- How it works


How to Write the Thesis Or Dissertation Introduction – Guide
Published by Carmen Troy at August 31st, 2021 , Revised On June 7, 2024
What would you tell someone if they asked you to introduce yourself? You’d probably start with your name, what you do for a living…etc., etc., etc. Think of your dissertation as the same. How would you go about it if you had to introduce it to the world for the first time?
Keep this forefront in your mind for the remainder of this guide: you are introducing your research to the world that doesn’t even know it exists. Every word, phrase and line you write in your introduction will stand for the strength of your dissertation’s character.
This is not very different from how, in real life, if someone fails to introduce themselves properly (such as leaving out what they do for a living, where they live, etc.) to a stranger, it leaves a lasting impression on the stranger.
Don’t leave your dissertation a stranger among other strangers. Let’s review the little, basic concepts we already have at the back of our minds, perhaps, to piece them together in one body: an introduction.
What Goes Inside an Introduction
The exact ingredients of a dissertation or thesis introduction chapter vary depending on your chosen research topic, your university’s guidelines, and your academic subject – but they are generally mixed in one sequence or another to introduce an academic argument.
The critical elements of an excellent dissertation introduction include a definition of the selected research topic , a reference to previous studies on the subject, a statement of the value of the subject for academic and scientific communities, a clear aim/purpose of the study, a list of your objectives, a reference to viewpoints of other researchers and a justification for the research.
Steps of Writing a Dissertation Introduction
- Research background
- Significance of the research
- Research problem
- Research questions
- The research aims and objectives
- Limitations of the research
- Outline of dissertation
1. Research Background – Writing a Dissertation Introduction
This is the very first section of your introduction. Building a background of your chosen topic will help you understand more about the topic and help readers know why the general research area is problematic, interesting, central, important, etc.
Your research background should include significant concepts related to your dissertation topic. This will give your supervisor and markers an idea that you’ve investigated the research problem thoroughly and know the various aspects of your topic.
The introduction to a dissertation shouldn’t talk only about other research work in the same area, as this will be discussed in the literature review section. Moreover, this section should not include the research design and data collection method(s) .
All about research strategy should be covered in the methodology chapter . Research background only helps to build up your research in general.
For instance, if your research is based on job satisfaction measures of a specific country, the content of the introduction chapter will generally be about job satisfaction and its impact.
Hire an Expert Writer
Orders completed by our expert writers are
- Formally drafted in academic style
- Plagiarism free
- Never resold
- Include unlimited free revisions
- Completed to match exact client requirements

2. Significance of the Research
As a researcher, you must demonstrate how your research will provide value to the scientific and academic communities. If your dissertation is based on a specific company or industry, you need to explain why that industry and company were chosen.
If you’re comparing, explain why you’re doing so and what this research will yield. Regardless of your chosen research topic, explain thoroughly in this section why this research is being conducted and what benefits it will serve.
The idea here is to convince your supervisor and readers that the concept should be researched to find a solution to a problem.
3. Research Problem
Once you’ve described the main research problem and the importance of your research, the next step would be to present your problem statement , i.e., why this research is being conducted and its purpose.
This is one of the essential aspects of writing a dissertation’s introduction. Doing so will help your readers understand what you intend to do in this research and what they should expect from this study.
Presenting the research problem competently is crucial in persuading your readers to read other parts of the dissertation paper . This research problem is the crux of your dissertation, i.e., it gives a direction as to why this research is being carried out, and what issues the study will consider. The research problem should be a clear and concise statement that identifies the gap in the existing knowledge that your research aims to fill. It should be specific enough to guide your research, but broad enough to allow for a comprehensive investigation.
For example, if your dissertation is based on measuring the job satisfaction of a specific organisation, your research problem should talk about the problem the company is facing and how your research will help the company to solve that.
If your dissertation is not based on any specific organisation, you can explain the common issues that companies face when they do not consider job satisfaction as a pillar of business growth and elaborate on how your research will help them realise its importance.
Citing too many references in the introduction chapter isn’t recommended because here, you must explain why you chose to study a specific area and what your research will accomplish. Any citations only set the context, and you should leave the bulk of the literature for a later section.
4. Research Question(s)
The central part of your introduction is the research question , which should be based on your research problem and the dissertation title. Combining these two aspects will help you formulate an exciting yet manageable research question. Your research question is what your research aims to answer and around which your dissertation will revolve. The research question should be specific and concise.
Your research question is what your research aims to answer and around which your dissertation will revolve. The research question should be specific and concise.
It should be a one- or two-line question you’ve set out to answer through your dissertation. For the job satisfaction example, a sample research question could be, how does job satisfaction positively impact employee performance?
Look up dissertation introduction examples online or ask your friends to get an idea of how an ideal research question is formed. Or you can review our dissertation introduction example here and research question examples here .
Once you’ve formed your research question, pick out vital elements from it, based on which you will then prepare your theoretical framework and literature review. You will come back to your research question again when concluding your dissertation .
Sometimes, you might have to formulate a hypothesis in place of a research question. The hypothesis is a simple statement you prove with your results , discussion and analysis .
A sample hypothesis could be job satisfaction is positively linked to employee job performance . The results of your dissertation could be in favour of this dissertation or against it.
Tip: Read up about what alternative, null, one-tailed and two-tailed hypotheses are so you can better formulate the hypothesis for your dissertation. Following are the definitions for each term, as retrieved from Trochim et al.’s Research Methods: The Essential Knowledge Base (2016):
- Alternative hypothesis (H 1 ): “A specific statement of prediction that usually states what you expect will happen in your study.”
- Null hypothesis (H 0 ): “The hypothesis that describes the possible outcomes other than the alternative hypothesis. Usually, the null hypothesis predicts there will be no effect of a program or treatment you are studying.”
- One-tailed hypothesis: “A hypothesis that specifies a direction; for example, when your hypothesis predicts that your program will increase the outcome.”
- Two-tailed hypothesis: “A hypothesis that does not specify a direction. For example, if you hypothesise that your program or intervention will affect an outcome, but you are unwilling to specify whether that effect will be positive or negative, you are using a two-tailed hypothesis.”
Get Help with Any Part of Your Dissertation!
UK’s best academic support services. How would you know until you try?
Interesting read: 10 ways to write a practical introduction fast .
Get Help With Any Part of Your Dissertation!
Uk’s best academic support services. how would you know until you try, 5. research aims and objectives.
Next, the research aims and objectives. Aims and objectives are broad statements of desired results of your dissertation . They reflect the expectations of the topic and research and address the long-term project outcomes.
These statements should use the concepts accurately, must be focused, should be able to convey your research intentions and serve as steps that communicate how your research question will be answered.
You should formulate your aims and objectives based on your topic, research question, or hypothesis. These are simple statements and are an extension of your research question.
Through the aims and objectives, you communicate to your readers what aspects of research you’ve considered and how you intend to answer your research question.
Usually, these statements initiate with words like ‘to explore’, ‘to study’, ‘to assess’, ‘to critically assess’, ‘to understand’, ‘to evaluate’ etc.
You could ask your supervisor to provide some thesis introduction examples to help you understand better how aims and objectives are formulated. More examples are here .
Your aims and objectives should be interrelated and connect to your research question and problem. If they do not, they’ll be considered vague and too broad in scope.
Always ensure your research aims and objectives are concise, brief, and relevant.
Once you conclude your dissertation , you will have to revert back to address whether your research aims and objectives have been met.
You will have to reflect on how your dissertation’s findings , analysis, and discussion related to your aims and objectives and how your research has helped in achieving them.
6. Research Limitations
This section is sometimes a part of the dissertation methodology section ; however, it is usually included in the introduction of a dissertation.
Every research has some limitations. Thus, it is normal for you to experience certain limitations when conducting your study.
You could experience research design limitations, data limitations or even financial limitations. Regardless of which type of limitation you may experience, your dissertation would be impacted. Thus, it would be best if you mentioned them without any hesitation.
When including this section in the introduction, make sure that you clearly state the type of constraint you experienced. This will help your supervisor understand what problems you went through while working on your dissertation.
However, one aspect that you should take care of is that your results, in no way, should be influenced by these restrictions. The results should not be compromised, or your dissertation will not be deemed authentic and reliable.
After you’ve mentioned your research limitations, discuss how you overcame them to produce a perfect dissertation .
Also, mention that your limitations do not adversely impact your results and that you’ve produced research with accurate results the academic community can rely on.
Also read: How to Write Dissertation Methodology .
7. Outline of the Dissertation
Even though this isn’t a mandatory sub-section of the introduction chapter, good introductory chapters in dissertations outline what’s to follow in the preceding chapters.
It is also usual to set out an outline of the rest of the dissertation . Depending on your university and academic subject, you might also be asked to include it in your research proposal .
Because your tutor might want to glance over it to see how you plan your dissertation and what sections you’d include; based on what sections you include and how you intend to research and cover them, they’d provide feedback for you to improve.
Usually, this section discusses what sections you plan to include and what concepts and aspects each section entails. A standard dissertation consists of five sections : chapters, introduction, literature review , methodology , results and discussion , and conclusion .
Some dissertation assignments do not use the same chapter for results and discussion. Instead, they split it into two different chapters, making six chapters. Check with your supervisor regarding which format you should follow.
When discussing the outline of your dissertation , remember that you’d have to mention what each section involves. Discuss all the significant aspects of each section to give a brief overview of what your dissertation contains. This is precisely what our dissertation outline service provides.
Writing a dissertation introduction might seem complicated, but it is not if you understand what is expected of you. To understand the required elements and make sure that you focus on all of them.
Include all the aspects to ensure your supervisor and other readers can easily understand how you intend to undertake your research.
“If you find yourself stuck at any stage of your dissertation introduction, get introduction writing help from our writers! At ResearchProspect, we offer a dissertation writing service , and our qualified team of writers will also assist you in conducting in-depth research for your dissertation.
Topic Discussion versus Topic Introduction
Discussing and introducing a topic are two highly different aspects of dissertation introduction writing. You might find it easy to discuss a topic, but introducing it is much trickier.
The introduction is the first thing a reader reads; thus, it must be to the point, informative, engaging, and enjoyable. Even if one of these elements is missing, the reader will not be motivated to continue reading the paper and will move on to something different.
So, it’s critical to fully understand how to write the introduction of a dissertation before starting the actual write-up.
When writing a dissertation introduction, one has to explain the title, discuss the topic and present a background so that readers understand what your research is about and what results you expect to achieve at the end of the research work.
As a standard practice, you might work on your dissertation introduction chapter several times. Once when you’re working on your proposal and the second time when writing your actual dissertation.
“Want to keep up with the progress of the work done by your writer? ResearchProspect can deliver your dissertation order in three parts; outline, first half, and final dissertation delivery. Here is the link to our online order form .
Many academics argue that the Introduction chapter should be the last section of the dissertation paper you should complete, but by no means is it the last part you would think of because this is where your research starts from.
Write the draft introduction as early as possible. You should write it at the same time as the proposal submission, although you must revise and edit it many times before it takes the final shape.
Considering its importance, many students remain unsure of how to write the introduction of a dissertation. Here are some of the essential elements of how to write the introduction of a dissertation that’ll provide much-needed dissertation introduction writing help.
Here are some guidelines for you to learn to write a flawless first-class dissertation paper.
Dissertation Introduction Samples & Examples
Check out some basic samples of dissertation introduction chapters to get started.
FAQs about Dissertation Introduction
How to write a dissertation introduction.
- Capture the attention of your reader
- Add the following sections:
- Learn from others
What is the purpose of an introduction chapter?
It’s used to introduce key constructs, ideas, models and/or theories etc. relating to the topic; things that you will be basing the remainder of your dissertation on.
How do you start an introduction in a dissertation?
There is more than one way of starting a dissertation’s introductory chapter. You can begin by stating a problem in your area of interest, review relevant literature, identify the gap, and introduce your topic. Or, you can go the opposite way, too. It’s all entirely up to your discretion. However, be consistent in the format you choose to write in.
How long should a dissertation introduction be?
It can range from 1000 to 2000 words for a master’s dissertation , but for a higher-level dissertation, it mostly ranges from 8,000 to 10,000 words ’ introduction chapter. In the end, though, it depends on the guidelines provided to you by your department.
Dissertation Introduction Checklist
You may also like.
If your dissertation includes many abbreviations, it would make sense to define all these abbreviations in a list of abbreviations in alphabetical order.
How to Structure a Dissertation or Thesis Need interesting and manageable Finance and Accounting dissertation topics? Here are the trending Media dissertation titles so you can choose one most suitable to your needs.
Learn how to write a good declaration page for your thesis with the help of our step-by-step comprehensive guide. Read now.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
La Classe du Littéraire
Explications de textes, biographies d'auteurs, méthodologie, grammaire … Tout pour le Bac de Français et les études littéraires.
Comment faire l’introduction d’une dissertation en français ?
Pourquoi travailler spécifiquement l’introduction de la dissertation en français ?
Parce que très peu d’élèves le font !
En fait, très peu (trop peu ?) de candidats choisissent le sujet de dissertation au bac de français .
Maintenant, mettez-vous à la place du correcteur. Vous venez de corriger 3 commentaires moyens, vous lisez toujours les mêmes erreurs, vous êtes fatigué …
Une dernière copie pour aujourd’hui … tiens, une dissert’ !
Votre attention remonte d’un cran. Si le candidat fait montre d’une bonne réflexion et maîtrise bien la méthode, il a toutes les chances d’obtenir une bonne note.
En optant pour le sujet de dissertation, vous sortez du lot . C’est une épreuve où vous êtes moins amené à dire la même chose que les autres candidats puisque vous ne mobiliserez pas les mêmes exemples ni les mêmes références.
Cependant, comme pour le commentaire, une bonne introduction est primordiale .
Dans cet article, je vous donne toutes les clés pour réussir à coup sûr à donner une bonne impression au correcteur dès le début du devoir .
En effet, une introduction de qualité, c’est la garantie de mettre le correcteur dans de bonnes dispositions pour la lecture de la suite du travail !
Et avant de commencer à lire cet article, je vous invite, si ce n’est pas déjà fait, à vous reporter à ma méthode générale de la dissertation .

