- Action Verbs
- Auxiliary (or Helping) Verbs
- Stative Verbs
- Modal Verbs
- Phrasal Verbs
- Verb Tenses
- Irregular Verbs
- Irregular Verbs List
- Confusing Verbs
- Gerunds and Infinitives
- Infinitive Definition & Examples
- Do, Does, Did
- An Extensive List of Phrasal Verbs
- The Present Simple Tense
- The Present Progressive Tense
- The Past Simple Tense
- The Past Progressive Tense
- The Present Perfect Simple Verb Tense
- The Future Tense
- The Present Perfect Progressive Tense

The Past Perfect Simple Tense
- The Past Perfect Progressive Tense
- The Future Perfect Tense
- Passive Voice
- Conjugation
- Conjunctions
- Preposition
- Use after, as soon as, the moment that, until before using the past perfect simple. Ex: After she had moved out , I found her notes./ I didn’t say anything until she had finished talking.
- Use before, when, by the time before the past simple: Ex. Before I knew it, she had run out the door. / By the time he phoned her, she had found someone new.
Write better and faster Ginger helps you write confidently. Start writing with Ginger
- The past perfect simple, to refer to the action that happened first or earlier
- The past simple to refer to the action that happened second or later
- After Sofie had finished her work, she went to lunch. (First she finished her work and then she went to eat lunch.)
- I washed the floor when the painter had gone. (First the painter left and then I washed the floor.)
- Harold had known about it for a while. (First he knew about it, then others knew about it)
- walk > walk ed / study > stud ied / stop > stop ped / create > creat ed
| Subject | had +Verb(V3) (Past Participle) | Rest of Sentence |
| I / You / We / They He / She / It | had met | him before he became famous |
| had lived | here for three years by the time we met |
- By the time Doris got to the party, everyone had gone home.
- Everyone had gone home by the time Doris had got to the party.
Contractions in the Past Perfect Simple
Punctuation tip.
- I had > I'd - After I'd used the phone, I paid the bill.
- He had > He'd / She has > She'd / It has > It'd - It'd happened so quickly, I didn't notice.
- We had > We'd / You have > You'd /They are > They'd – We'd just gotten home, when we heard the blast outside.
Negative Sentences in the Past Perfect Simple Tense
| Subject | Auxillery Verb | Verb in V3 (Past Participle) | Rest of Sentence |
| I / You / We / They He / She / It | hadn't (had not) | driven | a car before then |
| had never | driven | a car before then |
- I had not eaten at that restaurant before today.
- Samantha hadn't had time to explain her side of the story.
- My friends hadn't ever gone to France.
- My friends had never gone to the USA either.
Yes/No Questions in the Past Perfect Simple
| Auxiliary Verb | Subject | Verb in V3 (Past Participle) | Rest of Sentence |
| Had | I / you / we / they he / she / it | had | time to rehearse you're the song |
| Had | he / she / it | eaten | there before |
- Had you cleaned up the mess by the time they came home?
- Had Adam ever spoken to the CEO before he was fired?
Wh-Questions in the Past Perfect Simple
| Wh-Word | Auxiliary Verb | Subject | Verb in V3 (Past Participle) | Rest of Sentence |
| What | had | I / you / we / they he / she / it | taught | before leaving education |
| Why | had | changed | the subject |
- What had they said that made him so angry?
- Why had he agreed to work for that salary?
- How much had he drunk before you got to him?
Tag Questions in the Past Perfect Simple
- John had known about the cancer for a couple of years, hadn't he ?
- They had been in business together, hadn't they ?
- Jennifer hadn't spoken to you about it, had she ?
- They had never eaten a proper Indian meal, had they ?
Exercises – Past Perfect Simple
- After Loren had turned on the alarm, she locked the door. (turn on)
- By the time Simone arrived , the police had already left. (arrive)
- Had you known about the contract they signed? (know)
- After the company _____Joe, he began to work on his first project. (hire)
- _____you _______ the news before you saw it on TV? (hear)
- Michael didn’t want to see the movie because he _______ the book yet. (not read)
- The concert ______ already _______when we _______ the stadium. (begin/ enter)
- Until Anne ________ Mark, she ____ never ______in love. (meet, be)
- Bill __________ for years before he finally _______. (smoke/ quit)
- _______ Sara ever _______to London by herself before then? (drive)
- How many fish ______ the boys _____ by the time it started raining? (catch)
- You ________ them to go to the beach, hadn’t you? (forbid)
- The girls _______ in weeks? That’s why they ______ so much afterwards. (exercise / hurt)
- hadn't read
- had/begun/entered
- met/had/been
- had smoked/quit
- had forbidden
- hadn’t exercised / hurt
Examples - Past Perfect Simple
- After Sofie had finished her work, she went to lunch.
- I washed the floor when the painter had gone.
- Harold had known about it for a while.
- I didn't say anything until she had finished talking.
- After she had moved out, I found her notes.
- Before I knew it, she had run out the door.
- By the time he phoned her, she had found someone new.
- I had had enough of his complaining.
- After I'd used the phone, I paid the bill.
- It'd happened so quickly, I didn't notice.
- We'd just gotten home, when we heard the blast outside.
Yes/No Questions
Wh- questions, tag questions.
- John had known about the cancer for a couple of years, hadn't he?
- They had been in business together, hadn't they?
- Jenifer hadn't spoken to you about it, had she?
- They had never eaten a proper Indian meal, had they?
- Most answers
- No selected answer
- No upvoted answer
- Ask a question
- Post a note
- Register Login Remember
Past simple or past continuous?
Please log in or register to add a comment.
The first one is more natural if you are referring to an action that was in progress at 8 o'clock. But it is not possible to omit the subject in English, pronoun " I " in this case.
If you are referring to an action that was concluded before 8 o'clock, you should use Past Perfect and a different preposition, " by 8 o'clock" in this case.
E.g.: I had finished my homework by 8 o'clock last night.
Both sentences are syntactically incorrect, i.e. the word order is not respected.
You have two options: 1) to use a comma for emphasis: At 8 o'clock last night , I was doing my homework; 2) to put the whole adverbial phrase after the object: I was doing my homework at 8 o'clock last night .
Your answer
- Share on Twitter
- Share on Google+
- Share on Facebook
Related questions
- When can you use present continuous? Difference between the present simple and the present continuous.
- What's the difference between 'Present Perfect Simple Tense' and 'Present Perfect Continuous Tense?
- when should i use past perfect and past simple?
- What's the difference when you use past simple and present perfect?
- Could someone give me examples about Past,Present and Future Perfect Continuous?
Latest Questions
Cpelle asked.
I need some english lessons
ahmad4altamimi asked
Speak english
Jasmins96 asked
Wegen viel Arbeit oder wegen vieler Arbeit?
Jahangir Alom asked
English speaking practice
The difference between "has + been + p.p" and "had + been + p.p"
LanguageLearningBase.com ( short: llb.re ) is an online community for learning foreign languages. It represents an open knowledge base. Every member can share and gain knowledge about a new language. Read more -->
Get the Reddit app
A subreddit for questions and discussions about grammar, language, style, conventions[,] and punctuation.
"They have finished their homework" vs "They finished their homework"
How does the meaning of the two sentences differ, if it all. And is one more correct than the other?
English With Ashish
THE PAST CONTINUOUS TENSE
The Past Continuous tense is one of the most used tenses we have in English. In this lesson, we learn when to use the Past Continuous tense, how to use it, and its different usages
NOTE : the Past Continuous tense is commonly known as the Past Progressive tense either.
When to use the Past Continuous tense ?
We use the Past Continuous tense when we want to talk about what was happening at a particular time in the past. Imagine you just got home from a party, and your father confronts you. He tells you that he had been waiting for you for an hour and asks, “What were you doing when I called you?”
Now, you are going to use the Past Continuous tense to frame the answer to the question as he is asking about what you were doing that time.
Possible replies:
• My phone was getting charged, and I was discussing something with Ron. • I was eating dinner. • I was driving the car.
Notice in all these sentences, we are using the Past Continuous tense to talk about what was happening at a certain time in the past. We haven’t mentioned the past time marker as he (father) already knows the time.
Structure: subject + was/were + V1+ing + past time marker
WAS : singular subjects (I, he, she, it & singular noun names) WERE : plural subjects (We, they, you & plural noun names)
PAST TIME MARKERS: last night, yesterday, in the morning, two hours ago, 7 pm, when you called, some time back, last year, last month, etc.
• I was partying with my friends last night. • He was sleeping when you called. • They were playing cricket in the morning. • She was calling me an hour ago. • My friends were talking about you last night. • Were you sleeping in the exam room? • Some kids were fighting in front of my house.
Note : It’s important to mention the time of the action in the Past Continuous tense. If the time of the action is not mentioned, understand that it is understood by the listener or the reader.
Now, let’s look at all the usages of the Past Continuous tense in English.

