

Understanding Assignments
What this handout is about.
The first step in any successful college writing venture is reading the assignment. While this sounds like a simple task, it can be a tough one. This handout will help you unravel your assignment and begin to craft an effective response. Much of the following advice will involve translating typical assignment terms and practices into meaningful clues to the type of writing your instructor expects. See our short video for more tips.
Basic beginnings
Regardless of the assignment, department, or instructor, adopting these two habits will serve you well :
- Read the assignment carefully as soon as you receive it. Do not put this task off—reading the assignment at the beginning will save you time, stress, and problems later. An assignment can look pretty straightforward at first, particularly if the instructor has provided lots of information. That does not mean it will not take time and effort to complete; you may even have to learn a new skill to complete the assignment.
- Ask the instructor about anything you do not understand. Do not hesitate to approach your instructor. Instructors would prefer to set you straight before you hand the paper in. That’s also when you will find their feedback most useful.
Assignment formats
Many assignments follow a basic format. Assignments often begin with an overview of the topic, include a central verb or verbs that describe the task, and offer some additional suggestions, questions, or prompts to get you started.
An Overview of Some Kind
The instructor might set the stage with some general discussion of the subject of the assignment, introduce the topic, or remind you of something pertinent that you have discussed in class. For example:
“Throughout history, gerbils have played a key role in politics,” or “In the last few weeks of class, we have focused on the evening wear of the housefly …”
The Task of the Assignment
Pay attention; this part tells you what to do when you write the paper. Look for the key verb or verbs in the sentence. Words like analyze, summarize, or compare direct you to think about your topic in a certain way. Also pay attention to words such as how, what, when, where, and why; these words guide your attention toward specific information. (See the section in this handout titled “Key Terms” for more information.)
“Analyze the effect that gerbils had on the Russian Revolution”, or “Suggest an interpretation of housefly undergarments that differs from Darwin’s.”
Additional Material to Think about
Here you will find some questions to use as springboards as you begin to think about the topic. Instructors usually include these questions as suggestions rather than requirements. Do not feel compelled to answer every question unless the instructor asks you to do so. Pay attention to the order of the questions. Sometimes they suggest the thinking process your instructor imagines you will need to follow to begin thinking about the topic.
“You may wish to consider the differing views held by Communist gerbils vs. Monarchist gerbils, or Can there be such a thing as ‘the housefly garment industry’ or is it just a home-based craft?”
These are the instructor’s comments about writing expectations:
“Be concise”, “Write effectively”, or “Argue furiously.”
Technical Details
These instructions usually indicate format rules or guidelines.
“Your paper must be typed in Palatino font on gray paper and must not exceed 600 pages. It is due on the anniversary of Mao Tse-tung’s death.”
The assignment’s parts may not appear in exactly this order, and each part may be very long or really short. Nonetheless, being aware of this standard pattern can help you understand what your instructor wants you to do.
Interpreting the assignment
Ask yourself a few basic questions as you read and jot down the answers on the assignment sheet:
Why did your instructor ask you to do this particular task?
Who is your audience.
- What kind of evidence do you need to support your ideas?
What kind of writing style is acceptable?
- What are the absolute rules of the paper?
Try to look at the question from the point of view of the instructor. Recognize that your instructor has a reason for giving you this assignment and for giving it to you at a particular point in the semester. In every assignment, the instructor has a challenge for you. This challenge could be anything from demonstrating an ability to think clearly to demonstrating an ability to use the library. See the assignment not as a vague suggestion of what to do but as an opportunity to show that you can handle the course material as directed. Paper assignments give you more than a topic to discuss—they ask you to do something with the topic. Keep reminding yourself of that. Be careful to avoid the other extreme as well: do not read more into the assignment than what is there.
Of course, your instructor has given you an assignment so that they will be able to assess your understanding of the course material and give you an appropriate grade. But there is more to it than that. Your instructor has tried to design a learning experience of some kind. Your instructor wants you to think about something in a particular way for a particular reason. If you read the course description at the beginning of your syllabus, review the assigned readings, and consider the assignment itself, you may begin to see the plan, purpose, or approach to the subject matter that your instructor has created for you. If you still aren’t sure of the assignment’s goals, try asking the instructor. For help with this, see our handout on getting feedback .
Given your instructor’s efforts, it helps to answer the question: What is my purpose in completing this assignment? Is it to gather research from a variety of outside sources and present a coherent picture? Is it to take material I have been learning in class and apply it to a new situation? Is it to prove a point one way or another? Key words from the assignment can help you figure this out. Look for key terms in the form of active verbs that tell you what to do.
Key Terms: Finding Those Active Verbs
Here are some common key words and definitions to help you think about assignment terms:
Information words Ask you to demonstrate what you know about the subject, such as who, what, when, where, how, and why.
- define —give the subject’s meaning (according to someone or something). Sometimes you have to give more than one view on the subject’s meaning
- describe —provide details about the subject by answering question words (such as who, what, when, where, how, and why); you might also give details related to the five senses (what you see, hear, feel, taste, and smell)
- explain —give reasons why or examples of how something happened
- illustrate —give descriptive examples of the subject and show how each is connected with the subject
- summarize —briefly list the important ideas you learned about the subject
- trace —outline how something has changed or developed from an earlier time to its current form
- research —gather material from outside sources about the subject, often with the implication or requirement that you will analyze what you have found
Relation words Ask you to demonstrate how things are connected.
- compare —show how two or more things are similar (and, sometimes, different)
- contrast —show how two or more things are dissimilar
- apply—use details that you’ve been given to demonstrate how an idea, theory, or concept works in a particular situation
- cause —show how one event or series of events made something else happen
- relate —show or describe the connections between things
Interpretation words Ask you to defend ideas of your own about the subject. Do not see these words as requesting opinion alone (unless the assignment specifically says so), but as requiring opinion that is supported by concrete evidence. Remember examples, principles, definitions, or concepts from class or research and use them in your interpretation.
- assess —summarize your opinion of the subject and measure it against something
- prove, justify —give reasons or examples to demonstrate how or why something is the truth
- evaluate, respond —state your opinion of the subject as good, bad, or some combination of the two, with examples and reasons
- support —give reasons or evidence for something you believe (be sure to state clearly what it is that you believe)
- synthesize —put two or more things together that have not been put together in class or in your readings before; do not just summarize one and then the other and say that they are similar or different—you must provide a reason for putting them together that runs all the way through the paper
- analyze —determine how individual parts create or relate to the whole, figure out how something works, what it might mean, or why it is important
- argue —take a side and defend it with evidence against the other side
More Clues to Your Purpose As you read the assignment, think about what the teacher does in class:
- What kinds of textbooks or coursepack did your instructor choose for the course—ones that provide background information, explain theories or perspectives, or argue a point of view?
- In lecture, does your instructor ask your opinion, try to prove their point of view, or use keywords that show up again in the assignment?
- What kinds of assignments are typical in this discipline? Social science classes often expect more research. Humanities classes thrive on interpretation and analysis.
- How do the assignments, readings, and lectures work together in the course? Instructors spend time designing courses, sometimes even arguing with their peers about the most effective course materials. Figuring out the overall design to the course will help you understand what each assignment is meant to achieve.
Now, what about your reader? Most undergraduates think of their audience as the instructor. True, your instructor is a good person to keep in mind as you write. But for the purposes of a good paper, think of your audience as someone like your roommate: smart enough to understand a clear, logical argument, but not someone who already knows exactly what is going on in your particular paper. Remember, even if the instructor knows everything there is to know about your paper topic, they still have to read your paper and assess your understanding. In other words, teach the material to your reader.
Aiming a paper at your audience happens in two ways: you make decisions about the tone and the level of information you want to convey.
- Tone means the “voice” of your paper. Should you be chatty, formal, or objective? Usually you will find some happy medium—you do not want to alienate your reader by sounding condescending or superior, but you do not want to, um, like, totally wig on the man, you know? Eschew ostentatious erudition: some students think the way to sound academic is to use big words. Be careful—you can sound ridiculous, especially if you use the wrong big words.
- The level of information you use depends on who you think your audience is. If you imagine your audience as your instructor and they already know everything you have to say, you may find yourself leaving out key information that can cause your argument to be unconvincing and illogical. But you do not have to explain every single word or issue. If you are telling your roommate what happened on your favorite science fiction TV show last night, you do not say, “First a dark-haired white man of average height, wearing a suit and carrying a flashlight, walked into the room. Then a purple alien with fifteen arms and at least three eyes turned around. Then the man smiled slightly. In the background, you could hear a clock ticking. The room was fairly dark and had at least two windows that I saw.” You also do not say, “This guy found some aliens. The end.” Find some balance of useful details that support your main point.
You’ll find a much more detailed discussion of these concepts in our handout on audience .
The Grim Truth
With a few exceptions (including some lab and ethnography reports), you are probably being asked to make an argument. You must convince your audience. It is easy to forget this aim when you are researching and writing; as you become involved in your subject matter, you may become enmeshed in the details and focus on learning or simply telling the information you have found. You need to do more than just repeat what you have read. Your writing should have a point, and you should be able to say it in a sentence. Sometimes instructors call this sentence a “thesis” or a “claim.”
So, if your instructor tells you to write about some aspect of oral hygiene, you do not want to just list: “First, you brush your teeth with a soft brush and some peanut butter. Then, you floss with unwaxed, bologna-flavored string. Finally, gargle with bourbon.” Instead, you could say, “Of all the oral cleaning methods, sandblasting removes the most plaque. Therefore it should be recommended by the American Dental Association.” Or, “From an aesthetic perspective, moldy teeth can be quite charming. However, their joys are short-lived.”
Convincing the reader of your argument is the goal of academic writing. It doesn’t have to say “argument” anywhere in the assignment for you to need one. Look at the assignment and think about what kind of argument you could make about it instead of just seeing it as a checklist of information you have to present. For help with understanding the role of argument in academic writing, see our handout on argument .
What kind of evidence do you need?
There are many kinds of evidence, and what type of evidence will work for your assignment can depend on several factors–the discipline, the parameters of the assignment, and your instructor’s preference. Should you use statistics? Historical examples? Do you need to conduct your own experiment? Can you rely on personal experience? See our handout on evidence for suggestions on how to use evidence appropriately.
Make sure you are clear about this part of the assignment, because your use of evidence will be crucial in writing a successful paper. You are not just learning how to argue; you are learning how to argue with specific types of materials and ideas. Ask your instructor what counts as acceptable evidence. You can also ask a librarian for help. No matter what kind of evidence you use, be sure to cite it correctly—see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial .
You cannot always tell from the assignment just what sort of writing style your instructor expects. The instructor may be really laid back in class but still expect you to sound formal in writing. Or the instructor may be fairly formal in class and ask you to write a reflection paper where you need to use “I” and speak from your own experience.
Try to avoid false associations of a particular field with a style (“art historians like wacky creativity,” or “political scientists are boring and just give facts”) and look instead to the types of readings you have been given in class. No one expects you to write like Plato—just use the readings as a guide for what is standard or preferable to your instructor. When in doubt, ask your instructor about the level of formality they expect.
No matter what field you are writing for or what facts you are including, if you do not write so that your reader can understand your main idea, you have wasted your time. So make clarity your main goal. For specific help with style, see our handout on style .
Technical details about the assignment
The technical information you are given in an assignment always seems like the easy part. This section can actually give you lots of little hints about approaching the task. Find out if elements such as page length and citation format (see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial ) are negotiable. Some professors do not have strong preferences as long as you are consistent and fully answer the assignment. Some professors are very specific and will deduct big points for deviations.
Usually, the page length tells you something important: The instructor thinks the size of the paper is appropriate to the assignment’s parameters. In plain English, your instructor is telling you how many pages it should take for you to answer the question as fully as you are expected to. So if an assignment is two pages long, you cannot pad your paper with examples or reword your main idea several times. Hit your one point early, defend it with the clearest example, and finish quickly. If an assignment is ten pages long, you can be more complex in your main points and examples—and if you can only produce five pages for that assignment, you need to see someone for help—as soon as possible.
Tricks that don’t work
Your instructors are not fooled when you:
- spend more time on the cover page than the essay —graphics, cool binders, and cute titles are no replacement for a well-written paper.
- use huge fonts, wide margins, or extra spacing to pad the page length —these tricks are immediately obvious to the eye. Most instructors use the same word processor you do. They know what’s possible. Such tactics are especially damning when the instructor has a stack of 60 papers to grade and yours is the only one that low-flying airplane pilots could read.
- use a paper from another class that covered “sort of similar” material . Again, the instructor has a particular task for you to fulfill in the assignment that usually relates to course material and lectures. Your other paper may not cover this material, and turning in the same paper for more than one course may constitute an Honor Code violation . Ask the instructor—it can’t hurt.
- get all wacky and “creative” before you answer the question . Showing that you are able to think beyond the boundaries of a simple assignment can be good, but you must do what the assignment calls for first. Again, check with your instructor. A humorous tone can be refreshing for someone grading a stack of papers, but it will not get you a good grade if you have not fulfilled the task.
Critical reading of assignments leads to skills in other types of reading and writing. If you get good at figuring out what the real goals of assignments are, you are going to be better at understanding the goals of all of your classes and fields of study.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift

Assignment of Contract
Jump to section, what is an assignment of contract.
An assignment of contract is a legal term that describes the process that occurs when the original party (assignor) transfers their rights and obligations under their contract to a third party (assignee). When an assignment of contract happens, the original party is relieved of their contractual duties, and their role is replaced by the approved incoming party.
How Does Assignment of Contract Work?
An assignment of contract is simpler than you might think.
The process starts with an existing contract party who wishes to transfer their contractual obligations to a new party.
When this occurs, the existing contract party must first confirm that an assignment of contract is permissible under the legally binding agreement . Some contracts prohibit assignments of contract altogether, and some require the other parties of the agreement to agree to the transfer. However, the general rule is that contracts are freely assignable unless there is an explicit provision that says otherwise.
In other cases, some contracts allow an assignment of contract without any formal notification to other contract parties. If this is the case, once the existing contract party decides to reassign his duties, he must create a “Letter of Assignment ” to notify any other contract signers of the change.
The Letter of Assignment must include details about who is to take over the contractual obligations of the exiting party and when the transfer will take place. If the assignment is valid, the assignor is not required to obtain the consent or signature of the other parties to the original contract for the valid assignment to take place.
Check out this article to learn more about how assigning a contract works.
Contract Assignment Examples
Contract assignments are great tools for contract parties to use when they wish to transfer their commitments to a third party. Here are some examples of contract assignments to help you better understand them:
Anna signs a contract with a local trash company that entitles her to have her trash picked up twice a week. A year later, the trash company transferred her contract to a new trash service provider. This contract assignment effectively makes Anna’s contract now with the new service provider.
Hasina enters a contract with a national phone company for cell phone service. The company goes into bankruptcy and needs to close its doors but decides to transfer all current contracts to another provider who agrees to honor the same rates and level of service. The contract assignment is completed, and Hasina now has a contract with the new phone company as a result.
Here is an article where you can find out more about contract assignments.
Assignment of Contract in Real Estate
Assignment of contract is also used in real estate to make money without going the well-known routes of buying and flipping houses. When real estate LLC investors use an assignment of contract, they can make money off properties without ever actually buying them by instead opting to transfer real estate contracts .
This process is called real estate wholesaling.
Real Estate Wholesaling
Real estate wholesaling consists of locating deals on houses that you don’t plan to buy but instead plan to enter a contract to reassign the house to another buyer and pocket the profit.
The process is simple: real estate wholesalers negotiate purchase contracts with sellers. Then, they present these contracts to buyers who pay them an assignment fee for transferring the contract.
This process works because a real estate purchase agreement does not come with the obligation to buy a property. Instead, it sets forth certain purchasing parameters that must be fulfilled by the buyer of the property. In a nutshell, whoever signs the purchase contract has the right to buy the property, but those rights can usually be transferred by means of an assignment of contract.
This means that as long as the buyer who’s involved in the assignment of contract agrees with the purchasing terms, they can legally take over the contract.
But how do real estate wholesalers find these properties?
It is easier than you might think. Here are a few examples of ways that wholesalers find cheap houses to turn a profit on:
- Direct mailers
- Place newspaper ads
- Make posts in online forums
- Social media posts
The key to finding the perfect home for an assignment of contract is to locate sellers that are looking to get rid of their properties quickly. This might be a family who is looking to relocate for a job opportunity or someone who needs to make repairs on a home but can’t afford it. Either way, the quicker the wholesaler can close the deal, the better.
Once a property is located, wholesalers immediately go to work getting the details ironed out about how the sale will work. Transparency is key when it comes to wholesaling. This means that when a wholesaler intends to use an assignment of contract to transfer the rights to another person, they are always upfront about during the preliminary phases of the sale.
In addition to this practice just being good business, it makes sure the process goes as smoothly as possible later down the line. Wholesalers are clear in their intent and make sure buyers know that the contract could be transferred to another buyer before the closing date arrives.
After their offer is accepted and warranties are determined, wholesalers move to complete a title search . Title searches ensure that sellers have the right to enter into a purchase agreement on the property. They do this by searching for any outstanding tax payments, liens , or other roadblocks that could prevent the sale from going through.
Wholesalers also often work with experienced real estate lawyers who ensure that all of the legal paperwork is forthcoming and will stand up in court. Lawyers can also assist in the contract negotiation process if needed but often don’t come in until the final stages.
If the title search comes back clear and the real estate lawyer gives the green light, the wholesaler will immediately move to locate an entity to transfer the rights to buy.
One of the most attractive advantages of real estate wholesaling is that very little money is needed to get started. The process of finding a seller, negotiating a price, and performing a title search is an extremely cheap process that almost anyone can do.
On the other hand, it is not always a positive experience. It can be hard for wholesalers to find sellers who will agree to sell their homes for less than the market value. Even when they do, there is always a chance that the transferred buyer will back out of the sale, which leaves wholesalers obligated to either purchase the property themselves or scramble to find a new person to complete an assignment of contract with.
Learn more about assignment of contract in real estate by checking out this article .
Who Handles Assignment of Contract?
The best person to handle an assignment of contract is an attorney. Since these are detailed legal documents that deal with thousands of dollars, it is never a bad idea to have a professional on your side. If you need help with an assignment of contract or signing a business contract , post a project on ContractsCounsel. There, you can connect with attorneys who know everything there is to know about assignment of contract amendment and can walk you through the whole process.
ContractsCounsel is not a law firm, and this post should not be considered and does not contain legal advice. To ensure the information and advice in this post are correct, sufficient, and appropriate for your situation, please consult a licensed attorney. Also, using or accessing ContractsCounsel's site does not create an attorney-client relationship between you and ContractsCounsel.
Meet some of our Lawyers
Experienced in-house attorney with focus on acquisitions, divestitures, general corporate matters and litigation support.
After starting my professional career in Human Resources in the Healthcare and Non-profit fields, I decided to expand my options and attended law school, passing the North Carolina bar in 2016. Since then, I have practiced in-house for healthcare companies, in the civil rights arena, and run my own business. I am currently looking to return to my legal roots and am excited to practice business law again.
A veteran real estate attorney with experience ranging from drafting and negotiating land development agreements, to purchase and sale and lease agreements for multifamily and large commercial proects.
I have been practicing law in Minnesota for the past 17 years, in general civil practice. My primary focus is employment law and contracts.
I have 13+ years of experience as a real estate, construction, and general transactional lawyer focused on drafting and negotiating commercial leases, purchase and sale agreements, contractor and design professional agreements, etc.
I'm in general practice with an emphasis on real estate, litigation, and contracts
Hailing from Central Texas, Jordan Pender graduated from Baylor University in 2017 with his Bachelor of Arts degree and in 2021 he graduated from Baylor Law School with his Juris Doctor. Since August of 2021, Jordan has been working as an associate attorney for The Law Office of Gregory K. Simmons in Killeen, Texas focusing in general civil litigation. Areas of expertise include: Family Law, Contractual disputes, Business entity formation and planning, and Landlord & Tenant disputes.
Find the best lawyer for your project

