
- Search 85832
- Search 15378
- Search 64684


Tesla Business Model (2023) | Tesla Business Model Canvas
Last updated: Oct 9, 2021
Company: TESLA, Inc. CEO: Elon Reeve Musk Subsidiary: SolarCity, Tesla Grohmann Automation, Maxwell Technologies Founders: Elon Musk, Martin Eberhard, JB Straubel, Marc Tarpenning, Ian Wright Year founded: 2003 Headquarter: Palo Alto, California Type: Public Ticker Symbol: TSLA Annual Revenue (2021): $53.82 Billion Profit |Net income (2021): $5.64 Billion
Products & Services: Tesla Motor Vehicles | Auto service | Financial Services | Energy Storage (Power battery packs) | Solar panels | Lifestyle products | Retail merchandise
Competitors: Kia Soul EV | BMW i3 | Nissan Leaf | Volkswagen e-Golf | Hyundai Ioniq EV | Tesla Model S | Chevrolet Volt EV.
Table of Contents
Introduction to Tesla, Inc.
Tesla, Inc. (formerly known as Tesla Motors, Inc.) is an American automotive, lifestyle and energy company that was originally founded in July of 2003 . The company launched its products specifically in the automotive industry and began to design and supply lifestyle products as well. The company was originally founded by engineers Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning prior to changing its name to just Tesla, Inc. in February of 2017.
During the Series A funding phase, Elon Reeve Musk, J. B. Straubel, and Ian Wright were also accredited with the recognition as the founding fathers of Tesla Motors. Elon Reeve Musk is currently the serving CEO of the company, overlooking all the operations and the structures of the business.
In August of 2015, Tesla, Inc. aimed its focus towards on safety, autopilot, charging networks and motors. Tesla operated a combination of 260 galleries/retails across the United States in 2016. One of the most exciting years for Tesla was 2017.
Tesla was able to focus its markets in the Germany sectors, providing a Dutch RDQ-issued Whole Vehicle type approval (WVTA) which should be accepted as a legal compliance document, without grounds to a national type of approvals in EU member States.
This significantly reduced any compliance check and excelled deliverance exponentially, since the vehicle was already under Germany vehicle standard compliance.
In the same year, Tesla launched additional international locations in Dubai and South Korea, which increased its brand visibility and helped increase revenue streams.
During that year Tesla had a budget of $52 million as a marketing budget and used a referral program and a word of mouth tactic to help attract customers that would be interested in purchasing a Tesla vehicle.
By 2018, Tesla, Inc. was ranked as the bestselling plug-in passenger car manufacturer in the electric car industry. It sold over 245,240 units in total. With over 200k+ units sold, Tesla was responsible for capturing the market shares of 12% in the electric-plug-in vehicle industry. In Q2 of 2020, Tesla delivered 90,650 vehicles to customers and is expected to deliver more than 500,000 cars by the end of 2020. [ 1 ]
The company’s market capitalization increased to nearly $208 billion and surpassed Toyota’s $202 market cap to become the world’s most valuable automaker by market value. [ 2 ]
The following is the complete Tesla Business Model Canvas report and how it is different from the rest of its competition.

Tesla Business Model Canvas
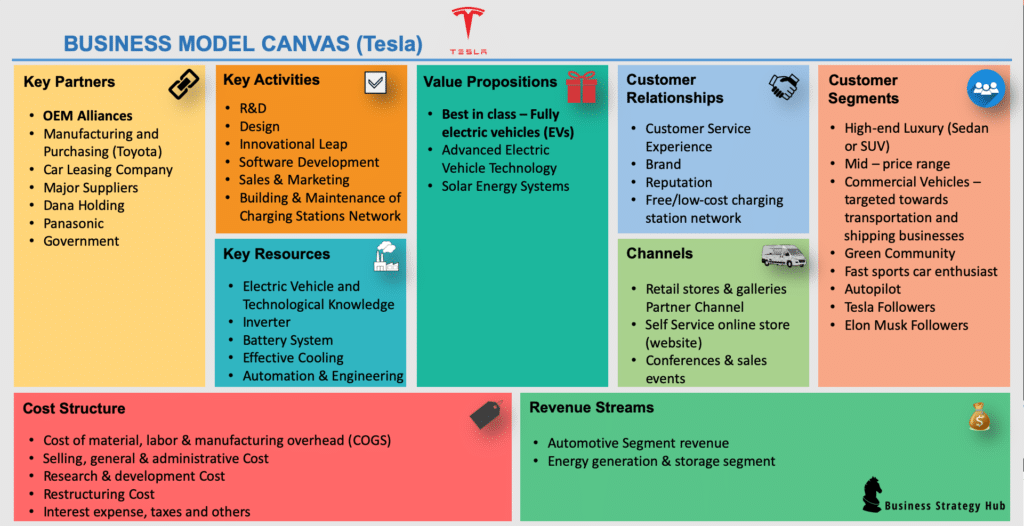
1. Value Propositions of Tesla
Best in class – Fully electric vehicles (EVs)
- Tesla aims to provide some of the best in class EV models that offers high performance, energy efficient, long range (with convenient recharge stations), and sleek designs.
- Model S (Luxury sedan) – June 2012
- Model X (SUV) – September 2015
- Model 3 (Lower priced sedan for the mass market) – July 2017
- Model Y (Compact Crossover) – expected to deliver in 2020
- Semi-Truck (Commercial Heavy-duty truck) – expected to deliver in 2020-21
- Tesla Pickup Truck – expected to deliver in 2020-21
- Tesla Roadster (Sports car) – Original model was in production from 2008-2012. A newer version is expected to deliver in 2020.
- Tesla Cybertruck – Tesla’s angular-designed Cybertruck was unveiled in November 2019 and is expected to hit the market in 2021. [ 3 ]

Advanced Electric Vehicle Technology
- Supercharging and destination recharging station network
- High miles per charge
- All wheel drives
- Free or low-cost electric charging stations or battery swap.
- To support open source movement, Tesla has opened the use of all its patents for other auto-manufacturer to advance EV technology.
- Autopilot option
- Free software updates
- Solar Energy Systems – Tesla is known for its Electric vehicles, also sells solar panels to residential and commercial customers.

2. Customer Segments of Tesla
Tesla’s engineers and designers have designed vehicles appropriate for every customer groups. Vehicle class type is based on the following segments:
- High-end Luxury (Sedan or SUV)
- Mid – price range
- Commercial Vehicles – targeted towards transportation and shipping businesses
- Green Community
- Fast sports car enthusiast
- Autopilot enthusiast
- Tesla Followers
- Elon Musk Followers
3. Key Partners of Tesla
OEM Alliances
- 2009 – Tesla, Inc. aligned a partnership with OEM manufacturer ( Daimler ), which helped to provide Tesla, Inc. with access to superior research and engineering development and a cash infusion that helped Tesla to escape the potential bankruptcy.
- 2010 – Tesla, Inc. signed an alliance with Toyota , which enabled them to buy former NUMMI factory which positioned Tesla professionals to learn the large-scale, high-quality manufacturing from a pioneer of lean manufacturing.
- 2014- Tesla, Inc. joined Osaka (Japan) investments to develop and improve its battery designs.
- 2020 – Tesla, Inc. entered into a partnership with LG Chem Ltd and China’s CATL to develop batteries for its electric cars. [ 4 ]
- 2020 – Tesla, Inc. partnered with Huston-Tillotson University to collaborate in research and provide opportunities for students from disadvantaged communities to engage in the sector. [ 5 ]
Manufacturing and Purchasing (Toyota)
- Toyota and Tesla, Inc. joined forces announcing to the public that they are to build an alliance that would be dedicated to developing electric vehicles , parts and production systems for electric cars and accessories.
- In return, Toyota bought $50 Million of Tesla stocks and Tesla purchased an assembly factory in California to continue its endeavor towards facilitating the process of manufacturing electric vehicles.
- “ Tesla has quite a clear business strategy for developing a better battery ,” said Osamu Nagata , president, and CEO of Toyota Motor Engineering & Manufacturing North America. “
Car Leasing Company
- March 2012 – Athlon Car Lease Company built an alliance with Tesla for Tesla’s premium electric sedan specifically for corporate fleet services throughout the European regions. The model consists of the Model S and the 150 Model S Sedans to ensure early availability of the Model S for its clients.
- Tesla’s strategic alliance helped to pave the way for making the first Model S fleet reservation possible for leasing worldwide.
- Athlon VP Richard Sikkel confirms : “Our collaboration with Tesla has been very well perceived by the market. Almost 50 % of our initial order have already been pre-reserved by several of Athlon’s existing customers – an example that demonstrates the increasing need for electric vehicles in the industry.”
Major Suppliers
Tesla, Inc. is commonly responsible for manufacturing the electric car’s basics, which include the electric motor, the battery pack and the charger. Rest are provided by suppliers from the US, Europe, and Asia.
The following are Tesla’s main designers and suppliers:
- AGC Automotive: windshields
- Brembo: brakes
- Fisher Dynamics: power seats
- Inteva Products: instrument panel
- Modine Manufacturing Co. battery chiller
- Sika: acoustic dampers
- Stabilus: liftgate gas spring
- ZF Lenksysteme: a power steering mechanism
- LG Chem LTD: Batteries [ 6 ]
Other suppliers include:
- Angell-Demmel
- Hitachi Cable America
- Hope Global
- MacLean-Fogg
- Magna International
- Methode Electronics
- PSM International
- T1 Automotive
- Zanini Auto Group
Dana Holding
- Dana Holdings provided Tesla, Inc. with Dana Cooling Technology for further implementation of the Tesla engine and the overall cooling system design .
- Panasonic’s current lithium-ion batteries showed to serve sufficiently; Tesla confirms that it is seeking more batteries for its Model S in which Panasonic is currently supplying.
- In this effort, Panasonic is collaborating to build Tesla’s Gigafactorys – a large scale battery and solar cells manufacturing plant in Nevada and New York.
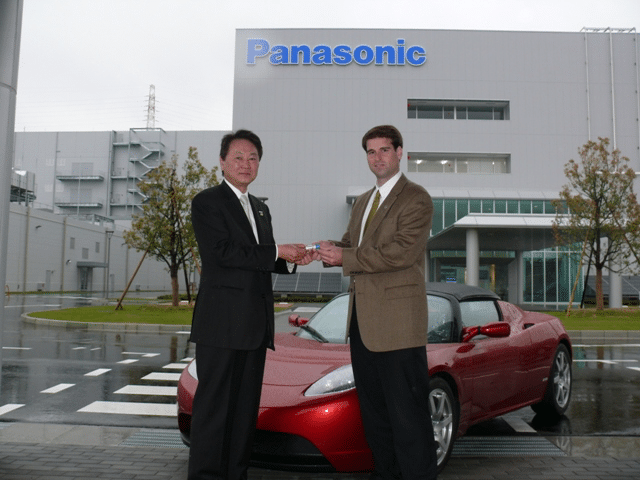

- Government-funded Tesla with a $465 Million loan for its electric Sedan
- $365 Million of the loan shall be allocated towards the production of it’s Model S Sedan.
- Remaining $100 Million will be allocated towards its electric power train manufacturing plant in California.
- Due to Tesla’s Electric Vehicle development and improvements, the US government provides federal tax incentives of about $3750 to customers depending upon the state .
4. Key Activities of Tesla
- R&D helped Tesla attain its milestones by providing breakthrough technologies and innovational designs that were in association with the engine design of Tesla vehicles.
- Tesla’s innovative design helped to produce reliable electric plug-in cars made affordable for all.
- Modern design that includes lightweight body , durable and long-lasting battery life
- Designs range from small, to classy, to luxurious classes – there is a vehicle type for every customer segment at different price points.
Innovational Leap
- Tesla continues to work around the building blocks of Tesla vehicles to better improve and sufficiently design vehicles that are built with eco-friendly materials, ensure future sustainability and invoke reliability of its line of manufacturers.
Software Development
- One of the most crucial movements for Tesla was its dedication towards the vital software programs that helped shaped the electric vehicle industry to what it is today.
- Tesla does not follow the long development software product lifecycles that many automotive specialists follow; instead, Tesla worked around these hurdles to create diverse software programs that improved the sufficiency of each of their model make series.
- Tesla uses agile principles like “scrums” or also known as regular meetings that are designed to work and improve the structures of its core software.
- Through this breakthrough, it has aided Tesla to minimize errors and bring innovation into progressing leaps.
- Tesla, Inc. regularly evaluates customer experience and feedback that helps to pave the next generation in improving its software spectrum and the sufficiency of its vehicles.
- Technological errors are expected but shall improve in the long run to perfection.
Sales & Marketing
- Tesla invests heavily in executing its sales and marketing efforts, which includes establishing company-owned stores , galleries and service centers known as “Service Plus.”
Building & Maintenance of Charging Stations Network
- Tesla has been building an extensive network of the supercharger and destination recharge stations around the world to expand the widespread adoption of its Electric Vehicles.
- There are 1441 Supercharger stations worldwide with 12,888 superchargers and thousands of Destination charging stations at hotels, restaurants, shopping centers, parking garages, office building, etc.
- MOAT – A Tesla, Inc. project that is geared to provide EV charging stations
- Tesla, Inc. plans on launching a network specifically for other automaker brands for EV charging supply. However, this is still to happen.
- First to launch a portable home charger that costs about $500
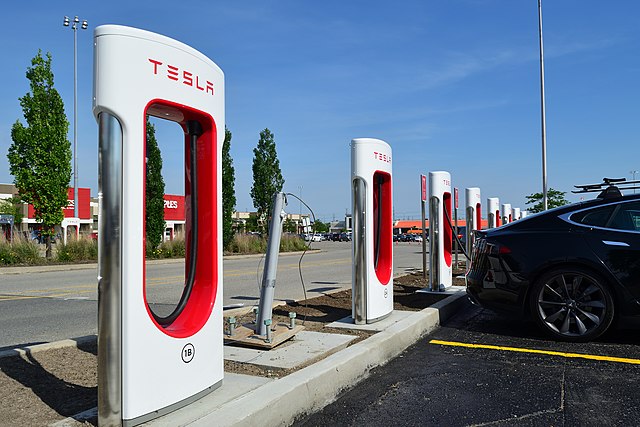