1. An ongoing action in the past
This is the most common usage of the Past Continuous tense to talk about what was continuing/happening at a certain time in the past.
- She was teaching digital marketing.
- I was talking to your mother in the morning.
- Yesterday at the time, I was writing an article.
- They were drinking on the terrace last night.
- He was talking to students one by one between 7 pm and 8 pm.
- At 11 ‘0 clock, we were eating dinner.
- What were you doing 10 minutes ago?
NOTE : you can use another past action ( simple past tense ) to refer to the time of the action.
- We were partying when you were in the office.
- When she reached the station, I was watching my favorite series: FRIENDS.
2. Interrupted action
We commonly use the Past Continuous tense to talk about actions that were going on in the past and got interrupted by a short action (shorter than the progressive action) in the Simple past tense..
- I was sleeping when you called. (The continuous action of sleeping got interrupted/stopped because of another action: you called.)
- We were watching movies when my parents came back home.
- She was eating dinner when the bell rang.
- They were playing games on their phones when the boss entered into the meeting.
3 . Multiple progressive actions (parallel actions)
We also use this tense to talk about two or more actions happening simultaneously at some time in the past.
- While you were playing games on your phone, I was taking notes.
- While all of you were enjoying the food, I was working hard on my project.
- Last night, we were drinking on the terrace, making fun of each other, calling each other by funny names, and playing games.
- Ron was doing his homework while Nancy was talking to her friends.
4. To paint a picture of a past scene
We could also use the Past Continuous tense to talk about the scene or the atmosphere of an event in the past.
- When I entered the office, my manager was shouting at my team, the HR was explaining the company’s policy to a freshman, some employees were talking to their clients, and the others were sitting idle.
- When the party started, everyone was having fun. Some people were dancing; some were having snacks; my friends were sitting in a circle and cracking jokes at each other; waiters were serving food at the tables, and a man was yelling at a woman who seemed like his wife.
5. Habitual action in the past
We can also use the past continuous tense to talk about actions that were repeated in the past using constantly and always .
- As much as I can recall, he was always cracking jokes and making everybody laugh.
- She was always coming late to the class and irritating the teacher.
- My mother was constantly giving me lectures on the importance of food at the time of eating dinner.
- Jenny was always changing her boyfriends.
POSITIVE SENTENCE
| Subject | Auxiliary verb (was/were) | Present participle (V1+ing) | object/modifier |
| I | was | sleeping | at this time yesterday. |
| We | were | partying | last night. |
NEGATIVE SENTENCE
| Subject | was/were + not | Present participle (V1+ing) | object/modifier |
| I | was not | doing | anything. |
| He | was not | working out | in the morning. |
INTERROGATIVE SENTENCE
| Was/were | subject | Present participle (V1+ing) | object/modifier + ? |
| Were | you | partying | last night? |
| Was | he | sleeping | with you? |
Note : we can use question words (what, where, when, why, how) before the auxiliary verb.
- What were you doing with my laptop the other day?
- Why was he arguing with you?
- When were you making this project?
- Where were they partying last night?
- How was she doing it?
The Past Continuous tense + the Simple past tense
We generally use the Simple past tense with the Past Continuous tense in two cases:
- When the Simple past tense refers to a specific time when the continuous tense was taking place.
- When the Simple past tense interrupts the continuous tense.
- I was sleeping. (Past continuous)
- He woke up. (Simple past)
We can combine these sentences together and use the simple past tense to refer to a specific time when the ongoing action was happening. We will use the conjunction ‘when’ before the simple past tense.
- I was sleeping when he woke up. OR
- When he woke up, I was sleeping.
Notice “when you woke up” is also referring to a past time, working as a past time marker.
- You rang the bell. (Simple past)
Let’s join them together.
- I was sleeping when you rang the bell. OR
- When you rang the bell, I was sleeping.
Notice “when you rang the bell” is referring to a past action that interrupts the continuous action. I was sleeping until something happened (you rang the bell).
WHILE vs WHEN
Both while and when are used in the beginning of a clause . ‘ When’ is generally used before a clause in simple past tense and while is used before a clause showing past continuous tense. Look at the following examples to understand their usages in the past tense:
- While I was recording a lesson , a bike exploded outside my house.
- I was recording a lesson when a bike exploded outside my house .
Both the sentences render the same meaning but are focusing on different parts. The first one is emphasizing the longer action (past continuous tense), and the second one is focusing on the shorter action (simple past tense).
Active/passive voice
- I was writing a book last year. (active voice)
- He was beating the kids. (active voice)
- A book was being written by me last year. (passive voice)
- The kids were being by him. (passive voice)
Hope you enjoyed the lesson! Feel free to share your question, doubt, or feedback in the comment section, and also, share the post with the people that need it.
For one-on-one classes, contact me at [email protected] .
Detailed post on the Past Continuous tense (active to passive voice).
Ashish Sharma
Ashish found his first love—the English language—a few years back. Since then, he has been immersed in the language, breaking down the language and teaching it to passionate English learners. He has a flair for listening to the English language (podcasts, sitcoms, stories), observing the nuances, and making it easy for English learners. He is known for breaking down complex English topics and making them easy to be understood.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
Grammar: When to Use Do, Does, and Did

