

How to Write a Nursing Case Study Analysis – Guide, Format, and Examples for Nursing Students
Wilson logan.
- August 6, 2022
- Nursing Writing Guides

What is a Nursing Case Study Analysis?
A case study analysis is a detailed examination of a specific real-world situation or event.
It is typically used in nursing school to help students learn how to analyze complex problems and make decisions based on limited information to support nursing care.
Preparing a good case study analysis is difficult and requires much time and effort. This article provides some tips on how to write a case study analysis that will help you get the most out of your research and provide a solid foundation for your writing.
A case study analysis requires you to investigate a nursing scenario, examine the alternative solutions, and propose the most effective solution using supporting evidence.
Nurses constantly make decisions that affect the lives of their patients. Nurses need strong problem-solving and critical-thinking skills to make these decisions correctly. Case studies are an excellent way for nurses to hone these skills.
This guide will help BSN, MSN, and DNP nursing students navigate the process of writing a nursing case study analysis, focusing on the format, steps, and key components.
How do you analyze a case study in nursing?
A nursing case study is an in-depth examination of a single individual. It is usually used to identify new areas of knowledge or to validate existing knowledge.
When analyzing a nursing case study, it is important to consider the following elements:
- The patient’s medical history. This includes any prior illnesses, treatments, and medications.
- The patient’s current condition. This includes symptoms, vital signs, and laboratory results.
- The nurse’s observations. This includes the nurse’s notes on the patient’s condition and behavior.
- The patient’s family and social history. This includes information on the patient’s family, friends, and social support network.
- The patient’s response to treatment, including any changes in the patient’s condition or symptoms after receiving treatment.
How Nursing Practitioners Can Analyze Patient’s Cases
As a nurse practitioner, you will often be asked to provide a case analysis for your patients. This can be a daunting task, but there are some key elements that you should always include in your analysis.
- The first element is the patient history. This should include any relevant medical history and any personal information that may be pertinent to the case.
- The second element is the physical examination. This should include a thorough patient examination, including any relevant test results.
- The third element is the diagnosis. This is where you will assess the patient’s condition and identify potential problems.
- The fourth element is the treatment plan. This is where you will outline the course of treatment you recommend for the patient.
- The fifth and final element is the prognosis. In this section, you will assess the likely outcome of the case based on the information you have gathered.
How to Write a Nursing Case Study Analysis
Format of a nursing case study analysis.
A nursing case study analysis typically follows a standard format, which includes:
- Introduction: Provide a brief overview of the patient, the diagnosis, and the purpose of the case study (Hooper, 2014).
- Patient History: Present the patient’s background, including age, gender, medical history, and any relevant social or family history (Smith, 2017).
- Nursing Assessment: Describe the patient’s current condition, including vital signs, physical examination findings, and any diagnostic tests or procedures (Jones, 2015).
- Nursing Diagnosis: Identify the primary nursing diagnosis based on the assessment findings, using NANDA International terminology (Herdman & Kamitsuru, 2019).
- Care Plan: Develop a comprehensive care plan that addresses the patient’s needs, including nursing interventions, rationale, and expected outcomes (Thompson, 2018).
- Evaluation: Discuss the patient’s response to the interventions and any modifications made to the care plan (Brown, 2016).
- Conclusion: Summarize the key points of the case study and discuss the implications for nursing practice (Davis, 2014).
Steps for conducting a case study in nursing research papers
- Choose a relevant case: Select a patient case that aligns with the purpose of your research paper and highlights important nursing concepts (Taylor, 2015).
- Gather information: Collect data from the patient’s medical record, nursing assessments, and any additional sources, such as interviews with the patient or family members (Wilson, 2017).
- Analyze the data: Identify patterns, trends, and significant findings in the patient’s data to inform your nursing diagnosis and care plan (Lee, 2016).
- Develop a nursing diagnosis: Use the NANDA International taxonomy to formulate a nursing diagnosis that accurately reflects the patient’s condition (Herdman & Kamitsuru, 2019).
- Create a care plan: Develop a comprehensive care plan that addresses the patient’s needs, including specific nursing interventions, rationale, and expected outcomes (Thompson, 2018).
- Evaluate the outcome: Discuss the patient’s response to the interventions and any modifications made to the care plan based on the patient’s progress (Brown, 2016).
- Write the case study: Follow the standard format for a nursing case study analysis, ensuring that each section is well-organized and supported by evidence from primary sources (Hooper, 2014).
- First, you will need to read over the case study thoroughly.
- Ensure you understand all of the information presented in the case study and note any key points or details that may be important.
- Once you understand the case study well, you must start planning your analysis. Consider your overall argument.
- What points do you want to make in your analysis?
- What evidence will you use to support these points?
- Once you have a good idea of what you want to say in your analysis, start organizing your thoughts and putting them into a coherent structure.
- Once you have a rough case study analysis outline, start filling in the details. Flesh out your arguments and provide evidence to support them. In addition, make sure to address any counterarguments that could be made against your points.
- Finally, conclude your analysis by summarizing your main points and providing any recommendations or suggestions for further action.
Presenting a Care plan and Nursing Assessment of the patient in a Case Study
When presenting a care plan and nursing assessment in a case study, it is essential to:
- Use a systematic approach: Follow a standardized format like the Nursing Process to ensure a comprehensive assessment and care plan.
- Include relevant data: Present pertinent information from the patient’s history, physical examination, diagnostic tests, and nursing assessments.
- Prioritize nursing diagnoses: Based on the patient’s condition, identify the most important nursing diagnoses and prioritize them according to urgency and significance.
- Develop patient-centered interventions: Create nursing interventions that are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) and tailored to the patient’s individual needs.
- Provide rationale: Explain the reasoning behind each nursing intervention, linking it to evidence-based practice and the expected outcomes.
- Evaluate outcomes: Discuss the patient’s response to the interventions and any modifications made to the care plan based on the patient’s progress.
How to write case study analysis in nursing
To write a case study analysis in nursing, follow these steps:
- Introduction: Begin with a brief overview of the patient, the diagnosis, and the purpose of the case study.
- Patient History: Present the patient’s background, including age, gender, medical history, and any relevant social or family history.
- Nursing Assessment: Describe the patient’s current condition, including vital signs, physical examination findings, and any diagnostic tests or procedures.
- Nursing Diagnosis: Using NANDA International terminology, identify the primary nursing diagnosis based on the assessment findings.
- Care Plan: Develop a comprehensive care plan that addresses the patient’s needs, including nursing interventions, rationale, and expected outcomes.
- Evaluation: Discuss the patient’s response to the interventions and any modifications to the care plan.
- Conclusion: Summarize the key points of the case study and discuss the implications for nursing practice.
How to Structure a Nursing Case Study Analysis Paper
When structuring a nursing case study paper, it is essential to include specific information in each section to ensure a comprehensive and well-organized analysis. Here’s an extensive guide on what should be included in each section of the nursing case study analysis paper:
- The title of the case study should be concise, descriptive, and reflective of its main focus
- Include your name, academic credentials, and the institution where you are studying.
- Provide the date of submission
- Write a brief summary (usually 150-300 words) of the case study
- Include the purpose of the study, the main methods used, key results, and conclusions
- Highlight the most important points that will be discussed in the paper
Introduction
- Provide background information on the patient, including age, gender, and the primary reason for seeking medical care.
- Briefly describe the patient’s diagnosis and any relevant medical history.
- State the purpose of the case study and its significance to nursing practice.
Patient History
- Present a detailed account of the patient’s background, including past medical history, family history, social history, and any relevant lifestyle factors.
- Discuss the patient’s medications, allergies, and recent hospitalizations or surgeries.
- Include pertinent information about the patient’s physical, emotional, and cognitive status.
Nursing Assessment:
- Describe the patient’s condition, including vital signs, physical examination findings, and relevant diagnostic tests or procedures.
- Use a systematic approach, such as the head-to-toe assessment, to ensure a comprehensive patient evaluation.
- Discuss the patient’s chief complaint, symptoms, and any changes in their condition since admission.
Nursing Diagnosis
- Using NANDA International terminology, identify the primary nursing diagnosis based on the assessment findings.
- Provide a clear, concise statement that describes the patient’s health problem or potential risk.
- Include the related factors and defining characteristics that support the nursing diagnosis.
- Based on the nursing diagnosis, develop a comprehensive care plan that addresses the patient’s needs.
- Include specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals for each nursing intervention.
- Explain each intervention’s rationale, explaining how it will help achieve the desired outcomes.
- Discuss the implementation of the interventions, including any collaborative efforts with other healthcare professionals.
- Assess the patient’s response to the nursing interventions and discuss any changes in their condition (Brown, 2016).
- Evaluate the effectiveness of the care plan in achieving the desired outcomes (Wilson, 2017).
- Discuss any modifications to the care plan based on the patient’s progress or changes in their condition (Lee, 2016).
- Reflect on the overall nursing care provided and identify areas for improvement (Jones, 2015).
- Analyze the case study, applying relevant nursing theories and evidence-based practice guidelines.
- Compare the patient’s case to similar cases in the literature and discuss any unique aspects.
- Identify the strengths and weaknesses of the nursing care provided and recommend improvement.
- Discuss the implications of the case study for nursing practice, education, and research.
- Summarize the key points of the case study, including the primary nursing diagnoses, interventions, and outcomes.
- Emphasize the importance of the case study for nursing practice and patient care.
- Provide a final reflection on the learning experience and how it contributes to your growth as a nursing professional.
- List all sources cited in the case study using the appropriate citation style (e.g., APA, MLA).
- Ensure that all references are current, reliable, and relevant to the case study.
- Include a mix of primary and secondary sources, such as research articles, textbooks, and clinical guidelines.
10 Nursing Case Study Examples for Nursing Students
Tips for writing a nursing case study analysis.
When writing a nursing case study analysis, applying your theoretical knowledge, critical thinking skills, and clinical reasoning is essential to provide a thorough and evidence-based evaluation of the patient’s condition. Here are some tips to help you write a comprehensive nursing case study analysis:
- Start with a clear introduction that includes patient information, such as age, gender, and chief complaint. This will give the reader a clear picture of the patient’s background and medical situation.
- Provide a detailed medical history, including any chronic conditions, medications, allergies, and surgeries. This information will help you formulate nursing diagnoses and develop an appropriate nursing care plan.
- Include a family history section to identify any genetic diseases or chronic conditions that may be relevant to the patient’s current condition. This will help you understand potential complications and adjust treatment accordingly.
- Discuss the patient’s social history, including employment status, living situation, and alcohol/drug use. This information can provide insight into the patient’s lifestyle and its impact on their health.
- Perform a thorough physical examination and review of symptoms to identify any abnormalities contributing to the patient’s condition. This will help you determine the need for further medical attention or diagnostic testing.
- Analyze diagnostic test results, such as blood work, imaging tests, and biopsies, to confirm or rule out a diagnosis. This will help you develop an evidence-based treatment plan.
- Develop a comprehensive nursing care plan that includes nursing diagnoses, interventions, and expected outcomes. Ensure that the plan is based on evidence-based guidelines and tailored to the patient’s specific needs.
- Describe the rationale behind each intervention in the nursing care plan. This will demonstrate your application of theoretical knowledge and clinical reasoning skills.
- Evaluate the patient’s response to treatment and discuss any changes in their condition. This will help you assess the effectiveness of the nursing care plan and make necessary adjustments.
- Conclude with a clear prognosis based on your analysis of the patient’s condition and response to treatment. This will demonstrate your ability to synthesize information and make informed predictions about the patient’s outcomes.
- Use a logical and organized structure throughout your case study analysis. This will ensure that your document flows logically and is easy to follow.
- Engage in reflective practice by discussing what you found interesting or challenging about the case study. This will help you identify areas for further learning and professional growth.
- Collaborate with the healthcare team to ensure the patient receives comprehensive and coordinated care. This will help bridge the gap between theory and practice and promote optimal patient outcomes.
By following these tips, you can write a thorough and evidence-based nursing case study analysis demonstrating your critical thinking skills, clinical reasoning, and application of theoretical knowledge. Whether you are working on a free nursing case study or a more complex case, these tips will help you comprehensively evaluate the patient’s condition and develop an appropriate care plan.
- Brown, S. (2016). Evaluating nursing interventions in case studies. Journal of Nursing Education, 55(6), 345-351.
- Davis, L. (2014). Writing effective case study conclusions. Nursing Education Perspectives, 35(4), 268-269.
- Doenges, M. E., Moorhouse, M. F., & Murr, A. C. (2016). Nursing care plans: Guidelines for individualizing client care across the life span. F.A. Davis.
- Herdman, T. H., & Kamitsuru, S. (Eds.). (2019). NANDA International nursing diagnoses: Definitions & classification, 2021-2023. Thieme Medical Publishers.
- Hooper, V. D. (2014). How to write a nursing case study. American Nurse Today, 9(8), 44-47.
- Jones, C. (2015). The importance of nursing assessments in case studies. Nursing Standard, 29(50), 42-48.
- Lee, J. (2016). Analyzing nursing care in case studies: A beginner’s guide. Nursing Education Today, 45, 142-146.
- Potter, P. A., Perry, A. G., Hall, A., & Stockert, P. A. (2019). Fundamentals of nursing. Elsevier.
- Smith, J. (2017). Presenting patient history in nursing case studies. Journal of Nursing Education and Practice, 7(11), 44-49.
- Taylor, C. R. (2015). Selecting relevant cases for nursing case studies. Nurse Educator, 40(4), 204-206.
- Thompson, C. J. (2018). Developing patient-centered care plans in nursing case studies. Nursing Education Perspectives, 39(3), 158-161.
- Wilson, L. (2017). Gathering data for nursing case studies: Best practices. Journal of Nursing Education, 56(10), 609-614.
Working On an Assignment With Similar Concepts Or Instructions?
A Page will cost you $12, however, this varies with your deadline.
We have a team of expert nursing writers ready to help with your nursing assignments. They will save you time, and improve your grades.
Whatever your goals are, expect plagiarism-free works, on-time delivery, and 24/7 support from us.
Here is your 15% off to get started. Simply:
- Place your order ( Place Order )
- Click on Enter Promo Code after adding your instructions
- Insert your code – Get20
All the Best,
Have a subject expert Write for You Now
Have a subject expert finish your paper for you, edit my paper for me, have an expert write your dissertation's chapter, what you'll learn.
- Nursing Careers
- Nursing Paper Solutions
- Nursing Theories
- Nursing Topics and Ideas
Related Posts
- How to Write a DNP Project Proposal with Examples
- Capstone vs Thesis vs Dissertation in Nursing
- 266+ Nursing Capstone Project Ideas and Topics for BSN, MSN – DNP [With Examples – updated]
Important Links
Knowledge base, paper examples, nursing writing services.
Nursingstudy.org helps students cope with college assignments and write papers on various topics. We deal with academic writing, creative writing, and non-word assignments.
All the materials from our website should be used with proper references. All the work should be used per the appropriate policies and applicable laws.
Our samples and other types of content are meant for research and reference purposes only. We are strongly against plagiarism and academic dishonesty.
Phone: +1 628 261 0844
Mail: [email protected]

We Accept:

@2015-2024, Nursingstudy.org

How to Write a Nursing Case Study Paper (A Guide)

