
21 Research Objectives Examples (Copy and Paste)

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process

Research objectives refer to the definitive statements made by researchers at the beginning of a research project detailing exactly what a research project aims to achieve.
These objectives are explicit goals clearly and concisely projected by the researcher to present a clear intention or course of action for his or her qualitative or quantitative study.
Research objectives are typically nested under one overarching research aim. The objectives are the steps you’ll need to take in order to achieve the aim (see the examples below, for example, which demonstrate an aim followed by 3 objectives, which is what I recommend to my research students).
Research Objectives vs Research Aims
Research aim and research objectives are fundamental constituents of any study, fitting together like two pieces of the same puzzle.
The ‘research aim’ describes the overarching goal or purpose of the study (Kumar, 2019). This is usually a broad, high-level purpose statement, summing up the central question that the research intends to answer.
Example of an Overarching Research Aim:
“The aim of this study is to explore the impact of climate change on crop productivity.”
Comparatively, ‘research objectives’ are concrete goals that underpin the research aim, providing stepwise actions to achieve the aim.
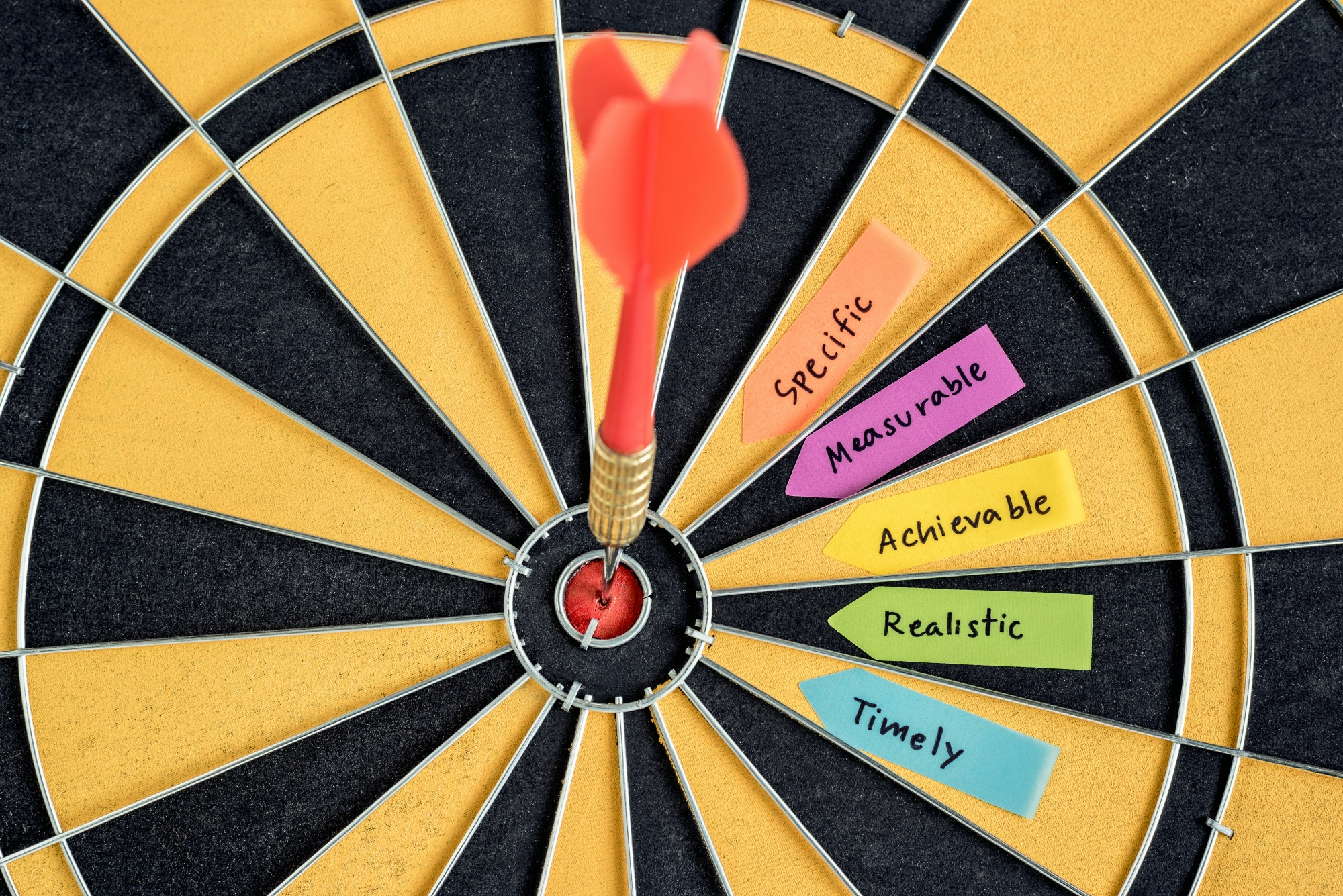
Objectives break the primary aim into manageable, focused pieces, and are usually characterized as being more specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
Examples of Specific Research Objectives:
1. “To examine the effects of rising temperatures on the yield of rice crops during the upcoming growth season.” 2. “To assess changes in rainfall patterns in major agricultural regions over the first decade of the twenty-first century (2000-2010).” 3. “To analyze the impact of changing weather patterns on crop diseases within the same timeframe.”
The distinction between these two terms, though subtle, is significant for successfully conducting a study. The research aim provides the study with direction, while the research objectives set the path to achieving this aim, thereby ensuring the study’s efficiency and effectiveness.
How to Write Research Objectives
I usually recommend to my students that they use the SMART framework to create their research objectives.
SMART is an acronym standing for Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. It provides a clear method of defining solid research objectives and helps students know where to start in writing their objectives (Locke & Latham, 2013).
Each element of this acronym adds a distinct dimension to the framework, aiding in the creation of comprehensive, well-delineated objectives.
Here is each step:
- Specific : We need to avoid ambiguity in our objectives. They need to be clear and precise (Doran, 1981). For instance, rather than stating the objective as “to study the effects of social media,” a more focused detail would be “to examine the effects of social media use (Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter) on the academic performance of college students.”
- Measurable: The measurable attribute provides a clear criterion to determine if the objective has been met (Locke & Latham, 2013). A quantifiable element, such as a percentage or a number, adds a measurable quality. For example, “to increase response rate to the annual customer survey by 10%,” makes it easier to ascertain achievement.
- Achievable: The achievable aspect encourages researchers to craft realistic objectives, resembling a self-check mechanism to ensure the objectives align with the scope and resources at disposal (Doran, 1981). For example, “to interview 25 participants selected randomly from a population of 100” is an attainable objective as long as the researcher has access to these participants.
- Relevance : Relevance, the fourth element, compels the researcher to tailor the objectives in alignment with overarching goals of the study (Locke & Latham, 2013). This is extremely important – each objective must help you meet your overall one-sentence ‘aim’ in your study.
- Time-Bound: Lastly, the time-bound element fosters a sense of urgency and prioritization, preventing procrastination and enhancing productivity (Doran, 1981). “To analyze the effect of laptop use in lectures on student engagement over the course of two semesters this year” expresses a clear deadline, thus serving as a motivator for timely completion.
You’re not expected to fit every single element of the SMART framework in one objective, but across your objectives, try to touch on each of the five components.
Research Objectives Examples
1. Field: Psychology
Aim: To explore the impact of sleep deprivation on cognitive performance in college students.
- Objective 1: To compare cognitive test scores of students with less than six hours of sleep and those with 8 or more hours of sleep.
- Objective 2: To investigate the relationship between class grades and reported sleep duration.
- Objective 3: To survey student perceptions and experiences on how sleep deprivation affects their cognitive capabilities.
2. Field: Environmental Science
Aim: To understand the effects of urban green spaces on human well-being in a metropolitan city.
- Objective 1: To assess the physical and mental health benefits of regular exposure to urban green spaces.
- Objective 2: To evaluate the social impacts of urban green spaces on community interactions.
- Objective 3: To examine patterns of use for different types of urban green spaces.
3. Field: Technology
Aim: To investigate the influence of using social media on productivity in the workplace.
- Objective 1: To measure the amount of time spent on social media during work hours.
- Objective 2: To evaluate the perceived impact of social media use on task completion and work efficiency.
- Objective 3: To explore whether company policies on social media usage correlate with different patterns of productivity.
4. Field: Education
Aim: To examine the effectiveness of online vs traditional face-to-face learning on student engagement and achievement.
- Objective 1: To compare student grades between the groups exposed to online and traditional face-to-face learning.
- Objective 2: To assess student engagement levels in both learning environments.
- Objective 3: To collate student perceptions and preferences regarding both learning methods.
5. Field: Health
Aim: To determine the impact of a Mediterranean diet on cardiac health among adults over 50.
- Objective 1: To assess changes in cardiovascular health metrics after following a Mediterranean diet for six months.
- Objective 2: To compare these health metrics with a similar group who follow their regular diet.
- Objective 3: To document participants’ experiences and adherence to the Mediterranean diet.
6. Field: Environmental Science
Aim: To analyze the impact of urban farming on community sustainability.
- Objective 1: To document the types and quantity of food produced through urban farming initiatives.
- Objective 2: To assess the effect of urban farming on local communities’ access to fresh produce.
- Objective 3: To examine the social dynamics and cooperative relationships in the creating and maintaining of urban farms.
7. Field: Sociology
Aim: To investigate the influence of home offices on work-life balance during remote work.
- Objective 1: To survey remote workers on their perceptions of work-life balance since setting up home offices.
- Objective 2: To conduct an observational study of daily work routines and family interactions in a home office setting.
- Objective 3: To assess the correlation, if any, between physical boundaries of workspaces and mental boundaries for work in the home setting.
8. Field: Economics
Aim: To evaluate the effects of minimum wage increases on small businesses.
- Objective 1: To analyze cost structures, pricing changes, and profitability of small businesses before and after minimum wage increases.
- Objective 2: To survey small business owners on the strategies they employ to navigate minimum wage increases.
- Objective 3: To examine employment trends in small businesses in response to wage increase legislation.
9. Field: Education
Aim: To explore the role of extracurricular activities in promoting soft skills among high school students.
- Objective 1: To assess the variety of soft skills developed through different types of extracurricular activities.
- Objective 2: To compare self-reported soft skills between students who participate in extracurricular activities and those who do not.
- Objective 3: To investigate the teachers’ perspectives on the contribution of extracurricular activities to students’ skill development.
10. Field: Technology
Aim: To assess the impact of virtual reality (VR) technology on the tourism industry.
- Objective 1: To document the types and popularity of VR experiences available in the tourism market.
- Objective 2: To survey tourists on their interest levels and satisfaction rates with VR tourism experiences.
- Objective 3: To determine whether VR tourism experiences correlate with increased interest in real-life travel to the simulated destinations.
11. Field: Biochemistry
Aim: To examine the role of antioxidants in preventing cellular damage.
- Objective 1: To identify the types and quantities of antioxidants in common fruits and vegetables.
- Objective 2: To determine the effects of various antioxidants on free radical neutralization in controlled lab tests.
- Objective 3: To investigate potential beneficial impacts of antioxidant-rich diets on long-term cellular health.
12. Field: Linguistics
Aim: To determine the influence of early exposure to multiple languages on cognitive development in children.
- Objective 1: To assess cognitive development milestones in monolingual and multilingual children.
- Objective 2: To document the number and intensity of language exposures for each group in the study.
- Objective 3: To investigate the specific cognitive advantages, if any, enjoyed by multilingual children.
13. Field: Art History
Aim: To explore the impact of the Renaissance period on modern-day art trends.
- Objective 1: To identify key characteristics and styles of Renaissance art.
- Objective 2: To analyze modern art pieces for the influence of the Renaissance style.
- Objective 3: To survey modern-day artists for their inspirations and the influence of historical art movements on their work.
14. Field: Cybersecurity
Aim: To assess the effectiveness of two-factor authentication (2FA) in preventing unauthorized system access.
- Objective 1: To measure the frequency of unauthorized access attempts before and after the introduction of 2FA.
- Objective 2: To survey users about their experiences and challenges with 2FA implementation.
- Objective 3: To evaluate the efficacy of different types of 2FA (SMS-based, authenticator apps, biometrics, etc.).
15. Field: Cultural Studies
Aim: To analyze the role of music in cultural identity formation among ethnic minorities.
- Objective 1: To document the types and frequency of traditional music practices within selected ethnic minority communities.
- Objective 2: To survey community members on the role of music in their personal and communal identity.
- Objective 3: To explore the resilience and transmission of traditional music practices in contemporary society.
16. Field: Astronomy
Aim: To explore the impact of solar activity on satellite communication.
- Objective 1: To categorize different types of solar activities and their frequencies of occurrence.
- Objective 2: To ascertain how variations in solar activity may influence satellite communication.
- Objective 3: To investigate preventative and damage-control measures currently in place during periods of high solar activity.
17. Field: Literature
Aim: To examine narrative techniques in contemporary graphic novels.
- Objective 1: To identify a range of narrative techniques employed in this genre.
- Objective 2: To analyze the ways in which these narrative techniques engage readers and affect story interpretation.
- Objective 3: To compare narrative techniques in graphic novels to those found in traditional printed novels.
18. Field: Renewable Energy
Aim: To investigate the feasibility of solar energy as a primary renewable resource within urban areas.
- Objective 1: To quantify the average sunlight hours across urban areas in different climatic zones.
- Objective 2: To calculate the potential solar energy that could be harnessed within these areas.
- Objective 3: To identify barriers or challenges to widespread solar energy implementation in urban settings and potential solutions.
19. Field: Sports Science
Aim: To evaluate the role of pre-game rituals in athlete performance.
- Objective 1: To identify the variety and frequency of pre-game rituals among professional athletes in several sports.
- Objective 2: To measure the impact of pre-game rituals on individual athletes’ performance metrics.
- Objective 3: To examine the psychological mechanisms that might explain the effects (if any) of pre-game ritual on performance.
20. Field: Ecology
Aim: To investigate the effects of urban noise pollution on bird populations.
- Objective 1: To record and quantify urban noise levels in various bird habitats.
- Objective 2: To measure bird population densities in relation to noise levels.
- Objective 3: To determine any changes in bird behavior or vocalization linked to noise levels.
21. Field: Food Science
Aim: To examine the influence of cooking methods on the nutritional value of vegetables.
- Objective 1: To identify the nutrient content of various vegetables both raw and after different cooking processes.
- Objective 2: To compare the effect of various cooking methods on the nutrient retention of these vegetables.
- Objective 3: To propose cooking strategies that optimize nutrient retention.
The Importance of Research Objectives
The importance of research objectives cannot be overstated. In essence, these guideposts articulate what the researcher aims to discover, understand, or examine (Kothari, 2014).
When drafting research objectives, it’s essential to make them simple and comprehensible, specific to the point of being quantifiable where possible, achievable in a practical sense, relevant to the chosen research question, and time-constrained to ensure efficient progress (Kumar, 2019).
Remember that a good research objective is integral to the success of your project, offering a clear path forward for setting out a research design , and serving as the bedrock of your study plan. Each objective must distinctly address a different dimension of your research question or problem (Kothari, 2014). Always bear in mind that the ultimate purpose of your research objectives is to succinctly encapsulate your aims in the clearest way possible, facilitating a coherent, comprehensive and rational approach to your planned study, and furnishing a scientific roadmap for your journey into the depths of knowledge and research (Kumar, 2019).
Kothari, C.R (2014). Research Methodology: Methods and Techniques . New Delhi: New Age International.
Kumar, R. (2019). Research Methodology: A Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners .New York: SAGE Publications.
Doran, G. T. (1981). There’s a S.M.A.R.T. way to write management’s goals and objectives. Management review, 70 (11), 35-36.
Locke, E. A., & Latham, G. P. (2013). New Developments in Goal Setting and Task Performance . New York: Routledge.

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 15 Body Language Signs He Likes You
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 25 Classroom Wall Decoration Ideas
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 31 Cute & Cozy Play Corner Ideas
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 24 Steiner-Waldorf Classroom Design Ideas
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

- Aims and Objectives – A Guide for Academic Writing
- Doing a PhD
One of the most important aspects of a thesis, dissertation or research paper is the correct formulation of the aims and objectives. This is because your aims and objectives will establish the scope, depth and direction that your research will ultimately take. An effective set of aims and objectives will give your research focus and your reader clarity, with your aims indicating what is to be achieved, and your objectives indicating how it will be achieved.
Introduction
There is no getting away from the importance of the aims and objectives in determining the success of your research project. Unfortunately, however, it is an aspect that many students struggle with, and ultimately end up doing poorly. Given their importance, if you suspect that there is even the smallest possibility that you belong to this group of students, we strongly recommend you read this page in full.
This page describes what research aims and objectives are, how they differ from each other, how to write them correctly, and the common mistakes students make and how to avoid them. An example of a good aim and objectives from a past thesis has also been deconstructed to help your understanding.
What Are Aims and Objectives?
Research aims.
A research aim describes the main goal or the overarching purpose of your research project.
In doing so, it acts as a focal point for your research and provides your readers with clarity as to what your study is all about. Because of this, research aims are almost always located within its own subsection under the introduction section of a research document, regardless of whether it’s a thesis , a dissertation, or a research paper .
A research aim is usually formulated as a broad statement of the main goal of the research and can range in length from a single sentence to a short paragraph. Although the exact format may vary according to preference, they should all describe why your research is needed (i.e. the context), what it sets out to accomplish (the actual aim) and, briefly, how it intends to accomplish it (overview of your objectives).
To give an example, we have extracted the following research aim from a real PhD thesis:
Example of a Research Aim
The role of diametrical cup deformation as a factor to unsatisfactory implant performance has not been widely reported. The aim of this thesis was to gain an understanding of the diametrical deformation behaviour of acetabular cups and shells following impaction into the reamed acetabulum. The influence of a range of factors on deformation was investigated to ascertain if cup and shell deformation may be high enough to potentially contribute to early failure and high wear rates in metal-on-metal implants.
Note: Extracted with permission from thesis titled “T he Impact And Deformation Of Press-Fit Metal Acetabular Components ” produced by Dr H Hothi of previously Queen Mary University of London.
Research Objectives
Where a research aim specifies what your study will answer, research objectives specify how your study will answer it.
They divide your research aim into several smaller parts, each of which represents a key section of your research project. As a result, almost all research objectives take the form of a numbered list, with each item usually receiving its own chapter in a dissertation or thesis.
Following the example of the research aim shared above, here are it’s real research objectives as an example:
Example of a Research Objective
- Develop finite element models using explicit dynamics to mimic mallet blows during cup/shell insertion, initially using simplified experimentally validated foam models to represent the acetabulum.
- Investigate the number, velocity and position of impacts needed to insert a cup.
- Determine the relationship between the size of interference between the cup and cavity and deformation for different cup types.
- Investigate the influence of non-uniform cup support and varying the orientation of the component in the cavity on deformation.
- Examine the influence of errors during reaming of the acetabulum which introduce ovality to the cavity.
- Determine the relationship between changes in the geometry of the component and deformation for different cup designs.
- Develop three dimensional pelvis models with non-uniform bone material properties from a range of patients with varying bone quality.
- Use the key parameters that influence deformation, as identified in the foam models to determine the range of deformations that may occur clinically using the anatomic models and if these deformations are clinically significant.
It’s worth noting that researchers sometimes use research questions instead of research objectives, or in other cases both. From a high-level perspective, research questions and research objectives make the same statements, but just in different formats.
Taking the first three research objectives as an example, they can be restructured into research questions as follows:
Restructuring Research Objectives as Research Questions
- Can finite element models using simplified experimentally validated foam models to represent the acetabulum together with explicit dynamics be used to mimic mallet blows during cup/shell insertion?
- What is the number, velocity and position of impacts needed to insert a cup?
- What is the relationship between the size of interference between the cup and cavity and deformation for different cup types?
Difference Between Aims and Objectives
Hopefully the above explanations make clear the differences between aims and objectives, but to clarify:
- The research aim focus on what the research project is intended to achieve; research objectives focus on how the aim will be achieved.
- Research aims are relatively broad; research objectives are specific.
- Research aims focus on a project’s long-term outcomes; research objectives focus on its immediate, short-term outcomes.
- A research aim can be written in a single sentence or short paragraph; research objectives should be written as a numbered list.
How to Write Aims and Objectives
Before we discuss how to write a clear set of research aims and objectives, we should make it clear that there is no single way they must be written. Each researcher will approach their aims and objectives slightly differently, and often your supervisor will influence the formulation of yours on the basis of their own preferences.
Regardless, there are some basic principles that you should observe for good practice; these principles are described below.
Your aim should be made up of three parts that answer the below questions:
- Why is this research required?
- What is this research about?
- How are you going to do it?
The easiest way to achieve this would be to address each question in its own sentence, although it does not matter whether you combine them or write multiple sentences for each, the key is to address each one.
The first question, why , provides context to your research project, the second question, what , describes the aim of your research, and the last question, how , acts as an introduction to your objectives which will immediately follow.
Scroll through the image set below to see the ‘why, what and how’ associated with our research aim example.

Note: Your research aims need not be limited to one. Some individuals per to define one broad ‘overarching aim’ of a project and then adopt two or three specific research aims for their thesis or dissertation. Remember, however, that in order for your assessors to consider your research project complete, you will need to prove you have fulfilled all of the aims you set out to achieve. Therefore, while having more than one research aim is not necessarily disadvantageous, consider whether a single overarching one will do.
Research Objectives
Each of your research objectives should be SMART :
- Specific – is there any ambiguity in the action you are going to undertake, or is it focused and well-defined?
- Measurable – how will you measure progress and determine when you have achieved the action?
- Achievable – do you have the support, resources and facilities required to carry out the action?
- Relevant – is the action essential to the achievement of your research aim?
- Timebound – can you realistically complete the action in the available time alongside your other research tasks?
In addition to being SMART, your research objectives should start with a verb that helps communicate your intent. Common research verbs include:
Table of Research Verbs to Use in Aims and Objectives
| (Understanding and organising information) | (Solving problems using information) | (reaching conclusion from evidence) | (Breaking down into components) | (Judging merit) |
| Review Identify Explore Discover Discuss Summarise Describe | Interpret Apply Demonstrate Establish Determine Estimate Calculate Relate | Analyse Compare Inspect Examine Verify Select Test Arrange | Propose Design Formulate Collect Construct Prepare Undertake Assemble | Appraise Evaluate Compare Assess Recommend Conclude Select |
Last, format your objectives into a numbered list. This is because when you write your thesis or dissertation, you will at times need to make reference to a specific research objective; structuring your research objectives in a numbered list will provide a clear way of doing this.
To bring all this together, let’s compare the first research objective in the previous example with the above guidance:
Checking Research Objective Example Against Recommended Approach
Research Objective:
1. Develop finite element models using explicit dynamics to mimic mallet blows during cup/shell insertion, initially using simplified experimentally validated foam models to represent the acetabulum.
Checking Against Recommended Approach:
Q: Is it specific? A: Yes, it is clear what the student intends to do (produce a finite element model), why they intend to do it (mimic cup/shell blows) and their parameters have been well-defined ( using simplified experimentally validated foam models to represent the acetabulum ).
Q: Is it measurable? A: Yes, it is clear that the research objective will be achieved once the finite element model is complete.
Q: Is it achievable? A: Yes, provided the student has access to a computer lab, modelling software and laboratory data.
Q: Is it relevant? A: Yes, mimicking impacts to a cup/shell is fundamental to the overall aim of understanding how they deform when impacted upon.
Q: Is it timebound? A: Yes, it is possible to create a limited-scope finite element model in a relatively short time, especially if you already have experience in modelling.
Q: Does it start with a verb? A: Yes, it starts with ‘develop’, which makes the intent of the objective immediately clear.
Q: Is it a numbered list? A: Yes, it is the first research objective in a list of eight.
Mistakes in Writing Research Aims and Objectives
1. making your research aim too broad.
Having a research aim too broad becomes very difficult to achieve. Normally, this occurs when a student develops their research aim before they have a good understanding of what they want to research. Remember that at the end of your project and during your viva defence , you will have to prove that you have achieved your research aims; if they are too broad, this will be an almost impossible task. In the early stages of your research project, your priority should be to narrow your study to a specific area. A good way to do this is to take the time to study existing literature, question their current approaches, findings and limitations, and consider whether there are any recurring gaps that could be investigated .
Note: Achieving a set of aims does not necessarily mean proving or disproving a theory or hypothesis, even if your research aim was to, but having done enough work to provide a useful and original insight into the principles that underlie your research aim.
2. Making Your Research Objectives Too Ambitious
Be realistic about what you can achieve in the time you have available. It is natural to want to set ambitious research objectives that require sophisticated data collection and analysis, but only completing this with six months before the end of your PhD registration period is not a worthwhile trade-off.
3. Formulating Repetitive Research Objectives
Each research objective should have its own purpose and distinct measurable outcome. To this effect, a common mistake is to form research objectives which have large amounts of overlap. This makes it difficult to determine when an objective is truly complete, and also presents challenges in estimating the duration of objectives when creating your project timeline. It also makes it difficult to structure your thesis into unique chapters, making it more challenging for you to write and for your audience to read.
Fortunately, this oversight can be easily avoided by using SMART objectives.
Hopefully, you now have a good idea of how to create an effective set of aims and objectives for your research project, whether it be a thesis, dissertation or research paper. While it may be tempting to dive directly into your research, spending time on getting your aims and objectives right will give your research clear direction. This won’t only reduce the likelihood of problems arising later down the line, but will also lead to a more thorough and coherent research project.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.
Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey

What Are Research Objectives and How to Write Them (with Examples)

