
- A+ A- Text Size
- About the Court
- Judicial Conference
- Courts4Civics /
- Essay Contest

Banner Graphic Images: Background: U.S. Supreme Court Building, Washington, D.C. - Left: Excerpt from page 9 (emphasis added) of the unanimous Supreme Court ruling in Brown v. Board of Education , May 17, 1954. Courtesy of the National Archives & Records Administration - Right: A nearly empty hallway at Central High School, Little Rock, Arkansas, during the time that it was closed to avoid integrating, Sept. 1958. Thomas J. O'Halloran, Courtesy of the Library of Congress
*Entries for the 2024 Essay Contest are closed.*
*CONTEST DEADLINE EXTENDED TO ...*
*2024 Essay Contest Winners Announced*
Seventy years ago, the Supreme Court held in Brown v. Board of Education , 347 U.S. 483 (1954), that racial segregation in public schools violates the United States Constitution. The Court recognized that public education is "the very foundation of good citizenship," and Brown 's impact on education and society has been the subject of much discussion and debate in our nation's history.
Has the decision in Brown , viewed through the lens of 2024, achieved its purpose of ensuring equal opportunity in public education?
Consider one or more of these questions in preparing your essay:
- What purpose, or purposes, does Brown 's goal of diversity in schools serve in educating citizens in a democracy?
- What is the importance of Brown and the equal protection of the laws in later educational or societal changes?
- What institutions or groups should play a role in ensuring racial diversity in education, and how?
- How did the decision in Brown impact other landmark Supreme Court decisions?
- In deciding cases with a major impact on society, like Brown , should the Supreme Court consider public opinion on the subject at issue? If so, how would the Court evaluate the public opinion in making its decision?

Who May Enter
The Fourth Circuit Student Essay Contest is open to all students currently in grades 6 through 12 from Maryland, North Carolina, South Carolina, Virginia, and West Virginia.
Note: Prior award winners as well as children, grandchildren, stepchildren, and members of the household of a federal judge or federal judiciary employee are excluded from the competition.
Submission Deadline
Your essay and entry form must be submitted by 11:59 p.m. Eastern Time on Friday, May 31, 2024 . The contest entry form has instructions for submitting your essay. Your essay must be submitted at the same time as your entry form.
- Understanding of constitutional principles (35 points) Demonstrates a clear understanding of the historical context and significance of Brown v. Board of Education .
- Analysis and interpretation (25 points) Provides thoughtful analysis and considers competing viewpoints before reaching a conclusion.
- Clarity and organization (20 points) Presents ideas clearly and in well-structured paragraphs. Maintains focus on a central theme.
- Evidence and support (10 points) Identifies and attributes information from credible sources. Students will not be graded based on citation format, but the reader should be able to easily identify the source.
- Grammar, spelling, and composition (10 points) Uses appropriate vocabulary and sentence structure, with minimal spelling or grammatical errors.
Exceeding the word limit, missing the submission deadline, using AI-generated content, plagiarizing content, providing false entry information, and not adhering to the rules are grounds for disqualification.
Length & Format
Essays are limited to the length indicated for each grade group . Citations should be placed in footnotes, endnotes, works cited, or a bibliography and are excluded from the word count. Submit your essay without your name in the following format:
- Grades 9–12: Microsoft Word or Adobe Acrobat PDF document
- Grades 6–8: Text typed or pasted into form section
- Do not submit your essay as a link.
Winners will be announced in August 2024, and the winning essays will be presented at the Fourth Circuit's Constitution Day Program in September 2024.
Contest Flyer
Contact the Clerk's Office at [email protected] or (804) 916-2715.

Submit Your Entry Form & Essay
Background Essay: The Supreme Court and the Bill of Rights

Guiding Question: How has the Supreme Court decided cases in controversies related to the Bill of Rights?
- I can identify the role of the Supreme Court in protecting civil liberties.
- I can explain how the Supreme Court’s role has changed over time.
Essential Vocabulary
During the last 60 years, the Supreme Court has become perhaps the central defender of civil liberties, or freedoms that government is not allowed to restrict, in the United States. This role has been a relatively recent development that marked a distinct change from the Founding, when the Court mostly addressed government powers. The evolution of this role for the Court has greatly expanded popular expectations of enjoying individual rights. However, it has also been fraught with numerous difficulties, both for the constitutional order and for the Supreme Court itself, as it has become the center of controversy about rights.
Limited Government and the Supreme Court
The original Founding understanding of the Bill of Rights was that it limited the powers of the federal government to violate the rights of the people. When originally ratified, the Bill of Rights only applied to the national government, not to state governments. State governments had their own bills of rights to protect their citizens. This reflected the constitutional principle of federalism, or the separation of powers between state and national governments. The Supreme Court endorsed this Founding view that the Bill of Rights applied only to the national government in the case Barron v. Baltimore (1833).
Moreover, this also represented the principle of limited government, one of the foundations of protecting liberties. The national government had certain enumerated and implied powers that the three branches—legislative, executive, and judicial—exercised in making, executing, and interpreting the law. Enumerated powers are those listed explicitly in the Constitution. Implied powers are those that government has that are not written in the document. The national government could not exceed these powers to violate the liberties of the people. To further this protection, states had their own bills of rights. The Declaration of Independence asserted that the ultimate protection of the people’s liberties is the overthrow of a tyrannical government after a long train of abuses.
The role of the Court was to hear all cases arising under the Constitution. After the case of Marbury v. Madison (1803), the Court’s role expanded to include determining the constitutionality of governmental laws and actions. However, there was debate over whether or not the other branches also had the responsibility of interpreting the Constitution.
It is important to note that although the Court could rule a law or action unconstitutional, it was not necessarily the final word on the Constitution. In a speech critical of the Dred Scott v. Sandford (1857) decision, Abraham Lincoln quoted Andrew Jackson, saying, “The Congress, the executive and the court, must each for itself be guided by its own opinion of the Constitution.” Lincoln was arguing that the Court’s authority and just precedents , or earlier laws or rulings, should be respected, but the Supreme Court was not necessarily the final word on the meaning of the Constitution and could make errors, as it did in Dred Scott . All the branches must interpret the document in the exercise of their constitutional powers for the ends of liberty, equality, and justice.
The Supreme Court, Incorporation, and the Bill of Rights from the Twentieth Century to Today
The due process clause of the 14th Amendment led to the incorporation of the Bill of Rights, which meant that the Supreme Court applied the Bill of Rights to the states. During the first half of the twentieth century, the Court incorporated the Bill of Rights selectively in a few cases. For example, it extended the First Amendment right of free speech against state violation in Gitlow v. New York (1925) and freedom of the press in Near v. Minnesota (1931).
The popular understanding of the Court as the protector of individual rights became widely accepted during the Warren Court (1953–1969) and after. Many of the decisions were controversial because Americans viewed the issues involved differently. Some Americans questioned whether the Court was the appropriate branch to define rights or whether it should be left to the other branches of government or the amendment process. The Court also controversially overturned the laws and common values of states and local communities for one uniform, national standard.
The Court expanded the application of the Bill of Rights (incorporated) to the states in several areas and protected civil liberties in new ways. For example, the Court banned school-sponsored prayer and Bible reading in public schools in Engel v. Vitale (1962) and Abington School District v. Schempp (1963), respectively, for violating the establishment clause of the First Amendment.
The Court protected the rights of students in local public schools in other ways. In Tinker v. Des Moines (1969), the Court decided that students had the right of free speech to protest the Vietnam War under the First Amendment. The students had worn black armbands to protest the war despite a warning not to, and the school suspended them.
The Court protected the rights of the accused in major cases during the mid-1960s. The Court stated that criminal defendants are entitled to an attorney in Gideon v. Wainwright (1963). The Court excluded, or left out, illegally seized criminal evidence under the Fourth Amendment in Mapp v. Ohio (1964). In Miranda v. Arizona (1966), the Court decided that police officers must provide a “Miranda warning” informing accused people of their rights before questioning them about a crime.
The Court also made key decisions on moral issues that were fiercely debated in American society. In Griswold v. Connecticut (1965), the Court asserted that a “right to privacy” exists and is implicit in several amendments of the Bill of Rights. Therefore, the Court declared a state law banning birth control unconstitutional. The decision was a precedent for the use of the right to privacy argument in Roe v. Wade (1973), which established a right to abortion.
In recent decades, the Court helped protect gay rights. In Lawrence v. Texas (2003), the Court invalidated state laws banning homosexual acts. In Obergefell v. Hodges (2015), the Court made gay marriage a right when it required states to recognize the same-sex marriages of other states.
The Supreme Court has left a mixed record regarding its decisions related to the Bill of Rights. On one hand, Court rulings have protected what seem like reasonable and fundamental individual liberties. On the other hand, the Court has made rulings on cultural, social, and moral disputes that often did little to resolve the wider debate over the issues and maybe even fueled division among Americans. In recent decades, for better or worse, Americans have increasingly looked to the Supreme Court as the protector of civil liberties and the final word on the Constitution.
Related Content

Background Essay Questions: The Supreme Court and the Bill of Rights

Supreme Court Case Scenarios: How Would You Decide?

The Supreme Court and the Bill of Rights
How has the Supreme Court decided cases in controversies related to the Bill of Rights?

Presentations made painless
- Get Premium
124 Court Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
Inside This Article
The court system is a fundamental pillar of any democratic society, serving as the ultimate arbiter of justice and the protector of individual rights. Writing an essay on court-related topics can be a fascinating and thought-provoking task. Whether you are studying law, political science, or simply interested in the legal system, here are 124 court essay topic ideas and examples to inspire your writing:
The evolution of the court system throughout history.
The role of the Supreme Court in shaping constitutional interpretations.
The impact of landmark court decisions on society.
The difference between civil and criminal courts.
The pros and cons of the jury system.
The role of judges in the court system.
The influence of public opinion on court decisions.
The role of technology in modern courtrooms.
The impact of judicial activism on the court system.
The challenges of ensuring a fair trial in high-profile cases.
The role of plea bargains in the criminal justice system.
The benefits and drawbacks of alternative dispute resolution methods.
The impact of social media on court proceedings.
The role of expert witnesses in court cases.
The debate over the use of capital punishment.
The impact of the court system on marginalized communities.
The challenges faced by self-represented litigants in court.
The ethical dilemmas of being a defense attorney.
The role of the court system in protecting individual rights.
The impact of judicial appointments on court decisions.
The challenges of ensuring a diverse and representative judiciary.
The relationship between the court system and law enforcement.
The impact of court decisions on public policy.
The role of the court system in combating corruption.
The influence of international law on domestic court decisions.
The challenges of balancing national security and civil liberties in court cases.
The impact of jury selection methods on trial outcomes.
The role of public defenders in the criminal justice system.
The impact of court decisions on corporate accountability.
The challenges of prosecuting white-collar crimes in court.
The role of the court system in protecting intellectual property rights.
The impact of court decisions on environmental regulations.
The challenges of ensuring a fair trial for individuals with mental illnesses.
The role of the court system in addressing discrimination and inequality.
The impact of court decisions on reproductive rights.
The challenges of balancing freedom of speech and hate speech in court cases.
The role of the court system in protecting journalists and whistleblowers.
The impact of court decisions on LGBTQ+ rights.
The challenges of ensuring a fair trial in cases involving police misconduct.
The role of the court system in addressing cybercrime.
The impact of court decisions on privacy rights in the digital age.
The challenges of prosecuting and sentencing juvenile offenders in court.
The role of the court system in addressing domestic violence cases.
The impact of court decisions on immigration policies.
The challenges of ensuring a fair trial for individuals accused of terrorism.
The role of the court system in protecting religious freedoms.
The impact of court decisions on gun control regulations.
The challenges of prosecuting and sentencing drug offenders in court.
The role of the court system in addressing human trafficking cases.
The impact of court decisions on the rights of individuals with disabilities.
The challenges of ensuring a fair trial for individuals accused of war crimes.
The role of the court system in addressing hate crimes.
The impact of court decisions on the rights of indigenous peoples.
The challenges of prosecuting and sentencing perpetrators of sexual assault in court.
The role of the court system in addressing child custody disputes.
The impact of court decisions on prison conditions and rehabilitation programs.
The challenges of ensuring a fair trial for individuals accused of corruption.
The role of the court system in addressing workplace discrimination cases.
The impact of court decisions on workers' rights.
The challenges of prosecuting and sentencing individuals involved in organized crime in court.
The role of the court system in addressing international human rights violations.
The impact of court decisions on the rights of refugees and asylum seekers.
The challenges of ensuring a fair trial for individuals accused of treason.
The role of the court system in addressing animal rights cases.
The impact of court decisions on the rights of prisoners.
The challenges of prosecuting and sentencing individuals involved in cybercrime in court.
The role of the court system in addressing copyright infringement cases.
The impact of court decisions on the rights of homeless individuals.
The challenges of ensuring a fair trial for individuals accused of genocide.
The role of the court system in addressing elder abuse cases.
The impact of court decisions on the rights of undocumented immigrants.
The challenges of prosecuting and sentencing individuals involved in human trafficking in court.
The role of the court system in addressing environmental crimes.
The impact of court decisions on the rights of workers in the gig economy.
The challenges of ensuring a fair trial for individuals accused of espionage.
The role of the court system in addressing discrimination against the LGBTQ+ community.
The impact of court decisions on the rights of individuals with mental disabilities.
The challenges of prosecuting and sentencing individuals involved in drug trafficking in court.
The role of the court system in addressing child labor cases.
The impact of court decisions on the rights of individuals in detention centers.
The challenges of ensuring a fair trial for individuals accused of human rights violations.
The role of the court system in addressing gender-based violence cases.
The impact of court decisions on the rights of individuals with HIV/AIDS.
The challenges of prosecuting and sentencing individuals involved in arms trafficking in court.
The role of the court system in addressing racial profiling cases.
The impact of court decisions on the rights of individuals with disabilities in education.
The role of the court system in addressing international labor rights violations.
The impact of court decisions on the rights of individuals with mental illnesses in healthcare.
The challenges of prosecuting and sentencing individuals involved in environmental crimes in court.
The role of the court system in addressing discrimination against individuals with tattoos and piercings.
The impact of court decisions on the rights of individuals with substance use disorders.
The challenges of ensuring a fair trial for individuals accused of child abuse.
The role of the court system in addressing discrimination against individuals with obesity.
The impact of court decisions on the rights of individuals with eating disorders.
The challenges of prosecuting and sentencing individuals involved in animal cruelty in court.
The role of the court system in addressing discrimination against individuals with mental disabilities.
The impact of court decisions on the rights of individuals with autism.
The challenges of ensuring a fair trial for individuals accused of elder abuse.
The role of the court system in addressing discrimination against individuals with physical disabilities.
The impact of court decisions on the rights of individuals with visual impairments.
The challenges of prosecuting and sentencing individuals involved in child labor in court.
The role of the court system in addressing discrimination against individuals with speech disorders.
The impact of court decisions on the rights of individuals with learning disabilities.
The challenges of ensuring a fair trial for individuals accused of discrimination.
The role of the court system in addressing discrimination against individuals with hearing impairments.
The impact of court decisions on the rights of individuals with intellectual disabilities.
The challenges of prosecuting and sentencing individuals involved in cyberbullying in court.
The role of the court system in addressing discrimination against individuals with gender dysphoria.
The impact of court decisions on the rights of individuals with bipolar disorder.
The challenges of ensuring a fair trial for individuals accused of sexual harassment.
The role of the court system in addressing discrimination against individuals with depression.
The impact of court decisions on the rights of individuals with anxiety disorders.
The challenges of prosecuting and sentencing individuals involved in identity theft in court.
The role of the court system in addressing discrimination against individuals with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
The impact of court decisions on the rights of individuals with addiction disorders.
The challenges of ensuring a fair trial for individuals accused of workplace harassment.
The role of the court system in addressing discrimination against individuals with schizophrenia.
The impact of court decisions on the rights of individuals with obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD).
The challenges of prosecuting and sentencing individuals involved in online harassment in court.
The role of the court system in addressing discrimination against individuals with HIV/AIDS.
The impact of court decisions on the rights of individuals with multiple sclerosis.
The challenges of ensuring a fair trial for individuals accused of stalking.
The role of the court system in addressing discrimination against individuals with physical disabilities in housing.
These essay topics cover a wide range of court-related issues, allowing you to explore various aspects of the legal system and its impact on society. Choose a topic that interests you the most, conduct thorough research, and present a well-structured and compelling argument in your essay. Remember, the court system plays a crucial role in the administration of justice, and your essay has the potential to shed light on important issues and contribute to the ongoing conversation about the law.
Want to create a presentation now?
Instantly Create A Deck
Let PitchGrade do this for me
Hassle Free
We will create your text and designs for you. Sit back and relax while we do the work.
Explore More Content
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
© 2023 Pitchgrade
- Supreme Court
Trump wants the Supreme Court to toss out his conviction. Will they?
It’s hard to see how they’d do it legally, but this Court has a history of reading the law creatively.
by Ian Millhiser

Then-President Donald Trump greets Justice Brett Kavanaugh as he departs after delivering a State of the Union address to a joint session of Congress at the U.S. Capitol in Washington, DC, on February 5, 2019.
On Sunday, Trump wrote on Truth Social, his personal social media site, that the Supreme Court “MUST” intervene after a New York jury found him guilty of 34 counts of falsifying business records. Though Trump’s post wasn’t written with the precision of a legal brief, he appeared to float two separate theories that could justify tossing out his conviction: that the judge was impermissibly biased and that the prosecutor was out to get Trump.
Trump’s rant was echoed by many Republicans, including US House Speaker Mike Johnson, who claimed that he knows many of the justices personally and that “they are deeply concerned about” Trump’s conviction .