3-minute read
- 12th August 2022
Verbs are essential to creating complete sentences, as they help us express physical actions ( She jumped in the puddle) , mental actions ( He thought about puppies) , and states of being ( I am hungry) .
There are several types of verbs that can each be written in different tenses, so they can be tricky to work with, especially if English isn’t your first language . We’ve put together a guide to help you use one of the most common verbs, do , in your writing . Read on below to learn more!
Action Verbs
As the name suggests, action verbs are used to express actions completed by the subject of a sentence. The base verb do is conjugated according to the tense:
1. Present Tense
In the present tense, do takes the form do or does, depending on the subject:
| Subject: | Verb: |
| I/you/we/they | Do |
| He/she/it | Does |
Consider the following examples:
We do our homework every night.
She does her homework every night.
2. Past Tense
In the simple past tense , the base verb do takes the form did with all subjects:
| Subject: | Verb: |
| I/you/we/they | Did |
| He/she/it | Did |
We did our homework last night.
She did her homework last night.
Auxiliary Verbs
Auxiliary , or helping verbs, are used with another base verb to create negative sentences, questions, or add emphasis. Here’s how do should be used as an auxiliary verb:
1. Negative Sentences
Following the same subject–verb pairings introduced above, we combine the auxiliaries do , does , and did with the adverb not to create negative sentences:
We do not do our homework every night.
She did not do her homework last night.
Note that we can combine the auxiliary and the adverb to create the contractions don’t , doesn’t , and didn’t . You simply remove the space between the two words and replace the letter o in not with an apostrophe (’).
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Contractions are more common in conversations and informal writing and typically shouldn’t be used in formal writing (e.g., academic or business).
2. Questions
To create questions, the auxiliary is combined with the infinitive of another verb in this way: auxiliary verb + subject + infinitive verb .
● Simple present questions:
Do they sell children’s books?
Does he speak English?
Note that the third person verb speaks isn’t spelled with the s when paired with the auxiliary to form a question.
● Simple past questions:
Did you buy anything at the bookstore?
Did he learn how to speak English?
Note that did indicates the past tense, so the main verbs don’t also take the past tense (i.e., bought and learned ).
3. Emphasis
In positive sentences, we can also combine the auxiliaries do , does , and did with the main verb to emphasize that something is true:
We do sell children’s books.
He did learn to speak English.
Try saying these sentences aloud and adding emphasis to the auxiliary terms with your tone. It adds a dramatic effect!
Proofreading and Editing Services
Hopefully, this guide will help you feel more confident when using different forms of the verb do in your writing. If you’re still learning or want to be sure your work is error-free, our editors are ready to help. You can upload a free trial document today to learn more!
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
4-minute read
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
T086 - Past Tense Simple or Progressive
Gap-fill exercise.
Fill in the correct form of the PAST TENSE : Simple or Progressive !
- My brother ( DRINK ) while he ( DO ) his homework.
- He ( WALK ) into the classroom, then he (SAT) down.
- Harry ( SING ) a song when Jane ( COME ) in.
- Nothing ( HAPPEN ) when I turned on the radio.
- It ( START ) to rain while I ( WALK ) through the park.
- Jackie ( LISTEN ) to the radio when the doorbell ( RING ).
- He ( FIND ) some money when he ( CLEAN ) the cupboards.
- He ( SEE ) the accident when he (DRIVE) home from work.
- While Jimmy ( TELL ) a joke his teacher ( WALK ) in.
- The Smiths ( FLY ) to Italy yesterday.
- It ( BEGIN ) to snow while we ( PLAY ) football.
- They ( LIVE ) in Portugal when the earthquake ( HAPPEN )
- Ako sa učiť

Past Perfect Tense
- Forming Past Perfect Simple
- Use of Past Perfect Simple
- Vocabulary related to Past Perfect Simple
- Forming Past Perfect Continuous
- Use of Past Perfect Continuous
- Past Perfect compared to other tenses
- Instructions
- Follow-up questions
Introduction
The Past Perfect tense is often feared by students. It is one of the complicated tenses. However, it is not that tricky. This chapter examines the Past Perfect Simple and the Past Perfect Continuous. Let’s first look at the way they are formed and then the situations in which we use them.
1 Past perfect simple
The Past Perfect Simple expresses what happened before the past event – hence the name Past Perfect. Therefore, this tense rarely occurs without the context:
- How do we know which part of a sentence the Past Perfect Simple will be in? It is in the one where the first event happened. Something happened in the past (I went to the party – Past tense), but BEFORE that I was doing something (I had bought a gift – Past Perfect).

Before we talk in more detail about the situations in which we use this tense, let’s explore its formation.
1.1 Forming Past Perfect Simple
What do we need to form Past Perfect Simple? subject + auxiliary verb HAD + regular verb with -ed / 3. form of irregular verb
| Positive form | ||
|---|---|---|
| I | . | |
| You | . | |
| He | . | |
| She | . | |
| We | . | |
| You | . | |
| They | . |
- The negative of the Past Perfect Simple is formed by adding NOT to the auxiliary verb HAD (I had not exercised.) HAD (I had not exercised.)
- The short form is HADN‘T (I hadn‘t exercised.)
| Negative form | ||
|---|---|---|
| I | . | |
| You | . | |
| He | . | |
| She | . | |
| We | . | |
| You | . | |
| They | . |
- When forming a question, we just switch the subject of the sentence with the auxiliary verb HAD
| Question | ||
|---|---|---|
| I | ? | |
| you | ? | |
| he | ? | |
| she | ? | |
| we | ? | |
| you | ? | |
| they | ? |
1.2 Use of Past Perfect Simple
When do we use the Past Perfect Simple? When something had happened before a certain moment in the past
- As can be seen from the sentence, the doctor first examined the patient and then recommended more movement.

- As we can see from the sentence, firstly, she left her purse at home and then had to return for it.

- Here, for example, is a mother who makes sure that her son did his homework and then went to the cinema.

