
Assessing the Sustainability of Slum Tourism
Student thesis : Master thesis
Slums have always tempted the imagination, portrayed as adventurous places that display authenticity, culture and diversity. The phenomenon of slum tourism first made its appearance in Victorian London and since then has been the focal center of journalists, academics and social reformers, raising questions about poverty, power and ethics. More recently, slum tourism reappeared in many cities of the Global South drawing the attention of the academia and international media, and while it is criticized for commodifying poverty and promoting voyeurism, its advocates stress the benefits it produces for the poor. The impact slum tourism has on local communities, however, remains relatively undocumented. Driven by the declaration of 2017 as the ‘’International Year for Sustainable Tourism Development’’ by the United Nations, this paper explores the potential of slum tourism as a tool for poverty alleviation, focusing on the cases of Cape Town and Rio de Janeiro. The sustainability of this ‘’new’’ phenomenon is examined in a post-developmental approach, through a lens of ethical controversies, conceptual ambiguities and asymmetrical power relations, in hope that slum tourism is a means to an end, and not an end in itself.
| Educations | MSocSc in Service Management, (Graduate Programme) Final Thesis |
|---|---|
| Language | English |
| Publication date | 2016 |
| Number of pages | 82 |
| Supervisors | Mogens Bjerre |
Documents & Links
File : application/pdf, 1.61 MB
Type : Text file
Advertisement
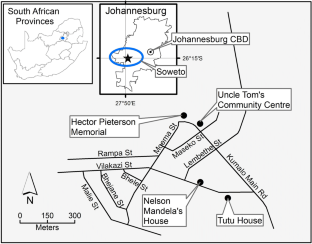
Tourist and resident perspectives on ‘slum tourism’: the case of the Vilakazi precinct, Soweto
- Published: 06 May 2019
- Volume 85 , pages 1133–1149, ( 2020 )
Cite this article

- Gijsbert Hoogendoorn ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7969-7952 1 ,
- Nthabiseng Letsatsi 1 ,
- Thabisile Malleka 1 &
- Irma Booyens 2 , 3
1968 Accesses
13 Citations
Explore all metrics
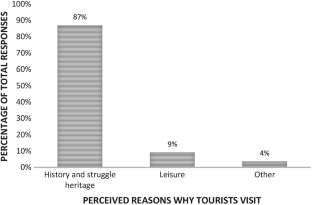
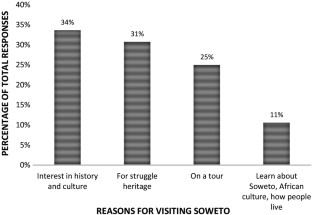
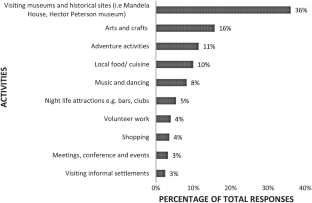
Slum tourism as a topic of investigation has seen significant growth since the beginning of this decade with increasing theoretical and empirical depth. With this growth, some inconsistencies in conceptual framing and use of terminology have emerged. The purpose of this paper is to argue for township tourism in Soweto to be regarded as a form of heritage tourism rather than slum tourism—a notion which has entered the township tourism literature in recent years. This argument is presented through two sections of analysis and debate, using Vilakazi precinct in Soweto as a case study. Firstly, the paper analyses the emergence of township tourism as an academic focus in the literature and how it came to be classified as slum tourism, considering definitional conundrums. Various South African authors emphasise the struggle heritage character of township tourism. Secondly, the historical development of townships and tourism in these areas are interrogated. The empirical data offer the perspectives on tourism in their area from: (a) residents living in and around Vilakazi Street; and (b) tourists visiting the Vilakazi precinct. The analysis reveals that neither residents nor visitors consider the Vilakazi precinct or the larger area of Orlando West as a slum; rather they perceive tourism is the area to be connected to its struggle heritage. We accordingly stress that the term ‘slum tourism’ to describe township tourism in Soweto is inaccurate and is inconsistent with the views not only of residents and visitors, but also South African authors.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
( source : authors)
( source : resident survey)

( source : visitor survey)*. *Figures subject to rounding error
( source : visitor survey)
Similar content being viewed by others