Most nursing students dread writing a nursing case study analysis paper, yet it is a mandatory assignment; call it a rite of passage in nursing school. This is because it is a somewhat tricky process that is often overwhelming for nursing students. Nevertheless, by reading this guide prepared by our best nursing students, you should be able to easily and quickly write a nursing case study that can get you an excellent grade.
How different is this guide from similar guides all over the internet? Very different!
This guide provides all the pieces of information that one would need to write an A-grade nursing case study. These include the format for a nursing case study, a step-by-step guide on how to write a nursing case study, and all the important tips to follow when writing a nursing case study.
This comprehensive guide was developed by the top nursing essay writers at NurseMyGrade, so you can trust that the information herein is a gem that will catapult your grades to the next level. Expect updates as we unravel further information about writing a nursing case study.
Now that you know you’ve discovered a gold mine , let’s get right into it.
What Is a Nursing Case Study?
A nursing case study is a natural or imagined patient scenario designed to test the knowledge and skills of student nurses. Nursing case study assignments usually focus on testing knowledge and skills in areas of nursing study related to daily nursing practice.
As a nursing student, you must expect a nursing case study assignment at some point in your academic life. The fact that you are reading this post means that point is now.
While there is no standard structure for writing a nursing case study assignment, some things or elements must be present in your nursing assignment for your professor to consider it complete.
In the next section, you will discover what your instructor n expects in your nursing case study analysis. Remember, these are assignments where you are given a case study and are expected to write a case analysis report explaining how to handle such scenarios in real-life settings.
The Nursing Case Study Template
The typical nursing case study has nine sections. These are:
- Introduction
- Case presentation (Patient info, history, and medical condition)
- Diagnosis/Nursing assessment
- Intervention/Nursing care plan
- Discussion and recommendations
The Structure of a Nursing Case Study Analysis
You now know what nursing professors expect in a nursing case study analysis. In this section, we will explain what to include in each section of your nursing case study analysis to make it an excellent one.
1. Title page
The title page is essential in all types of academic writing. You must include it in your nursing case study analysis or any other essay or paper. And you must include it in the format recommended by your college.
If your college has no specific title page format, use the title page format of the style requested in the assignment prompt. In nursing college, virtually all assignments should be written in Harvard or APA format .
So, check your assignment prompt and create your title page correctly. The typical title page should include the topic of your paper, your name, the name of your professor, the course name, the date you are submitting the paper, and the name of your college.
2. Abstract
Most nursing professors require you to include an abstract in your nursing case study analysis. And even when you are not explicitly required to write one, it is good to do so. Of course, you should consult with your professor before doing so.
When writing an abstract for your paper, make sure it is about 200 words long. The abstract should include a brief summary of the case study, including all the essential information in the patient presentation, such as the history, age, and current diagnosis.
The summary should also include the nursing assessment, the current interventions, and recommendations.
3. Introduction
After writing the title page and the abstract, start writing the introduction. The introduction of a nursing case study analysis must briefly include the patient’s presentation, current diagnosis and medication, and recommendations. It must also include a strong thesis statement that shows what the paper is all about.
You shouldn’t just write an introduction for the sake of it. If you do so, your introduction will be bland. You need to put in good effort when writing your introduction. The best way to do this is to use your introduction to show you understand the case study perfectly and that you will analyze it right.
You can always write your introduction last. Many students do this because they believe writing an introduction last makes it more precise and accurate.
4. Case Presentation (Status of the Patient)
After introducing your nursing case study analysis, you should present the case where you outline the patient's status. It is usually straightforward to present a case.
You must paraphrase the patient scenario in the assignment prompt or brief. Focus on the demographic data of the patient (who they are, age, race, height, skin tone, occupation, relationships, marital status, appearance, etc.), why they are in the case study or scenario, reasons they sought medical attention, chief complaint, and current diagnosis and treatment. You should also discuss the actions performed on the patient, such as admission to the ICU, taking vital signs, recommending tests, etc.
In short, everything necessary in the patient scenario should be in your case presentation. You only need to avoid copying the patient scenario or case study word-for-word when writing your case presentation.
5. Diagnosis and Assessment
After the case presentation, you should explain the diagnosis. In other words, you should explain the condition, disease, or medical situation highlighted in the case presentation. For example, if the patient is a heavy smoker and he has COPD, it is at this point that you explain how COPD is linked to heavy smoking.
This is the section where you thoroughly discuss the disease process (pathophysiology) by highlighting the causes, symptoms, observations, and treatment methods. You should relate these to the patient’s status and give concrete evidence. You should describe the progression of the disease from when the client was admitted to a few hours or days after they were stabilized. Consider the first indication of the disease that prompted the patient to seek further medical assistance.
Your paper should also elucidate the diagnostic tests that should be conducted and the differential diagnosis. Ensure that each is given a well-founded rationale.
When explaining the condition, go deep into the pathophysiology. Focus specifically on the patient’s risk factors. Ensure you get your explanation from recent nursing literature (peer-reviewed scholarly journals published in the last 5 years). And do not forget to cite all the literature you get your facts from.
In short, this section should explain the patient’s condition or suffering.
6. Nursing Intervention
After the diagnosis and nursing assessment section, your nursing case study analysis should have an intervention section. This section is also known as the nursing care planning section. What you are supposed to do in this section is to present a nursing care plan for the patient presented in the patient scenario. You should describe the nursing care plan and goals for the patient. Record all the anticipated positive changes and assess whether the care plan addresses the patient's condition.
A good nursing care plan details the patient’s chief complaints or critical problems. It then describes the causes of these problems using evidence from recent medical or nursing literature. It then details the potential intervention for each problem. Lastly, it includes goals and evaluation strategies for the measures. Most professors, predominantly Australian and UK professors, prefer if this section is in table format.
Some nursing professors regard the intervention section (or nursing care plan section) as the most critical part of a nursing case study. This is because this part details precisely how the student nurse will react to the patient scenario (which is what the nursing professors want to know). So, ensure you make a reasonable effort when developing this section to get an excellent grade.
7. Discussion and Recommendations
The intervention section in a nursing case study is followed by a discussion and recommendations section. In this section, you are supposed to expound on the patient scenario, the diagnosis, and the nursing care plan. You should also expound on the potential outcomes if the care plan is followed correctly. The discussion should also explain the rationale for the care plan or its significant bits.
Recommendations should follow the discussion. Recommendations usually involve everything necessary that can be done or changed to manage a patient’s condition or prevent its reoccurrence. Anything that enhances the patient’s well-being can be a recommendation. Just make sure your key recommendations are supported by evidence.
8. Conclusion
This is the second last section of a typical nursing case study. What you need here is to summarize the entire case study. Ensure your summary has at least the case presentation, the nursing assessment/diagnosis, the intervention, and the key recommendations.
At the very end of your conclusion, add a closing statement. The statement should wrap up the whole thing nicely. Try to make it as impressive as possible.
9. References
This is the last section of a nursing case study. No nursing case study is complete without a references section. You should ensure your case study has in-text citations and a references page.
And you should make sure both are written as recommended in the assignment. The style section is usually Harvard or APA. Follow the recommended style to get a good grade on your essay.
Step-By-Step Guide to Writing a Nursing Case Study
You know all the key sections you must include in a nursing case study. You also know what exactly you need to do in each section. It is time to learn how to write a nursing case study. The process detailed below should be easy to follow because you know the typical nursing case study structure.
1. Understand the Assignment
When given a nursing case study assignment, the first thing you need to do is to read. You need to read two pieces of information slowly and carefully.
First, you need to read the prompt itself slowly and carefully. This is important because the prompt will have essential bits of information you need to know, including the style, the format, the word count, and the number of references needed. All these bits of information are essential to ensure your writing is correct.
Second, you need to read the patient scenario slowly and carefully. You should do this to understand it clearly so that you do not make any mistakes in your analysis.
2. Create a Rough Outline
Failure to plan is a plan to fail. That is not what you are in it for anyway! In other words, do not fail to create an outline for your case study analysis. Use the template provided in this essay to create a rough outline for your nursing case study analysis.
Ensure your outline is as detailed as it can be at this stage. You can do light research to achieve this aim. However, this is not exactly necessary because this is just a rough outline.
3. Conduct thorough research
After creating a rough outline, you should conduct thorough research. Your research should especially focus on providing a credible and evidence-based nursing assessment of the patient problem(s). You should only use evidence from recent nursing or medical literature.
You must also conduct thorough research to develop an effective intervention or nursing care plan. So when researching the patient’s problem and its diagnosis, you should also research the most suitable intervention or do it right after.
When conducting research, you should always note down your sources. So for every piece of information you find, and what to use, you should have its reference.
After conducting thorough research, you should enhance your rough outline using the new information you have discovered. Make sure it is as comprehensive as possible.
4. Write your nursing case study
You must follow your comprehensive outline to write your case study analysis at this stage. If you created a good outline, you should find it very easy to write your nursing case study analysis.
If you did not, writing your nursing case study will be challenging. Whenever you are stuck writing your case study analysis paper, you should re-read the part where we explain what to include in every section of your analysis. Doing so will help you know what to write to continue your essay. Writing a nursing case study analysis usually takes only a few hours.
5. Reference your case study
After writing your case study, ensure you add all in-text citations if you have not already. And when adding them, you should follow the style/format recommended in the assignment prompt (usually APA or Harvard style).
After adding in-text citations exactly where they need to be and in the correct format, add all the references you have used in a references page. And you should add them correctly as per the rules of the style you were asked to use.
Do not forget to organize your references alphabetically after creating your references page.
6. Thoroughly edit your case study
After STEP 5 above, you need to edit your case study. You should edit it slowly and carefully. Do this by proofreading it twice. Proofread it slowly each time to discover all the grammar, style, and punctuation errors. Remove all the errors you find.
After proofreading your essay twice, recheck it to ensure every sentence is straightforward. This will transform your ordinary case study into an A-grade one. Of course, it must also have all the standard sections expected in a case study.
Recheck your case study using a grammarly.com or a similar computer grammar checker to ensure it is perfect. Doing this will help you catch and eliminate all the remaining errors in your work.
7. Submit your case study analysis
After proofreading and editing your case study analysis, it will be 100% ready for submission. Just convert it into the format it is required in and submit it.
Nursing Case Study Tips and Tricks
The guide above and other information in this article should help you develop a good nursing case study analysis. Note that this guide focuses entirely on nursing case scenario-based papers, not research study-based nursing case studies. The tips and tricks in this section should help you ensure that the nursing case study analysis you create is excellent.
1. Begin early
The moment you see a nursing case study assignment prompt, identify a date to start writing it and create your own deadline to beat before the deadline stated in the prompt.
Do this and start writing your case study analysis early before your deadline. You will have plenty of time to do excellent research, develop an excellent paper, and edit your final paper as thoroughly as you want.
Most student nurses combine work and study. Therefore, if you decide to leave a nursing case study assignment until late to complete it, something could come up, and you could end up failing to submit it or submitting a rushed case study analysis.
2. Use the proper terminology
When writing an essay or any other academic paper, you are always encouraged to use the most straightforward language to make your work easy to understand. However, this is not true when writing a nursing case study analysis. While your work should certainly be easy to understand, you must use the right nursing terminology at every point where it is necessary. Failure to do this could damage your work or make it look less professional or convincing.
3. Avoid copying and pasting
If you are a serious nursing student, you know that copying and pasting are prohibited in assignments. However, sometimes copying and pasting can seem okay in nursing case studies. For example, it can seem okay to copy-paste the patient presentation. However, this is not okay. You are supposed to paraphrase the verbatim when presenting the patient presentation in your essay. You should also avoid copy-pasting information or texts directly. Every fact or evidence you research and find should be paraphrased to appear in your work. And it should be cited correctly.
4. Always ask for help if stuck
This is very important. Students are usually overwhelmed with academic work, especially a month or two to the end of the semester. If you are overwhelmed and think you will not have the time to complete your nursing case study analysis or submit a quality one, ask for help. Ask for help from a nursing assignment-help website like ours, and you will soon have a paper ready that you can use as you please. If you choose to get help from us, you will get a well-researched, well-planned, well-developed, and fully edited nursing case study.
5. Format your paper correctly
Many students forget to do proper formatting after writing their nursing case study analyses. Before you submit your paper, make sure you format it correctly. If you do not format your paper correctly, you will lose marks because of poor formatting. If you feel you are not very confident with your APA or Harvard formatting skills, send your paper to us to get it correctly formatted and ready for submission.
Now that you are all set up …
Our company has been among the best-rated nursing homework help companies in the last few years. Thousands of students have benefitted from our many academic writing guides. Many more have benefitted from direct help given by our experts.
- How to write a nursing philosophy statement.
- Writing an abstract poster presentation.
We have experienced nursing experts available every day of the week to provide nursing assignment help. They can easily research and write virtually any nursing assignment, including a nursing case study. So, if the information provided in this article isn’t making you feel any optimistic about writing an excellent nursing case study, get help from us.
Get help by ordering a custom nursing case study through this very website. If you do so, you will get a 100% original paper that is well-researched, well-written, well-formatted, and adequately referenced. Since the paper is original, you can use it anywhere without problems.
Thousands of students trust our company every week, month, and year. Be like them! Trust us for 100% confidentiality and speedy delivery.
Struggling with
Related Articles

Tips to help you Succeed in Nursing School

How to Ace Online Nursing Classes: Tips & Tricks

AMA Citation and Formatting Style for Medical Paper
NurseMyGrades is being relied upon by thousands of students worldwide to ace their nursing studies. We offer high quality sample papers that help students in their revision as well as helping them remain abreast of what is expected of them.

Nursing Case Study
Ai generator.

ScienceDirect posted a nursing ethics case study where an end-stage prostate cancer patient, Mr. Green, confided to nursing staff about his plan to commit suicide. The patient asked the nurse to keep it a secret. The ethical problem is whether the nurse should tell the health care team members about the patient’s thought without his permission. The best ethical decision for this nursing case study was to share this critical information with other health care professionals, which was the action the nurse took. The team adhered to the proper self-harm and suicide protocol. The appropriate team performed a palliative therapy. As a result, the patient didn’t harm himself and died peacefully a few months after he was discharged.
What Is a Nursing Case Study? A nursing case study is a detailed study of an individual patient. Through this type of research, you can gain more information about the symptoms and the medical history of a patient. It will also allow you to provide the proper diagnoses of the patient’s illness based on the symptoms he or she experienced and other affecting factors. Nursing students usually perform this study as part of their practicum, making it an essential experience because, through this research methodology , they can apply the lessons they have learned from school. The situation mentioned above was an excellent example of a nursing case study.
Nursing Case Study Format
1. introduction.
Purpose: Briefly introduces the case study, including the main health issue or condition being explored. Background: Provides context for the patient scenario, outlining the significance of the case in nursing practice. Objectives: Lists the learning objectives or goals that the case study aims to achieve.
2. Patient Information
Demographics: Age, gender, ethnicity, and relevant personal information. Medical History: Past medical history, including any chronic conditions, surgeries, or significant health events. Current Health Assessment: Presents the patient’s current health status, including symptoms, vital signs, and results from initial examinations.
3. Case Description
Clinical Presentation: Detailed description of the patient’s presentation, including physical examination findings and patient-reported symptoms. Diagnostic Findings: Summarizes diagnostic tests that were performed, including lab tests, imaging studies, and other diagnostic procedures, along with their results. Treatment Plan: Outlines the initial treatment provided to the patient, including medications, therapies, surgeries, or other interventions.
4. Nursing Care Plan
Nursing Diagnoses: Identifies the nursing diagnoses based on the assessment data. Goals and Outcomes: Establishes short-term and long-term goals for the patient’s care, including expected outcomes. Interventions: Describes specific nursing interventions planned or implemented to address each nursing diagnosis and achieve the stated goals. Evaluation: Discusses the effectiveness of the nursing interventions, including patient progress and any adjustments made to the care plan.
5. Analysis
Critical Analysis: Analyzes the case in depth, considering different aspects of patient care, decision-making processes, and the application of nursing theories and principles. Reflection: Reflects on the nursing practice, lessons learned, and how the case study has impacted the understanding and application of nursing knowledge.
6. Conclusion
Summary: Provides a concise summary of the key points from the case study, including the patient outcome and the nursing care impact. Implications for Practice: Discusses the implications of the case for nursing practice, including any changes to practice or policy that could improve patient care. Recommendations: Offers recommendations for future care or areas for further study based on the case study findings.
Examples of Nursing Case Study
Management of Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMI) Introduction: A 58-year-old male with a history of hypertension and smoking presents to the emergency department with chest pain. This case study explores the nursing management for patients with AMI. Patient Information: Demographics: 58-year-old male, smoker. Medical History: Hypertension, no previous diagnosis of heart disease. Current Health Assessment: Reports severe chest pain radiating to his left arm, sweating, and nausea. Case Description: Clinical Presentation: Patient appeared in distress, clutching his chest. Diagnostic Findings: ECG showed ST-elevation in anterior leads. Troponin levels were elevated. Treatment Plan: Immediate administration of aspirin, nitroglycerin, and morphine for pain. Referred for emergency coronary angiography. Nursing Care Plan: Nursing Diagnoses: Acute pain related to myocardial ischemia. Goals: Relieve pain and prevent further myocardial damage. Interventions: Monitoring vital signs, administering prescribed medications, and providing emotional support. Evaluation: Pain was managed effectively, and the patient was stabilized for angiography. Analysis: The timely nursing interventions contributed to stabilizing the patient’s condition, showcasing the critical role nurses play in acute care settings. Conclusion: This case highlights the importance of quick assessment and intervention in patients with AMI, emphasizing the nurse’s role in pain management and support.
Managing Type 1 Diabetes in a Pediatric Patient Introduction: A 10-year-old female diagnosed with type 1 diabetes presents for a routine check-up. This case study focuses on the nursing care plan for managing diabetes in pediatric patients. Patient Information: Demographics: 10-year-old female. Medical History: Diagnosed with type 1 diabetes six months ago. Current Health Assessment: Well-controlled blood glucose levels, but expresses difficulty with frequent insulin injections. Case Description: Clinical Presentation: Patient is active, engaging in school activities but struggles with diabetes management. Diagnostic Findings: HbA1c is 7.2%, indicating good control. Treatment Plan: Insulin therapy, carbohydrate counting, and regular blood glucose monitoring. Nursing Care Plan: Nursing Diagnoses: Risk for unstable blood glucose levels. Goals: Maintain blood glucose within target range and increase patient comfort with diabetes management. Interventions: Education on insulin pump use, dietary advice, and coping strategies. Evaluation: Patient showed interest in using an insulin pump and understood dietary recommendations. Analysis: This case emphasizes the importance of education and emotional support in managing chronic conditions in pediatric patients. Conclusion: Effective management of type 1 diabetes in children requires a comprehensive approach that includes education, technological aids, and psychological support.
Elderly Care for Alzheimer’s Disease Introduction: An 82-year-old female with Alzheimer’s disease presents with increased confusion and agitation. This case study examines the complexities of caring for elderly patients with Alzheimer’s. Patient Information: Demographics: 82-year-old female. Medical History: Alzheimer’s disease, osteoarthritis. Current Health Assessment: Increased confusion, agitation, and occasional aggression. Case Description: Clinical Presentation: Patient exhibits signs of advanced Alzheimer’s with memory loss and disorientation. Diagnostic Findings: Cognitive tests confirm the progression of Alzheimer’s. Treatment Plan: Non-pharmacological interventions for agitation, memory aids, and safety measures in the home. Nursing Care Plan: Nursing Diagnoses: Impaired memory related to Alzheimer’s disease. Goals: Reduce agitation and prevent harm. Interventions: Use of calming techniques, establishing a routine, and environmental modifications. Evaluation: Agitation was reduced, and the patient’s safety was improved through environmental adjustments. Analysis: The case underscores the need for tailored interventions to manage Alzheimer’s symptoms and improve the quality of life for the elderly. Conclusion: Nursing care for Alzheimer’s patients requires a multifaceted approach focusing on safety, symptom management, and patient dignity.
Nursing Case Study Topics with Samples to Edit & Download
- Telehealth Nursing
- Mental Health and Psychiatric Nursing
- Geriatric Nursing Care
- Palliative and End-of-Life Care
- Pediatric Nursing
- Emergency and Critical Care Nursing
- Chronic Disease Management
- Nursing Ethics and Patient Rights
- Infection Control and Prevention
- Oncology Nursing
- Nursing Leadership and Management
- Cultural Competence in Nursing
- Substance Abuse and Addiction Nursing
- Technological Innovations in Nursing
- Nursing Education and Training
Nursing Case Study Examples & Templates
1. nursing case study template.

2. Free Nursing Student Care Plan Template
3. Nursing Action Case Study Example

4. Hospital Nursing Care Case Study Example

5. Printable Nursing Health Case Study Example

professays.com
6. Fundamentals of Nursing Case Study Example

secure-ecsd.elsevier.com
7. Sample Nursing Case Study Example

caresearch.com.au
8. Nursing Research Case Study Example
9. Standard Nursing Case Study Example

resourcecenter.ovid.com
10. Nursing Disability Case Study Example

careerswales.com
11. Nursing care Patients Case Study Example

12. School of Nursing Case Study Example

ebn.bmj.com
13. Evaluation of Nursing Care Case Study Example
philadelphia.edu
Nursing Case Study Segments
Typically, a nursing case study contains three main categories, such as the items below.
1. The Status of a Patient
In this section, you will provide the patient’s information, such as medical history, and give the current patient’s diagnosis, condition, and treatment. Always remember to write down all the relevant information about the patient. Other items that you can collect in this stage are the reasons for the patient to seek medical care and the initial symptoms that he or she is experiencing. After that, based on the gathered information, you will explain the nature and cause of the illness of the patient.
2. The Nursing Assessment of the Patient
In this stage, you will need to prepare your evaluation of the patient’s condition. You should explain each observation that you have collected based on the vital signs and test results. You will also explain each nursing diagnosis that you have identified and determine the proper nursing care plan for the patient.
3. The Current Care Plan and Recommendations
Describe the appropriate care plan that you can recommend to the patient based on the diagnosis, current status, and prognosis in detail, including how the care plan will affect his or her life quality. If needed, you can also evaluate the patient’s existing care plan and give recommendations to enhance it. It is also crucial to cite relevant authoritative sources that will support your recommendations .
Objectives of Nursing Case Study
Nursing case studies are integral educational tools that bridge theoretical knowledge with practical application in patient care. They serve several key objectives essential for the development of nursing students and professionals. Here are the primary objectives of nursing case studies:
1. Enhance Critical Thinking and Clinical Reasoning
Case studies encourage nurses to analyze complex patient scenarios, make informed decisions, and apply critical thinking skills to solve problems. They simulate real-life situations, requiring nurses to evaluate data, consider multiple outcomes, and choose the best course of action.
2. Improve Diagnostic Skills
Through the detailed analysis of patient information, symptoms, and diagnostic results, nursing case studies help improve diagnostic skills. They allow nurses to practice interpreting clinical data to identify patient conditions and understand the underlying causes of symptoms.
3. Facilitate Application of Theoretical Knowledge
Nursing case studies provide a direct bridge between classroom learning and clinical practice. They offer a practical venue for applying theoretical knowledge about anatomy, physiology, pharmacology, and nursing theories to real-world patient care situations.
4. Promote Understanding of Comprehensive Patient Care
These studies emphasize the importance of holistic care, considering the physical, emotional, social, and psychological aspects of patient well-being. Nurses learn to develop comprehensive care plans that address all facets of a patient’s health.
5. Encourage Reflective Practice and Self-Assessment
Reflecting on case study outcomes enables nurses to evaluate their own decision-making processes, clinical judgments, and actions. This self-assessment promotes continuous learning and professional growth by identifying areas for improvement.
6. Foster Interdisciplinary Collaboration
Case studies often involve scenarios that require collaboration among healthcare professionals from various disciplines. They teach nurses the value of teamwork, communication, and the integration of different expertise to achieve optimal patient outcomes.
7. Enhance Patient Education and Advocacy Skills
By working through case studies, nurses improve their ability to educate patients and families about health conditions, treatment plans, and preventive measures. They also learn to advocate for their patients’ needs and preferences within the healthcare system.
8. Prepare for Real-Life Challenges
Nursing case studies prepare students and new nurses for the unpredictability and challenges of real-life clinical settings. They provide safe, controlled environments to practice responses to emergencies, ethical dilemmas, and complex patient needs without the risk of actual harm.
Steps in Nursing Process
Whether you are handling a patient with schizophrenia, pneumonia, diabetes, appendicitis, hypertension, COPD, etc, you will need to follow specific steps to ensure that you are executing the critical nursing process.
1. Assess the Patient
The first step of the nursing process requires critical thinking skills as it involves gathering both subjective and objective data. Subjective data includes verbal statements that you can collect from the patient or caregiver. In contrast, objective information refers to measurable and tangible data, such as vital signs, height, weight, etc. You can also use other sources of information, such as electronic health records, and friends that are in direct contact with the patient.
2. Diagnose the Patient
This critical step will help you in the next steps, such as planning and implementation of patient care. In this step, you will formulate a nursing diagnosis by applying clinical judgment. As a nurse, the North American Nursing Diagnosis Association (NANDA) will give you an up-to-date nursing diagnosis list, which will allow you to form a diagnosis based on the actual health problem.
3. Plan for a Proper Patient Care Plan
This part is where you will plan out the appropriate care plan for the patient. You will set this goal following the evidence-based practice (EDP) guidelines. The goal you will set should be specific, measurable, attainable, realistic, and timely ( SMART ).
4. Implement the Plan
In this stage, you can execute the plan that you have developed in the previous step. The implementation may need interventions such as a cardiac monitor, medication administration, etc.
5. Evaluate the Results
It is crucial to remember that every time the team does an intervention, you must do a reassessment to ensure that the process will lead to a positive result. You may need to reassess the patient depending on his progress, and the care plan may be modified based on the reassessment result.
Where to find nursing case studies?
Nursing case studies can be found in a variety of academic, professional, and medical resources. Here are some key places to look for nursing case studies:
- Academic Journals : Many academic journals focus on nursing and healthcare and publish case studies regularly. Examples include the “Journal of Clinical Nursing,” “Nursing Case Studies,” and “American Journal of Nursing.”
- University and College Libraries : Many academic institutions provide access to databases and journals that contain nursing case studies. Libraries often have subscriptions to these resources.
- Online Medical Libraries : Websites like PubMed, ScienceDirect, and Wiley Online Library offer a vast collection of nursing and medical case studies.
- Professional Nursing Organizations : Organizations such as the American Nurses Association (ANA) and the National League for Nursing (NLN) often provide resources, including case studies, for their members.
- Nursing Education Websites : Websites dedicated to nursing education, such as Lippincott NursingCenter and Nurse.com, often feature case studies for educational purposes.
- Government Health Websites : The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the World Health Organization (WHO) sometimes publish case studies related to public health nursing and disease outbreaks.
- Nursing Textbooks and eBooks : Many nursing textbooks and eBooks include case studies to illustrate key concepts and scenarios encountered in practice.
- Online Nursing Forums and Communities : Forums and online communities for nursing professionals may share or discuss case studies as part of their content.
- Conference Proceedings : Nursing and healthcare conferences often include presentations of case studies. Many of these are published in the conference proceedings, which may be accessible online.
Carrying out a nursing case study can be a delicate task since it puts the life of a person at stake. Thus, it requires a thorough investigation. With that said, it is essential to gain intensive knowledge about this type of study. Today, we have discussed an overview of how to conduct a nursing case study. However, if you think that you are having problems with your writing skills , we recommend you to consider looking for an essay writing service from the experts in the nursing department to ensure that the output follows the appropriate writing style and terminology.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting

Step-By-Step Guide to Writing a Nursing Case Study
You now know all the key sections you need to include in a nursing case study. You also know what exactly you need to do in each section. It is now time to know how exactly to write a nursing case study. The process detailed below should be easy to follow because you now know the typical structure of nursing case studies.
When given a nursing case study assignment, the first thing you need to do is to read. You need to read two pieces of information slowly and carefully.
First, you need to read the prompt itself slowly and carefully. This is important because the prompt will have important bits of information that you need to know, including the style, the format, the word count, and the number of references needed. All these bits of information are important to know to ensure what you are writing is the right thing.
Second, you need to read the patient scenario slowly and carefully. You should do this to understand it clearly so that you do not make any mistakes in your analysis.
- Create a rough outline
Failure to plan is a plan to fail. So do not fail to plan. In other words, do not fail to create an outline for your case study analysis. Use the template provided in this essay to create a rough outline for your nursing case study analysis.
Make sure your outline is as detailed as it can be at this stage. You can do light research to achieve this aim. However, this is not exactly necessary because this is just a rough outline.
- Conduct thorough research
After creating a rough outline, you should conduct thorough research. Your research should especially focus on providing a credible and evidence-based nursing assessment on the patient problem(s). The evidence you should use should only be from recent nursing or medical literature.
You will also need to conduct thorough research to come up with an effective intervention or nursing care plan. So when researching the patient’s problem and its diagnosis, you should also research the most suitable intervention or you should do it right after.
When conducting research, you should always note down your sources. So for every piece of information you find and what to use, you should have its reference.
After conducting thorough research, you should enhance your rough outline using the new pieces of information you have discovered. Make sure it is as comprehensive as possible.
- Write your nursing case study
At this stage, you simply need to follow your comprehensive outline to write your case study analysis. If you created a good outline, you should find it very easy to write your nursing case study analysis.
If you did not, you will find it difficult to write your nursing case study. Whenever you are stuck when writing your case study analysis paper, you should re-read the part of this article where we explain what to include in every section of your analysis. Doing so will help you know what exactly to write to continue with your essay. Writing a nursing case study analysis usually takes only a few hours.
- Reference your case study
After writing your case study, make sure you add all in-text citations if you had not added them already. And when adding them, you should make sure you follow the style/format recommended in the assignment prompt (usually APA or Harvard style).
After adding in-text citations exactly where they need to be and in the right format, add all the references you have used in a references page. And you should add them correctly as per the rules of the style you were asked to use.
Do not forget to organize your references alphabetically after you are done creating your references page.
- Thoroughly edit your case study
After STEP 5 above, you need to edit your case study. You should edit it slowly and carefully. Do this by proofreading it twice. Proofread it slowly each time to discover all the grammar, style, and punctuation errors. Remove all the errors you find.
After proofreading your essay twice, check it one more time to make sure every sentence is very easy to understand. This is what will transform your ordinary case study into an A-grade case study. Of course, it must also have all the standard sections expected in a case study.
Just to make sure your case study is absolutely perfect, check it one more time using a grammarly.com or a similar computer grammar checker. Doing this will help you catch and eliminate all the remaining errors in your work.
- Submit your case study analysis
After you are done proofreading and editing your case study analysis, it will be 100% ready for submission. Just convert it into the format it is required in and submit it.
Published by laura
View all posts by laura
📕 Studying HQ
10 nursing case study analysis examples [format + structure], bob cardens.
- August 6, 2022
If you are a nursing student, you may be asked to write a case study analysis. This can be a daunting task, but it is possible to do if you follow some simple steps. Here we include Nursing Case Study Analysis Examples to help you get started.
First, read the case study and make sure you understand the situation. Next, identify the key players involved and their role in the case. Finally, analyze the data presented and draw your own conclusions.
Writing a case study analysis can be challenging, but it is also an excellent way to learn more about nursing care. By taking the time to understand the situation and identify the key players, you will be able to gain valuable insights that can be applied to future cases.
What You'll Learn
10 Nursing Case Study Analysis Examples
Nursing case study analysis format and structure.
When it comes to writing a case study analysis, there is no one-size-fits-all approach. However, there is a general format and structure that you can follow to ensure your analysis is well-organized and flows smoothly. Here are the basics:
A nursing case study is a detailed study of a patient that is encountered by a nurse. The purpose of the case study is to provide a comprehensive view of the patient’s health condition and history. Nurse practitioners use case studies to enhance their ability to care for patients by providing them with a more complete picture of the patient’s health. Nurse practitioners may use different formats for their nursing case studies. However, all case studies should include certain key elements. These key elements include:
As a nursing practitioner, you will be responsible for analyzing patient cases and providing care based on your findings. There are key elements that you must take into account when performing a case analysis in order to ensure that you are providing the best possible care for your patients.
- The first element is the patient’s history. You will need to obtain a complete medical history in order to understand the background of the case and identify any potential risk factors.
- Next, you will need to perform a physical examination of the patient. This will help you to identify any physical signs or symptoms that may be related to the case.
- You will also need to order and review any laboratory tests or imaging studies that have been performed on the patient. These results can provide valuable information about the patient’s condition.
- Once you have gathered all of this information, you will need to start piecing together the puzzle to form a diagnosis. This process will involve synthesizing all of the information you have gathered and making a determination about what is causing the patient’s symptoms.
- Once you have made a diagnosis, you can start developing a treatment plan. This plan should be tailored specifically to the needs of the individual patient.
When writing a nursing case study, nurse practitioners should use a clear and concise format. The format should be easy to follow and understand. Nurse practitioners should also include all of the key elements in their nursing case studies. Nursing Case Study Analysis Examples
![10 nursing case study analysis examples [format + structure] 1 Nursing case study analysis examples](https://i0.wp.com/studyinghq.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/113124-84-CHECK.png?resize=84%2C84&ssl=1)
How to write a case study assignment
A case study is an in-depth analysis of a real-life situation or incident, as a way to illustrate content and theory to students. It is usually presented as a written report, but can also be done in the form of a presentation, video, or multimedia production.
Case studies are used in many different disciplines, including business, law, psychology, nursing, social work, and medical sciences.
A case study assignment is a type of paper that requires you to analyze a real-life or fictional situation and offer possible solutions. This can be a challenging task, but if you follow some basic guidelines, you can write a successful case study assignment.
Here are some tips on how to write a case study assignment:
- Read the case study carefully. Make sure you understand the situation and the problem that needs to be solved.
- Research the subject matter. You will need to have a good understanding of the relevant theories and concepts in order to offer possible solutions.
- Read the case study carefully. This may seem obvious, but it is important to get a clear understanding of the situation before you start writing. Make sure you have all the relevant facts and figures to hand before you start.
- Identify the key issues. Once you have read and understood the case study, you need to identify the key issues that it raises. These will form the basis of your analysis.
- Research the law/theory applicable to the key issues. Once you have identified the key issues, you need to research the law or theory that applies to them. This will help you to form your arguments and conclusions.
- Write your paper. Be sure to present your analysis in a clear and concise manner. Your paper should be well-organized and well-written
Start by filling this short order form order.studyinghq.com
And then follow the progressive flow.
Having an issue, chat with us here
Cathy, CS.
New Concept ? Let a subject expert write your paper for You
Have a subject expert write for you now, have a subject expert finish your paper for you, edit my paper for me, have an expert write your dissertation's chapter, popular topics.
Business Analysis Examples Essay Topics and Ideas How to Guides Nursing
- Nursing Solutions
- Study Guides
- Free College Essay Examples
- Privacy Policy
- Writing Service
- Discounts / Offers
Study Hub:
- Studying Blog
- Topic Ideas
- How to Guides
- Business Studying
- Nursing Studying
- Literature and English Studying
Writing Tools
- Citation Generator
- Topic Generator
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Conclusion Maker
- Research Title Generator
- Thesis Statement Generator
- Summarizing Tool
- Terms and Conditions
- Confidentiality Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Refund and Revision Policy
Our samples and other types of content are meant for research and reference purposes only. We are strongly against plagiarism and academic dishonesty.
Contact Us:
📞 +15512677917
2012-2024 © studyinghq.com. All rights reserved
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- v.24(6); 2019 Sep

