Essay on Bullying in Schools
School bullying can be defined as the situation in which one or more students (The Bullies) single out a child (victim) and intend in behavior intended to cause discomfort or harm the child. A bully will repeatedly target the same victim several times. Under all circumstances, bullies have an advantage over the victim as they possess more power. Compared to the victim, bullies usually have physically stronger with a large circle of friends or higher social standing. Bullying can inflict emotional distress, humiliation, and physical harm. More than 95% of learning institutions experience bullying globally. Bullying must be meet a specific rationale to be considered bullying. Such requirements include repetitiveness, recurrent imbalance of power, and provocation. Bullying can occur in schools, on campus, or the outskirts of school, but its setting must have been created within the school. Regardless of the position, all the stakeholders in a school context, such as parents, educators, children, and community members, are required to contribute to the prevention of bullying in schools. School bullying is increasingly becoming a social problem in modern society. Ideally, there are several types of school bullying attached to different causes. The effects of school bullying can be classified in psychological, economical, and academic dimensions.
Types of Bullying in Schools
The common types of bullying in a school setting include verbal, sexual, cyber, psychological, physical, and higher education bullying. Notably, victims in a learning context can experience bullying regardless of age. The aforementioned types of bullying are further classified as either direct or indirect bullying. Direct bullying is defined as an attack that is openly targeted to a victim. Direct bullying is either verbal or physical. Contrary, indirect bullying involves different forms of relational aggression that leads to social isolation through defaming one’s reputation and manipulating the conscience of others into falsehood. Indirect bullying is usually hard and subtle to detect in a school setting (Goodwin et al. 330). If undertaken by a group of bullies, direct and indirect bullying can be referred to as pack bullying. The different types of bullying can be defined either directly or indirectly relative to the implication to the victim.
Physical bullying occurs when there is unwanted physical contact between the victim and the bully. Physical contact can be hand to hand or tripping and throwing items at others that can cause physical harm. The second is emotional bullying. Emotional bullying can be defined as hurting others emotionally by negatively influencing their moods and psyche. The primary examples of emotional bullying include; belittling, spreading false information, and defamation. Verbal bullying can be defined as the usage of slanderous language or statements causing emotional distress to other people. Examples of verbal bullying include harassing, mocking, teasing, and threatening to cause harm. Finally, Cyberbullying is attached to the evolution of the internet and computers. The use of computers in bullying at schoolyards is on the surge. In most instances, schools experience difficulties in controlling cyberbullying as experiences are beyond the school fraternity.
The other common types of school bullying are sexual bullying and higher education bullying. Sexual bullying is either non-physical or physical, grounded on the gender or sexuality of the victim. In most instances, sexual bullying is undertaken by the male gender. The United States department of education reports an average of 60% of expulsions and suspensions from learning institutions attached to sexual bullying (Goodwin et al. 328). In most instances, the young ones are frames into tricks to share their nudes, after which there are forced to fulfill specific sexual demands at the expense of exposure. Higher education bullying occurs at the campus or college level. Around 95% of students have reported having been bullied at the college level. Higher education bullying results in depression and suicide in most cases.
Measures to Control Bullying
The main approaches in controlling bullying in school settings include the implementation of educative programs, creating a positive school climate, engaging parents, encouraging open communication and punishments. These techniques, however, vary depending on the learning level and the prevalence of bullying in the particular period. Education programs involve creating awareness to parents, students, and teachers regarding what constitutes bullying. Educative programs are instrumental in creating insight into the harmful nature of whichever kind of bullying. All the stakeholders within the school fraternity are enrolled in sessions of creating awareness on the signs of bullying and the most appropriate intervention criteria. The most common ways in educating on bullying include role-play, identification and reporting discussions, and other approaches to decline being involved in bullying. Nickerson(19) argued that educative programs are 62% effective in curbing the prevalence of bullying in learning institutions.
Secondly, schools can help in the prevention of bullying by promoting a positive school climate. Schools with a positive climate are presumed to have a healthy development, while the negative school climate results in a surge in bullying cases, unsafe feelings, victimization, and aggression. While the elements of positive school culture vary from norms relative to power, relationships, and feelings, it’s evident that a positive climate is a product of a conscious process that becomes self-reinforcing (Goodwin et al. 330). The main determinants of a positive climate include leadership and integrity in learning institutions. Therefore, the ability to have cognitive leaders is an advantage of coping with bullying in schools.
Third, schools should engage parents. Parents spend most of their time with children at the primary level. While there are many stakeholders involved in the lives of the children, parents play an essential role in understanding their behavior. Engaging parents in bullying scenarios means initiating communication on the progress of the children in terms of behavior and performance. Integration between parents and teachers is essential in providing consistent approaches that help yield a more productive and appropriate behavior (Nickerson 22). Parents can help their children recognize while being bullied by others. However, the approach is not viable in urban schools as parents experience difficulties establishing trust with schools.
Finally, schools should initiate open communication techniques. Open communication is essential in building rapport. Having open communication means that students can disclose their problems to teachers. Open communication helps the teachers gain more insight into existing bullies in the school (Nickerson 20). For instance, classroom meetings in grade 4 will enable teachers to obtain crucial information in enacting more controls to curb bullying in schools. Teachers are expected to listen carefully during the class meetings to avoid inflicting fear on the learners. Students should be assured of confidentiality and privacy of the information obtained as any disclosure might attract further bullying.
Effects of School Bullying
The effect of school bullying can be categorized in psychological and academic dimensions. Bullying results in poor performance in school. More than 70% of learners subjected to bullying ends up recording a decline in academic performance. The results are more severe at a young age. Bullying would result in fading of interest and participation of learners in school activities as it results in unexplained injuries linked to affecting concentration (Menesini and Christina 246). The impact of bullying on educational performance is increasingly becoming imminent. Bullying installs fear in learners from attending school regularly, thus affecting their consistency and concentration in class. Based on this explanation, it’s evident that bullied students will experience difficulties in achieving their academic goals. Moreover, bullying is linked with an unsafe learning environment that creates a negative climate of fear and insecurities and the perception that teachers do not care about the welfare of learners, thus decline in quality of education.
Secondly, bullying is associated with psychological problems. While bullying to individuals helps them enhance their personality and perceptions as they grow, it’s presumed that bullying can risk an individual developing an antisocial personality disorder linked to committing crimes. Bullying leads to depression, anxiety, and psychosomatic symptoms, which often leads to alcohol and substance abuse by the victims at a later stage in their lives. It’s argued that victims of depression feel free and open to share their experience with others, unlike in bullying, where the victims would choose to shy talking about the feeling in fear of being bullied again. In the short run, bystanders of the bullying experience may develop the fear, guiltiness, and sadness, and if the experience persists, they might get psychologically drained (Sampson). Therefore, the victims of bullying experiences struggle with insomnia, suicidal thoughts, health problems, and depression. Bullying does affect not only the students but also their classmates and family. Feeling powerless, parents and immediate family members might fall victim to depression and emotional distress. Some parents would invest more time in protecting their children, thus affecting them psychologically and economically.
Causes of Bullying
There are numerous causes of school bullying attached to religion, socioeconomic status, race, and gender. Understanding the reasons why students chose to bully their classmates is significant to teachers in combating bullying. The National Center for Educational Statistics report established that 25% of Blacks, 22% of Caucasians, 17% of Hispanics, and 9% of Asian students were bullied in 2017 (Divecha). Some of the students that bully others have higher levels of courage and confidence and can respond aggressively if threatened by the behavior. Students at the college level get bullied on sexual matters. For instance, the subscribers to LGBTQA sexual orientation get bullied based on their decision as gay or lesbians. Moreover, bullying in schools is caused by other factors attached to families. Students from abuse and divorced families are likely to bully others due to jealousy, anger, and despair.
From the above discussion, it’s evident that school bullying in whichever capacity is detrimental to human dignity. School bullying is increasingly becoming a social problem in modern society. Ideally, there are several types of school bullying attached to different causes. The effects of school bullying can be classified in psychological, economical, and academic dimensions. The primary forms of school form such as verbal, sexual, cyber, psychological, physical, and higher education bullying are categorized into direct and indirect bullying. The intervention strategies to curb bullying should involve all the stakeholders, such as parents, teachers, and students. The main approaches in controlling bullying in school settings include implementing educative programs, creating a positive school climate, engaging parents, and encouraging open communication and punishments.
Works Cited
Divecha, Diana. “What Are the Best Ways to Prevent Bullying in Schools?” Greater Good , https://greatergood.berkeley.edu/article/item/what_are_the_best_ways_to_prevent_bullyi ng_in_schools
Sampson, Rana. “Center for Problem-Oriented Policing.” Arizona State University, https://popcenter.asu.edu/content/bullying-schools-0
Menesini, Ersilia, and Christina Salmivalli. “Bullying in schools: the state of knowledge and effective interventions.” Psychology, health & medicine 22.sup1 (2017): 240-253.
Goodwin, John, et al. “Bullying in schools: an evaluation of the use of drama in bullying prevention.” Journal of Creativity in Mental Health 14.3 (2019): 329-342.
Nickerson, Amanda B. “Preventing and intervening with bullying in schools: A framework for evidence- based practice.” School Mental Health 11.1 (2019): 15-28.

Cite this page
Similar essay samples.
- Essay on Personal Epistemology
- Essay on How Can Human Trafficking Be Reduced in the US
- Embracing the CRT
- The female body as vessel of memory/hope in Platonov’s Dzhan
- Essay on Motor Skills
- Essay on the Fighting During the Revolutionary War

The Broad Impact of School Bullying, and What Must Be Done
Major interventions are required to make schools safe learning environments..
Posted May 2, 2021 | Reviewed by Hara Estroff Marano
- How to Handle Bullying
- Find a therapist to support kids or teens
- At least one in five kids is bullied, and a significant percentage are bullies. Both are negatively affected, as are bystanders.
- Bullying is an epidemic that is not showing signs of improvement.
- Evidence-based bullying prevention programs can be effective, but school adoption is inconsistent.
According to the U.S. federal government website StopBullying.gov :
There is no federal law that specifically applies to bullying . In some cases, when bullying is based on race or ethnicity , color, national origin, sex, disability, or religion, bullying overlaps with harassment and schools are legally obligated to address it.
The National Bullying Prevention Center reports data suggesting that one in five children have been bullied. There are many risk factors for being targeted, including being seen as weak, being different from peers including being LGBT or having learning differences or visible disabilities, being depressed or anxious, and having few friends. It's hard to measure how many engage in bullying, but estimates range from one in twenty, to much higher .
The American Association of University Women reports that in grades 7-12, 48 percent of students (56 percent of girls and 40 percent of boys) are sexually harassed. In college, rates of sexual harassment rise to 66 percent. Eleven percent are raped or sexually assaulted.
Silence facilitates traumatization
Only 20 percent of attacked young women report sexual assault . And 89 percent of undergraduate schools report zero sexual harassment. This means that children, adolescents, young adults and their friends are at high risk for being victimized. It means that many kids know what is happening, and don't do anything.
This may be from fear of retaliation and socialization into a trauma-permissive culture, and it may be from lack of proper education and training. Institutional betrayal , when organizations fail to uphold their promises and responsibilities, adds to the problem.
In some states such as New York, laws like “ the Dignity for All Students Act ” (DASA) apply only to public schools. Private, religious, and denominational schools are not included, leaving 20 percent of students in NYC and 10 percent throughout the state unprotected. Research shows that over the last decade, bullying in U.S. high schools has held steady around 20 percent, and 15 percent for cyberbullying.
The impact of bullying
While there is much research on how bullying affects mental health, social function, and academics, the results are scattered across dozens of papers. A recent paper in the Journal of School Violence (Halliday et al., 2021) presents a needed systematic literature review on bullying’s impact in children aged 10-18.
1. Psychological: Being a victim of bullying was associated with increased depression , anxiety , and psychosis . Victims of bullying reported more suicidal thinking and engaged in greater self-harming behaviors. They were more likely to experience social anxiety , body-image issues, and negative conduct. Simultaneous cyberbullying and conventional bullying were associated with more severe depression.
2. Social: Bullying victims reported greater problems in relationships with family, friends and in day-to-day social interactions. They reported they enjoyed time with family and friends less, felt they were being treated unfairly more easily, and liked less where they lived. Victimized children were less popular and likeable, and experienced more social rejection. They tended to be friends with other victims, potentially heightening problems while also providing social support.
3. Academic achievement: Victimized kids on average had lower grades. Over time, they did worse especially in math. They tended to be more proficient readers, perhaps as a result of turning to books for comfort in isolation (something people with a history of being bullied commonly report in therapy ).

4. School attitudes: Bullied children and adolescents were less engaged in education, had poorer attendance, felt less belonging, and felt more negatively about school.
5. What happens with age? Researchers studied adult psychiatric outcomes of bullying, looking at both victims and bullies, reported in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) Psychiatry (Copeland et al., 2013). After controlling for other childhood hardships, researchers found that young adults experience increased rates of agoraphobia (fear of leaving the house), generalized anxiety, panic disorder, and increased depression risk. Men had higher suicide risk.
The impact of bullying does not stop in early adulthood. Research in the Journals of Gerontology (Hu, 2021) found that people over the age of 60 who were bullied as children had more severe depression and had lower life satisfaction.
6. Bullying and the brain: Work reported in Frontiers in Psychiatry (Muetzel et al., 2019) found that victims of bullying had thickening of the fusiform gyrus, an area of the cerebral cortex involved with facial recognition, and sensing emotions from facial expressions. 1 For those with posttraumatic stress disorder, brain changes may be extensive.
7. Bystanders are affected: Research also shows that bystanders have higher rates of anxiety and depression (Midgett et al., 2019). The problem is magnified for bystanders who are also victims. It is likely that taking appropriate action is protective.
Given that victims of bullying are at risk for posttraumatic stress disorder ( PTSD ; Idsoe et al., 2012), it’s important to understand that many of the reported psychiatric findings may be better explained by PTSD than as a handful of overlapping but separate diagnoses. Trauma often goes unrecognized.
What can be done?
The psychosocial and academic costs of unmitigated bullying are astronomical, to say nothing of the considerable economic cost. Change is needed, but resistance to change, as with racism, gender bias, and other forms of discrimination , is built into how we see things.
Legislation: There is no federal antibullying legislation, and state laws may be weak and inconsistently applied. Given that bullying rates are no longer falling, it’s important for lawmakers and advocates to seek immediate changes.
Bullying prevention: Schools can adopt antibullying programs, though they are not universally effective and sometimes may backfire. Overall, however, research in JAMA Pediatrics (Fraguas et al., 2021) shows that antibullying programs reduce bullying, improve mental health outcomes, and stay effective over time. 2
Trauma-informed education creates an environment in which all participants are aware of the impact of childhood trauma and the need for specific modifications given how trauma is common among children and how it affects development.
According to the National Child Traumatic Stress Network (NCTSN):
"The primary mission of schools is to support students in educational achievement. To reach this goal, children must feel safe, supported, and ready to learn. Children exposed to violence and trauma may not feel safe or ready to learn. Not only are individual children affected by traumatic experiences, but other students, the adults on campus, and the school community can be impacted by interacting or working with a child who has experienced trauma. Thus, as schools maintain their critical focus on education and achievement, they must also acknowledge that mental health and wellness are innately connected to students’ success in the classroom and to a thriving school environment."
Parenting makes a difference. Certain parenting styles may set kids up for emotional abuse in relationships , while others may be protective. A 2019 study reported in Frontiers in Public Health (Plexousakis et al.) found that children with anxious, overprotective mothers were more likely to be victims.
Those with cold or detached mothers were more likely to become bullies. Overprotective fathering was associated with worse PTSD symptoms, likely by getting in the way of socialization. The children of overprotective fathers were also more likely to be aggressive.
Quality parental bonding, however, appeared to help protect children from PTSD symptoms. A healthy home environment is essential both for helping victims of bullying and preventing bullying in at-risk children.
Parents who recognize the need to learn more positive approaches can help buffer again the all-too-common cycle of passing trauma from generation to generation, building resilience and nurturing secure attachment to enjoy better family experiences and equip children to thrive.
State-by-state legislation
Bullying prevention programs (the KiVA program is also notable)
Measuring Bullying Victimization, Perpetration and Bystander Experiences , Centers for Disease Control
Trauma-informed teaching
US Government Stop Bullying
1. Such differences could both result from being bullied (e.g. needing to scan faces for threat) and could also make being bullied more likely (e.g. misreading social cues leading to increased risk of being targeted).
2. Such programs focus on reducing negative messaging in order to keep stakeholders engaged, monitor and respond quickly to bullying, involve students in bullying prevention and detection in positive ways (e.g. being an “upstander” instead of a bystander), monitor more closely for bullying when the risk is higher (e.g. after anti-bullying trainings), respond fairly with the understanding that bullies often have problems of their own and need help, involved parents and teachers in anti-bullying education, and devote specific resources for anti-bullying.
Sarah Halliday, Tess Gregory, Amanda Taylor, Christianna Digenis & Deborah Turnbull (2021): The Impact of Bullying Victimization in Early Adolescence on Subsequent Psychosocial and Academic Outcomes across the Adolescent Period: A Systematic Review, Journal of School Violence, DOI: 10.1080/15388220.2021.1913598
Copeland WE, Wolke D, Angold A, Costello EJ. Adult Psychiatric Outcomes of Bullying and Being Bullied by Peers in Childhood and Adolescence. JAMA Psychiatry. 2013;70(4):419–426. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2013.504
Bo Hu, PhD, Is Bullying Victimization in Childhood Associated With Mental Health in Old Age, The Journals of Gerontology: Series B, Volume 76, Issue 1, January 2021, Pages 161–172, https://doi.org/10.1093/geronb/gbz115
Muetzel RL, Mulder RH, Lamballais S, Cortes Hidalgo AP, Jansen P, Güroğlu B, Vernooiji MW, Hillegers M, White T, El Marroun H and Tiemeier H (2019) Frequent Bullying Involvement and Brain Morphology in Children. Front. Psychiatry 10:696. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00696
Midgett, A., Doumas, D.M. Witnessing Bullying at School: The Association Between Being a Bystander and Anxiety and Depressive Symptoms. School Mental Health 11, 454–463 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12310-019-09312-6
Idsoe, T., Dyregrov, A. & Idsoe, E.C. Bullying and PTSD Symptoms. J Abnorm Child Psychol 40, 901–911 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-012-9620-0
Fraguas D, Díaz-Caneja CM, Ayora M, Durán-Cutilla M, Abregú-Crespo R, Ezquiaga-Bravo I, Martín-Babarro J, Arango C. Assessment of School Anti-Bullying Interventions: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. JAMA Pediatr. 2021 Jan 1;175(1):44-55. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.3541. PMID: 33136156; PMCID: PMC7607493.
Plexousakis SS, Kourkoutas E, Giovazolias T, Chatira K and Nikolopoulos D (2019) School Bullying and Post-traumatic Stress Disorder Symptoms: The Role of Parental Bonding. Front. Public Health 7:75. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2019.00075
Note: An ExperiMentations Blog Post ("Our Blog Post") is not intended to be a substitute for professional advice. We will not be liable for any loss or damage caused by your reliance on information obtained through Our Blog Post. Please seek the advice of professionals, as appropriate, regarding the evaluation of any specific information, opinion, advice, or other content. We are not responsible and will not be held liable for third-party comments on Our Blog Post. Any user comment on Our Blog Post that in our sole discretion restricts or inhibits any other user from using or enjoying Our Blog Post is prohibited and may be reported to Sussex Publishers/Psychology Today. Grant H. Brenner. All rights reserved.

Grant Hilary Brenner, M.D., a psychiatrist and psychoanalyst, helps adults with mood and anxiety conditions, and works on many levels to help unleash their full capacities and live and love well.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

At any moment, someone’s aggravating behavior or our own bad luck can set us off on an emotional spiral that threatens to derail our entire day. Here’s how we can face our triggers with less reactivity so that we can get on with our lives.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
Greater Good Science Center • Magazine • In Action • In Education
What Are the Best Ways to Prevent Bullying in Schools?
All 50 U.S. states require schools to have a bullying prevention policy.
But a policy, alone, is not enough. Despite the requirement, there’s been a slight uptick in all forms of bullying during the last three years. Bullying can look like experienced basketball players systematically intimidating novice players off the court, kids repeatedly stigmatizing immigrant classmates for their cultural differences, or a middle-school girl suddenly being insulted and excluded by her group of friends.
Bullying occurs everywhere, even in the highest-performing schools, and it is hurtful to everyone involved, from the targets of bullying to the witnesses—and even to bullies themselves. October is National Bullying Prevention Month, so it’s a good time to ask ourselves: What are the best practices for preventing bullying in schools? That’s a question I explored with my colleague Marc Brackett from the Yale Center for Emotional Intelligence, in a recent paper, Rethinking School-Based Bullying Prevention Through the Lens of Social and Emotional Learning , that reviewed dozens of studies of real-world bullying prevention efforts.

