
Peer Recognized
Make a name in academia

How to Write a Research Paper: the LEAP approach (+cheat sheet)
In this article I will show you how to write a research paper using the four LEAP writing steps. The LEAP academic writing approach is a step-by-step method for turning research results into a published paper .
The LEAP writing approach has been the cornerstone of the 70 + research papers that I have authored and the 3700+ citations these paper have accumulated within 9 years since the completion of my PhD. I hope the LEAP approach will help you just as much as it has helped me to make an real, tangible impact with my research.
What is the LEAP research paper writing approach?
I designed the LEAP writing approach not only for merely writing the papers. My goal with the writing system was to show young scientists how to first think about research results and then how to efficiently write each section of the research paper.
In other words, you will see how to write a research paper by first analyzing the results and then building a logical, persuasive arguments. In this way, instead of being afraid of writing research paper, you will be able to rely on the paper writing process to help you with what is the most demanding task in getting published – thinking.
The four research paper writing steps according to the LEAP approach:

I will show each of these steps in detail. And you will be able to download the LEAP cheat sheet for using with every paper you write.
But before I tell you how to efficiently write a research paper, I want to show you what is the problem with the way scientists typically write a research paper and why the LEAP approach is more efficient.
How scientists typically write a research paper (and why it isn’t efficient)
Writing a research paper can be tough, especially for a young scientist. Your reasoning needs to be persuasive and thorough enough to convince readers of your arguments. The description has to be derived from research evidence, from prior art, and from your own judgment. This is a tough feat to accomplish.
The figure below shows the sequence of the different parts of a typical research paper. Depending on the scientific journal, some sections might be merged or nonexistent, but the general outline of a research paper will remain very similar.

Here is the problem: Most people make the mistake of writing in this same sequence.
While the structure of scientific articles is designed to help the reader follow the research, it does little to help the scientist write the paper. This is because the layout of research articles starts with the broad (introduction) and narrows down to the specifics (results). See in the figure below how the research paper is structured in terms of the breath of information that each section entails.
How to write a research paper according to the LEAP approach
For a scientist, it is much easier to start writing a research paper with laying out the facts in the narrow sections (i.e. results), step back to describe them (i.e. write the discussion), and step back again to explain the broader picture in the introduction.
For example, it might feel intimidating to start writing a research paper by explaining your research’s global significance in the introduction, while it is easy to plot the figures in the results. When plotting the results, there is not much room for wiggle: the results are what they are.
Starting to write a research papers from the results is also more fun because you finally get to see and understand the complete picture of the research that you have worked on.
Most importantly, following the LEAP approach will help you first make sense of the results yourself and then clearly communicate them to the readers. That is because the sequence of writing allows you to slowly understand the meaning of the results and then develop arguments for presenting to your readers.
I have personally been able to write and submit a research article in three short days using this method.
Step 1: Lay Out the Facts

You have worked long hours on a research project that has produced results and are no doubt curious to determine what they exactly mean. There is no better way to do this than by preparing figures, graphics and tables. This is what the first LEAP step is focused on – diving into the results.
How to p repare charts and tables for a research paper
Your first task is to try out different ways of visually demonstrating the research results. In many fields, the central items of a journal paper will be charts that are based on the data generated during research. In other fields, these might be conceptual diagrams, microscopy images, schematics and a number of other types of scientific graphics which should visually communicate the research study and its results to the readers. If you have reasonably small number of data points, data tables might be useful as well.
Tips for preparing charts and tables
- Try multiple chart types but in the finished paper only use the one that best conveys the message you want to present to the readers
- Follow the eight chart design progressions for selecting and refining a data chart for your paper: https://peerrecognized.com/chart-progressions
- Prepare scientific graphics and visualizations for your paper using the scientific graphic design cheat sheet: https://peerrecognized.com/tools-for-creating-scientific-illustrations/
How to describe the results of your research
Now that you have your data charts, graphics and tables laid out in front of you – describe what you see in them. Seek to answer the question: What have I found? Your statements should progress in a logical sequence and be backed by the visual information. Since, at this point, you are simply explaining what everyone should be able to see for themselves, you can use a declarative tone: The figure X demonstrates that…
Tips for describing the research results :
- Answer the question: “ What have I found? “
- Use declarative tone since you are simply describing observations
Step 2: Explain the results

The core aspect of your research paper is not actually the results; it is the explanation of their meaning. In the second LEAP step, you will do some heavy lifting by guiding the readers through the results using logic backed by previous scientific research.
How to define the Message of a research paper
To define the central message of your research paper, imagine how you would explain your research to a colleague in 20 seconds . If you succeed in effectively communicating your paper’s message, a reader should be able to recount your findings in a similarly concise way even a year after reading it. This clarity will increase the chances that someone uses the knowledge you generated, which in turn raises the likelihood of citations to your research paper.
Tips for defining the paper’s central message :
- Write the paper’s core message in a single sentence or two bullet points
- Write the core message in the header of the research paper manuscript
How to write the Discussion section of a research paper
In the discussion section you have to demonstrate why your research paper is worthy of publishing. In other words, you must now answer the all-important So what? question . How well you do so will ultimately define the success of your research paper.
Here are three steps to get started with writing the discussion section:
- Write bullet points of the things that convey the central message of the research article (these may evolve into subheadings later on).
- Make a list with the arguments or observations that support each idea.
- Finally, expand on each point to make full sentences and paragraphs.
Tips for writing the discussion section:
- What is the meaning of the results?
- Was the hypothesis confirmed?
- Write bullet points that support the core message
- List logical arguments for each bullet point, group them into sections
- Instead of repeating research timeline, use a presentation sequence that best supports your logic
- Convert arguments to full paragraphs; be confident but do not overhype
- Refer to both supportive and contradicting research papers for maximum credibility
How to write the Conclusions of a research paper
Since some readers might just skim through your research paper and turn directly to the conclusions, it is a good idea to make conclusion a standalone piece. In the first few sentences of the conclusions, briefly summarize the methodology and try to avoid using abbreviations (if you do, explain what they mean).
After this introduction, summarize the findings from the discussion section. Either paragraph style or bullet-point style conclusions can be used. I prefer the bullet-point style because it clearly separates the different conclusions and provides an easy-to-digest overview for the casual browser. It also forces me to be more succinct.
Tips for writing the conclusion section :
- Summarize the key findings, starting with the most important one
- Make conclusions standalone (short summary, avoid abbreviations)
- Add an optional take-home message and suggest future research in the last paragraph
How to refine the Objective of a research paper
The objective is a short, clear statement defining the paper’s research goals. It can be included either in the final paragraph of the introduction, or as a separate subsection after the introduction. Avoid writing long paragraphs with in-depth reasoning, references, and explanation of methodology since these belong in other sections. The paper’s objective can often be written in a single crisp sentence.
Tips for writing the objective section :
- The objective should ask the question that is answered by the central message of the research paper
- The research objective should be clear long before writing a paper. At this point, you are simply refining it to make sure it is addressed in the body of the paper.
How to write the Methodology section of your research paper
When writing the methodology section, aim for a depth of explanation that will allow readers to reproduce the study . This means that if you are using a novel method, you will have to describe it thoroughly. If, on the other hand, you applied a standardized method, or used an approach from another paper, it will be enough to briefly describe it with reference to the detailed original source.
Remember to also detail the research population, mention how you ensured representative sampling, and elaborate on what statistical methods you used to analyze the results.
Tips for writing the methodology section :
- Include enough detail to allow reproducing the research
- Provide references if the methods are known
- Create a methodology flow chart to add clarity
- Describe the research population, sampling methodology, statistical methods for result analysis
- Describe what methodology, test methods, materials, and sample groups were used in the research.
Step 3: Advertize the research
Step 3 of the LEAP writing approach is designed to entice the casual browser into reading your research paper. This advertising can be done with an informative title, an intriguing abstract, as well as a thorough explanation of the underlying need for doing the research within the introduction.

How to write the Introduction of a research paper
The introduction section should leave no doubt in the mind of the reader that what you are doing is important and that this work could push scientific knowledge forward. To do this convincingly, you will need to have a good knowledge of what is state-of-the-art in your field. You also need be able to see the bigger picture in order to demonstrate the potential impacts of your research work.
Think of the introduction as a funnel, going from wide to narrow, as shown in the figure below:
- Start with a brief context to explain what do we already know,
- Follow with the motivation for the research study and explain why should we care about it,
- Explain the research gap you are going to bridge within this research paper,
- Describe the approach you will take to solve the problem.
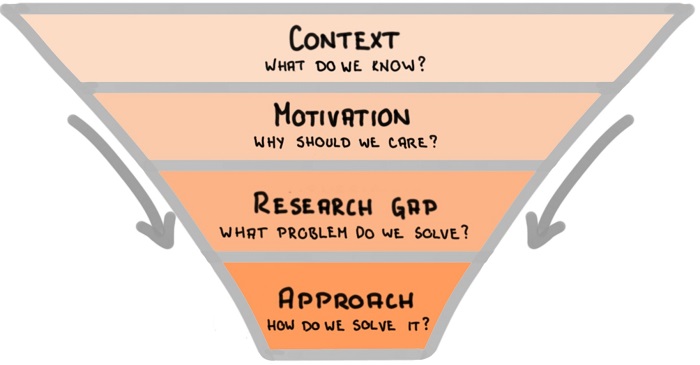
Tips for writing the introduction section :
- Follow the Context – Motivation – Research gap – Approach funnel for writing the introduction
- Explain how others tried and how you plan to solve the research problem
- Do a thorough literature review before writing the introduction
- Start writing the introduction by using your own words, then add references from the literature
How to prepare the Abstract of a research paper
The abstract acts as your paper’s elevator pitch and is therefore best written only after the main text is finished. In this one short paragraph you must convince someone to take on the time-consuming task of reading your whole research article. So, make the paper easy to read, intriguing, and self-explanatory; avoid jargon and abbreviations.
How to structure the abstract of a research paper:
- The abstract is a single paragraph that follows this structure:
- Problem: why did we research this
- Methodology: typically starts with the words “Here we…” that signal the start of own contribution.
- Results: what we found from the research.
- Conclusions: show why are the findings important
How to compose a research paper Title
The title is the ultimate summary of a research paper. It must therefore entice someone looking for information to click on a link to it and continue reading the article. A title is also used for indexing purposes in scientific databases, so a representative and optimized title will play large role in determining if your research paper appears in search results at all.
Tips for coming up with a research paper title:
- Capture curiosity of potential readers using a clear and descriptive title
- Include broad terms that are often searched
- Add details that uniquely identify the researched subject of your research paper
- Avoid jargon and abbreviations
- Use keywords as title extension (instead of duplicating the words) to increase the chance of appearing in search results
How to prepare Highlights and Graphical Abstract
Highlights are three to five short bullet-point style statements that convey the core findings of the research paper. Notice that the focus is on the findings, not on the process of getting there.
A graphical abstract placed next to the textual abstract visually summarizes the entire research paper in a single, easy-to-follow figure. I show how to create a graphical abstract in my book Research Data Visualization and Scientific Graphics.
Tips for preparing highlights and graphical abstract:
- In highlights show core findings of the research paper (instead of what you did in the study).
- In graphical abstract show take-home message or methodology of the research paper. Learn more about creating a graphical abstract in this article.
Step 4: Prepare for submission

Sometimes it seems that nuclear fusion will stop on the star closest to us (read: the sun will stop to shine) before a submitted manuscript is published in a scientific journal. The publication process routinely takes a long time, and after submitting the manuscript you have very little control over what happens. To increase the chances of a quick publication, you must do your homework before submitting the manuscript. In the fourth LEAP step, you make sure that your research paper is published in the most appropriate journal as quickly and painlessly as possible.
How to select a scientific Journal for your research paper
The best way to find a journal for your research paper is it to review which journals you used while preparing your manuscript. This source listing should provide some assurance that your own research paper, once published, will be among similar articles and, thus, among your field’s trusted sources.
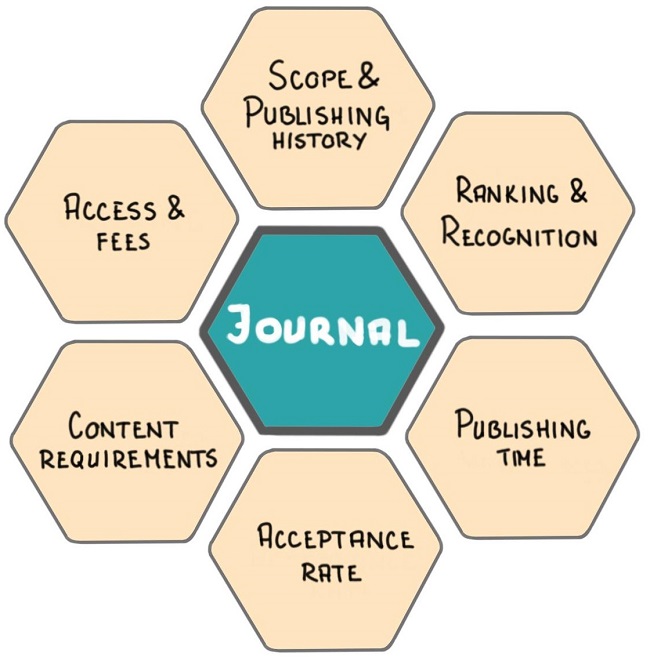
After this initial selection of hand-full of scientific journals, consider the following six parameters for selecting the most appropriate journal for your research paper (read this article to review each step in detail):
- Scope and publishing history
- Ranking and Recognition
- Publishing time
- Acceptance rate
- Content requirements
- Access and Fees
How to select a journal for your research paper:
- Use the six parameters to select the most appropriate scientific journal for your research paper
- Use the following tools for journal selection: https://peerrecognized.com/journals
- Follow the journal’s “Authors guide” formatting requirements
How to Edit you manuscript
No one can write a finished research paper on their first attempt. Before submitting, make sure to take a break from your work for a couple of days, or even weeks. Try not to think about the manuscript during this time. Once it has faded from your memory, it is time to return and edit. The pause will allow you to read the manuscript from a fresh perspective and make edits as necessary.
I have summarized the most useful research paper editing tools in this article.
Tips for editing a research paper:
- Take time away from the research paper to forget about it; then returning to edit,
- Start by editing the content: structure, headings, paragraphs, logic, figures
- Continue by editing the grammar and language; perform a thorough language check using academic writing tools
- Read the entire paper out loud and correct what sounds weird
How to write a compelling Cover Letter for your paper
Begin the cover letter by stating the paper’s title and the type of paper you are submitting (review paper, research paper, short communication). Next, concisely explain why your study was performed, what was done, and what the key findings are. State why the results are important and what impact they might have in the field. Make sure you mention how your approach and findings relate to the scope of the journal in order to show why the article would be of interest to the journal’s readers.
I wrote a separate article that explains what to include in a cover letter here. You can also download a cover letter template from the article.
Tips for writing a cover letter:
- Explain how the findings of your research relate to journal’s scope
- Tell what impact the research results will have
- Show why the research paper will interest the journal’s audience
- Add any legal statements as required in journal’s guide for authors
How to Answer the Reviewers
Reviewers will often ask for new experiments, extended discussion, additional details on the experimental setup, and so forth. In principle, your primary winning tactic will be to agree with the reviewers and follow their suggestions whenever possible. After all, you must earn their blessing in order to get your paper published.
Be sure to answer each review query and stick to the point. In the response to the reviewers document write exactly where in the paper you have made any changes. In the paper itself, highlight the changes using a different color. This way the reviewers are less likely to re-read the entire article and suggest new edits.
In cases when you don’t agree with the reviewers, it makes sense to answer more thoroughly. Reviewers are scientifically minded people and so, with enough logical and supported argument, they will eventually be willing to see things your way.
Tips for answering the reviewers:
- Agree with most review comments, but if you don’t, thoroughly explain why
- Highlight changes in the manuscript
- Do not take the comments personally and cool down before answering
The LEAP research paper writing cheat sheet
Imagine that you are back in grad school and preparing to take an exam on the topic: “How to write a research paper”. As an exemplary student, you would, most naturally, create a cheat sheet summarizing the subject… Well, I did it for you.
This one-page summary of the LEAP research paper writing technique will remind you of the key research paper writing steps. Print it out and stick it to a wall in your office so that you can review it whenever you are writing a new research paper.

Now that we have gone through the four LEAP research paper writing steps, I hope you have a good idea of how to write a research paper. It can be an enjoyable process and once you get the hang of it, the four LEAP writing steps should even help you think about and interpret the research results. This process should enable you to write a well-structured, concise, and compelling research paper.
Have fund with writing your next research paper. I hope it will turn out great!
Learn writing papers that get cited
The LEAP writing approach is a blueprint for writing research papers. But to be efficient and write papers that get cited, you need more than that.
My name is Martins Zaumanis and in my interactive course Research Paper Writing Masterclass I will show you how to visualize your research results, frame a message that convinces your readers, and write each section of the paper. Step-by-step.
And of course – you will learn to respond the infamous Reviewer No.2.

Hey! My name is Martins Zaumanis and I am a materials scientist in Switzerland ( Google Scholar ). As the first person in my family with a PhD, I have first-hand experience of the challenges starting scientists face in academia. With this blog, I want to help young researchers succeed in academia. I call the blog “Peer Recognized”, because peer recognition is what lifts academic careers and pushes science forward.
Besides this blog, I have written the Peer Recognized book series and created the Peer Recognized Academy offering interactive online courses.
Related articles:
One comment
- Pingback: Research Paper Outline with Key Sentence Skeleton (+Paper Template)
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
I want to join the Peer Recognized newsletter!
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Privacy Overview
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
Copyright © 2024 Martins Zaumanis
Contacts: [email protected]
Privacy Policy
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Research Paper

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Research Paper
There will come a time in most students' careers when they are assigned a research paper. Such an assignment often creates a great deal of unneeded anxiety in the student, which may result in procrastination and a feeling of confusion and inadequacy. This anxiety frequently stems from the fact that many students are unfamiliar and inexperienced with this genre of writing. Never fear—inexperience and unfamiliarity are situations you can change through practice! Writing a research paper is an essential aspect of academics and should not be avoided on account of one's anxiety. In fact, the process of writing a research paper can be one of the more rewarding experiences one may encounter in academics. What is more, many students will continue to do research throughout their careers, which is one of the reasons this topic is so important.
Becoming an experienced researcher and writer in any field or discipline takes a great deal of practice. There are few individuals for whom this process comes naturally. Remember, even the most seasoned academic veterans have had to learn how to write a research paper at some point in their career. Therefore, with diligence, organization, practice, a willingness to learn (and to make mistakes!), and, perhaps most important of all, patience, students will find that they can achieve great things through their research and writing.
The pages in this section cover the following topic areas related to the process of writing a research paper:
- Genre - This section will provide an overview for understanding the difference between an analytical and argumentative research paper.
- Choosing a Topic - This section will guide the student through the process of choosing topics, whether the topic be one that is assigned or one that the student chooses themselves.
- Identifying an Audience - This section will help the student understand the often times confusing topic of audience by offering some basic guidelines for the process.
- Where Do I Begin - This section concludes the handout by offering several links to resources at Purdue, and also provides an overview of the final stages of writing a research paper.
How To Write A Research Paper
Step-By-Step Tutorial With Examples + FREE Template
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewer: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | March 2024
For many students, crafting a strong research paper from scratch can feel like a daunting task – and rightly so! In this post, we’ll unpack what a research paper is, what it needs to do , and how to write one – in three easy steps. 🙂
Overview: Writing A Research Paper
What (exactly) is a research paper.
- How to write a research paper
- Stage 1 : Topic & literature search
- Stage 2 : Structure & outline
- Stage 3 : Iterative writing
- Key takeaways
Let’s start by asking the most important question, “ What is a research paper? ”.
Simply put, a research paper is a scholarly written work where the writer (that’s you!) answers a specific question (this is called a research question ) through evidence-based arguments . Evidence-based is the keyword here. In other words, a research paper is different from an essay or other writing assignments that draw from the writer’s personal opinions or experiences. With a research paper, it’s all about building your arguments based on evidence (we’ll talk more about that evidence a little later).
Now, it’s worth noting that there are many different types of research papers , including analytical papers (the type I just described), argumentative papers, and interpretative papers. Here, we’ll focus on analytical papers , as these are some of the most common – but if you’re keen to learn about other types of research papers, be sure to check out the rest of the blog .
With that basic foundation laid, let’s get down to business and look at how to write a research paper .

Overview: The 3-Stage Process
While there are, of course, many potential approaches you can take to write a research paper, there are typically three stages to the writing process. So, in this tutorial, we’ll present a straightforward three-step process that we use when working with students at Grad Coach.
These three steps are:
- Finding a research topic and reviewing the existing literature
- Developing a provisional structure and outline for your paper, and
- Writing up your initial draft and then refining it iteratively
Let’s dig into each of these.
Need a helping hand?
Step 1: Find a topic and review the literature
As we mentioned earlier, in a research paper, you, as the researcher, will try to answer a question . More specifically, that’s called a research question , and it sets the direction of your entire paper. What’s important to understand though is that you’ll need to answer that research question with the help of high-quality sources – for example, journal articles, government reports, case studies, and so on. We’ll circle back to this in a minute.
The first stage of the research process is deciding on what your research question will be and then reviewing the existing literature (in other words, past studies and papers) to see what they say about that specific research question. In some cases, your professor may provide you with a predetermined research question (or set of questions). However, in many cases, you’ll need to find your own research question within a certain topic area.
Finding a strong research question hinges on identifying a meaningful research gap – in other words, an area that’s lacking in existing research. There’s a lot to unpack here, so if you wanna learn more, check out the plain-language explainer video below.
Once you’ve figured out which question (or questions) you’ll attempt to answer in your research paper, you’ll need to do a deep dive into the existing literature – this is called a “ literature search ”. Again, there are many ways to go about this, but your most likely starting point will be Google Scholar .
If you’re new to Google Scholar, think of it as Google for the academic world. You can start by simply entering a few different keywords that are relevant to your research question and it will then present a host of articles for you to review. What you want to pay close attention to here is the number of citations for each paper – the more citations a paper has, the more credible it is (generally speaking – there are some exceptions, of course).

Ideally, what you’re looking for are well-cited papers that are highly relevant to your topic. That said, keep in mind that citations are a cumulative metric , so older papers will often have more citations than newer papers – just because they’ve been around for longer. So, don’t fixate on this metric in isolation – relevance and recency are also very important.
Beyond Google Scholar, you’ll also definitely want to check out academic databases and aggregators such as Science Direct, PubMed, JStor and so on. These will often overlap with the results that you find in Google Scholar, but they can also reveal some hidden gems – so, be sure to check them out.
Once you’ve worked your way through all the literature, you’ll want to catalogue all this information in some sort of spreadsheet so that you can easily recall who said what, when and within what context. If you’d like, we’ve got a free literature spreadsheet that helps you do exactly that.

Step 2: Develop a structure and outline
With your research question pinned down and your literature digested and catalogued, it’s time to move on to planning your actual research paper .
It might sound obvious, but it’s really important to have some sort of rough outline in place before you start writing your paper. So often, we see students eagerly rushing into the writing phase, only to land up with a disjointed research paper that rambles on in multiple
Now, the secret here is to not get caught up in the fine details . Realistically, all you need at this stage is a bullet-point list that describes (in broad strokes) what you’ll discuss and in what order. It’s also useful to remember that you’re not glued to this outline – in all likelihood, you’ll chop and change some sections once you start writing, and that’s perfectly okay. What’s important is that you have some sort of roadmap in place from the start.

At this stage you might be wondering, “ But how should I structure my research paper? ”. Well, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution here, but in general, a research paper will consist of a few relatively standardised components:
- Introduction
- Literature review
- Methodology
Let’s take a look at each of these.
First up is the introduction section . As the name suggests, the purpose of the introduction is to set the scene for your research paper. There are usually (at least) four ingredients that go into this section – these are the background to the topic, the research problem and resultant research question , and the justification or rationale. If you’re interested, the video below unpacks the introduction section in more detail.
The next section of your research paper will typically be your literature review . Remember all that literature you worked through earlier? Well, this is where you’ll present your interpretation of all that content . You’ll do this by writing about recent trends, developments, and arguments within the literature – but more specifically, those that are relevant to your research question . The literature review can oftentimes seem a little daunting, even to seasoned researchers, so be sure to check out our extensive collection of literature review content here .
With the introduction and lit review out of the way, the next section of your paper is the research methodology . In a nutshell, the methodology section should describe to your reader what you did (beyond just reviewing the existing literature) to answer your research question. For example, what data did you collect, how did you collect that data, how did you analyse that data and so on? For each choice, you’ll also need to justify why you chose to do it that way, and what the strengths and weaknesses of your approach were.
Now, it’s worth mentioning that for some research papers, this aspect of the project may be a lot simpler . For example, you may only need to draw on secondary sources (in other words, existing data sets). In some cases, you may just be asked to draw your conclusions from the literature search itself (in other words, there may be no data analysis at all). But, if you are required to collect and analyse data, you’ll need to pay a lot of attention to the methodology section. The video below provides an example of what the methodology section might look like.
By this stage of your paper, you will have explained what your research question is, what the existing literature has to say about that question, and how you analysed additional data to try to answer your question. So, the natural next step is to present your analysis of that data . This section is usually called the “results” or “analysis” section and this is where you’ll showcase your findings.
Depending on your school’s requirements, you may need to present and interpret the data in one section – or you might split the presentation and the interpretation into two sections. In the latter case, your “results” section will just describe the data, and the “discussion” is where you’ll interpret that data and explicitly link your analysis back to your research question. If you’re not sure which approach to take, check in with your professor or take a look at past papers to see what the norms are for your programme.
Alright – once you’ve presented and discussed your results, it’s time to wrap it up . This usually takes the form of the “ conclusion ” section. In the conclusion, you’ll need to highlight the key takeaways from your study and close the loop by explicitly answering your research question. Again, the exact requirements here will vary depending on your programme (and you may not even need a conclusion section at all) – so be sure to check with your professor if you’re unsure.
Step 3: Write and refine
Finally, it’s time to get writing. All too often though, students hit a brick wall right about here… So, how do you avoid this happening to you?
Well, there’s a lot to be said when it comes to writing a research paper (or any sort of academic piece), but we’ll share three practical tips to help you get started.
First and foremost , it’s essential to approach your writing as an iterative process. In other words, you need to start with a really messy first draft and then polish it over multiple rounds of editing. Don’t waste your time trying to write a perfect research paper in one go. Instead, take the pressure off yourself by adopting an iterative approach.
Secondly , it’s important to always lean towards critical writing , rather than descriptive writing. What does this mean? Well, at the simplest level, descriptive writing focuses on the “ what ”, while critical writing digs into the “ so what ” – in other words, the implications . If you’re not familiar with these two types of writing, don’t worry! You can find a plain-language explanation here.
Last but not least, you’ll need to get your referencing right. Specifically, you’ll need to provide credible, correctly formatted citations for the statements you make. We see students making referencing mistakes all the time and it costs them dearly. The good news is that you can easily avoid this by using a simple reference manager . If you don’t have one, check out our video about Mendeley, an easy (and free) reference management tool that you can start using today.
Recap: Key Takeaways
We’ve covered a lot of ground here. To recap, the three steps to writing a high-quality research paper are:
- To choose a research question and review the literature
- To plan your paper structure and draft an outline
- To take an iterative approach to writing, focusing on critical writing and strong referencing
Remember, this is just a b ig-picture overview of the research paper development process and there’s a lot more nuance to unpack. So, be sure to grab a copy of our free research paper template to learn more about how to write a research paper.
You Might Also Like:

