Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey


What is a Research Problem? Characteristics, Types, and Examples

A research problem is a gap in existing knowledge, a contradiction in an established theory, or a real-world challenge that a researcher aims to address in their research. It is at the heart of any scientific inquiry, directing the trajectory of an investigation. The statement of a problem orients the reader to the importance of the topic, sets the problem into a particular context, and defines the relevant parameters, providing the framework for reporting the findings. Therein lies the importance of research problem s.
The formulation of well-defined research questions is central to addressing a research problem . A research question is a statement made in a question form to provide focus, clarity, and structure to the research endeavor. This helps the researcher design methodologies, collect data, and analyze results in a systematic and coherent manner. A study may have one or more research questions depending on the nature of the study.

Identifying and addressing a research problem is very important. By starting with a pertinent problem , a scholar can contribute to the accumulation of evidence-based insights, solutions, and scientific progress, thereby advancing the frontier of research. Moreover, the process of formulating research problems and posing pertinent research questions cultivates critical thinking and hones problem-solving skills.
Table of Contents
What is a Research Problem ?
Before you conceive of your project, you need to ask yourself “ What is a research problem ?” A research problem definition can be broadly put forward as the primary statement of a knowledge gap or a fundamental challenge in a field, which forms the foundation for research. Conversely, the findings from a research investigation provide solutions to the problem .
A research problem guides the selection of approaches and methodologies, data collection, and interpretation of results to find answers or solutions. A well-defined problem determines the generation of valuable insights and contributions to the broader intellectual discourse.
Characteristics of a Research Problem
Knowing the characteristics of a research problem is instrumental in formulating a research inquiry; take a look at the five key characteristics below:
Novel : An ideal research problem introduces a fresh perspective, offering something new to the existing body of knowledge. It should contribute original insights and address unresolved matters or essential knowledge.
Significant : A problem should hold significance in terms of its potential impact on theory, practice, policy, or the understanding of a particular phenomenon. It should be relevant to the field of study, addressing a gap in knowledge, a practical concern, or a theoretical dilemma that holds significance.
Feasible: A practical research problem allows for the formulation of hypotheses and the design of research methodologies. A feasible research problem is one that can realistically be investigated given the available resources, time, and expertise. It should not be too broad or too narrow to explore effectively, and should be measurable in terms of its variables and outcomes. It should be amenable to investigation through empirical research methods, such as data collection and analysis, to arrive at meaningful conclusions A practical research problem considers budgetary and time constraints, as well as limitations of the problem . These limitations may arise due to constraints in methodology, resources, or the complexity of the problem.
Clear and specific : A well-defined research problem is clear and specific, leaving no room for ambiguity; it should be easily understandable and precisely articulated. Ensuring specificity in the problem ensures that it is focused, addresses a distinct aspect of the broader topic and is not vague.
Rooted in evidence: A good research problem leans on trustworthy evidence and data, while dismissing unverifiable information. It must also consider ethical guidelines, ensuring the well-being and rights of any individuals or groups involved in the study.

Types of Research Problems
Across fields and disciplines, there are different types of research problems . We can broadly categorize them into three types.
- Theoretical research problems
Theoretical research problems deal with conceptual and intellectual inquiries that may not involve empirical data collection but instead seek to advance our understanding of complex concepts, theories, and phenomena within their respective disciplines. For example, in the social sciences, research problem s may be casuist (relating to the determination of right and wrong in questions of conduct or conscience), difference (comparing or contrasting two or more phenomena), descriptive (aims to describe a situation or state), or relational (investigating characteristics that are related in some way).
Here are some theoretical research problem examples :
- Ethical frameworks that can provide coherent justifications for artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms, especially in contexts involving autonomous decision-making and moral agency.
- Determining how mathematical models can elucidate the gradual development of complex traits, such as intricate anatomical structures or elaborate behaviors, through successive generations.
- Applied research problems
Applied or practical research problems focus on addressing real-world challenges and generating practical solutions to improve various aspects of society, technology, health, and the environment.
Here are some applied research problem examples :
- Studying the use of precision agriculture techniques to optimize crop yield and minimize resource waste.
- Designing a more energy-efficient and sustainable transportation system for a city to reduce carbon emissions.
- Action research problems
Action research problems aim to create positive change within specific contexts by involving stakeholders, implementing interventions, and evaluating outcomes in a collaborative manner.
Here are some action research problem examples :
- Partnering with healthcare professionals to identify barriers to patient adherence to medication regimens and devising interventions to address them.
- Collaborating with a nonprofit organization to evaluate the effectiveness of their programs aimed at providing job training for underserved populations.
These different types of research problems may give you some ideas when you plan on developing your own.
How to Define a Research Problem
You might now ask “ How to define a research problem ?” These are the general steps to follow:
- Look for a broad problem area: Identify under-explored aspects or areas of concern, or a controversy in your topic of interest. Evaluate the significance of addressing the problem in terms of its potential contribution to the field, practical applications, or theoretical insights.
- Learn more about the problem: Read the literature, starting from historical aspects to the current status and latest updates. Rely on reputable evidence and data. Be sure to consult researchers who work in the relevant field, mentors, and peers. Do not ignore the gray literature on the subject.
- Identify the relevant variables and how they are related: Consider which variables are most important to the study and will help answer the research question. Once this is done, you will need to determine the relationships between these variables and how these relationships affect the research problem .
- Think of practical aspects : Deliberate on ways that your study can be practical and feasible in terms of time and resources. Discuss practical aspects with researchers in the field and be open to revising the problem based on feedback. Refine the scope of the research problem to make it manageable and specific; consider the resources available, time constraints, and feasibility.
- Formulate the problem statement: Craft a concise problem statement that outlines the specific issue, its relevance, and why it needs further investigation.
- Stick to plans, but be flexible: When defining the problem , plan ahead but adhere to your budget and timeline. At the same time, consider all possibilities and ensure that the problem and question can be modified if needed.

Key Takeaways
- A research problem concerns an area of interest, a situation necessitating improvement, an obstacle requiring eradication, or a challenge in theory or practical applications.
- The importance of research problem is that it guides the research and helps advance human understanding and the development of practical solutions.
- Research problem definition begins with identifying a broad problem area, followed by learning more about the problem, identifying the variables and how they are related, considering practical aspects, and finally developing the problem statement.
- Different types of research problems include theoretical, applied, and action research problems , and these depend on the discipline and nature of the study.
- An ideal problem is original, important, feasible, specific, and based on evidence.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is it important to define a research problem?
Identifying potential issues and gaps as research problems is important for choosing a relevant topic and for determining a well-defined course of one’s research. Pinpointing a problem and formulating research questions can help researchers build their critical thinking, curiosity, and problem-solving abilities.
How do I identify a research problem?
Identifying a research problem involves recognizing gaps in existing knowledge, exploring areas of uncertainty, and assessing the significance of addressing these gaps within a specific field of study. This process often involves thorough literature review, discussions with experts, and considering practical implications.
Can a research problem change during the research process?
Yes, a research problem can change during the research process. During the course of an investigation a researcher might discover new perspectives, complexities, or insights that prompt a reevaluation of the initial problem. The scope of the problem, unforeseen or unexpected issues, or other limitations might prompt some tweaks. You should be able to adjust the problem to ensure that the study remains relevant and aligned with the evolving understanding of the subject matter.
How does a research problem relate to research questions or hypotheses?
A research problem sets the stage for the study. Next, research questions refine the direction of investigation by breaking down the broader research problem into manageable components. Research questions are formulated based on the problem , guiding the investigation’s scope and objectives. The hypothesis provides a testable statement to validate or refute within the research process. All three elements are interconnected and work together to guide the research.
R Discovery is a literature search and research reading platform that accelerates your research discovery journey by keeping you updated on the latest, most relevant scholarly content. With 250M+ research articles sourced from trusted aggregators like CrossRef, Unpaywall, PubMed, PubMed Central, Open Alex and top publishing houses like Springer Nature, JAMA, IOP, Taylor & Francis, NEJM, BMJ, Karger, SAGE, Emerald Publishing and more, R Discovery puts a world of research at your fingertips.
Try R Discovery Prime FREE for 1 week or upgrade at just US$72 a year to access premium features that let you listen to research on the go, read in your language, collaborate with peers, auto sync with reference managers, and much more. Choose a simpler, smarter way to find and read research – Download the app and start your free 7-day trial today !
Related Posts

How Publishers Can Enhance Reader Engagement with R Discovery’s Article Recommendation System

Turabian Format: A Beginner’s Guide
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Problem – Examples, Types and Guide
Research Problem – Examples, Types and Guide
Table of Contents

Research Problem
Definition:
Research problem is a specific and well-defined issue or question that a researcher seeks to investigate through research. It is the starting point of any research project, as it sets the direction, scope, and purpose of the study.
Types of Research Problems
Types of Research Problems are as follows:
Descriptive problems
These problems involve describing or documenting a particular phenomenon, event, or situation. For example, a researcher might investigate the demographics of a particular population, such as their age, gender, income, and education.
Exploratory problems
These problems are designed to explore a particular topic or issue in depth, often with the goal of generating new ideas or hypotheses. For example, a researcher might explore the factors that contribute to job satisfaction among employees in a particular industry.
Explanatory Problems
These problems seek to explain why a particular phenomenon or event occurs, and they typically involve testing hypotheses or theories. For example, a researcher might investigate the relationship between exercise and mental health, with the goal of determining whether exercise has a causal effect on mental health.
Predictive Problems
These problems involve making predictions or forecasts about future events or trends. For example, a researcher might investigate the factors that predict future success in a particular field or industry.
Evaluative Problems
These problems involve assessing the effectiveness of a particular intervention, program, or policy. For example, a researcher might evaluate the impact of a new teaching method on student learning outcomes.
How to Define a Research Problem
Defining a research problem involves identifying a specific question or issue that a researcher seeks to address through a research study. Here are the steps to follow when defining a research problem:
- Identify a broad research topic : Start by identifying a broad topic that you are interested in researching. This could be based on your personal interests, observations, or gaps in the existing literature.
- Conduct a literature review : Once you have identified a broad topic, conduct a thorough literature review to identify the current state of knowledge in the field. This will help you identify gaps or inconsistencies in the existing research that can be addressed through your study.
- Refine the research question: Based on the gaps or inconsistencies identified in the literature review, refine your research question to a specific, clear, and well-defined problem statement. Your research question should be feasible, relevant, and important to the field of study.
- Develop a hypothesis: Based on the research question, develop a hypothesis that states the expected relationship between variables.
- Define the scope and limitations: Clearly define the scope and limitations of your research problem. This will help you focus your study and ensure that your research objectives are achievable.
- Get feedback: Get feedback from your advisor or colleagues to ensure that your research problem is clear, feasible, and relevant to the field of study.
Components of a Research Problem
The components of a research problem typically include the following:
- Topic : The general subject or area of interest that the research will explore.
- Research Question : A clear and specific question that the research seeks to answer or investigate.
- Objective : A statement that describes the purpose of the research, what it aims to achieve, and the expected outcomes.
- Hypothesis : An educated guess or prediction about the relationship between variables, which is tested during the research.
- Variables : The factors or elements that are being studied, measured, or manipulated in the research.
- Methodology : The overall approach and methods that will be used to conduct the research.
- Scope and Limitations : A description of the boundaries and parameters of the research, including what will be included and excluded, and any potential constraints or limitations.
- Significance: A statement that explains the potential value or impact of the research, its contribution to the field of study, and how it will add to the existing knowledge.
Research Problem Examples
Following are some Research Problem Examples:
Research Problem Examples in Psychology are as follows:
- Exploring the impact of social media on adolescent mental health.
- Investigating the effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy for treating anxiety disorders.
- Studying the impact of prenatal stress on child development outcomes.
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to addiction and relapse in substance abuse treatment.
- Examining the impact of personality traits on romantic relationships.
Research Problem Examples in Sociology are as follows:
- Investigating the relationship between social support and mental health outcomes in marginalized communities.
- Studying the impact of globalization on labor markets and employment opportunities.
- Analyzing the causes and consequences of gentrification in urban neighborhoods.
- Investigating the impact of family structure on social mobility and economic outcomes.
- Examining the effects of social capital on community development and resilience.
Research Problem Examples in Economics are as follows:
- Studying the effects of trade policies on economic growth and development.
- Analyzing the impact of automation and artificial intelligence on labor markets and employment opportunities.
- Investigating the factors that contribute to economic inequality and poverty.
- Examining the impact of fiscal and monetary policies on inflation and economic stability.
- Studying the relationship between education and economic outcomes, such as income and employment.
Political Science
Research Problem Examples in Political Science are as follows:
- Analyzing the causes and consequences of political polarization and partisan behavior.
- Investigating the impact of social movements on political change and policymaking.
- Studying the role of media and communication in shaping public opinion and political discourse.
- Examining the effectiveness of electoral systems in promoting democratic governance and representation.
- Investigating the impact of international organizations and agreements on global governance and security.
Environmental Science
Research Problem Examples in Environmental Science are as follows:
- Studying the impact of air pollution on human health and well-being.
- Investigating the effects of deforestation on climate change and biodiversity loss.
- Analyzing the impact of ocean acidification on marine ecosystems and food webs.
- Studying the relationship between urban development and ecological resilience.
- Examining the effectiveness of environmental policies and regulations in promoting sustainability and conservation.
Research Problem Examples in Education are as follows:
- Investigating the impact of teacher training and professional development on student learning outcomes.
- Studying the effectiveness of technology-enhanced learning in promoting student engagement and achievement.
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to achievement gaps and educational inequality.
- Examining the impact of parental involvement on student motivation and achievement.
- Studying the effectiveness of alternative educational models, such as homeschooling and online learning.
Research Problem Examples in History are as follows:
- Analyzing the social and economic factors that contributed to the rise and fall of ancient civilizations.
- Investigating the impact of colonialism on indigenous societies and cultures.
- Studying the role of religion in shaping political and social movements throughout history.
- Analyzing the impact of the Industrial Revolution on economic and social structures.
- Examining the causes and consequences of global conflicts, such as World War I and II.
Research Problem Examples in Business are as follows:
- Studying the impact of corporate social responsibility on brand reputation and consumer behavior.
- Investigating the effectiveness of leadership development programs in improving organizational performance and employee satisfaction.
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful entrepreneurship and small business development.
- Examining the impact of mergers and acquisitions on market competition and consumer welfare.
- Studying the effectiveness of marketing strategies and advertising campaigns in promoting brand awareness and sales.
Research Problem Example for Students
An Example of a Research Problem for Students could be:
“How does social media usage affect the academic performance of high school students?”
This research problem is specific, measurable, and relevant. It is specific because it focuses on a particular area of interest, which is the impact of social media on academic performance. It is measurable because the researcher can collect data on social media usage and academic performance to evaluate the relationship between the two variables. It is relevant because it addresses a current and important issue that affects high school students.
To conduct research on this problem, the researcher could use various methods, such as surveys, interviews, and statistical analysis of academic records. The results of the study could provide insights into the relationship between social media usage and academic performance, which could help educators and parents develop effective strategies for managing social media use among students.
Another example of a research problem for students:
“Does participation in extracurricular activities impact the academic performance of middle school students?”
This research problem is also specific, measurable, and relevant. It is specific because it focuses on a particular type of activity, extracurricular activities, and its impact on academic performance. It is measurable because the researcher can collect data on students’ participation in extracurricular activities and their academic performance to evaluate the relationship between the two variables. It is relevant because extracurricular activities are an essential part of the middle school experience, and their impact on academic performance is a topic of interest to educators and parents.
To conduct research on this problem, the researcher could use surveys, interviews, and academic records analysis. The results of the study could provide insights into the relationship between extracurricular activities and academic performance, which could help educators and parents make informed decisions about the types of activities that are most beneficial for middle school students.
Applications of Research Problem
Applications of Research Problem are as follows:
- Academic research: Research problems are used to guide academic research in various fields, including social sciences, natural sciences, humanities, and engineering. Researchers use research problems to identify gaps in knowledge, address theoretical or practical problems, and explore new areas of study.
- Business research : Research problems are used to guide business research, including market research, consumer behavior research, and organizational research. Researchers use research problems to identify business challenges, explore opportunities, and develop strategies for business growth and success.
- Healthcare research : Research problems are used to guide healthcare research, including medical research, clinical research, and health services research. Researchers use research problems to identify healthcare challenges, develop new treatments and interventions, and improve healthcare delivery and outcomes.
- Public policy research : Research problems are used to guide public policy research, including policy analysis, program evaluation, and policy development. Researchers use research problems to identify social issues, assess the effectiveness of existing policies and programs, and develop new policies and programs to address societal challenges.
- Environmental research : Research problems are used to guide environmental research, including environmental science, ecology, and environmental management. Researchers use research problems to identify environmental challenges, assess the impact of human activities on the environment, and develop sustainable solutions to protect the environment.
Purpose of Research Problems
The purpose of research problems is to identify an area of study that requires further investigation and to formulate a clear, concise and specific research question. A research problem defines the specific issue or problem that needs to be addressed and serves as the foundation for the research project.
Identifying a research problem is important because it helps to establish the direction of the research and sets the stage for the research design, methods, and analysis. It also ensures that the research is relevant and contributes to the existing body of knowledge in the field.
A well-formulated research problem should:
- Clearly define the specific issue or problem that needs to be investigated
- Be specific and narrow enough to be manageable in terms of time, resources, and scope
- Be relevant to the field of study and contribute to the existing body of knowledge
- Be feasible and realistic in terms of available data, resources, and research methods
- Be interesting and intellectually stimulating for the researcher and potential readers or audiences.
Characteristics of Research Problem
The characteristics of a research problem refer to the specific features that a problem must possess to qualify as a suitable research topic. Some of the key characteristics of a research problem are:
- Clarity : A research problem should be clearly defined and stated in a way that it is easily understood by the researcher and other readers. The problem should be specific, unambiguous, and easy to comprehend.
- Relevance : A research problem should be relevant to the field of study, and it should contribute to the existing body of knowledge. The problem should address a gap in knowledge, a theoretical or practical problem, or a real-world issue that requires further investigation.
- Feasibility : A research problem should be feasible in terms of the availability of data, resources, and research methods. It should be realistic and practical to conduct the study within the available time, budget, and resources.
- Novelty : A research problem should be novel or original in some way. It should represent a new or innovative perspective on an existing problem, or it should explore a new area of study or apply an existing theory to a new context.
- Importance : A research problem should be important or significant in terms of its potential impact on the field or society. It should have the potential to produce new knowledge, advance existing theories, or address a pressing societal issue.
- Manageability : A research problem should be manageable in terms of its scope and complexity. It should be specific enough to be investigated within the available time and resources, and it should be broad enough to provide meaningful results.
Advantages of Research Problem
The advantages of a well-defined research problem are as follows:
- Focus : A research problem provides a clear and focused direction for the research study. It ensures that the study stays on track and does not deviate from the research question.
- Clarity : A research problem provides clarity and specificity to the research question. It ensures that the research is not too broad or too narrow and that the research objectives are clearly defined.
- Relevance : A research problem ensures that the research study is relevant to the field of study and contributes to the existing body of knowledge. It addresses gaps in knowledge, theoretical or practical problems, or real-world issues that require further investigation.
- Feasibility : A research problem ensures that the research study is feasible in terms of the availability of data, resources, and research methods. It ensures that the research is realistic and practical to conduct within the available time, budget, and resources.
- Novelty : A research problem ensures that the research study is original and innovative. It represents a new or unique perspective on an existing problem, explores a new area of study, or applies an existing theory to a new context.
- Importance : A research problem ensures that the research study is important and significant in terms of its potential impact on the field or society. It has the potential to produce new knowledge, advance existing theories, or address a pressing societal issue.
- Rigor : A research problem ensures that the research study is rigorous and follows established research methods and practices. It ensures that the research is conducted in a systematic, objective, and unbiased manner.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Future Research – Thesis Guide

Research Contribution – Thesis Guide

Theoretical Framework – Types, Examples and...