As we discovered, not all approaches to bullying prevention are equally effective. Most bullying prevention programs focus on raising awareness of the problem and administering consequences. But programs that rely on punishment and zero tolerance have not been shown to be effective in the U.S.; and they often disproportionately target students of color. Programs like peer mediation that place responsibility on the children to work out conflicts can increase bullying. (Adult victims of abuse are never asked to “work it out” with their tormentor, and children have an additional legal right to protections due to their developmental status.) Bystander intervention, even among adults, only works for some people—extroverts, empaths, and people with higher social status and moral engagement. Many approaches that educators adopt have not been evaluated through research; instead, educators tend to select programs based on what their colleagues use.
We found two research-tested approaches that show the most promise for reducing bullying (along with other forms of aggression and conflict). They are a positive school climate, and social and emotional learning.
Building a positive school climate
School climate can be difficult to define, though possible to measure . It is the “felt sense” of being in a school, which can arise from a greeting, the way a problem is resolved, or how people work together; it is a school’s “heart and soul,” its “quality and character.” Schools with a positive climate foster healthy development, while a negative school climate is associated with higher rates of student bullying, aggression, victimization, and feeling unsafe.

GGSC Online Courses for Educators
A suite of practical, self-paced courses to help build kinder, happier schools
The elements of a positive climate may vary, but may often include norms about feelings and relationships, power and how it is expressed, and media consumption. Social norm engineering is a conscious process that builds a positive culture among student peers and school adults that becomes self-reinforcing. Like a healthy immune system, a positive school climate promotes optimal health and reduces the chances of dysfunction or disease.
Leadership is key to a positive climate. Is bullying minimized as a “normal rite of childhood,” or is it recognized as the harmful peer abuse that it is? Do leaders understand that uninterrupted, severe bullying can confer lifelong negative consequences on targets of bullies, bullies, and witnesses? Are school leaders committed to promoting all children’s positive psychological health, or do they over-rely on punishing misbehavior? Can they discern between typical developmental processes that need guidance versus bullying that needs assertive intervention? Are educators empathic to their students, and do they value children’s feelings?
Next, are teachers prepared to deal with bullying? Students consistently report that teachers miss most incidents of bullying and fail to help students when asked. A majority of teachers report that they feel unprepared to deal with classroom bullying. Some teachers bully students themselves , or show a lack of empathy toward children who are bullied. Teachers report that they receive little guidance in “classroom management,” and sometimes default to the disciplinary strategies they learned in their own families growing up.
However, reforming school climate should involve all stakeholders—students and parents, as well as the administrators and teachers—so a school’s specific issues can be addressed, and the flavor of local cultures retained. School climate assessments can be completed periodically to track the impact of improvements.
Advancing social and emotional learning
Social and emotional learning (SEL) is well known, and involves teaching skills of self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, responsible decision making, and relationships management. (Full disclosure: Brackett and I are affiliated with the SEL program RULER .)
Evidence-based SEL approaches have been shown to deliver cost-effective, solid results. Numerous meta-analyses , research reviews , and individual studies of hundreds of thousands of K-12 students show that SEL improves emotional well-being, self-regulation, classroom relationships, and kind and helpful behavior among students. It reduces a range of problems like anxiety, emotional distress, and depression; reduces disruptive behaviors like conflicts, aggression, bullying, anger, and hostile attribution bias; and it improves academic achievement, creativity, and leadership.
A 2012 study of 36 first-grade teachers showed that when teachers were more emotionally supportive of students, children were less aggressive and had greater behavioral self-control, compared to the use of behavior management, which did not improve student self-control. One 2018 meta-analysis showed that developing emotional competence was protective against becoming a victim of bullying; social competence and academic performance were protective against becoming a bully; and positive peer interactions were protective against becoming a bully-victim (one who has been bullied and bullies others). A series of longitudinal studies showed positive effects into midlife (e.g., fewer divorces, less unemployment) and even cross-generational effects of early SEL. Compared to a matched control group, the children of the adults who participated in the Perry Preschool Project had less criminal involvement and higher educational and employment achievement. A cost-benefit analysis of six SEL programs found them to be good investments, with $11 saved for every $1 spent.
Teachers also benefit from SEL. Those with emotional and social skills training have higher job satisfaction and less burnout, show more positive emotions toward their students, manage their classrooms better, and use more strategies that cultivate creativity, choice, and autonomy in their students. Teachers report that they want more SEL support to cultivate their own emotional and social skills, and to better understand their students’ feelings. But few teacher training programs focus on growing the teachers’ emotion regulation skills.
Bullying at different age levels
SEL approaches should be developmentally wise , since what is salient and possible for children changes at different ages.
For example, preschoolers are expelled from school at the highest rates of all, but the neurological hardware for their self-control is only just developing. Only then are the connections between the emotion circuitry and the more thinking regions of the prefrontal cortex beginning to be myelinated (insulated for faster connectivity), something that will take until the mid 20s to complete. An SEL program like PATHS or RULER that teaches young children language for feelings, and strategies for thinking before acting, can develop better self-regulation.
Sometimes, adults confuse normal developmental processes with bullying. For example, children begin to reorganize their friendships midway through elementary school, something that can naturally create hurt feelings and interpersonal conflict. It should not be misconstrued as bullying, though, which involves intentional, repeated aggression within an imbalance of power. Normal development also includes experimenting with power, and these normal dynamics should be guided safely toward developing a healthy sense of agency, rather than a hurtful exertion of power over someone else.
Finally, the onset of puberty marks the beginning of heightened sensitivity to social relationships, an especially important time to cultivate skills for kinder, gentler relationships. Unfortunately, this is the period when bullying spikes the highest. And while some strategies work well for younger children (for example, advising them to “tell a trusted adult”), this option may fail with teens, and the breakpoint seems to be around the eighth grade. Older teens require approaches that are less didactic and leverage their need for autonomy, while affirming their values and search for meaning. Physiologically, the brain changes during puberty confer a second chance for recalibrating their stress regulation system. That opportunity should be constructively seized.
Approaches should also take into account individual differences between children. Even SEL programs can stumble here, over-relying on just one or two emotion regulation strategies, like breathing or mindfulness. But children vary in their temperaments, sensitivities, strengths, and vulnerabilities. The best SEL approaches guide students toward discovering strategies that work best for them—strategies that are emotion- and context-specific, personalized, and culturally responsive. This approach requires unconventional flexibility on the part of the educators.
And, finally, approaches work best if they are not standalone pedagogies or from kits that end up in the classroom closet at the end of the year. In order to be effective, skills should become fully embedded across the curricula and the entire day, in all settings, and implemented by all adults—in other words, infiltrating the ecosystem. Only approaches used and taught as intended are successful.
Schools can’t do this alone
Families matter, too. Bullying in schools sometimes arises from harsh parenting practices or sibling bullying at home.
Even parents’ workplaces matter. Adults experience bullying in their workplaces at about the same rate as children in schools, and it’s even found among teachers and in senior living communities . In other words, bullying is not just a childhood problem; it is a pervasive human problem. And children are not buffered from the wider social world—bullying of children who belong to groups targeted in the national political discourse has spiked on playgrounds nationwide.
Ultimately, we need a substantial shift in our mindsets about the importance of children and their feelings. Children are more likely to thrive when we nurture their humanity, and offer them language and strategies and values to help them identify, express, and, thus, regulate their feelings. When parents, teachers, and administrators gain new awareness into the complex roots of bullying and adopt new strategies for addressing it, schools can lead the way. The kids are counting on us.

Courage in Education: Facing Challenges with Strength, Determination, and Hope
A new online course to help educators cultivate courage in schools and classrooms.
About the Author

Diana Divecha
Diana Divecha, Ph.D. , is a developmental psychologist, an assistant clinical professor at the Yale Child Study Center and Yale Center for Emotional Intelligence, and on the advisory board of the Greater Good Science Center. Her blog is developmentalscience.com .
You May Also Enjoy

Playground Heroes

How to Bullyproof Your Kid

How Bullied Children Grow into Wounded Adults

The Bully Problem

Could Gay-Straight Alliances Reduce Bullying?
Eight keys to end bullying.
What you need to know about school violence and bullying

Bullying in schools deprives millions of children and young people of their fundamental right to education. A recent UNESCO report revealed that more than 30% of the world's students have been victims of bullying, with devastating consequences on academic achievement, school dropout, and physical and mental health.
The world is marking the first International Day against Violence and Bullying at School Including Cyberbullying , on 5 November. Here is what you need to know about school violence and bullying.
What is school violence?
School violence refers to all forms of violence that takes place in and around schools and is experienced by students and perpetrated by other students, teachers and other school staff. This includes bullying and cyberbullying. Bullying is one of the most pervasive forms of school violence, affecting 1 in 3 young people.
What forms may school violence take?
Based on existing international surveys that collect data on violence in schools, UNESCO recognizes the following forms of school violence:
- Physical violence, which is any form of physical aggression with intention to hurt perpetrated by peers, teachers or school staff.
- Psychological violence as verbal and emotional abuse, which includes any forms of isolating, rejecting, ignoring, insults, spreading rumors, making up lies, name-calling, ridicule, humiliation and threats, and psychological punishment.
- Sexual violence, which includes intimidation of a sexual nature, sexual harassment, unwanted touching, sexual coercion and rape, and it is perpetrated by a teacher, school staff or a schoolmate or classmate.
- Physical bullying, including hitting, kicking and the destruction of property;
- Psychological bullying, such as teasing, insulting and threatening; or relational, through the spreading of rumours and exclusion from a group; and
- Sexual bullying, such as making fun of a victim with sexual jokes, comments or gestures, which may be defined as sexual ‘harassment’ in some countries.
- Cyberbullying is a form of psychological or sexual bullying that takes place online. Examples of cyberbullying include posting or sending messages, pictures or videos, aimed at harassing, threatening or targeting another person via a variety of media and social media platforms. Cyberbullying may also include spreading rumours, posting false information, hurtful messages, embarrassing comments or photos, or excluding someone from online networks or other communications.
Who perpetrates school violence?
School violence is perpetrated by students, teachers and other school staff. However, available evidence shows that violence perpetrated by peers is the most common.
What are the main reasons why children are bullied?
All children can be bullied, yet evidence shows that children who are perceived to be “different” in any way are more at risk. Key factors include physical appearance, ethnic, linguistic or cultural background, gender, including not conforming to gender norms and stereotypes; social status and disability.
What are the consequences of school violence?
Educational consequences: Being bullied undermines the sense of belonging at school and affects continued engagement in education. Children who are frequently bullied are more likely to feel like an outsider at school, and more likely to want to leave school after finishing secondary education. Children who are bullied have lower academic achievements than those who are not frequently bullied.
Health consequences: Children’s mental health and well-being can be adversely impacted by bullying. Bullying is associated with higher rates of feeling lonely and suicidal, higher rates of smoking, alcohol and cannabis use and lower rates of self-reported life satisfaction and health. School violence can also cause physical injuries and harm.
What are the linkages between school violence and bullying, school-related gender-based violence and violence based on sexual orientation and gender identity or expression?
School violence may be perpetrated as a result of gender norms and stereotypes and enforced by unequal power dynamics and is therefore referred to as school-related gender-based violence. It includes, in particular, a specific type of gender-based violence that is linked to the actual or perceived sexual orientation and gender identity or expression of victims, including homophobic and transphobic bullying. School-related gender-based violence is a significant part of school violence that requires specific efforts to address.
Does school-related gender-based violence refer to sexual violence against girls only?
No. School-related gender-based violence refers to all forms of school violence that is based on or driven by gender norms and stereotypes, which also includes violence against and between boys.
Is school violence always gender-based?
There are many factors that drive school violence. Gender is one of the significant drivers of violence but not all school violence is based on gender. Moreover, international surveys do not systematically collect data on the gendered nature of school violence, nor on violence based on sexual orientation and gender identity or expression.
Based on the analysis of global data, there are no major differences in the prevalence of bullying for boys and girls. However, there are some differences between boys and girls in terms of the types of bullying they experience. Boys are much more exposed to physical bullying, and to physical violence in general, than girls. Girls are slightly more exposed to psychological bullying, particularly through cyberbullying. According to the same data, sexual bullying the same proportion of boys and girls. Data coming from different countries, however, shows that girls are increasingly exposed to sexual bullying online.
How does UNESCO help prevent and address school violence and bullying?
The best available evidence shows that responses to school violence and bullying that are effective should be comprehensive and include a combination of policies and interventions. Often this comprehensive response to school violence and bullying is referred to as a whole-school approach. Based on an extensive review of existing conceptual frameworks that describe that whole-school approach, UNESCO has identified nine key components of a response that goes beyond schools and could be better described as a whole-education system or whole-education approach. These components are the following:
- Strong political leadership and robust legal and policy framework to address school violence and bullying;
- Training and support for teachers on school violence and bullying prevention and positive classroom management
- Curriculum, learning & teaching to promote, a caring (i.e. anti- school violence and bullying) school climate and students’ social and emotional skills
- A safe psychological and physical school and classroom environment
- Reporting mechanisms for students affected by school violence and bullying, together with support and referral services
- Involvement of all stakeholders in the school community including parents
- Student empowerment and participation
- Collaboration and partnerships between the education sector and a wide range of partners (other government sectors, NGOs, academia)
- Evidence: monitoring of school violence and bullying and evaluation of responses
More on UNESCO’s work to prevent and address school violence and bullying
Read UNESCO's publication Behind the numbers: Ending school violence and bullying
Photo: Eakachai Leesin/Shutterstock.com

Event International Conference of the Memory of the World Programme, incorporating the 4th Global Policy Forum 28 October 2024 - 29 October 2024

Other recent articles

Articles on Bullying in schools
Displaying 1 - 20 of 21 articles.

Emotional problems in young people were rising rapidly even before the pandemic
Rebecca E Anthony , Cardiff University

Disruptive kindergartners are likely to be bullied later in elementary school
Paul L. Morgan , Penn State

School students who had COVID-19 report stigma and bullying. How can we stop it?
Brian Moore , Charles Sturt University and Stuart Woodcock , Griffith University
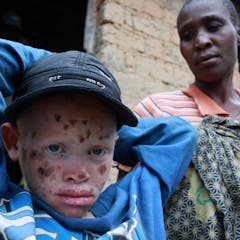
Taunts and bullying drive children with albinism from Tanzanian schools
Simon Ngalomba , University of Dar es Salaam
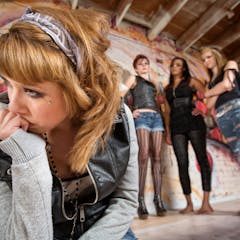
Bullying linked to gender and sexuality often goes unchecked in schools
Victoria Rawlings , University of Sydney

Is your child less likely to be bullied in a private school?
Karyn Healy , The University of Queensland

Cutting down the tall poppies: female athletes bullied in Aussie schools
Maureen O'Neill , University of the Sunshine Coast and Angie Calder , University of the Sunshine Coast

How to reduce prejudice among groups of children at school
Luke McGuire , Goldsmiths, University of London

It shouldn’t take legal action for schools to act on bullying
Sally Varnham , University of Technology Sydney

Nearly a third of early adulthood depression linked to bullying in teenage years
Lucy Bowes , University of Oxford

What to do when your child is the bully, rather than the victim
Natalie Swayn, University of New England ; Christopher Boyle , University of New England , and Dr Joanna Anderson , University of New England

What should parents do if their child is bullied at school?

Telling kids homophobia is wrong won’t stop bullying in schools
Mary Lou Rasmussen , Monash University ; Fida Sanjakdar , Monash University ; Kathleen Quinlivan , University of Canterbury , and Louisa Allen , University of Auckland, Waipapa Taumata Rau

Everyone has a part to play in managing classroom bullying
Barbara Spears , University of South Australia

How parents can prevent and deal with bullying
Sheryl Hemphill , Australian Catholic University

How to handle bullies
Phillip Slee , Flinders University

The difference between ‘bullying’ and ‘everyday life’
Marilyn Campbell , Queensland University of Technology

What works best to help stop bullying in schools?
Peter K Smith , Goldsmiths, University of London and Fran Thompson , Goldsmiths, University of London

It’s the permanence of online abuse that makes cyberbullying so damaging for children
Chris Kyriacou , University of York

Who are more likely to be bullies – poor kids or rich kids?
Neil Tippett , University of Warwick and Dieter Wolke , University of Warwick
Related Topics
- Author Q&A
- Bullying prevention
- Child behaviour
- Cyberbullying
- Mental health
- Non-government schools
- School bullying
- Special needs
Top contributors
Researcher, The University of Queensland
Professor, School of Sociology, Australian National University
Professor of Psychology, University of Warwick
Leverhulme Early Career Research Fellow, University of Oxford
Professor in Educational Psychology, University of York
Research Fellow, Manchester Institute of Education, University of Manchester
PhD student, University of Warwick
Adjunct Professor of Education and Social Development, University of South Australia
Professor, School of Early Childhood & Inclusive Education, Queensland University of Technology
Professor, Human Development, School of Education, Flinders University
Emeritus Professor, Unit for School and Family Studies, Department of Psychology, Goldsmiths, University of London
Researcher, Unit for School and Family Studies, Department of Psychology, Goldsmiths, University of London
Associated professor at the Department of Education at Federal University of São Carlos, Brazil and academic visiting scholar, department of education, University of York
Professor of Psychology, Australian Catholic University
Senior Lecturer in Inclusive Education, University of New England
- X (Twitter)
- Unfollow topic Follow topic