Can you help me with a full paper template for this Abstract:
Background: Energy and sports drinks have gained popularity among diverse demographic groups, including adolescents, athletes, workers, and college students. While often used interchangeably, these beverages serve distinct purposes, with energy drinks aiming to boost energy and cognitive performance, and sports drinks designed to prevent dehydration and replenish electrolytes and carbohydrates lost during physical exertion.
Objective: To assess the nutritional quality of energy and sports drinks in Egypt.
Material and Methods: A cross-sectional study assessed the nutrient contents, including energy, sugar, electrolytes, vitamins, and caffeine, of sports and energy drinks available in major supermarkets in Cairo, Alexandria, and Giza, Egypt. Data collection involved photographing all relevant product labels and recording nutritional information. Descriptive statistics and appropriate statistical tests were employed to analyze and compare the nutritional values of energy and sports drinks.
Results: The study analyzed 38 sports drinks and 42 energy drinks. Sports drinks were significantly more expensive than energy drinks, with higher net content and elevated magnesium, potassium, and vitamin C. Energy drinks contained higher concentrations of caffeine, sugars, and vitamins B2, B3, and B6.
Conclusion: Significant nutritional differences exist between sports and energy drinks, reflecting their intended uses. However, these beverages’ high sugar content and calorie loads raise health concerns. Proper labeling, public awareness, and responsible marketing are essential to guide safe consumption practices in Egypt.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- How to write a research paper
Last updated
11 January 2024
Reviewed by
With proper planning, knowledge, and framework, completing a research paper can be a fulfilling and exciting experience.
Though it might initially sound slightly intimidating, this guide will help you embrace the challenge.
By documenting your findings, you can inspire others and make a difference in your field. Here's how you can make your research paper unique and comprehensive.
- What is a research paper?
Research papers allow you to demonstrate your knowledge and understanding of a particular topic. These papers are usually lengthier and more detailed than typical essays, requiring deeper insight into the chosen topic.
To write a research paper, you must first choose a topic that interests you and is relevant to the field of study. Once you’ve selected your topic, gathering as many relevant resources as possible, including books, scholarly articles, credible websites, and other academic materials, is essential. You must then read and analyze these sources, summarizing their key points and identifying gaps in the current research.
You can formulate your ideas and opinions once you thoroughly understand the existing research. To get there might involve conducting original research, gathering data, or analyzing existing data sets. It could also involve presenting an original argument or interpretation of the existing research.
Writing a successful research paper involves presenting your findings clearly and engagingly, which might involve using charts, graphs, or other visual aids to present your data and using concise language to explain your findings. You must also ensure your paper adheres to relevant academic formatting guidelines, including proper citations and references.
Overall, writing a research paper requires a significant amount of time, effort, and attention to detail. However, it is also an enriching experience that allows you to delve deeply into a subject that interests you and contribute to the existing body of knowledge in your chosen field.
- How long should a research paper be?
Research papers are deep dives into a topic. Therefore, they tend to be longer pieces of work than essays or opinion pieces.
However, a suitable length depends on the complexity of the topic and your level of expertise. For instance, are you a first-year college student or an experienced professional?
Also, remember that the best research papers provide valuable information for the benefit of others. Therefore, the quality of information matters most, not necessarily the length. Being concise is valuable.
Following these best practice steps will help keep your process simple and productive:
1. Gaining a deep understanding of any expectations
Before diving into your intended topic or beginning the research phase, take some time to orient yourself. Suppose there’s a specific topic assigned to you. In that case, it’s essential to deeply understand the question and organize your planning and approach in response. Pay attention to the key requirements and ensure you align your writing accordingly.
This preparation step entails
Deeply understanding the task or assignment
Being clear about the expected format and length
Familiarizing yourself with the citation and referencing requirements
Understanding any defined limits for your research contribution
Where applicable, speaking to your professor or research supervisor for further clarification
2. Choose your research topic
Select a research topic that aligns with both your interests and available resources. Ideally, focus on a field where you possess significant experience and analytical skills. In crafting your research paper, it's crucial to go beyond summarizing existing data and contribute fresh insights to the chosen area.
Consider narrowing your focus to a specific aspect of the topic. For example, if exploring the link between technology and mental health, delve into how social media use during the pandemic impacts the well-being of college students. Conducting interviews and surveys with students could provide firsthand data and unique perspectives, adding substantial value to the existing knowledge.
When finalizing your topic, adhere to legal and ethical norms in the relevant area (this ensures the integrity of your research, protects participants' rights, upholds intellectual property standards, and ensures transparency and accountability). Following these principles not only maintains the credibility of your work but also builds trust within your academic or professional community.
For instance, in writing about medical research, consider legal and ethical norms , including patient confidentiality laws and informed consent requirements. Similarly, if analyzing user data on social media platforms, be mindful of data privacy regulations, ensuring compliance with laws governing personal information collection and use. Aligning with legal and ethical standards not only avoids potential issues but also underscores the responsible conduct of your research.
3. Gather preliminary research
Once you’ve landed on your topic, it’s time to explore it further. You’ll want to discover more about available resources and existing research relevant to your assignment at this stage.
This exploratory phase is vital as you may discover issues with your original idea or realize you have insufficient resources to explore the topic effectively. This key bit of groundwork allows you to redirect your research topic in a different, more feasible, or more relevant direction if necessary.
Spending ample time at this stage ensures you gather everything you need, learn as much as you can about the topic, and discover gaps where the topic has yet to be sufficiently covered, offering an opportunity to research it further.
4. Define your research question
To produce a well-structured and focused paper, it is imperative to formulate a clear and precise research question that will guide your work. Your research question must be informed by the existing literature and tailored to the scope and objectives of your project. By refining your focus, you can produce a thoughtful and engaging paper that effectively communicates your ideas to your readers.
5. Write a thesis statement
A thesis statement is a one-to-two-sentence summary of your research paper's main argument or direction. It serves as an overall guide to summarize the overall intent of the research paper for you and anyone wanting to know more about the research.
A strong thesis statement is:
Concise and clear: Explain your case in simple sentences (avoid covering multiple ideas). It might help to think of this section as an elevator pitch.
Specific: Ensure that there is no ambiguity in your statement and that your summary covers the points argued in the paper.
Debatable: A thesis statement puts forward a specific argument––it is not merely a statement but a debatable point that can be analyzed and discussed.
Here are three thesis statement examples from different disciplines:
Psychology thesis example: "We're studying adults aged 25-40 to see if taking short breaks for mindfulness can help with stress. Our goal is to find practical ways to manage anxiety better."
Environmental science thesis example: "This research paper looks into how having more city parks might make the air cleaner and keep people healthier. I want to find out if more green spaces means breathing fewer carcinogens in big cities."
UX research thesis example: "This study focuses on improving mobile banking for older adults using ethnographic research, eye-tracking analysis, and interactive prototyping. We investigate the usefulness of eye-tracking analysis with older individuals, aiming to spark debate and offer fresh perspectives on UX design and digital inclusivity for the aging population."
6. Conduct in-depth research
A research paper doesn’t just include research that you’ve uncovered from other papers and studies but your fresh insights, too. You will seek to become an expert on your topic––understanding the nuances in the current leading theories. You will analyze existing research and add your thinking and discoveries. It's crucial to conduct well-designed research that is rigorous, robust, and based on reliable sources. Suppose a research paper lacks evidence or is biased. In that case, it won't benefit the academic community or the general public. Therefore, examining the topic thoroughly and furthering its understanding through high-quality research is essential. That usually means conducting new research. Depending on the area under investigation, you may conduct surveys, interviews, diary studies , or observational research to uncover new insights or bolster current claims.
7. Determine supporting evidence
Not every piece of research you’ve discovered will be relevant to your research paper. It’s important to categorize the most meaningful evidence to include alongside your discoveries. It's important to include evidence that doesn't support your claims to avoid exclusion bias and ensure a fair research paper.
8. Write a research paper outline
Before diving in and writing the whole paper, start with an outline. It will help you to see if more research is needed, and it will provide a framework by which to write a more compelling paper. Your supervisor may even request an outline to approve before beginning to write the first draft of the full paper. An outline will include your topic, thesis statement, key headings, short summaries of the research, and your arguments.
9. Write your first draft
Once you feel confident about your outline and sources, it’s time to write your first draft. While penning a long piece of content can be intimidating, if you’ve laid the groundwork, you will have a structure to help you move steadily through each section. To keep up motivation and inspiration, it’s often best to keep the pace quick. Stopping for long periods can interrupt your flow and make jumping back in harder than writing when things are fresh in your mind.
10. Cite your sources correctly
It's always a good practice to give credit where it's due, and the same goes for citing any works that have influenced your paper. Building your arguments on credible references adds value and authenticity to your research. In the formatting guidelines section, you’ll find an overview of different citation styles (MLA, CMOS, or APA), which will help you meet any publishing or academic requirements and strengthen your paper's credibility. It is essential to follow the guidelines provided by your school or the publication you are submitting to ensure the accuracy and relevance of your citations.
11. Ensure your work is original
It is crucial to ensure the originality of your paper, as plagiarism can lead to serious consequences. To avoid plagiarism, you should use proper paraphrasing and quoting techniques. Paraphrasing is rewriting a text in your own words while maintaining the original meaning. Quoting involves directly citing the source. Giving credit to the original author or source is essential whenever you borrow their ideas or words. You can also use plagiarism detection tools such as Scribbr or Grammarly to check the originality of your paper. These tools compare your draft writing to a vast database of online sources. If you find any accidental plagiarism, you should correct it immediately by rephrasing or citing the source.
12. Revise, edit, and proofread
One of the essential qualities of excellent writers is their ability to understand the importance of editing and proofreading. Even though it's tempting to call it a day once you've finished your writing, editing your work can significantly improve its quality. It's natural to overlook the weaker areas when you've just finished writing a paper. Therefore, it's best to take a break of a day or two, or even up to a week, to refresh your mind. This way, you can return to your work with a new perspective. After some breathing room, you can spot any inconsistencies, spelling and grammar errors, typos, or missing citations and correct them.
- The best research paper format
The format of your research paper should align with the requirements set forth by your college, school, or target publication.
There is no one “best” format, per se. Depending on the stated requirements, you may need to include the following elements:
Title page: The title page of a research paper typically includes the title, author's name, and institutional affiliation and may include additional information such as a course name or instructor's name.
Table of contents: Include a table of contents to make it easy for readers to find specific sections of your paper.
Abstract: The abstract is a summary of the purpose of the paper.
Methods : In this section, describe the research methods used. This may include collecting data , conducting interviews, or doing field research .
Results: Summarize the conclusions you drew from your research in this section.
Discussion: In this section, discuss the implications of your research . Be sure to mention any significant limitations to your approach and suggest areas for further research.
Tables, charts, and illustrations: Use tables, charts, and illustrations to help convey your research findings and make them easier to understand.
Works cited or reference page: Include a works cited or reference page to give credit to the sources that you used to conduct your research.
Bibliography: Provide a list of all the sources you consulted while conducting your research.
Dedication and acknowledgments : Optionally, you may include a dedication and acknowledgments section to thank individuals who helped you with your research.
- General style and formatting guidelines
Formatting your research paper means you can submit it to your college, journal, or other publications in compliance with their criteria.
Research papers tend to follow the American Psychological Association (APA), Modern Language Association (MLA), or Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS) guidelines.
Here’s how each style guide is typically used:
Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS):
CMOS is a versatile style guide used for various types of writing. It's known for its flexibility and use in the humanities. CMOS provides guidelines for citations, formatting, and overall writing style. It allows for both footnotes and in-text citations, giving writers options based on their preferences or publication requirements.
American Psychological Association (APA):
APA is common in the social sciences. It’s hailed for its clarity and emphasis on precision. It has specific rules for citing sources, creating references, and formatting papers. APA style uses in-text citations with an accompanying reference list. It's designed to convey information efficiently and is widely used in academic and scientific writing.
Modern Language Association (MLA):
MLA is widely used in the humanities, especially literature and language studies. It emphasizes the author-page format for in-text citations and provides guidelines for creating a "Works Cited" page. MLA is known for its focus on the author's name and the literary works cited. It’s frequently used in disciplines that prioritize literary analysis and critical thinking.
To confirm you're using the latest style guide, check the official website or publisher's site for updates, consult academic resources, and verify the guide's publication date. Online platforms and educational resources may also provide summaries and alerts about any revisions or additions to the style guide.
Citing sources
When working on your research paper, it's important to cite the sources you used properly. Your citation style will guide you through this process. Generally, there are three parts to citing sources in your research paper:
First, provide a brief citation in the body of your essay. This is also known as a parenthetical or in-text citation.
Second, include a full citation in the Reference list at the end of your paper. Different types of citations include in-text citations, footnotes, and reference lists.
In-text citations include the author's surname and the date of the citation.
Footnotes appear at the bottom of each page of your research paper. They may also be summarized within a reference list at the end of the paper.
A reference list includes all of the research used within the paper at the end of the document. It should include the author, date, paper title, and publisher listed in the order that aligns with your citation style.
10 research paper writing tips:
Following some best practices is essential to writing a research paper that contributes to your field of study and creates a positive impact.
These tactics will help you structure your argument effectively and ensure your work benefits others:
Clear and precise language: Ensure your language is unambiguous. Use academic language appropriately, but keep it simple. Also, provide clear takeaways for your audience.
Effective idea separation: Organize the vast amount of information and sources in your paper with paragraphs and titles. Create easily digestible sections for your readers to navigate through.
Compelling intro: Craft an engaging introduction that captures your reader's interest. Hook your audience and motivate them to continue reading.
Thorough revision and editing: Take the time to review and edit your paper comprehensively. Use tools like Grammarly to detect and correct small, overlooked errors.
Thesis precision: Develop a clear and concise thesis statement that guides your paper. Ensure that your thesis aligns with your research's overall purpose and contribution.
Logical flow of ideas: Maintain a logical progression throughout the paper. Use transitions effectively to connect different sections and maintain coherence.
Critical evaluation of sources: Evaluate and critically assess the relevance and reliability of your sources. Ensure that your research is based on credible and up-to-date information.
Thematic consistency: Maintain a consistent theme throughout the paper. Ensure that all sections contribute cohesively to the overall argument.
Relevant supporting evidence: Provide concise and relevant evidence to support your arguments. Avoid unnecessary details that may distract from the main points.
Embrace counterarguments: Acknowledge and address opposing views to strengthen your position. Show that you have considered alternative arguments in your field.
7 research tips
If you want your paper to not only be well-written but also contribute to the progress of human knowledge, consider these tips to take your paper to the next level:
Selecting the appropriate topic: The topic you select should align with your area of expertise, comply with the requirements of your project, and have sufficient resources for a comprehensive investigation.
Use academic databases: Academic databases such as PubMed, Google Scholar, and JSTOR offer a wealth of research papers that can help you discover everything you need to know about your chosen topic.
Critically evaluate sources: It is important not to accept research findings at face value. Instead, it is crucial to critically analyze the information to avoid jumping to conclusions or overlooking important details. A well-written research paper requires a critical analysis with thorough reasoning to support claims.
Diversify your sources: Expand your research horizons by exploring a variety of sources beyond the standard databases. Utilize books, conference proceedings, and interviews to gather diverse perspectives and enrich your understanding of the topic.
Take detailed notes: Detailed note-taking is crucial during research and can help you form the outline and body of your paper.
Stay up on trends: Keep abreast of the latest developments in your field by regularly checking for recent publications. Subscribe to newsletters, follow relevant journals, and attend conferences to stay informed about emerging trends and advancements.
Engage in peer review: Seek feedback from peers or mentors to ensure the rigor and validity of your research . Peer review helps identify potential weaknesses in your methodology and strengthens the overall credibility of your findings.
- The real-world impact of research papers
Writing a research paper is more than an academic or business exercise. The experience provides an opportunity to explore a subject in-depth, broaden one's understanding, and arrive at meaningful conclusions. With careful planning, dedication, and hard work, writing a research paper can be a fulfilling and enriching experience contributing to advancing knowledge.
How do I publish my research paper?
Many academics wish to publish their research papers. While challenging, your paper might get traction if it covers new and well-written information. To publish your research paper, find a target publication, thoroughly read their guidelines, format your paper accordingly, and send it to them per their instructions. You may need to include a cover letter, too. After submission, your paper may be peer-reviewed by experts to assess its legitimacy, quality, originality, and methodology. Following review, you will be informed by the publication whether they have accepted or rejected your paper.
What is a good opening sentence for a research paper?
Beginning your research paper with a compelling introduction can ensure readers are interested in going further. A relevant quote, a compelling statistic, or a bold argument can start the paper and hook your reader. Remember, though, that the most important aspect of a research paper is the quality of the information––not necessarily your ability to storytell, so ensure anything you write aligns with your goals.
Research paper vs. a research proposal—what’s the difference?
While some may confuse research papers and proposals, they are different documents.
A research proposal comes before a research paper. It is a detailed document that outlines an intended area of exploration. It includes the research topic, methodology, timeline, sources, and potential conclusions. Research proposals are often required when seeking approval to conduct research.
A research paper is a summary of research findings. A research paper follows a structured format to present those findings and construct an argument or conclusion.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 18 April 2023
Last updated: 27 February 2023
Last updated: 6 February 2023
Last updated: 6 October 2023
Last updated: 5 February 2023
Last updated: 16 April 2023
Last updated: 7 March 2023
Last updated: 9 March 2023
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next.

Users report unexpectedly high data usage, especially during streaming sessions.

Users find it hard to navigate from the home page to relevant playlists in the app.

It would be great to have a sleep timer feature, especially for bedtime listening.

I need better filters to find the songs or artists I’m looking for.
- 10 research paper
Log in or sign up
Get started for free
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Paper
Definition:
Research Paper is a written document that presents the author’s original research, analysis, and interpretation of a specific topic or issue.
It is typically based on Empirical Evidence, and may involve qualitative or quantitative research methods, or a combination of both. The purpose of a research paper is to contribute new knowledge or insights to a particular field of study, and to demonstrate the author’s understanding of the existing literature and theories related to the topic.
Structure of Research Paper
The structure of a research paper typically follows a standard format, consisting of several sections that convey specific information about the research study. The following is a detailed explanation of the structure of a research paper:
The title page contains the title of the paper, the name(s) of the author(s), and the affiliation(s) of the author(s). It also includes the date of submission and possibly, the name of the journal or conference where the paper is to be published.
The abstract is a brief summary of the research paper, typically ranging from 100 to 250 words. It should include the research question, the methods used, the key findings, and the implications of the results. The abstract should be written in a concise and clear manner to allow readers to quickly grasp the essence of the research.
Introduction
The introduction section of a research paper provides background information about the research problem, the research question, and the research objectives. It also outlines the significance of the research, the research gap that it aims to fill, and the approach taken to address the research question. Finally, the introduction section ends with a clear statement of the research hypothesis or research question.
Literature Review
The literature review section of a research paper provides an overview of the existing literature on the topic of study. It includes a critical analysis and synthesis of the literature, highlighting the key concepts, themes, and debates. The literature review should also demonstrate the research gap and how the current study seeks to address it.
The methods section of a research paper describes the research design, the sample selection, the data collection and analysis procedures, and the statistical methods used to analyze the data. This section should provide sufficient detail for other researchers to replicate the study.
The results section presents the findings of the research, using tables, graphs, and figures to illustrate the data. The findings should be presented in a clear and concise manner, with reference to the research question and hypothesis.
The discussion section of a research paper interprets the findings and discusses their implications for the research question, the literature review, and the field of study. It should also address the limitations of the study and suggest future research directions.
The conclusion section summarizes the main findings of the study, restates the research question and hypothesis, and provides a final reflection on the significance of the research.
The references section provides a list of all the sources cited in the paper, following a specific citation style such as APA, MLA or Chicago.
How to Write Research Paper
You can write Research Paper by the following guide:
- Choose a Topic: The first step is to select a topic that interests you and is relevant to your field of study. Brainstorm ideas and narrow down to a research question that is specific and researchable.
- Conduct a Literature Review: The literature review helps you identify the gap in the existing research and provides a basis for your research question. It also helps you to develop a theoretical framework and research hypothesis.
- Develop a Thesis Statement : The thesis statement is the main argument of your research paper. It should be clear, concise and specific to your research question.
- Plan your Research: Develop a research plan that outlines the methods, data sources, and data analysis procedures. This will help you to collect and analyze data effectively.
- Collect and Analyze Data: Collect data using various methods such as surveys, interviews, observations, or experiments. Analyze data using statistical tools or other qualitative methods.
- Organize your Paper : Organize your paper into sections such as Introduction, Literature Review, Methods, Results, Discussion, and Conclusion. Ensure that each section is coherent and follows a logical flow.
- Write your Paper : Start by writing the introduction, followed by the literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. Ensure that your writing is clear, concise, and follows the required formatting and citation styles.
- Edit and Proofread your Paper: Review your paper for grammar and spelling errors, and ensure that it is well-structured and easy to read. Ask someone else to review your paper to get feedback and suggestions for improvement.
- Cite your Sources: Ensure that you properly cite all sources used in your research paper. This is essential for giving credit to the original authors and avoiding plagiarism.
Research Paper Example
Note : The below example research paper is for illustrative purposes only and is not an actual research paper. Actual research papers may have different structures, contents, and formats depending on the field of study, research question, data collection and analysis methods, and other factors. Students should always consult with their professors or supervisors for specific guidelines and expectations for their research papers.
Research Paper Example sample for Students:
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health among Young Adults
Abstract: This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults. A literature review was conducted to examine the existing research on the topic. A survey was then administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Introduction: Social media has become an integral part of modern life, particularly among young adults. While social media has many benefits, including increased communication and social connectivity, it has also been associated with negative outcomes, such as addiction, cyberbullying, and mental health problems. This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults.
Literature Review: The literature review highlights the existing research on the impact of social media use on mental health. The review shows that social media use is associated with depression, anxiety, stress, and other mental health problems. The review also identifies the factors that contribute to the negative impact of social media, including social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Methods : A survey was administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The survey included questions on social media use, mental health status (measured using the DASS-21), and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and regression analysis.
Results : The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Discussion : The study’s findings suggest that social media use has a negative impact on the mental health of young adults. The study highlights the need for interventions that address the factors contributing to the negative impact of social media, such as social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Conclusion : In conclusion, social media use has a significant impact on the mental health of young adults. The study’s findings underscore the need for interventions that promote healthy social media use and address the negative outcomes associated with social media use. Future research can explore the effectiveness of interventions aimed at reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health. Additionally, longitudinal studies can investigate the long-term effects of social media use on mental health.
Limitations : The study has some limitations, including the use of self-report measures and a cross-sectional design. The use of self-report measures may result in biased responses, and a cross-sectional design limits the ability to establish causality.
Implications: The study’s findings have implications for mental health professionals, educators, and policymakers. Mental health professionals can use the findings to develop interventions that address the negative impact of social media use on mental health. Educators can incorporate social media literacy into their curriculum to promote healthy social media use among young adults. Policymakers can use the findings to develop policies that protect young adults from the negative outcomes associated with social media use.
References :
- Twenge, J. M., & Campbell, W. K. (2019). Associations between screen time and lower psychological well-being among children and adolescents: Evidence from a population-based study. Preventive medicine reports, 15, 100918.
- Primack, B. A., Shensa, A., Escobar-Viera, C. G., Barrett, E. L., Sidani, J. E., Colditz, J. B., … & James, A. E. (2017). Use of multiple social media platforms and symptoms of depression and anxiety: A nationally-representative study among US young adults. Computers in Human Behavior, 69, 1-9.
- Van der Meer, T. G., & Verhoeven, J. W. (2017). Social media and its impact on academic performance of students. Journal of Information Technology Education: Research, 16, 383-398.
Appendix : The survey used in this study is provided below.
Social Media and Mental Health Survey
- How often do you use social media per day?
- Less than 30 minutes
- 30 minutes to 1 hour
- 1 to 2 hours
- 2 to 4 hours
- More than 4 hours
- Which social media platforms do you use?
- Others (Please specify)
- How often do you experience the following on social media?
- Social comparison (comparing yourself to others)
- Cyberbullying
- Fear of Missing Out (FOMO)
- Have you ever experienced any of the following mental health problems in the past month?
- Do you think social media use has a positive or negative impact on your mental health?
- Very positive
- Somewhat positive
- Somewhat negative
- Very negative
- In your opinion, which factors contribute to the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Social comparison
- In your opinion, what interventions could be effective in reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Education on healthy social media use
- Counseling for mental health problems caused by social media
- Social media detox programs
- Regulation of social media use
Thank you for your participation!
Applications of Research Paper
Research papers have several applications in various fields, including:
- Advancing knowledge: Research papers contribute to the advancement of knowledge by generating new insights, theories, and findings that can inform future research and practice. They help to answer important questions, clarify existing knowledge, and identify areas that require further investigation.
- Informing policy: Research papers can inform policy decisions by providing evidence-based recommendations for policymakers. They can help to identify gaps in current policies, evaluate the effectiveness of interventions, and inform the development of new policies and regulations.
- Improving practice: Research papers can improve practice by providing evidence-based guidance for professionals in various fields, including medicine, education, business, and psychology. They can inform the development of best practices, guidelines, and standards of care that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- Educating students : Research papers are often used as teaching tools in universities and colleges to educate students about research methods, data analysis, and academic writing. They help students to develop critical thinking skills, research skills, and communication skills that are essential for success in many careers.
- Fostering collaboration: Research papers can foster collaboration among researchers, practitioners, and policymakers by providing a platform for sharing knowledge and ideas. They can facilitate interdisciplinary collaborations and partnerships that can lead to innovative solutions to complex problems.
When to Write Research Paper
Research papers are typically written when a person has completed a research project or when they have conducted a study and have obtained data or findings that they want to share with the academic or professional community. Research papers are usually written in academic settings, such as universities, but they can also be written in professional settings, such as research organizations, government agencies, or private companies.
Here are some common situations where a person might need to write a research paper:
- For academic purposes: Students in universities and colleges are often required to write research papers as part of their coursework, particularly in the social sciences, natural sciences, and humanities. Writing research papers helps students to develop research skills, critical thinking skills, and academic writing skills.
- For publication: Researchers often write research papers to publish their findings in academic journals or to present their work at academic conferences. Publishing research papers is an important way to disseminate research findings to the academic community and to establish oneself as an expert in a particular field.
- To inform policy or practice : Researchers may write research papers to inform policy decisions or to improve practice in various fields. Research findings can be used to inform the development of policies, guidelines, and best practices that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- To share new insights or ideas: Researchers may write research papers to share new insights or ideas with the academic or professional community. They may present new theories, propose new research methods, or challenge existing paradigms in their field.
Purpose of Research Paper
The purpose of a research paper is to present the results of a study or investigation in a clear, concise, and structured manner. Research papers are written to communicate new knowledge, ideas, or findings to a specific audience, such as researchers, scholars, practitioners, or policymakers. The primary purposes of a research paper are:
- To contribute to the body of knowledge : Research papers aim to add new knowledge or insights to a particular field or discipline. They do this by reporting the results of empirical studies, reviewing and synthesizing existing literature, proposing new theories, or providing new perspectives on a topic.
- To inform or persuade: Research papers are written to inform or persuade the reader about a particular issue, topic, or phenomenon. They present evidence and arguments to support their claims and seek to persuade the reader of the validity of their findings or recommendations.
- To advance the field: Research papers seek to advance the field or discipline by identifying gaps in knowledge, proposing new research questions or approaches, or challenging existing assumptions or paradigms. They aim to contribute to ongoing debates and discussions within a field and to stimulate further research and inquiry.
- To demonstrate research skills: Research papers demonstrate the author’s research skills, including their ability to design and conduct a study, collect and analyze data, and interpret and communicate findings. They also demonstrate the author’s ability to critically evaluate existing literature, synthesize information from multiple sources, and write in a clear and structured manner.
Characteristics of Research Paper
Research papers have several characteristics that distinguish them from other forms of academic or professional writing. Here are some common characteristics of research papers:
- Evidence-based: Research papers are based on empirical evidence, which is collected through rigorous research methods such as experiments, surveys, observations, or interviews. They rely on objective data and facts to support their claims and conclusions.
- Structured and organized: Research papers have a clear and logical structure, with sections such as introduction, literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. They are organized in a way that helps the reader to follow the argument and understand the findings.
- Formal and objective: Research papers are written in a formal and objective tone, with an emphasis on clarity, precision, and accuracy. They avoid subjective language or personal opinions and instead rely on objective data and analysis to support their arguments.
- Citations and references: Research papers include citations and references to acknowledge the sources of information and ideas used in the paper. They use a specific citation style, such as APA, MLA, or Chicago, to ensure consistency and accuracy.
- Peer-reviewed: Research papers are often peer-reviewed, which means they are evaluated by other experts in the field before they are published. Peer-review ensures that the research is of high quality, meets ethical standards, and contributes to the advancement of knowledge in the field.
- Objective and unbiased: Research papers strive to be objective and unbiased in their presentation of the findings. They avoid personal biases or preconceptions and instead rely on the data and analysis to draw conclusions.
Advantages of Research Paper
Research papers have many advantages, both for the individual researcher and for the broader academic and professional community. Here are some advantages of research papers:
- Contribution to knowledge: Research papers contribute to the body of knowledge in a particular field or discipline. They add new information, insights, and perspectives to existing literature and help advance the understanding of a particular phenomenon or issue.
- Opportunity for intellectual growth: Research papers provide an opportunity for intellectual growth for the researcher. They require critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity, which can help develop the researcher’s skills and knowledge.
- Career advancement: Research papers can help advance the researcher’s career by demonstrating their expertise and contributions to the field. They can also lead to new research opportunities, collaborations, and funding.
- Academic recognition: Research papers can lead to academic recognition in the form of awards, grants, or invitations to speak at conferences or events. They can also contribute to the researcher’s reputation and standing in the field.
- Impact on policy and practice: Research papers can have a significant impact on policy and practice. They can inform policy decisions, guide practice, and lead to changes in laws, regulations, or procedures.
- Advancement of society: Research papers can contribute to the advancement of society by addressing important issues, identifying solutions to problems, and promoting social justice and equality.
Limitations of Research Paper
Research papers also have some limitations that should be considered when interpreting their findings or implications. Here are some common limitations of research papers:
- Limited generalizability: Research findings may not be generalizable to other populations, settings, or contexts. Studies often use specific samples or conditions that may not reflect the broader population or real-world situations.
- Potential for bias : Research papers may be biased due to factors such as sample selection, measurement errors, or researcher biases. It is important to evaluate the quality of the research design and methods used to ensure that the findings are valid and reliable.
- Ethical concerns: Research papers may raise ethical concerns, such as the use of vulnerable populations or invasive procedures. Researchers must adhere to ethical guidelines and obtain informed consent from participants to ensure that the research is conducted in a responsible and respectful manner.
- Limitations of methodology: Research papers may be limited by the methodology used to collect and analyze data. For example, certain research methods may not capture the complexity or nuance of a particular phenomenon, or may not be appropriate for certain research questions.
- Publication bias: Research papers may be subject to publication bias, where positive or significant findings are more likely to be published than negative or non-significant findings. This can skew the overall findings of a particular area of research.
- Time and resource constraints: Research papers may be limited by time and resource constraints, which can affect the quality and scope of the research. Researchers may not have access to certain data or resources, or may be unable to conduct long-term studies due to practical limitations.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Future Research – Thesis Guide

Background of The Study – Examples and Writing...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Context of the Study – Writing Guide and Examples