5. Customer Relationships of Tesla
Customer Service Experience
- Tesla provides digitally driven Omni-channel experience (stores, website, social media) to its customers.
- Company Owned Stores – Tesla utilizes direct to customer sales model . Tesla sells its cars to customers directly through its stores and galleries, instead of selling through auto dealers. It provides an enhanced level of shopping experience for customers.
- Self Service website – Often times, customer place orders directly on the Tesla website. Customers can build their own car, add features, choose different color combinations, various financing options; which is an again a unique shopping experience.
- Tesla is considered as a luxury brand in the automotive industry. For those that know about Tesla, and what it stands for understands the value and quality that it provides to loyal customers.
- Due to the continuous innovation and the design, Tesla has built a reputation unlike any other technology in the EV automobile industry.
- Customers feel that Tesla is well ahead in its innovation and production electric vehicle ecosystem that is like no other competitors in the industry.
Free/low-cost charging station network
- Extension chargers provided for Model S, Model X and Model 3
- A built-in navigation system that helps to identify and locate the charger stations
- Charging stations are designed to supercharge Tesla vehicles that get charged in just 30 minutes
- Tesla charging stations and app system indicates when the vehicle charging is complete

6. Key Resources of Tesla
Electric Vehicle and Technological Knowledge
A) Superior Engine Design:
- High-Performance Vehicle
- Pollution & Noise free Vehicle
- Super-Fast vehicle
B) Engine components:
- Lithium-ion battery system
- Induction motor. (Rotor Speed < RMF Speed)
- Uniform induction, power, and speed.
- Brushless and requires no magnets, instead the induction creates magnetism through rotational movement
- 3-phase. Ac power input.
- Speed is dependent on the amount of voltages that are fed to the 3-phase AC power Input. Speed can range from 0-18000 RPM.
- No Transmission required a direct mount of the engine to the axel is sufficient.
Comparison Chart of the Tesla Induction Motor VS. Typical IC Engine
Battery System
- Lithium-ion Batteries. (DC Power)
- 7,000 individual battery cells constituted into the design into 16 compartments
- A range of 16 compartments that act as one big cell.
Effective Cooling
- The use of small individual cells is a guarantee of sufficient cooling, instead of using a few big batteries
- This also increases the battery duration and lifeline.
- Glycol is used as the cooling medium that is bypassed through the gaps between the rows of the cells in each of the 16 lithium-ion compartments.
- Battery alignment and frame offers the vehicle side skirt support from a vehicle collision.
Automation & Engineering
- Induction motor. (Rotor Speed < RMF Speed) Uniform induction, power, and speed.
- Brushless and requires no magnets.
- Inverter system = 3 phase. Ac power input.
- Speed is dependent on the amount of voltages that are fed to the 3-phase AC power Input.
- Speed can range from 0-18000 RPM.
- No Transmission required a direct mount of the engine to the axel is sufficient
- Another positive aspect of Tesla that helped progressed its success is the reliability of its big data , which is derived from its in-vehicle software, and strategic partnerships.
- Through channeling new departments, opportunities and the new business operations, Tesla was able to generate potential clients and aim at different business endeavors successfully such as solar energy systems, retail merchandise, etc.
7. Channels of Tesla
The following are the set of channels that Tesla utilizes to channel and market its technology:
- Retail stores & galleries – Tesla, Inc. retail stores and galleries are designed and built to showcase Tesla vehicles and maximize customer experience. In early 2019, there were around 276 Tesla stores worldwide of which around 130 were based in the US but the company has closed most of its stores globally and moved to online sales channels . [ 7 ]
- Self Service online store (website)
- Conferences & sales events

8. Cost Structure of Tesla
In FY 2019, Tesla’s annual revenue was $24.578 Billion with a net expense of about $24.72 Billion, which leaves the company with a net loss of $144 Million. [ 8 ]
The following are Tesla expense and cost structure;
- Cost of Goods and Services (COGS): $20.509 Billion equal to 83% of the revenue
- Selling, General & Administrative Cost: $2.646 Billion equal to 11% of the revenue
- Research & Development Cost: $1.343 Billion equal to 6% of the revenue
- Restructuring Cost: $149 Million equal to less than 1% of the revenue
- Interest Expense, Taxes, and Others: approx. 3% of revenue
9. Revenue Streams of Tesla
Tesla not only sells Electric vehicles but also has created an eco-system of a top of the line green vehicles. Also, it has introduced solar energy systems, and lifestyle products for its loyal customers and the fans of Tesla, Inc;
Here is a high level break down of Tesla’s revenue. In FY2019, the total annual revenue of Tesla was $24.578 Billion .
Automotive Segment revenue – it includes sales of all vehicle models, access to charging network, software updates, after – sales services, sales of EV components, retail merchandise, etc. Here is a further breakdown in the automotive segment.
- Vehicle sales: $19.952 Billion
- Vehicle leasing: $869 Million
Total: $20.821 Billion
Energy generation & storage segment – it includes sales of solar energy systems and storage products such as solar roof panels, etc.
Total Revenue from Energy Generation & Storage: $1.531 Billion
Services – Includes car services, repairs, consultations, and other general services
Total Revenue from Services and other: $2.226 Billion
Tesla, Inc. started its business as offering reliable ways of providing transportation. By reviving the theory of utilizing electric vehicles instead of gasoline combustion chamber engines helped to pave the recognition of sufficient EV system, which also contributed to revolutionize the automobile industry from mechanical drives to all smart computer driven electric vehicles.
Because of the strategic steps taken to design a sound EV engine system, the possibilities of actualizing an electric car that serves sufficiently and safely, Tesla, Inc. is one of the most successful EV company in today’s automobile industries and continues to develop and innovate the methods of transportation.
References & more information
- Wagner, I. (2020, July 15). Tesla’s vehicle deliveries by the quarter – YTD Q2 2020 . Statista
- Korosec, K. (2020, July 1). Tesla Blows Past Toyota to become Most Valuable Automaker in the World . Tech Crunch
- Brown, M. (2020, July 23). Tesla Cybertruck: Elon Musk Reveals where It will be Built . Inverse
- Talia, S. (2020, January 30). Tesla partners with LG Chem, CATL for battery supply . Reuters
- Crider, J. (2020, July 31). Tesla’s Newest Partnership With An HBCU Is A Great Thing . Clean Technica
- Contemporary Amperex Technology Co. Limited (CATL): Batteries
- Williams, M. (2019, March 4). Tesla to close showrooms and move sales online . Automotive Logistics
- Investing Alerts (2020, January). Tesla Inc. Financials . Market Watch
Tell us what you think? Did you find this article interesting? Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below.
A management consultant and entrepreneur. S.K. Gupta understands how to create and implement business strategies. He is passionate about analyzing and writing about businesses.
Cancel reply
Loved this!
You may also like

How Does Popmoney Work ?
Last updated: May 18, 2020 Company: Popmoney (Division of Fiserv) CEO: Jeffery W. Yabuki Founders: Sanjeev Dheer Year founded: 2010 Headquarter: New York, NY Products & Services: Peer...
What is ProctorU, how it works and makes money?
Company: ProctorU Founders: Jarrod Morgan Year founded: 2008 CEO: Scott McFarland Headquarter: Birmingham, Alabama Number of Employees (Dec 2018): 400+ Type: Private Ticker Symbol: NYSE: UBER Annual Revenue (Dec...

How Does Snapchat Make Money?
Company: Snapchat CEO: Evan Spiegel Year founded: 2011 Headquarter: Santa Monica, California, USA Number of Employees (Dec 2018): 2884 Public or Private: Public Ticker Symbol: SNAP Market Cap (April...

How does DealDash work & make money?
Company: DealDash Founders: William Wolfram CEO: Pasi Lohi Year founded: 2009 Headquarter: Minneapolis, MN Number of Employees (Dec 2018): 50 Type: Private Annual Revenue (Dec 2018): Estimated $9.7M Products...

How does Hinge work & make money? – In a nutshell
Company: Hinge (a subsidiary of Match Group) Founders & CEO: Justin McLeod Year founded: 2012 Headquarter: New York, New York Number of Employees (2018): 18 Type: Private Downloads (2018): 5.5 Million...
Walmart Business Model | How does Walmart Make Money ?
Company: Walmart Inc. (NYSE: WMT) Founders: Sam Walton Year founded: 1962 CEO: Doug McMillan Headquarter: Bentonville, Arkansas Number of Employees (2023): 2.1 million Type: Public Market Capitalization (July...
How Does HQ Trivia Make Money?
Last updated: Feb 18, 2020 Company: HQ Trivia Founders: Rus Yusupov and Colin Kroll Year founded: 2017 CEO: Rus Yusupov Headquarter: New York, NY Number of Employees (2019): 25 Annual Revenue (2019): $10 million...

How Does eBay Make Money? (2022)
Last updated: May 23, 2020 Company: eBay Founder: Pierre Omidyar CEO: Devin Wenig Year founded: 1995 Headquarter: San Jose, California, USA Number of Employees (Dec 2019): 13,300 Type: Public Ticker Symbol: EBAY Market...

How Does Waze Make Money?
Company: Waze Inc. (a subsidiary of Google Inc) Industry: GPS Navigation Software Founder(s): Amir Shinar, Ehud Shabtai, Uri Levine Year founded: 2006 CEO(s): Noam Bardin Headquarter: Palo Alto, CA, USA Acquisition...

OYO Business Model | How Does Oyo Make Money?
Last updated: September 30, 2021 Company: Oyo Rooms CEO: Ritesh Agarwal Year founded: 2013 Headquarter: Gurgaon, Haryana, India. Number of Employees (2019): 25,000+ Type: Private Valuation (Aug 2020): $8...
Recent Posts
- Who Owns 1440 News?
- Who Owns PNC Bank?
- Who Owns The Shade Room?
- Who Owns Professional Fighters League (PFL)?
- Who Owns Ulta Beauty?
- Who Owns History Channel?
- Who Owns Cheesecake Factory?
- Who Owns Westin Hotels & Resorts?
- Who Owns Truist Bank?
- Who Owns Alfa Romeo?
Business Strategy Hub
- A – Z Companies
- Privacy Policy
Subscribe to receive updates from the hub!
- Red Queen Effect
- Blue Ocean Strategy
- Only the paranoid survives
- Co-opetition Strategy
- Mintzberg’s 5 Ps
- Ansoff Matrix
- Target Right Customers
- Product Life Cycle
- Diffusion of Innovation Theory
- Bowman’s Strategic Clock
- Pricing Strategies
- 7S Framework
- Porter’s Five Forces
- Strategy Diamond
- Value Innovation
- PESTLE Analysis
- Gap Analysis
- SWOT Analysis
- Strategy Canvas
- Business Model
- Mission & Vision
- Competitors
A Deep Dive Into Tesla Business Strategy

Based in Palo Alto, California, Tesla Inc. is an American automaker, energy storage and solar manufacturer. The company is probably the dawn of the greatest revolution in the automotive industry that the world has witnessed since Karl Benz .
Only a few years old, Tesla has gained much attention and significant success. Its market value is about $48 billion (surpassing Ford at $45 billion). Most people think that Elon Musk (the current CEO of Tesla) is the founder of the company. But this is far from the truth. In reality, it was founded by a group of Silicon Valley engineers who later collaborated with the billionaire.
Since its inception Tesla’s growth and business strategies have been nothing short of inspirational. So let us take a look into that.
The Business of Tesla
Tesla was founded in 2003 by Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning. Later on, Elon Musk, JB Straubel and Ian Wright were also considered founders of the company. The company deals in electric cars, lithium-ion battery energy storage and residential solar panels. The first great success of the company was the Roadster in 2008, an electric sports car.