Preventing Bullying Through Science, Policy, and Practice (2016)
Chapter: 1 introduction, 1 introduction.
Bullying, long tolerated by many as a rite of passage into adulthood, is now recognized as a major and preventable public health problem, one that can have long-lasting consequences ( McDougall and Vaillancourt, 2015 ; Wolke and Lereya, 2015 ). Those consequences—for those who are bullied, for the perpetrators of bullying, and for witnesses who are present during a bullying event—include poor school performance, anxiety, depression, and future delinquent and aggressive behavior. Federal, state, and local governments have responded by adopting laws and implementing programs to prevent bullying and deal with its consequences. However, many of these responses have been undertaken with little attention to what is known about bullying and its effects. Even the definition of bullying varies among both researchers and lawmakers, though it generally includes physical and verbal behavior, behavior leading to social isolation, and behavior that uses digital communications technology (cyberbullying). This report adopts the term “bullying behavior,” which is frequently used in the research field, to cover all of these behaviors.
Bullying behavior is evident as early as preschool, although it peaks during the middle school years ( Currie et al., 2012 ; Vaillancourt et al., 2010 ). It can occur in diverse social settings, including classrooms, school gyms and cafeterias, on school buses, and online. Bullying behavior affects not only the children and youth who are bullied, who bully, and who are both bullied and bully others but also bystanders to bullying incidents. Given the myriad situations in which bullying can occur and the many people who may be involved, identifying effective prevention programs and policies is challenging, and it is unlikely that any one approach will be ap-
propriate in all situations. Commonly used bullying prevention approaches include policies regarding acceptable behavior in schools and behavioral interventions to promote positive cultural norms.
STUDY CHARGE
Recognizing that bullying behavior is a major public health problem that demands the concerted and coordinated time and attention of parents, educators and school administrators, health care providers, policy makers, families, and others concerned with the care of children, a group of federal agencies and private foundations asked the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine to undertake a study of what is known and what needs to be known to further the field of preventing bullying behavior. The Committee on the Biological and Psychosocial Effects of Peer Victimization:
Lessons for Bullying Prevention was created to carry out this task under the Academies’ Board on Children, Youth, and Families and the Committee on Law and Justice. The study received financial support from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, the Health Resources and Services Administration, the Highmark Foundation, the National Institute of Justice, the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, Semi J. and Ruth W. Begun Foundation, and the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. The full statement of task for the committee is presented in Box 1-1 .
Although the committee acknowledges the importance of this topic as it pertains to all children in the United States and in U.S. territories, this report focuses on the 50 states and the District of Columbia. Also, while the committee acknowledges that bullying behavior occurs in the school
environment for youth in foster care, in juvenile justice facilities, and in other residential treatment facilities, this report does not address bullying behavior in those environments because it is beyond the study charge.
CONTEXT FOR THE STUDY
This section of the report highlights relevant work in the field and, later in the chapter under “The Committee’s Approach,” presents the conceptual framework and corresponding definitions of terms that the committee has adopted.
Historical Context
Bullying behavior was first characterized in the scientific literature as part of the childhood experience more than 100 years ago in “Teasing and Bullying,” published in the Pedagogical Seminary ( Burk, 1897 ). The author described bullying behavior, attempted to delineate causes and cures for the tormenting of others, and called for additional research ( Koo, 2007 ). Nearly a century later, Dan Olweus, a Swedish research professor of psychology in Norway, conducted an intensive study on bullying ( Olweus, 1978 ). The efforts of Olweus brought awareness to the issue and motivated other professionals to conduct their own research, thereby expanding and contributing to knowledge of bullying behavior. Since Olweus’s early work, research on bullying has steadily increased (see Farrington and Ttofi, 2009 ; Hymel and Swearer, 2015 ).
Over the past few decades, venues where bullying behavior occurs have expanded with the advent of the Internet, chat rooms, instant messaging, social media, and other forms of digital electronic communication. These modes of communication have provided a new communal avenue for bullying. While the media reports linking bullying to suicide suggest a causal relationship, the available research suggests that there are often multiple factors that contribute to a youth’s suicide-related ideology and behavior. Several studies, however, have demonstrated an association between bullying involvement and suicide-related ideology and behavior (see, e.g., Holt et al., 2015 ; Kim and Leventhal, 2008 ; Sourander, 2010 ; van Geel et al., 2014 ).
In 2013, the Health Resources and Services Administration of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services requested that the Institute of Medicine 1 and the National Research Council convene an ad hoc planning committee to plan and conduct a 2-day public workshop to highlight relevant information and knowledge that could inform a multidisciplinary
___________________
1 Prior to 2015, the National Academy of Medicine was known as the Institute of Medicine.
road map on next steps for the field of bullying prevention. Content areas that were explored during the April 2014 workshop included the identification of conceptual models and interventions that have proven effective in decreasing bullying and the antecedents to bullying while increasing protective factors that mitigate the negative health impact of bullying. The discussions highlighted the need for a better understanding of the effectiveness of program interventions in realistic settings; the importance of understanding what works for whom and under what circumstances, as well as the influence of different mediators (i.e., what accounts for associations between variables) and moderators (i.e., what affects the direction or strength of associations between variables) in bullying prevention efforts; and the need for coordination among agencies to prevent and respond to bullying. The workshop summary ( Institute of Medicine and National Research Council, 2014c ) informs this committee’s work.
Federal Efforts to Address Bullying and Related Topics
Currently, there is no comprehensive federal statute that explicitly prohibits bullying among children and adolescents, including cyberbullying. However, in the wake of the growing concerns surrounding the implications of bullying, several federal initiatives do address bullying among children and adolescents, and although some of them do not primarily focus on bullying, they permit some funds to be used for bullying prevention purposes.
The earliest federal initiative was in 1999, when three agencies collaborated to establish the Safe Schools/Healthy Students initiative in response to a series of deadly school shootings in the late 1990s. The program is administered by the U.S. Departments of Education, Health and Human Services, and Justice to prevent youth violence and promote the healthy development of youth. It is jointly funded by the Department of Education and by the Department of Health and Human Services’ Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. The program has provided grantees with both the opportunity to benefit from collaboration and the tools to sustain it through deliberate planning, more cost-effective service delivery, and a broader funding base ( Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, 2015 ).
The next major effort was in 2010, when the Department of Education awarded $38.8 million in grants under the Safe and Supportive Schools (S3) Program to 11 states to support statewide measurement of conditions for learning and targeted programmatic interventions to improve conditions for learning, in order to help schools improve safety and reduce substance use. The S3 Program was administered by the Safe and Supportive Schools Group, which also administered the Safe and Drug-Free Schools and Communities Act State and Local Grants Program, authorized by the
1994 Elementary and Secondary Education Act. 2 It was one of several programs related to developing and maintaining safe, disciplined, and drug-free schools. In addition to the S3 grants program, the group administered a number of interagency agreements with a focus on (but not limited to) bullying, school recovery research, data collection, and drug and violence prevention activities ( U.S. Department of Education, 2015 ).
A collaborative effort among the U.S. Departments of Agriculture, Defense, Education, Health and Human Services, Interior, and Justice; the Federal Trade Commission; and the White House Initiative on Asian Americans and Pacific Islanders created the Federal Partners in Bullying Prevention (FPBP) Steering Committee. Led by the U.S. Department of Education, the FPBP works to coordinate policy, research, and communications on bullying topics. The FPBP Website provides extensive resources on bullying behavior, including information on what bullying is, its risk factors, its warning signs, and its effects. 3 The FPBP Steering Committee also plans to provide details on how to get help for those who have been bullied. It also was involved in creating the “Be More than a Bystander” Public Service Announcement campaign with the Ad Council to engage students in bullying prevention. To improve school climate and reduce rates of bullying nationwide, FPBP has sponsored four bullying prevention summits attended by education practitioners, policy makers, researchers, and federal officials.
In 2014, the National Institute of Justice—the scientific research arm of the U.S. Department of Justice—launched the Comprehensive School Safety Initiative with a congressional appropriation of $75 million. The funds are to be used for rigorous research to produce practical knowledge that can improve the safety of schools and students, including bullying prevention. The initiative is carried out through partnerships among researchers, educators, and other stakeholders, including law enforcement, behavioral and mental health professionals, courts, and other justice system professionals ( National Institute of Justice, 2015 ).
In 2015, the Every Student Succeeds Act was signed by President Obama, reauthorizing the 50-year-old Elementary and Secondary Education Act, which is committed to providing equal opportunities for all students. Although bullying is neither defined nor prohibited in this act, it is explicitly mentioned in regard to applicability of safe school funding, which it had not been in previous iterations of the Elementary and Secondary Education Act.
The above are examples of federal initiatives aimed at promoting the
2 The Safe and Drug-Free Schools and Communities Act was included as Title IV, Part A, of the 1994 Elementary and Secondary Education Act. See http://www.ojjdp.gov/pubs/gun_violence/sect08-i.html [October 2015].
3 For details, see http://www.stopbullying.gov/ [October 2015].
healthy development of youth, improving the safety of schools and students, and reducing rates of bullying behavior. There are several other federal initiatives that address student bullying directly or allow funds to be used for bullying prevention activities.
Definitional Context
The terms “bullying,” “harassment,” and “peer victimization” have been used in the scientific literature to refer to behavior that is aggressive, is carried out repeatedly and over time, and occurs in an interpersonal relationship where a power imbalance exists ( Eisenberg and Aalsma, 2005 ). Although some of these terms have been used interchangeably in the literature, peer victimization is targeted aggressive behavior of one child against another that causes physical, emotional, social, or psychological harm. While conflict and bullying among siblings are important in their own right ( Tanrikulu and Campbell, 2015 ), this area falls outside of the scope of the committee’s charge. Sibling conflict and aggression falls under the broader concept of interpersonal aggression, which includes dating violence, sexual assault, and sibling violence, in addition to bullying as defined for this report. Olweus (1993) noted that bullying, unlike other forms of peer victimization where the children involved are equally matched, involves a power imbalance between the perpetrator and the target, where the target has difficulty defending him or herself and feels helpless against the aggressor. This power imbalance is typically considered a defining feature of bullying, which distinguishes this particular form of aggression from other forms, and is typically repeated in multiple bullying incidents involving the same individuals over time ( Olweus, 1993 ).
Bullying and violence are subcategories of aggressive behavior that overlap ( Olweus, 1996 ). There are situations in which violence is used in the context of bullying. However, not all forms of bullying (e.g., rumor spreading) involve violent behavior. The committee also acknowledges that perspective about intentions can matter and that in many situations, there may be at least two plausible perceptions involved in the bullying behavior.
A number of factors may influence one’s perception of the term “bullying” ( Smith and Monks, 2008 ). Children and adolescents’ understanding of the term “bullying” may be subject to cultural interpretations or translations of the term ( Hopkins et al., 2013 ). Studies have also shown that influences on children’s understanding of bullying include the child’s experiences as he or she matures and whether the child witnesses the bullying behavior of others ( Hellström et al., 2015 ; Monks and Smith, 2006 ; Smith and Monks, 2008 ).
In 2010, the FPBP Steering Committee convened its first summit, which brought together more than 150 nonprofit and corporate leaders,
researchers, practitioners, parents, and youths to identify challenges in bullying prevention. Discussions at the summit revealed inconsistencies in the definition of bullying behavior and the need to create a uniform definition of bullying. Subsequently, a review of the 2011 CDC publication of assessment tools used to measure bullying among youth ( Hamburger et al., 2011 ) revealed inconsistent definitions of bullying and diverse measurement strategies. Those inconsistencies and diverse measurements make it difficult to compare the prevalence of bullying across studies ( Vivolo et al., 2011 ) and complicate the task of distinguishing bullying from other types of aggression between youths. A uniform definition can support the consistent tracking of bullying behavior over time, facilitate the comparison of bullying prevalence rates and associated risk and protective factors across different data collection systems, and enable the collection of comparable information on the performance of bullying intervention and prevention programs across contexts ( Gladden et al., 2014 ). The CDC and U.S. Department of Education collaborated on the creation of the following uniform definition of bullying (quoted in Gladden et al., 2014, p. 7 ):
Bullying is any unwanted aggressive behavior(s) by another youth or group of youths who are not siblings or current dating partners that involves an observed or perceived power imbalance and is repeated multiple times or is highly likely to be repeated. Bullying may inflict harm or distress on the targeted youth including physical, psychological, social, or educational harm.
This report noted that the definition includes school-age individuals ages 5-18 and explicitly excludes sibling violence and violence that occurs in the context of a dating or intimate relationship ( Gladden et al., 2014 ). This definition also highlighted that there are direct and indirect modes of bullying, as well as different types of bullying. Direct bullying involves “aggressive behavior(s) that occur in the presence of the targeted youth”; indirect bullying includes “aggressive behavior(s) that are not directly communicated to the targeted youth” ( Gladden et al., 2014, p. 7 ). The direct forms of violence (e.g., sibling violence, teen dating violence, intimate partner violence) can include aggression that is physical, sexual, or psychological, but the context and uniquely dynamic nature of the relationship between the target and the perpetrator in which these acts occur is different from that of peer bullying. Examples of direct bullying include pushing, hitting, verbal taunting, or direct written communication. A common form of indirect bullying is spreading rumors. Four different types of bullying are commonly identified—physical, verbal, relational, and damage to property. Some observational studies have shown that the different forms of bullying that youths commonly experience may overlap ( Bradshaw et al., 2015 ;
Godleski et al., 2015 ). The four types of bullying are defined as follows ( Gladden et al., 2014 ):
- Physical bullying involves the use of physical force (e.g., shoving, hitting, spitting, pushing, and tripping).
- Verbal bullying involves oral or written communication that causes harm (e.g., taunting, name calling, offensive notes or hand gestures, verbal threats).
- Relational bullying is behavior “designed to harm the reputation and relationships of the targeted youth (e.g., social isolation, rumor spreading, posting derogatory comments or pictures online).”
- Damage to property is “theft, alteration, or damaging of the target youth’s property by the perpetrator to cause harm.”
In recent years, a new form of aggression or bullying has emerged, labeled “cyberbullying,” in which the aggression occurs through modern technological devices, specifically mobile phones or the Internet ( Slonje and Smith, 2008 ). Cyberbullying may take the form of mean or nasty messages or comments, rumor spreading through posts or creation of groups, and exclusion by groups of peers online.
While the CDC definition identifies bullying that occurs using technology as electronic bullying and views that as a context or location where bullying occurs, one of the major challenges in the field is how to conceptualize and define cyberbullying ( Tokunaga, 2010 ). The extent to which the CDC definition can be applied to cyberbullying is unclear, particularly with respect to several key concepts within the CDC definition. First, whether determination of an interaction as “wanted” or “unwanted” or whether communication was intended to be harmful can be challenging to assess in the absence of important in-person socioemotional cues (e.g., vocal tone, facial expressions). Second, assessing “repetition” is challenging in that a single harmful act on the Internet has the potential to be shared or viewed multiple times ( Sticca and Perren, 2013 ). Third, cyberbullying can involve a less powerful peer using technological tools to bully a peer who is perceived to have more power. In this manner, technology may provide the tools that create a power imbalance, in contrast to traditional bullying, which typically involves an existing power imbalance.
A study that used focus groups with college students to discuss whether the CDC definition applied to cyberbullying found that students were wary of applying the definition due to their perception that cyberbullying often involves less emphasis on aggression, intention, and repetition than other forms of bullying ( Kota et al., 2014 ). Many researchers have responded to this lack of conceptual and definitional clarity by creating their own measures to assess cyberbullying. It is noteworthy that very few of these
definitions and measures include the components of traditional bullying—i.e., repetition, power imbalance, and intent ( Berne et al., 2013 ). A more recent study argues that the term “cyberbullying” should be reserved for incidents that involve key aspects of bullying such as repetition and differential power ( Ybarra et al., 2014 ).
Although the formulation of a uniform definition of bullying appears to be a step in the right direction for the field of bullying prevention, there are some limitations of the CDC definition. For example, some researchers find the focus on school-age youth as well as the repeated nature of bullying to be rather limiting; similarly the exclusion of bullying in the context of sibling relationships or dating relationships may preclude full appreciation of the range of aggressive behaviors that may co-occur with or constitute bullying behavior. As noted above, other researchers have raised concerns about whether cyberbullying should be considered a particular form or mode under the broader heading of bullying as suggested in the CDC definition, or whether a separate defintion is needed. Furthermore, the measurement of bullying prevalence using such a definiton of bullying is rather complex and does not lend itself well to large-scale survey research. The CDC definition was intended to inform public health surveillance efforts, rather than to serve as a definition for policy. However, increased alignment between bullying definitions used by policy makers and researchers would greatly advance the field. Much of the extant research on bullying has not applied a consistent definition or one that aligns with the CDC definition. As a result of these and other challenges to the CDC definition, thus far there has been inconsistent adoption of this particular definition by researchers, practitioners, or policy makers; however, as the definition was created in 2014, less than 2 years is not a sufficient amount of time to assess whether it has been successfully adopted or will be in the future.
THE COMMITTEE’S APPROACH
This report builds on the April 2014 workshop, summarized in Building Capacity to Reduce Bullying: Workshop Summary ( Institute of Medicine and National Research Council, 2014c ). The committee’s work was accomplished over an 18-month period that began in October 2014, after the workshop was held and the formal summary of it had been released. The study committee members represented expertise in communication technology, criminology, developmental and clinical psychology, education, mental health, neurobiological development, pediatrics, public health, school administration, school district policy, and state law and policy. (See Appendix E for biographical sketches of the committee members and staff.) The committee met three times in person and conducted other meetings by teleconferences and electronic communication.
Information Gathering
The committee conducted an extensive review of the literature pertaining to peer victimization and bullying. In some instances, the committee drew upon the broader literature on aggression and violence. The review began with an English-language literature search of online databases, including ERIC, Google Scholar, Lexis Law Reviews Database, Medline, PubMed, Scopus, PsycInfo, and Web of Science, and was expanded as literature and resources from other countries were identified by committee members and project staff as relevant. The committee drew upon the early childhood literature since there is substantial evidence indicating that bullying involvement happens as early as preschool (see Vlachou et al., 2011 ). The committee also drew on the literature on late adolescence and looked at related areas of research such as maltreatment for insights into this emerging field.
The committee used a variety of sources to supplement its review of the literature. The committee held two public information-gathering sessions, one with the study sponsors and the second with experts on the neurobiology of bullying; bullying as a group phenomenon and the role of bystanders; the role of media in bullying prevention; and the intersection of social science, the law, and bullying and peer victimization. See Appendix A for the agendas for these two sessions. To explore different facets of bullying and give perspectives from the field, a subgroup of the committee and study staff also conducted a site visit to a northeastern city, where they convened four stakeholder groups comprised, respectively, of local practitioners, school personnel, private foundation representatives, and young adults. The site visit provided the committee with an opportunity for place-based learning about bullying prevention programs and best practices. Each focus group was transcribed and summarized thematically in accordance with this report’s chapter considerations. Themes related to the chapters are displayed throughout the report in boxes titled “Perspectives from the Field”; these boxes reflect responses synthesized from all four focus groups. See Appendix B for the site visit’s agenda and for summaries of the focus groups.
The committee also benefited from earlier reports by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine through its Division of Behavioral and Social Sciences and Education and the Institute of Medicine, most notably:
- Reducing Risks for Mental Disorders: Frontiers for Preventive Intervention Research ( Institute of Medicine, 1994 )
- Community Programs to Promote Youth Development ( National Research Council and Institute of Medicine, 2002 )
- Deadly Lessons: Understanding Lethal School Violence ( National Research Council and Institute of Medicine, 2003 )
- Preventing Mental, Emotional, and Behavioral Disorders Among Young People: Progress and Possibilities ( National Research Council and Institute of Medicine, 2009 )
- The Science of Adolescent Risk-Taking: Workshop Report ( Institute of Medicine and National Research Council, 2011 )
- Communications and Technology for Violence Prevention: Workshop Summary ( Institute of Medicine and National Research Council, 2012 )
- Building Capacity to Reduce Bullying: Workshop Summary ( Institute of Medicine and National Research Council, 2014c )
- The Evidence for Violence Prevention across the Lifespan and Around the World: Workshop Summary ( Institute of Medicine and National Research Council, 2014a )
- Strategies for Scaling Effective Family-Focused Preventive Interventions to Promote Children’s Cognitive, Affective, and Behavioral Health: Workshop Summary ( Institute of Medicine and National Research Council, 2014b )
- Investing in the Health and Well-Being of Young Adults ( Institute of Medicine and National Research Council, 2015 )
Although these past reports and workshop summaries address various forms of violence and victimization, this report is the first consensus study by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine on the state of the science on the biological and psychosocial consequences of bullying and the risk and protective factors that either increase or decrease bullying behavior and its consequences.
Terminology
Given the variable use of the terms “bullying” and “peer victimization” in both the research-based and practice-based literature, the committee chose to use the current CDC definition quoted above ( Gladden et al., 2014, p. 7 ). While the committee determined that this was the best definition to use, it acknowledges that this definition is not necessarily the most user-friendly definition for students and has the potential to cause problems for students reporting bullying. Not only does this definition provide detail on the common elements of bullying behavior but it also was developed with input from a panel of researchers and practitioners. The committee also followed the CDC in focusing primarily on individuals between the ages of 5 and 18. The committee recognizes that children’s development occurs on a continuum, and so while it relied primarily on the CDC defini-
tion, its work and this report acknowledge the importance of addressing bullying in both early childhood and emerging adulthood. For purposes of this report, the committee used the terms “early childhood” to refer to ages 1-4, “middle childhood” for ages 5 to 10, “early adolescence” for ages 11-14, “middle adolescence” for ages 15-17, and “late adolescence” for ages 18-21. This terminology and the associated age ranges are consistent with the Bright Futures and American Academy of Pediatrics definition of the stages of development. 4
A given instance of bullying behavior involves at least two unequal roles: one or more individuals who perpetrate the behavior (the perpetrator in this instance) and at least one individual who is bullied (the target in this instance). To avoid labeling and potentially further stigmatizing individuals with the terms “bully” and “victim,” which are sometimes viewed as traits of persons rather than role descriptions in a particular instance of behavior, the committee decided to use “individual who is bullied” to refer to the target of a bullying instance or pattern and “individual who bullies” to refer to the perpetrator of a bullying instance or pattern. Thus, “individual who is bullied and bullies others” can refer to one who is either perpetrating a bullying behavior or a target of bullying behavior, depending on the incident. This terminology is consistent with the approach used by the FPBP (see above). Also, bullying is a dynamic social interaction ( Espelage and Swearer, 2003 ) where individuals can play different roles in bullying interactions based on both individual and contextual factors.
The committee used “cyberbullying” to refer to bullying that takes place using technology or digital electronic means. “Digital electronic forms of contact” comprise a broad category that may include e-mail, blogs, social networking Websites, online games, chat rooms, forums, instant messaging, Skype, text messaging, and mobile phone pictures. The committee uses the term “traditional bullying” to refer to bullying behavior that is not cyberbullying (to aid in comparisons), recognizing that the term has been used at times in slightly different senses in the literature.
Where accurate reporting of study findings requires use of the above terms but with senses different from those specified here, the committee has noted the sense in which the source used the term. Similarly, accurate reporting has at times required use of terms such as “victimization” or “victim” that the committee has chosen to avoid in its own statements.
4 For details on these stages of adolescence, see https://brightfutures.aap.org/Bright%20Futures%20Documents/3-Promoting_Child_Development.pdf [October 2015].
ORGANIZATION OF THE REPORT
This report is organized into seven chapters. After this introductory chapter, Chapter 2 provides a broad overview of the scope of the problem.
Chapter 3 focuses on the conceptual frameworks for the study and the developmental trajectory of the child who is bullied, the child who bullies, and the child who is bullied and also bullies. It explores processes that can explain heterogeneity in bullying outcomes by focusing on contextual processes that moderate the effect of individual characteristics on bullying behavior.
Chapter 4 discusses the cyclical nature of bullying and the consequences of bullying behavior. It summarizes what is known about the psychosocial, physical health, neurobiological, academic-performance, and population-level consequences of bullying.
Chapter 5 provides an overview of the landscape in bullying prevention programming. This chapter describes in detail the context for preventive interventions and the specific actions that various stakeholders can take to achieve a coordinated response to bullying behavior. The chapter uses the Institute of Medicine’s multi-tiered framework ( National Research Council and Institute of Medicine, 2009 ) to present the different levels of approaches to preventing bullying behavior.
Chapter 6 reviews what is known about federal, state, and local laws and policies and their impact on bullying.
After a critical review of the relevant research and practice-based literatures, Chapter 7 discusses the committee conclusions and recommendations and provides a path forward for bullying prevention.
The report includes a number of appendixes. Appendix A includes meeting agendas of the committee’s public information-gathering meetings. Appendix B includes the agenda and summaries of the site visit. Appendix C includes summaries of bullying prevalence data from the national surveys discussed in Chapter 2 . Appendix D provides a list of selected federal resources on bullying for parents and teachers. Appendix E provides biographical sketches of the committee members and project staff.
Berne, S., Frisén, A., Schultze-Krumbholz, A., Scheithauer, H., Naruskov, K., Luik, P., Katzer, C., Erentaite, R., and Zukauskiene, R. (2013). Cyberbullying assessment instruments: A systematic review. Aggression and Violent Behavior, 18 (2), 320-334.
Bradshaw, C.P., Waasdorp, T.E., and Johnson, S.L. (2015). Overlapping verbal, relational, physical, and electronic forms of bullying in adolescence: Influence of school context. Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology, 44 (3), 494-508.
Burk, F.L. (1897). Teasing and bullying. The Pedagogical Seminary, 4 (3), 336-371.
Currie, C., Zanotti, C., Morgan, A., Currie, D., de Looze, M., Roberts, C., Samdal, O., Smith, O.R., and Barnekow, V. (2012). Social determinants of health and well-being among young people. Copenhagen, Denmark: World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe.
Eisenberg, M.E., and Aalsma, M.C. (2005). Bullying and peer victimization: Position paper of the Society for Adolescent Medicine. Journal of Adolescent Health, 36 (1), 88-91.
Espelage, D.L., and Swearer, S.M. (2003). Research on school bullying and victimization: What have we learned and where do we go from here? School Psychology Review, 32 (3), 365-383.
Farrington, D., and Ttofi, M. (2009). School-based programs to reduce bullying and victimization: A systematic review. Campbell Systematic Reviews, 5 (6).
Finkelhor, D., Ormrod, R.K., and Turner, H.A. (2007). Poly-victimization: A neglected component in child victimization. Child Abuse & Neglect , 31 (1), 7-26.
Gladden, R.M., Vivolo-Kantor, A.M., Hamburger, M.E., and Lumpkin, C.D. (2014). Bullying Surveillance among Youths: Uniform Definitions for Public Health and Recommended Data Elements, Version 1.0 . Atlanta, GA: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and U.S. Department of Education.
Godleski, S.A., Kamper, K.E., Ostrov, J.M., Hart, E.J., and Blakely-McClure, S.J. (2015). Peer victimization and peer rejection during early childhood. Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology, 44 (3), 380-392.
Hamburger, M.E., Basile, K.C., and Vivolo, A.M. (2011). Measuring Bullying Victimization, Perpetration, and Bystander Experiences: A Compendium of Assessment Tools. Atlanta, GA: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Injury Prevention and Control.
Hellström, L., Persson, L., and Hagquist, C. (2015). Understanding and defining bullying—Adolescents’ own views. Archives of Public Health, 73 (4), 1-9.
Holt, M.K., Vivolo-Kantor, A.M., Polanin, J.R., Holland, K.M., DeGue, S., Matjasko, J.L., Wolfe, M., and Reid, G. (2015). Bullying and suicidal ideation and behaviors: A meta-analysis. Pediatrics, 135 (2), e496-e509.
Hopkins, L., Taylor, L., Bowen, E., and Wood, C. (2013). A qualitative study investigating adolescents’ understanding of aggression, bullying and violence. Children and Youth Services Review, 35 (4), 685-693.
Hymel, S., and Swearer, S.M. (2015). Four decades of research on school bullying: An introduction. American Psychologist, 70 (4), 293.
Institute of Medicine. (1994). Reducing Risks for Mental Disorders: Frontiers for Preventive Intervention Research. Committee on Prevention of Mental Disorders. P.J. Mrazek and R.J. Haggerty, Editors. Division of Biobehavioral Sciences and Mental Disorders. Washington, DC: National Academy Press.
Institute of Medicine and National Research Council. (2011). The Science of Adolescent Risk-taking: Workshop Report . Committee on the Science of Adolescence. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press.
Institute of Medicine and National Research Council. (2012). Communications and Technology for Violence Prevention: Workshop Summary . Washington, DC: The National Academies Press.
Institute of Medicine and National Research Council. (2014a). The Evidence for Violence Prevention across the Lifespan and around the World: Workshop Summary . Washington, DC: The National Academies Press.
Institute of Medicine and National Research Council. (2014b). Strategies for Scaling Effective Family-Focused Preventive Interventions to Promote Children’s Cognitive, Affective, and Behavioral Health: Workshop Summary . Washington, DC: The National Academies Press.
Institute of Medicine and National Research Council. (2014c). Building Capacity to Reduce Bullying: Workshop Summary . Washington, DC: The National Academies Press.
Institute of Medicine and National Research Council. (2015). Investing in the Health and Well-Being of Young Adults . Washington, DC: The National Academies Press.
Kim, Y.S., and Leventhal, B. (2008). Bullying and suicide. A review. International Journal of Adolescent Medicine and Health, 20 (2), 133-154.
Koo, H. (2007). A time line of the evolution of school bullying in differing social contexts. Asia Pacific Education Review, 8 (1), 107-116.
Kota, R., Schoohs, S., Benson, M., and Moreno, M.A. (2014). Characterizing cyberbullying among college students: Hacking, dirty laundry, and mocking. Societies, 4 (4), 549-560.
McDougall, P., and Vaillancourt, T. (2015). Long-term adult outcomes of peer victimization in childhood and adolescence: Pathways to adjustment and maladjustment. American Psychologist, 70 (4), 300.
Monks, C.P., and Smith, P.K. (2006). Definitions of bullying: Age differences in understanding of the term and the role of experience. British Journal of Developmental Psychology, 24 (4), 801-821.
National Institute of Justice. (2015). Comprehensive School Safety Initiative. 2015. Available: http://nij.gov/topics/crime/school-crime/Pages/school-safety-initiative.aspx#about [October 2015].
National Research Council and Institute of Medicine. (2002). Community Programs to Promote Youth Development . Committee on Community-Level Programs for Youth. J. Eccles and J.A. Gootman, Editors. Board on Children, Youth, and Families, Division of Behavioral and Social Sciences and Education. Washington, DC: National Academy Press.
National Research Council and Institute of Medicine. (2003). Deadly Lessons: Understanding Lethal School Violence . Case Studies of School Violence Committee. M.H. Moore, C.V. Petrie, A.A. Barga, and B.L. McLaughlin, Editors. Division of Behavioral and Social Sciences and Education. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press.
National Research Council and Institute of Medicine. (2009). Preventing Mental, Emotional, and Behavioral Disorders among Young People: Progress and Possibilities. Committee on the Prevention of Mental Disorders and Substance Abuse Among Children, Youth, and Young Adults: Research Advances and Promising Interventions. M.E. O’Connell, T. Boat, and K.E. Warner, Editors. Board on Children, Youth, and Families, Division of Behavioral and Social Sciences and Education. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press.
Olweus, D. (1978). Aggression in the Schools: Bullies and Whipping Boys. Washington, DC: Hemisphere.
Olweus, D. (1993). Bullying at School. What We Know and Whal We Can Do. Oxford, UK: Blackwell.
Olweus, D. (1996). Bully/victim problems in school. Prospects, 26 (2), 331-359.
Slonje, R., and Smith, P.K. (2008). Cyberbullying: Another main type of bullying? Scandinavian Journal of Psychology, 49 (2), 147-154.
Smith, P. ., and Monks, C. . (2008). Concepts of bullying: Developmental and cultural aspects. International Journal of Adolescent Medicine and Health, 20 (2), 101-112.
Sourander, A. (2010). The association of suicide and bullying in childhood to young adulthood: A review of cross-sectional and longitudinal research findings. Canadian Journal of Psychiatry, 55 (5), 282.
Sticca, F., and Perren, S. (2013). Is cyberbullying worse than traditional bullying? Examining the differential roles of medium, publicity, and anonymity for the perceived severity of bullying. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 42 (5), 739-750.
Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. (2015). Safe Schools/Healthy Students. 2015. Available: http://www.samhsa.gov/safe-schools-healthy-students/about [November 2015].
Tanrikulu, I., and Campbell, M. (2015). Correlates of traditional bullying and cyberbullying perpetration among Australian students. Children and Youth Services Review , 55 , 138-146.
Tokunaga, R.S. (2010). Following you home from school: A critical review and synthesis of research on cyberbullying victimization. Computers in Human Behavior, 26 (3), 277-287.
U.S. Department of Education. (2015). Safe and Supportive Schools . Available: http://www.ed.gov/news/press-releases/us-department-education-awards-388-million-safe-and-supportive-school-grants [October 2015].
Vaillancourt, T., Trinh, V., McDougall, P., Duku, E., Cunningham, L., Cunningham, C., Hymel, S., and Short, K. (2010). Optimizing population screening of bullying in school-aged children. Journal of School Violence, 9 (3), 233-250.
van Geel, M., Vedder, P., and Tanilon, J. (2014). Relationship between peer victimization, cyberbullying, and suicide in children and adolescents: A meta-analysis. Journal of the American Medical Association. Pediatrics, 168 (5), 435-442.
Vivolo, A.M., Holt, M.K., and Massetti, G.M. (2011). Individual and contextual factors for bullying and peer victimization: Implications for prevention. Journal of School Violence, 10 (2), 201-212.
Vlachou, M., Andreou, E., Botsoglou, K., and Didaskalou, E. (2011). Bully/victim problems among preschool children: A review of current research evidence. Educational Psychology Review, 23 (3), 329-358.
Wolke, D., and Lereya, S.T. (2015). Long-term effects of bullying. Archives of Disease in Childhood, 100 (9), 879-885.
Ybarra, M.L., Espelage, D.L., and Mitchell, K.J. (2014). Differentiating youth who are bullied from other victims of peer-aggression: The importance of differential power and repetition. Journal of Adolescent Health, 55 (2), 293-300.
This page intentionally left blank.
Bullying has long been tolerated as a rite of passage among children and adolescents. There is an implication that individuals who are bullied must have "asked for" this type of treatment, or deserved it. Sometimes, even the child who is bullied begins to internalize this idea. For many years, there has been a general acceptance and collective shrug when it comes to a child or adolescent with greater social capital or power pushing around a child perceived as subordinate. But bullying is not developmentally appropriate; it should not be considered a normal part of the typical social grouping that occurs throughout a child's life.
Although bullying behavior endures through generations, the milieu is changing. Historically, bulling has occurred at school, the physical setting in which most of childhood is centered and the primary source for peer group formation. In recent years, however, the physical setting is not the only place bullying is occurring. Technology allows for an entirely new type of digital electronic aggression, cyberbullying, which takes place through chat rooms, instant messaging, social media, and other forms of digital electronic communication.
Composition of peer groups, shifting demographics, changing societal norms, and modern technology are contextual factors that must be considered to understand and effectively react to bullying in the United States. Youth are embedded in multiple contexts and each of these contexts interacts with individual characteristics of youth in ways that either exacerbate or attenuate the association between these individual characteristics and bullying perpetration or victimization. Recognizing that bullying behavior is a major public health problem that demands the concerted and coordinated time and attention of parents, educators and school administrators, health care providers, policy makers, families, and others concerned with the care of children, this report evaluates the state of the science on biological and psychosocial consequences of peer victimization and the risk and protective factors that either increase or decrease peer victimization behavior and consequences.
READ FREE ONLINE
Welcome to OpenBook!
You're looking at OpenBook, NAP.edu's online reading room since 1999. Based on feedback from you, our users, we've made some improvements that make it easier than ever to read thousands of publications on our website.
Do you want to take a quick tour of the OpenBook's features?
Show this book's table of contents , where you can jump to any chapter by name.
...or use these buttons to go back to the previous chapter or skip to the next one.
Jump up to the previous page or down to the next one. Also, you can type in a page number and press Enter to go directly to that page in the book.
Switch between the Original Pages , where you can read the report as it appeared in print, and Text Pages for the web version, where you can highlight and search the text.
To search the entire text of this book, type in your search term here and press Enter .
Share a link to this book page on your preferred social network or via email.
View our suggested citation for this chapter.
Ready to take your reading offline? Click here to buy this book in print or download it as a free PDF, if available.
Get Email Updates
Do you enjoy reading reports from the Academies online for free ? Sign up for email notifications and we'll let you know about new publications in your areas of interest when they're released.
Home — Essay Samples — Social Issues — Bullying — Consequences of Bullying in Schools
Consequences of Bullying in Schools
- Categories: Art and Religion Bullying
About this sample