Research Techniques – Methods, Types and Examples

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

How to Write a Research Paper
Use the links below to jump directly to any section of this guide:
Research Paper Fundamentals
How to choose a topic or question, how to create a working hypothesis or thesis, common research paper methodologies, how to gather and organize evidence , how to write an outline for your research paper, how to write a rough draft, how to revise your draft, how to produce a final draft, resources for teachers .
It is not fair to say that no one writes anymore. Just about everyone writes text messages, brief emails, or social media posts every single day. Yet, most people don't have a lot of practice with the formal, organized writing required for a good academic research paper. This guide contains links to a variety of resources that can help demystify the process. Some of these resources are intended for teachers; they contain exercises, activities, and teaching strategies. Other resources are intended for direct use by students who are struggling to write papers, or are looking for tips to make the process go more smoothly.
The resources in this section are designed to help students understand the different types of research papers, the general research process, and how to manage their time. Below, you'll find links from university writing centers, the trusted Purdue Online Writing Lab, and more.
What is an Academic Research Paper?
"Genre and the Research Paper" (Purdue OWL)
There are different types of research papers. Different types of scholarly questions will lend themselves to one format or another. This is a brief introduction to the two main genres of research paper: analytic and argumentative.
"7 Most Popular Types of Research Papers" (Personal-writer.com)
This resource discusses formats that high school students commonly encounter, such as the compare and contrast essay and the definitional essay. Please note that the inclusion of this link is not an endorsement of this company's paid service.
How to Prepare and Plan Out Writing a Research Paper
Teachers can give their students a step-by-step guide like these to help them understand the different steps of the research paper process. These guides can be combined with the time management tools in the next subsection to help students come up with customized calendars for completing their papers.
"Ten Steps for Writing Research Papers" (American University)
This resource from American University is a comprehensive guide to the research paper writing process, and includes examples of proper research questions and thesis topics.
"Steps in Writing a Research Paper" (SUNY Empire State College)
This guide breaks the research paper process into 11 steps. Each "step" links to a separate page, which describes the work entailed in completing it.
How to Manage Time Effectively
The links below will help students determine how much time is necessary to complete a paper. If your sources are not available online or at your local library, you'll need to leave extra time for the Interlibrary Loan process. Remember that, even if you do not need to consult secondary sources, you'll still need to leave yourself ample time to organize your thoughts.
"Research Paper Planner: Timeline" (Baylor University)
This interactive resource from Baylor University creates a suggested writing schedule based on how much time a student has to work on the assignment.
"Research Paper Planner" (UCLA)
UCLA's library offers this step-by-step guide to the research paper writing process, which also includes a suggested planning calendar.
There's a reason teachers spend a long time talking about choosing a good topic. Without a good topic and a well-formulated research question, it is almost impossible to write a clear and organized paper. The resources below will help you generate ideas and formulate precise questions.
"How to Select a Research Topic" (Univ. of Michigan-Flint)
This resource is designed for college students who are struggling to come up with an appropriate topic. A student who uses this resource and still feels unsure about his or her topic should consult the course instructor for further personalized assistance.
"25 Interesting Research Paper Topics to Get You Started" (Kibin)
This resource, which is probably most appropriate for high school students, provides a list of specific topics to help get students started. It is broken into subsections, such as "paper topics on local issues."
"Writing a Good Research Question" (Grand Canyon University)
This introduction to research questions includes some embedded videos, as well as links to scholarly articles on research questions. This resource would be most appropriate for teachers who are planning lessons on research paper fundamentals.
"How to Write a Research Question the Right Way" (Kibin)
This student-focused resource provides more detail on writing research questions. The language is accessible, and there are embedded videos and examples of good and bad questions.
It is important to have a rough hypothesis or thesis in mind at the beginning of the research process. People who have a sense of what they want to say will have an easier time sorting through scholarly sources and other information. The key, of course, is not to become too wedded to the draft hypothesis or thesis. Just about every working thesis gets changed during the research process.
CrashCourse Video: "Sociology Research Methods" (YouTube)
Although this video is tailored to sociology students, it is applicable to students in a variety of social science disciplines. This video does a good job demonstrating the connection between the brainstorming that goes into selecting a research question and the formulation of a working hypothesis.
"How to Write a Thesis Statement for an Analytical Essay" (YouTube)
Students writing analytical essays will not develop the same type of working hypothesis as students who are writing research papers in other disciplines. For these students, developing the working thesis may happen as a part of the rough draft (see the relevant section below).
"Research Hypothesis" (Oakland Univ.)
This resource provides some examples of hypotheses in social science disciplines like Political Science and Criminal Justice. These sample hypotheses may also be useful for students in other soft social sciences and humanities disciplines like History.
When grading a research paper, instructors look for a consistent methodology. This section will help you understand different methodological approaches used in research papers. Students will get the most out of these resources if they use them to help prepare for conversations with teachers or discussions in class.
"Types of Research Designs" (USC)
A "research design," used for complex papers, is related to the paper's method. This resource contains introductions to a variety of popular research designs in the social sciences. Although it is not the most intuitive site to read, the information here is very valuable.
"Major Research Methods" (YouTube)
Although this video is a bit on the dry side, it provides a comprehensive overview of the major research methodologies in a format that might be more accessible to students who have struggled with textbooks or other written resources.
"Humanities Research Strategies" (USC)
This is a portal where students can learn about four methodological approaches for humanities papers: Historical Methodologies, Textual Criticism, Conceptual Analysis, and the Synoptic method.
"Selected Major Social Science Research Methods: Overview" (National Academies Press)
This appendix from the book Using Science as Evidence in Public Policy , printed by National Academies Press, introduces some methods used in social science papers.
"Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper: 6. The Methodology" (USC)
This resource from the University of Southern California's library contains tips for writing a methodology section in a research paper.
How to Determine the Best Methodology for You
Anyone who is new to writing research papers should be sure to select a method in consultation with their instructor. These resources can be used to help prepare for that discussion. They may also be used on their own by more advanced students.
"Choosing Appropriate Research Methodologies" (Palgrave Study Skills)
This friendly and approachable resource from Palgrave Macmillan can be used by students who are just starting to think about appropriate methodologies.
"How to Choose Your Research Methods" (NFER (UK))
This is another approachable resource students can use to help narrow down the most appropriate methods for their research projects.
The resources in this section introduce the process of gathering scholarly sources and collecting evidence. You'll find a range of material here, from introductory guides to advanced explications best suited to college students. Please consult the LitCharts How to Do Academic Research guide for a more comprehensive list of resources devoted to finding scholarly literature.
Google Scholar
Students who have access to library websites with detailed research guides should start there, but people who do not have access to those resources can begin their search for secondary literature here.
"Gathering Appropriate Information" (Texas Gateway)
This resource from the Texas Gateway for online resources introduces students to the research process, and contains interactive exercises. The level of complexity is suitable for middle school, high school, and introductory college classrooms.
"An Overview of Quantitative and Qualitative Data Collection Methods" (NSF)
This PDF from the National Science Foundation goes into detail about best practices and pitfalls in data collection across multiple types of methodologies.
"Social Science Methods for Data Collection and Analysis" (Swiss FIT)
This resource is appropriate for advanced undergraduates or teachers looking to create lessons on research design and data collection. It covers techniques for gathering data via interviews, observations, and other methods.
"Collecting Data by In-depth Interviewing" (Leeds Univ.)
This resource contains enough information about conducting interviews to make it useful for teachers who want to create a lesson plan, but is also accessible enough for college juniors or seniors to make use of it on their own.
There is no "one size fits all" outlining technique. Some students might devote all their energy and attention to the outline in order to avoid the paper. Other students may benefit from being made to sit down and organize their thoughts into a lengthy sentence outline. The resources in this section include strategies and templates for multiple types of outlines.
"Topic vs. Sentence Outlines" (UC Berkeley)
This resource introduces two basic approaches to outlining: the shorter topic-based approach, and the longer, more detailed sentence-based approach. This resource also contains videos on how to develop paper paragraphs from the sentence-based outline.
"Types of Outlines and Samples" (Purdue OWL)
The Purdue Online Writing Lab's guide is a slightly less detailed discussion of different types of outlines. It contains several sample outlines.
"Writing An Outline" (Austin C.C.)
This resource from a community college contains sample outlines from an American history class that students can use as models.
"How to Structure an Outline for a College Paper" (YouTube)
This brief (sub-2 minute) video from the ExpertVillage YouTube channel provides a model of outline writing for students who are struggling with the idea.
"Outlining" (Harvard)
This is a good resource to consult after completing a draft outline. It offers suggestions for making sure your outline avoids things like unnecessary repetition.
As with outlines, rough drafts can take on many different forms. These resources introduce teachers and students to the various approaches to writing a rough draft. This section also includes resources that will help you cite your sources appropriately according to the MLA, Chicago, and APA style manuals.
"Creating a Rough Draft for a Research Paper" (Univ. of Minnesota)
This resource is useful for teachers in particular, as it provides some suggested exercises to help students with writing a basic rough draft.
Rough Draft Assignment (Duke of Definition)
This sample assignment, with a brief list of tips, was developed by a high school teacher who runs a very successful and well-reviewed page of educational resources.
"Creating the First Draft of Your Research Paper" (Concordia Univ.)
This resource will be helpful for perfectionists or procrastinators, as it opens by discussing the problem of avoiding writing. It also provides a short list of suggestions meant to get students writing.
Using Proper Citations
There is no such thing as a rough draft of a scholarly citation. These links to the three major citation guides will ensure that your citations follow the correct format. Please consult the LitCharts How to Cite Your Sources guide for more resources.
Chicago Manual of Style Citation Guide
Some call The Chicago Manual of Style , which was first published in 1906, "the editors' Bible." The manual is now in its 17th edition, and is popular in the social sciences, historical journals, and some other fields in the humanities.
APA Citation Guide
According to the American Psychological Association, this guide was developed to aid reading comprehension, clarity of communication, and to reduce bias in language in the social and behavioral sciences. Its first full edition was published in 1952, and it is now in its sixth edition.
MLA Citation Guide
The Modern Language Association style is used most commonly within the liberal arts and humanities. The MLA Style Manual and Guide to Scholarly Publishing was first published in 1985 and (as of 2008) is in its third edition.
Any professional scholar will tell you that the best research papers are made in the revision stage. No matter how strong your research question or working thesis, it is not possible to write a truly outstanding paper without devoting energy to revision. These resources provide examples of revision exercises for the classroom, as well as tips for students working independently.
"The Art of Revision" (Univ. of Arizona)
This resource provides a wealth of information and suggestions for both students and teachers. There is a list of suggested exercises that teachers might use in class, along with a revision checklist that is useful for teachers and students alike.
"Script for Workshop on Revision" (Vanderbilt University)
Vanderbilt's guide for leading a 50-minute revision workshop can serve as a model for teachers who wish to guide students through the revision process during classtime.
"Revising Your Paper" (Univ. of Washington)
This detailed handout was designed for students who are beginning the revision process. It discusses different approaches and methods for revision, and also includes a detailed list of things students should look for while they revise.
"Revising Drafts" (UNC Writing Center)
This resource is designed for students and suggests things to look for during the revision process. It provides steps for the process and has a FAQ for students who have questions about why it is important to revise.
Conferencing with Writing Tutors and Instructors
No writer is so good that he or she can't benefit from meeting with instructors or peer tutors. These resources from university writing, learning, and communication centers provide suggestions for how to get the most out of these one-on-one meetings.
"Getting Feedback" (UNC Writing Center)
This very helpful resource talks about how to ask for feedback during the entire writing process. It contains possible questions that students might ask when developing an outline, during the revision process, and after the final draft has been graded.
"Prepare for Your Tutoring Session" (Otis College of Art and Design)
This guide from a university's student learning center contains a lot of helpful tips for getting the most out of working with a writing tutor.
"The Importance of Asking Your Professor" (Univ. of Waterloo)
This article from the university's Writing and Communication Centre's blog contains some suggestions for how and when to get help from professors and Teaching Assistants.
Once you've revised your first draft, you're well on your way to handing in a polished paper. These resources—each of them produced by writing professionals at colleges and universities—outline the steps required in order to produce a final draft. You'll find proofreading tips and checklists in text and video form.
"Developing a Final Draft of a Research Paper" (Univ. of Minnesota)
While this resource contains suggestions for revision, it also features a couple of helpful checklists for the last stages of completing a final draft.
Basic Final Draft Tips and Checklist (Univ. of Maryland-University College)
This short and accessible resource, part of UMUC's very thorough online guide to writing and research, contains a very basic checklist for students who are getting ready to turn in their final drafts.
Final Draft Checklist (Everett C.C.)
This is another accessible final draft checklist, appropriate for both high school and college students. It suggests reading your essay aloud at least once.
"How to Proofread Your Final Draft" (YouTube)
This video (approximately 5 minutes), produced by Eastern Washington University, gives students tips on proofreading final drafts.
"Proofreading Tips" (Georgia Southern-Armstrong)
This guide will help students learn how to spot common errors in their papers. It suggests focusing on content and editing for grammar and mechanics.
This final set of resources is intended specifically for high school and college instructors. It provides links to unit plans and classroom exercises that can help improve students' research and writing skills. You'll find resources that give an overview of the process, along with activities that focus on how to begin and how to carry out research.
"Research Paper Complete Resources Pack" (Teachers Pay Teachers)
This packet of assignments, rubrics, and other resources is designed for high school students. The resources in this packet are aligned to Common Core standards.
"Research Paper—Complete Unit" (Teachers Pay Teachers)
This packet of assignments, notes, PowerPoints, and other resources has a 4/4 rating with over 700 ratings. It is designed for high school teachers, but might also be useful to college instructors who work with freshmen.
"Teaching Students to Write Good Papers" (Yale)
This resource from Yale's Center for Teaching and Learning is designed for college instructors, and it includes links to appropriate activities and exercises.
"Research Paper Writing: An Overview" (CUNY Brooklyn)
CUNY Brooklyn offers this complete lesson plan for introducing students to research papers. It includes an accompanying set of PowerPoint slides.
"Lesson Plan: How to Begin Writing a Research Paper" (San Jose State Univ.)
This lesson plan is designed for students in the health sciences, so teachers will have to modify it for their own needs. It includes a breakdown of the brainstorming, topic selection, and research question process.
"Quantitative Techniques for Social Science Research" (Univ. of Pittsburgh)
This is a set of PowerPoint slides that can be used to introduce students to a variety of quantitative methods used in the social sciences.
- PDFs for all 136 Lit Terms we cover
- Downloads of 1956 LitCharts Lit Guides
- Teacher Editions for every Lit Guide
- Explanations and citation info for 41,253 quotes across 1956 books
- Downloadable (PDF) line-by-line translations of every Shakespeare play
Need something? Request a new guide .
How can we improve? Share feedback .
LitCharts is hiring!

Writing a Research Paper
This page lists some of the stages involved in writing a library-based research paper.
Although this list suggests that there is a simple, linear process to writing such a paper, the actual process of writing a research paper is often a messy and recursive one, so please use this outline as a flexible guide.
Discovering, Narrowing, and Focusing a Researchable Topic
- Try to find a topic that truly interests you
- Try writing your way to a topic
- Talk with your course instructor and classmates about your topic
- Pose your topic as a question to be answered or a problem to be solved
Finding, Selecting, and Reading Sources
You will need to look at the following types of sources:
- library catalog, periodical indexes, bibliographies, suggestions from your instructor
- primary vs. secondary sources
- journals, books, other documents
Grouping, Sequencing, and Documenting Information
The following systems will help keep you organized:
- a system for noting sources on bibliography cards
- a system for organizing material according to its relative importance
- a system for taking notes
Writing an Outline and a Prospectus for Yourself
Consider the following questions:
- What is the topic?
- Why is it significant?
- What background material is relevant?
- What is my thesis or purpose statement?
- What organizational plan will best support my purpose?
Writing the Introduction
In the introduction you will need to do the following things:
- present relevant background or contextual material
- define terms or concepts when necessary
- explain the focus of the paper and your specific purpose
- reveal your plan of organization
Writing the Body
- Use your outline and prospectus as flexible guides
- Build your essay around points you want to make (i.e., don’t let your sources organize your paper)
- Integrate your sources into your discussion
- Summarize, analyze, explain, and evaluate published work rather than merely reporting it
- Move up and down the “ladder of abstraction” from generalization to varying levels of detail back to generalization
Writing the Conclusion
- If the argument or point of your paper is complex, you may need to summarize the argument for your reader.
- If prior to your conclusion you have not yet explained the significance of your findings or if you are proceeding inductively, use the end of your paper to add your points up, to explain their significance.
- Move from a detailed to a general level of consideration that returns the topic to the context provided by the introduction.
- Perhaps suggest what about this topic needs further research.
Revising the Final Draft
- Check overall organization : logical flow of introduction, coherence and depth of discussion in body, effectiveness of conclusion.
- Paragraph level concerns : topic sentences, sequence of ideas within paragraphs, use of details to support generalizations, summary sentences where necessary, use of transitions within and between paragraphs.
- Sentence level concerns: sentence structure, word choices, punctuation, spelling.
- Documentation: consistent use of one system, citation of all material not considered common knowledge, appropriate use of endnotes or footnotes, accuracy of list of works cited.

Academic and Professional Writing
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Analysis Papers
Reading Poetry
A Short Guide to Close Reading for Literary Analysis
Using Literary Quotations
Play Reviews
Writing a Rhetorical Précis to Analyze Nonfiction Texts
Incorporating Interview Data
Grant Proposals
Planning and Writing a Grant Proposal: The Basics
Additional Resources for Grants and Proposal Writing
Job Materials and Application Essays
Writing Personal Statements for Ph.D. Programs
- Before you begin: useful tips for writing your essay
- Guided brainstorming exercises
- Get more help with your essay
- Frequently Asked Questions
Resume Writing Tips
CV Writing Tips
Cover Letters
Business Letters
Proposals and Dissertations
Resources for Proposal Writers
Resources for Dissertators
Research Papers
Planning and Writing Research Papers
Quoting and Paraphrasing
Writing Annotated Bibliographies
Creating Poster Presentations
Writing an Abstract for Your Research Paper
Thank-You Notes
Advice for Students Writing Thank-You Notes to Donors
Reading for a Review
Critical Reviews
Writing a Review of Literature
Scientific Reports
Scientific Report Format
Sample Lab Assignment
Writing for the Web
Writing an Effective Blog Post
Writing for Social Media: A Guide for Academics
Home / Guides / Writing Guides / Paper Types / How to Write a Research Paper
How to Write a Research Paper
Research papers are a requirement for most college courses, so knowing how to write a research paper is important. These in-depth pieces of academic writing can seem pretty daunting, but there’s no need to panic. When broken down into its key components, writing your paper should be a manageable and, dare we say it, enjoyable task.
We’re going to look at the required elements of a paper in detail, and you might also find this webpage to be a useful reference .
Guide Overview
- What is a research paper?
- How to start a research paper
- Get clear instructions
- Brainstorm ideas
- Choose a topic
- Outline your outline
- Make friends with your librarian
- Find quality sources
- Understand your topic
- A detailed outline
- Keep it factual
- Finalize your thesis statement
- Think about format
- Cite, cite and cite
- The editing process
- Final checks
What is a Research Paper?
A research paper is more than just an extra long essay or encyclopedic regurgitation of facts and figures. The aim of this task is to combine in-depth study of a particular topic with critical thinking and evaluation by the student—that’s you!
There are two main types of research paper: argumentative and analytical.
Argumentative — takes a stance on a particular topic right from the start, with the aim of persuading the reader of the validity of the argument. These are best suited to topics that are debatable or controversial.
Analytical — takes no firm stance on a topic initially. Instead it asks a question and should come to an answer through the evaluation of source material. As its name suggests, the aim is to analyze the source material and offer a fresh perspective on the results.
If you wish to further your understanding, you can learn more here .
A required word count (think thousands!) can make writing that paper seem like an insurmountable task. Don’t worry! Our step-by-step guide will help you write that killer paper with confidence.
How to Start a Research Paper
Don’t rush ahead. Taking care during the planning and preparation stage will save time and hassle later.
Get Clear Instructions
Your lecturer or professor is your biggest ally—after all, they want you to do well. Make sure you get clear guidance from them on both the required format and preferred topics. In some cases, your tutor will assign a topic, or give you a set list to choose from. Often, however, you’ll be expected to select a suitable topic for yourself.
Having a research paper example to look at can also be useful for first-timers, so ask your tutor to supply you with one.
Brainstorm Ideas
Brainstorming research paper ideas is the first step to selecting a topic—and there are various methods you can use to brainstorm, including clustering (also known as mind mapping). Think about the research paper topics that interest you, and identify topics you have a strong opinion on.
Choose a Topic
Once you have a list of potential research paper topics, narrow them down by considering your academic strengths and ‘gaps in the market,’ e.g., don’t choose a common topic that’s been written about many times before. While you want your topic to be fresh and interesting, you also need to ensure there’s enough material available for you to work with. Similarly, while you shouldn’t go for easy research paper topics just for the sake of giving yourself less work, you do need to choose a topic that you feel confident you can do justice to.
Outline Your Outline
It might not be possible to form a full research paper outline until you’ve done some information gathering, but you can think about your overall aim; basically what you want to show and how you’re going to show it. Now’s also a good time to consider your thesis statement, although this might change as you delve into your source material deeper.
Researching the Research
Now it’s time to knuckle down and dig out all the information that’s relevant to your topic. Here are some tips.
Make Friends With Your Librarian
While lots of information gathering can be carried out online from anywhere, there’s still a place for old-fashioned study sessions in the library. A good librarian can help you to locate sources quickly and easily, and might even make suggestions that you hadn’t thought of. They’re great at helping you study and research, but probably can’t save you the best desk by the window.
Find Quality Sources
Not all sources are created equal, so make sure that you’re referring to reputable, reliable information. Examples of sources could include books, magazine articles, scholarly articles, reputable websites, databases and journals. Keywords relating to your topic can help you in your search.
As you search, you should begin to compile a list of references. This will make it much easier later when you are ready to build your paper’s bibliography. Keeping clear notes detailing any sources that you use will help you to avoid accidentally plagiarizing someone else’s work or ideas.
Understand Your Topic
Simply regurgitating facts and figures won’t make for an interesting paper. It’s essential that you fully understand your topic so you can come across as an authority on the subject and present your own ideas on it. You should read around your topic as widely as you can, before narrowing your area of interest for your paper, and critically analyzing your findings.
A Detailed Outline
Once you’ve got a firm grip on your subject and the source material available to you, formulate a detailed outline, including your thesis statement and how you are going to support it. The structure of your paper will depend on the subject type—ask a tutor for a research paper outline example if you’re unsure.
Get Writing!
If you’ve fully understood your topic and gathered quality source materials, bringing it all together should actually be the easy part!
Keep it Factual
There’s no place for sloppy writing in this kind of academic task, so keep your language simple and clear, and your points critical and succinct. The creative part is finding innovative angles and new insights on the topic to make your paper interesting.
Don’t forget about our verb , preposition , and adverb pages. You may find useful information to help with your writing!
Finalize Your Thesis Statement
You should now be in a position to finalize your thesis statement, showing clearly what your paper will show, answer or prove. This should usually be a one or two sentence statement; however, it’s the core idea of your paper, and every insight that you include should be relevant to it. Remember, a thesis statement is not merely a summary of your findings. It should present an argument or perspective that the rest of your paper aims to support.
Think About Format
The required style of your research paper format will usually depend on your subject area. For example, APA format is normally used for social science subjects, while MLA style is most commonly used for liberal arts and humanities. Still, there are thousands of more styles . Your tutor should be able to give you clear guidance on how to format your paper, how to structure it, and what elements it should include. Make sure that you follow their instruction. If possible, ask to see a sample research paper in the required format.
Cite, Cite and Cite
As all research paper topics invariably involve referring to other people’s work, it’s vital that you know how to properly cite your sources to avoid unintentional plagiarism. Whether you’re paraphrasing (putting someone else’s ideas into your own words) or directly quoting, the original source needs to be referenced. What style of citation formatting you use will depend on the requirements of your instructor, with common styles including APA and MLA format , which consist of in-text citations (short citations within the text, enclosed with parentheses) and a reference/works cited list.
The Editing Process
It’s likely that your paper will go through several drafts before you arrive at the very best version. The editing process is your chance to fix any weak points in your paper before submission. You might find that it needs a better balance of both primary and secondary sources (click through to find more info on the difference), that an adjective could use tweaking, or that you’ve included sources that aren’t relevant or credible. You might even feel that you need to be clearer in your argument, more thorough in your critical analysis, or more balanced in your evaluation.
From a stylistic point of view, you want to ensure that your writing is clear, simple and concise, with no long, rambling sentences or paragraphs. Keeping within the required word count parameters is also important, and another thing to keep in mind is the inclusion of gender-neutral language, to avoid the reinforcement of tired stereotypes.
Don’t forget about our other pages! If you are looking for help with other grammar-related topics, check out our noun , pronoun , and conjunction pages.
Final Checks
Once you’re happy with the depth and balance of the arguments and points presented, you can turn your attention to the finer details, such as formatting, spelling, punctuation, grammar and ensuring that your citations are all present and correct. The EasyBib Plus plagiarism checker is a handy tool for making sure that your sources are all cited. An EasyBib Plus subscription also comes with access to citation tools that can help you create citations in your choice of format.
Also, double-check your deadline date and the submissions guidelines to avoid any last-minute issues. Take a peek at our other grammar pages while you’re at it. We’ve included numerous links on this page, but we also have an interjection page and determiner page.
So you’ve done your final checks and handed in your paper according to the submissions guidelines and preferably before deadline day. Congratulations! If your schedule permits, now would be a great time to take a break from your studies. Maybe plan a fun activity with friends or just take the opportunity to rest and relax. A well-earned break from the books will ensure that you return to class refreshed and ready for your next stage of learning—and the next research paper requirement your tutor sets!
EasyBib Writing Resources
Writing a paper.
- Academic Essay
- Argumentative Essay
- College Admissions Essay
- Expository Essay
- Persuasive Essay
- Research Paper
- Thesis Statement
- Writing a Conclusion
- Writing an Introduction
- Writing an Outline
- Writing a Summary
EasyBib Plus Features
- Citation Generator
- Essay Checker
- Expert Check Proofreader
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tools
Plagiarism Checker
- Spell Checker
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Grammar and Plagiarism Checkers
Grammar Basics
Plagiarism Basics
Writing Basics
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
Summer 2024 Admissions for 1-on-1 Research Mentorship is OPEN. Watch information session recording here (featuring former and current Admission Officers at Havard and UPenn).
How to Write a Research Paper

Undergrads often write research papers each semester, causing stress. Yet, it’s simpler than believing if you know how to write a research paper . Divide the task, get tips, a plan, and tools for an outstanding paper. Simplify research, writing, topic choice, and illustration use!
A research paper is an academic document that involves deep, independent research to offer analysis, interpretation, and argument. Unlike academic essays, research papers are lengthier and more detailed, aiming to evaluate your writing and scholarly research abilities. To write one, you must showcase expertise in your subject, interact with diverse sources, and provide a unique perspective to the discussion.
Research papers are a foundational element of contemporary science and the most efficient means of disseminating knowledge throughout a broad network. Nonetheless, individuals usually encounter research papers during their education; they are frequently employed in college courses to assess a student’s grasp of a specific field or their aptitude for research.
Given their significance, research papers adopt a research paper format – a formal, unadorned style that eliminates any subjective influence from the writing. Scientists present their discoveries straightforwardly, accompanied by relevant supporting proof, enabling other researchers to integrate the paper into their investigations.
This guide leads you through every steps to write a research paper , from grasping your task to refining your ultimate draft and will teach you how to write a research paper.
Understanding The Research Paper
A research paper is a meticulously structured document that showcases the outcomes of an inquiry, exploration, or scrutiny undertaken on a specific subject. It embodies a formal piece of academic prose that adds novel information, perspectives, or interpretations to a particular domain of study. Typically authored by scholars, researchers, scientists, or students as part of their academic or professional pursuits, these papers adhere to a well-defined format. This research paper format encompasses an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion.
The introduction provides context and outlines the study’s significance, while the literature review encapsulates existing research and situates the study within the broader academic discourse. The methodology section elucidates the research process, encompassing data collection and analysis techniques. Findings are presented in the results section, often complemented by graphical and statistical representations. Interpretation of findings, implications, and connection to existing knowledge transpire in the discussion section.
Ultimately, the conclusion encapsulates pivotal discoveries and their wider import.
Research papers wield immense significance in advancing knowledge across diverse disciplines, enabling researchers to disseminate findings, theories, and revelations to a broader audience. Before publication in academic journals or presentations at conferences, these papers undergo a stringent peer review process conducted by domain experts, ensuring their integrity, precision, and worth.
Academic and non-academic research papers diverge across several dimensions. Academic papers are crafted for scholarly circles to expand domain knowledge and theories. They maintain a formal, objective tone and heavily rely on peer-reviewed sources for credibility. In contrast, non-academic papers, employing a more flexible writing style, target a broader audience or specific practical goals. These papers might incorporate persuasive language, anecdotes, and various sources beyond academia. While academic papers rigorously adhere to structured formats and established citation styles, non-academic papers prioritize practicality, adapting their structure and citation methods to suit the intended readership.
The purpose of a research paper revolves around offering fresh insights, knowledge, or interpretations within a specific field. This formal document serves as a conduit for scholars, researchers, scientists, and students to communicate their investigative findings and actively contribute to the ongoing academic discourse.

Research Paper Writing Process – How To Write a Good Research Paper
Selecting a suitable research topic .
Your initial task is to thoroughly review the assignment and carefully absorb the writing prompt’s details. Pay particular attention to technical specifications like length, formatting prerequisites (such as single- vs. double-spacing, indentation, etc.), and the required citation style. Also, pay attention to specifics, including an abstract or a cover page.
Once you’ve a clear understanding of the assignment, the subsequent steps to write a research paper are aligned with the conventional writing process. However, remember that research papers have rules, adding some extra considerations to the process.
When given some assignment freedom, the crucial task of choosing a topic rests on you. Despite its apparent simplicity, this choice sets the foundation for your entire research paper, shaping its direction. The primary factor in picking a research paper topic is ensuring it has enough material to support it. Your chosen topic should provide ample data and complexity for a thorough discussion. However, it’s important to avoid overly broad subjects and focus on specific ones that cover all relevant information without gaps. Yet, approach topic selection more slowly; choosing something that genuinely interests you is still valuable. Aim for a topic that meets both criteria—delivering substantial content while maintaining engagement.
Conducting Thorough Research
Commence by delving into your research early to refine your topic and shape your thesis statement. Swift engagement with available research aids in dispelling misconceptions and unveils optimal paths and strategies to gather more material. Typically, research sources can be located either online or within libraries. When navigating online sources, exercise caution and opt for reputable outlets such as scientific journals or academic papers. Specific search engines, outlined below in the Tools and Resources section, exclusively enable exploring accredited sources and academic databases.
While pursuing information, it’s essential to differentiate between primary and secondary sources. Primary sources entail firsthand accounts, encompassing published articles or autobiographies, while secondary sources, such as critical reviews or secondary biographies, are more distanced. Skimming sources instead of reading each part proves more efficient during the research phase. If a source shows promise, set it aside for more in-depth reading later. Doing so prevents you from investing excessive time in sources that won’t contribute substantively to your work. You should present a literature review detailing your references and submit them for validation in certain instances.
Organizing And Structuring The Research Paper
According to the research paper format , an outline for a research paper is a catalogue of essential topics, arguments, and evidence you intend to incorporate. These elements are divided into sections with headings, offering a preliminary overview of the paper’s structure before commencing the writing process. Formulating a structural outline can significantly enhance writing efficiency, warranting an investment of time to establish one.
Start by generating a list encompassing crucial categories and subtopics—a preliminary outline. Reflect on the amassed information while gathering supporting evidence, pondering the most effective means of segregation and categorization.
Once a discussion list is compiled, deliberate on the optimal information presentation sequence and identify related subtopics that should be placed adjacent. Consider if any subtopic loses coherence when presented out of order. Adopting a chronological arrangement can be suitable if the information follows a straightforward trajectory.
Given the potential complexity of research papers, consider breaking down the outline into paragraphs. This aids in maintaining organization when dealing with copious information and provides better control over the paper’s progression. Rectifying structural issues during the outline phase is preferable to addressing them after writing.
Remember to incorporate supporting evidence within the outline. Since there’s likely a substantial amount to include, outlining helps prevent overlooking crucial elements.
Writing The Introduction
According to the research paper format , the introduction of a research paper must address three fundamental inquiries: What, why, and how? Upon completing the introduction, the reader should clearly understand the paper’s subject matter, its relevance, and the approach you’ll use to construct your arguments.
What? Offer precise details regarding the paper’s topic, provide context, and elucidate essential terminology or concepts.
Why? This constitutes the most crucial yet challenging aspect of the introduction. Endeavour to furnish concise responses to the subsequent queries: What novel information or insights do you present? Which significant matters does your essay assist in defining or resolving?
How? To provide the reader with a preview of the paper’s forthcoming content, the introduction should incorporate a “guide” outlining the upcoming discussions. This entails briefly outlining the paper’s principal components in chronological sequence.

Developing The Main Body
One of the primary challenges that many writers grapple with is effectively organizing the wealth of information they wish to present in their papers. This is precisely why an outline can be an invaluable tool. However, it’s essential to recognize that while an outline provides a roadmap, the writing process allows flexibility in determining the order in which information and arguments are introduced.
Maintaining cohesiveness throughout the paper involves anchoring your writing to the thesis statement and topic sentences. Here’s how to ensure a well-structured paper:
- Alignment with Thesis Statement: Regularly assess whether your topic sentences correspond with the central thesis statement. This ensures that your arguments remain on track and directly contribute to the overarching message you intend to convey.
- Consistency and Logical Flow: Review your topic sentences concerning one another. Do they follow a logical order that guides the reader through a coherent narrative? Ensuring a seamless flow from one topic to another helps maintain engagement and comprehension.
- Supporting Sentence Alignment: Each sentence within a paragraph should align with the topic sentence of that paragraph. This alignment reinforces the central idea, preventing tangential or disjointed discussions.
Additionally, identify paragraphs that cover similar content. While some overlap might be inevitable, it’s essential to approach shared topics from different angles, offering fresh insights and perspectives. Creating these nuanced differences helps present a well-rounded exploration of the subject matter.
An often-overlooked aspect of effective organization is the art of crafting smooth transitions. Transitions between sentences, paragraphs, and larger sections are the glue that holds your paper together. They guide the reader through the progression of ideas, enhancing clarity and creating a seamless reading experience.
Ultimately, while the struggle to organize information is accurate, employing these strategies not only aids in addressing the challenge but also contributes to the overall quality and impact of your writing.
Crafting A Strong Conclusion
The purpose of the research paper’s conclusion is to guide your reader out of the realm of the paper’s argument, leaving them with a sense of closure.
Trace the paper’s trajectory, underscoring how all the elements converge to validate your thesis statement. Impart a sense of completion by ensuring the reader comprehends the resolution of the issues introduced in the paper’s introduction.
In addition, you can explore the broader implications of your argument, outline your paper’s contributions to future students studying the subject, and propose questions that your argument raises—ones that might not be addressed in the paper itself. However, it’s important to avoid:
- Introducing new arguments or crucial information that wasn’t covered earlier.
- Extending the conclusion unnecessarily.
- Employing common phrases that signal the decision (e.g., “In conclusion”).
By adhering to these guidelines, your conclusion can serve as a fitting and impactful conclusion to your research paper, leaving a lasting impression on your readers.
Refining The Research Paper
- Editing And Proofreading
Eliminate unnecessary verbiage and extraneous content. In tandem with the comprehensive structure of your paper, focus on individual words, ensuring your language is robust. Verify the utilization of active voice rather than passive voice, and confirm that your word selection is precise and tangible.
The passive voice, exemplified by phrases like “I opened the door,” tends to convey hesitation and verbosity. In contrast, the active voice, as in “I opened the door,” imparts strength and brevity.
Each word employed in your paper should serve a distinct purpose. Strive to eschew the inclusion of surplus words solely to occupy space or exhibit sophistication.
For instance, the statement “The author uses pathos to appeal to readers’ emotions” is superior to the alternative “The author utilizes pathos to appeal to the emotional core of those who read the passage.”
Engage in thorough proofreading to rectify spelling, grammatical, and formatting inconsistencies. Once you’ve refined the structure and content of your paper, address any typographical and grammatical inaccuracies. Taking a break from your paper before proofreading can offer a new perspective.
Enhance error detection by reading your essay aloud. This not only aids in identifying mistakes but also assists in evaluating the flow. If you encounter sections that seem awkward during this reading, consider making necessary adjustments to enhance the overall coherence.
- Formatting And Referencing
Citations are pivotal in distinguishing research papers from informal nonfiction pieces like personal essays. They serve the dual purpose of substantiating your data and establishing a connection between your research paper and the broader scientific community. Given their significance, citations are subject to precise formatting regulations; however, the challenge lies in the existence of multiple sets of rules.
It’s crucial to consult the assignment’s instructions to determine the required formatting style. Generally, academic research papers adhere to either of two formatting styles for source citations:
- MLA (Modern Language Association)
- APA (American Psychological Association)
Moreover, aside from MLA and APA styles, occasional demands might call for adherence to CMOS (The Chicago Manual of Style), AMA (American Medical Association), and IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) formats.
Initially, citations might appear intricate due to their numerous regulations and specific details. However, once you become adept at them, citing sources accurately becomes almost second nature. It’s important to note that each formatting style provides detailed guidelines for citing various sources, including photographs, websites, speeches, and YouTube videos.