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Chapter Summary & Overview – Writing Guide...
45 Research Problem Examples & Inspiration

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process
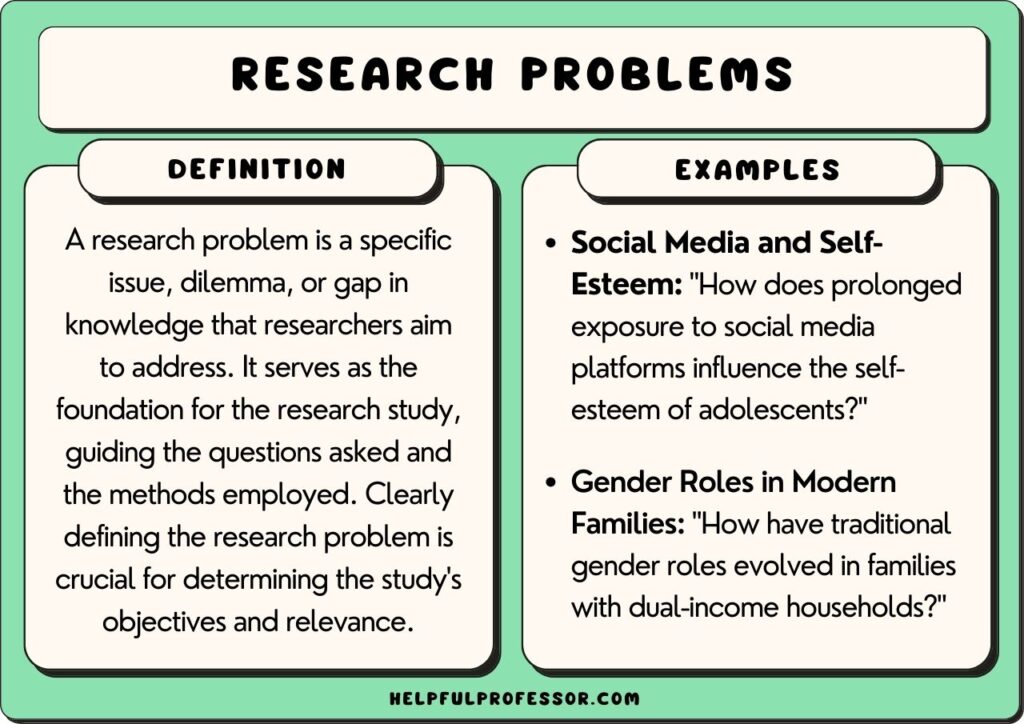
A research problem is an issue of concern that is the catalyst for your research. It demonstrates why the research problem needs to take place in the first place.
Generally, you will write your research problem as a clear, concise, and focused statement that identifies an issue or gap in current knowledge that requires investigation.
The problem will likely also guide the direction and purpose of a study. Depending on the problem, you will identify a suitable methodology that will help address the problem and bring solutions to light.
Research Problem Examples
In the following examples, I’ll present some problems worth addressing, and some suggested theoretical frameworks and research methodologies that might fit with the study. Note, however, that these aren’t the only ways to approach the problems. Keep an open mind and consult with your dissertation supervisor!

Psychology Problems
1. Social Media and Self-Esteem: “How does prolonged exposure to social media platforms influence the self-esteem of adolescents?”
- Theoretical Framework : Social Comparison Theory
- Methodology : Longitudinal study tracking adolescents’ social media usage and self-esteem measures over time, combined with qualitative interviews.
2. Sleep and Cognitive Performance: “How does sleep quality and duration impact cognitive performance in adults?”
- Theoretical Framework : Cognitive Psychology
- Methodology : Experimental design with controlled sleep conditions, followed by cognitive tests. Participant sleep patterns can also be monitored using actigraphy.
3. Childhood Trauma and Adult Relationships: “How does unresolved childhood trauma influence attachment styles and relationship dynamics in adulthood?
- Theoretical Framework : Attachment Theory
- Methodology : Mixed methods, combining quantitative measures of attachment styles with qualitative in-depth interviews exploring past trauma and current relationship dynamics.
4. Mindfulness and Stress Reduction: “How effective is mindfulness meditation in reducing perceived stress and physiological markers of stress in working professionals?”
- Theoretical Framework : Humanist Psychology
- Methodology : Randomized controlled trial comparing a group practicing mindfulness meditation to a control group, measuring both self-reported stress and physiological markers (e.g., cortisol levels).
5. Implicit Bias and Decision Making: “To what extent do implicit biases influence decision-making processes in hiring practices?
- Theoretical Framework : Cognitive Dissonance Theory
- Methodology : Experimental design using Implicit Association Tests (IAT) to measure implicit biases, followed by simulated hiring tasks to observe decision-making behaviors.
6. Emotional Regulation and Academic Performance: “How does the ability to regulate emotions impact academic performance in college students?”
- Theoretical Framework : Cognitive Theory of Emotion
- Methodology : Quantitative surveys measuring emotional regulation strategies, combined with academic performance metrics (e.g., GPA).
7. Nature Exposure and Mental Well-being: “Does regular exposure to natural environments improve mental well-being and reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression?”
- Theoretical Framework : Biophilia Hypothesis
- Methodology : Longitudinal study comparing mental health measures of individuals with regular nature exposure to those without, possibly using ecological momentary assessment for real-time data collection.
8. Video Games and Cognitive Skills: “How do action video games influence cognitive skills such as attention, spatial reasoning, and problem-solving?”
- Theoretical Framework : Cognitive Load Theory
- Methodology : Experimental design with pre- and post-tests, comparing cognitive skills of participants before and after a period of action video game play.
9. Parenting Styles and Child Resilience: “How do different parenting styles influence the development of resilience in children facing adversities?”
- Theoretical Framework : Baumrind’s Parenting Styles Inventory
- Methodology : Mixed methods, combining quantitative measures of resilience and parenting styles with qualitative interviews exploring children’s experiences and perceptions.
10. Memory and Aging: “How does the aging process impact episodic memory , and what strategies can mitigate age-related memory decline?
- Theoretical Framework : Information Processing Theory
- Methodology : Cross-sectional study comparing episodic memory performance across different age groups, combined with interventions like memory training or mnemonic strategies to assess potential improvements.
Education Problems
11. Equity and Access : “How do socioeconomic factors influence students’ access to quality education, and what interventions can bridge the gap?
- Theoretical Framework : Critical Pedagogy
- Methodology : Mixed methods, combining quantitative data on student outcomes with qualitative interviews and focus groups with students, parents, and educators.
12. Digital Divide : How does the lack of access to technology and the internet affect remote learning outcomes, and how can this divide be addressed?
- Theoretical Framework : Social Construction of Technology Theory
- Methodology : Survey research to gather data on access to technology, followed by case studies in selected areas.
13. Teacher Efficacy : “What factors contribute to teacher self-efficacy, and how does it impact student achievement?”
- Theoretical Framework : Bandura’s Self-Efficacy Theory
- Methodology : Quantitative surveys to measure teacher self-efficacy, combined with qualitative interviews to explore factors affecting it.
14. Curriculum Relevance : “How can curricula be made more relevant to diverse student populations, incorporating cultural and local contexts?”
- Theoretical Framework : Sociocultural Theory
- Methodology : Content analysis of curricula, combined with focus groups with students and teachers.
15. Special Education : “What are the most effective instructional strategies for students with specific learning disabilities?
- Theoretical Framework : Social Learning Theory
- Methodology : Experimental design comparing different instructional strategies, with pre- and post-tests to measure student achievement.
16. Dropout Rates : “What factors contribute to high school dropout rates, and what interventions can help retain students?”
- Methodology : Longitudinal study tracking students over time, combined with interviews with dropouts.
17. Bilingual Education : “How does bilingual education impact cognitive development and academic achievement?
- Methodology : Comparative study of students in bilingual vs. monolingual programs, using standardized tests and qualitative interviews.
18. Classroom Management: “What reward strategies are most effective in managing diverse classrooms and promoting a positive learning environment?
- Theoretical Framework : Behaviorism (e.g., Skinner’s Operant Conditioning)
- Methodology : Observational research in classrooms , combined with teacher interviews.
19. Standardized Testing : “How do standardized tests affect student motivation, learning, and curriculum design?”
- Theoretical Framework : Critical Theory
- Methodology : Quantitative analysis of test scores and student outcomes, combined with qualitative interviews with educators and students.
20. STEM Education : “What methods can be employed to increase interest and proficiency in STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) fields among underrepresented student groups?”
- Theoretical Framework : Constructivist Learning Theory
- Methodology : Experimental design comparing different instructional methods, with pre- and post-tests.
21. Social-Emotional Learning : “How can social-emotional learning be effectively integrated into the curriculum, and what are its impacts on student well-being and academic outcomes?”
- Theoretical Framework : Goleman’s Emotional Intelligence Theory
- Methodology : Mixed methods, combining quantitative measures of student well-being with qualitative interviews.
22. Parental Involvement : “How does parental involvement influence student achievement, and what strategies can schools use to increase it?”
- Theoretical Framework : Reggio Emilia’s Model (Community Engagement Focus)
- Methodology : Survey research with parents and teachers, combined with case studies in selected schools.
23. Early Childhood Education : “What are the long-term impacts of quality early childhood education on academic and life outcomes?”
- Theoretical Framework : Erikson’s Stages of Psychosocial Development
- Methodology : Longitudinal study comparing students with and without early childhood education, combined with observational research.
24. Teacher Training and Professional Development : “How can teacher training programs be improved to address the evolving needs of the 21st-century classroom?”
- Theoretical Framework : Adult Learning Theory (Andragogy)
- Methodology : Pre- and post-assessments of teacher competencies, combined with focus groups.
25. Educational Technology : “How can technology be effectively integrated into the classroom to enhance learning, and what are the potential drawbacks or challenges?”
- Theoretical Framework : Technological Pedagogical Content Knowledge (TPACK)
- Methodology : Experimental design comparing classrooms with and without specific technologies, combined with teacher and student interviews.
Sociology Problems
26. Urbanization and Social Ties: “How does rapid urbanization impact the strength and nature of social ties in communities?”
- Theoretical Framework : Structural Functionalism
- Methodology : Mixed methods, combining quantitative surveys on social ties with qualitative interviews in urbanizing areas.
27. Gender Roles in Modern Families: “How have traditional gender roles evolved in families with dual-income households?”
- Theoretical Framework : Gender Schema Theory
- Methodology : Qualitative interviews with dual-income families, combined with historical data analysis.
28. Social Media and Collective Behavior: “How does social media influence collective behaviors and the formation of social movements?”
- Theoretical Framework : Emergent Norm Theory
- Methodology : Content analysis of social media platforms, combined with quantitative surveys on participation in social movements.
29. Education and Social Mobility: “To what extent does access to quality education influence social mobility in socioeconomically diverse settings?”
- Methodology : Longitudinal study tracking educational access and subsequent socioeconomic status, combined with qualitative interviews.
30. Religion and Social Cohesion: “How do religious beliefs and practices contribute to social cohesion in multicultural societies?”
- Methodology : Quantitative surveys on religious beliefs and perceptions of social cohesion, combined with ethnographic studies.
31. Consumer Culture and Identity Formation: “How does consumer culture influence individual identity formation and personal values?”
- Theoretical Framework : Social Identity Theory
- Methodology : Mixed methods, combining content analysis of advertising with qualitative interviews on identity and values.
32. Migration and Cultural Assimilation: “How do migrants negotiate cultural assimilation and preservation of their original cultural identities in their host countries?”
- Theoretical Framework : Post-Structuralism
- Methodology : Qualitative interviews with migrants, combined with observational studies in multicultural communities.
33. Social Networks and Mental Health: “How do social networks, both online and offline, impact mental health and well-being?”
- Theoretical Framework : Social Network Theory
- Methodology : Quantitative surveys assessing social network characteristics and mental health metrics, combined with qualitative interviews.
34. Crime, Deviance, and Social Control: “How do societal norms and values shape definitions of crime and deviance, and how are these definitions enforced?”
- Theoretical Framework : Labeling Theory
- Methodology : Content analysis of legal documents and media, combined with ethnographic studies in diverse communities.
35. Technology and Social Interaction: “How has the proliferation of digital technology influenced face-to-face social interactions and community building?”
- Theoretical Framework : Technological Determinism
- Methodology : Mixed methods, combining quantitative surveys on technology use with qualitative observations of social interactions in various settings.
Nursing Problems
36. Patient Communication and Recovery: “How does effective nurse-patient communication influence patient recovery rates and overall satisfaction with care?”
- Methodology : Quantitative surveys assessing patient satisfaction and recovery metrics, combined with observational studies on nurse-patient interactions.
37. Stress Management in Nursing: “What are the primary sources of occupational stress for nurses, and how can they be effectively managed to prevent burnout?”
- Methodology : Mixed methods, combining quantitative measures of stress and burnout with qualitative interviews exploring personal experiences and coping mechanisms.
38. Hand Hygiene Compliance: “How effective are different interventions in improving hand hygiene compliance among nursing staff, and what are the barriers to consistent hand hygiene?”
- Methodology : Experimental design comparing hand hygiene rates before and after specific interventions, combined with focus groups to understand barriers.
39. Nurse-Patient Ratios and Patient Outcomes: “How do nurse-patient ratios impact patient outcomes, including recovery rates, complications, and hospital readmissions?”
- Methodology : Quantitative study analyzing patient outcomes in relation to staffing levels, possibly using retrospective chart reviews.
40. Continuing Education and Clinical Competence: “How does regular continuing education influence clinical competence and confidence among nurses?”
- Methodology : Longitudinal study tracking nurses’ clinical skills and confidence over time as they engage in continuing education, combined with patient outcome measures to assess potential impacts on care quality.
Communication Studies Problems
41. Media Representation and Public Perception: “How does media representation of minority groups influence public perceptions and biases?”
- Theoretical Framework : Cultivation Theory
- Methodology : Content analysis of media representations combined with quantitative surveys assessing public perceptions and attitudes.
42. Digital Communication and Relationship Building: “How has the rise of digital communication platforms impacted the way individuals build and maintain personal relationships?”
- Theoretical Framework : Social Penetration Theory
- Methodology : Mixed methods, combining quantitative surveys on digital communication habits with qualitative interviews exploring personal relationship dynamics.
43. Crisis Communication Effectiveness: “What strategies are most effective in managing public relations during organizational crises, and how do they influence public trust?”
- Theoretical Framework : Situational Crisis Communication Theory (SCCT)
- Methodology : Case study analysis of past organizational crises, assessing communication strategies used and subsequent public trust metrics.
44. Nonverbal Cues in Virtual Communication: “How do nonverbal cues, such as facial expressions and gestures, influence message interpretation in virtual communication platforms?”
- Theoretical Framework : Social Semiotics
- Methodology : Experimental design using video conferencing tools, analyzing participants’ interpretations of messages with varying nonverbal cues.
45. Influence of Social Media on Political Engagement: “How does exposure to political content on social media platforms influence individuals’ political engagement and activism?”
- Theoretical Framework : Uses and Gratifications Theory
- Methodology : Quantitative surveys assessing social media habits and political engagement levels, combined with content analysis of political posts on popular platforms.
Before you Go: Tips and Tricks for Writing a Research Problem
This is an incredibly stressful time for research students. The research problem is going to lock you into a specific line of inquiry for the rest of your studies.
So, here’s what I tend to suggest to my students:
- Start with something you find intellectually stimulating – Too many students choose projects because they think it hasn’t been studies or they’ve found a research gap. Don’t over-estimate the importance of finding a research gap. There are gaps in every line of inquiry. For now, just find a topic you think you can really sink your teeth into and will enjoy learning about.
- Take 5 ideas to your supervisor – Approach your research supervisor, professor, lecturer, TA, our course leader with 5 research problem ideas and run each by them. The supervisor will have valuable insights that you didn’t consider that will help you narrow-down and refine your problem even more.
- Trust your supervisor – The supervisor-student relationship is often very strained and stressful. While of course this is your project, your supervisor knows the internal politics and conventions of academic research. The depth of knowledge about how to navigate academia and get you out the other end with your degree is invaluable. Don’t underestimate their advice.
I’ve got a full article on all my tips and tricks for doing research projects right here – I recommend reading it:
- 9 Tips on How to Choose a Dissertation Topic

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 119 Bloom’s Taxonomy Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ All 6 Levels of Understanding (on Bloom’s Taxonomy)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 15 Self-Actualization Examples (Maslow's Hierarchy)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Forest Schools Philosophy & Curriculum, Explained!
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
The Research Problem & Statement
What they are & how to write them (with examples)
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewed By: Eunice Rautenbach (DTech) | March 2023
If you’re new to academic research, you’re bound to encounter the concept of a “ research problem ” or “ problem statement ” fairly early in your learning journey. Having a good research problem is essential, as it provides a foundation for developing high-quality research, from relatively small research papers to a full-length PhD dissertations and theses.
In this post, we’ll unpack what a research problem is and how it’s related to a problem statement . We’ll also share some examples and provide a step-by-step process you can follow to identify and evaluate study-worthy research problems for your own project.
Overview: Research Problem 101
What is a research problem.
- What is a problem statement?
Where do research problems come from?
- How to find a suitable research problem
- Key takeaways
A research problem is, at the simplest level, the core issue that a study will try to solve or (at least) examine. In other words, it’s an explicit declaration about the problem that your dissertation, thesis or research paper will address. More technically, it identifies the research gap that the study will attempt to fill (more on that later).
Let’s look at an example to make the research problem a little more tangible.
To justify a hypothetical study, you might argue that there’s currently a lack of research regarding the challenges experienced by first-generation college students when writing their dissertations [ PROBLEM ] . As a result, these students struggle to successfully complete their dissertations, leading to higher-than-average dropout rates [ CONSEQUENCE ]. Therefore, your study will aim to address this lack of research – i.e., this research problem [ SOLUTION ].
A research problem can be theoretical in nature, focusing on an area of academic research that is lacking in some way. Alternatively, a research problem can be more applied in nature, focused on finding a practical solution to an established problem within an industry or an organisation. In other words, theoretical research problems are motivated by the desire to grow the overall body of knowledge , while applied research problems are motivated by the need to find practical solutions to current real-world problems (such as the one in the example above).
As you can probably see, the research problem acts as the driving force behind any study , as it directly shapes the research aims, objectives and research questions , as well as the research approach. Therefore, it’s really important to develop a very clearly articulated research problem before you even start your research proposal . A vague research problem will lead to unfocused, potentially conflicting research aims, objectives and research questions .