Speaker Johnson is undoubtedly correct that many of the justices are upset that the leader of their political party was convicted of multiple felony counts, a fact that could lead some voters to favor President Joe Biden over Trump in the 2024 election.
Last March, five of the Court’s six Republicans voted to effectively neutralize a provision of the Constitution that prohibits former officials who “engaged in insurrection or rebellion” against the United States from seeking high office again. (All nine justices voted to reverse a state court decision tossing Trump off the ballot, but only five voted to effectively immunize Trump from accountability under this provision of the Constitution.)
Similarly, the Supreme Court has for months delayed Trump’s federal criminal trial for attempting to overturn Biden’s victory in the 2020 election, all but ensuring that it won’t take place until after the November election.
SCOTUS, Explained
Get the latest developments on the US Supreme Court from senior correspondent Ian Millhiser.
But will the justices step in to nullify the one Trump criminal trial that was tried to conviction before the election? And can the Court’s Republican majority intervene fast enough to throw out the conviction before voters cast their ballots this fall?
Let’s take these questions in reverse order.
How fast could a partisan Supreme Court move to bail out Trump if it wanted to?
Assume, for just a moment, that a majority of the justices are partisan hacks who are determined to remove the stigma of a felony conviction from the Republican presidential candidate before the election. Could they actually invalidate his conviction before the November election?
The answer to this question should be “no.” Under the rules that apply to criminal defendants who are not named Donald Trump, two state-level appeals courts should review Trump’s conviction before the justices could intervene. Both of those courts would ordinarily take months or longer to review a criminal appeal.
To toss out Trump’s conviction before the election, the Court would have to take such extraordinary procedural liberties that this outcome is probably unlikely. But it’s also not possible to rule it out entirely. Not that long ago, it seemed unthinkable that the Court would give serious thought to Trump’s argument that he is immune from prosecution for his attempt to overthrow the 2020 election. At oral argument in that case, however, most of the justices appeared eager to rule that former presidents have, at least, some immunity from criminal prosecution.
The Roberts Court also has a history of embracing legal arguments that were widely viewed as risible by the legal community after those arguments were adopted by the Republican Party . So, with a wide range of elected Republicans now calling for Trump’s conviction to be tossed out, there is a real risk that the GOP-appointed justices will leap on this bandwagon.
This Supreme Court also has a history of manipulating its calendar to achieve substantive results. During the Trump administration, for example, when a lower court blocked one of Trump’s immigration policies, the Court would often race to reinstate that policy days or weeks after the administration’s lawyers asked the justices to do so. After Biden became president, however, the Court started sitting on similar cases for nearly a year, even in cases where the Court ultimately concluded that the lower court was wrong to block one of Biden’s policies.
Similarly, after the Colorado Supreme Court held that Trump must be removed from the 2024 ballot because of his role in the January 6 insurrection, the Supreme Court reversed that decision on an extraordinarily expedited time frame, hearing oral arguments and deciding the case a little more than two months after the Colorado court’s decision.
By contrast, the Court has now delayed Trump’s federal election theft trial for nearly six months . And, based on the questions many justices asked during an April oral argument, the Court appears likely to hand down a decision that will force more delay and ensure that Trump is not tried before the November election.
Even so, to bypass the two state-level appeals courts that are supposed to consider Trump’s conviction before the Supreme Court weighs in, the justices would have to engage in some truly extraordinary procedural gymnastics. Even Speaker Johnson didn’t expect the Supreme Court to move quickly when he predicted that the justices would eventually step in to help Trump: Johnson told Fox News that “ it’s going to take a while .”
Trump’s conviction will first appeal to New York’s intermediate appeals court (which, somewhat confusingly, is called the “appellate division” of the state’s “Supreme Court”). After the appellate division weighs in, the losing party can then appeal that decision to the highest court in New York, which is known as the “Court of Appeals.”
Except in very rare cases, any appeal of any trial court decision will take months. Trump’s lawyers will need time to review the record in the trial and decide which issues they want to appeal, and they will need more time to brief the case. Then, the prosecutors will also need sufficient time to review Trump’s briefs and prepare their own responsive brief, which Trump’s lawyers will then be given some time to respond to. Once the briefs are ready, they will be distributed to a panel of judges, who ordinarily spend months reviewing the case, conducting oral arguments, and writing an opinion. This process can take even longer if a judge dissents.
This is just a brief summary of the process that will take place in the appellate division. If Trump plans to bring this case to the US Supreme Court, he will have to repeat this lengthy process in both the New York Court of Appeals and in the Supreme Court itself, and both of those courts have their own time-consuming process to decide which cases they will hear in the first place.
The Supreme Court does have a process, known as “certiorari before judgment,” which can be used to bypass an appellate court and bring a case directly to the justices, but cert before judgment is supposed to be granted only in the most exceptional cases, and it’s only supposed to be available to parties challenging a federal (not a state) court decision .
The Court’s rules provide that it “will be granted only upon a showing that the case is of such imperative public importance as to justify deviation from normal appellate practice and to require immediate determination in this Court.” (Notably, when the shoe was on the other foot, the Supreme Court denied special counsel Jack Smith’s request for cert before judgment in the Trump immunity case.)
It’s hard to see what earth-shattering legal issue could be raised by a state-level prosecution over falsified business records that could justify such a deviation from normal procedures — unless, of course, the justices believe that there is a moral imperative to rescue the Republican candidate from an embarrassing news story.
Meanwhile, some of Trump’s allies have suggested that Trump could invoke even more obscure procedures, such as asking the Court to use its “ original jurisdiction ” to free him without going through the ordinary appeals process at all. But there are any number of problems with this approach — among other things, as law professor Lee Kovarsky points out on Twitter, the Supreme Court hasn’t granted this kind of relief to someone convicted of a crime since 1925 .
In any event, even if the justices are inclined to move fast enough to toss out Trump’s conviction before the election, Trump’s lawyers would need to formally ask them to do so. So the thing to watch right now is whether Trump’s legal team takes the audacious step of filing such a request in the Supreme Court.
What would be the legal basis of a Supreme Court decision tossing out Trump’s conviction?
As a general rule, each state’s highest court has the final word on questions of state law, and the Supreme Court is only supposed to get involved in a case if there is some allegation that the lower courts either violated the Constitution or a federal law. This matters because, while there are some plausible legal arguments Trump could raise on appeal, these arguments largely turn on the proper way to understand New York’s laws.
Trump’s strongest argument , for example, turns on the question of whether he was properly convicted of violating the felony version of New York’s business records law, as opposed to a weaker misdemeanor version. But, while there is genuine uncertainty about how to read this law, the question of how to read a New York criminal statute is a question of state law and thus should be resolved exclusively by New York’s state courts.
In his Truth Social post , Trump does hint, in his own way, at two legal arguments that could be raised under federal law. He claims that the prosecutor was improperly biased (“Radical Left Soros backed D.A., who ran on a platform of ‘I will get Trump’”) and that the judge is also too biased to hear his case (“appointed by Democrats, who is HIGHLY CONFLICTED”).
Yet, while it is theoretically possible to challenge a conviction on the grounds that the judge or the prosecutor was unconstitutional biased, as a practical matter these sorts of cases are almost impossible to win.
Before we get into that, it’s important to note that Trump’s allegations against prosecutor Alvin Bragg and Judge Juan Merchan are, to put it mildly, exaggerated. Bragg did not run on an “I will get Trump” platform. He did, while he was campaigning for his current job, highlight his previous experience bringing civil lawsuits against Donald Trump , but that’s because Bragg’s predecessor had already opened a criminal investigation into Trump. So it appears that Bragg was trying to convince voters that he had the experience necessary to take over supervision of this ongoing investigation.
As a candidate, Bragg also emphasized that he will “follow the facts” in that investigation and that “every case still has to be judged by the facts and I don’t know all the facts.”
Similarly, it’s unclear what could be the basis of a recusal motion against Justice Merchan. The fact that Merchan was “appointed by Democrats” is not a valid reason to remove him from the case , any more than Judge Aileen Cannon, the Trump appointee overseeing a different Trump prosecution, can be removed from that case solely because she was appointed by Trump.
Similarly, some of Merchan’s critics have questioned a $35 donation the judge made to a pro-Biden organization. This donation is not ideal, but it also is not a basis for recusal. If judges could be forced off of cases solely because of such a small-dollar political donation, many judges would be forced off of countless cases.
That’s because most judges are either political appointees or elected officials, and people with political ambitions donate to political candidates and organizations all the time. Cannon, for example, gave $100 to Republican Florida Gov. Ron DeSantis . Judge Tanya Chutkan, the judge overseeing the election theft case that the Supreme Court has put on hold, made multiple donations to President Barack Obama , in addition to a 2008 donation to Democratic Sen. Kirsten Gillibrand.
So let’s walk through what the law actually says about when a prosecutor or judge can be removed from a case because of unconstitutional bias.
For prosecutors, the leading case is United States v. Armstrong (1996). Armstrong did hold that the Constitution places some limits on “selective prosecution,” such as if a criminal defendant were targeted because of their race or religion. Because the First Amendment typically prohibits “ viewpoint discrimination ,” it follows that a politician could not be targeted because of their political beliefs.
As a practical matter, however, Armstrong laid out a legal standard that is almost impossible for anyone challenging an allegedly selective prosecution to overcome. “Our cases delineating the necessary elements to prove a claim of selective prosecution have taken great pains to explain that the standard is a demanding one.” To prevail, Trump would have to show that “similarly situated individuals” who do not share his political views “were not prosecuted.”
Selective prosecution claims are so hard to win that several scholars have argued that no court has ruled in favor of a party claiming they were impermissibly prosecuted because of their race since Yick Wo v. Hopkins (1886). Admittedly, the most recent paper I was able to find examining these cases was published in 2008 , so it’s possible that such a party has prevailed since then. Still, the fact that more than a century passed without such a case succeeding suggests that the bar in these cases is virtually impossible to clear.
There are good reasons, moreover, why it is so hard to prevail in a selective prosecution case. For starters, prosecutors are supposed to be biased in favor of convicting criminal defendants. It is literally their job to do so. Defendants, moreover, enjoy a wide range of protections, such as the requirement that the prosecution must prove their case beyond a reasonable doubt to a unanimous jury. So even if a prosecutor does bring a case for unjust reasons, they don’t have the power to convict that defendant on their own.
The constitutional rules governing judicial recusals are a bit more nuanced, but it is still very difficult to remove a judge from a case because of allegations of bias. Just look at Cannon, the Trump appointee who has behaved like she is a member of Trump’s defense team in his stolen documents case but who has not yet been forced off the case.
Generally speaking, the Constitution only requires a judge to be removed from a case when they have a financial stake in the case’s outcome or when the judge has an unusual personal stake in the case. In Mayberry v. Pennsylvania (1971), for example, the Court held that a judge who was “cruelly slandered” by a criminal defendant should not preside over that defendant’s trial for contempt of court because the target of these insults was unlikely to “maintain that calm detachment necessary for fair adjudication.”
In Caperton v. Massey (2009), the Court did hold that, in extreme cases, campaign donations can justify recusal. But, as the Court emphasized in Caperton , that case involved an “extraordinary situation” that went well beyond any ordinary case involving a judge who gave or accepted political donations: A wealthy businessman, who had a case pending before the West Virginia Supreme Court, spent $3 million to elect a justice who then ruled in favor of the businessman’s company.
That’s a far cry from Merchan’s (or Cannon’s, or Chutkan’s) much smaller donations to political causes.
Caperton , moreover, also emphasized “States may choose to ‘adopt recusal standards more rigorous than due process requires.’” The Constitution has very little to say about judicial recusals because codes of judicial conduct are the “principal safeguard” against unethical judges. But that also means that the US Supreme Court should play virtually no role in policing claims that a state judge is impermissibly biased.
So it’s hard to imagine a legitimate reason why the Supreme Court might get involved in Trump’s New York case.
Given the justices’ previous behavior in other cases involving Donald Trump, however, we cannot rule out the possibility that they may get involved anyway.
Update, June 5, 10:55 am: This piece was originally published on June 4 and has been updated to clarify the process someone convicted in state court can use to bypass the ordinary appeals process and bring a case directly to the Supreme Court.
Most Popular
The hottest place on earth is cracking from the stress of extreme heat, the backlash against children’s youtuber ms rachel, explained, take a mental break with the newest vox crossword, an artist snuck an anti-semitic message into marvel’s newest x-men comic book, openai insiders are demanding a “right to warn” the public, today, explained.
Understand the world with a daily explainer plus the most compelling stories of the day.
More in Supreme Court

The NRA just won a big Supreme Court victory. Good.

Alito says the Supreme Court’s fake ethics code allows him to be unethical

The Comstock Act, the long-dead law Trump could use to ban abortion, explained

The Supreme Court's new voting rights decision is a love letter to gerrymandering

The Republican Party's man inside the Supreme Court

The Supreme Court decides not to trigger a second Great Depression

The messy discussion around Caitlin Clark, Chennedy Carter, and the WNBA, explained

Modi won the Indian election. So why does it seem like he lost?

Baby Reindeer’s “Martha” is, inevitably, suing Netflix

Where AI predictions go wrong

The failure of the college president

- IBPS SO LAW
- Civil Judge (Pre+Mains)
- Hotel Management
- CAT & OMETs
- Udaan Programs
- Udaan Webinar
- Jaipur [Bapu Nagar]
- Jaipur [Vaishali Nagar]
- Jaipur [JLN Marg]
- Delhi (South Extension)
- Delhi (Pitampura)
- Delhi (CP Center)
- Delhi (Dwarka)
- Gurugram (Sector 27)
- Gurugram (Sector 50)
- Gurugram(Sector 14)
- Mumbai (Andheri)
- Mumbai (Navi Mumbai)
- Mumbai (Thane)
- Chandigarh Sector 8C
- Lucknow Hazratganj
- Lucknow Aliganj
- Jaipur (Bapu Nagar)
- Jaipur (Vaishali Nagar)
- Gurugram (Sector 14)
- Chandigarh 8C Sector
- Jaipur[Vaishali Nagar]
- Navi Mumbai
- Lucknow [Aliganj]
- Lucknow [Hazratganj]
- CLAT Super 30
- IPMAT Indore
- IPMAT Rohtak
- Christ University
- St. Xaviers
- Judiciary Study Material
- Chhattisgarh (CGPSC)
- Haryana (HJS)
- Uttar Pradesh (UP PCSJ)
- Rajasthan (RJS)
- Madhya Pradesh [MP]
- Delhi [DJS]
- Bihar [BPSC]
- Uttarakhand [UKPSC]
- Jharkhand [JKPSC]
- Himachal Pradesh [HPPSC]
- LegalEdge AISAT
- LegalEdge IST
- Judiciary Gold AIJSAT
- Judiciary Gold IST
- SuperGrads IPM AISAT
- SuperGrads IPM IST
- Supergrads CUET AISAT
- SuperGrads CUET IST
- SuperGrads CAT
- Creative Edge
- LegalEdge AIOM
- SuperGrads AICUET
- Judiciary AIOMC
- Supergrads IPM AIOM
- CreativEdge AIOM
Free Videos
- CLAT Free Videos
- UGC NET LAW
- RBI Grade B
- Uttarakhand
- Judiciary Notes
- Judiciary Videos
- KAUN BANEGA JUDGE
- Daily Current Affairs
- Weekly Current Affairs
- Monthly Current Affairs
- LegalEdge UG
- SuperGrads Webinar
- SuperGrads CUET Webinar
- Creative Edge Webinar
- Judiciary (Beginners)
- UDAAN Webinar
- LAW Entrances
- Management Entrances
- CUET Exam [UG & PG]
- Design & Architecture
- LAW & Judiciary
- Franchise Enquiry [Join Us]
50 Most Expected Essay Topics for Judiciary Exams 2024
Author : Yogricha
Updated On : May 9, 2024
Overview: Essay writing is one of the most important skill that you must work on if you are planning to crack Judiciary. In most State Judiciary Examinations essay writing is an important part in Mains examination.
To help you with the preparation of essay writing for Judiciary Mains examination then we have made a list of important topics that you should know and we have also curated a list of tips and tricks that will help you socre better in essay writing in Judiciary Mains Examination.
Before writing an essay you should know things like, details of the topics, how to start wirting, how to give examples, etc. therefore, in this blog we will cover:
- How to start your preparation for essay writing?
- Important Essay Topics for Judiciary Exams 2024
- Topics from Previous year question papers
- Expected essay topics in 2024 Judiciary Exams
Download FREE Notes for Judiciary Exams by Judiciary Gold
How to start your preparation for essay writing for 2024 Judiciary Exams?
If you want to crack judiciary exams in 2024 then you must master the art of essay writing. This article will discuss some important essay topics you should be prepared for, along with tips and strategies to help you write effective essays.
So, whether it's analyzing social issues, addressing legal topics, or exhibiting language proficiency, mastering the art of essay writing is crucial to excelling in judiciary exams. Prepare to sharpen your writing skills and delve into the 50 most expected essay topics for Judiciary Exams 2024.
Download FREE Notes of Transfer of Property Act by Judiciary Gold
Most Important Essay Topics for Judiciary Exams 2024
Writing an essay on legal topics for a judicial exam becomes more challenging since research and sufficient legal understanding are required. In such scenarios, practice is the only key to writing a good essay in the Upcoming Judiciary Exams .
The following are some of the most critical essay topics for a judiciary or current essay topics in 2024 for Judiciary exams that you need to focus on to score well in essay writing:
Read Now: Note-making ti ps suggested by the judiciary exam toppers
Download FREE Notes of Indian Contract Act for Judiciary
Apart from the above-mentioned topics, here are more topics for your reference:
- Lawyers' Role in Speedy Justice-delivery
- Capital Punishment
- Human Rights in India
- Empowering a woman empowers the next generations.
- Marriage - an institution of great social relevance
- Farmers' stir - more than a loan waiver
- The drug, drinking and driving never go together
- Cyberbullying - more extreme than face-to-face taunts
- Global warming is warning us through sea level rising and ice caps melting
- With value education, build the pillars of character
- Lawyers' Role in Speedy Justice-delivery
- Apolitical Education
- Skilling the youth of India
- Education is a weapon that can change the world
- Right to education - challenges and prospects
- The dark disparity gap between rich and poor
Read More: When to begin Judiciary Exam Preparation
Download Smart Study Plan for Judiciary Exams 2024
- Why is the administration insensitive to the plight of slum dwellers
- Environment vs Growth
- Is communalism a challenge to peace or propagation of religion or something else
- Right to privacy
- Young Indian's preferences from job search to job creation
- Should educational qualifications be made mandatory for politicians
- Reservations and Human Development in India
- Beto Bachao - Beti Padhao, India ko aage badhao
- India & China, from rivalry to enmity
- How the internet changed the way we live
- Cybernation - a threat or a convivial to employment
- Be the change you want to see in others
- Justice delayed Justice denied
Know more: How to prepare for Judiciary in 2024?
Download 1 Year Preparation Strategy for 2024 Judiciary Exams
Previous Year's Essays Topics in Judiciary Exams
Here is the table of the essay topics that were asked in the previous year's PCS J Exams:
Understand Now: Judiciary Exam Pattern
Download Functions of Judiciary Notes
50 Most Expected Essay Topics for Upcoming Judiciary Exams 2024
Essays can increase your score and improve your final rank with little effort and the proper technique. Follwong the fifty most important essay topics for PCS J exams. Prepare these topics well in advance to excel in the Essay section of the Judicial Services Exam :
- Role of courts/courts during a pandemic
- Violence against women
- Child rights during lockdown
- Digitalisation of education
- Right to digital education
- Vaccination Policy of India
- Contempt of court
- Power of court to order relief for covid affected patients
- Labourer's/daily wage workers' rights
- Women's Rights during lockdown
- Hate speech
- Organizing mass gatherings during a pandemic
- Essential services during lockdown
- Restriction of rights of citizens during pandemic/lockdown
- Freedom of religion vis a vis pandemic
- Role of social media in the Pandemic
- Growing unemployment
- Medical infrastructure of the country
- Participation of the Judiciary in Politics
- Mental health
- Freedom of speech and expression
- Freedom of movement
- Sustainable environment
- Growing intolerance
- Social and legal ramifications of CAA/UAPA
- Right to protest
- Rights of the LGBTQIA+ community
- Too much democracy
- Atmanirbhar Bharat
- Terrorism (talibanism)
- Problem of malnutrition
- New India - Why Still A Union Territory?
- Debate on nationalism
- Pollution crises
- Article 370
- Water disputes between states
- Fugitive economic offender bill
- Labour Reform
- White collar crime
- Women Empowerment
- Triple Talaq
- Cyberbullying
- Global Warming
- Right to Education
- Gender disparity in the social sector
- Justice delayed justice denied
- Protection of Child Rights in India
- Social Justice in Indian Democracy
- Alternate Dispute Redressal (ADR)
- Right to Constitutional Remedy
Know About: Best Books for Judiciary Exams
Download Hindu Law Notes for Judiciary by Judiciary Gold
Important Current Legal Essay Topics for Judiciary Exam 2024
Solving previous year's Questions Papers for Judiciary Exams will help you know the difficulty level and the type of questions asked in the essay paper. Refer to the following list of essays on current legal topics in India:
- Importance of Uniform Civil Code in India
- Role of Media in protecting democratic values in India
- Causes and Consequences of Violence Against Women in India
- Protection of human rights; Indian scenario
- How gender inequality affects the progress of our country
- The education system in India
- Causes and Consequences of Corruption in India
- The Practice of Child Labour In India
- The right to privacy is a fundamental right in India
- Right to Education in India
Read More : How to Read Bare Acts for Judiciary Exams?
- Barriers to Access to Justice in India
- Social Justice in Indian Democracy: An Overview
- The law relating to contempt of courts in India
- Review of administrative law in India
- Alternative dispute resolution in India
- Child Rights in India
- Right to constitutional remedies under the Constitution of India
- Emergency provisions of the Constitution of India
- Role and Powers of Governor
- Functions of Parliament in India: An overview
- Right to a fair trial in India
Important English Essay Topics for Judiciary Exams 2024
English is a subject where you can improve your grades in the judicial services examination.
Following a few English preparation tips for Judiciary Exams will help enhance your grammar and vocabulary, which are essential for writing a good essay.
The following are essential English essay topics for the Civil Judge exam:
- Role of Media
- Demonetisation
- Cyber Security
- Child Labour
- Industrial Development/Pollution
- Farmers suicide
- Water disputes
- Social Media
- Globalization
- Recent Laws
- World meetings
- Social issues
Read More : Short Tricks to Memorize Bare Acts for Judiciary exams
Mastering the Art of Writing An Excellent Essay for Judiciary Exams 2024
While an essay is a large project, there are many steps a student can take to break down the task into manageable chunks.
Following are the six steps to drafting an essay:
- Read and understand the topic : Know precisely what is being asked of you.
- Plan: Prepare an outline or diagram of your ideas around the selected topic. To write a successful essay, you must organize your thoughts. You must see connections and links between ideas more clearly by taking what's already in your head and putting it to paper.
- Write the body: The body of your essay argues, explains, or describes your topic. Each main idea that you wrote in bullets.
- Write the introduction: The introduction should attract the reader's attention and show the focus of your essay. Your diagram or outline will become a separate section within the body of your essay.
- Write the conclusion: The conclusion brings closure to the topic and sums up your overall ideas while providing a final perspective on your topic.
- Proofread : Read your response carefully to ensure there are no mistakes and you didn't miss anything.
How to Write a Good Essay in Judiciary Exam 2024?
Essay writing is an art that cannot be learned overnight or in a month. To write a good essay, you must read books, love reading and writing, and follow good authors. An Essay mainly depends on your command of the language and how much you know about the topic .
The following are some of the best essay writing preparation tips for the Judiciary exam :
First, you should read newspapers, magazines, etc., as it will help improve your vocabulary, knowledge, and viewpoint.
1. Selection of Topic
- Generally, you will be given 3 to 4 topics in the exam.
- You have to choose the one per your knowledge of the particular topic.
2. Planning
- After finalizing the topic, you must plan your writing with a balanced approach.
- Jot down the key points to be mentioned in your essay.
- Your views must be presented in objective nature rather than presenting them in subjective nature.
- Also, mention your opinions and arguments with examples in your essay.
- Include facts and figures to support your approach.
Read more : Judiciary Exam Syllabus
3. Prioritize Important Points
- Highlight the essential points in the initial paragraph of the essay.
- Try to include all the critical points related to the topic in the essay.
- Make text bold or italics to highlight the critical points in the middle of the paragraph.
4. Interlink Each Point
- Try to interlink each point in the essay.
- The second paragraph must continue the first paragraph; the third paragraph must relate to the second one, and so on.
- Do not repeat the content of the introduction.
- The essay topics encompass diverse areas of law, including constitutional law, criminal law, and civil law.
- Understanding key concepts and recent developments in these areas is crucial for success.
- Candidates should enhance their analytical and critical thinking skills to address these topics effectively.
- Regular practice and mock essay writing will help candidates develop their writing style and time management.
- Familiarity with landmark judgments and relevant case laws will strengthen essay arguments.
- Continuous self-assessment and revision will ensure a well-rounded preparation for the judiciary exams.
By utilizing these key takeaways, candidates can confidently and competently approach the essay section of the judiciary exams.
Download Judiciary Study Material
Fill your details
Recently Published
NALSAR Team Interview on Launch of IPMAT Program
Updated On : June 7, 2024
International Organizations Notes for UP Judiciary Aspirants [Download PDF]
Commercial Court Act Notes And Insights For Judiciary Preparation
Partnership Act Notes and Study Material For Judiciary Preparation 2024
Copyright Act Notes for Judiciary Preparation 2024
Frequently Asked Questions
Is there any recommended newspaper for essay preparation of judiciary exam?