Comment faire une bonne introduction de dissertation en français ?
Mais alors, comment fait-on pour faire une bonne introduction ? Existe-t-il une recette miracle qui marche à chaque fois ?
La réponse est oui.
Une bonne introduction de dissertation en français est rédigée de manière fluide et naturelle. Elle comporte une phrase d’accroche et une analyse du sujet suivie d’une problématisation et d’une annonce d’un plan d’étude. Le tout dans le même paragraphe sans oublier l’alinéa au début.
Oui, mais c’est un peu vague, me direz-vous.
Que signifie exactement “rédigée de manière fluide et naturelle” ?
Ça veut dire que vous passez facilement d’une idée à l’autre et que le correcteur peut oublier un instant qu’il est en train de lire un devoir. Il doit avoir l’impression de suivre votre pensée.
Pour cela, un outil principal : les mots de liaison.
L’importance des mots de liaison
Dans une introduction de dissertation en français, ce sont les mots de liaison qui vont vous permettre d’apporter structure et cohérence à votre style. Plutôt que de passer de manière abrupte d’une idée à une autre, cimentez l’ensemble avec les mots de liaison adaptés.
Voici quelques mots que vous pouvez utiliser dans toutes les introductions que vous rédigerez (en français, mais aussi en philo ou HGGSP, par exemple) :
- D’abord, ensuite, enfin …
- Dans un premier temps, dans un second temps, dans un temps final …
- Et, puis, par la suite …
- Ainsi, donc, par conséquent …
- Cependant, mais, toutefois …
- Bien que, en revanche, néanmoins …
- d’une part … d’autre part …
Faites preuve de logique
Une introduction bien construite, c’est une introduction où chaque idée mène à la suivante.
Le sujet mène à la problématique ; la problématique mène au plan … C’est logique puisque le plan a pour but de répondre à la problématique.
Cependant, trop peu d’élèves perçoivent la logique interne de l’introduction .
On voit souvent une problématique suivie de l’annonce soudaine du plan.
Il suffirait pourtant d’expliciter le lien entre la problématique et le plan. Le plan sert à répondre à la problématique : donc ajoutons un complément circonstanciel de but pour expliciter le lien entre les deux ! “ pour répondre à cette question , nous verrons d’abord que …”
Vous voyez, rien de bien difficile, mais avec cette formule simple à retenir, mon introduction vient de gagner en fluidité.
L’image de l’avion
Avant de voir les 4 étapes de l’introduction, j’aimerais vous parler de l’image de l’avion.
Il s’agit d’un moyen mnémotechnique que l’on m’a appris quand j’étais élève, et qui permet de mieux comprendre la logique d’une introduction (pour tous types d’exercices)

Il faut s’imaginer que l’on survole une ville en avion. Au début on la regarde de loin, c’est l’accroche .
Ensuite, on prend des jumelles et on la voit de plus près, c’est l’annonce du sujet , de la problématique et du plan .
Ensuite, on zoom au maximum, et on regarde différents détails de la ville, c’est le développement .
Quand on en a assez vu, on repose les jumelles, on regarde une dernière fois la ville, c’est la conclusion du devoir.
Même si cet article ne porte que sur l’introduction, je pense que cette image permet de comprendre la logique de l’introduction : c’est la première vue que vous avez sur la ville, avant de décrire les quartiers, il faut commencer par annoncer à votre voisin de siège (le correcteur) ce que vous voyez !
Mais laissons pour le moment derrière nous ces considérations d’ordre général, et entrons dans le vif du sujet en voyant de quoi se compose une introduction de dissertation pour le bac de français .
Quelles sont les 4 étapes d’une introduction de dissertation en français ?
Les 4 étapes d’une introduction de dissertation en français sont d’abord la phrase d’accroche , puis l’annonce du sujet suivie d’une problématisation de ce sujet qui donne lieu à l’annonce d’un plan d’étude. Chaque étape doit mener logiquement à la suivante.
Nous allons maintenant voir comment réussir chacune des 4 étapes constitutives d’une bonne introduction, avant d’examiner les mots qui permettent de gagner en fluidité stylistique.
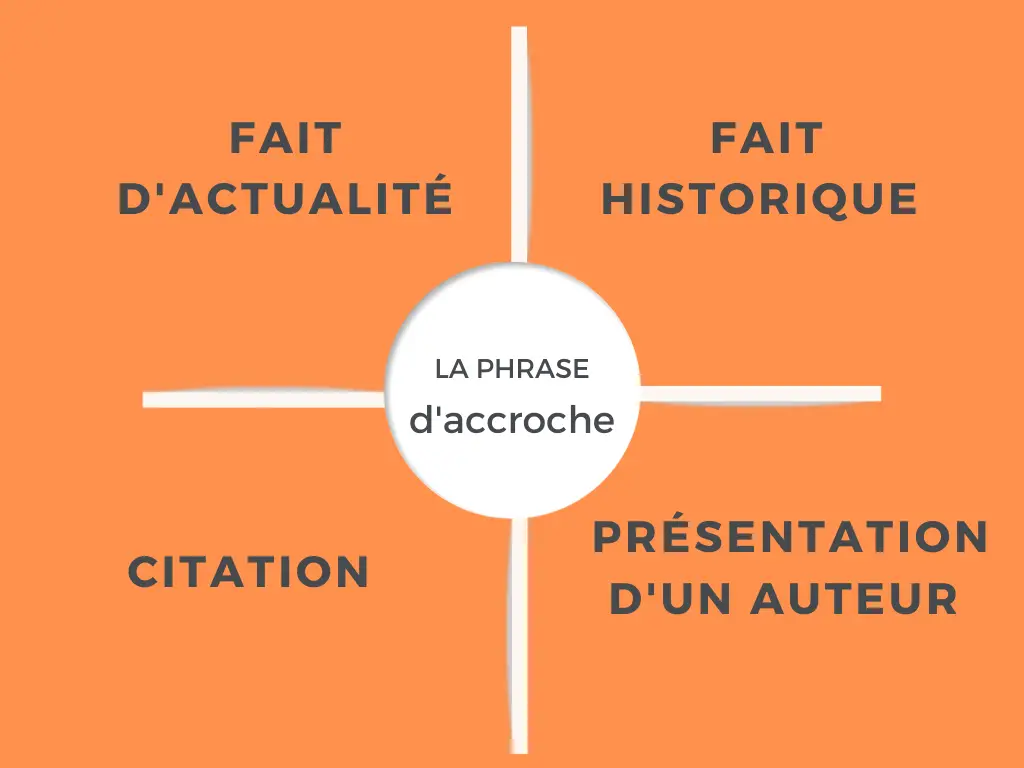
Comment faire une phrase d’accroche ?
Pour réussir à faire une bonne phrase d’accroche dans une dissertation, il faut trouver un angle d’entrée dans le sujet qui permette de susciter l’intérêt du lecteur. Si vous arrivez à introduire le sujet donné tout en sortant du lot, c’est gagné !
Alors, quels sont les différents types de phrase d’accroche possibles ?
En règle générale, on en distingue 4 :
La difficulté réside dans le fait de trouver celui qui est le plus appropriée au sujet sur lequel vous composez.
Mais rassurez-vous, dans la plupart des cas, vous devriez pouvoir les utiliser indifféremment ; c’est plus une question de préférence personnelle que de pertinence par rapport au sujet.
Ce qui signifie que vous pouvez préparer votre phrase d’accroche à l’avance , et l’affiner le jour J pour qu’elle colle parfaitement au sujet.
Comme la dissertation porte sur une oeuvre travaillée pendant l’année, vous pouvez anticiper et préparer votre réserve d’accroches selon les sujets vus en classe.
Le mieux est de préparer une idée pour chacun des types d’accroche :
Entrée historique dans le sujet
C’est une entrée en matière sérieuse, mais pas toujours originale, car vous risquez de tous dire la même chose.
Il faut maîtriser le contexte d’écriture et de parution de chacune des oeuvres au programme .
Ainsi, vous pourrez utiliser votre culture dès la première phrase de votre devoir. Par exemple, pour un sujet comme celui ci dessous, vous pourriez commencer par parler du libertinage au XVIIIe siècle.

Entrée par une citation
Apprenez quelques citations autour de différents thèmes liés à chacune des oeuvres du programme.
En fonction du sujet, voyez si une citation que vous avez retenue est adaptée : si oui, jackpot ! Vous ferez bonne impression en donnant le sentiment que vous maîtrisez vraiment votre sujet.
Entrée par un sujet d’actualité
C’est peut-être l’entrée la plus originale, mais c’est surtout la plus périlleuse.
Si le sujet vous fait penser à un fait d’actualité, vous pouvez attirer l’attention du correcteur en mentionnant d’emblée ce fait, ce qui est inattendu dans un devoir qui porte normalement sur un ouvrage ancien.
Cependant, deux points de vigilance :
- S’assurer que l’on ne fait pas d’anachronisme, c’est à dire que l’on ne lit pas le texte avec des codes sociaux qui lui sont postérieurs
- S’assurer que le fait d’actualité choisi est vraiment en rapport avec le sujet
Entrée par une présentation de l’auteur
Si vous n’avez pas d’idée, vous aurez toujours cette sécurité.
Pour un sujet sur Manon Lescaut , vous pouvez dire deux mots de l’Abbé Prévost. Par exemple, avec le sujet ci-dessus, essayez de cibler ce qui, dans sa biographie, peut avoir un rapport avec l’immoralité.
Cela suppose bien entendu que vous ayez travaillé la biographie de chacun des auteurs des oeuvres lues en classe !
Les mots à éviter dans l’accroche d’une introduction de dissertation en français
Il n’y a pas vraiment de mots interdits dans une phrase d’accroche, mais il y a des formules à éviter à tout prix pour commencer une dissertation.
Ne commencez pas votre devoir par une formule générale et vague :
- De tout temps
- Depuis la nuit des temps
- Depuis très longtemps
Évitez aussi absolument de commencer comme cela : “je vais vous parler de …” ou “le sujet est …”
Exemples d’accroches d’introduction de dissertation en français
Voici 3 exemples de phrases d’accroche tirées de mon article sur les phrases d’accroche . Pour approfondir le sujet, je vous en conseille la lecture.
Actualité : Chaque année, au mois de novembre, on entend que les femmes vont finir l’année en travaillant sans être payées. En effet, selon des chiffres fournis par l’organisme Eurostat , les femmes touchent en moyenne un salaire 15% moins important que celui des hommes. Face à cette inégalité entre les sexes, de nombreux auteurs ont cherché à prendre la plume pour éveiller les consciences, comme Pénélope Bagieu avec sa série de BD « Les Culotées ». Cela peut nous amener à réfléchir au rôle de l’écrit dans les luttes égalitaires. Nous nous intéresserons en particulier au sujet suivant : …………
Citation : Molière affirmait que « le devoir de la comédie (est) de corriger les hommes en les divertissant », ce qu’il s’attachait à faire dans nombre de ses pièces. Seulement, cette correction n’était pas au goût de tous, et rarement à celui des corrigés. Cela peut nous amener à réfléchir au sujet suivant ………..
Historique : Les livres ne sont pas inoffensifs. C’est pourquoi, tout au long de l’Histoire, on assiste à des bûchers de livres. En Italie au XVe siècle, on brûle les œuvres de Pétrarque, en Russie à l’époque Bolchévique, c’est Kant et Descartes qui sont passés par les flammes, et en Allemagne, pendant la montée du nazisme, on brûle les ouvrages écrits par des juifs. Pourquoi brûler un livre, si ce n’est parce qu’il représente un danger pour l’ordre établi ? Cela peut nous amener à réfléchir au rôle de l’écrit dans les luttes égalitaires. Nous nous intéresserons en particulier au sujet suivant : ….
Vous l’aurez compris, une phrase d’accroche, c’est court, mais extrêmement important ! Les premiers mots lus doivent résonner dans votre correcteur, lui montrer votre originalité et votre culture.
L’étape de la présentation du sujet
Ce qu’on attend également d’une accroche, c’est qu’elle mène naturellement au sujet.
Ne vous lancez pas dans la biographie complète de Rimbaud pour ensuite passer du coq à l’âne en introduisant un sujet qui n’a rien à voir.
Le correcteur doit absolument comprendre le lien entre votre accroche et le sujet .
À la fin de l’accroche, utilisez une formule du type : “cela peut nous amener à nous demander …” ou “nous nous intéresserons au sujet suivant …”
Le sujet doit ensuite être recopié tel quel. Ne changez rien, cela viendra au moment de l’étape de problématisation.
Une fois le sujet introduit, vous pouvez définir les mots qui vous semblent importants, et expliquer son sens si la question n’est pas parfaitement claire. Par exemple, dans le sujet sur Manon Lescaut , vous pouvez rappeler qui sont Tiberge et Manon et pourquoi Manon est taxée d’immoralité.
C’est uniquement si l’étape de présentation et d’analyse du sujet est bien effectuée que la problématique aura du sens (cohérence et fluidité, toujours).
La problématique
La problématique est une question que vous allez vous poser pendant tout le devoir.
Elle vous servira de guide car chaque sous-partie proposera un élément de réponse. Vous ferez une synthèse de votre travail dans la conclusion pour finalement donner une réponse complète.
Autant dire qu’ une bonne problématique est la colonne vertébrale de votre dissertation .
Le but n’est pas simplement de reformuler la question du sujet, mais d’exprimer l’ampleur du questionnement qui en découle.
Voici un exemple de problématisation pour le sujet sur Manon Lescaut :
Dans Manon Lescaut , le personnage de Tiberge incarne la morale et cherche sans cesse à ramener Des Grieux dans le droit chemin en l’éloignant de Manon. C’est pourquoi Musset, dans son poème « Namouna », en fait un personnage ennuyeux.
Aussi, on peut se demander si ce personnage droit est condamné à la platitude. En d’autres termes, la saveur du personnage de Manon et de la lecture du roman tient-elle à l’immoralité qui y est mise en scène ?
Attention à la double interrogation !
Erreur commune à laquelle vous devez veiller : ne pas faire à la fois une interrogation directe et une interrogation indirecte dans la même phrase.
Pour faire simple, soit vous posez une question directe avec inversion sujet verbe : ” la saveur du personnage de Manon et de la lecture du roman tient-elle à l’immoralité qui y est mise en scène ?”
Soit vous formulez une interrogation indirecte avec un mot interrogatif : “on se demandera si la saveur du personnage de Manon et de la lecture du roman tient à l’immoralité qui y est mise en scène.”
Dans le cas d’une interrogation indirecte, il ne faut pas mettre de point d’interrogation à la fin de la phrase ni utiliser l’inversion sujet-verbe.
Comment annoncer la problématique dans une introduction de dissertation en français ?
L’introduction de la problématique doit découler directement et logiquement de l’analyse du sujet. Comme la problématique est au centre de votre dissertation, elle doit être mise en valeur par une formulation claire ; elle ne doit jamais passer inaperçu.
Heureusement, comme avec les mots de liaison, il existe quelques phrases toutes faites que vous pouvez reprendre pour réussir à introduire votre problématique à coup sûr !
Quelle phrase pour introduire une problématique ?