What is a research problem statement?
As the name suggests, a problem statement (within a research context, at least) is an explicit statement that clearly and concisely articulates the specific research problem your study will address. While your research problem can span over multiple paragraphs, your problem statement should be brief , ideally no longer than one paragraph . Importantly, it must clearly state what the problem is (whether theoretical or practical in nature) and how the study will address it.
Here’s an example of a statement of the problem in a research context:
Rural communities across Ghana lack access to clean water, leading to high rates of waterborne illnesses and infant mortality. Despite this, there is little research investigating the effectiveness of community-led water supply projects within the Ghanaian context. Therefore, this study aims to investigate the effectiveness of such projects in improving access to clean water and reducing rates of waterborne illnesses in these communities.
As you can see, this problem statement clearly and concisely identifies the issue that needs to be addressed (i.e., a lack of research regarding the effectiveness of community-led water supply projects) and the research question that the study aims to answer (i.e., are community-led water supply projects effective in reducing waterborne illnesses?), all within one short paragraph.
Need a helping hand?
Wherever there is a lack of well-established and agreed-upon academic literature , there is an opportunity for research problems to arise, since there is a paucity of (credible) knowledge. In other words, research problems are derived from research gaps . These gaps can arise from various sources, including the emergence of new frontiers or new contexts, as well as disagreements within the existing research.
Let’s look at each of these scenarios:
New frontiers – new technologies, discoveries or breakthroughs can open up entirely new frontiers where there is very little existing research, thereby creating fresh research gaps. For example, as generative AI technology became accessible to the general public in 2023, the full implications and knock-on effects of this were (or perhaps, still are) largely unknown and therefore present multiple avenues for researchers to explore.
New contexts – very often, existing research tends to be concentrated on specific contexts and geographies. Therefore, even within well-studied fields, there is often a lack of research within niche contexts. For example, just because a study finds certain results within a western context doesn’t mean that it would necessarily find the same within an eastern context. If there’s reason to believe that results may vary across these geographies, a potential research gap emerges.
Disagreements – within many areas of existing research, there are (quite naturally) conflicting views between researchers, where each side presents strong points that pull in opposing directions. In such cases, it’s still somewhat uncertain as to which viewpoint (if any) is more accurate. As a result, there is room for further research in an attempt to “settle” the debate.
Of course, many other potential scenarios can give rise to research gaps, and consequently, research problems, but these common ones are a useful starting point. If you’re interested in research gaps, you can learn more here .
How to find a research problem
Given that research problems flow from research gaps , finding a strong research problem for your research project means that you’ll need to first identify a clear research gap. Below, we’ll present a four-step process to help you find and evaluate potential research problems.
If you’ve read our other articles about finding a research topic , you’ll find the process below very familiar as the research problem is the foundation of any study . In other words, finding a research problem is much the same as finding a research topic.
Step 1 – Identify your area of interest
Naturally, the starting point is to first identify a general area of interest . Chances are you already have something in mind, but if not, have a look at past dissertations and theses within your institution to get some inspiration. These present a goldmine of information as they’ll not only give you ideas for your own research, but they’ll also help you see exactly what the norms and expectations are for these types of projects.
At this stage, you don’t need to get super specific. The objective is simply to identify a couple of potential research areas that interest you. For example, if you’re undertaking research as part of a business degree, you may be interested in social media marketing strategies for small businesses, leadership strategies for multinational companies, etc.
Depending on the type of project you’re undertaking, there may also be restrictions or requirements regarding what topic areas you’re allowed to investigate, what type of methodology you can utilise, etc. So, be sure to first familiarise yourself with your institution’s specific requirements and keep these front of mind as you explore potential research ideas.
Step 2 – Review the literature and develop a shortlist
Once you’ve decided on an area that interests you, it’s time to sink your teeth into the literature . In other words, you’ll need to familiarise yourself with the existing research regarding your interest area. Google Scholar is a good starting point for this, as you can simply enter a few keywords and quickly get a feel for what’s out there. Keep an eye out for recent literature reviews and systematic review-type journal articles, as these will provide a good overview of the current state of research.
At this stage, you don’t need to read every journal article from start to finish . A good strategy is to pay attention to the abstract, intro and conclusion , as together these provide a snapshot of the key takeaways. As you work your way through the literature, keep an eye out for what’s missing – in other words, what questions does the current research not answer adequately (or at all)? Importantly, pay attention to the section titled “ further research is needed ”, typically found towards the very end of each journal article. This section will specifically outline potential research gaps that you can explore, based on the current state of knowledge (provided the article you’re looking at is recent).
Take the time to engage with the literature and develop a big-picture understanding of the current state of knowledge. Reviewing the literature takes time and is an iterative process , but it’s an essential part of the research process, so don’t cut corners at this stage.
As you work through the review process, take note of any potential research gaps that are of interest to you. From there, develop a shortlist of potential research gaps (and resultant research problems) – ideally 3 – 5 options that interest you.

Step 3 – Evaluate your potential options
Once you’ve developed your shortlist, you’ll need to evaluate your options to identify a winner. There are many potential evaluation criteria that you can use, but we’ll outline three common ones here: value, practicality and personal appeal.
Value – a good research problem needs to create value when successfully addressed. Ask yourself:
- Who will this study benefit (e.g., practitioners, researchers, academia)?
- How will it benefit them specifically?
- How much will it benefit them?
Practicality – a good research problem needs to be manageable in light of your resources. Ask yourself:
- What data will I need access to?
- What knowledge and skills will I need to undertake the analysis?
- What equipment or software will I need to process and/or analyse the data?
- How much time will I need?
- What costs might I incur?
Personal appeal – a research project is a commitment, so the research problem that you choose needs to be genuinely attractive and interesting to you. Ask yourself:
- How appealing is the prospect of solving this research problem (on a scale of 1 – 10)?
- Why, specifically, is it attractive (or unattractive) to me?
- Does the research align with my longer-term goals (e.g., career goals, educational path, etc)?
Depending on how many potential options you have, you may want to consider creating a spreadsheet where you numerically rate each of the options in terms of these criteria. Remember to also include any criteria specified by your institution . From there, tally up the numbers and pick a winner.
Step 4 – Craft your problem statement
Once you’ve selected your research problem, the final step is to craft a problem statement. Remember, your problem statement needs to be a concise outline of what the core issue is and how your study will address it. Aim to fit this within one paragraph – don’t waffle on. Have a look at the problem statement example we mentioned earlier if you need some inspiration.
Key Takeaways
We’ve covered a lot of ground. Let’s do a quick recap of the key takeaways:
- A research problem is an explanation of the issue that your study will try to solve. This explanation needs to highlight the problem , the consequence and the solution or response.
- A problem statement is a clear and concise summary of the research problem , typically contained within one paragraph.
- Research problems emerge from research gaps , which themselves can emerge from multiple potential sources, including new frontiers, new contexts or disagreements within the existing literature.
- To find a research problem, you need to first identify your area of interest , then review the literature and develop a shortlist, after which you’ll evaluate your options, select a winner and craft a problem statement .

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

I APPRECIATE YOUR CONCISE AND MIND-CAPTIVATING INSIGHTS ON THE STATEMENT OF PROBLEMS. PLEASE I STILL NEED SOME SAMPLES RELATED TO SUICIDES.
Very pleased and appreciate clear information.
Your videos and information have been a life saver for me throughout my dissertation journey. I wish I’d discovered them sooner. Thank you!
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- How it works

Research Problem – Definition, Steps & Tips
Published by Jamie Walker at August 12th, 2021 , Revised On October 3, 2023
Once you have chosen a research topic, the next stage is to explain the research problem: the detailed issue, ambiguity of the research, gap analysis, or gaps in knowledge and findings that you will discuss.
Here, in this article, we explore a research problem in a dissertation or an essay with some research problem examples to help you better understand how and when you should write a research problem.
“A research problem is a specific statement relating to an area of concern and is contingent on the type of research. Some research studies focus on theoretical and practical problems, while some focus on only one.”
The problem statement in the dissertation, essay, research paper, and other academic papers should be clearly stated and intended to expand information, knowledge, and contribution to change.
This article will assist in identifying and elaborating a research problem if you are unsure how to define your research problem. The most notable challenge in the research process is to formulate and identify a research problem. Formulating a problem statement and research questions while finalizing the research proposal or introduction for your dissertation or thesis is necessary.
Why is Research Problem Critical?
An interesting research topic is only the first step. The real challenge of the research process is to develop a well-rounded research problem.
A well-formulated research problem helps understand the research procedure; without it, your research will appear unforeseeable and awkward.
Research is a procedure based on a sequence and a research problem aids in following and completing the research in a sequence. Repetition of existing literature is something that should be avoided in research.
Therefore research problem in a dissertation or an essay needs to be well thought out and presented with a clear purpose. Hence, your research work contributes more value to existing knowledge. You need to be well aware of the problem so you can present logical solutions.
Formulating a research problem is the first step of conducting research, whether you are writing an essay, research paper, dissertation , or research proposal .
Looking for dissertation help?
Researchprospect to the rescue then.
We have expert writers on our team who are skilled at helping students with dissertations across a variety of STEM disciplines. Guaranteeing 100% satisfaction!