Quick, user friendly and one of the better ways I've come across to get ahold of lawyers willing to take new clients.
Need help with a Contract Agreement?
Post Your Project
Get Free Bids to Compare
Hire Your Lawyer
CONTRACT LAWYERS BY TOP CITIES
- Austin Contracts Lawyers
- Boston Contracts Lawyers
- Chicago Contracts Lawyers
- Dallas Contracts Lawyers
- Denver Contracts Lawyers
- Houston Contracts Lawyers
- Los Angeles Contracts Lawyers
- New York Contracts Lawyers
- Phoenix Contracts Lawyers
- San Diego Contracts Lawyers
- Tampa Contracts Lawyers
ASSIGNMENT OF CONTRACT LAWYERS BY CITY
- Austin Assignment Of Contract Lawyers
- Boston Assignment Of Contract Lawyers
- Chicago Assignment Of Contract Lawyers
- Dallas Assignment Of Contract Lawyers
- Denver Assignment Of Contract Lawyers
- Houston Assignment Of Contract Lawyers
- Los Angeles Assignment Of Contract Lawyers
- New York Assignment Of Contract Lawyers
- Phoenix Assignment Of Contract Lawyers
- San Diego Assignment Of Contract Lawyers
- Tampa Assignment Of Contract Lawyers
Contracts Counsel was incredibly helpful and easy to use. I submitted a project for a lawyer's help within a day I had received over 6 proposals from qualified lawyers. I submitted a bid that works best for my business and we went forward with the project.
I never knew how difficult it was to obtain representation or a lawyer, and ContractsCounsel was EXACTLY the type of service I was hoping for when I was in a pinch. Working with their service was efficient, effective and made me feel in control. Thank you so much and should I ever need attorney services down the road, I'll certainly be a repeat customer.
I got 5 bids within 24h of posting my project. I choose the person who provided the most detailed and relevant intro letter, highlighting their experience relevant to my project. I am very satisfied with the outcome and quality of the two agreements that were produced, they actually far exceed my expectations.
How It Works
Want to speak to someone.
Get in touch below and we will schedule a time to connect!
Find lawyers and attorneys by city
- assignments basic law
Assignments: The Basic Law
The assignment of a right or obligation is a common contractual event under the law and the right to assign (or prohibition against assignments) is found in the majority of agreements, leases and business structural documents created in the United States.
As with many terms commonly used, people are familiar with the term but often are not aware or fully aware of what the terms entail. The concept of assignment of rights and obligations is one of those simple concepts with wide ranging ramifications in the contractual and business context and the law imposes severe restrictions on the validity and effect of assignment in many instances. Clear contractual provisions concerning assignments and rights should be in every document and structure created and this article will outline why such drafting is essential for the creation of appropriate and effective contracts and structures.
The reader should first read the article on Limited Liability Entities in the United States and Contracts since the information in those articles will be assumed in this article.
Basic Definitions and Concepts:
An assignment is the transfer of rights held by one party called the “assignor” to another party called the “assignee.” The legal nature of the assignment and the contractual terms of the agreement between the parties determines some additional rights and liabilities that accompany the assignment. The assignment of rights under a contract usually completely transfers the rights to the assignee to receive the benefits accruing under the contract. Ordinarily, the term assignment is limited to the transfer of rights that are intangible, like contractual rights and rights connected with property. Merchants Service Co. v. Small Claims Court , 35 Cal. 2d 109, 113-114 (Cal. 1950).
An assignment will generally be permitted under the law unless there is an express prohibition against assignment in the underlying contract or lease. Where assignments are permitted, the assignor need not consult the other party to the contract but may merely assign the rights at that time. However, an assignment cannot have any adverse effect on the duties of the other party to the contract, nor can it diminish the chance of the other party receiving complete performance. The assignor normally remains liable unless there is an agreement to the contrary by the other party to the contract.
The effect of a valid assignment is to remove privity between the assignor and the obligor and create privity between the obligor and the assignee. Privity is usually defined as a direct and immediate contractual relationship. See Merchants case above.
Further, for the assignment to be effective in most jurisdictions, it must occur in the present. One does not normally assign a future right; the assignment vests immediate rights and obligations.
No specific language is required to create an assignment so long as the assignor makes clear his/her intent to assign identified contractual rights to the assignee. Since expensive litigation can erupt from ambiguous or vague language, obtaining the correct verbiage is vital. An agreement must manifest the intent to transfer rights and can either be oral or in writing and the rights assigned must be certain.
Note that an assignment of an interest is the transfer of some identifiable property, claim, or right from the assignor to the assignee. The assignment operates to transfer to the assignee all of the rights, title, or interest of the assignor in the thing assigned. A transfer of all rights, title, and interests conveys everything that the assignor owned in the thing assigned and the assignee stands in the shoes of the assignor. Knott v. McDonald’s Corp ., 985 F. Supp. 1222 (N.D. Cal. 1997)
The parties must intend to effectuate an assignment at the time of the transfer, although no particular language or procedure is necessary. As long ago as the case of National Reserve Co. v. Metropolitan Trust Co ., 17 Cal. 2d 827 (Cal. 1941), the court held that in determining what rights or interests pass under an assignment, the intention of the parties as manifested in the instrument is controlling.
The intent of the parties to an assignment is a question of fact to be derived not only from the instrument executed by the parties but also from the surrounding circumstances. When there is no writing to evidence the intention to transfer some identifiable property, claim, or right, it is necessary to scrutinize the surrounding circumstances and parties’ acts to ascertain their intentions. Strosberg v. Brauvin Realty Servs., 295 Ill. App. 3d 17 (Ill. App. Ct. 1st Dist. 1998)
The general rule applicable to assignments of choses in action is that an assignment, unless there is a contract to the contrary, carries with it all securities held by the assignor as collateral to the claim and all rights incidental thereto and vests in the assignee the equitable title to such collateral securities and incidental rights. An unqualified assignment of a contract or chose in action, however, with no indication of the intent of the parties, vests in the assignee the assigned contract or chose and all rights and remedies incidental thereto.
More examples: In Strosberg v. Brauvin Realty Servs ., 295 Ill. App. 3d 17 (Ill. App. Ct. 1st Dist. 1998), the court held that the assignee of a party to a subordination agreement is entitled to the benefits and is subject to the burdens of the agreement. In Florida E. C. R. Co. v. Eno , 99 Fla. 887 (Fla. 1930), the court held that the mere assignment of all sums due in and of itself creates no different or other liability of the owner to the assignee than that which existed from the owner to the assignor.
And note that even though an assignment vests in the assignee all rights, remedies, and contingent benefits which are incidental to the thing assigned, those which are personal to the assignor and for his sole benefit are not assigned. Rasp v. Hidden Valley Lake, Inc ., 519 N.E.2d 153, 158 (Ind. Ct. App. 1988). Thus, if the underlying agreement provides that a service can only be provided to X, X cannot assign that right to Y.
Novation Compared to Assignment:
Although the difference between a novation and an assignment may appear narrow, it is an essential one. “Novation is a act whereby one party transfers all its obligations and benefits under a contract to a third party.” In a novation, a third party successfully substitutes the original party as a party to the contract. “When a contract is novated, the other contracting party must be left in the same position he was in prior to the novation being made.”
A sublease is the transfer when a tenant retains some right of reentry onto the leased premises. However, if the tenant transfers the entire leasehold estate, retaining no right of reentry or other reversionary interest, then the transfer is an assignment. The assignor is normally also removed from liability to the landlord only if the landlord consents or allowed that right in the lease. In a sublease, the original tenant is not released from the obligations of the original lease.
Equitable Assignments:
An equitable assignment is one in which one has a future interest and is not valid at law but valid in a court of equity. In National Bank of Republic v. United Sec. Life Ins. & Trust Co. , 17 App. D.C. 112 (D.C. Cir. 1900), the court held that to constitute an equitable assignment of a chose in action, the following has to occur generally: anything said written or done, in pursuance of an agreement and for valuable consideration, or in consideration of an antecedent debt, to place a chose in action or fund out of the control of the owner, and appropriate it to or in favor of another person, amounts to an equitable assignment. Thus, an agreement, between a debtor and a creditor, that the debt shall be paid out of a specific fund going to the debtor may operate as an equitable assignment.
In Egyptian Navigation Co. v. Baker Invs. Corp. , 2008 U.S. Dist. LEXIS 30804 (S.D.N.Y. Apr. 14, 2008), the court stated that an equitable assignment occurs under English law when an assignor, with an intent to transfer his/her right to a chose in action, informs the assignee about the right so transferred.
An executory agreement or a declaration of trust are also equitable assignments if unenforceable as assignments by a court of law but enforceable by a court of equity exercising sound discretion according to the circumstances of the case. Since California combines courts of equity and courts of law, the same court would hear arguments as to whether an equitable assignment had occurred. Quite often, such relief is granted to avoid fraud or unjust enrichment.
Note that obtaining an assignment through fraudulent means invalidates the assignment. Fraud destroys the validity of everything into which it enters. It vitiates the most solemn contracts, documents, and even judgments. Walker v. Rich , 79 Cal. App. 139 (Cal. App. 1926). If an assignment is made with the fraudulent intent to delay, hinder, and defraud creditors, then it is void as fraudulent in fact. See our article on Transfers to Defraud Creditors .
But note that the motives that prompted an assignor to make the transfer will be considered as immaterial and will constitute no defense to an action by the assignee, if an assignment is considered as valid in all other respects.
Enforceability of Assignments:
Whether a right under a contract is capable of being transferred is determined by the law of the place where the contract was entered into. The validity and effect of an assignment is determined by the law of the place of assignment. The validity of an assignment of a contractual right is governed by the law of the state with the most significant relationship to the assignment and the parties.
In some jurisdictions, the traditional conflict of laws rules governing assignments has been rejected and the law of the place having the most significant contacts with the assignment applies. In Downs v. American Mut. Liability Ins. Co ., 14 N.Y.2d 266 (N.Y. 1964), a wife and her husband separated and the wife obtained a judgment of separation from the husband in New York. The judgment required the husband to pay a certain yearly sum to the wife. The husband assigned 50 percent of his future salary, wages, and earnings to the wife. The agreement authorized the employer to make such payments to the wife.
After the husband moved from New York, the wife learned that he was employed by an employer in Massachusetts. She sent the proper notice and demanded payment under the agreement. The employer refused and the wife brought an action for enforcement. The court observed that Massachusetts did not prohibit assignment of the husband’s wages. Moreover, Massachusetts law was not controlling because New York had the most significant relationship with the assignment. Therefore, the court ruled in favor of the wife.
Therefore, the validity of an assignment is determined by looking to the law of the forum with the most significant relationship to the assignment itself. To determine the applicable law of assignments, the court must look to the law of the state which is most significantly related to the principal issue before it.
Assignment of Contractual Rights:
Generally, the law allows the assignment of a contractual right unless the substitution of rights would materially change the duty of the obligor, materially increase the burden or risk imposed on the obligor by the contract, materially impair the chance of obtaining return performance, or materially reduce the value of the performance to the obligor. Restat 2d of Contracts, § 317(2)(a). This presumes that the underlying agreement is silent on the right to assign.
If the contract specifically precludes assignment, the contractual right is not assignable. Whether a contract is assignable is a matter of contractual intent and one must look to the language used by the parties to discern that intent.
In the absence of an express provision to the contrary, the rights and duties under a bilateral executory contract that does not involve personal skill, trust, or confidence may be assigned without the consent of the other party. But note that an assignment is invalid if it would materially alter the other party’s duties and responsibilities. Once an assignment is effective, the assignee stands in the shoes of the assignor and assumes all of assignor’s rights. Hence, after a valid assignment, the assignor’s right to performance is extinguished, transferred to assignee, and the assignee possesses the same rights, benefits, and remedies assignor once possessed. Robert Lamb Hart Planners & Architects v. Evergreen, Ltd. , 787 F. Supp. 753 (S.D. Ohio 1992).
On the other hand, an assignee’s right against the obligor is subject to “all of the limitations of the assignor’s right, all defenses thereto, and all set-offs and counterclaims which would have been available against the assignor had there been no assignment, provided that these defenses and set-offs are based on facts existing at the time of the assignment.” See Robert Lamb , case, above.
The power of the contract to restrict assignment is broad. Usually, contractual provisions that restrict assignment of the contract without the consent of the obligor are valid and enforceable, even when there is statutory authorization for the assignment. The restriction of the power to assign is often ineffective unless the restriction is expressly and precisely stated. Anti-assignment clauses are effective only if they contain clear, unambiguous language of prohibition. Anti-assignment clauses protect only the obligor and do not affect the transaction between the assignee and assignor.
Usually, a prohibition against the assignment of a contract does not prevent an assignment of the right to receive payments due, unless circumstances indicate the contrary. Moreover, the contracting parties cannot, by a mere non-assignment provision, prevent the effectual alienation of the right to money which becomes due under the contract.
A contract provision prohibiting or restricting an assignment may be waived, or a party may so act as to be estopped from objecting to the assignment, such as by effectively ratifying the assignment. The power to void an assignment made in violation of an anti-assignment clause may be waived either before or after the assignment. See our article on Contracts.
Noncompete Clauses and Assignments:
Of critical import to most buyers of businesses is the ability to ensure that key employees of the business being purchased cannot start a competing company. Some states strictly limit such clauses, some do allow them. California does restrict noncompete clauses, only allowing them under certain circumstances. A common question in those states that do allow them is whether such rights can be assigned to a new party, such as the buyer of the buyer.
A covenant not to compete, also called a non-competitive clause, is a formal agreement prohibiting one party from performing similar work or business within a designated area for a specified amount of time. This type of clause is generally included in contracts between employer and employee and contracts between buyer and seller of a business.
Many workers sign a covenant not to compete as part of the paperwork required for employment. It may be a separate document similar to a non-disclosure agreement, or buried within a number of other clauses in a contract. A covenant not to compete is generally legal and enforceable, although there are some exceptions and restrictions.
Whenever a company recruits skilled employees, it invests a significant amount of time and training. For example, it often takes years before a research chemist or a design engineer develops a workable knowledge of a company’s product line, including trade secrets and highly sensitive information. Once an employee gains this knowledge and experience, however, all sorts of things can happen. The employee could work for the company until retirement, accept a better offer from a competing company or start up his or her own business.
A covenant not to compete may cover a number of potential issues between employers and former employees. Many companies spend years developing a local base of customers or clients. It is important that this customer base not fall into the hands of local competitors. When an employee signs a covenant not to compete, he or she usually agrees not to use insider knowledge of the company’s customer base to disadvantage the company. The covenant not to compete often defines a broad geographical area considered off-limits to former employees, possibly tens or hundreds of miles.
Another area of concern covered by a covenant not to compete is a potential ‘brain drain’. Some high-level former employees may seek to recruit others from the same company to create new competition. Retention of employees, especially those with unique skills or proprietary knowledge, is vital for most companies, so a covenant not to compete may spell out definite restrictions on the hiring or recruiting of employees.
A covenant not to compete may also define a specific amount of time before a former employee can seek employment in a similar field. Many companies offer a substantial severance package to make sure former employees are financially solvent until the terms of the covenant not to compete have been met.
Because the use of a covenant not to compete can be controversial, a handful of states, including California, have largely banned this type of contractual language. The legal enforcement of these agreements falls on individual states, and many have sided with the employee during arbitration or litigation. A covenant not to compete must be reasonable and specific, with defined time periods and coverage areas. If the agreement gives the company too much power over former employees or is ambiguous, state courts may declare it to be overbroad and therefore unenforceable. In such case, the employee would be free to pursue any employment opportunity, including working for a direct competitor or starting up a new company of his or her own.
It has been held that an employee’s covenant not to compete is assignable where one business is transferred to another, that a merger does not constitute an assignment of a covenant not to compete, and that a covenant not to compete is enforceable by a successor to the employer where the assignment does not create an added burden of employment or other disadvantage to the employee. However, in some states such as Hawaii, it has also been held that a covenant not to compete is not assignable and under various statutes for various reasons that such covenants are not enforceable against an employee by a successor to the employer. Hawaii v. Gannett Pac. Corp. , 99 F. Supp. 2d 1241 (D. Haw. 1999)
It is vital to obtain the relevant law of the applicable state before drafting or attempting to enforce assignment rights in this particular area.
Conclusion:
In the current business world of fast changing structures, agreements, employees and projects, the ability to assign rights and obligations is essential to allow flexibility and adjustment to new situations. Conversely, the ability to hold a contracting party into the deal may be essential for the future of a party. Thus, the law of assignments and the restriction on same is a critical aspect of every agreement and every structure. This basic provision is often glanced at by the contracting parties, or scribbled into the deal at the last minute but can easily become the most vital part of the transaction.
As an example, one client of ours came into the office outraged that his co venturer on a sizable exporting agreement, who had excellent connections in Brazil, had elected to pursue another venture instead and assigned the agreement to a party unknown to our client and without the business contacts our client considered vital. When we examined the handwritten agreement our client had drafted in a restaurant in Sao Paolo, we discovered there was no restriction on assignment whatsoever…our client had not even considered that right when drafting the agreement after a full day of work.
One choses who one does business with carefully…to ensure that one’s choice remains the party on the other side of the contract, one must master the ability to negotiate proper assignment provisions.
Founded in 1939, our law firm combines the ability to represent clients in domestic or international matters with the personal interaction with clients that is traditional to a long established law firm.
Read more about our firm
© 2024, Stimmel, Stimmel & Roeser, All rights reserved | Terms of Use | Site by Bay Design
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Options and Derivatives
- Strategy & Education
Assignment: Definition in Finance, How It Works, and Examples
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
Yarilet Perez is an experienced multimedia journalist and fact-checker with a Master of Science in Journalism. She has worked in multiple cities covering breaking news, politics, education, and more. Her expertise is in personal finance and investing, and real estate.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/YariletPerez-d2289cb01c3c4f2aabf79ce6057e5078.jpg)
What Is an Assignment?
Assignment most often refers to one of two definitions in the financial world:
- The transfer of an individual's rights or property to another person or business. This concept exists in a variety of business transactions and is often spelled out contractually.
- In trading, assignment occurs when an option contract is exercised. The owner of the contract exercises the contract and assigns the option writer to an obligation to complete the requirements of the contract.
Key Takeaways
- Assignment is a transfer of rights or property from one party to another.
- Options assignments occur when option buyers exercise their rights to a position in a security.
- Other examples of assignments can be found in wages, mortgages, and leases.
Uses For Assignments
Assignment refers to the transfer of some or all property rights and obligations associated with an asset, property, contract, or other asset of value. to another entity through a written agreement.
Assignment rights happen every day in many different situations. A payee, like a utility or a merchant, assigns the right to collect payment from a written check to a bank. A merchant can assign the funds from a line of credit to a manufacturing third party that makes a product that the merchant will eventually sell. A trademark owner can transfer, sell, or give another person interest in the trademark or logo. A homeowner who sells their house assigns the deed to the new buyer.
To be effective, an assignment must involve parties with legal capacity, consideration, consent, and legality of the object.
A wage assignment is a forced payment of an obligation by automatic withholding from an employee’s pay. Courts issue wage assignments for people late with child or spousal support, taxes, loans, or other obligations. Money is automatically subtracted from a worker's paycheck without consent if they have a history of nonpayment. For example, a person delinquent on $100 monthly loan payments has a wage assignment deducting the money from their paycheck and sent to the lender. Wage assignments are helpful in paying back long-term debts.
Another instance can be found in a mortgage assignment. This is where a mortgage deed gives a lender interest in a mortgaged property in return for payments received. Lenders often sell mortgages to third parties, such as other lenders. A mortgage assignment document clarifies the assignment of contract and instructs the borrower in making future mortgage payments, and potentially modifies the mortgage terms.
A final example involves a lease assignment. This benefits a relocating tenant wanting to end a lease early or a landlord looking for rent payments to pay creditors. Once the new tenant signs the lease, taking over responsibility for rent payments and other obligations, the previous tenant is released from those responsibilities. In a separate lease assignment, a landlord agrees to pay a creditor through an assignment of rent due under rental property leases. The agreement is used to pay a mortgage lender if the landlord defaults on the loan or files for bankruptcy . Any rental income would then be paid directly to the lender.
Options Assignment
Options can be assigned when a buyer decides to exercise their right to buy (or sell) stock at a particular strike price . The corresponding seller of the option is not determined when a buyer opens an option trade, but only at the time that an option holder decides to exercise their right to buy stock. So an option seller with open positions is matched with the exercising buyer via automated lottery. The randomly selected seller is then assigned to fulfill the buyer's rights. This is known as an option assignment.
Once assigned, the writer (seller) of the option will have the obligation to sell (if a call option ) or buy (if a put option ) the designated number of shares of stock at the agreed-upon price (the strike price). For instance, if the writer sold calls they would be obligated to sell the stock, and the process is often referred to as having the stock called away . For puts, the buyer of the option sells stock (puts stock shares) to the writer in the form of a short-sold position.
Suppose a trader owns 100 call options on company ABC's stock with a strike price of $10 per share. The stock is now trading at $30 and ABC is due to pay a dividend shortly. As a result, the trader exercises the options early and receives 10,000 shares of ABC paid at $10. At the same time, the other side of the long call (the short call) is assigned the contract and must deliver the shares to the long.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/investor-viewing-company-share-price-market-data-on-a-laptop-computer-713768437-c4eda9ee28224ad6be4f6912822227af.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy

In order to continue enjoying our site, we ask that you confirm your identity as a human. Thank you very much for your cooperation.
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
The Definition of Random Assignment According to Psychology
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Emily is a board-certified science editor who has worked with top digital publishing brands like Voices for Biodiversity, Study.com, GoodTherapy, Vox, and Verywell.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Emily-Swaim-1000-0f3197de18f74329aeffb690a177160c.jpg)
Materio / Getty Images
Random assignment refers to the use of chance procedures in psychology experiments to ensure that each participant has the same opportunity to be assigned to any given group in a study to eliminate any potential bias in the experiment at the outset. Participants are randomly assigned to different groups, such as the treatment group versus the control group. In clinical research, randomized clinical trials are known as the gold standard for meaningful results.
Simple random assignment techniques might involve tactics such as flipping a coin, drawing names out of a hat, rolling dice, or assigning random numbers to a list of participants. It is important to note that random assignment differs from random selection .
While random selection refers to how participants are randomly chosen from a target population as representatives of that population, random assignment refers to how those chosen participants are then assigned to experimental groups.
Random Assignment In Research
To determine if changes in one variable will cause changes in another variable, psychologists must perform an experiment. Random assignment is a critical part of the experimental design that helps ensure the reliability of the study outcomes.
Researchers often begin by forming a testable hypothesis predicting that one variable of interest will have some predictable impact on another variable.
The variable that the experimenters will manipulate in the experiment is known as the independent variable , while the variable that they will then measure for different outcomes is known as the dependent variable. While there are different ways to look at relationships between variables, an experiment is the best way to get a clear idea if there is a cause-and-effect relationship between two or more variables.
Once researchers have formulated a hypothesis, conducted background research, and chosen an experimental design, it is time to find participants for their experiment. How exactly do researchers decide who will be part of an experiment? As mentioned previously, this is often accomplished through something known as random selection.
Random Selection
In order to generalize the results of an experiment to a larger group, it is important to choose a sample that is representative of the qualities found in that population. For example, if the total population is 60% female and 40% male, then the sample should reflect those same percentages.
Choosing a representative sample is often accomplished by randomly picking people from the population to be participants in a study. Random selection means that everyone in the group stands an equal chance of being chosen to minimize any bias. Once a pool of participants has been selected, it is time to assign them to groups.
By randomly assigning the participants into groups, the experimenters can be fairly sure that each group will have the same characteristics before the independent variable is applied.
Participants might be randomly assigned to the control group , which does not receive the treatment in question. The control group may receive a placebo or receive the standard treatment. Participants may also be randomly assigned to the experimental group , which receives the treatment of interest. In larger studies, there can be multiple treatment groups for comparison.
There are simple methods of random assignment, like rolling the die. However, there are more complex techniques that involve random number generators to remove any human error.
There can also be random assignment to groups with pre-established rules or parameters. For example, if you want to have an equal number of men and women in each of your study groups, you might separate your sample into two groups (by sex) before randomly assigning each of those groups into the treatment group and control group.
Random assignment is essential because it increases the likelihood that the groups are the same at the outset. With all characteristics being equal between groups, other than the application of the independent variable, any differences found between group outcomes can be more confidently attributed to the effect of the intervention.
Example of Random Assignment
Imagine that a researcher is interested in learning whether or not drinking caffeinated beverages prior to an exam will improve test performance. After randomly selecting a pool of participants, each person is randomly assigned to either the control group or the experimental group.
The participants in the control group consume a placebo drink prior to the exam that does not contain any caffeine. Those in the experimental group, on the other hand, consume a caffeinated beverage before taking the test.
Participants in both groups then take the test, and the researcher compares the results to determine if the caffeinated beverage had any impact on test performance.
A Word From Verywell
Random assignment plays an important role in the psychology research process. Not only does this process help eliminate possible sources of bias, but it also makes it easier to generalize the results of a tested sample of participants to a larger population.
Random assignment helps ensure that members of each group in the experiment are the same, which means that the groups are also likely more representative of what is present in the larger population of interest. Through the use of this technique, psychology researchers are able to study complex phenomena and contribute to our understanding of the human mind and behavior.
Lin Y, Zhu M, Su Z. The pursuit of balance: An overview of covariate-adaptive randomization techniques in clinical trials . Contemp Clin Trials. 2015;45(Pt A):21-25. doi:10.1016/j.cct.2015.07.011
Sullivan L. Random assignment versus random selection . In: The SAGE Glossary of the Social and Behavioral Sciences. SAGE Publications, Inc.; 2009. doi:10.4135/9781412972024.n2108
Alferes VR. Methods of Randomization in Experimental Design . SAGE Publications, Inc.; 2012. doi:10.4135/9781452270012
Nestor PG, Schutt RK. Research Methods in Psychology: Investigating Human Behavior. (2nd Ed.). SAGE Publications, Inc.; 2015.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."