Furthermore, in 2012, the Model S, an electric luxury sedan, was another milestone in its widely gained success. In 2015 and 2016, the Model S was the world’s best-selling plug-in electric car. Succeeding the Model S is the Model X, a crossover SUV. The Model 3 (at a mid-range price point), which is Tesla’s fourth vehicle, has been designed for the mass market and has been put into production since July 2017.
Since the very first model: Roadster, Tesla has sold over 186,000 electric cars and went on to be the world’s second-best-selling manufacturer of plug-in electric cars in 2015 and 2016. Apart from this, Tesla has given its customers a network of high-powered Superchargers across North America, Asia and Europe for Tesla vehicles.
Other than vehicles, Tesla also ventures into highly efficient solar roof systems .
Tesla Business Strategy
Tesla entered the market with expensive high-end cars targeted at the more financially privileged class of people. Once it is more established and widely known as a successful idea, it would venture into a more competitive market of lower-level priced models. So the first model was launched to get the company’s mission out in the marketplace.
All Tesla needed was to make a name for their brand to get its concept widely accepted. After that, it reinforced its business model . Tesla’s business model is based on a three-pronged approach to selling, servicing, and charging its electric vehicles.
Direct Sales
Tesla doesn’t adopt the approach of franchise dealerships, unlike most manufacturers. They prefer selling their product directly to customers through self-owned showrooms across many of the major urban centres in the world. They believe that this method of selling can speed up product development. But more significant is the customer’s buying experience. Tesla has showrooms, Service Plus centres (a combination of retail and service centres), and service facilities. Tesla has also made use of Internet sales—consumers can customise and purchase a Tesla online.
As mentioned above, Tesla has combined direct sales with service centres. They believe opening service centres have a positive effect on customer demand. Thus the “Service Plus” retail centres. Customers can service their cars or charge them at the service centres or the Service Plus locations. They also have mobile technicians who can come to your home, called Tesla Rangers. With the Model S, they can wirelessly upload data so technicians can view and fix certain problems online without even physically touching the car.
Charger’s network
Tesla has a wide network where its customers can charge their vehicles. Supercharger Stations: a place where customers can charge their vehicles in about 30 minutes for free. It is their belief that this will increase the rate of the customers’ product adoption.
It doesn’t end here, apart from the three-pronged business model, Tesla also provides financial services like granting loans and leases. If the customer wants to resell a vehicle, some of the loan programs have a resale value guarantee provision, which provides some downside protection on a vehicle’s value. Tesla’s other products include a line of home batteries called the Powerwall , which serve as energy storage systems in homes or businesses, and solar roof systems as well. Another very important part of Tesla’s business strategy is that Tesla takes customer deposits upfront—a year, two years, or three years in advance of production and delivery, unlike other car companies. Tesla has sold $500 million in stock to the public.
The Face of Tesla: Elon Musk
Elon Musk is the co-founder, CEO and Product Architect at Tesla. He oversees all product development, engineering, and design of the company’s electric vehicles, battery products, and solar roofs.
He joined Tesla in 2004 as the chairman of the board of directors. Initially, he wasn’t much involved in the day-to-day activities of the company (although he did oversee Roadster’s product design). Post-2008 crisis, Elon took on the task of leading the company as the CEO and product architect. Ever since he has been shaping the future of electric cars and the automotive industry radically through Tesla.
Tesla’s homepage was changed to Tesla.com in February 2016 after Elon acquired it from Stu Grossman, who had owned it since 1992. In December 2016, Musk was ranked 21st on the Forbes list of The World’s Most Powerful People. Because all of the many accolades of Elon and his achievements in SpaceX, he’s gained a lot of attention and popularity. This has made him a famous personality and a credible one.
Most car companies spend billions on advertising and publicity . However, Tesla just needs a tweet from Elon announcing a new model or an idea to get crazy ravenous publicity. The next thing you know, everyone’s talking about Elon tweet and Tesla, and it has become a big deal already. And the best part of it is all of it is free of charge. It would also be fitting to say that, on quite a level, people believe in Tesla because of Elon.
Let me conclude by leading you with a question:
What makes Tesla, Inc. different from other automotive companies or rather, companies in general?
Tesla, Inc. doesn’t have its goals set in producing and manufacturing high-end electric cars for the affluent to make money and move up on the charts. The mission of the company is this: to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy.
They also put it like this:
- Build a sports car
- Use that money to build an affordable car
- Use that money to build an even more affordable car
- While doing the above, also provide zero-emission electric power generation options
- Don’t tell anyone.
Tesla’s goals are far beyond that of most automotive companies. They envision building a world with cars void of harmful emissions. Every day they work to draw this future closer to the present.
The Superchargers were made to overcome one of the biggest challenges impeding the future of electric cars: for electric cars to really be able to take a road trip without much inconvenience.
With its no-pressure sales approach, Tesla salesmen aim at furnishing the customer with the details of their cars instead of trying to force a sale. Unlike other electric car retail outlets, Tesla staff know more about their car than the customers that visit.
The performance of Tesla cars is also superior.
Whichever Tesla you buy, not any comparatively priced car from a competitor, whether gas or electric, in the same class is going to beat the Tesla to 100 km/h. What Tesla has done is it has not only manufactured electric cars successfully, but it has revolutionised the future of emission-free travel and has made long-distance travel through electric cars possible.
What could be considered the greatest achievement of Tesla is that it made a successful business model to bring the electric car into the market rather than just manufacturing one.
Go On, Tell Us What You Think!
Did we miss something? Come on! Tell us what you think of our article on the Tesla business strategy and business model in the comments section.
A social entrepreneur who loves to read books on self-help, motivation, businesses, entrepreneurship, and social dynamics. To me a life without health, wealth, love, and happiness is a life not worth living.
Related Posts:

Growth Navigate
- Team Growth Navigate
Tesla Business Model: Comprehensive Guide
The automotive industry has undergone a significant transformation in recent years, driven by the rise of electric vehicles (EVs) and the push towards sustainable transportation. At the forefront of this revolution is Tesla , an American company founded in 2003 with a mission to accelerate the world's transition to sustainable energy. Tesla's unique business model has not only disrupted the automotive industry but has also expanded into other sectors, making it a force to be reckoned with. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the Tesla business model, exploring its history, value propositions, key activities, customer relationships, and more.
About Tesla Motors and Business Model
Tesla Motors , now known simply as Tesla, was founded in 2003 by a group of visionary engineers, including Martin Eberhard, Marc Tarpenning, Ian Wright, JB Straubel, and Elon Musk. The company's initial focus was on developing electric vehicles, with the goal of commercializing sustainable transportation. In 2008, Tesla made its first breakthrough with the launch of the Tesla Roadster , a high-performance electric sports car that garnered attention for its impressive range and acceleration.