1.3 Vocabulary related to Past Perfect Simple
The Past Perfect Simple is characterized by the frequent use of the following adverbs:
AFTER, WHEN Both of these adverbs can be placed at the beginning of a sentence or in the middle:
- When I had finished cooking , I called my friend.
- I called my friend after I had finished cooking .
BEFORE The adverb BEFORE can be placed at the beginning of a sentence or in the middle.
- Before I went to lunch, I had had an interview .
- I had had an interview before I went to lunch.
In the case that an event took place at a particular time, the Past Perfect Simple is not a rerequisite and we can use the Past Simple tense. The same is true for the adverb AFTER. Therefore, both of these options are possible:
- I had seen them only once in 2015 before I went on a road trip with them in 2017.
- I saw them only once in 2015 before I went on a road trip with them in 2017.
However, if it is not an event occurring at a particular time, we need to use the Ppat Perfect Simple. In the following sentence we see that this is not an event, but an experience:
- Not: I worked for several companies before I started working for you.
We use the conjunction BECAUSE for so-called reason sentences. The subordinate clause is in the Past Perfect Simple if we want to express that it had happened before a certain moment in the past. Again, we can place it at the beginning of the sentence or in the middle:
- Because I hadn’t studied , I failed the test.
- I failed the test because I hadn’t studied .
We often come across related subordinate clauses:
- The girl, who I had met last summer , called me.
- The movie which you had recommended to me was really good!
The Past Perfect also appears with object subordinate sentences:
- I realized that somebody had broken into our house .
2 Past Perfect Continuous
If you have studied the rules about the Past Perfect Simple, the Past Perfect Continuous won’t be so complicated for you. While we can tell by the Past Perfect Simple what had happened at a particular moment in the past, the Past Perfect Continuous serves to tell us what had been happening before a certain moment in the past.
- We emphasize the course of this event- so we also add that it took the whole afternoon.

Before we take a closer look at the situations in which we use this tense, let’s explain how it is formed.
2.1 Forming Past Perfect Continuous
What do we need to form Past Perfect Continuous? subject + HAD + BEEN + action verb with ending -ING + rest of sentence
| Positive form | ||
|---|---|---|
| I | wait . | |
| You | wait . | |
| He | wait . | |
| She | wait . | |
| We | wait . | |
| You | wait . | |
| They | wait . |
- We create the negative form by putting NOT after HAD (the auxiliary verb)
- The short form is HADN‘T (You hadn’t been waiting (nečekal jsi)).
| Negative form | ||
|---|---|---|
| I | wait . | |
| You | wait . | |
| He | wait . | |
| She | wait . | |
| We | wait . | |
| You | wait . | |
| They | wait . |
- We form a question by switching the subject with the auxiliary verb HAD
- The verb BEEN follows the subject:
| Question | ||
|---|---|---|
| I | wait ? | |
| you | wait ? | |
| he | wait ? | |
| she | wait ? | |
| we | wait ? | |
| you | wait ? | |
| they | wait ? |
2.2 Use of Past Perfect Continuous
Now we know how to form Past Perfect Continuous, we can now look at the situations where we use it:
We are talking about something that has been going on for some time before a specific point in the past
- The exercise has lasted for two hours and it made the person exhausted.
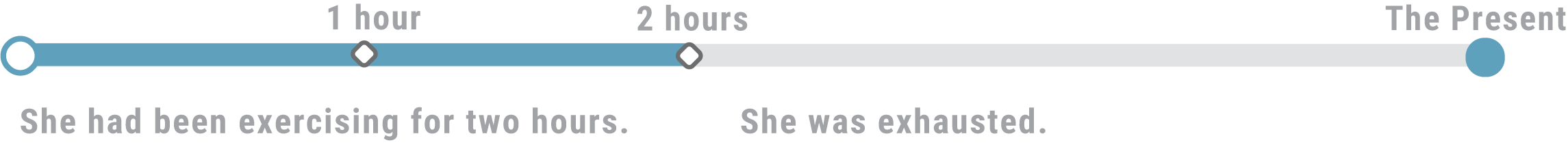
We want to emphasize the duration of a certain event We don’t just use only Past Perfect Continuous with a specific expression of time. We also use it when we want to say that the event took a longer time:
- They had been playing really well (all the time) before the football match was cancelled.

We are talking about a state that was caused by a certain event
- He was wet (state) because it had been raining the whole afternoon (event).

3 Past tense compared to other tenses
Now let’s look at the same sentence in different tenses. Notice how its meaning changes.
- The actions happened one after the other, we use simple past tense.
- His activity was in progress at the moment I entered the room, so we use past continuous tense.
- Father had completed the activity before I entered the room. To express this sequence, we use past perfect tense.
4 Practicing past perfect tense
Try the following exercises and test your newly acquired knowledge.
4.1 Instructions
Exercise 1: Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the verb Fill in the blank with the correct form of the verb in past and past perfect tense:
1) By the time I __________ (arrive) at the party, everyone __________ (leave). 2) She __________ (study) for two hours before she __________ (take) a break. 3) They __________ (already eat) by the time we __________ (get) to the restaurant. 4) The movie __________ (start) before we __________ (arrive) at the cinema. 5) He __________ (never see) a bear before he __________ (go) to Alaska.
Exercise 2: Sentence transformation
Change the following sentences to the past perfect tense:
1) I woke up early this morning. 2) They started the project last week. 3) She bought a new car yesterday. 4) He had a sandwich for lunch. 5) We went to bed late last night.
Exercise 3: Answers the questions Answer the following questions in the past perfect tense:
1) Had you ever been to New York before your trip last year? – Yes,… 2) Had she finished the book before she saw the movie? – Yes,… 3) Had they seen the movie before they read the book? – No,… 4) Had he eaten breakfast before he left for work? – Yes,… 5) Had we met before the party last week? – No,…
4.2 Solution
Exercise 1: Filling in the blanks with the correct verb form
1) By the time arrived at the party, everyone had left . 2) She had studied / had been studying for two hours before she took a break. 3) They had already eaten by the time we got to the restaurant. 4) The movie had started before we arrived at the cinema. 5) He had never seen a bear before he went to Alaska.
1) I had woken up early this morning. 2) They had started the project last week. 3) She had bought a new car yesterday. 4) He had had a sandwich for lunch. 5) We had gone to bed late last night.
Exercise 3: Answering questions
1) Had you ever been to New York before your trip last year? Yes, I had been to New York before my trip last year. 2) Had she finished the book before she saw the movie? Yes, she had finished the book before she saw the movie. 3) Had they seen the movie before they read the book? No, they had not seen the movie before they read the book. 4) Had he eaten breakfast before he left for work? Yes, he had eaten breakfast before he left for work. 5) Had we met before the party last week? No, we had not met before the party last week.

5 A story using Past Perfect Tense
And what does the past perfect tense look like in the context of a story? Read and listen to the story. Do you dare to try the comprehension questions too?
Alice had always dreamed of becoming a successful author, but it wasn’t until she had graduated from college that she started to pursue her passion for writing. After completing a few short stories, she had decided to write her first novel. For months, Alice had been working tirelessly, pouring her heart and soul into her writing. She had spent countless hours researching and developing her characters, creating the perfect plot, and editing and revising her work.By the time Alice had submitted her manuscript to various publishing houses, she had been writing for over a year. During this time, she had faced many rejections and setbacks, but she had never given up. She had continued to work hard, honing her craft, and perfecting her novel.
Finally, after what had felt like an eternity, Alice had received an email from a publishing house expressing their interest in publishing her book. She had been overjoyed, and the hours, days, and months she had spent writing had all been worth it. Alice had been ecstatic to see her dream come to fruition.
From that day on, Alice had been known as a successful author, and her book had become a bestseller. Looking back, she had realized that all the hard work, dedication, and perseverance had been worth it.
5.1 Follow-up questions
5.2 answers.
Alice had been dreaming of becoming a successful author.
Alice had started pursuing her passion for writing after graduating from college.
Yes, Alice had completed a few short stories before deciding to write her first novel.
Alice had been working tirelessly on her writing for months.
Alice had spent countless hours researching and developing her characters, creating the perfect plot, and editing and revising her work.
By the time Alice submitted her manuscript to publishing houses, she had been writing for over a year.
Yes, Alice had faced many rejections and setbacks during her writing process.
Alice had continued to work hard, honing her craft and perfecting her novel.
Alice had been writing for over a year before receiving an email from a publishing house expressing their interest in publishing her book.
Alice had realized that all the hard work, dedication, and perseverance had been worth it when looking back on her journey to becoming a successful author.