Table of Contents
Introduction
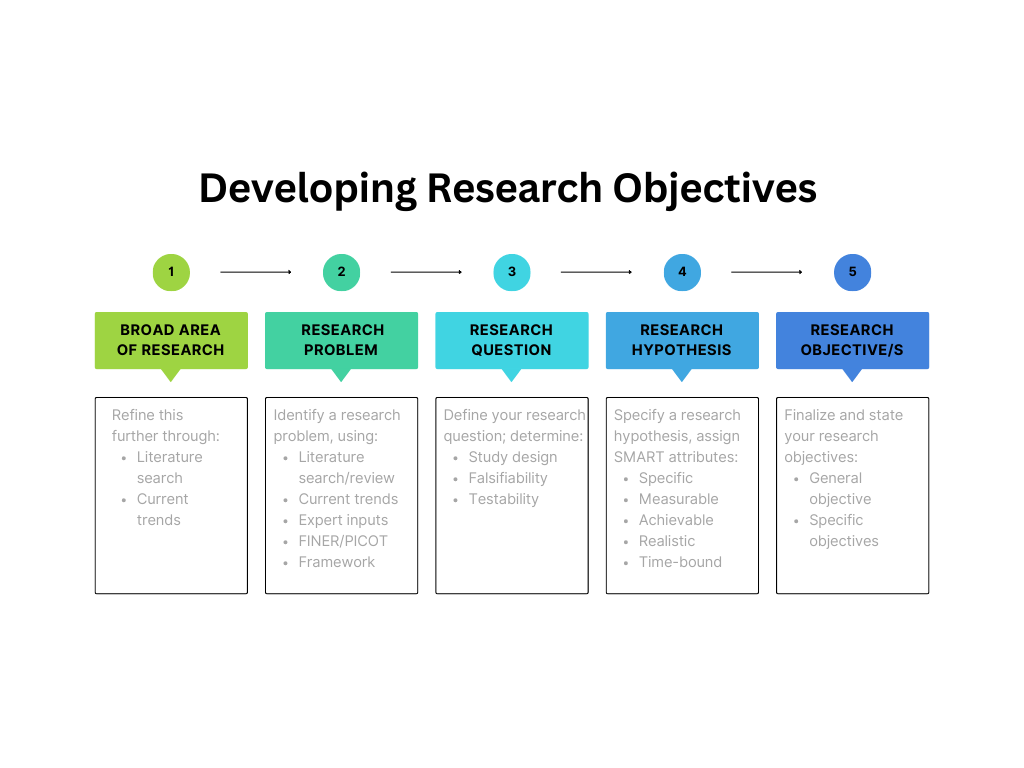
Research is at the center of everything researchers do, and setting clear, well-defined research objectives plays a pivotal role in guiding scholars toward their desired outcomes. Research papers are essential instruments for researchers to effectively communicate their work. Among the many sections that constitute a research paper, the introduction plays a key role in providing a background and setting the context. 1 Research objectives, which define the aims of the study, are usually stated in the introduction. Every study has a research question that the authors are trying to answer, and the objective is an active statement about how the study will answer this research question. These objectives help guide the development and design of the study and steer the research in the appropriate direction; if this is not clearly defined, a project can fail!
Research studies have a research question, research hypothesis, and one or more research objectives. A research question is what a study aims to answer, and a research hypothesis is a predictive statement about the relationship between two or more variables, which the study sets out to prove or disprove. Objectives are specific, measurable goals that the study aims to achieve. The difference between these three is illustrated by the following example:
- Research question : How does low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) compare with a placebo device in managing the symptoms of skeletally mature patients with patellar tendinopathy?
- Research hypothesis : Pain levels are reduced in patients who receive daily active-LIPUS (treatment) for 12 weeks compared with individuals who receive inactive-LIPUS (placebo).
- Research objective : To investigate the clinical efficacy of LIPUS in the management of patellar tendinopathy symptoms.
This article discusses the importance of clear, well-thought out objectives and suggests methods to write them clearly.
What is the introduction in research papers?
Research objectives are usually included in the introduction section. This section is the first that the readers will read so it is essential that it conveys the subject matter appropriately and is well written to create a good first impression. A good introduction sets the tone of the paper and clearly outlines the contents so that the readers get a quick snapshot of what to expect.
A good introduction should aim to: 2,3
- Indicate the main subject area, its importance, and cite previous literature on the subject
- Define the gap(s) in existing research, ask a research question, and state the objectives
- Announce the present research and outline its novelty and significance
- Avoid repeating the Abstract, providing unnecessary information, and claiming novelty without accurate supporting information.
Why are research objectives important?
Objectives can help you stay focused and steer your research in the required direction. They help define and limit the scope of your research, which is important to efficiently manage your resources and time. The objectives help to create and maintain the overall structure, and specify two main things—the variables and the methods of quantifying the variables.
A good research objective:
- defines the scope of the study
- gives direction to the research
- helps maintain focus and avoid diversions from the topic
- minimizes wastage of resources like time, money, and energy
Types of research objectives
Research objectives can be broadly classified into general and specific objectives . 4 General objectives state what the research expects to achieve overall while specific objectives break this down into smaller, logically connected parts, each of which addresses various parts of the research problem. General objectives are the main goals of the study and are usually fewer in number while specific objectives are more in number because they address several aspects of the research problem.
Example (general objective): To investigate the factors influencing the financial performance of firms listed in the New York Stock Exchange market.
Example (specific objective): To assess the influence of firm size on the financial performance of firms listed in the New York Stock Exchange market.
In addition to this broad classification, research objectives can be grouped into several categories depending on the research problem, as given in Table 1.
Table 1: Types of research objectives
| Exploratory | Explores a previously unstudied topic, issue, or phenomenon; aims to generate ideas or hypotheses |
| Descriptive | Describes the characteristics and features of a particular population or group |
| Explanatory | Explains the relationships between variables; seeks to identify cause-and-effect relationships |
| Predictive | Predicts future outcomes or events based on existing data samples or trends |
| Diagnostic | Identifies factors contributing to a particular problem |
| Comparative | Compares two or more groups or phenomena to identify similarities and differences |
| Historical | Examines past events and trends to understand their significance and impact |
| Methodological | Develops and improves research methods and techniques |
| Theoretical | Tests and refines existing theories or helps develop new theoretical perspectives |
Characteristics of research objectives
Research objectives must start with the word “To” because this helps readers identify the objective in the absence of headings and appropriate sectioning in research papers. 5,6
- A good objective is SMART (mostly applicable to specific objectives):
- Specific—clear about the what, why, when, and how
- Measurable—identifies the main variables of the study and quantifies the targets
- Achievable—attainable using the available time and resources
- Realistic—accurately addresses the scope of the problem
- Time-bound—identifies the time in which each step will be completed
- Research objectives clarify the purpose of research.
- They help understand the relationship and dissimilarities between variables.
- They provide a direction that helps the research to reach a definite conclusion.
How to write research objectives?
Research objectives can be written using the following steps: 7
- State your main research question clearly and concisely.
- Describe the ultimate goal of your study, which is similar to the research question but states the intended outcomes more definitively.
- Divide this main goal into subcategories to develop your objectives.
- Limit the number of objectives (1-2 general; 3-4 specific)
- Assess each objective using the SMART
- Start each objective with an action verb like assess, compare, determine, evaluate, etc., which makes the research appear more actionable.
- Use specific language without making the sentence data heavy.
- The most common section to add the objectives is the introduction and after the problem statement.
- Add the objectives to the abstract (if there is one).
- State the general objective first, followed by the specific objectives.
Formulating research objectives
Formulating research objectives has the following five steps, which could help researchers develop a clear objective: 8
- Identify the research problem.
- Review past studies on subjects similar to your problem statement, that is, studies that use similar methods, variables, etc.
- Identify the research gaps the current study should cover based on your literature review. These gaps could be theoretical, methodological, or conceptual.
- Define the research question(s) based on the gaps identified.
- Revise/relate the research problem based on the defined research question and the gaps identified. This is to confirm that there is an actual need for a study on the subject based on the gaps in literature.
- Identify and write the general and specific objectives.
- Incorporate the objectives into the study.
Advantages of research objectives
Adding clear research objectives has the following advantages: 4,8
- Maintains the focus and direction of the research
- Optimizes allocation of resources with minimal wastage
- Acts as a foundation for defining appropriate research questions and hypotheses
- Provides measurable outcomes that can help evaluate the success of the research
- Determines the feasibility of the research by helping to assess the availability of required resources
- Ensures relevance of the study to the subject and its contribution to existing literature
Disadvantages of research objectives
Research objectives also have few disadvantages, as listed below: 8
- Absence of clearly defined objectives can lead to ambiguity in the research process
- Unintentional bias could affect the validity and accuracy of the research findings
Key takeaways
- Research objectives are concise statements that describe what the research is aiming to achieve.
- They define the scope and direction of the research and maintain focus.
- The objectives should be SMART—specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, and time-bound.
- Clear research objectives help avoid collection of data or resources not required for the study.
- Well-formulated specific objectives help develop the overall research methodology, including data collection, analysis, interpretation, and utilization.
- Research objectives should cover all aspects of the problem statement in a coherent way.
- They should be clearly stated using action verbs.
Frequently asked questions on research objectives
Q: what’s the difference between research objectives and aims 9.
A: Research aims are statements that reflect the broad goal(s) of the study and outline the general direction of the research. They are not specific but clearly define the focus of the study.
Example: This research aims to explore employee experiences of digital transformation in retail HR.
Research objectives focus on the action to be taken to achieve the aims. They make the aims more practical and should be specific and actionable.
Example: To observe the retail HR employees throughout the digital transformation.
Q: What are the examples of research objectives, both general and specific?
A: Here are a few examples of research objectives:
- To identify the antiviral chemical constituents in Mumbukura gitoniensis (general)
- To carry out solvent extraction of dried flowers of Mumbukura gitoniensis and isolate the constituents. (specific)
- To determine the antiviral activity of each of the isolated compounds. (specific)
- To examine the extent, range, and method of coral reef rehabilitation projects in five shallow reef areas adjacent to popular tourist destinations in the Philippines.
- To investigate species richness of mammal communities in five protected areas over the past 20 years.
- To evaluate the potential application of AI techniques for estimating best-corrected visual acuity from fundus photographs with and without ancillary information.
- To investigate whether sport influences psychological parameters in the personality of asthmatic children.
Q: How do I develop research objectives?
A: Developing research objectives begins with defining the problem statement clearly, as illustrated by Figure 1. Objectives specify how the research question will be answered and they determine what is to be measured to test the hypothesis.
Q: Are research objectives measurable?
A: The word “measurable” implies that something is quantifiable. In terms of research objectives, this means that the source and method of collecting data are identified and that all these aspects are feasible for the research. Some metrics can be created to measure your progress toward achieving your objectives.
Q: Can research objectives change during the study?
A: Revising research objectives during the study is acceptable in situations when the selected methodology is not progressing toward achieving the objective, or if there are challenges pertaining to resources, etc. One thing to keep in mind is the time and resources you would have to complete your research after revising the objectives. Thus, as long as your problem statement and hypotheses are unchanged, minor revisions to the research objectives are acceptable.
Q: What is the difference between research questions and research objectives? 10
| Broad statement; guide the overall direction of the research | Specific, measurable goals that the research aims to achieve |
| Identify the main problem | Define the specific outcomes the study aims to achieve |
| Used to generate hypotheses or identify gaps in existing knowledge | Used to establish clear and achievable targets for the research |
| Not mutually exclusive with research objectives | Should be directly related to the research question |
| Example: | Example: |
Q: Are research objectives the same as hypotheses?
A: No, hypotheses are predictive theories that are expressed in general terms. Research objectives, which are more specific, are developed from hypotheses and aim to test them. A hypothesis can be tested using several methods and each method will have different objectives because the methodology to be used could be different. A hypothesis is developed based on observation and reasoning; it is a calculated prediction about why a particular phenomenon is occurring. To test this prediction, different research objectives are formulated. Here’s a simple example of both a research hypothesis and research objective.
Research hypothesis : Employees who arrive at work earlier are more productive.
Research objective : To assess whether employees who arrive at work earlier are more productive.
To summarize, research objectives are an important part of research studies and should be written clearly to effectively communicate your research. We hope this article has given you a brief insight into the importance of using clearly defined research objectives and how to formulate them.
- Farrugia P, Petrisor BA, Farrokhyar F, Bhandari M. Practical tips for surgical research: Research questions, hypotheses and objectives. Can J Surg. 2010 Aug;53(4):278-81.
- Abbadia J. How to write an introduction for a research paper. Mind the Graph website. Accessed June 14, 2023. https://mindthegraph.com/blog/how-to-write-an-introduction-for-a-research-paper/
- Writing a scientific paper: Introduction. UCI libraries website. Accessed June 15, 2023. https://guides.lib.uci.edu/c.php?g=334338&p=2249903
- Research objectives—Types, examples and writing guide. Researchmethod.net website. Accessed June 17, 2023. https://researchmethod.net/research-objectives/#:~:text=They%20provide%20a%20clear%20direction,track%20and%20achieve%20their%20goals .
- Bartle P. SMART Characteristics of good objectives. Community empowerment collective website. Accessed June 16, 2023. https://cec.vcn.bc.ca/cmp/modules/pd-smar.htm
- Research objectives. Studyprobe website. Accessed June 18, 2023. https://www.studyprobe.in/2022/08/research-objectives.html
- Corredor F. How to write objectives in a research paper. wikiHow website. Accessed June 18, 2023. https://www.wikihow.com/Write-Objectives-in-a-Research-Proposal
- Research objectives: Definition, types, characteristics, advantages. AccountingNest website. Accessed June 15, 2023. https://www.accountingnest.com/articles/research/research-objectives
- Phair D., Shaeffer A. Research aims, objectives & questions. GradCoach website. Accessed June 20, 2023. https://gradcoach.com/research-aims-objectives-questions/
- Understanding the difference between research questions and objectives. Accessed June 21, 2023. https://board.researchersjob.com/blog/research-questions-and-objectives
R Discovery is a literature search and research reading platform that accelerates your research discovery journey by keeping you updated on the latest, most relevant scholarly content. With 250M+ research articles sourced from trusted aggregators like CrossRef, Unpaywall, PubMed, PubMed Central, Open Alex and top publishing houses like Springer Nature, JAMA, IOP, Taylor & Francis, NEJM, BMJ, Karger, SAGE, Emerald Publishing and more, R Discovery puts a world of research at your fingertips.
Try R Discovery Prime FREE for 1 week or upgrade at just US$72 a year to access premium features that let you listen to research on the go, read in your language, collaborate with peers, auto sync with reference managers, and much more. Choose a simpler, smarter way to find and read research – Download the app and start your free 7-day trial today !
Related Posts

Simple Random Sampling: Definition, Methods, and Examples

What is a Case Study in Research? Definition, Methods, and Examples
- How it works

How to Write the Dissertation Aims and Objectives – Guide & Examples
Published by Grace Graffin at January 27th, 2023 , Revised On October 9, 2023
Aims and objectives are among the essential aspects of a dissertation. If you write aims and objectives effectively, they can act as a foundation to give your research clarity and focus.
This article will provide you with all the necessary information regarding aims and objectives, their differences, writing tips , and the common mistakes you should avoid while writing them.
The aim is often a single sentence or a short paragraph that describes your dissertation’s main goal and intent. It tells what you hope to achieve at the end. You should write the aim so that it becomes identifiable when it is achieved with the completion of your dissertation .
The aim is written in a subsection of the introduction to clarify the overall purpose of the dissertation .
Example: It is often observed that employees in culturally diverse workplaces struggle to work effectively in a team. A probable cause of this issue is bullying at the workplace. This research investigates the impact of bullying on employee job satisfaction at culturally diverse workplaces and the resulting loss of employee productivity. This research will use surveys and case study analysis to analyze the impact of bullying on employees.
The objectives in a dissertation describe the ways through which you intend to achieve the research aim. They are specific statements that break down the aim into several smaller key sections of the overall research. Suitable objectives can help you stay focused and conduct research in the direction of your aim.
The number of objectives should be realistic; usually, between three to six, and each one should be possible to achieve. The following example shows the objectives for the previously-mentioned dissertation aim.
1. identification of the behaviors that are considered as bullying 2. exploring the factors that cause bullying at a culturally diverse workplace 3. analyzing the relationship between bullying and job satisfaction of employees 4. providing suitable recommendations on minimizing the bullying at the workplace
The objectives of a dissertation should be SMART.
- Specific: should be precise, focused, and well-defined
- Measurable: the progress should be measurable, and you should be able to determine when you have achieved an objective.
- Achievable: you should be able to carry out the required action within your available resources
- Relevant: should be related to the dissertation aim
- Time-bound: should be possible within the available time
Differences between aims and objectives
Aims and objectives are often mixed, but there are clear differences between them.
| Aims | Objectives |
|---|---|
| describes “what” you intend to achieve through your research | focus on “how” you will achieve the aim |
| usually written in broad terms covering the entire dissertation | are specific statements describing steps through which the research aim will be achieved |
| is written as a single sentence or a small paragraph | should be written as a numbered list. |
| focuses on long-term outcomes | focus on short-term and immediate outcomes. |
Hire an Expert Writer
Orders completed by our expert writers are
- Formally drafted in an academic style
- Free Amendments and 100% Plagiarism Free – or your money back!
- 100% Confidential and Timely Delivery!
- Free anti-plagiarism report
- Appreciated by thousands of clients. Check client reviews

How to write aims and objectives?
There is no particular way or standard to write the aims and objectives. Different researchers have different writing styles, and often it can be influenced by your research supervisor. However, you should follow certain basic principles while writing aims and objectives in a dissertation.
Writing the aim statement
The aim statement should cover the following essential elements.
- Why is the research necessary? (covers the underlying problem on which the study is to be conducted)
- What is the research about? (description of the research title)
- How are you going to conduct it? (a brief statement of intended research methods)
An appropriate aim clearly defines the research purpose without confusing the reader. If you struggle to explain your research and its importance in simpler terms, you should consider refining your research to clarify it further.
Writing objectives
The objectives describe how you would achieve your research aim. You can do this through the following steps,
- The first one to two objectives can be applied to the literature review . (Verbs to be used: investigate, examine, study)
- One objective can be applied to the methodology portion. (Verbs to be used: collect, select, demonstrate, estimate)
- Two to three objectives can cover the critical evaluation or discussion chapters (Verbs to be used: analyze, compare, evaluate)
- The final objective will cover the conclusion or recommendation portion. (Verbs to be used: conclude, recommend)
Instead of writing like a paragraph, the objectives should be written as a numbered list to give them more clarity.
How many aims and objectives should be there?
It depends upon the topic of your research and mainly upon your supervisor’s requirements. Generally, a dissertation has a single broad statement as the research aim. However, it is acceptable to include a main aim along with two to three subsidiary aims.
Similarly, the number of objectives should be realistic and sufficient to measure the progress regarding the achievement of the research aim. Their number can generally vary from three to six depending upon the aim.
Common mistakes to avoid while writing research aims and objectives
- Writing a broad research aim
Writing a broad research aim is a common mistake, and it often becomes difficult to achieve. It may create a problem when you are asked to prove how you have achieved your aims during your viva defense . It would be best to narrow your study to a specific area in the early stages of the dissertation.
- Formulating overlapping research objectives
The objectives should be written such that they are measurable and distinct from each other. If they overlap, it makes it difficult to structure your dissertation properly in specific chapters.
- Setting unrealistic aims
Students often get over-ambitious while describing the research aim and face problems afterward in achieving those aims. You should avoid this mistake and be realistic about what you can achieve in the available time and resources.
Aims and objectives are the sections that require significant time and attention to avoid future hassles while conducting research and writing your dissertation.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to set dissertation aims and objectives.
To set dissertation aims and objectives, define your research goals clearly. Aims state what you want to achieve, while objectives outline specific, measurable steps to reach those goals. Ensure they align with your research question and contribute to your study’s significance.
You May Also Like
Technology is an important part of our lives these days. Here are ten powerful applications for students to be productive.
Struggling to write a high quality research paper? Here is all you need to know if you need help with writing research paper for your degree programme.
Elevate your professional profile with the CapCut Creative Suite! Craft compelling video resumes that captivate employers in the job market.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works

Handy Tips To Write A Clear Research Objectives With Examples
Introduction.
Research objectives play a crucial role in any research study. They provide a clear direction and purpose for the research, guiding the researcher in their investigation. Understanding research objectives is essential for conducting a successful study and achieving meaningful results.
In this comprehensive review, we will delve into the definition of research objectives, exploring their characteristics, types, and examples. We will also discuss the relationship between research objectives and research questions, as well as provide insights into how to write effective research objectives. Additionally, we will examine the role of research objectives in research methodology and highlight the importance of them in a study. By the end of this review, you will have a comprehensive understanding of research objectives and their significance in the research process.
Definition of Research Objectives: What Are They?

A research objective is defined as a clear and concise statement that outlines the specific goals and aims of a research study. These objectives are designed to be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART), ensuring they provide a structured pathway to accomplishing the intended outcomes of the project. Each objective serves as a foundational element that summarizes the purpose of your study, guiding the research activities and helping to measure progress toward the study’s goals. Additionally, research objectives are integral components of the research framework , establishing a clear direction that aligns with the overall research questions and hypotheses. This alignment helps to ensure that the study remains focused and relevant, facilitating the systematic collection, analysis, and interpretation of data.
Characteristics of Effective Research Objectives
Characteristics of research objectives include:
- Specific: Research objectives should be clear about the what, why, when, and how of the study.
- Measurable: Research objectives should identify the main variables of the study that can be measured or observed.
- Relevant: Research objectives should be relevant to the research topic and contribute to the overall understanding of the subject.
- Feasible: Research objectives should be achievable within the constraints of time, resources, and expertise available.
- Logical: Research objectives should follow a logical sequence and build upon each other to achieve the overall research goal.
- Observable: Research objectives should be observable or measurable in order to assess the progress and success of the research project.
- Unambiguous: Research objectives should be clear and unambiguous, leaving no room for interpretation or confusion.
- Measurable: Research objectives should be measurable, allowing for the collection of data and analysis of results.
By incorporating these characteristics into research objectives, researchers can ensure that their study is focused, achievable, and contributes to the body of knowledge in their field.
Types of Research Objectives
Research objective can be broadly classified into general and specific objectives. General objectives are broad statements that define the overall purpose of the research. They provide a broad direction for the study and help in setting the context. Specific objectives, on the other hand, are detailed objectives that describe what will be researched during the study. They are more focused and provide specific outcomes that the researcher aims to achieve. Specific objectives are derived from the general objectives and help in breaking down the research into smaller, manageable parts. The specific objectives should be clear, measurable, and achievable. They should be designed in a way that allows the researcher to answer the research questions and address the research problem.
In addition to general and specific objectives, research objective can also be categorized as descriptive or analytical objectives. Descriptive objectives focus on describing the characteristics or phenomena of a particular subject or population. They involve surveys, observations, and data collection to provide a detailed understanding of the subject. Analytical objectives, on the other hand, aim to analyze the relationships between variables or factors. They involve data analysis and interpretation to gain insights and draw conclusions.
Both descriptive and analytical objectives are important in research as they serve different purposes and contribute to a comprehensive understanding of the research topic.
Examples of Research Objectives
Here are some examples of research objectives in different fields:
1. Objective: To identify key characteristics and styles of Renaissance art.
This objective focuses on exploring the characteristics and styles of art during the Renaissance period. The research may involve analyzing various artworks, studying historical documents, and interviewing experts in the field.
2. Objective: To analyze modern art trends and their impact on society.
This objective aims to examine the current trends in modern art and understand how they influence society. The research may involve analyzing artworks, conducting surveys or interviews with artists and art enthusiasts, and studying the social and cultural implications of modern art.
3. Objective: To investigate the effects of exercise on mental health.
This objective focuses on studying the relationship between exercise and mental health. The research may involve conducting experiments or surveys to assess the impact of exercise on factors such as stress, anxiety, and depression.
4. Objective: To explore the factors influencing consumer purchasing decisions in the fashion industry.
This objective aims to understand the various factors that influence consumers’ purchasing decisions in the fashion industry. The research may involve conducting surveys, analyzing consumer behavior data, and studying the impact of marketing strategies on consumer choices.
5. Objective: To examine the effectiveness of a new drug in treating a specific medical condition.
This objective focuses on evaluating the effectiveness of a newly developed drug in treating a particular medical condition. The research may involve conducting clinical trials, analyzing patient data, and comparing the outcomes of the new drug with existing treatment options.
These examples demonstrate the diversity of research objectives across different disciplines. Each objective is specific, measurable, and achievable, providing a clear direction for the research study.
Aligning Research Objectives with Research Questions
Research objectives and research questions are essential components of a research project. Research objective describe what you intend your research project to accomplish. They summarize the approach and purpose of the project and provide a clear direction for the research. Research questions, on the other hand, are the starting point of any good research. They guide the overall direction of the research and help identify and focus on the research gaps .
The main difference between research questions and objectives is their form. Research questions are stated in a question form, while objectives are specific, measurable, and achievable goals that you aim to accomplish within a specified timeframe. Research questions are broad statements that provide a roadmap for the research, while objectives break down the research aim into smaller, actionable steps.
Research objectives and research questions work together to form the ‘golden thread’ of a research project. The research aim specifies what the study will answer, while the objectives and questions specify how the study will answer it. They provide a clear focus and scope for the research project, helping researchers stay on track and ensure that their study is meaningful and relevant.
When writing research objectives and questions, it is important to be clear, concise, and specific. Each objective or question should address a specific aspect of the research and contribute to the overall goal of the study. They should also be measurable, meaning that their achievement can be assessed and evaluated. Additionally, research objectives and questions should be achievable within the given timeframe and resources of the research project. By clearly defining the objectives and questions, researchers can effectively plan and execute their research, leading to valuable insights and contributions to the field.
Guidelines for Writing Clear Research Objectives
Writing research objective is a crucial step in any research project. The objectives provide a clear direction and purpose for the study, guiding the researcher in their data collection and analysis. Here are some tips on how to write effective research objective:
1. Be clear and specific
Research objective should be written in a clear and specific manner. Avoid vague or ambiguous language that can lead to confusion. Clearly state what you intend to achieve through your research.
2. Use action verbs
Start your research objective with action verbs that describe the desired outcome. Action verbs such as ‘investigate’, ‘analyze’, ‘compare’, ‘evaluate’, or ‘identify’ help to convey the purpose of the study.
3. Align with research questions or hypotheses
Ensure that your research objectives are aligned with your research questions or hypotheses. The objectives should address the main goals of your study and provide a framework for answering your research questions or testing your hypotheses.
4. Be realistic and achievable
Set research objectives that are realistic and achievable within the scope of your study. Consider the available resources, time constraints, and feasibility of your objectives. Unrealistic objectives can lead to frustration and hinder the progress of your research.
5. Consider the significance and relevance
Reflect on the significance and relevance of your research objectives. How will achieving these objectives contribute to the existing knowledge or address a gap in the literature? Ensure that your objectives have a clear purpose and value.
6. Seek feedback
It is beneficial to seek feedback on your research objectives from colleagues, mentors, or experts in your field. They can provide valuable insights and suggestions for improving the clarity and effectiveness of your objectives.
7. Revise and refine
Research objectives are not set in stone. As you progress in your research, you may need to revise and refine your objectives to align with new findings or changes in the research context. Regularly review and update your objectives to ensure they remain relevant and focused.
By following these tips, you can write research objectives that are clear, focused, and aligned with your research goals. Well-defined objectives will guide your research process and help you achieve meaningful outcomes.
The Role of Research Objectives in Research Methodology
Research objectives play a crucial role in the research methodology . In research methodology, research objectives are formulated based on the research questions or problem statement. These objectives help in defining the scope and focus of the study, ensuring that the research is conducted in a systematic and organized manner.
The research objectives in research methodology act as a roadmap for the research project. They help in identifying the key variables to be studied, determining the research design and methodology, and selecting the appropriate data collection methods .
Furthermore, research objectives in research methodology assist in evaluating the success of the study. By setting clear objectives, researchers can assess whether the desired outcomes have been achieved and determine the effectiveness of the research methods employed. It is important to note that research objectives in research methodology should be aligned with the overall research aim. They should address the specific aspects or components of the research aim and provide a framework for achieving the desired outcomes.
Understanding The Dynamic of Research Objectives in Your Study
The research objectives of a study play a crucial role in guiding the research process, ensuring that the study is focused, purposeful, and contributes to the advancement of knowledge in the field. It is important to note that the research objectives may evolve or change as the study progresses. As new information is gathered and analyzed, the researcher may need to revise the objectives to ensure that they remain relevant and achievable.
In summary, research objectives are essential components in writing an effective research paper . They provide a roadmap for the research process, guiding the researcher in their investigation and helping to ensure that the study is purposeful and meaningful. By understanding and effectively utilizing research objectives, researchers can enhance the quality and impact of their research endeavors.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related articles
Writing engaging introduction in research papers : tips and tricks.