How to Assign Tasks Dynamically: Role Assignments in Process Street
Assigning team members to their tasks is a duty which is as vital as it is tedious.
Everyone pretty much knows what they should be doing, so there’s no need to directly assign them to everything when you could be spending time on more important tasks, right?
Human error (of which memory plays a huge part) affects 1/100 routine tasks where care is needed . This means that the people responsible either makes a mistake or forgets what they need to do (hence why documented processes are so important).
That’s why we here at Process Street have a role assignment feature in our checklists.
Role assignments let you dictate who each task in your process checklists needs to be assigned to without fail every time. All you need to do is set up the role which will have the task assigned, then Process Street does the rest.
Ready to assign your tasks without fail, fuss or tedious fiddling? Then let’s dive right in.
Defined roles make processes flexible
Having documented processes is a great way to make sure that your teams get their tasks done on time and to a high standard. Checklists allow everyone to focus on what they’re doing rather than relying on memory for their next task or training for how to carry out their current duties.
However, recording your processes doesn’t automatically mean that your team will be successful in carrying them out.
One of the biggest problems with adopting new processes is making sure that everyone knows what they need to do, and who they’re relying on and reporting to. They need to know their place in the process in order to be able to plan their schedule and manage their time effectively around those tasks.
This is another reason why it’s important to assign your team members to their tasks in some way. They may well have 10 or more different processes to carry out, and chances are they won’t be able to remember precisely which tasks they’re supposed to do by heart.
Here’s where we run into the bus factor .
People need to be assigned to tasks to know what they’re doing but what happens if they leave the company or change roles? You’re left having to go through every process they were involved with to assign the new employee to their tasks.
That’s why it’s better to assign roles rather than people to your processes.
The team manager might leave but the tasks they carry out will always need to be performed by the next team manager. The person changes but the role doesn’t.
This nullifies the bus factor entirely – it doesn’t matter who is and isn’t available to complete your processes if you can define on the spot (and en masse) who will be completing various tasks.
What are role assignments in Process Street?
Role assignments in Process Street are built to make assigning people to their tasks easier than ever.
Instead of having to edit your process templates to assign a new person, you can define a role to assign to a task and then define who will fill that role using a couple of different parameters.
For example, let’s say that you have an employee onboarding checklist . Let’s say that this checklist has the HR manager doing some initial setup, the new employee filling out some details, and the employee’s trainer/mentor filling out other tasks.
Assigning the various tasks to these three team members would usually be time-consuming and tedious, as each task would need assigning manually for every new checklist (due to the employee and mentor changing). With role assignments, you could instead assign tasks to the role of the manager, employee, and mentor, and then record who will fill those roles at the start of each new checklist.
How to set up role assignments
Before I get into the nitty-gritty, let’s make it clear that role assignments are a Business Pro payment plan feature .
With that out of the way, there are three ways to define a role which can be assigned to your tasks:
Using the checklist creator
Using the members form field, using the email form field.
All of these options can be accessed via clicking the “Assign” button in a task while editing your process template, then clicking the “Roles” submenu.
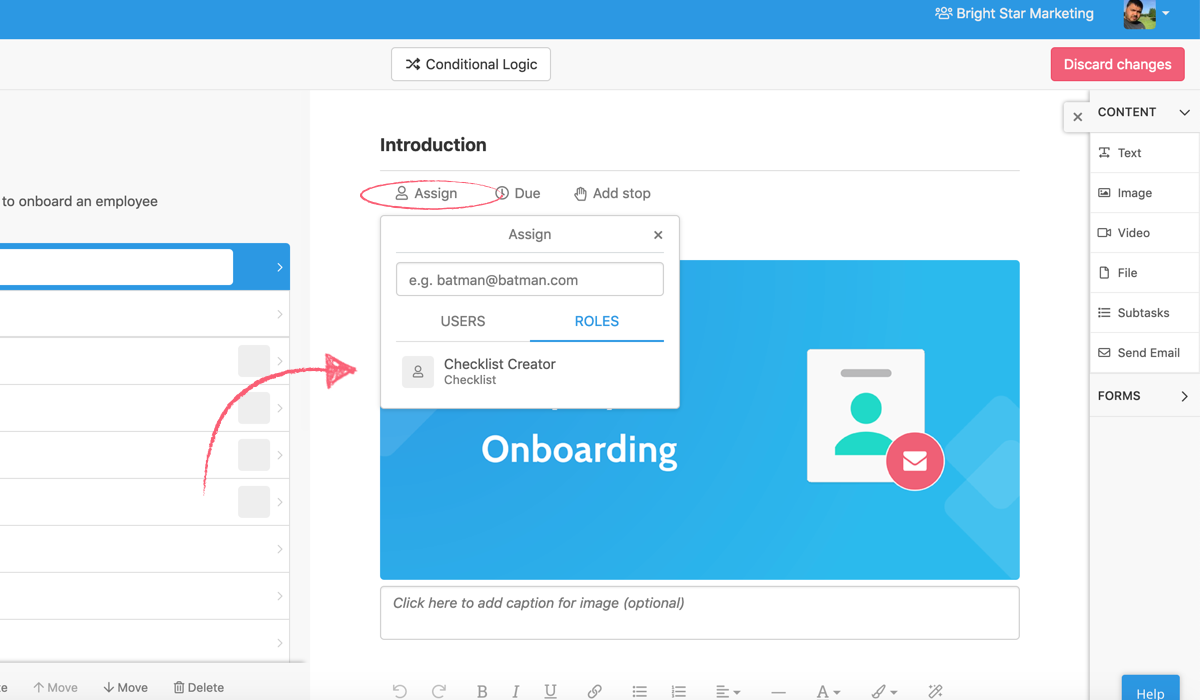
The “Checklist Creator” role does exactly what it says on the tin; it assigns the person who created the checklist to a task.
Using this you can pre-emptively assign yourself to the tasks in a checklist which are relevant to you, letting you see which tasks you need to complete at a glance and track them from your inbox .
For example, let’s say that you need to work through a pre-publish checklist for your latest blog post. Most of the tasks are relevant to whoever’s writing the post, aside from a few at the end which let the editor take over, make changes, and finally push it live.
This is a perfect example of where the checklist creator role saves you time, effort, and covers a potentially messy area of assignment.
By assigning all tasks relevant to the blog post’s writer to the checklist creator, you can automatically have them be attached to the relevant tasks to follow when crafting a great post. As soon as they run the checklist for their work they’ll be assigned, leaving no room for error.
This way your process is flexible enough to allow different writers to get stuck in at their own pace but still provides the value of a set of core instructions and guidelines to follow.
The members form field is a little more complicated, as it provides the person working through the checklist a chance to record who should be assigned to a particular role.
A members form field allows users to select a team member from your Process Street organization (or a particular group within it) while providing a label to indicate who needs to be chosen.
For example, you could have a field with the label “HR Manager” and limit the field’s selection to only show members from the HR group in your organization.
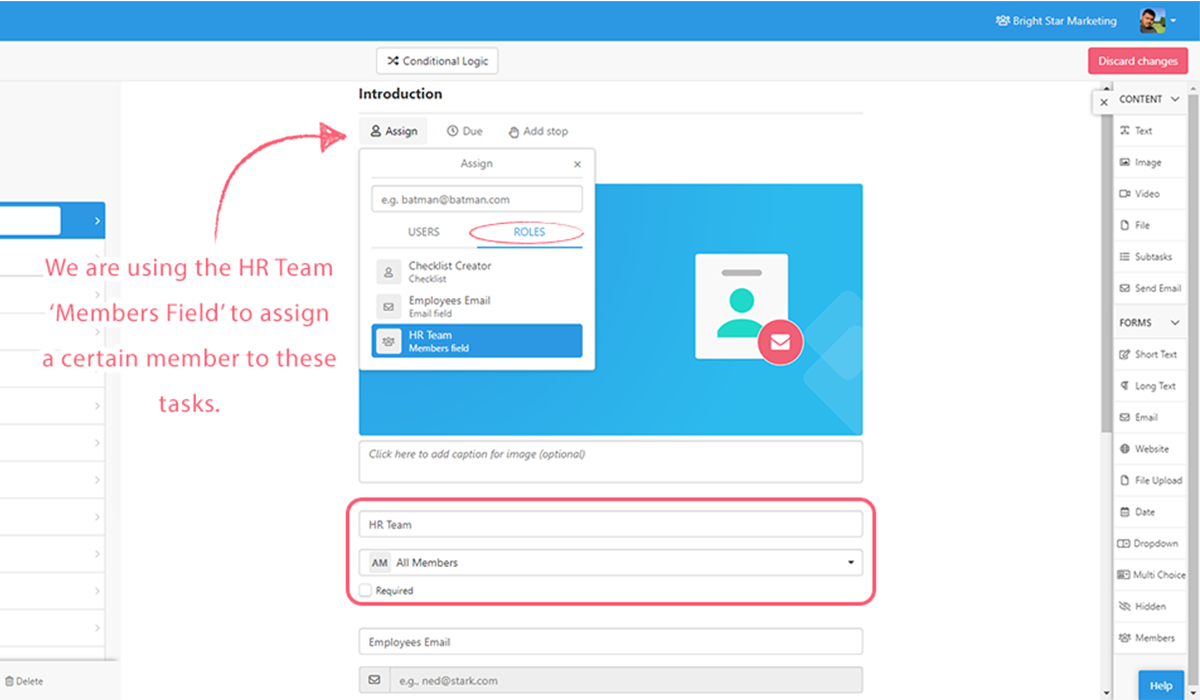
Whatever label you use for this members field will then show up as a role which you can assign to a task.
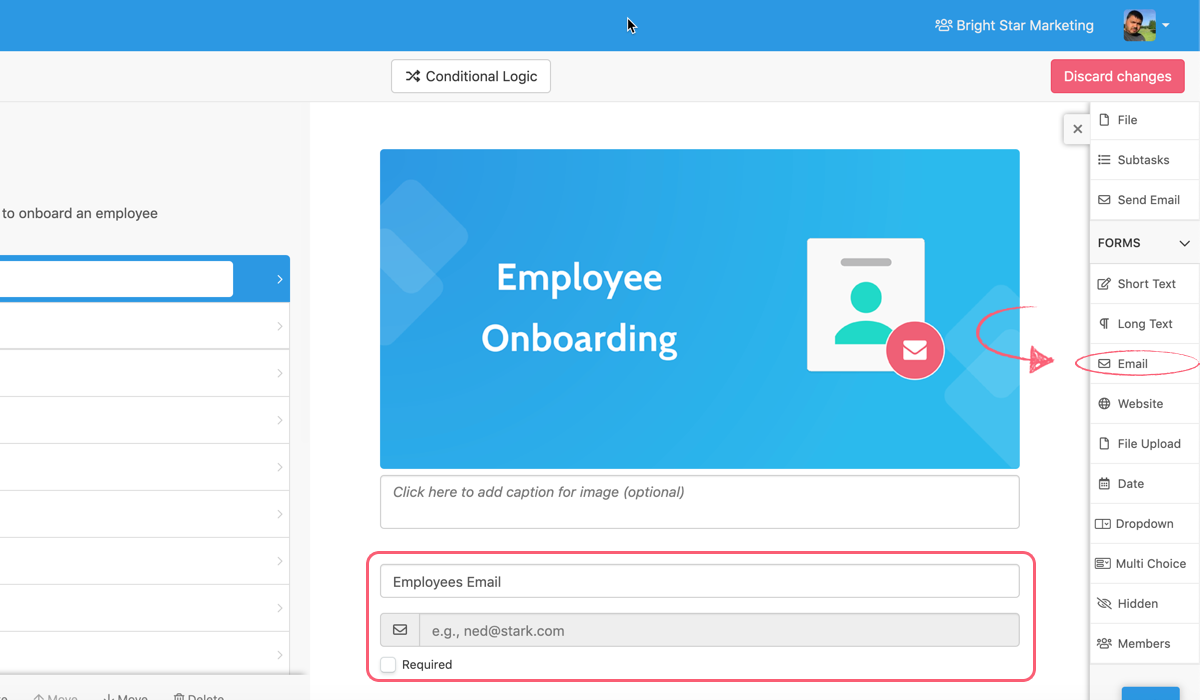
To go back to our blog pre-publish checklist example, let’s say you have multiple editors on the team but only one will be assigned to review any given post at the end of the checklist.
This can be easily accommodated for by providing the writer with a members form field labeled “Post Editor” or something of the like. To make it easier to find the editor in question, you could then limit their selection to only be people within your “Content Creation” team.
Once the field is set up, you then just need to go into each task the editor needs to carry out, click “Assign”, click “Roles”, and then click “Post Editor” (or whatever you named the members form field).
Email form fields are one of the most useful features in our repertoire due to their flexibility, and this is partly due to their power in role assignments.
Any email form field in your process can be used as a role which can be assigned to any task you like. The tasks will then be assigned to whatever email address is put into the form field while working through the checklist.
“But Ben,” I hear you say, “how does that work? Would it break if the email address didn’t belong to a Process Street account already?”
Absolutely not! Role assignments through an email field don’t require the email address to already be tied to an account. You can use an email address even if they’ve never heard of Process Street and they’ll still be assigned to the task.
This is because we’ll first search your organization for an email address matching the one you enter. If there’s an existing user with that email address, we’ll assign that user to the relevant tasks.
If the user doesn’t exist in your organization already, we’ll invite them to your organization as a guest and assign them as per usual.
That way you don’t have multiple users with the same email address in your organization, anyone assigned doesn’t have to be part of your Process Street organization.
Whether it’s a client who you need to fill out a few steps in a feedback checklist or a warehouse employee signing for a package, this is an ideal solution for roles which don’t belong to someone who’s a regular member of your processes.
Automating your role assignments
If you’ve never used business process automation before, you’re missing out on one of the best ways to streamline your work and eliminate basic tasks.
If you already automate your processes, you know just how much time and effort you can save, letting your team focus on the work that actually needs their attention.
Either way, role assignments can also be automated to make assigning tasks to the correct people even more efficient!
Zapier allows you to automatically trigger checklists to run and even fill form fields with customizable data based on certain triggers.
Let’s use an employee onboarding process as our example once again to make things simple.
Zapier could detect when a new employee is added to your database and run an employee onboarding checklist in response. This would also allow Zapier access to the new employee’s data, meaning that their email address could be pushed into your email form field for “New Employee Email”.
In other words, as soon as the new employee is entered into your system, Zapier could automatically create an onboarding checklist for them in Process Street and (through an email form field) assign them to all of the tasks they need to complete.
Going further, if tasks are set up to be assigned to the role of the checklist’s creator, Zapier will take care of this role assignment too.
This is because Zapier works by using a team member’s account to gain access to your apps. In this instance, your HR manager could have the Zap (the automation in Zapier) set up using their account, meaning that they will be automatically assigned to any task labeled as being for the checklist’s creator.
It can take a while to wrap your head around at first but automation is an incredibly powerful tool if you learn how to use it. To learn more, check out our free ebook on the topic:
- The Ultimate Guide to Business Process Automation [Free eBook]
Role assignment use cases
You know how role assignments work. You know why they’re useful and how they can save your team time and effort while making sure that everything is assigned to the right people to perform their tasks.
So, just to prove the point and demonstrate the span of use cases, let’s get stuck into a few core examples of role assignments in action.
Specifically, I’ll show you how you could use role assignments in the following examples:
Employee onboarding
Blog pre-publish checklist, vehicle inspection checklist.
While I’ve already highlighted how this process could be broken up earlier in the post, role assignments are worth their weight in gold when it comes to as delicate and time-sensitive a process as employee onboarding .
The process above is a great way to get started but, with role assignments, you can take it one step further to making sure that the employee is fully on board and ready to tackle their tasks effectively.
All tasks in the “Before first day” and “First day” segments should be tackled by the HR manager to make sure that you make the best first impression and give the employee the best chance of success.
After that, almost everything can be handled by the employee’s mentor in order to lessen the load on the HR manager while still giving the new hire the training and attention they need.
These assignments (especially the mentor) will vary depending on who needs to be assigned. So, rather than manually assigning each task every time, you can use role assignments.
The HR manager can either manually or automatically (through Zapier) trigger the checklist to run, and their tasks can be set to automatically assign to the “checklist creator”. Nice and easy.
The mentor’s tasks can all be set to be assigned to the role of “Employee mentor”. Then, when the mentor is selected in the “Assign a mentor” task (using the members form field), this will automatically make them responsible for every following task.
It’s simple, it’s easy, and it makes sure that everyone knows exactly what they have to do despite potential variation in the person who needs assigning.
Similar to employee onboarding, a blog pre-publish checklist will always need at least two people to work on it. The writer of the post and the editor who will give feedback and (ultimately) approve it for publication.
While it doesn’t quite have the same complexity in terms of the tasks that need to be assigned, it serves as a great example of how role assignments can save you time even in processes where the majority (if not entirely) of the checklist needs to be completed by one person.
You don’t need to assign your entire team to different tasks to save time. A huge amount of tedious work goes into assigning each and every task to the same person, yet, with role assignments, this no longer has to be an issue.
Practically every task can be set to assign itself to the role of “checklist creator” here. That way the writer only has to run the checklist in order to be assigned to each and every task to see it in their task inbox.
The only task that needs assigning to someone else would be the “Have the post approved” task towards the end of the checklist. This could be set to automatically assign to the member’s field for “Person approving the post” in the same task, who can then fill in the final dropdown form field with their final approval.
Let’s have a change of pace and show off how tasks can be assigned via an email form field.
A vehicle inspection is a pretty standard affair. However, an issue arises in this (and any other similar situation) if the inspection is generated by anyone other than the person carrying out the main tasks. This means that you can’t just set everything to be assigned to the role of “checklist creator”.
Enter our email form field. By including one of these you can assign tasks to the person with the email address entered in the form field, whether they’re a member of your Process Street organization or not.
Setting up each task to be assigned to the role of the “Vehicle Inspector’s Email Address” in the first actionable task means that, as soon as their details are filled in by the checklist creator (which could be automatically done via Zapier) the rest of the checklist will assign itself to them. This, in turn, sends an email notification to let them know that they’ve been assigned and provide them a link with which they can get to work on the checklist.
Don’t get bogged down assigning tasks manually every time
It’s time to say goodbye to tedious individual task assignments and the human error that comes with no assignments at all.
Take advantage of role assignments with Process Street and see just how much time and effort you can save!
Sign up for a free account today .
Have any questions about or interesting uses for role assignments? Let me know in the comments below!
Get our posts & product updates earlier by simply subscribing
Ben Mulholland
Ben Mulholland is an Editor at Process Street , and winds down with a casual article or two on Mulholland Writing . Find him on Twitter here .