Slum Tourism and Urban Regeneration: Touring Inner Johannesburg

The Other Half of Urban Tourism: Research Directions in the Global South

The Process of Tourism Transition and the Tourism Social Contract in Indigenous Territory: The Case of the Nova Esperança Indigenous Community (Rio Cuieiras, Brazil)
This was in response to one of the authors’ presentations at the South African Cultural Observatory’s 2018 conference in Port Elizabeth, 7–8 March 2018.
Resident No. 46 (hereafter R with the questionnaire number), young female (18–30), unemployed.
Young female (18–30), relying on remittances.
Male, aged 41–50, informal income.
Female, aged 31–40, informal income.
Young male (18–30), relying on remittances.
Young female (18–30), informal income.
Visitor No. 30 (hereafter V with the questionnaire number), female, aged 30, on holiday.
Female, aged 30, on holiday.
Note that Youth Day is a National Holiday to commemorate the June 16th uprising, and it was coincidental that some of the fieldwork fell over this holiday. While the fieldwork was carried out over a three weeks in June and July 2018, 44% of the visitor responses (42 international and 17 domestic visitors) were collected on Youth Day due to the number of visitors on the day. We did not detect notable differences in the responses collected on Youth Day in comparison with the overall responses.
Male, aged 52, business owner from Germany.
Female, aged 52, on holiday.
Female, aged 18, student.
Female, aged 40, visiting family.
Male, aged 20, student from France.
Aitchison, C. (2001). Theorizing Other discourses of tourism, gender and culture: Can the subaltern speak (in tourism)? Tourist Studies, 1 (2), 133–147.
Google Scholar
BBC (British Broadcasting Cooperation). (2014). Favela life: Rio’s city within a city . https://www.bbc.com/news/world-latin-america-27635554 . Accessed January 8, 2019.
Beavon, K., & Rogerson, C. M. (1990). Temporary trading for temporary people: The making of hawking in Soweto. In D. Drakakis-Smith (Ed.), Economic growth and urbanization in developing areas (pp. 263–286). London: Routledge.
Bolay, J. C. (2006). Slums and urban development: Questions on society and globalisation. The European Journal of Development Research, 18 (2), 284–298.
Booyens, I. (2010). Rethinking township tourism: Towards responsible tourism development in South African townships. Development Southern Africa, 27 (2), 273–287.
Booyens, I., & Rogerson, C. M. (2018). Creative tourism: South African township explorations. Tourism Review, 74 (2), 256–267. https://doi.org/10.1108/TR-12-2017-0200 .
Article Google Scholar
Booyens, I., & Rogerson, C. M. (2019). Recreating slum tourism: Perspectives from South Africa. Urbani izziv, 30, S52–S63.
Bourdieu, P. (1971). Systems of education and systems of thought. In M. Young (Ed.), Knowledge and control: New directions for the sociology of education (pp. 189–207). London: Collier-Macmillan.
Briedenhann, J., & Ramchander, P. (2006). Township tourism: Blessing or blight? The case of Soweto in South Africa. In M. K. Smith & M. Robinson (Eds.), Cultural tourism in a changing world: Politics, participation (re)presentation (pp. 124–142). Clevedon: Channel View.
Butler, R. W. (1980). The concept of a tourist area cycle of evolution: Implications for management of resources. The Canadian Geographer, 24 (1), 5–12.
Butler, S. R. (2010). Should I stay or should I go? Negotiating township tours in post-apartheid South Africa. Journal of Tourism and Cultural Change, 8 (1/2), 15–30.
Census. (2011). Orlando West. Statistics South Africa. https://census2011.adrianfrith.com/place/798026032 . Accessed January 7, 2019.
Choplin, A. (2016). Rethinking precarious neighborhoods, rethinking the future city. In A. Deboulet (Ed.), Rethinking precarious neighbourhoods (pp. 245–250). Paris: Agence Française De Développement.
Cirolia, L. R., & Scheba, S. (2019). Towards a multi-scalar reading of informality in Delft South Africa: Weaving the ‘everyday’ with wider structural tracings. Urban Studies, 56 (3), 594–611.
City of Johannesburg. (2004). Soweto tourism plan . Johannesburg: Site Solutions, Tourism Intelligence and Open Transcommunication.
Deboulet, A. (2016). Introduction, Rethinking precarious neighbourhoods. Knowledge and recognition. In A. Deboulet (Ed.), Rethinking precarious neighbourhoods (pp. 9–35). Paris: Agence Française De Développement.
Department of Environmental Affairs and Tourism. (2005). Vilakazi Precinct Project . Johannesburg: Interfaith Community Development Association and Holicki and Associates JV.
Dürr, E. (2012). Urban poverty, spatial representation and mobility: Touring a slum in Mexico. International Journal of Urban and Regional Research, 36 (4), 706–724.
Dyson, P. (2012). Slum tourism: Representing and interpreting ‘reality’ in Dharavi. Mumbai. Tourism Geographies, 14 (2), 254–274.
Freire-Medeiros, B. (2009). The favela and touristic transits. Geoforum, 40 (4), 580–588.
Freire-Medeiros, B. (2014). Touring poverty . Abingdon: Routledge.
Frenzel, F. (2013). Slum tourism in the context of the tourism and poverty (relief) debate. Die Erde, 144 (2), 117–128.
Frenzel, F. (2014). Slum tourism and urban regeneration: Touring inner Johannesburg. Urban Forum, 25 (4), 431–447.
Frenzel, F. (2016). Slumming it: The tourist valorization of urban poverty . London: Zed.
Frenzel, F. (2018). On the question of using the concept ‘slum tourism’ for urban tourism in stigmatised neighbourhoods in inner city Johannesburg. Urban Forum, 21 (1), 51–62.
Frenzel, F., & Koens, K. (2012). Slum tourism: Developments in a young field of interdisciplinary tourism research. Tourism Geographies, 14 (2), 195–212.
Frenzel, F., Koens, K., Steinbrink, M., & Rogerson, C. M. (2015). Slum tourism: State of the art. Tourism Review International, 18 (4), 237–252.
Frisch, T. (2012). Glimpses of another world: The Favela as a tourist attraction. Tourism Geographies, 14 (2), 320–338.
Gastrow, C. (2015). Thinking futures through the slum. The Avery Review, 9 . http://www.averyreview.com/issues/9/thinking-futures .