Tips For Writing An Effective Research Paper
By following these research paper writing tips , you’ll be well-equipped to create a well-structured, well-researched, and impactful research paper:
- Select a Clear and Manageable Topic: Choose a topic that is specific and focused enough to be thoroughly explored within the scope of your paper.
- Conduct In-Depth Research: Gather information from reputable sources such as academic journals, books, and credible websites. Take thorough notes to keep track of your sources.
- Create a Strong Thesis Statement: Craft a clear and concise thesis statement that outlines the main argument or purpose of your paper.
- Develop a Well-Structured Outline: Organize your ideas into a logical order by creating an outline that outlines the main sections and their supporting points.
- Compose a Captivating Introduction: Hook the reader with an engaging introduction that provides background information and introduces the thesis statement.
- Provide Clear and Relevant Evidence: Support your arguments with reliable and relevant evidence, such as statistics, examples, and expert opinions.
- Maintain Consistent Tone and Style: Keep a consistent tone and writing style throughout the paper, adhering to the formatting guidelines of your chosen citation style.
- Craft Coherent Paragraphs: Each paragraph should focus on a single idea or point, and transitions should smoothly guide the reader from one idea to the next.
- Use Active Voice: Write in the active voice to make your writing more direct and engaging.
- Revise and Edit Thoroughly: Proofread your paper for grammatical errors, spelling mistakes, and sentence structure. Revise for clarity and coherence.
- Seek Peer Feedback: Have a peer or instructor review your paper for feedback and suggestions.
- Cite Sources Properly: Accurately cite all sources using the required citation style (e.g., MLA, APA) to avoid plagiarism and give credit to original authors.
- Be Concise and Avoid Redundancy: Strive for clarity by eliminating unnecessary words and redundancies.
- Conclude Effectively: Summarize your main points and restate your thesis in the conclusion. Provide a sense of closure without introducing new ideas.
- Stay Organized: Keep track of your sources, notes, and drafts to ensure a structured and organized approach to the writing process.
- Proofread with Fresh Eyes: Take a break before final proofreading to review your paper with a fresh perspective, helping you catch any overlooked errors.
- Edit for Clarity: Ensure that your ideas are conveyed clearly and that your arguments are easy to follow.
- Ask for Feedback: Don’t hesitate to ask for feedback from peers, instructors, or writing centers to improve your paper further.
In conclusion, we’ve explored the essential steps to write a research paper . From selecting a focused topic to mastering the intricacies of citations, we’ve navigated through the key elements of this process.
It’s vital to recognize that adhering to the research paper writing tips is not merely a suggestion, but a roadmap to success. Each stage contributes to the overall quality and impact of your paper. By meticulously following these steps, you ensure a robust foundation for your research, bolster your arguments, and present your findings with clarity and conviction.
As you embark on your own research paper journey, I urge you to put into practice the techniques and insights shared in this guide. Don’t shy away from investing time in organization, thorough research, and precise writing. Embrace the challenge, for it’s through this process that your ideas take shape and your voice is heard within the academic discourse.
Remember, every exceptional research paper begins with a single step. And with each step you take, your ability to articulate complex ideas and contribute to your field of study grows. So, go ahead – apply these tips, refine your skills, and witness your research papers evolve into compelling narratives that inspire, inform, and captivate.
In the grand tapestry of academia, your research paper becomes a thread of insight, woven into the larger narrative of human knowledge. By embracing the writing process and nurturing your unique perspective, you become an integral part of this ever-expanding tapestry.
Happy writing, and may your research papers shine brightly, leaving a lasting mark on both your readers and the world of scholarship.
Related Posts

How To Write Enduring Issues Essay
Our Exceptional Alumni: College Admission Results 2020-2023
The ccir minerva scholarship opens doors to exceptional student researchers worldwide.

High School Student Researcher Claudia on Viewing the Musical Theatre Industry in China

High School Student Researcher Rithwik’s Paper on Multi-Class Anomaly Detection for Astronomical Transients Accepted at 243rd Meeting of the American Astronomical Society

Steps To Write A Great Research Paper
Download Programme Prospectus
- Programme structure
- Research course catalogue
- Professor biographies
- Tuition and Scholarship
Start Your Application
Cambridge Future Scholar (Fall 24)
Pre-Application is OPEN.
Rolling Admissions.
1-on-1 Research Mentorship Admission is open all year.

How to Write a Research Paper: Your Top Guide

A research paper is a comprehensive document presenting the findings, analysis, and interpretation of an original study or investigation.
It typically follows a structured format, including an introduction outlining the research question or problem, a review of relevant literature, methodology detailing the approach used to collect and analyze data, results presenting the findings of the study, discussion interpreting the results in the context of existing knowledge, and a conclusion summarizing the implications and potential future directions of the research.
Research papers contribute new knowledge to a specific field, undergo rigorous peer review, and are often published in academic journals to disseminate findings to the broader scholarly community. Below, you will find effective steps you should take to learn how to write an effective research paper.

How Long Should a Research Paper Be
A research paper typically ranges from 6,000 to 8,000 words , equivalent to approximately 15 to 20 pages , double-spaced. However, the specific length can vary depending on factors such as the academic discipline, journal requirements, and the topic's complexity. It's vital to follow the research paper guidelines the instructor or publisher provides to ensure the paper meets the required length and format.
Feeling Like a Detective with Zero Clues for Your Research Paper?
Well, order our research paper service , and let us be your Watson to brilliance!
Sample Research Paper
Before we dive into the specifics of writing a research paper, let’s explore some of its main components and how the information is structured.
How to Write a Research Paper: A Step-by-Step Guide
With the following guidelines, you can quickly produce a strong research paper without spending too much time on technicalities.
.webp)
Understand the Research Paper Types
Research papers come in various types, each serving different purposes and methodologies. Here's a breakdown:
| 📄 Paper Type | 📝 Description |
|---|---|
| Original Papers | Report new findings. |
| Review Papers | Summarize existing research. |
| Meta-analysis Papers | Analyze data from multiple studies. |
| Perspective Papers | Present unique viewpoints. |
| Case Studies | Analyze specific cases. |
| Conceptual Papers | Discuss theoretical frameworks. |
| Short Communications | Brief reports on significant findings. |
| Methodological Papers | Introduce new research methods. |
| Commentaries | Offer critical analysis of existing research. |
Depending on the type of research paper, you will have to carefully read the assignment and understand how it correlates with your assignment.
Choose a Topic
A good topic for a research paper involves several considerations. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you:
- Follow Your Passion: Choose a topic that genuinely interests you.
- Check Relevance: Ensure your topic is relevant to your field or area of study.
- Narrow Your Focus: Specify a clear research question or problem.
- Review Existing Literature: To refine your focus, see what's already been studied.
- Assess Feasibility: Ascertain you have the resources and time to research the topic.
- Seek Feedback: Discuss your ideas with peers or mentors.
- Consider Impact: Think about how your research can contribute to knowledge or practice.
- Stay Flexible: Be open to refining your topic as you learn more.
Conduct Preliminary Research
When you’re writing a research paper, preliminary research involves exploring existing literature to understand the landscape of your topic. Start by defining your broad area of interest and then delve into academic databases, journals, books, and credible websites to gather information. Identify key concepts, theories, and recent studies related to your topic.
Evaluate the credibility and relevance of the sources you find and take notes on important findings. Use this information to identify potential research questions or hypotheses and refine your topic to focus on a specific aspect that interests you and aligns with the existing literature.
During the preliminary research stage, it's important to ask questions that help guide your exploration and understanding of the topic. Here are some questions to consider:
- What is the current state of research on my topic?
- What are the key concepts, theories, and approaches in this area?
- Are there any recent developments or trends related to my topic?
- What gaps or unanswered questions exist in the literature?
- What methodologies and research techniques have been used in previous studies?
- What are the main arguments or perspectives on this topic?
- Are there any controversies or debates surrounding my topic?
- What are the practical implications or real-world applications of this research?
- How might my interests or expertise contribute to this field?
- Are there any interdisciplinary connections or related areas of study worth exploring?
Formulate a Thesis Statement
To formulate a thesis statement, start by identifying your research paper's main argument or central claim. This statement should provide a concise summary of the purpose and scope of your study. Here's a general formula for how to write a thesis for a research paper:
- Identify the Topic: Start by clearly stating the topic or subject of your research paper.
- State Your Position: Express your perspective or stance on the topic. What is the main argument you will be making?
- Preview Your Main Points: Provide a brief overview of the key points or arguments that will support your thesis.
Here's an example:
"Despite the proliferation of stress management techniques in modern society, there is a growing need for research that evaluates the effectiveness of mindfulness-based interventions in reducing workplace stress. This paper argues that mindfulness practices, when integrated into organizational settings, can significantly improve employee well-being, productivity, and job satisfaction. By analyzing recent studies and case examples, this research will demonstrate the potential benefits of mindfulness interventions for addressing workplace stress and offer recommendations for implementation."
This thesis statement clearly identifies the topic (mindfulness-based interventions for workplace stress), states the position (advocating for their effectiveness), and previews the main points (benefits and recommendations). Overall, a thesis is the first thing you have to consider if you want to learn how to start a research paper.
Gather and Evaluate Sources
Gathering and evaluating sources for a research paper involves several steps to ensure that you use credible, relevant, and reliable information.
- Use Keywords: Start with relevant keywords for your topic.
- Utilize Academic Databases: Search in databases like PubMed, JSTOR, or Google Scholar.
- Check Library Catalogs: Look for books and journals in your library.
- Evaluate Credibility : Consider author credentials, publication date, and source reputation.
- Review Abstracts: Check abstracts to see if the source is relevant.
- Skim for Key Information: Quickly scan for main arguments and findings.
- Check Citations: Look for references to other relevant works.
- Consider Bias: Be aware of potential bias or conflicts of interest.
- Take Notes: Keep track of sources for accurate citations.
Create a Research Paper Outline
A research paper outline is a structured plan that serves as a roadmap for your writing process. It organizes your ideas, arguments, and supporting evidence into a coherent and logical framework. Here's how to write a research paper outline:
- Choose a formatting style.
- Identify main sections.
- Break down sections into subsections.
- Provide supporting details.
- Arrange points logically.
Research Paper Outline Structure
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| Title Page | Include the title of your paper, your name, the course name, instructor's name, and the date. |
| Abstract (optional) | Summarize the key points of your paper, including the research question, methods, results, and conclusions. |
| Introduction | Introduce the topic, provides background information, and states the research question or thesis statement. |
| Literature Review | Survey existing research and literature relevant to your topic, highlighting key findings, theories, and methodologies. |
| Methodology | Describe the methods and techniques used to conduct your research, including data collection and analysis procedures. |
| Results | Present your research findings, often using tables, graphs, or figures to illustrate key findings. |
| Discussion | Analyze and interpret the results, discussing their implications and relevance to the research question or hypothesis. |
| Conclusion | Summarize the study's main findings, restate the thesis statement, and discuss the broader implications of the research. |
| References | List all the sources cited in your paper, formatted according to the style guidelines (e.g., APA, MLA). |
| Appendices (if necessary) | Include any additional materials or data relevant to your study but not essential for understanding the main text. |
Collect and Analyze Supporting Data
Before writing a research paper, you have to determine the type of data needed for your research, whether qualitative (such as interviews or observations) or quantitative (such as surveys or experiments).
Then, design data collection methods that align with your research objectives, ensuring they are reliable and valid. Implement these methods to gather the necessary data, ensuring proper documentation and ethical considerations. Once data is collected, organize and prepare it for analysis, which may involve coding qualitative data or entering quantitative data into statistical software.
Analyze the data using appropriate techniques, such as thematic analysis for qualitative data or statistical tests for quantitative data, to identify patterns, trends, and relationships.
For all kinds of research papers, always interpret the results in the context of your research question and draw conclusions based on them, ensuring that they support your research objectives and contribute to a broader understanding of the topic.
Write a Research Paper Introduction
The research paper introduction is crucial as it sets the stage, contextualizes the study, and engages readers by outlining the significance, research question, and objectives.
Here's a step-by-step guide on how to write an effective introduction:
- Contextualize the Topic: Introduce the research topic and briefly explain its significance in the field or its relevance to current issues.
- State the Research Question: Clearly articulate the thesis for research paper your paper addresses.
- Highlight Research Gap: Briefly mention any gaps or limitations in current literature that your study aims to address.
- Outline Objectives: Describe the objectives or goals of your research and what you aim to achieve.
- Preview Structure: Provide a brief overview of the paper's organization to guide the reader through its content.
Write Every Research Paper Body Paragraph
The main body of a research paper involves presenting and supporting your arguments, analyzing data, and discussing findings.
Organize Your Content
Plan the structure of your main body based on the outline you created earlier. Each main section should correspond to a key point or argument that supports your thesis statement.
Start with a Topic Sentence
Begin each paragraph with a topic sentence that introduces the main point or argument you will discuss in that paragraph.

Provide Evidence and Analysis
Support your arguments with evidence from credible sources, such as research studies, data, statistics, or expert opinions. Analyze and interpret the evidence to demonstrate its relevance to your thesis statement and research question.
Use Clear and Logical Transitions
Ensure smooth transitions between paragraphs and sections to maintain coherence and flow. Use transition words and phrases to guide readers through your argumentation.
Consider Counterarguments
Acknowledge and address potential counterarguments or alternative perspectives related to your topic. This demonstrates critical thinking and strengthens your argument by showing that you have considered different viewpoints.
Use Visual Aids (if applicable)
If you have data or information that can be better presented visually, consider including tables, graphs, or charts to enhance clarity and understanding.
Maintain Objectivity and Clarity
Write clearly, concisely, and objectively, avoiding bias or subjective language. Present your arguments logically and systematically, ensuring that each point contributes to the overall coherence of your paper.
Summarize and Synthesize
Summarize key findings or arguments at the end of each section or paragraph. Synthesize information from different sources or perspectives to understand the topic comprehensively.
Conclude Each Section Thoughtfully
Conclude all parts of research paper that go in the main body with a brief summary or transition that connects back to your thesis statement and previews the next section.
How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper
A conclusion for a research paper must summarize key findings, reiterate the study's significance, and suggest avenues for future research. In the conclusion section, it is crucial to use words and phrases such as "in summary," "overall," "conclusively," "implications," "future research," and "contributions to the field."
Here are three examples of a research paper conclusion:
- “To sum up, this study provides valuable insights into the impact of climate change on global biodiversity, highlighting the urgent need for conservation efforts to mitigate its effects. Overall, our findings underscore the importance of implementing adaptive management strategies to safeguard ecosystems and enhance resilience in environmental change. Conclusively, this research contributes to the growing body of literature on climate change ecology and provides a foundation for future research aimed at addressing this critical global challenge.”
- “In conclusion, this study's results demonstrate the effectiveness of mindfulness-based interventions in reducing workplace stress and improving employee well-being. Our findings suggest that integrating mindfulness practices into organizational settings can significantly improve productivity, job satisfaction, and overall workplace functioning. Moving forward, further research is needed to explore the long-term effects of mindfulness interventions and identify best practices for implementation in diverse workplace environments.”
- “In summary, this research paper has investigated the relationship between social media usage and adolescent mental health outcomes, revealing both positive and negative effects. Overall, our findings suggest that while social media can provide valuable social support and connectivity, excessive use may also contribute to feelings of loneliness and depression. Looking ahead, it is essential for policymakers, educators, and parents to work collaboratively to promote healthy social media habits and provide support for adolescents navigating the digital landscape.”
Cite Sources
Sources in a research paper are essential for acknowledging the ideas and work of others and avoiding plagiarism.
Choose a Citation Style
Determine which citation style you'll use for your paper, such as APA, MLA, Chicago, or others. Each style has a specific research paper format, so it's essential to use the appropriate style for your discipline or your assignment's requirements.
In-text Citations
Within the body of your paper, provide in-text citations to acknowledge the sources of your information. Include the author's last name and the publication year in parentheses at the end or within the sentence itself if the author's name is mentioned.
Create a Works Cited or References Page
At the end of your paper, include a separate page titled "Works Cited" (for MLA) or "References" (for APA and other styles). List all the sources you cited in your paper alphabetically by the author's last name.
Format Citations
Format each citation according to the guidelines of your chosen citation style. Pay attention to details such as punctuation, italics, and capitalization, as these can vary between styles.
Use Citation Tools
Consider using citation management tools such as Zotero, Mendeley, or EndNote to help you automatically organize and format your citations. These tools can save you time and ensure accuracy in your citations.
Check Citation Guides
Refer to citation guides and manuals provided by your institution, library, or online resources for specific examples and instructions on how to cite different types of sources (e.g., books, journal articles, and websites).
Proofread, Edit, and Revise
Proofreading, editing, and revising a research paper are crucial to ensure clarity, coherence, and accuracy. Here are effective tips on how to effectively polish the final draft of your paper:
- Step back after writing to refresh your perspective.
- Listen for awkward phrasing and errors by reading aloud.
- Ensure ideas flow logically and transitions are smooth.
- Confirm your paper follows a clear structure from start to finish.
- Double-check citations for accuracy and formatting.
- Correct any grammar, punctuation, or spelling mistakes.
- Add clarity and depth to key points as needed.
- Remove unnecessary repetition or wordiness.
- Get input from peers or instructors for fresh insights.
- Make necessary changes based on feedback and your observations.
- Do a final check for any lingering errors before submission.
Research Paper Writing Tips
Here are 6 in-depth tips that will bring your research paper writing prowess to the next level, which will be likely noticed by your teachers:
Formulate Hypotheses with Testable Predictions
Develop hypotheses that make specific, testable predictions about the relationships between variables in your research. Ensure hypotheses are grounded in theory and previous research, guiding your empirical investigation toward meaningful results and insights.
Design Robust Methodologies
Design your research methodologies with meticulous attention to detail, ensuring they are valid, reliable, and replicable. Select appropriate research designs, sampling techniques, and data collection methods that align with your research questions and objectives. Anticipate potential confounding variables and implement controls to mitigate their effects, enhancing the internal validity of your study.
Analyze Data Using Advanced Statistical Techniques
Employ advanced statistical techniques to analyze your data rigorously and uncover meaningful patterns or associations. To examine complex relationships among variables, utilize multivariate analyses, such as regression, factor analysis, or structural equation modeling. Interpret results critically, considering statistical and practical significance to draw robust conclusions.
Synthesize Findings with Theoretical Frameworks
Synthesize your empirical findings with relevant theoretical frameworks to generate novel insights and contribute to theoretical advancement within your field. Situate your research within broader theoretical debates and paradigms, identifying theoretical implications and avenues for future research.
Engage in Peer Review and Scholarly Dialogue
Seek opportunities to engage in peer review and scholarly dialogue to receive constructive feedback on your research and contribute to advancing knowledge. Submit your work to reputable academic journals, present at conferences, and participate in scholarly communities to receive critical appraisal and refine your ideas through intellectual exchange.
Communicate Results Effectively
Structure your paper following the IMRAD (Introduction, Methods, Results, and Discussion) format, adhering to the conventions of scientific writing. Present findings objectively, using empirical evidence to support your claims and acknowledge limitations transparently.
In conclusion, with these effective steps and techniques, you can confidently write a research paper. Dive into research, organize your thoughts, support your arguments, revise diligently, and embrace improvement. Let your ideas flow and create papers that make a meaningful impact in your field.
Tired of Trying to Crack the Code of a Perfect Research Paper?
Take control, grab your metaphorical sword, and order now! It's time to turn those sleepless nights into peaceful slumbers and make your professor go 'Wow!' in sheer awe!
When Will I Need to Write a Research Paper in College?
Where can i find ideas for research paper topics.

Daniel Parker
is a seasoned educational writer focusing on scholarship guidance, research papers, and various forms of academic essays including reflective and narrative essays. His expertise also extends to detailed case studies. A scholar with a background in English Literature and Education, Daniel’s work on EssayPro blog aims to support students in achieving academic excellence and securing scholarships. His hobbies include reading classic literature and participating in academic forums.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
- How to Start (and Complete) a Research Paper - TIP Sheet - Butte College. (n.d.). Copyright Butte College, All Rights Reserved. https://www.butte.edu/departments/cas/tipsheets/research/research_paper.html
- Developersid. (2021, April 7). How to Write a Research Paper - Enago Academy. Enago Academy. https://www.enago.com/academy/how-to-write-research-paper/
- Writing a Research Paper - Purdue OWL® - Purdue University. (n.d.). https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/common_writing_assignments/research_papers/
.webp)
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write a Research Essay
Last Updated: January 12, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Michelle Golden, PhD . Michelle Golden is an English teacher in Athens, Georgia. She received her MA in Language Arts Teacher Education in 2008 and received her PhD in English from Georgia State University in 2015. There are 11 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 386,203 times.
Research essays are extremely common assignments in high school, college, and graduate school, and are not unheard of in middle school. If you are a student, chances are you will sooner or later be faced with the task of researching a topic and writing a paper about it. Knowing how to efficiently and successfully do simple research, synthesize information, and clearly present it in essay form will save you many hours and a lot of frustration.
Researching a Topic

- Be sure to stay within the guidelines you are given by your teacher or professor. For example, if you are free to choose a topic but the general theme must fall under human biology, do not write your essay on plant photosynthesis.
- Stick with topics that are not overly complicated, especially if the subject is not something you plan to continue studying. There's no need to make things harder on yourself!

- Specialty books; these can be found at your local public or school library. A book published on your topic is a great resource and will likely be one of your most reliable options for finding quality information. They also contain lists of references where you can look for more information.
- Academic journals; these are periodicals devoted to scholarly research on a specific field of study. Articles in academic journals are written by experts in that field and scrutinized by other professionals to ensure their accuracy. These are great options if you need to find detailed, sophisticated information on your topic; avoid these if you are only writing a general overview.
- Online encyclopedias; the most reliable information on the internet can be found in online encyclopedias like Encyclopedia.com and Britannica.com. While online wikis can be very helpful, they sometimes contain unverified information that you should probably not rely upon as your primary resources.
- Expert interviews; if possible, interview an expert in the subject of your research. Experts can be professionals working in the field you are studying, professors with advanced degrees in the subject of interest, etc.

- Organize your notes by sub-topic to keep them orderly and so you can easily find references when you are writing.
- If you are using books or physical copies of magazines or journals, use sticky tabs to mark pages or paragraphs where you found useful information. You might even want to number these tabs to correspond with numbers on your note sheet for easy reference.
- By keeping your notes brief and simple, you can make them easier to understand and reference while writing. Don't make your notes so long and detailed that they essentially copy what's already written in your sources, as this won't be helpful to you.

- Sometimes the objective of your research will be obvious to you before you even begin researching the topic; other times, you may have to do a bit of reading before you can determine the direction you want your essay to take.
- If you have an objective in mind from the start, you can incorporate this into online searches about your topic in order to find the most relevant resources. For example, if your objective is to outline the environmental hazards of hydraulic fracturing practices, search for that exact phrase rather than just "hydraulic fracturing."

- Avoid asking your teacher to give you a topic. Unless your topic was assigned to you in the first place, part of the assignment is for you to choose a topic relevant to the broader theme of the class or unit. By asking your teacher to do this for you, you risk admitting laziness or incompetence.
- If you have a few topics in mind but are not sure how to develop objectives for some of them, your teacher can help with this. Plan to discuss your options with your teacher and come to a decision yourself rather than having him or her choose the topic for you from several options.
Organizing your Essay

- Consider what background information is necessary to contextualize your research topic. What questions might the reader have right out of the gate? How do you want the reader to think about the topic? Answering these kinds of questions can help you figure out how to set up your argument.
- Match your paper sections to the objective(s) of your writing. For example, if you are trying to present two sides of a debate, create a section for each and then divide them up according to the aspects of each argument you want to address.

- An outline can be as detailed or general as you want, so long as it helps you figure out how to construct the essay. Some people like to include a few sentences under each heading in their outline to create a sort of "mini-essay" before they begin writing. Others find that a simple ordered list of topics is sufficient. Do whatever works best for you.
- If you have time, write your outline a day or two before you start writing and come back to it several times. This will give you an opportunity to think about how the pieces of your essay will best fit together. Rearrange things in your outline as many times as you want until you have a structure you are happy with.

- Style guides tell you exactly how to quote passages, cite references, construct works cited sections, etc. If you are assigned a specific format, you must take care to adhere to guidelines for text formatting and citations.
- Some computer programs (such as EndNote) allow you to construct a library of resources which you can then set to a specific format type; then you can automatically insert in-text citations from your library and populate a references section at the end of the document. This is an easy way to make sure your citations match your assigned style format.

- You may wish to start by simply assigning yourself a certain number of pages per day. Divide the number of pages you are required to write by the number of days you have to finish the essay; this is the number of pages (minimum) that you must complete each day in order to pace yourself evenly.
- If possible, leave a buffer of at least one day between finishing your paper and the due date. This will allow you to review your finished product and edit it for errors. This will also help in case something comes up that slows your writing progress.
Writing your Essay

- Keep your introduction relatively short. For most papers, one or two paragraphs will suffice. For really long essays, you may need to expand this.
- Don't assume your reader already knows the basics of the topic unless it truly is a matter of common knowledge. For example, you probably don't need to explain in your introduction what biology is, but you should define less general terms such as "eukaryote" or "polypeptide chain."

- You may need to include a special section at the beginning of the essay body for background information on your topic. Alternatively, you can consider moving this to the introductory section, but only if your essay is short and only minimal background discussion is needed.
- This is the part of your paper where organization and structure are most important. Arrange sections within the body so that they flow logically and the reader is introduced to ideas and sub-topics before they are discussed further.
- Depending upon the length and detail of your paper, the end of the body might contain a discussion of findings. This kind of section serves to wrap up your main findings but does not explicitly state your conclusions (which should come in the final section of the essay).
- Avoid repetition in the essay body. Keep your writing concise, yet with sufficient detail to address your objective(s) or research question(s).

- Always use quotation marks when using exact quotes from another source. If someone already said or wrote the words you are using, you must quote them this way! Place your in-text citation at the end of the quote.
- To include someone else's ideas in your essay without directly quoting them, you can restate the information in your own words; this is called paraphrasing. Although this does not require quotation marks, it should still be accompanied by an in-text citation.

- Except for very long essays, keep your conclusion short and to the point. You should aim for one or two paragraphs, if possible.
- Conclusions should directly correspond to research discussed in the essay body. In other words, make sure your conclusions logically connect to the rest of your essay and provide explanations when necessary.
- If your topic is complex and involves lots of details, you should consider including a brief summary of the main points of your research in your conclusion.

- Making changes to the discussion and conclusion sections instead of the introduction often requires a less extensive rewrite. Doing this also prevents you from removing anything from the beginning of your essay that could accidentally make subsequent portions of your writing seem out of place.
- It is okay to revise your thesis once you've finished the first draft of your essay! People's views often change once they've done research on a topic. Just make sure you don't end up straying too far from your assigned topic if you do this.
- You don't necessarily need to wait until you've finished your entire draft to do this step. In fact, it is a good idea to revisit your thesis regularly as you write. This can save you a lot of time in the end by helping you keep your essay content on track.

- Computer software such as EndNote is available for making citation organization as easy and quick as possible. You can create a reference library and link it to your document, adding in-text citations as you write; the program creates a formatted works cited section at the end of your document.
- Be aware of the formatting requirements of your chosen style guide for works cited sections and in-text citations. Reference library programs like EndNote have hundreds of pre-loaded formats to choose from.

- Create a catchy title. Waiting until you have finished your essay before choosing a title ensures that it will closely match the content of your essay. Research papers don't always take on the shape we expect them to, and it's easier to match your title to your essay than vice-versa.
- Read through your paper to identify and rework sentences or paragraphs that are confusing or unclear. Each section of your paper should have a clear focus and purpose; if any of yours seem not to meet these expectations, either rewrite or discard them.
- Review your works cited section (at the end of your essay) to ensure that it conforms to the standards of your chosen or assigned style format. You should at least make sure that the style is consistent throughout this section.
- Run a spell checker on your entire document to catch any spelling or grammar mistakes you may not have noticed during your read-through. All modern word processing programs include this function.

- Note that revising your draft is not the same as proofreading it. Revisions are done to make sure the content and substantive ideas are solid; editing is done to check for spelling and grammar errors. Revisions are arguably a more important part of writing a good paper.
- You may want to have a friend, classmate, or family member read your first draft and give you feedback. This can be immensely helpful when trying to decide how to improve upon your first version of the essay.
- Except in extreme cases, avoid a complete rewrite of your first draft. This will most likely be counterproductive and will waste a lot of time. Your first draft is probably already pretty good -- it likely just needs some tweaking before it is ready to submit.
Community Q&A
- Avoid use of the word "I" in research essay writing, even when conveying your personal opinion about a subject. This makes your writing sound biased and narrow in scope. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Even if there is a minimum number of paragraphs, always do 3 or 4 more paragraphs more than needed, so you can always get a good grade. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

- Never plagiarize the work of others! Passing off others' writing as your own can land you in a lot of trouble and is usually grounds for failing an assignment or class. Thanks Helpful 12 Not Helpful 1
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/common_writing_assignments/research_papers/choosing_a_topic.html
- ↑ https://libguides.mit.edu/select-topic
- ↑ https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/research-objectives
- ↑ https://www.hunter.cuny.edu/rwc/handouts/the-writing-process-1/organization/Organizing-an-Essay
- ↑ https://www.lynchburg.edu/academics/writing-center/wilmer-writing-center-online-writing-lab/the-writing-process/organizing-your-paper/
- ↑ https://www.mla.org/MLA-Style
- ↑ http://www.apastyle.org/
- ↑ https://writing.wisc.edu/Handbook/PlanResearchPaper.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/apa6_style/apa_formatting_and_style_guide/in_text_citations_the_basics.html
- ↑ https://opentextbc.ca/writingforsuccess/chapter/chapter-12-peer-review-and-final-revisions/
- ↑ https://openoregon.pressbooks.pub/wrd/back-matter/creating-a-works-cited-page/
About This Article

The best way to write a research essay is to find sources, like specialty books, academic journals, and online encyclopedias, about your topic. Take notes as you research, and make sure you note which page and book you got your notes from. Create an outline for the paper that details your argument, various sections, and primary points for each section. Then, write an introduction, build the body of the essay, and state your conclusion. Cite your sources along the way, and follow the assigned format, like APA or MLA, if applicable. To learn more from our co-author with an English Ph.D. about how to choose a thesis statement for your research paper, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Nov 18, 2018
Did this article help you?