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Take control of your workflows today

What is Cost Assignment?
Share This...
Cost assignment.
Cost assignment is the process of associating costs with cost objects, such as products, services, departments, or projects. It encompasses the identification, measurement, and allocation of both direct and indirect costs to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the resources consumed by various cost objects within an organization. Cost assignment is a crucial aspect of cost accounting and management accounting, as it helps organizations make informed decisions about pricing, resource allocation, budgeting, and performance evaluation.
There are two main components of cost assignment:
- Direct cost assignment: Direct costs are those costs that can be specifically traced or identified with a particular cost object. Examples of direct costs include direct materials, such as raw materials used in manufacturing a product, and direct labor, such as the wages paid to workers directly involved in producing a product or providing a service. Direct cost assignment involves linking these costs directly to the relevant cost objects, typically through invoices, timesheets, or other documentation.
- Indirect cost assignment (Cost allocation): Indirect costs, also known as overhead or shared costs, are those costs that cannot be directly traced to a specific cost object or are not economically feasible to trace directly. Examples of indirect costs include rent, utilities, depreciation, insurance, and administrative expenses. Since indirect costs cannot be assigned directly to cost objects, organizations use various cost allocation methods to distribute these costs in a systematic and rational manner. Some common cost allocation methods include direct allocation, step-down allocation, reciprocal allocation, and activity-based costing (ABC).
In summary, cost assignment is the process of associating both direct and indirect costs with cost objects, such as products, services, departments, or projects. It plays a critical role in cost accounting and management accounting by providing organizations with the necessary information to make informed decisions about pricing, resource allocation, budgeting, and performance evaluation.
Example of Cost Assignment
Let’s consider an example of cost assignment at a bakery called “BreadHeaven” that produces two types of bread: white bread and whole wheat bread.
BreadHeaven incurs various direct and indirect costs to produce the bread. Here’s how the company would assign these costs to the two types of bread:
- Direct cost assignment:
Direct costs can be specifically traced to each type of bread. In this case, the direct costs include:
- Direct materials: BreadHeaven purchases flour, yeast, salt, and other ingredients required to make the bread. The cost of these ingredients can be directly traced to each type of bread.
- Direct labor: BreadHeaven employs bakers who are directly involved in making the bread. The wages paid to these bakers can be directly traced to each type of bread based on the time spent working on each bread type.
For example, if BreadHeaven spent $2,000 on direct materials and $1,500 on direct labor for white bread, and $3,000 on direct materials and $2,500 on direct labor for whole wheat bread, these costs would be directly assigned to each bread type.
- Indirect cost assignment (Cost allocation):
Indirect costs, such as rent, utilities, equipment maintenance, and administrative expenses, cannot be directly traced to each type of bread. BreadHeaven uses a cost allocation method to assign these costs to the two types of bread.
Suppose the total indirect costs for the month are $6,000. BreadHeaven decides to use the number of loaves produced as the allocation base , as it believes that indirect costs are driven by the production volume. During the month, the bakery produces 3,000 loaves of white bread and 2,000 loaves of whole wheat bread, totaling 5,000 loaves.
The allocation rate per loaf is:
Allocation Rate = Total Indirect Costs / Total Loaves Allocation Rate = $6,000 / 5,000 loaves = $1.20 per loaf
BreadHeaven allocates the indirect costs to each type of bread using the allocation rate and the number of loaves produced:
- White bread: 3,000 loaves × $1.20 per loaf = $3,600
- Whole wheat bread: 2,000 loaves × $1.20 per loaf = $2,400
After completing the cost assignment, BreadHeaven can determine the total costs for each type of bread:
- White bread: $2,000 (direct materials) + $1,500 (direct labor) + $3,600 (indirect costs) = $7,100
- Whole wheat bread: $3,000 (direct materials) + $2,500 (direct labor) + $2,400 (indirect costs) = $7,900
By assigning both direct and indirect costs to each type of bread, BreadHeaven gains a better understanding of the full cost of producing each bread type, which can inform pricing decisions, resource allocation, and performance evaluation.
Other Posts You'll Like...