Lessons learnt: examining the use of case study methodology for nursing research in the context of palliative care
Paula brogan.
School of Communication and Media, University of Ulster, Northern Ireland, UK
Felicity Hasson
Institute of Nursing Research, University of Ulster, Northern Ireland, UK
An empirical social research approach, facilitating in-depth exploration of complex, contemporary contextualised phenomena, case study research has been used internationally in healthcare studies across clinical settings, to explore systems and processes of care delivery. In the United Kingdom, case study methods have been championed by nurse researchers, particularly in the context of community nursing and palliative care provision, where its applicability is well established. Yet, dogged by conceptual confusion, case study remains largely underutilised as a research approach.
Drawing on examples from nursing and palliative care studies, this paper clarifies case study research, identifies key concepts and considers lessons learned about its potential for nursing research within the unique and complex palliative and end of life context.
A case study approach offers nurse researchers the opportunity for in-depth, contextualised understanding of the systems and processes which influence their role in palliative care delivery across settings. However, philosophical and conceptual understandings are needed and further training in case study methodology is required to enable researchers to articulate and conduct case study.
Introduction
An empirical social research approach, facilitating in-depth exploration of a contemporary phenomenon ( Yin, 2009 ), case study research has been used internationally in healthcare studies ( Anthony and Jack, 2009 ) to explore systems of palliative care ( Lalor et al., 2013 ), diverse contexts for palliative care delivery ( Sussman et al., 2011 ), roles of professional groups such as pharmacy ( O’Connor et al., 2011 ), the impact of services such as complementary therapy ( Maddalena et al., 2010 ) and nursing (Kaasalainen et al., 2013). In the United Kingdom, case study methods have been championed by nurse researchers ( Payne et al., 2006 ), particularly in the context of community nursing and palliative care provision ( Kennedy, 2005 ; Walshe et al., 2004 , 2008 ) and its applicability to palliative and end-of-life care research is established ( Goodman et al., 2012 ). Suited to the study of complex processes ( Walshe, 2011 ), case study methodology is embedded in professional guidance on the development of complex interventions ( Medical Research Council, 2008 ). Yet, case study is dogged by conceptual confusion (Flyvberg, 2006), and, despite sporadic use, remains underutilised as a research approach in healthcare settings ( Froggatt et al., 2003 ).
Illustrated by examples from nursing and palliative care studies, this paper aims to clarify conceptual understanding and identify key lessons for its application within these unique and complex contexts and, more broadly, for nursing research.
Origins and definitions
French sociologist Frederic Le Play (1806–1882) is associated with the origin of the case study approach ( Hamel et al., 1993 ). Using a purposive sample of working class families and fieldwork methods of observation and individual interview, he sought a contextualised and in-depth understanding of their individual experiences. Each family case study uncovered the unique experience of that family, but each additional family studied was another ‘ case of the lived experience’ of working class families in mid-18th century France. Thereby, Le Play used the lens of individual experience ( Yin, 2013 ) to build comparisons across families and enrich overall understanding of that complex society.
This early glimpse of the case study approach showed it to be a straightforward ‘field investigation’ ( Hamel et al., 1993 ); epistemologically pragmatic as it generated knowledge through data drawn from diverse sources, such as family members, and used the best available data collection methods then, to inform a holistic and contextualised understanding of how people operated within a complex social system ( Stake, 1995 ).
However, defining case study has become increasingly challenging since its expansion into North America in the 1800s ( Platt, 1992 ), and its use across a range of disciplines such as politics ( Gerring, 2004 ), social science ( George and Bennett, 2005 ), education ( Merriam, 1998 ) and healthcare ( Yin, 2013 ). Variously characterised as a case report, data collection method and methodology ( Anthony and Jack, 2009 ), the development of case histories as illustrations in health and social care and in education ( Merriam, 1998 ) has contributed to further confusion for researchers and readers of case study research ( Gomm et al., 2000 ). Critiques of case study note that it lacks a single definition, such that a plethora of discipline dependant interpretations ( Simons, 2009 ) and loose use of the term case study ( Tight, 2010 ) have contributed to confusion and undermined case study credibility. However, Simons ( 2009 , p. 63) advises researchers that case study must be seen within the complex nexus of political, methodological and epistemological convictions that constitute the field of enquiry, and variations of these may be glimpsed in Table 1 as definitions from four eminent and frequently cited case study authors illustrate philosophical and discipline-influenced differences in emphasis. Consequently, the case study definition selected, with its underpinning ontology and epistemology has important implications for the coherent outworking of the overall research design. It is therefore notable that many of the palliative care case studies contained in Table 2 fail to identify any such definition and this may have implications for interpretation of the quality of studies.
Definitions of case study by four key authors, showing the variation in meaning and interpretation.
Examples of Case Studies (CS) conducted in palliative care contexts.
Case study as a philosophy for the epistemology of knowledge generation
Although frequently linked to naturalistic inquiry ( Lincoln and Guba, 1986 ), interpretative/constructivist philosophy and qualitative methodology ( Stake, 1995 ), case study is not in fact bound to any single research paradigm ( Creswell, 2013 ). It is philosophically pragmatic, such that the case study design should reflect the ontological positions and epistemological considerations of the researchers and their topic of interest ( Luck et al., 2006 ). In practice, this means that case study research may pragmatically employ both qualitative and quantitative methods independently or together in order to respond to the research objectives ( Cooper et al., 2012 ; Simons, 1987 ; Stake, 2006 ). So whilst Table 2 shows that qualitative case studies are common in palliative care, epistemological variation is evident and reflects the study topic, purpose and context of the research. For example, Maddalena et al. (2010) used in-depth interview and discourse analysis to understand individual patient meaning-making; Brogan et al. (2017) used focus groups and thematic analysis as part of an embedded element of a multiple case study, to contrast the diverse perspectives of multi-disciplinary healthcare practitioners on end-of-life decision-making; Sussman et al. (2011) incorporated survey data into a mixed methods multiple case study which explored health system characteristics and quality of care delivery for cancer patients across four regions of Canada. Consequently, it is useful to ‘conceptualise (case study) as an approach to research rather than a methodology in its own right’ ( Rosenberg and Yates, 2007 , p. 448), so that a non-standardised approach exists and the case study design, its boundaries, numbers of cases and methods are guided by the stated underpinning ontological perspectives of the researcher and their topic of interest. The study then flexibly adopts the best methods to gain an in-depth, holistic and contextualised understanding of the phenomenon of interest – the latter objectives being at the core of any definition of case study research.
Key case study concepts and lessons for practice
When considering the utility of a case study approach, research conducted in complex palliative care contexts offers several insights into how central concepts translate to practice.
Contextualised understanding
Drawing on the definitions in Table 1 , Stake emphasised the particularity and intrinsic value of each individual case ( Stake, 1995 ), to emphasise the usefulness of multiple cases to increase insight ( Stake, 2006 ), analyse patterns ( Gerring, 2004 ; George and Bennett, 2005 ) and develop causal hypotheses ( Yin, 2013 ). Yet, whatever the purpose, all case studies are concerned with the crucial relationship between a phenomenon and the environment in which it has occurred. In practice therefore, case study researchers must be concerned with understanding the background systems, structures and processes that influence and interact with the phenomenon under study. This capacity for contextualised and holistic understanding is underpinned by use of multiple data collection methods, such as observation, interview and document review, used simultaneously or sequentially ( Stake, 2006 ; Scholz and Tietje, 2002 ), to mine multiple sources of data, such as participant experience ( Brogan et al., 2017 ; Kaasalainen et al., 2012 ), documents (Lalor et al., 2003) service evaluations ( Walshe et al., 2008 ), and diaries ( Skilbeck and Seymour, 2002 ). This is exemplified in a study by Walshe et al. (2011) , who investigated referral decisions made by community palliative care nurses in the UK, by capturing interview data on the self-reported perspectives of healthcare professionals, in combination with observed team meetings in which decisions were influenced, and review of the written referral policies, protocols and palliative healthcare strategies specific to those decisions. This comprehensive and complex data enabled comparison of decisional processes and their influencing factors both within and across three Primary Care Trusts, thus providing a contemporaneous understanding of the complex relationship between individual nurse's referral decisions and the impact of the organisational and professional systems that underpinned them. Enhancing rigor, such methodological triangulation importantly contributed to the richness of data analysis and the development of assertions which might be drawn from the findings ( Cooper et al., 2012 ; Stake, 2006 ).
Process-focused
Flexible data collection methods, linked to the research purpose, enables case study researchers to gather both historical and real-time data in a variety of ways. For example, Kennedy’s longitudinal case study ( Kennedy, 2002 ) observed snapshots of the initial and follow-up assessment conducted by 11 district nurses over the subsequent 12 months, enabling an exploration of the outcome and impact of their decision-making, demonstrating the usefulness of case study to understand complex roles and processes which are fluid and elusive ( Yin, 2013 ), or otherwise difficult to capture, particularly in the intimate interpersonal contexts where nursing happens.
Analytic frame
Palliative care studies reviewed frequently report the use of thematic analysis. However, whilst this approach is certainly useful to process data generated in qualitative case studies, the approach to analysis must be congruent with the research design and reflect the purpose of the research and methods used. Moreover, beyond decisions about use of thematic analysis or descriptive statistics etc., in case study, important decisions must be made about the analytic frame of the research. Gerring’s definition (2004) set out the analytic frame in which the cases studied might be understood, explaining that each unit of analysis (or case), sheds light on other units (or cases). Thus defined, an individual case offers intrinsically valuable information about a phenomenon ( Stake, 1995 ) and the purposeful selection of cases is central to case study design. This is because, viewed from a certain angle, each case is also a case of something else, such that the findings have broader implications ( Gerring, 2004 ; Simons, 2009 , 1987 ; Yin, 2013 ). In practice, this means that the case and what it is a case of, must be clearly identified and well defined at the outset of a study, since this has implications for the relevance of findings. This can be seen in a study by O’Connor et al., (2011) , who considered the perceived role of community pharmacists in palliative care teams in Australia. Each unique case included multi-disciplinary healthcare team members, such as pharmacists, doctors and nurses working in localities, whose perspectives were sought. Each locality group was a case of community pharmacy provision in palliative care settings in Australia, and findings had implications for the planning of community services overall. So, insight development was possible at an individual, group and organisational level, and inferences were made directly in relation to the parameters of that case study.
The addition of several carefully selected cases, as in multiple case studies, offers the opportunity to analyse data gained within and across cases ( Stake, 2006 ). Case selection may be made in order to explore similarities and contrasting perspectives ( Brogan et al., 2017 ), understand the various impacts of geographical differences ( Sussman et al., 2011 ), and different organisational influences ( Walshe et al., 2008 ). However, whilst repetition of data across cases may reinforce propositions made at the outset of a study, the purpose of increasing the number of cases in case study research is primarily about increasing insight development into the complexity of a phenomenon ( Stake, 2006 ). Since case study is the study of a boundaried phenomenon ( Yin, 2013 ), establishing the analytic frame then underpins the selection criteria for potentially useful cases. Such clarification is essential since it provides the lens through which to focus research ( Gerring, 2004 ; Scholz and Tietje, 2002 ; Stake, 2006 ) and permits key decisions to be made about data which may be included and that which is not applicable.
However, significantly, this information is rarely articulated within published case studies in palliative care. This is an important issue for the quality of case study research, since description of the process of refining case study parameters, establishing clear boundaries of the case, articulating propositions based on existing literature, identifying the sources of data (people, records, policies, etc.) and the ways in which data would be captured, establishes clarity and underpins a rigorous, systematic and comprehensive process ( Gibbert et al., 2008 ), which can usefully contribute to practice and policy development ( George and Bennett, 2005 ).
Shaped by organisational systems, intimate settings and significant life stage contexts, the interconnection between context and participant experience of palliative care is one example of a process of healthcare provision that is often complex, subtle and elusive ( Walshe et al., 2011 ). Case studies conducted in these swiftly changing contexts illustrate several characteristics of case study research, which make it an appropriate methodological option for nurse researchers, providing the opportunity for in-depth, contextualised understanding of the systems and processes which influence their role in palliative care delivery across settings ( Walshe et al., 2004 ) and many others who seek a contextualised, contemporaneous understanding of any complex role or process ( Yin, 2013 ; Simons, 2009 ). This fieldwork-based approach has the potential to achieve depth and breadth of insight through the pragmatic, but carefully planned and articulated, use of multiple methods of data collection in order to answer the research question ( Stake, 2006 ) when analysed systematically within a frame determined at the outset by the definition of the case and its boundaries ( Gerring, 2004 ). Yet, the methodological flexibility that is advantageous in complex contexts, may be misunderstood ( Hammersley, 2012 ), particularly where terminology is unclear ( Lather, 1996 ) or where description of the systematic and rigorous application of the approach is missing from the report ( Morrow, 2005 ). Taken as an example of one area of healthcare research, evidence suggests that palliative care studies that deal meaningfully with underpinning philosophical perspectives for their selected case study approach, or which articulate coherent links between the defined case, its boundaries and the analytical frame are rare. The impact of such omissions may be the perpetuation of confusion and out-dated perceptions about the personality and quality of case study research ( King et al., 1994 ), with implications for its wider adoption by nurses in healthcare research. Further training in case study methodology is required to promote philosophical and conceptual understanding, and to enable researchers to fully articulate, conduct and report case study, to underpin its credibility, relevance and future use ( Hammersley et al., 2000 ; Stake and Turnbull, 1982).
Key points for policy, practice and/or research
- Case study is well suited to nursing research in palliative care contexts, where in-depth understanding of participant experience, complex systems and processes of care within changing contexts is needed.
- Not bound to any single paradigm, nor defined by any methodology, case study’s pragmatism and flexibility makes it useful for studies in palliative care.
- Training is needed in the underpinning philosophical and conceptual basis of case study methodology, in order to articulate, conduct and report credible case study research, and take advantage of the opportunities it offers for the conduct of palliative and end-of-life care research.
Paula Brogan is a Lecturer in counselling and communication in the School of Communication and Media, and was recently appointed as Faculty Partnership Manager, University of Ulster. Dual qualified as a Registered Nurse with specialism in District Nursing and as a Counsellor/couple psychotherapist (Reg MBACPaccred), she has over 30 years’ clinical practice experience in community palliative care nursing and the provision of psychological care to patients and families dealing with palliative and chronic illness. Having worked across statutory, voluntary and private sectors, her PhD focused on multi-disciplinary decision-making at the end of life with patients and families in the community setting. Currently secretary of the Palliative Care Research Forum for Northern Ireland (PCRFNI), Paula’s ongoing research interests include communication and co-constructed decision-making in palliative and chronic illness, and the psychological support of individuals, couples, patient-family groups and multi-disciplinary staff responding to challenges of advanced progressive illness.
Felicity Hasson is a Senior Lecturer in the Institute of Nursing Research at the University of Ulster with 20 years’ experience in research. A social researcher by background, she has extensive experience and knowledge of qualitative, quantitative and mixed method research and has been involved in numerous research studies in palliative and end-of-life care. She completed her MSc in 1996 and her PhD from University of Ulster in 2012. Felicity sits on the Council of Partners for the All Ireland Institute of Hospice and the Palliative Care Palliative Care Research Network (PCRN) and is an executive board member for the UK Palliative Care Research Society. She holds an editorial board position on Futures and Foresight Science. Felicity has an established publication track recorded and successful history of grant applications. Her research interests include nurse and assistant workforce, workforce training, palliative care and chronic illness (malignant and non-malignant with patients, families and multi-disciplinary health care professionals) and public awareness of palliative care and end of life issues.
Sonja McIlfatrick is a Professor in Nursing and Palliative Care and has recently been appointed as the Head of School of Nursing at University of Ulster. She is an experienced clinical academic with experience in nursing and palliative care practice, education and research. She previously worked as the Head of Research for the All Ireland Institute of Hospice and Palliative Care (2011-2014) and led the establishment of the All Ireland Palliative Care Research Network (PCRN) and is the current Chair of the Strategic Scientific Committee for the PCRN (AIIHPC). Sonja is an Executive Board member for the UK, Palliative Care Research Society and is member of the Research Scientific Advisory Committee for Marie Curie, UK. Sonja holds an Editorial Board position on the International Journal of Palliative Nursing and Journal of Research in Nursing. Professor McIlfatrick has published widely in academic and professional journals focused on palliative care research and has a successful history of grant acquisition. Sonja has a keen interest in doctoral education and is the current President of the International Network of Doctoral Education in Nursing (INDEN). Her research interests include, palliative care in chronic illness, decision making at end of life; public awareness of palliative care and psychosocial support for family caregivers affected by advanced disease.
Declaration of conflicting interests
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Ethics statement
Ethical permission was not required for this paper.
The author(s) received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
- Anthony S, Jack S. (2009) Qualitative case-study methodology in nursing research: An integrative review . Journal of Advanced Nursing 65 ( 6 ): 1171–1181. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Brogan P, Hasson F, McIlfatrick S. (2017) Shared decision-making at the end of life: A focus group study exploring the perceptions and experiences of multi-disciplinary healthcare professionals working in a home setting . Palliative Medicine 32 ( 1 ): 123–132. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cooper B, Glaesser J, Gomm R, et al. (2012) Challenging the Qualitative-Quantitative Divide: Explorations in Case-focused Causal Analysis , London: Continuum. [ Google Scholar ]
- Creswell JW. (2013) Qualitative Inquiry and Research Design: Choosing among five approaches , 3rd ed. Thousand Oaks: SAGE. [ Google Scholar ]
- Flyvbjerg B. (2006) Five misunderstandings about case-study research . Qualitative Inquiry 12 ( 2 ): 219–245. [ Google Scholar ]
- Froggatt KA, Field D, Bailey C, et al. (2003) Qualitative research in palliative care 1990–1999: A descriptive review . International Journal of Palliative Nursing 9 ( 3 ): 98–104. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- George AL, Bennett A. (2005) Case Studies and Theory Development in the Social Sciences , Cambridge, MA: MIT Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gerring J. (2004) What is case-study and what is it good for? The American Political Science Review 98 ( 2 ): 341–354. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gibbert M, Ruigrok W, Wicki B. (2008) What passes as rigorous case-study? Strategic Management Journal 29 : 1465–1474. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gomm R, Hammersley M, Foster P. (2000) Case Study Method: Key Issues, Key Texts , London: SAGE. [ Google Scholar ]
- Goodman C, Froggatt KA, Mathie E. (2012) End-of-life Care. Methods Review 12 , London: National Institute for Health Research and School for Social Care Research. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hamel J, Defour S, Fortin D. (1993) Case-study Methods. Qualitative Research Methods Series. 32 , Newbury Park: SAGE. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hammersley M, Foster P, Gomm R. (2000) Case study and generalisation . In: Gomm R, Hammersley M, Foster P. (eds) Case Study Method: Key Issues, Key Texts , London: SAGE, pp. 98–115. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hammersley M. (2012) Troubling theory in case study research . Higher Education Research and Development 31 ( 3 ): 393–405. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kaasalainen S, Ploeg J, McAiney C, et al. (2012) Role of the nurse practitioners in providing palliative care in long-term care homes . International Journal of Palliative Nursing 19 ( 10 ): 477–485. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kennedy C. (2005) District nursing support for patients with cancer requiring palliative care . British Journal of Community Nursing 10 ( 12 ): 566–574. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kennedy C. (2002) The decision-making process in a district nursing assessment . British Journal of Community Nursing 7 ( 10 ): 505–513. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- King G, Keohane RO, Verba S. (1994) Designing Social Inquiry: Scientific Inference in Qualitative Research , Princeton: Princeton University Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lalor JG, Casey D, Elliott N, et al. (2013) Using case-study within a sequential explanatory design to evaluate the impact of specialist and advanced practice roles on clinical outcomes: The SCAPE study . BMC Medical Research Methodology 13 ( 1 ): 55. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lather P. (1996) Troubling clarity: The politics of accessible language . Harvard Educational Review 66 ( 3 ): 525–554. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lincoln YS, Guba EG. (1986) But is it rigorous? Trustworthiness and authenticity in naturalistic evaluation . In: Williams DD. (eds) Naturalistic Evaluation , San Francisco: Josey-Bass, pp. 73–84. [ Google Scholar ]
- Luck L, Jackson D, Usher K. (2006) Case-study: A bridge across paradigms . Nursing Inquiry 13 ( 2 ): 103–109. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Maddalena VJ, Bernard WT, Etowa J, et al. (2010) Cancer care experiences and the use of complementary and alternative medicine at the end-of-life in Nova Scotia’s black communities . J Transcultural Nursing 21 ( 2 ): 114–122. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Medical Research Council (2008) Complex Interventions Guidance, www.mrc.ac.uk/complexinterventionsguidance (accessed 14 March 2014).
- Merriam SB. (1998) Qualitative research and case-study applications in education , San Francisco: Jossey-Bass. [ Google Scholar ]
- Morrow SL. (2005) Quality and trustworthiness in qualitative research in counselling psychology . Journal of Counseling Psychology 52 ( 2 ): 256–260. [ Google Scholar ]
- O’Connor M, Fisher C, French L, et al. (2011) Exploring the community pharmacist’s role in palliative care: Focusing on the person not just the prescription . Patient Education and Counseling 83 : 458–464. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Payne S, Field D, Rolls L, et al. (2006) Case-study research methods in end-of-life care: Reflections on three studies . Journal of Advanced Nursing 58 ( 3 ): 236–245. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Platt J. (1992) Case study in American methodological thought . Current Sociology 40 ( 1 ): 17–48. [ Google Scholar ]
- Rosenberg JP, Yates PM. (2007) Schematic representation of case-study research designs . Journal of Advanced Nursing 60 ( 4 ): 447–452. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Scholz RW, Tietje O. (2002) Embedded Case Study Methods: Integrating Quantitative and Qualitative Knowledge , Los Angeles: SAGE. [ Google Scholar ]
- Simons H. (1987) The paradox of case-study . Cambridge Journal of Education 26 ( 2 ): 225–240. [ Google Scholar ]
- Simons H. (2009) Case-study Research in Practice , Thousand Oaks: SAGE. [ Google Scholar ]
- Skilbeck J, Seymour J. (2002) Meeting complex needs: And analysis of Macmillan nurses’ work with patients . International Journal of Palliative Nursing 8 ( 12 ): 574–582. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Stake RE. (1995) The Art of Case-study Research , Thousand Oaks: SAGE. [ Google Scholar ]
- Stake RE, Trumbull DJ. (1987) Naturalistic generalizations . Review Journal of Philosophy and Social Science 7 : 1–12. [ Google Scholar ]
- Stake RE. (2006) Multiple case-study analysis , New York: The Guilford Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sussman J, Barbera L, Bainbridge D, et al. (2011) Health system characteristics and quality of care delivery: A comparative case-study examination of palliative care for cancer patients in four regions in Ontario, Canada . Palliative Medecine 26 ( 4 ): 322–335. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tight M. (2010) The curious case of case study: A viewpoint . International Journal of Social Research Methodology 13 ( 4 ): 329–339. [ Google Scholar ]
- Walshe C. (2011) The evaluation of complex interventions in palliative care: An exploration of the potential of case-study . Palliative Medicine 25 ( 8 ): 774–781. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Walshe C, Chew-Graham C, Todd C, et al. (2008) What influences referrals within community palliative care services? A qualitative case-study . Social Science and Medicine 6 : 137–146. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Walshe CE, Caress AL, Chew-Graham C, et al. (2004) Case studies: A research strategy appropriate for palliative care?’ . Palliative Medicine 18 : 677–684. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yin RK. (2013) Case-study Research: Design and Methods (Applied Social Research Methods) , Newbury Park: SAGE. [ Google Scholar ]
- Yin RK. (2009) Case-study Research: Design and Methods , 4th ed. Newbury Park: SAGE. [ Google Scholar ]
Connect on WhatsApp: +91 74786 38563 , Uninterrupted Access, 24x7 Availability, 100% Confidential. Connect Now
Writing Tips
A comprehensive nursing case study writing guide.

Aug. 4, 2023 • 7 min read

Nursing Case Study Writing Step-By-Step Guide
Nursing case studies play a vital role in the education and training of aspiring nurses in the USA, UK, UAE, and Canada. These real-life scenarios provide students with a unique opportunity to apply theoretical knowledge to practical situations, enhancing their critical thinking, clinical reasoning, and decision-making skills. In this guide, we'll walk you through the essential steps to creating effective and insightful nursing case studies that meet the academic standards of these countries.
1. Choosing a Relevant Case
The foundation of a successful nursing case study is the selection of an appropriate case. Look for scenarios that align with your course's learning objectives and reflect the wide range of healthcare challenges that nurses may face. Select cases involving ethical quandaries, complex patient interactions, or situations requiring interdisciplinary collaboration.
2. Gathering Information
Thorough research is key to crafting a detailed and accurate nursing case study. Collect data from reputable sources such as medical journals, textbooks, and evidence-based practice guidelines. Ensure that the patient's medical history, current condition, and relevant clinical data are well-documented. Protect patient confidentiality by de-identifying information.
3. Setting the Stage
Introduce the case by providing basic details on the patient, the healthcare setting, and any other relevant information. Describe the patient's demographics, medical history, current symptoms, and reason for seeking medical help. This establishes the context for readers to comprehend the situation and its significance.
4. Clinical Assessment
Detail the nursing assessment process, including physical examinations, diagnostic tests, and the collection of subjective and objective data. Highlight the nurse's role in observing, interviewing, and evaluating the patient's condition. Discuss the data collected and its implications for the patient's care.
5. Diagnosis and Planning
Based on the assessment, outline the nursing diagnoses and collaborative problems. Clearly explain the rationale behind each diagnosis and present a well-reasoned plan of care. Discuss short-term and long-term goals, potential interventions, and the expected outcomes of nursing interventions.
6. Implementation and Evaluation
Describe how the nursing care plan was executed and the interventions that were implemented. Include details about the nurse's interactions with the patient, families, and other healthcare team members. Evaluate the effectiveness of the interventions, discussing any changes in the patient's condition, responses to treatment, and unexpected challenges.
7. Reflection and Learning
Encourage critical thinking by incorporating a reflection section. Invite students to analyze the case, consider alternative approaches, and reflect on what they have learned from the experience. Discuss the ethical, cultural, and emotional aspects of the case, promoting a holistic understanding of patient care.

8. References and Citations
Maintain academic integrity by properly citing all sources used in your case study. Follow the appropriate citation style (such as APA, MLA, or Chicago) as required by your institution.
Writing nursing case studies is an essential skill for nursing students in the USA, UK, and Canada. Through these case studies, students can bridge the gap between theory and practice, preparing them for the complex and dynamic healthcare environments they will encounter in their careers. By carefully selecting cases, conducting thorough research, and presenting well-structured and reflective analyses, nursing students can create case studies that not only meet academic standards but also contribute to their growth as competent and compassionate healthcare professionals.
Our platform has been giving quality services to our students from the very beginning, all thanks to our highly-trained and professional Nursing case study helpers, who complete every task with utmost sincerity and dedication by applying all their knowledge to your projects so that you can raise your head confidently while presenting in front of your class. TutorGenix has always been ranked as the Best Nursing Case Study help in the USA, the UK, Canada, and the UAE. Our Nursing project writers will complete your academic reports, essays, homework, and whatnot, so just order us and we will help with everything we’ve got. You will get instant solutions for nursing homeworks or any other subject homework you need help with, as we have 24/7 available tutors.
Stuck With Your Homework? Get Your Homework Done From Our Expert Writers
Is there any desired work length (in words)?
No. of pages (1 page = 250 words)
Fill Your Mobile Number & Get 5$
I accept the T&C and other policies of the website and agree to receive offers and updates.
Useful Links:
- Homework Help
- Assignment Help
- Live Session Help
- Lab Report Writing
- Project Report Writing
- PowerPoint Presentation
- Case Study Writing
- Essay Writing
- Coursework Writing
Related Articles

How to Write a Freedom Essay in 9 Steps
June 23, 2023 • 10 min read

What are the 4 types of sentences?
June 13, 2023 • 10 min read

How to write a Lab Report?
Nov. 28, 2022 • 10 min read
How to Write a Nursing Case Study [Examples, Format, & Tips]
✒️ case study topics for nursing students.
- 🩺️ The Basics
- 💉 Nursing Case Study: Writing Rules
📑 Nursing Case Study Format
📝 nursing case study examples.
- ⏱️ Tips on Quick Writing
🔗 References
A nursing case study is an in-depth analysis of the health situation of an individual patient.

The analysis is based on:
- medical history,
- other relevant criteria.
In most cases, you will be asked to diagnose to suggest the first aid measures. Alternatively, nurses can be asked to describe a patient in their practice and analyze the correctness of their actions. The purpose is to recreate a realistic hospital setting in the classroom and make students reflect on the treatment process from diagnosis to treatment.
- Anaphylactic shock in a teenager with peanut allergy.
- Non-compliant patient with diabetes: ways to improve adherence.
- Telehealth intervention for managing chronic disease.
- Communication strategies to address vaccine hesitancy in a rural community.
- Postpartum hemorrhage in a new mother: risk factors and interventions.
- Ways to improve recognition of dehydration in aging adults.
- The effective ways of maintaining work-life balance for nurses.
- Cultural competency in providing care to migrants and refugees.
- Why should every patient’s medical history remain confidential?
- The use of massage therapy in relieving pain.
- The challenges facing medicine in 2024.
- How does modern technology impact nursing?
- The significance of regular follow-up appointments with the healthcare provider.
- What are the primary treatments for postpartum depression?
- The use of steroids in cancer treatment.
🩺️ Nursing Case Study: What Is It About?
As a nursing student, you should understand that no two patients are the same. Each has a unique clinical record and condition. And although most nursing case study tasks will ask you to suggest a diagnosis or treatment, your focus should rest on the patient.
Busy nurses can sometimes see their patients in the framework of an illness to be treated or a procedure to be fulfilled. But you should do your best to remember that each patient is a living person with a complex set of needs, emotions, and preferences. A ready-made textbook answer is rarely the best solution for them. Moreover, it rarely helps to analyze a condition in isolation from the patient.
In a nursing case study, your task is to analyze a disorder or illness as a part of a specific medical situation. If you don’t do that, your case study becomes an essay (theoretical and generalized). It is the difference between the two assignment types.
Once again:
A case study in nursing emphasizes the particular patient’s condition. Meanwhile, a nursing essay will explore the disease, prevention methods, treatment, or possible consequences of the disease.
Even if the case is hypothetical, it should focus on the suggested reality. On the other hand, essays are usually literature-based. You are expected to do some reading for a case study too, but you should research and present the information within the context of the patient. In simple terms, a case study uses information in the actual application, and an essay uses it for the sake of generalized suggestions.
💉 How to Write a Nursing Case Study: 3 Key Rules
- Do the fieldwork. Before setting your hands to writing, you should collect all of the available materials: clinical notes, results of medical tests, x-rays, sickness records, etc. Use this information to draw a clear picture of the story. It is always helpful to ask yourself, “What is interesting or unusual about this patient’s condition?” In the course of writing, recall your answer from time to time not to get lost in words. It will help you to convey a definite and appropriate message.
- Stick to the facts. A nursing case study should be an accurate description of the actual situation. Restrain from speculating about the inherent mechanisms of the illness or the general treatment methodology. In fact, students are rarely prepared enough to discuss pathology and physiology. Leave this to reputable experts. The best result you can provide in a case study is an honest account of clinical events.
- Concentrate on the patients and their progress. Remember that a nursing case study is a story of a patient’s progress and not a narrative about their nurse. No matter how efficiently the medical specialist acted, it would be incorrect to add any praiseful remarks. The optimal way is to tell the story in its logical and time order and outline the result of treatment. In this case, the outcome will speak for itself.
Introduction
It is where you should tell the reader why this case is interesting . Place your study in a social or historical context. If, during your preliminary research, you found some similar cases, describe them briefly. If you had a hard time diagnosing the patient or your proposed treatment is complicated, mention it here. Don’t forget to cite the references to each of them!
The introduction should not exceed several paragraphs. The purpose is to explain why the reader will benefit from reading about the case.