Step 1: Identifying Problem Area – What is Research Problem
The most significant step in any research is to look for unexplored areas, topics, and controversies . You aim to find gaps that your work will fill. Here are some research problem examples for you to better understand the concept.
Practical Research Problems
To conduct practical research, you will need practical research problems that are typically identified by analysing reports, previous research studies, and interactions with the experienced personals of pertinent disciplines. You might search for:
- Problems with performance or competence in an organization
- Institutional practices that could be enhanced
- Practitioners of relevant fields and their areas of concern
- Problems confronted by specific groups of people within your area of study
If your research work relates to an internship or a job, then it will be critical for you to identify a research problem that addresses certain issues faced by the firm the job or internship pertains to.
Examples of Practical Research Problems
Decreased voter participation in county A, as compared to the rest of the country.
The high employee turnover rate of department X of company Y influenced efficiency and team performance.
A charity institution, Y, suffers a lack of funding resulting in budget cuts for its programmes.
Theoretical Research Problems
Theoretical research relates to predicting, explaining, and understanding various phenomena. It also expands and challenges existing information and knowledge.
Identification of a research problem in theoretical research is achieved by analysing theories and fresh research literature relating to a broad area of research. This practice helps to find gaps in the research done by others and endorse the argument of your topic.
Here are some questions that you should bear in mind.
- A case or framework that has not been deeply analysed
- An ambiguity between more than one viewpoints
- An unstudied condition or relationships
- A problematic issue that needs to be addressed
Theoretical issues often contain practical implications, but immediate issues are often not resolved by these results. If that is the case, you might want to adopt a different research approach to achieve the desired outcomes.
Examples of Theoretical Research Problems
Long-term Vitamin D deficiency affects cardiac patients are not well researched.
The relationship between races, sex, and income imbalances needs to be studied with reference to the economy of a specific country or region.
The disagreement among historians of Scottish nationalism regarding the contributions of Imperial Britain in the creation of the national identity for Scotland.
Hire an Expert Writer
Proposal and dissertation orders completed by our expert writers are
- Formally drafted in academic style
- Plagiarism free
- 100% Confidential
- Never Resold
- Include unlimited free revisions
- Completed to match exact client requirements
Step 2: Understanding the Research Problem
The researcher further investigates the selected area of research to find knowledge and information relating to the research problem to address the findings in the research.
Background and Rationale
- Population influenced by the problem?
- Is it a persistent problem, or is it recently revealed?
- Research that has already been conducted on this problem?
- Any proposed solution to the problem?
- Recent arguments concerning the problem, what are the gaps in the problem?
How to Write a First Class Dissertation Proposal or Research Proposal
Particularity and Suitability
- What specific place, time, and/or people will be focused on?
- Any aspects of research that you may not be able to deal with?
- What will be the concerns if the problem remains unresolved?
- What are the benefices of the problem resolution (e.g. future researcher or organisation’s management)?
Example of a Specific Research Problem
A non-profit institution X has been examined on their existing support base retention, but the existing research does not incorporate an understanding of how to effectively target new donors. To continue their work, the institution needs more research and find strategies for effective fundraising.
Once the problem is narrowed down, the next stage is to propose a problem statement and hypothesis or research questions.
If you are unsure about what a research problem is and how to define the research problem, then you might want to take advantage of our dissertation proposal writing service. You may also want to take a look at our essay writing service if you need help with identifying a research problem for your essay.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is research problem with example.
A research problem is a specific challenge that requires investigation. Example: “What is the impact of social media on mental health among adolescents?” This problem drives research to analyse the relationship between social media use and mental well-being in young people.
How many types of research problems do we have?
- Descriptive: Describing phenomena as they exist.
- Explanatory: Understanding causes and effects.
- Exploratory: Investigating little-understood phenomena.
- Predictive: Forecasting future outcomes.
- Prescriptive: Recommending actions.
- Normative: Describing what ought to be.
What are the principles of the research problem?
- Relevance: Addresses a significant issue.
- Re searchability: Amenable to empirical investigation.
- Clarity: Clearly defined without ambiguity.
- Specificity: Narrowly framed, avoiding vagueness.
- Feasibility: Realistic to conduct with available resources.
- Novelty: Offers new insights or challenges existing knowledge.
- Ethical considerations: Respect rights, dignity, and safety.
Why is research problem important?
A research problem is crucial because it identifies knowledge gaps, directs the inquiry’s focus, and forms the foundation for generating hypotheses or questions. It drives the methodology and determination of study relevance, ensuring that research contributes meaningfully to academic discourse and potentially addresses real-world challenges.
How do you write a research problem?
To write a research problem, identify a knowledge gap or an unresolved issue in your field. Start with a broad topic, then narrow it down. Clearly articulate the problem in a concise statement, ensuring it’s researchable, significant, and relevant. Ground it in the existing literature to highlight its importance and context.
How can we solve research problem?
To solve a research problem, start by conducting a thorough literature review. Formulate hypotheses or research questions. Choose an appropriate research methodology. Collect and analyse data systematically. Interpret findings in the context of existing knowledge. Ensure validity and reliability, and discuss implications, limitations, and potential future research directions.
You May Also Like
Make sure that your selected topic is intriguing, manageable, and relevant. Here are some guidelines to help understand how to find a good dissertation topic.
How to write a hypothesis for dissertation,? A hypothesis is a statement that can be tested with the help of experimental or theoretical research.
To help students organise their dissertation proposal paper correctly, we have put together detailed guidelines on how to structure a dissertation proposal.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 1. Choosing a Research Problem
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
In the social and behavioral sciences, the subject of analysis is most often framed as a problem that must be researched in order to obtain a greater understanding, formulate a set of solutions or recommended courses of action, and/or develop a better approach to practice. The research problem, therefore, is the main organizing principle guiding the analysis of your research. The problem under investigation establishes an occasion for writing and a focus that governs what you want to say. It represents the core subject matter of scholarly communication and the means by which scholars arrive at other topics of conversation and the discovery of new knowledge and understanding.
Alvesson, Mats and Jörgen Sandberg. Constructing Research Questions: Doing Interesting Research . London: Sage, 2013; Jacobs, Ronald L. “Developing a Dissertation Research Problem: A Guide for Doctoral Students in Human Resource Development and Adult Education.” New Horizons in Adult Education and Human Resource Development 25 (Summer 2013): 103-117; Chapter 1: Research and the Research Problem. Nicholas Walliman . Your Research Project: Designing and Planning Your Work . 3rd edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 2011.
Choosing a Research Problem / How to Begin
Do not assume that identifying a research problem to investigate will be a quick and easy task! You should be thinking about it during the beginning of the course. There are generally three ways you are asked to write about a research problem : 1) your professor provides you with a general topic from which you study a particular aspect; 2) your professor provides you with a list of possible topics to study and you choose a topic from that list; or, 3) your professor leaves it up to you to choose a topic and you only have to obtain permission to write about it before beginning your investigation. Here are some strategies for getting started for each scenario.
I. How To Begin: You are given the topic to write about
Step 1 : Identify concepts and terms that make up the topic statement . For example, your professor wants the class to focus on the following research problem: “Is the European Union a credible security actor with the capacity to contribute to confronting global terrorism?" The main concepts in this problem are: European Union, security, global terrorism, credibility [ hint : focus on identifying proper nouns, nouns or noun phrases, and action verbs in the assignment description]. Step 2 : Review related literature to help refine how you will approach examining the topic and finding a way to analyze it . You can begin by doing any or all of the following: reading through background information from materials listed in your course syllabus; searching the USC Libraries Catalog to find a recent book on the topic and, if appropriate, more specialized works about the topic; conducting a preliminary review of the research literature using multidisciplinary databases such as ProQuest or subject-specific databases from the " By Subject Area " drop down menu located above the list of databases.
Choose the advanced search option in the database and enter into each search box the main concept terms you developed in Step 1. Also consider using their synonyms to retrieve additional relevant records. This will help you refine and frame the scope of the research problem. You will likely need to do this several times before you can finalize how to approach writing about the topic. NOTE: Always review the references from your most relevant research results cited by the authors in footnotes, endnotes, or a bibliography to locate related research on your topic. This is a good strategy for identifying important prior research about the topic because titles that are repeatedly cited indicate their significance in laying a foundation for understanding the problem. However, if you’re having trouble at this point locating relevant research literature, ask a librarian for help!
ANOTHER NOTE: If you find an article from a database that's particularly helpful, paste it into Google Scholar , placing the title of the article in quotes. If the article record appears, look for a "cited by" reference followed by a number [e.g., C ited by 37] just below the record. This link indicates how many times other scholars have subsequently cited that article in their own research since it was first published. This is an effective strategy for identifying more current, related research on your topic. Finding additional cited by references from your original list of cited by references helps you navigate through the literature and, by so doing, understand the evolution of thought around a particular research problem. Step 3 : Since social science research papers are generally designed to encourage you to develop your own ideas and arguments, look for sources that can help broaden, modify, or strengthen your initial thoughts and arguments. For example, if you decide to argue that the European Union is inadequately prepared to take on responsibilities for broader global security because of the debt crisis in many EU countries, then focus on identifying sources that support as well as refute this position. From the advanced search option in ProQuest , a sample search would use "European Union" in one search box, "global security" in the second search box, and adding a third search box to include "debt crisis."
There are least four appropriate roles your related literature plays in helping you formulate how to begin your analysis :
- Sources of criticism -- frequently, you'll find yourself reading materials that are relevant to your chosen topic, but you disagree with the author's position. Therefore, one way that you can use a source is to describe the counter-argument, provide evidence from your own review of the literature as to why the prevailing argument is unsatisfactory, and to discuss how your approach is more appropriate based upon your interpretation of the evidence.
- Sources of new ideas -- while a general goal in writing college research papers in the social sciences is to examine a research problem with some basic idea of what position you'd like to take and on what basis you'd like to defend your position, it is certainly acceptable [and often encouraged] to read the literature and extend, modify, and refine your own position in light of the ideas proposed by others. Just make sure that you cite the sources !
- Sources for historical context -- another role your related literature plays in formulating how to begin your analysis is to place issues and events in proper historical context. This can help to demonstrate familiarity with developments in relevant scholarship about your topic, provide a means of comparing historical versus contemporary issues and events, and identifying key people, places, and events that had an important role related to the research problem. Given its archival journal coverage, a good multidisciplnary database to use in this case is JSTOR .
- Sources of interdisciplinary insight -- an advantage of using databases like ProQuest to begin exploring your topic is that it covers publications from a variety of different disciplines. Another way to formulate how to study the topic is to look at it from different disciplinary perspectives. If the topic concerns immigration reform, for example, ask yourself, how do studies from sociological journals found by searching ProQuest vary in their analysis from those in political science journals. A goal in reviewing related literature is to provide a means of approaching a topic from multiple perspectives rather than the perspective offered from just one discipline.
NOTE: Remember to keep careful notes at every stage or utilize a citation management system like EndNotes or RefWorks . You may think you'll remember what you have searched and where you found things, but it’s easy to forget or get confused. Most databases have a search history feature that allows you to go back and see what searches you conducted previously as long as you haven't closed your session. If you start over, that history could be deleted.
Step 4 : Assuming you have done an effective job of synthesizing and thinking about the results of your initial search for related literature, you're ready to prepare a detailed outline for your paper that lays the foundation for a more in-depth and focused review of relevant research literature [after consulting with a librarian, if needed!]. How will you know you haven't done an effective job of synthesizing and thinking about the results of our initial search for related literature? A good indication is that you start composing the outline and gaps appear in how you want to approach the study. This indicates the need to gather further background information and analysis about the research problem.
II. How To Begin: You are provided a list of possible topics to choose from Step 1 : I know what you’re thinking--which topic on this list will be the easiest to find the most information on? An effective instructor would never include a topic that is so obscure or complex that no research is available to examine and from which to design an effective study. Therefore, don't approach a list of possible topics to study from the perspective of trying to identify the path of least resistance; choose a topic that you find interesting in some way, that is controversial and that you have a strong opinion about, that has some personal meaning for you, or relates to your major or a minor. You're going to be working on the topic for quite some time, so choose one that you find interesting and engaging or that motivates you to take a position. Embrace the opportunity to learn something new! Once you’ve settled on a topic of interest from the list provided by your professor, follow Steps 1 - 4 listed above to further develop it into a research paper.
NOTE: It’s ok to review related literature to help refine how you will approach analyzing a topic, and then discover that the topic isn’t all that interesting to you. In that case, choose a different topic from the list. Just don’t wait too long to make a switch and, of course, be sure to inform your professor that you are changing your topic.
III. How To Begin: Your professor leaves it up to you to choose a topic
Step 1 : Under this scenario, the key process is turning an idea or general thought into a topic that can be configured into a research problem. When given an assignment where you choose the topic, don't begin by thinking about what to write about, but rather, ask yourself the question, "What do I want to understand or learn about?" Treat an open-ended research assignment as an opportunity to gain new knowledge about something that's important or exciting to you in the context of the overall subject of the course.
Step 2 : If you lack ideas, or wish to gain focus, try any or all of the following strategies:
- Review your course readings, particularly the suggested readings, for topic ideas. Don't just review what you've already read, but jump ahead in the syllabus to readings that have not been covered yet.
- Search the USC Libraries Catalog for a recently published book and, if appropriate, more specialized works related to the discipline area of the course [e.g., for the course SOCI 335: Society and Population, search for books on "population and society" or "population and social impact"]. Reviewing the contents of a book about your area of interest can give you insight into what conversations scholars are having about the topic and, thus, how you might want to contribute your own ideas to these conversations through the research paper you write for the class.
- Browse through some current scholarly [a.k.a., academic, peer reviewed] journals in your subject discipline. Even if most of the articles are not relevant, you can skim through the contents quickly. You only need one to be the spark that begins the process of wanting to learn more about a topic. Consult with a librarian and/or your professor about what constitutes the core journals within the subject area of the writing assignment.
- Think about essays you have written for other courses you have taken or academic lectures and programs you have attended outside of class. Thinking back, ask yourself why did you want to take this class or attend this event? What interested you the most? What would you like to know more about? Place this question in the context of the current course assignment. Note that this strategy also applies to anything you've watched on TV or has been shared on social media.
- Search online news media sources, such as CNN , the Los Angeles Times , Huffington Post , MSNBC , Fox News , or Newsweek , to see if your idea has been covered by the media. Use this coverage to refine your idea into something that you'd like to investigate further, but in a more deliberate, scholarly way in relation to a particular problem that needs to be researched.
Step 3 : To build upon your initial idea, use the suggestions under this tab to help narrow , broaden , or increase the timeliness of your idea so you can write it out as a research problem.
Once you are comfortable with having turned your idea into a research problem, follow Steps 1 - 4 listed in Part I above to further develop it into an outline for a research paper.
Alderman, Jim. "Choosing a Research Topic." Beginning Library and Information Systems Strategies. Paper 17. Jacksonville, FL: University of North Florida Digital Commons, 2014; Alvesson, Mats and Jörgen Sandberg. Constructing Research Questions: Doing Interesting Research . London: Sage, 2013; Chapter 2: Choosing a Research Topic. Adrian R. Eley. Becoming a Successful Early Career Researcher . New York: Routledge, 2012; Answering the Question. Academic Skills Centre. University of Canberra; Brainstorming. Department of English Writing Guide. George Mason University; Brainstorming. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Chapter 1: Research and the Research Problem. Nicholas Walliman . Your Research Project: Designing and Planning Your Work . 3rd edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 2011; Choosing a Topic. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Mullaney, Thomas S. and Christopher Rea. Where Research Begins: Choosing a Research Project That Matters to You (and the World) . Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press, 2022; Coming Up With Your Topic. Institute for Writing Rhetoric. Dartmouth College; How To Write a Thesis Statement. Writing Tutorial Services, Center for Innovative Teaching and Learning. Indiana University; Identify Your Question. Start Your Research. University Library, University of California, Santa Cruz; The Process of Writing a Research Paper. Department of History. Trent University; Trochim, William M.K. Problem Formulation. Research Methods Knowledge Base. 2006.
Resources for Identifying a Topic
Resources for Identifying a Research Problem
If you are having difficulty identifying a topic to study or need basic background information, the following web resources and databases can be useful:
- CQ Researcher -- a collection of single-themed public policy reports that provide an overview of an issue. Each report includes background information, an assessment of the current policy situation, statistical tables and maps, pro/con statements from representatives of opposing positions, and a bibliography of key sources.
- New York Times Topics -- each topic page collects news articles, reference and archival information, photos, graphics, audio and video files. Content is available without charge on articles going back to 1981.
- Opposing Viewpoints In Context -- an online resource covering a wide range of social issues from a variety of perspectives. The database contains a media-rich collection of materials, including pro/con viewpoint essays, topic overviews, primary source materials, biographies of social activists and reformers, journal articles, statistical tables, charts and graphs, images, videos, and podcasts.
- Policy Commons -- platform for objective, fact-based research from the world’s leading policy experts, nonpartisan think tanks, and intergovernmental and non-governmental organizations. The database provides advanced searching across millions of pages of books, articles, working papers, reports, policy briefs, data sets, tables, charts, media, case studies, and statistical publications, including archived reports from more than 200 defunct think tanks. Coverage is international in scope.
Descriptions of resources are adapted or quoted from vendor websites.
Writing Tip
Not Finding Anything on Your Topic? Ask a Librarian!
Don't assume or jump to the conclusion that your topic is too narrowly defined or obscure just because your initial search has failed to identify relevant research. Librarians are experts in locating and critically assessing information and how it is organized. This knowledge will help you develop strategies for analyzing existing knowledge in new ways. Therefore, always consult with a librarian before you consider giving up on finding information about the topic you want to investigate. If there isn't a lot of information about your topic, a librarian can help you identify a closely related topic that you can study. Use the Ask-A-Librarian link above to identify a librarian in your subject area.
Another Writing Tip
Don't be a Martyr!
In thinking about what to study, don't adopt the mindset of pursuing an esoteric or overly complicated topic just to impress your professor but that, in reality, does not have any real interest to you. Choose a topic that is challenging but that has at least some interest to you or that you care about. Obviously, this is easier for courses within your major, but even for those nasty prerequisite classes that you must take in order to graduate [and that provide an additional tuition revenue for the university], try to apply issues associated with your major to the general topic given to you. For example, if you are an international relations major taking a GE philosophy class where the assignment asks you to apply the question of "what is truth" to some aspect of life, you could choose to study how government leaders attempt to shape truth through the use of nationalistic propaganda.
Still Another Writing Tip
A Research Problem is Not a Thesis Statement
A thesis statement and a research problem are two different parts of the introduction section of your paper. The thesis statement succinctly describes in one or two sentences, usually in the last paragraph of the introduction, what position you have reached about a topic. It includes an assertion that requires evidence and support along with your opinion or argument about what you are researching. There are three general types of thesis statements: analytical statements that break down and evaluate the topic; argumentative statements that make a claim about the topic and defend that claim; and, expository statements that present facts and research about the topic. Each are intended to set forth a claim that you will seek to validate through the research you describe in your paper.
Before the thesis statement, your introduction must include a description of a problem that describes either a key area of concern, a condition to be improved upon, a difficulty to be eliminated, or a troubling issue that exists . The research problem describes something that can be empirically verified and measured; it is often followed by a set of questions that underpin how you plan to approach investigating that problem. In short, the thesis statement states your opinion or argument about the research problem and summarizes how you plan to address it.
Tips and Examples for Writing Thesis Statements. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Write a Strong Thesis Statement! The Writing Center, University of Evansville; Thesis Statements. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Tutorial #26: Thesis Statements and Topic Sentences. Writing Center, College of San Mateo; Creswell, John W. and J. David Creswell. Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches . 5th edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2017.
- << Previous: Glossary of Research Terms
- Next: Reading Research Effectively >>
- Last Updated: Jun 17, 2024 9:29 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
- 10 Research Question Examples to Guide Your Research Project
10 Research Question Examples to Guide your Research Project
Published on October 30, 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on October 19, 2023.
The research question is one of the most important parts of your research paper , thesis or dissertation . It’s important to spend some time assessing and refining your question before you get started.
The exact form of your question will depend on a few things, such as the length of your project, the type of research you’re conducting, the topic , and the research problem . However, all research questions should be focused, specific, and relevant to a timely social or scholarly issue.
Once you’ve read our guide on how to write a research question , you can use these examples to craft your own.
| Research question | Explanation |
|---|---|
| The first question is not enough. The second question is more , using . | |
| Starting with “why” often means that your question is not enough: there are too many possible answers. By targeting just one aspect of the problem, the second question offers a clear path for research. | |
| The first question is too broad and subjective: there’s no clear criteria for what counts as “better.” The second question is much more . It uses clearly defined terms and narrows its focus to a specific population. | |
| It is generally not for academic research to answer broad normative questions. The second question is more specific, aiming to gain an understanding of possible solutions in order to make informed recommendations. | |
| The first question is too simple: it can be answered with a simple yes or no. The second question is , requiring in-depth investigation and the development of an original argument. | |
| The first question is too broad and not very . The second question identifies an underexplored aspect of the topic that requires investigation of various to answer. | |
| The first question is not enough: it tries to address two different (the quality of sexual health services and LGBT support services). Even though the two issues are related, it’s not clear how the research will bring them together. The second integrates the two problems into one focused, specific question. | |
| The first question is too simple, asking for a straightforward fact that can be easily found online. The second is a more question that requires and detailed discussion to answer. | |
| ? dealt with the theme of racism through casting, staging, and allusion to contemporary events? | The first question is not — it would be very difficult to contribute anything new. The second question takes a specific angle to make an original argument, and has more relevance to current social concerns and debates. |
| The first question asks for a ready-made solution, and is not . The second question is a clearer comparative question, but note that it may not be practically . For a smaller research project or thesis, it could be narrowed down further to focus on the effectiveness of drunk driving laws in just one or two countries. |
Note that the design of your research question can depend on what method you are pursuing. Here are a few options for qualitative, quantitative, and statistical research questions.
| Type of research | Example question |
|---|---|
| Qualitative research question | |
| Quantitative research question | |
| Statistical research question |
Other interesting articles
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, October 19). 10 Research Question Examples to Guide your Research Project. Scribbr. Retrieved June 18, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/research-question-examples/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, how to choose a dissertation topic | 8 steps to follow, evaluating sources | methods & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Artificial Intelligence
- Market Research
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
Academic Experience
How to identify and resolve research problems
Updated July 12, 2023
In this article, we’re going to take you through one of the most pertinent parts of conducting research: a research problem (also known as a research problem statement).
When trying to formulate a good research statement, and understand how to solve it for complex projects, it can be difficult to know where to start.
Not only are there multiple perspectives (from stakeholders to project marketers who want answers), you have to consider the particular context of the research topic: is it timely, is it relevant and most importantly of all, is it valuable?
In other words: are you looking at a research worthy problem?
The fact is, a well-defined, precise, and goal-centric research problem will keep your researchers, stakeholders, and business-focused and your results actionable.
And when it works well, it's a powerful tool to identify practical solutions that can drive change and secure buy-in from your workforce.
Free eBook: The ultimate guide to market research
What is a research problem?
In social research methodology and behavioral sciences , a research problem establishes the direction of research, often relating to a specific topic or opportunity for discussion.
For example: climate change and sustainability, analyzing moral dilemmas or wage disparity amongst classes could all be areas that the research problem focuses on.
As well as outlining the topic and/or opportunity, a research problem will explain:
- why the area/issue needs to be addressed,
- why the area/issue is of importance,
- the parameters of the research study
- the research objective
- the reporting framework for the results and
- what the overall benefit of doing so will provide (whether to society as a whole or other researchers and projects).
Having identified the main topic or opportunity for discussion, you can then narrow it down into one or several specific questions that can be scrutinized and answered through the research process.
What are research questions?
Generating research questions underpinning your study usually starts with problems that require further research and understanding while fulfilling the objectives of the study.
A good problem statement begins by asking deeper questions to gain insights about a specific topic.
For example, using the problems above, our questions could be:
"How will climate change policies influence sustainability standards across specific geographies?"
"What measures can be taken to address wage disparity without increasing inflation?"
Developing a research worthy problem is the first step - and one of the most important - in any kind of research.
It’s also a task that will come up again and again because any business research process is cyclical. New questions arise as you iterate and progress through discovering, refining, and improving your products and processes. A research question can also be referred to as a "problem statement".
Note: good research supports multiple perspectives through empirical data. It’s focused on key concepts rather than a broad area, providing readily actionable insight and areas for further research.
Research question or research problem?
As we've highlighted, the terms “research question” and “research problem” are often used interchangeably, becoming a vague or broad proposition for many.
The term "problem statement" is far more representative, but finds little use among academics.
Instead, some researchers think in terms of a single research problem and several research questions that arise from it.
As mentioned above, the questions are lines of inquiry to explore in trying to solve the overarching research problem.
Ultimately, this provides a more meaningful understanding of a topic area.
It may be useful to think of questions and problems as coming out of your business data – that’s the O-data (otherwise known as operational data) like sales figures and website metrics.
What's an example of a research problem?
Your overall research problem could be: "How do we improve sales across EMEA and reduce lost deals?"
This research problem then has a subset of questions, such as:
"Why do sales peak at certain times of the day?"
"Why are customers abandoning their online carts at the point of sale?"
As well as helping you to solve business problems, research problems (and associated questions) help you to think critically about topics and/or issues (business or otherwise). You can also use your old research to aid future research -- a good example is laying the foundation for comparative trend reports or a complex research project.
(Also, if you want to see the bigger picture when it comes to research problems, why not check out our ultimate guide to market research? In it you'll find out: what effective market research looks like, the use cases for market research, carrying out a research study, and how to examine and action research findings).
The research process: why are research problems important?
A research problem has two essential roles in setting your research project on a course for success.
1. They set the scope
The research problem defines what problem or opportunity you’re looking at and what your research goals are. It stops you from getting side-tracked or allowing the scope of research to creep off-course .
Without a strong research problem or problem statement, your team could end up spending resources unnecessarily, or coming up with results that aren’t actionable - or worse, harmful to your business - because the field of study is too broad.
2. They tie your work to business goals and actions
To formulate a research problem in terms of business decisions means you always have clarity on what’s needed to make those decisions. You can show the effects of what you’ve studied using real outcomes.
Then, by focusing your research problem statement on a series of questions tied to business objectives, you can reduce the risk of the research being unactionable or inaccurate.
It's also worth examining research or other scholarly literature (you’ll find plenty of similar, pertinent research online) to see how others have explored specific topics and noting implications that could have for your research.
Four steps to defining your research problem
Image credit: http://myfreeschooltanzania.blogspot.com/2014/11/defining-research-problem.html
1. Observe and identify
Businesses today have so much data that it can be difficult to know which problems to address first. Researchers also have business stakeholders who come to them with problems they would like to have explored. A researcher’s job is to sift through these inputs and discover exactly what higher-level trends and key concepts are worth investing in.
This often means asking questions and doing some initial investigation to decide which avenues to pursue. This could mean gathering interdisciplinary perspectives identifying additional expertise and contextual information.
Sometimes, a small-scale preliminary study might be worth doing to help get a more comprehensive understanding of the business context and needs, and to make sure your research problem addresses the most critical questions.
This could take the form of qualitative research using a few in-depth interviews , an environmental scan, or reviewing relevant literature.
The sales manager of a sportswear company has a problem: sales of trail running shoes are down year-on-year and she isn’t sure why. She approaches the company’s research team for input and they begin asking questions within the company and reviewing their knowledge of the wider market.
2. Review the key factors involved
As a marketing researcher, you must work closely with your team of researchers to define and test the influencing factors and the wider context involved in your study. These might include demographic and economic trends or the business environment affecting the question at hand. This is referred to as a relational research problem.
To do this, you have to identify the factors that will affect the research and begin formulating different methods to control them.
You also need to consider the relationships between factors and the degree of control you have over them. For example, you may be able to control the loading speed of your website but you can’t control the fluctuations of the stock market.
Doing this will help you determine whether the findings of your project will produce enough information to be worth the cost.
You need to determine:
- which factors affect the solution to the research proposal.
- which ones can be controlled and used for the purposes of the company, and to what extent.
- the functional relationships between the factors.
- which ones are critical to the solution of the research study.
The research team at the running shoe company is hard at work. They explore the factors involved and the context of why YoY sales are down for trail shoes, including things like what the company’s competitors are doing, what the weather has been like – affecting outdoor exercise – and the relative spend on marketing for the brand from year to year.
The final factor is within the company’s control, although the first two are not. They check the figures and determine marketing spend has a significant impact on the company.
3. Prioritize
Once you and your research team have a few observations, prioritize them based on their business impact and importance. It may be that you can answer more than one question with a single study, but don’t do it at the risk of losing focus on your overarching research problem.
Questions to ask:
- Who? Who are the people with the problem? Are they end-users, stakeholders, teams within your business? Have you validated the information to see what the scale of the problem is?
- What? What is its nature and what is the supporting evidence?
- Why? What is the business case for solving the problem? How will it help?
- Where? How does the problem manifest and where is it observed?
To help you understand all dimensions, you might want to consider focus groups or preliminary interviews with external (including consumers and existing customers) and internal (salespeople, managers, and other stakeholders) parties to provide what is sometimes much-needed insight into a particular set of questions or problems.
After observing and investigating, the running shoe researchers come up with a few candidate questions, including:
- What is the relationship between US average temperatures and sales of our products year on year?
- At present, how does our customer base rank Competitor X and Competitor Y’s trail running shoe compared to our brand?
- What is the relationship between marketing spend and trail shoe product sales over the last 12 months?
They opt for the final question, because the variables involved are fully within the company’s control, and based on their initial research and stakeholder input, seem the most likely cause of the dive in sales. The research question is specific enough to keep the work on course towards an actionable result, but it allows for a few different avenues to be explored, such as the different budget allocations of offline and online marketing and the kinds of messaging used.
Get feedback from the key teams within your business to make sure everyone is aligned and has the same understanding of the research problem and questions, and the actions you hope to take based on the results. Now is also a good time to demonstrate the ROI of your research and lay out its potential benefits to your stakeholders.
Different groups may have different goals and perspectives on the issue. This step is vital for getting the necessary buy-in and pushing the project forward.
The running shoe company researchers now have everything they need to begin. They call a meeting with the sales manager and consult with the product team, marketing team, and C-suite to make sure everyone is aligned and has bought into the direction of the research topic. They identify and agree that the likely course of action will be a rethink of how marketing resources are allocated, and potentially testing out some new channels and messaging strategies .
Can you explore a broad area and is it practical to do so?
A broader research problem or report can be a great way to bring attention to prevalent issues, societal or otherwise, but are often undertaken by those with the resources to do so.
Take a typical government cybersecurity breach survey, for example. Most of these reports raise awareness of cybercrime, from the day-to-day threats businesses face to what security measures some organizations are taking. What these reports don't do, however, is provide actionable advice - mostly because every organization is different.
The point here is that while some researchers will explore a very complex issue in detail, others will provide only a snapshot to maintain interest and encourage further investigation. The "value" of the data is wholly determined by the recipients of it - and what information you choose to include.
To summarize, it can be practical to undertake a broader research problem, certainly, but it may not be possible to cover everything or provide the detail your audience needs. Likewise, a more systematic investigation of an issue or topic will be more valuable, but you may also find that you cover far less ground.
It's important to think about your research objectives and expected findings before going ahead.
Ensuring your research project is a success
A complex research project can be made significantly easier with clear research objectives, a descriptive research problem, and a central focus. All of which we've outlined in this article.
If you have previous research, even better. Use it as a benchmark
Remember: what separates a good research paper from an average one is actually very simple: valuable, empirical data that explores a prevalent societal or business issue and provides actionable insights.
And we can help.
Sophisticated research made simple with Qualtrics
Trusted by the world's best brands, our platform enables researchers from academic to corporate to tackle the hardest challenges and deliver the results that matter.
Our CoreXM platform supports the methods that define superior research and delivers insights in real-time. It's easy to use (thanks to drag-and-drop functionality) and requires no coding, meaning you'll be capturing data and gleaning insights in no time.
It also excels in flexibility; you can track consumer behavior across segments , benchmark your company versus competitors , carry out complex academic research, and do much more, all from one system.
It's one platform with endless applications, so no matter your research problem, we've got the tools to help you solve it. And if you don't have a team of research experts in-house, our market research team has the practical knowledge and tools to help design the surveys and find the respondents you need.
Of course, you may want to know where to begin with your own market research . If you're struggling, make sure to download our ultimate guide using the link below.
It's got everything you need and there’s always information in our research methods knowledge base.
Scott Smith
Scott Smith, Ph.D. is a contributor to the Qualtrics blog.
Related Articles
April 1, 2023
How to write great survey questions (with examples)
February 8, 2023
Smoothing the transition from school to work with work-based learning
December 6, 2022
How customer experience helps bring Open Universities Australia’s brand promise to life
August 18, 2022
School safety, learning gaps top of mind for parents this back-to-school season
August 9, 2022
3 things that will improve your teachers’ school experience
August 2, 2022
Why a sense of belonging at school matters for K-12 students
July 14, 2022
Improve the student experience with simplified course evaluations
March 17, 2022
Understanding what’s important to college students
Stay up to date with the latest xm thought leadership, tips and news., request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
- QUICK LINKS
- How to enroll
- Career services
How to Identify an Appropriate Research Problem