Tesla's Mission Statement
At the core of the Tesla business model is its mission to accelerate the world's transition to sustainable energy. This mission statement drives every aspect of the company's operations, from product development to customer relationships. By prioritizing sustainability and innovation, Tesla has positioned itself as a leader in the electric vehicle market.
Tesla's Value Propositions
Tesla's success can largely be attributed to its unique value propositions, which cater to a diverse range of customer segments. The company offers greener solutions that combine high performance, modern design, energy efficiency, long-range recharging flexibility, and low-cost or free charging options. Tesla's vehicles are not only environmentally friendly but also technologically advanced, providing customers with a premium driving experience.
In addition to its electric vehicles, Tesla has expanded its product portfolio to include solar energy systems, such as solar panels and home batteries. These offerings provide customers with convenient and sustainable power solutions, further enhancing Tesla's value proposition.
Tesla's Customer Segments
Tesla has carefully targeted multiple customer segments, ensuring that its products cater to a wide range of needs and preferences. The company's vehicles are designed for mid-market consumers seeking affordable electric cars, as well as luxury car enthusiasts who prioritize performance and design. Tesla has also entered the commercial vehicle sector, providing greener transportation options for businesses and fleet operators. Furthermore, Tesla has amassed a loyal following of environmentally conscious consumers who are passionate about sustainable energy and technology.
Tesla's Distribution Channels
Tesla's distribution channels are a crucial component of its business model . Unlike traditional car manufacturers that rely on franchised dealerships, Tesla sells its vehicles directly to consumers. The company operates a network of company-owned stores and galleries, allowing customers to experience and purchase Tesla vehicles firsthand. In addition to physical stores, Tesla also utilizes online sales channels, where customers can customize and order their desired vehicles.
Furthermore, Tesla has established a comprehensive charging network to support its electric vehicles. The Supercharger Network, consisting of thousands of charging stations globally, enables Tesla owners to recharge their vehicles quickly and conveniently. These charging stations are strategically located in high-traffic areas, ensuring accessibility for Tesla customers.
Tesla's Revenue Streams
Tesla generates revenue through multiple streams, primarily through the sale of its electric vehicles. Automotive sales account for the majority of the company's revenue, with additional income derived from automotive services, vehicle leasing, and sales of energy storage products, such as solar panels and home batteries. Furthermore, Tesla benefits from carbon credits, which are tradable certificates that reward companies for reducing carbon dioxide emissions. These revenue streams collectively contribute to Tesla's financial success and sustainability.
For the twelve months ending September 30, 2023, Tesla's total revenue amounted to $95.924 billion, representing a year-over-year increase of 28.13%. Source: MacroTrends
Key Resources and Key Activities
Tesla's key resources and activities are integral to its ability to deliver its value proposition and achieve its mission. The company leverages cutting-edge technology, advanced engineering, and design expertise to develop innovative and high-quality electric vehicles. Tesla's key activities include car manufacturing, research and development, building and maintaining charging stations, software development, and sales and marketing. By investing in these core activities, Tesla continuously enhances its product offerings, customer experience, and overall business performance.
Tesla's Key Partners
Collaboration with strategic partners is a crucial aspect of the Tesla business model. Tesla has formed alliances with original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) like Daimler, Toyota, and Panasonic, allowing the company to access superior engineering, research, and manufacturing capabilities. These partnerships have played a vital role in Tesla's growth and expansion, enabling the company to leverage the expertise of established industry players. Additionally, Tesla has partnered with various suppliers, charging point hosts, and leasing companies to enhance its operations and customer reach.
Tesla's Customer Relationships
Tesla places a strong emphasis on customer relationships, aiming to provide an exceptional experience throughout the entire customer journey. The company's direct-to-consumer sales model allows for personalized interactions and direct feedback, enabling Tesla to continuously improve its products and services. Tesla's website serves as a self-service platform where customers can explore and customize their desired vehicle, further enhancing the convenience and accessibility of the purchasing process. Furthermore, Tesla's commitment to sustainability and innovation fosters a sense of community among its customers, creating a loyal and passionate customer base.
Tesla's Cost Structure
As a global manufacturer, Tesla has a complex cost structure that encompasses various elements. Manufacturing infrastructure, general administration and sales expenses, research and development budget, distribution costs, and materials procurement all contribute to Tesla's overall cost structure. However, the company's focus on efficiency, economies of scale, and technological advancements helps mitigate costs and ensure competitive pricing for its products.
Tesla's Competitors
While Tesla has established itself as a leader in the electric vehicle market, it faces competition from both traditional automakers and emerging players in the industry. Competitors such as Nio, Ford, Volkswagen, Li Auto, Nikola Corp, and Workhorse Group are vying for a share of the electric vehicle market. However, Tesla's strong brand reputation, technological innovation, and extensive charging network give it a competitive edge in the industry.
SWOT Analysis: Assessing Tesla's Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats
To gain a comprehensive understanding of the Tesla business model, it is essential to conduct a SWOT analysis. This analysis examines Tesla's internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats in the market.
Brand Reputation : Tesla has cultivated a strong brand reputation as a pioneer in electric vehicles, known for its innovative technology, performance, and commitment to sustainability.
Technological Innovation : Tesla's continuous investment in research and development has resulted in technological advancements, such as autonomous driving features and over-the-air software updates.
Charging Infrastructure : The extensive Supercharger Network provides Tesla owners with convenient and fast charging options, addressing one of the major barriers to electric vehicle adoption.
Strong Customer Base : Tesla has a loyal and passionate customer base that values sustainability, innovation, and superior driving experience.
Production Constraints : Tesla has faced challenges in scaling its production capacity to meet the growing demand for its vehicles, resulting in delays and customer dissatisfaction.
High Production Costs : The development and production of electric vehicles require significant investments, and Tesla's high production costs have impacted its profitability.
Dependence on Government Incentives : Tesla's sales and profitability are partially reliant on government incentives and regulations, which can be subject to change.
Opportunities
Growing Electric Vehicle Market : The increasing global demand for electric vehicles presents a significant opportunity for Tesla to expand its market share and revenue.
Expansion into New Markets : Tesla has the potential to enter emerging markets and tap into new customer segments, further diversifying its revenue streams.
Advancements in Battery Technology : As battery technology improves, Tesla can leverage these advancements to enhance the range, performance, and affordability of its vehicles.
Intense Competition : The electric vehicle market is becoming increasingly competitive, with traditional automakers investing heavily in electric vehicle technology and infrastructure.
Regulatory Changes : Shifts in government policies and regulations can impact Tesla's business operations, including incentives, emissions standards, and manufacturing requirements.
Supply Chain Disruptions : Tesla's reliance on a complex global supply chain exposes it to risks such as raw material shortages, trade disputes, and geopolitical tensions.
Wrapping Up
The Tesla business model has revolutionized the automotive industry, paving the way for sustainable transportation and driving technological advancements. By prioritizing innovation, customer experience, and sustainability, Tesla has positioned itself as a leader in the electric vehicle market. Through its unique value propositions, direct-to-consumer sales model, comprehensive charging network, and strategic partnerships, Tesla has built a strong brand and a loyal customer base. As the demand for electric vehicles continues to grow, Tesla is well-positioned to capitalize on this market opportunity and shape the future of transportation.
- Business Model
WhatsApp Business Model - How Does WhatsApp Make Money?
Walmart Business Model: How Walmart Makes Money?
What is Concierge Service? Meaning, Types and Examples
- March 30, 2023
Unraveling the Tesla Business Model. How does Tesla Make money?
In this article, we unravel the tesla business model using the business model canvas and learn about how tesla makes money..
Tesla, the American electric vehicle and clean energy company, has revolutionized the automotive industry and become a symbol of sustainable innovation. Founded in 2003 by a group of engineers and entrepreneurs, including Elon Musk, JB Straubel, Martin Eberhard, Ian Wright, and Marc Tarpenning, Tesla’s mission is to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy.
In this blog post, we will dive deep into Tesla’s business model using Alexander Osterwalder’s Business Model Canvas as our framework. This will enable us to better understand the key components that have contributed to Tesla’s remarkable success and how they have disrupted the automotive industry. Let’s start by introducing the Business Model Canvas and its nine building blocks before we delve into the fascinating story of Tesla’s origins and growth.
Explore our podcast
The business model canvas of tesla – explained.
Alexander Osterwalder’s Business Model Canvas is a strategic management tool that helps organizations visualize, design, and test their business models. It consists of nine building blocks: customer segments, value propositions, channels, customer relationships, revenue streams, key resources, key activities, key partnerships, and cost structure. By examining each component, we can gain valuable insights into the inner workings of Tesla’s business model.
- Customer Segments
Tesla targets a wide range of customer segments, including individual buyers, businesses, and government agencies. Initially, they focused on affluent customers willing to pay a premium for luxury electric vehicles (EVs). The Roadster, Tesla’s first vehicle, was a high-performance sports car with a six-figure price tag. This allowed the company to build brand awareness and generate revenue for future vehicle development.
As Tesla expanded its product lineup, it started targeting broader customer segments. The Model S and Model X catered to luxury sedan and SUV buyers, while the more affordable Model 3 and Model Y expanded Tesla’s reach to the mass market. Tesla also targets commercial customers with its Semi truck and energy products, such as solar panels and energy storage solutions, for residential, commercial, and utility-scale applications.
- Value Propositions
Tesla’s primary value proposition is offering high-quality electric vehicles that combine performance, design, and sustainability. By developing cutting-edge battery technology, Tesla has been able to achieve industry-leading range and charging times. Tesla’s vehicles also stand out for their exceptional performance, with some models reaching 0-60 mph in under 3 seconds.
In addition to its vehicles, Tesla’s value proposition includes its Supercharger network, providing fast and convenient charging for long-distance travel. Tesla also leverages its software expertise to deliver unique features, such as over-the-air updates and advanced driver assistance systems, like Autopilot.
Another key component of Tesla’s value proposition is its commitment to sustainability. This is reflected in its solar and energy storage products, as well as its Gigafactories, which aim to minimize the environmental impact of battery production.
Tesla uses a direct-to-consumer sales model, which enables it to maintain control over the entire customer experience. This approach differentiates Tesla from traditional automakers that rely on third-party dealerships. Tesla customers can purchase vehicles online or at one of the company’s retail stores, which also serve as showrooms and service centers.
For charging, Tesla has built a vast Supercharger network, making long-distance travel more convenient for EV owners. Tesla owners can also charge their vehicles at home using the company’s Wall Connector or a standard electrical outlet.
- Customer Relationships
Tesla fosters strong customer relationships through its direct sales model, personalized service, and online community. Tesla owners have access to the company’s mobile app, which enables them to monitor and control their vehicles remotely. Additionally, Tesla offers over-the-air software updates, ensuring that its vehicles are continuously improved and updated with new features.
Tesla’s online community is another significant aspect of its customer relationships. Forums, social media, and owner clubs provide Tesla enthusiasts with a platform to share experiences, ask questions, and connect with fellow owners. Tesla also hosts events and programs, such as factory tours and referral programs, to further engage its customer base.
- Revenue Streams
Tesla generates revenue from several sources, including vehicle sales, energy products, and services. Vehicle sales are the primary driver of revenue, encompassing the Model S, Model 3, Model X, Model Y, and the upcoming Cybertruck and Roadster. As Tesla continues to expand its product lineup, it will be able to capture additional market segments and generate more revenue.
Energy products, such as solar panels and energy storage solutions, represent another revenue stream for Tesla. Its acquisition of SolarCity in 2016 allowed Tesla to offer an integrated clean energy solution to residential, commercial, and utility customers.
Lastly, Tesla generates revenue from its service centers and Supercharger network. Although Supercharging is free for some Tesla owners, others pay a fee based on the amount of energy consumed during charging. Moreover, Tesla offers maintenance and repair services, as well as an extended service agreement and extended battery warranty for its vehicles.
- Key Resources
Tesla’s key resources include its intellectual property, manufacturing facilities, workforce, and brand. The company’s patents, trademarks, and trade secrets protect its innovations in battery technology, electric powertrain, and software. Tesla’s Gigafactories are essential for manufacturing batteries, electric motors, and vehicles at scale, allowing the company to reduce production costs and increase output.
Tesla’s workforce, led by CEO Elon Musk, is another crucial resource. The company’s engineers, designers, and software developers drive innovation and product development, while its sales and service teams ensure a positive customer experience. Tesla’s strong brand, synonymous with innovation, sustainability, and performance, is a valuable resource that differentiates it from competitors and attracts customers.
- Key Activities
Tesla’s key activities include research and development (R&D), vehicle manufacturing, and infrastructure expansion. The company invests heavily in R&D to develop cutting-edge technologies, such as battery systems, powertrains, and autonomous driving software. This focus on innovation enables Tesla to stay ahead of the competition and continue to improve its products.
Vehicle manufacturing is another essential activity, as Tesla strives to increase production capacity and lower costs. The construction of new Gigafactories and manufacturing facilities, such as the ones in Nevada, New York, Berlin, Shanghai, and Texas, is crucial for achieving these goals.
Finally, Tesla continuously expands its Supercharger network and service centers, ensuring that customers have convenient access to charging and maintenance services.
- Key Partnerships
Tesla has formed strategic partnerships to support its growth and enhance its capabilities. Some notable partnerships include:
- Panasonic: Tesla’s collaboration with Panasonic involves producing batteries at the Nevada Gigafactory and jointly developing next-generation battery technology.
- CATL and LG Chem: Tesla sources batteries from these suppliers to diversify its supply chain and meet the growing demand for its vehicles.
- Daimler and Toyota: Both automakers have invested in Tesla in the past, providing the company with capital and strategic support.
- State and local governments: Tesla has received tax incentives, grants, and low-interest loans for building Gigafactories and manufacturing facilities in different regions.
- Cost Structure
Tesla’s cost structure includes R&D, manufacturing, infrastructure, and personnel expenses. R&D costs are significant, as the company constantly innovates to improve its products and maintain its competitive edge. Manufacturing costs encompass raw materials, components, and labor for vehicle and battery production.
Infrastructure costs include the construction and operation of Gigafactories, Super charger stations, and service centers. Lastly, personnel costs encompass salaries, wages, and benefits for Tesla’s workforce, including engineers, designers, sales, and service staff.
The Tesla Story
Tesla’s story began in 2003 when engineers Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning decided to start a company focused on electric vehicles. They were inspired by the poor performance of traditional automakers in developing clean and sustainable transportation solutions. Eberhard and Tarpenning were later joined by JB Straubel, Ian Wright, and Elon Musk, who provided crucial funding and became the company’s chairman.
Tesla’s first vehicle, the Roadster, was introduced in 2008. This all-electric sports car was built on the Lotus Elise chassis and utilized a unique electric powertrain developed by Tesla. The Roadster showcased the potential of electric vehicles by offering an impressive range of over 200 miles and acceleration capabilities comparable to high-performance gasoline-powered cars. This success set the stage for Tesla’s future vehicles and its mission to make electric cars accessible to the mass market.
In 2012, Tesla launched the Model S, a luxury electric sedan that quickly became the best-selling electric car globally. The Model S established Tesla as a major player in the automotive industry and demonstrated that electric vehicles could compete with traditional cars in terms of performance, range, and design.
Tesla continued to expand its product lineup with the Model X, an all-electric SUV, in 2015, and the more affordable Model 3 sedan in 2017. The Model 3, in particular, played a crucial role in Tesla’s growth, as it targeted a broader customer base and significantly increased the company’s production volume.
In 2016, Tesla acquired SolarCity, a leading solar energy company, and integrated its solar and energy storage products into its offerings. This acquisition aligned with Tesla’s mission to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy and provided customers with a complete clean energy solution for their homes and vehicles.
Today, Tesla continues to innovate and disrupt the automotive and energy industries. With upcoming vehicles like the Cybertruck and the second-generation Roadster, as well as ongoing advancements in battery technology, Tesla is well-positioned to lead the global transition towards electric vehicles and clean energy.
Tesla’s business model, as examined through the lens of Alexander Osterwalder’s Business Model Canvas, provides valuable insights into the company’s success and disruptive potential. By targeting a wide range of customer segments, offering innovative and high-quality products, and controlling its sales and service channels, Tesla has established itself as a dominant player in the electric vehicle market.
Tesla’s commitment to research and development, manufacturing, and infrastructure expansion has allowed it to stay ahead of competitors and continuously improve its products. The company’s key partnerships, resources, and customer relationships have further strengthened its position in the market.
As Tesla continues to grow and innovate, it will play a critical role in shaping the future of transportation and sustainable energy. Its unique business model, combined with its bold mission and vision, ensures that Tesla remains a fascinating and inspiring case study for entrepreneurs, business leaders, and sustainability advocates alike.
Did you know? Tech Startups like to use our private theatre in Bangalore.
Learn more about our coworking space in Bangalore on YouTube where we talk about a variety of topics including entrepreneurship, business and life.
You'll also like this...


Private Karaoke Studio in Bangalore
Unleash Your Inner Star at Work Theater’s Premier Karaoke Studio in Bangalore! Welcome to the ultimate karaoke experience where your

Everything about Nagarbhavi in Bangalore. Explored
Explore Nagarbhavi in Bangalore: Discover landmarks, educational hubs, car showrooms and Work Theater, the ultimate coworking space with virtual office

What is Coworking? The Rise of Coworking in India
Today let’s explore what is coworking in depth. Also, let’s look into the rise of virtual offices and coworking in

Differences between Ltd and Pvt Ltd Companies in India
Explore the key differences between Ltd and Pvt Ltd companies in India in this detailed article. Here’s a comprehensive guide
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Work Theater is a coworking space in Bangalore for startups, individuals, teams and creatives.
© 2023 Work Theater (A unit of Chaitra Ventures )
Terms of service
© 2022 Work Theater (A unit of Chaitra Ventures )
designed by KatMantra Webdesign
Hey there, We're open for bookings. Do fill in your details and we will get in touch with you soon.