Jun 11, 2017
Christina Wonodi
Oct 12, 2016
Caroline Scott
Jan 28, 2017
Fhatuwani Musinyali
Mar 14, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter

4 Research Essay
Jeffrey Kessler
By the end of this chapter, you will be able to do the following:
- Construct a thesis based upon your research
- Use critical reading strategies to analyze your research
- Defend a position in relation to the range of ideas surrounding a topic
- Organize your research essay in order to logically support your thesis
I. Introduction
The goal of this book has been to help demystify research and inquiry through a series of genres that are part of the research process. Each of these writing projects—the annotated bibliography, proposal, literature review, and research essay—builds on each other. Research is an ongoing and evolving process, and each of these projects help you build towards the next.
In your annotated bibliography, you started your inquiry into a topic, reading widely to define the breadth of your inquiry. You recorded this by summarizing and/or evaluating the first sources you examined. In your proposal, you organized a plan and developed pointed questions to pursue and ideas to research. This provided a good sense of where you might continue to explore. In your literature review, you developed a sense of the larger conversations around your topic and assessed the state of existing research. During each of these writing projects, your knowledge of your topic grew, and you became much more informed about its key issues.
You’ve established a topic and assembled sources in conversation with one another. It’s now time to contribute to that conversation with your own voice. With so much of your research complete, you can now turn your focus to crafting a strong research essay with a clear thesis. Having the extensive knowledge that you have developed across the first three writing projects will allow you to think more about putting the pieces of your research together, rather than trying to do research at the same time that you are writing.
This doesn’t mean that you won’t need to do a little more research. Instead, you might need to focus strategically on one or two key pieces of information to advance your argument, rather than trying to learn about the basics of your topic.
But what about a thesis or argument? You may have developed a clear idea early in the process, or you might have slowly come across an important claim you want to defend or a critique you want to make as you read more into your topic. You might still not be sure what you want to argue. No matter where you are, this chapter will help you navigate the genre of the research essay. We’ll examine the basics of a good thesis and argument, different ways to use sources, and strategies to organize your essay.
While this chapter will focus on the kind of research essay you would write in the college classroom, the skills are broadly applicable. Research takes many different forms in the academic, professional, and public worlds. Depending on the course or discipline, research can mean a semester-long project for a class or a few years’ worth of research for an advanced degree. As you’ll see in the examples below, research can consist of a brief, two-page conclusion or a government report that spans hundreds of pages with an overwhelming amount of original data.
Above all else, good research is engaged with its audience to bring new ideas to light based on existing conversations. A good research essay uses the research of others to advance the conversation around the topic based on relevant facts, analysis, and ideas.
II. Rhetorical Considerations: Contributing to the Conversation
The word “essay” comes from the French word essayer , or “attempt.” In other words, an essay is an attempt—to prove or know or illustrate something. Through writing an essay, your ideas will evolve as you attempt to explore and think through complicated ideas. Some essays are more exploratory or creative, while some are straightforward reports about the kind of original research that happens in laboratories.
Most research essays attempt to argue a point about the material, information, and data that you have collected. That research can come from fieldwork, laboratories, archives, interviews, data mining, or just a lot of reading. No matter the sources you use, the thesis of a research essay is grounded in evidence that is compelling to the reader.
Where you described the conversation in your literature review, in your research essay you are contributing to that conversation with your own argument. Your argument doesn’t have to be an argument in the cable-news-social-media-shouting sense of the word. It doesn’t have to be something that immediately polarizes individuals or divides an issue into black or white. Instead, an argument for a research essay should be a claim, or, more specifically, a claim that requires evidence and analysis to support. This can take many different forms.
Example 4.1: Here are some different types of arguments you might see in a research essay:
- Critiquing a specific idea within a field
- Interrogating an assumption many people hold about an issue
- Examining the cause of an existing problem
- Identifying the effects of a proposed program, law, or concept
- Assessing a historical event in a new way
- Using a new method to evaluate a text or phenomenon
- Proposing a new solution to an existing problem
- Evaluating an existing solution and suggesting improvements
These are only a few examples of the kinds of approaches your argument might take. As you look at the research you have gathered throughout your projects, your ideas will have evolved. This is a natural part of the research process. If you had a fully formed argument before you did any research, then you probably didn’t have an argument based on strong evidence. Your research now informs your position and understanding, allowing you to form a stronger evidence-based argument.
Having a good idea about your thesis and your approach is an important step, but getting the general idea into specific words can be a challenge on its own. This is one of the most common challenges in writing: “I know what I want to say; I just don’t know how to say it.”
Example 4.2: Here are some sample thesis statements. Examine them and think about their arguments.
Whether you agree, disagree, or are just plain unsure about them, you can imagine that these statements require their authors to present evidence, offer context, and explain key details in order to argue their point.
- Artificial intelligence (AI) has the ability to greatly expand the methods and content of higher education, and though there are some transient shortcomings, faculty in STEM should embrace AI as a positive change to the system of student learning. In particular, AI can prove to close the achievement gap often found in larger lecture settings by providing more custom student support.
- I argue that while the current situation for undocumented college students remains tumultuous, there are multiple routes—through financial and social support programs like the Fearless Undocumented Alliance—that both universities and colleges can utilize to support students affected by the reality of DACA’s shortcomings.
While it can be argued that massive reform of the NCAA’s bylaws is needed in the long run, one possible immediate improvement exists in the form of student-athlete name, image, and likeness rights. The NCAA should amend their long-standing definition of amateurism and allow student athletes to pursue financial gains from the use of their names, images, and likenesses, as is the case with amateur Olympic athletes.
Each of these thesis statements identifies a critical conversation around a topic and establishes a position that needs evidence for further support. They each offer a lot to consider, and, as sentences, are constructed in different ways.
Some writing textbooks, like They Say, I Say (2017), offer convenient templates in which to fit your thesis. For example, it suggests a list of sentence constructions like “Although some critics argue X, I will argue Y” and “If we are right to assume X, then we must consider the consequences of Y.”
More Resources 4.1: Templates
Templates can be a productive start for your ideas, but depending on the writing situation (and depending on your audience), you may want to expand your thesis beyond a single sentence (like the examples above) or template. According to Amy Guptill in her book Writing in Col lege (2016) , a good thesis has four main elements (pp. 21-22). A good thesis:
- Makes a non-obvious claim
- Poses something arguable
- Provides well-specified details
- Includes broader implications
Consider the sample thesis statements above. Each one provides a claim that is both non-obvious and arguable. In other words, they present something that needs further evidence to support—that’s where all your research is going to come in. In addition, each thesis identifies specifics, whether these are teaching methods, support programs, or policies. As you will see, when you include those specifics in a thesis statement, they help project a starting point towards organizing your essay.
Finally, according to Guptill, a good thesis includes broader implications. A good thesis not only engages the specific details of its argument, but also leaves room for further consideration. As we have discussed before, research takes place in an ongoing conversation. Your well-developed essay and hard work won’t be the final word on this topic, but one of many contributions among other scholars and writers. It would be impossible to solve every single issue surrounding your topic, but a strong thesis helps us think about the larger picture. Here’s Guptill:
Putting your claims in their broader context makes them more interesting to your reader and more impressive to your professors who, after all, assign topics that they think have enduring significance. Finding that significance for yourself makes the most of both your paper and your learning. (p. 23)
Thinking about the broader implications will also help you write a conclusion that is better than just repeating your thesis (we’ll discuss this more below).
Example 4.3: Let’s look at an example from above:
This thesis makes a key claim about the rights of student athletes (in fact, shortly after this paper was written, NCAA athletes became eligible to profit from their own name, image, and likeness). It provides specific details, rather than just suggesting that student athletes should be able to make money. Furthermore, it provides broader context, even giving a possible model—Olympic athletes—to build an arguable case.
Remember, that just like your entire research project, your thesis will evolve as you write. Don’t be afraid to change some key terms or move some phrases and clauses around to play with the emphasis in your thesis. In fact, doing so implies that you have allowed the research to inform your position.
Example 4.4: Consider these examples about the same topic and general idea. How does playing around with organization shade the argument differently?
- Although William Dowling’s amateur college sports model reminds us that the real stakeholders are the student athletes themselves, he highlights that the true power over student athletes comes from the athletic directors, TV networks, and coaches who care more about profits than people.
- While William Dowling’s amateur college sports model reminds us that the real stakeholders in college athletics are not the athletic directors, TV networks, and coaches, but the students themselves, his plan does not seem feasible because it eliminates the reason many people care about student athletes in the first place: highly lucrative bowl games and March Madness.
- Although William Dowling’s amateur college sports model has student athletes’ best interests in mind, his proposal remains unfeasible because financial stakeholders in college athletics, like athletic directors, TV networks, and coaches, refuse to let go of their power.
When you look at the different versions of the thesis statements above, the general ideas remain the same, but you can imagine how they might unfold differently in a paper, and even how those papers might be structured differently. Even after you have a good version of your thesis, consider how it might evolve by moving ideas around or changing emphasis as you outline and draft your paper.
More Resources 4.2: Thesis Statements
Looking for some additional help on thesis statements? Try these resources:
- How to Write a Thesis Statement
- Writing Effective Thesis Statements.
Library Referral: Your Voice Matters!
(by Annie R. Armstrong)
If you’re embarking on your first major college research paper, you might be concerned about “getting it right.” How can you possibly jump into a conversation with the authors of books, articles, and more, who are seasoned experts in their topics and disciplines? The way they write might seem advanced, confusing, academic, irritating, and even alienating. Try not to get discouraged. There are techniques for working with scholarly sources to break them down and make them easier to work with (see How to Read a Scholarly Article ). A librarian can work with you to help you find a variety of source types that address your topic in a meaningful way, or that one specific source you may still be trying to track down.
Furthermore, scholarly experts are not the only voices welcome at the research table! This research paper and others to come are an invitation to you to join the conversation; your voice and lived experience give you one-of-a-kind expertise equipping you to make new inquiries and insights into your topic. Sure, you’ll need to wrestle how to interpret difficult academic texts and how to piece them together. That said, your voice is an integral and essential part of the puzzle. All of those scholarly experts started closer to where you are than you might think.
III. The Research Essay Across the Disciplines
Example 4.5: Academic and Professional Examples
These examples are meant to show you how this genre looks in other disciplines and professions. Make sure to follow the requirements for your own class or to seek out specific examples from your instructor in order to address the needs of your own assignment.
As you will see, different disciplines use language very differently, including citation practices, use of footnotes and endnotes, and in-text references. (Review Chapter 3 for citation practices as disciplinary conventions.) You may find some STEM research to be almost unreadable, unless you are already an expert in that field and have a highly developed knowledge of the key terms and ideas in that field. STEM fields often rely on highly technical language and assume a high level of knowledge in the field. Similarly, humanities research can be hard to navigate if you don’t have a significant background in the topic or material.
As we’ve discussed, highly specialized research assumes its readers are other highly specialized researchers. Unless you read something like The Journ al of American Medicine on a regular basis, you usually learn about scientific or medical breakthroughs when they are reported by another news outlet, where a reporter makes the highly technical language of a scientific discovery more accessible for non-specialists.
Even if you are not an expert in multiple disciplines of study, you will find that research essays contain a lot of similarities in their structure and organization. Most research essays have an abstract that summarizes the entire article at the beginning. Introductions provide the necessary setup for the article. Body sections can vary. Some essays include a literature review section that describes the state of research about the topic. Others might provide background or a brief history. Many essays in the sciences will have a methodology section that explains how the research was conducted, including details such as lab procedures, sample sizes, control populations, conditions, and survey questions. Others include long analyses of primary sources, sets of data, or archival documents. Most essays end with conclusions about what further research needs to be completed or what their research further implies.
As you examine some of the different examples, look at the variations in arguments and structures. Just as in reading research about your own topic, you don’t need to read each essay from start to finish. Browse through different sections and see the different uses of language and organization that are possible.
IV. Research Strategies: When is Enough?
At this point, you know a lot about your topic. You’ve done a lot of research to complete your first three writing projects, but when do you have enough sources and information to start writing? Really, it depends.
If you’re writing a dissertation, you may have spent months or years doing research and still feel like you need to do more or to wait a few months until that next new study is published. If you’re writing a research essay for a class, you probably have a schedule of due dates for drafts and workshops. Either way, it’s better to start drafting sooner rather than later. Part of doing research is trying on ideas and discovering things throughout the drafting process.
That’s why you’ve written the other projects along the way instead of just starting with a research essay. You’ve built a foundation of strong research to read about your topic in the annotated bibliography, planned your research in the proposal, and understood the conversations around your topic in the literature review. Now that you are working on your research essay, you are far enough along in the research process where you might need a few more sources, but you will most likely discover this as you are drafting your essay. In other words, get writing and trust that you’ll discover what you need along the way.
V. Reading Strategies: Forwarding and Countering
Using sources is necessary to a research essay, and it is essential to think about how you use them. At this point in your research, you have read, summarized, analyzed, and made connections across many sources. Think back to the literature review. In that genre, you used your sources to illustrate the major issues, topics, and/or concerns among your research. You used those sources to describe and make connections between them.
For your research essay, you are putting those sources to work in a different way: using them in service of supporting your own contribution to the conversation. According to Joseph Harris in his book Rewriting (2017), we read texts in order to respond to them: “drawing from, commenting on, adding to […] the works of others” (p. 2). The act of writing, according to Harris, takes place among the different texts we read and the ways we use them for our own projects. Whether a source provides factual information or complicated concepts, we use sources in different ways. Two key ways to do so for Harris are forwarding and countering .
Forwarding a text means taking the original concept or idea and applying it to a new context. Harris writes: “In forwarding a text you test the strength of its insights and the range and flexibility of its phrasings. You rewrite it through reusing some of its key concepts and phrasings” (pp. 38-39). This is common in a lot of research essays. In fact, Harris identifies different types of forwarding:
- Illustrating: using a source to explain a larger point
- Authorizing: appealing to another source for credibility
- Borrowing: taking a term or concept from one context or discipline and using it in a new one
- Extending: expanding upon a source or its implications
It’s not enough in a research essay to include just sources with which you agree. Countering a text means more than just disagreeing with it, but it allows you to do more with a text that might not initially support your argument. This can include for Harris:
- Arguing the other side: oftentimes called “including a naysayer” or addressing objections
- Uncovering values: examining assumptions within the text that might prove problematic or reveal interesting insights
- Dissenting: finding the problems in or the limits of an argument (p. 58)
While the categories above are merely suggestions, it is worth taking a moment to think a little more about sources with which you might disagree. The whole point of an argument is to offer a claim that needs to be proved and/or defended. Essential to this is addressing possible objections. What might be some of the doubts your reader may have? What questions might a reasonable person have about your argument? You will never convince every single person, but by addressing and acknowledging possible objections, you help build the credibility of your argument by showing how your own voice fits into the larger conversation—if other members of that conversation may disagree.
VI. Writing Strategies: Organizing and Outlining
At this point you likely have a draft of a thesis (or the beginnings of one) and a lot of research, notes, and three writing projects about your topic. How do you get from all of this material to a coherent research essay? The following section will offer a few different ideas about organizing your essay. Depending on your topic, discipline, or assignment, you might need to make some necessary adjustments along the way, depending on your audience. Consider these more as suggestions and prompts to help in the writing and drafting of your research essay.
Sometimes, we tend to turn our research essay into an enthusiastic book report: “Here are all the cool things I read about my topic this semester!” When you’ve spent a long time reading and thinking about a topic, you may feel compelled to include every piece of information you’ve found. This can quickly overwhelm your audience. Other times, we as writers may feel so overwhelmed with all of the things we want to say that we don’t know where to start.
Writers don’t all follow the same processes or strategies. What works for one person may not always work for another, and what worked in one writing situation (or class) may not be as successful in another. Regardless, it’s important to have a plan and to follow a few strategies to get writing. The suggestions below can help get you organized and writing quickly. If you’ve never tried some of these strategies before, it’s worth seeing how they will work for you.
Think in Sections, Not Paragraphs
For smaller papers, you might think about what you want to say in each of the five to seven paragraphs that paper might require. Sometimes writing instructors even tell students what each paragraph should include. For longer essays, it’s much easier to think about a research essay in sections, or as a few connected short papers. In a short essay, you might need a paragraph to provide background information about your topic, but in longer essays—like the ones you have read for your project—you will likely find that you need more than a single paragraph, sometimes a few pages.
You might think about the different types of sections you have encountered in the research you have already gathered. Those types of sections might include: introduction, background, the history of an issue, literature review, causes, effects, solutions, analysis, limits, etc. When you consider possible sections for your paper, ask yourself, “What is the purpose of this section?” Then you can start to think about the best way to organize that information into paragraphs for each section.
Build an Outline
After you have developed what you want to argue with your thesis (or at least a general sense of it), consider how you want to argue it. You know that you need to begin with an introduction (more on that momentarily). Then you’ll likely need a few sections that help lead your reader through your argument.
Your outline can start simple. In what order are you going to divide up your main points? You can slowly build a larger outline to include where you will discuss key sources, as well as what are the main claims or ideas you want to present in each section. It’s much easier to move ideas and sources around when you have a larger structure in place.
Example 4.6: A Sample Outline for a Research Paper
- College athletics is a central part of American culture
- Few of its viewers fully understand the extent to which players are mistreated
- Thesis: While William Dowling’s amateur col lege sports model does not seem feasible to implement in the twenty-first century, his proposal reminds us that the real stakeholders in college athletics are not the athletic directors, TV networks, and coaches, but the students themselves, who deserve th e chance to earn a quality education even more than the chance to play ball.
- While many student athletes are strong students, many D-1 sports programs focus more on elite sports recruits than academic achievement
- Quotes from coaches and athletic directors about revenue and building fan bases (ESPN)
- Lowered admissions standards and fake classes (Sperber)
- Scandals in academic dishonesty (Sperber and Dowling)
- Some elite D-1 athletes are left in a worse place than where they began
- Study about athletes who go pro (Knight Commission, Dowling, Cantral)
- Few studies on after-effects (Knight Commission)
- Dowling imagines an amateur sports program without recruitment, athletic scholarships, or TV contracts
- Without the presence of big money contracts and recruitment, athletics programs would have less temptation to cheat in regards to academic dishonesty
- Knight Commission Report
- Is there any incentive for large-scale reform?
- Is paying student athletes a real possibility?
Some writers don’t think in as linear a fashion as others, and starting with an outline might not be the first strategy to employ. Other writers rely on different organizational strategies, like mind mapping, word clouds, or a reverse outline.
More Resources 4.3: Organizing Strategies
At this point, it’s best to get some writing done, even if writing is just taking more notes and then organizing those notes. Here are a few more links to get your thoughts down in some fun and engaging ways:
- Concept Mapping
- The Mad Lib from Hell: Three Alternatives to Traditional Outlining
- Thinking Outside the Formal Outline
- Mind Mapping in Research
- Reverse Outlining
Start Drafting in the Middle
This may sound odd to some people, but it’s much easier to get started by drafting sections from the middle of your paper instead of starting with the introduction. Sections that provide background or more factual information tend to be more straightforward to write. Sections like these can even be written as you are still finalizing your argument and organizational structure.
If you’ve completed the three previous writing projects, you will likely also funnel some of your work from those projects into the final essay. Don’t just cut and paste entire chunks of those other assignments. That’s called self-plagiarism, and since those assignments serve different purposes in different genres, they won’t fit naturally into your research essay. You’ll want to think about how you are using the sources and ideas from those assignments to serve the needs of your argument. For example, you may have found an interesting source for your literature review paper, but that source may not help advance your final paper.
Draft your Introduction and Conclusion towards the End
Your introduction and conclusion are the bookends of your research essay. They prepare your reader for what’s to come and help your reader process what they have just read. The introduction leads your reader into your paper’s research, and the conclusion helps them look outward towards its implications and significance.
Many students think you should write your introduction at the beginning of the drafting stage because that is where the paper starts. This is not always the best idea. An introduction provides a lot of essential information, including the paper’s method, context, organization, and main argument. You might not have all of these details figured out when you first start drafting your paper. If you wait until much later in the drafting stage, the introduction will be much easier to write. In fact, most academic writers and researchers wait until the rest of their project—a paper, dissertation, or book—is completed before they write the introduction.
A good introduction does not need to be long. In fact, short introductions can impressively communicate a lot of information about a paper when the reader is most receptive to new information. You don’t need to have a long hook or anecdote to catch the reader’s attention, and in many disciplines, big, broad openings are discouraged. Instead, a good introduction to a research essay usually does the following:
- defines the scope of the paper
- indicates its method or approach
- gives some brief context (although more significant background may be saved for a separate section)
- offers a road map
If we think about research as an ongoing conversation, you don’t need to think of your conclusion as the end—or just a repetition of your argument. No matter the topic, you won’t have the final word, and you’re not going to tie up a complicated issue neatly with a bow. As you reach the end of your project, your conclusion can be a good place to reflect about how your research contributes to the larger conversations around your issue.
Think of your conclusion as a place to consider big questions. How does your project address some of the larger issues related to your topic? How might the conversation continue? How might it have changed? You might also address limits to existing research. What else might your readers want to find out? What do we need to research or explore in the future?
You need not answer every question. You’ve contributed to the conversation around your topic, and this is your opportunity to reflect a little about that. Still looking for some additional strategies for introductions and conclusions? Try this additional resource:
More Resources 4.4: Introductions and Conclusions
If you’re a bit stuck on introductions and conclusions, check out these helpful links:
- Introductions & Writing Effective Introductions
- Guide to Writing Introductions and Conclusions
- Conclusions & Writing Effective Conclusions
Putting It All Together
This chapter is meant to help you get all the pieces together. You have a strong foundation with your research and lots of strategies at your disposal. That doesn’t mean you might not still feel overwhelmed. Two useful strategies are making a schedule and writing out a checklist.
You likely have a due date for your final draft, and maybe some additional dates for submitting rough drafts or completing peer review workshops. Consider expanding this schedule for yourself. You might have specific days set aside for writing or for drafting a certain number of words or pages. You can also schedule times to visit office hours, the library, or the writing center (especially if your writing center takes appointments—they fill up quickly at the end of the semester!). The more you fill in specific dates and smaller goals, the more likely you will be to complete them. Even if you miss a day that you set aside to write four hundred words, it’s easier to make that up than saying you’ll write an entire draft over a weekend and not getting much done.
Another useful strategy is assembling a checklist, as you put together all the pieces from your research, citations, key quotes, data, and different sections. This allows you to track what you have done and what you still need to accomplish. You might review your assignment’s requirements and list them out so you know when you’ve hit the things like required sources or minimum length. It also helps remind you towards the end to review things like your works cited and any other key grammar and style issues you might want to revisit.
You’re much closer to completing everything than you think. You have all the research, you have all the pieces, and you have a good foundation. You’ve developed a level of understanding of the many sources you have gathered, along with the writing projects you have written. Time to put it all together and join the conversation.
Key Takeaways
- Your research essay adds to the conversation surrounding your topic.
- Begin drafting your essay and trust that your ideas will continue to develop and evolve.
- As you assemble your essay, rely on what works for you, whether that is outlining, mindmapping, checklists, or anything else.
- You have come far. The end is in sight.