Words: 523 |
Published: Mar 16, 2024
Words: 523 | Page: 1 | 3 min read
Table of contents
Mental health impact, social development impact, physical consequences.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: Arts & Culture Social Issues

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!

Related Essays
2 pages / 799 words
6 pages / 2868 words
3 pages / 1194 words
3 pages / 1351 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Bullying
Bullying is a prevalent issue in educational institutions and society at large. According to the National Center for Education Statistics, 20.8% of students reported being bullied in 2019. Bullying is defined as intentional [...]
School bullies represent a persistent and troubling issue in educational institutions worldwide. The negative consequences of bullying extend beyond the classroom, affecting the well-being and academic performance of both [...]
In this essay, readers can expect to delve into the pervasive issue of bullying and its detrimental consequences on mental health and well-being. The essay explores how bullying not only affects individuals but also has [...]
Bullying is a pervasive problem that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a form of aggressive behavior that is intended to harm, intimidate, or humiliate someone. Bullying can take many forms, including physical, verbal, [...]
Do you know how many innocent souls are shattered in the hands of ruthless bullies? Even in the most civilized countries, bullying causes grief to many young teens. A 2004 study published in the medical Journal of Pediatrics [...]
This essay aims to explore "what are the causes and effects of bullying," a critical issue that continues to plague various segments of society. Among the most common and neglected problems in the world, bullying is on top of [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Bullying Essay for Students and Children
500+ words essay on bullying.
Bullying refers to aggressive behavior so as to dominate the other person. It refers to the coercion of power over others so that one individual can dominate others. It is an act that is not one time, instead, it keeps on repeating over frequent intervals. The person(s) who bullies others can be termed as bullies, who make fun of others due to several reasons. Bullying is a result of someone’s perception of the imbalance of power.

Types of bullying :
There can be various types of bullying, like:
- Physical bullying: When the bullies try to physically hurt or torture someone, or even touch someone without his/her consent can be termed as physical bullying .
- Verbal bullying: It is when a person taunts or teases the other person.
- Psychological bullying: When a person or group of persons gossip about another person or exclude them from being part of the group, can be termed as psychological bullying.
- Cyber bullying: When bullies make use of social media to insult or hurt someone. They may make comments bad and degrading comments on the person at the public forum and hence make the other person feel embarrassed. Bullies may also post personal information, pictures or videos on social media to deteriorate some one’s public image.
Read Essay on Cyber Bullying
Bullying can happen at any stage of life, such as school bullying, College bullying, Workplace bullying, Public Place bullying, etc. Many times not only the other persons but the family members or parents also unknowingly bully an individual by making constant discouraging remarks. Hence the victim gradually starts losing his/her self-esteem, and may also suffer from psychological disorders.
A UNESCO report says that 32% of students are bullied at schools worldwide. In our country as well, bullying is becoming quite common. Instead, bullying is becoming a major problem worldwide. It has been noted that physical bullying is prevalent amongst boys and psychological bullying is prevalent amongst girls.
Prevention strategies:
In the case of school bullying, parents and teachers can play an important role. They should try and notice the early symptoms of children/students such as behavioral change, lack of self-esteem, concentration deficit, etc. Early recognition of symptoms, prompt action and timely counseling can reduce the after-effects of bullying on the victim.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Anti-bullying laws :
One should be aware of the anti-bullying laws in India. Awareness about such laws may also create discouragement to the act of bullying amongst children and youngsters. Some information about anti-bullying laws is as follows:
- Laws in School: To put a notice on the notice board that if any student is found bullying other students then he/she can be rusticated. A committee should be formed which can have representatives from school, parents, legal, etc.
- Laws in Colleges: The government of India, in order to prevent ragging , has created guideline called “UGC regulations on curbing the menace of ragging in Higher Education Institutions,2009”.
- Cyber Bullying Laws: The victim can file a complaint under the Indian Penal Code .
Conclusion:
It is the duty of the parents to constantly preach their children about not bullying anyone and that it is wrong. Hence, if we, as a society need to grow and develop then we have to collectively work towards discouraging the act of bullying and hence make our children feel secure.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov
A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock ( ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

Effects of Bullying
Bullying can affect everyone—those who are bullied, those who bully, and those who witness bullying. Bullying is linked to many negative outcomes including impacts on mental health, substance use, and suicide. It is important to talk to kids to determine whether bullying—or something else—is a concern.
Kids Who are Bullied
Kids who are bullied can experience negative physical, social, emotional, academic, and mental health issues. Kids who are bullied are more likely to experience:
- Depression and anxiety, increased feelings of sadness and loneliness, changes in sleep and eating patterns, and loss of interest in activities they used to enjoy. These issues may persist into adulthood.
- Health complaints
- Decreased academic achievement—GPA and standardized test scores—and school participation. They are more likely to miss, skip, or drop out of school.
A very small number of bullied children might retaliate through extremely violent measures. In 12 of 15 school shooting cases in the 1990s, the shooters had a history of being bullied.
Kids Who Bully Others
Kids who bully others can also engage in violent and other risky behaviors into adulthood. Kids who bully are more likely to:
- Abuse alcohol and other drugs in adolescence and as adults
- Get into fights, vandalize property, and drop out of school
- Engage in early sexual activity
- Have criminal convictions and traffic citations as adults
- Be abusive toward their romantic partners, spouses, or children as adults
Kids who witness bullying are more likely to:
- Have increased use of tobacco, alcohol, or other drugs
- Have increased mental health problems, including depression and anxiety
- Miss or skip school
The Relationship between Bullying and Suicide
Media reports often link bullying with suicide. However, most youth who are bullied do not have thoughts of suicide or engage in suicidal behaviors.
Although kids who are bullied are at risk of suicide, bullying alone is not the cause. Many issues contribute to suicide risk, including depression, problems at home, and trauma history. Additionally, specific groups have an increased risk of suicide, including American Indian and Alaskan Native, Asian American, lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender youth. This risk can be increased further when these kids are not supported by parents, peers, and schools. Bullying can make an unsupportive situation worse.
Click through the PLOS taxonomy to find articles in your field.
For more information about PLOS Subject Areas, click here .
Loading metrics
Open Access
Peer-reviewed
Research Article
The relationship between teachers’ disciplinary practices and school bullying and students’ satisfaction with school: The moderated mediation effects of sex and school belonging
Roles Conceptualization, Methodology, Project administration, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing
* E-mail: [email protected]
Affiliation Institute for Educational Research, Belgrade, Serbia
Roles Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing
Roles Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing
Affiliation University of Belgrade, Faculty of Special Education and Rehabilitation, Belgrade, Serbia
Roles Conceptualization, Data curation, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Resources
Roles Conceptualization, Data curation, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Project administration
Roles Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing
Roles Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation
Affiliation Institute of Criminological and Sociological Research, Belgrade, Serbia
Roles Formal analysis, Software, Visualization
- Marina Kovacevic Lepojevic,
- Marija Trajkovic,
- Luka Mijatovic,
- Branislava Popovic-Citic,
- Lidija Bukvic,
- Milica Kovacevic,
- Ana Parausic Marinkovic,
- Mladen Radulovic