Case Presentation
- Why did the patient seek medical help? (Describe the symptoms.)
- What is known about the patient? (Mention only the information that influenced your diagnosis. Otherwise, explain why some information is irrelevant to the diagnosis.)
- Stick to the narrative form. (Make it a story!)
- What are the variants for diagnosis? (Make a shortlist of possible disorders that fall under the patient’s symptoms. But make it specific: not just “pneumonia” but “bilateral pneumonia,” for example. Besides, this point is optional.)
- What were the results of your clinical examination? (If you saw the patient in person.)
- Explain the results of lab tests. (The words “positive” or “negative” are not always clear.)
Actions and Their Results
This section describes the care that has been provided and/or is planned. You can answer the following questions in narrative form . If some information is missing, skip the point:
- What preliminary actions have been taken? (Be specific: not just “wound care,” but “wound cleaning and dressing.”)
- How long has the patient been under care?
- Has the previous treatment given any visible result?
- Why was it suspended or finished?
- Why did the patient withdraw from treatment (if applicable)?
- How could you improve the patient’s condition if the result was negative?
- If the disease is incurable (like in the case of diabetes), which activities would stabilize the patient’s condition?
- If possible, include the patient’s reports of their own physical and mental health.
In this section, you should identify your questions about the case. It is impossible to answer all of them in one case study. Likewise, it is unreal to suggest all the relevant hypotheses explaining the patient’s condition. Your purpose is to show your critical thinking and observation skills. Finalize your conclusion by summarizing the lessons you learned from the nursing case study.
Whenever you directly or indirectly cite other sources or use data from them, add these books and documents to the references list. Follow the citation style assigned by your professor. Besides, 15 items are already too much. Try to make a list of up to 10. Using textbooks as references can be viewed as bad manners.
Include all the tables, photographs, x-rays, figures, and the journal of medication usage in this section. Unless required otherwise in the assignment, start each item from a new page, naming them “Appendix A,” “Appendix B…”.
Below you will find case study samples for various topics. Using them as a reference will improve your writing. If you need more ideas, you are welcome to use our free title-generating tool .
- Case study: healing and autonomy.
- Sara’s case study: maternal and child nursing.
- COPD medical diagnostics: case study.
- Care standards in healthcare institutions: case study.
- Acute bacterial prostatitis: case study analysis.
- Alzheimer disease: the patient case study.
- The treatment of foot ulcers in diabetic patients: case study.
- Hypertension: C.D’s case study.
- Myocardial infarction: cardiovascular case study.
- Major depressive disorder case.
- Case study of the patient with metabolic syndrome .
- Pulmonary analysis case study .
- Older adults isolation: Case study .
- The holistic care: Case study .
- Obesity in the Elderly: The Case Study.
- Medical ethics: Case study .
- Patient diagnoses and treatment: Case study .
- Obesity case study: Mr. C .
- Nurse Joserine: Case study problems .
- Chronic stable angina: Case study .
- Fetal abnormality: Case study .
- Researching SOAP: Case study .
- Case study for a patient with hormonal disorders .
- “Walking the Tightrope”: A case study analysis .
- ARNP approach: Case study analysis .
- Case study on biomedical ethics in the Christian narrative .
- Thermal injury: Case study .
- Ethical dilemma in nursing: Case study .
- Asthma: A case study of the patient .
- Asthma discharge plan: Mini case study .
- Case study: An ethics of euthanasia .
- Case study: Head-to-toe assessment steps .
- Pain management strategies: Case study .
- Case study: Inflammatory bowel disease .
- Sleep deprivation and insomnia: The case study .
- The case study of a heart failure .
- Porphyria cutanea tarda: Disease case study .
- Case study: Hardy Hospital case summary .
- Obesity and its complications: Case study .
- Angina disease case study .
- Nursing ethics case study .
- Case study of a patient: Assessment and treatment plan .
- Cecile case study: Mrs. J .
- Nursing power in the emergency department: Case study .
- Heart failure case study: Mrs. J .
- Application of ethics in nursing: Case study .
- Sudden visual impairment: Case study .
- Epidemiology case study: Outbreak at Watersedge — Public health discovery game .
- Wellness of senior citizens: Case study .
- Healthcare organization evaluation: Case study of Banner Health .
⏱️ Bonus: Tips on Writing a Case Study in Record Time
Need to prepare a case study on nursing or in another field? Below you’ll find a collection fo tips that will help you do it as quickly as possible!
3 Shortcuts for a Quick Start
If you’re about to start writing a case study, you should check yourself if you’re not doing any of the following:
- spending too much time on selecting a topic;
- reading too much before selecting a topic;
- making conclusions too early – creating bias.
Instead of killing time doing the three useless things discussed above, consider these:
- Choose approach. Note that there are 2 major approaches to case studies: the analytical approach (investigating possible reasons without making any conclusions) and problem-oriented approach (focusing on a particular problem and investigating it).
- Skim some sources (DON’T READ THEM). Select several sources. Simply skim abstracts and conclusions.
- Start making notes early. Simply reading is ineffective unless you’re lucky to have a phenomenal memory. Always make notes of any useful arguments.
4 Shortcuts Not to Get Stuck in the Middle
Even if you kick started your case study, it’s too early to celebrate it. Consider the following traps in the middle of the project:
- Watch the structure. The classic logical structure is your formula of success. It will help you move from one point to another without the unnecessary procrastination:
- Respect the logic. Make your case study flow – make logical transitions between the different parts and make it consistent. Avoid changing your position throughout the paper.
- Be detail-oriented. Any trifle deserves attention when you write a case study.
- Avoid bias. Be sure that all your opinions are based on the specific arguments form the case study. Avoid pouring your biased views into the project.
3 Shortcuts for a Happy Ending
- Offer a realistic solution. College case study is a rehearsal of real-life situations. Take the responsibility for your suggestions.
- Keep your conclusion short. Avoid repeating the details and don’t include any new information.
- Consider creating a Power Point. If your task is not only writing a case study, but also presenting it – why not create PowerPoint slides to help you?
As the last step on your way to a perfect nursing case study, prepare the title page. Its format usually depends on the professor’s requirements. But if you know the citation style, our Title Page Maker is a perfect tool to apply the right formatting and accelerate the process. And if you have any know-how on how to write a medical case study, you are very welcome to share it with other students in the comments below.
❓ Nursing Case Study: FAQ
What is a case study in nursing.
A nursing case study explores the condition of a patient. It is based on previous clinical records, lab reports, and other medical and personal information. A case study focuses on the patient and describes the treatment that was (or should be) applied and its (expected) outcome.
How to Write a Nursing Case Study?
- Collect the bulk of data available about the patient.
- Read literature about the diagnosed condition.
- Focus on the individual patient and their symptoms.
- Describe the situation and outline its development in time.
- Analyze the actions of the medical personnel that have been done.
- Plan further treatment of the patient.
Why Are Case Studies Good for Nursing Students?
Nursing case studies offer you a priceless opportunity to gain experience of different patient conditions and cure methods without visiting the clinic. You can think about whether the proposed treatment was appropriate or wrong and suggest a better solution. And the best thing, your teacher will indicate your mistakes (and no patient will be hurt in the process).
Why Are Case Studies Important in Nursing?
- You learn to distinguish the relevant data and analyze it.
- You learn to ask the right questions.
- You learn to evaluate the severity of symptoms.
- You learn to make better diagnoses.
- You train your critical thinking in terms of treatment methods
- Case studies are in-class simulators of authentic atmosphere in a clinical ward.
- What is a case study? | Evidence-Based Nursing
- Case Studies – Johns Hopkins Medicine
- Case Study Research Design in Nursing
- Case study report for Nursing | Learning Lab – RMIT University
- Case Study or Nursing Care Study? – jstor
Research Paper Analysis: How to Analyze a Research Article + Example
Film analysis: example, format, and outline + topics & prompts.
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Book Title: Nursing Case Studies by and for Student Nurses
Author: jaimehannans

Book Information
Nursing Case Studies by and for Student Nurses Copyright © by jaimehannans is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
- RMIT Australia
- RMIT Europe
- RMIT Vietnam
- RMIT Global
- RMIT Online
- Alumni & Giving

- What will I do?
- What will I need?
- Who will help me?
- About the institution
- New to university?
- Studying efficiently
- Time management
- Mind mapping
- Note-taking
- Reading skills
- Argument analysis
- Preparing for assessment
- Critical thinking and argument analysis
- Online learning skills
- Starting my first assignment
- Researching your assignment
- What is referencing?
- Understanding citations
- When referencing isn't needed
- Paraphrasing
- Summarising
- Synthesising
- Integrating ideas with reporting words
- Referencing with Easy Cite
- Getting help with referencing
- Acting with academic integrity
- Artificial intelligence tools
- Understanding your audience
- Writing for coursework
- Literature review
- Academic style
- Writing for the workplace
- Spelling tips
- Writing paragraphs
- Writing sentences
- Academic word lists
- Annotated bibliographies
- Artist statement
- Case studies
- Creating effective poster presentations
- Essays, Reports, Reflective Writing
- Law assessments
- Oral presentations
- Reflective writing
- Art and design
- Critical thinking
- Maths and statistics
- Sustainability
- Educators' guide
- Learning Lab content in context
- Latest updates
- Students Alumni & Giving Staff Library
Learning Lab
Getting started at uni, study skills, referencing.
- When referencing isn't needed
- Integrating ideas
Writing and assessments
- Critical reading
- Poster presentations
- Postgraduate report writing
Subject areas
For educators.
- Educators' guide
- Case study report for nursing
Part 1: What is it and why?
This video introduces the concept of the case study and identifies how case studies differ to other written assignments.
The most important thing in writing up a case study report is that first, second, and thirdly: It is about the patient, not the condition nor the treatment. Students often put the emphasis on the condition or the treatment because the question usually focuses on this. While you need to explore these things, you still have to bring it back to the patient, and keep the patient central to the whole assignment.
We can understand if busy medical professionals start to see their patients in terms of a condition to be fixed, or a procedure to be performed. But ideally, we should remember that a patient is a person with a complex array of needs and preferences. This means that a simple textbook answer is not always best for them.
In your career, you will need to negotiate adjustments and anticipate problems particular to the patient. It does not make sense to discuss a condition in isolation from the individual. Each patient has their own unique kaleidoscope of history, personality type, fears, medical challenges, needs during recovery, so forth and so on. You need to see their condition or their treatment overall, as part of the whole person. Writing a case study teaches you to do that, if you don’t explore the condition or treatment as part of a holistic system, you case study becomes theoretical, it becomes another essay.
Let’s compare the case study to the essays you might have already written. The case study in nursing explores a particular patient’s situation, while your essays will more likely have focused on disease, a treatment, a concept, or a system. A case study is very grounded in the real and the now, even if the patient is a hypothetical invention. It still provides some fairly authentic experience with dealing with an individual patient.
Essays, on the other hand, tend to be literature-based. Of course, you need to do a lot of research and reading for your case study too, but the difference is for a case study you must always view and evaluate the information in the context of your patient. So in a case study, you need to show that you can find and apply information to you patient. For an essay you need to look at the information itself, pull it apart and evaluate it for its own sake.
So even if the question looks like an essay, don’t be distracted. There is still an expectation to relate this to the patient. It is possible to explore the content and theory in a generalised way throughout the assignment, but the beginning of the assignment (and the beginning of each paragraph, in fact) should foreground you're patient and their relationship to this theory.
Part 2: Research and writing
This video provides tips on how to research and structure paragraphs in order to keep a patient centred emphasis in the writing.
An essay, as opposed to a case study, usually has an question or a thesis which defines the boundaries of what you research, You aim to keep it within those parameters. and you delve as deeply as you can into the material. It loses focus if you include stuff outside of the topic.
With a case study, however, your focus is the patient so you need to cast your net widely and generously at first to find something that is relevant to them. And then when you find something relevant, you need to research deeply. So, doing a good case study report involves a lot more reading than you might think. You’ll have to research both generally and deeply.
There can be a lot of research, and fairly unguided research involved in a case study. Don’t assume it’s like a reading comprehension exercise, the problems are not always clearly defined and the solutions have not necessarily been covered in lectures. Think of your case study as a mystery puzzle with a few clues scattered through it.
In reality, patients do not arrive with instructions, so it’s up to the professional to notice that it is obvious and to think outside of the box. It is up to you to anticipate problems for the patient, it is up to you to follow through with the threads of any clues, and to see if they offer any valuable information, and these may only be hinted at indirectly. With years of nursing experience, the clues and danger signs get easier to spot, but it is very challenging for a beginner if you don’t know what to look for, and that is why the broad reading is important.
So, every piece of information about your patient is valuable. When the information is given in the assignment, the facts are not random facts, they have usually been included for a reason, so use them and use them as much as you can. You may, on the other hand, have been told very little in the assignment and be expected to elicit the information yourself from the patient, through a blog, or a question-and-answer session. Asking for more details about their own condition just gives you more details about their condition, and unless you have some reasoning in mind for asking about that, more details per se is usually not that very helpful.
Instead, ask about things that may affect the treatment or recovery; ask about things that may complicate matters. Smoking, relevant illnesses, lack of family support, strenuous lifestyles or jobs are all factors that may generate important decisions about how the patient is treated or cared for. The secret to keeping it about the patient is to keep them foremost into the discussion. You do this by making them the subject of each paragraph, and you do this by making them feature in the topic sentence: at the beginning and, if possible, a summary sentence at the end.
In the middle of a paragraph, you have more flexibility to talk about the procedure or the condition in a more general way. But, at the end of the day, you need to remind us of how this is important for your patient. If you don’t, your writing becomes an essay rather than a case study. And if you feel like you’re being asked to research and to discuss material that is not directly relevant to your patient, you can make it relevant by at least explaining why it is not relevant. Remember, everything you write about should be in relation to your patient.
So remember, it is all about the patient, keep everything relevant to the patient; keep the patient in mind throughout the research and the writing. Explore and discuss what the question requires, but theory for the sake of theory should be avoided. Your mission is to find the best solutions available for your patient, and develop the best understanding that you can of your patient.
You have now complete the Case Study module. We hope you have enjoyed the content. For more study skill resources, please visit the RMIT Learning Lab.
- Writing a case study
Still can't find what you need?
The RMIT University Library provides study support , one-on-one consultations and peer mentoring to RMIT students.
- Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Twitter (opens in a new window)
- Instagram (opens in a new window)
- Linkedin (opens in a new window)
- YouTube (opens in a new window)
- Weibo (opens in a new window)
- Copyright © 2024 RMIT University |
- Accessibility |
- Learning Lab feedback |
- Complaints |
- ABN 49 781 030 034 |
- CRICOS provider number: 00122A |
- RTO Code: 3046 |
- Open Universities Australia
- AI Content Shield
- AI KW Research
- AI Assistant
- SEO Optimizer
- AI KW Clustering
- Customer reviews
- The NLO Revolution
- Press Center
- Help Center
- Content Resources
- Facebook Group
How to Write a Thorough Nursing Case Study
Table of Contents
Case studies are common requirements for nursing schools and healthcare institutions. But learning how to write a nursing case study can be challenging. If you’re stuck on how to get started, we’ve got your back! In this article, we’ll be guiding you through all the necessary elements you should include ensuring your study is clear and thorough. We’ll also share some key tips to make your work more professional. When done right, a case study can enhance your knowledge base and help identify better healthcare practices. And this can greatly improve overall healthcare standards.
What is a Nursing Case Study?
A nursing case study is a detailed assessment of a patient’s medical history, diagnosis, and treatment . It seeks to identify the causes of an illness or injury and analyze how they have been addressed. This helps assess the overall quality of care given. These case studies aim to understand the cause of certain illnesses, how to prevent them, and how to best treat them. The data gathered from these studies can inform policy changes and develop effective strategies for improving patient outcomes.

How to Write a Nursing Case Study
Writing a nursing case study requires thoughtful consideration of relevant information and resources. You must select a single subject, conduct research on it, interview experts, analyze the data collected, and present your findings. That may seem like a lot, but let us break it down for you. Here’s a look at the key elements that your case study structure should cover:
A title page should be concise yet informative, helping readers understand what the focus of the study is. It includes the following elements:
- Title of the case study
- Author’s name
- Any collaborators or contributors to the work
- An abstract summarizing the contents
An abstract is a summary of the content of the case study, which outlines its purpose, methods used, results, and conclusions. It aims to provide readers with a clear overview of the studied topic without reading through the entire document.
Introduction
The introduction sets the stage for the case study by introducing the main subject and providing background information. It should include the research question(s) or hypothesis that will guide the investigation.
Case Presentation
Your case presentation needs to include as much relevant detail as possible while maintaining clarity and brevity. It details the following:
- Patient’s history
- Physical exam findings
- Laboratory values
- Imaging studies
- Treatments received
- Clinical course
Pathophysiology
Pathophysiology discusses how diseases affect normal body processes and functions. Try to explain the pathology behind the observed symptoms to understand how they can be managed. This may involve discussing anatomy, physiology, biochemistry, genetics, pharmacology, immunology, and pathogenesis.
Nursing Care Plan
A nursing care plan should provide an overview of the patient’s current condition, including any pre-existing medical conditions. It should also outline the desired goals for the patient’s health, such as stabilizing vital signs or reducing pain levels. The plan will usually include a list of interventions to be carried out by nurses. It can also outline monitoring steps to evaluate whether these interventions are effective in achieving the desired outcomes.
Discussion and Recommendations
This section provides an opportunity to discuss any issues or suggestions related to the patient’s case study. Experienced professionals can provide valuable input regarding the best strategies to improve the treatment outcome.
The conclusion is where you can summarize all the findings from the study and provide your final thoughts regarding the results. It should draw attention to any successes achieved during the investigation and identify areas for improvement. Your conclusion should also make clear how the results relate to the overall objective of providing quality care for the patient.
The references section is where sources used throughout the case study are listed. These may include textbooks, reports, journal entries, and other forms of documentation that were consulted for the project. All entries must adhere to proper citation standards (e.g., APA style) and appear alphabetically according to the author’s name.
Final Words
Learning how to write a nursing case study has far more applications than just fulfilling a course requirement. These case studies can be invaluable tools in advocating for improved healthcare for individuals and communities. Hopefully, this quick guide has helped you better understand how to write a more comprehensive and clearer work. Good luck!