The past perfect event happened first in time.
FIRST: The thief the money.
THEN: The police the thief.
The thief the money before the police him.
OR: Before the police the thief, he the money.
" " tells us that event happened first in time.
Past perfect key words: already, yet
| 1. | First: Diego ate dinner. Then: Pablo came over. Diego (eat) |
| 2. | First: I finished my homework. Then: I went to bed. I (go) |
| 3. | First: Sam washed the dishes. Then: Sam turned on the TV. Sam (turn) |
| 4. | First: Frank threw the football. Then: Frank fell down. Frank (fall) |
| 5. | First: I bought an airplane ticket. Then: Sara found a really good price. After I (buy) |
| 6. | Last night I started to make dinner at 5:30, and finished at 5:50. At 6:00, my husband came home. By the time my husband (come) |
| 7. | Yesterday Maria fed the cat and then she went to work. Maria (go) |
| 8. | Peter was late. By the time he (get) |
| 9. | The teacher (give) |
| 10. | We (play) |
Simple Past or Present Perfect Simple
Put the verbs into the correct tense (simple past or present perfect simple).
- I (just / finish) my homework.
- Mary (already / write) five letters.
- Tom (move) to this town in 1994.
- My friend (be) in Canada two years ago.
- I (not / be) to Canada so far.
- But I (already / travel) to London a couple of times.
- Last week, Mary and Paul (go) to the cinema.
- I can't take any pictures because I (not / buy) a new film yet.
- (they / spend) their holiday in New Zealand last summer?
- (you / ever / see) a whale?
| |
- 📝 VOCABULARY
- 🚀 GAMES/ACTIVITIES
Simple Past Tense (Did) – With Explanations Pictures and Exercises

Simple past tense (past simple tense) is a verb tense that describes completed actions or past habits before now. It is also used to talk about a series of events in the past. “Did” is the helping verb of simple past tense. For affirmative (positive) sentences we use past simple form of a verb.
⬤ Formation of simple past tense
For affirmative sentences we use the formation of “verb + ed” . For negative sentences and questions we use the auxiliary “did” or “did not”. See the chart below to learn the structure of simple past tense.