- Published: May 28, 2024
- https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0303466
- Reader Comments
An authoritative school climate, along with greater teacher support and warm relations among peers are frequently connected with less school bullying. The main aim of this paper is to examine the direct link as perceived by students between teachers’ disciplinary practices and bullying in school and students’ satisfaction with school. The indirect relationships are explored via the mediation of school belonging and the moderation of sex. High school students (N = 860, 40.4% male students) completed the Delaware School Climate Survey, the Multidimensional Students’ Life Satisfaction Scale, and the Psychological Sense of School Membership Scale at a single time point. In general, teachers’ disciplinary practices have significant direct effects on perceptions of bullying and satisfaction with school. Positive disciplinary (direct effect = .28, SE = .04) and SEL techniques (direct effect = .22, SE = .04) are related to bullying only among males, while punitive techniques are directly linked to school bullying unrelated to sex (b = .03, SE = .05). Similarly, the effect of positive disciplinary (direct effect = .27, SE = .08) and SEL (direct effect = .21, SE = .08) techniques on satisfaction with school was significant only among males. A direct relationship between punitive disciplinary techniques and satisfaction with school was not recognized. The mediation analysis revealed the indirect effects of teachers’ disciplinary practices on the dependent variables via school belonging to be stronger among females. Teachers’ negative modeling through punitive disciplinary practices leads to more bullying. School belonging may serve as a protective factor related to the negative impact of teachers’ disciplinary practices on school bullying as well as satisfaction with school, especially among females. Interventions should be focused on fostering school belonging along with the development of positive sex-specific disciplinary practices.
Citation: Kovacevic Lepojevic M, Trajkovic M, Mijatovic L, Popovic-Citic B, Bukvic L, Kovacevic M, et al. (2024) The relationship between teachers’ disciplinary practices and school bullying and students’ satisfaction with school: The moderated mediation effects of sex and school belonging. PLoS ONE 19(5): e0303466. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0303466
Editor: Gianpiero Greco, University of Study of Bari Aldo Moro, ITALY
Received: September 15, 2023; Accepted: April 25, 2024; Published: May 28, 2024
Copyright: © 2024 Kovacevic Lepojevic et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Data Availability: All relevant data are within the manuscript and its Supporting Information files.
Funding: The data collection was funded by the Council of Europe and the European Union within the project Promotion of Diversity and Equality in Serbia, Horizontal Facility for the Western Balkans and Turkey (Horizontal Facility II, 2019-2022), BH4674/2021/7, and preparation of the manuscript was funded by the Ministry of Science, Technological Development and Innovation of the Republic of Serbia (Contract No. 451-03-47/2023-01/200018 and No. 451-03-66/2024-03/200039). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Competing interests: NO: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Introduction
By its definition school bullying involves the repeated intent to harm and an imbalance of power between the aggressor and the victim [ 1 ]. Such an imbalance of power may stem from physical strength, social status within the group, or a certain vulnerability (e.g. appearance, learning difficulties, family situation, personality characteristics) [ 2 ]. Less school bullying is frequently connected with an authoritative school climate, and more teacher, peer and parental support [ 3 – 5 ]. Scientific results imply that instead of being considered in terms of the individual’s behaviour, bullying should be considered as a structural issue [ 6 ]. Harsh discipline in schools is generally directly related to more experiences of bullying as a consequence of negative teacher-student modeling [ 7 ]. Punishment is often used in traditionally oriented schools and reflects a policy of zero tolerance and the frequent use of suspensions and exclusions from school. Research results indicate that a supportive disciplinary framework is recognized in effective bullying prevention programmes [ 8 ], and even punitive discipline may be successful in achieving the short-term effects of managing student behaviour [ 9 ]. Teachers’ SEL disciplinary practices are the most effective in developing students’ self-discipline and long-term positive developmental changes [ 10 ]. The results of evaluation studies show that SEL in combination with positive disciplinary techniques achieves better results than without them [ 11 , 12 ]. Certain authors stress that in an authoritative school climate, both responsiveness (support) and demandingness (structure) are equally valued, and together are viewed as instrumental for effective discipline in both the short and long term [ 13 ]. There has been a notable shift in school programmes from bullying prevention to the systemic integration of the evidence-based practices of social and emotional learning (SEL) [ 14 ]
One of the frequently examined indicators of positive youth developmental outcomes is student life satisfaction [ 15 ]. Subjective well-being is most often interpreted as experiencing a high level of positive affect, a low level of negative affect, and a high degree of satisfaction with one’s life [ 16 ]. The concept of subjective well-being has frequently been used synonymously with ‘‘happiness”, meaning that maximising one’s well-being has been viewed as maximising one’s feelings of happiness [ 16 ]. However, self- reports of being happy do not necessarily mean that people are psychologically well [ 16 ]. As represented in the Eudaimonic Activity Model, eudaimonic and hedonic aspects of well-being are closely related [ 17 ]. Life satisfaction is one of the most important indicators of youth well-being and represents their cognitive evaluation of their quality of life [ 18 ]). This might be conceptualized as a general life satisfaction assessment or within specific life domains (e.g. satisfaction with friends, family, and school experiences) [ 19 , 20 ]. The author suggests the variability in satisfaction ratings across life domains, with adolescents reporting the greatest dissatisfaction with their school experiences [ 21 ]. Creating a balance between responsiveness and demandingness in the classroom is connected to higher student satisfaction with school [ 22 ]. The interpersonal relations between students and teachers and among peers has been found to be the most important school climate factor which affects student satisfaction with school [ 22 ]. The research results suggest that teachers should focus more on positive disciplinary practices as they are linked to improved outcomes for both students and teachers [ 23 ]. Monitoring the effects of the RULER program–an evidence-based approach to social and emotional learning, significant improvements in multiple dimensions of the school climate, including disciplinary practice, were found to be related to satisfaction with school [ 24 ].
Previous research recognized school belonging as a good mediator in explaining the link between different aspects of the school climate and various positive and negative student outcomes such as problematic internet use [ 25 ]; academic success [ 26 ]; bullying, and symptoms of depression [ 27 ], etc. School belonging is defined as the extent to which students feel personally accepted, respected, included, and supported by others in the school social environment [ 28 ]. The research results indicate that school belonging is closely related to many positive developmental outcomes such as higher student cognitive and behavioural engagement, higher motivation and academic success [ 29 , 30 ]; fewer problems and higher prosocial behaviour [ 31 , 32 ], and higher life satisfaction [ 33 ]. The results show that students in positive school climates report higher levels of school belonging and fewer physical, emotional, and cyberbullying behaviours [ 27 , 34 ]. School belonging mediates certain school climate aspects (e.g. teacher-student relationships, and a sense of fairness) in relation to students’ life satisfaction [ 35 ]. School belonging may not be relevant for negative disciplinary practices. Supportive teaching practices are closely linked to school connectedness, while punitive disciplinary practice has no significant correlation with school connectedness [ 36 ]. Class level path analysis showed that the effect of the student-teacher relationship on bullying behaviour is mediated by the student-student relationship [ 37 ].
Numerous differences in peer socialization and variances between males and females have been recognized to date, starting from girls’ relational orientation, a tendency to build more meaningful relationships, interpersonal sensitivity and prosocial orientation [ 38 ], suggesting greater male engagement in bullying [ 5 , 39 ], less connectedness with school [ 40 ], and less positive relationships with teachers [ 41 , 42 ]. To our knowledge, sex moderation of the mediation of school belonging in examining the relationship between teacher disciplinary practices and school bullying behaviour and satisfaction with school has not yet been explored.
The main aim of this paper is to examine the links between teachers’ disciplinary practices perceived by students with bullying in school and with students’ satisfaction with school. The indirect relationships are explored via the mediation of school belonging and the moderating role of sex. The proposed model includes how (the mediating effect), when (the moderating effect), and when and how (moderated mediating effect) teachers’ disciplinary practices affect both bullying and students’ school satisfaction ( Fig 1 ).
- PPT PowerPoint slide
- PNG larger image
- TIFF original image
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0303466.g001
Based on authoritative discipline theory [ 43 , 44 ] and Stockard and Mayberry’s [ 45 ] theoretical framework for the school climate which imply that a healthy balance between responsiveness (support) and demandingness (structure) lead to more self-discipline [ 46 ] we hypothesized that: punitive discipline is negatively related to satisfaction with school and positively to bullying; teachers’ socio-emotional techniques as well positive disciplinary techniques are negatively related to school bullying and positively to students’ satisfaction with school. School belonging is expected to have mediating potential in the explanation of the relationship between disciplinary practices and bullying in schools and disciplinary practices and students’ satisfaction with school. Additionally, we expect to find that the proposed interactions differ by sex We hypothesized that socioemotional learning and positive disciplinary techniques can help to develop school belonging, especially at females. Also, we expect that teachers’ negative modeling via the use of punitive discipline is expected to affect males more directly. We consider that further exploring of the sex moderation between teacher practices and school belonging can help to the developing of school belonging, greater satisfaction of students and prevention of school bullying.
Materials and methods
Students from 11 Belgrade (Serbia) high schools from the first to the fourth grade (N = 860, 40.4% male students) completed the Delaware School Climate Survey [ 47 ], the Multidimensional Students’ Life Satisfaction Scale [ 19 ], and the Psychological Sense of School Membership Scale [ 28 ] at a single time point from April 5 th to May 28 th 2021. Measures The Delaware Positive, Punitive, and SEL Techniques Scale [ 47 ] measures students’ perceptions of the extent to which three types of techniques are used in their school to manage student behaviour. The positive behaviour techniques consist of 4 items (e.g. Students are often praised), the use of punitive/corrective techniques of 4 items (e.g. Students are punished a lot), and the use of SEL techniques of 5 items (e.g. Students are taught to feel responsible for their behaviour). In the current study, Cronbach’s alpha coefficient ranged from 0.77 (Punitive Techniques), 0.83 (Positive Techniques) to 0.85 (SEL Techniques) and McDonald’s omega from 0.77 (Punitive Techniques), 0.84 (Positive Techniques) to 0.85 (SEL Techniques) for the student sample. The Bullying School-Wide subscale comprises 4 items which explore students’ perceptions of bullying in their schools (e.g. In this school, bullying is a problem). The rating response range was from 1 (strongly disagree) to 4 (strongly agree). The internal consistency measured by Cronbach’s alpha and McDonald’s omega coefficient is 0.76. The Multidimensional Students’ Life Satisfaction Scale (MSLSS) [ 19 ] is a 6-point Likert-type self-report scale (ranging from strongly disagree (1) to strongly agree (6)), designed for children aged 8 to 18. The MSLSS is designed to provide a holistic assessment of the wellbeing of young people. It has five subscales: family, friends, school, the living environment and self. The school domain items rep-resent satisfaction with school life (e.g. I enjoy school activities). The value of Cronbach’s alpha is 0.84 and McDonald’s omega is 0.85. The Psychological Sense of School Membership Scale (PSSM) comprises 18 items (e.g. Most teachers at this school are interested in me.) to be assessed on a 5-point Likert-type scale from 1 (strongly disagree) to 5 (strongly agree) [ 28 ]. The internal consistency is 0.84 measured by Cronbach’s alpha and 0.90 measured by McDonald’s omega.
Procedure . Verbal informed consent from participants is obtained. At first we presented the research and relevant procedures involve with data collection and usage, and ask to declare if someone doesn’t want to participate. It was witnessed by school psychologist. One school hour was necessary for completing the questionnaire. In the Republic of Serbia there is no regulation at all about parental consent for children participating in scientific research, but Family law, Official Gazette, no 18/2005, 72/11 and 6/2015,and Law about protection of the rights of the patients, Official Gazette, no 45/2013-19, 25/2019-3, respect privacy of children above 15 years (e.g. they make decisions about medical treatments by their own). This study was approved by the Research Ethics and Conduct Committee of the CEPORA–Center for Positive Youth Development (no. 12/2021 ES)
Descriptive statistics and the intercorrelations of the variables
Descriptive and correlation analyses were conducted using SPSS 21.0. PROCESS analyses were performed to test the mediating role of school belonging in predicting bullying and students’ school satisfaction by teachers’ disciplinary practices (positive, punitive and SEL techniques) along with the moderating role of sex. The entire model was previously tested in IBM AMOS version 25.
Table 1 presents the means and standard deviations of the study variables: positive, punitive and SEL techniques, school belonging, bullying and students’ school satisfaction and their intercorrelations.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0303466.t001
The correlation results indicated that bullying was negatively associated with SEL techniques, school belonging and students’ school satisfaction (p < 0.01) and positively with punitive techniques (p < 0.01). Students’ school satisfaction was negatively related to punitive techniques, bullying and age (p < 0.01) and positively to the other study variables. The correlations of age with positive techniques, SEL techniques, school be-longing and students’ school satisfaction were negative and weak (p < 0.01).
Moderated mediation analyses results
The entire model was previously tested in IBM AMOS version 25. Results suggested the model can be considered unsatisfactory: Chi-square value was significant (χ2 = 780.396, p < .001), the TLI and CFI values were below the recommended threshold of 0.90, while the RMSEA was far above the prescribed value of 0.08 (TLI =.-.111, CFI = .704, RMSEA = .339). For that reason, direct and indirect effects were separately tested using the SPSS macro PROCESS suggested by Hayes [ 48 ]. Using proposed model number 59, six PROCESS analyses were conducted–one for each pair of predictor and dependent variables. In this way the independent contribution of the predictors and their relations with the mediator were examined with sex as the moderator. Age was treated as a covariate and its role will not be presented within the results or discussed. A full information maximum likelihood estimator was used which could also handle missing values. The direct, indirect, and total effects were calculated. 5000 bootstrap samples were used. Bootstrapping is a non-parametric method which bypasses the is-sue of non-normality distribution [ 49 ]. All used variables (except sex) were standardized prior to test and effects and their standard errors (SE) are shown.
As regards the first model (F(5,688) = 40.86, p < .01), positive techniques positively predicted school belonging (b = .36, SE = .11, p < .01), sex also predicted the mediator variable (b = -.16, SE = .007, p < .05), while the interaction between positive techniques and sex on school belonging was not significant. Bullying was negatively predicted by school belonging (b = -.38, SE = .15, p < .05) and positively by positive techniques (b = .69, SE = .14, p < .01). Interaction of sex and positive techniques negatively predicted bullying (b = -.3, SE = .08, p < .01) which explained 1.5% of the variance in predicting bullying, while interaction of sex and belonging didn’t have significant effect on dependent variable. Further probing of the significant interaction indicated that the conditional direct effect was significant (and positive) only for males (direct effect = .39, SE = .06, p < .01), while the indirect effects of positive techniques on bullying did not differ between males and females–the index of moderated mediation was not significant (index = -.09, bootSE = .052, 95% BootLLCI = -.2—BootULCI = .01). The entire first model explained 22,9.% of the variance in bullying ( Fig 2 ).
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0303466.g002
Within the second model (F(5,692) = 80.09, p < .01), punitive techniques (b = .11, SE = .38, p = .47) and sex (b = -.13, SE = .07, p = .06) as the predictors did not affect school belonging, while the interaction of sex and punitive techniques (b = -.30, SE = .07, p < .01) was significant in predicting the mediator. This interaction explained an additional proportion of the variance in school belonging (2%) with significant effects in both males (effect = -.22, SE = .05, p < .01) and females (effect = -.52, SE = .04, p < .01), showing that punitive techniques exerted a stronger negative effect on school belonging among females. Bullying was positively predicted by punitive techniques (b = .49, SE = .1, p < .01) and sex (b = .22, SE = .06, p < .001), while belonging didn’t have significant effect on bullying in context of these variables (b = .16, SE = .12, p = .18). Interaction of sex and punitive techniques (b = -.03, SE = .06, p = .63) did not influence the criterion, but interaction between belonging and sex did (b = -.23, SE = .07, p < .01), explaining an additional proportion of the variance in bullying (1%) and showing that there is significant negative effect of belonging on bullying among girls (effect = -.31, SE = .04, p < .01) and no such effect among boys. Consequently, the indirect effects of punitive techniques on bullying were positive and significant females (indirect effect = .16, bootSE = .02, 95% BootLLCI = .12—BootULCI = .21) and unsignificant for males (indirect effect = .02, bootSE = .01, 95% BootLLCI = -.01—BootULCI = .04). The index of moderated mediation was significant (index = .14, bootSE = .03, 95% BootLLCI = .09—BootULCI = .20). The entire second model explained 37% of the variance in bullying ( Fig 3 ).
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0303466.g003
As regards the third model (F(5,682) = 37.65, p < .01), school belonging was predicted by SEL techniques (b = .29, SE = .1, p < .01), sex (b = -.24, SE = .06, p < .01) and their interaction (b = .2, SE = .06, p < .01). The sex-SEL interaction explained an additional 1% of the variance in the mediator with significant positive effects in both males (effect = .49, SE = .05, p < .01) and females (effect = .69, SE = .04, p < .01), indicating again a stronger effect among females. Bullying was positively predicted by SEL techniques (b = .68, SE = .14, p < .01) and negatively by school belonging (b = -.42, SE = .16, p < .01). Sex (b = .1, SE = .07, p = .15) and the sex x belonging interaction (b = -.02, SE = .09, p = .81) didn’t significantly influence the criterion, while sex x SEL techniques interaction had significant affect (b = -.36, SE = .09, p < .01) This interaction explained 2% of the variance in bullying. The conditional direct effect of SEL techniques on bullying was significant for males (direct effect = .32, SE = .06, p < .01), but not for females. The indirect effects were significant for both males (indirect effect = -.22, bootSE = .04, 95% BootLLCI = -.30—BootULCI = -.13) and females (indirect effect = -.32, bootSE = .04, 95% BootLLCI = -.40—BootULCI = - .25). and they did not significantly differ between males and females (index = -.11, bootSE = .06, 95% BootLLCI = -.22—BootULCI = .01). The entire first model explained 22,93% of the variance in bullying ( Fig 4 ).
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0303466.g004
As regards the fourth model (F(5,690) = 192.73, p < .01), the prediction of the mediator was significant for positive techniques (b = .3, SE = .11, p < .01), sex (b = -.19, SE = .06, p < .01) and their interaction (b = .14, SE = .07, p < .05), while the effects on the mediator were significant among both males (effect = .44, SE = .05, p < .01) and females (effect = .58, SE = .04, p < .01). This interaction is significantly higher among females. When it comes to predicting students’ school satisfaction, significant effects were found for positive techniques (b = .32, SE = .1, p < .01), school belonging (b = .62, SE = .12, p < .01), sex (b = .15, SE = .05, p < .01), and the sex x positive techniques interaction (b = -.16, SE = .06, p < .01), while sex x school belonging interaction didn’t predict school satisfaction. The conditional direct effect was significant just for males (direct effect = .16, SE = .05, p < .001). The indirect effects were significant for both males (indirect effect = .30, boot SE = .04, 95% BootLLCI = .23—BootULCI = .38) and females (indirect effect = .43, bootSE = .04, 95% BootLLCI = .36—BootULCI = .5), again indicating a stronger effect among females. The index of moderated mediation was significant (index = .13, bootSE = .05, 95% BootLLCI = .03—BootULCI = .23), while the whole model explained 58% of the variance in students’ school satisfaction ( Fig 5 ).
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0303466.g005
In the fifth model (F(5,698) = 198.93, p < .01), the mediator variable was predicted by sex (b = -.17, SE = .07, p < .01) and the interaction of sex and punitive techniques (b = -.24, SE = .07, p < .01), which explained 2% of the variance in school belonging. The independent variable alone did not affect the mediator (b = .07, SE = .11, p = .57). The negative effects of the interaction on the mediator were significant in both males (effect = -.22 SE = .05, p < .01) and females (effect = -.5, SE = .04, p < .01), but higher among females. Students’ school satisfaction was directly predicted by school belonging (b = .84, SE = .1, p < .01) and sex (b = .15, SE = .05, p < .001), while the influences of punitive techniques (b = .02, SE = .09, p = .86), and interaction and sex (b = -.05, SE = .05, p = .35) and interaction of school belonging and sex (b = -.06, SE = .06, p = .3) were insignificant. Due to the latter results, the conditional direct effects were not shown. The indirect effects were significantly higher among females (indirect effect = -.36, bootSE = .04, 95% BootLLCI = -.44—BootULCI = -.29) than males (indirect effect = -.17, bootSE = .04, 95% BootLLCI = -.25—BootULCI = -.1). The index of moderated mediation was significant (index = -.19, bootSE = .05, 95% BootLLCI = -.3—BootULCI = -.09), while the model in total explained 59% of the variance in students’ school satisfaction ( Fig 6 ).
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0303466.g006
As regards the sixth model (F(5,690) = 203.05, p < .01), SEL techniques (b = .23, SE = .1, p < .05), sex (b = -.27, SE = .06, p < .01) and their interaction (b = .22, SE = .06, p < .001) predicted the mediator. The SEL techniques x sex interaction explained 1% of the variance of school belonging, while the positive effects on the mediator were significant and lower for males (effect = .45 SE = .05, p < .01) compared to females (effect = .68, SE = .04, p < .01). The effects of SEL techniques (b = .26, SE = .1, p < .01), school belonging (b = .68, SE = .12, p < .001), sex (b = .13, SE = .05, p < .01) and sex x SEL techniques (b = -.13, SE = .06, p < .05) were significant predictors of school satisfaction, while school belonging x sex interaction didn’t have effect. Sex influenced the relation between the independent and criterion variables, where the conditional direct effect was significant only for males (direct effect = .12, SE = .05, p < .01). The indirect effects were significant for both males (indirect effect = .32, bootSE = .04, 95% BootLLCI = .25—BootULCI = .4) and females (indirect effect = .51, bootSE = .04, 95% BootLLCI = .43—BootULCI = .59), with a stronger effect among females once again. The index of moderated mediation was significant (index = .19, bootSE = .05, 95% BootLLCI = .08—BootULCI = .31), while the model in total explained 60% of the variance in students’ school satisfaction ( Fig 7 ).
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0303466.g007
As expected, punitive discipline is directly and positively related to school bullying unrelated to sex, indicating the impact of teachers’ negative modeling on student-student behaviour and bullying as its negative manifestation [ 7 , 43 ]. Unexpectedly, positive disciplinary and SEL techniques are positively related to bullying, and that link is found to be relevant only for male students which is contrary to previous findings [ 24 , 50 , 51 ]. One of the explanations for this is that SEL might be perceived as a Trojan horse to increase classroom management and social control, instead of cultivating the positive, full development of the child and the adult educator, including care-givers [ 31 ]. The positive relation between positive disciplinary techniques and SEL with school bullying might be explained by difficulties in implementation at secondary school level if such techniques are not applied appropriately at previous educational levels and simultaneously in other ecological contexts. These findings might imply the need to apply systemic SEL as an approach to create equitable learning conditions which actively involve all Pre-K to Grade 12 students in learning and developing social, emotional, and academic competencies [ 52 , 53 ]. Difficulties in school staff motivation and capabilities are also recognized [ 54 ]. Positive and SEL disciplinary techniques which are not properly implemented might be perceived as more teacher- oriented [ 54 ]. Teachers are then perceived to have a greater share of the power similar to punitive school discipline. These positive relations might be additionally explained in a reactive way, meaning that teachers respond to severe bullying behaviour inappropriately. Teachers might not recognize when incidents of bullying should be considered as severe, requiring help from other agencies and services. The author has already noticed that the severity of peer victimization may moderate the relationship between socio-emotional learning and school bullying [ 51 ]. As the victims of bullying have said, teachers often react to the perpetrator, without offering any support to the victim and the whole class after such incidents [ 55 ]. Teachers may underestimate verbal incidents of bullying, even suffer from bullying themselves, or enable bullying by their inappropriate reaction to the bulling incidents which occur in the classroom [ 56 , 57 ]. As has already been noted in previous research, male students tend to “ignore incidents”, or report only more severe incidents of bullying compared to female students who are more sensitive to minor incidents, which might affect findings about gen-der-specific interactions [ 58 ].
The interesting finding that positive discipline and SEL directly relate to student satisfaction with school only for male students might be explained by the fact that although females are more rationally oriented, have positive relations with teachers [ 41 , 42 ], and build better relations with their peers [ 58 ], parents [ 59 ] and other important figures, supportive teacher relationships might mean more to male students than their female counterparts. Even punitive disciplinary practice was not directly related to satisfaction with school, while school belonging was found to be a good protective factor especially among female students, which is not surprising because of their relational and contextual orientation [ 38 ]. The full mediation of school belonging established in relation to SEL and positive disciplinary techniques on students’ satisfaction with school implies that interventions focused on fostering school belonging along with efforts toward establishing a positive school climate might positively affect students’ wellbeing and have a negative effect on school bullying [ 24 , 32 ]. According to the current study, school belonging is sex-specific and partly explains bullying behaviour [ 27 , 58 ] and student wellbeing [ 34 , 35 ]. The qualitative differences between female and male students indicate that both might use bullying as a tool to feel a sense of belonging, girls to prevent being excluded from the group and boys to avoid being perceived as weak [ 58 ].
As has already been noted, bullying does not occur in a vacuum [ 60 ]. This study highlights the importance of the disciplinary strategies used by teachers in schools, how they manage their classrooms and how this is related to bullying and satisfaction with school. The data about sex relevance within the examined interactions are of special value in this study. The research results are in line with a noticeable shift in bullying prevention towards evidence-based practices of social and emotional learning (SEL) leading to a variety of positive outcomes for students and teachers alike [ 14 , 50 ]. Interventions for developing school belonging are highly recommended in order to prevent school bullying and improve students’ positive developmental outcomes. We recommend that a good fit for bullying prevention in middle and high schools might have teacher practice of adopting greater youth participation at classroom level along with practicing SEL. It’s expected that greater youth participation, and more group discussion will strengthen school belonging, equity impact and less bullying [ 61 ].
This study is limited by its cross-sectional design. Longitudinal or intervention re-search is necessary to provide more detailed answers to the research question regarding the relation between school climate aspects and school bullying. A further limitation relates to the lack of a class level analysis which could provide more exact data. Longitudinal data could provide some evidence of both the short and long term effects of teachers’ disciplinary practices. This research is mono-informant in nature with the measurements being restricted to student self-rating scales. For future studies we recommend involving more global measures of students’ life satisfaction so as to avoid the similarity between the school belonging and satisfaction with school constructs used in the current study. Additionally, measuring bullying victimization as well as disciplinary infractions would be important in order to gain a better under-standing of the mechanisms underlying teachers’ disciplinary practices.
Supporting information
S1 dataset..
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0303466.s001
- 1. Olweus D. Bullying at School. In: Aggressive Behavior. Huesmann L.R, editor. The Plenum Series in Social/Clinical Psychology. Boston, MA: Springer; 1994. 97–130. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4757-9116-7_5
- View Article
- PubMed/NCBI
- Google Scholar
- 9. Landrum T. J, Kauffman J. M. Behavioral approaches to classroom management. In: Evertson C. M. Weinstein C.M, C, Mahwah S, editors, Handbook of classroom management: Research, practice, and contemporary issues. NJ: Erlbaum. 2006; pp: 47–71.
- 12. Gueldner B. A, Feuerborn L. L, Merrell K. W. Social and emotional learning in the classroom: Promoting mental health and academic success. Second Edition. London, NY: Guilford Publications; 2020.
- 13. Bear G. G, Whitcomb S. A, Elias M. J, Blank J. C. SEL and schoolwide positive behavioral interventions and supports. In: Durlak J. A., Domintrovich C. E., editors. Handbook of social and emotional learning (SEL): Research and practice, New York, NY: Guilford; 2015; pp: 453–467.
- 20. Huebner S. Manual for the Multidimensional Students’ Life Satisfaction Scale. Available from: https://ww2.cas.sc.edu/psyc/sites/default/files/directory_files/huebslssmanual_0.pdf , 2001
- 45. Stockard J, Mayberry M. Effective educational environments. Newbury Park, CA: Corwin; 1992.
- 46. Bear G. G. School discipline and self-discipline: A practical guide to promoting prosocial student behavior. New York: Guilford Press; 2010.
- 48. Hayes A. F. Introduction to mediation, moderation, and conditional process analysis: A regression-based approach. Guilford Press; 2013.
- 50. Fredrick S. S, Traudt S, Nickerson A. Social emotional learning practices in schools and bullying prevention. Encyclopedia of Education. New York: Routledge; 2022.
- 53. Rosario-Ramos E. M, Rivas-Drake D, Jagers R. J. Implementing SEL with an Equity Lens: The Role of “Stretching” in Teachers’ Practice. In Motivating the SEL field forward through equity (Vol. 21, pp. 113–126). Emerald Publishing Limited; 2021.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
How Do You Respond to a Young Person Upset by Racist Jokes at School?
When you talk to students about social media radicalization, racism and bullying, you learn how desperate they are for some guidance.