Abir Ghenaiet
Abir is a data analyst and researcher. Among her interests are artificial intelligence, machine learning, and natural language processing. As a humanitarian and educator, she actively supports women in tech and promotes diversity.
Explore All Write A Case Study Articles
How to write a leadership case study (sample) .
Writing a case study isn’t as straightforward as writing essays. But it has proven to be an effective way of…
- Write A Case Study
Top 5 Online Expert Case Study Writing Services
It’s a few hours to your deadline — and your case study college assignment is still a mystery to you.…
Examples Of Business Case Study In Research
A business case study can prevent an imminent mistake in business. How? It’s an effective teaching technique that teaches students…
How to Write a Multiple Case Study Effectively
Have you ever been assigned to write a multiple case study but don’t know where to begin? Are you intimidated…
How to Write a Case Study Presentation: 6 Key Steps
Case studies are an essential element of the business world. Understanding how to write a case study presentation will give…
How to Write a Case Study for Your Portfolio
Are you ready to showcase your design skills and move your career to the next level? Crafting a compelling case…
- Reviews / Why join our community?
- For companies
- Frequently asked questions

How to write the conclusion of your case study
You worked on an amazing UX project. You documented every detail and deliverable and when the time came, you began to write a UX case study about it. In the case study, you highlighted how you worked through a Design Thinking process to get to the end result; so, can you stop there and now move on to the next thing? Well, no! There’s just one more bit left to finish up and make the perfect case study. So, get ready; we will now explore how you can write the perfect conclusion to wrap it all up and leave a lasting great impression.
Every start has an end – we’re not just repeating the famous quote here, because for case studies, a proper end is your last and final chance to leave a lasting great (at the very least, good) impression with whoever is reading your work (typically, recruiters!). Many junior UX designers often forget about the conclusion part of the case study, but this is a costly mistake to make. A well-written case study must end with an appropriate final section, in which you should summarize the key takeaways that you want others to remember about you and your work. Let’s see why.
Last impressions are just as important as first ones
We’ll go to some length here to convince you about the importance of last impressions, especially as we can understand the reason behind not wanting to pay very much attention to the end of your case study, after all the hard work you put into writing the process section. You are tired, and anyone who’s read your work should already have a good idea about your skills, anyway. Surely—you could be forgiven for thinking, at least—all that awesome material you put in the start and middle sections must have built up the momentum to take your work into orbit and make the recruiter’s last impression of you a lasting—and very good—one, and all you need to do now is take your leave. However, psychologist Saul McLeod (2008) explains how early work by experimental psychology pioneers Atkinson & Shriffin (1968) demonstrated that when humans are presented with information, they tend to remember the first and last elements and are more likely to forget the middle ones.
This is known as the “ serial position effect ” (more technically, the tendency to remember the first elements is known as the “ primacy effect ”, while the tendency to remember the last elements is known as the “ recency effect ”). Further work in human experiences discovered that the last few things we see or hear at the end of an experience can generate the most powerful memories that come back to us when we come across a situation or when we think about it. For example, let’s say you stayed in a hotel room that left a bit to be desired. Maybe the room was a little cramped, or the towels were not so soft. But if the receptionist, as you leave, shakes your hand warmly, smiles and thanks you sincerely for your custom, and goes out of his way to help you with your luggage, or to get you a taxi, you will remember that person’s kind demeanor more than you will remember the fact that the room facilities could be improved.
A good ending to your case study can help people forget some of the not-so-good points about your case study middle. For example, if you missed out a few crucial details but can demonstrate some truly interesting takeaways, they can always just ask you about these in an interview. Inversely, a bad ending leaves the recruiter with some doubt that will linger. Did this person learn nothing interesting from all this work? Did their work have no impact at all? Did they even write the case study themselves? A bad last impression can certainly undo much of the hard work you’ve put into writing the complicated middle part of your case study.
What to put in your case study conclusions
A case study ending is your opportunity to bring some closure to the story that you are writing. So, you can use it to mention the status of the project (e.g., is it ongoing or has it ended?) and then to demonstrate the impact that your work has had. By presenting some quantifiable results (e.g., data from end evaluations, analytics, key performance indicators ), you can demonstrate this impact. You can also discuss what you learned from this project, making you wiser than the next applicant – for example, something about a special category of users that the company might be interested in developing products for, or something that is cutting-edge and that advances the frontiers of science or practice.
As you can see, there are a few good ways in which you can end your case study. Next, we will outline four options that can be part of your ending: lessons learned, the impact of the project, reflections, and acknowledgements.
Lessons learned
A recruiter wants to see how you improve yourself by learning from the projects you work on. You can discuss interesting insights that you learned from user research or the evaluation of your designs – for example, surprising behaviors that you found out about the technology use in a group of users who are not typically considered to be big proponents of technology (e.g., older adults), or, perhaps, the reasons a particular design pattern didn’t work as well as expected under the context of your project.
Another thing you can discuss is your opinion on what the most difficult challenge of the project was, and comment on how you managed to overcome it. You can also discuss here things that you found out about yourself as a professional – for example, that you enjoyed taking on a UX role that you didn’t have previous experience with, or that you were able to overcome some personal limitations or build on your existing skills in a new way.
Impact of the project
Showing impact is always good. How did you measure the impact of your work? By using analytics, evaluation results, and even testimonials from your customers or users, or even your development or marketing team, you can demonstrate that your methodical approach to work brought about some positive change. Use before-after comparison data to demonstrate the extent of your impact. Verbatim positive quotes from your users or other project stakeholders are worth their weight (or rather, sentence length) in gold. Don’t go overboard, but mix and match the best evidence for the quality of your work to keep the end section brief and to the point.

Copyright holder: Andreas Komninos, Interaction Design Foundation. Copyright terms and license: CC BY-SA 3.0
User reviews from app stores are a great source of obtaining testimonials to include in your case studies. Overall app ratings and download volumes are also great bits of information to show impact.

An excerpt from a case study ending section. Here, text and accompanying charts are used to demonstrate the impact of the work done by the UX professional.
Reflections on your experiences
You can include some information that shows you have a clear understanding of how further work can build on the success of what you’ve already done. This demonstrates forward thinking and exploratory desire. Something else you can reflect on is your choices during the project. In every project, there might be things you could do differently or improve upon. But be aware that the natural question that follows such statements is this: “Well, so why haven’t you done it?”
Don’t shoot yourself in the foot by listing all the things you wish you could have done, but focus on what you’ve actually done and lay out future directions. For example, if you’ve done the user research in an ongoing project, don’t say, “ After all this user research, it would have been great to progress to a prototype, but it’s not yet done ”; instead, say, “ This user research is now enabling developers to quickly progress to the prototyping stage. ”
Acknowledgments
The end of the case study section is where you should put in your acknowledgments to any other members of your team, if this wasn’t a personal project. Your goal by doing so is to highlight your team spirit and humility in recognizing that great projects are most typically the result of collaboration . Be careful here, because it’s easy to make the waters muddy by not being explicit about what YOU did. So, for example, don’t write something like “ I couldn’t have done it without John X. and Jane Y. ”, but instead say this: “ My user research and prototype design fed into the development work carried out by John X. User testing was carried out by Jane Y., whose findings informed further re-design that I did on the prototypes. ”
What is a good length for a UX case study ending?
UX case studies must be kept short, and, when considering the length of your beginning, process and conclusion sections, it’s the beginning and the conclusion sections that should be the shortest of all. In some case studies, you can keep the ending to two or three short phrases. Other, longer case studies about more complex projects may require a slightly longer section.
Remember, though, that the end section is your chance for a last, short but impactful impression. If the hotel receptionist from our early example started to say goodbye and then went on and on to ask you about your experience, sharing with you the comments of other clients, or started talking to you about where you are going next, and why, and maybe if he had been there himself, started to tell you all about where to go and what to see, well… you get the point. Keep it short, sincere and focused. And certainly, don’t try to make the project sound more important than it was. Recruiters are not stupid – they’ve been there and done that, so they know.
Putting it all together
In the example below, we will show how you can address the points above using text. We are going to focus on the three main questions here, so you can see an example of this in action, for a longer case study.

An example ending section for a longer case study, addressing all aspects: Lessons, impact, reflection and acknowledgments.
Here is how we might structure the text for a shorter version of the same case study, focusing on the bare essentials:

An example ending section for a shorter case study, addressing the most critical aspects: Lessons, impact and reflection. Acknowledgments are being sacrificed for the sake of brevity here, but perhaps that’s OK – you might mention it in the middle part of the case study.
The Take Away
The end part of your case study needs as much care and attention as the rest of it does. You shouldn’t neglect it just because it’s the last thing in the case study. It’s not hard work if you know the basics, and here, we’ve given you the pointers you need to ensure that you don’t miss out anything important. The end part of the case study should leave your recruiters with a good (hopefully, very good) last impression of you and your work, so give it the thorough consideration it needs, to ensure it doesn’t undo all the hard work you’ve put into the case study.
References & Where to Learn More
Copyright holder: Andrew Hurley, Flickr. Copyright terms and license: CC BY-SA 2.0
Atkinson, R. C., & Shiffrin, R. M. (1968). Chapter: Human memory : A proposed system and its control processes. In Spence, K. W., & Spence, J. T. The psychology of learning and motivation (Volume 2). New York: Academic Press. pp. 89–195.
McLeod, S. (2008). Serial Position Effect
How to Create a UX Portfolio

Get Weekly Design Tips
Topics in this article, what you should read next, how to change your career from graphic design to ux design.
- 1.4k shares
How to Change Your Career from Marketing to UX Design
- 1.1k shares
- 3 years ago
How to Change Your Career from Web Design to UX Design
The Ultimate Guide to Understanding UX Roles and Which One You Should Go For
7 Tips to Improve Your UX Design Practice
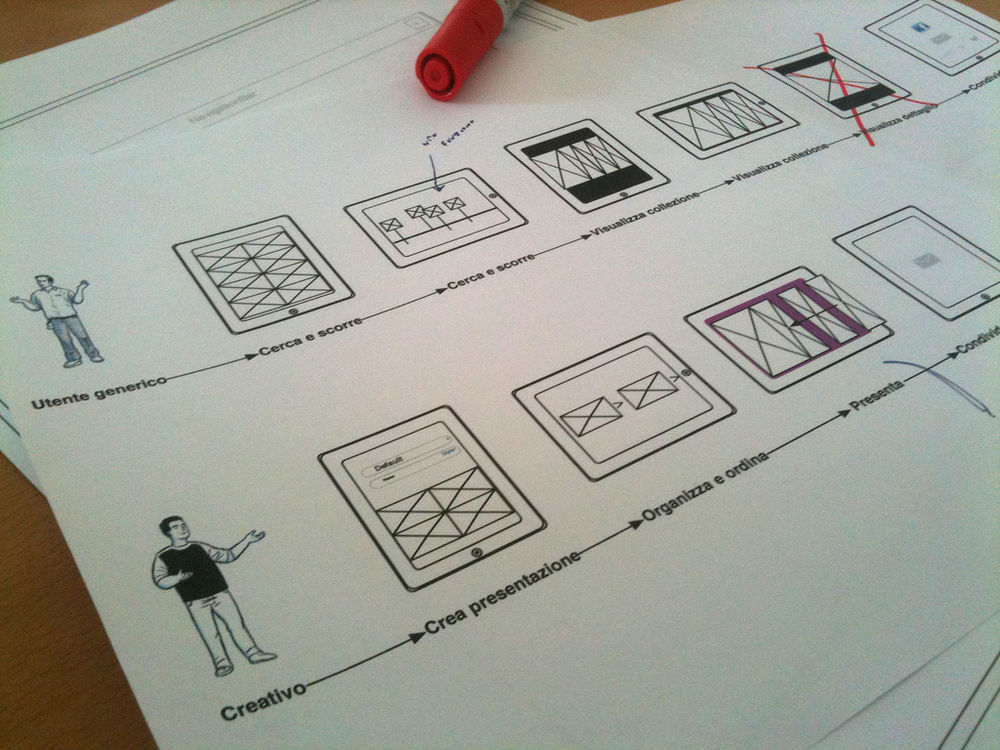
How to create the perfect structure for a UX case study

7 Powerful Steps for Creating the Perfect Freelance CV
Tips for Writing a CV for a UX Job Application
15 Popular Reasons to Become a Freelancer or Entrepreneur

- 4 years ago
The Design Career Map – Learn How to Get Ahead in Your Work

Open Access—Link to us!
We believe in Open Access and the democratization of knowledge . Unfortunately, world-class educational materials such as this page are normally hidden behind paywalls or in expensive textbooks.
If you want this to change , cite this article , link to us, or join us to help us democratize design knowledge !
Privacy Settings
Our digital services use necessary tracking technologies, including third-party cookies, for security, functionality, and to uphold user rights. Optional cookies offer enhanced features, and analytics.
Experience the full potential of our site that remembers your preferences and supports secure sign-in.
Governs the storage of data necessary for maintaining website security, user authentication, and fraud prevention mechanisms.
Enhanced Functionality
Saves your settings and preferences, like your location, for a more personalized experience.
Referral Program
We use cookies to enable our referral program, giving you and your friends discounts.
Error Reporting
We share user ID with Bugsnag and NewRelic to help us track errors and fix issues.
Optimize your experience by allowing us to monitor site usage. You’ll enjoy a smoother, more personalized journey without compromising your privacy.
Analytics Storage
Collects anonymous data on how you navigate and interact, helping us make informed improvements.
Differentiates real visitors from automated bots, ensuring accurate usage data and improving your website experience.
Lets us tailor your digital ads to match your interests, making them more relevant and useful to you.
Advertising Storage
Stores information for better-targeted advertising, enhancing your online ad experience.
Personalization Storage
Permits storing data to personalize content and ads across Google services based on user behavior, enhancing overall user experience.
Advertising Personalization
Allows for content and ad personalization across Google services based on user behavior. This consent enhances user experiences.
Enables personalizing ads based on user data and interactions, allowing for more relevant advertising experiences across Google services.
Receive more relevant advertisements by sharing your interests and behavior with our trusted advertising partners.
Enables better ad targeting and measurement on Meta platforms, making ads you see more relevant.
Allows for improved ad effectiveness and measurement through Meta’s Conversions API, ensuring privacy-compliant data sharing.
LinkedIn Insights
Tracks conversions, retargeting, and web analytics for LinkedIn ad campaigns, enhancing ad relevance and performance.
LinkedIn CAPI
Enhances LinkedIn advertising through server-side event tracking, offering more accurate measurement and personalization.
Google Ads Tag
Tracks ad performance and user engagement, helping deliver ads that are most useful to you.
Share Knowledge, Get Respect!
or copy link
Cite according to academic standards
Simply copy and paste the text below into your bibliographic reference list, onto your blog, or anywhere else. You can also just hyperlink to this article.
New to UX Design? We’re giving you a free ebook!