Understanding Comparative Frameworks: Their Importance, Components, Examples and 8 Best Practices

Revolutionizing Effective Thesis Writing for PhD Students Using Artificial Intelligence!

3 Types of Interviews in Qualitative Research: An Essential Research Instrument and Handy Tips to Conduct Them

Highlight Abstracts: An Ultimate Guide For Researchers!

Crafting Critical Abstracts: 11 Expert Strategies for Summarizing Research

Crafting the Perfect Informative Abstract: Definition, Importance and 8 Expert Writing Tips

Descriptive Abstracts: A Complete Guide to Crafting Effective Summaries in Research Writing

What are you doing and how are you doing it? Articulating your aims and objectives.
Mar 6, 2019

Have you checked out the rest of The PhD Knowledge Base ? It’s home to hundreds more free resources and guides, written especially for PhD students.
How long does it take the person reading your thesis to understand what you’re doing and how you’re doing it? If the answer is anything other than ’in the opening paragraphs of the thesis’ then keep reading.
If you tell them as early as possible what you’re doing and how you’re doing it – and do so in clear and simple terms – whatever you write after will make much more sense. If you leave them guessing for ten pages, everything they read in those ten pages has no coherence. You’ll know where it is all leading, but they won’t.
Unless you tell them.
If you tell the reader what you’re doing as early as possible in clear and simple terms, whatever you write after will make much more sense.
What are aims & objectives?
If you build a house without foundations, it’s pretty obvious what will happen. It’ll collapse. Your thesis is the same; fail to build the foundations and your thesis just won’t work .
Your aims and objectives are those foundations. That’s why we’ve put them right at the top of our PhD Writing Template (if you haven’t already downloaded it, join the thousands who have by clicking here ).
If you write your aims and objectives clearly then you’ll make your reader’s life easier.
A lot of students fail to clearly articulate their aims and objectives because they aren’t sure themselves what they actually are.
Picture this: if there’s one thing that every PhD student hates it’s being asked by a stranger what their research is on.

Your PhD thesis. All on one page.
Use our free PhD structure template to quickly visualise every element of your thesis.
Hello, Doctor…
Sounds good, doesn’t it? Be able to call yourself Doctor sooner with our five-star rated How to Write A PhD email-course. Learn everything your supervisor should have taught you about planning and completing a PhD.
Now half price. Join hundreds of other students and become a better thesis writer, or your money back.
Research aims
Your research aims are the answer to the question, ‘What are you doing?’
1. You need to clearly describe what your intentions are and what you hope to achieve. These are your aims.
2. Your aims may be to test theory in a new empirical setting, derive new theory entirely, construct a new data-set, replicate an existing study, question existing orthodoxy, and so on. Whatever they are, clearly articulate them and do so early. Definitely include them in your introduction and, if you’re smart, you’ll write them in your abstract .
3. Be very explicit . In the opening paragraphs, say, in simple terms, ‘ the aim of this thesis is to …’
4. Think of your aims then as a statement of intent. They are a promise to the reader that you are going to do something. You use the next two hundred pages or so to follow through on that promise. If you don’t make the promise, the reader won’t understand your follow-through. Simple as that.
Because they serve as the starting point of the study, there needs to be a flow from your aims through your objectives (more on this below) to your research questions and contribution and then into the study itself. If you have completed your research and found that you answered a different question (not that uncommon), make sure your original aims are still valid. If they aren’t, refine them.
If you struggle to explain in simple terms what your research is about and why it matters, you may need to refine your aims and objectives to make them more concise.
When writing up your aims, there are a number of things to bear in mind.
1. Avoid listing too many. Your PhD isn’t as long as you think it is and you won’t have time or room for more than around two or three.
2. When you write them up, be very specific. Don’t leave things so vague that the reader is left unsure or unclear on what you aim to achieve.
3. Make sure there is a logical flow between each of your aims. They should make sense together and should each be separate components which, when added together, are bigger than the sum of their parts.
Research objectives
Your aims answer the question, ‘What are you doing?’ The objectives are the answer to the question, ‘How are you doing it?’
Research objectives refer to the goals or steps that you will take to achieve your aims.
When you write them, make sure they are SMART.
- S pecific: talk in a precise and clear way about what you are going to do.
- M easurable: how will you know when you have achieved your aim?
- A chievable: make sure that you aren’t overly ambitious.
- R ealistic: recognise the time and resource constraints that come with doing a PhD and don’t attempt to do too much.
- T ime constrained: determine when each objective needs to be completed.
You need to be as explicit as possible here. Leave the reader in no doubt about what you will do to achieve your aims. Step by step. Leave no ambiguity. At the same time, be careful not to repeat your methods chapter here. Just hint at your methods by presenting the headlines. You’ll have plenty of space in your methods discussion to flesh out the detail.
Elsewhere in the thesis you will necessarily have to talk in a complex language and juggle complex ideas. Here you don’t. You can write in clear, plain sentences.
What is the difference between research aims and objectives?
The aims of a study describe what you hope to achieve. The objectives detail how you are going to achieve your aims.
Let’s use an example to illustrate.
- To understand the contribution that local governments make to national level energy policy.
Objectives:
- Conduct a survey of local politicians to solicit responses.
- Conduct desk-research of local government websites to create a database of local energy policy.
- Interview national level politicians to understand the impact these local policies have had.
- Data will be coded using a code book derived from dominant theories of governance.
If you’re still struggling, Professor Pat Thompson’s great blog has a guide that will help.
Leave the reader in no doubt about what you will do to achieve your aims. Step by step. Leave no ambiguity.
I can’t articulate them clearly, my research is complicated!
Of course your research is complex. That’s the name of the game. But the sign of someone being able to master complexity is their ability to summarise it . Sure, you’re not looking to capture all the richness and detail in a short summary of aims and objectives, but you are looking to tell the reader what you’re doing and how you’re doing it.
If you’re struggling to clearly articulate your aims and objectives, then try the following task. At the top of a Post-it note write the sentence: ‘In this research I will…’. Then keep trying until you can fit an answer onto one single Post-it note. The answer should answer two questions: what are are you doing and how are you doing it?
Remember – whenever you write, make it as clear as possible. Pay attention to the words ‘as possible’ there. That means you should write as clearly as you can given the fact that your subject and research is necessarily complex. Think of it the other way: it’s about not making things more complicated and unclear than they need to be.
In other words, make your reader’s job as easy as you can. They’ll thank you for it.
If you’re still having trouble, get in touch to arrange a one-on-one coaching session and we can work through your aims and objectives together.
Share this:
32 comments.
The write up is quite inspiring.
My topic is setting up a healing gardens in hospitals Need a aim and objectives for a dissertation
Dis is really good and more understandable thanks
Crisp, concise, and easy to understnad. Thank you for posint this. I now know how to write up my report.
Great. Glad you found it useful.
Good piece of work! Very useful
Great. Glad you found it useful!
The write up makes sense
Great. Thanks!
I love this article. Amazing, outstanding and incredible facts.
Glad you found it useful!
Well written and easy to follow
Thank you for the comment, I’m really glad you found it valuable.
I’m currently developing a dissertation proposal for my PhD in organizational leadership. I need guidance in writing my proposal
Hey – have you checked out this guide? https://www.thephdproofreaders.com/writing/how-to-write-a-phd-proposal/
Indeed I’m impressed and gained a lot from this and I hope I can write an acceptable thesis with this your guide. Bello, H.K
Great. Thanks for the kind words. Good luck with the thesis.
Thumbs up! God job, well done. The information is quite concise and straight to the point.
Glad you thought so – good luck with the writing.
Dear Max, thank you so much for your work and efforts!
Your explanation about Aims and Objectives really helped me out. However, I got stuck with other parts of the Aims and Objectives Work Sheet: Scope, Main Argument, and Contribution.
Could you please explain these as well, preferably including some examples?
Thanks for your kind words. Your question is a big one! Without knowing lots about your topics/subject I’m not able to provide tailored advice, but broadly speaking your scope is the aims/objectives, your main argument is the thread running through the thesis (i.e. what your thesis is trying to argue) and the contribution (again, broadly speaking) is that gap you are filling.
I love your website and you’ve been so SO helpful..
DUMB QUESTION ALERT: Is there supposed to be a difference between aims and research question?
I mean, using your own example.. if the aim of my research is: “To understand the contribution that local governments make to national level energy policy” then wouldn’t the research question be: “How do local governments contribute to energy policy at national level”?
I am sorry if this comes out as completely obvious but I am at that stage of confusion where I am starting to question everything I know.
Sorry it’s taken me so long to reply! It’s not a dumb question at all. The aim of the study is what the study as a whole is seeking to achieve. So that might be the gap it is filling/the contribution it is making. The research questions are your means to achieving that aim. Your aim might be to fill a gap in knowledge, and you then may have a small number of questions that help you along that path. Does that make sense?
Thank you Max for this post! So helpful!
Thanks Anna!
Thanks so much this piece. I have written both bachelor’s and master’s thesis but haven’t read this made me feel like I didn’t know anything about research at all. I gained more insight into aims and objectives of academic researches.
Interesting explanation. Thank you.
I’m glad you found it useful.
Hi… I really like the way it is put “What are you going?” (Aims) and “How are you doing it?” (Objectives). Simple and straightforward. Thanks for making aims and objectives easy to understand.
Thank you for the write up it is insightful. if you are ask to discuss your doctoral aims. that means: what you are doing how you are doing it.
I was totally lost and still in the woods to the point of thinking I am dull, but looking at how you are coaching it tells me that i am just a student who needs to understand the lesson. I now believe that with your guidance i will pass my PhD. I am writing on an otherwise obvious subject, Value addition to raw materials, why Africa has failed to add value to raw materials? Difficult question as answers seem to abound, but that is where i differ and i seem to be against the general tide. However with your guidance I believe i will make it. Thanks.
Thanks for your lovely, kind words. So kind.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Search The PhD Knowledge Base
Most popular articles from the phd knowlege base.
The PhD Knowledge Base Categories
- Your PhD and Covid
- Mastering your theory and literature review chapters
- How to structure and write every chapter of the PhD
- How to stay motivated and productive
- Techniques to improve your writing and fluency
- Advice on maintaining good mental health
- Resources designed for non-native English speakers
- PhD Writing Template
- Explore our back-catalogue of motivational advice
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Write Research Objectives

3-minute read
- 22nd November 2021
Writing a research paper, thesis, or dissertation ? If so, you’ll want to state your research objectives in the introduction of your paper to make it clear to your readers what you’re trying to accomplish. But how do you write effective research objectives? In this post, we’ll look at two key topics to help you do this:
- How to use your research aims as a basis for developing objectives.
- How to use SMART criteria to refine your research objectives.
For more advice on how to write strong research objectives, see below.
Research Aims and Objectives
There is an important difference between research aims and research objectives:
- A research aim defines the main purpose of your research. As such, you can think of your research aim as answering the question “What are you doing?”
- Research objectives (as most studies will have more than one) are the steps you will take to fulfil your aims. As such, your objectives should answer the question “How are you conducting your research?”
For instance, an example research aim could be:
This study will investigate the link between dehydration and the incidence of urinary tract infections (UTIs) in intensive care patients in Australia.
To develop a set of research objectives, you would then break down the various steps involved in meeting said aim. For example:
This study will investigate the link between dehydration and the incidence of urinary tract infections (UTIs) in intensive care patients in Australia. To achieve this, the study objectives w ill include:
- Replicat ing a small Singaporean study into the role of dehydration in UTIs in hospital patients (Sepe, 2018) in a larger Australian cohort.
- Trialing the use of intravenous fluids for intensive care patients to prevent dehydration.
- Assessing the relationship between the age of patients and quantities of intravenous fluids needed to counter dehydration.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Note that the objectives don’t go into any great detail here. The key is to briefly summarize each component of your study. You can save details for how you will conduct the research for the methodology section of your paper.
Make Your Research Objectives SMART
A great way to refine your research objectives is to use SMART criteria . Borrowed from the world of project management, there are many versions of this system. However, we’re going to focus on developing specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and timebound objectives.
In other words, a good research objective should be all of the following:
- S pecific – Is the objective clear and well-defined?
- M easurable – How will you know when the objective has been achieved? Is there a way to measure the thing you’re seeking to do?
- A chievable – Do you have the support and resources necessary to undertake this action? Are you being overly ambitious with this objective?
- R elevant – Is this objective vital for fulfilling your research aim?
- T imebound – Can this action be realistically undertaken in the time you have?
If you follow this system, your research objectives will be much stronger.
Expert Research Proofreading
Whatever your research aims and objectives, make sure to have your academic writing proofread by the experts!
Our academic editors can help you with research papers and proposals , as well as any other scholarly document you need checking. And this will help to ensure that your academic writing is always clear, concise, and precise.
Submit a free sample document today to trial our services and find out more.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
4-minute read
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.

Formulating Research Aims and Objectives
Formulating research aim and objectives in an appropriate manner is one of the most important aspects of your thesis. This is because research aim and objectives determine the scope, depth and the overall direction of the research. Research question is the central question of the study that has to be answered on the basis of research findings.
Research aim emphasizes what needs to be achieved within the scope of the research, by the end of the research process. Achievement of research aim provides answer to the research question.
Research objectives divide research aim into several parts and address each part separately. Research aim specifies WHAT needs to be studied and research objectives comprise a number of steps that address HOW research aim will be achieved.
As a rule of dumb, there would be one research aim and several research objectives. Achievement of each research objective will lead to the achievement of the research aim.
Consider the following as an example:
Research title: Effects of organizational culture on business profitability: a case study of Virgin Atlantic
Research aim: To assess the effects of Virgin Atlantic organizational culture on business profitability
Following research objectives would facilitate the achievement of this aim:
- Analyzing the nature of organizational culture at Virgin Atlantic by September 1, 2022
- Identifying factors impacting Virgin Atlantic organizational culture by September 16, 2022
- Analyzing impacts of Virgin Atlantic organizational culture on employee performances by September 30, 2022
- Providing recommendations to Virgin Atlantic strategic level management in terms of increasing the level of effectiveness of organizational culture by October 5, 2022
Figure below illustrates additional examples in formulating research aims and objectives:

Formulation of research question, aim and objectives
Common mistakes in the formulation of research aim relate to the following:
1. Choosing the topic too broadly . This is the most common mistake. For example, a research title of “an analysis of leadership practices” can be classified as too broad because the title fails to answer the following questions:
a) Which aspects of leadership practices? Leadership has many aspects such as employee motivation, ethical behaviour, strategic planning, change management etc. An attempt to cover all of these aspects of organizational leadership within a single research will result in an unfocused and poor work.
b) An analysis of leadership practices in which country? Leadership practices tend to be different in various countries due to cross-cultural differences, legislations and a range of other region-specific factors. Therefore, a study of leadership practices needs to be country-specific.
c) Analysis of leadership practices in which company or industry? Similar to the point above, analysis of leadership practices needs to take into account industry-specific and/or company-specific differences, and there is no way to conduct a leadership research that relates to all industries and organizations in an equal manner.
Accordingly, as an example “a study into the impacts of ethical behaviour of a leader on the level of employee motivation in US healthcare sector” would be a more appropriate title than simply “An analysis of leadership practices”.
2. Setting an unrealistic aim . Formulation of a research aim that involves in-depth interviews with Apple strategic level management by an undergraduate level student can be specified as a bit over-ambitious. This is because securing an interview with Apple CEO Tim Cook or members of Apple Board of Directors might not be easy. This is an extreme example of course, but you got the idea. Instead, you may aim to interview the manager of your local Apple store and adopt a more feasible strategy to get your dissertation completed.
3. Choosing research methods incompatible with the timeframe available . Conducting interviews with 20 sample group members and collecting primary data through 2 focus groups when only three months left until submission of your dissertation can be very difficult, if not impossible. Accordingly, timeframe available need to be taken into account when formulating research aims and objectives and selecting research methods.
Moreover, research objectives need to be formulated according to SMART principle,
where the abbreviation stands for specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, and time-bound.
| Study employee motivation of Coca-Cola | To study the impacts of management practices on the levels of employee motivation at Coca-Cola US by December 5, 2022
|
| Analyze consumer behaviour in catering industry
| Analyzing changes in consumer behaviour in catering industry in the 21 century in the UK by March 1, 2022 |
| Recommend Toyota Motor Corporation management on new market entry strategy
| Formulating recommendations to Toyota Motor Corporation management on the choice of appropriate strategy to enter Vietnam market by June 9, 2022
|
| Analyze the impact of social media marketing on business
| Assessing impacts of integration of social media into marketing strategy on the level of brand awareness by March 30, 2022
|
| Finding out about time management principles used by Accenture managers | Identifying main time-management strategies used by managers of Accenture France by December 1, 2022 |
Examples of SMART research objectives
At the conclusion part of your research project you will need to reflect on the level of achievement of research aims and objectives. In case your research aims and objectives are not fully achieved by the end of the study, you will need to discuss the reasons. These may include initial inappropriate formulation of research aims and objectives, effects of other variables that were not considered at the beginning of the research or changes in some circumstances during the research process.

John Dudovskiy
Writing the Research Objectives: 5 Straightforward Examples
The research objective of a research proposal or scientific article defines the direction or content of a research investigation. Without the research objectives, the proposal or research paper is in disarray. It is like a fisherman riding on a boat without any purpose and with no destination in sight. Therefore, at the beginning of any research venture, the researcher must be clear about what he or she intends to do or achieve in conducting a study.
How do you define the objectives of a study? What are the uses of the research objective? How would a researcher write this essential part of the research? This article aims to provide answers to these questions.
Table of Contents
Definition of a research objective.
A research objective describes, in a few words, the result of the research project after its implementation. It answers the question,
The research objective provides direction to the performance of the study.
What are the Uses of the Research Objective?
The uses of the research objective are enumerated below:
The research design serves as the “blueprint” for the research investigation. The University of Southern California describes the different types of research design extensively. It details the data to be gathered, data collection procedure, data measurement, and statistical tests to use in the analysis.
The variables of the study include those factors that the researcher wants to evaluate in the study. These variables narrow down the research to several manageable components to see differences or correlations between them.
Specifying the data collection procedure ensures data accuracy and integrity . Thus, the probability of error is minimized. Generalizations or conclusions based on valid arguments founded on reliable data strengthens research findings on particular issues and problems.
In data mining activities where large data sets are involved, the research objective plays a crucial role. Without a clear objective to guide the machine learning process, the desired outcomes will not be met.
How is the Research Objective Written?
A research objective must be achievable, i.e., it must be framed keeping in mind the available time, infrastructure required for research, and other resources.
Before forming a research objective, you should read about all the developments in your area of research and find gaps in knowledge that need to be addressed. Readings will help you come up with suitable objectives for your research project.
5 Examples of Research Objectives
The following examples of research objectives based on several published studies on various topics demonstrate how the research objectives are written:
Finally, writing the research objectives requires constant practice, experience, and knowledge about the topic investigated. Clearly written objectives save time, money, and effort.
Evans, K. L., Rodrigues, A. S., Chown, S. L., & Gaston, K. J. (2006). Protected areas and regional avian species richness in South Africa. Biology letters , 2 (2), 184-188.
Yeemin, T., Sutthacheep, M., & Pettongma, R. (2006). Coral reef restoration projects in Thailand. Ocean & Coastal Management , 49 (9-10), 562-575.
© 2020 March 23 P. A. Regoniel Updated 17 November 2020 | Updated 18 January 2024
Related Posts
Designing a study: 5 key components of a research goal, multiple regression analysis example with conceptual framework, confounding variables: 3 examples and 5 case studies, about the author, patrick regoniel.
Dr. Regoniel, a hobbyist writer, served as consultant to various environmental research and development projects covering issues and concerns on climate change, coral reef resources and management, economic valuation of environmental and natural resources, mining, and waste management and pollution. He has extensive experience on applied statistics, systems modelling and analysis, an avid practitioner of LaTeX, and a multidisciplinary web developer. He leverages pioneering AI-powered content creation tools to produce unique and comprehensive articles in this website.
SimplyEducate.Me Privacy Policy
Aims and Objectives for Master’s Dissertations

Aims and Objectives for Master’s Dissertations. This blog will look at writing an ‘Aim’ statement and ‘Objectives’ for a Master’s thesis. It should also be helpful for final year projects at undergraduate level.
I have done 2 previous blogs on ‘Topic Selection’ and ‘Dissertation Title Writing’ that may also be of interest.
Here is a short video clip on writing the Aims and Objectives.
Where should the Aims and Objectives be?
The Aims and Objectives for your Master’s Dissertations need to be in chapter 1, the introduction to the research project. Chapter 1 should be an introduction to the project, and not an introduction to the topic. The topic is covered in the Literature Review, usually chapter 2. However, there needs to be a few pages of background introduction to set the scene and the reasons for the research. Therefore, the Aims and Objectives should be around page 2, 3, or 4.
Tips for Writing the AIM Statement
There will be one overall AIM statement as described here. Sometimes a research project may contain several distinct aims. However, they need to fit together to an overall research AIM.
The AIM is really just a longer and more explanatory version of the research title. The AIM can be an expansion of the title to 3 to 6 sentences. Make sure you cover these three elements:
- Why is this research necessary – some background showing a problem.
- What is this research about – an expansion of the title.
- How is the research to be performed – a brief statement of the intended research methods.
Initially aim for 1 sentence for each item. Expanding to two sentences for each will be OK. The AIM statement should not exceed a paragraph or a quarter to a third of a page.
Example of an Aim Statement
Example: I will take a project title: “An investigation into Project Management Life-Cycles in the Automotive Industry: Honda as a case study.”
The AIM will need to include:
- Why: Oversupply and unfilled manufacturing capacity, and increasing innovation in the industry are causing all automotive companies problems. This states the problem.
- What: This project seeks to examine how Project Life Cycles are implemented in the Honda Motor Company.
- How: By case study analysis and comparison with other automotive companies.
Put those three sentences together and the AIM statement becomes:
Aim Statement: Oversupply and unfilled manufacturing capacity is leading to increasing innovation in the automotive industry. This requires all automotive companies to reduce their project life cycles to remain competitive. This project seeks to examine how Project Life Cycles are implemented in the Honda Motor Company. The research will use case study analysis and comparison of Honda Project Life Cycles implementation with that of other automotive companies.
The first part of the aim statement – the problem – is what needs to be covered in the first 2 or 3 pages of the introduction chapter. Some researchers may then introduce a secondary aim statement to complement the first. In this example there may be a secondary AIM to distribute or publish the research findings.
Writing Objectives for a Master’s Dissertation

Nine Objectives
I suggest that 6-9 Objectives is an initial target. There are often comments that 9 may be too many. However, as a Project Manager my natural inclination is to break a project into manageable chunks of work. Also, if there are 9 objectives and one objective is not met, then there are still 8 objectives that are met.
The objectives when read alone should tell a story through the dissertation. This can be done by ensuring:
- 2 or 3 Objectives apply to the Literature Review – Demonstrating knowledge. Verbs such as Research, Examine, Study, and Investigate are suitable.
- 1 Objectives apply to the Research Methodology – How the research is performed. These might include: Collect data, Select interviewees, Analyse results as examples.
- 2 or 3 Objectives focus on the Critical Evaluation or Discussion chapters. Verbs such as Analyse, Compare, Discuss, and Evaluate would be appropriate.
- There may be one or two final objectives. To Conclude, and/or To Recommend.
I have already issued blogs about the requirements of a Master’s Dissertation from the QAA perspective and the three elements of a Master’s Dissertation . Using the above approach to write the objectives will demonstrate that these requirements have been met.
When writing objectives, keep to just one verb, and avoid the use of ‘and’. If you are using ‘and’ then perhaps this objective should be broken into two separate objectives.
Don’t forget that the objectives will need to be repeated and commented on in the conclusion chapter of the dissertation.
Examples of Research Objectives
For the example AIM from earlier, here are some suggested project objectives. Note how they start broad, and become more specific:
- To examine the current status of the Automotive Industry
- Study Project Management as it applies to the Automotive Industry
- To research Project Life Cycles specifically as used within the Automotive Industry
- Identify suitable case studies concerning Automotive Project Life Cycles for evaluation
- To analyse the case studies
- Compare Project Life Cycles as demonstrated b the case study companies
- To critical evaluate the use of Project Life Cycles at Honda Motor Company
- Recommend improvements to the Honda Motor Company in their use of Project Life Cycles
Just reading the verbs tells a story through the dissertation. To examine, to study, to research, to identify, to analyse, to compare, to evaluate and to recommend.

Honda Motor Car
Higher Level Verbs
Don’t forget to use Blooms Higher level verbs when looking at the critical evaluation section. It is also important not to duplicate a verb. There are around 40-50 different verbs that you could use to write your objectives, and therefore it looks lazy to use the same verb more than once.
The Project Aim is an expansion of the title covering Why, What and How. The objectives should cover the whole dissertation from the Literature Review, through the Research Methodology, and to the Critical Evaluation and Conclusions.
AbleSim Project Management Simulations YouTube Channel
AbleSim have a YouTube channel dedicated to work with Project Management Simulations, Masters Dissertation Support and MS Project.
Subscribe to this channel here!
Project Management Training YouTube Channel
Andrew Bell has a YouTube channel dedicated to Project Management Training with over 10 hours of video arranged by 97 videos in 20 playlists.
Follow 🔔 AbleSim 🔔 on twitter @AbleSim
Join the conversation #pmsim
- Tweets could not be loaded at this time.
Like us on Facebook

- Privacy Overview
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
- 3rd Party Cookies
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible.
Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly necessary cookies should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.
This website uses Google Analytics to collect anonymous information such as the number of visitors to the site, and the most popular pages.
Keeping this cookie enabled helps us to improve our website.
Please enable Strictly Necessary Cookies first so that we can save your preferences!