How are Judiciary Exams Question Papers useful in preparing for the essay writing?
Is the Judiciary Exam easy?
What is the best way to prepare for important essay topics for Judiciary Exams?
Which book to refer for Important Essay Topics for Judiciary Exams?
What are good topics for essays in Judiciary Exams 2023?
May 9, 2024
Online Coaching
Test Series
Trending Exams
- Architecture
- Career Counselling
Scholarship Tests
- Judiciary Gold
- Supergrads IPM
- SuperGrads CUET
- LegalEdge After College
Mentor Tips
- CLAT Prep Tips
- AILET Prep Tips
- IPMAT Prep Tips
- NATA Prep Tips
- NID Prep Tips
- Judiciary Prep Tips
- CAT Prep Tips
ABOUT TOP RANKERS
Toprankers, launched in 2016, is India’s most preferred digital counselling & preparation platform for careers beyond engineering & medicine. We envision to build awareness and increase the success rate for lucrative career options after 12th. We offer best learning practices and end-to-end support to every student preparing for management, humanities, law, judiciary & design entrances.
: +91-7676564400
Social Channels
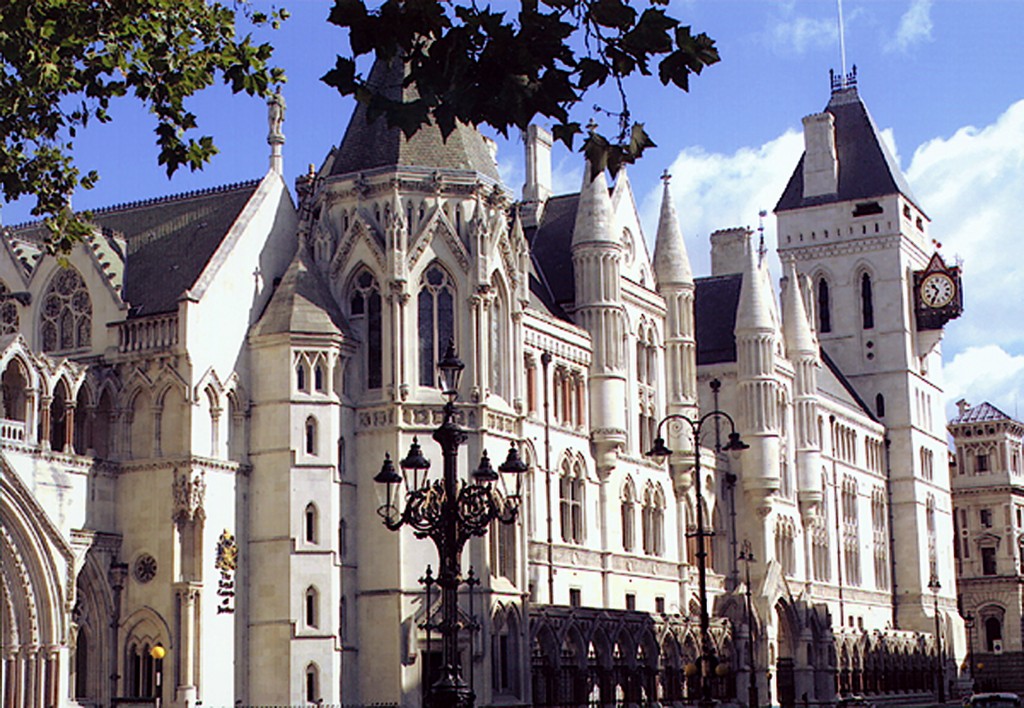