By Mansureh Kebritchi, Ph.D.
A research problem is the heart of the study. It is a clear, definite statement of the area of concern or investigation and is backed by evidence (Bryman, 2007). It drives the research questions and processes and provides the framework for understanding the research findings. To begin, you will need to know where to look for your research problem and how to evaluate when a research problem for success.
Where to Find a Research Problem
Ideas for research problems tend to come from two sources: real life and the scholarly arena. First, identifying a research problem can be as simple as observing the complications and issues in your local workplace. You may encounter ongoing issues on a daily basis in your workplace or observe your colleagues struggle with major issues or questions in your field. These ongoing obstacles and issues in the workplace can be the catalyst for developing a research problem.
Alternatively, research problems can be identified by reviewing recent literature, reports, or databases in your field. Often the section on “recommendations for future studies” provided at the end of journal articles or doctoral dissertations suggests potential research problems. In addition, major reports and databases in the field may reveal findings or data-based facts that call for additional investigation or suggest potential issues to be addressed. Looking at what theories need to be tested is another opportunity to develop a research problem.
How to Evaluate a Research Problem
Once you find your potential research problem, you will need to evaluate the problem and ensure that it is appropriate for research. A research problem is deemed appropriate when it is supported by the literature and considered significant, timely, novel, specific, and researchable. Stronger research problems are more likely to succeed in publication, presentation, and application.
Supported by the Literature
Your research problem should be relevant to the field and supported by a number of recent peer-reviewed studies in the field. Even if you identify the problem based on the recommendation of one journal article or dissertation, you will still need to conduct a literature search and ensure that other researchers support the problem and the need for conducting research to further address the problem.
Significant
Your research problem should have a positive impact on the field. The impact can be practical, in the form of direct application of the results in the field, or conceptual, where the work advances the field by filling a knowledge gap.
Your research problem should be related to the current needs in the field and well-suited for the present status of the issues in your field. Explore what topics are being covered in current journals in the field. Look at calls from relevant disciplinary organizations. Review your research center agenda and focused topics. For example, the topics of the Research Labs at the Center for Educational and Instructional Technology Research including critical thinking, social media and cultural competency, diversity, and Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM) in higher education are representative of the current timely topics in the field of education. Identifying a current question in the field and supporting the problem with recent literature can justify the problem's timeliness.
Your research problem should be original and unique. It should seek to address a gap in our knowledge or application. An exhaustive review of the literature can help you identify whether the problem has already been addressed with your particular sample and/or context. Talking to experts in the research area can illuminate a problem. Replication of an existing study warrants a discussion of value elsewhere, but the novelty can be found in determining if an already-resolved problem holds in a new sample and/or context.
Specific and Clear
Your research problem should be specific enough to set the direction of the study, raise research question(s), and determine an appropriate research method and design. Vague research problems may not be useful to specify the direction of the study or develop research questions.
Researchable
Research problems are solved through the scientific method. This means researchability, or feasibility of the problem, is more important than all of the above characteristics. You as the researcher should be able to solve the problem with your abilities and available research methods, designs, research sites, resources, and timeframe. If a research problem retains all of the aforementioned characteristics but it is not researchable, it may not be an appropriate research problem.
References and More Information
Bryman, Alan. “The Research Question in Social Research: What is its Role?” International Journal of Social Research Methodology 10 (2007): 5-20.

- Foundations
- Write Paper
Search form
- Experiments
- Anthropology
- Self-Esteem
- Social Anxiety

Defining a Research Problem
Defining a research problem is the fuel that drives the scientific process, and is the foundation of any research method and experimental design, from true experiment to case study.
This article is a part of the guide:
- Null Hypothesis
- Research Hypothesis
- Selecting Method
- Test Hypothesis
Browse Full Outline
- 1 Scientific Method
- 2.1.1 Null Hypothesis
- 2.1.2 Research Hypothesis
- 2.2 Prediction
- 2.3 Conceptual Variable
- 3.1 Operationalization
- 3.2 Selecting Method
- 3.3 Measurements
- 3.4 Scientific Observation
- 4.1 Empirical Evidence
- 5.1 Generalization
- 5.2 Errors in Conclusion
It is one of the first statements made in any research paper and, as well as defining the research area, should include a quick synopsis of how the hypothesis was arrived at.
Operationalization is then used to give some indication of the exact definitions of the variables, and the type of scientific measurements used.
This will lead to the proposal of a viable hypothesis . As an aside, when scientists are putting forward proposals for research funds, the quality of their research problem often makes the difference between success and failure.

Structuring the Research Problem
Look at any scientific paper, and you will see the research problem, written almost like a statement of intent.
Defining a research problem is crucial in defining the quality of the answers, and determines the exact research method used. A quantitative experimental design uses deductive reasoning to arrive at a testable hypothesis .
Qualitative research designs use inductive reasoning to propose a research statement.
Formulating the research problem begins during the first steps of the scientific process .
As an example, a literature review and a study of previous experiments, and research, might throw up some vague areas of interest.
Many scientific researchers look at an area where a previous researcher generated some interesting results, but never followed up. It could be an interesting area of research, which nobody else has fully explored.
A scientist may even review a successful experiment, disagree with the results , the tests used, or the methodology , and decide to refine the research process, retesting the hypothesis .
This is called the conceptual definition, and is an overall view of the problem. A science report will generally begin with an overview of the previous research and real-world observations. The researcher will then state how this led to defining a research problem.
The Operational Definitions
The operational definition is the determining the scalar properties of the variables .
For example, temperature, weight and time are usually well known and defined, with only the exact scale used needing definition. If a researcher is measuring abstract concepts, such as intelligence, emotions, and subjective responses, then a system of measuring numerically needs to be established, allowing statistical analysis and replication.
For example, intelligence may be measured with IQ and human responses could be measured with a questionnaire from ‘1- strongly disagree’, to ‘5 - strongly agree’.
Behavioral biologists and social scientists might design an ordinal scale for measuring and rating behavior. These measurements are always subjective, but allow statistics and replication of the whole research method. This is all an essential part of defining a research problem.
Examples of Defining a Research Problem
An anthropologist might find references to a relatively unknown tribe in Papua New Guinea. Through inductive reasoning , she arrives at the research problem and asks,
‘How do these people live and how does their culture relate to nearby tribes?’
She has found a gap in knowledge, and she seeks to fill it, using a qualitative case study , without a hypothesis.
The Bandura Bobo Doll Experiment is a good example of using deductive reasoning to arrive at a research problem and hypothesis.
Anecdotal evidence showed that violent behavior amongst children was increasing. Bandura believed that higher levels of violent adult role models on television, was a contributor to this rise. This was expanded into a hypothesis , and operationalization of the variables, and scientific measurement scale , led to a robust experimental design.
- Psychology 101
- Flags and Countries
- Capitals and Countries
Martyn Shuttleworth (Oct 2, 2008). Defining a Research Problem. Retrieved Jun 18, 2024 from Explorable.com: https://explorable.com/defining-a-research-problem
You Are Allowed To Copy The Text
The text in this article is licensed under the Creative Commons-License Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) .
This means you're free to copy, share and adapt any parts (or all) of the text in the article, as long as you give appropriate credit and provide a link/reference to this page.
That is it. You don't need our permission to copy the article; just include a link/reference back to this page. You can use it freely (with some kind of link), and we're also okay with people reprinting in publications like books, blogs, newsletters, course-material, papers, wikipedia and presentations (with clear attribution).

Want to stay up to date? Follow us!
Get all these articles in 1 guide.
Want the full version to study at home, take to school or just scribble on?
Whether you are an academic novice, or you simply want to brush up your skills, this book will take your academic writing skills to the next level.

Download electronic versions: - Epub for mobiles and tablets - For Kindle here - PDF version here
Save this course for later
Don't have time for it all now? No problem, save it as a course and come back to it later.
Footer bottom
- Privacy Policy

- Subscribe to our RSS Feed
- Like us on Facebook
- Follow us on Twitter

What is Research Problem? Components, Identifying, Formulating,
- Post last modified: 13 August 2023
- Reading time: 10 mins read
- Post category: Research Methodology

What is Research Problem?
A research problem refers to an area or issue that requires investigation, analysis, and resolution through a systematic and scientific approach. It is a specific question, gap, or challenge within a particular field of study that researchers aim to address through their research endeavors.
Table of Content
- 1 What is Research Problem?
- 2 Concept of a Research Problem
- 3 Need to Define a Research Problem
- 4 Conditions and Components of a Research Problem
- 5 Identifying a Research Problem
- 6 Formulating a Research Problem
Concept of a Research Problem
The first step in any research project is to identify the problem. When we specifically talk about research related to a business organisation, the first step is to identify the problem that is being faced by the concerned organisation. The researchers need to develop a concrete, unambiguous and easily comprehensible definition of the problem that requires research.
If the research problem is not well-defined, the research project may be affected. You may also consider defining research problem and carrying out literature review as the foundation on which the entire research process is based.
In general, a research problem refers to a problem that a researcher has witnessed or experienced in a theoretical or real-life situation and wants to develop a solution for the same. The research problem is only a problem statement and it does not describe how to do something. It must be remembered that a research problem is always related to some kind of management dilemma
Need to Define a Research Problem
The researchers must clearly define or formulate the research problem in order to represent a clear picture of what they wish to achieve through their research. When a researcher starts off his research with a well-formulated research problem, it becomes easier to carry out the research.
Some of the major reasons for which a research problem must be defined are:
- Select useful information for research
- Segregate useful information from irrelevant information
- Monitor the research progress
- Ensure research is centred around a problem
- What data should be collected?
- What data attributes are relevant and need to be analysed?
- What relationships should be investigated?
- Determine the structure of the study
- Ensure that the research is centred around the research problem only
Defining a research problem well helps the decision makers in getting good research results if right questions are asked. On the contrary, correct answer to a wrong question will lead to bad research results.
Conditions and Components of a Research Problem
Conditions necessary for the existence of a research problem are:
- Existence of a problem whose solution is not known currently
- Existence of an individual, group or organisation to which the given problem can be attributed
- Existence of at least two alternative courses of action that can be pursued by a researcher
- At least two feasible outcomes of the course of action and out of two outcomes, one outcome should be more preferable to the other
A research problem consists of certain specific components as follows:
- Manager/Decision-maker (individual/group/institution) and his/ her objectives The individual, group or an institution is the one who is facing the problem. At times, the different individuals or groups related to a problem do not agree with the problem statement as their objectives differ from one another. The decision makers must agree on a concrete and clearly worded problem statemen.
- Environment or context of the problem
- Nature of the problem
- Alternative courses of problem
- A set of consequences related to courses of action and the occurrence of events that are not under the control of the manager/decision maker
- A state of uncertainty for which a course of action is best
Identifying a Research Problem
Identifying a research problem is an important and time-consuming activity. Research problem identification involves understanding the given social problem that needs to be investigated in order to solve it. In most cases, the researchers usually identify a research problem by using their observation, knowledge, wisdom and skills. Identifying a research problem can be as simple as recognising the difficulties and problems in your workplace.
Certain other factors that are considered while identifying a research problem include:
- Potential research problems raised at the end of journal articles
- Large-scale reports and data records in the field may disclose the findings or facts based on data that require further investigation
- Personal interest of the researcher
- Knowledge and competence of the researcher
- Availability of resources such as large-scale data collection, time and finance
- Relative importance of different problems
- Practical utility of finding answers to a problem
- Data availability for a problem
Formulating a Research Problem
Formulating a research problem is usually done under the first step of research process, i.e., defining the research problem. Identification, clarification and formulation of a research problem is done using different steps as:
- Discover the Management Dilemma
- Define the Management Question
- Define the Research Question
- Refine the Research Question(s)
You have already studied why it is important to clarify a research question. The next step is to discover the management dilemma. The entire research process starts with a management dilemma. For instance, an organisation facing increasing number of customer complaints may want to carry out research.
At most times, the researchers state the management dilemma followed by developing questions which are then broken down into specific set of questions. Management dilemma, in most cases, is a symptom of the actual problem being faced by an organisation.
A few examples of management dilemma are low turnover, high attrition, high product defect rate, low quality, increasing costs, decreasing profits, low employee morale, high absenteeism, flexibility and remote work issues, use of technology, increasing market share of a competitor, decline in plant/production capacity, distribution of profit between dividends and retained earnings, etc.
If an organisation tracks its performance indicators on a regular basis, it is quite easy to identify the management dilemma. Now, the difficult task for a researcher to choose a particular management dilemma among the given set of management dilemmas.
Business Ethics
( Click on Topic to Read )
- What is Ethics?
- What is Business Ethics?
- Values, Norms, Beliefs and Standards in Business Ethics
- Indian Ethos in Management
- Ethical Issues in Marketing
- Ethical Issues in HRM
- Ethical Issues in IT
- Ethical Issues in Production and Operations Management
- Ethical Issues in Finance and Accounting
- What is Corporate Governance?
- What is Ownership Concentration?
- What is Ownership Composition?
- Types of Companies in India
- Internal Corporate Governance
- External Corporate Governance
- Corporate Governance in India
- What is Enterprise Risk Management (ERM)?
- What is Assessment of Risk?
- What is Risk Register?
- Risk Management Committee
Corporate social responsibility (CSR)
- Theories of CSR
- Arguments Against CSR
- Business Case for CSR
- Importance of CSR in India
- Drivers of Corporate Social Responsibility
- Developing a CSR Strategy
- Implement CSR Commitments
- CSR Marketplace
- CSR at Workplace
- Environmental CSR
- CSR with Communities and in Supply Chain
- Community Interventions
- CSR Monitoring
- CSR Reporting
- Voluntary Codes in CSR
- What is Corporate Ethics?
Lean Six Sigma
- What is Six Sigma?
- What is Lean Six Sigma?
- Value and Waste in Lean Six Sigma
- Six Sigma Team
- MAIC Six Sigma
- Six Sigma in Supply Chains
- What is Binomial, Poisson, Normal Distribution?
- What is Sigma Level?
- What is DMAIC in Six Sigma?
- What is DMADV in Six Sigma?
- Six Sigma Project Charter
- Project Decomposition in Six Sigma
- Critical to Quality (CTQ) Six Sigma
- Process Mapping Six Sigma
- Flowchart and SIPOC
- Gage Repeatability and Reproducibility
- Statistical Diagram
- Lean Techniques for Optimisation Flow
- Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
- What is Process Audits?
- Six Sigma Implementation at Ford
- IBM Uses Six Sigma to Drive Behaviour Change
- Research Methodology
- What is Research?
- What is Hypothesis?
- Sampling Method
- Research Methods
- Data Collection in Research
- Methods of Collecting Data
Application of Business Research
- Levels of Measurement
- What is Sampling?
Hypothesis Testing
- Research Report
- What is Management?
- Planning in Management
- Decision Making in Management
- What is Controlling?
- What is Coordination?
- What is Staffing?
- Organization Structure
- What is Departmentation?
- Span of Control
- What is Authority?
- Centralization vs Decentralization
- Organizing in Management
- Schools of Management Thought
- Classical Management Approach
- Is Management an Art or Science?
- Who is a Manager?
Operations Research
- What is Operations Research?
- Operation Research Models
- Linear Programming
- Linear Programming Graphic Solution
- Linear Programming Simplex Method
- Linear Programming Artificial Variable Technique
- Duality in Linear Programming
- Transportation Problem Initial Basic Feasible Solution
- Transportation Problem Finding Optimal Solution
- Project Network Analysis with Critical Path Method
- Project Network Analysis Methods
- Project Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT)
- Simulation in Operation Research
- Replacement Models in Operation Research
Operation Management
- What is Strategy?
- What is Operations Strategy?
- Operations Competitive Dimensions
- Operations Strategy Formulation Process
- What is Strategic Fit?
- Strategic Design Process
- Focused Operations Strategy
- Corporate Level Strategy
- Expansion Strategies
- Stability Strategies
- Retrenchment Strategies
- Competitive Advantage
- Strategic Choice and Strategic Alternatives
- What is Production Process?
- What is Process Technology?
- What is Process Improvement?
- Strategic Capacity Management
- Production and Logistics Strategy
- Taxonomy of Supply Chain Strategies
- Factors Considered in Supply Chain Planning
- Operational and Strategic Issues in Global Logistics
- Logistics Outsourcing Strategy
- What is Supply Chain Mapping?
- Supply Chain Process Restructuring
- Points of Differentiation
- Re-engineering Improvement in SCM
- What is Supply Chain Drivers?
- Supply Chain Operations Reference (SCOR) Model
- Customer Service and Cost Trade Off
- Internal and External Performance Measures
- Linking Supply Chain and Business Performance
- Netflix’s Niche Focused Strategy
- Disney and Pixar Merger
- Process Planning at Mcdonald’s
Service Operations Management
- What is Service?
- What is Service Operations Management?
- What is Service Design?
- Service Design Process
- Service Delivery
- What is Service Quality?
- Gap Model of Service Quality
- Juran Trilogy
- Service Performance Measurement
- Service Decoupling
- IT Service Operation
- Service Operations Management in Different Sector
Procurement Management
- What is Procurement Management?
- Procurement Negotiation
- Types of Requisition
- RFX in Procurement
- What is Purchasing Cycle?
- Vendor Managed Inventory
- Internal Conflict During Purchasing Operation
- Spend Analysis in Procurement
- Sourcing in Procurement
- Supplier Evaluation and Selection in Procurement
- Blacklisting of Suppliers in Procurement
- Total Cost of Ownership in Procurement
- Incoterms in Procurement
- Documents Used in International Procurement
- Transportation and Logistics Strategy
- What is Capital Equipment?
- Procurement Process of Capital Equipment
- Acquisition of Technology in Procurement
- What is E-Procurement?
- E-marketplace and Online Catalogues
- Fixed Price and Cost Reimbursement Contracts
- Contract Cancellation in Procurement
- Ethics in Procurement
- Legal Aspects of Procurement
- Global Sourcing in Procurement
- Intermediaries and Countertrade in Procurement
Strategic Management
- What is Strategic Management?
- What is Value Chain Analysis?
- Mission Statement
- Business Level Strategy
- What is SWOT Analysis?
- What is Competitive Advantage?
- What is Vision?
- What is Ansoff Matrix?
- Prahalad and Gary Hammel
- Strategic Management In Global Environment
- Competitor Analysis Framework
- Competitive Rivalry Analysis
- Competitive Dynamics
- What is Competitive Rivalry?
- Five Competitive Forces That Shape Strategy
- What is PESTLE Analysis?
- Fragmentation and Consolidation Of Industries
- What is Technology Life Cycle?
- What is Diversification Strategy?
- What is Corporate Restructuring Strategy?
- Resources and Capabilities of Organization
- Role of Leaders In Functional-Level Strategic Management
- Functional Structure In Functional Level Strategy Formulation
- Information And Control System
- What is Strategy Gap Analysis?
- Issues In Strategy Implementation
- Matrix Organizational Structure
- What is Strategic Management Process?
Supply Chain
- What is Supply Chain Management?
- Supply Chain Planning and Measuring Strategy Performance
- What is Warehousing?
- What is Packaging?
- What is Inventory Management?
- What is Material Handling?
- What is Order Picking?
- Receiving and Dispatch, Processes
- What is Warehouse Design?
- What is Warehousing Costs?
You Might Also Like
What is parametric tests types: z-test, t-test, f-test, primary data and secondary data, what is measure of dispersion, what is hypothesis testing procedure, data processing in research, what is measure of skewness, what is experiments variables, types, lab, field, steps in questionnaire design, types of charts used in data analysis, data analysis in research, leave a reply cancel reply.
You must be logged in to post a comment.
World's Best Online Courses at One Place
We’ve spent the time in finding, so you can spend your time in learning
Digital Marketing
Personal Growth