Clemson Libaries. (2016). “Joining the (Scholarly) Conversation.” YouTube . https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=79WmzNQvAZY
Fosslien, L. Remember how much progress you’ve made [Image].
Graff, G. & Birkenstein, C. (2017). They Say, I Say: The Moves that Matter in Academic Writing . W. W. Norton and Co.
Guptill, A. (2016). Constructing the Thesis and Argument—From the Ground Up : Writing in College . Open SUNY Textbooks.
Harris, Joseph. Rewriting: How to Do Things with Texts . Second Edition. Utah State University Press, 2017.
Writing for Inquiry and Research Copyright © 2023 by Jeffrey Kessler is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
)
How to write a research paper: A step-by-step guide
Published July 20, 2020. Updated May 19, 2022.
Research Paper Definition
A research paper is an essay that evaluates or argues a perception or a point.
Overview of research paper
Research papers are papers written as in-depth analyses of the academic literature on a selected topic. A research paper outline consists of planning out the main sections of the paper, including the points and evidence, so that the drafting and editing processes are much easier. The research paper should have an introduction paragraph, at least three body paragraphs, a conclusion paragraph, and a Works Cited page. Some important steps should be followed while writing a research paper. The steps include understanding the instructor’s expectations for how to write a research paper, brainstorming research paper ideas, conducting research, defining the thesis statement, making a research paper outline, writing, editing again if required, creating a title page, and writing an abstract.
Key takeaways
- A research paper is an essay that analyzes or argues a perspective or a point.
- A research paper outline involves planning out the main sections of your paper, including your points and evidence, so that the drafting and editing processes go a lot smoother.
- Before you write your research paper outline, consult your instructor, research potential topics, and define your thesis statement.
- Your research paper should include an introduction paragraph, at least three body paragraphs, a conclusion paragraph, and a Works Cited page.
What are the steps to writing a research paper?
Here are 7 steps on how to write a research paper, plus two optional steps on creating a title page and an abstract:
Step 1: Understand your instructor’s expectations for how to write a research paper
Step 2: brainstorm research paper ideas, step 3: conduct research, step 4: define your thesis statement, step 5: make a research paper outline, step 6: write, step 7: edit, edit, and edit again, step 8 (optional): create a title page, step 9 (optional): write an abstract.
- Additional tips
Worried about your writing? Submit your paper for a Chegg Writing essay check , or for an Expert Check proofreading . Both can help you find and fix potential writing issues.
First, read and reread the rubric for the assignment. Depending on your field of study, the guidelines will vary. For instance, psychology, education, and the sciences tend to use APA research paper format, while the humanities, language, and the fine arts tend to use MLA or Chicago style.
Once you know which research paper format to use, take heed of any specific expectations your instructor has for this assignment. For example:
- When is it due?
- What is the expected page count?
- Will your instructor expect to see a research paper outline before the draft?
- Is there a set topic list or can you choose your own?
- Is there someplace to look at sample research papers that got A’s?
If anything isn’t clear about how to write a research paper, don’t hesitate to ask your instructor.
Being aware of the assignment’s details is a good start! However, even after reading them, you may still be asking some of the following questions:
- How do you think of topics for research papers?
- How do you think of interesting research paper topics?
- How do I structure an outline?
- Where can you find examples of research papers?
We’ll answer all of these questions (and more) in the steps below.
Some instructors offer a set of research paper topics to choose from. That makes it easy for you—just pick the research paper idea that intrigues you the most! Since all the topics have been approved by your instructor, you shouldn’t have to worry about any of them being too “broad” or “narrow.” (But remember, there are no easy research paper topics!)
On the other hand, many instructors expect students to brainstorm their own topics for research papers. In this case, you will need to ensure your topic is relevant as well as not too broad or narrow.
An example of a research paper topic that is too broad is “The History of Modernist Literature.” An expert would be hard-pressed to write a book on this topic, much less a school essay.
An example of a research paper topic that is too narrow is “Why the First Line of Ulysses Exemplifies Modernist Literature.” It may take a page or two to outline the ways in which the first line of Ulysses exemplifies traits of modernist literature, but there’s only so much you can write about one line!
Good research paper topics fall somewhere in the middle . An example of this would be “Why Ulysses ’ Stephen Exemplifies Modernist Literature.” Analyzing a character in a novel is broader than analyzing a single line, but it is narrower than examining an entire literary movement.
Next, conduct research and use an adequate number of reputable sources to back up your argument or analysis. This means that you need to evaluate the credibility of all your sources and probably include a few peer-reviewed journal articles (tip: use a database).
A lot of good sources can be found online or at your school’s library (in-person and online). If you’re stuck finding sources or would like to see a sample research paper, ask your librarian for help. If you’re having trouble finding useful sources, it may be a warning sign that your idea is too broad or narrow. For a more comprehensive look at research, check this out .
Your thesis statement is the most important line of your research paper! It encompasses in one sentence what your paper is all about. Having a concrete thesis statement will help you organize your thoughts around a defined point, and it will help your readers understand what they’re reading about.
If you could boil your paper down into a single line, what would that line be?
Here is an example of a working thesis:
In George Orwell’s 1984 , the Party manipulates citizens into total submission to the Party’s ideals through Newspeak, propaganda, and altered history.
For more information, see this guide on thesis statements .
Even if you think you chose an easy research paper topic, a structured, outlined research paper format is still necessary to help you stay organized and on-track while you draft. The traditional research paper outline example looks something like this:
Introduction
- Main point #1
- Main point #2
- Main point #3
Works cited
Let’s examine each section in detail.
Wondering how to start a research paper that gets an A? One good step is to have a strong introduction. Your research paper introduction will include the following elements:
- state your thesis (the one or two-line gist of your paper)
- explain the question you will answer or argument you will make
- outline your research methodology
1. Open with a hook
Keep your readers reading—hook them! A handy tip for writing a hook is to think about what made you choose this topic. What about your topic captured your interest enough to research it and write a paper about it?
A hook might sound something like the following examples:
Did you know that babies have around a hundred more bones than adults?
A language dies every fourteen days.
Of course, by no means does your opening line have to be so shocking. It could be as simple as you’d like, as long as it pulls your readers in and gives them an idea of what your paper is going to be about.
2. Introduce relevant background context
After you’ve hooked your readers, introduce them to the topic at hand. What is already known about it? What is still a mystery? Why should we care? Finally, what work have you done to advance knowledge on this topic?
You can include a relevant quotation or paraphrase here, but keep it short and sweet. Your introduction should not be bogged down with anything less than essential.
3. End on your thesis statement
Finally, end your introduction paragraph with your thesis statement, which is a concise sentence (just one, two max) summarizing the crux of your research paper.
Research paper introduction example
As John Wilkes Booth fled the scene of his assassination of President Abraham Lincoln, he yelled, “ Sic semper tyrannis ! The South is avenged!” Booth was an ardent supporter of the Southern cause during the Civil War era, but what made him passionate enough to assassinate a sitting president? Although Booth’s ire can be traced mostly to his backing of the South, there is more to the story than just that. John Wilkes Booth had three primary motives for assassinating Abraham Lincoln.
The body of your paper is not limited to three points, as shown below, but three is typically considered the minimum. A good rule of thumb is to back up each main point with three arguments or pieces of evidence. To present a cogent argument or make your analysis more compelling , present your points and arguments in a “strong, stronger, strongest” research paper format.
- Main point #1 – A strong point
- Strong supporting argument or evidence #1
- Stronger supporting argument or evidence #2
- Strongest supporting argument or evidence #3
- Main point #2 – A stronger point
- Main point #3 – Your strongest point
The conclusion is crucial for helping your readers reflect on your main arguments or analyses and understand why what they just read was worthwhile.
- restate your topic
- synthesize your most important points
- restate your thesis statement
- tie it all into the bigger picture
1. Restate your topic
Before you wrap up your paper, it helps to remind your readers of the main idea at hand. This is different than restating your thesis. While your thesis states the specific argument or analysis at hand, the main idea of your research paper might be much broader. For instance, your thesis statement might be “John Wilkes Booth had three primary motives for assassinating Abraham Lincoln.” The main idea of the paper is Booth’s assassination of Lincoln. Even broader, the research paper is about American history.
2. Synthesize your most important points
The key here is to synthesize , not summarize . Many students don’t see the point of conclusions because they look at them as mere repetition of points that already have been made. They’re right—that’s not what a conclusion paragraph should do! To summarize is to objectively restate what you’ve already said in your paper. What you want to do instead is offer a new viewpoint. Take the points you’ve made and develop a unique understanding or perspective.
For example, assume the main points you made in your paper are the following:
John Wilkes Booth was loyal to the South and the Confederate States of America.
John Wilkes Booth strongly opposed the abolition of slavery.
John Wilkes Booth was vocal about his hatred of Abraham Lincoln.
Instead of simply restating those three points in your conclusion, you could synthesize the points:
John Wilkes Booth’s outspoken loyalty to the South and opposition to abolition motivated him to assassinate Lincoln, who was one of the most prominent proponents of the abolition of slavery and the Union side of the Civil War. If Lincoln’s cause succeeded, the economy and culture of the antebellum South that Booth advocated for would not survive. All of those reasons combined were why Booth saw it as imperative that Lincoln be killed.
3. Restate your thesis statement
After you’ve synthesized the main points of your research paper, restate your thesis statement. This helps bring your paper full circle back to where you began.
4. Tie it all into the bigger picture
Answer the “so what?” question of your argument or analysis in order to end your research paper by tying it into a bigger picture. What implications does your argument or analysis have on the research of others? Why does your discovery matter? If you’re not sure, ask a friend to ask you (or ask yourself) “so what?” until you’ve figured it out. Here’s how it might look:
Friend: What is your paper about?
You: John Wilkes Booth assassinated Abraham Lincoln for three main reasons.
Friend: So what?
You: It’s important to know why he killed Lincoln.
Friend: Why is it important?
You: So we know what kind of things motivate assassins to kill presidents so we can avoid it happening in the future.
Just like that, you have tied your paper into the bigger picture. Your paper is more likely to have a strong impact on your readers (and receive a better grade) if you end it with a strong “take-home” message.
Tips for writing a great conclusion to your paper
- Link your conclusion to your introduction.
- Don’t give away all the answers. Remember, you don’t have to have all the answers. You can conclude your research paper with some questions for your readers to ponder.
- Propose a call to action. After conducting all this research and formulating some great arguments or analyses, you might believe something needs to be done. For example, if you wrote the aforementioned research paper about Abraham Lincoln’s assassination, you might suggest a call to action that we all keep an eye out for potential presidential assassins like John Wilkes Booth.
Mistakes to avoid when concluding your research paper
- Being too wordy. Keep the conclusion concise.
- Failure to relate it back to your intro.
- Failure to reflect on the bigger picture. Provide a compelling synthesis of what was just written.
Research paper conclusion example
Presidential assassinations are particularly sad and defining points in American history. They shake the country and make the people ask, “How could this happen to the most powerful figure in our nation?” In this paper, we explored some of the reasons why assassinations happen. John Wilkes Booth’s outspoken loyalty to the South and opposition to abolition motivated him to assassinate Lincoln, who was one of the most prominent proponents of the abolition of slavery and the Union side of the Civil War. If Lincoln’s cause succeeded, the economy and culture of the antebellum South that Booth advocated for would not survive. Those three motives combined were why Booth saw it as imperative that Lincoln be killed. As history scholars, we should remember why and how this happened so that we can avoid it happening in the future.
A works cited or bibliography page (or pages) should be the final section of your paper. This section includes a list of the resources you consulted, quoted, or cited within the body of your work, as well as those which influenced your ideas on the topic.
This is only a basic research paper outline template, which can be altered depending on the length and purpose of your paper. Argumentative papers aim to prove a point through well-researched, persuasive argument, while analytical papers posit a question and explore possible answers throughout the paper. Either way, your goal as a writer is to find and share the truth, whether you do so before you start writing a research paper or while you’re writing it.
Once you have an outline in the above research paper format, it’s a good idea to consult with your teacher or a writing tutor to find ways to strengthen it. They’ll also be able to give you good writing advice, from how to start a research paper to how to find research paper ideas conducive to strong arguments. As you write, you might find yourself tweaking (or overhauling) your outline. That’s okay!
You already have a rock-solid topic, credible sources, and intuitive outline. Now, you just have to flesh it out into pages of flowing, articulate prose. (Okay, it won’t exactly be easy.)
Before you begin writing, you might find it helpful to look at sample research papers in your school’s library or writing center (many research paper examples can also be found online). This will give you an idea of how to do a research paper outline, build a research paper outline template, as well as give you several research paper introduction examples. Here is one example research paper .
Examples of research papers you’ll see will look crazy long. But remember, those weren’t completed in one sitting! So, don’t wait until the last minute to get started. You’ll need to factor in time for breaks, writing tutor consultations, and the dreaded writer’s block.
You will probably write multiple drafts. Don’t expect your first draft to be perfect. You may even need to change your main argument halfway through your draft. That’s okay! Be ready to re-brainstorm, re-outline, and rewrite.
This might just be the most important step. Even if you brainstorm the perfect topic, create a brilliant research paper outline, and write a strong first draft. None of that brilliance will shine through if your paper is full of typos, grammar errors, and rambling tangents.
You’ll want to complete these kinds of editing, in this order:
- line editing
- spell-checking
- proofreading
Revision deals with broad issues, such as an argument that doesn’t make sense or a source that doesn’t support your thesis. Line editing, spell-checking, and proofreading are more to do with your writing itself—the flow of your sentences and the presence of any spelling or grammatical errors.
Paper formatting
The format of your paper will depend largely on what paper or citation style your instructor has told you to use (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago, Harvard, etc.). In general though, here are some good paper formatting guidelines to follow:
- Use 1-inch margins around your paper.
- Use a standard font like Times New Roman, Arial, etc.
- Use a standard font size between 10-12 points.
- Make sure that the title of your paper, date you turn it in, course name, and your name appear somewhere on the first page. If this is for APA, you’ll create a title page. If for MLA, you’ll create a header.
After you finish, it also doesn’t hurt to check your paper for plagiarism .
Before you turn in that paper, don’t forget to cite your sources in APA format , MLA format , or a style of your choice.
A title page is not always needed but is sometimes requested by an instructor or required by a paper format (example: APA style). It is always the first page of a paper and is the cover that communicates what’s in store for a reader. Let’s discuss what a title page is, why it’s important, how to create one, and tips on writing a good title.
What is a title page?
A title page is the first page of the paper that displays the title, the author’s name, and other required information such as thhe course number, the instructor’s name, or the date .
Why have a title page?
The main purpose of title page is like the purpose of a book cover or a news article headline. Its purpose is to allow the reader to easily understand what the paper is about .
This makes it especially important for you to have an effective and well-written title for your essay. You want to capture the reader’s attention, so they feel that your work is worth reading.
A title page can also indicate that the paper is academic in nature. The structured nature of a title page is an indicator that a paper has been created using certain academic guidelines or standards.
What is included on the title page besides the title?
There are two title page formats that you may be asked to use for academic papers. One is called American Psychological Association, which is commonly known as APA, and the second is called Modern Language Association, generally referred to as MLA. APA is typically used for research involving technical and scientific topics while MLA is more likely to be used for humanities or literature topics. Even though they are similar, each has a different set of requirements for the title page.
APA requirements:
- Research Paper Title
- Author’s full name (first name, middle initial, last name)
- Department and university name/Affiliation
- Course number and name
- Instructor’s/Professor’s name
- Assignment due date
- Page number
- All information is to be double spaced and centered
- Use Times New Roman font with 12 point size
MLA requirements:
It is important to note that usually a cover page is not required when using the MLA format. Instead, all the same points are found at the top of the first page of the research paper. However, if a title page is requested, it must meet the following requirements:
- Name of the school or university
- Title of the paper
- Subtitle of the paper (if necessary)
- Author’s/Student’s name
- Appropriate course number and name
- Use Times New Roman font with 12 as the font size
- Except for small words such as a, the, or, etc.
- The first letter of the first word should always be capitalized
- For BOTH formats, the first line should be spaced down three or four lines from the top margin.
Now, look at examples of both APA and MLA college research paper title page formats.
College research paper title page examples
Effects of Depression Symptoms on Quality of Sleep
Jane A. Doe and John Z. Smith
Michigan State University
Jack Peterson, Instructor
March 11, 2021
Effects of Depression Symptoms on Quality of Sleep
Jane A. Doe and Joe Z. Smith
Professor Jack Peterson
Tips on writing a great title
There are few things to consider when creating the title of your research paper:
- Succinctly communicate what the topic of the paper is.
- Be concise.
- Give your reader a preview of your approach to the subject.
- Gain the reader’s interest in learning about your subject.
Below are two examples of titles. Think about which title is more effective and why.
- Student Loan Debt
- The Vanishing American Middle Class: How Student Loan Debt is Destroying the Next Generation and What Can Be Done About It
Hopefully, you noticed that while Title 1 is concise, it is not informative. It does not give information on the writer’s approach to research on the topic. Title 2 is more interesting and precise than Title 1, and it communicates what problem the writer has researched. It is, however, very long. An ideal title would be something in the middle like this:
Student Loan Debt and Its Impact on the Vanishing American Middle Class
Here are a few examples of bad titles:
- Television is Influential
(the title is very vague and doesn’t make the reader want to learn more)
- The Most Poisonous Snakes
(This title is too broad.)
- Outsourcing in the 21st Century
While this title is not terrible, it should include more detail. For example, what is being outsourced exactly?
A good paper title should convey your specific topic or argument and can hint at the conclusions. Here are some general guidelines to follow:
- Your title should be grammatically correct and in Title Case
- It should be formatted correctly
- It should not be a quote by someone else
- The title is not your thesis statement
- The title is not just rephrasing the topic or assignment
- Always follow your professor’s preferences
- Do not put your title in All CAPS or Italics
An abstract is a concise overview or summary of your research paper. The abstract is a paragraph that states the central question behind the research, describes the research methods, and summarizes the findings. After reading your abstract, readers should understand exactly what your paper is all about.
Abstracts are used in papers meant for publication in journals and are not typically required for student papers.
What’s the difference between an abstract and an introduction?
Many students have trouble understanding the difference between an abstract and an introduction. While it’s true that both may seem quite similar at first glance, an abstract is distinct from an introduction in several ways.
An abstract is a concise summary, whereas an introduction is much more detailed. When writing an introduction, you will provide an overview of the “why, what, when and how” of your study. On the other hand, an abstract provides readers with a quick overview of your paper without them having to read the entire paper. It will also provide a preview so they can better understand the paper when reading it or deciding whether or not they want to read it.
Why are abstracts necessary for research papers?
Abstracts help researchers to quickly identify studies relevant to subjects they need information on. If abstracts didn’t exist, people would have to sift through pages and pages of each study just to find this important information. In the modern era, abstracts are even more important because they contain keywords that make papers easier to find on the web. In addition, abstracts allow researchers to absorb key information without paying any money if the paper is not an open-source document.
Planning your abstract
Write the abstract after you have finished writing your paper. You can’t summarize until you have written the paper. The organization of an abstract is determined by the type of research paper.
Scientific abstracts include a concise summary of the following:
- OBJECTIVE: Clearly define the purpose of your research and the central question you aimed to answer.
- METHODS: Briefly explain research methods you used to answer your central question.
- RESULTS: Summarize the most important and relevant results of your study. Don’t include all of your results if there are too many to realistically fit.
- FINDINGS: Explain how your research answered your central problem or question. What the significance of your research? What kind of argument are you making in light of your results?
Abstracts for research in humanities and the social sciences contain the following:
- The background and overview of your general topic
- A concise summary of your central argument and claims
- The rationale and purpose for your research in this specific area
- Your method and strategy for researching this topic and primary sources used to support your claims
There are different types of abstracts you may be asked to write, depending on the assignment. Common types of abstracts for the social sciences include the following:
- Critical Abstract: This type of abstract provides a judgment or comment on how reliable the study is. These types of abstracts are quite rare.
- Descriptive Abstract: A descriptive abstract simply summarizes the information found in a paper. There is no judgment involved, and these abstracts can be as short as 100 words.
- Informative Abstract: This is the most common type of abstract. It includes the main arguments, the evidence presented and the most important findings. In most cases, this is the type of abstract you will be writing.
- Highlight Abstract: The purpose of a highlight abstract is to grab the reader’s attention. These are often incomplete, biased, and full of leading remarks intended only to attract readers. These are not used in academic writing.
Writing your abstract
Abstracts are usually between 150 and 300 words. An abstract for a research paper in the humanities or social sciences should be formatted as a single paragraph. For the sciences, you will need to clearly outline each section (Objective, Methods, Results, Conclusion). The abstract follows the title page.
When it comes to actually writing your abstract, you can simply copy and paste key sentences from your paper and place them in a sequence. This is a good way to organize and outline your ideas before writing the abstract. You may prefer to write it another way – just be sure to include your main objective, method, and overall conclusion. Regardless, be sure to make your abstract a clear and concise explanation of your rationale for the essay and primary findings.
Below is a sample APA abstract that a freshman college student taking psychology and studying addictive disorders might provide for her research.
Sample Psychology Abstract
The purpose of this essay is to analyze the overall efficacy of Medicated Assisted Treatment (MAT) in individuals with opioid use disorder compared with those individuals who only receive treatment in the form of 12-step recovery style meetings and counseling. From 2017-present, most people who seek assistance for opiate addiction in the United States receive treatment in the form of MAT or 12-step (and related) forms of treatment. Some are provided with both. Using recent data from recognized and credible scientific and medical literature and peer-reviewed journals, I provide an analysis of current trends in how opioid-dependent individuals are likely to be treated and make an argument that MAT combined with counseling/therapy of any recovery model (not only 12-step type, e. g., Narcotics Anonymous or NA) is much more effective than recovery programs using 12-step meetings and fellowship as the primary method of treatment. Furthermore, I demonstrate that individuals with private insurance and access to private treatment (inpatient rehabilitation with medical detoxification and post-acute support) are more likely to receive MAT combined with therapy and, therefore, achieve long term success/ sobriety. Success is measured in the percentage of subjects who show long-term abstinence from opioids after 5 years compared to those who do not survive — or return to their opioid use disorder. The rationale for this research project is to find out how most Americans are treated for this debilitating health issue during the current “opioid epidemic” that resulted in 50,000 overdose-related deaths in 2019 alone. My hope is that my argument might increase awareness of the higher success rates of MAT compared to that of predominately 12-step only recovery as well as prompt discussion of making MAT more accessible to those without private medical insurance and the financial means to pay for it.
Sample Scientific Abstract
“The relationship between habitat use by voles (Rodentia: Microtus) and the density of vegetative cover was studied to determine if voles select forage areas at the microhabitat level. Using live traps, I trapped, powdered, and released voles at 10 sites. At each trap site I analyzed the type and height of the vegetation in the immediate area. Using a black light, I followed the trails left by powdered voles through the vegetation. I mapped the trails using a compass to ascertain the tortuosity, or amount the trail twisted and turned, and visually checked the trails to determine obstruction of the movement path by vegetation. I also checked vegetative obstruction on 4 random paths near the actual trail, to compare the cover on the trail with other nearby alternative pathways. There was not a statistically significant difference between the amount of cover on a vole trail and the cover off to the sides of the trail when completely covered; there was a significant difference between on and off the trail when the path was completely open. These results indicate that voles are selectively avoiding bare areas, while not choosing among dense patches at a fine microhabitat scale.”
Source: http://www.umt.edu/ugresearch/umcur/sample_abstracts.php
Additional tips for writing a research paper abstract
- Imagine you are another researcher looking at your abstract for the first time. Does it adequately summarize your research, or is essential information missing?
- Avoid redundancy.
- Do not use acronyms or abbreviations.
- Do not reference other literature.
- Do not use confusing terminology that new readers will not understand.
- Do not use images, graphs, or tables.
- Only describe the paper – do not defend your research in the abstract.
- No need to cite sources.
- Write in past tense, as the research is already complete.
- Use active tense when possible.
Example research paper on student stress
Why it’s worth learning how to write a research paper.
Learning how to write a research paper will allow you to strengthen your time management, communication, and analytical skills. What is a research paper for, after all, if not to help you grow as a student and a writer? Believe it or not, with enough practice, you’ll become a pro at finding interesting research paper topics, creating an organized research paper outline, and writing a clean draft that flows from introduction to conclusion.
Research paper template and example
- Research paper template
- Research paper example
- How to write a research paper
- Research paper topics
- Research paper outline
By Jolee McManus. Jolee earned a BA in English from the University of Georgia. She has several years of experience as a writing tutor and freelance copywriter and editor
Common Writing Assignments, Apps & Tests
- Analytical Essay
- AP synthesis Essay
- Argumentative Essay
- Book Report
- Compare and Contrast Essay
- Cause and Effect Essay
- College Admissions Essay
- Critical Analysis Essay
- Definition Essay
- Descriptive Essay
- Dissertation
- Explanatory Essay
- Expository Essay
- Informative Essay
- Narrative Essay
- Opinion Essay
- Personal Essay
- Persuasive Essay
- Reflective Essay
- Research Paper
- Rhetorical Analysis
- Scholarship Essay
- Short Essay
- Thesis Paper

What’s included with a Chegg Writing subscription
- Unlimited number of paper scans
- Plagiarism detection: Check against billions of sources
- Expert proofreading for papers on any subject
- Grammar scans for 200+ types of common errors
- Automatically create & save citations in 7,000+ styles
- Cancel subscription anytime, no obligation
.png)
How to Write a Research Paper
How To Write A Research Paper – The Clear-Cut and Error-Free Way!
To write a research paper, select a topic, gather and organize information, and formulate a thesis. Create an outline, draft the main content, reassess your thesis, and revise the draft. Finally, write the introduction and conclusion, then thoroughly proofread and edit.
Writing a research paper is a pivotal academic endeavor that deepens your understanding of a topic while contributing to your field of study. It involves selecting a relevant topic, conducting thorough research, and presenting your findings clearly.
This guide provides a step-by-step approach to navigate through this process, from choosing your subject to drafting and refining your paper, ensuring you create a work that is both informative and engaging. Whether for academic purposes or personal inquiry, this guide aims to equip you with the tools needed for effective research writing.
Guide to Writing a Research Paper: The Basics
1. Know Your Expertise : Understand your strengths within your field of study. Look for underrepresented or novel areas that could benefit from further research.
2. Brainstorming Related Ideas : Generate ideas related to your main topic. Look for peculiar aspects or gaps that could form the basis of your research.
3. Narrowing Down the Topic One Last Time : Refine your topic to its most specific and polished form, ensuring it provides clear context for your study.
4. Be a Savant for Evidence :
- Gathering initial information : Acquire prior knowledge about your topic from personal experiences or known issues.
- Exploring Relevant Sources : Seek out credible and scientific sources from reputable organizations, academic institutions, and validated print materials.
- Note-Take and Organize : Process and organize the gathered information using tools like mind maps or fishbone diagrams.
5. Create a Storyline : Develop a research narrative by connecting different relevant information and formulating a central point.
6. Create an Outline Like a PRO : Construct a specific, relevant, and strategic outline to provide a clear framework for your paper.
7. Structuring the Paper’s Framework : Ensure your outline is specific, relevant, and strategically organized to guide both the researcher and the readers.
8. Organizing Main Points, Subpoints, and a Thesis Statement : Break down your content into manageable subpoints to maintain clarity and coherence.
9. Maintaining a Logical Flow while Writing Research Papers : Ensure ideas are coherent and transitions are smooth for easy navigation.
10. Write the Draft Without Repeating it 100 Times : Utilize different writing strategies, focused draft creation, and content elaboration to develop a comprehensive manuscript.
11. Understanding Citation Styles and Bibliographies :
- Knowing your Citation Styles : Choose the appropriate citation style based on your discipline or publication requirements.
- Create a bibliography or reference list : Compile a comprehensive list of sources used in your research to reflect your academic integrity and provide a resource for others.
Choose a Topic– Carefully
A topic may be the first thing to remember when starting to write your research paper, but most of the time, this phase is also a period of unexplainable agony and distress. Want to know why?
The bigger the universal body of knowledge that we strive to explore, the more we ask questions and get curious about exploring its depths, which may lead to endless thinking and unfinished progress.
The good news about this, though, is that this agony may meet its deserving end by narrowing things out. By choosing topics carefully, we also mean that we need to end countless unnecessary thoughts and focus on the most realistic, feasible, and specific things that you can explore as a researcher that you know you are.
To do this and hopefully choose the best topic for your research project, read through the following tips:
1. Know Your Expertise
A particular field of study has subcomponents. Exploring the entirety of it is nearly impossible unless you are Aristotle for Biology or Hawking for Physics. You have to know where you are good at, and there is definitely a stream of fields that you may find interesting or noteworthy.
Sometimes, these streams are often underrepresented because of their novelty, or maybe some phenomena are yet to be discovered through considerable amounts of literature that could either approve or reject their existence.
For example, exoplanets , or planets that orbit stars outside our solar system, were believed to be theoretical or speculative entities rather than confirmed astronomical entities. This concept was not widely embraced by experts due to the lack of empirical evidence and the limited technological capacities to detect such planets.
This changed through astronomy in 1995 when Michel Mayor and Didier Queloz, both Swiss astronomers, announced the discovery of an exoplanet named 51 Pegasi b, circling a sun-like star outside our solar system.
2. Brainstorming Related Ideas
Finding a suitable topic for writing a research paper does not end here. Generating related ideas to that topic may surely be of great help in writing a research paper in its easiest sense. In doing so, you may use the cardinal rule in formulating a complete research topic: find something peculiar about the topic.
This peculiarity may be in the form of a problem, novelty, or even something that does not even exist yet. Even when you think your topic in the first step is already specific, brainstorming related ideas may find new gaps that could be the groundwork for your research endeavor.
For instance, if you have "The Efficiency of Solar Panels in Residential Settings” as your proposed topic, you may explore other related ideas attached to it, such as its impact on homeowners, the intermittence which could be one of its problems, or its connection with the environment– whether the latter benefits from it or the other way around.
From this, you are not just expanding your options, but you are seeing exactly how your research will pan out should you choose to go two steps further in the topic.
3. Narrowing Down the Topic One Last Time
Once you get to this part, it means that you are doing well in filtering down your topic. The last “funnel” is needed to bring your topic to its most polished– and fool-proof– form! By narrowing down your topic one last time, you are ensuring that you provide the context of your study.
You may identify the type, locale, or even the dynamics of the variables included in your supposed research project.
Suppose the proposed topic of interest is "The Influence of Social Media on Teenagers' Mental Health." To polish this topic further and present the study's context, you might dwell on "Instagram Use and Its Impact on Anxiety Levels in Adolescents from Urban Areas."
This polished version specifies the platform (Instagram), the demographic (adolescents), and a specific facet of mental health (anxiety levels). Furthermore, the study focuses on the demographics of teenagers living in urban areas, possibly opening the knowledge for comparisons between urban and rural settings or highlighting urban-specific stressors that impact mental health.
Struggling with your Research Paper?
Get your assignments done by real pros. Save your precious time and boost your marks with ease.
Be a Savant for Evidence
You help yourself write a research paper by ensuring that your paper is an authority– leaving no trace of fraud or senseless information in it. In doing so, you have to prepare the information that MATTERS.
1. Gathering initial information
You have to have a piece of prior knowledge about the issue. This prior knowledge may come from a personal experience, or something that you have known that you think affects a considerable number of individuals, regardless of whether you are included in it.
Going back to the example of solar power, you may have experienced using that kind of energy before, letting you know how it works and benefits you somehow.
2. Exploring Relevant Sources
There are BUNCH (I could not emphasize this enough) of stuff on the Internet that have impressions to be used as a source of information to write a research paper. However, only a few can be as relevant, objective, scientific, and sensible to be included rightfully in an academic masterpiece.
The best relevant source may be found in reputable organizations, academic institutions, government-run pages, print materials, such as academic journals, and other validated print sources.
While blogs and newspapers can be enticing because of their eye-catching titles and claims, they are less superior than those mentioned in terms of credibility. You may still use them, however, when you want to provide raw data or anecdotal evidence related to a phenomenon.
3. Note-Take and Organize
This is where the ambivalent feeling of becoming a pseudo-detective begins. The information and evidence you have just gathered will not sit there to wait for a miracle to transpire.
You, as a researcher, must process them!
You need to take everything in a single base (a notebook may be handy at this part) and filter things out (yes, you need to remove some). For a good start, you may use graphic organizers like a mind map or a fishbone diagram– depending on the nature of your study.
These organizers will help you find the relationship between the concepts that potentially make up your study and minimize overcrowding of thoughts (because sometimes, too much information may overwhelm you).
4. Create a Storyline
Now comes the fun part of writing research papers! A good research paper is laid out as a story - with the preliminary research you've done, it's time to do more research, but that of a mental kind. It's time to connect different relevant information you've found and think of a central point of their convergence.
For the first draft, it's enough to come up with a research paper outline that takes your preliminary research and puts it into academic writing.
Our step by step guide guides your journey through the entire paper, including thesis statements, materials and methods section, and answering research questions. We'll also include a guide on how to properly cite resources and come up with a good introductory paragraph.
Create an Outline Like a PRO
A day will surely last without you asking the classic question, “How do I write a research paper?” if you have an outline from the get-go. Just like what was reiterated at the very beginning of this blog, all you need to do to breeze through this task of how to make a research paper is to create an outline. Creating one requires your keen eye for specificity, importance, and strategy.
You must be specific to ensure you are targeting the right answer to your question 100%– leaving no cookie crumbs. You have to make sure you are relaying the most important pointers, leaving no room for any senseless or incoherent details in your outline.
Lastly, you have to strategically place these pointers in a position where your readers can easily appreciate them while the lucid flow of your paper is carrying them.
Having a keen eye for these criteria might be easy for a one-man team like you, but a research paper writing service like Studyfy can lay its hand for you in just a few days. With its roster of writers equipped with style knowledge, writing experience, and a keen eye for detail and nuances, your paper will never miss the harshest beat of success.
1. Structuring the Paper’s Framework
A specific, relevant, and strategic outline provides a strong framework for a paper. It provides a clear roadmap to the researcher on what to do methodically, and with clarity being considered, the paper’s framework ensures that the process maximizes finding the answer to the questions being asked by the researcher.
The harshness of having these three conditions for the outline (specificity, importance, and strategy) always comes with a prize: having a framework that guides the researcher and the readers on how the answers were extracted brilliantly.
2. Organizing Main Points, Subpoints and a Thesis Statement
A bulk of words in a paragraph can be a challenge for both the researcher and the audience. Breaking them down by dividing the points into components may ease this common writing problem.
ou may separate information into subpoints whenever you feel that they tackle an isolated topic that is distinct from one another. Subpoints may be regarded as “transition markers,” familiarizing readers with “where” they are in the paper.
3. Maintaining a Logical Flow while Writing Research Papers
The logical flow of a research paper can be seen in the way (a) ideas are coherent with each other and (b) visible transition devices connect these strings of ideas.
When you have these ticked inside the boxes, you have a paper that is easy to navigate, and ideas come off as united, giving you a singular impression even when you have read a lot of it in a single sitting.
Write the Draft Without Repeating it 100 Times
Now that you have a specific outline that will help writing a research paper, all you need to do is to start a manuscript. Writing a draft does not ideally happen overnight– unless you work in an exceptional and highly-tailored writing service that offers quality-laden research papers for sale – will not just make you monitor your progress.
Still, it will also help you check the parts you are having trouble with and strategically prioritize one over the other (you may start with the harder ones or the other way around, depending on your liking).
Other than time management, these are the other things to consider on how to do a research paper with the help of a draft:
1. Applying different writing strategies
Learning the different writing strategies is one of the best ways how to write a research essay in its initial stages. You can use various strategies interchangeably throughout the manuscript writing process.
These are, but are not limited to, definition, synthesis, critical analysis, argumentation, evidence integration, and storytelling, which are the approaches you can employ on the different parts of your paper.
2. Focused draft creation
A focused draft creation approach is a specialized strategy in completing a manuscript where the writer divides the writing process into sections. It does not necessarily have to be adherent to the topics or “chunks” that you have in mind before writing the manuscript.
You may divide them according to difficulty, nature of idea generation, or the recency of information. The main goal of this approach is to focus on one section before jumping to the next for clarity.
3. Content Elaboration
While this strategy may be included in the first pointer, the art of elaboration can stand on its own and possibly be imperative in the completion of a research manuscript. It often dictates how long should a research paper be due to its contribution to the word count.
However, one should not focus solely on this benefit, as elaboration has more profound work of substantiating the quality of the paper and ensuring that processes, concepts, and terminology are explained and elucidated well.
What's important for elaboration is the nature of the research question, the stance in your central argument, and the background information. A good research paper utilizes background information to provide a stream of cohesive data (which you get when you conduct research) and creates an elaborative story that simply makes sense.
Understanding Citation Styles and Bibliographies
1. knowing your citation styles.
APA, Chicago, MLA, Vancouver, and many more– you may choose freely— or NOT! The rule of thumb in this situation is the discipline of your study. Vancouver is mostly used in Natural Science, while APA and MLA are often employed in Social Sciences and Humanities. Aside from the field of study, the requirements for journal publication can affect your choice of citation style. These styles follow distinct citation and referencing formats, so be sure to know at least their basic features and iterations.
2. Create a bibliography or reference list
Although this part of the paper is the last (in most cases, if the Appendix page is not necessary) one to appear, it still holds significance, especially when the reader wants to see a copy of the work you previously used.
The reference list, aside from being the reflection of your integrity and commitment to sharing the knowledge with the academic community, also acts as a repository for people to find sources that they can likewise use for reference and counter-checking efforts.
Steps of Writing a Research Paper
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Expertise | Identify strengths and research gaps in your field. |
| 2. Idea Brainstorming | Generate and explore ideas around your topic. |
| 3. Topic Refinement | Refine your topic for specificity and clarity. |
| 4. Evidence Gathering | Gather information from credible sources. |
| 5. Storyline Creation | Connect information to form a research narrative. |
| 6. Outline Development | Create a clear and strategic paper outline. |
| 7. Framework Structuring | Structure the paper with a specific outline. |
| 8. Content Organization | Organize main points and thesis clearly. |
| 9. Logical Flow | Ensure coherence and smooth transitions. |
| 10. Draft Writing | Develop the draft using various writing strategies. |
| 11. Citation Styles | Select the right citation style for your discipline. |
Did you like our inspiring Research Paper Guide?
For more help, tap into our pool of professional writers and get expert research paper writing services!
Frequently Asked Questions
How to write a good research paper if you do not have a clear outline.
Writing a research paper without a clear outline involves understanding the assignment, selecting a topic, conducting preliminary research, and drafting a tentative thesis. Start by writing sections that form a basic structure: introduction, body, and conclusion. Take detailed notes during research and focus on developing your argument. Revise your draft, ensuring coherence and logical flow. Finally, seek feedback and proofread for errors. The writing process is iterative, so be prepared to refine your paper as your ideas evolve.
If you find yourself struggling with this process, considering the option to pay for a research paper can be a practical solution.
Can literary devices or other styles of writing help on research papers?
In some parts of the paper, such as the background of the study, the creative style of writing and the use of literary devices can escape the formality of research papers. If executed well, it can complement the rigid nature of the writing process. However, it must be used sparingly.
How do you write a research paper if you do not have sufficient literature to prove the existence of a gap?
The lack of literature on a research topic is already a sign of a novelty or unexplored aspect of the phenomenon. All you need to do is provide a clear context on the phenomenon, narrow down the topic into the said limitation, acknowledge it, and provide a strong rationale that will also prove why the insufficiency calls for further development of your proposed topic.
Is it possible for a specialized service to craft a research paper tailored to my preferences?
Indeed, a service such as Studyfy offers the capability to produce a research paper that seems as though you've meticulously crafted it yourself. Their team of skilled writers can adapt their expertise to fit your specific requirements, ensuring your paper is of the highest quality, following the IMRAD format or any other structure you need.
Opting for such a service for your " write my research paper " need means receiving a professionally crafted document, with thorough citations, grammatical precision, correct formatting, and a well-chosen research topic.
Featured Posts
How to write a term paper.
.png)
How To Make An Essay Longer
.png)
How to Write a Dissertation

How to Write an Essay

How to Write a Discussion Post

How to Write a Lab Report


Traffic engineers build roads that invite crashes because they rely on outdated research and faulty data
Professor of Civil Engineering, University of Colorado Denver
Disclosure statement
Wes Marshall receives funding from the US Department of Transportation's University Transportation Centers program and various state transportation departments.
View all partners
“Can you name the truck with four-wheel drive, smells like a steak, and seats 35?”
Back in 1998, “The Simpsons” joked about the Canyonero, an SUV so big that they were obviously kidding. At that time, it was preposterous to think anyone would drive something that was “12 yards long, two lanes wide, 65 tons of American Pride.”
In 2024, that joke isn’t far from reality.
And our reality is one where more pedestrians and bicyclists are getting killed on U.S. streets than at any time in the past 45 years – over 1,000 bicyclists and 7,500 pedestrians in 2022 alone.
Vehicle size is a big part of this problem. A recent paper by urban economist Justin Tyndall found that increasing the front-end height of a vehicle by roughly 4 inches (10 centimeters) increases the chance of a pedestrian fatality by 22% . The risk increases by 31% for female pedestrians or those over 65 years, and by 81% for children.
It’s hard to argue with physics, so there is a certain logic in blaming cars for rising traffic deaths. In fact, if a bicyclist is hit by a pickup truck instead of a car, Tyndall suggests that they are 291% more likely to die.
Yet automakers have long asserted that if everyone simply followed the rules of the road, nobody would die. Vehicle size is irrelevant to that assertion.
My discipline, traffic engineering , acts similarly. We underestimate our role in perpetuating bad outcomes, as well as the role that better engineering can play in designing safer communities and streets.