The High Court of Justice in London, together with the Court of Appeal and the Crown Court, are the Senior Courts of England and Wales. Its name is abbreviated as EWHC for legal citation purposes.
It deals at first instance with all high value and high importance civil law (non-criminal) cases, and also has a supervisory jurisdiction over all subordinate courts and tribunals, with a few statutory exceptions.
The High Court consists of 3 divisions: the King’s Bench Division, the Family Division, and the Chancery Division.
Find out more
Read about the different types of court, and their specialist types of casework
King’s Bench Division
Find out more about the work and the judges of the King’s Bench Division
Family Division
The family justice system exists to help families resolve disputes arising in respect of family matters quickly and with the minimum of disruption to those involved
Chancery Division
The Chancery Division undertakes civil work of many kinds, including disputes relating to business, property or land, intellectual property issues, insolvency, bankruptcy, tax and the validity of wills
Business and Property Courts
Judges from both the King’s Bench and Chancery Divisions sit in the Business and Property Courts
218 Essay about Court Examples & Topics
Need to write an essay about court system? Looking for a court case essay example? The issues of law and crimes are crucial in society are fascinating and worth exploring!
🏆 Best Court Topics for Essays
⚖️ court system essay topics, 👍 a+ court case essay examples, 👨⚖️ essay about court: samples, 💡 top judicial essay topics, ✍️ court essay topics for college.
In your court system essay, you might want to focus on American judicial system. Another idea is to discuss the theory and functions of criminal courts. One more option is to find some interesting legal issues and discuss them. Whether you’re planning to write an argumentative or analysis essay, this article will be helpful. It contains interesting court system essay examples, judicial essay topics, and ideas for your court essay.
- The Criminal Trial: Court Observation Report In this case, the accused was found guilty of the crime and the outcome of the judgment was that he would serve a minimum of ten years in prison.
- Casebrief, Based on the Supreme Court: State V Hoying W L Hoying fully acknowledging the violation of writing to the victim, which is in violation of the civil protection order asked Ms.
- Dow Jones & Company Inc. vs. Gutnick: The Australian Court’s Conclusion The paper starts with the details of the case, including the factual and procedural background thereof, proceeds to the judgment summary of the case and the analysis of the questions that the court ruling have […]
- Greenman vs. Yuba Supreme Court Case As the result of the trial before the jury, the court acquitted the third party of this conflict the retailer where Mr.
- Joseph Haydn’s Contract With the Esterhazy Court Joseph Haydn’s contract for work at the Esterhazy Court is a distinctive document that needs to be preserved because it explains the authorities’ attitudes to the music and composers in the eighteenth century.
- “Supreme Revenge: Battle for the Court”: Documentary Analysis The content of the documentary is proof that the Judiciary is a political playfield for the Democratic and the Republican parties as they struggle for control.
- The Texas Court System and How Its Impact on Americans In Texas all the judges are selected using the partisan elections with the exception of the municipal judges who are appointed by the mayor or the city council.
- Court for Mentally Ill: Commonwealth vs. Bobbitt Apparently, the actions and circumstances which took place prior to Lorena’s act of severing her husband’s penis, namely, the rape of Lorena Bobbitt by her husband, as well as the constant domestic violence of John […]
- Harris vs. Forklift Systems Supreme Court Case The inference from this view is that Charles Hardy did not deprive Teresa Harris of equal rights for employment and was a person who was taught to disrespect women.
- International Court of Justice: Definition, History and Importance The purpose of the court is to serve as the organ of judicial arbitration between countries that are members of the United Nations; it is also the organ that gives legal advice to the UN […]
- Hearsay Evidence and Witness Testimony in Court A statement is only considered as hearsay if the objective of the testimony being presented is to prove the truth of its contents.
- Court Structure in England and Wales The article below illustrates the hierarchical arrangement of the court structure in England and Wales. In England and Wales, the Supreme Court is the utmost court of petition.
- Benefits of Three-Tier Court System In the three-tier court system, there are the trial courts, the first appellate courts, and the U.S. Thus, the three-tier court system consists of a regional court, an appellate court, and a supreme court.
- Vehicle Searches: The Carroll vs. US Court Case However, the court upheld that in line with the Fourth Amendment of the constitution, the security agents had to prove that they had a legitimate lead making them believe that the particular vehicle had contraband […]
- The United States State and Federal Court Systems For example, if a person has a bank account in a particular state, then he or she is under the jurisdiction of this state’s court.
- Intake Officers in Juvenile Court System The final duty of the Intake officer is to determine whether it would be safe to release the juvenile or not.
- The R v Gordon Wood Case and Court Decision It was brought to the attention of the judge that a week before Caroline was found dead, she had been seen in the company of the accused at a city fitness centre.
- Portrait of Kangxi Emperor in Court Dress Review The painting belongs to the Late Kangxi period.”Portrait of Kangxi Emperor in Court Dress” is depicted with the help of color on silk on a hanging scroll.
- Larry Hillblom: Should Larry Junior Go to Court or Settle? Due to the fact that he did not stipulate that illegitimate children would be unable to receive an inheritance, anyone who could prove themselves to be a child of Larry Hillblom would be a legitimate […]
- Cyber Crimes: Court – United States vs. Ancheta Reasoning: The jury argued that the defendant conspired to violate the Computer Fraud Abuse Act as well as the CAN-SPAM Act, caused havoc to computer networks of the national defense department of the federal government, […]
- A Case Against Polygraph Evidence Admissibility in Court The survival of any civilization depends on the establishment of laws of conduct and the following of the same by all the members of the society.
- Court Observation in Courts of Sydney Once inside the courtroom, he sits at the bench facing the rest of the court.the defense lawyers sit in the left side of the court, close to the dock, while the prosecution sits on the […]
- People vs. O’Neil Supreme Court Desicion In addition to the murder and involuntary manslaughter charges, the jury also charged the individual and corporate defendants with reckless conduct. Secondly, the defendants argued that the murder charges were inconsistent with the involuntary manslaughter […]
- Loving vs. Virginia Supreme Court Case Since the couple pled guilty, the judge refused the appeal which led the case to be taken to the Virginia Supreme Court of Appeals.
- Court Hearing Visit Report Despite the need to uphold the principle of the open justice, some courts are held in camera, that is, they are not open to the public.
- The International Criminal Court Thus, it is essential to formulate the strengths and weaknesses of the ICC and Victor’s justice and to describe the relationship with the U.S.
- United States Supreme Court Justices It should be noted that the role of judges is to guarantee fair decisions to the parties to the process. Accordingly, in an adversarial process, the role of the judge is to control the process […]
- Supreme Court’s Decision in McGirt v. Oklahoma In my view, the ruling revealed the fact that Oklahoma has, for a long time, ignored the requirement that Congress is the sole entity with the power to establish the boundaries of a tribal reservation.
- Nurses in the Court, Licensure, and Regulation Nursing licensure refers to the process in various regulatory bodies, such as the Board of Nursing, to ensure that the nursing practices are within its jurisdiction.
- “The Supreme Court: Home to America’s Highest Court” Documentary In this documentary, Chief Justice John Roberts discusses the principal goal of the Supreme Court and the West Plaza, the site of several public protests.
- The American Government and Supreme Court Composition If the current Supreme Court judges were to hear the case, they still would uphold the ruling because it reflects their beliefs of defining the US as a haven dedicated to respecting human rights and […]
- Court Cases Concerning Nursing Education In the process, the question is whether the court’s ruling in favor of the nurse and against the doctor can be justified by a sufficient purpose.
- Enea vs. Superior Court of Monterey County: Case Analysis The issue for determination is if actions that have a negative impact on the profits of the business constitute a breach of fiduciary duty, even though the partnership agreement does not specifically ban such behavior.
- The Griffin vs. California Supreme Court Case In the court, Griffin refused to testify, and according to a prosecutor, the defendant’s choice was evidence of guilt. In turn, it is the responsibility of the prosecution to prove the defendant’s guilt based on […]
- Discussion Thread: International Court As well known, in the aftermath of World War II, the Allies proposed the creation of an international court for the persecution of war criminals, which became known as the International Court of Justice, later […]
- State vs. Anderson: Supreme Court Summary With its main purposes to obtain, store, and review information received from fingerprints, the AFIS system is fundamental in the investigation of criminal cases.
- European Court of Justice Case Analysis Therefore, the company’s vehicles that featured the defeat device in the engine were prohibited per Article 5 of Regulation No 715/2007.
- Being Outside International Criminal Court Jurisdiction The regime gives the ICC power to assert its jurisdiction in that particular nation as long it is a member nation of the court.
- Employee Benefits Program for Supreme Court Justice They are also a guarantee of the independence of the Supreme Court Justice representative in the performance of his duties. In case of the death of a representative of the Supreme Court Justice related to […]
- United States vs. Nixon Landmark Supreme Court Decision Nixon case happened in 1974 is one of the most critical decisions of the Supreme Court of the United States because it rejected the privileges that the head of the state supposedly had.
- The Supreme Court Chief Justice Position: Recruitment Plan Afterward, the Chief Justice of the Supreme Court must be appointed by the President, with the following approval by the Senate. As a result, fairness and the absence of bias in court judgment will be […]
- Transferring a Defendant to an Adult Court In the given case, it seems pretty challenging to transfer the defendant to the adult court due to the number of mental challenges.
- Legal Trends of In-Court Accommodations This study by Celik owes that disclosure of cases of child sexual abuse is directly related to the individual and environmental factors in different age groups.
- Section 2339B of the US Code in Court Case To begin, the court concluded that the legislation was clear since the sections of the Act that pertained to the plaintiffs’ anticipated behavior were specified explicitly.
- The Sanowicz vs. Bacal Court Appeal Case I would like to appeal to the decision made by the Court that has concluded that a referral fee must be paid despite the lack of the necessary agreement.
- Addressing and Respecting Citizens’ Rights in Supreme Court Facts of The Case: Harriet Louise Adderley is the representative of the group of protesting students. The primary aim of the students was to protest for the releasing their black friends from the non-public prison.
- The Supreme Court’s Cancellation of Vaccines One of the points of view is that the COVID situation is getting worse, and the mandate was a logical continuation of Biden’s policy to combat coronavirus.
- The Brewer vs. Williams Supreme Court Case Williams became the main suspect of the young girls’ abduction after a young boy confessed to have seen him at the YMCA packing his car a large bundle of clothes with “skinny and white legs” […]
- McKinney vs. Arizona Case and Court Decision The Arizona Supreme Court upheld the state appellate jury’s ruling, holding that a court may perform a re-evaluation of the contributing instead of a jury in cases involving the death sentence.
- The Supreme Court Decision on the Right to Same-Sex Marriage The decision of the Supreme Court on the constitutional right of citizens to same-sex marriage is a significant event in the history of the development of modern democratic society.
- Diana Levine vs. Wyeth at the Supreme Court Diana Levine sued Wyeth at the Vermont Supreme Court, seeking compensation from the defendant for improperly written instructions to Phenergan that resulted in the amputation of one of the plaintiff’s limbs; litigation continued in the […]
- Washington vs. Texas Court Case No. 649: Issue, Facts, and Summary Still, the court authorities denied him a request to listen and consider the testimony of a witness or an accomplice, because of which the court’s verdict turned in the opposite direction.
- Marbury vs. Madison: A Landmark Supreme Court Case However, one of these judges, William Marbury, wanted to ask the Supreme Court to issue a writ of mandamus, a mandate, meaning that something that happened in case of his appointment would not be delivered […]
- Supreme Court’s Decision in Tinker vs. Des Moines Nevertheless, the court protected the school and claimed the reasonability and fairness of its actions regarding the suspension of the students.
- Criminal Court System in U.S. As a result, one gains an in-depth insight into the subject matter and becomes capable of improving it to reduce the threat of a mistrial, The stages of a court process may vary depending on […]
- Louisiana District Court: Role, Structure, and Jurisdiction Criminal District Court in Orleans Parish has supervisory jurisdiction over the municipal and traffic courts. There is a total of 42 district courts in the state, executing jurisdiction of criminal and property-related cases.
- Court Proceedings Experiential Report The practical experiences of the proceedings both confirmed and challenged some of the information that I have learned about the structure of a trial.
- Intellectual Property: The Supreme Court’s Ruling in Eldred vs. Ashcroft The other relevant information to be shared on the basis of this case encompasses the copyright and patent clause that accords the Congress with the power to provide authors the authority of controlling the use […]
- The Institution of the US Supreme Court The institution was designed as a check on the power of the legislative and the executive branches of the federal government.
- The Supreme Court’s Internet Sales Tax Decision The added input leads to an increase in products’ prices, making it hard for e-commerce startups to compete with other large-scale retailers and wholesalers.
- A Comparison and Contrast of Two Court Rulings Furthermore, he or she has a duty to act in the protection of others should a patient present a threat. In a situation closer to that in Estates of Morgan v.
- Using Victim Impact Statements and Defendant’s Sentencing Memorandums in Court Thus, I consider these documents to be of high importance, and the jurisdiction should give it more attention the punishments will only become more realistic.
- Alternative to Incarceration (ATI), Treatment Court The Los Angeles County Department of Mental Health later developed a forensic mental health court diversion program that offered consultation services to courts on the management of criminals with psychiatric illnesses.
- Court Observation: Ausar Walcott’s Trial Some of the information to be presented includes the names of the parties in the suit, a summary of key facts, the jury’s verdict, and the relevant legal issues.
- How Canada’s Supreme Court Affected Administrative Law Principles The protection of the rights of a claimant should respond to the statutory scheme in an administrative decision and expectations of procedural protection.
- Conflicting Cases and the Contemporary Court Systems This paper will compare the constitutional framework of the U.S.and the UK, The cases in which the existing regulations collide with the essential Constitutional premises are quite few, yet they set the prime example of […]
- Court Rulings on Confidentiality in Healthcare In both Tarasoff and Morgan, the therapists contacted the relevant authorities in favor of the victim’s safety. The cases showed that individuals have a moral obligation to make decisions that infringe private information in favor […]
- Current Issues of Supreme Court Confirmation Process This fact ensures that the confirmation process is impartial, which contributes to the effectiveness of the Supreme Court by endorsing the candidates who have the most suitable skills and knowledge to occupy this position.
- Bordenkircher vs. Hayes, the United States Supreme Court, 1978 Is the Due Process Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment violated if, in the course of plea bargaining, a state prosecutor threatens the accused to be indicted on more severe charges if the respondent does not […]
- Court Cases Showing Various Law Arguments After further inquisitives, the Supreme Court realized that the need for the second appeal by the plaintiff was of no need.
- Current and Future Issues Facing Courts and Court Administrators The system of courts is structured in a way that both the innocent and the guilty have a chance to be heard.
- Court of Justice of the European Union (CJEU) and Consumer Contracts According to the European Commission, the solutions to such complex systems are in the freedom of contract. Rules may limit freedom of contract in some member states of the EU.
- The Practice of Sealing Juvenile Court Records The practice of sealing juvenile’s court records is indeed acceptable practice to some extent in most countries in the world. Recent surveys as analyzed in the article indicate that the locations where juvenile records are […]
- The Role of Expert Witness in Court Some court cases may require the services of an expert to enable the jurors and judges to have a better understanding of the underlying principles of the case in question.
- Design of a Drug Court System Offenders have a strong incentive in being members of the Drug Court in that they have the prospect of avoiding being in jail for as long as they abide by the rules and cooperate in […]
- Trial Court Functions, the Concepts of Schlichmann The term preponderance of the evidence means that the side that would provide greater evidence concerning the case would lead either the judge or the jury to take one side as opposed to the other.
- Juvenile Court System: 15-Year-Old Larceny Offender The facts of the case show that the juvenile is a first offender and is yet to attain the minimum age for criminal prosecution according to the state’s juvenile justice system.
- Supreme Court Eras. Brown vs. Board of Education The primary purpose of the paper is to provide the in-depth analysis regarding a possible decision made by the Supreme Court of the United States regarding the case Brown v.
- Court Unification and Juvenile Delinquency Speaking about the given issue, it is important to give the clear definition of this category and determine who could be judged by the juvenile court.
- The Warren Court’s Rulings and Criminal Procedure Police also inform the suspects that they have the right to an attorney that will be provided to them by the state if they cannot afford one.
- Court Requirements in Aguilar and Gates Cases However, the Supreme Court’s requirements for testing the validity of the evidence were not congruent: the major diversion point was the reliability of the source of information used in the process of the investigation.
- Policing and the Bill of Rights: Supreme Court Cases Jones case, the placement of a GPS device under a suspect’s car was interpreted as a violation of the Fourth amendment by the Supreme Court. In the United States v.
- Lechmere vs. National Labor Relations Board: Supreme Court’s Decision Lechmere Inc did not allow the organizers to use the lot, and they opted to use the public strip of land to distribute the handbills to employees entering in the morning and leaving in the […]
- Complex Foundations: Nottingham Magistrate Court The glass material used to form the walls of the court requires a strong support, hence the choice of the piling method.
- FCT V Stone : Court Case Analysis In particular, the court had to decide if the athletic activities of this person could be regarded as a form of business.
- Bail and Pre-Trial Release Conditions Impact on Court Systems In this journal, Clark informs the world how the state of pre-trial release in tribal jurisdiction operates in the United States.
- Systematic Review of Drug Court Effects on Recidivism Although the article does not state the specific research question or hypothesis for the study, it is clear that the study wanted to address the question “what is the impact of drug courts on recidivism […]
- Effectiveness of the DUI Court In the last one decade, the relative success of drug courts has led to the establishment of a growing number of driving while impaired or driving under the influence courts across the U.S.
- The Structure of the US Court System and Determination of Truth There have been suggestions to study the inquisitorial system and adopt some of its features that could help to improve the determination of truth under the US adversarial system. It is thus advisable to redesign […]
- Jury Selection in Court First of all, some attorneys will hire psychologists to analyze the prospective jury pool and help pick out which jurors would be the most effective for the case at hand.
- In re Yamashita Case and Supreme Court’s Decision As a result, General Yamashita was the commander of all Japanese forces that were operating in Philippine, so he was responsible for their actions.
- Analysis of a Specific Supreme Court Decision The issue of fetal protection and the safety of pregnant mothers as provided in the Johnsons’ Control fetal policy is one that, not only draws particular attention to the parties that it seeks to address, […]
- Accountability of Court Officials Therefore, just like the politicians and the government which is accountable to the citizens of the country, the judicial system is accountable to the citizens.
- Court Decisions that Influence Juvenile Justice System Supreme Court that postulated that an underage person is eligible to the rights of due process, namely the right to obtain counsel, the right to be notified about the charges, and the right to encounter […]
- Is There a Gender Bias in the USA Court System? The truth of the matter is there is gender bias in the United States court system. Another factor that underlines gender bias in United States courtroom is the number of female lawyers as compared to […]
- State Court Statistics Project Statistics show that the state of California has one of the highest court case filings, there are three different courts in California; these courts are spread around the 58 counties of California. Except for California, […]
- Juvenile Court Philosophy This philosophy states that a rehabilitation program can prevent the children from committing crimes since it attempts to transform cognitively the distorted cognitive behavior of the child involved in criminal acts.
- Gender Bias in Family Court This research study wishes to consider the current scope and resultant impacts of gender bias in the context of family courts in the United States of America.
- Court Watch Expectation: Personal Experience Apart from the court staff, I expect to learn about the sections of the courtroom and the function of each. I am hoping to observe how, in the initial court proceedings, the charges are filed […]
- Business and Corporate Law: Federal Court of Australia ASIC was provided with the notice of the application and it advised the Federal Court of Australia that it did not oppose the application; neither did it propose to attend the hearing of the application.
- Court Proceedings: Pretrial Motion and Its Aspects Any request, defense or objections which are competent of resolution devoid of any court proceedings of the common matter may be pleaded at any time before trial by motions. At the discretion of the judge […]
- Mr. Charles Dempsey Court Case: Cause and Consequences of the Crime The case had gone through the plea hearing, the preliminary hearing the trial hearing and was to be decided on this day during the sentencing hearing where the judge was supposed to deliver the Judgment.
- Court Sentencing: Juvenile Status and Unemployment These provisions allowed that based on prior criminal history and in consideration of the current offense, they could be transferred for trial in adults courts.
- The Introduction of the New British Supreme Court The introduction of the new British Supreme Court has involved different constitutional implications, such as changing the role of the Lord Chancellor and creating a position of President of the Court of England and Wales; […]
- Apprendi vs. New Jersey: Decision Made by the Highest Court of the United States On the other hand, Apprendi had the right to challenge the alteration of the sentence claiming that it was against the constitution.
- Supreme Court Decision in the US vs. Bass Case of 2001 In the case of the defendant, race should not be a contributory factor and if this is so, then it can be concluded that the ruling was unfair.
- Examples of Court Cases Involving Alcohol On the day the deed was executed, the plaintiff was driven in an automobile from his farm to Reno, Nevada for the purpose of the plaintiff and defendant being married in said city.
- US Constitutional Law & Supreme Court’s Decisions It is not only necessary to have the necessary knowledge about principles and judgments of Constitutional Law by the Supreme Court, but it is also important to know how the Court has arrived at such […]
- Court System and Prosecutors Office The state of New Jersey is not an exception to this rule, and the relation of the Morris County Prosecutors Office in Morristown, NJ to the current US court system is the relation of a […]
- Rights and Freedoms: The Court Case Terry vs. Ohio All these rights are noted in the constitutions of the countries along with the obligations of the citizens.”The Bill of Rights” is a very important document in the life of Americans, as this Bill guarantees […]
- Ruth Bader Ginsburg Documentary of Supreme Court Justice Ginsburg, who became the 107th judge of the Supreme Court and the second woman on the bench, was a sensation with the younger generations.
- 2017 ICC Moot Court Case Prosecution Argument In the court case, the Counsel for the Government of Yunkel has requested that Judge Rosemelle Hasty, one of the three Pre-Trial Chamber members assigned to the matter, be disqualified.
- Drug Courts and Detoxification: Approach to Drug Abuse Treatment However, since 1989, the US federal system has been providing the majority of drug abusers with proper treatment or education with the help of a drug court option.
- Thurgood Marshall: Supreme Court of the United States Thurgood Marshall, serving on the Supreme Court of the United States, was one of the prominent American jurists who played a pivotal role in shaping the history of civil rights in America.
- Court Case of Swain vs. Geoffrey Osborne Limited The court was to resolve whether the defendant and the second defendant were liable for personal injuries sustained by the lorry driver in the accident. On the day of the accident, the driver had driven […]
- Supreme Court: The Case Research The national-traffic and motor-vehicle-safety act was established in the US in the year 1966 and it was meant to facilitate the federal government to provide and enforce safety standards meant to ensure that road safety […]
- Supreme Court’s Interpretation of Democracy This was seen in the Free Exercise Clause of the First Amendment in a case involving Sherbert and Verner. The court mentioned the importance of a compelling interest from the state in regard to employment […]
- Does Understanding Body Language in Court Hearing Influence Interpreting Process When the other parties receive the coded message, they go through the process of decoding or interpreting it to understand and meaning”.”Effective ways of communicating exists between the sender of the information and the receiver […]
- Supreme Court Decision: Corporations and Freedom of Speech The Constitution is the framework for the Government of the United States that protects and guarantees the basic rights of the people.
- Maltreated Children’s and Court Involvement In this study, independent variables included the age of the children involved in the proceedings, the gender of the children, duration of time that the child has been involved in the proceedings and the in […]
- Witnesses’ Role in the Court Trial In conclusion, eyewitnesses’ evidences are very important during the court procedure, but judges should be very careful with these evidences and to check them carefully.
- Public Interest Immunity in Court Process Before attempt to evaluate the current operation of the law of public interest immunity in civil trials it is necessary to discuss the definition of public interest immunity, current situation and the judgement of few […]
- The Model of the International Criminal Court The basis of the functioning and jurisdiction of the ICC is the Rome Statute. The irony of the matter is that in comparison to other modern states, the United States has considered itself as not […]
- Morse vs. Frederick: Decisions of the United States Supreme Court This court is independent; this gives it the mandate to check the other two arms of the government that is the Legislature and the Executive.
- Three-Tiered Court Structure in the United States S is a three tiered judicial system divided into the Supreme Court, The Courts of appeal and the Federal District Courts.
- Pennsylvania State Court System In regard to the terms of the Appellate Court Judges, their length of terms for Supreme Court, Superior Court and Commonwealth Court are 10 years in all cases.
- Washington County Court Services The former held notion about unaccepted restorative justice and the victim offender mediation has been reviewed and now the aim of this Court is to restore the relationship between the offenders and the victims and […]
- Top Court Rules Against Police in Search Case In the case in point, there are several issues which must be considered: in cases of domestic disturbance, who has the right to grant entrance to police; if police enter to protect one occupant, can […]
- Global Human Rights: The European Court of Human Rights The European Convention on Human Rights, or officially called Convention for the Protection of Human Rights and Fundamental Freedoms became one of the most significant documents accepted by the Council of Europe.
- European Union & Court of Justice The sixth most important developmental trend in the history of Europe has been visualized by Europeanization since the 16th century in a broad historical sense.”The primary and overarching objective of EU development cooperation is the […]
- Juvenile Delinquents in Adult Court We are all aware of the existence of social standards concerning the status of children and adolescents, as well as the nature of punishment and justice.
- Supreme Court and Local Governments Unfortunately, the ruling on the property by the Supreme Court is characteristic of a regulated market. To preserve a free market and the right of property ownership, the ruling should be reviewed.
- Forensic Experts in Court: Pros and Cons The forensic psychologist, in this case, does not employ the notion of empathizing any action in the defendant’s favor but being closer to the gathered evidence from the particular defendant’s reasons and provide the sources […]
- Business Law & Court System in Virginia The General District Courts and J&DR Courts are parts of District courts and they are courts of limited jurisdiction. Only the Chief Judges can appoint clerks of J & DR and General District Courts.
- Appeal Process in the Supreme Court in the U.S It is the duty of the Supreme Court to correct errors in trial court proceedings, interpret case law and statutes, and the state and federal constitutions and administrators of the courts.
- Forensic Science and Law: The U.S. Supreme Court’s Decision in Daubert According to the Daubert decision, the Supreme Court took a broad view of “science ” based on the data and reasoning facts considered as expert evidence.
- The World Court or International Court of Justice All of the cases of the Court are submitted to the Registrar and when the Registrar receives the case, it is dated based on the date of receipt by the Registrar.
- President’s Power in Supreme Court Cases The Humphrey’s case and the Myers case test the powers of the president of the United States to hire and fire individuals at will.
- Necessity of a New International Environmental Court For example, the international court of justice which is the Judicial Wing of the United Nation is in a position to hear environmental cases and fully attend to them.
- Lomanno: Tax Law and Court Rulings Report The second fact is that the husband of a petitioner did not have the permission to sign her name to income tax in the years that are discussed and there was also no approval to […]
- Arizona Court System to Sue Uber Technologies Inc. The use of automated cars by Uber led to several accidents that resulted in the death of one of the pedestrians in Arizona.
- Relationship Between the Supreme Court and the High Court Justice The given article utilizes the empirical and quantitative methods of studying the relationship between the Supreme Court and the High Court Justice.
- People vs. Goetz: Court Decision and Implications The court case of the appellant in the face of the People of the State of New York and the respondent in the face of Bernhard Goetz was argued and decided in the year 1986.
- Dual Court System Definition After the State Supreme Court or the Federal Circuit Court of Appeals, there is the final avenue of appeal, to the United States Supreme Court.
- Court Alternatives for Mentally Ill Criminals
- Electronic Surveillance and Related Court Rulings
- The Supreme Court Saves Cell Phone Privacy
- State Court Organization and Structure
- Felony Court System Administration
- Expert Witnesses and Testimony in Four Court Cases
- Mock Trial Experience at Brooklyn Federal Court
- Constitutional Law: Supreme Court and Stare Decisis
- International Court Punishing Rape in Armed Conflict
- Supreme Court Decisions That Affect Victim Handing
- The Crown Court Case: Drug and Weapons Trafficking
- Supreme Court: Elk Grove Unified School District vs. Newdow
- Understanding the Court System: People vs. Turner Case
- “Punishment” and “Conscience of the Court” Comparison
- Criminal Court: Ahmad Al-Faqi Al-Mahdi Case
- Women Roles in the Ptolemaic Court
- Court Problem and Its Future
- The Supreme Court of the United States
- Court System vs. the United States Constitution
- Court Process: Interview Eith the Prosecuting Attorneys
- Project Reset and the Domestic Violence Court
- The Eighth Amendment and the US Supreme Court
- US Supreme Court’s Role in Criminal Justice System
- Criminal Cases in the Supreme Court’s Jurisdiction
- Home Firearms in McDonald vs. Chicago Court Case
- US Supreme Court’s Ideological Tendencies
- Supreme Court in New York Times Co. vs. United States
- Obergefell vs. Hodge: Supreme Court Case
- Syrian War Crimes and International Criminal Court
- Roberts Court and Its Political Relations
- Trials and Verdicts in the Court Proceedings
- The Juvenile Division of the Court
- Brown vs. Plata Case and Supreme Court’s Decision
- European Court of Justice and Regional Integration
- The Supreme Court Role in Canadian Politics
- Supreme Court and State of the U.S. Justice System
- Law: Court Issue Analysis
- Law: Court Purposes and Responsibilities
- Supreme Court Ruling: The Louisiana Purchase
- Analyzing Data in HR and Presenting Findings to Make Decisions in Crown Prince Court
- Analysis: “Governing From the Bench: The Supreme Court of Canada and the Judicial Role” by Emmett Macfarlane
- Albert Court Motor Lodge
- The New Deal and the Role of the Supreme Court
- The United States Supreme Court: Marbury vs. Madison
- U.S. Supreme Court: Antonin Scalia as a Textualist
- Oral Arguments and Decision-Making on the Supreme Court
- Supreme Court in Israel
- Theory of Negligence Advance in High Court in Australia
- Personal Jurisdiction of a Court
- Civil Rights Court Case: Griggs vs. Duke Power Co
- The Role of the High Court in Australia’s System of Government
- High Court of Australia
- Emperor Xiaowen and His Court
- The Supreme Court: Justice Clarence Thomas
- The Relationship Between the International Criminal Court and the African Union
- Prima Facie Case: Home Country vs. Foreign Country
- International Court of Justice in Hague
- Supreme Court in the United States
- Roe vs. Wade Ruling – The Result of the Supreme Court
- As Supreme Court Reconvenes, Civil Rights Issues in the Fore
- Case Brief on Reynolds vs. Sims
- Why Juveniles Should Be Tried in Adults’ Court?
- Gay Marriage and Decision Massachusetts Supreme Judicial Court
- The Warren Court in United States
- U.S. Supreme Court Operation
- Comparison of US Supreme Court Decisions
- Child Abuse and Neglect Children in Court
- Questioning and Criticizing Supreme Court Nominees
- The Supreme Court Decision: Bank of Augusta vs. Earle
- The Supreme Court, in the Case of Kelo vs. the City of New London
- Prison Paper Topics
- Civil Rights Movement Questions
- Social Policy Essay Ideas
- Constitution Research Ideas
- Supreme Court Essay Topics
- Criminal Procedure Titles
- Antitrust Law Research Topics
- Civil Law Paper Topics
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 26). 218 Essay about Court Examples & Topics. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/court-essay-topics/
"218 Essay about Court Examples & Topics." IvyPanda , 26 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/court-essay-topics/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '218 Essay about Court Examples & Topics'. 26 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "218 Essay about Court Examples & Topics." February 26, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/court-essay-topics/.
1. IvyPanda . "218 Essay about Court Examples & Topics." February 26, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/court-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "218 Essay about Court Examples & Topics." February 26, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/court-essay-topics/.
We will keep fighting for all libraries - stand with us!
Internet Archive Audio