Development

Organizing Academic Research Papers: The Research Problem/Question
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Executive Summary
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tertiary Sources
- What Is Scholarly vs. Popular?
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Annotated Bibliography
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- How to Manage Group Projects
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Essays
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Acknowledgements
A research problem is a statement about an area of concern, a condition to be improved, a difficulty to be eliminated, or a troubling question that exists in scholarly literature, in theory, or in practice that points to the need for meaningful understanding and deliberate investigation. In some social science disciplines the research problem is typically posed in the form of a question. A research problem does not state how to do something, offer a vague or broad proposition, or present a value question.
Importance of...
The purpose of a problem statement is to:
- Introduce the reader to the importance of the topic being studied . The reader is oriented to the significance of the study and the research questions or hypotheses to follow.
- Places the problem into a particular context that defines the parameters of what is to be investigated.
- Provides the framework for reporting the results and indicates what is probably necessary to conduct the study and explain how the findings will present this information.
In the social sciences, the research problem establishes the means by which you must answer the "So What?" question. The "So What?" question refers to a research problem surviving the relevancy test [the quality of a measurement procedure that provides repeatability and accuracy]. Note that answering the "So What" question requires a commitment on your part to not only show that you have researched the material, but that you have thought about its significance.
To survive the "So What" question, problem statements should possess the following attributes:
- Clarity and precision [a well-written statement does not make sweeping generalizations and irresponsible statements],
- Identification of what would be studied, while avoiding the use of value-laden words and terms,
- Identification of an overarching question and key factors or variables,
- Identification of key concepts and terms,
- Articulation of the study's boundaries or parameters,
- Some generalizability in regards to applicability and bringing results into general use,
- Conveyance of the study's importance, benefits, and justification [regardless of the type of research, it is important to address the “so what” question by demonstrating that the research is not trivial],
- Does not have unnecessary jargon; and,
- Conveyance of more than the mere gathering of descriptive data providing only a snapshot of the issue or phenomenon under investigation.
Castellanos, Susie. Critical Writing and Thinking . The Writing Center. Dean of the College. Brown University; Ellis, Timothy J. and Yair Levy Nova Framework of Problem-Based Research: A Guide for Novice Researchers on the Development of a Research-Worthy Problem. Informing Science: the International Journal of an Emerging Transdiscipline 11 (2008); Thesis and Purpose Statements . The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin, Madison; Thesis Statements . The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Tips and Examples for Writing Thesis Statements . The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Types and Content
There are four general conceptualizations of a research problem in the social sciences:
- Casuist Research Problem -- this type of problem relates to the determination of right and wrong in questions of conduct or conscience by analyzing moral dilemmas through the application of general rules and the careful distinction of special cases.
- Difference Research Problem -- typically asks the question, “Is there a difference between two or more groups or treatments?” This type of problem statement is used when the researcher compares or contrasts two or more phenomena.
- Descriptive Research Problem -- typically asks the question, "what is...?" with the underlying purpose to describe a situation, state, or existence of a specific phenomenon.
- Relational Research Problem -- suggests a relationship of some sort between two or more variables to be investigated. The underlying purpose is to investigate qualities/characteristics that are connected in some way.
A problem statement in the social sciences should contain :
- A lead-in that helps ensure the reader will maintain interest over the study
- A declaration of originality [e.g., mentioning a knowledge void, which would be supported by the literature review]
- An indication of the central focus of the study, and
- An explanation of the study's significance or the benefits to be derived from an investigating the problem.
II. Sources of Problems for Investigation
Identifying a problem to study can be challenging, not because there is a lack of issues that could be investigated, but due to pursuing a goal of formulating a socially relevant and researchable problem statement that is unique and does not simply duplicate the work of others. To facilitate how you might select a problem from which to build a research study, consider these three broad sources of inspiration:
Deductions from Theory This relates to deductions made from social philosophy or generalizations embodied in life in society that the researcher is familiar with. These deductions from human behavior are then fitted within an empirical frame of reference through research. From a theory, the research can formulate a research problem or hypothesis stating the expected findings in certain empirical situations. The research asks the question: “What relationship between variables will be observed if theory aptly summarizes the state of affairs?” One can then design and carry out a systematic investigation to assess whether empirical data confirm or reject the hypothesis and hence the theory.
Interdisciplinary Perspectives Identifying a problem that forms the basis for a research study can come from academic movements and scholarship originating in disciplines outside of your primary area of study. A review of pertinent literature should include examining research from related disciplines, which can expose you to new avenues of exploration and analysis. An interdisciplinary approach to selecting a research problem offers an opportunity to construct a more comprehensive understanding of a very complex issue than any single discipline might provide.
Interviewing Practitioners The identification of research problems about particular topics can arise from formal or informal discussions with practitioners who provide insight into new directions for future research and how to make research findings increasingly relevant to practice. Discussions with experts in the field, such as, teachers, social workers, health care providers, etc., offers the chance to identify practical, “real worl” problems that may be understudied or ignored within academic circles. This approach also provides some practical knowledge which may help in the process of designing and conducting your study.
Personal Experience Your everyday experiences can give rise to worthwhile problems for investigation. Think critically about your own experiences and/or frustrations with an issue facing society, your community, or in your neighborhood. This can be derived, for example, from deliberate observations of certain relationships for which there is no clear explanation or witnessing an event that appears harmful to a person or group or that is out of the ordinary.
Relevant Literature The selection of a research problem can often be derived from an extensive and thorough review of pertinent research associated with your overall area of interest. This may reveal where gaps remain in our understanding of a topic. Research may be conducted to: 1) fill such gaps in knowledge; 2) evaluate if the methodologies employed in prior studies can be adapted to solve other problems; or, 3) determine if a similar study could be conducted in a different subject area or applied to different study sample [i.e., different groups of people]. Also, authors frequently conclude their studies by noting implications for further research; this can also be a valuable source of problems to investigate.
III. What Makes a Good Research Statement?
A good problem statement begins by introducing the broad area in which your research is centered and then gradually leads the reader to the more narrow questions you are posing. The statement need not be lengthy but a good research problem should incorporate the following features:
Compelling topic Simple curiosity is not a good enough reason to pursue a research study. The problem that you choose to explore must be important to you and to a larger community you share. The problem chosen must be one that motivates you to address it. Supports multiple perspectives The problem most be phrased in a way that avoids dichotomies and instead supports the generation and exploration of multiple perspectives. A general rule of thumb is that a good research problem is one that would generate a variety of viewpoints from a composite audience made up of reasonable people. Researchable It seems a bit obvious, but you don't want to find yourself in the midst of investigating a complex research project and realize that you don't have much to draw on for your research. Choose research problems that can be supported by the resources available to you. Not sure? Seek out help from a librarian!
NOTE: Do not confuse a research problem with a research topic. A topic is something to read and obtain information about whereas a problem is something to solve or framed as a question that must be answered.
IV. Mistakes to Avoid
Beware of circular reasoning . Don’t state that the research problem as simply the absence of the thing you are suggesting. For example, if you propose, "The problem in this community is that it has no hospital."
This only leads to a research problem where:
- The need is for a hospital
- The objective is to create a hospital
- The method is to plan for building a hospital, and
- The evaluation is to measure if there is a hospital or not.
This is an example of a research problem that fails the "so what?" test because it does not reveal the relevance of why you are investigating the problem of having no hospital in the community [e.g., there's a hospital in the community ten miles away] and because the research problem does not elucidate the significance of why one should study the fact that no hospital exists in the community [e.g., that hospital in the community ten miles away has no emergency room].
Choosing and Refining Topics . Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Ellis, Timothy J. and Yair Levy Nova Framework of Problem-Based Research: A Guide for Novice Researchers on the Development of a Research-Worthy Problem. Informing Science: the International Journal of an Emerging Transdiscipline 11 (2008); How to Write a Research Question . The Writing Center. George Mason University; Invention: Developing a Thesis Statement . The Reading/Writing Center. Hunter College; Problem Statements PowerPoint Presentation . The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Procter, Margaret. Using Thesis Statements . University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Trochim, William M.K. Problem Formulation . Research Methods Knowledge Base. 2006; Thesis and Purpose Statements . The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin, Madison; Thesis Statements . The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Tips and Examples for Writing Thesis Statements . The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University.
- << Previous: Background Information
- Next: Theoretical Framework >>
- Last Updated: Jul 18, 2023 11:58 AM
- URL: https://library.sacredheart.edu/c.php?g=29803
- QuickSearch
- Library Catalog
- Databases A-Z
- Publication Finder
- Course Reserves
- Citation Linker
- Digital Commons
- Our Website
Research Support
- Ask a Librarian
- Appointments
- Interlibrary Loan (ILL)
- Research Guides
- Databases by Subject
- Citation Help
Using the Library
- Reserve a Group Study Room
- Renew Books
- Honors Study Rooms
- Off-Campus Access
- Library Policies
- Library Technology
User Information
- Grad Students
- Online Students
- COVID-19 Updates
- Staff Directory
- News & Announcements
- Library Newsletter
My Accounts
- Interlibrary Loan
- Staff Site Login
FIND US ON

The Best PhD and Masters Consulting Company

The Importance of a Well-Defined Research Problem.
In the labyrinthine world of academic research, a well-defined research problem serves as the North Star, guiding scholars and scientists on their intellectual voyages of discovery. It is the compass that steers research endeavors toward meaningful, impactful, and enlightening destinations. In this comprehensive blog, we will delve into the paramount significance of a well-defined research problem and explore why it stands as the bedrock of all scholarly pursuits.
The Essence of a Well-Defined Research Problem.
A well-defined research problem is more than just a question; it is a gateway to understanding, a key to unlocking the mysteries of the universe, and a catalyst for innovation. Here’s why it is so crucial:
1. Precision and Focus.
A research problem carves a path through the dense forest of potential research areas. It provides clarity and precision, helping researchers channel their efforts effectively. Without a well-defined problem, research can drift aimlessly, leading to inconclusive results or even dead ends.
2. Relevance and Significance.
An effective research problem doesn’t exist in a vacuum; it addresses real-world issues and concerns. It tackles questions or challenges that are pertinent to a specific field or even society at large. This relevance is what makes research meaningful and impactful.
3. Structured Research.
Think of a research problem as the blueprint for your research journey. It dictates the structure and organization of your study, determining what literature to review, which methodologies to employ, and how data should be analyzed. Without this foundation, research can become disjointed and chaotic.
4. Knowledge Advancement.
At its core, research aims to expand the boundaries of human knowledge. A well-defined problem encapsulates the gap in existing knowledge, highlighting precisely what needs to be explored or understood. This, in turn, propels the collective intellect forward.
5. Practical Application.
Many research problems have direct implications for practical applications. Whether it’s developing new medical treatments, optimizing renewable energy sources, or improving educational techniques, research problems lay the groundwork for solutions that can benefit society.
Formulating a Well-Defined Research Problem.
Creating a well-defined research problem is both an art and a science. It requires a thoughtful and systematic approach:
1. Choose Your Field.
Begin by selecting the academic field or domain you are passionate about. Your research problem should align with your interests and expertise.
2. Extensive Literature Review.
A thorough literature review is paramount. It helps you understand what has already been explored, what questions remain unanswered, and where the gaps in knowledge lie.
3. Identify the Gap.
Based on your literature review, pinpoint the specific gap or issue you want to investigate. Your research problem should be a concise, focused statement that encapsulates this gap.
4. Set Clear Objectives.
Define the objectives or goals of your research. What do you intend to achieve by addressing this problem? What are the expected outcomes?
5. Scope and Feasibility.
Determine the scope of your research and assess its feasibility. Ensure that your research problem can be tackled within the constraints of time, resources, and ethical considerations.
6. Seek Feedback.
Don’t hesitate to consult with mentors, peers, or experts in your field. Their input can help refine and validate your research problem.
The Ripple Effect of Well-Defined Research Problems.
A well-defined research problem has a far-reaching impact that extends beyond the confines of academia:
1. Scientific Progress.
Research problems are the driving force behind scientific advancements. They encourage researchers to push boundaries, challenge established theories, and pioneer new paradigms.
2. Technological Innovation.
Many of the technological marvels that shape our world today emerged from research endeavors aimed at solving specific problems. From the internet to medical breakthroughs, research problems drive innovation.
3. Societal Transformation.
Research that addresses pressing social, economic, or environmental issues can catalyze profound societal transformations. It can inform policies, drive advocacy, and empower communities.
4. Intellectual Growth.
Engaging with research problems fosters intellectual growth. It nurtures critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and a deeper understanding of the world.
Conclusion.
In the grand tapestry of human knowledge, a well-defined research problem is the warp and weft that weave together insights, discoveries, and innovations. It is the crucible in which curiosity transforms into wisdom, and the spark that ignites the fires of progress. Whether you are a researcher embarking on a new project or a curious mind seeking to understand the world, always remember that a well-defined research problem is your compass, your guide, and your ticket to the frontiers of knowledge.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- OU Homepage
- The University of Oklahoma
OU Biologist Reveals Wicked Problem in Global Plant Nutrition

Nutrient dilution, caused in large part by carbon dioxide, is leading to dramatic changes in global ecology
Josh DeLozier
Media Contact
Josh DeLozier (405) 325-1502 [email protected]
NORMAN, OKLA. – Michael Kaspari, a professor of biology in the University of Oklahoma School of Biological Sciences, has published research in the journal Trends in Ecology and Evolution that highlights nutrient dilution in plants and its cascading impact on the animals and insects that eat this less nutritious food.
“Every living thing on the planet is made out of chemical elements, including plants,” Kaspari said. “However, we now have ample, disturbing evidence that the concentration of these essential elements has been declining for the last 20-30 years. That means that every bite an herbivore takes has less and less nutrition.”
Kaspari explains that the quality of our food supply is decreasing at a time when the quantity is increasing. The research, which is funded by the National Science Foundation, shows that nutrient dilution is a widespread, global phenomenon.
“This situation is tied closely to the increase in carbon dioxide in the atmosphere,” he said. “The carbon dioxide is acting as its own fertilizer, but it’s adding empty carbohydrates to the world’s food supply. This results in ‘green deserts’ which are fields and forests full of plants with empty carbs.”
As the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere increases, plants grow larger. However, since there are no additional nutrients in the soil, the quality of the vegetation decreases.
“It’s the equivalent of taking a field of kale and converting it to iceberg lettuce,” he said. “And while we have perhaps 30% more plant matter on the planet today than we did 100 years ago, much of it is empty calories. This decline is leading to a loss of plant-eaters and is impacting the predators that eat the plant-eaters.”
Research shows that the global insect population is declining at approximately 1.5% annually, even though prairie vegetation is double what it was 20 years ago. This has led to a 37% decline in grasshopper populations in the Konza Prairie during that same period.
“Insect declines are a wicked problem that has a lot of moving parts,” he said. “To address this problem, some suggest eliminating pesticides or restoring habitats. Those things will help, but to make real strides, we must reduce the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. That will require a lot of ingenuity and cooperation.”
According to Kaspari, this situation is also impacting the human food supply and is likely already leading to poor health outcomes for impoverished communities around the globe.
“These communities, already dealing with famine and malnourishment, must now also contend with developmental abnormalities and higher fetal mortality due to the lack of essential micronutrients like zinc and iron that help them grow,” he said. “If we care about our fellow human beings, then we must take this seriously and act now.”
Learn more about the Kaspari Lab at the University of Oklahoma and read the full study, "Nutrient Dilution and the Future of Herbivore Populations," published in Trends in Ecology and Evolution , DOI no. 10.1016/j.tree.2024.05.001 .
About the project
Michael Kaspari is a George Lynn Cross Research Professor and a Fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science and the Ecological Society of America. He worked alongside Ellen Welti, a former postdoctoral researcher at the University of Oklahoma who is now a staff member and researcher associate at the Smithsonian, and three OU undergraduate student researchers. This research is rooted in an earlier publication in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences that received the Cozzarelli Prize from the National Academy of Sciences for being one of the top two environmental science papers in 2020.
About the University of Oklahoma
Founded in 1890, the University of Oklahoma is a public research university located in Norman, Oklahoma. As the state’s flagship university, OU serves the educational, cultural, economic and health care needs of the state, region and nation. OU was named the state’s highest-ranking university in U.S. News & World Report’s most recent Best Colleges list . For more information about the university, visit ou.edu .
Recent News
Ou researchers discover genetic collaboration in harmful algae.
A breakthrough study of freshwater harmful algal communities led by Dave Hambright, a Regents’ Professor of Biology, has discovered that complementary genes in bacteria and algae living in the same algal colonies coordinate the use and movement of nutrients within the colony. This research, funded by the National Science Foundation, has been published in the journal Microbiome.

OU Climbs in Engineering Graduate Program Rankings
U.S. News and World Report ranked the University of Oklahoma 106th among the best schools for engineering graduate programs, climbing four spots from 110th last year.

Potential New Treatment Option for Diabetic Retinopathy
Researchers at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center are studying a new, revolutionary treatment for diabetic retinopathy.