Examples with Pictures Dialogue exercise Sentence scramble game Translation exercise
| I watch . | I watch. | you watch? |
| You watch . | You watch. | you watch? |
⬤ Which auxiliary (helping verb) to use for simple past tense?
The auxiliary verb in simple past tense is “ did “. However we use “ was-were ” to talk about a state in the past. Examples:
- I walked in the park.
- I didn’t walk in the park.
- Did you walk in the park?
- I was in the park.
- I wasn’t in the park.
- Were you in the park?
⬤ Positive (Affirmative) sentences
For the formation of positive sentences in simple past tense we add “ -ed “, “ -ied ” or just “ -d ” to the verb. We do not use “ did ” for the positive sentences.
- I asked a question.
- She studied maths.
- She cleaned her room.
- Jack repaired the car last week.
- A traffic accident happened yesterday.
⬤ Negative sentences
For the formation of negative sentences in simple past tense we use “ not ” together with “ did “. The short form is “ didn’t ”
- He did not want tea.
- We didn’t wait for the bus.
- I didn’t use your pen.
- Susan didn’t lie.
⬤ Interrogative sentences
For the formation of question sentences (interrogative) in simple past tense we put “ did ” before the subject.
- Did you enjoy your holiday.
- Did she write an email.
- Where did Yuto go?
- What did Ali want?
⬤ Sentence forms in simple past tense
| I play | I play | I play? |
| You play | You play | you play? |
| He play | He play | he play? |
| She play | She play | she play? |
| It play | It play | it play? |
| We play | We play | we play? |
| They play | They play | they play? |
⬤ What are the regular verbs?
Regular verbs are the verbs that gets “ -ed “, “ -ied ” or “ -d ” for the the past simple forms.
| clean | clean | clean |
| play | play | play |
| study | stud | stud |
⬤ What are the irregular verbs?
Irregular verbs are the verbs which don’t get “ -ed “, “ -ied ” or “ -d ” to form past simple form or past participle form. There are a number of irregular verbs which needs to be memorized. Because the formation has no standard rule. Some verbs have the same form as bare form, past simple form or past participle form. For example “cut, put, let, hit”.
| find | found | found |
| go | went | gone |
| break | broke | broken |
| speak | spoke | spoken |
| put | put | put |
- (+) I visit ed my uncle.
- (-) I didn’t visit my uncle yesterday.
- (?) Did you visit your uncle yesterday?
- (+) They found the cat.
- (-) They didn’t find the cat.
- (?) Did they find the cat?
SIMILAR PAGES: ❯❯ Learn verb to be here ❯❯ Learn simple present tense here ❯❯ Learn present continuous tense here ❯❯ Learn future simple tense (will) here ❯❯ Learn be going to future tense here ❯❯ Learn past continuous tense here ❯❯ Learn present perfect tense here
⬤ Explanations and usages of Simple Past Tense
Let’s go on with the explanations, usages and time adverbs of simple past tense:
⬤ 1- Finished actions in the past
Simple Past Tense is used to describe a finished action in a specific time in the past. Examples: I watched a film yesterday. I did n’t watch a film yesterday. Last year, I traveled to Italy. Last year, I did n’t travel to Italy. She washed her hands. She did n’t wash her hands. I bought a hat yesterday. Did you like your cake? Where did you go? What did Ethan say? How did she get 100 points in the exam?
⬤ 2- A series of finished actions.
Simple Past Tense is also used to describe past actions that happen one after the other. The series of actions are all expressed in simple past tense. Examples: I went out, walked to the park, and watched the sky silently.
He arrived from the airport at 11:00, looked for someone to ask the way, and called a taxi.
⬤ 3- Past habits
We can also use simple past tense to talk about habits in the past. Examples: I always played basketball when I was a child. He often played the guitar. They never went to school, they always skipped . She worked at the hospital after school.
⬤ Using “was”, “were” to talk about past states.
If you want to talk about a past state or condition we use “was, were”. The negative form is “was not, were not” or “wasn’t weren’t”. To make questions we use “was/were” before the subject.
⬤ I lived in London. ⬤ I was in London.
Examples (did) Sally worked at the hospital. Sally didn’t work at the hospital. Did Sally work at the hospital? Where did Sally work?
Examples (was-were) Sally was at the hospital. Sally wasn’t at the hospital. Was Sally at the hospital? Where was Sally?
⬤ What are the time expressions in simple past tense?
⬤ yesterday I went to the cinema yesterday. ⬤ last week, last year, last Sunday, last month etc. He bought a car last week. ⬤ two years ago , four days ago , three minutes ago etc. I saw her five minutes ago. ⬤ in 1995, in 2003 etc. I had an accident in 2014.
⬤ Time adverbs exercise
You can see the simple past tense time adverbs below. Click on the cards and tell the meaning of them in your native language..
⬤ Images and example sentences
You can learn simple past tense with images and example sentences below.
⬤ A conversation example
Here is a dialogue to learn simple past tense. You can make similar conversations.
Did you win the match yesterday?
Yes, we did.
How was the game?
I don’t know.
What do you mean?
Didn’t you play?
Actually I didn’t.
I had a traffic accident
so I spent the night at a hospital.
We won the match.
My teammates dedicated the goals to me.
Well. Your team needs you. Get well soon.
⬤ Translate these sentences
You will see random examples of simple past tense below. Try to translate them into your own language.
⬤ Sentence scramble game
You will see scrambled words of simple past tense sentences. Click on them in order to make a sentence.
⬤ Example sentences about simple past tense
You can see many sentences below to learn simple past tense.
➔ 10 examples of about simple past tense
- I listened to the new pop album yesterday. It’s great.
- She liked the film but she didn’t like the music.
- There was a problem with the plug.
- I was happy to see her with a smile in her face.
- Her parents travelled by train from Istanbul to Moscow.
- I phoned you four times last night but you were out.
- There were many workers waiting outside.
- We walked along the beach yesterday. It was lovely.
- I had a problem. So I asked to my mother about it.
- Last week I was in Paris. I stayed in a hotel.
⬤ Questions and with answers
Read the questions and the answers below to learn how to use about simple past tense.
➔ 10 questions and answers about simple past tense
- Did you like the film? Yes, I liked it very much.
- Did they give her a present after the ceremony? Yes, they gave her a new camera.
- When did you start playing the guitar? I started playing the guitar when I was nine.
- Was there a guard at the door? No. They let us in.
- When did you leave school? I left school when I was sixteen.
- Who invented the radio? Guglielmo Marconi invented it.
- When did you give your first concert? We gave our first concert in a wedding in Liverpool.
- How many sandwiches did he eat? He ate 3 sandwiches.
- Were you with Sally when she had an accident? Yes, I was.
- What did she do with the book? She sat on a bench and started reading.
External resources: You can go to British Council page and study simple past tense , or watch a video from the popular movies about past simple tense .
related pages
Fill in the blanks quiz for simple past tense, sentence scramble game for simple past tense, accessories vocabulary 👓 exercises pictures audio, body parts in english 👨 with games and listed images, classroom objects vocabulary in english 📕 with games, clothes vocabulary in english 👕 learn with images and flashcards, colour names in english 🎈 with tests and images, computer parts (hardware) vocabulary: pictures audio, verb to be (am, is, are) – with examples and online exercises, modal “can” – with explanations exercises and activities, present continuous tense – with usage examples and pictures, simple present tense (do-does) – with usage, pictures and example sentences.
© www.english-learn-online.com All right reserved You can write us any mistakes or read our about page or see our privacy policy .
- Rules/Help/FAQ Help/FAQ
- Members Current visitors
- Interface Language
Follow along with the video below to see how to install our site as a web app on your home screen.
Note: This feature may not be available in some browsers.
- English Only
After doing/having done his homework, he watched TV
- Thread starter angelene001
- Start date Nov 26, 2019
angelene001
Senior member.
- Nov 26, 2019
Can the word "after" be followed by either the present participle or the perfect participle without any change in meaning? 1. After doing his homework, he watched TV. 2. After having done his homework, he watched TV. Is it similar to "after" + the past simple/ the past perfect, where we can use the past perfect but it isn't necessary because the word "after" makes the order of the events clear: 1. After he did his homework, he watched TV. 2. After he had done his homework, he watched TV.
Edinburgher
Thank you. What I've found in the grammar book (Grammarway 4) is: After taking/ having taken his Master's degree, he applied for a job. However, when I checked the key to the exercises in the same book, I found only "After doing" or just "Having done" as the correct answers. Just as you say. And that's what I've always thought: After doing, Having done, After somebody had done,

She ___ her homework last night. a. did b. made
Select your answer:
Next Quiz >
Other quiz:
What do … need to know before renting a car?
Billy will ride ____ bike to pick up milk for ____ mom
B. his, his
D. it’s him
How to use : Read the question carefully, then select one of the answers button.
GrammarQuiz.Net - Improve your knowledge of English grammar, the best way to kill your free time.
- Grammar Lessons
- Grammar Exercises
- Grammar Quizzes
- Mixed Tests
- PDF Worksheets
- Beginners Lessons
- Easy Worksheets
- Beginners Tests
- Reading Exercises
- Drag & Drop Grammar
- English For Kids
- Kids Word Games
- Picture Vocabulary
- Reading Tests
- Short Dialogues
- Short Sentences
- Closest in Meaning
- Irrelevant Sentence
- ESL Paragraphs
- GRE Reading
- Text Completion
- GRE Equivalence
- SAT Sentence
- Essay Writing
- Vocabulary Exercises
- Study Skills Tips
- Drag & Drop Vocab
Present Perfect / Simple Past Key
| GrammarBank Video Exercises |
|---|