REG CPA Exam: Example Scenarios to Identify the Remedy Available for a Breach of Contract

REG CPA Exam: Example Scenarios Involving a Breach of Contract

REG CPA Exam: Understanding the Available Remedies for the Breach of a Contract

REG CPA Exam: Understanding Whether Both Parties to a Contract Have Fulfilled Their Performance Obligations

REG CPA Exam: Example Scenarios of Whether a Contract Has Been Discharged

REG CPA Exam: Understanding the Ways a Contract Can Be Discharged
Helpful links.
- Learn to Study "Strategically"
- How to Pass a Failed CPA Exam
- Samples of SFCPA Study Tools
- SuperfastCPA Podcast

“I Shouldn’t Be Able to Do This”: How Colbi Passed Her CPA Exams

The 5 Biggest Myths About CPA Exam Study

From 8 Hours a Day to 8 Hours a Week, How Branden Passed His CPA Exams

5 High Impact CPA Study Strategies

How Melodie Passed Her CPA Exams by Making Every Morning Count

Inconsistent CPA Study? Try These 4 Strategies
Want to pass as fast as possible, ( and avoid failing sections ), watch one of our free "study hacks" trainings for a free walkthrough of the superfastcpa study methods that have helped so many candidates pass their sections faster and avoid failing scores....

Make Your Study Process Easier and more effective with SuperfastCPA
Take Your CPA Exams with Confidence
- Free "Study Hacks" Training
- SuperfastCPA PRO Course
- SuperfastCPA Review Notes
- SuperfastCPA Audio Notes
- SuperfastCPA Quizzes
Get Started
- Free "Study Hacks Training"
- Read Reviews of SuperfastCPA
- Busy Candidate's Guide to Passing
- Subscribe to the Podcast
- Purchase Now
- Nate's Story
- Interviews with SFCPA Customers
- Our Study Methods
- SuperfastCPA Reviews
- CPA Score Release Dates
- The "Best" CPA Review Course
- Do You Really Need the CPA License?
- 7 Habits of Successful Candidates
- "Deep Work" & CPA Study
- More from M-W
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
assignation
Definition of assignation
- appointment
Examples of assignation in a Sentence
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'assignation.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Word History
15th century, in the meaning defined at sense 1
Dictionary Entries Near assignation
assigned risk
Cite this Entry
“Assignation.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/assignation. Accessed 9 Jul. 2024.
More from Merriam-Webster on assignation
Nglish: Translation of assignation for Spanish Speakers
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
Plural and possessive names: a guide, commonly misspelled words, how to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), absent letters that are heard anyway, how to use accents and diacritical marks, popular in wordplay, it's a scorcher words for the summer heat, flower etymologies for your spring garden, 12 star wars words, 'swash', 'praya', and 12 more beachy words, 8 words for lesser-known musical instruments, games & quizzes.

- Marketing Strategy
- Five Forces
- Business Lists
- Competitors
- Business Concepts
- Human Resources (HR)
- Global Assignment
Global Assignment - Meaning, Importance, Steps & Example
What is global assignment.
Global assignments are business projects which are allotted to some employees outside the home country. Global assignments are employers assigning their employees on projects which are globally implemented. Global assignments are mostly taken place in multinational companies and may involve employees to relocate from their current country to a different country where the assignment is assigned.
Since globalization has taken place rapidly and the world has become more connected, it has become a very common phenomenon. Many countries face skill shortage or require an expert for a particular assignment so they would hire the person with the requisite skills or knowledge from other countries and pay the person a hefty compensation as demanded by the person.
Steps in Managing Global Assignment
Some steps in managing global assignments & international projects are:
1. Evaluating objectives of the international project
2. Identifying team members & giving pre-requisite training
3. Pre-departure preparation of activities & work to be done
4. On job activities on global assignment at international location
5. Project completion
6. Evaluation & reassignment if required
Importance of Global Assignment
Global assignments as identified by experts in international human resource management are of three types
1. Technical assignments: Employees may be assigned global assignments if they have the technical skills that are required by the MNC for a particular assignment and the MNC is not able to find anyone as capable as that person internally and in that particular country, if a person is located within the MNC in another country then that person is sent on a technical assignment.
2. Developmental assignments: Developmental assignments are typically used to develop a project or concept that is new to a different location or develop skills in a different location which is not implemented in that location, it is also used by institutes to bring in faculties from different parts of the globe to give the students an exposure to different perspectives and cultures and their thoughts on the scenario of the subject.
3. Strategic Assignments are global assignments in which a key partner is sent to launch a product in a key location, develop the market or get necessary changes in the business strategy or even sign Memorandum of Understandings and Joint Venture deals.
Advantages of Global Assignments
Some advantages of global assignments are
1. Skills and knowledge which are not available in a country can be brought from other countries.
2. MNC’s are able to get their projects done more effectively and not having the problem of talent not being available.
3. Employees may be motivated to join an MNC which assigns global assignments to its employees regularly.
Example of Global Assignment
Here is an example of global assignment for a hypothetical organization Company A. Company A could not find a person who could communicate in French, German and Hindi in their main headquarters in USA as they felt that there would be a gap in understanding if the language is translated to English, and then to either of these languages. So, since they did not find the any person who had proficiency in these three languages in their headquarters and started finding for a person with the language skills throughout all their office. Company A found a person in their international office in India with the knowledge in these three languages. So, they assigned her the project under a global assignment and she was asked to relocate to the main headquarters located in the United States for the duration of the project.
Hence, this concludes the definition of Global Assignment along with its overview.
This article has been researched & authored by the Business Concepts Team . It has been reviewed & published by the MBA Skool Team. The content on MBA Skool has been created for educational & academic purpose only.
Browse the definition and meaning of more similar terms. The Management Dictionary covers over 1800 business concepts from 5 categories.
Continue Reading:
- Job Description
- Compensation and Benefits
- Career Development
- 360 Degree Feedback
- Employee Training
- Marketing & Strategy Terms
- Human Resources (HR) Terms
- Operations & SCM Terms
- IT & Systems Terms
- Statistics Terms
What is MBA Skool? About Us
MBA Skool is a Knowledge Resource for Management Students, Aspirants & Professionals.
Business Courses
- Operations & SCM
- Human Resources
Quizzes & Skills
- Management Quizzes
- Skills Tests
Quizzes test your expertise in business and Skill tests evaluate your management traits
Related Content
- Inventory Costs
- Sales Quota
- Quality Control
- Training and Development
- Capacity Management
- Work Life Balance
- More Definitions
All Business Sections
- SWOT Analysis
- Marketing Strategy & Mix
- PESTLE Analysis
- Five Forces Analysis
- Top Brand Lists
Write for Us
- Submit Content
- Privacy Policy
- Contribute Content
- Web Stories
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Meaning of assign in English
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
assign verb [T] ( CHOOSE )
- Every available officer will be assigned to the investigation .
- The textbooks were assigned by the course director .
- Part of the group were assigned to clear land mines .
- Each trainee is assigned a mentor who will help them learn more about the job .
- We were assigned an interpreter for the duration of our stay .
- accommodate
- accommodate someone with something
- administration
- arm someone with something
- be good for something idiom
- hand something around
- hand something back
- hand something down
- hand something in
- put something on
- re-equipment
- reassignment
You can also find related words, phrases, and synonyms in the topics:
assign verb [T] ( SEND )
- She was assigned to the Paris office .
- All the team were assigned to Poland.
- advertisement
- employment agency
- recruitment drive
- reinstatement
- relocation expenses
assign verb [T] ( COMPUTING )
- 3-D printing
- adaptive learning
- additive manufacturing
- hexadecimal
- hill climbing
- telerobotics
- word processing
assign verb [T] ( GIVE LEGALLY )
Phrasal verb, assign | american dictionary, assign | business english, examples of assign, translations of assign.
Get a quick, free translation!

Word of the Day
an expression of surprise or feeling sorry about a mistake or slight accident

Fakes and forgeries (Things that are not what they seem to be)