The Business Strategy of Tesla

Tesla has made Elon Musk one of the richest people in the world. This American multinational automotive and clean energy company has been at the forefront of technological developments for electric vehicles and battery energy storage while also expanding further its photovoltaic solutions for residential and commercial applications.
It has also been considered one of the most valuable companies in the world and has retained its status as the most valuable automaker in terms of market capitalization. Nevertheless, considering its accomplishments, understanding the success of Tesla requires understanding the role of innovation and efficiency in its overall business strategy
Key Principles in the Business Strategy of Tesla
Engineers and entrepreneurs Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning founded Tesla in 2003. Their goal was to become an electric vehicle manufacturer that leverages technological innovation. Note that electric vehicles around this time were expensive. Eberhard and Tarpenning aspired to commercialize and mass produce these vehicles.
A series A round enabled the company to raise USD 7.5 million in February 2004. Musk entered the company during the same time using a portion of the proceeds he received from the sale of PayPal in 2002. His initial investment an amount of USD 6.5 million. This made him the largest shareholder of Tesla and the chairperson of its board of directors.
The PayPal founder took a more active role beginning in 2005 until he became its chief executive officer and product architect in 2008. Tesla saw the introduction of the Roadster, its first electric sports car, in 2008, and the Model S, a four-door sedan, in 2012. It also ventured into energy storage technologies and further into photovoltaic solutions.
Understanding the evolution and expansion of Tesla from a small and aspirational electric vehicle manufacturer to a full-blown tech company involves taking a look at the intentional steps and tactics developed and undertaken by Musk and his executives. The following are the key principles in the business strategy of Tesla:
1. Safeguarding the Supply Chain Through a Vertical Integration Strategy
Remember that electric vehicles were expensive compared to gas-powered vehicles. The costs associated with manufacturing these vehicles were too high due to the lack of a substantial market and undeveloped technological requirements. Part of the business strategy of Tesla is to cover all the grounds needed to manufacture electric vehicles.
Achieving the aforementioned involves a vertical integration strategy . Note that vertical integration is rare for automakers. Most of these companies outsource more than 50 percent of their supplies and other business requirements to third-party providers. Of course, outsourcing has notable advantages but it also has disadvantages and limitations.
Vertical integration addresses the drawbacks of outsourcing and issues related to supply chain management. Tesla does not only build electric vehicles but also produces specific vehicle components. Remember that the company also develops and manufactures battery technologies both for its vehicles and for commercial and residential markets.
Having better control over its supply chain allows Tesla to lessen its dependence on third parties or other providers of production inputs. This translates to a competitive advantage due to a better control over the production schedule and the absence of reliance on the bargaining power of suppliers. It also lowers transaction costs, removes switching costs, and captures profit margins.
2. Maximizing Profitability Through Business and Product Diversification
Aligned with the vertical integration strategy of Tesla is its diversification into several business lines outside the manufacturing of electric vehicles. Tesla Energy is the clean energy subsidiary of Tesla responsible for developing, manufacturing, and marketing energy storage technologies and products and photovoltaic or solar cell solutions.
The clean energy brand was founded in 2015 with the launch of the Tesla Energy brand of energy storage products. and the specific Tesla Powerwall product. It has expanded its capabilities and product offerings to include photovoltaic solutions and systems after the acquisition of SolarCity Corporation in 2016.
It now targets residential, commercial, and industrial segments. Its product offerings include the home energy storage device Powerwall and the large-scale energy storage systems Powerpack and Megapack, as well as the Tesla Solar Roof and Tesla Solar Inverter. It has also developed software for monitoring and controlling its clean energy systems.
Tesla also generates revenues from its after-sales services for its electric vehicles. These include overall vehicle servicing, charging through its Supercharger and Destination Charging networks, software upgrades, wireless connectivity services, and insurance. These services earned a combined revenue of USD 1.47 billion in the first quarter of 2022 alone.
It makes sense for Tesla to create its Tesla Energy subsidiary and capitalize further on its after-sales services for its electric vehicle customers. Expanding its business and product offerings behind electric vehicles allows the company to take full advantage of its vertical integration strategy and maximize its earning potential by capitalizing on its capabilities.
3. Expanding Tesla and its Capabilities Through Strategic Acquisitions
Acquisitions are an important aspect of the specific vertical integration and expansion strategies of Tesla. Its acquisition of solar energy solutions provider SolarCity Corporation in 2016 for about USD 2.6 billion has allowed it to venture further into the clean energy business and expand its specific photovoltaic solutions business.
The company also acquired several entities for its energy storage business. These include the acquisition of Hibar Systems in 2021 and SilLion Company in 2014 for undisclosed amounts, and Maxwell Technologies in 2019 for USD 218 million to obtain relevant technologies and capabilities for designing and producing rechargeable lithium-ion batteries .
Other acquisitions intended to build its manufacturing capabilities include the American stamping die manufacturer Riviera Tool in 2015, the German engineering automation company Grohmann Automation in 2016 for USD 136 million, and the Canadian ATS Automation Tooling Systems in 2020 for an undisclosed amount.
Tesla has two reasons for acquiring other companies. The first is to expand its product lines or offerings through the acquisition of companies and their products or technologies. The second is to cut down costs and lessen its dependence on the bargaining powers of its suppliers by purchasing businesses that feed into its supply chain.
4. Capturing the Market and Customers through an Evolving Marketing Strategy
Must laid down the primary marketing strategy for Tesla in 2006. He was aware that electric vehicles are more expensive than gas-powered vehicles. Hence, to capture the market and appeal to its target customers, the company focused on low-volume but high-priced luxury vehicles to target specific customers that are less sensitive to price,
The initial strategy worked. It allowed the company to generate enough revenues from minimal sales to explore technologies and solutions that would allow it to cut down the cost of rechargeable batteries. Tesla eventually succeeded in bringing down the cost of its electric vehicles, thus enabling high-volume production and cheaper end-use price.
Note that the Roadster was priced at over USD 100,000. There were fewer than 2500 units produced. The Model S and Model X retailed at more affordable price points although they are still positioned as luxury vehicles. More recent models such as the Model 3 and Model Y have lower price points and are produced at high volumes each quarter.
Another important principle in the marketing strategy of Tesla is its refusal to course its sales through auto dealerships. It sells through company-owned stores and its websites. The company also has minimal to zero advertising expenses because it focuses on setting up stores or “galleries” in high-traffic locations such as retail districts or inside malls.
Tesla has also brought in strategies utilized by Apple . Some observers noted that its electric vehicles are the “iPhone on wheels” because it has created a close ecosystem in which it can sell other products or services to Tesla vehicle owners. The fact that the company generates billions of dollars each year from its after-sales business is a testament.
5. Positioning Tesla as a Tech Company Further Through Continuous Innovation
Another critical component of the business strategy of Tesla is its strong technological innovation. Remember that the company has positioned itself as both an automaker and a clean energy company, as well as a technology company. At the heart of its business is innovation. It has even branded itself as an energy-innovation company.
Of course, most companies can claim that they are also technology companies. However, Tesla takes its innovative pursuits seriously. It has its own chief technical officer responsible for spearheading research and development, guiding its team of engineers and scientists, and partaking in overseeing production and other related processes.
The company is at the forefront of developing and introducing technologies relevant to electric vehicles. Furthermore, it has been developing true self-autonomous vehicles through artificial intelligence that involves both hardware and software capabilities. Note that Tesla vehicles have operating systems that are continuously improved by Tesla employees.
It is also worth reiterating the fact that the company also develops and produces other technologies outside of its electric vehicle business. These include battery storage technologies that it has opened to its competitors for licensing. It has also developed solutions for improving charge speed, as well as products relevant to its photovoltaic solutions.
FURTHER READINGS AND REFERENCES
- Garcia, C. “Tesla Stock: Advantages and Disadvantages.” Fincier . Available online
- Garcia, C. 2023. “Porter’s 5 Forces Analysis of Tesla.” Konsyse . Available online
- Garcia, C. 2023. “SWOT Analysis of Tesla.” Konsyse . Available online
- Martinez, I. 2023. “Competitive Advantage of Tesla.” Konsyse . Available online
- Neuman, R. 2023. “How To Invest in Tesla.” Fincier . Available online

- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Company News
Tesla (TSLA) Plans for Future, Makes Changes to Business
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/profilepic__rakesh_sharma-5bfc262dc9e77c00517eda0b.jpg)
Even as it reported record earnings this past week, electric carmaker Tesla, Inc. ( TSLA ) is already reorganizing its business strategy to boost profits. Two recent reports—one relating to its pricing tactics in China and another about a pivot in retail sales experience—provide clues to Tesla's business strategy. Together, they could set the direction for the car company's future earnings reports.
Key Takeaways
- Tesla is lowering the price of its cars in China to garner market share.
- According to reports, the company is also planning to overhaul its retail sales strategy to emphasize online sales.
- Together, these strategy changes could have a major impact on its future earnings.
Cheaper Teslas in China
A substantial portion of Tesla's deliveries this past quarter occurred in China. Almost all of them were for Model Y—its compact SUV. Amid increased competition from cheaper original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), the company has reduced the car's price in China to boost sales. That strategy contrasts with Tesla's approach in the United States, where it has raised prices on its Model 3 and Model Y cars about a dozen times in the past year alone, according to a Reuters report.
This Tesla playbook is not a new one. The company reduced prices on several of its models after launch in the United States, only to hike them subsequently. It is likely that Tesla is following a similar strategy in China.
But the company might have to play a long game there. Gene Munster from Loup Ventures estimates that the company's cars are three times the cost of a typical electric vehicle (EV) made in China. "Price of Teslas in China will be below rest of the world for the next decade," he told Reuters.
China accounted for slightly more than half of all electric car sales last year. Consulting firm McKinsey has predicted that it will remain the biggest market for electric vehicles, reaching 9 million by 2030, in the years to come.
Tesla has already become an important player in the Chinese market. By the middle of last year, the company's China sales accounted for nearly a quarter of the overall figure, according to McKinsey. Its Model 3 was the single best-selling premium battery-operated electric vehicle model in China in the same year. Some analysts say China is the "linchpin" to Tesla's earnings.
While reduced prices may help Tesla garner market share in China, they also have the potential to crimp its margins. The Palo Alto, California-based company will have to carefully balance sales volumes for its cars with production costs. It has plenty of leeway to play around in that arena. According to analysis by Guosen Securities released in January this year, a Model Y produced at Tesla's Shanghai Gigafactory has a 29.4% gross profit margin . The Model S, according to the same report, has a gross profit margin of approximately 40%.
An Online Sales Experience
The other big change occurring at Tesla is related to its sales division. According to a report in online publication Electrek, the company is planning to overhaul its sales experience by emphasizing an online sales experience over offline sales. As part of this strategy, it will get rid of expensive showroom space, instead renting out inexpensive space in mall parking lots, warehouses, and "other locations" for test drives and delivery of its cars.
A Tesla central virtual store will be primarily responsible for sales. Online advisors at the store will coordinate the sales experience, from enabling potential buyers to unlock cars for test drives to ensuring physical delivery of a purchased car, virtually. The move will help Tesla cut down on expensive real estate rent. Electrek states that the company plans to use those savings to open car delivery centers in less expensive areas.
Tesla had already announced this sales plan, with accompanying store closures and layoffs, earlier in 2019. But it held off on getting rid of its real estate as it focused on growing its market and business in China. Tesla's operating expenses have ballooned in recent years as it expands its geographic footprint. During its most recent quarter, they were $10.6 billion, up 86% from the previous year. A virtual sales strategy will help the company expand without incurring significant costs to its bottom line.
Bloomberg. Tesla Unveils Cheaper Model of Model Y After Backlash .
WHBL. Analysis: Tesla Hikes Car Prices in the US, Holds Line in China .
Yahoo Finance. Tesla Keeps Getting More Expensive.
Weforum. Which Countries Sell the Most Electric Cars?
McKinsey. Winning the Chinese BEV Market.
CNBC. China is Linchpin to Tesla Bull Story.
Inside EVs. Tesla Model Y Made in China Has 29.4% Margin.
Electrek. Tesla Launches Major Shift in Retail Operations .
Electrek. Tesla Changes Entire Sales Strategy .
Macrotrends. Tesla Operating Expenses .
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/self-driving-car-drive-thru-FT-BLOG0420-62c67b665c4d4af490e83ba2b737574d.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Lessons from Tesla’s Approach to Innovation
- Nathan Furr