Millions of road deaths
How bad are the bad outcomes? The U.S. has been tracking car-related road deaths since 1899. As a country, we hit the threshold of 1 million cumulative deaths in 1953, 2 million in 1975 and 3 million in 1998. While the past several years of data have not yet been released, I estimate that the U.S. topped 4 million total road deaths sometime in the spring of 2024.
How many of those are pedestrians and bicyclists? Analysts didn’t do a great job of separating out the pedestrian and cyclist deaths in the early years , but based on later trends, my estimate is that some 930,000 pedestrians and bicyclists have been killed by automobiles in the U.S.
How many of those deaths do we blame on big cars or bad streets? The answer is, very few.
As I show in my new book, “ Killed by a Traffic Engineer: Shattering the Delusion that Science Underlies our Transportation System ,” the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration calls road user error the “ critical reason” behind 94% of crashes, injuries and deaths .
Crash data backs that up.
Police investigate crashes and inevitably look to see which road users, including drivers, pedestrians and cyclists, are most at fault. It’s easy to do because in almost any crash, road user error appears to be the obvious problem.
This approach helps insurance companies figure out who needs to pay. It also helps automakers and traffic engineers rationalize away all these deaths. Everyone – except the families and friends of these 4 million victims – goes to sleep at night feeling good that bad-behaving road users just need more education or better enforcement.
But road user error only scratches the surface of the problem.
Who creates dangerous streets?
When traffic engineers build an overly wide street that looks more like a freeway , and a speeding driver in a Canyonero crashes, subsequent crash data blames the driver for speeding.
When traffic engineers provide lousy crosswalks separated by long distances , and someone jaywalks and gets hit by that speeding Canyonero driver, one or both of these road users will be blamed in the official crash report.
And when automakers build gargantuan vehicles that can easily go double the speed limit and fill them with distracting touchscreens , crash data will still blame the road users for almost anything bad that happens.
These are the sorts of systemic conditions that lead to many so-called road user errors. Look just below the surface, though, and it becomes clear that many human errors represent the typical, rational behaviors of typical, rational road users given the transportation system and vehicle options we put in front of them.
Look more deeply, and you can start to see how our underlying crash data gives everyone a pass but the road users themselves. Everyone wants a data-driven approach to road safety, but today’s standard view of crash data lets automakers, insurance companies and policymakers who shape vehicle safety standards off the hook for embiggening these ever-larger cars and light-duty trucks.
It also absolves traffic engineers, planners and policymakers of blame for creating a transportation system where for most Americans, the only rational choice for getting around is a car .
Understanding road behavior
Automakers want to sell cars and make money. And if bigger SUVs seem safer to potential customers, while also being much more profitable , it’s easy to see how interactions between road users and car companies – making seemingly rational decisions – have devolved into an SUV arms race.
Even though these same vehicles are less safe for pedestrians, bicyclists and those in opposing vehicles , the current data-driven approach to road safety misses that part of the story.
This can’t all be fixed at once. But by pursuing business as usual, automakers and traffic engineers will continue wasting money on victim-blaming campaigns or billboards placed high over a road telling drivers to pay attention to the road .
A better starting point would be remaking the U.S.’s allegedly data-driven approach to road safety by reinventing our understanding of the crash data that informs it all.
The key is starting to ask why. Why did these road users act as they did? Why didn’t they follow the rules that were laid out for them? Bad road user behavior shouldn’t be excused, but a bit of digging below the surface of crash data unearths a completely different story.
Figuring out which road user is most at fault may be useful for law enforcement and insurance companies, but it doesn’t give transportation engineers, planners, policymakers or automakers much insight into what they can do better. Even worse, it has kept them from realizing that they might be doing anything wrong.
- Urban policy
- Civil engineering
- Pedestrians
- Car accidents
- Sustainable cities
- Transportation policy
- Safe streets
- Bicycle safety
- Motorcycles

Lecturer in Indigenous Health (Identified)

Social Media Producer

Lecturer in Physiotherapy

PhD Scholarship

Senior Lecturer, HRM or People Analytics
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
- Americans’ Views of Government’s Role: Persistent Divisions and Areas of Agreement
Wide majorities of Biden and Trump supporters oppose cuts to Social Security
Table of contents.
- Views on the efficiency of government
- Views on the government’s regulation of business
- Confidence in the nation’s ability to solve problems
- Views on the effect of government aid to the poor
- Views on government’s role in health care
- Views on the future of Social Security
- Trust in government
- Feelings toward the federal government
- Acknowledgments
- The American Trends Panel survey methodology

Pew Research Center conducted this study to understand Americans’ attitudes about U.S. government, such as its size and role.
This report is based primarily on a survey of 8,709 adults, including 7,166 registered voters, from April 8 to 14, 2024. Some of the analysis in this report is based on a survey of 8,638 adults from May 13 to 19, 2024.
Everyone who took part in these surveys is a member of the Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. This way nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology .
Here are the questions used for the report and its methodology .
While the economy, immigration and abortion have emerged as major issues in the 2024 election, Joe Biden and Donald Trump also have dramatically different ideas about the size and role of government.
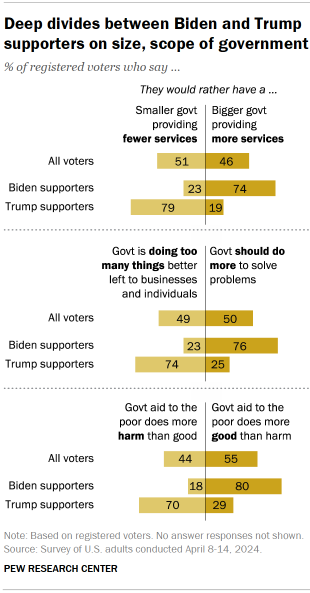
These differences reflect decades-old divisions between Democrats and Republicans over the scope of government.
Among registered voters, large majorities of Biden supporters – roughly three-quarters or more – favor a bigger, more activist government.
- 74% say they would rather have a bigger government providing more services.
- 76% say government should do more to solve problems.
- 80% say government aid to the poor “does more good than harm.”
Trump supporters, by comparable margins, take the opposing view on all three questions.
The Pew Research Center survey of 8,709 adults – including 7,166 registered voters – conducted April 8-14, 2024, examines Americans’ views of the role and scope of government , the social safety net and long-term trends in trust in the federal government .
Democratic support for bigger government is little changed in the last five years but remains higher than it was a decade ago. Republicans’ views have shifted less over the last 10 years.
Among all adults, about three-quarters of Democrats and Democratic-leaning independents favor a bigger government, up from about six-in-ten in 2014 and 2015. The share of Republicans and Republican leaners who prefer a bigger government has increased only modestly over the same period.
Democratic support for bigger government, while slightly lower than in 2021 (78%), remains at nearly its highest level in five decades. During Bill Clinton’s presidency in the 1990s, fewer than half of Democrats said they preferred a bigger government with more services.
Voters continue to express very different views about government’s role in specific areas than about the government generally.
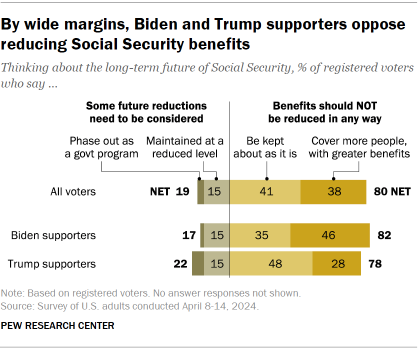
A large majority of voters (80%) – including 82% of Biden supporters and 78% of Trump supporters – say that in thinking about the long-term future of Social Security, benefits should not be reduced in any way.
However, Biden supporters are more likely than Trump supporters to say Social Security should cover more people with greater benefits.
- 46% of Biden supporters favor expanding Social Security coverage and benefits, compared with 28% of Trump supporters.
Most Americans (65%) continue to say the federal government has a responsibility to make sure all Americans have health care coverage.
Democrats overwhelmingly (88%) say the federal government has this responsibility, compared with 40% of Republicans.
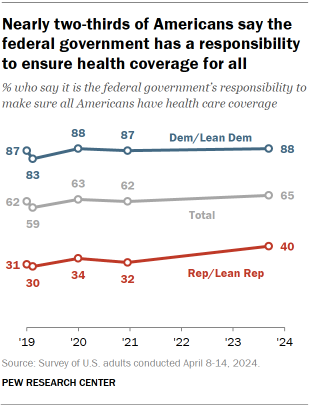
The share of Republicans who say the government has a responsibility to provide health coverage has increased 8 percentage points since 2021, from 32% to 40%.
There are wide income differences among Republicans in opinions about the government’s role in health care:
- 56% of Republicans with lower family incomes say the government has a responsibility to provide health coverage for all, compared with 36% of those with middle incomes and 29% of higher-income Republicans.
When asked how the government should provide health coverage, 36% of Americans say it should be provided through a single national program, while 28% say it should be through a mix of government and private programs. These views have changed little in recent years.
Democrats continue to be more likely than Republicans to favor a “single payer” government health insurance program (53% vs. 18%).
Other key findings in this report
- Americans’ trust in the federal government remains low but has modestly increased since last year. Today, 22% of American adults say they trust the government to do what is right always or most of the time, which is up from 16% in June 2023.
- While the public overall is divided over the nation’s ability to solve important problems, young adults are notably pessimistic about the country’s ability to solve problems . About half of Americans (52%) say the U.S. can’t solve many of its important problems, while 47% say it can find a way to solve problems and get what it wants. Roughly six-in-ten adults under age 30 (62%) say the nation can’t solve major problems, the highest share in any age group and 16 points higher than two years ago.
Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivery Saturday mornings
Sign up for The Briefing
Weekly updates on the world of news & information
- Election 2024
- Federal Government
- Government Spending & the Deficit
- Health Care
- Partisanship & Issues
- Social Security & Medicare
- Trust in Government
Third-party and independent candidates for president often fall short of early polling numbers
6 facts about presidential and vice presidential debates, biden, trump are least-liked pair of major party presidential candidates in at least 3 decades, cultural issues and the 2024 election, more than half of americans are following election news closely, and many are already worn out, most popular, report materials.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
© 2024 Pew Research Center

- Advanced Search
GEEF: : A neural network model for automatic essay feedback generation by integrating writing skills assessment
New citation alert added.
This alert has been successfully added and will be sent to:
You will be notified whenever a record that you have chosen has been cited.
To manage your alert preferences, click on the button below.
New Citation Alert!
Please log in to your account
Information & Contributors
Bibliometrics & citations, view options, recommendations, an elitist non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm enhanced with a neural network applied to the multi-objective optimization of a polysiloxane synthesis process.
This paper presents an original software implementation of the elitist non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm (NSGA-II) applied and adapted to the multi-objective optimization of a polysiloxane synthesis process. An optimized feed-forward neural ...
Original Contribution: Cluster network for recognition of handwritten, cursive script characters
A neural net structure was developed to recognize isolated cursive script characters. Characters were composed of features suggested by an established model of handwriting. The model assumes that handwritten characters are formed from a limited number ...
Segmentation of touching characters using an MLP
In this paper, we propose a method of character extraction from documents in which both Hangul (Korean characters) and alphanumeric characters are written. In order to ensure accurate segmentation of touching characters, character segmentation and ...
Information
Published in.
Pergamon Press, Inc.
United States
Publication History
Author tags.
- Essay feedback generation
- Student essay grading
- Neural network
- Seq2seq models
- Research-article
Contributors
Other metrics, bibliometrics, article metrics.
- 0 Total Citations
- 0 Total Downloads
- Downloads (Last 12 months) 0
- Downloads (Last 6 weeks) 0
View options
Login options.
Check if you have access through your login credentials or your institution to get full access on this article.
Full Access
Share this publication link.
Copying failed.
Share on social media
Affiliations, export citations.
- Please download or close your previous search result export first before starting a new bulk export. Preview is not available. By clicking download, a status dialog will open to start the export process. The process may take a few minutes but once it finishes a file will be downloadable from your browser. You may continue to browse the DL while the export process is in progress. Download
- Download citation
- Copy citation
We are preparing your search results for download ...
We will inform you here when the file is ready.
Your file of search results citations is now ready.
Your search export query has expired. Please try again.
Forgot Your Password?
New to The Nation ? Subscribe
Print subscriber? Activate your online access
Current Issue

The President Can Now Assassinate You, Officially
Under this new standard, a president can go on a four-to-eight-year crime spree and then retire from public life, never to be held accountable.

United States Supreme Court justices pose for their official portrait on October 7, 2022, in Washington, DC.
Welp, Donald Trump won. The Supreme Court today ruled that presidents are entitled to “absolute immunity” from criminal prosecution for official acts, then contended that pressuring the vice president and the Department of Justice to overthrow the government was an “official act,” then said that talking to advisers or making public statements are “official acts” as well, and then determined that evidence of what presidents say and do cannot be used against them to establish that their acts are “unofficial.”
The ruling from the Supreme Court was 6-3, written by Chief Justice John Roberts, on a straight party-line vote, with all the Republican-appointed justices joining to give the president the power of a king. While some parts of the federal indictment against Trump will be remanded back down to the district-court trial judge to determine whether any of Trump’s actions were “unofficial” (“unofficial” acts, the court says, are not entitled to immunity), Trump’s victory in front of the Supreme Court is total. Essentially, all he has to do is claim that everything he did to plot a coup was part of his “official” duties, and the Supreme Court provided no clear method or evidentiary standard that can be used to challenge that presumption.
Legally, there are two critical things to understand about the totality of the court’s ruling here:
- The immunity is absolute
- There is no legislative way to get rid of what the court has given
On the first point, the immunity granted to Trump in this case far exceeds the immunity granted to, say, police officers or other government officials, when they act in their official capacities. Those officials are granted “qualified” immunity from civil penalties. Because the immunity is “qualified,” it can be taken away (“pierced” is the legal jargon for taking away an official’s qualified immunity). People can bring evidence against officials and argue that they shouldn’t be given immunity because of the gravity or depravity of their acts.
Not so with Trump. Presidents are now entitled to “absolute” immunity, which means that no matter what they do, the immunity cannot be lost. They are always and forever immune, no matter what evidence is brought to bear.
Moreover, unlike other officials, presidents are now entitled to absolute immunity from criminal charges. Even a cop can be charged with, say, murder , even if they argue that killing people is part of their jobs. But not presidents. Presidents can murder, rape, steal, and pretty much do whatever they want, so long as they argue that murdering, raping, or stealing is part of the official job of the president of the United States. There is no crime that pierces the veil of absolute immunity.
And there is essentially nothing we can do to change it. The courts created qualified immunity for public officials, but it can be undone by state or federal legislatures if they pass a law removing that protection. Not so with absolute presidential immunity. The court here says that absolute immunity is required by the separation of powers inherent in the Constitution, meaning that Congress cannot take it away. Congress, according to the Supreme Court, does not have the power to pass legislation saying “the president can be prosecuted for crimes.” Impeachment, and only impeachment, is the only way to punish presidents, and, somewhat obviously, impeachment does nothing to a president who is already no longer in office.
The Nation Weekly
Under this new standard, a president can go on a four-to-eight-year crime spree, steal all the money and murder all the people they can get their hands on, all under guise of presumptive “official” behavior, and then retire from public life, never to be held accountable for their crimes while in office. That, according to the court, is what the Constitution requires.
There will be Republicans and legal academics and whatever the hell job Jonathan Turley has who will go into overdrive arguing that the decision isn’t as bad as all that. These bad-faith actors will be quoted or even published in The Washington Post and The New York Times . They will argue that presidents can still be prosecuted for “unofficial acts,” and so they will say that everything is fine.
But they will be wrong, because while the Supreme Court says “unofficial” acts are still prosecutable, the court has left nearly no sphere in which the president can be said to be acting “unofficially.” And more importantly, the court has left virtually no vector of evidence that can be deployed against a president to prove that their acts were “unofficial.” If trying to overthrow the government is “official,” then what isn’t? And if we can’t use the evidence of what the president says or does, because communications with their advisers, other government officials, and the public is “official,” then how can we ever show that an act was taken “unofficially”?
Take the now-classic example of a president ordering Seal Team Six to assassinate a political rival. According to the logic of the Republicans on the Supreme Court, that would likely be an official act. According to their logic, there is also no way to prove it’s “unofficial,” because any conversation the president has with their military advisers (where, for instance, the president tells them why they want a particular person assassinated) is official and cannot be used against them.
There will doubtless be people still wondering if Trump can somehow be prosecuted: The answer is “no.” Special counsel Jack Smith will surely argue that presenting fake electors in connection with his cadre of campaign sycophants was not an “official act.” Lower-court judges may well agree. But when that appeal gets back to the Supreme Court next year, the same justices who just ruled that Trump is entitled to absolute immunity will surely rule that submitting fake electors was also part of Trump’s “official” responsibilities.
The President Can Now Assassinate You, Officially The President Can Now Assassinate You, Officially
Elie mystal, a senior dnc member says there’s a way to replace biden and beat trump a senior dnc member says there’s a way to replace biden and beat trump.
John Nichols
Will Arizona Be MAGA’s Last Stand? Will Arizona Be MAGA’s Last Stand?
Feature / Sasha Abramsky
“I Heard a Machine Gun Being Loaded”: A Harrowing Escape From Gaza “I Heard a Machine Gun Being Loaded”: A Harrowing Escape From Gaza
Comment / Mohammed R. Mhawish
There is no way to change that outcome in the short term. In the long term, the only way to undo the authoritarianism the court has just ushered in is to expand the Supreme Court . Democrats would have to win the upcoming presidential election and the House and the Senate. Then Congress would have to pass a law expanding the number of justices on the Supreme Court; then the Senate would have to pass that law as well, which, at a minimum, would likely have to include getting rid of the filibuster. Then the president would have to sign such a bill, and appoint additional Supreme Court justices who do not think that presidents should be kings—and then those justices would have to be confirmed. And all of that would have to happen before the current Supreme Court hears whatever Trump appeal from his January 6 charges comes up next, because if court expansion happens after the current Supreme Court dismisses the charges against him, double jeopardy will attach and Trump can never be prosecuted again under a less-fascist court.
So, since that’s not going to happen, Trump won. He won completely. He tried to overthrow the government, and he got away with it. I cannot even imagine what he’ll try if he is actually given power again, knowing full well that he will never be held accountable for literal crimes.
If you ever wondered what you’d have done in ancient Rome, when the Roman Republic was shuttered and Augustus Caesar declared himself the “first” citizen of Rome, the answer is: whatever you’re doing right now. It’s what you would have done during the Restoration of King Charles II in England, and what you would have done when Napoleon declared himself emperor of France. This, right here, is how republics die.
And the answer that cries out from the abyss of history is that most people, in real time, don’t care. Republics fall because most citizens are willing to give it away. Most people think that it won’t be that bad to lose the rule of law, and the people who stand to benefit from the ending of republican self-government tell everybody that it will be OK. When the Imperium came to be, the Romans didn’t realize that they were seeing the last form of European self-government for 2,000 years, and the ones who did were largely happy about it.
For my part, I assume that like Mark Antony’s wife, Fulvia, defiling the decapitated head of Cicero, Martha-Ann Alito will be jabbing her golden hairpin into my tongue for criticizing the powerful soon enough. But I’m just a writer. I wonder what the rest of you will do as the last vestiges of democracy are taken away by the Imperial Supreme Court and the untouchable executive officer they’ve just created.
- Submit a correction
- Send a letter to the editor
- Reprints & permissions
Thank you for reading The Nation
We hope you enjoyed the story you just read, just one of the many incisive, deeply-reported articles we publish daily. Now more than ever, we need fearless journalism that shifts the needle on important issues, uncovers malfeasance and corruption, and uplifts voices and perspectives that often go unheard in mainstream media.
Throughout this critical election year and a time of media austerity and renewed campus activism and rising labor organizing, independent journalism that gets to the heart of the matter is more critical than ever before. Donate right now and help us hold the powerful accountable, shine a light on issues that would otherwise be swept under the rug, and build a more just and equitable future.
For nearly 160 years, The Nation has stood for truth, justice, and moral clarity. As a reader-supported publication, we are not beholden to the whims of advertisers or a corporate owner. But it does take financial resources to report on stories that may take weeks or months to properly investigate, thoroughly edit and fact-check articles, and get our stories into the hands of readers.
Donate today and stand with us for a better future. Thank you for being a supporter of independent journalism.
Elie Mystal is The Nation ’s justice correspondent and the host of its legal podcast, Contempt of Court . He is also an Alfred Knobler Fellow at the Type Media Center. His first book is the New York Times bestseller Allow Me to Retort: A Black Guy’s Guide to the Constitution, published by The New Press. Elie can be followed @ElieNYC .
More from The Nation

The Roberts Supreme Court’s Decision on Netchoice Was Righteous The Roberts Supreme Court’s Decision on Netchoice Was Righteous
No, that is not a typo. Amid the deluge this week, Big Tech didn't get what it wanted. And the court left open the possibility that we might get social media regulation right.
Zephyr Teachout

Prison Innovations Prison Innovations
Writer James Kilgore and information artist Vic Liu demonstrate the improvisations and ingenuities that allow incarcerated people to experience some small human comforts.
Visualization / James Kilgore and Vic Liu

We’re Caught in Another Cycle of Racial Progress and Backlash We’re Caught in Another Cycle of Racial Progress and Backlash
The racial justice uprisings in 2020 led to some minor achievements—and a major backlash.
The Front Burner / Kali Holloway

There Is No Universal Free Speech There Is No Universal Free Speech
PEN America hides behind the false universalism of free speech, but institutions always choose whom to protect.
Comment / P.E. Moskowitz

Do July Jitters Mean a Nightmare in November? Do July Jitters Mean a Nightmare in November?
The center may have held in the EU elections, but Americans are starting to tug their shirt collars.
Editorial / D.D. Guttenplan
Letters From the July 2024 Issue Letters From the July 2024 Issue
The cost of psychotherapy… The Yemen script… Surface beauty… Correction…
Letters / Our Readers
Latest from the nation
The roberts supreme court’s decision on netchoice was righteous, democrats are running interference for biden. voters aren't convinced., campaigns and elections, gun accessories, what does it mean to be a labor leader for this moment, a senior dnc member says there’s a way to replace biden and beat trump, editor's picks.

VIDEO: People in Denmark Are a Lot Happier Than People in the United States. Here’s Why.

Historical Amnesia About Slavery Is a Tool of White Supremacy
- Library of Congress
- Research Guides
- Main Reading Room
Federalist Papers: Primary Documents in American History
Full text of the federalist papers.
- Introduction
- Federalist Nos. 1-10
- Federalist Nos. 11-20
- Federalist Nos. 21-30
- Federalist Nos. 31-40
- Federalist Nos. 41-50
- Federalist Nos. 51-60
- Federalist Nos. 61-70
- Federalist Nos. 71-80
- Federalist Nos. 81-85
- Related Digital Resources
- External Websites
- Print Resources
History, Humanities & Social Sciences : Ask a Librarian
Have a question? Need assistance? Use our online form to ask a librarian for help.
Chat with a librarian , Monday through Friday, 12-4pm Eastern Time (except Federal Holidays).
The Federalist , commonly referred to as the Federalist Papers, is a series of 85 essays written by Alexander Hamilton, John Jay, and James Madison between October 1787 and May 1788. The essays were published anonymously, under the pen name "Publius," in various New York state newspapers of the time.
The Federalist Papers were written and published to urge New Yorkers to ratify the proposed United States Constitution, which was drafted in Philadelphia in the summer of 1787. In lobbying for adoption of the Constitution over the existing Articles of Confederation, the essays explain particular provisions of the Constitution in detail. For this reason, and because Hamilton and Madison were each members of the Constitutional Convention, the Federalist Papers are often used today to help interpret the intentions of those drafting the Constitution.
The Federalist Papers were published primarily in two New York state newspapers: The New York Packet and The Independent Journal . They were reprinted in other newspapers in New York state and in several cities in other states. A bound edition, with revisions and corrections by Hamilton, was published in 1788 by printers J. and A. McLean. An edition published by printer Jacob Gideon in 1818, with revisions and corrections by Madison, was the first to identify each essay by its author's name. Because of its publishing history, the assignment of authorship, numbering, and exact wording may vary with different editions of The Federalist .
The electronic text of The Federalist used here was compiled for Project Gutenberg by scholars who drew on many available versions of the papers.
One printed edition of the text is The Federalist , edited by Jacob E. Cooke (Middletown, Conn., Wesleyan University Press, 1961). Cooke's introduction provides background information on the printing history of The Federalist; the information provided above comes in part from his work.
This web-friendly presentation of the original text of the Federalist Papers (also known as The Federalist) was obtained from the e-text archives of Project Gutenberg. Any irregularities with regard to grammar, syntax, spelling, or punctuation are as they exist in the original e-text archives.
Table of Contents
| No. | Title | Author | Publication | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Hamilton | For the | -- | |
| 2. | Jay | For the | -- | |
| 3. | Jay | For the | -- | |
| 4. | Jay | For the | -- | |
| 5. | Jay | For the | -- | |
| 6. | Hamilton | For the | -- | |
| 7. | Hamilton | For the | -- | |
| 8. | Hamilton | From the | Tuesday, November 20, 1787 | |
| 9. | Hamilton | For the | -- | |
| 10. | Madison | Frm the | Friday, November 27, 1787 | |
| 11. | Hamilton | For the | -- | |
| 12. | Hamilton | From the | Tuesday, November 27, 1787 | |
| 13. | Hamilton | For the | -- | |
| 14. | Madison | From the | Friday, November 30, 1787 | |
| 15. | Hamilton | For the | -- | |
| 16. | Hamilton | From the | Tuesday, December 4, 1787 | |
| 17. | Hamilton | For the | -- | |
| 18. | Hamilton and Madison | For the | -- | |
| 19. | Hamilton and Madison | For the | -- | |
| 20. | Hamilton and Madison | From the | Tuesday, December 11, 1787 | |
| 21. | Hamilton | For the | -- | |
| 22. | Hamilton | From the | Friday, December 14, 1787 | |
| 23. | Hamilton | From the | Tuesday, December 17, 1787 | |
| 24. | Hamilton | For the | -- | |
| 25. | Hamilton | From the | Friday, December 21, 1787 | |
| 26. | Hamilton | For the | -- | |
| 27. | Hamilton | From the | Tuesday, December 25, 1787 | |
| 28. | Hamilton | For the | -- | |
| 29. | Hamilton | From the | Thursday, January 10, 1788 | |
| 30. | Hamilton | From the | Friday, December 28, 1787 | |
| 31. | Hamilton | From the | Tuesday, January 1, 1788 | |
| 32. | Hamilton | From the | Thursday, January 3, 1788 | |
| 33. | Hamilton | From the | Thursday, January 3, 1788 | |
| 34. | Hamilton | From the | Friday, January 4, 1788 | |
| 35. | Hamilton | For the | -- | |
| 36. | Hamilton | From the | Tuesday, January 8, 1788 | |
| 37. | Madison | From the | Friday, January 11, 1788 | |
| 38. | Madison | From the | Tuesday, January 15, 1788 | |
| 39. | Madison | For the | -- | |
| 40. | Madison | From the | Friday, January 18, 1788 | |
| 41. | Madison | For the | -- | |
| 42. | Madison | From the | Tuesday, January 22, 1788 | |
| 43. | Madison | For the | -- | |
| 44. | Madison | From the | Friday, January 25, 1788 | |
| 45. | Madison | For the | -- | |
| 46. | Madison | From the | Tuesday, January 29, 1788 | |
| 47. | Madison | From the | Friday, February 1, 1788 | |
| 48. | Madison | From the | Friday, February 1, 1788 | |
| 49. | Hamilton or Madison | From the | Tuesday, February 5, 1788 | |
| 50. | Hamilton or Madison | From the | Tuesday, February 5, 1788 | |
| 51. | Hamilton or Madison | From the | Friday, February 8, 1788 | |
| 52. | Hamilton or Madison | From the | Friday, February 8, 1788 | |
| 53. | Hamilton or Madison | From the | Tuesday, February 12, 1788 | |
| 54. | Hamilton or Madison | From the | Tuesday, February 12, 1788 | |
| 55. | Hamilton or Madison | From the | Friday, February 15, 1788 | |
| 56. | Hamilton or Madison | From the | Tuesday, February 19, 1788 | |
| 57. | Hamilton or Madison | From the | Tuesday, February 19, 1788 | |
| 58. | Madison | -- | -- | |
| 59. | Hamilton | From the | Friday, February 22, 1788 | |
| 60. | Hamilton | From the | Tuesday, February 26, 1788 | |
| 61. | Hamilton | From the | Tuesday, February 26, 1788 | |
| 62. | Hamilton or Madison | For the | -- | |
| 63. | Hamilton or Madison | For the | -- | |
| 64. | Jay | From the | Friday, March 7, 1788 | |
| 65. | Hamilton | From the | Friday, March 7, 1788 | |
| 66. | Hamilton | From the | Tuesday, March 11, 1788 | |
| 67. | Hamilton | From the | Tuesday, March 11, 1788 | |
| 68. | Hamilton | From the | Friday, March 14, 1788 | |
| 69. | Hamilton | From the | Friday, March 14, 1788 | |
| 70. | Hamilton | From the | Friday, March 14, 1788 | |
| 71. | Hamilton | From the | Tuesday, March 18, 1788 | |
| 72. | Hamilton | From the | Friday, March 21, 1788 | |
| 73. | Hamilton | From the | Friday, March 21, 1788 | |
| 74. | Hamilton | From the | Tuesday, March 25, 1788 | |
| 75. | Hamilton | For the | -- | |
| 76. | Hamilton | From the | Tuesday, April 1, 1788 | |
| 77. | Hamilton | From the | Friday, April 4, 1788 | |
| 78. | Hamilton | From McLEAN's Edition, New York | -- | |
| 79. | Hamilton | From McLEAN's Edition, New York | -- | |
| 80. | Hamilton | From McLEAN's Edition, New York | -- | |
| 81. | Hamilton | From McLEAN's Edition | -- | |
| 82. | Hamilton | From McLEAN's Edition | -- | |
| 83. | Hamilton | From McLEAN's Edition | -- | |
| 84. | Hamilton | From McLEAN's Edition | -- | |
| 85. | Hamilton | From McLEAN's Edition | -- |
- << Previous: Introduction
- Next: Federalist Nos. 1-10 >>
- Last Updated: Apr 25, 2024 10:16 AM
- URL: https://guides.loc.gov/federalist-papers
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research paper
- Research Paper Format | APA, MLA, & Chicago Templates
Research Paper Format | APA, MLA, & Chicago Templates
Published on November 19, 2022 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on January 20, 2023.
The formatting of a research paper is different depending on which style guide you’re following. In addition to citations , APA, MLA, and Chicago provide format guidelines for things like font choices, page layout, format of headings and the format of the reference page.
Scribbr offers free Microsoft Word templates for the most common formats. Simply download and get started on your paper.
APA | MLA | Chicago author-date | Chicago notes & bibliography
- Generate an automatic table of contents
- Generate a list of tables and figures
- Ensure consistent paragraph formatting
- Insert page numbering
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Formatting an apa paper, formatting an mla paper, formatting a chicago paper, frequently asked questions about research paper formatting.
The main guidelines for formatting a paper in APA Style are as follows:
- Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman or 11 pt Arial.
- Set 1 inch page margins.
- Apply double line spacing.
- If submitting for publication, insert a APA running head on every page.
- Indent every new paragraph ½ inch.
Watch the video below for a quick guide to setting up the format in Google Docs.
The image below shows how to format an APA Style title page for a student paper.
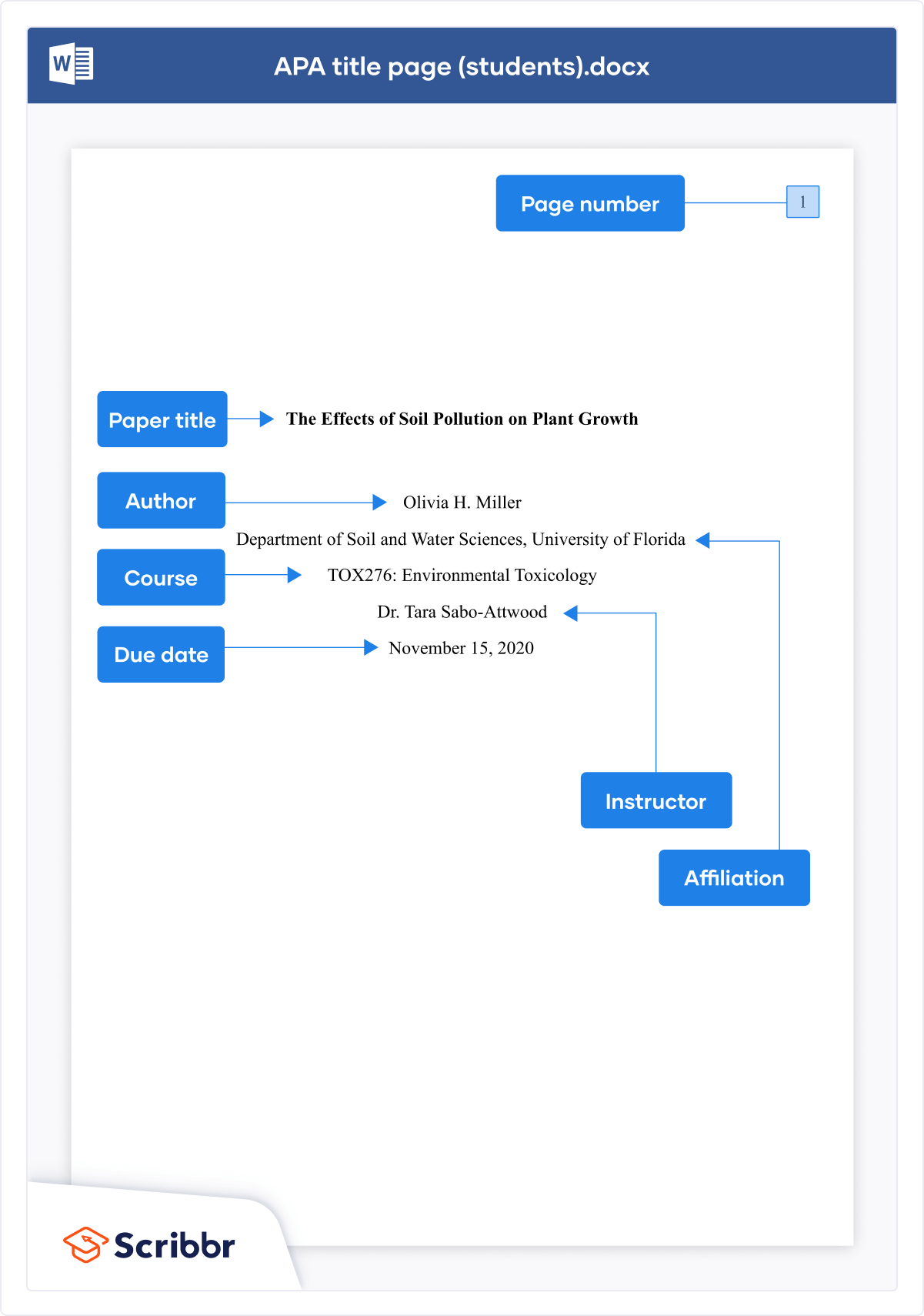
Running head
If you are submitting a paper for publication, APA requires you to include a running head on each page. The image below shows you how this should be formatted.
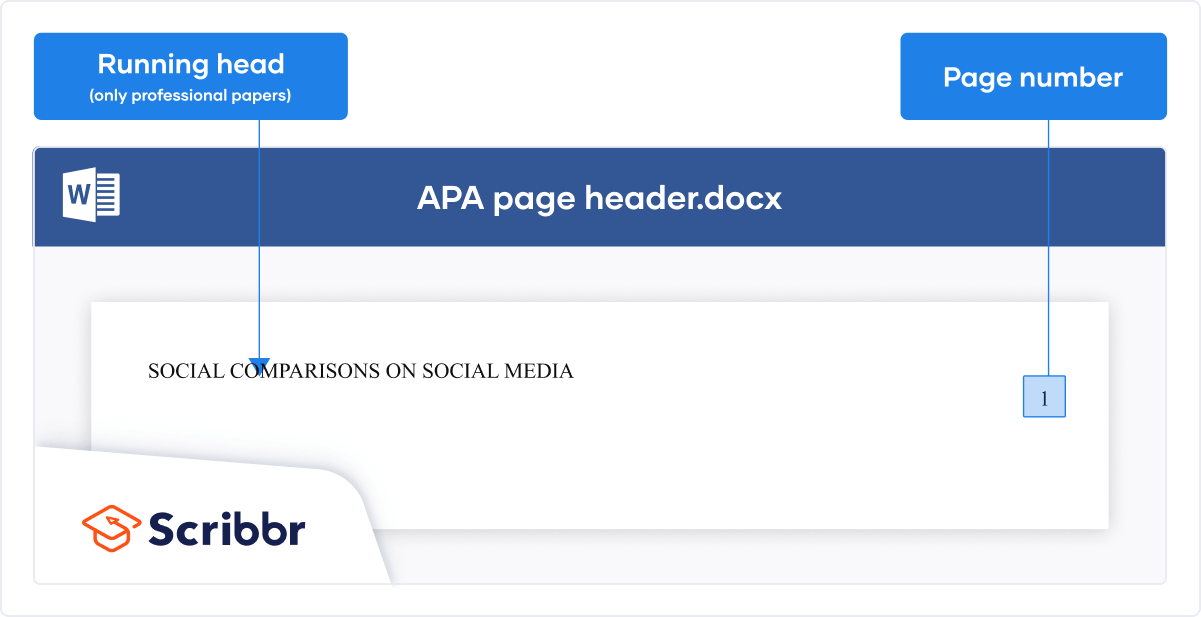
For student papers, no running head is required unless you have been instructed to include one.
APA provides guidelines for formatting up to five levels of heading within your paper. Level 1 headings are the most general, level 5 the most specific.
Reference page
APA Style citation requires (author-date) APA in-text citations throughout the text and an APA Style reference page at the end. The image below shows how the reference page should be formatted.
Note that the format of reference entries is different depending on the source type. You can easily create your citations and reference list using the free APA Citation Generator.
Generate APA citations for free
Don't submit your assignments before you do this
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students. Free citation check included.