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
- assign (CHOOSE)
- assign (SEND)
- assign (COMPUTING)
- assign (GIVE LEGALLY)
- American Verb
- Business Verb
- Translations
- All translations
To add assign to a word list please sign up or log in.
Add assign to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- Random Assignment in Experiments | Introduction & Examples
Random Assignment in Experiments | Introduction & Examples
Published on March 8, 2021 by Pritha Bhandari . Revised on June 22, 2023.
In experimental research, random assignment is a way of placing participants from your sample into different treatment groups using randomization.
With simple random assignment, every member of the sample has a known or equal chance of being placed in a control group or an experimental group. Studies that use simple random assignment are also called completely randomized designs .
Random assignment is a key part of experimental design . It helps you ensure that all groups are comparable at the start of a study: any differences between them are due to random factors, not research biases like sampling bias or selection bias .
Table of contents
Why does random assignment matter, random sampling vs random assignment, how do you use random assignment, when is random assignment not used, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about random assignment.
Random assignment is an important part of control in experimental research, because it helps strengthen the internal validity of an experiment and avoid biases.
In experiments, researchers manipulate an independent variable to assess its effect on a dependent variable, while controlling for other variables. To do so, they often use different levels of an independent variable for different groups of participants.
This is called a between-groups or independent measures design.
You use three groups of participants that are each given a different level of the independent variable:
- a control group that’s given a placebo (no dosage, to control for a placebo effect ),
- an experimental group that’s given a low dosage,
- a second experimental group that’s given a high dosage.
Random assignment to helps you make sure that the treatment groups don’t differ in systematic ways at the start of the experiment, as this can seriously affect (and even invalidate) your work.
If you don’t use random assignment, you may not be able to rule out alternative explanations for your results.
- participants recruited from cafes are placed in the control group ,
- participants recruited from local community centers are placed in the low dosage experimental group,
- participants recruited from gyms are placed in the high dosage group.
With this type of assignment, it’s hard to tell whether the participant characteristics are the same across all groups at the start of the study. Gym-users may tend to engage in more healthy behaviors than people who frequent cafes or community centers, and this would introduce a healthy user bias in your study.
Although random assignment helps even out baseline differences between groups, it doesn’t always make them completely equivalent. There may still be extraneous variables that differ between groups, and there will always be some group differences that arise from chance.
Most of the time, the random variation between groups is low, and, therefore, it’s acceptable for further analysis. This is especially true when you have a large sample. In general, you should always use random assignment in experiments when it is ethically possible and makes sense for your study topic.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Random sampling and random assignment are both important concepts in research, but it’s important to understand the difference between them.
Random sampling (also called probability sampling or random selection) is a way of selecting members of a population to be included in your study. In contrast, random assignment is a way of sorting the sample participants into control and experimental groups.
While random sampling is used in many types of studies, random assignment is only used in between-subjects experimental designs.
Some studies use both random sampling and random assignment, while others use only one or the other.
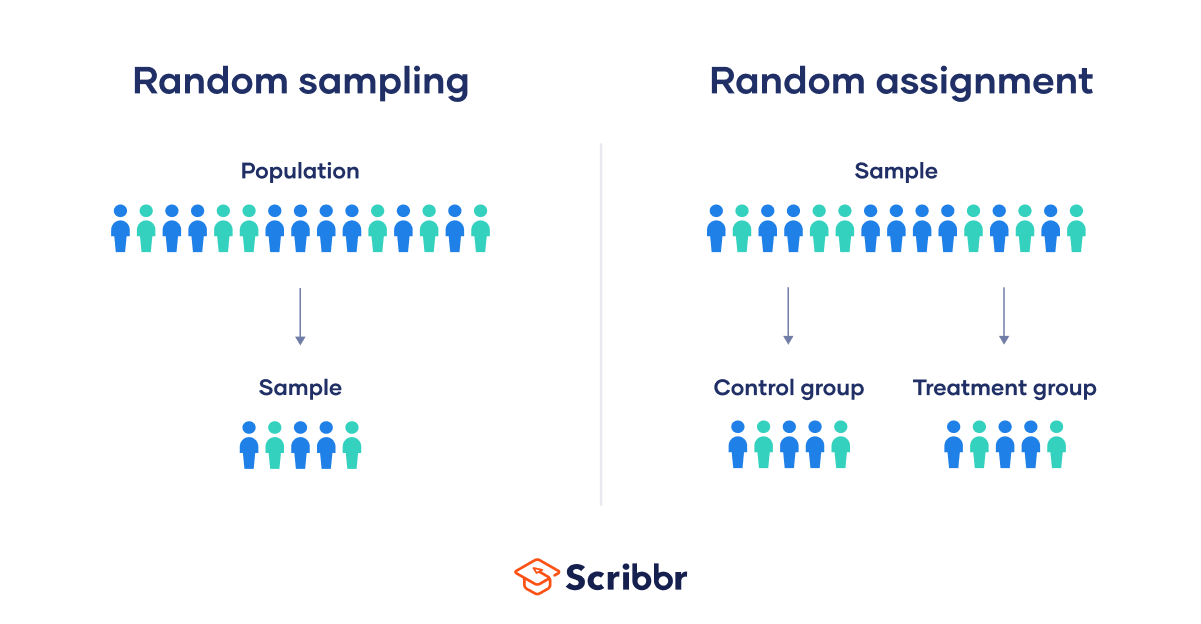
Random sampling enhances the external validity or generalizability of your results, because it helps ensure that your sample is unbiased and representative of the whole population. This allows you to make stronger statistical inferences .
You use a simple random sample to collect data. Because you have access to the whole population (all employees), you can assign all 8000 employees a number and use a random number generator to select 300 employees. These 300 employees are your full sample.
Random assignment enhances the internal validity of the study, because it ensures that there are no systematic differences between the participants in each group. This helps you conclude that the outcomes can be attributed to the independent variable .
- a control group that receives no intervention.
- an experimental group that has a remote team-building intervention every week for a month.
You use random assignment to place participants into the control or experimental group. To do so, you take your list of participants and assign each participant a number. Again, you use a random number generator to place each participant in one of the two groups.
To use simple random assignment, you start by giving every member of the sample a unique number. Then, you can use computer programs or manual methods to randomly assign each participant to a group.
- Random number generator: Use a computer program to generate random numbers from the list for each group.
- Lottery method: Place all numbers individually in a hat or a bucket, and draw numbers at random for each group.
- Flip a coin: When you only have two groups, for each number on the list, flip a coin to decide if they’ll be in the control or the experimental group.
- Use a dice: When you have three groups, for each number on the list, roll a dice to decide which of the groups they will be in. For example, assume that rolling 1 or 2 lands them in a control group; 3 or 4 in an experimental group; and 5 or 6 in a second control or experimental group.
This type of random assignment is the most powerful method of placing participants in conditions, because each individual has an equal chance of being placed in any one of your treatment groups.
Random assignment in block designs
In more complicated experimental designs, random assignment is only used after participants are grouped into blocks based on some characteristic (e.g., test score or demographic variable). These groupings mean that you need a larger sample to achieve high statistical power .
For example, a randomized block design involves placing participants into blocks based on a shared characteristic (e.g., college students versus graduates), and then using random assignment within each block to assign participants to every treatment condition. This helps you assess whether the characteristic affects the outcomes of your treatment.
In an experimental matched design , you use blocking and then match up individual participants from each block based on specific characteristics. Within each matched pair or group, you randomly assign each participant to one of the conditions in the experiment and compare their outcomes.
Sometimes, it’s not relevant or ethical to use simple random assignment, so groups are assigned in a different way.
When comparing different groups
Sometimes, differences between participants are the main focus of a study, for example, when comparing men and women or people with and without health conditions. Participants are not randomly assigned to different groups, but instead assigned based on their characteristics.
In this type of study, the characteristic of interest (e.g., gender) is an independent variable, and the groups differ based on the different levels (e.g., men, women, etc.). All participants are tested the same way, and then their group-level outcomes are compared.
When it’s not ethically permissible
When studying unhealthy or dangerous behaviors, it’s not possible to use random assignment. For example, if you’re studying heavy drinkers and social drinkers, it’s unethical to randomly assign participants to one of the two groups and ask them to drink large amounts of alcohol for your experiment.
When you can’t assign participants to groups, you can also conduct a quasi-experimental study . In a quasi-experiment, you study the outcomes of pre-existing groups who receive treatments that you may not have any control over (e.g., heavy drinkers and social drinkers). These groups aren’t randomly assigned, but may be considered comparable when some other variables (e.g., age or socioeconomic status) are controlled for.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Student’s t -distribution
- Normal distribution
- Null and Alternative Hypotheses
- Chi square tests
- Confidence interval
- Quartiles & Quantiles
- Cluster sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Data cleansing
- Reproducibility vs Replicability
- Peer review
- Prospective cohort study
Research bias
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Placebo effect
- Hawthorne effect
- Hindsight bias
- Affect heuristic
- Social desirability bias
In experimental research, random assignment is a way of placing participants from your sample into different groups using randomization. With this method, every member of the sample has a known or equal chance of being placed in a control group or an experimental group.
Random selection, or random sampling , is a way of selecting members of a population for your study’s sample.
In contrast, random assignment is a way of sorting the sample into control and experimental groups.
Random sampling enhances the external validity or generalizability of your results, while random assignment improves the internal validity of your study.
Random assignment is used in experiments with a between-groups or independent measures design. In this research design, there’s usually a control group and one or more experimental groups. Random assignment helps ensure that the groups are comparable.
In general, you should always use random assignment in this type of experimental design when it is ethically possible and makes sense for your study topic.
To implement random assignment , assign a unique number to every member of your study’s sample .
Then, you can use a random number generator or a lottery method to randomly assign each number to a control or experimental group. You can also do so manually, by flipping a coin or rolling a dice to randomly assign participants to groups.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Bhandari, P. (2023, June 22). Random Assignment in Experiments | Introduction & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved July 8, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/random-assignment/
Is this article helpful?

Pritha Bhandari
Other students also liked, guide to experimental design | overview, steps, & examples, confounding variables | definition, examples & controls, control groups and treatment groups | uses & examples, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
- Administering Payroll for the United Kingdom
How the Local and Global Transfer Process Handles Copy Failures
The Local and Global Transfer process logs any success, warning, and error messages in the Change Legal Employer Dashboard.
As part of transferring a worker, the Local and Global Transfer process:
Creates the appropriate employment records on the target, including an assignment, payroll definition, and payroll relationship.
If the process encounters an error when creating these records, it logs the error in the Change Legal Employer Dashboard and stops.
Copies the payroll data to the target.
This includes personal payment methods, person costing overrides, and element entries.
If a payment method encounters an error, the process doesn't copy the data.
For all other payroll data, the copy continues even if one of the records fails. It doesn't reverse the transaction.
Related Topics
- What Happens to Calculation Cards During Employee Transfers
- What Happens to Costing Overrides During Person Transfers
- What Happens to Element Entries During Person Transfers
- What Happens to Payment Methods During Person Transfers
- Dashboard for Legal Employer Change
- How the Local and Global Transfer Process Handles Payroll Details

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Assignment (law) Assignment [a] is a legal term used in the context of the laws of contract and of property. In both instances, assignment is the process whereby a person, the assignor, transfers rights or benefits to another, the assignee. [1] An assignment may not transfer a duty, burden or detriment without the express agreement of the assignee.
What this handout is about. The first step in any successful college writing venture is reading the assignment. While this sounds like a simple task, it can be a tough one. This handout will help you unravel your assignment and begin to craft an effective response. Much of the following advice will involve translating typical assignment terms ...
An assignment of contract is a legal term that describes the process that occurs when the original party (assignor) transfers their rights and obligations under their contract to a third party (assignee). When an assignment of contract happens, the original party is relieved of their contractual duties, and their role is replaced by the ...
The meaning of ASSIGNMENT is the act of assigning something. How to use assignment in a sentence. Synonym Discussion of Assignment.
Assignments: The Basic Law. The assignment of a right or obligation is a common contractual event under the law and the right to assign (or prohibition against assignments) is found in the majority of agreements, leases and business structural documents created in the United States. As with many terms commonly used, people are familiar with the ...
Table of contents. Step 1: Prewriting. Step 2: Planning and outlining. Step 3: Writing a first draft. Step 4: Redrafting and revising. Step 5: Editing and proofreading. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the writing process.
Assignment Method Explained. The assignment method in operation research is a strategy for allocating organizational resources to tasks to increase profit via efficiency gains, cost reductions, and improved handling of operations that might create bottlenecks.It is an operations management tool that, by allocating jobs to the appropriate individual, minimizes expenses, time, and effort.
IP Assignment Agreement has the meaning set forth in Section 3.2 (a) (iii). Assignment and Acceptance means an assignment and acceptance entered into by a Lender and an Eligible Assignee, and accepted by the Agent, in substantially the form of Exhibit C hereto. Define Assignment Process. Included in the "Assignment Process" are all teachers ...
Assignment: An assignment is the transfer of an individual's rights or property to another person or business. For example, when an option contract is assigned, an option writer has an obligation ...
Assignment definition: something assigned, as a particular task or duty. See examples of ASSIGNMENT used in a sentence.
assignment meaning: a piece of work or job that you are given to do: . Learn more.
assign: [verb] to transfer (property) to another especially in trust or for the benefit of creditors.
ASSIGNMENT definition: 1. a piece of work given to someone, typically as part of their studies or job: 2. a job that…. Learn more.
7 meanings: 1. something that has been assigned, such as a mission or task 2. a position or post to which a person is assigned.... Click for more definitions.
The writing process refers to a series of actions taken by writers to move from an assignment or idea to a polished product. The writing process definition outlines stages used by most writers to ...
The Definition of Random Assignment According to Psychology. Random assignment refers to the use of chance procedures in psychology experiments to ensure that each participant has the same opportunity to be assigned to any given group in a study to eliminate any potential bias in the experiment at the outset. Participants are randomly assigned ...
ASSIGNMENT meaning: 1. a piece of work given to someone, typically as part of their studies or job: 2. a job that…. Learn more.
Role assignments in Process Street are built to make assigning people to their tasks easier than ever. Instead of having to edit your process templates to assign a new person, you can define a role to assign to a task and then define who will fill that role using a couple of different parameters.
Cost Assignment. Cost assignment is the process of associating costs with cost objects, such as products, services, departments, or projects. It encompasses the identification, measurement, and allocation of both direct and indirect costs to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the resources consumed by various cost objects within an organization.
assignation: [noun] the act of assigning or the assignment made.
Some steps in managing global assignments & international projects are: 1. Evaluating objectives of the international project. 2. Identifying team members & giving pre-requisite training. 3. Pre-departure preparation of activities & work to be done. 4. On job activities on global assignment at international location.
ASSIGN definition: 1. to give a particular job or piece of work to someone: 2. If you assign a time for a job or…. Learn more.
Random sampling (also called probability sampling or random selection) is a way of selecting members of a population to be included in your study. In contrast, random assignment is a way of sorting the sample participants into control and experimental groups. While random sampling is used in many types of studies, random assignment is only used ...
If a payment method encounters an error, the process doesn't copy the data. For all other payroll data, the copy continues even if one of the records fails. It doesn't reverse the transaction.