How To Write A Research Proposal
A Straightforward How-To Guide (With Examples)
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By: Dr. Eunice Rautenbach | August 2019 (Updated April 2023)
Writing up a strong research proposal for a dissertation or thesis is much like a marriage proposal. It’s a task that calls on you to win somebody over and persuade them that what you’re planning is a great idea. An idea they’re happy to say ‘yes’ to. This means that your dissertation proposal needs to be persuasive , attractive and well-planned. In this post, I’ll show you how to write a winning dissertation proposal, from scratch.
Before you start:
– Understand exactly what a research proposal is – Ask yourself these 4 questions
The 5 essential ingredients:
- The title/topic
- The introduction chapter
- The scope/delimitations
- Preliminary literature review
- Design/ methodology
- Practical considerations and risks
What Is A Research Proposal?
The research proposal is literally that: a written document that communicates what you propose to research, in a concise format. It’s where you put all that stuff that’s spinning around in your head down on to paper, in a logical, convincing fashion.
Convincing is the keyword here, as your research proposal needs to convince the assessor that your research is clearly articulated (i.e., a clear research question) , worth doing (i.e., is unique and valuable enough to justify the effort), and doable within the restrictions you’ll face (time limits, budget, skill limits, etc.). If your proposal does not address these three criteria, your research won’t be approved, no matter how “exciting” the research idea might be.
PS – if you’re completely new to proposal writing, we’ve got a detailed walkthrough video covering two successful research proposals here .

How do I know I’m ready?
Before starting the writing process, you need to ask yourself 4 important questions . If you can’t answer them succinctly and confidently, you’re not ready – you need to go back and think more deeply about your dissertation topic .
You should be able to answer the following 4 questions before starting your dissertation or thesis research proposal:
- WHAT is my main research question? (the topic)
- WHO cares and why is this important? (the justification)
- WHAT data would I need to answer this question, and how will I analyse it? (the research design)
- HOW will I manage the completion of this research, within the given timelines? (project and risk management)
If you can’t answer these questions clearly and concisely, you’re not yet ready to write your research proposal – revisit our post on choosing a topic .
If you can, that’s great – it’s time to start writing up your dissertation proposal. Next, I’ll discuss what needs to go into your research proposal, and how to structure it all into an intuitive, convincing document with a linear narrative.
The 5 Essential Ingredients
Research proposals can vary in style between institutions and disciplines, but here I’ll share with you a handy 5-section structure you can use. These 5 sections directly address the core questions we spoke about earlier, ensuring that you present a convincing proposal. If your institution already provides a proposal template, there will likely be substantial overlap with this, so you’ll still get value from reading on.
For each section discussed below, make sure you use headers and sub-headers (ideally, numbered headers) to help the reader navigate through your document, and to support them when they need to revisit a previous section. Don’t just present an endless wall of text, paragraph after paragraph after paragraph…
Top Tip: Use MS Word Styles to format headings. This will allow you to be clear about whether a sub-heading is level 2, 3, or 4. Additionally, you can view your document in ‘outline view’ which will show you only your headings. This makes it much easier to check your structure, shift things around and make decisions about where a section needs to sit. You can also generate a 100% accurate table of contents using Word’s automatic functionality.

Ingredient #1 – Topic/Title Header
Your research proposal’s title should be your main research question in its simplest form, possibly with a sub-heading providing basic details on the specifics of the study. For example:
“Compliance with equality legislation in the charity sector: a study of the ‘reasonable adjustments’ made in three London care homes”
As you can see, this title provides a clear indication of what the research is about, in broad terms. It paints a high-level picture for the first-time reader, which gives them a taste of what to expect. Always aim for a clear, concise title . Don’t feel the need to capture every detail of your research in your title – your proposal will fill in the gaps.
Need a helping hand?
Ingredient #2 – Introduction
In this section of your research proposal, you’ll expand on what you’ve communicated in the title, by providing a few paragraphs which offer more detail about your research topic. Importantly, the focus here is the topic – what will you research and why is that worth researching? This is not the place to discuss methodology, practicalities, etc. – you’ll do that later.
You should cover the following:
- An overview of the broad area you’ll be researching – introduce the reader to key concepts and language
- An explanation of the specific (narrower) area you’ll be focusing, and why you’ll be focusing there
- Your research aims and objectives
- Your research question (s) and sub-questions (if applicable)
Importantly, you should aim to use short sentences and plain language – don’t babble on with extensive jargon, acronyms and complex language. Assume that the reader is an intelligent layman – not a subject area specialist (even if they are). Remember that the best writing is writing that can be easily understood and digested. Keep it simple.

Note that some universities may want some extra bits and pieces in your introduction section. For example, personal development objectives, a structural outline, etc. Check your brief to see if there are any other details they expect in your proposal, and make sure you find a place for these.
Ingredient #3 – Scope
Next, you’ll need to specify what the scope of your research will be – this is also known as the delimitations . In other words, you need to make it clear what you will be covering and, more importantly, what you won’t be covering in your research. Simply put, this is about ring fencing your research topic so that you have a laser-sharp focus.
All too often, students feel the need to go broad and try to address as many issues as possible, in the interest of producing comprehensive research. Whilst this is admirable, it’s a mistake. By tightly refining your scope, you’ll enable yourself to go deep with your research, which is what you need to earn good marks. If your scope is too broad, you’re likely going to land up with superficial research (which won’t earn marks), so don’t be afraid to narrow things down.
Ingredient #4 – Literature Review
In this section of your research proposal, you need to provide a (relatively) brief discussion of the existing literature. Naturally, this will not be as comprehensive as the literature review in your actual dissertation, but it will lay the foundation for that. In fact, if you put in the effort at this stage, you’ll make your life a lot easier when it’s time to write your actual literature review chapter.
There are a few things you need to achieve in this section:
- Demonstrate that you’ve done your reading and are familiar with the current state of the research in your topic area.
- Show that there’s a clear gap for your specific research – i.e., show that your topic is sufficiently unique and will add value to the existing research.
- Show how the existing research has shaped your thinking regarding research design . For example, you might use scales or questionnaires from previous studies.
When you write up your literature review, keep these three objectives front of mind, especially number two (revealing the gap in the literature), so that your literature review has a clear purpose and direction . Everything you write should be contributing towards one (or more) of these objectives in some way. If it doesn’t, you need to ask yourself whether it’s truly needed.
Top Tip: Don’t fall into the trap of just describing the main pieces of literature, for example, “A says this, B says that, C also says that…” and so on. Merely describing the literature provides no value. Instead, you need to synthesise it, and use it to address the three objectives above.

Ingredient #5 – Research Methodology
Now that you’ve clearly explained both your intended research topic (in the introduction) and the existing research it will draw on (in the literature review section), it’s time to get practical and explain exactly how you’ll be carrying out your own research. In other words, your research methodology.
In this section, you’ll need to answer two critical questions :
- How will you design your research? I.e., what research methodology will you adopt, what will your sample be, how will you collect data, etc.
- Why have you chosen this design? I.e., why does this approach suit your specific research aims, objectives and questions?
In other words, this is not just about explaining WHAT you’ll be doing, it’s also about explaining WHY. In fact, the justification is the most important part , because that justification is how you demonstrate a good understanding of research design (which is what assessors want to see).
Some essential design choices you need to cover in your research proposal include:
- Your intended research philosophy (e.g., positivism, interpretivism or pragmatism )
- What methodological approach you’ll be taking (e.g., qualitative , quantitative or mixed )
- The details of your sample (e.g., sample size, who they are, who they represent, etc.)
- What data you plan to collect (i.e. data about what, in what form?)
- How you plan to collect it (e.g., surveys , interviews , focus groups, etc.)
- How you plan to analyse it (e.g., regression analysis, thematic analysis , etc.)
- Ethical adherence (i.e., does this research satisfy all ethical requirements of your institution, or does it need further approval?)
This list is not exhaustive – these are just some core attributes of research design. Check with your institution what level of detail they expect. The “ research onion ” by Saunders et al (2009) provides a good summary of the various design choices you ultimately need to make – you can read more about that here .
Don’t forget the practicalities…
In addition to the technical aspects, you will need to address the practical side of the project. In other words, you need to explain what resources you’ll need (e.g., time, money, access to equipment or software, etc.) and how you intend to secure these resources. You need to show that your project is feasible, so any “make or break” type resources need to already be secured. The success or failure of your project cannot depend on some resource which you’re not yet sure you have access to.
Another part of the practicalities discussion is project and risk management . In other words, you need to show that you have a clear project plan to tackle your research with. Some key questions to address:
- What are the timelines for each phase of your project?
- Are the time allocations reasonable?
- What happens if something takes longer than anticipated (risk management)?
- What happens if you don’t get the response rate you expect?
A good way to demonstrate that you’ve thought this through is to include a Gantt chart and a risk register (in the appendix if word count is a problem). With these two tools, you can show that you’ve got a clear, feasible plan, and you’ve thought about and accounted for the potential risks.
Tip – Be honest about the potential difficulties – but show that you are anticipating solutions and workarounds. This is much more impressive to an assessor than an unrealistically optimistic proposal which does not anticipate any challenges whatsoever.
Final Touches: Read And Simplify
The final step is to edit and proofread your proposal – very carefully. It sounds obvious, but all too often poor editing and proofreading ruin a good proposal. Nothing is more off-putting for an assessor than a poorly edited, typo-strewn document. It sends the message that you either do not pay attention to detail, or just don’t care. Neither of these are good messages. Put the effort into editing and proofreading your proposal (or pay someone to do it for you) – it will pay dividends.
When you’re editing, watch out for ‘academese’. Many students can speak simply, passionately and clearly about their dissertation topic – but become incomprehensible the moment they turn the laptop on. You are not required to write in any kind of special, formal, complex language when you write academic work. Sure, there may be technical terms, jargon specific to your discipline, shorthand terms and so on. But, apart from those, keep your written language very close to natural spoken language – just as you would speak in the classroom. Imagine that you are explaining your project plans to your classmates or a family member. Remember, write for the intelligent layman, not the subject matter experts. Plain-language, concise writing is what wins hearts and minds – and marks!
Let’s Recap: Research Proposal 101
And there you have it – how to write your dissertation or thesis research proposal, from the title page to the final proof. Here’s a quick recap of the key takeaways:
- The purpose of the research proposal is to convince – therefore, you need to make a clear, concise argument of why your research is both worth doing and doable.
- Make sure you can ask the critical what, who, and how questions of your research before you put pen to paper.
- Title – provides the first taste of your research, in broad terms
- Introduction – explains what you’ll be researching in more detail
- Scope – explains the boundaries of your research
- Literature review – explains how your research fits into the existing research and why it’s unique and valuable
- Research methodology – explains and justifies how you will carry out your own research
Hopefully, this post has helped you better understand how to write up a winning research proposal. If you enjoyed it, be sure to check out the rest of the Grad Coach Blog . If your university doesn’t provide any template for your proposal, you might want to try out our free research proposal template .

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Research Proposal Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .

30 Comments
Thank you so much for the valuable insight that you have given, especially on the research proposal. That is what I have managed to cover. I still need to go back to the other parts as I got disturbed while still listening to Derek’s audio on you-tube. I am inspired. I will definitely continue with Grad-coach guidance on You-tube.
Thanks for the kind words :). All the best with your proposal.
First of all, thanks a lot for making such a wonderful presentation. The video was really useful and gave me a very clear insight of how a research proposal has to be written. I shall try implementing these ideas in my RP.
Once again, I thank you for this content.
I found reading your outline on writing research proposal very beneficial. I wish there was a way of submitting my draft proposal to you guys for critiquing before I submit to the institution.
Hi Bonginkosi
Thank you for the kind words. Yes, we do provide a review service. The best starting point is to have a chat with one of our coaches here: https://gradcoach.com/book/new/ .
Hello team GRADCOACH, may God bless you so much. I was totally green in research. Am so happy for your free superb tutorials and resources. Once again thank you so much Derek and his team.
You’re welcome, Erick. Good luck with your research proposal 🙂
thank you for the information. its precise and on point.
Really a remarkable piece of writing and great source of guidance for the researchers. GOD BLESS YOU for your guidance. Regards
Thanks so much for your guidance. It is easy and comprehensive the way you explain the steps for a winning research proposal.
Thank you guys so much for the rich post. I enjoyed and learn from every word in it. My problem now is how to get into your platform wherein I can always seek help on things related to my research work ? Secondly, I wish to find out if there is a way I can send my tentative proposal to you guys for examination before I take to my supervisor Once again thanks very much for the insights
Thanks for your kind words, Desire.
If you are based in a country where Grad Coach’s paid services are available, you can book a consultation by clicking the “Book” button in the top right.
Best of luck with your studies.
May God bless you team for the wonderful work you are doing,
If I have a topic, Can I submit it to you so that you can draft a proposal for me?? As I am expecting to go for masters degree in the near future.
Thanks for your comment. We definitely cannot draft a proposal for you, as that would constitute academic misconduct. The proposal needs to be your own work. We can coach you through the process, but it needs to be your own work and your own writing.
Best of luck with your research!
I found a lot of many essential concepts from your material. it is real a road map to write a research proposal. so thanks a lot. If there is any update material on your hand on MBA please forward to me.
GradCoach is a professional website that presents support and helps for MBA student like me through the useful online information on the page and with my 1-on-1 online coaching with the amazing and professional PhD Kerryen.
Thank you Kerryen so much for the support and help 🙂
I really recommend dealing with such a reliable services provider like Gradcoah and a coach like Kerryen.
Hi, Am happy for your service and effort to help students and researchers, Please, i have been given an assignment on research for strategic development, the task one is to formulate a research proposal to support the strategic development of a business area, my issue here is how to go about it, especially the topic or title and introduction. Please, i would like to know if you could help me and how much is the charge.
This content is practical, valuable, and just great!
Thank you very much!
Hi Derek, Thank you for the valuable presentation. It is very helpful especially for beginners like me. I am just starting my PhD.
This is quite instructive and research proposal made simple. Can I have a research proposal template?
Great! Thanks for rescuing me, because I had no former knowledge in this topic. But with this piece of information, I am now secured. Thank you once more.
I enjoyed listening to your video on how to write a proposal. I think I will be able to write a winning proposal with your advice. I wish you were to be my supervisor.
Dear Derek Jansen,
Thank you for your great content. I couldn’t learn these topics in MBA, but now I learned from GradCoach. Really appreciate your efforts….
From Afghanistan!
I have got very essential inputs for startup of my dissertation proposal. Well organized properly communicated with video presentation. Thank you for the presentation.
Wow, this is absolutely amazing guys. Thank you so much for the fruitful presentation, you’ve made my research much easier.
this helps me a lot. thank you all so much for impacting in us. may god richly bless you all
How I wish I’d learn about Grad Coach earlier. I’ve been stumbling around writing and rewriting! Now I have concise clear directions on how to put this thing together. Thank you!
Fantastic!! Thank You for this very concise yet comprehensive guidance.
Even if I am poor in English I would like to thank you very much.
Thank you very much, this is very insightful.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

Research Voyage
Research Tips and Infromation
How to Write Aims and Objectives for your Dissertation or Thesis?

Introduction
Understanding aims and objectives, crafting aims, break it down into objectives, developing specific objectives, align with research questions, consider feasibility, review and refine, seek feedback, documenting aims and objectives.
In a PhD or Post Graduate dissertation, the aims and objectives play a crucial role in shaping the research process and ensuring focus. They provide a clear roadmap for your study and serve as the guiding principles that steer your research in the right direction.
Aims represent the broader purpose or the overarching goal of your research. They define what you want to achieve with your dissertation. For example, let’s say you’re conducting a study on renewable energy sources. Your aim could be to analyze the economic viability and environmental impact of solar energy adoption in residential areas.
Objectives, on the other hand, break down the aim into specific, measurable, and achievable targets that help you accomplish your research goal. They outline the specific steps or tasks you need to undertake to fulfill the aim. Continuing with the previous example, some objectives could be:
- Evaluate the current state of solar energy technologies and their efficiency.
- Assess the economic costs and benefits associated with the installation of solar panels in residential areas.
- Analyze the environmental impact of solar energy adoption in terms of carbon emissions reduction.
- Investigate the potential barriers to the widespread adoption of solar energy in residential communities.
- Develop recommendations for policymakers and stakeholders to promote the use of solar energy in residential areas.
These objectives, when combined, address different aspects related to the aim of analyzing the economic viability and environmental impact of solar energy adoption. Each objective guides a specific aspect of the research and contributes to answering the research questions.
By having clear aims and objectives, you establish a solid framework for your study. They help you stay focused on the main purpose of your research and prevent you from getting sidetracked or overwhelmed by tangential topics. Moreover, they provide clarity to both you and your readers, ensuring that your research remains coherent and well-structured.
In summary, clear aims and objectives are instrumental in guiding the research process of a PhD dissertation. They provide a roadmap, define the research goal, and break it down into specific targets. Through the example provided, it is evident how aims and objectives bring focus to a study on renewable energy sources and solar energy adoption in residential areas.
If you are in paucity of time, not confident of your writing skills and in a hurry to complete the writing task then you can think of hiring a research consultant that solves all your problems. Please visit my article on Hiring a Research consultant for your PhD tasks for further details.
Aims and objectives play a crucial role in guiding research projects. It’s important to define these terms and differentiate between them to ensure a clear focus in your work.
Aims represent the broader purpose or goal of your study. They define what you aim to achieve through your research project. Aims provide the overarching context and direction for your work, guiding the selection of topics, methodologies, and outcomes.
Example: Suppose you’re working on a PhD dissertation in computer science with a focus on natural language processing. Your aim could be: “To develop an efficient and accurate algorithm for sentiment analysis in social media data.”
In this example, the aim highlights the objective of creating an algorithm specifically for sentiment analysis in social media data, indicating the main objective of your research.
Objectives break down the aim into specific, measurable, and achievable targets that contribute to achieving the overall goal. They are more focused and concrete than aims, outlining the steps or tasks necessary to fulfill the aim. Objectives serve as the building blocks of your research, guiding the implementation and evaluation of your work.
Example: Continuing with the previous aim, let’s define some specific objectives:
- Collect and preprocess a large dataset of social media posts for sentiment analysis.
- Explore and compare existing sentiment analysis techniques to identify their limitations and strengths.
- Design and develop a novel algorithm that addresses the limitations of current approaches.
- Implement the algorithm and evaluate its performance on the collected dataset.
- Analyze the results and compare them with existing state-of-the-art sentiment analysis methods.
These objectives, when combined, address different aspects necessary to fulfill the aim of developing an efficient and accurate sentiment analysis algorithm for social media data. Each objective represents a specific task or milestone that contributes to the overall research goal.
The relationship between aims and objectives is critical in driving research. Objectives are derived from the aim and provide the means to accomplish it. They act as stepping stones, guiding the researcher towards achieving the broader aim.
In summary, aims provide the broader context and goal, while objectives break down the aim into specific tasks and milestones. Together, they ensure focus and direction in your research, guiding the selection of topics, methodologies, and outcomes. The objectives serve as the means to achieve the overall aim, highlighting the relationship between aims and objectives in driving research in the computer science domain.
Formulating the overarching aim of your research is a crucial step in defining the direction and purpose of your dissertation. The aim represents the primary goal or intention of your study, and crafting it effectively is essential for setting the foundation of your research.
Research Topic: Enhancing cybersecurity in cloud computing environments.
In this example, the aim focuses on improving cybersecurity in the context of cloud computing. The aim should be formulated in a concise and focused manner that aligns with the research topic. Here’s an example of how the aim could be crafted effectively:
Aim: Develop an efficient and robust security framework for ensuring data confidentiality, integrity, and availability in cloud computing environments.
The above aim encapsulates the overall goal of the research, which is to develop a security framework for enhancing cybersecurity in cloud computing. It clearly states the intention to address key aspects such as data confidentiality, integrity, and availability. The aim is concise, specific, and directly aligned with the research topic.
The significance of a well-defined aim cannot be overstated. It serves as a guiding beacon throughout your research journey, providing a clear direction and purpose. A well-crafted aim helps you stay focused and ensures that your efforts are aligned with the research’s core objectives. It also helps you communicate the purpose of your study to others, including your advisor, peers, and potential readers of your dissertation.
Additionally, an effective aim sets the stage for the subsequent development of specific objectives and research questions. It serves as a foundation upon which you can break down the aim into smaller, manageable objectives that contribute to achieving the overall research goal. Each objective should align with the aim and work together harmoniously to address the research questions and gaps in the field.
Moreover, a concise and aligned aim allows readers to quickly grasp the essence of your research. It provides them with a clear understanding of the research’s scope and purpose. By stating the aim concisely and aligning it with the research topic, you demonstrate your ability to articulate the core objective of your study in a succinct manner.
In summary, crafting effective aims involves formulating the overarching goal or intention of your research in a concise and focused manner. A well-defined aim sets the direction for your dissertation, guiding your efforts and ensuring alignment with the research topic. It serves as a foundation for the development of specific objectives and research questions. By presenting a clear and aligned aim, you convey the purpose of your study to others and demonstrate your ability to articulate the core objective of your research.
After defining the aim of your research, it’s important to break it down into smaller, manageable objectives. These objectives should address key research questions or subtopics that are necessary to achieve the overall aim. Additionally, objectives should be specific, measurable, and utilize action verbs to describe the intended actions or achievements.
Example: Suppose the aim of your research is to develop a recommendation system for an e-commerce platform. Here are some examples of specific objectives:
- Action Verbs: Analyze, Identify
- Description: Gather and analyze user preferences and historical data from the e-commerce platform to identify patterns in user behavior and item preferences.
- Action Verbs: Design, Implement
- Description: Develop and implement collaborative filtering algorithms, such as user-based or item-based methods, to generate personalized recommendations based on user similarities or item similarities.
- Action Verbs: Incorporate
- Description: Integrate machine learning techniques, such as matrix factorization or deep learning models, into the recommendation system to improve the accuracy and personalization of the recommendations.
- Action Verbs: Evaluate
- Description: Conduct experiments and evaluate the performance of the recommendation system using appropriate evaluation metrics, such as precision, recall, or mean average precision, to assess the effectiveness and efficiency of the system.
- Action Verbs: Optimize
- Description: Identify and implement optimization techniques, such as parallel computing or distributed systems, to enhance the scalability and efficiency of the recommendation algorithm, allowing it to handle large-scale datasets and real-time recommendations.
By breaking down the aim into these specific objectives, you address key components of developing a recommendation system, such as data analysis, algorithm design, evaluation, and optimization. Each objective represents a distinct step that contributes to achieving the overall aim.
Importantly, these objectives are specific and measurable, allowing you to determine whether you have successfully achieved them. For instance, you can measure the accuracy of the recommendation system, evaluate its performance against baseline models, or assess its scalability in terms of handling large datasets.
In summary, when conducting research, breaking down the aim into specific objectives helps in managing the workload and providing a clear roadmap for your research. These objectives should address key research questions or subtopics, be specific and measurable, and use action verbs to describe the intended actions or achievements. By following this approach, you can ensure a systematic and focused research process.
To develop specific objectives for your research, you need to break down the overarching aim into smaller, measurable objectives. These objectives should be clear, specific, and actionable, providing a roadmap for your research and guiding the entire research process.
Aim: Develop a machine learning-based system for automated sentiment analysis in social media data.
Objective 1: Conduct a comprehensive literature review on existing sentiment analysis techniques and methodologies.
- Breakdown: This objective focuses on reviewing the literature in the field of sentiment analysis, specifically examining the various techniques and methodologies that have been developed and applied. It involves gathering and analyzing research papers, books, and other relevant sources to gain a comprehensive understanding of the existing knowledge in sentiment analysis.
Objective 2: Collect a large dataset of social media posts for training and evaluation.
- Breakdown: This objective entails the collection of a substantial amount of social media data that will be used as input for training and evaluating the machine learning model. It involves designing data collection mechanisms, such as web scraping or utilizing available APIs, to gather a diverse set of social media posts from platforms like Twitter or Facebook.
Objective 3: Design and implement a machine learning algorithm capable of accurately detecting sentiment polarity in social media text.
- Breakdown: This objective focuses on the development of a machine learning algorithm tailored for sentiment analysis in social media text. It involves designing and implementing the necessary algorithms, selecting appropriate feature representations, and training a model to accurately classify sentiment polarity (positive, negative, or neutral) of social media posts.
Objective 4: Evaluate the performance of the developed sentiment analysis system against benchmark datasets and compare it with existing state-of-the-art approaches.
- Breakdown: This objective involves assessing the performance of the developed sentiment analysis system by evaluating it against established benchmark datasets. It requires selecting appropriate evaluation metrics and comparing the system’s performance with existing state-of-the-art approaches in sentiment analysis, such as accuracy, precision, recall, or F1 score.
The importance of clear, specific objectives cannot be overstated. These objectives provide a clear roadmap and direction for your research, guiding your efforts and ensuring that you stay on track. They help you structure your research activities, allocate resources effectively, and measure progress along the way.
Using action verbs to articulate objectives effectively is another crucial aspect. Action verbs convey specific actions or achievements that need to be accomplished. They provide clarity and precision, leaving no room for ambiguity. For example:
By using action verbs, you explicitly state what needs to be done or achieved in each objective, making it easier to track progress and assess the completion of objectives.
In summary, developing specific objectives involves breaking down the overarching aim into smaller, measurable objectives. Clear and specific objectives provide a roadmap for your research and guide the entire research process. By using action verbs, you articulate objectives effectively, leaving no room for ambiguity. These objectives help structure your research activities, allocate resources effectively, and measure progress, ultimately leading to the successful completion of your research.
When formulating objectives for your research, it is essential to ensure that they align with the research questions you have formulated. Each objective should contribute to addressing or answering a specific research question, creating a cohesive and focused research framework.
Example: Suppose your research in computer science focuses on developing an automated system for detecting and preventing cybersecurity threats. Here are examples of objectives aligned with research questions:
Research Question: How can machine learning algorithms be utilized to detect and mitigate cybersecurity threats effectively?
Objective 1: Evaluate and compare different machine learning algorithms for cybersecurity threat detection.
- Description: Explore and assess various machine learning algorithms, such as decision trees, random forests, or neural networks, to identify the most suitable approach for detecting cybersecurity threats accurately and efficiently.
Objective 2: Develop a dataset representative of diverse cybersecurity threats.
- Description: Create a comprehensive dataset containing various types of cybersecurity threats, including malware, phishing attacks, and network intrusions, to train and evaluate the machine learning models effectively.
Research Question: What are the key challenges and vulnerabilities in existing cybersecurity systems that need to be addressed?
Objective 3: Conduct a systematic analysis of existing cybersecurity systems and identify vulnerabilities.
- Description: Analyze and evaluate existing cybersecurity systems, such as intrusion detection systems or antivirus software, to identify vulnerabilities, weaknesses, and potential areas of improvement that can inform the development of a more robust automated system.
Objective 4: Propose novel techniques to enhance the resilience of the cybersecurity system.
- Description: Develop innovative approaches, such as anomaly detection algorithms or behavior-based analysis techniques, to enhance the resilience of the automated cybersecurity system and address the identified vulnerabilities.
By aligning the objectives with the research questions, you ensure that each objective contributes to addressing a specific aspect of your research. For example, Objective 1 directly addresses the research question regarding the utilization of machine learning algorithms for cybersecurity threat detection. Objective 3 focuses on analyzing existing systems to identify vulnerabilities, which is in line with the question about challenges and vulnerabilities in existing cybersecurity systems.
The alignment between research questions and objectives helps maintain a clear focus on the research objectives and ensures that your efforts are directed towards addressing the research questions. It also enhances the coherence of your research, as each objective becomes a stepping stone towards answering the research questions and achieving the overall aim of your study.
In summary, aligning objectives with research questions is crucial in research. It ensures that each objective contributes to answering or addressing a specific research question, creating a logical and cohesive framework for your study. By establishing this alignment, you can maintain a clear focus on the research objectives and make meaningful contributions to the field.
When setting objectives for your research, it is important to consider their feasibility. Feasibility refers to the realistic achievability of your objectives within the scope of your PhD research, taking into account available resources, time constraints, and other practical limitations.
Example: Suppose your research focuses on developing a new algorithm for real-time video processing and analysis. Here are examples of objectives that consider feasibility:
Objective 1: Implement the real-time video processing algorithm on a high-performance computing cluster.
- Feasibility Considerations: Before setting this objective, assess whether you have access to a high-performance computing cluster and the necessary resources (e.g., hardware, software, computational power) to support the implementation and testing of the algorithm. If such resources are available within your research environment or institution, this objective is feasible.
Objective 2: Collect and annotate a large-scale video dataset for algorithm training and evaluation.
- Feasibility Considerations: Consider the practical aspects of collecting and annotating a large-scale video dataset. Evaluate the time, manpower, and equipment required for this task. Assess whether you have access to the necessary resources (e.g., cameras, storage, annotation tools) and the capability to manage and process such a dataset. If these resources and capabilities are available within your research context, this objective is feasible.
Objective 3: Collaborate with industry partners to obtain real-world video data for testing and validation.
- Feasibility Considerations: Evaluate the feasibility of establishing collaborations with industry partners to obtain real-world video data. Consider factors such as data sharing agreements, legal and privacy considerations, and the willingness of industry partners to provide access to their data. Assess the potential challenges and limitations that may arise during this collaboration process. If such collaborations are feasible and can be established within the constraints of your research, this objective is feasible.
By considering feasibility, you ensure that your objectives are realistically achievable within the resources, time, and other constraints of your PhD research. It helps you avoid setting objectives that are too ambitious or beyond the scope of what you can reasonably accomplish.
Feasibility assessment is crucial in ensuring the successful completion of your research project. It allows you to allocate resources effectively, manage your time, and avoid potential pitfalls or setbacks that could hinder your progress. By setting feasible objectives, you can maintain a practical and manageable research plan that is more likely to lead to meaningful outcomes within the given constraints.
In summary, considering feasibility when setting objectives in computer science research is essential. Assess the available resources, time constraints, and practical limitations to ensure that your objectives are realistically achievable within the scope of your PhD research. By doing so, you can plan and execute your research effectively, making the most of the resources at your disposal and increasing the likelihood of successful outcomes.
Once you have defined your aims and objectives for your research, it’s important to review and refine them to ensure clarity, coherence, and logical flow. This step allows you to make any necessary revisions to ensure that your aims and objectives accurately reflect the scope and purpose of your research.
Example: Suppose your research in computer science focuses on developing a mobile application for enhancing cybersecurity awareness among smartphone users. Here’s an example of reviewing and refining aims and objectives:
Aim: Develop a mobile application for enhancing cybersecurity awareness among smartphone users.
Objective 1: Conduct a comprehensive literature review on cybersecurity awareness strategies and mobile application design principles.
- Review and Refinement: Upon review, you find that the objective is clear and aligned with the aim. However, you decide to refine it to include specific aspects you intend to cover in the literature review, such as user education techniques, persuasive design elements, and existing cybersecurity awareness mobile applications.
Objective 2: Design and develop a user-friendly mobile application prototype that delivers educational content and interactive features.
- Review and Refinement: During the review, you realize that the objective lacks specificity regarding the educational content and interactive features. You refine it to explicitly mention the inclusion of topics like phishing prevention, password management, and interactive quizzes to reinforce learning.
Objective 3: Conduct usability testing and collect feedback from potential users to evaluate the effectiveness of the mobile application.
- Review and Refinement: While reviewing, you realize that the objective could benefit from additional information. You refine it to include details such as the target user group (e.g., smartphone users aged 18-35), the number of participants you plan to involve in the usability testing, and the specific metrics you will use to evaluate the effectiveness of the application.
By reviewing and refining your aims and objectives, you ensure that they accurately capture the scope and purpose of your research. It helps you identify any gaps, ambiguities, or areas that need further clarification. Through this process, you can enhance the clarity, coherence, and logical flow of your aims and objectives, making them more robust and aligned with your research goals.
Additionally, reviewing and refining your aims and objectives allows you to align them with the current state of knowledge in the field. As you conduct literature reviews and gain more insights into existing research, you may discover the need to make adjustments to your aims and objectives to reflect the most relevant and up-to-date information.
In summary, reviewing and refining aims and objectives in research is essential to ensure clarity, coherence, and logical flow. By carefully reviewing each aim and objective, you can identify areas for improvement, refine them to include specific details, and align them with the current state of knowledge in the field. This process enhances the accuracy and effectiveness of your aims and objectives, providing a strong foundation for your research.
Once you have developed your aims and objectives for your research, it is important to seek feedback from your supervisor or peers. Sharing your aims and objectives with others allows you to gather valuable insights, suggestions, and perspectives that can help refine and improve your objectives, ensuring they are appropriate and aligned with your research.
Imagine you have formulated the following objectives for your computer science research on developing an intelligent tutoring system:
Objective 1: Conduct a literature review on existing intelligent tutoring systems and their effectiveness in enhancing student learning outcomes.
Objective 2: Design and develop an adaptive learning algorithm to personalize the tutoring experience based on individual student needs.
Objective 3: Implement a user-friendly interface for the intelligent tutoring system that provides an intuitive and engaging learning environment.
Objective 4: Evaluate the effectiveness of the developed intelligent tutoring system through a series of user studies and compare it with traditional tutoring methods.
At this stage, it would be beneficial to share your aims and objectives with your supervisor or peers to receive feedback. They can provide valuable insights and suggestions to help you refine and improve your objectives. For example:
- Your supervisor may suggest including a specific research question to further clarify the focus of Objective 1, such as “What are the key features and techniques used in successful intelligent tutoring systems?”
- Peers may provide feedback on the clarity and specificity of Objective 2, suggesting adding details on the specific adaptability mechanisms to be incorporated.
- Your supervisor might suggest considering the inclusion of usability testing as part of Objective 3 to ensure the interface meets the needs and preferences of the target users.
- Peers may offer suggestions on additional evaluation metrics or experimental setups to strengthen Objective 4 and provide more robust comparisons.
By seeking feedback, you open yourself up to constructive criticism and valuable perspectives that can help enhance the quality and effectiveness of your aims and objectives. Feedback from experienced researchers or knowledgeable peers can help you identify any potential gaps or weaknesses in your objectives and provide suggestions for improvement.
Remember that feedback is an iterative process, and it is important to carefully consider the suggestions provided while also critically evaluating them in the context of your research. Incorporating constructive feedback will help you refine your aims and objectives, ensuring they are robust, relevant, and aligned with your research goals.
In summary, seeking feedback on your aims and objectives is a valuable step in the process of developing your research. Sharing your objectives with your supervisor or peers allows you to gather insights, suggestions, and perspectives that can help refine and improve your objectives. Feedback helps ensure that your objectives are appropriate, clear, and aligned with your research goals, ultimately strengthening the overall quality of your research.
When writing your dissertation, it is crucial to properly document and present your aims and objectives. The placement and presentation of aims and objectives play a significant role in providing readers with a clear understanding of the research’s purpose and direction.
Placement: The aims and objectives of your research should be presented early on in your dissertation, typically within the introduction chapter. This allows readers to grasp the overall scope and intent of your research from the beginning. Placing them in the introduction helps set the context and provides a roadmap for the rest of the dissertation.
Presentation: When presenting aims and objectives, it is important to clearly distinguish between the two and articulate their role in driving the research. Here’s an example of how you can document aims and objectives:
Aims: Start by presenting the overarching aim of your research, which represents the primary goal or intention of your study. It should be a concise statement that captures the essence of your research focus.
For example:
Aim: The aim of this research is to develop a machine learning-based system for automated sentiment analysis in social media data.
Objectives: Following the aim, present a list of specific objectives that outline the key steps or milestones required to achieve the aim. Each objective should be clear, specific, and measurable. Here’s an example:
Objectives:
- Analyze existing sentiment analysis techniques and methodologies in the literature to identify their limitations and challenges.
- Collect and preprocess a large dataset of social media posts to serve as the training and evaluation data for the sentiment analysis system.
- Design and implement a machine learning algorithm capable of accurately detecting sentiment polarity in social media text.
- Evaluate the performance of the developed sentiment analysis system against existing state-of-the-art approaches, using appropriate evaluation metrics.
- Optimize the system for scalability and efficiency, allowing it to handle large volumes of real-time social media data.
By clearly documenting the aims and objectives in your dissertation, you provide readers with a clear understanding of the purpose and direction of your research. This enables them to follow your thought process and evaluate the relevance and significance of your study. Aims and objectives serve as guideposts that help readers navigate through your dissertation and understand the specific research questions you seek to address.
Moreover, the well-documented aims and objectives help you maintain focus throughout your research journey and provide a framework for organizing your dissertation. They establish the foundation upon which your methodology, analysis, and conclusions are built.
In summary, when documenting aims and objectives in a dissertation, it is important to place them in the introduction chapter and clearly present their role in guiding the research. Aims and objectives should be distinct, with the aim of capturing the overarching goal and the objectives outlining the specific steps or milestones to achieve it. By effectively documenting aims and objectives, you provide readers with a clear understanding of the research’s purpose and direction, facilitating their engagement with your work.
Crafting clear and well-defined aims and objectives is a critical aspect of writing a PhD or Post Graduate dissertation. These aims and objectives provide a solid foundation for your research, guiding your efforts and ensuring a focused and coherent study. Through this discussion, we have explored the importance of aims and objectives in a PhD dissertation and how they contribute to the research process.
Upcoming Events
- Visit the Upcoming International Conferences at Exotic Travel Destinations with Travel Plan
- Visit for Research Internships Worldwide