Gauteng Province. (2014). Gauteng township economy revitalisation strategy 2014–2019 . Johannesburg: Gauteng Province.
George, R., & Booyens, I. (2014). Township tourism demand: Tourists’ perceptions of safety and security. Urban Forum, 25 (4), 449–467.
Giddy, J. K., & Hoogendoorn, G. (2018). Ethical concerns around inner city walking tours. Urban Geography, 39 (9), 1293–1299. https://doi.org/10.1080/02723638.2018.1446884 .
Giliomee, H. B., & Mbenga, B. (2007). New history of South Africa . Cape Town: Tafelberg.
Hernandez-Garcia, J. (2013). Slum tourism, city branding and social urbanism: The case of Medellin, Colombia. Journal of Place Management and Development, 6 (1), 43–51.
Hlongwane, A. K. (2007). The mapping of June 16 1976 Soweto student uprising routes: Past recollections and present reconstruction(s). Journal of African Cultural Studies, 19 (1), 7–36.
Holst, T. (2018). The affective negotiation of slum tourism: City walks in Delhi . London: Routledge.
Hoogendoorn, G., & Giddy, J. K. (2017). “Does this look like a slum?” Walking tours in the inner city of Johannesburg. Urban Forum, 28 (3), 315–328.
Jones, G. A., & Sanyal, R. (2015). Spectacle and suffering: The Mumbai slum as a worlded space. Geoforum, 65, 431–439.
Koens, K., & Thomas, R. (2016). “You know that’s a rip off”: Policies and practices surrounding micro-enterprises and poverty alleviation in South African township tourism. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 24 (12), 1641–1654.
Lejano, R. P., & Del Bianco, C. (2018). The logic of informality: Pattern and process in a São Paulo favela. Geoforum, 91, 195–205.
Linke, U. (2012). Mobile imaginaries, portable signs: Global consumption and representations of slum life. Tourism Geographies, 14 (2), 294–319.
Lombard, M. (2014). Constructing ordinary places: Place-making in urban informal settlements in Mexico. Progress in Planning, 94, 1–53.
Ma, M., & Hassink, R. (2013). An evolutionary perspective on tourism area development. Annals of Tourism Research, 41, 89–109.
Magubane, P., & Lee, M. (1979). Soweto . Cape Town: Don Nelson.
Marschall, S. (2006). Visualizing memories: The Hector Pieterson Memorial in Soweto. Visual Anthropology, 19 (2), 145–169.
Masilo, H., & van der Merwe, C. D. (2016). Heritage tourist’s experiences of ‘Struggle Heritage’ at Liliesleaf Farm Museum and Hector Pieterson Memorial & Museum South Africa. African Journal of Hospitality, Tourism and Leisure, 5 (3), 1–20.
Mekawy, M. A. (2012). Responsible slum tourism: Egyptian experience. Annals of Tourism Research, 39 (4), 2092–2113.
Meschkank, J. (2011). Investigations into slum tourism in Mumbai: Poverty tourism and the tensions between different constructions of reality. GeoJournal, 76 (1), 47–62.
Mkono, M. (2016). The reflexive tourist. Annals of Tourism Research, 57, 206–209.
Muldoon, M. (2018). Gazing back: A feminist postcolonial lens on tourism in the townships of South Africa . Unpublished PhD, University of Waterloo, Canada.
Ndlovu, S. (2006). Mapping the Soweto uprising routes . Johannesburg: Emba Project Management on behalf to the Gauteng Department of Public Works.
Nisbett, M. (2017). Empowering the empowered? Slum tourism and the depoliticization of poverty. Geoforum, 85, 37–45.
Pieterse, E. (2011). Grasping the unknowable: Coming to grips with African urbanisms. Social Dynamics, 37 (1), 5–23.
Poria, Y., Butler, R., & Airey, D. (2003). The core of heritage tourism. Annals of Tourism Research, 30 (1), 238–254.
Poria, Y., Butler, R., & Airey, D. (2004). Links between tourists, heritage and reasons for visiting heritage sites. Journal of Travel Research, 43 (1), 20–28.
Pott, A., & Steinbrink, M. (2009). Die kultur des Slum(ming)s. Zur historischen Rekonstruktion eines globalen Phänomens. In H. Wöhler, A. Pott, & V. Denzer (Eds.), Tourismusräume. Zur soziokulturellen Konstruktion eines globalen Phänomens . Bielefeld: Springer.
Pratt, A. (2019). Formality as exception. Urban Studies, 56 (3), 612–615.
Ramchander, P. (2003). Towards the responsible management of socio-cultural impact of township tourism. In P. M. Burns & M. Novelli (Eds.), Tourism and politics: Global frameworks and local realities (pp. 149–172). Oxford: Elsevier.
Ramchander, P. (2004). Towards the responsible management of the social - cultural impact of township tourism. Unpublished PhD thesis, Department of Tourism Management, University of Pretoria.
Rogerson, C. M. (2004). Urban tourism and small tourism enterprise development in Johannesburg: The case of township tourism. GeoJournal, 60 (3), 249–257.
Rogerson, C. M. (2013). Urban tourism, economic regeneration and inclusion: Evidence from South Africa. Local Economy, 28 (2), 188–202.
Rogerson, C. M. (2014). Rethinking slum tourism: Tourism in South Africa’s rural slumlands. Bulletin of Geography: Socio-Economic Series, 26 (26), 19–34.
Rogerson, C. M. (2015). Revisiting VFR tourism in South Africa. South African Geographical Journal, 97 (2), 139–157.
Rogerson, C. M. (2019). The economic development of South Africa’s townships. In J. Knight & C. M. Rogerson (Eds.), The geography of South Africa—Contemporary changes and new directions (pp. 187–194). Cham: Springer.
Rogerson, C. M., & Hoogendoorn, G. (2014). VFR travel and second home tourism: The missing link? The case of South Africa. Tourism Review International, 18 (3), 167–178.
Rolfes, M. (2010). Poverty tourism: Theoretical reflections and empirical findings regarding an extraordinary form of tourism. GeoJournal, 75 (5), 421–442.
Scheyvens, R. (2001). Poverty tourism. Development Bulletin, 55, 18–21.
Selinger, E., & Outterson, K. (2010). The ethics of poverty tourism. Environmental Philosophy, 7 (2), 93–114.
Silberg, T. (1995). Cultural tourism and business opportunity for museums and heritage sites. Tourism Management, 16 (5), 361–365.
Slikker, N., & Koens, K. (2015). “Breaking the silence”: Local perceptions of slum tourism in Dharavi. Tourism Review International, 19 (1–2), 75–86.
South Africa. (1999). National Heritage Resources Act 25 of 1999 . Pretoria: Government Printer.
Spivak, G. C. (1994). Can the subaltern speak? In P. Williams & L. Chrisman (Eds.), Colonial discourse and post-colonial theory (pp. 66–111). New York: Columbia University Press.