There is a method to the madness.
Tesla has shifted the auto industry toward electric vehicles, achieved consistently growing revenues, and at the start of 2020 was the highest-performing automaker in terms of total return, sales growth, and long-term shareholder value. As a technology and innovation scholar, the author has studied how innovators commercialize new technologies and found that Tesla’s strategy offers enduring lessons for any innovator, especially in terms of how to win support for an idea and how to bring new technologies to market. To understand Tesla’s strategy, one must separate its two primary pillars: headline-grabbing moves like launching the Cybertruck or the Roadster 2.0 and the big bets it is making on its core vehicles, the models S, X, 3, and Y.
Few companies have attracted as much scorn and adoration as Tesla. When Tesla launches a product like the Cybertruck, the reception tends to be divisive: Critics see it as further evidence that founder Elon Musk is out of touch and doomed to fail, while supporters buy in — within a month Tesla received 200,000 preorders for the new vehicle. Compare that with the Ford-150, the world’s best-selling car in 2018, which sold just over 1 million vehicles that year.
- Nathan Furr is a Professor of Strategy at INSEAD and a coauthor of five best-selling books, including The Upside of Uncertainty, The Innovator’s Method, Leading Transformation, Innovation Cap i tal , and Nail It then Scale It .
- Jeff Dyer is the Horace Beesley Professor of Strategy at BYU’s Marriott School of Management. He is the lead author of the best-selling book, The Innovator’s DNA , and coauthor of The Innovator’s Method .
Partner Center
The Secret Tesla Motors Master Plan (just between you and me)
As you know, the initial product of Tesla Motors is a high performance electric sports car called the Tesla Roadster. However, some readers may not be aware of the fact that our long term plan is to build a wide range of models, including affordably priced family cars. This is because the overarching purpose of Tesla Motors (and the reason I am funding the company) is to help expedite the move from a mine-and-burn hydrocarbon economy towards a solar electric economy, which I believe to be the primary, but not exclusive, sustainable solution.
Critical to making that happen is an electric car without compromises, which is why the Tesla Roadster is designed to beat a gasoline sports car like a Porsche or Ferrari in a head to head showdown. Then, over and above that fact, it has twice the energy efficiency of a Prius. Even so, some may question whether this actually does any good for the world. Are we really in need of another high performance sports car? Will it actually make a difference to global carbon emissions?
Well, the answers are no and not much. However, that misses the point, unless you understand the secret master plan alluded to above. Almost any new technology initially has high unit cost before it can be optimized and this is no less true for electric cars. The strategy of Tesla is to enter at the high end of the market, where customers are prepared to pay a premium, and then drive down market as fast as possible to higher unit volume and lower prices with each successive model.
Without giving away too much, I can say that the second model will be a sporty four door family car at roughly half the $89k price point of the Tesla Roadster and the third model will be even more affordable. In keeping with a fast growing technology company, all free cash flow is plowed back into R&D to drive down the costs and bring the follow on products to market as fast as possible. When someone buys the Tesla Roadster sports car, they are actually helping pay for development of the low cost family car.
Now I’d like to address two repeated arguments against electric vehicles — battery disposal and power plant emissions. The answer to the first is short and simple, the second requires a bit of math:
Batteries that are not toxic to the environment! I wouldn’t recommend them as a dessert topping, but the Tesla Motors Lithium-Ion cells are not classified as hazardous and are landfill safe. However, dumping them in the trash would be throwing money away, since the battery pack can be sold to recycling companies (unsubsidized) at the end of its greater than 100,000-mile design life. Moreover, the battery isn’t dead at that point, it just has less range.
Power Plant Emissions aka “The Long Tailpipe”
A common rebuttal to electric vehicles as a solution to carbon emissions is that they simply transfer the CO 2 emissions to the power plant. The obvious counter is that one can develop grid electric power from a variety of means , many of which, like hydro, wind, geothermal, nuclear, solar, etc. involve no CO 2 emissions. However, let’s assume for the moment that the electricity is generated from a hydrocarbon source like natural gas, the most popular fuel for new US power plants in recent years.
The H-System Combined Cycle Generator from General Electric is 60% efficient in turning natural gas into electricity. "Combined Cycle" is where the natural gas is burned to generate electricity and then the waste heat is used to create steam that powers a second generator. Natural gas recovery is 97.5% efficient, processing is also 97.5% efficient and then transmission efficiency over the electric grid is 92% on average. This gives us a well-to-electric-outlet efficiency of 97.5% x 97.5% x 60% x 92% = 52.5%.
Despite a body shape, tires and gearing aimed at high performance rather than peak efficiency, the Tesla Roadster requires 0.4 MJ per kilometer or, stated another way, will travel 2.53 km per mega-joule of electricity. The full cycle charge and discharge efficiency of the Tesla Roadster is 86%, which means that for every 100 MJ of electricity used to charge the battery, about 86 MJ reaches the motor.
Bringing the math together, we get the final figure of merit of 2.53 km/MJ x 86% x 52.5% = 1.14 km/MJ. Let’s compare that to the Prius and a few other options normally considered energy efficient.
The fully considered well-to-wheel efficiency of a gasoline powered car is equal to the energy content of gasoline (34.3 MJ/liter) minus the refinement & transportation losses (18.3%), multiplied by the miles per gallon or km per liter. The Prius at an EPA rated 55 mpg therefore has an energy efficiency of 0.56 km/MJ. This is actually an excellent number compared with a “normal” car like the Toyota Camry at 0.28 km/MJ.
Note the term hybrid as applied to cars currently on the road is a misnomer. They are really just gasoline powered cars with a little battery assistance and, unless you are one of the handful who have an aftermarket hack, the little battery has to be charged from the gasoline engine. Therefore, they can be considered simply as slightly more efficient gasoline powered cars. If the EPA certified mileage is 55 mpg, then it is indistinguishable from a non-hybrid that achieves 55 mpg. As a friend of mine says, a world 100% full of Prius drivers is still 100% addicted to oil.
The CO 2 content of any given source fuel is well understood. Natural gas is 14.4 grams of carbon per mega-joule and oil is 19.9 grams of carbon per mega-joule. Applying those carbon content levels to the vehicle efficiencies, including as a reference the Honda combusted natural gas and Honda fuel cell natural gas vehicles, the hands down winner is pure electric:
The Tesla Roadster still wins by a hefty margin if you assume the average CO 2 per joule of US power production. The higher CO 2 content of coal compared to natural gas is offset by the negligible CO 2 content of hydro, nuclear, geothermal, wind, solar, etc. The exact power production mixture varies from one part of the country to another and is changing over time, so natural gas is used here as a fixed yardstick.
Becoming Energy Positive I should mention that Tesla Motors will be co-marketing sustainable energy products from other companies along with the car. For example, among other choices, we will be offering a modestly sized and priced solar panel from SolarCity , a photovoltaics company (where I am also the principal financier). This system can be installed on your roof in an out of the way location, because of its small size, or set up as a carport and will generate about 50 miles per day of electricity.
If you travel less than 350 miles per week, you will therefore be “energy positive” with respect to your personal transportation. This is a step beyond conserving or even nullifying your use of energy for transport – you will actually be putting more energy back into the system than you consume in transportation! So, in short, the master plan is:
- Build sports car
- Use that money to build an affordable car
- Use that money to build an even more affordable car
- While doing above, also provide zero emission electric power generation options
Don't tell anyone.
Tesla Business Model | How Does Tesla Make Money
8 minutes read
Learning how a successful business works is integral to growing your business. As you already know, these companies did not attain success overnight. It surely took them effort, business strategies, and failures.
This article will tackle how the Tesla business model transformed the company into one of the more popular ones, the automotive industry and other sectors where it also provides its services. Being this big, the company can be overwhelming as you look at its strategies, but you’ll surely learn essential things from its business model.

A Brief History of Tesla
Tesla was initially called Tesla Motors, Inc., founded in July 2003 . It was founded by Marc Tarpenning and Martin Eberhard, who introduced products catering specifically to the automotive industry. Elon Musk, Ian Wright, and J.B Straubel were also accredited as the founders of Tesla Motors. Musk is currently the company’s serving CEO, who spearheads all the operations and business structures.
In 2008, Tesla launched its first product, the Tesla Roadster - a high-performance electric car. The company introduced its target market as a luxury car instead of going for the cheaper first car. The following years saw Tesla investing heavily in research, development, and research, prioritizing studies in autopilot, safe, and charging cars. It was in 2018 when Tesla became the largest electronic car seller globally, with 250,000 vehicles sold, which took up to 12% of the market.
Tesla Business Model Canvas
While the Tesla business model canvas may encompass several sections, it fundamentally relies on three distinct pillars: servicing, selling model, and charging network. These core foundations are intricately woven into Tesla’s operational framework, ensuring efficient maintenance and support services, an innovative selling model tailored to the electric vehicle market, and a comprehensive charging network that underpins the convenience of Tesla’s vehicles for customers.
Value Propositions of Tesla
The company’s value propositions in the Tesla business model include greener solutions that add high performance, modern design, energy efficiency, cost of ownership, and long-range recharging flexibility. We can look deeper into its value chain . Besides the cars that Tesla sells, which is what they’re known for, it has also launched solar panels and home batteries for commercial and residential customers. These products aim to provide convenience in terms of power resources. More than that, the company also has systems and components they sell to other automobile manufacturers. Generally, Tesla has grown so much since it started, as it also provides financial services with leases and loans.
Customer Segments of Tesla
Tesla might have introduced its first car as a luxury, but the Tesla business model canvas shows that the company designs vehicles for every customer group. This includes high-net-worth customers, green buyers who prefer eco-friendly cars, commercial fleet buyers, sports car enthusiasts, corporate executives, and fans of Elon Musk. As you know, Musk has a significant following today, especially now that he’s acquired a popular social networking site.
Also, one cannot take away the fact that more and more people are looking into environmentally conscious modes of transportation. That is why Tesla made an excellent decision to invest in designing and producing electric cars. These cars need no gas to run. You only have to charge them.
Key Partners of Tesla
The Tesla business model canvas won’t be complete without its partners. These can be sectors, organizations, or individuals. They ensure the company’s processes run smoothly to ensure customer satisfaction. Some of the company’s key partners are the following:
- OEM Alliances. In 2009, Tesla partnered with OEM manufacturer Daimler, which helped the company access superior engineering and research development. It also provided Tesla with a cash infusion to help the company from potential bankruptcy. Along the way, Tesla has allied with other large companies like Toyota, which opened the doors to buying the NUMMI factory. The battery designs were from Tesla’s joint investments with Osaka and its partnership with LG Chem Ltd and CATL of China.
- Manufacturing and purchasing. Surely, Tesla produces the entire base of cars they sell. However, some parts are sourced from third parties. The company joined forces with Toyota to create electric vehicles, including production systems and components for electric cars and their accessories.
- Tesla continues to receive tax incentives from the federal government of the United States due to the company’s focus on developing eco-friendly energies and vehicles.
- Charging points. Like gas stations, Tesla cars must be charged to run. The company partners with resorts, restaurants, shopping centers, and hotels to mount fast car charging spaces.
- Leasing companies. Tesla partners with Athlon Car Lease Company for the company’s premium electric sedan, which is dedicated to fleet services within the European regions.
Key Activities of Tesla
Based on the Tesla business model canvas, the company has four key activities, including the following.
- Car manufacturing. You can consider cars as the bread and butter of Tesla. After all, it’s the company’s main activity. Along with producing electric cars are accessories and systems that come with every unit.
- R&D. To provide innovative and advanced electric cars, Tesla must explore its options through research and development.
- Building and maintenance of various charging stations. For the electric cars to run, Tesla must also provide accessible charging stations. There are more than a thousand Supercharger stations in public places like restaurants, hotels, shopping centers, and parking spaces.
- Electric power technologies. The company uses agile principles in developing and improving its software.
Customer Relationships of Tesla
You might be wondering, ‘How does Tesla make money?’ One of the reasons for the company’s success is making customer relationships its foundation. From its founding, Tesla focused on its efforts on customer experiences. This is why it does not support dealerships. Instead, the company builds company-owned stores and develops a self-service website where it’s easy to choose, order, and customize the cars. As you know, it heavily invests in its charging networks for more accessible and cost-effective car charging.
Most importantly, Tesla has solidified its position and reputation with its target markets for being a provider of luxury, innovative, and technological vehicles while considering the environmental impact.
Key Resources of Tesla
The Tesla business model canvas relies on several essential resources to facilitate key activities and deliver Tesla’s unique value proposition. These critical resources encompass Tesla’s cutting-edge technology for electric vehicles, robust battery production capabilities, top-notch engineering and design expertise, and advanced software systems. These elements synergize to drive innovation and fulfill Tesla’s commitment to sustainable transportation solutions.
Channels of Tesla
As you know, Tesla focuses more on reaching out to customers directly and getting immediate and organic from them after the purchase. With this, its retail stores and galleries are one of the primary channels it uses to market its vehicles and technology. Data in 2019 revealed that there were about 276 Tesla stores globally.
While some of these stores have halted operation, they have moved to online sales channels through the Tesla website. It’s a self-service platform where customers can shop for cars. Of course, many want to see the vehicles in person before buying them, but the website allows Tesla’s markets to explore their options before visiting its retail stores. It takes off the hassle of spending hours choosing car models in physical stores.
Besides the conferences and sales events that the company utilizes to reach customers, the popularity of Elon Musk is also an excellent marketing strategy to expand Tesla’s market.
Cost Structure of Tesla
Like any global manufacturer, Tesla comes with a very broad cost structure. As of June 2023, the company has a total operating expense of $81.376B, about a 40% increase from 2022. The total expenditure covers the following process and aspects.
- Manufacturing infrastructure
- General admin and sales
- Human resources
- Research and development budget
- Distribution
Revenue Streams of Tesla
Tesla is a company offering diverse products for its target markets. Besides its electric vehicles, the company has developed an ecosystem of innovative and cutting-edge green cars. Moreover, it launched lifestyle products and solar energy systems for Tesla’s loyal customers and fans of the company. Essentially, Tesla has two significant revenue streams.
- Automotive segment revenue. This segment includes all the sales from vehicle models, software updates, charging network access, sales services, retail merchandise, and EV components sales.
- Storage and energy generation segment. The segment includes revenues from storage products like solar panels and Tesla’s solar energy systems.
As Tesla continues to expand, you can also expect more revenue streams. This is relatively similar in all other businesses, whether for startups or a company as big as Tesla.
How Does Tesla Make Money?
With the tough competition in the automotive industry, how does Tesla make money? As you look at its business model, you’ll know that the company’s primary revenue stream is through selling cars. Tesla generated a revenue of $81.46 billion in 2022, with almost 80% of the sales coming from automotive sales. In short, they make money from selling vehicle models. Besides manufacturing luxury cars, the unique thing about Tesla is they’re branding themselves as an environmentally-conscious vehicle provider. More and more people are getting curious about electric vehicles, and customers are willing to pay more to own one of Tesla’s car models.
However, Tesla is more than just an automotive company. It operates with a diverse and comprehensive business model which manufactures various clean energy products. China is Tesla’s largest growth market, with a continuous expansion worldwide.
The following are other products and services Tesla offers to properly understand ‘how does Tesla make money?’
- Tesla provides servicing facilities for its electric vehicles and energy solutions. Owners of Tesla car models can only go to Tesla-approved servicing centers. It also offers green energy solution installations like Tesla’s Powerwall.
- Energy solutions. Businesses and households can also avail of Tesla’s unique green energy solutions. Solar Roof, Powerwall, and Powerpack are some of its products. However, if you’re curious about the Solar Roof service, Tesla has stopped manufacturing it because of supplier complications.
- Carbon credits. Tesla also makes money from carbon credits, which they receive from the US government since Tesla manufactures electric vehicles. In fact, about 20% of Tesla’s revenue is from this segment, which are tradable certificates that give companies a chance to emit a specific amount of carbon dioxide into the environment.
- Public charging. Tesla has a Supercharger Network mounted across the US and globally. A fully-charged 85kWh Tesla Model S would cost about $20-$25.
Key Takeaways
When examining Tesla’s business model canvas, it’s crucial to understand how the company generates revenue. Tesla ventured into manufacturing a premium all-electric sedan in 2008, driven by a vision of electric vehicles becoming mainstream in the future. This strategic decision was underpinned by relentless research and development efforts, which have been instrumental in creating innovative and appealing electric vehicles that cater to a growing market segment seeking sustainable and technologically advanced transportation solutions.
Along the way, Tesla found a solid position and developed a reputation as the pioneer company that produced EVs. The EV system somehow changed the landscape of the automobile industry - what used to be just mechanical drives can now be smart and computer-driven electric vehicles. Tesla also did the right thing by expanding its services, which are still associated with its main revenue stream - the EVs. Tesla might be a global company, but other businesses can take inspiration from how they manage to create their own brand identity . Keeping products innovative, unique, and relevant all at once is essential to keeping that edge amid tough competition in any industry.
Try Boardmix for Free
You, too, can create a comprehensive business model with the help of a diagramming and collaboration tool. Boardmix lets you explore its templates library and use the predesigned business model canvas template. It’s customizable, so you can tweak some elements on the template to make it your own.
Features of Creating a Business Model Canvas on Boardmix
Developing a Business Model Canvas is a strategic activity often undertaken by startups and established businesses to identify and plan out different business aspects. Boardmix online whiteboard has numerous features that make this process more intuitive, efficient, and collaborative.
1. Interactive Whiteboard Interface Boardmix's digital whiteboard allows users to visually layout and connect various components of the Business Model Canvas, like Key Partners, Value Propositions, Customer Segments, etc. The ability to write, draw, or annotate on the board facilitates clear expression of ideas. 2. Real-time Collaboration Boardmix’s collaboration feature enables teams to work on the same Business Model Canvas simultaneously. This real-time interaction allows for immediate feedback, brainstorming, and iteration, which can significantly enhance the canvas’s quality and relevance. 3. Drag-and-Drop Functionality Reorganizing ideas and elements is made easy with Boardmix’s drag-and-drop functionality. This feature helps to effortlessly structure or restructure the canvas, making the modeling process flexible and adaptive to evolving business strategies. 4. Multimedia Integration Supplement your Business Model Canvas with rich multimedia content. Integrate images, documents, or even video clips directly into the canvas to provide additional context or explanation, enhancing comprehension and engagement. 5. AI-Enhanced Brainstorming Boardmix’s AI enhancement feature can stimulate brainstorming by suggesting related concepts based on the inputs you provide for your Business Model Canvas. This innovative feature can contribute to the development of a comprehensive and robust business model. 6. Ready-to-use Templates Boardmix offers pre-made Business Model Canvas templates, accelerating the modeling process. These templates provide a well-structured format that can be readily filled in with business-specific details. 7. Secure Cloud Storage With Boardmix, you never have to worry about losing your work. Your Business Model Canvas gets auto-saved and stored securely in the cloud. This means you can access your canvas from anywhere and at any time. By utilizing these features of Boardmix Online Whiteboard, developing a comprehensive and visually engaging Business Model Canvas becomes an enjoyable and effective process.
References:
https://bstrategyhub.com/tesla-business-model-tesla-business-model-canvas/
https://finty.com/us/business-models/tesla/#:~:text=Tesla%20makes%20money%20by%20selling,there’s%20the%20investment%20in%20Bitcoin .
https://businessmodelanalyst.com/tesla-business-model/#How_Tesla_makes_money
https://www.investopedia.com/tesla-s-largest-revenue-source-is-automotive-sales-4799069
Join Boardmix to collaborate with your team.
Microsoft Value Chain Analysis: A Comprehensive Breakdown
Google Value Chain Analysis
KFC Value Chain Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide

The Leading Source of Insights On Business Model Strategy & Tech Business Models

Tesla Mission Statement and Vision Statement Analysis
Tesla’s vision is to “create the most compelling car company of the 21st century by driving the world’s transition to electric vehicles,” while its mission is “to accelerate the advent of sustainable transport by bringing compelling mass-market electric cars to market as soon as possible.” Tesla used a transitional business model as its ecosystem grew.
Table of Contents
Breaking down the Tesla mission and vision
In an official presentation in 2011, Tesla highlighted its vision as:
Create the most compelling car company of the 21st century by driving the world’s transition to electric vehicles
While as highlighted by Elon Musk on Tesla’s blog its mission was:
To accelerate the advent of sustainable transport by bringing compelling mass-market electric cars to market as soon as possible.
To understand what it means, we need to look at Tesla’s history and how it developed.
Tesla was founded in 2003 by a group of engineers. The central idea was to prove that electric cars could be as good, if not better, than gasoline alternatives.
As Elon Musk took over as a CEO, he started to roll out a strategy where Tesla could have an entry price competitive with other cars in the market.
That is why the first car Tesla launched was a sports car, as its pricing was in line with the market.
If Tesla were to launch a premium car, it would not have made it because the costs of producing the first prototypes turned out so much higher, and Tesla would have seen all its orders canceled.

Instead, by narrowing down the market, at the point of figuring out a microniche, Tesla could sell a high-priced sports car in a market segment that was much less elastic to price changes, as those were innovators interested in the technology.
Tesla could envision its next step in this evolution only after launching a successful sports car.
Indeed, once it had figured out the prototyping of the car, it could start to manufacture a premium car model at proper pricing for the market, which could be a bit wider.
This targeted a market segment that could be labeled, according to the tech adoption curve , as early adopters.
Those were people interested in the technology but much more in its value proposition , which was about an alternative to gas-powered cars with zero emissions.

Where are we today? Tesla, with its Model 3, is ready to tackle mass manufacturing.

Of course, as Tesla has scaled and launched the new Model 3, its value proposition and scope also changed.
Tesla is now working on achieving economies of scale, and the people buying a Tesla now are doing it for different reasons.
It’s about status, looking good with peers, saving on gas, and of course, for some, it’s still about the environment.
Indeed, it’s critical to notice that when a company scales, the value proposition for consumers also changes dramatically.
From a more tech-based and practical pay-off, the value proposition morphs into demand generation when it adds into the mix social status and how the consumer feels about her/himself while driving a Tesla!|
To remember the early days, as highlighted by Elon Musk back in 2013:
Our first product was going to be expensive no matter what it looked like, so we decided to build a sports car, as that seemed like it had the best chance of being competitive with its gasoline alternatives.
Therefore, as a go-to-market and entry strategy , Tesla used a higher-priced segment of the market, in seemingly sharp contrast with its mission .
Yet this was a transitional business model that enabled Tesla to be viable in the short term and yet achieve its mission in the long run.
That’s because, in order to become fully viable as a business model, Tesla needed to create an entire ecosystem, also made of energy solutions that could enable electric cars to become competitive in terms of convenience (meant the ability to charge anywhere) in respect to gasoline vehicles.
Therefore, as Tesla rolls out its business model , by enabling this ecosystem to grow year over year, the company can enter larger and larger segments of the markets by offering lower-priced options that might make it possible for Tesla’s vehicles to achieve mass adoption.
Where is Tesla today?
It took years for Tesla to roll out its business strategy , at the point of going through various near-death experiences.
And yet, by 2022, this is where Tesla stands.

In fact, after many years of rolling outs its strategy , finally, the car segment of Tesla has become highly profitable as result of scale.

Thus, today Tesla is a completely different company, with a changed cost and margin structure.

And profitability.

Of course, things might slightly change as the EV market gets more competitive, and Tesla might have to leverage short-term price wars to win market shares.
However, the company, overall, has become way more efficient over the years.

History of Tesla
The history of Tesla is one of the most interesting corporate histories of the last century.
Starting as an attempt to show the viability of EVs, by starting from a sub-segment of the sports car performance market, Tesla produced its first viable EV in 2008.
From there, the company scaled up its operations in a story with plenty of twists and turns and many near-death experiences.
Elon Musk explained how, in 2018, Tesla was a few days away from bankruptcy and how the company managed to survive and thrive.
Yet, while Tesla’s story might make sense in hindsight, it was a very unpredictable turn of events that transformed Telsa into one of the most interesting companies of the last century!
Starting from a microniche to kick off the business
At the introduction of the Tesla Roadster, Elon Musk, in 2006, as the prototype was introduced, highlighted:
The opportunity is now and the need is now to have a car company of this nature and you know one thing I’d say to anyone who’s considering buying this car is you know you’re not just buying a sports car you’re actually helping pay for the development of the mass-market vehicles. The tesla collectives are not paid high salaries we don’t issue dividends all money all free cash flow goes completely into driving the technology to lower and lower costs and make it more more available and also we’re going to be working with solar panel companies to offer solar options along with the vehicles so that if you buy the solar option and you buy the vehicle you’ll actually be energy positive. You’ll generate more miles in electricity than you use in your daily commute and so I really I think we should all aspire to be the energy positive in that way.
After a very complex history, made of many near-death experiences, Tesla’s pieces came together in a company that goes way beyond cars!
And while the path seems easy and linear in hindsight, in reality, it was very messy and hard to predict.
I like to say over and over that it takes a decade or more to roll out a business strategy fully.
And when you look at it in hindsight, it looks like a linear journey, when instead, it was a very messy endeavor.

Indeed, when Musk set the master plan for Tesla, it was a very simple plan, which took fifteen years to execute!
Indeed, by 2006, Musk would lay out the foundation for Tesla’s plan for the next decade. It was a four points master plan structured as below:
- Build sports car
- Use that money to build an affordable car
- Use that money to build an even more affordable car
- While doing above, also provide zero emission electric power generation options
Breaking down the Tesla business model
To understand Tesla’s business model, it’s critical to look at a few key ingredients:
- In-house manufacturing: when Tesla started to execute its business model back in the early 2000s, it thought it could mainly outsource parts of the car, and create an electric vehicle out of those. Yet, they soon realized this assumption was completely off. Not only did they not manage to secure proper parts for the vehicles, but none wanted to risk having electric vehicles that could have caught fire. Instead, if Tesla wanted to make its business plan viable it had to build its own manufacturing centers. It took years for the company to do that, and it’s starting to pay off today. Now Tesla has various manufacturing facilities, called gigafactories.
- Energy storage and generation : another key element to make the Tesla business model scalable is the ability of drivers to find electric stations around the country, and to quickly charge the cars. That is why, over the years, Tesla has been ramping up its electric generation and storage arm.
- Direct distribution : another key element of the Tesla business model which the company started to build early on, is direct distribution or the ability to sell Tesla vehicles either through its online stores, or via its Tesla stores.
- And financing models : as explained in real-time insurance , a combination of lower insurance premiums and better leasing rates can ramp up Tesla’s demand side, making it possible for many millions of Americans to own a Tesla.

Manufacturing, together with energy storage and generation, and direct distribution are some of the key ingredients of Tesla’s business model.
Key Highlights
- Vision: To create the most compelling car company of the 21st century by driving the world’s transition to electric vehicles.
- Mission: To accelerate the advent of sustainable transport by bringing compelling mass-market electric cars to market as soon as possible.
- Founded in 2003 by a group of engineers with the goal of proving the viability of electric cars.
- Initial focus on building high-priced sports cars, starting with the Tesla Roadster.
- Aimed to demonstrate that electric vehicles (EVs) could compete with gasoline alternatives.
- Tesla’s early emphasis on sports cars was a transitional strategy to establish brand credibility and generate revenue.
- Recognized the need to build its manufacturing facilities (Gigafactories) to ensure EV production.
- Developed an entire ecosystem, including energy solutions, to support EV convenience and competitiveness.
- Gradually expanded its market by offering lower-priced options as it achieved economies of scale.
- Tesla’s value proposition evolved over the years.
- Initially, it was technology-focused, targeting innovators interested in new tech.
- Expanded to include social status, cost savings, and environmental considerations as the company scaled.
- Demonstrated how the value proposition changes as a company grows.
- In 2022, Tesla achieved a profit margin of $9,580 per car, driven by increased scale and efficiency.
- Automotive sales accounted for over $71.4 billion in revenue, with a 28.5% gross margin.
- Gross margin improved from 19% in 2017 to over 25% in 2022.
- The company achieved profitability, with over $12.5 billion in profits in 2022.
- Tesla went through various phases, from proving EV viability with the Roadster to achieving mass production with the Model 3.
- Faced numerous challenges and near-death experiences.
- The company’s transformation was marked by unpredictability and adaptation.
- Build a high-priced sports car (Roadster).
- Use the profits to create an affordable car (Model S).
- Repeat step 2 to produce even more affordable vehicles (Model 3, Model Y).
- Develop zero-emission electric power generation options (Solar, Energy products).
- In-house manufacturing: Tesla realized the need to establish its own manufacturing facilities (Gigafactories) to control production.
- Energy solutions: Tesla invested in electric generation and storage solutions, including solar products and Powerwalls.
- Direct distribution : Tesla adopted a direct-to-consumer sales model, combining online and physical stores.
- Financing models: Lower insurance premiums and leasing options were part of Tesla’s strategy to make EVs accessible.
- Tesla is vertically integrated, overseeing its manufacturing plants, including Gigafactories, and directly selling products to consumers.
- Vertical integration allows Tesla to have greater control over production and customer experience.
Read Also: Tesla Business Model
Related to Tesla
Is Tesla Profitable?