By Dashka Slater
The sixth-grade boy who raised his hand was wiry and small. “People at my school make racist jokes,” he said, when I called on him. His voice had yet to change. “How do I get them to stop?”
I was sitting on a high school stage in Piedmont, Calif., where I had finished a conversation with two high school seniors about my new book, “Accountable,” which was adapted in The New York Times Magazine last August . Both the article and the book tell the story of the turmoil that befell a California high school and its community after some students created and shared racist material on an Instagram account. Since the article and book came out, I have spoken at schools around the country about the issues the story raises: social media radicalization, racism, humor, boy culture, the impacts of bullying and the vexing question of how to respond effectively.
This particular audience was made up mostly of adults, and they responded with applause, as if the boy’s mere desire to stop racist jokes was triumph enough. Perhaps it was. But this sixth grader wasn’t looking for approval. He wanted an actual answer , not the platitudes that adults fall back on when asked about the toxic social dynamics of middle and high school: “Be kind!” “Speak up!” “Be an upstander!” He wanted to know how to get people at his school to stop making racist jokes without becoming the butt of the jokes himself.
I talked about having a firm but nonconfrontational phrase ready, something like “Dude, that’s messed up.” I talked about how to identify which classmates had the social clout to influence their peers and how to approach those people. I talked about when to get an adult involved and how to choose the right one. But even as I spoke, I was thinking: “You know I’m just a journalist, right? I’m the one who asks the questions. What makes you think I have the answers ?”
This is both the joy and the terror of talking to young people about hot-button topics. I usually start by asking students to raise their hands if they’ve seen or heard hate speech online, whether it’s the use of slurs on gaming platforms; racist memes or videos on social media; or ugly remarks in the comment section of an article or video. They all have, of course. We all have.
If I’ve managed to engage their attention — tougher to do just before lunch or during first period, when they’re barely awake — students will respond to my presentation with questions that reveal both how pertinent the topic is to their lives and how eager they are for guidance.
Sometimes the questions are philosophical: “How do you know if someone is a good person or a bad person?” “You say that everyone has the capacity to transform, but what if it’s a mass murderer?”
Sometimes they are practical: “What should we do when we see something racist online?”
And often the questions are deeply personal. Usually, at the end of my presentation, there is a small group of students waiting to talk with me. With the sensitivity that is characteristic of their generation, they will keep some space between one another so that the person speaking with me won’t be overheard.
Within that small cocoon of privacy, I’ve had a young woman sob in my arms after saying: “Those girls you wrote about must have felt so heard. But nobody listened when it happened to me!” I’ve heard the stories of young people who were the targets of everything from racist remarks to violent bullying. I’ve fielded questions about free speech and the role anger plays in the emotional health of victims.
“I did not want to write about my experiences with racism,” Jeena Ann Kidambi, an eighth grader from Framingham, Mass., wrote in an essay about the girls, Ana and A., featured in the Times article because they were targeted by the racist Instagram account. Like A., she wrote, “I did not want to dwell on those memories. However, by writing this essay and embracing my emotions on the subject, I gained closure and released myself from anger’s chokehold.” (The essay won a contest in her school district sponsored by the Swiacki Children’s Literature Festival at Framingham State University.)
At one school, a girl spoke so softly that I had to lean close to hear her. Haltingly, with her eyes fixed on the ground, she asked how people could make amends for a harm they caused if the person harmed wouldn’t speak to them. She didn’t tell me what she had done, but I could see that it haunted her — both the guilt over the injury she had caused and the fear she would be punished in perpetuity.
I think about this girl often, wishing I had a better answer to give her. At every school I visit, I remind students that they are works in progress, that during their teenage years they will both be harmed and cause harm, and that they have the capacity to survive both. And each time, I walk away struck by how vulnerable they are to forces that they neither created nor control.
Dashka Slater is a writer in California with a focus on teenagers and criminal justice. Her book “The 57 Bus,” a New York Times best seller, was based on an article she wrote for the magazine in 2015 and went on to win a 2018 Stonewall Book Award from the American Library Association.
The Great Read
Here are more fascinating tales you can’t help reading all the way to the end..
Two close friends had run side by side for more than 10,000 miles. Both vied for a place in the marathon at the Paris Olympics .
Responding to fears of a “honeybee collapse,” 30 states have passed laws to protect the pollinators. But when they invaded our reporter’s house, she learned that the honeybees didn’t need saving .
In Littleton, N.H., one reaction to a piece of public art prompted a community-wide uproar about gay rights, free speech and the separation of church and state.
After two decades, Shelley Duvall, known for her roles in era defining films like “The Shining” and “Nashville,” has returned to acting. But what happened to her ?
In the age of Ozempic, the “fat activist” Virginia Sole-Smith has hit a nerve at a moment when there is no neutral ground .
Online bullying and playground taunts can lead to teen mental health issues. Here's how the experts recommend handling a bully
Matt Purcell was just six years old when a group of older boys stuffed him in a council bin and left him to stew in the juices.
It was the final act following months of daily school bus bullying that the Korean-Australian had been keeping to himself.
"I was an adoptee from South Korea and my parents were nothing like me, and that was targeted by bullies at my school," he said.
When his adopted parents learned about the behaviour they called the school and the boys were punished.
The physical assaults stopped, but the school bus taunts continued.
"What bullying does, it dehumanises you," Mr Purcell said.
"Being bullied at the age of six right through to high school made me feel like not a human. I struggled with my identity for years.
"My life was pretty sad for a long time."
His father enrolled him in Kung Fu classes, but that also caused problems when Mr Purcell responded to the bullies with his own violence.
"If it wasn't for mentors in my life who pursued me, I wouldn't be here today."
This week an international study found Australia's teens experience bullying at the second highest rate among developed countries.
The Australian Council for Educational Research analysed data from the OECD's Program for International Student Assessment (PISA) test which surveyed more than 13,437 Australian students in 2022.
It found Australia ranked number two for bullying, with 17 per cent of students reporting that "other students made fun of me" but the overall trend was down compared to 2018.
Students in Tasmania reported the highest levels of bullying with the lowest in Victoria, NSW and the ACT.
The study found teen girls were reporting anxiety, fear and panic at twice the rate of boys, but boys appeared more resilient to stress than girls.
Bullying can send some teens to the brink
Bullying is a type of trauma that falls under the banner of Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACE) and it may be contributing to the current surge in youth mental health problems.
"These mental health issues that appear in adolescence, they don't just happen overnight. Usually there's been precursors through the early childhood years," Children's Commissioner Anne Hollonds said.
Numerous studies have found bullying, including cyberbullying, is widespread and more than two-thirds of children aged 12 to 13 have experienced at least one bullying-like behaviour in a 12-month period.
Online, approximately one in four Australians aged between 14 and 17 have been the victim of cyberbullying in the past year.
A major 2021 Australian review found that of all the Adverse Childhood Experiences, bullying — including cyberbullying — was associated with double the risk of suicide in later life.
Teens who were victims of cyberbullying were more likely to report elevated symptoms of depression or anxiety, and the use of social media in particular, was also associated with a high risk of depression and anxiety.
The impact of being left out
Dr Deirdre Gartland leads the Resilience and Mental Health research program at Murdoch Children's Research Institute and says long term bullying could impact how children regulate their emotions, causing them to miss school or disengage at home.
"Ongoing stresses that are persistent and significant for a young person are going to affect how the pathways in the brain develop," she said.
Commissioner Hollonds said greater focus was needed on what she called "the middle years" — ages 8 to 14.
"What we now know is that in those years children are really looking for a sense of belonging," she said.
"If they're not able to build that sense of belonging at school, then that will lead to them starting to disengage from school or to behave in ways that causes them actually to be pushed out."
In a bid to address the impacts of bullying, funding of $4.2 million for school resources and programs such as the Anti-Bullying Collective and the National Day of Action against Bullying and Violence, was allocated in last week's federal budget.
What can parents do?
Dr Gartland said there were facets of life that proved to have a protective effect when it came to resilience and coping with traumatic events like bullying.
These include:
- Fostering a positive sense of self-identity
- Maintaining a good connection to family and friends
- Maintaining a strong connection to culture
- Ensuring teens are enjoying hobbies or activities outside of school hours
- Family guidance
- Ensuring there's a positive engagement with the school and the teachers there
- Fostering a sense of optimism for the future; and
- Helping teens build the capacity to identify and regulate their emotions
She said parents could facilitate some of these by having family traditions like birthdays or family holidays or enrol children in language courses to help them connect to their culture as well as extra-curricular activities such as sport, music or art.
"Connecting in with something that your child or young person really enjoys doing is a really wonderful way to build their resilience," she said.
Parents also needed to be role models and help children understand their emotions during turbulent times.
"Parents can be helping children and young people to both name and recognise their feelings," she said.
Commissioner Hollonds said parents should try to find creative ways to stay connected with teens — whether it be watching trashy television together or cooking a meal.
"Don't think that just because they don't seem to want to spend time with you that that means they don't want you around. Teenagers want you around. That's a fact," she said.
"The more time you spend with them and have those incidental conversations, the more you get a sense of what that child's well-being is over time."
Resilience isn't about 'bouncing back'
Dr Gartland said it was important to remember that resilience did not mean "bouncing back".
"Resilience is about a child or a young person drawing on their internal strengths and drawing on the strengths and resources that sit around them," she said.
"When children do have access to these resources, they are much more likely to have positive mental health and well-being irrespective of what's happening to them in their lives."
Mr Purcell urged parents to become detectives in their teens' lives and use "I statements" such as, "I noticed you've not being going to basketball" to try to draw out what was wrong while sitting shoulder to shoulder with their teen.
"So you've got to get the information out — who's doing what and is this a pattern?" he said.
"Make a decision. Do I need to make my kid move school? Do I need to have a conversation?"
He suggested parents relate their own school experiences to help connect with their teen and even use themselves as a soft target to role play ways to deal with bullies.
"It's a verbal dojo. We practice questioning back to each other. How could I come back to that? Is that actually true?" he explained.
And what not to do…
A key message from the experts to parents is to avoid common cliches like "just ignore them" or "well, just hit them back".
Dr Gartland said those kinds of messages could be damaging.
"It's really important to acknowledge the challenges that young people and children may be going through."
Years after his own bullying experience Mr Purcell became a youth worker and noticed other young people also didn't have the skills to combat verbal abuse.
As a result, he created Social Kung Fu, a program designed to give young people the words and phrases to combat schoolyard and online bullying.
Teens are given mock scripts and taught to use questions like, "what do you mean by that?" and "how do you know it's true?" as verbal blocks to put those spreading rumours and making accusations on the back foot.
Mr Purcell said responding with violence escalated the situation instead of resolving it, and while ignoring bullies may work for one-off incidents, he believed it was less effective for ongoing targeting.
"By being passive you're teaching the bully it's okay," he said.
Mr Purcell said the answer lay in teaching young people that their words could have tremendous impact.
"If we can help people use their words to defend themselves and to give value, then I believe that [good] mental health will increase," he said.
Mental health disorders among young people have soared by nearly 50 per cent in 15 years. The ABC is talking to youth, parents, and researchers about what's driving this pattern, and what can be done to turn things around.
- X (formerly Twitter)
154 Bullying Topics & Bullying Essay Examples
Looking for an exciting research topic about bullying? This problem is very controversial, sensitive, and definitely worth studying
🏆 Top 10 Bullying Topics for Research Papers
📃 bullying essay: writing tips, 🏆 best bullying topics to write about, ⚡ most shocking bullying topics to write about, ✅ simple & easy shocking bullying essay titles, ✍️ bullying essay topics for college, ❓ research questions about bullying.
Examples of bullying can be found everywhere: in schools, workplaces, and even on the Internet (in the form of cyberbullying).
In this article, we’ve collected top bullying research paper topics and questions, as well as bullying essay samples and writing tips. Get inspired with us!
- Direct and indirect bullying: compare & contrast
- The causes of bullying
- Classroom bullying and its effects
- Social isolation as a form of bullying
- Bullying and academic performance
- Passive and active victims of bullying: compare and contrast
- The role of social agencies in bullying prevention
- Public policy for bullying and aggression
- Bullying behavior and psychological health
- Aggressive children and their family background
A bullying essay is a popular assignment in various subjects, including psychology, sociology, and education. Writing an excellent paper on the matter requires more than just in-depth research and planning. Don’t worry; there are some tips that will make writing an essay on bullying much easier:
- Choose a topic that allows analyzing and interpreting the problem. Instead of merely describing what bullying is, try to dig deeper into its causes, consequences, and solutions. If your professor didn’t suggest any topics, you may research bullying essay topics online and select one that would be exciting for you to explore.
- Read sample articles and papers online to see how other students approached the subject. Notice the bits that work and don’t work, and write them out to make the process of creating your essay easier. If you’re struggling with finding enough examples online, you may want to expand your search to discrimination essay topics and materials.
- Research what scholars say about bullying. Articles in scholarly journals are an excellent source of information because they are usually trustworthy. If you’re still in school, your ability to navigate the library or online databases will also impress your tutor. As you start researching, you will find that there is a great variety of studies, and it’s challenging to find the relevant ones. Narrowing down your search would help you to do that. For instance, if you are writing a cyber bullying essay, try searching for social media bullying or online anti-bullying services.
- Include real-life experiences where relevant. Unfortunately, bullying is a common problem in many institutions, and if you haven’t experienced it, your friends or family members probably have. If your tutor allows personal input, explore real-life experiences with bullying. Note the effects, preventive measures that worked or didn’t work, and what a person used to cope with bullying. If personal input is not allowed, you could ask your friends or relatives for ideas and then find high-quality sources that discuss similar problems.
- If you can, be creative about it! A powerful bullying essay example draws from a variety of sources to present material in a creative way and engage readers. Hence, this might be an excellent opportunity for you to include images or graphs in your paper. For example, anti-bullying posters could complement the sections of your work that talks about solutions to the problem. Quotes about bullying coming from famous persons would also be influential, especially if you include them at the beginning of your piece. If you like drawing or painting, you could try to put some of your ideas in graphic form – this will definitely earn you some extra marks! Just make sure to check with your tutor to see whether or not creative input is allowed.
- Structure your paper well to avoid gaps or inconsistencies. It would be beneficial to create a detailed bullying essay outline before you start working. A typical essay should include an introduction, two to three main paragraphs, and a conclusion. The first paragraph of your work should consist of some background information, whereas the last one should restate the points and close up the paper. A good bullying essay introduction should also feature a thesis statement that shows what the piece is about.
These tips will help you to write top-notch essays on bullying, as well as on related subjects. Don’t forget to browse our blog some more to find other helpful materials, including essay titles!
- The Problem of Bullying and Possible Solutions In general, bullying is a critical and complex issue prevailing among children; thus, it is essential to adopt different solutions to tackle it.
- Cyber Bullying Issue Therefore, the goal of this paper is to analyse who the victims of cyber bullying are and the influence it has on them.
- Bullying and Its Effects in Society Secondary research is critical in the development of a background to the research, which helps in determining the validity of the problem and suggested research methodologies.
- Bullying and Child Development Bullying is one of the common vices in schools that influences a lot of growth and development of children. Bullying also affects the ability of children to concentrate in school because they are always on […]
- Social Influence on Bullying in Schools The theory helps us to understand why the stronger members of the school population are likely to “rule” over the weaker members of the school as described in the social hierarchy concept in the theory.
- School Bullying and Moral Development The middle childhood is marked by the development of basic literacy skills and understanding of other people’s behavior that would be crucial in creating effective later social cognitions. Therefore, addressing bullying in schools requires strategies […]
- Bullying on Social Media Platforms It is consistent and repeating, taking advantage of the Internet’s anonymity with the main goal to anger, scare, or shame a victim.
- The Impact of Workplace Bullying The negative impacts of bullying in the workplace develop as a result of ignorance among employees regarding the vice, unreported cases, as well as the negligence of organizational leaders.
- Cyber Bullying and Positivist Theory of Crime Learning theory approaches to the explanation of criminal behavior have been associated with one of the major sociological theories of crime, the differential association theory.
- Is Cyber Bullying Against Teenagers More Detrimental Than Face-To-Face Bullying? Social networking has also contributed greatly to the issue of cyber bullying especially in making it more harmful as compared to face-to-face bullying.
- Verbal Bullying at School: How It Should Be Stopped This paper highlights some of the best practices that can be used by teachers in order to address this problem. So, this information can be of great benefit to them.
- Cyber-Bullying Is a Crime: Discussion It is easy to see the effects of cyber-bullying but it is hard to find out who is the bully making it hard for authorities to pin the blame on the perpetrator of a crime […]
- School Bullying: Causes and Police Prevention It is for this reason that there has been need for the intervention of the community and the government to address the issue of bullying schools lest the school environment becomes the worst place to […]
- Moral Development and Bullying in Children The understanding of moral development following the theories of Kohlberg and Gilligan can provide useful solutions to eliminating bullying in American schools.
- Nature of Bullying In this paper, central focus is going to be on the nature of bullying of children in my hometown, Orlando Florida, how it can be solved, and most importantly; establishing the importance of having knowledge […]
- Bullying and Cyberbullying in Modern Society Cyberbullying among adolescents and teenagers is defined as the purposeful and repetitive harm done by one or more peers in cyberspace as a result of using digital devices and social media platforms.
- Cyber Bullying Prevention in Learning Institutions: Systematic Approach To start with, the students are provided with ways of reporting their concern to the educational institution, and when the staff members of the institution receive the report, they evaluate the information together with the […]
- School Bullying: Methods for Managing the Problem The investigation of relevant studies on the methods for stopping school bullying reveals that the most effective ways of eliminating this type of behavior include providing training for teachers, encouraging students to participate in the […]
- Problem of Childhood Bullying in Modern Society To begin with, the family which is the basic and the most important unit in the society as well as the primary socializing agent plays a major role in shaping behavior of children include bullying.
- The Effects of Cyber-Bullying and Cyber-Stalking on the Society In particular, one should focus on such issues as the disrespect for a person’s autonomy, the growing intensity of domestic violence and deteriorating mental health in the country.
- Behaviour Management: Bullying The typical behaviors which I saw in the child who got bullied are: The victim of this bullying is physically weak and a soft-natured one.
- Social Psychological Concepts of Bullying and Its Types Some of the factors that contribute to bullying include poor parenting, economic challenges, lack of mentorship, and jealousy among others. One of the main concepts used to explain bullying is that of parenting roles and […]
- Bullying Through Social Media: Research Proposal The hypothesis of the study is as follows: the role of adolescents in a cyberbullying situation is interconnected with their psychological characteristics.
- The Issue of Bullying in the Schools It gives me joy to know that the issue of bullying is now a pubic affair since bullying stories were unheard of when I was growing up.
- The ABC Model of Crisis: Bullying at School The next step is the identification of the nature of the crisis, and thus questions are as follows: Who is bullying you?
- Fights and Bullying Among Middle School Learners Alongside the positivist philosophy, the research adopted the survey strategy that involved the use of self-administered questionnaires to collect from the participants.
- Bullying as a Relational Aggression This resistance has been one of the obstacles to eliminating the cyber bullying in the schools. Schools and districts have been involved in the Challenge Day activities where children are advised on how to handle […]
- Bullying in School Face-to-face bullying is an interesting area of study because it clearly demonstrates bullying in school. Students consider bullying as a school culture even though it is contrary to the school rules and regulations of schools.
- Racist Bullying Among Black Students in US Universities This research focuses on the impact of bullying and racism among African American students in the country. What are the impacts of bullying and racism among Black students in U.S.universities?
- The Essence of Bullying: Healthy Societal Relations The aggressor frequently abuses the victim’s lower social standing to gain control of the situation and cause harm, which is another characteristic of the phenomenon.
- Bullying: Violence in Children and Adolescents Bullying is one of the most common manifestations of peer violence in children and adolescents. Prevention of bullying, cyberbullying included, has to occur in accordance with the IBSE Standards of social and emotional learning.