Steinbrink, M. (2012). ‘We did the slum!’—Urban poverty tourism in historical perspective. Tourism Geographies, 14 (2), 213–234.
Torres, I. (2012). Branding slums: A community-driven strategy for urban inclusion in Rio de Janeiro. Journal of Place Management and Development, 5 (3), 198–211.
Turok, I., & Visagie J. (2018). Inclusive urban development in South Africa: What does it mean and how can it be measured? IDS Working Paper, 512.
Turok, I., Budlender, J., & Visagie, J. (2017). Urban ‘slums’ and social mobility. Development Policy Review, 36 (6), 703–725. https://doi.org/10.1111/dpr.12325 .
Tzanelli, R. (2018). Slum tourism: A review of state-of-the-art scholarship. Tourism, Culture & Communication, 18 (2), 149–155.
Urry, J., & Larsen, J. (2011). The tourist gaze 3.0 . London: Sage.
United Nations Habitat. (2003). Housing and slum upgrading . http://unhabitat.org/urban-themes/housing-slum-upgrading/ . Accessed July 16, 2018.
Vecco, M. (2010). A definition of cultural heritage: From the tangible to the intangible. Journal of Cultural Heritage, 11 (3), 321–324.
Waterton, E., & Smith, L. (2010). The recognition and misrecognition of community heritage. International Journal of Heritage Studies, 16 (1–2), 4–15.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the helpful comments of the reviewers.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Geography, Environmental Management and Energy Studies, University of Johannesburg, Johannesburg, South Africa
Gijsbert Hoogendoorn, Nthabiseng Letsatsi & Thabisile Malleka
Economic Performance and Development, Human Sciences Research Council, Cape Town, South Africa
Irma Booyens
School of Tourism and Hospitality, University of Johannesburg, Johannesburg, South Africa
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Gijsbert Hoogendoorn .
Ethics declarations
Ethical statement.
All ethical requirements as expected by the University of Johannesburg were followed. No under aged individuals were interviewed, no people that may be considered vulnerable because of economic or social reasons were interviewed. All respondents are kept completely confidential and due diligence was followed.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Hoogendoorn, G., Letsatsi, N., Malleka, T. et al. Tourist and resident perspectives on ‘slum tourism’: the case of the Vilakazi precinct, Soweto. GeoJournal 85 , 1133–1149 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10708-019-10016-2
Download citation
Published : 06 May 2019
Issue Date : August 2020
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10708-019-10016-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Slum tourism
- Township tourism
- Vilakazi Street
- Representation
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Print this article
Explorations | Exploraciones
Theorizing slum tourism: performing, negotiating and transforming inequality.
- Rivke Jaffe
- Rivke Jaffe , Assistant Professor at the Centre for Urban Studies at the Universityof Amsterdam, the Netherlands Rivke Jaffe is an Assistant Professor at the Centre for Urban Studies at the Universityof Amsterdam, the Netherlands. She previously held teaching and research positions at Leiden University, the University of the West Indies, and the Royal Netherlands Institute of Southeast Asian and Caribbean Studies (KITLV). She has conducted fieldwork in Jamaica, Curaçao and Suriname on topics ranging from the urban environment to the political economy of multiculturalism. Her current research, in Jamaica, studies how criminal organizations and the state share control over urban spaces and populations, and the formulations of governance and citizenship that result from this. She is the author of several peer-reviewed articles in journals such as Anthropological Quarterly, Ethnic and Racial Studies, and Social and Cultural Geography. In addition, she is the editor of The Caribbean City (Ian Randle, 2008) and the co-editor of Urban Pollution (with Eveline Dürr, Berghahn, 2010).
This Exploration focuses on the emerging field of slum tourism research, which has the potential to connect Latin American and Caribbean studies on tourism and urban inequality. Slum tourism involves transforming poverty, squalor and violence into a tourism product. Drawing on both altruism and voyeurism, this form of tourism is a complex phenomenon that raises various questions concerning power, inequality and subjectivity. This essay seeks to advance the theoretical debate on slum tourism research and to stimulate comparative studies. Introducing brief examples of slum tourism in Mexico and Jamaica, this contribution moves towards an initial theorization of the performance, negotiation and transformation of inequality in a framework of tourism and global mobilities.
Resumen: Teorizar el Turismo en las zonas marginadas: Construcción, negociación y transformación de la desigualdad
Esta Exploración se centra en el campo emergente del turismo en zonas marginadas, que tiene como potencial conectar a América Latina y el Caribe en los estudios sobre el turismo y la desigualdad urbana. Turismo 'Slum' implica la transformación de la pobreza, la miseria y la violencia en un producto turístico. Basándose tanto en el altruismo como en el voyerismo, esta forma de turismo es un fenómeno complejo que plantea diversas cuestiones relativas al poder, la desigualdad y la subjetividad. Con este ensayo se pretende avanzar en el debate teórico sobre la investigación de turismo en zonas marginadas y estimular estudios comparativos. Presentando ejemplos breves de turismo en barrios pobres en la ciudad de México y de Jamaica, esta contribución se mueve hacia una teorización inicial de la construcción, la negociación y la transformación de la desigualdad en el marco del turismo y la movilidad global.
- Page/Article: 113-123
- DOI: 10.18352/erlacs.8367
- Peer Reviewed
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Potential of Slum Tourism in Urban Ghana: A Case Study of Old Fadama (S odom and Gomorra) Slum in Accra