Download our free ebook The Basics of User Experience Design to learn about core concepts of UX design.
In 9 chapters, we’ll cover: conducting user interviews, design thinking, interaction design, mobile UX design, usability, UX research, and many more!
New to UX Design? We’re Giving You a Free ebook!
- Open access
- Published: 22 May 2024
Preparedness for a first clinical placement in nursing: a descriptive qualitative study
- Philippa H. M. Marriott 1 ,
- Jennifer M. Weller-Newton 2 nAff3 &
- Katharine J. Reid 4
BMC Nursing volume 23 , Article number: 345 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
208 Accesses
2 Altmetric
Metrics details
A first clinical placement for nursing students is a challenging period involving translation of theoretical knowledge and development of an identity within the healthcare setting; it is often a time of emotional vulnerability. It can be a pivotal moment for ambivalent nursing students to decide whether to continue their professional training. To date, student expectations prior to their first clinical placement have been explored in advance of the experience or gathered following the placement experience. However, there is a significant gap in understanding how nursing students’ perspectives about their first clinical placement might change or remain consistent following their placement experiences. Thus, the study aimed to explore first-year nursing students’ emotional responses towards and perceptions of their preparedness for their first clinical placement and to examine whether initial perceptions remain consistent or change during the placement experience.
The research utilised a pre-post qualitative descriptive design. Six focus groups were undertaken before the first clinical placement (with up to four participants in each group) and follow-up individual interviews ( n = 10) were undertaken towards the end of the first clinical placement with first-year entry-to-practice postgraduate nursing students. Data were analysed thematically.
Three main themes emerged: (1) adjusting and managing a raft of feelings, encapsulating participants’ feelings about learning in a new environment and progressing from academia to clinical practice; (2) sinking or swimming, comprising students’ expectations before their first clinical placement and how these perceptions are altered through their clinical placement experience; and (3) navigating placement, describing relationships between healthcare staff, patients, and peers.
Conclusions
This unique study of first-year postgraduate entry-to-practice nursing students’ perspectives of their first clinical placement adds to the extant knowledge. By examining student experience prior to and during their first clinical placement experience, it is possible to explore the consistency and change in students’ narratives over the course of an impactful experience. Researching the narratives of nursing students embarking on their first clinical placement provides tertiary education institutions with insights into preparing students for this critical experience.
Peer Review reports
First clinical placements enable nursing students to develop their professional identity through initial socialisation, and where successful, first clinical placement experiences can motivate nursing students to persist with their studies [ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 ]. Where the transition from the tertiary environment to learning in the healthcare workplace is turbulent, it may impact nursing students’ learning, their confidence and potentially increase attrition rates from educational programs [ 2 , 5 , 6 ]. Attrition from preregistration nursing courses is a global concern, with the COVID-19 pandemic further straining the nursing workforce; thus, the supply of nursing professionals is unlikely to meet demand [ 7 ]. The COVID-19 pandemic has also impacted nursing education, with student nurses augmenting the diminishing nursing workforce [ 7 , 8 ].
The first clinical placement often triggers immense anxiety and fear for nursing students [ 9 , 10 ]. Research suggests that among nursing students, anxiety arises from perceived knowledge deficiencies, role ambiguity, the working environment, caring for ‘real’ people, potentially causing harm, exposure to nudity and death, and ‘not fitting in’ [ 2 , 3 , 11 ]. These stressors are reported internationally and often relate to inadequate preparation for entering the clinical environment [ 2 , 10 , 12 ]. Previous research suggests that high anxiety before the first clinical placement can be related to factors likely to affect patient outcomes, such as self-confidence and efficacy [ 13 ]. High anxiety during clinical placement may impair students’ capacity to learn, thus compromising the value of the clinical environment for learning [ 10 ].
The first clinical placement often occurs soon after commencing nursing training and can challenge students’ beliefs, philosophies, and preconceived ideas about nursing. An experience of cultural or ‘reality’ shock often arises when entering the healthcare setting, creating dissonance between reality and expectations [ 6 , 14 ]. These experiences may be exacerbated by tertiary education providers teaching of ‘ideal’ clinical practice [ 2 , 6 ]. The perceived distance between theoretical knowledge and what is expected in a healthcare placement, as opposed to what occurs on clinical placement, has been well documented as the theory-practice gap or an experience of cognitive dissonance [ 2 , 3 ].
Given the pivotal role of the first clinical placement in nursing students’ trajectories to nursing practice, it is important to understand students’ experiences and to explore how the placement experience shapes initial perceptions. Existing research focusses almost entirely either on describing nursing students’ projected emotions and perceptions prior to undertaking a first clinical placement [ 3 ] or examines student perceptions of reflecting on a completed first placement [ 15 ]. We wished to examine consistency and change in student perception of their first clinical placement by tracking their experiences longitudinally. We focused on a first clinical placement undertaken in a Master of Nursing Science. This two-year postgraduate qualification provides entry-to-practice nursing training for students who have completed any undergraduate qualification. The first clinical placement component of the course aimed to orient students to the clinical environment, support students to acquire skills and develop their clinical reasoning through experiential learning with experienced nursing mentors.
This paper makes a significant contribution to understanding how nursing students’ perceptions might develop over time because of their clinical placement experiences. Our research addresses a further gap in the existing literature, by focusing on students completing an accelerated postgraduate two-year entry-to-practice degree open to students with any prior undergraduate degree. Thus, the current research aimed to understand nursing students’ emotional responses and expectations and their perceptions of preparedness before attending their first clinical placement and to contrast these initial perceptions with their end-of-placement perspectives.
Study design
A descriptive qualitative study was undertaken, utilising a pre- and post-design for data collection. Focus groups with first-year postgraduate entry-to-practice nursing students were conducted before the first clinical placement, with individual semi-structured interviews undertaken during the first clinical placement.
Setting and participants
All first-year students enrolled in the two-year Master of Nursing Science program ( n = 190) at a tertiary institution in Melbourne, Australia, were eligible to participate. There were no exclusion criteria. At the time of this study, students were enrolled in a semester-long subject focused on nursing assessment and care. They studied the theoretical underpinnings of nursing and science, theoretical and practical nursing clinical skills and Indigenous health over the first six weeks of the course. Students completed a preclinical assessment as a hurdle before commencing a three-week clinical placement in a hospital setting, a subacute or acute environment. Overall, the clinical placement aimed to provide opportunities for experiential learning, skill acquisition, development of clinical reasoning skills and professional socialisation [ 16 , 17 ].
In total, sixteen students participated voluntarily in a focus group of between 60 and 90 min duration; ten of these students also participated in individual interviews of between 30 and 60 min duration, a number sufficient to reach data saturation. Table 1 shows the questions used in the focus groups conducted before clinical placement commenced and the questions for the semi-structured interview questions conducted during clinical placement. Study participants’ undergraduate qualifications included bachelor’s degrees in science, arts and business. A small number of participants had previous healthcare experience (e.g. as healthcare assistants). The participants attended clinical placement in the Melbourne metropolitan, Victorian regional and rural hospital locations.
Data collection
The study comprised two phases. The first phase comprised six focus groups prior to the first clinical placement, and the second phase comprised ten individual semi-structured interviews towards the end of the first clinical placement. Focus groups (with a maximum of four participants) and individual interviews were conducted by the lead author online via Zoom and were audio-recorded. Capping group size to a relatively small number considered diversity of perceptions and opportunities for participants to share their insights and to confirm or contradict their peers, particularly in the online environment [ 18 , 19 ].
Focus groups and interview questions were developed with reference to relevant literature, piloted with volunteer final-year nursing students, and then verified with the coauthors. All focus groups and interviewees received the same structured questions (Table 1 ) to ensure consistency and to facilitate comparison across the placement experience in the development of themes. Selective probing of interviewees’ responses for clarification to gain in-depth responses was undertaken. Nonverbal cues, impressions, or observations were noted.
The lead author was a registered nurse who had a clinical teaching role within the nursing department and was responsible for coordinating clinical placement experiences. To ensure rigour during the data collection process, the lead author maintained a reflective account, exploring her experiences of the discussions, reflecting on her interactions with participants as a researcher and as a clinical educator, and identifying areas for improvement (for instance allowing participants to tell their stories with fewer prompts). These reflections in conjunction with regular discussion with the other authors throughout the data collection period, aided in identifying any researcher biases, feelings and thoughts that possibly influenced the research [ 20 ].
To maintain rigour during the data analysis phase, we adhered to a systematic process involving input from all authors to code the data and to identify, refine and describe the themes and subthemes reported in this work. This comprehensive analytic process, reported in detail in the following section, was designed to ensure that the findings arising from this research were derived from a rigorous approach to analysing the data.
Data analysis
Focus groups and interviews were transcribed using the online transcription service Otter ( https://otter.ai/ ) and then checked and anonymised by the first author. Preliminary data analysis was carried out simultaneously by the first author using thematic content analysis proposed by Braun and Clarke [ 21 ] using NVivo 12 software [ 22 ]. All three authors undertook a detailed reading of the first three transcripts from both the focus groups and interviews and independently identified major themes. This preliminary coding was used as the basis of a discussion session to identify common themes between authors, to clarify sources of disagreement and to establish guidelines for further coding. Subsequent coding of the complete data set by the lead author identified a total of 533 descriptive codes; no descriptive code was duplicated across the themes. Initially, the descriptive codes were grouped into major themes identified from the literature, but with further analysis, themes emerged that were unique to the current study.
The research team met frequently during data analysis to discuss the initial descriptive codes, to confirm the major themes and subthemes, to revise themes on which there was disagreement and to identify any additional themes. Samples of quotes were reviewed by the second and third authors to decide whether these quotes were representative of the identified themes. The process occurred iteratively to refine the thematic categories, to discuss the definitions of each theme and to identify exemplar quotes.
Ethical considerations
The lead author was a clinical teacher and the clinical placement coordinator in the nursing department at the time of the study. Potential risks of perceived coercion and power imbalances were identified because of the lead author’s dual roles as an academic and as a researcher. To manage these potential risks, an academic staff member who was not part of the research study informed students about the study during a face-to-face lecture and ensured that all participants received a plain language statement identifying the lead author’s role and how perceived conflicts of interest would be managed. These included the lead author not undertaking any teaching or assessment role for the duration of the study and ensuring that placement allocations were completed prior to undertaking recruitment for the study. All students who participated in the study provided informed written consent. No financial or other incentives were offered. Approval to conduct the study was granted by the University of Melbourne Human Research Ethics Committee (Ethics ID 1955997.1).
Three main themes emerged describing students’ feelings and perceptions of their first clinical placement. In presenting the findings, before or during has been assigned to participants’ quotes to clarify the timing of students’ perspectives related to the clinical placement.
Major theme 1: Adjusting and managing a raft of feelings
The first theme encompassed the many positive and negative feelings about work-integrated learning expressed by participants before and during their clinical placement. Positive feelings before clinical placement were expressed by participants who were comfortable with the unknown and cautiously optimistic.
I am ready to just go with the flow, roll with the punches (Participant [P]1 before).
Overwhelmingly, however, the majority of feelings and thoughts anticipating the first clinical placement were negatively oriented. Students who expressed feelings of fear, anxiety, lack of knowledge, lack of preparedness, uncertainty about nursing as a career, or strong concerns about being a burden were all classified as conveying negative feelings. These negative feelings were categorised into four subthemes.
Subtheme 1.1 I don’t have enough knowledge
All participants expressed some concerns and anxiety before their first clinical placement. These encompassed concerns about knowledge inadequacy and were linked to a perception of under preparedness. Participants’ fears related to harming patients, responsibility for managing ‘real’ people, medication administration, and incomplete understanding of the language and communication skills within a healthcare setting. Anxiety for many participants merged with the logistics and management of their life during the clinical placement.
I’m scared that they will assume that I have more knowledge than I do (P3 before). I feel quite similar with P10, especially when she said fear of unknown and fear that she might do something wrong (P9 before).
Subtheme 1.2 Worry about judgment, being seen through that lens
Participants voiced concerns that they would be judged negatively by patients or healthcare staff because they perceived that the student nurse belonged to specific social groups related to their cultural background, ethnicity or gender. Affiliation with these groups contributed to students’ sense of self or identity, with students often describing such groups as a community. Before the clinical placement, participants worried that such judgements would impact the support they received on placement and their ability to deliver patient care.
Some older patients might prefer to have nurses from their own background, their own ethnicity, how they would react to me, or if racism is involved (P10 before). I just don’t want to reinforce like, whatever negative perceptions people might have of that community (P16 before).
Participants’ concerns prior to the first clinical placement about judgement or poor treatment because of patients’ preconceived ideas about specific ethnic groups did not eventuate.
I mean, it didn’t really feel like very much of a thing once I was actually there. It is one of those things you stress about, and it does not really amount to anything (P16 during).
Some students’ placement experiences revealed the positive benefits of their cultural background to enhancing patient care. One student affirmed that the placement experience reinforced their commitment to nursing and that this was related to their ability to communicate with patients whose first language was not English.
Yeah, definitely. Like, I can speak a few dialects. You know, I can actually see a difference with a lot of the non-English speaking background people. As soon as you, as soon as they’re aware that you’re trying and you’re trying to speak your language, they, they just open up. Yeah, yes. And it improves the care (P10 during).
However, a perceived lack of judgement was sometimes attributed to wearing the full personal protective equipment required during the COVID-19 pandemic, which meant that their personal features were largely obscured. For this reason, it was more difficult for patients to make assumptions or attributions about students’ ethnic or gender identity based on their appearance.
People tend to assume and call us all girls, which was irritating. It was mostly just because all of us were so covered up, no one could see anyone’s faces (P16 during).
Subtheme 1.3 Is nursing really for me?
Prior to their first clinical placement experience, many participants expressed ambivalence about a nursing career and anticipated that undertaking clinical placement could determine their suitability for the profession. Once exposed to clinical placement, the majority of students were completely committed to their chosen profession, with a minority remaining ambivalent or, in rare cases, choosing to leave the course. Not yet achieving full commitment to a nursing career was related to not wishing to work in the ward they had for their clinical placement, while remaining open to trying different specialities.
I didn’t have an actual idea of what I wanted to do after arts, this wasn’t something that I was aiming towards specifically (P14 before). I think I’m still not 100%, but enough to go on, that I’m happy to continue the course as best as I can (P11 during).
Subtheme 1.4 Being a burden
Before clinical placement, participants had concerns about being burdensome and how this would affect their clinical placement experiences.
If we end up being a burden to them, an extra responsibility for them on top of their day, then we might not be treated as well (P10 before).
A sense of burden remained a theme during the clinical placement for participants for the first five to seven days, after which most participants acknowledged that their role became more active. As students contributed more productively to their placement, their feelings of being a burden reduced.
Major theme 2: Sinking or swimming
The second major theme, sinking or swimming, described participants’ expectations about a successful placement experience and identified themes related to students’ successes (‘swimming’) or difficulties (‘sinking’) during their placement experience. Prior to clinical placement, without a realistic preview of what the experience might entail, participants were uncertain of their role, hoped for ‘nice’ supervising nurses and anticipated an observational role that would keep them afloat.
I will focus on what I want to learn and see if that coincides with what is expected, I guess (P15 before).
During the clinical placement, the reality was very different, with a sense of sinking. Participants discovered, some with shock, that they were expected to participate actively in the healthcare team.
I got the sense that they were not going to muck around, and, you know, they’re ‘gonna’ use the free labour that came with me (P1 during).
Adding to the confusion about the expected placement experience, participants believed that healthcare staff were unclear about students’ scope of practice for a postgraduate entry-to-practice degree, creating misalignment between students’ and supervising nurses’ expectations.
It seems to me like the educators don’t really seem to have a clear picture of what the scope is, and what is actually required or expected of us (P10 during).
In exploring perceived expectations of the clinical placement and the modifying effect of placement on initial expectations, three subthemes were identified: translation to practice is overwhelming, trying to find the rhythm or jigsaw pieces, and individual agency.
Subtheme 2.1 Translation to practice is overwhelming
Before clinical placement, participants described concerns about insufficient knowledge to enable them to engage effectively with the placement experience.
If I am doing an assessment understanding what are those indications and why I would be doing it or not doing it at a certain time (P1 before).
Integrating and applying theoretical content while navigating an unfamiliar clinical environment created a significant gap between theory and practice during clinical placement. As the clinical placement experience proceeded and initial fears dissipated, students became more aware of applying their theoretical knowledge in the clinical context.
We’re learning all this theory and clinical stuff, but then we don’t really have a realistic idea of what it’s like until we’re kind of thrown into it for three weeks (P10 during).
Subtheme 2.2 Trying to find the rhythm or the jigsaw pieces
Before clinical placement, participants described learning theory and clinical skills with contextual unfamiliarity. They had the jigsaw pieces but did not know how to assemble it; they had the music but did not know the final song. When discussing their expectations about clinical placement, the small number of participants with a healthcare background (e.g. as healthcare assistants) proposed realistic answers, whereas others struggled to answer or cited stories from friends or television. With a lack of context, feelings of unpreparedness were exacerbated. Once in the clinical environment, participants further emphasised that they could not identify what they needed to know to successfully prepare for clinical placement.
It was never really pieced together. We’ve learned bits and pieces, and then we’re putting it together ourselves (P8 during). On this course I feel it was this is how you do it, but I did not know how it was supposed to be played, I did not know the rhythm (P4 during).
Subtheme 2.3 Individual agency
Participants’ individual agency, their attitude, self-efficacy, and self-motivation affected their clinical placement experiences. Participant perceptions in advance of the clinical placement experience remained consistent with their perspectives following clinical placement. Before clinical placement, participants who were highly motivated to learn exhibited a growth mindset [ 23 ] and planned to be proactive in delivering patient care. During their clinical placement, initially positive students remained positive and optimistic about their future. Participants who believed that their first clinical placement role would be largely observational and were less proactive about applying their knowledge and skills identified boredom and a lack of learning opportunities on clinical placement.
A shadowing position, we don’t have enough skills and authority to do any work, not do any worthwhile skills (P3 before). I thought it would be a lot busier, because we’re limited with our scope, so there’s not much we can do, it’s just a bit slower than I thought (P12 during).
Individual agency appears to influence a successful first clinical placement; other factors may also be implicated but were not the focus of this study. Further research exploring the relationships between students’ age, life experience, resilience, individual agency, and the use of coping strategies during a first clinical placement would be useful.
Major theme 3: The reality of navigating placement relationships
The third main theme emphasised the reality of navigating clinical placement relationships and explored students’ relationships with healthcare staff, patients, and peers. Before clinical placement, many participants, especially those with healthcare backgrounds, expressed fears about relationships with supervising nurses. They perceived that the dynamics of the team and the healthcare workplace might influence the support they received. Several participants were nervous about attending placement on their own without peers for support, especially if the experience was challenging. Participants identified expectations of being mistreated, believing that it was unavoidable, and prepared themselves to not take it personally.
For me it’s where we’re going to land, are we going to be in a supportive, kind of nurturing environment, or is it just kind of sink or swim? (P5 before). If you don’t really trust them, you’re nervous the entire time and you’ll be like what if I get it wrong (P16 before).
Despite these concerns, students strongly emphasised the value of relationships during their first clinical placement, with these perceptions unchanged by their clinical placement experience. Where relationships were positive, participants felt empowered to be autonomous, and their self-confidence increased.
You get that that instant reaction from the patients. And that makes you feel more confident. So that really got me through the first week (P14 during). I felt like I was intruding, then as I started to build a bit of rapport with the people, and they saw that I was around, I don’t feel that as much now (P1 during).
Such development hinged on the receptiveness and support of supervising nurses, the team on the ward, and patients and could be hindered by poor relationships.
He was the old-style buddy nurse in his fifties, every time I questioned him, he would go ssshh, just listen, no questions, it was very stressful (P10 during). It depends whether the buddy sees us as an extra pair of hands, or we’re learners (P11 during).
Where students experienced poor behaviour from supervising nurses, they described a range of emotional responses to these interactions and also coping strategies including avoiding unfriendly staff and actively seeking out those who were more inclusive.
If they weren’t very nice, it wouldn’t be very enjoyable and if they didn’t trust you, then it would be a bit frustrating, that like I can do this, but you won’t let me (P12 during). If another nurse was not nice to me, and I was their buddy, I would literally just not buddy with them and go and follow whoever was nice to me (P4 during).
Relationships with peers were equally important; students on clinical placement with peers valued the shared experience. In contrast, students who attended clinical placement alone at a regional or rural hospital felt disconnected from the opportunities that learning with peers afforded.
Our research explored the emotional responses and perceptions of preparedness of postgraduate entry-to-practice nursing students prior to and during their first clinical placement. In this study, we described how the perceptions of nursing students remained consistent or were modified by their clinical placement experiences. Our analysis of students’ experiences identified three major themes: adjusting and managing a raft of feelings; sinking or swimming; and the reality of navigating placement relationships. We captured similar themes identified in the literature; however, our study also identified novel aspects of nursing students’ experiences of their first clinical placement.
The key theme, adjusting and managing a raft of feelings, which encapsulates anxiety before clinical placement, is consistent with previous research. This theme included concerns in communicating with healthcare staff and managing registered nurses’ negative attitudes and expectations, in addition to an academic workload [ 11 , 24 ]. Concerns not previously identified in the literature included a fear of judgement or discrimination by healthcare staff or patients that might impact the reputation of marginalised communities. Fortunately, these initial fears largely dissipated during clinical placement. Some students discovered that a diverse cultural background was an asset during their clinical placement. Although these initial fears were ameliorated by clinical placement experiences, evidence of such fears before clinical placement is concerning. Further research to identify appropriate support for nursing students from culturally diverse or marginalised communities is warranted. For example, a Finnish study highlighted the importance of mentoring culturally diverse students, creating a pedagogical atmosphere during clinical placement and integrating cultural diversity into nursing education [ 25 ].