More OU News

- Accessibility
- Sustainability
- OU Job Search
- Legal Notices
- Resources and Offices
- OU Report It!
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research process
- How to Define a Research Problem | Ideas & Examples
How to Define a Research Problem | Ideas & Examples
Published on 8 November 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George.
A research problem is a specific issue or gap in existing knowledge that you aim to address in your research. You may choose to look for practical problems aimed at contributing to change, or theoretical problems aimed at expanding knowledge.
Some research will do both of these things, but usually the research problem focuses on one or the other. The type of research problem you choose depends on your broad topic of interest and the type of research you think will fit best.
This article helps you identify and refine a research problem. When writing your research proposal or introduction , formulate it as a problem statement and/or research questions .
Table of contents
Why is the research problem important, step 1: identify a broad problem area, step 2: learn more about the problem, frequently asked questions about research problems.
Having an interesting topic isn’t a strong enough basis for academic research. Without a well-defined research problem, you are likely to end up with an unfocused and unmanageable project.
You might end up repeating what other people have already said, trying to say too much, or doing research without a clear purpose and justification. You need a clear problem in order to do research that contributes new and relevant insights.
Whether you’re planning your thesis , starting a research paper , or writing a research proposal , the research problem is the first step towards knowing exactly what you’ll do and why.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
As you read about your topic, look for under-explored aspects or areas of concern, conflict, or controversy. Your goal is to find a gap that your research project can fill.
Practical research problems
If you are doing practical research, you can identify a problem by reading reports, following up on previous research, or talking to people who work in the relevant field or organisation. You might look for:
- Issues with performance or efficiency
- Processes that could be improved
- Areas of concern among practitioners
- Difficulties faced by specific groups of people
Examples of practical research problems
Voter turnout in New England has been decreasing, in contrast to the rest of the country.
The HR department of a local chain of restaurants has a high staff turnover rate.
A non-profit organisation faces a funding gap that means some of its programs will have to be cut.
Theoretical research problems
If you are doing theoretical research, you can identify a research problem by reading existing research, theory, and debates on your topic to find a gap in what is currently known about it. You might look for:
- A phenomenon or context that has not been closely studied
- A contradiction between two or more perspectives
- A situation or relationship that is not well understood
- A troubling question that has yet to be resolved
Examples of theoretical research problems
The effects of long-term Vitamin D deficiency on cardiovascular health are not well understood.
The relationship between gender, race, and income inequality has yet to be closely studied in the context of the millennial gig economy.
Historians of Scottish nationalism disagree about the role of the British Empire in the development of Scotland’s national identity.
Next, you have to find out what is already known about the problem, and pinpoint the exact aspect that your research will address.
Context and background
- Who does the problem affect?
- Is it a newly-discovered problem, or a well-established one?
- What research has already been done?
- What, if any, solutions have been proposed?
- What are the current debates about the problem? What is missing from these debates?
Specificity and relevance
- What particular place, time, and/or group of people will you focus on?
- What aspects will you not be able to tackle?
- What will the consequences be if the problem is not resolved?
Example of a specific research problem
A local non-profit organisation focused on alleviating food insecurity has always fundraised from its existing support base. It lacks understanding of how best to target potential new donors. To be able to continue its work, the organisation requires research into more effective fundraising strategies.
Once you have narrowed down your research problem, the next step is to formulate a problem statement , as well as your research questions or hypotheses .
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement.
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
The way you present your research problem in your introduction varies depending on the nature of your research paper . A research paper that presents a sustained argument will usually encapsulate this argument in a thesis statement .
A research paper designed to present the results of empirical research tends to present a research question that it seeks to answer. It may also include a hypothesis – a prediction that will be confirmed or disproved by your research.
Research objectives describe what you intend your research project to accomplish.
They summarise the approach and purpose of the project and help to focus your research.
Your objectives should appear in the introduction of your research paper , at the end of your problem statement .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2022, November 08). How to Define a Research Problem | Ideas & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 18 June 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/the-research-process/define-research-problem/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, dissertation & thesis outline | example & free templates, example theoretical framework of a dissertation or thesis, how to write a strong hypothesis | guide & examples.
Check for Recalls Search vehicles, car seats, tires and other equipment for safety recalls, investigations, complaints and manufacturer communication.
Where’s my vin.
Every vehicle has a unique vehicle identification number , often referred to as a VIN. Look on the lower left of your car’s windshield for your 17-character VIN. Your VIN is also located on your car’s registration card, and it may be shown on your insurance card.
What information will display in the search results?
- When searching by license plate or VIN, you’ll learn if a specific vehicle needs to be repaired as part of a recall.
- When searching by a vehicle’s year, make and model, or for car seats, tires or equipment, you'll get general results for recalls, investigations, complaints and manufacturer communications.
What will the license plate and VIN search show?
- An unrepaired recall for a vehicle from certain manufacturers .
- If the vehicle has no unrepaired recalls, you will see the message: "0 unrepaired recalls associated with this VIN."
What won’t the license plate and VIN search show?
- A safety recall that has already been repaired.
- Some recently announced safety recalls for which not all VINs have been identified. VINs are added continuously so please check regularly.
- Safety recalls that are more than 15 years old (except where a manufacturer offers more coverage).
- Safety recalls conducted by small vehicle manufacturers, including some ultra-luxury brands and specialty applications.
- Manufacturer customer service or other non-safety recall campaigns.
- A recall involving an international vehicle.
Why is the license plate search result showing a different vehicle?
License plate information is generated from state department of motor vehicles. If the search result shows a vehicle you previously owned, rather than your new vehicle with the same license plate, contact your state DMV to request your vehicle information be updated. In the meantime, you can search for recalls using your vehicle’s VIN.
Other search options, including by NHTSA ID
You can also search for recalls and safety issues information by NHTSA ID and complaints by keyword .
Get Recall Alerts
Download NHTSA's free SaferCar app. When SaferCar discovers a safety recall for the vehicle or equipment you entered, it will send you an alert on your phone.
You can also sign up for general recall alerts via email.
Report a Safety Problem by filing a complaint with NHTSA
Have you experienced a vehicle, tire, car seat, or equipment safety problem that could be a safety defect.
If so, you can file a complaint that we will carefully review — like we do with every safety problem submitted to NHTSA. Complaints like yours help us investigate possible defects, which could lead to a safety recall.
From complaints to recall
NHTSA issues vehicle safety standards and requires manufacturers to recall vehicles and equipment that have safety-related defects. Learn about NHTSA's recall process.
Reporting your problem is the important first step.
Your complaint will be added to a public NHTSA database after personally identifying information is removed.
If the agency receives similar reports from a number of people about the same product, this could indicate that a safety-related defect may exist that would warrant the opening of an investigation.
Investigations
Nhtsa conducts an investigation from reported complaints..
A. SCREENING
NHTSA reviews filed complaints from vehicle owners and other information related to alleged defects to decide whether to open an investigation.
B. ANALYSIS
NHTSA conducts an analysis of any petitions calling for defect investigations. If the petition is denied, the reasons for the denial are published in the Federal Register.
C. INVESTIGATION
NHTSA opens an investigation of alleged safety defects. It is closed when they notify the manufacturer of recall recommendations or they don’t identify a safety-related defect.
D. RECALL MANAGEMENT
NHTSA monitors the effectiveness and management of recalls, including the filing of recall notices with NHTSA, communicating with owners regarding the recalls and tracking the completion rate of each recall.
Initiated safety recalls require a manufacturer's action to announce and remedy the defects.
A recall is issued when a manufacturer or NHTSA determines that a vehicle, equipment, car seat, or tire creates an unreasonable safety risk or fails to meet minimum safety standards. Most decisions to conduct a recall and remedy a safety defect are made voluntarily by manufacturers prior to any involvement by NHTSA.
Manufacturers are required to fix the problem by repairing it, replacing it, offering a refund, or in rare cases repurchasing the vehicle.
Using our VIN lookup tool, you can access recall information provided by the manufacturer conducting the recall which may be not posted yet on NHTSA’s site.
Recall Spotlight
Recalls Spotlight monitors high-profile recalls and offers consumers resources to find and address vehicle recalls.
Defects Investigation and Recalls Resources
Quick links to databases, resources and reports related to defects investigations and recalls.
Roles in the Recall Process
Manufacturer
Manufacturers will notify registered owners by first class mail within 60 days of notifying NHTSA of a recall decision. Manufacturers should offer a proper remedy to the owner.
NHTSA will monitor each safety recall to make sure owners receive safe, free, and effective remedies from manufacturers according to the Safety Act and Federal regulations.
You (owner)
You’ll be notified via mail from the manufacturer. When you receive a notification, follow any interim safety guidance provided by the manufacturer and contact your local dealership to fix the recalled part for free.
Register your vehicle, tires, car seats & equipment and check recalls twice a year.
Motor Vehicle Safety Defects And Recalls - What Every Vehicle Owner Should Know
Download this brochure to get more information about how and why recall campaigns are initiated, and to know your rights and responsibilities when a vehicle or item of motor vehicle equipment is recalled.
Vehicle Comparison
Available manufacturers.
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper: The Research Problem/Question
- Purpose of Guide
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- The Research Problem/Question
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Evaluating Sources
- Reading Research Effectively
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- What Is Scholarly vs. Popular?
- Is it Peer-Reviewed?
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism [linked guide]
- Annotated Bibliography
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
A research problem is a definite or clear expression [statement] about an area of concern, a condition to be improved upon, a difficulty to be eliminated, or a troubling question that exists in scholarly literature, in theory, or within existing practice that points to a need for meaningful understanding and deliberate investigation. A research problem does not state how to do something, offer a vague or broad proposition, or present a value question.
Bryman, Alan. “The Research Question in Social Research: What is its Role?” International Journal of Social Research Methodology 10 (2007): 5-20; Guba, Egon G., and Yvonna S. Lincoln. “Competing Paradigms in Qualitative Research.” In Handbook of Qualitative Research . Norman K. Denzin and Yvonna S. Lincoln, editors. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 1994), pp. 105-117.
Importance of...
The purpose of a problem statement is to:
- Introduce the reader to the importance of the topic being studied . The reader is oriented to the significance of the study.
- Anchors the research questions, hypotheses, or assumptions to follow . It offers a concise statement about the purpose of your paper.
- Place the topic into a particular context that defines the parameters of what is to be investigated.
- Provide the framework for reporting the results and indicates what is probably necessary to conduct the study and explain how the findings will present this information.
In the social sciences, the research problem establishes the means by which you must answer the "So What?" question. This question refers to a research problem surviving the relevancy test [the quality of a measurement procedure that provides repeatability and accuracy]. Note that answering the "So What?" question requires a commitment on your part to not only show that you have reviewed the literature, but that you have thoroughly considered its significance and its implications applied to obtaining new knowledge or understanding.
To survive the "So What" question, problem statements should possess the following attributes:
- Clarity and precision [a well-written statement does not make sweeping generalizations and irresponsible pronouncements; it also does include unspecific determinates like "very" or "giant"],
- Demonstrate a researchable topic or issue [i.e., feasibility of conducting the study is based upon access to information that can be effectively acquired, gathered, interpreted, synthesized, and understood],
- Identification of what would be studied, while avoiding the use of value-laden words and terms,
- Identification of an overarching question or small set of questions accompanied by key factors or variables,
- Identification of key concepts and terms,
- Articulation of the study's boundaries or parameters or limitations,
- Some generalizability in regards to applicability and bringing results into general use,
- Conveyance of the study's importance, benefits, and justification [i.e., regardless of the type of research, it is important to demonstrate that the research is not trivial],
- Does not have unnecessary jargon or overly complex sentence constructions; and,
- Conveyance of more than the mere gathering of descriptive data providing only a snapshot of the issue or phenomenon under investigation.
Bryman, Alan. “The Research Question in Social Research: What is its Role?” International Journal of Social Research Methodology 10 (2007): 5-20; Castellanos, Susie. Critical Writing and Thinking . The Writing Center. Dean of the College. Brown University; Ellis, Timothy J. and Yair Levy Nova Framework of Problem-Based Research: A Guide for Novice Researchers on the Development of a Research-Worthy Problem. Informing Science: the International Journal of an Emerging Transdiscipline 11 (2008); Thesis and Purpose Statements . The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin, Madison; Thesis Statements . The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Tips and Examples for Writing Thesis Statements . The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University.
Structure and Writing Style
Sources of Problems for Investigation
The identification of a problem to study can be challenging, not because there's a lack of issues that could be investigated, but due to the challenge of formulating an academically relevant and researchable problem which is unique and does not simply duplicate the work of others. To facilitate how you might select a problem from which to build a research study, consider these sources of inspiration:
Deductions from Theory This relates to deductions made from social philosophy or generalizations embodied in life and in society that the researcher is familiar with. These deductions from human behavior are then placed within an empirical frame of reference through research. From a theory, the researcher can formulate a research problem or hypothesis stating the expected findings in certain empirical situations. The research asks the question: “What relationship between variables will be observed if theory aptly summarizes the state of affairs?” One can then design and carry out a systematic investigation to assess whether empirical data confirm or reject the hypothesis, and hence, the theory.
Interdisciplinary Perspectives Identifying a problem that forms the basis for a research study can come from academic movements and scholarship originating in disciplines outside of your primary area of study. This can be an intellectually stimulating exercise. A review of pertinent literature should include examining research from related disciplines that can reveal new avenues of exploration and analysis. An interdisciplinary approach to selecting a research problem offers an opportunity to construct a more comprehensive understanding of a very complex issue that any single discipline may be able to provide.
Interviewing Practitioners The identification of research problems about particular topics can arise from formal interviews or informal discussions with practitioners who provide insight into new directions for future research and how to make research findings more relevant to practice. Discussions with experts in the field, such as, teachers, social workers, health care providers, lawyers, business leaders, etc., offers the chance to identify practical, “real world” problems that may be understudied or ignored within academic circles. This approach also provides some practical knowledge which may help in the process of designing and conducting your study.
Personal Experience Don't undervalue your everyday experiences or encounters as worthwhile problems for investigation. Think critically about your own experiences and/or frustrations with an issue facing society, your community, your neighborhood, your family, or your personal life. This can be derived, for example, from deliberate observations of certain relationships for which there is no clear explanation or witnessing an event that appears harmful to a person or group or that is out of the ordinary.
Relevant Literature The selection of a research problem can be derived from a thorough review of pertinent research associated with your overall area of interest. This may reveal where gaps exist in understanding a topic or where an issue has been understudied. Research may be conducted to: 1) fill such gaps in knowledge; 2) evaluate if the methodologies employed in prior studies can be adapted to solve other problems; or, 3) determine if a similar study could be conducted in a different subject area or applied in a different context or to different study sample [i.e., different setting or different group of people].Also, authors frequently conclude their studies by noting implications for further research; read the conclusion of pertinent studies because statements about further research can be a valuable source for identifying new problems to investigate. The fact that a researcher has identified a topic worthy of further exploration validates the fact it is worth pursuing.
What Makes a Good Research Statement?
A good problem statement begins by introducing the broad area in which your research is centered, gradually leading the reader to the more specific issues you are investigating. The statement need not be lengthy, but a good research problem should incorporate the following features:
1. Compelling Topic The problem chosen should be one that motivates you to address it but simple curiosity is not a good enough reason to pursue a research study because this does not indicate significance. The problem that you choose to explore must be important to you, but it must also be viewed as important by your readers and to a the larger academic and/or social community that could be impacted by the results of your study. 2. Supports Multiple Perspectives The problem must be phrased in a way that avoids dichotomies and instead supports the generation and exploration of multiple perspectives. A general rule of thumb in the social sciences is that a good research problem is one that would generate a variety of viewpoints from a composite audience made up of reasonable people. 3. Researchability This isn't a real word but it represents an important aspect of creating a good research statement. It seems a bit obvious, but you don't want to find yourself in the midst of investigating a complex research project and realize that you don't have enough prior research to draw from for your analysis. There's nothing inherently wrong with original research, but you must choose research problems that can be supported, in some way, by the resources available to you. If you are not sure if something is researchable, don't assume that it isn't if you don't find information right away--seek help from a librarian !
NOTE: Do not confuse a research problem with a research topic. A topic is something to read and obtain information about, whereas a problem is something to be solved or framed as a question raised for inquiry, consideration, or solution, or explained as a source of perplexity, distress, or vexation. In short, a research topic is something to be understood; a research problem is something that needs to be investigated.
Asking Analytical Questions about the Research Problem
Research problems in the social and behavioral sciences are often analyzed around critical questions that must be investigated. These questions can be explicitly listed in the introduction [i.e., "This study addresses three research questions about women's psychological recovery from domestic abuse in multi-generational home settings..."], or, the questions are implied in the text as specific areas of study related to the research problem. Explicitly listing your research questions at the end of your introduction can help in designing a clear roadmap of what you plan to address in your study, whereas, implicitly integrating them into the text of the introduction allows you to create a more compelling narrative around the key issues under investigation. Either approach is appropriate.
The number of questions you attempt to address should be based on the complexity of the problem you are investigating and what areas of inquiry you find most critical to study. Practical considerations, such as, the length of the paper you are writing or the availability of resources to analyze the issue can also factor in how many questions to ask. In general, however, there should be no more than four research questions underpinning a single research problem.
Given this, well-developed analytical questions can focus on any of the following:
- Highlights a genuine dilemma, area of ambiguity, or point of confusion about a topic open to interpretation by your readers;
- Yields an answer that is unexpected and not obvious rather than inevitable and self-evident;
- Provokes meaningful thought or discussion;
- Raises the visibility of the key ideas or concepts that may be understudied or hidden;
- Suggests the need for complex analysis or argument rather than a basic description or summary; and,
- Offers a specific path of inquiry that avoids eliciting generalizations about the problem.
NOTE: Questions of how and why concerning a research problem often require more analysis than questions about who, what, where, and when. You should still ask yourself these latter questions, however. Thinking introspectively about the who, what, where, and when of a research problem can help ensure that you have thoroughly considered all aspects of the problem under investigation and help define the scope of the study in relation to the problem.
Mistakes to Avoid
Beware of circular reasoning! Do not state that the research problem as simply the absence of the thing you are suggesting. For example, if you propose the following, "The problem in this community is that there is no hospital," this only leads to a research problem where:
- The need is for a hospital
- The objective is to create a hospital
- The method is to plan for building a hospital, and
- The evaluation is to measure if there is a hospital or not.
This is an example of a research problem that fails the "So What?" test . In this example, the problem does not reveal the relevance of why you are investigating the fact there is no hospital in the community [e.g., there's a hospital in the community ten miles away]; it does not elucidate the significance of why one should study the fact there is no hospital in the community [e.g., that hospital in the community ten miles away has no emergency room]; the research problem does not offer an intellectual pathway towards adding new knowledge or clarifying prior knowledge [e.g., the county in which there is no hospital already conducted a study about the need for a hospital]; and, the problem does not offer meaningful outcomes that lead to recommendations that can be generalized for other situations or that could suggest areas for further research [e.g., the challenges of building a new hospital serves as a case study for other communities].
Alvesson, Mats and Jörgen Sandberg. “Generating Research Questions Through Problematization.” Academy of Management Review 36 (April 2011): 247-271 ; Choosing and Refining Topics . Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Ellis, Timothy J. and Yair Levy Nova. "Framework of Problem-Based Research: A Guide for Novice Researchers on the Development of a Research-Worthy Problem." Informing Science: the International Journal of an Emerging Transdiscipline 11 (2008); How to Write a Research Question . The Writing Center. George Mason University; Invention: Developing a Thesis Statement . The Reading/Writing Center. Hunter College; Problem Statements PowerPoint Presentation . The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Procter, Margaret. Using Thesis Statements . University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Trochim, William M.K. Problem Formulation . Research Methods Knowledge Base. 2006; Thesis and Purpose Statements . The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin, Madison; Thesis Statements . The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Tips and Examples for Writing Thesis Statements . The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Walk, Kerry. Asking an Analytical Question . [Class handout or worksheet]. Princeton University; White, Patrick. Developing Research Questions: A Guide for Social Scientists . New York: Palgrave McMillan, 2009.
- << Previous: Broadening a Topic Idea
- Next: Preparing to Write >>
- Last Updated: Sep 8, 2023 12:19 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.txstate.edu/socialscienceresearch
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
- Cultural Issues and the 2024 Election
Immigration, gender identity, racial diversity and views of a changing society
Table of contents.
- Voters’ views about race and society, the impact of the legacy of slavery
- Most voters, but not all, view the nation’s diversity as a strength
- How should the country handle undocumented immigrants currently in the U.S.?
- Attitudes toward hearing other languages in public places
- Biden and Trump supporters’ views about discussing America’s historical successes, failures
- How does the U.S. compare with other countries?
- Views of women’s progress
- How much of a priority should marriage and children be?
- Abortion, IVF access and birth control
- Views of gender identity
- Voters’ attitudes toward use of gender-neutral pronouns
- Societal impact of more social acceptance of lesbian, gay, bisexual people
- Religion and government policy
- How much influence should the Bible have on the nation’s laws, if any?
- Views on the federal government’s role in promoting Christian values
- Most voters say it is not necessary to believe in God to be moral
- Is the justice system too tough on criminals, or not tough enough?
- Policing and law enforcement
- How Trump, Biden supporters view gun rights and ownership
- Views on the increasing number of guns in the U.S.
- Acknowledgments
- The American Trends Panel survey methodology