Abstract : The paper assessed the state of tourism in the slum community of Old Fadama (Sodom and Gomorra) in Accra, Ghana. It goes without saying that Old Fadama vehemently referred to as Sodom and Gomorra is a full embodiment of the characteristics of informal settlements better known as slums. Semi structured questionnaires were administered randomly to 250 dwellers of Sodom and Gomorra. In - depth interviews were purposively held with officials of local Travel and Tour Firms and the regional Office of the National Tourism Authority. Data was analyzed descriptively and thematically. Observing residents’ life style and photograph taking were found as the main touris t activities. Tourism was promoted through security consciousness of residents. Low involvement of residents in tourism affairs/businesses were the major drawbacks to tourism development in the slum. Residents needs to be sensitized to take advantage of th eir living conditions to establish tourism businesses in the short - term to empower them move to more ‘formal’ settlements of Accra in the near future to decelerate the growth of the notorious slum in Ghana’s capital city

Related Papers
Gijsbert Hoogendoorn
Slum tourism as a topic of investigation has seen significant growth since the beginning of this decade with increasing theoretical and empirical depth. With this growth, some inconsistencies in conceptual framing and use of terminology have emerged. The purpose of this paper is to argue for township tourism in Soweto to be regarded as a form of heritage tourism rather than slum tourism – a notion which has entered the township tourism literature in recent years. This argument is presented through two sections of analysis and debate, using Vilakazi precinct in Soweto as a case study. Firstly, the paper analyses the emergence of township tourism as an academic focus in the literature and how it came to be classified as slum tourism, considering definitional conundrums. Various South African authors emphasise the struggle heritage character of township tourism. Secondly, the historical development of townships and tourism in these areas are interrogated. The empirical data offer the perspectives on tourism in their area from: a) residents living in and around Vilakazi street; and b) tourists visiting the Vilakazi precinct. The analysis reveals that neither residents nor visitors consider the Vilakazi precinct or the larger area of Orlando West as a slum; rather they perceive tourism is the area to be connected to its struggle heritage. We accordingly stress that the term ‘slum tourism’ to describe township tourism in Soweto is inaccurate and is inconsistent with the views not only of residents and visitors, but also South African authors.
Tourism Review International
Fabian Frenzel , Ko Koens , Malte Steinbrink
This article provides a view on the state-of-the-art literature on slum tourism. It points to the rapid growth of slum tourism research in recent years and highlights the main avenues that research has thus far explored in areas such as slum tourism history, slum tourist subjectivity, resident perspectives, slum tourism operations, economics, and mobilities. With the advent of slum tourism the relationship of poverty and tourism has changed. Tourism is no longer only a means to fight poverty, but poverty is an attraction of tourism. This has consequences for the relationship of slum tourism to other forms of tourism where poverty functions as an attraction, like volunteer or developmental tourism. The article identifies research gaps as well as avenues for further research.
Assoc. Prof. Ahmed A D E L Hammad
Slum tourism refers to that form of speciality tourism, which involves organising tours to impoverished areas in some cities. This research aims at activating slum tourism in Egypt for benefiting from its role in developing slums of Egypt 'applied on slums of Alexandria City'. The research depended on primary data through targeting 520 online questionnaire forms at a random sample of respondents. The questionnaire was designed for gathering answers on applying slum tourism to benefit from its role in transforming slums into developed urban areas. The research also depended on secondary data related to the subject of study. The findings revealed that slum tourism attracts high expenditure niche tourists which can affect positively on the Egyptian tourism sector. Furthermore, it can be a successful way towards developing slums in Egypt by donating a portion of its tours' profits in developing slums of Alexandria, and then other Egyptian cities can act accordingly. The rese...
Fabian Frenzel
Since 2012, there has been a significant growth in tourism in inner city Johannesburg. Some of this tourism materialises as walking tours in disadvantaged and relatively poor inner city neighbourhoods, some of which were until recently considered no-go areas. In a paper published in Urban Forum in 2014 (Frenzel 2014), I have analysed this new phenomenon in the context of slum tourism. I define slum tourism as such forms of tourism where poverty and associated signifiers become central themes and (part of the) attraction of the visited destination. Following a broad empirical research project, Hoogendoorn and Giddy (2017) have questioned whether the concept slum tourism should be used when discussing tourism in inner city Johannesburg. This paper forms a response to the paper of Hoogendoorn and Giddy (2017).
Hussein Medlej
Tourism Geographies
zahra mohammadi , Dr. Kamran Yeganegi ( PH.D.)
Today tourism is one of the most prevalent activities in cultural, economic, etc. sections. Tourism has many kinds. Slum tourism is of black tourisms that is popular in countries like India, Brazil, Kenya, etc. as a new kind of tourism that includes visiting slums and touching and feeling the conditions of poor people. This paper aims to determine the effects of tourism industry on the economy and culture, etc.
Lisandra Torres Hechavarría
The aim of this report is to discuss whether slum tourism is a good development or not. There have been some studies on this topic but it is still considered a young subject of research in tourism (Frenzel & Koens 2012). "Poverty tourism", "poorism", "slum tourism", "favela tours", "township tours" and "reality tours" are some of the names given to a product that focuses in taking tourists to get in different levels of contact with informal settlements or “slums” in urban areas (Tourism Concern 2013). It has also been described as a tourist experience that involves visiting urban areas characterized by poverty, squalor and violence (Dürr & Jaffe 2012) The focus of the concern related to this topic has been around whether the community of the slum really benefits from tourism or if it is just another way of exploiting this places for the benefit of tour operators. In order to accomplish the aim of this paper it has been carried out a literature review and several case studies in slum tours products have been used to illustrate and better support the arguments made.
Indonesian Journal of Tourism and Leisure
Ainnoun Kornita
Slum areas are often seen in urban spatial policy gaps. The slum area becomes a dilemma, it portrays the unsuccessful management of a city area, on the other hand the reality of the city has the potential to become slum area tourism as an alternative attraction for tourism in urban areas. Efforts made by stakeholders in terms of city management tend to ignore slum areas as a city reality that has never touched a solution to the problem. Slum areas with social problems require real solutions. Through tourism in slum areas, residents innovate to represent and interpret their territory to find solutions for themselves. So far, studies on slum area tourism regarding how local residents represent and interpret their territory are still rare. Therefore, this study tries to look at the initiative to practice representation and interpretation of local residents in their area, and how stakeholders represent slum areas in their area through a qualitative study using a city tourism approach....
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
Maximiliano E. Korstanje
FRANKLIN BORMANN
Alhassan Yahaya
Urbani izziv
Irma Booyens
Khevana Desai
Monica Inés Cejas
Nomfundo Mahomed
Perceptions of the Dharavi community regarding slum tourism and affiliated NGO operations
Nieck Slikker
Revista Brasileira de Pesquisa em Turismo
Apoena Mano
IJMRAP Editor
Taher Abdel-Ghani
julie zufferey
Foster Frempong
Christina Koutra
Global Dynamics in Travel, Tourism, and Hospitality
DONATELLA PRIVITERA
Journal of economics and sustainable development
tintswalo mthombeni
Ko Koens , Ko Koens , Nieck Slikker
Fabian Frenzel , Malte Steinbrink
Asian Social Science
Christopher Mensah
Reality Tours and Travel: A Community Perception on Slum Tourism in Dharavi
Rudra Rhodes
European Review of Latin American and Caribbean Studies
Eveline Dürr
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