Recent Posts
- 05 Quick Review, High Impact, Best Research Journals for Submissions for July 2024
- Top Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a Research Paper
- Average Stipend for Research/Academic Internships
- These Institutes Offer Remote Research/Academic Internships
- How to Include Your Journal in the UGC-CARE List? A Guide for Publishers
- All Blog Posts
- Research Career
- Research Conference
- Research Internship
- Research Journal
- Research Tools
- Uncategorized
- Research Conferences
- Research Journals
- Research Grants
- Internships
- Research Internships
- Email Templates
- Conferences
- Blog Partners
- Privacy Policy
Copyright © 2024 Research Voyage
Design by ThemesDNA.com

- Privacy Policy

Home » Thesis – Structure, Example and Writing Guide
Thesis – Structure, Example and Writing Guide
Table of contents.

Definition:
Thesis is a scholarly document that presents a student’s original research and findings on a particular topic or question. It is usually written as a requirement for a graduate degree program and is intended to demonstrate the student’s mastery of the subject matter and their ability to conduct independent research.
History of Thesis
The concept of a thesis can be traced back to ancient Greece, where it was used as a way for students to demonstrate their knowledge of a particular subject. However, the modern form of the thesis as a scholarly document used to earn a degree is a relatively recent development.
The origin of the modern thesis can be traced back to medieval universities in Europe. During this time, students were required to present a “disputation” in which they would defend a particular thesis in front of their peers and faculty members. These disputations served as a way to demonstrate the student’s mastery of the subject matter and were often the final requirement for earning a degree.
In the 17th century, the concept of the thesis was formalized further with the creation of the modern research university. Students were now required to complete a research project and present their findings in a written document, which would serve as the basis for their degree.
The modern thesis as we know it today has evolved over time, with different disciplines and institutions adopting their own standards and formats. However, the basic elements of a thesis – original research, a clear research question, a thorough review of the literature, and a well-argued conclusion – remain the same.
Structure of Thesis
The structure of a thesis may vary slightly depending on the specific requirements of the institution, department, or field of study, but generally, it follows a specific format.
Here’s a breakdown of the structure of a thesis:
This is the first page of the thesis that includes the title of the thesis, the name of the author, the name of the institution, the department, the date, and any other relevant information required by the institution.
This is a brief summary of the thesis that provides an overview of the research question, methodology, findings, and conclusions.
This page provides a list of all the chapters and sections in the thesis and their page numbers.
Introduction
This chapter provides an overview of the research question, the context of the research, and the purpose of the study. The introduction should also outline the methodology and the scope of the research.
Literature Review
This chapter provides a critical analysis of the relevant literature on the research topic. It should demonstrate the gap in the existing knowledge and justify the need for the research.
Methodology
This chapter provides a detailed description of the research methods used to gather and analyze data. It should explain the research design, the sampling method, data collection techniques, and data analysis procedures.
This chapter presents the findings of the research. It should include tables, graphs, and charts to illustrate the results.
This chapter interprets the results and relates them to the research question. It should explain the significance of the findings and their implications for the research topic.
This chapter summarizes the key findings and the main conclusions of the research. It should also provide recommendations for future research.
This section provides a list of all the sources cited in the thesis. The citation style may vary depending on the requirements of the institution or the field of study.
This section includes any additional material that supports the research, such as raw data, survey questionnaires, or other relevant documents.
How to write Thesis
Here are some steps to help you write a thesis:
- Choose a Topic: The first step in writing a thesis is to choose a topic that interests you and is relevant to your field of study. You should also consider the scope of the topic and the availability of resources for research.
- Develop a Research Question: Once you have chosen a topic, you need to develop a research question that you will answer in your thesis. The research question should be specific, clear, and feasible.
- Conduct a Literature Review: Before you start your research, you need to conduct a literature review to identify the existing knowledge and gaps in the field. This will help you refine your research question and develop a research methodology.
- Develop a Research Methodology: Once you have refined your research question, you need to develop a research methodology that includes the research design, data collection methods, and data analysis procedures.
- Collect and Analyze Data: After developing your research methodology, you need to collect and analyze data. This may involve conducting surveys, interviews, experiments, or analyzing existing data.
- Write the Thesis: Once you have analyzed the data, you need to write the thesis. The thesis should follow a specific structure that includes an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, conclusion, and references.
- Edit and Proofread: After completing the thesis, you need to edit and proofread it carefully. You should also have someone else review it to ensure that it is clear, concise, and free of errors.
- Submit the Thesis: Finally, you need to submit the thesis to your academic advisor or committee for review and evaluation.
Example of Thesis
Example of Thesis template for Students:
Title of Thesis
Table of Contents:
Chapter 1: Introduction
Chapter 2: Literature Review
Chapter 3: Research Methodology
Chapter 4: Results
Chapter 5: Discussion
Chapter 6: Conclusion
References:
Appendices:
Note: That’s just a basic template, but it should give you an idea of the structure and content that a typical thesis might include. Be sure to consult with your department or supervisor for any specific formatting requirements they may have. Good luck with your thesis!
Application of Thesis
Thesis is an important academic document that serves several purposes. Here are some of the applications of thesis:
- Academic Requirement: A thesis is a requirement for many academic programs, especially at the graduate level. It is an essential component of the evaluation process and demonstrates the student’s ability to conduct original research and contribute to the knowledge in their field.
- Career Advancement: A thesis can also help in career advancement. Employers often value candidates who have completed a thesis as it demonstrates their research skills, critical thinking abilities, and their dedication to their field of study.
- Publication : A thesis can serve as a basis for future publications in academic journals, books, or conference proceedings. It provides the researcher with an opportunity to present their research to a wider audience and contribute to the body of knowledge in their field.
- Personal Development: Writing a thesis is a challenging task that requires time, dedication, and perseverance. It provides the student with an opportunity to develop critical thinking, research, and writing skills that are essential for their personal and professional development.
- Impact on Society: The findings of a thesis can have an impact on society by addressing important issues, providing insights into complex problems, and contributing to the development of policies and practices.
Purpose of Thesis
The purpose of a thesis is to present original research findings in a clear and organized manner. It is a formal document that demonstrates a student’s ability to conduct independent research and contribute to the knowledge in their field of study. The primary purposes of a thesis are:
- To Contribute to Knowledge: The main purpose of a thesis is to contribute to the knowledge in a particular field of study. By conducting original research and presenting their findings, the student adds new insights and perspectives to the existing body of knowledge.
- To Demonstrate Research Skills: A thesis is an opportunity for the student to demonstrate their research skills. This includes the ability to formulate a research question, design a research methodology, collect and analyze data, and draw conclusions based on their findings.
- To Develop Critical Thinking: Writing a thesis requires critical thinking and analysis. The student must evaluate existing literature and identify gaps in the field, as well as develop and defend their own ideas.
- To Provide Evidence of Competence : A thesis provides evidence of the student’s competence in their field of study. It demonstrates their ability to apply theoretical concepts to real-world problems, and their ability to communicate their ideas effectively.
- To Facilitate Career Advancement : Completing a thesis can help the student advance their career by demonstrating their research skills and dedication to their field of study. It can also provide a basis for future publications, presentations, or research projects.
When to Write Thesis
The timing for writing a thesis depends on the specific requirements of the academic program or institution. In most cases, the opportunity to write a thesis is typically offered at the graduate level, but there may be exceptions.
Generally, students should plan to write their thesis during the final year of their graduate program. This allows sufficient time for conducting research, analyzing data, and writing the thesis. It is important to start planning the thesis early and to identify a research topic and research advisor as soon as possible.
In some cases, students may be able to write a thesis as part of an undergraduate program or as an independent research project outside of an academic program. In such cases, it is important to consult with faculty advisors or mentors to ensure that the research is appropriately designed and executed.
It is important to note that the process of writing a thesis can be time-consuming and requires a significant amount of effort and dedication. It is important to plan accordingly and to allocate sufficient time for conducting research, analyzing data, and writing the thesis.
Characteristics of Thesis
The characteristics of a thesis vary depending on the specific academic program or institution. However, some general characteristics of a thesis include:
- Originality : A thesis should present original research findings or insights. It should demonstrate the student’s ability to conduct independent research and contribute to the knowledge in their field of study.
- Clarity : A thesis should be clear and concise. It should present the research question, methodology, findings, and conclusions in a logical and organized manner. It should also be well-written, with proper grammar, spelling, and punctuation.
- Research-Based: A thesis should be based on rigorous research, which involves collecting and analyzing data from various sources. The research should be well-designed, with appropriate research methods and techniques.
- Evidence-Based : A thesis should be based on evidence, which means that all claims made in the thesis should be supported by data or literature. The evidence should be properly cited using appropriate citation styles.
- Critical Thinking: A thesis should demonstrate the student’s ability to critically analyze and evaluate information. It should present the student’s own ideas and arguments, and engage with existing literature in the field.
- Academic Style : A thesis should adhere to the conventions of academic writing. It should be well-structured, with clear headings and subheadings, and should use appropriate academic language.
Advantages of Thesis
There are several advantages to writing a thesis, including:
- Development of Research Skills: Writing a thesis requires extensive research and analytical skills. It helps to develop the student’s research skills, including the ability to formulate research questions, design and execute research methodologies, collect and analyze data, and draw conclusions based on their findings.
- Contribution to Knowledge: Writing a thesis provides an opportunity for the student to contribute to the knowledge in their field of study. By conducting original research, they can add new insights and perspectives to the existing body of knowledge.
- Preparation for Future Research: Completing a thesis prepares the student for future research projects. It provides them with the necessary skills to design and execute research methodologies, analyze data, and draw conclusions based on their findings.
- Career Advancement: Writing a thesis can help to advance the student’s career. It demonstrates their research skills and dedication to their field of study, and provides a basis for future publications, presentations, or research projects.
- Personal Growth: Completing a thesis can be a challenging and rewarding experience. It requires dedication, hard work, and perseverance. It can help the student to develop self-confidence, independence, and a sense of accomplishment.
Limitations of Thesis
There are also some limitations to writing a thesis, including:
- Time and Resources: Writing a thesis requires a significant amount of time and resources. It can be a time-consuming and expensive process, as it may involve conducting original research, analyzing data, and producing a lengthy document.
- Narrow Focus: A thesis is typically focused on a specific research question or topic, which may limit the student’s exposure to other areas within their field of study.
- Limited Audience: A thesis is usually only read by a small number of people, such as the student’s thesis advisor and committee members. This limits the potential impact of the research findings.
- Lack of Real-World Application : Some thesis topics may be highly theoretical or academic in nature, which may limit their practical application in the real world.
- Pressure and Stress : Writing a thesis can be a stressful and pressure-filled experience, as it may involve meeting strict deadlines, conducting original research, and producing a high-quality document.
- Potential for Isolation: Writing a thesis can be a solitary experience, as the student may spend a significant amount of time working independently on their research and writing.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Conceptual Framework – Types, Methodology and...

Research Summary – Structure, Examples and...

Thesis Format – Templates and Samples

Research Topics – Ideas and Examples

Research Findings – Types Examples and Writing...

Dissertation vs Thesis – Key Differences
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

What is a thesis | A Complete Guide with Examples

Table of Contents
A thesis is a comprehensive academic paper based on your original research that presents new findings, arguments, and ideas of your study. It’s typically submitted at the end of your master’s degree or as a capstone of your bachelor’s degree.
However, writing a thesis can be laborious, especially for beginners. From the initial challenge of pinpointing a compelling research topic to organizing and presenting findings, the process is filled with potential pitfalls.
Therefore, to help you, this guide talks about what is a thesis. Additionally, it offers revelations and methodologies to transform it from an overwhelming task to a manageable and rewarding academic milestone.
What is a thesis?
A thesis is an in-depth research study that identifies a particular topic of inquiry and presents a clear argument or perspective about that topic using evidence and logic.
Writing a thesis showcases your ability of critical thinking, gathering evidence, and making a compelling argument. Integral to these competencies is thorough research, which not only fortifies your propositions but also confers credibility to your entire study.
Furthermore, there's another phenomenon you might often confuse with the thesis: the ' working thesis .' However, they aren't similar and shouldn't be used interchangeably.
A working thesis, often referred to as a preliminary or tentative thesis, is an initial version of your thesis statement. It serves as a draft or a starting point that guides your research in its early stages.
As you research more and gather more evidence, your initial thesis (aka working thesis) might change. It's like a starting point that can be adjusted as you learn more. It's normal for your main topic to change a few times before you finalize it.
While a thesis identifies and provides an overarching argument, the key to clearly communicating the central point of that argument lies in writing a strong thesis statement.
What is a thesis statement?
A strong thesis statement (aka thesis sentence) is a concise summary of the main argument or claim of the paper. It serves as a critical anchor in any academic work, succinctly encapsulating the primary argument or main idea of the entire paper.
Typically found within the introductory section, a strong thesis statement acts as a roadmap of your thesis, directing readers through your arguments and findings. By delineating the core focus of your investigation, it offers readers an immediate understanding of the context and the gravity of your study.
Furthermore, an effectively crafted thesis statement can set forth the boundaries of your research, helping readers anticipate the specific areas of inquiry you are addressing.
Different types of thesis statements
A good thesis statement is clear, specific, and arguable. Therefore, it is necessary for you to choose the right type of thesis statement for your academic papers.
Thesis statements can be classified based on their purpose and structure. Here are the primary types of thesis statements:
Argumentative (or Persuasive) thesis statement
Purpose : To convince the reader of a particular stance or point of view by presenting evidence and formulating a compelling argument.
Example : Reducing plastic use in daily life is essential for environmental health.
Analytical thesis statement
Purpose : To break down an idea or issue into its components and evaluate it.
Example : By examining the long-term effects, social implications, and economic impact of climate change, it becomes evident that immediate global action is necessary.
Expository (or Descriptive) thesis statement
Purpose : To explain a topic or subject to the reader.
Example : The Great Depression, spanning the 1930s, was a severe worldwide economic downturn triggered by a stock market crash, bank failures, and reduced consumer spending.
Cause and effect thesis statement
Purpose : To demonstrate a cause and its resulting effect.
Example : Overuse of smartphones can lead to impaired sleep patterns, reduced face-to-face social interactions, and increased levels of anxiety.
Compare and contrast thesis statement
Purpose : To highlight similarities and differences between two subjects.
Example : "While both novels '1984' and 'Brave New World' delve into dystopian futures, they differ in their portrayal of individual freedom, societal control, and the role of technology."
When you write a thesis statement , it's important to ensure clarity and precision, so the reader immediately understands the central focus of your work.
What is the difference between a thesis and a thesis statement?
While both terms are frequently used interchangeably, they have distinct meanings.
A thesis refers to the entire research document, encompassing all its chapters and sections. In contrast, a thesis statement is a brief assertion that encapsulates the central argument of the research.
Here’s an in-depth differentiation table of a thesis and a thesis statement.
Aspect | Thesis | Thesis Statement |
Definition | An extensive document presenting the author's research and findings, typically for a degree or professional qualification. | A concise sentence or two in an essay or research paper that outlines the main idea or argument. |
Position | It’s the entire document on its own. | Typically found at the end of the introduction of an essay, research paper, or thesis. |
Components | Introduction, methodology, results, conclusions, and bibliography or references. | Doesn't include any specific components |
Purpose | Provides detailed research, presents findings, and contributes to a field of study. | To guide the reader about the main point or argument of the paper or essay. |
Now, to craft a compelling thesis, it's crucial to adhere to a specific structure. Let’s break down these essential components that make up a thesis structure
15 components of a thesis structure
Navigating a thesis can be daunting. However, understanding its structure can make the process more manageable.
Here are the key components or different sections of a thesis structure:
Your thesis begins with the title page. It's not just a formality but the gateway to your research.

Here, you'll prominently display the necessary information about you (the author) and your institutional details.
- Title of your thesis
- Your full name
- Your department
- Your institution and degree program
- Your submission date
- Your Supervisor's name (in some cases)
- Your Department or faculty (in some cases)
- Your University's logo (in some cases)
- Your Student ID (in some cases)
In a concise manner, you'll have to summarize the critical aspects of your research in typically no more than 200-300 words.

This includes the problem statement, methodology, key findings, and conclusions. For many, the abstract will determine if they delve deeper into your work, so ensure it's clear and compelling.
Acknowledgments
Research is rarely a solitary endeavor. In the acknowledgments section, you have the chance to express gratitude to those who've supported your journey.

This might include advisors, peers, institutions, or even personal sources of inspiration and support. It's a personal touch, reflecting the humanity behind the academic rigor.
Table of contents
A roadmap for your readers, the table of contents lists the chapters, sections, and subsections of your thesis.

By providing page numbers, you allow readers to navigate your work easily, jumping to sections that pique their interest.
List of figures and tables
Research often involves data, and presenting this data visually can enhance understanding. This section provides an organized listing of all figures and tables in your thesis.

It's a visual index, ensuring that readers can quickly locate and reference your graphical data.
Introduction
Here's where you introduce your research topic, articulate the research question or objective, and outline the significance of your study.