- Bullying, Its Forms, and Counteractions In addition, it is necessary to support those at the center of this bullying, as this can protect them from harmful effects and consequences.
- Incivility, Violence, and Bullying in the Healthcare Workplace The following step is to gather the team and communicate the necessity of change, assigning some individuals for the positions related to the change, in other terms, a support team.
- Effective Ways to Deal With Bullying in US Schools Teachers should ensure the bully is aware of the improper behavior, why it is improper, and the repercussions of the behavior.
- The Gay Teen Suicide & Bullying The article explains that the ones who survive may have access to extensive facilities, support, and status beyond their world of bullies, which sounds reasonable for me.
- Network Bullying: School Policy Framework The first step is to have a careful conversation with the student and an assessment by the school psychologist to ensure that there is a fright.
- How to Reduce Bullying in Senior Facilities One of the main reasons an individual may commit suicide due to bullying is because it may make an individual develop a negative self-image after the bullying incident. Some of the major bullying incidences that […]
- Active Shooter and Nursing Bullying Nurses should lock all doors and use tables and other objects to reinforce them to prevent any possibility of the active shooter getting to the patients’ room.
- Bullying and Autism Spectrum Disorder In fact, bullying as a social phenomenon can be characterized as a social and interaction issue; therefore, it is possible to analyze the connection between autism and acts of bullying and inappropriate behavior.
- Eliminating the Problem of Online Bullying Eliminating the problem of online bullying is vital for improving the mental health of adolescents and young adults and allowing them to build their lives free of adverse external influences. It is possible to see […]
- Sexual Bullying in Schools and Its Influence The author states the difference in the mental and physical maturation of girls and boys as one of the core roots of the issue.
- Bullying and Harassment in the Healthcare Workplace This paper is written to explore the origins of discrimination and harassment in the healthcare workplace. Bullying begins early in medical college and residencies; it has been referred to as an element of the learning […]
- Bullying in Healthcare and Its Consequences Nancy was big and the manager used that to tease her every opportunity she got. It was important to confront the bully and support the victim.
- Queer (LGBT) Teenage Bullying at School The importance of this source to the research is associated with the significant role that youth organizations have to play towards minimizing bullying among LGBT students.
- Bullying of Children: Misconceptions and Preventive Measures As a result, the density of shows and articles devoted to bullying creates an illusion that this event appears more often than it does in reality.
- Bullying Behavior and Impact of Hegemonic Masculinity Rosen and Nofziger applied a quantitative research design to explore the relationships between students’ bullying experiences and race, age, and socioeconomic status and identify the frequency of bullying.
- Bullying and Incivility in Clinical Setting The problem of bullying and incivility in a clinical setting can negatively affect the quality of care provided, so it needs to be managed.
- Bullying and Its Influences on a Person It is common for victims of bullying to develop mental health issues, as they were placed in stressful situations and had a constant fear along with depression in some cases. Making friends is one of […]
- Overview of the Problem of Bullying Undoubtedly, there is no way each person would be able to share and divide their opinion with everyone else because people are not identical, and they tend to have various perspectives.
- “Bullying in Schools”: The Aspects of Bullying In their article, Menesini and Salmivalli examine the current state of knowledge on the topic and thoroughly discuss all of the aspects of bullying.
- Analysis of Bullying and Parenting Style Since the given topic usually refers to children and adolescents, it is evident that their parents hold a portion of responsibility because the adults affect the growth and development of young individuals.
- Hate Crimes – Bullying More than two-thirds of children and adolescents experience bullying and more than one-fourth of them report extreme forms of coercion.
- Bullying Management: Mass Awareness Program Bulletin.”Teachers, trained to help to rebuild trust, confidence, growth, and commitment through mass awareness to arrest bullying in high schools”. The proposed mass action program is meant to promote awareness on the need to stop […]
- An Anti-Bullying Program Integrated With PRAISE by Ackerman I chose to describe bullying because of the importance of the topic and due to my personal interest in it. Education will eliminate most of the reasons for bullying and provide students with the E […]
- Bullying Through Social Media: Methods An Informed Consent Document will be provided to participants prior to the research, explaining the purpose of the study and promising to protect their identity.
- Bullying Through Social Media In particular, inequality in the position of the persecutor and the victim is evident – the aggressor can be anonymous, and there can be many of them.
- Bullying of Nurses During the COVID-19 Pandemic Then, the principles of adult learning will be used to develop and implement an information product to improve the nursing workforce’s bullying awareness and the knowledge of healthy conflict resolution in the workplace.
- Bullying in Healthcare Organizations: Impact on Nursing Practice Bullying in business entities is a common phenomenon, but the extent of its influence on the “production process” in healthcare and medicine institutions is only beginning to be recognized.
- Workplace Bullying Among Nurses in the Acute Setting Since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, the frequency of conflicts between nurses and their colleagues and managers has increased significantly in my workplace.
- Bullying Perpetration Among School-Aged Children Mucherah et al.examined how the school climate and teachers’ sanctions against bullying relate to the risk of becoming a victim or perpetrator of bullying.
- Programming for a Year 5 Class on Bullying As a result, in Lesson 6, they will offer their project addressing bullying behaviour and present it to their class, which is the main aim of the Unit Plan.
- Injury and Violence Prevention: – Bullying The aim of preventing injury and violence from bullying is to enable the student to have a healthy social and physical life that will enable them to perform well in their studies and live healthily.
- Cyber-Bullying vs. Traditional Bullying: Its Psychological Effects The researchers presented the recent statistics in order to illustrate the negative social and psychological effects of cyber-bullying in contrast to the traditional bullying in schools.
- Bullying in the Workplace Old Nurse to New Nurse This unvoiced scourge in nursing is characteristically encouraged by the need of bullies to have a total control of a person. Resignation of nurses due to bullying can lead to shortage of nurses in hospitals.
- Bullying and Peer Abuse Especially at work, targets fear coming to work and this will have an adverse result in the efficiency of the staff in the hospital.
- Bullying in the Nursing Workplace Bullying in the nursing workplace, in this case, causes the one bullied to have a feeling of defenselessness and takes away the nurses’ right to dignity at his or her workplace.
- Cyberbullying and Bullying: Similarities While deciding on fitting and balanced sanctions, it is vital to reflect on the ways in which cyberbullying events differ in effect in comparison to other forms of bullying.
- Protection From Bullying: Methods That Work Because of this, it is vital that parents, teachers, and guardians educate themselves on the nature of bullying and work together to develop effective methods and strategies that would help to overcome the problem.
- Psychology: Social Media and Bullying The purpose of this paper is to discuss the issue of social media and bullying and express the author’s opinion on the matter.
- Bullying of LGBTQ Students in American Schools The chosen article focuses on the issue of bullying of LGBTQ students in American schools and its legal repercussions. The author shows that students who are openly gay or bi, as well as those who […]
- Workplace Bullying and Its Impact on People and Society The paper follows a traditional structure with the introduction and body paragraphs that provide essential information devoted to the problem, and improve the understanding of the concept of bullying.
- “Bullying Behavior Among Radiation Therapists” by Johnson and Trad The literature review encompassed a considerable number of sources pertinent to the study and recent enough to be relevant; all the publications were dated within the last fifteen years.
- Human Rights Issues in Australia: Bullying Among School-Going Age and Young People The focus of the topic of the day is on bullying. It is used to prevent or avoid the occurrence of a bullying experience.
- Bullying and Worker’s Harassment in Western Australia In most of the armed services in Australia, new recruits and women are commonly the victims of bullying and harassment despite the fact that it is unacceptable.
- Aggression and Bullying in the Workplace Investigation Aggression, the effects of which are often equated with the death wish, is an instinct like any other and in natural conditions, it helps just as much as any other to ensure the survival of […]
- Bullying: History and Mechanisms for Prevention Students are encouraged to not participate in bullying and to help prevent bullying of others through positive social reactions to incidences of bullying” and Sharing of Scenarios: “Each group will give feedback and share other […]
- Conflict Resolution Tactics and Bullying This study is interesting to the extent that it shows how the social environment impacts the development of a child and how it shapes his or her conflict resolution techniques.
- School Bullying: Case Analysis Even today there is no generally accepted definition of bullying but it is thought that when an individual is for a long period of time is exposed to repeat negative actions and behavior by one […]
- Bullying in the Workplace as a Psychological Harassment Another form of bullying in the workplace is physical assault in the sense that if the workers are not at ease with each other and when the rules and regulations are not at all observed, […]
- “Adolescents’ Perception of Bullying” by Frisen et al. The second and the third aims of the study were “to describe how adolescents perceive bullies” and “to describe what adolescents believe to be important in order to stop bullying”, respectively.
- The Long Term Effects of Bullying in Elementary School Wolke and Lereya argue that the problem is that the majority of studies on bullying are cross-sectional and only use follow-ups after a short period of time.
- Anti-Bullying and Work Quality Improvement Initiative Given the specifics of the work of nurses, conflicts of this kind negatively affect both the whole process of work and the health of patients in particular.
- Workplace Bullying, Salivary Cortisol and Long-Term Sickness Absence The purpose of this cohort-based study was to investigate the extent to which cortisol levels were associated with sickness absence and the relationships between workplace bullying and sickness absence through the prism of cortisol use.
- Workplace Bullying in Australia It is possible to offer several recommendations that can reduce the risk of bullying in organisations. In this case, more attention should be paid to the absence of mechanisms that can protect the victims of […]
- Domestic Violence and Bullying in Schools It also states the major variables related to bullying in schools. They will confirm that social-economic status, gender, and race can contribute to bullying in schools.
- Staff Training as a Solution to Workplace Bullying Furthermore, it has an appeal to logos as the writer has facts about the prevalence of workplace bullying in the USA.
- The “Bully-Free” Initiative: Bullying in Education The students need to have a clear idea that bullying goes against the rules of the school and which actions may be considered bullying.
- Free Speech vs. Bullying Laws One of the topical aspects of modern democracy is the freedom of speech expressed in an ability to come up with personal ideas and the lack of restrictions on the right of expression through publicity.
- Gender and Bullying Issues in Nursing A lack of tolerance for workplace harassment and bullying is likely to lead to the deterioration of the situation and further misunderstanding and tension in an organization.
- Bullying and Cyberbullying Among Peers They are facing the dilemma of how to react, whether they have to fight a superior force of the enemy or to complain to teachers and parents, undermining their reputation.
- Bullying in Schools and Its Major Reasons As of now, the most important goal in research studies covering the topic of bullying in schools is to understand the mechanisms behind bullying promotion and prevention.
- Bullying in Schools: Worldwide Study and Survey The parents were asked to rate the frequency of the bullying that their children experience and to describe the experience of bullying that their children went through.
- Bullying Prevention Programs Some teachers and professors claim that their students cannot show their potential in their hobbies due to the limitations they experience because of bullies around them. As it is mentioned above, educators do not control […]
- Bullying and Its Impact Thus, the current paper is dedicated to the issue of bullying and its effects as well as anti-bullying practices as related to peer victimization.
- Dealing With Workplace Bullying According to the report presented by the University of Louisville, workplace bullying is a repeated action of one employee or a group of employees towards another individual or group. Dealing with bullying in the workplace […]
- Bullying Policies in Walton School District and Georgia University The sample bullying policy language in Walton School District is very similar to the language in the policy of the University of Georgia.
- Amanda Todd’s Bullying and Suicide Story She was fifteen years old, and her story created a major uproar in the press, as it showed the true nature of bullying and the effects it has on the person.
- Bullying in America: Causes and Prevention That is why it is important to pay attention to the reasons why bullying occurs and ways in which it can be reduced.
- Bullying, Facts and Countermeasures Whether it is the bully or the bullied, the parents will need to do a lot to see to it that their children are brought up in the best of the behaviors.
- Bullying as Social and Criminal Deviance The most important step in the student’s guide to research that I would need to analyze bullying is defining the topic.
- Bullying and Legislation in Australian Workplace According to the authors of the article, workplace bullying can be characterized as internal violence. According to the authors of the article, bullying is a widespread phenomenon and is a common attribute of many organizations.
- Bullying at Australian School: Causes and Solution The technological breakthrough that was witnessed in the late 90s and the early 2000s also contributed to the development of the phenomenon, sparking the concepts such as cyberbullying and online bullying.
- Workplace Bullying in The Playground Never Ends The primary reason for becoming a bully is primarily seen in fear to lose authority or formal positions in an organization and have more institutional power than that of the targets.
- Bullying and Suicide in High Schools The main limitation of this research is that the scholars surveyed the victims more often. The victims of cyberbullying also had a tendency to be depressed and contemplate suicide.
- School-Aged Children’ Bullying Behaviors It is due to this that the work of Janssen et al.sought to show just how potentially damaging this behavior could be and the potential psychological repercussions it could have on young children due to […]
- College Students: Suicide and Bullying-Methods The analysts used this tool to report the mood of the participants by posting quizzes, which the students answered while filling the questionnaire.
- Childhood Bullying and Adulthood Suicide Connection In this regard, the seriousness of the issue is depicted in research results that indicate that at least 50% of children and youth in the US have experienced bullying situations as either bullies or victims […]
- Girl-To-Girl Bullying and Mean Stinks Program The positive results can be achieved by the implementation of the multiple educational programs, the increase in public awareness, and promotion of the values of the healthy relationships.”Mean Stinks” is exactly the program with the […]
- Association of Parenting Factors With Bullying The lack of the parental support is the main cause of students’ deviant behaviors at school, including the cases of bullying, and those parents who pay much attention to developing their career cannot provide the […]
- Workplace Bullying and Its Impact on Performance Workplace bullying refers to a deliberate, repeated, and continuous mistreatment of a worker or a group of workers by one or more colleagues in the workplace.
- The Problem of Workplace Bullying In particular, this paper will include the discussion of the research articles, reports and case studies that describe the causes of workplace bullying and the strategies used by companies in an effort to overcome it.
- College Students: Suicide and Bullying The misconception that bullying is a minor issue among college students has contributed to the high number of students who suffer because of bullying.
- Homosexual Students and Bullying Specifically, the section addresses the prevalence of bullying in schools and the level of bullying in bisexuals, gay males, and lesbians.
- Social Psychology of Violence and Bullying in Schools Bullying is a common phenomenon in schools and it is reported that it results in violence in learning institutions in the end.
- Bullying and Suicide: The Correlation Between Bullying and Suicide Nonetheless, the extensive research shows that the correlation exists and bullying is one of the risk factors for development of suicidal ideas in adolescents.
- Cyber Bullying Reduction Program Table of Activities Activity Significance Assembling parents/guardians, students and teachers to announce and explain the program in the institution To enlighten parents/guardians, students and teachers about the rules and regulation enacted due to the threat […]
- Discouraging and Eliminating Cyber Bullying Resources Role of the resource/input Statement forms To facilitate information transfer to the staff Counseling Personnel To arm students against the problem Bullying report system To create efficient internet enhance report system Regulation implementation documents […]
- High School Bullying Effective Responses Emphasis will also be made on the kind of audience to read this article because the contents of this study need to be at par with other similar articles in the journal to be selected.
- Bullying and Suicide Among Teenagers Specific objectives Analyze the causes of bullying among teenagers in the country Analyze the effects of bullying among victims, perpetrators and by-standers Analyze the relationship between bullying in school and suicide among teenagers in the […]
- Bullying in the Workplace Organizational leaders have an ethical obligation to ensure that they deal with cases of bullying within the workplace in a professional manner that demonstrates equality, honesty, and high sensitivity to the needs of others.
- Social Bullying in Jeff Cohen’s “Monster Culture” It is clear that his part of character is mostly dominant in the childhood stages, as children are not able to develop a sense of morality and predict the consequences of their actions.
- Cyber Bullying and Its Forms The difference between the conventional way of bullying and cyber bullying is that in conventional bullying, there is contact between the bully and the victim.
- Problem of Workplace Bullying Authority intervention should occur when the employees fail to respond to awareness intervention, and thus decide to continue with their behaviors.
- Problem of the Managing Bullying and Harassment in the Workplace Employees in an organization have a specific role that they are supposed to play and this means that there might be shortcomings which should not lead to bullying.
- Cyber Bullying as a Virtual Menace The use of information and communication technologies to support a deliberate and most of the time repeated hostile behavior by an individual or groups of people with the sole intention of harming others, one is […]
- Does Bullying Cause Emotional Problems? However, the current study was relevant because of this design, for the scope of the study covered as well as the results were accurate, and the conclusions drawn were correct.
- Ban High School Bullying A number of stakeholders contribute to the high prevalence of bullying in American schools. Schools that ignore bullying are a big part of the problem and they need to be held accountable.
- The Problem of Bullying While most states in the United States of America have laws to protect people from bullying, the federal government is yet to enact an anti-bullying law.
- Ethical Case: Facebook Gossip or Cyberbullying? The best option to Paige is to apologize publicly and withdraw her comments. The final stage is to act and reflect the outcome of the choice made.
- Bullying on the Rise: Should Federal Government Enact Federal-Bullying Laws? This paper will thus use both primary and secondary data to discuss the prevalence of bullying in schools and whether the federal govern should enact federal laws to curb the social vice at school.
- Character Traits of Bullying Despite the fact that such characteristics may differ from child to child, it is the common feature of difference that makes the target children get noticed by the bullies.
- Bullying in the Schools Furthermore, the law states that training should be done to the teachers as well as the other members of staff on how to deal with bullying and the law also needs the schools to report […]
- Troubled Adolescent due to Bullying His lowered self-esteem would make him to observe the common behaviours of the older boys quietly and accept the situation as a cultural practice.
- Workplace bullying: does it exist?
- What are the three key elements of bullying?
- How does bullying affect those who observe it?
- Direct and indirect bullying: what is the difference?
- What families do bullies typically come from?
- Aggressive children: what is their future?
- How to prevent bullying in schools?
- School bullying and domestic violence: is there a connection?
- Cyberbullying: how to prevent it?
- What can parents do to prevent their children from bullying?
- Children’s Rights Research Ideas
- Equality Topics
- Homophobia Topics
- School Violence Ideas
- Respect Essay Topics
- Social Inequality Paper Topics
- Suicide Topics
- Youth Violence Research Topics
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 22). 154 Bullying Topics & Bullying Essay Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/bullying-essay-examples/
"154 Bullying Topics & Bullying Essay Examples." IvyPanda , 22 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/bullying-essay-examples/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '154 Bullying Topics & Bullying Essay Examples'. 22 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "154 Bullying Topics & Bullying Essay Examples." February 22, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/bullying-essay-examples/.
1. IvyPanda . "154 Bullying Topics & Bullying Essay Examples." February 22, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/bullying-essay-examples/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "154 Bullying Topics & Bullying Essay Examples." February 22, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/bullying-essay-examples/.
- Mission and Vision
- Scientific Advancement Plan
- Science Visioning
- Research Framework
- Minority Health and Health Disparities Definitions
- Organizational Structure
- Staff Directory
- About the Director
- Director’s Messages
- News Mentions
- Presentations
- Selected Publications
- Director's Laboratory
- Congressional Justification
- Congressional Testimony
- Legislative History
- NIH Minority Health and Health Disparities Strategic Plan 2021-2025
- Minority Health and Health Disparities: Definitions and Parameters
- NIH and HHS Commitment
- Foundation for Planning
- Structure of This Plan
- Strategic Plan Categories
- Summary of Categories and Goals
- Scientific Goals, Research Strategies, and Priority Areas
- Research-Sustaining Activities: Goals, Strategies, and Priority Areas
- Outreach, Collaboration, and Dissemination: Goals and Strategies
- Leap Forward Research Challenge
- Future Plans
- Research Interest Areas
- Research Centers
- Research Endowment
- Community Based Participatory Research Program (CBPR)
- SBIR/STTR: Small Business Innovation/Tech Transfer
- Solicited and Investigator-Initiated Research Project Grants
- Scientific Conferences
- Training and Career Development
- Loan Repayment Program (LRP)
- Data Management and Sharing
- Social and Behavioral Sciences
- Population and Community Health Sciences
- Epidemiology and Genetics
- Medical Research Scholars Program (MRSP)
- Coleman Research Innovation Award
- Health Disparities Interest Group
- Art Challenge
- Breathe Better Network
- Healthy Hearts Network
- DEBUT Challenge
- Healthy Mind Initiative
- Mental Health Essay Contest
- Science Day for Students at NIH
- Fuel Up to Play 60 en Español
- Brother, You're on My Mind
- Celebrating National Minority Health Month
- Reaching People in Multiple Languages
- Funding Strategy
- Active Funding Opportunities
- Expired Funding Opportunities
- Technical Assistance Webinars