Inside the Controversial World of Slum Tourism
People have toured the world’s most marginalized, impoverished districts for over a century.
Hundreds of shanty towns line the riverbanks, train tracks, and garbage dumps in the Filipino capital—the most jammed-packed areas in one of the world’s most densely populated cities. Around a quarter of its 12 million people are considered “informal settlers.”
Manila is starkly representative of a global problem. According to the United Nations , about a quarter of the world’s urban population lives in slums—and this figure is rising fast.
Rich cultural heritage brings visitors to Manila, but some feel compelled to leave the safety of the historic center sites to get a glimpse of the city’s inequality. Tour operators in the Philippines —as well as places like Brazil and India —have responded by offering “slum tours” that take outsiders through their most impoverished, marginalized districts.
Slum tourism sparks considerable debate around an uncomfortable moral dilemma. No matter what you call it—slum tours, reality tours, adventure tourism, poverty tourism—many consider the practice little more than slack-jawed privileged people gawking at those less fortunate. Others argue they raise awareness and provide numerous examples of giving back to the local communities. Should tourists simply keep their eyes shut?

Around a quarter of Manila's 12 million people are considered “informal settlers."

Rich cultural heritage brings visitors to Manila, but some feel compelled to leave the safety of the historic center sites to get a glimpse of the city’s inequality.
Slumming For Centuries
Slum tourism is not a new phenomenon, although much has changed since its beginning. “Slumming” was added to the Oxford English Dictionary in the 1860s, meaning “to go into, or frequent, slums for discreditable purposes; to saunter about, with a suspicion, perhaps, of immoral pursuits.” In September 1884, the New York Times published an article about the latest trend in leisure activities that arrived from across the pond, “‘Slumming’ will become a form of fashionable dissipation this winter among our Belles, as our foreign cousins will always be ready to lead the way.”
Usually under the pretense of charity and sometimes with a police escort, rich Londoners began braving the city’s ill-reputed East End beginning around 1840. This new form of amusement arrived to New York City from wealthy British tourists eager to compare slums abroad to those back home. Spreading across the coast to San Francisco, the practice creeped into city guide books. Groups wandered through neighborhoods like the Bowery or Five Points in New York to peer into brothels, saloons, and opium dens.
Visitors could hardly believe their eyes, and justifiably so. “I don’t think an opium den would have welcomed, or allowed access to, slummers to come through if they weren’t there to smoke themselves,” Chad Heap writes in his book Slumming: Sexual and Racial Encounters in American Nightlife , 1885–1940 . Recognizing the business opportunity, outsiders cashed in on the curiosity by hiring actors to play the part of addicts or gang members to stage shoot-’em-ups in the streets. After all, no one wanted the slum tourists to demand a refund or go home disappointed.

Smokey Tours does not allow participants to take photos, but this policy proves difficult to enforce.

The city of San Francisco eventually banned such mockery of the poor, the New York Times reported in 1909: “This is a heavy blow to Chinatown guides, who have collected a fee of two dollars each. The opium smokers, gamblers, blind paupers, singing children, and other curiosities were all hired.”
Tours also brought positive results, as Professor of History Seth Koven highlights in his research of slumming in Victorian London. Oxford and Cambridge Universities opened study centers in the late 19th-century to inform social policy, which was only possible by seeing the underprivileged neighborhoods firsthand.
Popularity waned after World War II with the creation of welfare and social housing—then rose again in the 1980s and 1990s as those state provisions declined and labor demands increased.
Presenting Poverty
Plastic arrives from all over India to the dark alleys and corrugated shacks of Dharavi in Mumbai —the second-largest slum on the continent of Asia (after Orangi Town in Pakistan ) and third-largest slum in the world. Ushered around by the company Reality Tour and Travel , tourists see a thriving recycling industry which employs around ten thousand to melt, reshape, and mould discarded plastic. They stop to watch the dhobiwallahs , or washermen, scrub sheets from the city’s hospitals and hotels in an open-air laundry area.
In a TripAdvisor review, one recent participant from Virginia appreciated the focus on community. “It was great to hear about the economy, education and livelihood of the residents,” she writes. “The tour group doesn't allow photography or shopping which I think is really important. It didn't feel exploitative, it felt educational.”
One traveler from London commented on the extremity of the scene. "Had to stop after about 20 minutes into it due to the overbearing nature of the surroundings. The tour is not for the faint hearted. I would've liked a few more disclaimers on the website to warn us about the nature of it." Another guest from the United Kingdom expressed disappointment over the so-called family meal. “This was in the home of one of the guides and, whilst his mum made lunch a delicious meal that we ate in her house, she didn’t eat with us so it wasn’t really what I had expected from a family lunch (or the photos promoting such on the website).”

Smokey Tours enters the Manila North Cemetery, inhabited by some of Manila's poorest people.