Preclinical expectations of being mistreated can be viewed as an unavoidable phenomenon for nursing students [ 26 ]. The existing literature highlights power imbalances and hierarchical differences within the healthcare system, where student nurses may be marginalised, disrespected, and ignored [ 9 , 27 , 28 ]. During their clinical placement, students in our study reported unintentional incivility by supervising nurses: feeling not wanted, ignored, or asked to remain quiet by supervising nurses who were unfriendly or highly critical. These findings were similar to those of Thomas et al.’s [ 29 ] UK study and were particularly heightened at the beginning of clinical placement. Several students acknowledged that nursing staff fatigue from a high turnover of students on their ward and the COVID-19 pandemic could be contributing factors. In response to such incivility, students reported decreased self-confidence and described becoming quiet and withdrawing from active participation with their patients. Students oriented their behaviour towards repetitive low-level tasks, aiming to please and help their supervising nurse, to the detriment of learning opportunities. Fortunately, these incidents did not appear to impact nursing students’ overall experience of clinical placement. Indeed, students found positive experiences with different supervising nurses and their own self-reflection assisted with coping. Other active strategies to combat incivility identified in the current study that were also identified by Thomas et al. [ 29 ] included avoiding nurses who were uncivil, asking to work with nurses who were ‘nice’ to them, and seeking out support from other staff as a coping strategy. The nursing students in our study were undertaking a postgraduate entry-to-practice qualification and already had an undergraduate degree. The likely greater levels of experience and maturity of this cohort may influence their resilience when working with unsupportive supervising nurses and identifying strategies to manage challenging situations.
The theory-practice gap emerged in the theme of sinking or swimming. A theory-practice gap describes the perceived dissonance between theoretical knowledge and expectations for the first clinical placement, as opposed to the reality of the experience, and has been reported in previous studies (see, for instance, 24 , 30 , 31 , 32 ). Existing research has shown that when the first clinical placement does not meet inexperienced student nurses’ expectations, a disconnect between theory and practice occurs, creating feelings of being lost and insecure within the new environment, potentially impacting students’ motivation and risk of attrition [ 19 , 33 ]. The current study identified further areas exacerbating the theory-practice gap. Before the clinical placement, students without a healthcare background lacked context for their learning. They lacked understanding of nurses’ shift work and were apprehensive about applying clinical skills learned in the classroom. Hence, some students were uncertain if they were prepared for their first clinical placement or even how to prepare, which increased their anxiety. Prior research has demonstrated that applying theoretical knowledge more seamlessly during clinical placement was supported when students knew what to expect [ 6 ]. For instance, a Canadian study exposed students as observers to the healthcare setting before starting clinical placement, enabling early theory to practice connections that minimised misconceptions and false assumptions during clinical placement [ 34 ].
In the current study, the theory-practice gap was further exacerbated during clinical placement, where healthcare staff were confused about students’ scope of practice and the course learning objectives and expectations in a postgraduate entry-to-practice nursing qualification. The central booking system for clinical placements classifies first-year nursing students who participated in this study as equivalent to second-year undergraduate nursing students. Such a classification could create a misalignment between clinical educators’ expectations and their delivery of education versus students’ actual learning needs and capacity [ 3 , 31 ]. Additional communication to healthcare partners is warranted to enhance understanding of the scope of practice and expectations of a first-year postgraduate entry-to-practice nursing student. Educating and empowering students to communicate their learning needs within their scope of practice is also required.
Our research identified a link between students’ personality traits or individual agency and their first clinical placement experience. The importance of a positive orientation towards learning and the nursing profession in preparedness for clinical placement has been highlighted in previous studies [ 31 ]. Students’ experience of their first clinical placement in our study appeared to be strongly influenced by their mindset [ 23 ]. Some students demonstrated motivation to learn, were happy to ‘roll with the punches’, yet remain active in their learning requirements, whereas others perceived their role as observational and expected supervising nurses to provide learning opportunities. Students who anticipated a passive learning approach prior to their first clinical placement reported boredom, limited activity, and lack of opportunities during their first clinical placement. These students could have a lowered sense of self-efficacy, which may lead to a greater risk of doubt, stress, and reduced commitment to the profession [ 35 ]. Self-efficacy theory explores self-perceived confidence and competence around people’s beliefs in their ability to influence events, which is associated with motivation and is key to nursing students progressing in their career path confidently [ 35 , 36 ]. In the current study, students who actively engaged in their learning process used strategies such as self-reflection and sought support from clinical educators, peers and family. Such active approaches to learning appeared to increase their resilience and motivation to learn as they progressed in their first clinical placement.
Important relationships with supervising nurses, peers, or patients were highlighted in the theme of the reality of navigating placement relationships. This theme links with previous research findings about belongingness. Belongingness is a fundamental human need and impacts students’ behaviour, emotions, cognitive processes, overall well-being, and socialisation into the profession [ 37 , 38 ]. Nursing students who experience belongingness feel part of a team and are more likely to report positive experiences. Several students in the current study described how feeling part of a team improved self-confidence and empowered work-integrated learning. Nonetheless, compared with previous literature (see for instance, 2), working as a team and belongingness were infrequent themes. Such infrequency could be related to the short duration of the clinical placement. In shorter clinical placements, nursing students learn a range of technical skills but have less time to develop teamwork skills and experience socialisation to the profession [ 29 , 39 ].
Positive relationships with supervising nurses appeared fundamental to students’ experiences. Previous research has shown that in wards with safe psycho-social climates, where the culture tolerates mistakes, regarding them as learning opportunities, a pedagogical atmosphere prevails [ 25 , 39 ]. Whereas, if nursing students experience insolent behaviours or incivility, this not only impacts learning it can also affect career progression [ 26 ]. Participants who felt safe asking questions were given responsibility, had autonomy to conduct skills within their scope of practice and thrived in their learning. This finding aligns with previous research affirming that a welcoming and supportive clinical placement environment, where staff are caring, approachable and helpful, enables student nurses to flourish [ 36 , 40 , 41 , 42 ]. Related research highlights that students’ perception of a good clinical placement is linked to participation within the community and instructor behaviour over the quality of the clinical environment and opportunities [ 27 , 28 ]. Over a decade ago, a large European study found that the single most important element for students’ clinical learning was the supervisory relationship [ 39 ]. In our study, students identified how supervising nurses impacted their emotions and this was critical to their experience of clinical placement, rather than how effective they were in their teaching, delivery of feedback, or their knowledge base.
Students’ relationships with patients were similarly important for a successful clinical placement. Before the clinical placement, students expressed anxiety and fears in communicating and interacting with patients, particularly if they were dying or acutely unwell, which is reflective of the literature [ 2 , 10 , 11 ]. However, during clinical placement, relationships with patients positively impacted nursing students’ experiences, especially at the beginning when they felt particularly vulnerable in a new environment. Towards the end of clinical placement, feelings of incompetence, nervousness and uncertainty had subsided. Students were more active in patient care, which increased self-confidence, empowerment, and independence, in turn further improving relationships with patients and creating a positive feedback loop [ 36 , 42 , 43 ].
Limitations
This study involved participants from one university and a single course, thus limiting the generalisability of the results. Thus, verification of the major themes identified in this research in future studies is needed. Nonetheless, the purpose of this study was to explore in detail the way in which the experiences of clinical placement for student nurses modified initial emotional responses towards undertaking placement and their perceptions of preparedness. Participants in this study undertook their clinical placement in a variety of different hospital wards in different specialties, which contributed to the rigour of the study in identifying similar themes in nursing students’ experiences across diverse placement contexts.
This study explored the narratives of first-year nursing students undertaking a postgraduate entry-to-practice qualification on their preparedness for clinical placement. Exploring students’ changing perspectives before and during the clinical placement adds to extant knowledge about nursing students’ emotional responses and perceptions of preparedness. Our research highlighted the role that preplacement emotions and expectations may have in shaping nursing students’ clinical placement experiences. Emerging themes from this study highlighted the importance students placed on relationships with peers, patients, and supervising nurses. Significant anxiety and other negative emotions experienced by nursing students prior to the first clinical placement suggests that further research is needed to explore the impact of contextual learning to scaffold students’ transition to the clinical environment. The findings of this research also have significant implications for educational practice. Additional educational support for nursing students prior to entering the clinical environment for the first time might include developing students’ understanding of the clinical environment, such as through increasing students’ understanding of the different roles of nurses in the clinical context through pre-recorded interviews with nurses. Modified approaches to simulated teaching prior to the first clinical placement would also be useful to increase the emphasis on students applying their learning in a team-based, student-led context, rather than emphasising discrete clinical skill competencies. Finally, increasing contact between students and university-based educators throughout the placement would provide further opportunities for students to debrief, to receive support and to manage some of the negative emotions identified in this study. Further supporting the transition to the first clinical placement could be fundamental to reducing the theory-practice gap and allaying anxiety. Such support is crucial during their first clinical placement to reduce attrition and boost the nursing workforce.
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analysed during the current study are not publicly available due to the conditions of our ethics approval but may be available from the corresponding author on reasonable request and subject to permission from the Human Research Ethics Committee.
Alshahrani Y, Cusack L, Rasmussen P. Undergraduate nursing students’ strategies for coping with their first clinical placement: descriptive survey study. Nurse Educ Today. 2018;69:104–8.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Brady M, Price J, Bolland R, Finnerty G. Needing to belong: first practice placement experiences of childrens’ nursing students. Compr Child Adolesc Nurs. 2019;421:24–39.
Article Google Scholar
Levett-Jones T, Pitt V, Courtney-Pratt H, Harbrow G, Rossiter R. What are the primary concerns of nursing students as they prepare for and contemplate their first clinical placement experience? Nurse Educ Pract. 2015;154:304–9.
McCloughen A, Levy D, Johnson A, Nguyen H, McKenzie H. Nursing students’ socialisation to emotion management during early clinical placement experiences: a qualitative study. J Clin Nurs. 2020;2913–14:2508–20.
Andrew N, McGuinness C, Reid G, Corcoran T. Greater than the sum of its parts: transition into the first year of undergraduate nursing. Nurse Educ Pract. 2009;91:13–21.
Leducq M, Walsh P, Hinsliff-Smith. K McGarry J. A key transition for student nurses: the first placement experience. Nurse Educ Today. 2012;327:779–81.
Spurlock D Jr. The nursing shortage and the future of nursing education is in our hands. J Nurs Educ. 2020;596:303–4.
Agu CF, Stewart J, McFarlane-Stewart N, Rae T. COVID‐19 pandemic effects on nursing education: looking through the lens of a developing country. Int Nurs Rev. 2021;682:153–8.
Nejad FM, Asadizaker M, Baraz S, Malehi AS. Investigation of nursing student satisfaction with the first clinical education experience in universities of medical sciences in Iran. J Med Life. 2019;121:75–82.
Sun FK, Long A, Tseng YS, Huang HM, You JH, Chiang CY. Undergraduate student nurses’ lived experiences of anxiety during their first clinical practicum: a phenomenological study. Nurse Educ Today. 2016;37:21–6.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Gurková E, Zeleníková R. Nursing students perceived stress coping strategies health and supervisory approaches in clinical practice: a Slovak and Czech perspective. Nurse Educ Today. 2018;65:4–10.
Hanson J, Walsh S, Mason M, Wadsworth D, Framp A, Watson K. Speaking up for safety: a graded assertiveness intervention for first year nursing students in preparation for clinical placement: thematic analysis. Nurse Educ Today. 2020;84:104252.
Khalaila R. Simulation in nursing education: an evaluation of students outcomes at their first clinical practice combined with simulations. Nurse Educ Today. 2014;342:252–8.
Cummins AM, Catling C, Hogan R, Homer CS. Addressing culture shock in first year midwifery students: maximising the initial clinical experience. Women Birth. 2014;274:271–5.
Chesser-Smyth PA. The lived experiences of general student nurses on their first clinical placement: a phenomenological study. Nurse Educ Pract. 2005;56:320–7.
Arkan B, Ordin Y, Yılmaz D. Undergraduate nursing students experience related to their clinical learning environment and factors affecting to their clinical learning process. Nurse Educ Pract. 2018;29:127–32.
Cowen KJ, Hubbard LJ, Hancock DC. Expectations and experiences of nursing students in clinical courses: a descriptive study. Nurse Educ Today. 2018;67:15–20.
Krueger RA, Casey MA. Focus groups: a practical guide for applied research. 5th ed. Thousand Oaks, California: Sage; 2014.
Jonsén E, Melender HL, Hilli Y. Finnish and Swedish nursing students experiences of their first clinical practice placement—A qualitative study. Nurse Educ Today. 2013;333:297–302.
Watt D. On becoming a qualitative researcher: the value of reflexivity. Qual Rep. 2007;121:82–101.
Google Scholar
Braun V, Clarke V. Thematic analysis. In: Cooper H, Camic PM, Long DL, Panter AT, Rindskopf DK, Sher J, editors. APA handbook of research methods in psychology Vol. 2. Research designs: quantitative qualitative neuropsychological and biological. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association; 2012. pp. 57–71.
Chapter Google Scholar
Lumivero. - Software Solutions for Data Analysis & Management [Internet]. Lumivero. http://www.lumivero.com .
Yeager DS, Dweck CS. Mindsets that promote resilience: when students believe that personal characteristics can be developed. Educ Psychol. 2012;47(4):302–14.
Kol E, İnce S. Determining the opinions of the first-year nursing students about clinical practice and clinical educators. Nurse Educ Pract. 2018;31:35–40.
Mikkonen K, Merilainen M, Tomietto M. Empirical model of clinical learning environment and mentoring of culturally and linguistically diverse nursing students. J Clin Nurs. 2020;29(3–4):653–61.
Ahn YH, Choi J. Incivility experiences in clinical practicum education among nursing students. Nurse Educ Today. 2019;73:48–53.
Molesworth M. Nursing students first placement: peripherality and marginality within the community of practice. J Nurs Educ. 2017;561:31–8.
Rafati F, Nouhi E, Sabzehvari S, Dehghan-Nayyeri N. Iranian nursing students’ experience of stressors in their first clinical experience. J Prof Nurs. 2017;333:250–7.
Thomas J, Jinks A, Jack B. Finessing incivility: the professional socialisation experiences of student nurses first clinical placement a grounded theory. Nurse Educ Today. 2015;3512:e4–9.
Astin F, McKenna L, Newton J, Moore-Coulson L. Registered nurses–expectations and experiences of first year students–clinical skills and knowledge. Contemp Nurse. 2005;183:279–91.
Kalyani MN, Jamshidi N, Molazem Z, Torabizadeh C, Sharif F. How do nursing students experience the clinical learning environment and respond to their experiences? A qualitative study. BMJ Open. 2019;97:e028052.
Maginnis C, Croxon L. Transfer of learning to the nursing clinical practice setting. Rural Remote Health. 2010;102:334–40.
Soler OM, Aguayo-González M, Gutiérrez SSR, Pera MJ, Leyva-Moral JM. Nursing students’ expectations of their first clinical placement: a qualitative study. Nurse Educ Today. 2021;98:104736.
Powell TL, Cooke J, Brakke A. Altered nursing student perspectives: impact of a pre-clinical observation experience at an outpatient oncology setting. Can Oncol Nurs J. 2019;291:34–9.
Bandura AJJW. Self-efficacy. In: Weiner IB, Craighead WE, editors. The Corsini encyclopedia of psychology. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons Inc; 2010.
Porteous DJ, Machin A. The lived experience of first year undergraduate student nurses: a hermeneutic phenomenological study. Nurse Educ Today. 2018;60:56–61.
Cooper J, Courtney-Pratt H, Fitzgerald M. Key influences identified by first year undergraduate nursing students as impacting on the quality of clinical placement: a qualitative study. Nurse Educ Today. 2015;359:1004–8.
Levett-Jones T, Lathlean J. The ascent to competence conceptual framework: an outcome of a study of belongingness. J Clin Nurs. 2009;1820:2870–9.
Warne T, Johansson UB, Papastavrou E, Tichelaar E, Tomietto M, Van den Bossche K. Saarikoski M. An exploration of the clinical learning experience of nursing students in nine European countries. Nurse Educ Today. 2010;308:809–15.
Laugaland K, Kaldestad K, Espeland E, McCormack B, Akerjordet K, Aase I. Nursing students experience with clinical placement in nursing homes: a focus group study. BMC Nurs. 2021;201:1–13.
Manninen K, Henriksson EW, Scheja M, Silén C. Authenticity in learning–nursing students experiences at a clinical education ward. Health Educ. 2013;1132:132–43.
Teskereci G, Boz İ. I try to act like a nurse: a phenomenological qualitative study. Nurse Educ Pract. 2019;37:39–44.
Chesser-Smyth PA, Long T. Understanding the influences on self‐confidence among first‐year undergraduate nursing students in Ireland. J Adv Nurs. 2013;691:145–57.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the first-year nursing students who participated in this study and generously shared their experiences of undertaking their first clinical placement.
No funding was received for this study.
Author information
Jennifer M. Weller-Newton
Present address: School of Nursing and Midwifery, University of Canberra, Kirinari Drive, Bruce, Canberra, ACT, 2617, Australia
Authors and Affiliations
Department of Nursing, The University of Melbourne, Grattan St, Parkville, VIC, 3010, Australia
Philippa H. M. Marriott
Department of Rural Health, The University of Melbourne, Grattan St, Shepparton, VIC, 3630, Australia
Present address: Department of Medical Education, Melbourne Medical School, The University of Melbourne, Grattan St, Parkville, VIC, 3010, Australia
Katharine J. Reid
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors made a substantial contribution to conducting the research and preparing the manuscript for publication. P.M., J.W-N. and K.R. conceptualised the research and designed the study. P.M. undertook the data collection, and all authors were involved in thematic analysis and interpretation. P.M. wrote the first draft of the manuscript, K.R. undertook a further revision and all authors contributed to subsequent versions. All authors approved the final version for submission. Each author is prepared to take public responsibility for the research.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Katharine J. Reid .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The research was undertaken in accordance with the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia’s National Statement on Ethical Conduct in Human Research and the Australian Code for the Responsible Conduct of Research. Ethical approval to conduct the study was obtained from the University of Melbourne Human Research Ethics Committee (Ethics ID 1955997.1). All participants received a plain language statement that described the requirements of the study. All participants provided informed written consent to participate, which was affirmed verbally at the beginning of focus groups and interviews.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Marriott, P.H.M., Weller-Newton, J.M. & Reid, K.J. Preparedness for a first clinical placement in nursing: a descriptive qualitative study. BMC Nurs 23 , 345 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-024-01916-x
Download citation
Received : 17 November 2023
Accepted : 04 April 2024
Published : 22 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-024-01916-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Postgraduate nursing education
- Nursing students
- Nursing schools
- Clinical skills
- Qualitative research
BMC Nursing
ISSN: 1472-6955
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
To write a case study analysis in nursing, follow these steps: Introduction: Begin with a brief overview of the patient, the diagnosis, and the purpose of the case study. Patient History: Present the patient's background, including age, gender, medical history, and any relevant social or family history.
A nursing case study analysis begins with a comprehensive exploration of a patient's health situation. This includes their health history, current symptoms, and previous treatments. This exploration phase involves collecting data from patient interviews, physical examinations, and diagnostic tests.
Ensure your summary has at least the case presentation, the nursing assessment/diagnosis, the intervention, and the key recommendations. At the very end of your conclusion, add a closing statement. The statement should wrap up the whole thing nicely. Try to make it as impressive as possible. 9.
Click on a case study below to view in our Nursing Case Study Examples course which holds all of our 40+ nursing case studies with answers. Acute Kidney Injury Nursing Case Study. Continue Case Study. Cardiogenic Shock Nursing Case Study. Continue Case Study. Breast Cancer Nursing Case Study. Continue Case Study. Respiratory Nursing Case Study.
A nursing case study is a detailed study of an individual patient, which allows you to gain more information about the symptoms and the medical history of a patient and provide the proper diagnoses of the patient's illness based on the symptoms he or she experienced and other affecting factors. ... Conclusion: Nursing care for Alzheimer's ...
Writing a nursing case study analysis usually takes only a few hours. Reference your case study. After writing your case study, make sure you add all in-text citations if you had not added them already. And when adding them, you should make sure you follow the style/format recommended in the assignment prompt (usually APA or Harvard style).
The nursing case study example on Death and Dying and answers questions on Suffering and the Fallenness of the World, Suffering and the Hope of Resurrection, Value of Life, Euthanasia, and Morally Justified Options, also offers an analysis of the sin of suicide. Explores Ethical end of life decision making.
Case study is a research methodology, typically seen in social and life sciences. There is no one definition of case study research.1 However, very simply… 'a case study can be defined as an intensive study about a person, a group of people or a unit, which is aimed to generalize over several units'.1 A case study has also been described as an intensive, systematic investigation of a ...
Conclusion. A case study approach offers nurse researchers the opportunity for in-depth, contextualised understanding of the systems and processes which influence their role in palliative care delivery across settings. ... Anthony S, Jack S. (2009) Qualitative case-study methodology in nursing research: An integrative review. Journal of ...
Conclusion. Writing nursing case studies is an essential skill for nursing students in the USA, UK, and Canada. Through these case studies, students can bridge the gap between theory and practice, preparing them for the complex and dynamic healthcare environments they will encounter in their careers. By carefully selecting cases, conducting ...
Below you will find case study samples for various topics. Using them as a reference will improve your writing. If you need more ideas, you are welcome to use our free title-generating tool. Case study: healing and autonomy. Sara's case study: maternal and child nursing. COPD medical diagnostics: case study.
Book Title: Nursing Case Studies by and for Student Nurses Author: jaimehannans. License: Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial. Read Book Contents. Show All Contents Hide All Contents. Book Contents Navigation. Introduction. I. Neurological. 1. Ischemic Stroke: Randall Swanson. 2.
The case study in nursing explores a particular patient's situation, while your essays will more likely have focused on disease, a treatment, a concept, or a system. A case study is very grounded in the real and the now, even if the patient is a hypothetical invention. It still provides some fairly authentic experience with dealing with an ...
Writing a nursing case study requires thoughtful consideration of relevant information and resources. You must select a single subject, conduct research on it, interview experts, analyze the data collected, and present your findings. That may seem like a lot, but let us break it down for you. Here's a look at the key elements that your case ...
Proper nursing abilities and competencies as well as reviewing the in-depth data of the patient may need for acquiring effective health outcomes for the patients (White and Ewan,2013). Conclusion This case study evaluated disease conditions of Mr George and also addressed two health priorities for him. Effective health education, guidance and ...
FULL ESSAY case study during one shift this case study will focus on the implementation and evaluation stages of the nursing process while doing one shift in ... It suggested that further research is necessary to address effective non- pharmacological and other nursing interventions. In conclusion, Alan's care was desired on his health and ...
Mrs P - A Clinical Case Study. Mrs P is a 78 year old lady who currently lives alone in a centrally located council owned property in a town in the West Midlands. Mrs P was married in the 1950's and her husband worked in an engineering factory until he had to retire due to ill health and he then unfortunately passed away in the mid 1990's.
A sample 2:1 nursing case study on an evidence-based approach to a patient with sepsis. A sample 2:1 nursing case study on an evidence-based approach to a patient with sepsis. UKE ssays.com. ... Conclusion Mr. K presented with an acute exacerbation of COPD which was secondary to lobar pneumonia and further complicated by sepsis and septic shock ...
Introduction. This reflective case study will provide an account of the nursing management of a Mr Singh a 79 year old gentleman who developed a pressure sore whilst a hospital inpatient. The aim of the case study is to enhance the reader's knowledge of the importance of a structured approach to the management of the complex problems he ...
Case study is a research methodology, typically seen in social and life sciences. There is no one definition of case study research.1 However, very simply... 'a case study can be defined as an intensive study about a person, a group of people or a unit, which is aimed to generalize over several units' .1 A case study has also been described ...
UX case studies must be kept short, and, when considering the length of your beginning, process and conclusion sections, it's the beginning and the conclusion sections that should be the shortest of all. In some case studies, you can keep the ending to two or three short phrases. Other, longer case studies about more complex projects may ...
Nursing Case Study 2200 - OB Ward Submitted By: Liana Monique San Lorenzo BSN3-2; RLE Group 2 Submitted to: Ms. Vicencio October 15, 2013 NURSING CASE STUDY ADMISSION DIAGNOSIS: G2P1 (1001) Pregnancy, Uterine,Term, Cephalic FINAL DIAGNOSIS: G2P2 (2002) Pregnancy, Uterine,Term, Cephalic Delivered, Live birth by VSD with right
First clinical placements enable nursing students to develop their professional identity through initial socialisation, and where successful, first clinical placement experiences can motivate nursing students to persist with their studies [1,2,3,4].Where the transition from the tertiary environment to learning in the healthcare workplace is turbulent, it may impact nursing students' learning ...