- Community Health and Population Sciences
- Clinical and Health Services Research
- Integrative Biological and Behavioral Sciences
- Intramural Research Program
- Training and Diverse Workforce Development
- Inside NIMHD
- ScHARe HDPulse PhenX SDOH Toolkit Understanding Health Disparities For Research Applicants For Research Grantees Research and Training Programs Reports and Data Resources Health Information for the Public Science Education

- NIMHD Programs
- Education and Outreach
- 2024 Awardees
- Raphael: 2024 Mental Health Essay
- Extramural Research
- Intramural Research
- NIMHD Collaborations
- Fuel Up to Play 60 en Espanol
- COVID-19 Information and Resources
2024 Mental Health Essay Contest Awardee: Gold
Let’s CHAT: Mental Health Impact on Teens Living with Speech Challenges
Raphael, hawaii.

Nearly everyone has experienced being tongue-tied. We try to engage in conversation, but the words come out wrong or not at all. Now, imagine being a teenager who always feels tongue-tied and the mental anguish that follows. This is how I felt in 2021. While searching for support groups for teens with speech challenges, I discovered there was no such group in my entire state. So, I founded a 501(c)(3) nonprofit, CHATS: Caring for Hawaii Teens with Speech Challenges. In speaking with fellow stutterers and others who had been teased, bullied, and mocked due to their communication differences, I began to realize the correlation between the societal treatment of those with speech challenges and the emotional scars it leaves. This ripple of abuse needed to stop. That was the moment I decided to be the change. In partnering with Mental Health America of Hawaii and Spill the Tea Café, a local mental health clinic for youth, I would spread a message of inclusiveness, anti-bullying, and mental wellness.
According to the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (2010), approximately 18.5 million Americans have a communication disorder, yet many know little about it. Lack of knowledge and the inability to understand leads to the fabrication of myths and misconceptions. These false beliefs negatively affect the mental well-being of those who have trouble communicating, especially teens and young children. According to Mental Health America, youth with speech differences are five times more likely to be bullied. Youth with a speech challenge, such as a stutter, are 61% more likely to be targeted by a bully. As a result, these targeted youth have an increased likelihood of depressive symptoms and suicidal ideations. Shame, discrimination, avoidance, lack of access to clinicians, and undiagnosed speech challenges can be a barrier to those seeking therapy. Through CHATS, I am working to bridge the gap between youth and the medical help they need and deserve.
As the first in my community to tackle the topic concerning the mental health of teens with speech challenges, I partnered with local speech and mental health organizations and spoke within the community. I filmed a video that aired on PBS Hawaii called “A Safe Place for Youth.” It featured CHATS partner, Spill the Tea Café, and highlighted the clinic’s innovative and welcoming approach to individual and group therapy. I was the youngest of four panelists on INSIGHTS PBS Hawaii: Mental Health of Hawaii’s Teens. INSIGHTS is Hawaii’s second most-watched locally produced program on PBS Hawaii. On INSIGHTS, I gave my perspective, as well as those of my peers, on the topics of bullying, anxiety, mental health, as well as my work with CHATS. To stress the importance of mental health, I, alongside CHATS partner Mental Health America of Hawaii, visited neighborhood schools to talk about anti-bullying and acceptance for those with communicational differences and to offer help and resources to those who felt alone. I spoke to a crowd of concertgoers at a Martin Luther King Jr. event, sat on the 2022 Hawaii State Children and Youth Summit panel to stress the importance of state legislature to do more to help our youth, and hosted family meet-and-greets. I was able to speak with over 1,700 students, parents, educators, and medical health professionals. I have reached thousands of households through television, printed periodicals, and online sources, spreading a message of awareness and inclusivity.
Reaching out to the local community, I needed a multi-teared approach. I formed a team that includes mental health advocates, educators, youth coordinators, parents, teens, government officials, and speech and language pathologists. Members of my team and I have made an educational video for schools about speech challenges and mental health. These videos enable teachers to share this information multiple times within multiple grade levels. Speech and language pathologists who support the Hawaii Department of Education are speaking with me to discuss ways to be better stewards for CHATS. Speech therapists and pediatricians are encouraging their young patients to seek out social support through CHATS. Our teen support group meets once a month where we share and help each other in a safe environment. Future plans include a six-week series addressing different aspects of speech challenges; psychological and social. The series will feature guest speakers and will involve both teens and their parents.
Taking action in my community has inspired others to advocate for CHATS as well. For example, a 100-year-old World War II veteran living with a stutter heard about CHATS. I had the privilege of meeting with him where I learned about his difficult life journey through stuttering. Overjoyed with the work CHATS is doing he volunteered as a guest speaker to encourage others who may be struggling. A teen CHATS member with a cleft palate decided to start her own CHATS fan club in her school. We have gained a teen base of volunteers who attend CHATS community events, speak to attendees about the problem, and discuss the solution. A faculty member at a local school has invited me to return to impact more students. Also, the medical community invited me as a guest speaker for the Continuing Medical Education (CME) Grand Rounds Presentations (a sort of TED Talk for doctors, nurses, interns, students, etc.) and to present a talk for Behavioral Health ECHO (Extension for Community Healthcare Outcomes). I presented to hundreds of psychiatrists, pediatricians, speech and language pathologists, and those involved with the overall well-being of our youth. The co-founder of Camp Ohana Foundation, a nonprofit organization dedicated to empowering youth in Africa, has agreed to partner with us to provide resources and therapy to kids in Kenya.
Through awareness and education, we can break the walls of misconception to create a society that views those with speech and communication differences with normalcy and acceptance. This will empower youth to raise their voice and teach the community to listen. It all starts with a conversation.
NIH recognizes these talented essay winners for their thoughtfulness and creativity in addressing youth mental health. These essays are written in the students' own words, are unedited, and do not necessarily represent the views of NIH, HHS, or the federal government.
Page published May 31, 2024
May 2024: NIH Announces Winners of High School Mental Health Essay Contest
Dec. 2023: High School Students Invited to Reflect on Mental Health Stigma in National Essay Contest
National Institute of Mental Health
National Institute on Minority Health and Health Disparities
Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development

Staying Connected
- Funding Opportunities
- News & Events
- HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
- Privacy/Disclaimer/Accessibility Policy
- Viewers & Players
- Alzheimer's disease & dementia
- Arthritis & Rheumatism
- Attention deficit disorders
- Autism spectrum disorders
- Biomedical technology
- Diseases, Conditions, Syndromes
- Endocrinology & Metabolism
- Gastroenterology
- Gerontology & Geriatrics
- Health informatics
- Inflammatory disorders
- Medical economics
- Medical research
- Medications
- Neuroscience
- Obstetrics & gynaecology
- Oncology & Cancer
- Ophthalmology
- Overweight & Obesity
- Parkinson's & Movement disorders
- Psychology & Psychiatry
- Radiology & Imaging
- Sleep disorders
- Sports medicine & Kinesiology
- Vaccination
- Breast cancer
- Cardiovascular disease
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Colon cancer
- Coronary artery disease
- Heart attack
- Heart disease
- High blood pressure
- Kidney disease
- Lung cancer
- Multiple sclerosis
- Myocardial infarction
- Ovarian cancer
- Post traumatic stress disorder
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Schizophrenia
- Skin cancer
- Type 2 diabetes
- Full List »
share this!
May 31, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
Sleep moderates the link between bullying and suicide in teens
by American Academy of Sleep Medicine

A new study to be presented at the SLEEP 2024 annual meeting found that sleep duration significantly moderates the association between bullying and suicide attempts among adolescents in the U.S. The research abstract was also published in an online supplement of the journal Sleep .
The study revealed that 15% of adolescents reported they were bullied at school, and 16% were bullied electronically; 10.2% reported they had attempted suicide during the past year; and 77.3% did not adhere to sleep duration recommendations.
Adolescents who reported four hours of sleep or less per night were two times as likely to attempt suicide, and sleep duration significantly moderated the association between bullying in school and suicide attempts .
"Adolescent suicide and suicide attempts constitute a serious public health crisis in the United States," said lead author Marie-Rachelle Narcisse, who has a doctorate in public health and is an assistant professor in the Warren Alpert School of Medicine of Brown University and a research scientist at the E.P. Bradley Hospital COBRE Center for Sleep and Circadian Rhythms in Child and Adolescent Mental Health in Providence, Rhode Island.
"The fact that sleep duration significantly modifies the association between bullying and suicide attempts is a remarkable finding."
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, suicide is the second-leading cause of death among teens between 14 and 18 years of age. The American Academy of Sleep Medicine recommends that teens should sleep eight to 10 hours on a regular basis to promote optimal health. Insufficient sleep in teenagers is associated with increased risk of self-harm, suicidal thoughts, and suicide attempts.
The study involved an analysis of data from the 2021 Youth Risk Behavior Surveillance System, comprising a nationally representative sample of 17,134 participants. The researchers analyzed the relationships among electronic or school bullying, sleep duration, and past-year suicide attempts among adolescents between 12 and 18 years of age. Results were adjusted for potential confounders including sex, age, race/ethnicity, screen time , and poor mental health.
Adolescents who were bullied in school or electronically were three times as likely to attempt suicide compared with those who were not bullied. Those reporting no bullying showed a reduced likelihood of suicide attempts as sleep duration increased to seven hours, and the likelihood remained constant with more hours of sleep.
According to Narcisse, the results emphasize that sleep duration is an important target for interventions to reduce suicide in teens.
"If improved sleep duration can inhibit the adverse effect of bullying on suicide attempts, then interventions aimed at improving sleep duration could potentially have a positive influence on lowering suicide risk among adolescents," said Narcisse.
Explore further
Feedback to editors
Cancer patients often do better with less intensive treatment, new research finds
5 hours ago
Study sheds new light on the contribution of dopamine to reinforcement learning
12 hours ago

Almost 1 in 3 Americans know someone who's died from a drug overdose
Jun 1, 2024

Antibody discovery promises new hope in influenza B battle, paves way for universal vaccine

Eye-tracking techniques could help primary care providers diagnose autism sooner, more accurately
This self-powered sensor could make MRIs more efficient

Not eating can hinder weight loss, study in fruit flies suggests
Neuroscience research suggests ketones can enhance cognitive function and protect brain networks
New research finds antidepressants may help deliver other drugs into the brain

Mediterranean diet tied to one-fifth lower risk of death in women
Related stories.

Three factors exacerbate suicidal behavior in bullied teens
Jun 3, 2021

Trauma begets trauma: Bullying associated with increased suicide attempts among 12-to-15-year-olds
Aug 15, 2019

Lack of sleep can be linked to depression and suicidal thoughts among young people
Dec 13, 2023

Sleep troubles tied to suicidal thoughts in teens
Jun 19, 2023

Sleep restriction tied to negative cognitive effects in teens with overweight, obesity
May 23, 2024

Being bullied is associated with mental distress and suicide attempts in teens
Feb 15, 2023
Recommended for you

Infants hear significantly more speech than music at home, study finds

Study shows phone use boosts mood of teenagers
May 30, 2024

Could ultra-processed foods be associated with your insomnia?

Study suggests vocal exploration in babies is important for speech development
May 29, 2024

Study shows more than just social media use may be causing depression in young adults
Let us know if there is a problem with our content.
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Medical Xpress in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Published: 2021/11/05. Number of words: 1829. School bullying can be defined as the situation in which one or more students (The Bullies) single out a child (victim) and intend in behavior intended to cause discomfort or harm the child. A bully will repeatedly target the same victim several times.
School violence, including bullying, is widespread: one in three learners is bullied at school every month globally. The growing use of digital devices has exacerbated cyberbullying. In 2019, at least 10% of learners aged 8-10 had experienced cyberbullying, rising to 20% of learners aged 12-14. School violence can leave long-lasting impacts on learners' safety, physical and mental health ...
Abstract. During the school years, bullying is one of the most common expressions of violence in the peer context. Research on bullying started more than forty years ago, when the phenomenon was defined as 'aggressive, intentional acts carried out by a group or an individual repeatedly and over time against a victim who cannot easily defend him- or herself'.
1. Psychological: Being a victim of bullying was associated with increased depression, anxiety, and psychosis. Victims of bullying reported more suicidal thinking and engaged in greater self ...
Published: Dec 16, 2021. It is common to see bullying happen in the high school age group. Many teenagers often believe they can get away with bullying due to their lack of consequences or unclear consequences. Due to the advancement of technology, kids now have another source of bullying; social media. Children are no longer able to escape the ...
It reduces a range of problems like anxiety, emotional distress, and depression; reduces disruptive behaviors like conflicts, aggression, bullying, anger, and hostile attribution bias; and it improves academic achievement, creativity, and leadership. A 2012 study of 36 first-grade teachers showed that when teachers were more emotionally ...
of the complexity of bullying among school-aged youth and di-rections for future research and intervention efforts. Keywords: bullying, victimization, school violence S chool bullying has been around for as long as any-one can remember, featured in Western literature for over 150 years—e.g., in Charles Dickens's Oliver Twist
This essay presents a succinct overview of bullying in schools and how it can be dealt with more effectively. The bullying of pupils by pupils in schools has been a concern for many years. In ...
School violence refers to all forms of violence that takes place in and around schools and is experienced by students and perpetrated by other students, teachers and other school staff. This includes bullying and cyberbullying. Bullying is one of the most pervasive forms of school violence, affecting 1 in 3 young people.
Bullying linked to gender and sexuality often goes unchecked in schools. Victoria Rawlings, University of Sydney. About 80% of students experience some kind of gender-based bullying in their ...
1 Introduction. Bullying, long tolerated by many as a rite of passage into adulthood, is now recognized as a major and preventable public health problem, one that can have long-lasting consequences (McDougall and Vaillancourt, 2015; Wolke and Lereya, 2015).Those consequences—for those who are bullied, for the perpetrators of bullying, and for witnesses who are present during a bullying event ...
The Effects of School Bullying. School bullying has far-reaching and detrimental effects on the lives of those involved. These effects extend beyond the school environment and can impact the mental, emotional, and physical well-being of individuals: Psychological Impact: Victims of bullying often experience anxiety, depression, low self-esteem ...
When bullying occurs, it causes oppression to the affected parties thus affecting their social life and studies in the case of students. This paper is therefore an analysis of the possible causes and ways of preventing instances of bullying in schools by the police. Past and present approaches of addressing the issue of bullying in schools will ...
Mental Health Impact. One of the primary consequences of bullying in schools is its impact on the mental health of the victims. Studies have shown that victims of bullying are more likely to experience depression, anxiety, and other mental health issues than their peers who have not been bullied. The constant fear and stress caused by bullying ...
Abstract Objective: Bullying threatens the mental and educational well-being of students. Although anti-bullying policies are prevalent, little is known about their effectiveness. This systematic review evaluates the methodological characteristics and summarizes substantive findings of studies examining the effectiveness of school bullying policies. Method: Searches of 11 bibliographic ...
Bullying has been part of school, and even workplaces, for years. More recently, though, technology and social media have created a new venue for bullying that has expanded its reach. Cyberbullying is bullying that happens online and via cell phones. Websites like YouTube, Instagram, and Snapchat allow kids to send hurtful, ongoing messages to ...
Bullying is mostly evident when there is an imbalance of power among individuals. We will write a custom essay on your topic. For instance, powerful or influential people are said to practice or bully other learners (Olweus, 1993, p. 20). In addition to this, those in power tend to bully others with an aim of making them feel less powerful.
This paper attempts to look at the issue of bullying in the schools. A personal story about how I was bullied when I was young is included. The paper looks at this issue by considering aspects like causes and forms of bullying as well as examples of bullying cases. We will write a custom essay on your topic. 812 writers online.
Students who are targeted for bullying are often members of historically marginalized groups, such as racial and ethnic minorities, the LGBTQ community, and children with different abilities. Students who are bullied can disengage from school, which can, in turn, negatively impacts their relationships and academic achievement.
Read Essay on Cyber Bullying. Bullying can happen at any stage of life, such as school bullying, College bullying, Workplace bullying, Public Place bullying, etc. Many times not only the other persons but the family members or parents also unknowingly bully an individual by making constant discouraging remarks.
Kids who are bullied are more likely to experience: Depression and anxiety, increased feelings of sadness and loneliness, changes in sleep and eating patterns, and loss of interest in activities they used to enjoy. These issues may persist into adulthood. Decreased academic achievement—GPA and standardized test scores—and school participation.
Long Essay on Bullying in Schools is usually given to classes 7, 8, 9, and 10. When a person is seen to use force, coercion and (or) threat to dominate, harm or abuse, someone is known as bullying. Bullying is characterized by an imbalance of social and (or) physical power, which differentiates it from conflicts and fights. It is a repeated ...
An authoritative school climate, along with greater teacher support and warm relations among peers are frequently connected with less school bullying. The main aim of this paper is to examine the direct link as perceived by students between teachers' disciplinary practices and bullying in school and students' satisfaction with school. The indirect relationships are explored via the ...
Since the article and book came out, I have spoken at schools around the country about the issues the story raises: social media radicalization, racism, humor, boy culture, the impacts of bullying ...
Reading of the heartbreaking suicides of 10-year-old Sammy Teusch in Greenfield, Ind., and 12-year-old Flora Martinez in Las Vegas due to relentless, unpunished public-school bullying makes me ...
Bullying at school can take a number of different forms. Common types of bullying behavior at school include:. name-calling and public humiliation; fighting and physical violence; excluding ...
In a bid to address the impacts of bullying, funding of $4.2 million for school resources and programs such as the Anti-Bullying Collective and the National Day of Action against Bullying and ...
Table of Contents. Examples of bullying can be found everywhere: in schools, workplaces, and even on the Internet (in the form of cyberbullying). In this article, we've collected top bullying research paper topics and questions, as well as bullying essay samples and writing tips. Get inspired with us!
To stress the importance of mental health, I, alongside CHATS partner Mental Health America of Hawaii, visited neighborhood schools to talk about anti-bullying and acceptance for those with communicational differences and to offer help and resources to those who felt alone.
The study revealed that 15% of adolescents reported they were bullied at school, and 16% were bullied electronically; 10.2% reported they had attempted suicide during the past year; and 77.3% did ...