- This Just In
- Grateful Dead
- Old Time Radio
- 78 RPMs and Cylinder Recordings
- Audio Books & Poetry
- Computers, Technology and Science
- Music, Arts & Culture
- News & Public Affairs
- Spirituality & Religion
- Radio News Archive

- Flickr Commons
- Occupy Wall Street Flickr
- NASA Images
- Solar System Collection
- Ames Research Center

- All Software
- Old School Emulation
- MS-DOS Games
- Historical Software
- Classic PC Games
- Software Library
- Kodi Archive and Support File
- Vintage Software
- CD-ROM Software
- CD-ROM Software Library
- Software Sites
- Tucows Software Library
- Shareware CD-ROMs
- Software Capsules Compilation
- CD-ROM Images
- ZX Spectrum
- DOOM Level CD

- Smithsonian Libraries
- FEDLINK (US)
- Lincoln Collection
- American Libraries
- Canadian Libraries
- Universal Library
- Project Gutenberg
- Children's Library
- Biodiversity Heritage Library
- Books by Language
- Additional Collections

- Prelinger Archives
- Democracy Now!
- Occupy Wall Street
- TV NSA Clip Library
- Animation & Cartoons
- Arts & Music
- Computers & Technology
- Cultural & Academic Films
- Ephemeral Films
- Sports Videos
- Videogame Videos
- Youth Media
Search the history of over 866 billion web pages on the Internet.
Mobile Apps
- Wayback Machine (iOS)
- Wayback Machine (Android)
Browser Extensions
Archive-it subscription.
- Explore the Collections
- Build Collections
Save Page Now
Capture a web page as it appears now for use as a trusted citation in the future.
Please enter a valid web address
- Donate Donate icon An illustration of a heart shape
The High Court of Parliament and its supremacy; an historical essay on the boundaries between legislation and adjudication in England
Bookreader item preview, share or embed this item, flag this item for.
- Graphic Violence
- Explicit Sexual Content
- Hate Speech
- Misinformation/Disinformation
- Marketing/Phishing/Advertising
- Misleading/Inaccurate/Missing Metadata
![[WorldCat (this item)] [WorldCat (this item)]](https://archive.org/images/worldcat-small.png)
plus-circle Add Review comment Reviews
1,852 Views
2 Favorites
DOWNLOAD OPTIONS
For users with print-disabilities
IN COLLECTIONS
Uploaded by liz ridolfo on May 3, 2007
SIMILAR ITEMS (based on metadata)
Protecting the NRA’s Freedom of Speech Rights Protects Us All

It should be obvious that government officials can’t deploy their regulatory authority to punish an advocacy group because they disagree with its point of view. Yet that is exactly what Gov. Andrew Cuomo (D-NY) and his chief financial regulator, Maria Vullo, set out to do in 2018.
They favored gun control, and therefore disfavored the National Rifle Association. Cuomo and Vullo were of course free to criticize the NRA. But rather than just rely on the persuasive force of their ideas, they deployed the coercive power of their offices to pressure banks and insurance companies to cut ties with the NRA, as alleged.
On May 30, the US Supreme Court in effect confirmed what should have been obvious, unanimously ruling that Vullo’s and Cuomo’s alleged words and actions stated a claim under the First Amendment. In doing so, the court overturned a unanimous decision from the Second Circuit against the NRA. The decision makes no new law, but reaffirms what’s been established since the Supreme Court announced, 60 years ago, that government officials can’t use informal coercion to punish speech they disfavor.
The critical facts alleged in NRA v. Vullo are stark. In February 2018, Vullo, New York’s top financial regulator, with direct oversight of every bank and insurance company in the state, told Lloyd’s, the insurance underwriter, that she’d go easy on unrelated insurance violations if it aided her campaign to weaken the NRA by halting all business with the group. Lloyd’s agreed, and did her bidding.
Six weeks later, Vullo issued formal guidance letters and a press release directing the thousands of banks and insurance companies she oversees to cut their ties with the NRA—not because of any alleged improprieties, but because it “promotes guns.” In the accompanying press release, Cuomo said he directed Vullo to issue the guidance because doing business with the NRA “sends the wrong message.”
This was not about enforcing insurance law; it was about using state power to coerce a boycott of a political group because the state’s highest officials disapproved of its speech. As Cuomo put it in a tweet responding to the NRA’s subsequent lawsuit, “The regulations NY put in place are working. We’re forcing the NRA into financial jeopardy. We won’t stop until we shut them down.”
Had the court accepted Vullo’s argument that this was merely “government speech” and ordinary law enforcement, as the US Court of Appeals for the Second Circuit did, the decision would have provided a playbook for state officials across the country to blacklist whichever groups they disfavor.
That’s why the American Civil Liberties Union agreed to represent the NRA in the Supreme Court. The ACLU disagrees profoundly with the NRA on many issues of law and policy, but we agree that government officials can’t punish advocacy groups simply because they disagree with what they say.
The court’s unanimous decision ensures that officials can’t achieve indirectly what they are barred from achieving directly: punishing speech simply because they disagree with its message. That principle is foundational to a free and democratic society. And the Vullo decision ensures that the First Amendment’s protection extends not just to direct penalties, but to the sorts of end runs that Vullo and Cuomo attempted in targeting the NRA.
The case is NRA v. Vullo , US, No. 22-842, 5/30/24.
This article does not necessarily reflect the opinion of Bloomberg Industry Group, Inc., the publisher of Bloomberg Law and Bloomberg Tax, or its owners.
Author Information
David Cole is national legal director of the ACLU and professor at Georgetown Law. The ACLU represented the NRA in NRA v. Vullo , and Cole argued the case before the Supreme Court.
Write for Us: Author Guidelines
To contact the editors responsible for this story: Alison Lake at [email protected] ; Jessie Kokrda Kamens at [email protected]
Learn more about Bloomberg Law or Log In to keep reading:
Learn about bloomberg law.
AI-powered legal analytics, workflow tools and premium legal & business news.
Already a subscriber?
Log in to keep reading or access research tools.

Enjoy fast, free delivery, exclusive deals, and award-winning movies & TV shows with Prime Try Prime and start saving today with fast, free delivery
Amazon Prime includes:
Fast, FREE Delivery is available to Prime members. To join, select "Try Amazon Prime and start saving today with Fast, FREE Delivery" below the Add to Cart button.
- Cardmembers earn 5% Back at Amazon.com with a Prime Credit Card.
- Unlimited Free Two-Day Delivery
- Streaming of thousands of movies and TV shows with limited ads on Prime Video.
- A Kindle book to borrow for free each month - with no due dates
- Listen to over 2 million songs and hundreds of playlists
- Unlimited photo storage with anywhere access
Important: Your credit card will NOT be charged when you start your free trial or if you cancel during the trial period. If you're happy with Amazon Prime, do nothing. At the end of the free trial, your membership will automatically upgrade to a monthly membership.
Return this item for free
Free returns are available for the shipping address you chose. You can return the item for any reason in new and unused condition: no shipping charges
- Go to your orders and start the return
- Select your preferred free shipping option
- Drop off and leave!

Download the free Kindle app and start reading Kindle books instantly on your smartphone, tablet, or computer - no Kindle device required .
Read instantly on your browser with Kindle for Web.
Using your mobile phone camera - scan the code below and download the Kindle app.


Image Unavailable

- To view this video download Flash Player

Follow the author

The High Court of Parliament and Its Supremacy: An Historical Essay on the Boundaries Between Legislation and Adjudication in England. Paperback – December 20, 2010
Purchase options and add-ons.
- Print length 434 pages
- Language English
- Publisher Gale, Making of Modern Law
- Publication date December 20, 2010
- Dimensions 7.44 x 0.88 x 9.69 inches
- ISBN-10 1240138490
- ISBN-13 978-1240138494
- See all details

Product details
- Publisher : Gale, Making of Modern Law (December 20, 2010)
- Language : English
- Paperback : 434 pages
- ISBN-10 : 1240138490
- ISBN-13 : 978-1240138494
- Item Weight : 1.7 pounds
- Dimensions : 7.44 x 0.88 x 9.69 inches
- #10,849 in General Constitutional Law
- #20,720 in England History
About the author
Charles howard mcilwain.
Discover more of the author’s books, see similar authors, read author blogs and more
Customer reviews
Customer Reviews, including Product Star Ratings help customers to learn more about the product and decide whether it is the right product for them.
To calculate the overall star rating and percentage breakdown by star, we don’t use a simple average. Instead, our system considers things like how recent a review is and if the reviewer bought the item on Amazon. It also analyzed reviews to verify trustworthiness.
No customer reviews
- Amazon Newsletter
- About Amazon
- Accessibility
- Sustainability
- Press Center
- Investor Relations
- Amazon Devices
- Amazon Science
- Sell on Amazon
- Sell apps on Amazon
- Supply to Amazon
- Protect & Build Your Brand
- Become an Affiliate
- Become a Delivery Driver
- Start a Package Delivery Business
- Advertise Your Products
- Self-Publish with Us
- Become an Amazon Hub Partner
- › See More Ways to Make Money
- Amazon Visa
- Amazon Store Card
- Amazon Secured Card
- Amazon Business Card
- Shop with Points
- Credit Card Marketplace
- Reload Your Balance
- Amazon Currency Converter
- Your Account
- Your Orders
- Shipping Rates & Policies
- Amazon Prime
- Returns & Replacements
- Manage Your Content and Devices
- Recalls and Product Safety Alerts
- Conditions of Use
- Privacy Notice
- Consumer Health Data Privacy Disclosure
- Your Ads Privacy Choices
The University of Chicago The Law School
College essays and diversity in the post-affirmative action era, sonja starr’s latest research adds data, legal analysis to discussion about race in college admissions essays.