- Present the research topic : Clearly articulate the central theme or subject of your research.
- Background information : Ground your research topic, providing any necessary context or background information your readers might need to understand the significance of your study.
- Define the scope : Clearly delineate the boundaries of your research, indicating what will and won't be covered.
- Literature review : Introduce any relevant existing research on your topic, situating your work within the broader academic conversation and highlighting where your research fits in.
- State the research Question(s) or objective(s) : Clearly articulate the primary questions or objectives your research aims to address.
- Outline the study's structure : Give a brief overview of how the subsequent sections of your work will unfold, guiding your readers through the journey ahead.
The introduction should captivate your readers, making them eager to delve deeper into your research journey.
Literature review section
Your study correlates with existing research. Therefore, in the literature review section, you'll engage in a dialogue with existing knowledge, highlighting relevant studies, theories, and findings.

It's here that you identify gaps in the current knowledge, positioning your research as a bridge to new insights.
To streamline this process, consider leveraging AI tools. For example, the SciSpace literature review tool enables you to efficiently explore and delve into research papers, simplifying your literature review journey.
Methodology
In the research methodology section, you’ll detail the tools, techniques, and processes you employed to gather and analyze data. This section will inform the readers about how you approached your research questions and ensures the reproducibility of your study.

Here's a breakdown of what it should encompass:
- Research Design : Describe the overall structure and approach of your research. Are you conducting a qualitative study with in-depth interviews? Or is it a quantitative study using statistical analysis? Perhaps it's a mixed-methods approach?
- Data Collection : Detail the methods you used to gather data. This could include surveys, experiments, observations, interviews, archival research, etc. Mention where you sourced your data, the duration of data collection, and any tools or instruments used.
- Sampling : If applicable, explain how you selected participants or data sources for your study. Discuss the size of your sample and the rationale behind choosing it.
- Data Analysis : Describe the techniques and tools you used to process and analyze the data. This could range from statistical tests in quantitative research to thematic analysis in qualitative research.
- Validity and Reliability : Address the steps you took to ensure the validity and reliability of your findings to ensure that your results are both accurate and consistent.
- Ethical Considerations : Highlight any ethical issues related to your research and the measures you took to address them, including — informed consent, confidentiality, and data storage and protection measures.
Moreover, different research questions necessitate different types of methodologies. For instance:
- Experimental methodology : Often used in sciences, this involves a controlled experiment to discern causality.
- Qualitative methodology : Employed when exploring patterns or phenomena without numerical data. Methods can include interviews, focus groups, or content analysis.
- Quantitative methodology : Concerned with measurable data and often involves statistical analysis. Surveys and structured observations are common tools here.
- Mixed methods : As the name implies, this combines both qualitative and quantitative methodologies.
The Methodology section isn’t just about detailing the methods but also justifying why they were chosen. The appropriateness of the methods in addressing your research question can significantly impact the credibility of your findings.
Results (or Findings)
This section presents the outcomes of your research. It's crucial to note that the nature of your results may vary; they could be quantitative, qualitative, or a mix of both.

Quantitative results often present statistical data, showcasing measurable outcomes, and they benefit from tables, graphs, and figures to depict these data points.
Qualitative results , on the other hand, might delve into patterns, themes, or narratives derived from non-numerical data, such as interviews or observations.
Regardless of the nature of your results, clarity is essential. This section is purely about presenting the data without offering interpretations — that comes later in the discussion.
In the discussion section, the raw data transforms into valuable insights.
Start by revisiting your research question and contrast it with the findings. How do your results expand, constrict, or challenge current academic conversations?
Dive into the intricacies of the data, guiding the reader through its implications. Detail potential limitations transparently, signaling your awareness of the research's boundaries. This is where your academic voice should be resonant and confident.
Practical implications (Recommendation) section
Based on the insights derived from your research, this section provides actionable suggestions or proposed solutions.
Whether aimed at industry professionals or the general public, recommendations translate your academic findings into potential real-world actions. They help readers understand the practical implications of your work and how it can be applied to effect change or improvement in a given field.
When crafting recommendations, it's essential to ensure they're feasible and rooted in the evidence provided by your research. They shouldn't merely be aspirational but should offer a clear path forward, grounded in your findings.
The conclusion provides closure to your research narrative.
It's not merely a recap but a synthesis of your main findings and their broader implications. Reconnect with the research questions or hypotheses posited at the beginning, offering clear answers based on your findings.

Reflect on the broader contributions of your study, considering its impact on the academic community and potential real-world applications.
Lastly, the conclusion should leave your readers with a clear understanding of the value and impact of your study.
References (or Bibliography)
Every theory you've expounded upon, every data point you've cited, and every methodological precedent you've followed finds its acknowledgment here.

In references, it's crucial to ensure meticulous consistency in formatting, mirroring the specific guidelines of the chosen citation style .
Proper referencing helps to avoid plagiarism , gives credit to original ideas, and allows readers to explore topics of interest. Moreover, it situates your work within the continuum of academic knowledge.
To properly cite the sources used in the study, you can rely on online citation generator tools to generate accurate citations!
Here’s more on how you can cite your sources.
Often, the depth of research produces a wealth of material that, while crucial, can make the core content of the thesis cumbersome. The appendix is where you mention extra information that supports your research but isn't central to the main text.

Whether it's raw datasets, detailed procedural methodologies, extended case studies, or any other ancillary material, the appendices ensure that these elements are archived for reference without breaking the main narrative's flow.
For thorough researchers and readers keen on meticulous details, the appendices provide a treasure trove of insights.
Glossary (optional)
In academics, specialized terminologies, and jargon are inevitable. However, not every reader is versed in every term.
The glossary, while optional, is a critical tool for accessibility. It's a bridge ensuring that even readers from outside the discipline can access, understand, and appreciate your work.

By defining complex terms and providing context, you're inviting a wider audience to engage with your research, enhancing its reach and impact.
Remember, while these components provide a structured framework, the essence of your thesis lies in the originality of your ideas, the rigor of your research, and the clarity of your presentation.
As you craft each section, keep your readers in mind, ensuring that your passion and dedication shine through every page.
Thesis examples
To further elucidate the concept of a thesis, here are illustrative examples from various fields:
Example 1 (History): Abolition, Africans, and Abstraction: the Influence of the ‘Noble Savage’ on British and French Antislavery Thought, 1787-1807 by Suchait Kahlon.
Example 2 (Climate Dynamics): Influence of external forcings on abrupt millennial-scale climate changes: a statistical modelling study by Takahito Mitsui · Michel Crucifix
Checklist for your thesis evaluation
Evaluating your thesis ensures that your research meets the standards of academia. Here's an elaborate checklist to guide you through this critical process.
Content and structure
- Is the thesis statement clear, concise, and debatable?
- Does the introduction provide sufficient background and context?
- Is the literature review comprehensive, relevant, and well-organized?
- Does the methodology section clearly describe and justify the research methods?
- Are the results/findings presented clearly and logically?
- Does the discussion interpret the results in light of the research question and existing literature?
- Is the conclusion summarizing the research and suggesting future directions or implications?
Clarity and coherence
- Is the writing clear and free of jargon?
- Are ideas and sections logically connected and flowing?
- Is there a clear narrative or argument throughout the thesis?
Research quality
- Is the research question significant and relevant?
- Are the research methods appropriate for the question?
- Is the sample size (if applicable) adequate?
- Are the data analysis techniques appropriate and correctly applied?
- Are potential biases or limitations addressed?
Originality and significance
- Does the thesis contribute new knowledge or insights to the field?
- Is the research grounded in existing literature while offering fresh perspectives?
Formatting and presentation
- Is the thesis formatted according to institutional guidelines?
- Are figures, tables, and charts clear, labeled, and referenced in the text?
- Is the bibliography or reference list complete and consistently formatted?
- Are appendices relevant and appropriately referenced in the main text?
Grammar and language
- Is the thesis free of grammatical and spelling errors?
- Is the language professional, consistent, and appropriate for an academic audience?
- Are quotations and paraphrased material correctly cited?
Feedback and revision
- Have you sought feedback from peers, advisors, or experts in the field?
- Have you addressed the feedback and made the necessary revisions?
Overall assessment
- Does the thesis as a whole feel cohesive and comprehensive?
- Would the thesis be understandable and valuable to someone in your field?
Ensure to use this checklist to leave no ground for doubt or missed information in your thesis.
After writing your thesis, the next step is to discuss and defend your findings verbally in front of a knowledgeable panel. You’ve to be well prepared as your professors may grade your presentation abilities.
Preparing your thesis defense
A thesis defense, also known as "defending the thesis," is the culmination of a scholar's research journey. It's the final frontier, where you’ll present their findings and face scrutiny from a panel of experts.
Typically, the defense involves a public presentation where you’ll have to outline your study, followed by a question-and-answer session with a committee of experts. This committee assesses the validity, originality, and significance of the research.
The defense serves as a rite of passage for scholars. It's an opportunity to showcase expertise, address criticisms, and refine arguments. A successful defense not only validates the research but also establishes your authority as a researcher in your field.
Here’s how you can effectively prepare for your thesis defense .
Now, having touched upon the process of defending a thesis, it's worth noting that scholarly work can take various forms, depending on academic and regional practices.
One such form, often paralleled with the thesis, is the 'dissertation.' But what differentiates the two?
Dissertation vs. Thesis
Often used interchangeably in casual discourse, they refer to distinct research projects undertaken at different levels of higher education.
To the uninitiated, understanding their meaning might be elusive. So, let's demystify these terms and delve into their core differences.
Here's a table differentiating between the two.
Aspect | Thesis | Dissertation |
Purpose | Often for a master's degree, showcasing a grasp of existing research | Primarily for a doctoral degree, contributing new knowledge to the field |
Length | 100 pages, focusing on a specific topic or question. | 400-500 pages, involving deep research and comprehensive findings |
Research Depth | Builds upon existing research | Involves original and groundbreaking research |
Advisor's Role | Guides the research process | Acts more as a consultant, allowing the student to take the lead |
Outcome | Demonstrates understanding of the subject | Proves capability to conduct independent and original research |
Wrapping up
From understanding the foundational concept of a thesis to navigating its various components, differentiating it from a dissertation, and recognizing the importance of proper citation — this guide covers it all.
As scholars and readers, understanding these nuances not only aids in academic pursuits but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the relentless quest for knowledge that drives academia.
It’s important to remember that every thesis is a testament to curiosity, dedication, and the indomitable spirit of discovery.
Good luck with your thesis writing!
Frequently Asked Questions
A thesis typically ranges between 40-80 pages, but its length can vary based on the research topic, institution guidelines, and level of study.
A PhD thesis usually spans 200-300 pages, though this can vary based on the discipline, complexity of the research, and institutional requirements.
To identify a thesis topic, consider current trends in your field, gaps in existing literature, personal interests, and discussions with advisors or mentors. Additionally, reviewing related journals and conference proceedings can provide insights into potential areas of exploration.
The conceptual framework is often situated in the literature review or theoretical framework section of a thesis. It helps set the stage by providing the context, defining key concepts, and explaining the relationships between variables.
A thesis statement should be concise, clear, and specific. It should state the main argument or point of your research. Start by pinpointing the central question or issue your research addresses, then condense that into a single statement, ensuring it reflects the essence of your paper.
You might also like

Boosting Citations: A Comparative Analysis of Graphical Abstract vs. Video Abstract

The Impact of Visual Abstracts on Boosting Citations

Introducing SciSpace’s Citation Booster To Increase Research Visibility
- The Open University
- Explore OpenLearn
- Get started
- Create a course
- Free courses
- Collections
My OpenLearn Create Profile
- Personalise your OpenLearn profile
- Save Your favourite content
- Get recognition for your learning
Already Registered?
- Health Management, Ethics and Research Module: Ethiopian Federal Ministry of Health
- Health Management, Ethics and Research Module: Acknowledgements
- Health Management, Ethics and Research Module: Introduction
- Health Management, Ethics and Research Module: 1. Health Services in Ethiopia
- Health Management, Ethics and Research Module: 2. Management and Leadership in Community Healthcare
- Health Management, Ethics and Research Module: 3. Planning Health Programmes
- Health Management, Ethics and Research Module: 4. Implementing your Health Plans
- Health Management, Ethics and Research Module: 5. Monitoring and Control
- Health Management, Ethics and Research Module: 6. Management of Supplies at Health Post Level
- Health Management, Ethics and Research Module: 7. Principles of Healthcare Ethics
- Health Management, Ethics and Research Module: 8. Ethical Dilemmas in Health Service Delivery
- Health Management, Ethics and Research Module: 9. Rights and Obligations of Health Extension Practitioners
- Health Management, Ethics and Research Module: 10. General Principles of Health Research and Introduction to Community Surveys
- Health Management, Ethics and Research Module: 11. Developing Your Community Profile
- Health Management, Ethics and Research: 12. Data Collection and Analysis for Your Baseline Community Survey
- Introduction
- Learning Outcomes for Study Session 13
- 13.1.1 Components of a community profile report
- 13.2.1 Clarifying the problem of malaria infection in your community
- 13.2.2 Criteria for choosing health problems to research
- 13.2.3 Poor sanitary conditions: creating a research question
- 13.2.4 Community participation in prioritising health issues
- 13.3 Choosing which topic to research
13.4.1 What other sources should you consult?
13.4.2 Research objectives
Summary of Study Session 13
- Self-Assessment Questions (SAQs) for Study Session 13
- Health Management, Ethics and Research: 14. Research Strategies and Study Designs for Small-Scale Research
- Health Management, Ethics and Research Module: 15. Sampling Methods and Sample Size in Small-Scale Research
- Health Management, Ethics and Research Module: 16. Extended Case Study on Health Management, Ethics and Research
- Download PDF version
- Health Management, Ethics and Research PDF (1.4MB)
About this course
- 40 hours study
- 1 Level 1: Introductory
- Course description

Health Management, Ethics and Research
If you create an account, you can set up a personal learning profile on the site.
The final part of clarifying your research project involves thinking in more detail about your research objectives . Research objectives should be closely related to the statement of the problem and summarise what you hope will be achieved by the study. For example, if the problem identified is low utilisation of antenatal care services, the general objective of the study could be to identify the reasons for this low uptake, in order to find ways of improving it.
Writing your research objectives clearly helps to:
- Define the focus of your study
- Clearly identify variables to be measured
- Indicate the various steps to be involved
- Establish the limits of the study
- Avoid collection of any data that is not strictly necessary.
What do you think might happen if you started a research project, but hadn’t written any clear research objectives?
Without clearly written research objectives, you might be confused about the limits of the study, what data should be collected, or how to conduct the research.
Objectives can be general or specific. The general objective of your study states what you expect to achieve in general terms. Specific objectives break down the general objective into smaller, logically connected parts that systematically address the various aspects of the problem. Your specific objectives should specify exactly what you will do in each phase of your study, how, where, when and for what purpose.
How should your objectives be stated?
Your objectives should be stated using action verbs that are specific enough to be measured, for example: to compare, to calculate, to assess, to determine, to verify, to calculate, to describe, to explain, etc. Avoid the use of vague non-active verbs such as: to appreciate, to understand, to believe, to study, etc., because it is difficult to evaluate whether they have been achieved.
Case Study 13.3 General and specific objectives for a counselling project
A research study designed to assess the accessibility and acceptability of the Voluntary Counselling and Testing (VCT) Services for HIV infection in kebele X had the following general and specific objectives:
General objective: To identify factors that affects the acceptability of VCT services and to assess community attitudes towards comprehensive care and support for people living with HIV/AIDS.
Specific objectives:
- To assess the knowledge, attitude and practice of the community towards HIV/AIDS and VCT services.
- To identify barriers and concerns related to VCT and its uptake.
- To assess the awareness and perception of the study community regarding comprehensive care and support for people living with HIV/AIDS.
What is the difference between the specific objectives and the general objective of a research project? You can use the example in Case Study 13.3 to help you answer this question.
Specific objectives are detailed objectives that describe what will be researched during the study, whereas the general objective is a much broader statement about what the study aims to achieve overall.
In the next study session, we will move on to teach you about research strategies and alternative study designs that you may choose to conduct for a small-scale research project in your community.
For further information, take a look at our frequently asked questions which may give you the support you need.
Have a question?
If you have any concerns about anything on this site please get in contact with us here.
Report a concern

What Makes a Thesis Statement Spectacular? — 5 things to know
Table of Contents
What Is a Thesis Statement?
A thesis statement is a declarative sentence that states the primary idea of an essay or a research paper . In this statement, the authors declare their beliefs or what they intend to argue in their research study. The statement is clear and concise, with only one or two sentences.
Thesis Statement — An Essential in Thesis Writing
A thesis statement distills the research paper idea into one or two sentences. This summary organizes your paper and develops the research argument or opinion. The statement is important because it lets the reader know what the research paper will talk about and how the author is approaching the issue. Moreover, the statement also serves as a map for the paper and helps the authors to track and organize their thoughts more efficiently.
A thesis statement can keep the writer from getting lost in a convoluted and directionless argument. Finally, it will also ensure that the research paper remains relevant and focused on the objective.
Where to Include the Thesis Statement?
The thesis statement is typically placed at the end of the introduction section of your essay or research paper. It usually consists of a single sentence of the writer’s opinion on the topic and provides a specific guide to the readers throughout the paper.
6 Steps to Write an Impactful Thesis Statement
Step 1 – analyze the literature.
Identify the knowledge gaps in the relevant research paper. Analyze the deeper implications of the author’s research argument. Was the research objective mentioned in the thesis statement reversed later in the discussion or conclusion? Does the author contradict themselves? Is there a major knowledge gap in creating a relevant research objective? Has the author understood and validated the fundamental theories correctly? Does the author support an argument without having supporting literature to cite? Answering these or related questions will help authors develop a working thesis and give their thesis an easy direction and structure.
Step 2 – Start with a Question
While developing a working thesis, early in the writing process, you might already have a research question to address. Strong research questions guide the design of studies and define and identify specific objectives. These objectives will assist the author in framing the thesis statement.
Step 3 – Develop the Answer
After initial research, the author could formulate a tentative answer to the research question. At this stage, the answer could be simple enough to guide the research and the writing process. After writing the initial answer, the author could elaborate further on why this is the chosen answer. After reading more about the research topic, the author could write and refine the answers to address the research question.
Step 4 – Write the First Draft of the Thesis Statement
After ideating the working thesis statement, make sure to write it down. It is disheartening to create a great idea for a thesis and then forget it when you lose concentration. The first draft will help you think clearly and logically. It will provide you with an option to align your thesis statement with the defined research objectives.
Step 5 – Anticipate Counter Arguments Against the Statement
After developing a working thesis, you should think about what might be said against it. This list of arguments will help you refute the thesis later. Remember that every argument has a counterargument, and if yours does not have one, what you state is not an argument — it may be a fact or opinion, but not an argument.
Step 6 – Refine the Statement
Anticipating counterarguments will help you refine your statement further. A strong thesis statement should address —
- Why does your research hold this stand?
- What will readers learn from the essay?
- Are the key points of your argumentative or narrative?
- Does the final thesis statement summarize your overall argument or the entire topic you aim to explain in the research paper?

5 Tips to Create a Compelling Thesis Statement
A thesis statement is a crucial part of any academic paper. Clearly stating the main idea of your research helps you focus on the objectives of your paper. Refer to the following tips while drafting your statement:
1. Keep it Concise
The statement should be short and precise. It should contain no more than a couple of sentences.
2. Make it Specific
The statement should be focused on a specific topic or argument. Covering too many topics will only make your paper weaker.
3. Express an Opinion
The statement should have an opinion on an issue or controversy. This will make your paper arguable and interesting to read.
4. Be Assertive
The statement should be stated assertively and not hesitantly or apologetically. Remember, you are making an argument — you need to sound convincing!
5. Support with Evidence
The thesis should be supported with evidence from your paper. Make sure you include specific examples from your research to reinforce your objectives.
Thesis Statement Examples *
Example 1 – alcohol consumption.
High levels of alcohol consumption have harmful effects on your health, such as weight gain, heart disease, and liver complications.
This thesis statement states specific reasons why alcohol consumption is detrimental. It is not required to mention every single detriment in your thesis.
Example 2 – Benefits of the Internet
The internet serves as a means of expediently connecting people across the globe, fostering new friendships and an exchange of ideas that would not have occurred before its inception.
While the internet offers a host of benefits, this thesis statement is about choosing the ability that fosters new friendships and exchange ideas. Also, the research needs to prove how connecting people across the globe could not have happened before the internet’s inception — which is a focused research statement.
*The following thesis statements are not fully researched and are merely examples shown to understand how to write a thesis statement. Also, you should avoid using these statements for your own research paper purposes.
A gripping thesis statement is developed by understanding it from the reader’s point of view. Be aware of not developing topics that only interest you and have less reader attraction. A harsh yet necessary question to ask oneself is — Why should readers read my paper? Is this paper worth reading? Would I read this paper if I weren’t its author?
A thesis statement hypes your research paper. It makes the readers excited about what specific information is coming their way. This helps them learn new facts and possibly embrace new opinions.
Writing a thesis statement (although two sentences) could be a daunting task. Hope this blog helps you write a compelling one! Do consider using the steps to create your thesis statement and tell us about it in the comment section below.
Great in impactation of knowledge
An interesting expository. Thanks for the concise explanation.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles
![examples of objectives in thesis What is Academic Integrity and How to Uphold it [FREE CHECKLIST]](https://www.enago.com/academy/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/FeatureImages-59-210x136.png)
Ensuring Academic Integrity and Transparency in Academic Research: A comprehensive checklist for researchers
Academic integrity is the foundation upon which the credibility and value of scientific findings are…

- Publishing Research
- Reporting Research
How to Optimize Your Research Process: A step-by-step guide
For researchers across disciplines, the path to uncovering novel findings and insights is often filled…

- Industry News
- Trending Now
Breaking Barriers: Sony and Nature unveil “Women in Technology Award”
Sony Group Corporation and the prestigious scientific journal Nature have collaborated to launch the inaugural…

Achieving Research Excellence: Checklist for good research practices
Academia is built on the foundation of trustworthy and high-quality research, supported by the pillars…

- Promoting Research
Plain Language Summary — Communicating your research to bridge the academic-lay gap
Science can be complex, but does that mean it should not be accessible to the…
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for…
Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right…
Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.

Postgraduate Thesis Statement
Ai generator.
Navigating the world of postgraduate research is a pivotal stage in one’s academic journey. As you advance into this realm, the emphasis on a well-structured thesis statement becomes even more crucial. A robust thesis statement not only anchors your research but also serves as a beacon, guiding your inquiries and arguments. Delve into these postgraduate thesis statement examples, along with an elucidative guide and valuable tips, to craft a statement that can stand the test of rigorous academic scrutiny.
What is a thesis statement for a Postgraduate? – Definition
A postgraduate thesis statement concise summary of the main point or claim of a research paper or essay at the postgraduate level. It serves as a roadmap for readers, outlining the central argument or purpose of the study. It’s typically more complex and in-depth than undergraduate thesis statements, reflecting the advanced nature of postgraduate research and the nuanced understanding required of the topic.
What is an example of a Postgraduate thesis statement?
Topic: The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Modern Healthcare Systems
Thesis Statement : “This research explores the transformative potential of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in modern healthcare, asserting that AI’s integration not only optimizes diagnostic accuracy and treatment efficacy but also presents challenges concerning patient data privacy and the role of human medical practitioners.”
100 Thesis Statement Examples for a Postgraduate