- Cela peut nous amener à nous demander de quelle manière …
- Il s’agira de s’interroger sur …
- Face à cette citation (ou opinion, vision, perception …) il est possible de se demander comment …
- Les propos de … posent la question suivante : …
Une fois que vous avez fait toutes les autres étapes de l’introduction, il ne vous reste qu’à annoncer votre plan, et c’est le plus facile.
Pour rappel, l’introduction s’écrit après l’étape du brouillon, donc vous avez déjà un plan sous la forme de notes au brouillon.
Tout ce que vous avez à faire, c’est reprendre les titres de vos axes (pas besoin d’annoncer les sous-parties) et les annoncer sous la formes d’une phrase entièrement rédigée (jamais de prise de notes).
Comment faire l’annonce du plan dans une introduction de dissertation en français ?
Voici 2 exemples de structures que vous pouvez réutiliser dans toutes vos introductions pour annoncer le plan :

- Afin de répondre à cette question, nous verrons d’abord que …, ensuite nous observerons …, enfin nous nous intéresserons à …
- Dans l’optique d’une réponse détaillée à cette interrogation, nous nous intéresserons dans un premier temps à … puis dans un second temps à …
Quelques mots pour conclure sur l’introduction …
Vous l’avez peut-être remarqué : l’introduction de la dissertation en français pour le bac de 1ère est similaire à celle du commentaire.
Vous n’avez pas besoin de tout réapprendre de zéro.
C’est pourquoi cet exercice ne devrait pas tant effrayer les candidats.
Il a de nombreux points communs avec le commentaire littéraire, massivement choisi, et massivement travaillé en classe.
Quand vous révisez votre méthode pour l’introduction de la dissertation du bac de français, gardez toujours à l’esprit l’importance de cette étape. Vous voulez vous montrer sous votre meilleur jour pour la première page de la copie.
Si votre style est un peu moins bon par la suite, c’est moins grave, mais soignez l’intro !
Les 4 étapes mentionnées ci-dessus doivent devenir un automatisme pour vous. Une fois que vous savez exactement les étapes à suivre et que vous avez votre réserve d’exemples, de références et de citations, vous n’avez plus qu’à vous concentrer sur l’articulation des 4 parties entre elles.
Vous verrez qu’avec un peu d’entraînement, vous serez capable de produire une introduction pour n’importe quel type d’exercice argumentatif en moins de 15 minutes !
Besoin d’une aide personnalisée ?
Je propose également des cours particuliers pour tous niveaux :
- Préparation d’examens
- Stages méthodologiques
- Révisions culture littéraire
- Grammaire et orthographe
- Et bien d’autres possibilités
Le tout en 100% distanciel (par WebCam) à partir de 50 euros / heure .
N’hésitez pas à me contacter ( [email protected] ) pour davantage de renseignements, et pour réserver votre premier cours !
Recommended Articles

Comment faire une phrase d’accroche ? (Commentaire, dissertation, essai)

La Méthode de la Dissertation pour le Bac de Français
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Most popular requests
- See full list of services at order form
- Essay Writing Service
- Write My Essay
- Law Essay Help
- HND Assignment Help
- Dissertation Service
- Write My Dissertation
- Buy Dissertation
- Thesis Service
- Literature Review Service
- Assignment Service
- Buy Assignments
- Do My Assignment
- Do My Homework
- Nursing Assignment Help
- Coursework Service
- Do My Coursework
- Research Paper Service
- Lab Report Service
- Personal Statement Service
- How it works
- Prices & discounts
- Client reviews
This site uses cookies to make sure you get the best experience. By continuing you are agreeing with our cookie policy .
- Vital Tips on How to Write a Dissertation Introduction

Most students start to wonder how to write a dissertation introduction after choosing their project topics. Now, they are sitting in front of their laptop, staring at the blank Word page and pondering where to begin. A dissertation is a lengthy, challenging work that determines how well you understand your subject, what original ideas you can contribute to it, and whether you deserve your degree. To succeed, students must face months of extensive research and brainstorming. Ironically, writing your first words is often the hardest part.
If you’ve been worrying about starting your dissertation, you’ve found the right guide. StateOfWriting team comprises talented experts who have written numerous powerful dissertations. They collaborated to create an academic guide featuring facts, insights, tips, and examples that will help you understand how to write introduction for dissertation. As Maya Angelou wisely said, " Do the best you can until you know better. Then when you know better, do better ." This guide is designed to help you learn more so that you can truly prepare your dissertation better. Examine it and say goodbye to your questions!
Key Suggestions on Writing a Solid Intro for Your Dissertation
What is an introduction? It’s the first section of a work with two major goals. First, it informs readers of what topic you intend to explore: they must feel interested and enlightened, forming a clear idea of what kind of research they’re about to delve into. Its second function is to provide a topic roadmap, showcasing what you’ll be doing to investigate it. Now let’s cover the key components each dissertation introduction should contain.
Dissertation Introduction Structure
Structure is one of the biggest problems with academic writing because most people loathe it. As a student, you’d probably prefer to present your thoughts naturally, giving idea after idea until you think you’ve said everything there was to say. Unfortunately, the education sphere is strict in this regard, especially in Great Britain. All dissertations must have a clearly defined structure; all students must stick to it. Cheer up, though! We will explain everything:
- Hook. What to include in introduction of dissertation first? An interesting sentence. Yes, it’s that simple. This sentence is called a hook because it has a similar purpose to a fish hook: it must reel readers in and catch their attention. When someone reads the first sentence of your introduction, they must feel immediately intrigued. You can achieve this effect by presenting a shocking fact, interesting statistics, or a line that uniquely resonates with people. Give it some thought.
- Context. The next element in our guide on how to write dissertation introduction is background. Give your audience some context on what you’re investigating. Start gradually, leading from general to more specific points. You need to show the context of your key theme, explaining why and how it emerged, its effect, and what can be done about it.
- Scope area. To learn how to write an introduction for a dissertation, you’ll have to see different examples. Once you do, you’ll realise that most of them mention other scholars’ research. That’s what you should include as well. Disclose whether your topic is popular, with many articles and books covering it, or if it’s rare and lacks a substantial body of research. Establish which area or population it affects.
- Overall relevance. Before writing an introduction for a dissertation, students should get dissertation proposal help and get this proposal approved by their professor. If you acquired it already, then you have nothing to worry about. If you were allowed to explore your topic, it must be relevant; now, all you have to do is confirm its relevance again, this time more profoundly. Reveal why researching it is a good idea. Indicate how many implications your study might have and what changes it may lead to. This highlights that a particular topic is not fully explored yet, hence why you chose it for your research.
- Research questions. Another part of the introduction dissertation structure is the leading research questions. At this point, you have formulated your topic and its background. Now you should demonstrate what exactly you’re trying to prove. Present the crucial questions you’ll be seeking to answer.
- Structure overview. This point is closely connected to the previous one. One of the keys to learning how to write a good introduction for a dissertation is being specific. You’ve described your main questions; now explain what each section of your introduction will do to answer them. Consider it a summary that goes through your entire project.
What Should a Dissertation Introduction Include
You’ve understood which elements the introduction consists of. That’s great, but you should know how a professional dissertation writer would approach this task. Every person has a unique vision, so they may spend more time describing some points while nearly omitting the others. Whatever you do, be sure to cover these aspects.
- Your personal interest. Before writing introduction for dissertation, all students decide on their topics. Hopefully, you can choose something you really like. Even if you have mixed thoughts about it, attempt to find something engaging that will allow you to feel at least some passion towards it. You must pour this passion into words, making your tone lively and compelling. If your readers sense your boredom in the disjoined ideas and dry language, they might lose interest in reading further.
- The central aim of the dissertation. What to write in dissertation introduction for certain? Its objectives. Dedicate significant attention to them because you should make it very clear what goals your research is pursuing. Check online examples if you’d like to see how professionals do it. We’ll come back to this little tip later.
- Other researchers’ studies. When writing dissertation introduction, include a couple of references to the major credible sources you’ll be relying on in your research. Don’t perform a literature review here, but present several facts supported by the articles or books you’ve located. This acquaints your audience with the sources they’ll encounter later in the body of your dissertation.
- Professional tone. What should a dissertation introduction include that we haven’t already mentioned? Your overall writing tone. As you probably understand, a dissertation is a serious project that requires a meticulous academic approach. Use more complex words and phrases than you normally do. Utilize synonyms and start your sentences in different ways to avoid repetitions — for example, switch between infinitives, gerunds, and nouns at the start of your lines.

Avoid This When Writing Introductions
You know how to start a dissertation introduction, but you should also learn what you should avoid when writing it. There are many rules. We chose the most relevant ones you should review.
- Direct quotes. Don’t use direct citations in your introduction unless absolutely necessary. This section showcases your ideas. You must present your own thoughts, not rely on someone else’s opinion.
- Topic discussion. Some students ramble in their introduction. Avoid doing the same. Tease your audience with some facts about your topic without giving much away. Introduce, don’t discuss. There’ll be space for it later.
- Informal language. When writing a dissertation introduction, avoid contractions, phrasal verbs, and first-person pronouns. Their usage will damage the validity of your project.
- Conclusion. Never present your study's conclusion in the first section. Even if you have all the numbers and facts, leave them for later sections. Like your readers, you’re supposed to be clueless at this point.
5 Suggestions from Top Dissertation Experts
Our British experts shared advice rooted in their experience with dissertation writing. Hopefully, you’ll find their tips beneficial.
- See online examples. Before writing your dissertation, see how other people did it.
- Write an introduction to dissertation last. Your plans and goals might change after you start performing research, so instead of re-writing your introduction later, create it last.
- Be aware of the size of this section. Typical introductions cannot exceed 10% of the total word count.
- Seek assistance if you feel insecure. If you start thinking, “I’d rather pay someone to write my dissertation instead of doing it myself”, perhaps you should do just that. Don’t rush, though. Order an introduction or any other chapter first, then see how it’ll make you feel. Perhaps, after getting support and seeing an introduction dissertation example, you’ll feel confident again and resume writing your project.
- Edit it at least twice. Re-read your dissertation a day and then preferably a week after writing it. This will give you different perspectives, letting you catch the mistakes your tired eyes might have missed.
Lack of inspiration? Want to Enjoy Free Time?
GRAB YOUR 20% DISCOUNT
Criteria Judging If You Learned How to Write a Good Dissertation Introduction
If you’ve ever seen the college grading rubric, you probably know how many categories it entails. In Great Britain, professors assess students’ dissertations part by part. The introduction has a separate column, which can either earn you points or make you lose them. Check it out and keep it close when you start your writing process.
- Length. Don’t let your dissertation exceed 10%.
- Fluency. It’s an inherent part of every work.
- Structure. It should be like in the dissertation introduction template we’ve shared above.
- Content. You get or lose points depending on how relevant your text is.
- Formatting. Follow the rules of APA or any other style you need. Watch out for commas and italics usage.