Try for free
The main guidelines for writing an MLA style paper are as follows:
- Use an easily readable font like 12 pt Times New Roman.
- Use title case capitalization for headings .
Check out the video below to see how to set up the format in Google Docs.
On the first page of an MLA paper, a heading appears above your title, featuring some key information:
- Your full name
- Your instructor’s or supervisor’s name
- The course name or number
- The due date of the assignment
Page header
A header appears at the top of each page in your paper, including your surname and the page number.
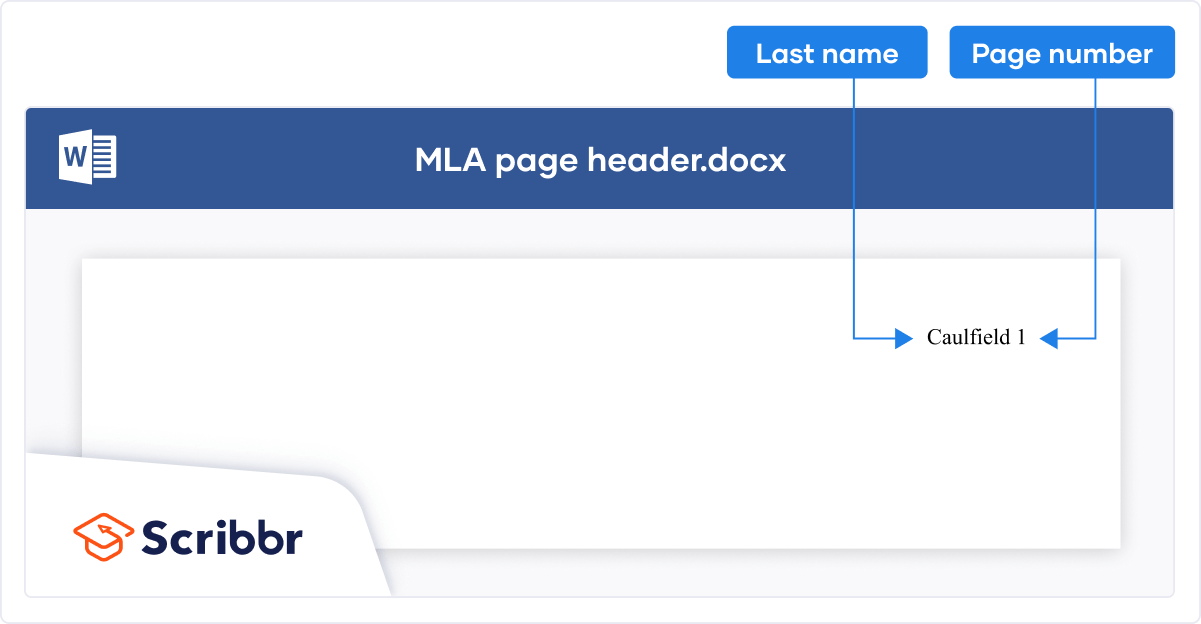
Works Cited page
MLA in-text citations appear wherever you refer to a source in your text. The MLA Works Cited page appears at the end of your text, listing all the sources used. It is formatted as shown below.
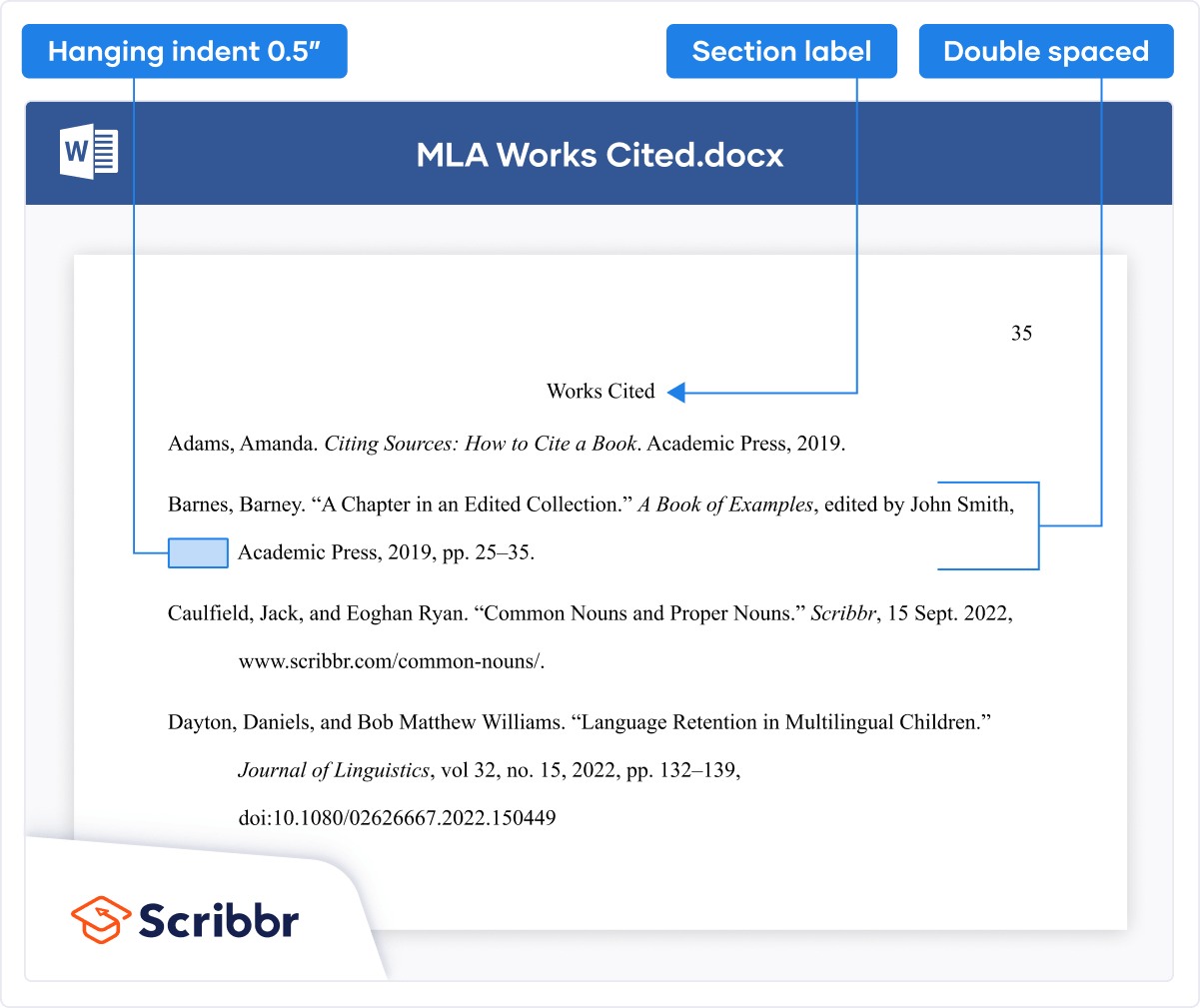
You can easily create your MLA citations and save your Works Cited list with the free MLA Citation Generator.
Generate MLA citations for free
The main guidelines for writing a paper in Chicago style (also known as Turabian style) are:
- Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman.
- Use 1 inch margins or larger.
- Place page numbers in the top right or bottom center.
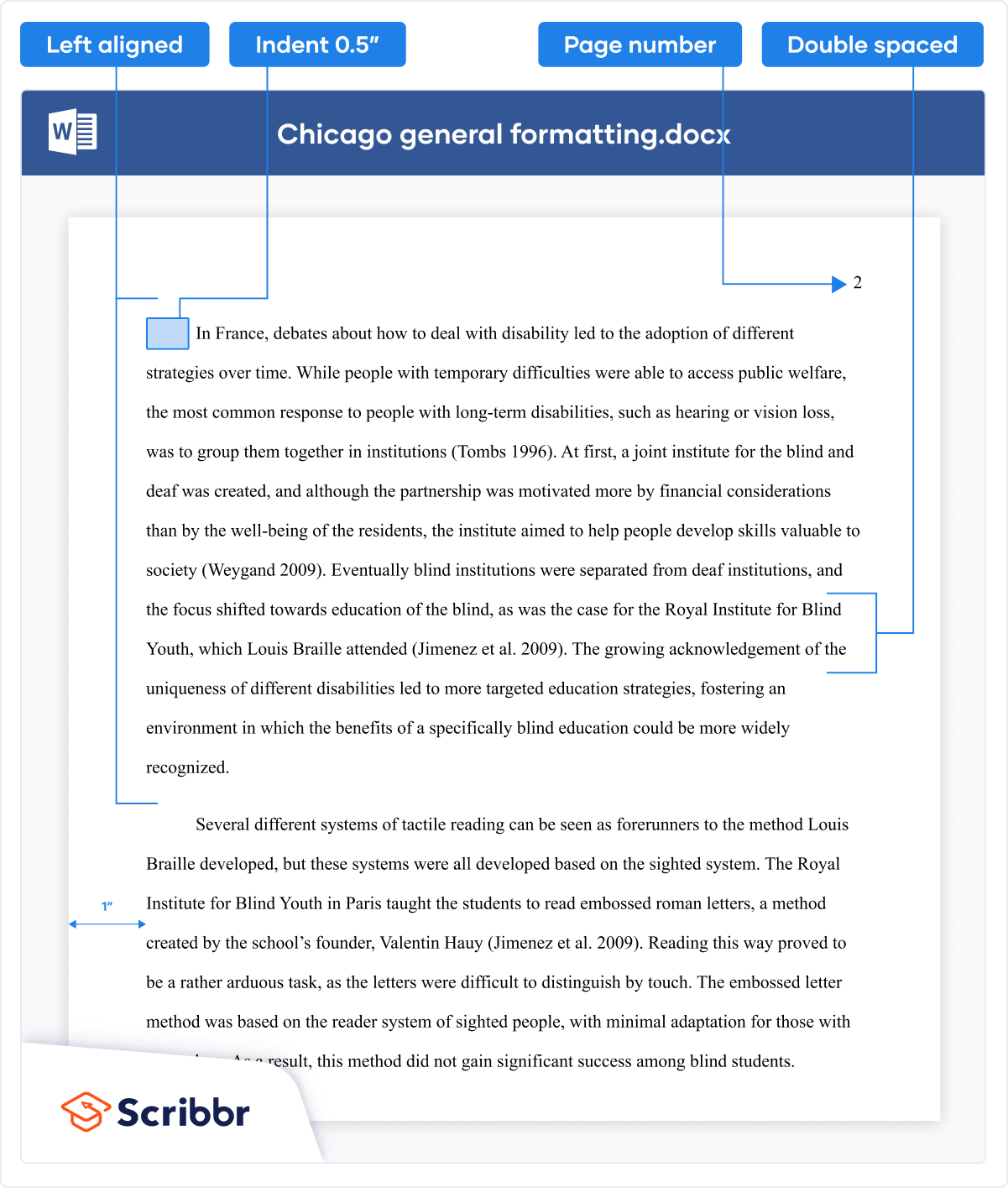
Chicago doesn’t require a title page , but if you want to include one, Turabian (based on Chicago) presents some guidelines. Lay out the title page as shown below.
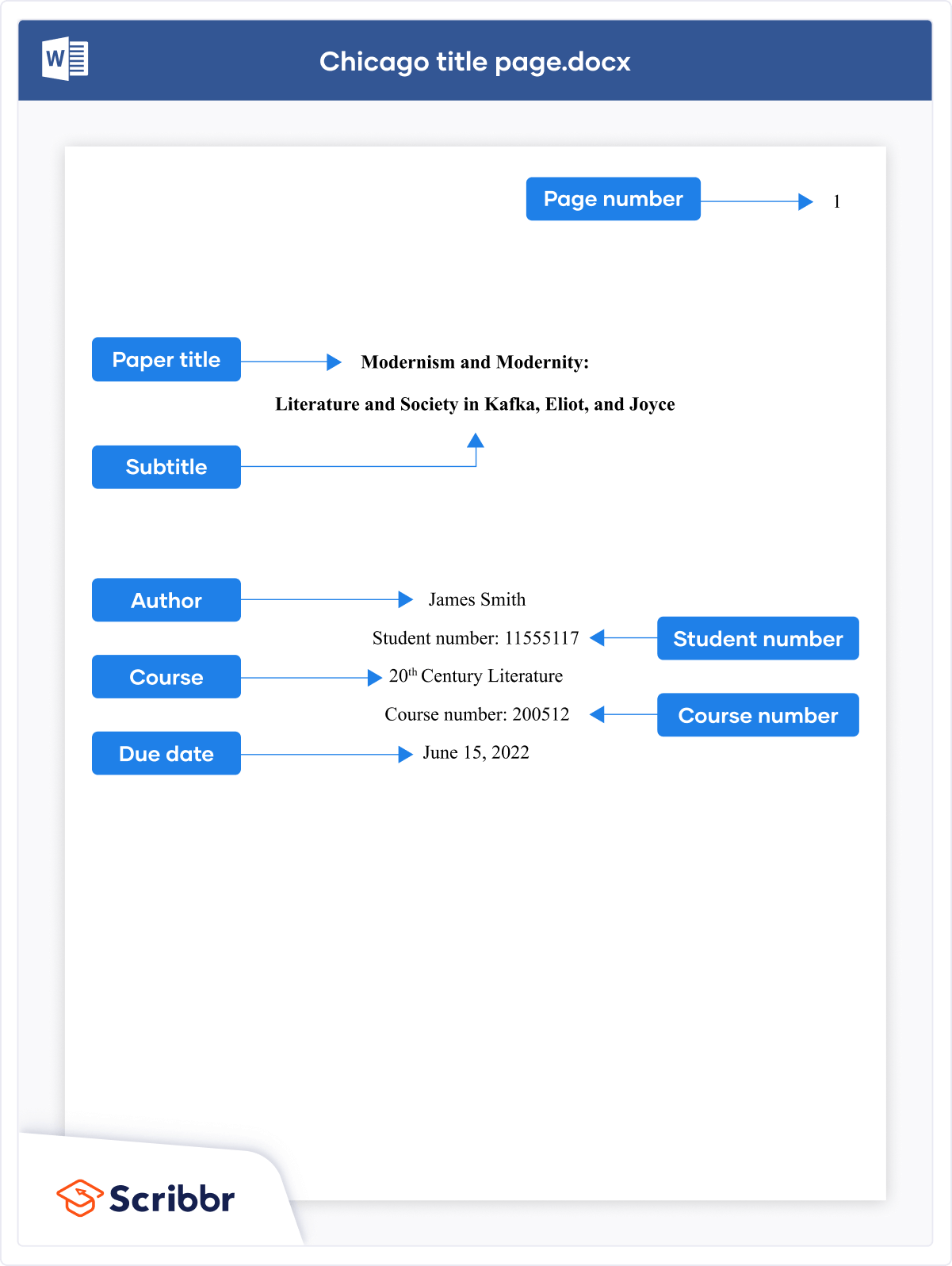
Bibliography or reference list
Chicago offers two citation styles : author-date citations plus a reference list, or footnote citations plus a bibliography. Choose one style or the other and use it consistently.
The reference list or bibliography appears at the end of the paper. Both styles present this page similarly in terms of formatting, as shown below.
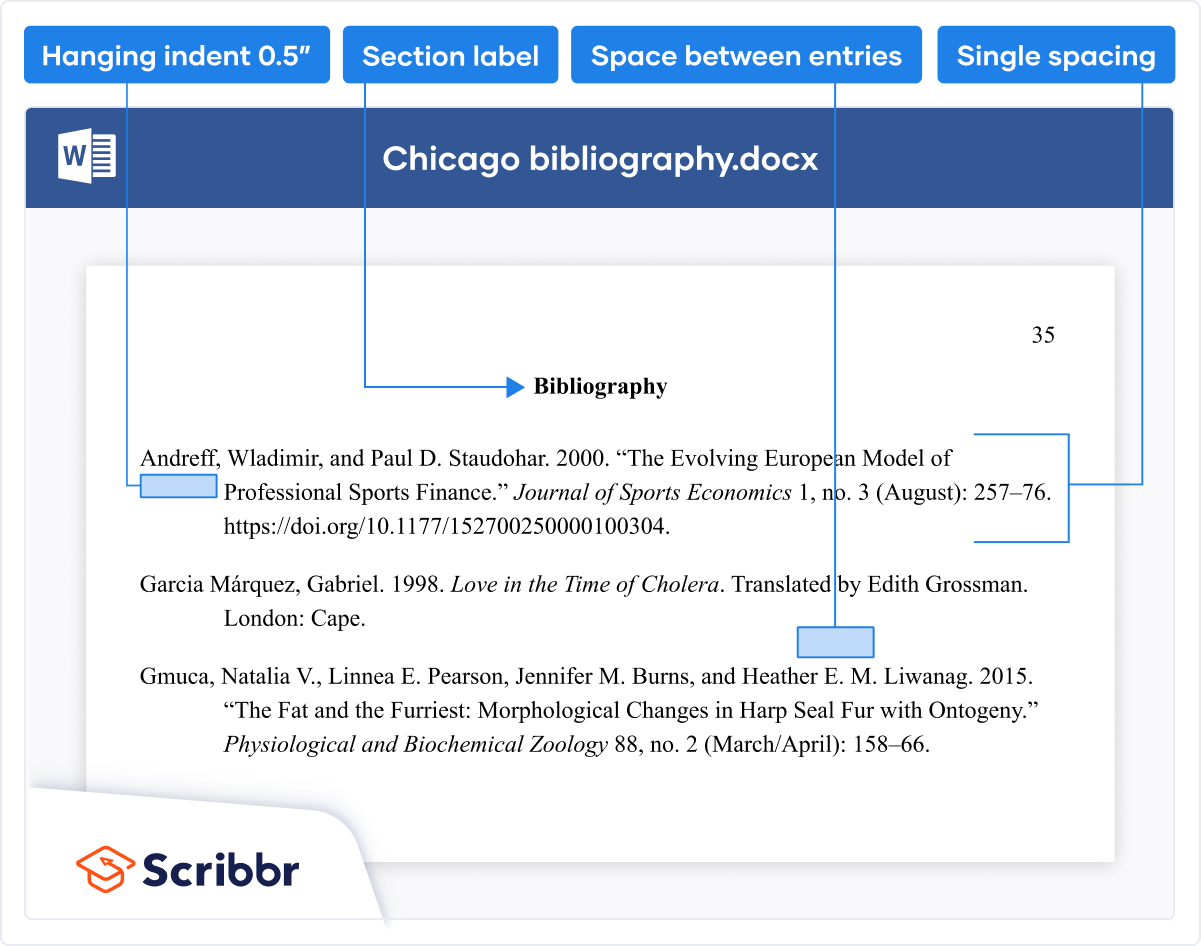
To format a paper in APA Style , follow these guidelines:
- Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman or 11 pt Arial
- Set 1 inch page margins
- Apply double line spacing
- Include a title page
- If submitting for publication, insert a running head on every page
- Indent every new paragraph ½ inch
- Apply APA heading styles
- Cite your sources with APA in-text citations
- List all sources cited on a reference page at the end
The main guidelines for formatting a paper in MLA style are as follows:
- Use an easily readable font like 12 pt Times New Roman
- Include a four-line MLA heading on the first page
- Center the paper’s title
- Use title case capitalization for headings
- Cite your sources with MLA in-text citations
- List all sources cited on a Works Cited page at the end
The main guidelines for formatting a paper in Chicago style are to:
- Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman
- Use 1 inch margins or larger
- Place page numbers in the top right or bottom center
- Cite your sources with author-date citations or Chicago footnotes
- Include a bibliography or reference list
To automatically generate accurate Chicago references, you can use Scribbr’s free Chicago reference generator .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, January 20). Research Paper Format | APA, MLA, & Chicago Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved July 2, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-paper/research-paper-format/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, apa format for academic papers and essays, mla format for academic papers and essays, chicago style format for papers | requirements & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Reading Time: 14 minutes In this article I will show you how to write a research paper using the four LEAP writing steps. The LEAP academic writing approach is a step-by-step method for turning research results into a published paper.. The LEAP writing approach has been the cornerstone of the 70 + research papers that I have authored and the 3700+ citations these paper have accumulated within ...
A research paper is a piece of academic writing that provides analysis, interpretation, and argument based on in-depth independent research. Research papers are similar to academic essays, but they are usually longer and more detailed assignments, designed to assess not only your writing skills but also your skills in scholarly research ...
Writing a research paper is an essential aspect of academics and should not be avoided on account of one's anxiety. In fact, the process of writing a research paper can be one of the more rewarding experiences one may encounter in academics. What is more, many students will continue to do research throughout their careers, which is one of the ...
We've covered a lot of ground here. To recap, the three steps to writing a high-quality research paper are: To choose a research question and review the literature. To plan your paper structure and draft an outline. To take an iterative approach to writing, focusing on critical writing and strong referencing.
Research papers are deep dives into a topic. Therefore, they tend to be longer pieces of work than essays or opinion pieces. The specific number of words or pages will depend on your college, school, or publication's requirements. According to ResearchersNetwork.org, research papers average around 4,000-6,000 words.
Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
Definition: Research Paper is a written document that presents the author's original research, analysis, and interpretation of a specific topic or issue. It is typically based on Empirical Evidence, and may involve qualitative or quantitative research methods, or a combination of both. The purpose of a research paper is to contribute new ...
This interactive resource from Baylor University creates a suggested writing schedule based on how much time a student has to work on the assignment. "Research Paper Planner" (UCLA) UCLA's library offers this step-by-step guide to the research paper writing process, which also includes a suggested planning calendar.
Writing a Research Paper. This page lists some of the stages involved in writing a library-based research paper. Although this list suggests that there is a simple, linear process to writing such a paper, the actual process of writing a research paper is often a messy and recursive one, so please use this outline as a flexible guide.
Do your research and gather sources. Come up with a thesis. Create an essay outline. Write the introduction. Write the main body, organized into paragraphs. Write the conclusion. Evaluate the overall organization. Revise the content of each paragraph. Proofread your essay or use a Grammar Checker for language errors.
Research papers are a requirement for most college courses, so knowing how to write a research paper is important. These in-depth pieces of academic writing can seem pretty daunting, but there's no need to panic. When broken down into its key components, writing your paper should be a manageable and, dare we say it, enjoyable task.
Unlock the secrets to crafting an outstanding research paper with our step-by-step guide. From choosing a compelling topic to refining your thesis statement, our expert tips will help you navigate the intricacies of research paper writing. Elevate your academic prowess and ensure success in your endeavors with this essential resource.
A research paper explores and evaluates previously and newly gathered information on a topic, then offers evidence for an argument. It follows academic writing standards, and virtually every college student will write at least one. Research papers are also integral to scientific fields, among others, as the most reliable way to share knowledge.
A research paper is a comprehensive document presenting the findings, analysis, and interpretation of an original study or investigation. It typically follows a structured format, including an introduction outlining the research question or problem, a review of relevant literature, methodology detailing the approach used to collect and analyze data, results presenting the findings of the study ...
Download Article. 1. Break up your essay into sub-topics. You will probably need to address several distinct aspects of your research topic in your essay. This is an important tactic for producing a well-organized research essay because it avoids 'stream of consciousness' writing, which typically lacks order.
The goal of this book has been to help demystify research and inquiry through a series of genres that are part of the research process. Each of these writing projects—the annotated bibliography, proposal, literature review, and research essay—builds on each other. Research is an ongoing and evolving process, and each of these projects help ...
Step 4: Create a Research Paper Outline. Outlining is a key part of crafting an effective essay. Your research paper outline should include a rough introduction to the topic, a thesis statement, supporting details for each main idea, and a brief conclusion. You can outline in whatever way feels most comfortable for you.
Here are 7 steps on how to write a research paper, plus two optional steps on creating a title page and an abstract: Step 1: Understand your instructor's expectations for how to write a research paper. Step 2: Brainstorm research paper ideas. Step 3: Conduct research. Step 4: Define your thesis statement.
Then, make sure the topic you choose can be discussed adequately in the prescribed essay length. Finally, decide on the approach you want to take while writing—expository, analytical, argumentative, or any other writing style. For more help, browse Bartleby's exhaustive reservoir of essay prompts and get a headstart on your next assignment.
To write a research paper, select a topic, gather and organize information, and formulate a thesis. Create an outline, draft the main content, reassess your thesis, and revise the draft. Finally, write the introduction and conclusion, then thoroughly proofread and edit. Writing a research paper is a pivotal academic endeavor that deepens your ...
As research essays have a beginning, so do they have an ending, generally called a conclusion. While the main purpose of an introduction is to get the reader's attention and to explain what the essay will be about, the goal of a conclusion is to bring the reader to a satisfying point of closure. In other words, a good conclusion does not ...
A decimal outline is similar in format to the alphanumeric outline, but with a different numbering system: 1, 1.1, 1.2, etc. Text is written as short notes rather than full sentences. Example: 1 Body paragraph one. 1.1 First point. 1.1.1 Sub-point of first point. 1.1.2 Sub-point of first point.
Tools for writing a research paper introduction. Now that we've introduced you to the basics of writing a research paper introduction, we'd like to introduce you to QuillBot. At every step of writing your intro, it can help you upgrade your writing skills: Cite sources using the Citation Generator. Avoid plagiarism using the Plagiarism Checker.
A recent paper by urban economist Justin Tyndall found that increasing the front-end height of a vehicle by roughly 4 inches (10 centimeters) increases the chance of a pedestrian fatality by 22% ...
Pew Research Center conducted this study to understand Americans' attitudes about U.S. government, such as its size and role. This report is based primarily on a survey of 8,709 adults, including 7,166 registered voters, from April 8 to 14, 2024. Some of the analysis in this report is based on a survey of 8,638 adults from May 13 to 19, 2024.
Assessing students' writing ability has always been an important component of research on automatic essay evaluation. The existing methods usually focus on outputting numerical scores, and there is little research on providing feedback on writing quality based on text generation techniques.
The ruling from the Supreme Court was 6-3, written by Chief Justice John Roberts, on a straight party-line vote, with all the Republican-appointed justices joining to give the president the power ...
The Federalist, commonly referred to as the Federalist Papers, is a series of 85 essays written by Alexander Hamilton, John Jay, and James Madison between October 1787 and May 1788.The essays were published anonymously, under the pen name "Publius," in various New York state newspapers of the time. The Federalist Papers were written and published to urge New Yorkers to ratify the proposed ...
Formatting a Chicago paper. The main guidelines for writing a paper in Chicago style (also known as Turabian style) are: Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman. Use 1 inch margins or larger. Apply double line spacing. Indent every new paragraph ½ inch. Place page numbers in the top right or bottom center. Title page
Review Essay on Climate Migration - Critical Perspectives for Law, Policy and Research and The Great Displacement - Climate Change and the Next American Migration Atmaja Gohain Baruah Comparative Asian Studies, National University of Singapore, Singapore, Singapore Correspondence [email protected] [email protected]