Editor’s Note: This story is part of an occasional series on research projects currently in the works at the Law School.
The Supreme Court’s decision in June 2023 to bar the use of affirmative action in college admissions raised many questions. One of the most significant is whether universities should consider applicants’ discussion of race in essays. The Court’s decision in Students for Fair Admissions (SFFA) v. Harvard did not require entirely race-blind admissions. Rather, the Court explicitly stated that admissions offices may weigh what students say about how race affected their lives. Yet the Court also warned that this practice may not be used to circumvent the bar on affirmative action.
Many university leaders made statements after SFFA suggesting that they take this passage seriously, and that it potentially points to a strategy for preserving diversity. But it’s not obvious how lower courts will distinguish between consideration of “race-related experience” and consideration of “race qua race.” Sonja Starr, Julius Kreeger Professor of Law & Criminology at the Law School, was intrigued by the implication of that question, calling the key passage of the Court’s opinion the “essay carveout.”
“Where is the line?” she wrote in a forthcoming article, the first of its kind to discuss this issue in depth in the post- SFFA era. “And what other potential legal pitfalls could universities encounter in evaluating essays about race?”
To inform her paper’s legal analysis, Starr conducted empirical analyses of how universities and students have included race in essays, both before and after the Court’s decision. She concluded that large numbers of applicants wrote about race, and that college essay prompts encouraged them to do so, even before SFFA .
Some thought the essay carveout made no sense. Justice Sonia Sotomayor called it “an attempt to put lipstick on a pig” in her dissent. Starr, however, disagrees. She argues that universities are on sound legal footing relying on the essay carveout, so long as they consider race-related experience in an individualized way. In her article, Starr points out reasons the essay carveout makes sense in the context of the Court’s other arguments. However, she points to the potential for future challenges—on both equal protection and First Amendment grounds—and discusses how colleges can survive them.
What the Empirical Research Showed
After SFFA , media outlets suggested that universities would add questions about race or identity in their admissions essays and that students would increasingly focus on that topic. Starr decided to investigate this speculation. She commissioned a professional survey group to recruit a nationally representative sample of recent college applicants. The firm queried 881 people about their essay content, about half of whom applied in 2022-23, before SFFA , and half of whom submitted in 2023-24.
The survey found that more than 60 percent of students in non-white groups wrote about race in at least some of their essays, as did about half of white applicants. But contrary to what the media suggested, there were no substantial changes between the pre-and post- SFFA application cycles.
Starr also reviewed essay prompts that 65 top schools have used over the last four years. She found that diversity and identity questions—as well as questions about overcoming adversity, which, for example, provide opportunities for students to discuss discrimination that they have faced—are common and have increased in frequency both before and after SFFA.
A Personally Inspired Interest
Although Starr has long written about equal protection issues, until about two years ago, she would have characterized educational admissions as a bit outside her wheelhouse. Her research has mostly focused on the criminal justice system, though race is often at the heart of it. In the past, for example, she has assessed the role of race in sentencing, the constitutionality of algorithmic risk assessment instruments in criminal justice, as well as policies to expand employment options for people with criminal records.
But a legal battle around admissions policies at Fairfax County’s Thomas Jefferson High School for Science and Technology—the high school that Starr attended—caught her attention. Starr followed the case closely and predicted that “litigation may soon be an ever-present threat for race-conscious policymaking” in a 2024 Stanford Law Review article on that and other magnet school cases.
“I got really interested in that case partly because of the personal connection,” she said. “But I ended up writing about it as an academic matter, and that got me entrenched in this world of educational admissions questions and their related implications for other areas of equal protection law.”
Implications in Education and Beyond
Starr’s forthcoming paper argues that the essay carveout provides a way for colleges to maintain diversity and stay on the right side of the Court’s decision.
“I believe there’s quite a bit of space that’s open for colleges to pursue in this area without crossing that line,” she said. “I lay out the arguments that colleges can put forth.”
Nevertheless, Starr expects future litigation targeting the essay carveout.
“I think we could see cases filed as soon as this year when the admissions numbers come out,” she said, pointing out that conservative legal organizations, such as the Pacific Legal Foundation, have warned that they’re going to be keeping a close eye on admissions numbers and looking for ways that schools are circumventing SFFA .
Starr envisions her paper being used as a resource for schools that want to obey the law while also maintaining diversity. “The preservation of diversity is not a red flag that something unconstitutional is happening,” she said. “There are lots of perfectly permissible ways that we can expect diversity to be maintained in this post- affirmative action era.”
Starr’s article, “Admissions Essays after SFFA ,” is slated to be published in Indiana Law Journal in early 2025.
The Importance and Challenges of a Speedy and Public Trial
This essay about the right to a speedy and public trial explains its importance in democratic justice systems. It highlights how a speedy trial prevents prolonged detention, protects defendants’ rights, and maintains the legal system’s integrity. Public trials ensure transparency and accountability, fostering trust in the judiciary. The essay discusses challenges in implementing these rights, such as balancing speed with quality of justice and managing privacy concerns. Technological advancements and international human rights law are suggested as potential solutions. Overall, the essay underscores the significance of upholding these rights to ensure fairness and transparency in the judicial process.
How it works
The right to a speedy and public trial is a cornerstone of democratic justice systems worldwide, enshrined in various constitutions and human rights documents. This principle aims to protect individuals from prolonged detention without trial and ensures transparency in the legal process. Its significance lies in balancing the scales of justice, preventing abuses of power, and maintaining public confidence in the judicial system.
The concept of a speedy trial ensures that a person accused of a crime is brought to trial within a reasonable timeframe.
This right prevents defendants from languishing in jail for extended periods, which can lead to loss of employment, disruption of family life, and deterioration of mental health. A delayed trial can also compromise the ability to mount an effective defense, as memories fade, evidence may be lost, and witnesses can become unavailable. Timeliness in the judicial process is crucial in maintaining the integrity of the legal system and upholding the rights of the accused.
A public trial, on the other hand, serves as a safeguard against judicial abuse and corruption. By allowing the public and media to observe the proceedings, transparency is promoted, which helps ensure that the trial is conducted fairly and according to the law. Public scrutiny acts as a check on the legal system, holding it accountable and fostering trust within the community. It also provides an educational function, informing the public about legal processes and the functioning of the judiciary.
However, implementing the right to a speedy and public trial presents several challenges. Ensuring speediness without compromising the quality of justice is a delicate balance. The judicial system must handle a large volume of cases, and resources such as judges, courtrooms, and legal personnel are often limited. This scarcity can lead to backlogs and delays, undermining the right to a speedy trial. Efforts to expedite proceedings must not come at the expense of thorough and fair consideration of each case.
Moreover, the requirement for public trials can sometimes clash with the need to protect the privacy and safety of those involved, particularly in cases involving sensitive issues such as sexual assault or national security. In some situations, extensive media coverage and public interest can create a circus-like atmosphere, which can influence the jury and affect the defendant’s right to a fair trial. Courts must find a balance between openness and the protection of the participants’ rights and safety.
Technological advancements offer potential solutions to some of these challenges. For instance, digital case management systems can help streamline court processes and reduce delays. Virtual courtrooms, which became more common during the COVID-19 pandemic, provide a way to conduct trials promptly while maintaining public access. These innovations can enhance the efficiency and transparency of the judicial system if implemented thoughtfully and with attention to the rights of all parties involved.
International human rights law also plays a significant role in upholding the right to a speedy and public trial. Documents such as the Universal Declaration of Human Rights and the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights outline these rights and serve as a benchmark for national legal systems. However, the extent to which these rights are realized can vary significantly between countries, influenced by legal traditions, resources, and political will.
In some jurisdictions, there are statutory limits on the time a defendant can be held before trial, which helps enforce the right to a speedy trial. For example, in the United States, the Speedy Trial Act sets specific time frames for the various stages of a criminal prosecution. While such measures provide a framework, the actual implementation can be affected by numerous factors, including the complexity of the case, the availability of legal counsel, and procedural issues.
In conclusion, the right to a speedy and public trial is fundamental to the administration of justice, protecting the rights of the accused and ensuring transparency in the judicial process. While there are significant challenges in balancing speed, fairness, and public access, continued efforts and innovations can help address these issues. Upholding these rights requires vigilance, resources, and a commitment to the principles of justice and human rights. As legal systems evolve, maintaining the delicate balance between expedience and thoroughness, openness and privacy, will remain a central concern in the pursuit of justice.
Remember, this essay is a starting point for inspiration and further research. For more personalized assistance and to ensure your essay meets all academic standards, consider reaching out to professionals at EduBirdie .
Cite this page
The Importance and Challenges of a Speedy and Public Trial. (2024, Jun 01). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/the-importance-and-challenges-of-a-speedy-and-public-trial/
"The Importance and Challenges of a Speedy and Public Trial." PapersOwl.com , 1 Jun 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/the-importance-and-challenges-of-a-speedy-and-public-trial/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). The Importance and Challenges of a Speedy and Public Trial . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-importance-and-challenges-of-a-speedy-and-public-trial/ [Accessed: 7 Jun. 2024]
"The Importance and Challenges of a Speedy and Public Trial." PapersOwl.com, Jun 01, 2024. Accessed June 7, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/the-importance-and-challenges-of-a-speedy-and-public-trial/
"The Importance and Challenges of a Speedy and Public Trial," PapersOwl.com , 01-Jun-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-importance-and-challenges-of-a-speedy-and-public-trial/. [Accessed: 7-Jun-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). The Importance and Challenges of a Speedy and Public Trial . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-importance-and-challenges-of-a-speedy-and-public-trial/ [Accessed: 7-Jun-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers
- IAS Preparation
- UPSC Preparation Strategy
High Courts of India - Number of High Courts in India, Jurisdiction & Composition (UPSC GS-II)
The highest judicial court in a state is the High Court. It is termed as the second-highest in the country after the Supreme Court of India. Currently, India has 25 High Courts established in different states of the country. As a vital part of the Indian Judiciary, High Court becomes an important topic with reference to the candidates preparing for the UPSC 2024 exam.
In this article, you shall find all the important information regarding the High Court in India, its powers, establishment, the appointment of Judges and Jurisdiction. You can also download the High Court notes PDF for the upcoming exam.
Aspirants would find this article very helpful while preparing for the IAS Exam .
How many High Courts are there in India?
There are 25 High Courts in India. Candidates can find the list of High Courts in India in the linked article.
It was in 1858 when on the recommendation of the Law Commission, the Parliament passed the Indian High Courts Act 1861 which suggested the establishment of High Courts in place of Supreme Court in three Presidencies: Calcutta, Madras, and Bombay. The Charter of High Court of Calcutta was ordered in May 1862 and that of Madras and Bombay were order in June 1862. Thereby, making the Calcutta High Court the first High Court of the country.
The reason for the implementation of this act was the need for a separate judiciary body for different states. The British Government, therefore, decided to abolish the then-existing Supreme Court and Sadar Adalat and replaced it with High Court.
Certain rules and eligibility criteria were set for the appointment of a Judge in any High Court and later after independence as per Article 214 of the Indian Constitution, it was declared that every Indian state must have their own High Court.
The British-created laws were different from the ones that were stated in the Indian Penal code and the entire legal system of the country changed after the independence of the country.
Which is the Newest High Court of India?
Andhra Pradesh is the recent state to have the High Court. High Court was established in Andhra Pradesh on 1st January 2019.
Constitution of High Court – Under British rule, each High Court has a Chief Justice and maximum 15 other puisne judges. But later certain changes were brought about in the composition of the High Court in India:
- Every High Court shall have a Chief Justice appointed by the President
- Unlike before, there was no fixed number of Judges who could be appointed for each High Court
- Additional Judges can also be appointed for the clearance of cases pending in the court. But their tenure cannot exceed more than two years
One thing that must be noted is that no one above the age of 62 years can be appointed as a High Court Judge. There is no uniformity among the High Courts regarding the number of Judges they will have. A smaller state shall have less number of judges in comparison to a larger state.
High Court Jurisdiction
The High Court is the highest court of appeal in the state vested with the power to interpret the Constitution. It is the protector of the Fundamental Rights of the citizens. Besides, it has supervisory and consultative roles. However, the Constitution does not contain detailed provisions with regard to the jurisdiction and powers of a high court.
At present, t he following jurisdictions are enjoyed by a High Court-
- Original jurisdiction
- Writ jurisdiction
- Appellate jurisdiction
- Supervisory jurisdiction
- Control over subordinate courts
- A court of record
- Power of judicial review
The Jurisdiction of Highcourt are as mentioned below –
- Original Jurisdiction – In such kind of cases the applicant can directly go to the High Court and does not require to raise an appeal. It is mostly applicable for cases related to the State Legislative Assembly, marriages, enforcement of fundamental rights and transfer cases from other courts.
- Power of Superintendence – It a special power enjoyed only by High Court and no other subordinate court has this power of superintendence. Under this, the High Court holds the right to order its subordinate offices and courts the way of maintaining records, prescribe rules for holding proceedings in the court and also settle the fees paid to sheriff clerks, officers and legal practitioners.
- Court of Record – It involves recording the judgments, proceedings and acts of high courts for perpetual memory. These records cannot be further questioned in any court. It has the power to punish for contempt of itself.
- Control over Subordinate Courts – This is an extension of the supervisory and appellate jurisdiction. It states that the High Court can withdraw a case pending before any subordinate court if it involves the substantial question of law. The case can be disposed of itself or solve the question of law and return back to the same court.
- Civil Jurisdiction – this includes orders and judgements of the district court, civil district court and subordinate court
- Criminal Jurisdiction – this includes judgements and orders of the sessions court and additional sessions court.
- Power of Judicial Review – This power of High Court includes the power to examine the constitutionality of legislative and executive orders of both central and state government. It is to be noted that the word judicial review is nowhere mentioned in our constitution but the Article 13 and 226 explicitly provide High Court with this power.
- Habeas Corpus
- Writ of Mandamus
- In the Chandra Kumar case (1997), the Supreme Court ruled that the writ jurisdiction of both the high court and the Supreme Court constitute a part of the basic structure of the Constitution. Hence, it cannot be ousted or excluded even by way of an amendment to the Constitution.
- In Shah Faesal’s Case, his case is justified because the cause of action happened in Delhi and then he was taken to outside the territory of Delhi.
High Court in India is one of the most important topics in terms of the UPSC exam and other government exams in India. Candidates can know the powers and function of a High Court , at the linked article.
How is a High Court Judge Appointed?
A High Court Judge is appointed by the President of India. He is solely responsible for the appointment of any judge in a High Court. However, he may consult the Governor of the State, the acting Chief Justice of India and Chief Justice of that particular state’s High Court.
A High Court judge is also liable to get transferred to other High Courts. This decision is entirely dependent on the Chief Justice of India. Transfer of judges is done with an aim to ensure proper and just trial for every case fought in the court of law.
Eligibility Criteria for High Court Judge
There are certain eligibility criteria that need to be fulfilled to be appointed as a judge in any High court in India. Given below are the set of eligibility criteria mandatory for the appointment of High Court judges:
- The person should have been a Barrister for more than five years
- Has been a civil servant for over 10 years along with serving the Zila court for at least 3 years
- A person who has been a pleader for over 10 years in any High Court.
- No judge should be of more than 62 years of age
The law states that every state must have a separate High Court, however, there still are certain states that do not have an individual High Court. For example – both Punjab and Haryana come under the jurisdiction of Punjab High Court sitting at Chandigarh. Besides, there is a common High Court for seven states – Assam, Nagaland, Manipur, Tripura, Meghalaya, Arunachal Pradesh and Mizoram.
Salary and Perks of High Court Judges
There has been a massive increase in the salary paid to a High Court judge. The table below gives the salary description of a judge in the High Court:
Apart from the salary, there are various other perks and allowances provided to a Judge in High Court.
Along with High Courts in India, IAS Exam aspirants can read other Polity Related Articles:
High Courts in India – UPSC Indian Polity Notes:- Download PDF Here
UPSC Preparation Articles:

Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
IAS 2024 - Your dream can come true!
Download the ultimate guide to upsc cse preparation, register with byju's & download free pdfs, register with byju's & watch live videos.
Essay on the High Courts of India
In this essay we will discuss about the high courts of India. After reading this essay you will learn about: 1. Jurisdictions of High Courts 2. Composition of the High Court 3. Salary and Allowances of the Judges 4. Oath or Affirmation by Judges of High Courts 5. Powers and Functions of the High Courts 6. Kinds of Writs 7. Subordinate Courts in India.
List of Essays on the High Courts of India
Essay Contents:
- Essay on the Subordinate Courts in India
1. Essay on the Jurisdictions of High Courts :
Judiciary is an integral part of every federal system. It inspires confidence of the federating units on the one hand and the masses on the other. In India constitution has provided for an integrated judiciary. Under this system at the top is Supreme Court of India, which is the highest judicial authority in the land. Its decisions are applicable all over the country. Down below in each state is a High Court.
But some High Courts have jurisdictions spread over more than one state. High Courts have jurisdictions over their respective states, but appeals against the judgment of a High Court can lie with the Supreme Court, which can reverse any of its decision. Still down below are District Courts, both civil and criminal.
At present in India there are 18 High Courts. Jurisdiction of each High Court is as under:
Thus, it will be seen that Bombay High Court is the oldest High Court in India which was founded in 1861 followed by Allahabad High Court set up in 1866. Sikkim High Court established in 1975 is the youngest High Court in the country. Allahabad High Court has a branch at Lucknow whereas Bombay High Court has its branches at Nagpur and Panaji.
Rajasthan High Court has its branch at Jodhpur and Patna High Court at Ranchi. Madhya Pradesh High Court has its branches at Gwalior and Indore whereas Gauhati High Court has set up its branches at Imphal and Agartala.
2. Essay on the Composition of the High Court :
Under the constitution each state in India shall have a High Court which shall consist of a Chief Justice and such other Judges as the President from time to time deem it necessary to appoint. In other words number of Judges will be decided by the President which even now varies from state to state depending upon the volume of the work.
Chief Justice of a High Court is appointed by the President of India in consultation with the Chief Justice of India, whereas he appoints other Judges in consultation with the concerned Governor and Chief Justice of the High Court and also Chief Justice of India. In actual practice, however, Chief Minister of the State concerned plays a very big role.
He is always consulted and his views weigh with the central government while making such appointments. Gradually an impression is being created that appointment of Judges of High Court has become a political affair. In case for any reason if the office of the Chief Justice falls vacant the President can ask one of the judges of that court to look after the duties of Chief Justice.
Qualifications for Appointment:
Any person can be appointed as Chief Justice of a State High Court provided he is an Indian citizen has for at least ten years held a judicial office in the territory of India or has for at least ten years been an advocate of a High Court or of two or more High Courts in succession.
By Forty-Second Constitution Amendment Act it was provided that any person who in the opinion of the President was an eminent jurist could also be appointed as Judge of the High Court.
But this was omitted by Forty-Fourth Constitution Amendment Act. He should be below the age of 62. In case any dispute arises about the age of judge, the matter shall be referred to the President who shall decide it in consultation with the Chief Justice of India and his decision shall be final.
In case the work of the High Court has gone in arrears or has temporarily increased, the President can appoint Additional Judges for a period not exceeding two years, from among those who possess qualifications prescribed for a High Court Judge. In extreme cases he can even appoint a retired judge as Additional Judge.
Removal of Judges:
A judge can remain in office till he has attained the age of 62 years but he can resign his office earlier if he so likes by writing under his hand a letter of resignation addressed to the President.
He can also be removed provided an address has been presented to the President by the Parliament supported by majority of the total membership of the House in which the motion of removal has been moved and by a majority of not less than two-third of that House present and voting has been presented to the President in the same session for such removal on the ground of proved misbehaviour or incapacity.
He shall also vacate his office when he is appointed by the President to be a judge of the Supreme Court or has been transferred to some other Court.
3. Essay on the Salary and Allowances of the Judges:
It is provided that the judges of the High Court shall draw such salaries and allowances, as the Parliament may by law fix from time to time, but until otherwise fixed those shall be as follows:
The Chief Justice Rs.9,000/- p.m.
Any other Judge Rs.8,000/- p.m.
In addition they will also be entitled to receive such other allowances as are admissible to other senior employees of the government. It is also provided that during the period of his appointment, the emoluments of a judge shall not be varied to his disadvantage, except of course when emergency conditions have been declared in the country.
Retired judges also get pension. It is provided that a retired judge cannot practice in Supreme Court or High Court of the state in which he was a permanent judge. In consultation with the Chief Justice of India, a judge of the High Court can be transferred from one court to the other in the Union Territory of India.
When the office of the Chief Justice of a High Court falls vacant or when any such Chief Justice is, by reason of absence or otherwise, unable to perform the duties of his office, the duties of his office shall be performed by one of the other judges of the court, who may be appointed by the President, to perform such duties.
As said earlier when the work in the High Court has increased, in order to cope with the increased volume of work, the President may appoint any qualified person as temporary judge. But such an appointment shall not exceed a period of 2 years.
Chief Justice of a High Court with the prior consent of President, can request a retired judge of the High Court whether of his own or any other state to sit and act as a judge of the High Court of the state. Such a judge shall enjoy and be entitled to such allowances as the President may by order determine and have all the jurisdictions, powers and privileges as any other judge of the High Court.
4. Essay on the Oath or Affirmation by Judges of High Courts :
Under the constitution every person appointed to be a judge of the High Court shall before he enters upon his office, make and subscribe before the Governor of the state, or before a person so appointed by him for the purpose an oath or affirmation in the following form:
“I, A.B. having been appointed Chief Justice (or a judge of the High Court at) (or of)……………………….. do………………….. that I will bear true faith and allegiance to the Constitution of India, as by law established, that I will uphold sovereignty and integrity of India, that I will truly and faithfully and to the best of my ability, knowledge and judgment perform the duties of my office without fear or favour, affection of ill will and I will uphold the Constitution and law.”
5. Essay on the Powers and Functions of High Courts :
One of the most essential features of Indian Judicial system is its impartiality. In the constitution it has been provided that the Judges should act impartially. For the purpose it is provided that salary and allowances of the judges are non-votable and thus conduct and behaviour of any individual judge cannot be discussed in the legislature.
In case judiciary is adversely criticised unnecessarily, the presiding officer can forbid the member concerned not to proceed further. Similarly procedure for the removal of a judge has been made complex and difficult, so that he is not afraid of the executive.
Similarly it is also provided that salaries and allowances of the Judges cannot be changed to their disadvantage, after the appointment has been made. Under Article 220 of the constitution it is provided that no person who has held office as a permanent judge of a High Court shall plead or act in any court or before any authority in India except the Supreme Court or High Court. This ban, however, applies only to permanent judges and is not to Acting or Additional judges.
Since High Courts in India were already in existence, before new constitution came into force, therefore, in the constitution it is provided that subject to such changes as may be made by different provisions of the constitution or otherwise by law, the powers of the judges of the High Courts shall be the same as immediately before the commencement of the constitution.
Article 225 of the constitution had a proviso which said that, “Any restriction to which the exercise of original jurisdiction of any of the High Courts with respect to any matter concerning the revenue or concerning any act ordered or any act done in the collection thereof was subject immediately before the commencement of this constitution shall no longer apply to the exercise of such jurisdiction.”
This provision of the constitution was omitted by Forty-Second Constitution Amendment Act but was again restored and incorporated in the constitution with the passing of Forty- Fourth Constitution Amendment Act.
High Court of a state is the highest judicial authority, whose decisions are binding over all citizens residing in the state.
The High Courts of Bombay, Calcutta and Madras have both original as well as appellate powers, whereas other High Courts have only appellate powers. Such powers extend both in civil as well as criminal cases. The High Courts are courts of record and have been authorised to issue directions, orders and writs in the nature of habeas corpus, mandamus, prohibition, quo warranto and certiorari, etc., for the enforcement of Fundamental Rights of citizens or any other purpose. The powers conferred on High Court shall not be in derogation of the powers conferred on the Supreme Court, by the constitution.
The Chief Justice of the High Court is competent to appoint officers and servants of the High Court. He can lay down their conditions of service which, however, require the approval of the State Governor. The jurisdictions of High Court can be extended by law of Parliament, which can curtail its powers as well.
Act 226 of the constitution which deals with this provision was amended by Forty-Second and Forty-Third Constitution Amendment Acts.
Forty-Fourth Constitution Amendment Act again amended this Article of the constitution, which is now as follows:
“Article 226:
Power of the High Court to issue certain writs:
(1) Not withstanding anything under Article 32, every High Court shall have power throughout the territory in relation to which it exercises jurisdictions, to issue to any person or authority, including in appropriate cases, any government, within these territories directions, orders or writs in the nature of habeas corpus, mandamus, prohibition, quo warranto, and certiorari, or any one of them, for the enforcement of any of the rights conferred by part III and for any other purpose;
(2) To issue directions, orders or writs to a government, authority or person may also be exercised by any High Court exercising jurisdictions in relation to the territories within which the cause of actions, wholly or in part, arise for the exercise of such power, not withstanding that the seat of such government or authority or the residence of such person is not within those territories.
(3) Where any party against whom an interim order whether by way of injunction or stay or in any other manner, is made on, or in any proceedings relating to, a petition under clause (1), without,
(a) Furnishing to such party-copies of such petition and all documents in support of the plea for such interim order;
(b) Giving such party an opportunity of being heard, makes an application to the High Court for the vacation of such order and furnishes a copy of such application to the party in whose favour such order has been made or the counsel of such party, the High Court shall dispose of the application within a period of two weeks from the date on which it is received or from the dale on which the copy of such application is so furnished, whichever is later, or where the High Court is closed on the last day of that period before the expiry of the next day afterwards on which the High Court is open; and if the application is not so disposed of, the interim order shall, on the expiry of that period, or as the case may be, the expiry of said next day, stand vacated.”
In this way the High Courts have been given back the power to issue writs and also to examine central laws, which had been taken away from them after the passing of constitution Forty-Second and Forty-Third Amendment Acts.
Before the commencement of constitution, in India only the High Courts of Bombay, Calcutta and Madras had the power to issue writs mentioned in the above said Article 226. But now all the courts have been given powers to issue these.
The writs are also known as prerogative writs. In the case of Election Commission of India Vs. Saka Venkata Subba Rao, it was ruled that High Court had no power to issue a writ to the Election Commission, which had its offices permanently located at New Delhi.
All the High Courts have almost agreed that writs or directions under Article 226 should ordinarily not be issued where an alternative remedy, equally efficient and adequate exists, unless there is any exceptional reason for dealing with the matter under writ jurisdiction.
The Supreme Court has held in the case of AB SK Sanga Vs. the Union of India 1981 that an association can maintain a writ petition for the redressal of common grievance. In Judges transfer case 1982, the Supreme Court has held that any member of the public having sufficient interest can approach the court for enforcing constitutional or legal proceedings where a specific legal injury has been caused to a determined group of persons when such group is unable to come before the court because of poverty, disability, etc., and the court will decide about relief. Thus, the scope of Art. 226 has been sufficiently widened.
6. Essay on the Kinds of Writs :
Certiorari may be described as an order issued by the High Court to an inferior court or body exercising what the High Court regards judicial or quasi-judicial function to have the decisions or acts of such courts or body removed to the High Court in order that its legality may be investigated.
It is discretionary and is not issued merely because it is lawful to do so. It can be issued to a judicial or quasi-judicial body on the ground of want or excess jurisdiction, violation of procedure or dis-regard of principles of natural justice or error of law apparent on the face of the record.
As regards writ of prohibition it is a type of a writ which commands the court or tribunal to whom it is issued to refrain from doing something which it is about to do or to assume jurisdictions which it does not possess. In other words such a writ lies both for excess of jurisdictions as well as absence of jurisdiction.
While differentiating between the two writs, Shukla says, “When an inferior court, takes up for hearing a matter over which it has no jurisdiction, the person against whom the proceedings are taken can move the superior court for a writ of prohibition, and on that, an order will issue prohibiting the inferior court from continuing the proceedings. On the other hand, if the court hears that case or matter and gives a decision, the party aggrieved will have to move the superior court for a writ of certiorari, and on that, an order will be made quashing the decision on the ground or want of jurisdiction.”
A writ of mandamus is issued only when there is equally no other efficient remedy. It is issued by the superior court, in the form of an order, to any government, corporation, court, etc., to do or forebear from doing some specific act which that body is obliged to do or refrain from doing, as the case may be, and which is in the nature of a public duty and in certain cases of statutory duty.
No mandamus will lie where the duty is of discretionary nature. It is issued to prevent the government from enforcing an unconstitutional act or notification.
Writ of Quo warranto is issued to prevent a person who has wrongfully usurped an office from continuing in that office. It calls upon the holder of the office to show to the court under what authority he holds the office. Before a citizen can claim this type of writ he must satisfy the court that the office in question is a public office. It will not lie in respect of an office of private nature and should be of substantive nature.
Writ of Corpus is very important. It is a process by which a person who is confined without legal justification may secure a release from his confinement. By this writ the High Court can order a person, who has kept in custody another person to bring the latter before the court and let it know on what grounds the prisoner is confined.
A person is not entitled to be released on the petition of habeas corpus if there is no illegal restraint. Physical confinement is not necessarily to constitute detention. Control and custody are sufficient.
Appellate Powers of High Courts:
Appeals from lower courts can lie in the High Court, both in civil and criminal matters, if the court is satisfied that some substantial question of law or interpretation of the constitution is involved or if any court below it has acted without or in excess of its jurisdiction or there has been some error of law.
If the High Court feels it necessary, it can withdraw some case pending before it and decide that and then return the lower court with a copy of the judgment to enable that court to proceed further in accordance with the judgment.
Power of Superintendence:
Article 227 of the constitution provides that, High Courts have power of superintendence over all other courts and tribunals throughout the state. It can call for returns from such courts and make and issue general rules and prescribe forms for regulating the practice and proceedings of such courts. It is also empowered to prescribe forms in which books, entries and accounts have been kept.
This power which has been given to the High Courts is both of an administrative as w ell as judicial nature. The High Courts, if need be, can interfere with the administrative orders of inferior courts. Such an interference can be for want of excess jurisdiction, failure to exercise jurisdiction violation of procedure, disregard of the principle of natural justice and error of law apparent on the face of record.
Such a superintendence also extends over tribunals which are not courts in the strict sense of the term.
In the case of B.N. Banerjee and P.R. Mukerji the Supreme Court has held that “Unless there was grave miscarriage of justice or flagrant violation of law the High Court could not interfere. The power should not ordinarily be exercised if some alternative remedy is available. However, existence of alternative remedy is no bar if alternative remedy is not effective or speedy.”
This Article too was amended by Forty-Second and Forty-Fourth Constitution Amendment Acts.
This Article of the constitution, as originally stood was:
“(1) Every High Court shall have superintendence over all court* and tribunals throughout the territories in relation to which it exercises jurisdictions.”
This was substituted by Forty-Second Constitution Amendment Act. It provided that:
“Every High Court shall have superintendence over all courts subject to appellate jurisdictions.”
It also inserted a new sub-clause in this Article which read as follows:
(5) Nothing in this Article shall be construed as giving to High Court any jurisdiction to question any judgment of any inferior courts which is not otherwise subject to appeal or revision.
Forty-Fourth Constitution Amendment Act, however, brought back the status quo and nullified the changes introduced by Forty-Second Constitution Amendment Act.
Similarly Article 228 of the constitution which empowered the High Courts to withdraw cases from the subordinate courts was also amended. The Article as it stood before amendment provided:
“If the High Court is satisfied that a case pending in a court subordinate to it involves a substantial question of law as to the interpretation of this constitution the determination of which is necessary for the disposal of the case, it shall withdraw the case and may…
Forty-Second Constitution Amendment Act omitted the words in italics and provided instead that
“It shall withdraw the case and subject to the provisions of Article 131 A, may.”…. shall be substituted. In other words by this provision, Article (131 A) imposed restrictions on the High Courts.
Forty-Third Constitution Amendment Act, however, nullified this amendment and restriction of Article 131A was removed from the courts.
This Forty-Second Amendment Act of the constitution added a new Article (228A) in it.
It provided that:
228 A: Special provision relating to constitutional validity of state laws:
(1) No High Court shall have jurisdiction to declare any central law to be constitutionally invalid;
(2) Subject to the provisions of Article 131A, the High Court may determine all questions relating to constitutional validity of any state law;
(3) The minimum number of judges who shall sit for the purpose of determining any question as to the constitutional validity of any state law shall be five; provided that where the High Courts consist of less than five judges, all the judges of the High Court may sit and determine such questions.
(4) A state law shall not be declared to be constitutionally invalid by the High Court unless.
(a) Where the High Court consists of five judges or more, not less than two-third of the judges sitting for the purpose of determining the validity of such law, hold it to be constitutionally invalid, and
(b) Where the High Court consists of less than five judges, all the judges of the High Court sitting for the purpose hold it to be constitutionally invalid.
(5) The provisions of this Article shall have effect not withstanding anything contained in this part.
Explanation:
In computing the number of judges of a High Court for the purpose of this Article, a judge who is disqualified by reason of personal or pecuniary bias shall be excluded.
Forty-Third Constitution Amendment Act also omitted this and thus powers of the High Courts which had been much reduced were given back to them.
As a court of record High Court has power to punish those who are adjudged guilty of contempt of court. All its decisions are binding and cannot be questioned in any lower court.
The constitution has empowered Chief Justice to appoint officers and servants of High Court, whose conditions of service are also to be decided by him with the approval of the Governor. Parliament by law can extend jurisdictions of a High Court to, or exclude the jurisdictions of a High Court, to any Union Territory.
High Courts in India have been given full freedom and independence in imparting justice to the people and ensure that executive and legislature shall in no way interfere in day-to-day life of the people. During emergency period of 19 months along with Supreme Court some powers of the High Courts were taken away and many such powers were restored with the passing of Forty-Third and Forty-Fourth Constitution Amendment Acts.
During this period of 19 months some excesses were alleged to have been committed and for this Janata party which came to power in 1977, set up some Commissions of Enquiry and Specials Courts.
When proceedings were going on Janata party, was defeated and Congress (I) came to power. In many cases the courts allowed the government to withdraw the cases, while in many other cases the decisions went in favour of the accused.
This left an impression on the minds of the people, that the courts were deciding cases in changed climate and not on the merits of the case. According to them the courts in India have started deciding cases after sensing political climate.
On the other hand, there are others who argue that the courts are to decide the case on the basis of documents and evidences made available to them. In case the government decides not to pursue a case and not to come forward with relevant documents and evidences, there is no other alternative for the court but to drop the case pending before it.
High Courts and States:
Of course under the constitution the High Courts are linked with states but in actual practice these too are very much linked with the Centre. The Judges of the High Court and Chief Justice of a High Court is appointed by the President.
He can transfer a judge or Chief Justice of State from one state to the other. He can decide dispute about retirement age of the judges and also promote them as judge of the Supreme Court. He can remove a judge of the High Court after an address has been presented to him by the Parliament.
Then the President can create a new High Court, thereby reduce the jurisdictions of some existing High Court. During financial emergency the Parliament can reduce or increase the salaries and allowances of judges of the High Court. Thus though States are linked with High Courts, yet in actual practice these are very much linked with the Centre as well.
Inter State Transfer of Judges:
For some time judges were not transferred from one High Court to the other but during 1975 emergency period the judges began to transferred from one High Court to the other. In 1977, in the case of Union of India Vs. Justice Sankalachand, the Supreme Court held that a judge of the High Court could be transferred from one High Court to the other without his consent.
In this case the Supreme Court asserted that the power to transfer a judge is conferred on the President in the public interest and not for the purpose of providing the executive with the weapon to punish a judge for any reason whatever.
It also made it clear that it was absolutely obligatory on the President to consult Chief Justice of India before transferring a judge from one High Court to another and that this consultation must be effective one.
In another case on 30th December, 1981 Supreme Court made it clear that a High Court judge may be transferred from one state to another without obtaining his consent, the only requirement being that there must be effective consultation and that the transfer must be in public interest and not by way of punishment.
On October 7, 1993 in the case of S.C. Advocate on Record Vs. the Union of India the Court held that in case of transfer of judges of High Courts the opinion of the Chief Justice of India has not the primacy but is determinative in the matter and that the consent of the transferred judge is not required. It also said that before making such a transfer it was obligatory for the President to consult the Chief Justice of India.
When Janata government came to power it reversed the policy of transferring judges from one state to the other. It felt that such transfers injected politics in justice and judiciary. In 1980 when Congress (I) came to power it again followed the old policy of transferring judges from one state to the other.
Its argument was that judges from outside the state are more impartial in their judicial pronouncements than those from within. National Front government of V.P. Singh however, was not in favour of transfer of High Court Judges from one state to the other, but judges are now being frequently followed from one state to the other without any difficulty.
7. Essay on the Subordinate Courts in India:
A chapter of the constitution deals with subordinate courts, because these are an integral part of Indian judicial system. There is hardly any other constitution of the world, which discusses at such a great length the composition and detailed working of subordinate courts.
It is provided in the constitution that appointment of judges, their postings and promotion at district level, in any state, shall be made by the Governor of the state, in consultation with the High Court, in whose jurisdiction such a court falls.
It is provided that any person who is not already in the service of state or Union shall be eligible to be appointed as District Judge provided, he has been an advocate or pleader for not less than seven years and has been recommended by the High Court for appointment. But judges, other than District Judges, are appointed by the Governor in accordance with the High Court and State Public Service Commission.
It is the duty and responsibility of High Courts to exercise control and supervision over the subordinate and district courts; in matters of leave, postings, promotion and transfers and also over the personnel belonging to state judicial service. For judicial purposes each state is divided into several districts. Even each district is headed by a District Magistrate. In each district there are civil, criminal and revenue courts.
i. Civil Courts:
At the district level, the highest civil court is district court, which is headed by a District Magistrate. He supervises the working of civil courts and has both original as well as appellate powers. Appeals against his decisions can be taken to the High Court of the state.
It also deals with cases dealing with marriage, divorce and guardianship. Below this court are courts of Senior Sub-Judges, Courts of Sub-Judges, and small causes courts, which are all in hierarchal order.
The last mentioned courts are also known as Munsif’s courts and are established in big cities to dispose of cases in which small sums of Rs.500/- are involved. Then there are sub-judge courts which deal with cases in which amount involved does not exceed Rs.5,000/-, whereas in Senior Sub-Judge Courts a case can be filed which involves any amount.
All these courts have original jurisdictions. Decisions of these courts can be challenged in the District Courts.
ii. Criminal Courts:
Criminal courts are organised in a hierarchal order. Court of Session Judge is at the top and is empowered to try all criminal cases involving murder and other serious offences duly committed to it by a First Class Magistrate. It can award even death penalty, but such a penalty must be confirmed by the State High Court.
Below this are First Class, Second Class and Third Class Magistrate Courts. Third Class Magistrate Court deals with minor offences. It can give punishments up to Rs.50/- and sentence a person up to one month, where as a Second Class Magistrate can impose a fine up to Rs.200/- and put a person behind bars for a period of six months.
Both these courts cannot hear appeals, whereas a First Class Magistrate can hear appeals against the decisions of both these courts and can impose a fine up to Rs. 1000/- and award imprisonment up to two years.
The Unique Burial of a Child of Early Scythian Time at the Cemetery of Saryg-Bulun (Tuva)
<< Previous page
Pages: 379-406
In 1988, the Tuvan Archaeological Expedition (led by M. E. Kilunovskaya and V. A. Semenov) discovered a unique burial of the early Iron Age at Saryg-Bulun in Central Tuva. There are two burial mounds of the Aldy-Bel culture dated by 7th century BC. Within the barrows, which adjoined one another, forming a figure-of-eight, there were discovered 7 burials, from which a representative collection of artifacts was recovered. Burial 5 was the most unique, it was found in a coffin made of a larch trunk, with a tightly closed lid. Due to the preservative properties of larch and lack of air access, the coffin contained a well-preserved mummy of a child with an accompanying set of grave goods. The interred individual retained the skin on his face and had a leather headdress painted with red pigment and a coat, sewn from jerboa fur. The coat was belted with a leather belt with bronze ornaments and buckles. Besides that, a leather quiver with arrows with the shafts decorated with painted ornaments, fully preserved battle pick and a bow were buried in the coffin. Unexpectedly, the full-genomic analysis, showed that the individual was female. This fact opens a new aspect in the study of the social history of the Scythian society and perhaps brings us back to the myth of the Amazons, discussed by Herodotus. Of course, this discovery is unique in its preservation for the Scythian culture of Tuva and requires careful study and conservation.
Keywords: Tuva, Early Iron Age, early Scythian period, Aldy-Bel culture, barrow, burial in the coffin, mummy, full genome sequencing, aDNA
Information about authors: Marina Kilunovskaya (Saint Petersburg, Russian Federation). Candidate of Historical Sciences. Institute for the History of Material Culture of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Dvortsovaya Emb., 18, Saint Petersburg, 191186, Russian Federation E-mail: [email protected] Vladimir Semenov (Saint Petersburg, Russian Federation). Candidate of Historical Sciences. Institute for the History of Material Culture of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Dvortsovaya Emb., 18, Saint Petersburg, 191186, Russian Federation E-mail: [email protected] Varvara Busova (Moscow, Russian Federation). (Saint Petersburg, Russian Federation). Institute for the History of Material Culture of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Dvortsovaya Emb., 18, Saint Petersburg, 191186, Russian Federation E-mail: [email protected] Kharis Mustafin (Moscow, Russian Federation). Candidate of Technical Sciences. Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology. Institutsky Lane, 9, Dolgoprudny, 141701, Moscow Oblast, Russian Federation E-mail: [email protected] Irina Alborova (Moscow, Russian Federation). Candidate of Biological Sciences. Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology. Institutsky Lane, 9, Dolgoprudny, 141701, Moscow Oblast, Russian Federation E-mail: [email protected] Alina Matzvai (Moscow, Russian Federation). Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology. Institutsky Lane, 9, Dolgoprudny, 141701, Moscow Oblast, Russian Federation E-mail: [email protected]
Shopping Cart Items: 0 Cart Total: 0,00 € place your order
Price pdf version
student - 2,75 € individual - 3,00 € institutional - 7,00 €

Copyright В© 1999-2022. Stratum Publishing House
Home — Essay Samples — Law, Crime & Punishment — Court — Reflecting on Courtroom Observations: Insights into Legal Proceedings
Reflecting on Courtroom Observations: Insights into Legal Proceedings
- Categories: Court Observation
About this sample

Words: 1701 |
Published: Dec 3, 2020
Words: 1701 | Pages: 4 | 9 min read

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Prof Ernest (PhD)
Verified writer
- Expert in: Law, Crime & Punishment Science

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
4 pages / 1641 words
3 pages / 1148 words
7 pages / 2974 words
1 pages / 820 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Court
The fair use copyright law enables people to use portions of material that is copyrighted for the purposes of criticism or as commentary. The hard part for many people is understanding what is permissible under the fair use [...]
Juror #5…A naive, very frightened young man who takes his obligations in the case seriously, but who finds it difficult to speak up when his elders have the floor.On page 36, juror #5 sees reasonable doubt in the case so he [...]
On 27th September 2018 I attended the provincial court of British Columbia inCourtenay. In the court, food, drinks and cell phones on are not allowed. I reached in the court at before 2:00pm. Before entering the court, I met [...]
Class by Professor Takeshi Tsunoda. Kenya’s system of courts is structured, in descending order, basically as follows: 1. Supreme Court 2. Court of Appeal 3. High Court (Including employment and labor court and the [...]
A numerus amount of cases is brought upon courtrooms every day and scheduled for the same time in different court rooms. DUI’s remain a big issue and concern to the public health and the safety of other as well as those under [...]
This research will this study did not look in detail at justice subdimensions. In a recent article, Scott et al. (2009) argued that the organizational justice dimensions would differ for employees based on their managerial [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free

Delhi High Court Personal Assistant Previous Papers (Download) JT, SJT Model Papers PDF
Delhi High Court Personal Assistant Previous Model Papers are provided on this page for Download: The Delhi High Court has released the Delhi High Court Personal Assistant Model Question Papers on its Official webpage @ delhihighcourt.nic.in . The Delhi High Court Personal Assistant Written Exam will be held soon. So the Candidates who had applied for Delhi High Court Personal Assistant Jobs 2023 and started their Exam preparation should check this article. This article is about the Delhi High Court Personal Assistant Previous Papers with Answers which help the Preparing candidates in their Exam preparation in order to get a good score in the Delhi High Court Personal Assistant Exam.
Contents in this Article
Delhi High Court Group B Previous Papers Highlights
Check delhi high court personal assistant exam pattern 2023, senior personal assistant, personal assistant, download delhi high court senior personal assistant previous papers pdf, download delhi high court senior personal assistants previous papers pdf, delhi high court personal assistant question papers- frequently asked questions(faq).
Stage – I (Qualifying Stage) – English Typing Test
- Typing Test of ten (10) minutes duration will be conducted on computers to assess candidates’ minimum speed of 40 words per minute in English Typing on a computer.
- The criterion of “characters with space” for calculating the typing speed will be adopted and a total number of mistakes permissible would be 3% of the total words typed.
- Only the successful/qualified candidates of Stage-I, i.e., the English Typing Test will be called for the next stage of Examination, i.e., Stage–II (English Shorthand Tests).
Stage – II – English Shorthand Tests
- Total Marks – 100 Marks
- Total Time – 5 Minutes for Dictation and 45 Minutes for Transcription
- 110 words per minute.
- The passage of 550 words will be dictated in five (5) minutes’ duration.
- Candidates will get forty five (45) minutes’ duration to transcribe the dictated passage on computers. No extra time will be given for reading the passage.
Stage – III – Main (Descriptive) Examination
Stage – IV – Interview
- Total Marks – 20 Marks
- Minimum passing marks for General Category candidates will be 10 Marks and for Reserved Category (including PwD) candidates will be 09 Marks.
Stage – I English Typing Test
- Typing Test of ten (10) minutes’ duration will be conducted on computers to assess candidates’ minimum speed of 40 words per minute in English Typing on computer.
- The criterion of “characters with space” for calculating the typing speed will be adopted and total number of mistakes permissible would be 3% of the total words typed.
- Only the successful/qualified candidates of Stage-I, i.e., English Typing Test will be called for the next stage of Examination, i.e., Stage – II (English Shorthand Tests).
Stage – II English Shorthand Tests
- 100 words per minute.
- The passage of 500 words will be dictated in five (5) minutes duration.
- Candidates will get forty-five (45) minutes duration to transcribe the dictated passage on computers. No extra time will be given for reading the passage.
Stage – III Main (Descriptive) Examination
Here we have uploaded the Subject wise Delhi High Court Personal Assistant Old Question papers along with the Detailed Delhi High Court Personal Assistant Syllabus and Exam Pattern. Check out this complete article and Get the Delhi High Court Personal Assistant Solved Question Papers from this page Questionpapersonline.com for Free of cost.
Delhi High Senior Personal Assistant Previous Papers – Reasoning
Hc of delhi senior personal assistant previous question papers – gk, delhi hc senior personal assistant practice papers free download, high court of delhi senior personal assistant question paper, delhi hc senior personal assistant previous papers – pdf english, delhi high court senior personal assistants exam previous papers – reasoning, delhi hc senior personal assistants exam previous question papers – gk, delhi high court examination practice papers free download, delhi hc senior personal assistants exam question paper, dhc senior personal assistants exam previous papers – pdf english, what is delhi high court personal assistant syllabus, what is the exam pattern for delhi high court 2023, where can i get the delhi high court personal assistant syllabus pdf, what are the total marks for delhi high court personal assistant exam, how many questions will be asked in the delhi high court personal assistant exam , more related articles.
Previous Years Paper.in
One Stop for the Question Papers
Jharkhand High Court Assistant Previous Year Papers, Download Free PDF Here!