A Well-Written Dissertation Introduction Example
Seeing something once is more impactful than learning theory. We prepared a brief sample of a dissertation introduction on the topic “ How Psychopathy Differs Between Children of Different Genders ”. Then, we analysed it to underline its strengths.
Introduction Example Psychopathy remains an understudied disorder with the power to alter people’s lives indefinitely. There is differing information on how early it emerges in a child, with some sources stating it happens within the first two years (Liren & Tyrell, 2022) and others insisting that it surfaces after age 5 (Makenshin, 2023). Regardless of the specific onset age, it is clear that psychopathy begins to unfold in young children, but few studies covered how it is displayed in males and females. It is important to understand if the genders have different manifestations because it will allow recognising psychopathy sooner as well as developing more appropriate therapy plans. This study aims to answer the following questions: “How does psychopathy differ in young males and females? Do psychopathic males show more aggressiveness?” The work will consist of five sections: a literature review, which analyses the available sources on the topic; methodology, which describes the process and means of investigation; findings, which present the results; discussion, which discusses these results; and conclusion. It will offer recommendations for future researchers.
Analysis of Good Dissertation Introduction
As you see from this example, the first sentence is a hook. It affects readers by addressing the lack of sufficient research on the topic and underlining its devastating effect. The following sentences establish the context and the scope, referencing two important sources. The last sentence of the first paragraph reveals the relevance of the topic and the implications of researching it. The second paragraph presents research questions and a quick dissertation overview. Note the use of complex words and formal language. If you have read this far, it means that you have decided to fully understand this issue. This article and bonus examples of dissertation chapters are for you.
FAQ on How to Start Dissertation Introduction
- How long should a dissertation introduction be?
Count what constitutes 10% of your total text and ensure that your introduction doesn’t exceed this number. For example, if your project has 5000 words, its starting section should be around 500 words.
- How many pages does an intro for a dissertation have?
Don’t consider the number of pages unless you’re ordering your introduction from a writing service (in which case 1 page equals 300 words). Focus on the word count. Remember the 10% rule: this is the maximum permissible length of your introduction.
- Other articles
- Unique Discursive Essay Topics To Try In 2024
- How to Start an Assignment Introduction Like an Expert
- How to Write a Personal Statement for College
- Top Tourist Attractions in England for Students
Writers are verified and tested to comply with quality standards.
Work is completed in time and delivered before deadline.
Wide range of subjects and topics of any difficulty covered.
Read testimonials to learn why customers trust us.
See how it works from order placement to delivery.
Client id #: 000229
You managed to please my supervisor on the first try! Whoa, I've been working with him for over a year and never turned in a paper without having to rewrite it at least once, lol I wonder if he thinks something's wrong with me now.
Client id #: 000154
Your attention to details cannot but makes me happy. Your professional writer followed every single instruction I gave and met the deadline. The text itself is full of sophisticated lexis and well-structured. I was on cloud nine when I looked through it. And my professor is satisfied as well. Million thanks!
Client id #: 000234
I contacted their call-center to specify the possible custom deadline dates prior to making an order decision and it felt like they hadn't even considered a possibility of going beyond the standard urgency. I didn't even want an additional discount for the extended time, just want to make sure I'll have enough time for editing if necessary. Made an order for standard 14 days, we'll see.
Client id #: 000098
I have no idea how you managed to do this research paper so quickly and professionally. But the result is magnificent. Well-structured, brilliantly written and with all the elements I asked for. I am already filling out my next order from you.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
What Is a Dissertation? | Guide, Examples, & Template
A dissertation is a long-form piece of academic writing based on original research conducted by you. It is usually submitted as the final step in order to finish a PhD program.
Your dissertation is probably the longest piece of writing you’ve ever completed. It requires solid research, writing, and analysis skills, and it can be intimidating to know where to begin.
Your department likely has guidelines related to how your dissertation should be structured. When in doubt, consult with your supervisor.
You can also download our full dissertation template in the format of your choice below. The template includes a ready-made table of contents with notes on what to include in each chapter, easily adaptable to your department’s requirements.
Download Word template Download Google Docs template
- In the US, a dissertation generally refers to the collection of research you conducted to obtain a PhD.
- In other countries (such as the UK), a dissertation often refers to the research you conduct to obtain your bachelor’s or master’s degree.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

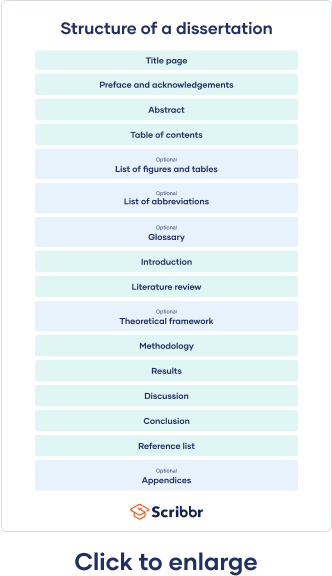
Table of contents
Dissertation committee and prospectus process, how to write and structure a dissertation, acknowledgements or preface, list of figures and tables, list of abbreviations, introduction, literature review, methodology, reference list, proofreading and editing, defending your dissertation, free checklist and lecture slides.
When you’ve finished your coursework, as well as any comprehensive exams or other requirements, you advance to “ABD” (All But Dissertation) status. This means you’ve completed everything except your dissertation.
Prior to starting to write, you must form your committee and write your prospectus or proposal . Your committee comprises your adviser and a few other faculty members. They can be from your own department, or, if your work is more interdisciplinary, from other departments. Your committee will guide you through the dissertation process, and ultimately decide whether you pass your dissertation defense and receive your PhD.
Your prospectus is a formal document presented to your committee, usually orally in a defense, outlining your research aims and objectives and showing why your topic is relevant . After passing your prospectus defense, you’re ready to start your research and writing.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
The structure of your dissertation depends on a variety of factors, such as your discipline, topic, and approach. Dissertations in the humanities are often structured more like a long essay , building an overall argument to support a central thesis , with chapters organized around different themes or case studies.
However, hard science and social science dissertations typically include a review of existing works, a methodology section, an analysis of your original research, and a presentation of your results , presented in different chapters.
Dissertation examples
We’ve compiled a list of dissertation examples to help you get started.
- Example dissertation #1: Heat, Wildfire and Energy Demand: An Examination of Residential Buildings and Community Equity (a dissertation by C. A. Antonopoulos about the impact of extreme heat and wildfire on residential buildings and occupant exposure risks).
- Example dissertation #2: Exploring Income Volatility and Financial Health Among Middle-Income Households (a dissertation by M. Addo about income volatility and declining economic security among middle-income households).
- Example dissertation #3: The Use of Mindfulness Meditation to Increase the Efficacy of Mirror Visual Feedback for Reducing Phantom Limb Pain in Amputees (a dissertation by N. S. Mills about the effect of mindfulness-based interventions on the relationship between mirror visual feedback and the pain level in amputees with phantom limb pain).
The very first page of your document contains your dissertation title, your name, department, institution, degree program, and submission date. Sometimes it also includes your student number, your supervisor’s name, and the university’s logo.
Read more about title pages
The acknowledgements section is usually optional and gives space for you to thank everyone who helped you in writing your dissertation. This might include your supervisors, participants in your research, and friends or family who supported you. In some cases, your acknowledgements are part of a preface.
Read more about acknowledgements Read more about prefaces

Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

The abstract is a short summary of your dissertation, usually about 150 to 300 words long. Though this may seem very short, it’s one of the most important parts of your dissertation, because it introduces your work to your audience.
Your abstract should:
- State your main topic and the aims of your research
- Describe your methods
- Summarize your main results
- State your conclusions
Read more about abstracts
The table of contents lists all of your chapters, along with corresponding subheadings and page numbers. This gives your reader an overview of your structure and helps them easily navigate your document.
Remember to include all main parts of your dissertation in your table of contents, even the appendices. It’s easy to generate a table automatically in Word if you used heading styles. Generally speaking, you only include level 2 and level 3 headings, not every subheading you included in your finished work.
Read more about tables of contents
While not usually mandatory, it’s nice to include a list of figures and tables to help guide your reader if you have used a lot of these in your dissertation. It’s easy to generate one of these in Word using the Insert Caption feature.
Read more about lists of figures and tables
Similarly, if you have used a lot of abbreviations (especially industry-specific ones) in your dissertation, you can include them in an alphabetized list of abbreviations so that the reader can easily look up their meanings.
Read more about lists of abbreviations
In addition to the list of abbreviations, if you find yourself using a lot of highly specialized terms that you worry will not be familiar to your reader, consider including a glossary. Here, alphabetize the terms and include a brief description or definition.
Read more about glossaries
The introduction serves to set up your dissertation’s topic, purpose, and relevance. It tells the reader what to expect in the rest of your dissertation. The introduction should:
- Establish your research topic , giving the background information needed to contextualize your work
- Narrow down the focus and define the scope of your research
- Discuss the state of existing research on the topic, showing your work’s relevance to a broader problem or debate
- Clearly state your research questions and objectives
- Outline the flow of the rest of your work
Everything in the introduction should be clear, engaging, and relevant. By the end, the reader should understand the what, why, and how of your research.
Read more about introductions
A formative part of your research is your literature review . This helps you gain a thorough understanding of the academic work that already exists on your topic.
Literature reviews encompass:
- Finding relevant sources (e.g., books and journal articles)
- Assessing the credibility of your sources
- Critically analyzing and evaluating each source
- Drawing connections between them (e.g., themes, patterns, conflicts, or gaps) to strengthen your overall point
A literature review is not merely a summary of existing sources. Your literature review should have a coherent structure and argument that leads to a clear justification for your own research. It may aim to:
- Address a gap in the literature or build on existing knowledge
- Take a new theoretical or methodological approach to your topic
- Propose a solution to an unresolved problem or advance one side of a theoretical debate
Read more about literature reviews
Theoretical framework
Your literature review can often form the basis for your theoretical framework. Here, you define and analyze the key theories, concepts, and models that frame your research.
Read more about theoretical frameworks
Your methodology chapter describes how you conducted your research, allowing your reader to critically assess its credibility. Your methodology section should accurately report what you did, as well as convince your reader that this was the best way to answer your research question.
A methodology section should generally include:
- The overall research approach ( quantitative vs. qualitative ) and research methods (e.g., a longitudinal study )
- Your data collection methods (e.g., interviews or a controlled experiment )
- Details of where, when, and with whom the research took place
- Any tools and materials you used (e.g., computer programs, lab equipment)
- Your data analysis methods (e.g., statistical analysis , discourse analysis )
- An evaluation or justification of your methods
Read more about methodology sections
Your results section should highlight what your methodology discovered. You can structure this section around sub-questions, hypotheses , or themes, but avoid including any subjective or speculative interpretation here.
Your results section should:
- Concisely state each relevant result together with relevant descriptive statistics (e.g., mean , standard deviation ) and inferential statistics (e.g., test statistics , p values )
- Briefly state how the result relates to the question or whether the hypothesis was supported
- Report all results that are relevant to your research questions , including any that did not meet your expectations.
Additional data (including raw numbers, full questionnaires, or interview transcripts) can be included as an appendix. You can include tables and figures, but only if they help the reader better understand your results. Read more about results sections
Your discussion section is your opportunity to explore the meaning and implications of your results in relation to your research question. Here, interpret your results in detail, discussing whether they met your expectations and how well they fit with the framework that you built in earlier chapters. Refer back to relevant source material to show how your results fit within existing research in your field.
Some guiding questions include:
- What do your results mean?
- Why do your results matter?
- What limitations do the results have?
If any of the results were unexpected, offer explanations for why this might be. It’s a good idea to consider alternative interpretations of your data.
Read more about discussion sections
Your dissertation’s conclusion should concisely answer your main research question, leaving your reader with a clear understanding of your central argument and emphasizing what your research has contributed to the field.
In some disciplines, the conclusion is just a short section preceding the discussion section, but in other contexts, it is the final chapter of your work. Here, you wrap up your dissertation with a final reflection on what you found, with recommendations for future research and concluding remarks.
It’s important to leave the reader with a clear impression of why your research matters. What have you added to what was already known? Why is your research necessary for the future of your field?
Read more about conclusions
It is crucial to include a reference list or list of works cited with the full details of all the sources that you used, in order to avoid plagiarism. Be sure to choose one citation style and follow it consistently throughout your dissertation. Each style has strict and specific formatting requirements.
Common styles include MLA , Chicago , and APA , but which style you use is often set by your department or your field.
Create APA citations Create MLA citations
Your dissertation should contain only essential information that directly contributes to answering your research question. Documents such as interview transcripts or survey questions can be added as appendices, rather than adding them to the main body.
Read more about appendices
Making sure that all of your sections are in the right place is only the first step to a well-written dissertation. Don’t forget to leave plenty of time for editing and proofreading, as grammar mistakes and sloppy spelling errors can really negatively impact your work.
Dissertations can take up to five years to write, so you will definitely want to make sure that everything is perfect before submitting. You may want to consider using a professional dissertation editing service , AI proofreader or grammar checker to make sure your final project is perfect prior to submitting.
After your written dissertation is approved, your committee will schedule a defense. Similarly to defending your prospectus, dissertation defenses are oral presentations of your work. You’ll present your dissertation, and your committee will ask you questions. Many departments allow family members, friends, and other people who are interested to join as well.
After your defense, your committee will meet, and then inform you whether you have passed. Keep in mind that defenses are usually just a formality; most committees will have resolved any serious issues with your work with you far prior to your defense, giving you ample time to fix any problems.
As you write your dissertation, you can use this simple checklist to make sure you’ve included all the essentials.
Checklist: Dissertation
My title page includes all information required by my university.
I have included acknowledgements thanking those who helped me.
My abstract provides a concise summary of the dissertation, giving the reader a clear idea of my key results or arguments.
I have created a table of contents to help the reader navigate my dissertation. It includes all chapter titles, but excludes the title page, acknowledgements, and abstract.
My introduction leads into my topic in an engaging way and shows the relevance of my research.
My introduction clearly defines the focus of my research, stating my research questions and research objectives .
My introduction includes an overview of the dissertation’s structure (reading guide).
I have conducted a literature review in which I (1) critically engage with sources, evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of existing research, (2) discuss patterns, themes, and debates in the literature, and (3) address a gap or show how my research contributes to existing research.
I have clearly outlined the theoretical framework of my research, explaining the theories and models that support my approach.
I have thoroughly described my methodology , explaining how I collected data and analyzed data.
I have concisely and objectively reported all relevant results .
I have (1) evaluated and interpreted the meaning of the results and (2) acknowledged any important limitations of the results in my discussion .
I have clearly stated the answer to my main research question in the conclusion .
I have clearly explained the implications of my conclusion, emphasizing what new insight my research has contributed.
I have provided relevant recommendations for further research or practice.
If relevant, I have included appendices with supplemental information.
I have included an in-text citation every time I use words, ideas, or information from a source.
I have listed every source in a reference list at the end of my dissertation.
I have consistently followed the rules of my chosen citation style .
I have followed all formatting guidelines provided by my university.
Congratulations!
The end is in sight—your dissertation is nearly ready to submit! Make sure it's perfectly polished with the help of a Scribbr editor.
If you’re an educator, feel free to download and adapt these slides to teach your students about structuring a dissertation.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
- Dissertation Table of Contents in Word | Instructions & Examples
- How to Choose a Dissertation Topic | 8 Steps to Follow
More interesting articles
- Checklist: Writing a dissertation
- Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates
- Dissertation Binding and Printing | Options, Tips, & Comparison
- Example of a dissertation abstract
- Figure and Table Lists | Word Instructions, Template & Examples
- How to Write a Discussion Section | Tips & Examples
- How to Write a Dissertation or Thesis Proposal
- How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples
- How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Conclusion
- How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Introduction
- How to Write an Abstract | Steps & Examples
- How to Write Recommendations in Research | Examples & Tips
- List of Abbreviations | Example, Template & Best Practices
- Operationalization | A Guide with Examples, Pros & Cons
- Prize-Winning Thesis and Dissertation Examples
- Purpose and structure of an advisory report
- Relevance of Your Dissertation Topic | Criteria & Tips
- Research Paper Appendix | Example & Templates
- Shorten your abstract or summary
- Theoretical Framework Example for a Thesis or Dissertation
- Thesis & Dissertation Acknowledgements | Tips & Examples
- Thesis & Dissertation Database Examples
- Thesis & Dissertation Title Page | Free Templates & Examples
- What is a Dissertation Preface? | Definition & Examples
- What is a Glossary? | Definition, Templates, & Examples
- What Is a Research Methodology? | Steps & Tips
- What Is a Theoretical Framework? | Guide to Organizing
- What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples
Get unlimited documents corrected
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