Adverb Clause of Time And Exercises

You might know that an adverb clause is a dependent clause that functions as an adverb in a sentence. There are different kinds of adverb clauses in English; in addition, the subordinators can distinguish the different types of adverb clauses. In this lesson, you will learn how to use an adverb clause of time.
Adverb Clause of Time
The adverb clause connectors, such as after, before, when, while/as, by the time, since, until/till, as soon as/once, as long as/so long as, and whenever can be used to form adverb clauses of time. Examples:
- After I am done with my homework, I will study the adverb clause of time.
- As soon as we finish Step 4, we will start the TOEFL iBT preparation program.
- As long as some troublemakers exist around here , you will not be able to improve your business.
Related Articles:
- Adverb Clause Of Contrast/ Concession
- Adverb Clause Of Purpose
- How To Use Adverb Clause Of Reason/ Cause?
Exercise 1:
Directions: Complete the following. Pay special attention to verb tenses.
- Last night, I went to bed after I ______________________________my homework.
- Tonight, I will go to bed after I _________________________my homework.
- Ever since I was a child, I ____________________________________ afraid of dogs.
- Jacquie’s contact lens popped out while she _____________________basketball.
- Be sure to reread your composition for errors before you _________________ it in to the teacher tomorrow.
- By the time, I left my apartment this morning, the mail carrier __________________________ the mail.
- I have known my best friend since her _____________________________ ten years old.
- A black cat ran across the road as I ____________________________my car to work this morning.
- By the time I leave this city, I _______________________________ here for four months.
- Whenever Mike __________________________________ angry, his nose gets red.
- I ____________________________ to the beach whenever the weather was nice, but now I do not have time to do that because I have to study.
- We will have a big party when __________________________________.
- The next time I ______________________________to Hawaii, I’m going to visit Mauna Loa, the world’s largest volcano.
- I had fried chicken the last time I ____________________________ at that restaurant.
Exercise 2:
Directions: Make sentences with until from the given situations.
- I can’t pay my bills. I haven’t gotten my paycheck yet.
I can’t pay my bills until my paycheck comes.
- We can’t leave yet. We have to wait for Carmen.
- Tell me the truth, or I am not going to leave this room.
- Finally, he arrived. Before that, it had been a dull party.
- Dinner won’t be ready for a while. I think we should just sit here by the fire.
- When I go to bed at night, I like to read. After a while, I get sleepy.
Exercise 3:
Directions: Combine the ideas by using either as soon as or once . ( As soon as and once basically have the same meaning. but as soon as is more immediate. Often, just is used with as soon as to emphasize the idea of “immediately”:
- I’ll call him just as soon as I get home.
- The taxi will get here in five minutes or so. Then we can leave for the airport.
As soon as the taxi gets here, we can leave for the airport.
- The rice will be done in about ten minutes. Immediately after that, we can eat.
- First, I have to graduate. Then I can return home.
- Spring will come and the weather will be nice again. Then we can start playing tennis every morning before class.
- My roommate walked into the room. Immediately, I knew that something was wrong.
- Your English will get better. Then you will begin to feel more comfortable living in the United States.
- Immediately after the singer finished her song, the audience burst into applause.
- I’m watching a baseball game on TV, but it will be over in a few minutes. Then I’ll take out the garbage.
Exercise 4:
Directions: Using the given information, make a sentence in which you use just after, just before , or just as . Notice that just adds the idea of “immediately.”
- I got to the airport at 8:15. My plane left ten minutes later. I got to the airport just before my plane left.
- You shouldn’t eat a heavy meal and then go to bed immediately afterward.
- I went to bed at 11:00. The phone rang at 11:05.
- We were sitting down to eat. At that moment, someone knocked on the door.
- I was getting on the bus. At that moment, I remembered that I had left my briefcase at home.
- I got up to give my speech. Immediately before that, I got butterflies in my stomach.
- The guests will come at 7:00. At 6:55, I’ll light the candles.
- I was bending over to pick up my pencil. My pants split.
Exercise 1.
- Last night, I went to bed after I did my homework.
- Tonight, I will go to bed after I do my homework.
- Ever since I was a child, I was afraid of dogs.
- Jacquie’s contact lens popped out while she was playing
- Be sure to reread your composition for errors before you give it to the teacher tomorrow.
- By the time I left my apartment this morning, the mail carrier had sent the mail.
- I have known my best friend since she was ten years old.
- A black cat ran across the road as I was driving my car to work this morning.
- By the time I leave this city, I will be here for four months.
- Whenever Mike is angry, his nose gets red.
- I was going to the beach whenever the weather was nice, but now I don’t have time to do that because I have to study.
- We will have a big party when you come .
- The next time I go to Hawaii, I’m going to visit Mauna Loa, the world’s largest volcano.
- I had fried chicken the last time I was at that restaurant.
Exercise 2.
- I can’t pay my bills until my paycheck comes.
- We can’t leave yet until Carmen come.
- Tell me the truth, until I leave this room.
- Finally, he arrived until it had been a dull party.
- Dinner won’t be ready for a while until we sit here by the fire.
- When I go to bed at night, I like to read until I get sleepy.
Exercise 3.
- As soon as the taxi gets here, we can leave for the airport.
- As soon as the rice is done, after that, we can eat.
- As soon as I graduate, I can return home.
- One the spring comes the weather will be nice again and then we can start playing tennis every morning before class.
- Once my roommate walked into the room immediately, then I knew that something was wrong.
- Once your English gets better, then you will feel more comfortable living in the United States.
- As soon as the singer finished her song, the audience burst into applause.
- I am watching a baseball game on TV, but as soon as it’s over, I’ll take out the garbage.
Exercise 4.
- I got to the airport just before my plane left.
- You shouldn’t go to the bed just after eating a heavy meal.
- I went to the bed just before the phone rang.
- Just as we sat down to eat, someone knocked on the door.
- Just as I got on the bus, I remember that I had left my briefcase at home.
- I got butterflies in my stomach just before I got up to give my speech.
- I will light the candles just before the guests come.
- My pants split just as I bent myself to pick up my pencil.
Conclusion:
Attempt the adverb clause of time exercises, then compare your answers with the given answers above. In addition, please feel free to write your feedback about the article (adverb clause of time) using the comment section below.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
Related posts
Best english books for english learners, direct and indirect of present perfect continuous tense, present continuous tense definition and examples.
Last night, I went to bed after I ______________________________my homework. Tonight, I will go to bed after I _________________________my homework. Ever since I was a child, I ____________________________________ afraid of dogs. Jacquie’s contact lens popped out while she _____________________basketball. Be sure to reread your composition for errors before you _________________ it in to the teacher tomorrow. By the time, I left my apartment this morning, the mail carrier __________________________ the mail. I have known my best friend since her _____________________________ ten years old. A black cat ran across the road as I ____________________________my car to work this morning. By the time I leave this city, I _______________________________ here for four months. Whenever Mike __________________________________ angry, his nose gets red. I ____________________________ to the beach whenever the weather was nice, but now I do not have time to do that because I have to study. We will have a big party when __________________________________. The next time I ______________________________to Hawaii, I’m going to visit Mauna Loa, the world’s largest volcano. I had fried chicken the last time I ____________________________ at that restaurant.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Tiếng Anh (mới)
It is certain that he didn’t finish his homework last night because he spent all night playing computer games.
A. He shouldn’t have finished his homework last night because he spent all night playing computer games.
B . He needn’t have finished his homework last night because he spent all night playing computer games.
C . He mustn’t have finished his homework last night because he spent all night playing computer games.
D . He can’t have finished his homework last night because he spent all night playing computer games.
Siêu phẩm 30 đề thi thử THPT quốc gia 2024 do thầy cô VietJack biên soạn, chỉ từ 100k trên Shopee Mall .
Đáp án: D