The Jharkhand High Court Assistant Previous Year Papers serves as an invaluable resource for aspirants preparing for the Assistant position within the esteemed Jharkhand High Court. These papers provide candidates with a comprehensive understanding of the exam pattern, syllabus, and the types of questions that are likely to be asked. By studying these previous year papers, candidates can familiarize themselves with the format of the exam and identify areas where they need to focus their preparation. Additionally, solving these papers under timed conditions helps in improving time management skills, which is crucial for success in any competitive examination. Overall, the Jharkhand High Court Assistant Previous Year Papers is an essential tool for aspirants striving to excel in their endeavors to secure a position in the esteemed Jharkhand High Court.
Download Jharkhand High Court Assistant Previous Year Papers PDF
The candidates can download the Jharkhand High Court Assistant Question Papers through the direct link mentioned below.
Jharkhand High Court Assistant Previous Year Papers Benefits
The benefits of utilizing Jharkhand High Court Assistant Previous Year Papers are manifold. Firstly, these papers provide a glimpse into the exam pattern, allowing aspirants to understand the structure of the test and the types of questions likely to be asked. By familiarizing themselves with the exam format, candidates can develop effective strategies for tackling the questions within the allocated time frame.
Understanding Exam Pattern: Utilizing Jharkhand High Court Assistant Previous Year Papers provides candidates with insights into the exam pattern, helping them understand the structure of the test and the distribution of marks across different sections.
Strategic Preparation: Familiarity with the exam format enables aspirants to develop effective strategies for tackling questions within the allocated time frame, enhancing their overall performance on the day of the exam.
Identifying Strengths and Weaknesses: Regular practice with previous year papers allows candidates to assess their strengths and weaknesses, enabling them to focus their preparation efforts on areas that require improvement.
Enhancing Problem-Solving Skills: Solving previous year papers aids in improving candidates’ problem-solving abilities, as they encounter a variety of questions that test their reasoning and analytical skills.
Conceptual Understanding: Repeatedly practicing with previous year papers helps in solidifying conceptual understanding across various topics covered in the syllabus, thereby reinforcing key concepts and principles.
Boosting Confidence: Regular practice with previous year papers boosts candidates’ confidence levels, making them feel more prepared and confident on the actual exam day, ultimately leading to better performance.
Stress Reduction: Familiarity with the exam format and the types of questions asked in previous years reduces exam-related stress and anxiety, allowing candidates to approach the exam with a calm and focused mindset.
Increased Chances of Success: Overall, utilizing Jharkhand High Court Assistant Previous Year Papers significantly enhances candidates’ preparation, increasing their chances of success in securing a position in the esteemed Jharkhand High Court.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Supreme Court Petition Filed Urging Re-Exam Over Alleged NEET UG 2024 Paper Leak
A mid many claims about question paper leak of the NEET UG 2024 exam, a group of candidates has asked the Supreme Court to conduct a new exam. The request, filed by Shivangi Mishra and others, mentions the National Testing Agency (NTA) and raises concerns about the alleged paper leak and the fairness of the test, asking for a fresh exam to be conducted, as reported by the news agency Press Trust of India (PTI).
They claim the NEET-UG exam held on May 5 had many cases of paper leaks, giving some students an unfair advantage, which violates Article 14 (right to equality) of the Constitution.
The plea was filed on June 1 by lawyer Usha Nandini V and may be reviewed by a vacation bench this week, PTI reported.
Wrong Question Papers Distributed At 1 Centre?
During the NEET (UG) 2024 examination, a singal incident of incorrect distribution of papers at the Girls Higher Secondary Model School, Mandir, Mantown, Sawai Madhopur, by the Center Superintendent came to light. The examination of approximately 120 affected candidates at the centre.
Despite efforts by invigilators to prevent it, some candidates left the examination center with question papers. However, the NTA had assured the public that apart from this isolated incident, the NEET (UG) 2024 examination commenced smoothly and is being conducted peacefully at all other examination centers across the country.
NTA Assured Fairness
NTA later released a notice stating that they are committed to ensuring the integrity and fairness of the National Eligibility cum Entrance Test (NEET) (UG) examination, held annually for medical aspirants across the country.
The NTA emphasises that this incident has not compromised the integrity of the examination process at other centers. In order to uphold the principles of fairness and equal opportunity for all candidates, the NTA has taken proactive measures.
"The NTA reaffirms its commitment to conducting examinations with transparency, integrity, and fairness. We extend our best wishes to all NEET (UG) 2024 candidates and assure them of our continued support throughout the examination process," it said in the public notice.
The NEET-UG exam is conducted by the NTA for admission to medical courses like MBBS, BDS, BAMS, and BHMS in government and private institutions across India. It is a vital exam for students wanting to pursue medical education. Each year, many science stream students take this exam.
This year, the NEET-UG exam was held on May 5, 2024, and over 24 lakh students from 14 international cities and 557 Indian cities participated. The exam was conducted in 13 different languages, and the results are expected to be announced on June 14.

- Yekaterinburg
- Novosibirsk
- Vladivostok
- Tours to Russia
- Practicalities
- Russia in Lists
Rusmania • Deep into Russia
Out of the Centre
Savvino-storozhevsky monastery and museum.

Zvenigorod's most famous sight is the Savvino-Storozhevsky Monastery, which was founded in 1398 by the monk Savva from the Troitse-Sergieva Lavra, at the invitation and with the support of Prince Yury Dmitrievich of Zvenigorod. Savva was later canonised as St Sabbas (Savva) of Storozhev. The monastery late flourished under the reign of Tsar Alexis, who chose the monastery as his family church and often went on pilgrimage there and made lots of donations to it. Most of the monastery’s buildings date from this time. The monastery is heavily fortified with thick walls and six towers, the most impressive of which is the Krasny Tower which also serves as the eastern entrance. The monastery was closed in 1918 and only reopened in 1995. In 1998 Patriarch Alexius II took part in a service to return the relics of St Sabbas to the monastery. Today the monastery has the status of a stauropegic monastery, which is second in status to a lavra. In addition to being a working monastery, it also holds the Zvenigorod Historical, Architectural and Art Museum.
Belfry and Neighbouring Churches

Located near the main entrance is the monastery's belfry which is perhaps the calling card of the monastery due to its uniqueness. It was built in the 1650s and the St Sergius of Radonezh’s Church was opened on the middle tier in the mid-17th century, although it was originally dedicated to the Trinity. The belfry's 35-tonne Great Bladgovestny Bell fell in 1941 and was only restored and returned in 2003. Attached to the belfry is a large refectory and the Transfiguration Church, both of which were built on the orders of Tsar Alexis in the 1650s.

To the left of the belfry is another, smaller, refectory which is attached to the Trinity Gate-Church, which was also constructed in the 1650s on the orders of Tsar Alexis who made it his own family church. The church is elaborately decorated with colourful trims and underneath the archway is a beautiful 19th century fresco.
Nativity of Virgin Mary Cathedral

The Nativity of Virgin Mary Cathedral is the oldest building in the monastery and among the oldest buildings in the Moscow Region. It was built between 1404 and 1405 during the lifetime of St Sabbas and using the funds of Prince Yury of Zvenigorod. The white-stone cathedral is a standard four-pillar design with a single golden dome. After the death of St Sabbas he was interred in the cathedral and a new altar dedicated to him was added.

Under the reign of Tsar Alexis the cathedral was decorated with frescoes by Stepan Ryazanets, some of which remain today. Tsar Alexis also presented the cathedral with a five-tier iconostasis, the top row of icons have been preserved.
Tsaritsa's Chambers

The Nativity of Virgin Mary Cathedral is located between the Tsaritsa's Chambers of the left and the Palace of Tsar Alexis on the right. The Tsaritsa's Chambers were built in the mid-17th century for the wife of Tsar Alexey - Tsaritsa Maria Ilinichna Miloskavskaya. The design of the building is influenced by the ancient Russian architectural style. Is prettier than the Tsar's chambers opposite, being red in colour with elaborately decorated window frames and entrance.

At present the Tsaritsa's Chambers houses the Zvenigorod Historical, Architectural and Art Museum. Among its displays is an accurate recreation of the interior of a noble lady's chambers including furniture, decorations and a decorated tiled oven, and an exhibition on the history of Zvenigorod and the monastery.
Palace of Tsar Alexis

The Palace of Tsar Alexis was built in the 1650s and is now one of the best surviving examples of non-religious architecture of that era. It was built especially for Tsar Alexis who often visited the monastery on religious pilgrimages. Its most striking feature is its pretty row of nine chimney spouts which resemble towers.

Plan your next trip to Russia
Ready-to-book tours.
Your holiday in Russia starts here. Choose and book your tour to Russia.
REQUEST A CUSTOMISED TRIP
Looking for something unique? Create the trip of your dreams with the help of our experts.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
The Fourth Circuit Student Essay Contest is open to all students currently in grades 6 through 12 from Maryland, North Carolina, South Carolina, Virginia, and West Virginia. Note: Prior award winners as well as children, grandchildren, stepchildren, and members of the household of a federal judge or federal judiciary employee are excluded from ...
The due process clause of the 14th Amendment led to the incorporation of the Bill of Rights, which meant that the Supreme Court applied the Bill of Rights to the states. During the first half of the twentieth century, the Court incorporated the Bill of Rights selectively in a few cases. For example, it extended the First Amendment right of free ...
Writing an essay on court-related topics can be a fascinating and thought-provoking task. Whether you are studying law, political science, or simply interested in the legal system, here are 124 court essay topic ideas and examples to inspire your writing: ... The challenges of ensuring a fair trial in high-profile cases. The role of plea ...
The jurisdiction of the High Court extends to all cases under the State or federal laws. In constitutional cases: if the High Court certifies that a case involves a substantial question of law. High Court Powers. Apart from the above, the High Courts have several functions and powers which are described below. As a Court of Record
The judiciary in India has a pyramidal structure with the Supreme Court (SC) at the top. High Courts are below the SC, and below them are the district and subordinate courts. The lower courts function under the direct superintendence of the higher courts. The diagram below gives the structure and organisation of the judicial system in the country.
The Calcutta High Court is the oldest high court in the country, established on 2 July 1862. High courts that handle numerous cases of a particular region have permanent benches established there. Benches are also present in states which come under the jurisdiction of a court outside its territorial limits. Smaller states with few cases may ...
A Lesson From the High Court. US Supreme Court Justice Samuel Alito is seen after a swearing in ceremony for Mark Esper to be the new US secretary of defense in 2019. (Alex Wong / Getty Images ...
The answer to this question should be "no.". Under the rules that apply to criminal defendants who are not named Donald Trump, two state-level appeals courts should review Trump's conviction ...
The Supreme Court Could Make the President a King. The high court's decision in the Trump immunity case appears to set the stage for future abuses of the pardon power. Supreme Court Police ...
The following are some of the most critical essay topics for a judiciary or current essay topics in 2024 for Judiciary exams that you need to focus on to score well in essay writing: Topic. Impact of social media on the Judiciary. Role of the Judiciary in the Fight against Corruption. Right to privacy in the digital age.
High Court. The High Court of Justice in London, together with the Court of Appeal and the Crown Court, are the Senior Courts of England and Wales. Its name is abbreviated as EWHC for legal citation purposes. It deals at first instance with all high value and high importance civil law (non-criminal) cases, and also has a supervisory ...
Child Abuse and Neglect Children in Court. Questioning and Criticizing Supreme Court Nominees. The Supreme Court Decision: Bank of Augusta vs. Earle. The Supreme Court, in the Case of Kelo vs. the City of New London. 148 Essay Samples and Topics on Corruption 117 Credit Essay Topic Ideas & Examples.
The High Court of Parliament and its supremacy; an historical essay on the boundaries between legislation and adjudication in England by McIlwain, Charles Howard, 1871-1968. Publication date 1910 Topics Great Britain. High Court of Justice, Great Britain. Parliament Publisher
Due to its age, it may contain imperfections such as marks, notations, marginalia and flawed pages. Because we believe this work is culturally important, we have made it available as part of our commitment for protecting, preserving, and promoting the world's literature in affordable, high quality, modern editions that are true to the original ...
On May 30, the US Supreme Court in effect confirmed what should have been obvious, unanimously ruling that Vullo's and Cuomo's alleged words and actions stated a claim under the First Amendment. In doing so, the court overturned a unanimous decision from the Second Circuit against the NRA. The decision makes no new law, but reaffirms what ...
The High Court of Parliament and Its Supremacy: An Historical Essay on the Boundaries Between Legislation and Adjudication in England. [McIlwain, Charles Howard] on Amazon.com. *FREE* shipping on qualifying offers. The High Court of Parliament and Its Supremacy: An Historical Essay on the Boundaries Between Legislation and Adjudication in England.
Editor's Note: This story is part of an occasional series on research projects currently in the works at the Law School. The Supreme Court's decision in June 2023 to bar the use of affirmative action in college admissions raised many questions. One of the most significant is whether universities should consider applicants' discussion of race in essays. The Court's decision in Students ...
This essay about the right to a speedy and public trial explains its importance in democratic justice systems. It highlights how a speedy trial prevents prolonged detention, protects defendants' rights, and maintains the legal system's integrity. ... For instance, digital case management systems can help streamline court processes and ...
The Federal Court of Malaysia is the highest judicial authority and the final court of appeal in Malaysia. Its decision binds all the courts below. The Federal Court consists of a president styled as the Chief Justice (formerly called the Lord President), the President of the Court of Appeal, the two Chief Judges of the High Courts in Malaya ...
High Court of India - There are 25 High Courts in India (Andhra Pradesh High Court is the newest.) high Court is the highest judiciary court of a state. Know the constitution and history of the establishment of High Courts. Also, get details like the salary, jurisdiction and eligibility of a High Court Judge for IAS Exam. Download High Court notes PDF for UPSC 2023.
In this essay we will discuss about the high courts of India. After reading this essay you will learn about: 1. Jurisdictions of High Courts 2. Composition of the High Court 3. Salary and Allowances of the Judges 4. Oath or Affirmation by Judges of High Courts 5. Powers and Functions of the High Courts 6. Kinds of Writs 7. Subordinate Courts in India. List of Essays on the High Courts of India ...
Burial 5 was the most unique, it was found in a coffin made of a larch trunk, with a tightly closed lid. Due to the preservative properties of larch and lack of air access, the coffin contained a well-preserved mummy of a child with an accompanying set of grave goods. The interred individual retained the skin on his face and had a leather ...
Related Essays on Court. ... High Court (Including employment and labor court and the [...] Reflections on Courtroom Observation: Analysis and Insight Essay. A numerus amount of cases is brought upon courtrooms every day and scheduled for the same time in different court rooms. DUI's remain a big issue and concern to the public health and the ...
Benefits of Solving Odisha High Court ASO Previous Year Papers. When preparing for the exam, use the Odisha High Court ASO Previous Year Paper as a study reference. As candidates solve Odisha High Court ASO's previous year papers, their accuracy, time management, and approach to various types of work will improve, allowing them to better grasp ...
May 4, 2023. Delhi High Court Personal Assistant Previous Model Papers are provided on this page for Download: The Delhi High Court has released the Delhi High Court Personal Assistant Model Question Papers on its Official webpage @ delhihighcourt.nic.in. The Delhi High Court Personal Assistant Written Exam will be held soon.
The Jharkhand High Court Assistant Previous Year Papers serves as an invaluable resource for aspirants preparing for the Assistant position within the esteemed Jharkhand High Court. These papers provide candidates with a comprehensive understanding of the exam pattern, syllabus, and the types of questions that are likely to be asked.
Amid many claims about question paper leak of the NEET UG 2024 exam, a group of candidates has asked the Supreme Court to conduct a new exam. The request, filed by Shivangi Mishra and others ...
Zvenigorod's most famous sight is the Savvino-Storozhevsky Monastery, which was founded in 1398 by the monk Savva from the Troitse-Sergieva Lavra, at the invitation and with the support of Prince Yury Dmitrievich of Zvenigorod. Savva was later canonised as St Sabbas (Savva) of Storozhev. The monastery late flourished under the reign of Tsar ...
In 1938, it was granted town status. [citation needed]Administrative and municipal status. Within the framework of administrative divisions, it is incorporated as Elektrostal City Under Oblast Jurisdiction—an administrative unit with the status equal to that of the districts. As a municipal division, Elektrostal City Under Oblast Jurisdiction is incorporated as Elektrostal Urban Okrug.
Elektrostal. Elektrostal ( Russian: Электроста́ль) is a city in Moscow Oblast, Russia. It is 58 kilometers (36 mi) east of Moscow. As of 2010, 155,196 people lived there.