Size: 277 KB
Crafting an impactful postgraduate thesis statement requires precision, depth, and a thorough understanding of your research domain. These examples span various disciplines, offering a glimpse into the intricacy and focus expected at this advanced academic level.
- Climate Change and Agriculture : “This study posits that climate change’s adverse effects significantly decrease agricultural yield, necessitating innovative adaptive measures for global food security.”
- Neuroscience and Memory : “This research delves into the neurobiological mechanisms underpinning memory retention, suggesting a pivotal role of the hippocampus in long-term memory consolidation.”
- Cultural Impacts on Marketing : “Examining Eastern versus Western marketing strategies reveals that cultural nuances significantly influence consumer behavior and brand perception.”
- Quantum Computing : “This thesis explores the potential of quantum computing in revolutionizing the computational landscape, emphasizing its superiority in solving specific algorithms compared to classical computers.”
- Mental Health and Social Media : “The correlation between social media usage and mental health outcomes among millennials suggests a significant increase in anxiety and depression rates.”
- Sustainable Architecture : “Green architectural practices not only reduce environmental footprints but also offer cost-efficient solutions in urban developments.”
- Blockchain in Banking : “Blockchain technology, with its decentralized nature, presents transformative prospects for banking security, transparency, and operational efficiency.”
- Child Psychology and Learning : “Play-based learning strategies in early childhood education yield superior cognitive and social development outcomes.”
- AI in Autonomous Vehicles : “Autonomous vehicles utilizing AI algorithms demonstrate a substantial reduction in road accidents compared to human-driven cars.”
- Genetic Engineering and Ethics : “The ethical ramifications of CRISPR technology in human gene editing necessitate stringent regulatory frameworks.”
- Migration and Global Economy : “Mass migrations, driven by socio-political factors, have a dual impact on global economies – rejuvenating labor markets while straining social services.”
- Gender Studies in Workplace Dynamics : “Gender diversity in corporate leadership roles directly correlates with increased creativity and profitability.”
- Astrophysics and Dark Matter : “The quest for understanding dark matter’s nature is pivotal in decoding the universe’s evolutionary trajectory.”
- Augmented Reality in Education : “Augmented Reality (AR) tools in educational settings foster immersive learning experiences, enhancing retention and engagement.”
- Global Health and Pandemics : “The global response to pandemics like COVID-19 underscores the necessity for unified international health protocols and rapid information dissemination.”
- Renewable Energy Adoption : “The transition to renewable energy sources is imperative for sustainable development, yet geopolitical and economic factors often hinder its large-scale adoption.”
- Linguistics and Language Evolution : “The evolution of human language is intrinsically linked to socio-cultural shifts, with technology playing a significant role in modern linguistic transformations.”
- Digital Transformation in Businesses : “Digital transformation, while streamlining operations, introduces challenges related to data privacy and workforce adaptation.”
- Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services : “A decline in global biodiversity directly impacts ecosystem services, affecting human sustenance and well-being.”
- Post-Colonial Literature : “Post-colonial literary works provide a lens to understand the enduring socio-cultural impacts of colonialism on previously colonized societies.
- Forensic Science and Crime : “Incorporating advanced forensic methodologies can significantly increase the conviction rate in criminal justice systems.”
- Space Exploration and Humanity : “The pursuit of interstellar travel holds implications not just for technological advancement but for understanding human resilience and adaptability.”
- Digital Art and Society : “The rise of digital art mediums challenges traditional art conventions, emphasizing the dynamic nature of artistic expression.”
- Nanotechnology in Medicine : “The infusion of nanotechnology in medicine offers prospects for targeted drug delivery, reducing side-effects.”
- Urban Planning and Mental Health : “Urban planning that incorporates green spaces directly influences inhabitants’ mental well-being.”
- Virtual Reality and Rehabilitation : “Virtual reality tools hold transformative potential in physical and psychological rehabilitation strategies.”
- Philosophy and Artificial Intelligence : “The evolution of AI compels a reexamination of philosophical constructs related to consciousness and autonomy.”
- Economics of Climate Change : “The economic ramifications of climate change encompass more than tangible damages, including the revaluation of assets and shifts in global labor markets.”
- Robotics in Healthcare : “Incorporating robotics in healthcare optimizes patient care, especially in surgeries and rehabilitation, but also raises ethical dilemmas.”
- Musicology and Emotions : “The intricate relationship between music and human emotion has neurobiological underpinnings, affecting mood regulation.
- Epigenetics and Disease : “Epigenetic modifications, though reversible, have profound implications in disease onset, progression, and potential therapeutic interventions.”
- Political Science and Media Influence : “The role of media in shaping public political opinions has intensified with the rise of social media platforms, necessitating a reevaluation of election campaign strategies.”
- Marine Biology and Coral Reefs : “The deteriorating health of coral reefs globally serves as an indicator of broader marine ecosystem imbalance and stresses the importance of conservation efforts.”
- Data Science and Privacy : “The surge in big data analytics offers unparalleled insights for businesses but simultaneously poses significant challenges to individual privacy.”
- Anthropology and Ancient Civilizations : “A study of ancient civilizations through anthropological lenses can unearth patterns of human social evolution and provide insights into contemporary societal structures.”
- Astrobiology and Extraterrestrial Life : “The quest for extraterrestrial life in astrobiology reshapes our understanding of life’s potential existence beyond Earth and its implications for humanity.”
- Sports Science and Athlete Performance : “Cutting-edge sports science technologies, from biomechanics to nutrition, have revolutionized athlete training, contributing to record-breaking performances.”
- Cryptography and Cybersecurity : “As cyber threats evolve, so does the field of cryptography, playing a pivotal role in ensuring data integrity and confidentiality in an increasingly digital world.”
- Sociology and Urbanization : “The rapid urbanization of modern societies presents challenges in social cohesion, demanding innovative solutions for ensuring inclusive growth.”
- Quantum Physics and Reality : “Quantum physics, with its counterintuitive principles, challenges classical notions of reality, necessitating a paradigm shift in our understanding of the universe.”
- Mathematical Modelling and Pandemics : “Mathematical models, especially when adapted promptly, provide critical insights into pandemic trajectories, aiding governments in crafting timely interventions.”
- Archaeology and Human Migration : “Modern archaeological techniques reveal intricate patterns of ancient human migrations, challenging conventional narratives of human history.”
- Psychology and Virtual Reality : “The immersion in virtual reality can have profound psychological effects, ranging from therapeutic benefits to potential mental health challenges.”
- Environmental Law and Conservation : “Contemporary environmental laws must adapt to the accelerating climate crisis, emphasizing both conservation and sustainable development.”
- Bioinformatics and Genomic Medicine : “Harnessing bioinformatics in genomic medicine allows for personalized medical treatments, revolutionizing patient care in the 21st century.”
- Space Technology and Satellite Communication : “The advancements in space technology have paved the way for more efficient satellite communication systems, reshaping global connectivity.”
- Geopolitics and Energy Resources : “The geopolitics of energy resources, especially in the Middle East, play a pivotal role in global economic dynamics and international relations.”
- Organic Chemistry and Drug Design : “Innovations in organic chemistry have revolutionized drug design, enabling the creation of targeted therapies for complex diseases.”
- Differential Equations and Engineering : “Differential equations serve as the backbone for modeling in engineering, from fluid dynamics to electrical circuits.”
- Sustainable Finance and Global Economy : “The rise of sustainable finance is not merely an ethical imperative but has tangible impacts on global economic stability and growth prospects.
- Ethnomusicology and Globalization : “Globalization has significantly influenced traditional music forms, introducing a confluence of styles while risking the erasure of unique cultural sounds.”
- Astronomy and Exoplanets : “The discovery of exoplanets challenges our understanding of planetary systems, suggesting myriad possibilities for life beyond Earth.”
- International Law and Cyber Warfare : “The increasing prevalence of cyber warfare necessitates the reevaluation and adaptation of international law to address virtual, borderless conflicts.”
- Biophysics and Cellular Mechanisms : “Biophysical studies reveal the intricate mechanics at cellular levels, promising potential breakthroughs in disease treatment.”
- Comparative Literature and Cultural Identity : “Exploring literature across cultures offers insights into evolving cultural identities in a rapidly globalizing world.”
- Environmental Engineering and Waste Management : “Advancements in environmental engineering have ushered in sustainable waste management practices, pivotal in combating pollution.”
- Metaphysics and Modern Physics : “Contemporary physics, especially quantum mechanics, intersects with metaphysical questions about the nature of reality and consciousness.”
- Robotics and Human Interaction : “The integration of robotics into daily life reshapes human interaction, posing questions about societal adaptation and ethical considerations.”
- Public Health and Aging Population : “With global populations aging, public health initiatives must recalibrate to address the unique challenges and healthcare needs of older adults.”
- Econometrics and Policy Making : “Econometrics, with its empirical analytical tools, plays a vital role in informing and refining economic policy-making.”
- Paleontology and Earth’s History : “Paleontological findings provide a window into Earth’s history, influencing our understanding of evolution and environmental changes.”
- Behavioral Economics and Consumer Behavior : “Behavioral economics uncovers the irrational patterns in consumer behavior, challenging traditional economic theories.”
- Human Rights and Globalization : “The trajectory of human rights in the age of globalization presents a paradox: while rights awareness has spread, violations persist and even intensify in some regions.”
- Topology and Quantum Computing : “The field of topology, focusing on properties of space, holds keys to advancements in quantum computing.”
- Comparative Politics and Democratization : “Comparative studies in politics reveal varying paths to democratization, shaped by historical, economic, and societal factors.”
- Bioethics and Genetic Engineering : “Bioethics emerges as a crucial field as genetic engineering capabilities advance, especially concerning human genome editing.”
- Nanoengineering and Material Science : “Nanoengineering has revolutionized material science, leading to the development of materials with unprecedented properties.”
- Migration Studies and Urban Development : “Migration patterns profoundly influence urban development, with cities evolving in response to diverse influxes of populations.”
- Cognitive Science and Artificial Intelligence : “Exploring the intersections of cognitive science and AI provides insights into replicating human-like learning and thinking in machines.”
- Art History and Digital Media : “Digital media has transformed art history, enabling immersive experiences of art and innovative methods of analysis.
- Oceanography and Climate Change : “The in-depth study of oceans reveals their critical role in regulating global climate, emphasizing the urgent need for marine conservation efforts.”
- Philosophy and Cognitive Sciences : “The intersections of philosophy and cognitive sciences offer profound insights into human consciousness, thought processes, and decision-making.”
- Microbiology and Antibiotic Resistance : “The rise of antibiotic-resistant pathogens necessitates urgent microbiological research to pave the way for new therapeutic approaches.”
- Linguistics and Neural Networks : “The relationship between linguistics and neural networks can provide insights into the development of advanced natural language processing tools in AI.”
- Forensic Science and Legal Systems : “Advancements in forensic science provide pivotal evidence in the legal system, but they also introduce ethical dilemmas related to privacy and potential misuse.”
- Criminology and Urban Safety : “Research in criminology indicates that urban safety strategies must evolve to address the changing dynamics of crime in densely populated areas.”
- Architecture and Sustainable Design : “Sustainable architectural practices are reshaping the built environment, ensuring energy efficiency and ecological harmony.”
- Biomedical Science and Personalized Medicine : “Personalized medicine, backed by biomedical research, holds the promise of tailor-made treatments, optimizing therapeutic outcomes for individual patients.”
- Agriculture and Food Security : “In the face of climate change, innovative agricultural techniques are paramount to ensuring global food security.”
- Dermatology and Nanotechnology : “Nanotechnology’s application in dermatology introduces potent solutions for skin ailments, but it also presents potential risks that require thorough investigation.”
- Political Economy and Global Inequalities : “The political economy framework reveals how power dynamics on a global scale perpetuate economic inequalities.”
- Aerospace Engineering and Interstellar Travel : “While interstellar travel remains a concept of science fiction, advancements in aerospace engineering gradually bring us closer to the possibility of exploring distant star systems.”
- Endocrinology and Metabolic Diseases : “Emerging research in endocrinology offers novel insights into metabolic diseases, opening avenues for innovative treatment protocols.”
- Theology and Interfaith Dialogue : “In an increasingly interconnected world, interfaith dialogues become essential to understanding and bridging theological differences.”
- Optometry and Digital Screen Usage : “Increased digital screen usage poses challenges to ocular health, necessitating innovations in optometry for prevention and management.”
- Veterinary Medicine and Zoonotic Diseases : “Understanding zoonotic diseases in veterinary medicine is crucial, given the increasing frequency of animal-human disease transmission events.”
- Urban Planning and Smart Cities : “The concept of smart cities, backed by technological innovations, promises to reshape urban planning to create more sustainable and efficient urban environments.”
- Quantum Mechanics and Classical Physics : “The divergence between quantum mechanics and classical physics continues to intrigue scientists, pushing the boundaries of our understanding of the universe.”
- Pedagogy and Digital Learning : “The rise of digital learning platforms challenges traditional pedagogy, calling for new educational strategies that cater to the digital generation.”
- Entomology and Ecosystem Balance : “Studying insects, especially their interactions within ecosystems, is essential to understand broader ecological balances and the impacts of environmental changes.”
- Neuroscience and Meditation : “Exploring the neural impacts of meditation uncovers its profound effects on cognitive function, stress reduction, and emotional regulation.”
- Maritime Studies and Global Trade : “The intricate world of maritime studies is pivotal in understanding the nuances of global trade, geopolitical tensions, and environmental challenges.”
- Sociology and Social Media : “The integration of social media into daily life has dramatically reshaped societal structures, influencing individual behavior, communal relationships, and even political movements.”
- Paleobotany and Climate Archives : “Studying ancient plant remains offers a unique window into Earth’s climatic history, assisting scientists in predicting future climatic shifts.”
- Film Studies and Cultural Representation : “Cinema serves as a mirror to society, and the study of films provides insights into cultural representation, societal norms, and evolving ideologies.”
- Epistemology and Artificial Intelligence : “The philosophical study of knowledge, or epistemology, prompts crucial questions about AI’s capacity for knowledge and understanding.”
- Chemical Engineering and Renewable Energy : “Innovations in chemical engineering hold the potential to revolutionize renewable energy sources, making them more efficient and widely accessible.”
- Ornithology and Biodiversity : “Studying birds, their habitats, and migratory patterns offers vital information on biodiversity, ecological health, and the impacts of climate change.”
- Pharmacology and Personalized Treatment : “Advanced pharmacological research paves the way for personalized treatments, optimizing drug efficacy based on individual genetic profiles.”
- Anthropology and Globalization : “Through the lens of anthropology, the impacts of globalization on indigenous cultures, traditions, and societal structures become evident, revealing both positive integrations and adverse assimilations.”
Thesis Statement Examples for Postgraduate Argumentative Essay
Postgraduate argumentative essays thesis statement challenge students to take a position on a contentious issue, supported by rigorous research and evidence. Here are thesis statements that showcase diverse angles on various subjects:
- Online Learning : “Despite its convenience, online learning can’t replicate the experiential richness of traditional classroom interactions.”
- Artificial Intelligence : “AI has the potential to outpace human intelligence, making its ethical implications a top priority.”
- Climate Change : “Global warming is the definitive challenge of our generation, and deniers are on the wrong side of science.”
- Mandatory Voting : “Compulsory voting infringes on personal freedoms and doesn’t guarantee a more engaged electorate.”
- Telemedicine : “The rise of telemedicine, accelerated by the pandemic, promises equitable healthcare access but also raises concerns about the quality of remote diagnoses.”
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) : “While CSR initiatives are often lauded, they can sometimes serve as mere PR strategies rather than genuine efforts for societal betterment.”
- Gene Editing : “CRISPR technology holds transformative medical potential, but unchecked edits might lead to unintended genetic consequences.”
- Work-from-Home : “Permanent work-from-home policies could revolutionize work-life balance, but might also blur boundaries leading to employee burnout.”
- Digital Privacy : “Given the increasing intrusiveness of tech giants, stringent data protection regulations are not just preferable but essential.”
- Nuclear Energy : “Nuclear energy, while a potent solution to energy crises, poses significant environmental and security risks.”
Postgraduate Thesis Statement Examples for Research paper
Postgraduate thesis statement for research papers delve deep into specialized areas of study, often contributing to existing academic literature. These thesis statements reflect some of these investigative pursuits:
- Microbiome and Health : “Gut microbiota plays a pivotal role in human health, influencing everything from digestion to mental well-being.”
- Quantum Computing : “Quantum computing promises computational power leaps but faces hurdles in practical, scalable applications.”
- Space Exploration : “The recent discovery of water on Mars rekindles debates about its potential habitability.”
- Renewable Energy Storage : “Efficient storage solutions are paramount to maximizing the benefits of renewable energy sources like solar and wind.”
- Mental Health in Adolescents : “The rise in adolescent mental health issues in the digital age hints at social media’s role in exacerbating anxiety and depression.”
- Sustainable Agriculture : “Permaculture practices present a sustainable solution to the global food crisis by promoting ecological balance and reducing dependence on non-renewable resources.”
- Virtual Reality (VR) : “VR technologies in medical training can revolutionize surgical techniques, offering risk-free practice environments.”
- Linguistics : “The rapid extinction of indigenous languages threatens cultural diversity, necessitating urgent preservation efforts.”
- Nanotechnology in Medicine : “Nanobots, while still in nascent stages, hold transformative potential in targeted drug delivery, potentially minimizing side-effects.”
- Blockchain : “Beyond cryptocurrency, blockchain technology offers potential solutions to issues of data transparency and authentication in various sectors.
Postgraduate 3 Point Thesis Statement Examples
Three-point thesis statements succinctly introduce the main points to be discussed in the paper, creating a roadmap for the reader. Here are some tailored to postgraduate topics:
- Augmented Reality : “Augmented Reality enhances user interaction, offers education opportunities, and revolutionizes business models.”
- Bioinformatics : “Bioinformatics streamlines drug discovery, aids in genome sequencing, and offers insights into evolutionary biology.”
- Cognitive Neuroscience : “Cognitive neuroscience sheds light on memory processes, decodes decision-making, and unravels the mysteries of perception.”
- Data Science and Business : “Through predicting consumer behavior, optimizing logistics, and enhancing product recommendations, data science drives business innovation.”
- Green Architecture : “Green architecture promotes energy efficiency, utilizes sustainable materials, and enhances residents’ overall well-being.”
- Healthcare Policies : “Effective healthcare policies reduce medical costs, improve patient outcomes, and ensure universal access.”
- International Relations in the Digital Age : “The digital age reshapes international diplomacy, alters state security dynamics, and fosters new global partnerships.”
- Machine Learning : “Machine learning optimizes automation, delivers personalized content, and aids scientific research.”
- Urban Planning and Sustainability : “Sustainable urban planning ensures efficient transportation, promotes green spaces, and prioritizes community welfare.”
- Zero-Waste Movement : “The zero-waste movement reduces environmental degradation, fosters sustainable consumer habits, and promotes circular economies.”
Thesis Statement Examples For Masters Degree
Masters’ theses delve into intricate research topics, combining comprehensive literature reviews with original research. Here are examples for various fields:
- Global Health : “Addressing global health disparities necessitates international cooperation, local stakeholder engagement, and technological innovations.”
- Marine Biology : “Coral reef bleaching, driven by climate change, jeopardizes marine biodiversity and the livelihoods of coastal communities.”
- Artificial Neural Networks : “Neural networks, mimicking human cognition, revolutionize sectors from finance to healthcare, but require careful calibration.”
- Pedagogical Strategies : “Innovative pedagogical strategies, blending traditional and digital learning, cater to diverse student needs and foster holistic development.”
- Financial Markets : “Algorithmic trading, while maximizing market efficiency, raises concerns about fairness and systemic risks.”
- Contemporary Literature : “Postcolonial narratives in contemporary literature unveil suppressed histories, challenge dominant discourses, and reimagine identity.”
- Green Chemistry : “Green chemistry practices, minimizing environmental footprints, are imperative in the modern industrial landscape.”
- Space Physics : “Explorations into heliophysics provide insights into solar phenomena and their implications for Earth’s space environment.”
- Clinical Psychology : “Mindfulness-based interventions offer promising results in treating anxiety disorders, promoting long-term well-being.”
- Cultural Anthropology : “The digital age reshapes cultural practices, offering a lens to examine evolving societal norms and values.
Thesis Statement Examples To Study Abroad
Studying abroad enriches educational experiences, broadens cultural horizons, and fosters personal growth. Here are thesis statements that explore various facets of international education:
- Language Acquisition : “Studying abroad accelerates language acquisition by immersing students in native-speaking environments, enhancing linguistic fluency.”
- Cultural Identity : “Navigating a new cultural context challenges students’ perceptions, prompting a deeper understanding of both self and others.”
- Global Networking : “Studying abroad fosters international networks, offering cross-cultural collaborations and global career opportunities.”
- Academic Excellence : “Experiencing diverse pedagogical approaches in foreign institutions enhances critical thinking and academic prowess.”
- Cultural Adaptation : “Navigating cultural differences and adapting to new norms sharpens students’ adaptability skills and global perspectives.”
- Career Advancement : “International education equips graduates with a global skillset, making them more attractive to multinational employers.”
- Cultural Exchange : “Cultural exchange programs promote cross-cultural understanding, challenging stereotypes and fostering mutual respect.”
- Personal Growth : “Navigating unfamiliar terrains encourages self-reliance, resilience, and personal development.”
- Global Perspectives : “A global education broadens perspectives, nurturing empathy and a more holistic understanding of global issues.”
- Interdisciplinary Learning : “Studying abroad encourages cross-disciplinary exploration, enriching students’ academic and personal journeys.”
Thesis Statement Examples for Grad School
Graduate school, whether master’s or doctoral, entails rigorous research and academic inquiry. Here are thesis statements that exemplify the depth of inquiry at the graduate level:
- Medicine and Ethics : “Bioethics in medical practice ensures patient autonomy, informed consent, and ethical decision-making, even in complex cases.”
- Literary Theory : “Poststructuralist literary theory deconstructs conventional narratives, revealing hidden power dynamics and challenging literary norms.”
- Economic Policy : “Monetary policies that prioritize financial stability must also consider their social and economic implications for vulnerable populations.”
- Medical Imaging Advances : “Emerging medical imaging technologies promise quicker diagnoses, reduced patient exposure, and enhanced medical insights.”
- Education and Technology : “Integrating technology into education offers opportunities for personalized learning, but also raises concerns about equity and privacy.”
- Sustainable Development : “Sustainable development policies must balance ecological preservation, social equity, and economic growth in a rapidly changing world.”
- Criminal Justice Reform : “Criminal justice reform requires interdisciplinary approaches, addressing systemic racism, rehabilitation, and restorative justice.”
- Artificial Intelligence and Ethics : “Ethical considerations in AI development ensure that AI algorithms align with human values and avoid perpetuating biases.”
- Medical Ethics : “Euthanasia debates revolve around autonomy, dignity, and the responsibilities of healthcare professionals in end-of-life decisions.”
- Social Work and Vulnerable Populations : “Social workers play a pivotal role in advocating for vulnerable populations, addressing systemic inequalities, and promoting social justice.”
Doctoral Thesis Statement Examples
Doctoral theses are pinnacle works of original research, often contributing significantly to their fields. Here are examples that reflect the rigor and innovation expected at the doctoral level:
- Neuroplasticity and Rehabilitation : “Investigating the brain’s adaptive capacities can revolutionize rehabilitation strategies for neurological injuries.”
- Quantum Mechanics and Gravity : “The unification of quantum mechanics and gravity remains elusive, demanding new theoretical paradigms to reconcile the two.”
- Sustainable Urban Design : “Creating eco-friendly, socially inclusive urban spaces requires holistic planning that incorporates environmental, economic, and societal factors.”
- Political Discourse Analysis : “Analyzing political discourse unveils power dynamics, linguistic strategies, and media’s role in shaping public opinion.”
- Cancer Immunotherapy : “Advancing cancer immunotherapy necessitates a deep understanding of the immune system’s complex interactions with tumor cells.”
- Modernist Literature and Identity : “Modernist literature’s fragmentation and ambivalence mirror the complexities of identity in the shifting modern world.”
- Nanomaterials for Clean Energy : “Designing nanomaterials with efficient energy conversion properties can revolutionize the clean energy landscape.”
- Historical Reconstruction through Archaeology : “Archaeological findings reconstruct historical narratives, offering insights into ancient societies, cultures, and practices.”
- Ethnobotany and Traditional Medicine : “Exploring ethnobotanical knowledge deepens our understanding of traditional medicines’ efficacy, informing modern healthcare practices.”
- Astrophysics and Dark Matter : “The elusive nature of dark matter challenges our fundamental understanding of the universe’s composition and gravitational forces.
Thesis Statement Examples for Postgraduate Nursing
Postgraduate nursing studies delve into advanced healthcare practices and research. Here are thesis statements encompassing diverse nursing topics:
- Telehealth in Nursing : “Integrating telehealth technologies enhances nursing care accessibility, especially in remote areas, while ensuring patient privacy and data security.”
- Mental Health Nursing : “Psychiatric-mental health nurses play a pivotal role in treating and destigmatizing mental health conditions, catering to holistic well-being.”
- Emergency Nursing Protocols : “Developing standardized emergency nursing protocols ensures timely, efficient care delivery in critical situations, optimizing patient outcomes.”
- Nursing Leadership : “Effective nursing leadership fosters a culture of collaboration, staff empowerment, and improved patient safety within healthcare institutions.”
- Pediatric Palliative Care : “Specialized pediatric palliative care addresses the unique needs of seriously ill children, offering comfort, pain relief, and emotional support.”
- Nurse Education Strategies : “Innovative nurse education approaches, from simulation-based learning to flipped classrooms, enhance critical thinking and clinical skills.”
- Nurse Advocacy in Policy : “Nurse advocacy in healthcare policy-making safeguards patient rights, promotes evidence-based care, and addresses healthcare disparities.”
- Nursing Research Impact : “Translating nursing research findings into clinical practice ensures evidence-based care, improving patient outcomes and healthcare quality.”
- Nursing Ethics : “Navigating ethical dilemmas in nursing involves balancing patient autonomy, beneficence, and non-maleficence while upholding professional integrity.”
- Global Health Nursing : “Global health nursing addresses disparities, infectious diseases, and healthcare access challenges across diverse cultures and settings.”
Thesis Statement Examples for Postgraduate Degree
Postgraduate degrees encompass a wide array of subjects. Here are thesis statements that highlight the advanced research and expertise required for various disciplines:
- Cultural Heritage Management : “Cultural heritage management requires interdisciplinary collaboration, legal frameworks, and community engagement to preserve diverse histories.”
- Digital Humanities : “Digital humanities marry technological advancements with humanistic inquiry, fostering new ways to analyze and understand cultural artifacts.”
- Environmental Economics : “Environmental economics evaluates the economic impacts of environmental policies, assessing trade-offs between growth and sustainability.”
- Organizational Psychology : “Organizational psychology studies human behavior in workplaces, aiding in employee motivation, team dynamics, and organizational performance.”
- Music Therapy : “Music therapy combines artistic expression and psychology, improving mental health outcomes and emotional well-being through musical interventions.”
- Fashion Sustainability : “Sustainable fashion integrates ethical practices, eco-friendly materials, and circular economies, reshaping the fashion industry’s ecological impact.”
- Robotics Engineering : “Robotics engineering advances automation, prosthetics, and AI, necessitating breakthroughs in mechanics, electronics, and artificial intelligence.”
- Comparative Literature : “Comparative literature transcends cultural and linguistic boundaries, analyzing narratives’ universal themes and cultural contexts.”
- Global Supply Chain Management : “Effective global supply chain management demands risk assessment, supplier collaboration, and dynamic logistical strategies.”
- Visual Communication Design : “Visual communication design merges aesthetics with functionality, influencing how information is conveyed and experienced in various media.”
Short Thesis Statement Examples for Postgraduate
Concise and impactful, short thesis statements convey the essence of postgraduate research topics. Here are succinct examples:
- Medical Ethics : “Balancing patient autonomy and medical beneficence raises pivotal ethical questions in healthcare.”
- Renewable Energy : “Advancing renewable energy technologies is vital for mitigating climate change and achieving energy security.”
- Diversity in Education : “Embracing diversity in education enriches learning environments, fostering global citizenship and empathy.”
- Cybersecurity : “Ensuring cybersecurity safeguards data integrity, privacy, and digital infrastructures from cyber threats.”
- Community Policing : “Community policing bridges gaps, enhancing police-public relations, and fostering safer neighborhoods.”
- Corporate Sustainability : “Corporate sustainability integrates profit with social responsibility, driving ethical business practices and ecological preservation.”
- Aging Population : “Adapting to an aging population requires comprehensive healthcare strategies and social support systems.”
- AI in Healthcare : “AI-driven diagnostics accelerate medical diagnoses, revolutionizing patient care and disease management.”
- Urban Resilience : “Building urban resilience addresses climate-related challenges, ensuring cities thrive despite environmental uncertainties.”
- Cancer Immunotherapy : “Immunotherapy’s personalized approach transforms cancer treatment, enhancing survival rates and patient quality of life.
Postgraduate Thesis Statement Examples for Biomedical Engineering
The field of biomedical engineering bridges the gap between medicine and engineering. It focuses on innovative solutions to medical problems, aiming to improve patient care and health outcomes. The following thesis statements reflect the intricate blend of engineering principles and biological sciences to address pressing health challenges.
- Prosthetics and AI : “The integration of AI into prosthetic limbs can significantly enhance functionality, mimicking natural movement more closely than ever before.”
- Tissue Engineering : “Advancements in tissue engineering promise revolutionary treatments for organ damage and loss, potentially reducing the need for donor transplants.”
- Neural Interfaces : “Creating efficient neural interfaces can transform treatments for neurological disorders, offering improved communication tools for patients with severe paralysis.”
- Medical Imaging : “Harnessing the power of quantum physics in medical imaging techniques can lead to earlier and more accurate disease diagnosis.”
- Wearable Health Monitors : “With the rise of wearable tech, biomedical engineering plays a crucial role in developing devices that offer real-time health monitoring outside of clinical settings.”
- Biomaterials for Drug Delivery : “Innovative biomaterials can revolutionize drug delivery systems, providing targeted treatment and reducing systemic side effects.”
- 3D Bioprinting : “3D bioprinting presents a promising future in regenerative medicine, potentially creating functional organs for transplantation.”
- Nanomedicine : “Harnessing nanotechnology in medicine offers targeted treatments at the molecular level, especially promising for cancer therapeutics.”
- Bioinformatics in Genomic Medicine : “Bioinformatics tools can decode complex genomic data, paving the way for personalized medicine and treatments tailored to individual genetic makeup.”
- Rehabilitation Robots : “Robot-assisted therapy, designed via biomedical engineering, can drastically improve recovery outcomes for patients post-stroke or traumatic injuries.”
Postgraduate Thesis Statement Examples for Environmental Law
Environmental law at the postgraduate level delves into the legal aspects of environmental protection and sustainable development. These thesis statements emphasize the regulatory, ethical, and global dimensions of laws formulated to protect our planet.
- International Treaties on Climate Change : “Analyzing international treaties reveals the challenges and successes in creating a global consensus on climate action.”
- Environmental Justice : “Environmental law must address the disproportionate environmental burdens faced by marginalized communities, ensuring justice and equity.”
- Marine Conservation Laws : “Stricter marine conservation laws are pivotal in preventing the ongoing degradation of marine ecosystems and ensuring sustainable fisheries.”
- Deforestation Regulations : “Strengthening deforestation regulations is imperative in preserving biodiversity, maintaining carbon sinks, and supporting indigenous communities.”
- Wildlife Trafficking : “Reinforced legal measures against wildlife trafficking can deter illicit activities, protecting endangered species from the brink of extinction.”
- Corporate Accountability in Pollution : “Enforcing stringent laws against corporate pollution can ensure companies prioritize sustainable practices over profit margins.”
- Land Use and Zoning Laws : “Refined land use and zoning regulations can guide sustainable urban development while preserving vital green spaces.”
- Freshwater Resource Laws : “Given escalating water crises, creating robust legal frameworks is essential in managing and preserving freshwater resources for future generations.”
- Genetic Resource Rights : “Legal measures concerning genetic resources can safeguard biodiversity and ensure fair benefit-sharing with indigenous communities.”
- Chemical Waste Disposal : “Enhanced legal frameworks governing chemical waste disposal can prevent environmental contamination and safeguard public health.
Postgraduate Thesis Statement Examples for Digital Marketing
Digital marketing harnesses the power of online platforms to connect businesses with their target audiences. It constantly evolves with technology and consumer behavior. The following thesis statements explore various facets of digital marketing in the modern era, from social media strategies to the implications of big data.
- Consumer Behavior in E-commerce : “Analyzing digital footprints offers a deeper understanding of consumer behavior, allowing e-commerce businesses to personalize shopping experiences.”
- SEO and Web Traffic : “Optimizing website content for search engines is a cornerstone of digital visibility, directly impacting web traffic and potential conversions.”
- Influencer Marketing : “Leveraging influencer partnerships can significantly boost brand awareness and credibility, especially among younger demographics.”
- Big Data in Marketing Strategy : “Harnessing big data analytics allows businesses to predict market trends and tailor marketing strategies for optimized engagement.”
- Video Content Engagement : “In the age of short attention spans, video content emerges as a leading tool for sustained audience engagement and brand retention.”
- Social Media Algorithms : “Understanding the intricacies of social media algorithms is pivotal for brands aiming to maintain visibility and engagement on platforms like Instagram and Facebook.”
- Digital Marketing Ethics : “As digital marketing tools become more invasive, ethical considerations must guide strategies to protect consumer privacy.”
- Augmented Reality Advertising : “Incorporating augmented reality (AR) into advertising campaigns offers immersive experiences, revolutionizing consumer-brand interactions.”
- Chatbots and Customer Service : “Integrating AI-powered chatbots on business platforms enhances customer service efficiency and accessibility.”
- Mobile-First Marketing : “With the ubiquity of smartphones, adopting a mobile-first approach in digital marketing strategies is no longer optional but essential.”
Postgraduate Thesis Statement Examples for Contemporary Literature
Contemporary literature offers a reflection of society, addressing its complexities, challenges, and transformations. The thesis statements below delve into various themes and narrative techniques that define modern literary works.
- Postcolonial Narratives : “Contemporary literature frequently revisits postcolonial themes, shedding light on the lasting impacts of colonialism and the complexities of identity.”
- Dystopian Literature in the Digital Age : “Modern dystopian narratives often address concerns related to digital technology, surveillance, and loss of individuality.”
- Gender and Sexuality : “Contemporary literary works play a pivotal role in challenging traditional gender norms and exploring diverse spectrums of sexuality.”
- Magical Realism and Cultural Identity : “Magical realism in literature serves as a bridge between cultural myths and contemporary realities, especially in postcolonial contexts.”
- Migration and Diaspora : “Modern literary works often tackle themes of migration and diaspora, reflecting global movements and the challenges of cultural integration.”
- Ecocriticism and Environmental Concerns : “Contemporary literature is increasingly colored by ecocritical perspectives, mirroring global concerns about environmental degradation.”
- Metafiction and Narrative Structure : “Metafictional techniques in modern literature challenge traditional narrative structures, prompting readers to question the nature of storytelling itself.”
- Posthumanism in Literature : “Recent literary works explore posthumanist themes, grappling with the implications of AI, biotechnology, and the blurring boundaries between human and machine.”
- Literature in the Age of Terrorism : “The post-9/11 world sees a surge in literary works addressing the socio-political implications of terrorism and its impact on global consciousness.”
- Digital Narratives and E-literature : “The rise of e-literature and digital narratives redefines the boundaries of literature, offering interactive and multimedia reading experiences.”
Postgraduate Thesis Statement Examples for Urban Planning
Urban planning shapes the physical layout of cities, aiming to improve the quality of life, sustainability, and functionality of urban spaces. The following thesis statements address various challenges and strategies in urban development and design.
- Sustainable Urban Design : “Incorporating sustainable practices in urban design is essential for creating eco-friendly, energy-efficient cities of the future.”
- Public Transportation Systems : “Developing efficient public transportation systems can drastically reduce urban congestion and environmental pollution.”
- Urban Green Spaces : “The integration of green spaces in urban layouts promotes biodiversity, enhances mental well-being, and mitigates the heat island effect.”
- Urban Regeneration : “Regenerating dilapidated urban areas not only revitalizes the physical space but also boosts socio-economic growth and community development.”
- Smart Cities and Technology : “Harnessing smart technologies in urban planning can lead to more efficient, adaptable, and user-friendly cities.”
- Housing and Affordability : “Addressing housing affordability in urban planning strategies ensures diverse, inclusive, and cohesive urban communities.”
- Historical Preservation : “Balancing modern urban development with historical preservation maintains a city’s cultural heritage while catering to contemporary needs.”
- Urban Agriculture : “Promoting urban agriculture can bolster local food systems, reduce transportation emissions, and offer green recreational spaces for residents.”
- Infrastructure and Climate Resilience : “Modern urban planning must prioritize climate-resilient infrastructure to mitigate risks posed by climate change-related events.”
- Pedestrian-Friendly Designs : “Designing pedestrian-friendly urban layouts promotes physical activity, reduces vehicular traffic, and fosters community interactions.
How to Write a Postgraduate Thesis Introduction
The introduction of your postgraduate thesis sets the stage for your research, capturing the reader’s interest while providing context for your study. Follow these steps to craft an engaging and informative introduction:
- Understand the Purpose : Clearly define the purpose of your thesis introduction. It should introduce your research topic, explain its significance, and outline the research questions you aim to address.
- Provide Background Information : Give the reader a solid foundation by providing relevant background information about the subject. Highlight key concepts, theories, and prior research that will help frame your study.
- State the Problem or Gap : Clearly articulate the problem, gap, or research question that your thesis addresses. Explain why this topic is worth investigating and how it contributes to the existing body of knowledge.
- Establish Relevance : Connect your research to broader contexts such as societal, academic, or practical implications. Show why your study matters and how it can address real-world challenges.
- State Your Hypothesis or Research Objectives : If applicable, state your thesis’s hypothesis or the objectives guiding your research. This provides a roadmap for what you’ll explore in the subsequent chapters.
- Outline the Methodology : Briefly describe the research methods and approaches you’ll employ. This helps the reader understand how you’ll gather data and analyze it to answer your research questions.
- Highlight Structure : Give a concise overview of the chapters that will follow in your thesis. This helps readers anticipate the organization of your work.
- Capture Attention : Craft a compelling opening paragraph that grabs the reader’s attention. This could be a relevant anecdote, a surprising fact, or a thought-provoking question.
- Maintain Clarity : Write in clear and concise language. Avoid jargon that might confuse readers who are not experts in your field.
- Revise and Polish : Your introduction is the first impression readers have of your thesis. Revise, edit, and proofread to ensure it’s well-structured, coherent, and free of grammatical errors.
How to Write a Postgraduate Thesis – Step by Step Guide
Writing a postgraduate thesis is a comprehensive endeavor that demands careful planning, research, and writing. Follow these steps to navigate the process effectively:
- Choose a Relevant Topic : Select a topic that aligns with your field of study, interests, and academic goals. Ensure it’s specific, researchable, and adds value to existing literature.
- Conduct Preliminary Research : Familiarize yourself with the existing literature on your chosen topic. Identify gaps, controversies, or unanswered questions that your research can address.
- Craft a Research Proposal : Outline your research objectives, research questions, methodology, and expected contributions. Seek feedback from mentors or advisors before proceeding.
- Formulate a Thesis Statement : Your thesis statement encapsulates the main argument of your thesis. It should be clear, concise, and specific, guiding your research and shaping your paper’s focus.
- Plan Your Research : Create a detailed research plan outlining the scope, methods, data sources, and timeline for each phase of your study.
- Gather and Analyze Data : Collect data through surveys, experiments, interviews, or archival research, depending on your field. Analyze the data using appropriate methods.
- Structure Your Thesis : Organize your thesis into sections such as introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion. Follow any specific formatting guidelines.
- Write Drafts of Each Section : Start writing early. Draft each section of your thesis, focusing on clarity, coherence, and logical flow. Revise and refine as you go.
- Cite Sources Properly : Adhere to the citation style required by your institution or field. Properly cite all sources to avoid plagiarism and give credit to prior research.
- Revise and Proofread : Once you have a complete draft, take time to revise for content, clarity, and coherence. Proofread meticulously for grammar and punctuation errors.
- Seek Feedback : Share your draft with mentors, advisors, or peers for constructive feedback. Address their suggestions and refine your thesis accordingly.
- Write the Introduction and Conclusion Last : Writing the introduction and conclusion becomes easier once you have a clear understanding of your entire thesis. These sections should succinctly summarize your work’s essence.
Tips for Writing a Thesis Statement for a Postgraduate
A strong thesis statement forms the foundation of your postgraduate thesis. Follow these tips to craft an effective and impactful thesis statement:
- Be Clear and Specific : Your thesis statement should convey a clear and specific argument or research question. Avoid vague or general statements.
- Reflect Your Focus : Your thesis statement should accurately reflect the main focus of your research. It sets the tone for your entire thesis.
- Make It Debatable : A good thesis statement is one that can be debated or challenged. Avoid statements that are universally accepted or obvious.
- Avoid Ambiguity : Ensure that your thesis statement is not open to multiple interpretations. Ambiguity can confuse readers.
- Use Concise Language : Keep your thesis statement concise, usually consisting of one or two sentences. Avoid unnecessary wordiness.
- Incorporate Key Terms : Include important keywords or concepts relevant to your field. This helps readers understand the context of your research.
- Highlight Significance : Your thesis statement should communicate why your research is significant and what contributions it will make to your field.
- Refine Through Revision : Your thesis statement may evolve as you progress in your research. Don’t hesitate to revise and refine it for accuracy and clarity.
- Align with Evidence : Ensure that your thesis statement aligns with the evidence you gather during your research. Avoid making claims that your data cannot support.
- Seek Feedback : Share your thesis statement with mentors or peers for feedback. Their input can help you refine and improve it before finalizing.
Writing a postgraduate thesis demands dedication, diligence, and a keen eye for detail. By following these guidelines, you can craft an engaging introduction, navigate the thesis writing process, and create a compelling thesis statement that captures the essence of your research. Remember that the journey of research and writing is as important as the final product, as it allows you to contribute to your field and showcase your expertise. You should also take a look at our thesis statement for review .
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Advertisement
Objective vs. Subjective Thinking and Applications
- Share Content on Facebook
- Share Content on LinkedIn
- Share Content on Flipboard
- Share Content on Reddit
- Share Content via Email