Research Voyage
Research Tips and Infromation
06 Essential Steps for Introduction Section of Dissertation or Thesis

Introduction
Stating the research problem or research question, brief overview of the structure of your dissertation, 1. starting with a compelling opening, 2. providing background information, 3. clearly stating the research problem, 4. stating the research objectives, 5. highlighting the research significance, 6. outlining the dissertation structure, avoiding unnecessary jargon or technical details, seeking feedback and revising the introduction multiple times, common academic phrases that can be used in the introduction section.
Are you on the journey of completing your PhD or Post Graduate dissertation? The introduction section plays a vital role in setting the stage for your research and capturing the reader’s attention from the very beginning. A well-crafted introduction is a gateway to showcasing the significance and value of your work.
In this blog post, we will guide you through the essential elements and expert tips to create an engaging and impactful introduction for your dissertation or thesis.
This comprehensive guide will equip you with the tools to write an introduction that stands out. From capturing the reader’s interest with a compelling opening to defining the research problem, stating objectives, and highlighting the research significance, we’ve got you covered.
Not only will you discover practical strategies for crafting an effective introduction, but you’ll also learn how to keep it concise, avoid jargon, and seek valuable feedback. Additionally, we’ll provide domain-specific examples to illustrate each point and help you better understand the application of these techniques.
By mastering the art of writing an engaging introduction, you’ll be able to captivate your readers, establish the context of your research, and demonstrate the value of your study. So, let’s dive in and unlock the secrets to crafting an introduction that sets the foundation for a remarkable PhD dissertation.
If you are in paucity of time, not confident of your writing skills and in a hurry to complete the writing task then you can think of hiring a research consultant that solves all your problems. Please visit my article on Hiring a Research consultant for your PhD tasks for further details.
Purpose of the Introduction
The introduction should introduce the specific topic of your research and provide the necessary background information. For example: “In recent years, artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as a transformative technology with applications in various domains. This study focuses on improving the accuracy of image recognition algorithms in computer vision, a crucial area within AI research.”
Clearly articulating the research problem or research question is essential. Here’s an example: “The objective of this study is to develop a more efficient algorithm for large-scale graph analysis, addressing the challenge of processing massive networks in real-time.”
It is important to state the specific objectives or goals of your research. Here’s an example: “The primary objectives of this research are to design and implement a secure communication protocol for Internet of Things (IoT) devices, evaluate its performance under different network conditions, and assess its resistance to potential cyber-attacks.”
It is helpful to provide a brief overview of the structure of your dissertation, indicating the main sections or chapters. Here’s an example: “This dissertation consists of six chapters. Chapter 1 presents the introduction, research problem, objectives, and methodology. Chapter 2 provides a comprehensive literature review of the existing algorithms for sentiment analysis. Chapter 3 details the proposed algorithm for sentiment classification. Chapter 4 presents the experimental setup and results. Chapter 5 discusses the findings and implications. Finally, Chapter 6 concludes the dissertation with recommendations for future research.”
Remember to adapt the examples to your specific research topic and ensure they accurately reflect the purpose of your introduction. By introducing the topic, stating the research problem, outlining the objectives, and providing an overview of the dissertation structure, you will establish the necessary foundation for your research.
Crafting an Effective Introduction in 06 Steps
By starting with a compelling opening, providing background information, clearly stating the research problem and objectives, highlighting the research significance, and outlining the dissertation structure, you will craft an effective introduction.
Starting with a compelling opening can capture the reader’s attention. Here are some examples:
- Anecdote: “Imagine a scenario where autonomous vehicles navigate through busy city streets, making split-second decisions to ensure passenger safety and optimize traffic flow.”
- Question: “Have you ever wondered how social media platforms use recommendation algorithms to personalize your news feed based on your interests and preferences?”
- Fact: “In 2020, the global cybersecurity market reached a value of $167.13 billion, highlighting the increasing need for robust and reliable security solutions in the digital age.”
Providing background information involves discussing existing literature, theories, and concepts. Here’s an example: “Previous studies in the field of natural language processing have focused on sentiment analysis, aiming to classify text into positive, negative, or neutral sentiments. However, current approaches face challenges in accurately capturing the contextual nuances and sarcasm often found in social media data.”
Clearly defining the research problem is crucial. Here’s an example: “The research problem addressed in this study is the efficient scheduling and resource allocation for cloud-based data-intensive applications, considering the dynamic nature of workloads and the varying availability of cloud resources.”
Presenting specific objectives is important in computer science. Here’s an example: “The primary objectives of this research are to develop an energy-efficient routing protocol for wireless sensor networks, investigate the impact of different routing metrics on network performance, and propose adaptive algorithms for dynamic topology changes.”
Explaining the importance and relevance of your research is essential. Here’s an example: “This research on blockchain technology has significant implications for enhancing data security, ensuring transparent and immutable transactions, and revolutionizing various sectors, including finance, supply chain management, and healthcare.”
Providing a brief overview of the main sections or chapters of your dissertation helps the reader understand the organization. Here’s an example: “This dissertation consists of five chapters. Chapter 1 introduces the research problem, objectives, and methodology. Chapter 2 provides a comprehensive literature review. Chapter 3 presents the proposed algorithm and its implementation. Chapter 4 discusses the experimental results and analysis. Finally, Chapter 5 concludes the dissertation, summarizing the findings and suggesting future research directions.”
Remember to tailor these examples to your specific research topic and ensure they align with your own introduction.
Tips for Writing a Strong Introduction
It’s essential to keep the introduction concise and focused on the main points. Avoid going into excessive detail or including unnecessary information. Here’s an example: “To achieve efficient data processing in distributed systems, this study focuses on developing a parallel algorithm for sorting large-scale datasets, aiming to reduce the computational time and improve overall system performance.”
While writing the introduction, it’s crucial to communicate your ideas clearly without overwhelming the reader with technical terms. Here’s an example: “This study investigates the usability of natural language interfaces for human-robot interaction, exploring the potential for seamless and intuitive communication between users and autonomous robotic systems.”
It’s important to seek feedback from your advisor or peers and revise your introduction based on their suggestions. .
Remember to adapt these examples to your specific research topic and ensure they align with your writing style. By keeping the introduction concise and focused, avoiding unnecessary jargon, and seeking feedback while revising multiple times, you will be able to write a strong introduction in any domain of research.
Here are some common academic phrases that can be used in the introduction section . I have included a table with examples to illustrate how these phrases might be used:
| Phrase | Example |
|---|---|
| Background/Context: This phrase is used to introduce the topic and provide some context or background information. | “With the increasing popularity of social media platforms, the problem of detecting and mitigating cyberbullying has become a pressing issue in the field of computer science.” |
| Motivation: This phrase is used to explain why the research is important or relevant. | “The increasing use of cloud computing and big data in business applications has led to growing concerns about the security and privacy of sensitive data, making it crucial to develop more effective data protection strategies.” |
| Problem statement/Research question: This phrase is used to state the specific research problem or question that the paper or research aims to address. | “This study investigates the following research question: How can machine learning techniques be used to improve the accuracy of traffic congestion prediction in urban areas?” |
| Objectives/Contributions: This phrase is used to explain the specific objectives or contributions of the research. | “The main objectives of this research are to develop a new algorithm for image segmentation and to evaluate its performance on a large dataset. The key contribution of this work is a novel approach that combines deep learning and traditional computer vision techniques to achieve high accuracy in image segmentation.” |
| Methodology/Approach: This phrase is used to explain the methods or approach used in the research. | “In this study, we used a case study approach to investigate the use of agile development methodologies in software engineering teams. We conducted interviews with team members and analyzed project data to identify the benefits and challenges of using agile methods in this context.” |
| Scope/Limitations: This phrase is used to define the scope of the research and any limitations or constraints. | “This research focuses on the use of blockchain technology in supply chain management applications. The limitations of this work include a small sample size and the limited generalizability of the results to other industries or contexts.” |
| Organization: This phrase is used to give an overview of the structure of the paper or research article. | “The rest of this thesis is organized as follows. Section 2 provides a literature review of existing approaches to cybersecurity risk management. Section 3 outlines the research methodology used in this study. Section 4 presents the results of our analysis, and Section 5 discusses the implications of these findings. Finally, Section 6 concludes the paper and suggests directions for future research.” |
Crafting a well-crafted introduction is paramount when it comes to writing a PhD or Post Graduate dissertation. The introduction serves as the gateway to your research, setting the stage for what follows and capturing the reader’s attention. By following the outlined guidelines and tips, you can create an introduction that engages the reader, establishes the context, and highlights the significance of your research.
Upcoming Events
- Visit the Upcoming International Conferences at Exotic Travel Destinations with Travel Plan
- Visit for Research Internships Worldwide

Recent Posts
- 05 Quick Review, High Impact, Best Research Journals for Submissions for July 2024
- Top Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a Research Paper
- Average Stipend for Research/Academic Internships
- These Institutes Offer Remote Research/Academic Internships
- How to Include Your Journal in the UGC-CARE List? A Guide for Publishers
- All Blog Posts
- Research Career
- Research Conference
- Research Internship
- Research Journal
- Research Tools
- Uncategorized
- Research Conferences
- Research Journals
- Research Grants
- Internships
- Research Internships
- Email Templates
- Conferences
- Blog Partners
- Privacy Policy
Copyright © 2024 Research Voyage
Design by ThemesDNA.com


Easily understand how to write a PhD thesis introduction
Feb 26, 2019

Have you checked out the rest of The PhD Knowledge Base ? It’s home to hundreds more free resources and guides, written especially for PhD students.
Get the introduction right and the rest of your dissertation will follow.

What is the purpose of a PhD thesis introduction?
1. establish your research territory (by situating your research in a broader context), 2. establish and justify your niche (by describing why your research is needed) , 3. explain the significance of your research (by describing how you conducted the research).
- What your thesis is about
- Why it is important
- How it was conducted
- How it is laid out
The introduction as a whole should outline the significance and relevance of the thesis. The main criteria for a PhD is its role as an original contribution to knowledge, so the introduction is the space in which you very clearly outline that contribution.
How to structure an PhD thesis introduction
A typical PhD thesis introduction follows the following format:
- Introduction to the introduction: a short version (of only a few paragraphs) of the thesis’ aims, research questions, contribution, objectives and findings.
- State the overarching topic and aims of the thesis in more detail Provide a brief review of the literature related to the topic (this will be very brief if you have a separate literature review chapter)
- Define the terms and scope of the topic
- Critically evaluate the current state of the literature on that topic and identify your gap
- Outline why the research is important and the contribution that it makes
- Outline your epistemological and ontological position
- Clearly outline the research questions and problem(s) you seek to address
- State the hypotheses (if you are using any)
- Detail the most important concepts and variables
- Briefly describe your methodology
- Discuss the main findings
- Discuss the layout of the thesis
Much like the abstract, the reader shouldn’t have to wait long before they understand the contribution, what you are doing and how you are doing it. So, you’ll start by presenting your research in a clear, concise way in the opening few paragraphs. These opening paragraphs should briefly summarise the aims, objectives, research questions, main argument and contribution.
The reader shouldn’t have to wait long before they understand the contribution, what you are doing and how you are doing it.
A useful exercise here is to try and write the core elements of an introduction on a Post-it note. Keep trying until they fit. When they do, use that as the basis for these first few paragraphs. This is the same technique you use when filling out the PhD Writing Template .
As you go through the chapter, you will dial down into more and more detail. That means that the next stage, after the first few paragraphs, is to provide some context (steps 2-10 above).
Here you provide all the detail necessary to situate the study and make sense of the opening few paragraphs.
But, there are two things to bear in mind.
You will need to ease into the detail gently. Don’t launch straight from your opening paragraphs into huge amounts of detail. Follow the order of the 13 steps above and you will gradually ease into your discussion.
The danger of presenting too much information too soon is that you will confuse the reader. They will struggle to understand how the information you present is relevant and will struggle to understand how it relates to your thesis aims and objectives.
Simply follow the steps above.
You need to bear in mind that the level of detail you will go into (and therefore the length of the introduction) depends on the structure of your thesis.
If you have a standalone literature review, you will go into less detail about the current state of the literature and the gaps within it.
Similarly, if you have a dedicated theory chapter, you will not need to spend too much time on developing your theory framework.
The same is true for your methods.
The goal in any case is to present enough context to situate and make sense of your research questions but not overburden the reader with information that is superfluous to the goal of situating the research and which you will repeat at a later juncture anyhow.