Tesla Business Model
How Does Tesla Make Money?

Tesla Cost Structure

Tesla Marketing Strategy

Tesla Revenue Per Employee

Tesla Profit Margin

Tesla Profit Margin Per Car

Tesla R&D Strategy

Tesla Market Cap vs. Revenue

Tesla Production

Tesla Production vs. Delivery

Who Is Elon Musk

Who Owns Tesla

Tesla Competitors

Real-Time Insurance

Read Also: Tesla Business Model , Elon Musk Companies, Who Owns Tesla , Transitional Business Models , Tesla Competitors .
Read Also: Who Is Elon Musk? The Elon Musk’s Story , How Does Elon Musk Make Money , Elon Musk Companies , Bill Gates Companies , Jeff Bezos Companies , Warren Buffett Companies .
How did Tesla use a transitional business model to thrive?
Mission Statement Case Studies
Adidas Mission Statement

Uber Mission Statement

Tesla Mission Statement

- Amazon Mission Statement

- Apple Mission Statement

Netflix Mission Statement

Coca-Cola Mission Statement
- Starbucks Mission Statement

Microsoft Mission Statement

Walmart Mission Statement

- Nike Mission Statement

- Google Mission Statement

Other resources:
- Successful Types of Business Models
- The Complete Guide To Business Development
- Business Strategy Examples
- Blitzscaling Business Model Innovation Canvas In A Nutshell
- What Is Market Segmentation? the Ultimate Guide to Market Segmentation
- Marketing Strategy: Definition, Types, And Examples
- Marketing vs. Sales: How to Use Sales Processes to Grow Your Business
- How To Write A Mission Statement
Case studies:
More Resources

About The Author
Gennaro Cuofano
Discover more from fourweekmba.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
- 70+ Business Models
- Airbnb Business Model
- Amazon Business Model
- Apple Business Model
- Google Business Model
- Facebook [Meta] Business Model
- Microsoft Business Model
- Netflix Business Model
- Uber Business Model
Tesla investors urged to vote against Musk's 'excessive' $56 billion pay package and proposed reincorporation in Texas
- Glass Lewis has advised Tesla shareholders to vote against Elon Musk's $56 billion pay package.
- The proxy advisor also urged them to reject a proposal to reincorporate the EV maker in Texas.
- Glass Lewis said in a report that the share options deal was of "excessive size" and "dilutive."

A top proxy advisory firm has urged Tesla shareholders to vote against Elon Musk's $56 billion pay deal and a proposal to reincorporate the EV maker in Texas.
Glass Lewis said in a report that the compensation package was of "excessive size" and "dilutive" while also raising concerns over Musk's numerous other projects — particularly the social media platform X .
"Mr. Musk's slate of extraordinarily time-consuming projects unrelated to the Company was well-documented before the 2018 grant, and only expanded with his high-profile purchase of the company now known as X," Glass Lewis said in the report, per Bloomberg .
The Tesla CEO also runs SpaceX, Neuralink, and the Boring Company.
Glass Lewis added that the proposed move to Texas offered shareholders "uncertain benefits and additional risk," the Financial Times reported.
Proxy advisor firms guide shareholders on how to vote at shareholder meetings, helping them "make educated decisions that benefit the company as well as their own investments," Glass Lewis says on its website .
A report published on the Harvard Law School Forum on Corporate Governance said that proxy advisory firms can have "significant influence" over institutional investors' voting decisions as well as the governance choices of publicly traded companies.
Related stories
The Glass Lewis report comes ahead of Tesla's annual meeting on June 13, when investors will vote on the proposed package of share options, which was initially outlined in 2018.
Musk has previously threatened to develop future products elsewhere if his bid to gain more control of Tesla by increasing his stake is blocked.
"I am uncomfortable growing Tesla to be a leader in AI & robotics without having ~25% voting control. Enough to be influential, but not so much that I can't be overturned," he wrote on X in January. "Unless that is the case, I would prefer to build products outside of Tesla."
Tesla's board has been attempting to persuade investors to support the controversial package since it was struck down by a Delaware judge in January over concerns about its size and the board's independence.
In the ruling, Court of Chancery Judge Kathleen St. J. McCormick said, "The process leading to the approval of Musk's compensation plan was deeply flawed," adding that "Musk had extensive ties with the persons tasked with negotiating on Tesla's behalf."
The SpaceX CEO was quick to express his view on the ruling on X, writing, "Never incorporate your company in the state of Delaware."
In 2018, 73% of investors approved Musk's pay proposal, per the FT.
If Tesla's board can now prove investors still back the deal, it may help an appeal case against the decision to void it.
Losing the vote would be a major blow to the board and could call Musk's leadership into question.
Tesla did not immediately respond to a request for comment from Business Insider, which was made outside regular working hours.
Watch: How Elon Musk makes and spends his billions
- Main content
- My View My View
- Following Following
- Saved Saved
Tesla stands by Musk pay after ISS urges shareholders to reject package
- Medium Text

- Company Tesla Inc Follow
Sign up here.
Reporting by Yuvraj Malik in Bengaluru; Editing by Arun Koyyur
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab

Business Chevron
Stellantis sees Italian plants running at full capacity in 2030
Stellantis sees its Italian plants running at full capacity in 2030 as plans for new models, including hybrid ones, are expected to support production, Chief Executive Carlos Tavares said on Tuesday.

We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
The Tesla business model operates as a Direct-to-Consumer (D2C) business model as it sells directly, cutting out middlemen such as dealerships and offering its own charging station network. Which of these names do you recognize more easily: Tesla or Elon Musk?While, in general, we identify the author by the work — that is, it would be normal for you to know Elon Musk as the CEO of Tesla ...
Tesla's business model is based on direct sales and service, not franchised dealerships. ... A business model is a company's profit-making plan which defines the products or services it will sell ...
In 2023, Tesla generated $96.77 Billion in revenues. Tesla's business model primarily relies on automotive sales, $78.5 billion (over 81% of the total revenues); services/others followed with over $8 billion; energy generation and storage generated over $6 billion in revenues. Tesla has four main sources of income:
A real-time insurance business model enables Tesla to build its own insurance arm, by dynamically adjusting the premiums, based on real-time driving behavior. Reduced insurance premiums hooked with the leasing arm, enable Tesla to scale its demand side of the business.. As explained in real-time insurance, a combination of lower insurance premiums and better leasing rates has the potential to ...
3. Key Partners of Tesla. OEM Alliances. 2009 - Tesla, Inc. aligned a partnership with OEM manufacturer (Daimler), which helped to provide Tesla, Inc. with access to superior research and engineering development and a cash infusion that helped Tesla to escape the potential bankruptcy.; 2010 - Tesla, Inc. signed an alliance with Toyota, which enabled them to buy former NUMMI factory which ...
The Tesla Team, April 5, 2023. Today, we are publishing Master Plan Part 3, which outlines a proposed path to reach a sustainable global energy economy through end-use electrification and sustainable electricity generation and storage. This paper outlines the assumptions, sources and calculations behind that proposal. Input and conversation are ...
A Five Year Business Strategic Plan for Tesla: An Introduction. Tesla Motors, Inc. (henceforth Tesla) did not exist in 2005. It was not until 2008 that its chairman, CEO, and founder, Elon Musk ...
Tesla's business model is based on a three-pronged approach to selling, servicing, and charging its electric vehicles. Direct Sales. Tesla doesn't adopt the approach of franchise dealerships, unlike most manufacturers. They prefer selling their product directly to customers through self-owned showrooms across many of the major urban centres ...
Tesla Motors, now known simply as Tesla, was founded in 2003 by a group of visionary engineers, including Martin Eberhard, Marc Tarpenning, Ian Wright, JB Straubel, and Elon Musk.The company's initial focus was on developing electric vehicles, with the goal of commercializing sustainable transportation. In 2008, Tesla made its first breakthrough with the launch of the Tesla Roadster, a high ...
Suffice it to say, these men laid the groundwork for Musk, Straubel and others to make Tesla's business plan of commercialising electric cars a reality. They had active roles within the company for several years before their ousting in 2008. Tesla's Branding Strategy
In this article, we unravel the Tesla Business Model using the Business Model Canvas and learn about how Tesla makes money. Tesla, the American electric vehicle and clean energy company, has revolutionized the automotive industry and become a symbol of sustainable innovation. Founded in 2003 by a group of engineers and entrepreneurs, including ...
These available subsidies help lower the cost of ownership for Tesla's high-priced vehicles, and has allowed the company to maintain its premium strategy. To summarize this quick overview of Tesla ...
How Tesla Sets Itself Apart. by. Lou Shipley. February 28, 2020. HBR Staff. Summary. Tesla and its flamboyant, and sometimes erratic, innovator Elon Musk have turned the more than a century old ...
5. Positioning Tesla as a Tech Company Further Through Continuous Innovation. Another critical component of the business strategy of Tesla is its strong technological innovation. Remember that the company has positioned itself as both an automaker and a clean energy company, as well as a technology company.
Published July 30, 2021. Even as it reported record earnings this past week, electric carmaker Tesla, Inc. ( TSLA) is already reorganizing its business strategy to boost profits. Two recent ...
Tesla has shifted the auto industry toward electric vehicles, achieved consistently growing revenues, and at the start of 2020 was the highest-performing automaker in terms of total return, sales ...
The Tesla Roadster still wins by a hefty margin if you assume the average CO 2 per joule of US power production. The higher CO 2 content of coal compared to natural gas is offset by the negligible CO 2 content of hydro, nuclear, geothermal, wind, solar, etc. The exact power production mixture varies from one part of the country to another and is changing over time, so natural gas is used here ...
As you look at its business model, you'll know that the company's primary revenue stream is through selling cars. Tesla generated a revenue of $81.46 billion in 2022, with almost 80% of the sales coming from automotive sales. In short, they make money from selling vehicle models.
Tesla, Inc. is the company chosen by me for doing the strategic business plan. In 2003 Tesla became the first car company to produce a fully electric vehicle which run solely on batteries and not using any internal combustion engine for traction purpose. Tesla is the only company to sell a zero greenhouse emission cars in successive production.
Tesla's "vertical integration" can be universally applied, and here are several takeaways for your building your business plan. Start with low volume production, and sell at higher price points ...
Using CB Insights data, we uncovered the 6 most important strategic priorities highlighted by Tesla's recent acquisitions and partnerships. We then categorized companies by their business relationships with Tesla across these priorities: Autonomous vehicles; Battery metal mining & materials processing; EV charging infrastructure
Common items to include are credit histories, resumes, product pictures, letters of reference, licenses, permits, patents, legal documents, and other contracts. Example traditional business plans. Before you write your business plan, read the following example business plans written by fictional business owners.
Tesla's vision is to "create the most compelling car company of the 21st century by driving the world's transition to electric vehicles," while its mission is "to accelerate the advent of sustainable transport by bringing compelling mass-market electric cars to market as soon as possible." Tesla used a transitional business model as its ecosystem grows.
Telsa faces investor pushback on reinstating Elon Musk's $55 billion pay package. The largest public pension fund in the US currently plans to vote against the pay plan. Musk called out the ...
Tesla was quick to fire back at Glass Lewis after the advisory firm encouraged shareholders to vote against the company's $55 billion compensation plan for Elon Musk. In a letter to shareholders ...
Top proxy advisor Institutional Shareholder Services on Friday recommended Tesla shareholders vote against the reapproval of CEO Elon Musk' s $56 billion pay package and withhold their support ...
Glass Lewis has advised Tesla shareholders to vote against Elon Musk's $56 billion pay package. The proxy advisor also urged them to reject a proposal to reincorporate the EV maker in Texas. Glass ...
Tesla on Monday defended a proposal to ratify CEO Elon Musk's $56 billion pay package and said a new compensation would be costlier, days after a top proxy advisory firm recommended shareholders ...
Elon Musk and the Tesla board are facing a shareholder suit over his sale of $7.5 billion worth of Tesla shares in late 2022, ahead of a January 2023 sales report that sent the price of that stock ...
Tesla Inc. is a company in disarray. Layoffs are mounting. Morale is shattered. Its stock is cratering and sales are anemic. And, some investors say, it's got a distracted leader at the helm ...