CÂU HỎI HOT CÙNG CHỦ ĐỀ
Mark the letter A, B, C, or D on your answer sheet to indicate the sentence that is closest in meaning. “Would you like a cup of coffee?” he said.
A . He asked me if I would like a cup of coffee.
B. He offered me a cup of coffee
C . He wondered if I would like a cup of coffee.
D. He wanted me to drink a cup of coffee.
Mark the letter A, B, C, or D on your answer sheet to indicate the word OPPOSITE in meaning to the underlined word(s) in each of the following questions. Question: Life on Earth is disappearing fast and will continue to do so unless urgent action is taken.
A . Polluting
B. destroying
C. vanishing
D . damaging
Choose the most suitable words or phrases to fill in the blanks. We’d better ________ early so as to avoid the heavy traffic.
B . go about
C. come apart
D . take up
The policeman wanted to know where he _________.
A. Was night before
B . Had been the previous night
C . was last night
D. had been the last night
Mark the letter A, B, C, or D on your answer sheet to indicate the word OPPOSITE in meaning to the underlined word(s) in each of the following questions. Question: Think about the interviewer’s comments because they may help you prepare better when you are called for the next job interview.
B . compliments
C . characters
D . behaviours
She suddenly left the job. We were all surprised at this.
A . As we were all surprised, she suddenly left the job.
B. Although she suddenly left the job, we weren’t all surprised.
C. She suddenly left the job in order to surprise us all.
D . That she suddenly left the job surprised us all.
Hãy Đăng nhập hoặc Tạo tài khoản để gửi bình luận

ĐỀ THI LIÊN QUAN

Gọi 084 283 45 85
Hỗ trợ đăng ký khóa học tại Vietjack
CHỌN BỘ SÁCH BẠN MUỐN XEM
Hãy chọn chính xác nhé!
Bạn đã có tài khoản? Đăng nhập
Bằng cách đăng ký, bạn đồng ý với Điều khoản sử dụng và Chính sách Bảo mật của chúng tôi.
Bạn chưa có tài khoản? Đăng ký
Quên mật khẩu
Số điện thoại hiện tại của bạn có vẻ không hợp lệ, vui lòng cập nhật số mới để hể thống kiểm tra lại.
Cambridge Proficiency (old book 5) Keyword transformations

Students also viewed


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The past perfect simple tense is formed by using the auxiliary verb had together with the V3 (past participle). The V3 (past participle) form of a regular verb looks just like a regular verb in the past simple: walk > walk ed / study > stud ied / stop > stop ped / create > creat ed. There are quite a few irregular verbs in English though.
I've lost my keys. We've been to a very nice restaurant. We use the past simple (NOT present perfect) when we mention or ask about when something happened or when the time is known by the speaker and the listener. We often use a past expression ( last week, yesterday, when I was a child, etc .) We've arrived yesterday.
E.g.: I had finished my homework by 8 o'clock last night. Both sentences are syntactically incorrect, i.e. the word order is not respected. You have two options: 1) to use a comma for emphasis: At 8 o'clock last night, I was doing my homework; 2) to put the whole adverbial phrase after the object: I was doing my homework at 8 o'clock last night.
The differences become more evident in other situations, eg when we introduce a specific past-time reference, like last week. The past perfect typically resists such past-time references: "The kids finished their homework last night" <-- OK. "The kids have finished their homework last night" <-- bad. 50.
Last night, we were drinking on the terrace, making fun of each other, calling each other by funny names, and playing games. Ron was doing his homework while Nancy was talking to her friends. 4. To paint a picture of a past scene. We could also use the Past Continuous tense to talk about the scene or the atmosphere of an event in the past ...
Consider the following examples: We did our homework last night. She did her homework last night.. Auxiliary Verbs. Auxiliary, or helping verbs, are used with another base verb to create negative sentences, questions, or add emphasis.Here's how do should be used as an auxiliary verb:. 1. Negative Sentences. Following the same subject-verb pairings introduced above, we combine the ...
Gap-fill exercise. Fill in the correct form of the PAST TENSE : Simple or Progressive ! My brother ( DRINK) while he ( DO) his homework. He ( WALK) into the classroom, then he (SAT) down. Nothing ( HAPPEN) when I turned on the radio. It ( START) to rain while I ( WALK) through the park. Jackie ( LISTEN) to the radio when the doorbell ( RING ).
2 Past Perfect Continuous. If you have studied the rules about the Past Perfect Simple, the Past Perfect Continuous won't be so complicated for you. While we can tell by the Past Perfect Simple what had happened at a particular moment in the past, the Past Perfect Continuous serves to tell us what had been happening before a certain moment in the past.
5. First: I bought an airplane ticket. Then: Sara found a really good price. After I (buy) an airplane ticket already, Sara (find) a really good price. 6. Last night I started to make dinner at 5:30, and finished at 5:50. At 6:00, my husband came home. By the time my husband (come) home, I (make) dinner already. 7.
Exercise 8. Put the verbs into the correct tense (simple past or present perfect simple). I (just / finish) my homework. Mary (already / write) five letters. Tom (move) to this town in 1994. My friend (be) in Canada two years ago. I (not / be) to Canada so far. But I (already / travel) to London a couple of times. Last week, Mary and Paul (go) to the cinema.
(why / you / clean) _____ the bathroom before you bathed the dog?
⬤ 1- Finished actions in the past. Simple Past Tense is used to describe a finished action in a specific time in the past. Examples: I watched a film yesterday. I did n't watch a film yesterday. Last year, I traveled to Italy. Last year, I did n't travel to Italy. She washed her hands. She did n't wash her hands. I bought a hat yesterday.
Its flavour differs a bit from "After he did", because the "had done" version more strongly suggests the completion aspect, i.e. he (had) finished all of his homework before watching TV. With "did", you are just reporting on his activities. First he did some homework (not necessarily all of it), and then he watched some TV.
A. him, it. B. his, his. C. his, my. D. it's him. How to use : Read the question carefully, then select one of the answers button. About grammarquiz.net. GrammarQuiz.Net - Improve your knowledge of English grammar, the best way to kill your free time. She ___ her homework last night. a.
He has just finished (just/finish) his second tragedy. 6. I flew (fly) over Loch Ness last week. Did you see (you/see) the Loch Ness monster? 7. I haven't seen (not see) him for three years. I wonder where he is. 8. He hasn't smoked (not smoke) for two weeks. He is trying to give it up. 9. Chopin composed (compose) some of his music in Majorca. 10.
Adverb Clause of Time. The adverb clause connectors, such as after, before, when, while/as, by the time, since, until/till, as soon as/once, as long as/so long as, and whenever can be used to form adverb clauses of time. Examples: After I am done with my homework, I will study the adverb clause of time. As soon as we finish Step 4, we will ...
1. He didn't go with us till he'd finished his homework. 2. They'd met each other before they came there. 3. My mother had worked as a farmer before she became a teacher. 4. We watched TV together after I'd finished all my chores. 5. Which channel had you watched before you tuned in this one? 6. By the time we graduated, he had worked ...
A. He shouldn't have finished his homework last night because he spent all night playing computer games. B. He needn't have finished his homework last night because he spent all night playing computer games. C. He mustn't have finished his homework last night because he spent all night playing computer games. D. He can't have finished ...
took my sister over three hours to finish. My sister needed more than three hours to finish her homework last night. over It _____ her homework last night. unable/ wasn't able to find anywhere. I couldn't find a parking space this morning. anywhere I was _____ to park this morning. have no intention of waiting (do not have/haven't got any ...