Your PhD thesis. All on one page.
Use our free PhD structure template to quickly visualise every element of your thesis.
Common problems when writing your introduction
When we proofread PhDs , we see the same mistakes again and again.
Providing too much detail
There is a tendency to provide too much background information in the introduction. As we saw above, quite how much information you present in your thesis will depend on whether you have a standalone literature review or methods chapter. What you want to avoid is any unnecessary repetition.
Sometimes there is necessary repetition though. You need to present just enough information to contextualise your study and to be able to situate your aims, research questions an argument, but not too much that you end up confusing and bombarding the reader. Keep things simple here; it’s fine to overlook some of the more technical detail at this stage. Think of a newspaper article: the first couple of paragraphs provide a brief overview of the story. The detail comes later.
Not providing enough detail
On the flip side, some students don’t provide enough detail. The danger here is that the reader is left asking questions at the end of the introduction. Remember: they should be able to understand what your thesis is about, how it was conducted and why it is important just from reading the introduction. If you present too little detail then they won’t be able to. Read through your own introduction; is it clear what your contribution is and why it is important? If not, you haven’t got enough detail.
Launching into too much detail
Make sure you introduce gently. Don’t suddenly rush into lots of detail. Instead, you should make the aims, questions and contribution clear in the opening lines and then gradually layer on more detail. That way, the reader can keep up. Present too much detail too soon and the reader will become confused. The last place you want confusion is in the introduction; if the reader can’t follow your introduction, they won’t understand the thesis.
Not following a coherent structure so that the reader is left confused
Some students don’t follow a coherent logic when they write their introductions, which means that the reader is left confused.
For example, if you present too much background information and literature review before you outline the aim and purpose of the research, the reader will struggle to follow, because they won’t know why the background information is important.
The same is true if you discuss the methods before your research questions.
What we see often is important information being spread throughout the introduction in such a way that the reader has to hunt for it. Follow our layout guide above so that each piece of vital information is contained in its own mini section. Make your reader’s job as easy as possible.
Using too much technical language not properly defined
It’s more than likely that your research relies upon lots of technical terms, concepts and techniques. If you must talk about any of these in the introduction, be sure to offer clear and concise definitions. A failure to do so means that the reader is left confused.
Conducting a literature review
Unless you are explicitly avoiding a standalone literature review chapter, the introduction is not the place to review the literature. Sure, you will need to situate your study in a body of literature, but the introduction isn’t the place to critically discuss it or justify its inclusion in that literature. It’s enough to say that you will contribute to X body of literature and briefly discuss its core features and shortcomings. The literature review is the place to justify that decision and elaborate upon its features. Read our guide to writing literature reviews and our guide to being critical when you do so.
Finalising your thesis introduction
Once you have finished your thesis, ask yourself the following questions:
- Does the first line of the introduction discuss the problem that your thesis is addressing and the contribution that it is making?
- Does the introduction provide an overview of the thesis and end with a brief discussion on the content of each chapter?
- Does the introduction make a case for the research?
- Have the research questions/problems/hypotheses been clearly outlined (preferably early on)?
Now you know how to present your research as clearly and concisely as possible. Your reader (and examiner) will thank you, because they’ll be able to understand exactly what your study is about just from reading the introductory pages. Keep this guide to hand, whatever stage of the writing process you are at.
Have you downloaded our free one page PhD Writing Template ? It’s a really effective way to visualise your entire thesis on one page.
If you’re still struggling to structure your introduction, or you need any other support as you write your thesis, check out our one-on-one PhD coaching . It’s like having a personal trainer, but for your PhD.
Share this:
12 comments.
I was struggling with writing the introduction chapter. Really had no idea on how to organise my ideas. Completely lost and desolate. I have no one to encourage or support me. I prayed to God to give me knowledge and wisdom and guide me. After a while I found this site. Praise the Lord. I can’t thank u enough for addressing exactly what’s in my mind. Thank you. Glory be to God for directing me to this site.
All we aim to do here is to make life a little bit easier for PhD students. I know how hard I found it when I was completing mine, so I want to give something back to the community. I’m so pleased you found it useful. Good luck with writing up. If you need any support or if you have any questions at all, email me: [email protected]
Thank you very very much for your information it is resourceful. I was having a problem how to start my introduction.
It’s great to hear you found it useful. Thanks!
Hey, this is so useful thankyou! I’m wondering does this apply broadly to all PhD’s including humanities?
Yep – it sure does.
I found this piece of information helpful. I am preparing for my proposal defense in two weeks and needed to refine my introduction. Thank you very much. God bless you richly. I wish we can have a skype conversation.
Thank you again.
thank you, learned from this
Your advice and guidance has become my constant companion in what has been a very stressful time. You write with empathy and understanding. What a wonderful job you are doing for those of us who are too proud to seek advice and support from supervisors or colleagues. Sincerest thanks for taking the loneliness out of writing.
Such nice words. Thank you so much.
this is really useful!!!
Thanks Nora! I’m glad you found it useful.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Search The PhD Knowledge Base
Most popular articles from the phd knowlege base.
The PhD Knowledge Base Categories
- Your PhD and Covid
- Mastering your theory and literature review chapters
- How to structure and write every chapter of the PhD
- How to stay motivated and productive
- Techniques to improve your writing and fluency
- Advice on maintaining good mental health
- Resources designed for non-native English speakers
- PhD Writing Template
- Explore our back-catalogue of motivational advice

- LEARNING SKILLS
- Writing a Dissertation or Thesis
- Introduction
Search SkillsYouNeed:
Learning Skills:
- A - Z List of Learning Skills
- What is Learning?
- Learning Approaches
- Learning Styles
- 8 Types of Learning Styles
- Understanding Your Preferences to Aid Learning
- Lifelong Learning
- Decisions to Make Before Applying to University
- Top Tips for Surviving Student Life
- Living Online: Education and Learning
- 8 Ways to Embrace Technology-Based Learning Approaches
- Critical Thinking Skills
- Critical Thinking and Fake News
- Understanding and Addressing Conspiracy Theories
- Critical Analysis
- Study Skills
- Exam Skills
- How to Write a Research Proposal
- Ethical Issues in Research
- Dissertation: The Introduction
- Researching and Writing a Literature Review
- Writing your Methodology
- Dissertation: Results and Discussion
- Dissertation: Conclusions and Extras
Writing Your Dissertation or Thesis eBook

Part of the Skills You Need Guide for Students .
- Research Methods
- Teaching, Coaching, Mentoring and Counselling
- Employability Skills for Graduates
Subscribe to our FREE newsletter and start improving your life in just 5 minutes a day.
You'll get our 5 free 'One Minute Life Skills' and our weekly newsletter.
We'll never share your email address and you can unsubscribe at any time.
Writing a Dissertation: The Introduction
The introduction to your dissertation or thesis may well be the last part that you complete, excepting perhaps the abstract. However, it should not be the last part that you think about.
You should write a draft of your introduction very early on, perhaps as early as when you submit your research proposal , to set out a broad outline of your ideas, why you want to study this area, and what you hope to explore and/or establish.
You can, and should, update your introduction several times as your ideas develop. Keeping the introduction in mind will help you to ensure that your research stays on track.
The introduction provides the rationale for your dissertation, thesis or other research project: what you are trying to answer and why it is important to do this research.
Your introduction should contain a clear statement of the research question and the aims of the research (closely related to the question).
It should also introduce and briefly review the literature on your topic to show what is already known and explain the theoretical framework. If there are theoretical debates in the literature, then the introduction is a good place for the researcher to give his or her own perspective in conjunction with the literature review section of the dissertation.
The introduction should also indicate how your piece of research will contribute to the theoretical understanding of the topic.
Drawing on your Research Proposal
The introduction to your dissertation or thesis will probably draw heavily on your research proposal.
If you haven't already written a research proposal see our page Writing a Research Proposal for some ideas.
The introduction needs to set the scene for the later work and give a broad idea of the arguments and/or research that preceded yours. It should give some idea of why you chose to study this area, giving a flavour of the literature, and what you hoped to find out.
Don’t include too many citations in your introduction: this is your summary of why you want to study this area, and what questions you hope to address. Any citations are only to set the context, and you should leave the bulk of the literature for a later section.
Unlike your research proposal, however, you have now completed the work. This means that your introduction can be much clearer about what exactly you chose to investigate and the precise scope of your work.
Remember , whenever you actually write it, that, for the reader, the introduction is the start of the journey through your work. Although you can give a flavour of the outcomes of your research, you should not include any detailed results or conclusions.
Some good ideas for making your introduction strong include:
- An interesting opening sentence that will hold the attention of your reader.
- Don’t try to say everything in the introduction, but do outline the broad thrust of your work and argument.
- Make sure that you don’t promise anything that can’t be delivered later.
- Keep the language straightforward. Although you should do this throughout, it is especially important for the introduction.
Your introduction is the reader’s ‘door’ into your thesis or dissertation. It therefore needs to make sense to the non-expert. Ask a friend to read it for you, and see if they can understand it easily.
At the end of the introduction, it is also usual to set out an outline of the rest of the dissertation.
This can be as simple as ‘ Chapter 2 discusses my chosen methodology, Chapter 3 sets out my results, and Chapter 4 discusses the results and draws conclusions ’.
However, if your thesis is ordered by themes, then a more complex outline may be necessary.
Drafting and Redrafting
As with any other piece of writing, redrafting and editing will improve your text.
This is especially important for the introduction because it needs to hold your reader’s attention and lead them into your research.
The best way to ensure that you can do this is to give yourself enough time to write a really good introduction, including several redrafts.
Do not view the introduction as a last minute job.
Continue to: Writing a Literature Review Writing the Methodology
See also: Dissertation: Results and Discussion Dissertation: Conclusions and Extra Sections Academic Referencing | Research Methods
University Libraries
Writing a dissertation or thesis proposal, what is a proposal, what is the purpose of a proposal.
- Video Tutorials
- Select a Topic
- Research Questions
- Search the Literature
- Plan Before Reviewing
- Review the Literature
- Write the Review
- IRB Approval
The proposal, sometimes called the prospectus, is composed mainly of the Introduction, Research Questions, Literature Review, Research Significance and Methodology. It may also include a dissertation/thesis outline and a timeline for your proposed research. You will be able to reuse the proposal when you actually write the entire dissertation or thesis.
In the graduate student timeline, the proposal comes after successfully passing qualifying or comprehensive exams and before starting the research for a dissertation or thesis.
Each UNT department has slightly different proposal requirements, so be sure to check with your advisor or the department's graduate advisor before you start!
- Examples of Proposals from UTexas More than 20 completed dissertation proposals are available to read at the UT Intellectual Entrepreneurship website.
- Dissertation Proposal Guidelines This document from the Department of Communication at the University of Washington is a good example of what you might be expected to include in a proposal.
The purpose of a proposal is to convince your dissertation or thesis committee that you are ready to start your research project and to create a plan for your dissertation or thesis work. You will submit your proposal to your committee for review and then you will do your proposal defense, during which you present your plan and the committee asks questions about it. The committee wants to know if your research questions have academic merit and whether you have chosen the right methods to answer the questions.
- How to Prepare a Successful Dissertation Proposal Defense Some general tips for a proposal defense from synonym.com
Need help? Then use the library's Ask Us service. Get help from real people face-to-face, by phone, or by email.
- Next: Resources >>
- Last Updated: Nov 13, 2023 4:28 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.unt.edu/Dissertation-thesis-proposal
Additional Links
UNT: Apply now UNT: Schedule a tour UNT: Get more info about the University of North Texas
UNT: Disclaimer | UNT: AA/EOE/ADA | UNT: Privacy | UNT: Electronic Accessibility | UNT: Required Links | UNT: UNT Home
Dissertation & Thesis Examples 📖
Real-world examples and samples from leading universities
Need some inspiration for your study? You’ve come to the right place. Here we showcase a collection of dissertation and thesis examples to help you get started. All of these are real-world studies from actual degrees (typically PhD and Master’s-level).
PS – If you’re looking for examples of specific dissertation chapters (e.g., literature review or methodology), you can also check out our collection of free templates .
Discipline-Specific Examples
- Business & management
- Political science
Stage-Specific Examples
- Proposal/pitch
- Literature review
- Methodology
Examples: Business & Management
Below you’ll find a sample of business and management-related dissertations and theses covering a range of topics.
Title: Interaction Among Supply Chains: Consumers, Firms and Policymakers Author: Yuanchen Li Year: 2020
This PhD thesis examines the dynamics of supply chain relationships across three levels: the interactions between firms and consumers, suppliers and buyers, and firms and governments. The research aims to provide insights into the complexities of supply chain dynamics and their implications for various stakeholders.
Title: Essays in Firm-Level Patenting Activities and Financial Outcomes Author: Michael J Woeppel Year: 2020
This doctoral dissertation explores financial dynamics in two key areas: investment valuation and the performance of small innovative firms. The first chapter introduces a new metric, PI q, which incorporates the replacement cost of patent capital into the traditional Tobin’s q calculation. The second chapter examines small innovative firms, finding that they achieve higher returns for up to five years compared to non-innovators.
Title: Analysis of Design Artifacts in Platform-Based Markets Author: Vandith Pamuru Subramanya Rama Year: 2020
This dissertation investigates design issues within digital platform-based markets through three essays. The first essay explores the economic impact of augmented-reality games like Pokémon Go on local businesses, specifically restaurants. The second essay delves into the sponsored search ad-market, examining the effects of market frictions on bidding behaviors in auctions. The third essay examines user-generated content platforms, focusing on how the loss of elite status affects user contributions.
Title: Gaming the IRS’s Third-Party Reporting System: Evidence From Pari-Mutuel Wagering Author: Victor Charles Ferguson Year: 2020
This dissertation investigates if taxpayers deliberately avoid IRS third-party reporting mechanisms, focusing on an IRS amendment in 2017 that changed how gambling winnings are reported. Specifically, it looks at the impact on thoroughbred racing wagers in the US, using Canadian tracks as a control.
Title: Essays on Product Innovation and Failures Author: Moonsik Shin Year: 2020
This dissertation delves into how strategic decisions made by firms can lead to innovation failures, a relatively underexplored area compared to studies on successful innovations. The research is structured into three essays. The first explores how inter-organisational relationships, specifically investments from venture capitalists, can influence innovation failures due to pressures such as time constraints imposed on portfolio companies. The second essay examines the role of acquisitions in innovation failures, suggesting that challenges like adverse selection and integration issues post-acquisition can significantly hinder a firm’s innovation outcomes. The third essay looks at how incremental product development can lead to failures if new products are too dependent on existing technologies, which may themselves be flawed.
Need a helping hand?
Examples: Psychology Dissertations
Title: Development and Validation of the Instrumental Support Inventory for Spouses Author: Ryan P. Egan Year: 2020
This research develops and validates the Instrumental Support Inventory for Spouses (ISI-s), a new tool to measure the practical support received from a romantic partner. The study involved two phases: initially, 372 married individuals helped refine the 39-item inventory across five categories through exploratory factor analysis, assessing reliability and validity. The second phase tested the inventory with 298 parents and their partners, using a longitudinal design, confirming its reliability and validity further.
Title: Dysfunctional Individuation, Spiritual Struggle and Identity in Emerging Adults: A Developmental Approach Author: Katheryn J. Klukow Kelley Year: 2020
This study investigates why emerging adults are participating less in organised religion, yet showing increased spirituality, attributing this shift to the process of religious identity development. The research involved a longitudinal survey of 788 students at a religious university, using structural equation models to analyse data collected at four points over an academic year.
Title: Depression Dynamics across a Decade: Density in Daily Depressive Affect and Yearly Depressive Symptoms Author: Raquael J. Joiner Year: 2020
This thesis investigates depression through a dynamic systems perspective, which views changes in depressive symptoms as part of an interconnected network of emotions and states, rather than isolated events. The research focuses on how the density of depressive affect—essentially the compactness and intensity of depressive symptoms—varies within individuals over a decade. By examining data at five different timepoints, the study aims to understand how these symptoms cluster daily and how this clustering influences transitions into or out of depressive states year by year.
Title: Maternal and Adolescent ADHD, Aggression, and Dysfunctional Discipline: Mediating Roles of Maternal Emotion Dysregulation and Stress Author: Natalie M. Ehret Year: 2020
This dissertation explores the challenges that parents face when both they and their children exhibit symptoms of ADHD, as well as oppositional defiant and aggressive behaviours. It investigates how these symptoms in mothers and adolescents may influence parenting discipline, focusing specifically on the roles of maternal emotion dysregulation and stress in shaping disciplinary practices. The study employs a process-oriented approach to better understand these complex dynamics.
Title: Linguistic Markers of Maternal Focus within Emotional Conversations: The Role of Depressive Symptoms and Maltreatment Author: Brigid Behrens Year: 2020
This study explores the relationship between maternal well-being and the language used during parent-child conversations about past emotional events. It specifically examines the use of first-person singular (“I”) and first-person plural (“we”) pronouns during a reminiscing task, to determine how maternal language might reflect cognitive biases. The research includes 229 mother-child dyads, both maltreating and non-maltreating, who are part of a larger clinical trial focused on Reminiscing and Emotion Training.