To grasp objective vs. subjective thinking, it's crucial to understand what makes each type of reasoning unique. Subjective information is based on personal opinions or feelings regarding a particular subject matter. In contrast, objective information is factual, data-based and unbiased.
Defining 'Subjective' and 'Objective'
Identifying objective statements, recognizing subjective influences, when to use subjective vs. objective statements, effective communication, subjective vs. objective perspectives in everyday life, blending personal insights with factual integrity.
Put simply, an objective statement is a verifiable fact and a subjective observation is an opinion.
The term "subjective" refers to personal preferences and feelings about someone or something. It often shows an individual’s unique perspective, shaped by their personal experiences.
On the other hand, the word "objective" refers to verifiable facts and irrefutable evidence, remaining free from personal biases.
Why We Need Both
Understanding the difference between subjective and objective thinking is essential for clear communication. You'd use objective thinking is situations pertaining to scientific research, journalism and decision-making processes.
In contrast, subjective thinking allows for personal expression and creativity. Without the ability to be subjective, any mode of personal expression would end up feeling robotic and unnecessarily conforming. Subjectivity is the lifeblood of the arts and literature.
Objective statements are unbiased, providing a reliable foundation for decision-making and analysis. Examples of objective statements include:
- The Earth revolves around the Sun.
- Water boils at 100°C at sea level.
- World War II ended in 1945.
These examples demonstrate how an objective perspective is rooted in factual data that can be independently verified.
Subjective information derives from personal beliefs, biases and opinions. An individual's unique vantage point, experiences and emotions shape subjective opinions. For example:
- I think the new policy is unfair.
- This is the best restaurant in town.
- She seems happy today.
These statements reflect personal interpretations and are unique to the individual making them. Subjective views can vary widely between different people, highlighting the role of personal preferences and biases.
Understanding the appropriate time to invoke these types of information ensures balanced communication and better reasoning.
Using Objective Data in Decision-making
In decision-making, objective data is essential for informed choices and developing accurate theories or models. Objective data provides cold hard facts, such as customer churn rate, cost per lead and click-through rate (CTR). These business metrics allow companies to base their strategies on evidence rather than opinions.
The same applies to journalism. When reporting details about a subject, location, event, policies and the like, it’s critical to stick to the facts. Ironclad reporting like this is what makes a difference when informing the public.
Balancing Objective and Subjective Insights
While being objective means is vital for accuracy, subjectivity is what makes creative writing (like a best-selling novel) interesting to read.
Balancing objective and subjective insights is also essential for high-quality data analytics and decision-making. For instance, customer feedback (subjective information) combined with sales data (objective information) can provide a comprehensive understanding of market trends.
Subjectivity refers to personal opinions and feelings, which are important in contexts where personal interpretation adds value. This balance ensures that both factual accuracy and personal perspective contribute to nuanced and well-rounded conclusions.
By focusing on objective language, individuals can enhance the clarity and reliability of their communications, whether in professional settings or everyday interactions.
Crafting an Objective Statement
When crafting messages, use objective language to ensure clarity and avoid influencing readers with personal biases. Objective messages are based solely on verifiable facts and are free from subjective language. For example:
- Objective statement : The company’s revenue increased by 20 percent last year.
- Subjective statement : The company did a fantastic job increasing its revenue.
The objective statement provides a clear, factual report without the influence of personal opinion.
Avoiding Unnecessary Subjective Language
To maintain objectivity, avoid using subjective language when reporting facts. This helps to ensure that the information remains unbiased and reliable.
For example, instead of saying, "The new policy is infuriating," you might say, "Joe said he's frustrated with the new policy." Joe's opinion is subjective — there's no such thing as an objective opinion — but the fact that he said he's frustrated with the policy is objective.
Of course, if you're writing an op-ed, the reverse would be true. You'd still want to draw on empirical data and objective facts, but injecting your personal take on the matter is why people would read what you have to say. Regardless, try to ensure that your audience receives accurate and trustworthy information.
When someone expresses a subjective opinion about a movie, it comes from their personal feelings and individual tastes. This subjective perspective can vary widely among different people; a child may love a Disney movie while her uncle finds it boring. An objective statement in this scenario could be: The movie was 96 minutes long.
The movie cannot be "objectively bad" — that's a subjective view — and knowing when certain statements are representing facts vs. opinions is key in preventing the spread of misinformation.
Subjective, objective — is there a right or wrong way to communicate? It's important to remain objective when discussing facts so that everyone in the conversation is working with the same foundation of truth. But that doesn't mean that being subjective means lying; it means there is no right or wrong expression of that feeling or opinion.
Stick to an objective assessment when the resulting statement can be deemed true or false, and make it known that your personal opinion is subjective.
Please copy/paste the following text to properly cite this HowStuffWorks.com article:
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Introduction
Published on September 7, 2022 by Tegan George and Shona McCombes. Revised on November 21, 2023.
The introduction is the first section of your thesis or dissertation , appearing right after the table of contents . Your introduction draws your reader in, setting the stage for your research with a clear focus, purpose, and direction on a relevant topic .
Your introduction should include:
- Your topic, in context: what does your reader need to know to understand your thesis dissertation?
- Your focus and scope: what specific aspect of the topic will you address?
- The relevance of your research: how does your work fit into existing studies on your topic?
- Your questions and objectives: what does your research aim to find out, and how?
- An overview of your structure: what does each section contribute to the overall aim?
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
How to start your introduction, topic and context, focus and scope, relevance and importance, questions and objectives, overview of the structure, thesis introduction example, introduction checklist, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about introductions.
Although your introduction kicks off your dissertation, it doesn’t have to be the first thing you write — in fact, it’s often one of the very last parts to be completed (just before your abstract ).
It’s a good idea to write a rough draft of your introduction as you begin your research, to help guide you. If you wrote a research proposal , consider using this as a template, as it contains many of the same elements. However, be sure to revise your introduction throughout the writing process, making sure it matches the content of your ensuing sections.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Begin by introducing your dissertation topic and giving any necessary background information. It’s important to contextualize your research and generate interest. Aim to show why your topic is timely or important. You may want to mention a relevant news item, academic debate, or practical problem.
After a brief introduction to your general area of interest, narrow your focus and define the scope of your research.
You can narrow this down in many ways, such as by:
- Geographical area
- Time period
- Demographics or communities
- Themes or aspects of the topic
It’s essential to share your motivation for doing this research, as well as how it relates to existing work on your topic. Further, you should also mention what new insights you expect it will contribute.
Start by giving a brief overview of the current state of research. You should definitely cite the most relevant literature, but remember that you will conduct a more in-depth survey of relevant sources in the literature review section, so there’s no need to go too in-depth in the introduction.
Depending on your field, the importance of your research might focus on its practical application (e.g., in policy or management) or on advancing scholarly understanding of the topic (e.g., by developing theories or adding new empirical data). In many cases, it will do both.
Ultimately, your introduction should explain how your thesis or dissertation:
- Helps solve a practical or theoretical problem
- Addresses a gap in the literature
- Builds on existing research
- Proposes a new understanding of your topic
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Perhaps the most important part of your introduction is your questions and objectives, as it sets up the expectations for the rest of your thesis or dissertation. How you formulate your research questions and research objectives will depend on your discipline, topic, and focus, but you should always clearly state the central aim of your research.
If your research aims to test hypotheses , you can formulate them here. Your introduction is also a good place for a conceptual framework that suggests relationships between variables .
- Conduct surveys to collect data on students’ levels of knowledge, understanding, and positive/negative perceptions of government policy.
- Determine whether attitudes to climate policy are associated with variables such as age, gender, region, and social class.
- Conduct interviews to gain qualitative insights into students’ perspectives and actions in relation to climate policy.
To help guide your reader, end your introduction with an outline of the structure of the thesis or dissertation to follow. Share a brief summary of each chapter, clearly showing how each contributes to your central aims. However, be careful to keep this overview concise: 1-2 sentences should be enough.
I. Introduction
Human language consists of a set of vowels and consonants which are combined to form words. During the speech production process, thoughts are converted into spoken utterances to convey a message. The appropriate words and their meanings are selected in the mental lexicon (Dell & Burger, 1997). This pre-verbal message is then grammatically coded, during which a syntactic representation of the utterance is built.
Speech, language, and voice disorders affect the vocal cords, nerves, muscles, and brain structures, which result in a distorted language reception or speech production (Sataloff & Hawkshaw, 2014). The symptoms vary from adding superfluous words and taking pauses to hoarseness of the voice, depending on the type of disorder (Dodd, 2005). However, distortions of the speech may also occur as a result of a disease that seems unrelated to speech, such as multiple sclerosis or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
This study aims to determine which acoustic parameters are suitable for the automatic detection of exacerbations in patients suffering from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) by investigating which aspects of speech differ between COPD patients and healthy speakers and which aspects differ between COPD patients in exacerbation and stable COPD patients.
Checklist: Introduction
I have introduced my research topic in an engaging way.
I have provided necessary context to help the reader understand my topic.
I have clearly specified the focus of my research.
I have shown the relevance and importance of the dissertation topic .
I have clearly stated the problem or question that my research addresses.
I have outlined the specific objectives of the research .
I have provided an overview of the dissertation’s structure .
You've written a strong introduction for your thesis or dissertation. Use the other checklists to continue improving your dissertation.
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Research bias
- Survivorship bias
- Self-serving bias
- Availability heuristic
- Halo effect
- Hindsight bias
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
The introduction of a research paper includes several key elements:
- A hook to catch the reader’s interest
- Relevant background on the topic
- Details of your research problem
and your problem statement
- A thesis statement or research question
- Sometimes an overview of the paper
Don’t feel that you have to write the introduction first. The introduction is often one of the last parts of the research paper you’ll write, along with the conclusion.
This is because it can be easier to introduce your paper once you’ve already written the body ; you may not have the clearest idea of your arguments until you’ve written them, and things can change during the writing process .
Research objectives describe what you intend your research project to accomplish.
They summarize the approach and purpose of the project and help to focus your research.
Your objectives should appear in the introduction of your research paper , at the end of your problem statement .
Scope of research is determined at the beginning of your research process , prior to the data collection stage. Sometimes called “scope of study,” your scope delineates what will and will not be covered in your project. It helps you focus your work and your time, ensuring that you’ll be able to achieve your goals and outcomes.
Defining a scope can be very useful in any research project, from a research proposal to a thesis or dissertation . A scope is needed for all types of research: quantitative , qualitative , and mixed methods .
To define your scope of research, consider the following:
- Budget constraints or any specifics of grant funding
- Your proposed timeline and duration
- Specifics about your population of study, your proposed sample size , and the research methodology you’ll pursue
- Any inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Any anticipated control , extraneous , or confounding variables that could bias your research if not accounted for properly.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. & McCombes, S. (2023, November 21). How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Introduction. Scribbr. Retrieved July 10, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/introduction-structure/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, how to choose a dissertation topic | 8 steps to follow, how to write an abstract | steps & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Research objectives refer to the definitive statements made by researchers at the beginning of a research project detailing exactly what a research project aims to achieve. These objectives are explicit goals clearly and concisely projected
Discover the correct way to write aims and objectives for your thesis, dissertation or research project. We share real examples, breakdowns and common mistakes.
Read this comprehensive article to understand what research objectives are and how to write them effectively. You'll also learn more about the characteristics and types of research objectives, with examples for each. Don't miss this!
Research objectives are essential for any research project, but how do you define and write them? In this article, you will learn what research objectives are, why they are important, and how to write them with clear and specific examples. Scribbr is your guide to academic writing and research.
Aims and objectives are among the essential aspects of a dissertation. If you write aims and objectives effectively, they can act as a foundation to give your research clarity and focus.
The golden thread simply refers to the collective research aims, research objectives, and research questions for any given project (i.e., a dissertation, thesis, or research paper ). These three elements are bundled together because it's extremely important that they align with each other, and that the entire research project aligns with them.
Research objectives refer to the specific goals or aims of a research study. They provide a clear and concise description of what the researcher hopes to achieve by conducting the research. The objectives are typically based on the research questions and hypotheses formulated at the beginning of the study and are used to guide the research process.
The objectives provide a clear direction and purpose for the study, guiding the researcher in their data collection and analysis. Here are some tips on how to write effective research objective: 1. Be clear and specific. Research objective should be written in a clear and specific manner.
Make your reader's life as easy as possible by writing your research aims and objectives clearly and concisely. Don't leave them guessing.
Writing a research paper, thesis, or dissertation? In this post we'll show you how to clearly state your research objectives!
Formulating research aim and objectives in an appropriate manner is one of the most important aspects of your thesis. This is because research aim and objectives determine the scope, depth and the overall direction of the research. Research question is the central question of the study that has to be answered on the basis of research findings.
The research objective of a research proposal or scientific article defines the direction or content of a research investigation. Here are 5 real examples.
Aims and Objectives for Master's Dissertations. How to write the aim statement for a research project, and a set of research objectives with examples.
Learn how to write a research proposal for a dissertation or thesis. Includes loads of examples plus our free research proposal template.
In a PhD dissertation, the aims and objectives provide a clear roadmap and serve as the guiding principles that steer your research in the right direction.
Learn how to write a thesis, a long essay or dissertation on a specific subject, with this comprehensive guide and examples.
A thesis is an in-depth research study that identifies a particular topic of inquiry and presents a clear argument or perspective about that topic using evidence and logic. Writing a thesis showcases your ability of critical thinking, gathering evidence, and making a compelling argument. Integral to these competencies is thorough research ...
A thesis or dissertation outline helps you to organize your ideas succinctly, and can provide you with a roadmap for your research.
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your essay. It usually comes at the end of the introduction.
The final part of clarifying your research project involves thinking in more detail about your research objectives. Research objectives should be closely related to the statement of the problem and summarise what you hope will be achieved by the study. For example, if the problem identified is low utilisation of antenatal care services, the general objective of the study could be to identify ...
Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Other than a dissertation, it is one of the longest pieces of writing students typically complete. It relies on your ability to conduct research from start to finish: choosing a relevant topic, crafting a proposal, designing your research, collecting data, developing a robust analysis, drawing strong conclusions, and writing concisely.
While developing a working thesis, early in the writing process, you might already have a research question to address. Strong research questions guide the design of studies and define and identify specific objectives. These objectives will assist the author in framing the thesis statement.
Elevate Your Postgraduate Thesis: From inspiration to execution, discover the art of writing effective thesis statements, along with tips and illustrative examples.
To grasp objective vs. subjective thinking, it's crucial to understand what makes each type of reasoning unique. Subjective information is based on personal opinions or feelings regarding a particular subject matter. In contrast, objective information is factual, data-based and unbiased.
The introduction is the first section of your thesis or dissertation, appearing right after the table of contents. Your introduction draws your reader in, setting the stage for your research with a clear focus, purpose, and direction on a relevant topic.