Children jump from grave to grave in the city’s largest cemetery.
Reality Tours hopes to challenge the stereotypical perception of slums as despairing places inhabited by hopeless people. The tour presented slum residents as productive and hardworking, but also content and happy. Analyzing more than 230 reviews of Reality Tour and Travel in her study , Dr. Melissa Nisbett of King’s College London realized that for many Dharavi visitors, poverty was practically invisible. “As the reviews show, poverty was ignored, denied, overlooked and romanticized, but moreover, it was depoliticized.” Without discussing the reason the slum existed, the tour decontextualized the plight of the poor and seemed only to empower the wrong people–the privileged, western, middle class visitors.
With good intentions, the company states that 80 percent of the profits benefit the community through the efforts of its NGO that works to provide access to healthcare, organize educational programs, and more. Co-founder Chris Way spoke to National Geographic after his company surged in popularity from the sleeper hit Slumdog Millionaire . “We do try and be as transparent as possible on our website, which does allay many people’s fears.” Way personally refuses a salary for his work.
No Two Cities Alike
The main question should be: Is poverty the central reason to visit?
Other cities take different approaches to slum tourism. In the early 1990s, when black South Africans began offering tours of their townships—the marginalized, racially-segregated areas where they were forced to live—to help raise global awareness of rampant human rights violations. Rather than exploitation inflicted by outsiders, local communities embraced slum tourism as a vehicle to take matters of their traditionally neglected neighborhoods into their own hands.
- Nat Geo Expeditions
Some free tours of favelas in Rio de Janeiro provided an accessible option to the crowds that infiltrated the city during the World Cup and Summer Olympics, while most companies continue to charge. Tour manager Eduardo Marques of Brazilian Expeditions explains how their authenticity stands out, “We work with some local guides or freelancers, and during the tour we stop in local small business plus [offer] capoeira presentations that [support] the locals in the favela. We do not hide any info from our visitors. The real life is presented to the visitors.”
Smokey Tours in Manila connected tourists with the reality facing inhabitants of a city landfill in Tondo (until 2014 when it closed) to tell their stories. Now the company tours around Baseco near the port, located in the same crowded district and known for its grassroots activism. Locally-based photographer Hannah Reyes Morales documented her experience walking with the group on assignment for National Geographic Travel. “I had permission to photograph this tour from both the operator and community officials, but the tour itself had a no photography policy for the tourists.” With the policy difficult to enforce, some guests secretly snapped photos on their phones. “I observed how differently tourists processed what they were seeing in the tour. There were those who were respectful of their surroundings, and those who were less so.”
All About Intention
Despite sincere attempts by tour operators to mitigate offense and give back to locals, the impact of slum tourism stays isolated. Ghettoized communities remain woven into the fabric of major cities around the world, each with their individual political, historical, and economic concerns that cannot be generalized. Similarly, the motivations behind the tourism inside them are as diverse as the tour participants themselves. For all participants involved, operators or guests, individual intentions matter most.

The Baseco neighborhood is located on the Pasig river near the city port, but lacks access to clean drinking water.
Better connections between cities allow more people to travel than ever before, with numbers of international tourists growing quickly every year. While prosperity and quality of life have increased in many cities, so has inequality. As travelers increasingly seek unique experiences that promise authentic experiences in previously off-limits places, access through tours helps put some areas on the map.
Travel connects people that would otherwise not meet, then provides potential to share meaningful stories with others back home. Dr. Fabian Frenzel, who studies tourism of urban poverty at the University of Leicester, points out that one of the key disadvantages of poverty is a lack of recognition and voice. “If you want to tell a story, you need an audience, and tourism provides that audience.” Frenzel argues that even taking the most commodifying tour is better than ignoring that inequality completely.
For the long-term future of these communities, the complex economic, legal, and political issues must be addressed holistically by reorganizing the distribution of resources. While illuminating the issue on a small scale, slum tourism is not a sufficient answer to a growing global problem.
Related Topics
- TRAVEL PHOTOGRAPHY
- PHOTOGRAPHY
You May Also Like

How I got the shot: Richard James Taylor on capturing Mekong sunset magic in Laos

Photo story: wild beauty in eastern Sardinia, from coast to mountains

How I got the shot: Dikpal Thapa on risking it all for one image

How to visit Grand Teton National Park

These are the best travel photos of 2022

How I got the shot: Richard James Taylor on capturing Dubrovnik's golden hour

The Masterclasses 2023: 10 practical tips to help you succeed as a travel photographer
- Environment
History & Culture
- History & Culture
- History Magazine
- Race in America
- Mind, Body, Wonder
- Destination Guide
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your US State Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
- Nat Geo Home
- Attend a Live Event
- Book a Trip
- Inspire Your Kids
- Shop Nat Geo
- Visit the D.C. Museum
- Learn About Our Impact
- Support Our Mission
- Advertise With Us
- Customer Service
- Renew Subscription
- Manage Your Subscription
- Work at Nat Geo
- Sign Up for Our Newsletters
- Contribute to Protect the Planet
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved
Slumtourism.net
Home of the slum tourism research network, tag archives: thesis, cultural tourism in the gambia.
Janet Thorne recently wrote a professional report on her experiences of cultural tourism in the Gambia. Her findings suggest that these tours bear similarities to slum tours and, similarly to slum tours are promoted with the promise of an insight into “the real Gambia” by certain tour operators and informal tour guides.
Thorne further shows how tourists on package holidays in this mass tourism destination certainly have an interest in such tours. What particularly surprised her on this matter was how similar the interests expressed by tourists in The Gambia were to those in the slum/poverty tourism literature. Among other things, tourists are hoping and expecting to see “everyday life” and have a more “authentic” tourist experience than is offered in general. Tourists are both intrigued as well as shocked by the poverty they see thus partially fulfilling this desire for authenticity.
While written as a more practical report rather than a purely academic work of tourism, the report contains much useful information on these cultural tours. The finding that there is demand from for these kinds of tours among package tourists in the Gambia alone is interesting. The destination is mainly known for its Sun, Sea and Sand package tours where tourists come specifically to relax. Thorne goes further however and also discusses different forms of interaction between locals and tourists as well as difficulties of market access and local participation.
All in all this professional report brings up the important question of when cultural tourist activites can be categorised as poverty or slum tourism? This may be easy in the case of favela or township tourism as the practices are limited to certain geographical areas. However as Thorne shows, similar practices take place elsewhere as well under a label of cultural tourism.
The report can be downloaded here and those wishing to contact Janet can do so at [email protected].
Thorne, J. (2011) Selling culture to package tourists: An exploration of demand for intangible heritage excursions in the Gambia. MSc. Leeds, Leeds Metropolitan University