Examples: Education Theses
Title: Functions and Purposes of Outdoor Education in Singaporean Education and Society: An Instrumental Case Study Author: Susanna Ho Year: 2011
This research aims to explore the roles outdoor education can play in Singapore, by conducting a case study of one school’s programme. Employing interviews, participant observations, and document analysis with tools like NVivo software, the study uses a grounded theory framework to interpret findings. It also incorporates Gert Biesta’s educational functions to assess outdoor education within Singapore’s specific context.
Title: The Impact of Internationalisation of Higher Education on Nursing Education in an Australian University: A Case Study Author: Elizabeth Alexandra Lavender Year: 2014
This study examines the impact of the rapid internationalisation of higher education on the School of Nursing and Midwifery at La Trobe University, Australia. It explores how global trends and policies, particularly the shift from ‘Aid to Trade’, have influenced educational practices within the school. The research uses a case study approach, incorporating document analysis and interviews with 15 university staff experienced in international education.
Title: Diabetes Education from the Podiatrist Perspective Author: Julia Yungken Year: 2020
This thesis investigates how diabetes education is delivered by podiatrists to patients, and the retention of this education over time. Through a series of four articles, the research first conducts a systematic review and meta-analysis to examine current educational practices. It then follows a study with three podiatrists and 24 patients over six months to observe educational retention. Additionally, a survey among Australian podiatrists assesses various educational methods and experiences. The study utilises diverse methodologies including observational studies, cognitive assessments, and surveys to understand and enhance the educational practices in diabetes care provided by podiatrists.
Title: Empowering Saudi Arabian Primary Teachers Through Participatory Action Research to Improve Their Professional Knowledge and Practices Regarding Gifted Learners Author: Faisal Yahya Alamiri Year: 2013
Title: Developing a National Assessment Model to Inform Educational Policy in Bhutan Author: Gembo Tshering Year: 2012

Examples: Healthcare-Related Dissertations
Title: Impact of the Increased Use of Telehealth on Health Care Management and Administration: The Case of New Care Management Practices Author: Immacula Pierre Year: 2024
This qualitative study explored the perceptions of healthcare managers on telehealth’s role and its influence on healthcare practices during the pandemic, focusing on aspects like provision and quality control. Through video-conferenced semi-structured interviews with 10 healthcare managers across various U.S. settings, the research aimed to understand the benefits, challenges, and the future role of telehealth.
Title: Healthcare Facilities Management Leadership Style Compared to Traditional Healthcare Business and Clinical Leaders Author: Joshua Ashlock Year: 2020
This dissertation explores leadership style differences between two groups within healthcare: traditional business and clinical leaders (represented by members of the American College of Healthcare Executives, ACHE) and healthcare facilities management leaders (represented by members of the American Society of Healthcare Engineers, ASHE). The research focuses on comparing transformational, transactional, and passive-avoidant leadership traits between these groups.
Title: Leadership Support as an Influence on Frontline Healthcare Employee Retention in the Washington Metropolitan Area (DMV) Author: Tamika Fair Year: 2023
This qualitative case study addresses the significant issue of high turnover rates among frontline healthcare employees in the DMV area, examining how the lack of support from healthcare leadership contributes to this problem. Through semi-structured interviews with 11 primary healthcare administrators in the DMV region, the research investigates how leaders engage with frontline workers and assesses their preparedness to tackle high staff turnover.
Title: Electronic Patient Portals: Promotion of Access by Healthcare Workers Increases Patient Engagement Author: Dena Todd Year: 2022
This integrative literature review examines strategies for promoting electronic patient portal (EPP) access in healthcare settings, a requirement highlighted by the Health Information for Economic and Clinical Health (HITECH) Act of 2010. The review underscores the importance of EPP systems in providing patients with access to their personal health information, including medications, lab results, diagnostics, and appointments. It discusses the potential risks for healthcare organisations that fail to offer such access, notably the loss of federal funding.
Title: Understanding Workplace Conditions Contributing to Physician Burnout Prevalence in Maryland State Author: Fatima Adefunke Queen Year: 2023
This dissertation utilises a qualitative multiple-case study to examine the workplace conditions that contribute to physician burnout in Maryland, particularly among primary care providers who show burnout rates of up to 50%. The study involved interviews with 21 physicians, including Medical Doctors (M.D.s), Doctors of Nursing Practice (DNPs), and Nurse Practitioners (NPs). Using Shanafelt’s well-being framework, the research aimed to understand the factors leading to burnout and its subsequent impact on physician attrition.

Examples: Political Science Theses
Title: The Influence of Peer Relationships on Political Socialisation Among College Students Author: Zachary Thomas Isaacs Year: 2021
This thesis investigates the role of peer relationships in the political socialisation of college students. This is an area not extensively covered by existing research, which primarily focuses on parental influence and often excludes the post-18 age group. A survey was conducted among college students aged 18 to 24, to explore how they communicate with their peers regarding politics and the effects of these interactions on their political socialisation.
Title: The Impact of Political Culture on Political Reactions: A Case Study of EU Sanctions on Russia Author: Kenzie Robin De Keyser Year: 2020
This dissertation examines the complex political impacts of European Union (EU) sanctions on Russia, taking into account the nuanced interplay between Russia’s political culture and the economic interdependencies between the EU and Russia. The research utilises the Cross-Cultural Competency (3Cs) Theorem to analyse key elements of Russian political culture—Russian Orthodox Christianity, geography, autocracy, and economic development— which are crucial in shaping the country’s political responses and governmental structure.
Title: Biased Representation: How Compulsory Voting and Campaign Finance Interact to Influence Government Responsiveness Author: Sarah Steinberg Year: 2016
This thesis investigates the interaction between compulsory voting and campaign finance, focusing on how they influence government responsiveness. It argues that the significant financial influence in political campaigns can lead to an elite bias, where government policies favour wealthier interests. The study uses statistical analysis and case studies from two countries to explore whether compulsory voting, which typically results in nearly universal voter turnout, can mitigate this bias.
Example: Dissertation Proposal
Example: literature review chapter, example: methodology chapter.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
-20% de remise automatique à partir de 3 outils

- 8 min de lecture
[DISSERTATION] La constitution, norme fondamentale
Cours et copies > Droit constitutionnel
Voici un exemple de dissertation en droit constitutionnel portant sur la constitution. La dissertation aborde la valeur de la constitution (texte fondamental dans un État de droit) ainsi que les libertés et droits fondamentaux qu'elle protège. Cette copie a obtenu la note de 15/20.
I/ La constitution, texte aux fondements de la vie politique des États de droit
A) la constitution aux fondements des caractéristiques essentielles de l'état.
B) La constitution, garante du bon fonctionnement de la séparation des pouvoirs
II/ La constitution, garantie des droits et libertés fondamentales
A) des droits et libertés inscrits dans des déclarations de droits, b) la constitution, texte organisant la défense des droits et libertés fondamentales.