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Finally, in the last part, the current state of slum tourism will be examined through the cases of Cape Town and Rio de Janeiro and the findings will be used along with the theoretical framework to assess the sustainability of slum tourism. Methodology. In order to investigate the phenomenon of slum tourism in depth and gain a better
Full version available upon request. Introduction. Slum tourism is an unsettling term. Touring impoverished areas has become a global phenomenon and has sparked intense controversy in recent years.
refer to this type of tourism as 'slum tourism'. Similarly, Ramchander (2004), in his PhD thesis which is one of the first and most authoritative studies on township tourism in South Africa, did not use the term 'slum' either. Briedenhann and Ramchander (2006) made the point that township tourists visit
Each thesis in the repository has been cleared where necessary by the author for third party ... Slum Tourism: developments in a young field of interdisciplinary tourism research Abstract This paper introduces the special issue on slum-tourism with a reflection on the state of the art on this new area of tourism research. After a review of the ...
increased in the past 20 years, so has the number. of tourists taking part in slum tourism. Recent esti-. mates by the authors point to an annual number of. over 1 million slum tourists. Most of ...
The impact slum tourism has on local communities, however, remains relatively undocumented. Driven by the declaration of 2017 as the ''International Year for Sustainable Tourism Development'' by the United Nations, this paper explores the potential of slum tourism as a tool for poverty alleviation, focusing on the cases of Cape Town and ...
Slum tourism as a topic of investigation has seen significant growth since the beginning of this decade with increasing theoretical and empirical depth. With this growth, some inconsistencies in conceptual framing and use of terminology have emerged. The purpose of this paper is to argue for township tourism in Soweto to be regarded as a form of heritage tourism rather than slum tourism—a ...
Slum tourism involves transforming poverty, squalor and violence into a tourism product. Drawing on both altruism and voyeurism, this form of tourism is a complex phenomenon that raises various questions concerning power, inequality and subjectivity. This essay seeks to advance the theoretical debate on slum tourism research and to stimulate ...
The widening scope and diversity of slum tourism is clearly reflected in the variety of papers presented at the conference and in this Special Issue. Whilst academic discussion on the theme is evolving rapidly, slum tourism is still a relatively young area of research. Most papers at the conference and, indeed, most slum tourism research as a ...
This study queries the notion of slum as an anathema to the growth and prosperity of cities in sub-Saharan Africa. Slum tourism is discussed as an emerging intervention to address the challenge of slums in the global south. Using ethnographic account and personal reflection of 5 slum settlements and key institutions in Lusaka, a novel
This dissertation is divided into two main parts, the theoretical frame and the study case, which altogether help accomplishing the objectives. The first one clarifies and explains the concepts on which this dissertation is based on, which are Slum tourism and ethics. The theoretical frame is based on scientific
Slum tourism, a controversial phenomenon in the tourism sector, has been the research subject of this thesis. ... but there is still a gap when it comes to the representations of the slum in (online) media. Therefore, this thesis will analyse how slum tours in Asia's biggest slum Dharavi are represented on two different tourist websites that ...
THESIS. The slums of rapidly growing cities in developing nations, specifically Villa 31 in Buenos Aires, Argentina, can provide positive lessons in urban sustainability and cultural vitality. Certain urban and architectural characteristics that incidentally occur in these settlements can form a basis for sustainable development.
This article provides a view on the state-of-the-art literature on slum tourism. It points to the rapid growth of slum tourism research in recent years and highlights the main avenues that research has thus far explored in areas such as slum tourism history, slum tourist subjectivity, resident perspectives, slum tourism operations, economics, and mobilities.
An aspect of slum tourism that has received much less attention is the perception local host communities to tourism. However, it would seem that we are missing a vital part of the puzzle with regards to slum tourism if we do not look at local resident's perspectives. ... If you have an interesting document, thesis or report regarding slum ...
Slum tourism's popularity began to wane somewhat around World War II, ... Slikker himself found the concept of slum tourism odd, and when he discussed his thesis topic with classmates, they ...
Slumming For Centuries. Slum tourism is not a new phenomenon, although much has changed since its beginning. "Slumming" was added to the Oxford English Dictionary in the 1860s, meaning "to ...
24/03/2011 Academic publication cultural tourism, perception, poverty tourism, The Gambia, thesis, tourists Ko Koens. Janet Thorne recently wrote a professional report on her experiences of cultural tourism in the Gambia. Her findings suggest that these tours bear similarities to slum tours and, similarly to slum tours are promoted with the ...
slum tourism discourses and investigations in South Africa and elsewhere in the Global South. Indeed, Muldoon ( 2018 : 13) observes that while ÔÔresearchers ... in his PhD thesis which is one of the Þrst and most authoritative studies on township tourism in South Africa, did not use the term ÔslumÕ either. Briedenhann and Ramchander (2006 ...
16. Churches & Cathedrals. Bratsk Museum of The History of The Development of The Angara River. 7. Speciality Museums. Orthodox Church of the Assumption of the Mother of God. 3. Churches & Cathedrals.
Bratsk Hydroelectric Power Station. 2. Church of the Nativity. 3. Orthodox Church of the Assumption of the Mother of God. 4. Glory Memorial. 5. Grace Church in Christ.
Top Things to Do in Bratsk, Russia. 1. Park of Culture and Leisure of Bratsk Municipality. 2. Bratsk Hydroelectric Power Station. 3. Architectural and Ethnographic Museum Angarskaya Derevnya im. O.Leonova. The place is a showcase to an Old Russian village of the Angara style.
Bratsk Reservoir is a popular tourist attraction, and due to this, Bratsk has a small, but notable, tourism industry. Modern Bratsk is classed as a 'high-density industrial region', producing around 20% of the industrial output of the Irkutsk oblast. In recent times, ...