N.B : cette copie est le fruit de la réflexion d’un étudiant en droit. La découvrir vous permettra de comprendre le raisonnement de ce dernier, qui lui a valu la note indiquée. Elle vous aidera à ce que vous ayez les outils pour formuler votre propre réflexion autour du sujet donné. Pour rappel, le plagiat est formellement interdit et n’est évidemment pas recommandé si vous voulez vous former au droit. En d’autres termes, réfléchissez vous-même ! Enfin, cette copie n’a pas eu 20/20, gardez un œil critique sur ce travail qui n’est donc pas parfait.
Disclaimer : attention ! N’oubliez pas que la méthodologie peut varier selon les facultés, mais aussi en fonction des enseignants. La méthodologie utilisée dans cette copie n'est donc pas universelle. Respectez la méthodologie enseignée par vos chargés de travaux dirigés et par vos enseignants.
Sujet : La constitution, norme fondamentale
[Accroche] « Une constitution doit être courte et obscure. Elle doit être faite pour ne pas gêner l'action du gouvernement ». Par cette citation, Napoléon Bonaparte cherche à nous montrer que pour lui, une constitution n'est qu'un texte servant à légitimer chaque action de l'État. Cependant, aujourd'hui, la Constitution est plutôt décrite comme la norme fondamentale à laquelle l’État doit se soumettre. Bien
[Définition] Au sens formel, une constitution est l'ensemble des textes organisant la vie politique des institutions (les pouvoirs publics) , les élections des représentants et les droits et libertés fondamentales. Au sens large, une constitution est la norme suprême d'un état. La hiérarchie des normes est une théorie de Hans Kelsen, dans laquelle chaque norme inférieure doit se conformer aux normes supérieures. (Oui) Dans cette pyramide , la constitution fait partie du bloc de constitutionnalité et est la plus haute norme existante. On dit donc qu'elle, ainsi que les textes qui lui sont rattachés, sont la norme fondamentale de l'État. Différentes formes de Constitution ?
[ Contextualisation historique ] Afin de nous concentrer sur la place de la Constitution dans l'État de droit, nous exclurons donc tous les contrôles visant à garantir la conformité des autres normes à la constitution ainsi que la relation de la constitution aux autres règle de droit. (Vous l’évoquez pourtant dans le II B !). Nous ne parlerons aussi donc pas de différents modes de rédaction des constitutions ainsi que de la distinction entre pouvoirs constituant originaire et dérivé et entre constitution coutumière et constitution écrite. (Ok) Nous nous concentrerons donc sur les constitutions tout autour de ??? et plus particulièrement sur celles apparues après 1945.
La place de la constitution comme norme fondamentale est aujourd'hui fortement remise en question, notamment par le droit européen qui dit se placer au-dessus des constitutions des États membres, ce qui a été accepté de manière différente par les juristes des dits États membres. De plus, avec la montée en puissance des revendications en faveur d'une VIème République, il peut être intéressant de regarder les caractéristiques faisant de la constitution une norme fondamentale et notamment sur ce que doit garantir une constitution afin de faire de l'État un État de droit . (Bien)
[ Problématique ] En quoi la constitution est-elle la norme fondamentale des États de droit ? (Pas que dans les États de droit !)
[ Annonce de plan ] La constitution a tout d'abord la place de norme fondamentale, car elle permet de régler différents points importants d’un État de droit [Ndlr : Voir une dissertation sur l'Etat de droit] . Mais cela permet aussi surtout de régler la question de la séparation des pouvoirs afin de savoir quels pouvoirs disposent de quelles attributions. Mais la constitution permet aussi et surtout de garantir les droits et libertés fondamentales ce qui est généralement fait dans les déclarations de droit. Mais la constitution ne se contente pas d’énoncer ces droits et libertés fondamentales, elle organise aussi leurs défenses.
Afin de traiter ces différents points, nous verrons dans un premier temps que la constitution organise la vie politique des États de droit (I). Puis, dans un second temps, nous montrerons que la constitution garantit des droits et libertés (II).
❤️ Recommandé pour vous :
Comment réussir sa dissertation juridique ?
« de la vie politique » → des pouvoirs publics ; « des États de droit » → pas nécessaire !
[Chapô] Tout d'abord, la constitution organise la vie politique des États de droit en réglant différents points importants dont les deux principaux sont les caractéristiques essentielles de l'État (A) ainsi que la question de la séparation des pouvoirs (B). Votre titre A est trop large ! Il englobe une partie de votre B !
Titre A trop similaire à votre titre I !
Tout d'abord, la constitution joue un rôle majeur dans la forme de l'État. En effet, c'est elle qui détermine si l'État est unitaire, régional ou fédéral ainsi que les différentes conséquences que cela entraîne. (Bien) Ainsi, la Constitution française de la Vème République prévoit que l'État français est un État unitaire décentralisé, c'est-à-dire que le pouvoir de décision est concentré en un seul endroit mais que certaines attributions sont néanmoins données aux collectivités territoriales. (Ok) La Constitution organise aussi le mode de scrutin afin de déterminer si celui-ci est restreint ou ouvert à toute la population sans distinction.
Mais la Constitution ne se limite pas à ces choix et permet aussi de déterminer les institutions qui seront actrices de la vie publique. (Affirmation de la souveraineté interne et externe de l’État ?) Ainsi, la Constitution fédérale allemande dispose que le Parlement allemand est divisé en deux chambres : le Bundestag et le Bundesrat. De plus, la Constitution permet aussi de fixer les modes de participation des citoyens à la vie politique en fixant notamment les modalités d'exercice du référendum ou bien les types de mandats exercés par les représentants du peuple . Ok
[ Transition ] Si la constitution fixe les caractéristiques essentielles d'un État de droit, elle a aussi pour tâche de régler la question de la séparation des pouvoirs et les conflits que celle-ci peut engendrer. Fonction intégrative et symbolique de la Constitution ?
B) La constitution, garantie du bon fonctionnement de la séparations des pouvoirs
« garantie » → « garante »
Dans L’esprit des lois , Montesquieu a théorisé que dans une démocratie, chaque pouvoir devait avoir une attribution propre. Cette théorie est aujourd'hui toujours mise en application dans les différentes constitutions autour du globe et permet même de mesurer si un État est un État de droit ou non. Cette théorie peut prendre deux formes qui se retrouvent dans deux types de constitutions. Ainsi, la Constitution américaine prévoit un régime présidentiel, c'est-à-dire que la fonction exécutive est exercée par un Président disposant de pouvoirs plutôt étendus et la séparation des pouvoirs est une séparation stricte des pouvoirs [Ndlr : Voir une dissertation sur le régime présidentiel ]. A contrario, un régime parlementaire comme le régime allemand va avoir une séparation des pouvoirs moins stricte et plus de coopération entre les pouvoirs. Ok
Après avoir réglé la question de comment sont séparés les pouvoirs, la constitution doit aussi réguler les conflits entre les différents pouvoirs. Pour cela, la Constitution va créer une institution qui a pour but de trancher les conflits d'attribution. Cette institution s'appelle le Conseil constitutionnel en France et va permettre de vérifier si les actions du Gouvernement n’outrepassent pas les prérogatives que lui donne la constitution. (Bien) En Allemagne, le Bundesverfassungsgericht, l’équivalent allemand, va aussi être amené à trancher donc les conflits d'attribution entre les États fédérés et l'État fédéral.
[ Transition ] La constitution joue donc un rôle important dans l'organisation de la vie politique de l'État de droit mais elle a aussi pour mission de garantir des droits et libertés fondamentales aux citoyens.
Dissertation juridique, les 10 conseils d'un chargé de TD
« garantie » → « garante », sinon ok
[Chapô] La constitution, afin de faire de l'État un État de droit, garantit donc aux citoyens un certain nombre de droits que l'on retrouve généralement dans une déclaration de droits (A), et assure surtout le respect de ces droits (B).
Titre trop descriptif !
Pour garantir ces droits et libertés fondamentales, la constitution utilise donc des déclarations de droits qui se trouvent généralement dans le préambule ou au début de la constitution. Ces déclarations de droit sont des listes de droits qui ont donc pour effet que tous les droits listés dans cette déclaration seront des droits à valeur constitutionnelle qui s'imposent donc aux institutions. En Allemagne, ces droits se trouvent garantis dans les articles 1 à 20 ce qui a donc pour effet de les placer tout au début de la loi fondamentale allemande ce qui montre l'attachement de la constitution allemande à ses droits fondamentaux. Bien
Pour le cas français, cette déclaration de droits ne se trouve pas explicitement marquée dans la Constitution ce qui fait du cas français une exception. En effet, c'est le Préambule de la Constitution de 1958 qui renvoie à des textes présentant ces différents droits, avec par exemple la Déclaration des droits de l'homme et du citoyen. Ces textes ont acquis une valeur constitutionnelle à la suite d'un arrêt (d’une décision) du Conseil constitutionnel et font donc désormais office de déclaration de droits. Ok → Décision Liberté d’association de 1971.
[ Transition ] Si les déclarations de droits permettent d'exposer ces différents droits fondamentaux, c'est bien la constitution qui assure le respect de ces droits par les institutions.
La constitution utilise en effet deux moyens pour garantir le respect de ces droits fondamentaux.
Le premier moyen ne se trouve que dans certaines démocraties et permet à la constitution d'interdire la modification et surtout la suppression des articles de la déclaration de droit. C'est le cas par exemple en Allemagne, où les articles 1 à 20 évoqués plus tôt ne peuvent pas être modifiés ou supprimés par une révision constitutionnelle. Ces interdictions sont appelées des clauses d’éternités. Ok
Le second moyen utilisé par la constitution est le juge constitutionnel. En effet, celui-ci peut vérifier qu’une loi ne porte pas atteinte aux droits garantis par la constitution. Si cette loi porte atteinte, elle sera abrogée et ne pourra plus être appliquée. Mais ce sont aussi les citoyens qui peuvent saisir le juge constitutionnel pour vérifier qu'une loi ne porte pas atteinte à ces droits constitutionnels. C'est le cas aux États-Unis où un citoyen peut saisir le juge lors d'un litige afin de vérifier qu’un de ces droits n'a pas été atteint par une loi ou une procédure. Ok, mais trop approximatif.
Commentaire général de l'enseignant : travail sérieux. Des connaissances malgré quelques oublis. Quelques maladresses sur la forme, notamment s’agissant de vos titres.

🧰 Parce que votre réussite nous tient à cœur, augmentez vos chances de valider votre année en découvrant toutes les ressources de la BOÎTE À OUTILS ( Flashcards Pamplemousse , Fiches de révisions , Livres de réussite ) .
💖 Recevez aussi des good vibes, des conseils confidentiels et réductions exclusives en recevant la NEWSLETTER DU BONHEUR.
[DISSERTATION] La séparation des pouvoirs aux USA (Droit constitutionnel)
[DISSERTATION] Exemple : un écart irréductible de la Constitution ? (Droit constitutionnel)
[DISSERTATION] Séparation des pouvoirs et régime présidentiel

File(s) under embargo
until file(s) become available
BISMUTH-BASED LAYERED SUPERCELL MULTIFERROIC THIN FILMS TOWARDS MULTIFUNCTIONALITY AND DEVICE APPLICATIONS
Multiferroics, which exhibit multiple ferroic orderings within a single material system, have substantial potential for applications in sensors, transducers, memory devices, and energy harvesters. However, the development of single-phase multiferroics that demonstrate roomtemperature properties remains limited by inherent contradictions in d-orbital occupancy between magnetic and ferroelectric materials. This dissertation focuses on addressing this challenge through the exploration of a novel bismuth-based, single-phase multiferroic thin film that features an exotic layered supercell (LSC) structure and displays multiferroic properties at room temperature. The primary aim is to deepen the understanding of LSC materials and advance their applications in practical devices. The dissertation is structured as follows: It begins with an introduction to the fundamental concepts of multiferroics, including their classifications and applications, the specific characteristics and growth mechanism of LSC materials, and other relevant background knowledge. This is followed by a detailed description of the experimental techniques employed. The core of this dissertation comprises four chapters that present a comprehensive study of LSC materials. The first chapter discusses a nanocomposite system combining an LSC material, Bi1.25AlMnO3.25, with Au nanoparticles (NPs), highlighting its tunable microstructure and multifunctional properties influenced by growth temperature. The second chapter explores the integration of Bi2NiMnO6 on a flexible mica substrate, demonstrating the potential of LSC materials for use in flexible electronics, with performance maintained across various bending conditions. The third chapter details the development of freestanding LSC thin films by utilizing a water-soluble sacrificial layer, which are shown to preserve their microstructure and properties after being transferred onto a silicon substrate. Building on this, the fourth chapter investigates the reuse of recycled SrTiO3 substrates for subsequent thin film growth, examining changes in surface strain states and chemistry to guide sustainable practices in complex oxide thin film processing. In summary, this dissertation presents an extensive examination of LSC multiferroics, revealing their significant promise for multifunctional applications and integration into flexible and silicon-based electronics. Additionally, the work explores sustainable methods for substrate reuse, contributing further to the field of material sciences.
N00014-20-1-2600
Degree type.
- Doctor of Philosophy
- Materials Engineering
Campus location
- West Lafayette
Advisor/Supervisor/Committee Chair
Additional committee member 2, additional committee member 3, additional committee member 4, usage metrics.
- Functional materials


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Overview of the structure. To help guide your reader, end your introduction with an outline of the structure of the thesis or dissertation to follow. Share a brief summary of each chapter, clearly showing how each contributes to your central aims. However, be careful to keep this overview concise: 1-2 sentences should be enough.
Craft an enticing and engaging opening section. Provide a background and context to the study. Clearly define the research problem. State your research aims, objectives and questions. Explain the significance of your study. Identify the limitations of your research. Outline the structure of your dissertation or thesis.
L'introduction de dissertation D'une longueur de 15 à 30 lignes, l'introduction doit être rédigée après ... entourée de normes et de lois qui la définissent au sein d'une société démocratique. Sujet : Être libre, est-ce faire ce que l'on veut ? 2. Définition et reformulation des
1. Research Background - Writing a Dissertation Introduction. This is the very first section of your introduction. Building a background of your chosen topic will help you understand more about the topic and help readers know why the general research area is problematic, interesting, central, important, etc.
La réponse est oui. Une bonne introduction de dissertation en français est rédigée de manière fluide et naturelle. Elle comporte une phrase d'accroche et une analyse du sujet suivie d'une problématisation et d'une annonce d'un plan d'étude. Le tout dans le même paragraphe sans oublier l'alinéa au début.
5. Keep the Reader in Mind. Always keep the reader in mind when writing your introduction. Consider what they need to know to understand your research and why it is important. Aim to engage and inform your reader, making them interested in your study and eager to read the rest of your dissertation.
Craft a convincing dissertation or thesis research proposal. Write a clear, compelling introduction chapter. Undertake a thorough review of the existing research and write up a literature review. Undertake your own research. Present and interpret your findings. Draw a conclusion and discuss the implications.
A Well-Written Dissertation Introduction Example. Seeing something once is more impactful than learning theory. We prepared a brief sample of a dissertation introduction on the topic "How Psychopathy Differs Between Children of Different Genders". Then, we analysed it to underline its strengths. Introduction Example
Crafting a snappy, interesting introduction, and putting efort into explaining the rationale of the study is key to creating this interest in your readers. Fig. 6.1. Introduction chapter as an inverted triangle. Secondly, you may have heard the advice "start broad and narrow the topic down" in your introduction.
Most dissertations run a minimum of 100-200 pages, with some hitting 300 pages or more. When editing your dissertation, break it down chapter by chapter. Go beyond grammar and spelling to make sure you communicate clearly and efficiently. Identify repetitive areas and shore up weaknesses in your argument.
A dissertation is a long-form piece of academic writing based on original research conducted by you. It is usually submitted as the final step in order to finish a PhD program. Your dissertation is probably the longest piece of writing you've ever completed. It requires solid research, writing, and analysis skills, and it can be intimidating ...
Stating the research problem or research question. Brief overview of the structure of your dissertation. Crafting an Effective Introduction in 06 Steps. 1. Starting with a compelling opening. 2. Providing Background Information. 3. Clearly stating the research problem.
An effective PhD thesis introduction does three things: 1. Establish your research territory (by situating your research in a broader context) One of the first things the introduction should do is to provide general statements that outline the importance of the topic and provide enough background information so that the reader can understand ...
Top Tip: Your introduction is the reader's 'door' into your thesis or dissertation. It therefore needs to make sense to the non-expert. Ask a friend to read it for you, and see if they can understand it easily. At the end of the introduction, it is also usual to set out an outline of the rest of the dissertation.
Generally, the chapter titles in a thesis are formatted as follows: Chapter X: Name of the chapter. You can choose to name the first chapter "Introduction" or something more imaginative if you feel like, depending on what is the norm in your field. However, if you choose to use more creative names, make sure they are not very informal.
Mastering these elements in your introduction can significantly enhance your examiner's initial impression and set a positive tone for the rest of your dissertation. Remember, a captivating introduction lays the groundwork for a compelling academic journey ahead.
Order and format of dissertation chapters may vary by institution and department. 1. Introduction 2. Literature review 3. Methodology 4. Findings 5. Analysis and synthesis 6. Conclusions and recommendations Chapter 1: Introduction This chapter makes a case for the signifi-cance of the problem, contextualizes the study, and provides an ...
The introduction is an integral and often overlooked part of the dissertation process. It not only introduces the topic, but it sets up the reader to understand what will be discussed in depth throughout the paper. Writing a compelling dissertation introduction can seem daunting, especially when facing such an important aspect of completing ...
The proposal, sometimes called the prospectus, is composed mainly of the Introduction, Research Questions, Literature Review, Research Significance and Methodology. It may also include a dissertation/thesis outline and a timeline for your proposed research. You will be able to reuse the proposal when you actually write the entire dissertation ...
The three preliminary pages that are required for all theses and dissertations are the title page, abstract, and table of contents. Lists of tables, figures, and attachments are required in some cases. All other pages are optional. Sample pages are available in the appendix of this document beginning on page 40.
This PhD thesis examines the dynamics of supply chain relationships across three levels: the interactions between firms and consumers, suppliers and buyers, and firms and governments. The research aims to provide insights into the complexities of supply chain dynamics and their implications for various stakeholders. Download Example.
La dissertation aborde la valeur de la constitution (texte fondamental dans un État de droit) ainsi que les libertés et droits fondamentaux qu'elle protège. Cette copie a obtenu la note de 15/20. N.B : cette copie est le fruit de la réflexion d'un étudiant en droit. La découvrir vous permettra de comprendre le raisonnement de ce dernier ...
The dissertation is structured as follows: It begins with an introduction to the fundamental concepts of multiferroics, including their classifications and applications, the specific characteristics and growth mechanism of LSC materials, and other relevant background knowledge. This is followed by a detailed description of the experimental ...