Pew Research Center conducted this study to understand voters’ political values related to cultural issues in the context of the 2024 election. For this analysis, we surveyed 8,709 adults, including 7,166 registered voters, from April 8 to 14, 2024. Everyone who took part in this survey is a member of the Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. This way nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology .
Here are the questions used for the report and its methodology .
The 2024 presidential campaign is taking place amid intense debates over such topics as immigration, growing racial and ethnic diversity in the United States, the changing American family, crime and reproductive issues.
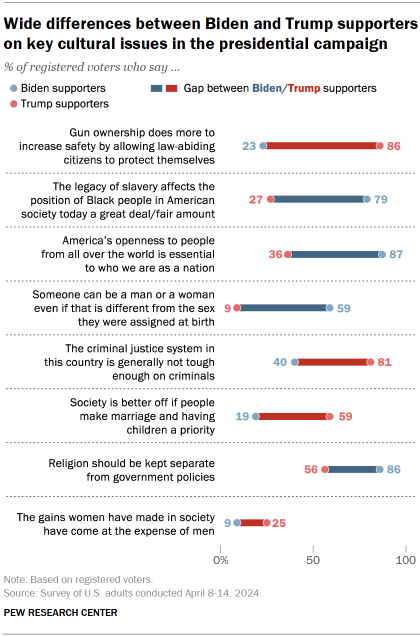
These topics sometimes are grouped together as “culture war” or “woke” issues.
On most – but not all – of these topics, voters who support President Joe Biden and former President Donald Trump have starkly different opinions. Yet in many cases, Biden and Trump supporters are themselves sharply divided.
Across more than 30 measures, some of the widest differences are on issues that have divided Americans for decades: the role of guns in society, as well as race and the legacy of slavery.
Yet, Biden and Trump supporters also have very different opinions across many other topics likely to be focal points in the campaign: gender identity and sexual orientation, crime and policing, reproductive issues, the influence of religion on society and the changes that have transformed life in the U.S. in recent decades.
A new survey by Pew Research Center of 8,709 adults – including 7,166 registered voters – conducted April 8-14, 2024, examines the political values of the Biden and Trump coalitions that underlie policy attitudes in many of these areas.
Jump to read about Biden and Trump supporters’ views on: Race and racial diversity | Immigration and language | American history | Gender and family | Gender identity and sexual orientation | Religion | Crime and policing | Guns
Among the major findings:
Enduring divisions on race and the legacy of slavery. Just 27% of registered voters who support Trump say the legacy of slavery affects the position of Black people in America today a great deal or fair amount; 73% say it has little or no impact.
Opinions among Biden supporters are nearly the opposite: 79% say slavery’s legacy still affects the position of Black people, while 20% say it has not too much or no effect.
Wide gaps on gender identity and same-sex marriage. While Americans have complex opinions on gender identity and transgender rights , a growing share of voters (65%) say that whether a person is a man or woman is determined by the sex they were assigned at birth. About a third (34%) say someone can be a man or woman, even if that differs from their sex at birth.
- Nearly all Trump supporters (90%) say gender is determined by sex at birth. By contrast, Biden supporters are more divided. About six-in-ten (59%) say gender can be different from sex at birth; 39% say gender is determined by sex at birth.
- Nearly a decade after the Supreme Court legalized same-sex marriage , Biden and Trump supporters have starkly different views of the impact of that historic ruling. Biden supporters are about five times as likely (57%) as Trump supporters (11%) to say legalization of same-sex marriage is good for society.
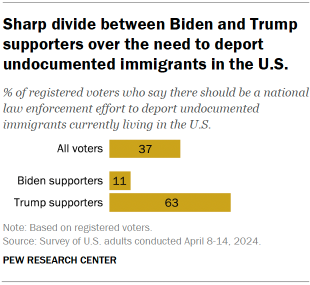
Most Trump voters now favor a “national effort to deport” all those in the U.S. illegally. Opposition to allowing undocumented immigrants to stay in the country legally if they meet certain requirements has risen in recent years, driven largely by Republican and Republican-leaning registered voters.
- Nearly two-thirds of Trump backers (63%) support a national effort to deport all those in the country illegally, compared with just 11% of Biden supporters.
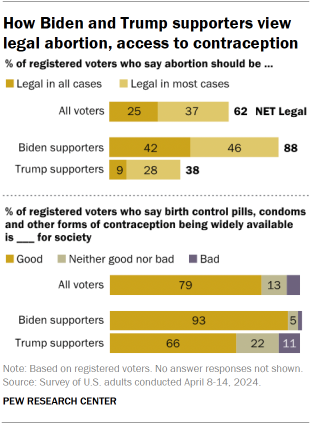
Divided views of the criminal justice system. A majority of voters (61%) say the criminal justice system is generally “not tough enough on criminals.” Just 13% say the system is too tough, while 25% say it treats criminals about right.
- Trump supporters (81%) are about twice as likely as Biden supporters (40%) to say the criminal justice system is not tough enough on criminals.
- Yet, there are much narrower differences in several priorities for the police and law enforcement: Overwhelming majorities of Biden and Trump supporters say it is extremely or very important for police and law enforcement to keep communities safe and to treat people of all racial and ethnic groups equally.
The changing American family. The structure of American family is very different than it was 40 or 50 years ago . Biden and Trump supporters view these changes very differently:
- Roughly three times as many Trump supporters as Biden supporters say society is better if people prioritize marriage and family (59% vs. 19%).
- And Trump supporters are far more likely to take a negative view of the nation’s falling birth rate: 47% say people having fewer children is a bad thing, compared with 23% of Biden supporters.
Divisions on abortion, more agreement on availability of contraceptives. Since the Supreme Court’s 2022 decision overturning Roe v. Wade, which guaranteed a right to abortion, support for legal abortion has ticked up in both parties.
- Today, 88% of Biden supporters say abortion should be legal in all or most cases; 38% of Trump supporters say the same.
By contrast, voters – including large majorities of both candidates’ supporters – overwhelmingly say the wide availability of birth control pills, condoms and other forms of contraception is good for society.
Broad support among voters for discussing America’s historical successes – and its flaws. The survey finds that while Biden and Trump supporters have profoundly different attitudes on many cultural issues, they mostly support the discussion of America’s historical successes, as well as its flaws.
- Nearly identical shares of Biden (74%) and Trump supporters (71%) say it is extremely or very important to have public discussions about the country’s historical successes and strengths.
- 78% of Biden supporters and 60% of Trump supporters say it is at least very important to have public discussions about the country’s failures and flaws.
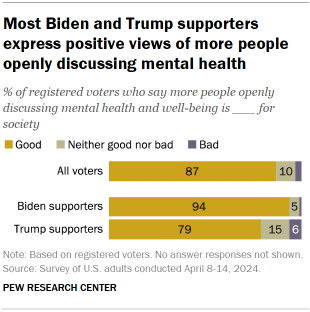
Voters are very positive about more open discussions of mental health. More than eight-in-ten voters (87%) say that more people openly discussing mental health and well-being is good for society. This includes large majorities of both Biden (94% good thing) and Trump supporters (79%).
Related: Who do Americans feel comfortable talking to about their mental health?
There is broad skepticism about the increased use of artificial intelligence (AI) in daily life. More than half of voters (55%) say this is bad for society, while 21% see this as a good thing (24% say it is neither good nor bad). There are only modest differences in these views between Trump supporters (59% say this is bad for society) and Biden supporters (51%).
Related: Growing public concern about the role of artificial intelligence in everyday life
Voters’ comfort level with some common – and less common – experiences
To some extent, voters’ political values are reflected in whether or not they’re comfortable with fairly common experiences.
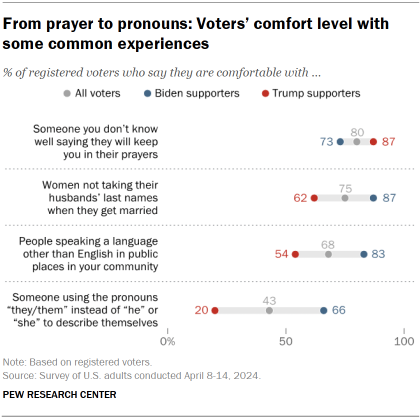
A large share of voters (80%), including sizable majorities of Biden and Trump supporters, say they are comfortable with someone they don’t know saying they will keep them in their prayers.
Most women in opposite-sex marriages continue to take their husbands’ last names when they marry. Still, three-quarters of voters say they are comfortable with women not taking their husbands names.
Trump supporters are less comfortable than Biden supporters with women not taking their husbands’ last names. And among men who support the former president, 44% are uncomfortable with this practice, compared with 29% of women who support Trump.
There is a wider gap between Biden and Trump voters in comfort with people speaking a language other than English in public places in their communities. More than eight-in-ten Biden supporters (83%) are comfortable hearing languages other than English, compared with a narrow majority of Trump supporters (54%).
And, reflecting the wide divide between the two sides in opinions on transgender issues, just 20% of Trump supporters say they are comfortable with someone using “they/them” instead of “he” or “she” to describe themselves. More than three times as many Biden supporters (66%) – including 79% of Biden supporters under age 50 – say they are comfortable with the use of these gender-neutral pronouns.
Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivery Saturday mornings
Sign up for The Briefing
Weekly updates on the world of news & information
- Criminal Justice
- Discrimination & Prejudice
- Donald Trump
- Election 2024
- Gender Equality & Discrimination
- Gender Identity
- Immigration & Language Adoption
- LGBTQ Attitudes & Experiences
- Marriage & Divorce
- Partisanship & Issues
- Political Issues
- Racial Bias & Discrimination
- Religion & Government
- Religion & Politics
- Unauthorized Immigration
Biden, Trump are least-liked pair of major party presidential candidates in at least 3 decades
More than half of americans are following election news closely, and many are already worn out, americans have mixed views about how the news media cover biden’s, trump’s ages, an early look at black voters’ views on biden, trump and election 2024, voters’ views of trump and biden differ sharply by religion, most popular, report materials.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
© 2024 Pew Research Center
- Alzheimer's disease & dementia
- Arthritis & Rheumatism
- Attention deficit disorders
- Autism spectrum disorders
- Biomedical technology
- Diseases, Conditions, Syndromes
- Endocrinology & Metabolism
- Gastroenterology
- Gerontology & Geriatrics
- Health informatics
- Inflammatory disorders
- Medical economics
- Medical research
- Medications
- Neuroscience
- Obstetrics & gynaecology
- Oncology & Cancer
- Ophthalmology
- Overweight & Obesity
- Parkinson's & Movement disorders
- Psychology & Psychiatry
- Radiology & Imaging
- Sleep disorders
- Sports medicine & Kinesiology
- Vaccination
- Breast cancer
- Cardiovascular disease
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Colon cancer
- Coronary artery disease
- Heart attack
- Heart disease
- High blood pressure
- Kidney disease
- Lung cancer
- Multiple sclerosis
- Myocardial infarction
- Ovarian cancer
- Post traumatic stress disorder
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Schizophrenia
- Skin cancer
- Type 2 diabetes
- Full List »
share this!
June 18, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
Potential new treatment option for diabetic retinopathy could address the problem much earlier
by Bonnier Rucker, University of Oklahoma
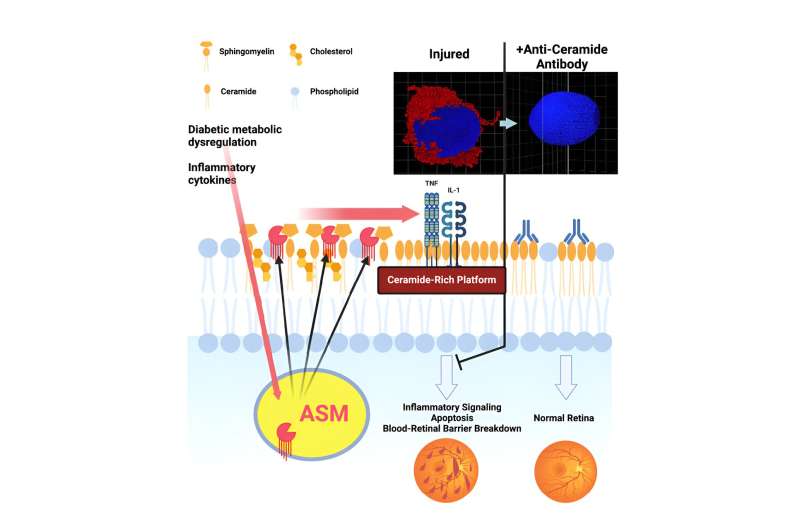
Patients with diabetes face a host of potential health problems as they work to manage the chronic disease. Still, one concern that seems to weigh heavily is the risk of losing their sight through a condition known as diabetic retinopathy.
Researchers at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences and Memorial Sloan Kettering (MSK) Cancer Center are studying a new, revolutionary treatment for diabetic retinopathy that could change the prognosis for these patients.
Julia Busik, Ph.D., professor and chair of the department of biochemistry and physiology in collaboration with Richard Kolesnick, MD of MSK Cancer Center, published a paper in the journal Cell Metabolism that details how anti-ceramide immunotherapy can address the root cause of the disease and stop progression toward blindness at an earlier stage than previous treatments.
"With the rise in diabetes, there's a rise in complications. One-third of adults over age 40 with diabetes have retinopathy," said Busik. "If left untreated, diabetic retinopathy can lead to blindness. Losing vision is one of the most feared complications for patients with diabetes."
This blindness is caused by hemorrhaging lipid, or fatty compound, build-ups. These start as dark spots in the field of view but can, as they multiply, become vision-threatening and eventually cause blindness.
There are currently two treatments for diabetic retinopathy, but both have serious health implications and are fairly invasive. One involves lasers that burn the vessels to stop the hemorrhaging; another involves injections directly into the eye that can stop the progression of the disease. According to Busik, these treatments are only sometimes effective.
The researchers are working on an exciting new treatment that could address the root cause of diabetic retinopathy. Continuing research that she began at Michigan State University, Busik has taken a closer look at lipids, specifically lipid pathways in the retina of the eye, and how they are affected by diabetes.
She and her team found that a certain, very damaging type of lipid, or ceramide, was present in the eyes of patients with diabetic retinopathy. In turn, they discovered that these ceramides, after stimulation by another type of cell—cytokines—stick together into large domains that cause damaging inflammatory signals to cells in the eye. This causes cell death and the progression of diabetic retinopathy .
In collaboration with the Kolesnick laboratory at MSK Cancer Center, Busik's team was then able to create an antibody against these lipids to prevent the ceramide buildup from happening and signaling the damage to healthy cells in the retina. The studies show great promise in animal and cell culture models.
Perhaps the most important advance from the current treatment is that it addresses the root cause of the disease, as opposed to late symptoms and stopping progression at the vision-threatening stage, explains Busik. It can also be administered systemically, so it does not have to be injected into the eye. Due to their invasive nature and safety concerns, currently available treatments are only used at very late stages of the disease when the vision is threatened.
"If we have this systemic safe treatment ," said Busik. "It could be given to a patient at a much earlier stage when they are just starting to progress, to make sure that they never get to that late stage."
Explore further
Feedback to editors
Researchers shed light on cause of 'happy hypoxia' in COVID-19 patients

Over-the-counter supplement found to improve walking for peripheral artery disease patients
Surprising origins for a rare cancer: Study finds overexpression of PKA protein causes fibrolamellar carcinoma

New global research aims to improve survival rates for pancreatic cancer patients

Study finds medication treatment for opioid use disorder offered at only a third of outpatient mental health facilities

Study reveals genetic basis of sepsis response variability

Discovery of 'new rules of the immune system' could improve treatment of inflammatory diseases, say scientists

Blood test could predict Parkinson's seven years before symptoms
Study suggests hepatitis E may be a sexually transmitted infection
Researchers unravel complexities of Alzheimer's disease in protein fragments and plaque diversity
Related stories.

Unexpected finding may deter disabling diabetic eye disease
Apr 6, 2018
Researchers discover link between cholesterol and diabetic retinopathy
Sep 5, 2023

Importance of routine eye care for patients with diabetes
Aug 18, 2023
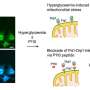
Research offers improved understanding of the biology of eye complications caused by diabetes
Mar 12, 2024
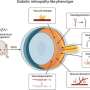
Uncovering the key process that contributes to vision loss and blindness in people with diabetes
Sep 23, 2022

Spotting the symptoms of diabetic retinopathy
Nov 2, 2020
Recommended for you

Drug approved as sickle cell disease treatment may help stabilize vision in rare genetic disease
Jun 17, 2024
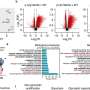
Researchers unveil impact of east Asian gene variant on type 2 diabetes risk
Jun 14, 2024

Study hints at tools to prevent diabetes associated with antipsychotic medications
Jun 13, 2024

Research on the visual rabbit illusion takes a leap forward
Jun 11, 2024

Robot radiotherapy could improve treatments for eye disease
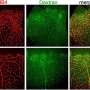
Genetic mechanisms may reveal retinal vascular disease therapeutic targets
Let us know if there is a problem with our content.
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Medical Xpress in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
Become an Insider
Sign up today to receive premium content.

Retailers Are Facing an IT Complexity Problem, New Research Finds

Lily is a Senior Editor at BizTech Magazine . She follows tech trends and the IT leaders who shape them — reporting on entrepreneurial business, security and thought leadership.
Retailers have long been a target for cyberattacks , whether through supply chain breaches or point-of-sale hacks. They also handle billions of dollars a day and are tasked with keeping consumer credit card data safe. To combat threats, 68 percent of these organizations operate between 10 and 49 security tools or platforms, according to the 2024 CDW Cybersecurity Research Report .
The report surveyed 97 IT decision-makers and influencers from U.S. retailers. Many respondents noted the difficulties in managing this many tech tools and said that simply creating more visibility into their enterprise’s IT system would help improve their cyber resilience .
Click the banner below to read the 2024 CDW Cybersecurity Research Report.

One respondent said the biggest challenge is “disparate systems, some of which are legacy, that impede the deployment of systemic cybersecurity measures.”
Another cited “the complexity of IT environments , the rapid evolution of cyberthreats, limited resources for cybersecurity, and the need to comply with various regulations and standards.”
Solutions such as security information and event management, threat hunting, incident response , multifactor authentication and next-generation firewalls were some of the most used tools, but less than 50 percent of respondents were very confident that these did enough to bolster their cybersecurity initiatives.
Instead, leaders favored wider-scale defenses such as network security and data security, which enable retailers to improve connections across the enterprise rather than solving one vulnerability at a time through patch management, for example.
With data reaching every endpoint, this approach is likely the next phase in zero trust and cybersecurity. “I think it will be mostly around data protection and data security, data governance , and ensuring that data is appropriately identified, classified and that the appropriate guardrails are put in place,” says Stephanie Hagopian, vice president of security for CDW .

Buck Bell Director, Global Security Strategy Office, CDW
Retailers Want More Visibility Into Their IT Systems
Retail respondents who were the most confident about their cybersecurity efforts had greater visibility into their IT systems. That’s no surprise, since seeing fault lines between integrations, network connection points or Internet of Things devices can help teams remediate threats before they escalate.
RELATED: Financial IT leaders share how they are managing data breaches in 2024.
Respondents agreed that being able to visualize possible security gaps in the system increased preparedness. Respondents also said that Software as a Service helped them achieve that visual picture, with 66 percent calling it their top choice for procuring new IT tools and services.
For Buck Bell, leader of CDW’s Global Security Strategy Office, visualizing the entire IT system is critical because cybersecurity touches on all aspects of the organization. “The more holistic your view of the enterprise as a whole — not only the specific cyber risk itself but also the business impacts that are associated with it — typically, the more successful you’re going to be in your cyber resilience aims. From my perspective, cyber risk is business risk .”
The percentage of surveyed retail IT leaders who feel “somewhat” prepared to respond to a cybersecurity incident
Getting to the Root of Cyber Incidents
Too often, IT leaders experience problems but fail to understand the root cause, the report reveals. Whether about IoT connectivity or artificial intelligence, this lack of understanding can also cut into a clear strategy for cyber resilience.
Retailers need to diagnose the issue before they can fix it, Hagopian explains. They can do that by talking with a tech partner for answers, connecting with peers or retracing the steps of a cyber incident.
Sometimes the culprit is an unlikely one. Take, for example, a new tool that is meant to simplify operations but instead causes disruption. “Various departments are purchasing their own technology and tools, so you have to retrofit that back into the central infrastructure and the centralized tooling that has been approved. And then there’s always shadow IT, where an end user could potentially purchase something in a silo,” Hagopian says.
READ MORE: Experts share what cyber resilience means and how to achieve it.
Focus on Mitigating Risks and Reducing Downtime Costs
Retailers know they need to respond to a cybersecurity incident when it happens, but what about defensive planning? This involves identifying the biggest risk and coming up with a plan to mitigate it, Bell says.
Right now, about 8 in 10 of the retail IT leaders surveyed felt at least somewhat prepared for a cybersecurity incident , even with the challenge of integrating legacy tools. For those who felt less prepared, negative consequences such as the cost of operational downtime and the impact on brand reputation may be bigger motivators than, say, data exfiltration or compliance issues, Bell says.
A quarter of respondents had suffered $5 million to $10 million in downtime to their organization after a data breach in the past five years — and that’s on the lower end. “Operational downtime can cost $100 million-plus a week in some scenarios,” Bell says.
These are the kinds of opportunity costs that linger long after an attack. But even more important is the “basic sense of trust that tends to be compromised when a breach occurs,” Bell says.

- Cloud Security
- Data-Driven Decisions
- Wireless Security
- Endpoint Security
- Identity Management
- Threat Prevention
- Unified Threat Management
Related Articles

Learn from Your Peers
What can you glean about security from other IT pros? Check out new CDW research and insight from our experts.
Copyright © 2024 CDW LLC 200 N. Milwaukee Avenue , Vernon Hills, IL 60061 Do Not Sell My Personal Information

COMMENTS
A research problem is a gap in existing knowledge, a contradiction in an established theory, or a real-world challenge that a researcher aims to address in their research. It is at the heart of any scientific inquiry, directing the trajectory of an investigation. The statement of a problem orients the reader to the importance of the topic, sets ...
A research problem is a specific issue or gap in existing knowledge that you aim to address in your research. You may choose to look for practical problems aimed at contributing to change, or theoretical problems aimed at expanding knowledge. Some research will do both of these things, but usually the research problem focuses on one or the other.
Feasibility: A research problem should be feasible in terms of the availability of data, resources, and research methods. It should be realistic and practical to conduct the study within the available time, budget, and resources. Novelty: A research problem should be novel or original in some way.
45 Research Problem Examples & Inspiration. A research problem is an issue of concern that is the catalyst for your research. It demonstrates why the research problem needs to take place in the first place. Generally, you will write your research problem as a clear, concise, and focused statement that identifies an issue or gap in current ...
A research problem is a definite or clear expression [statement] about an area of concern, a condition to be improved upon, a difficulty to be eliminated, or a troubling question that exists in scholarly literature, in theory, or within existing practice that points to a need for meaningful understanding and deliberate investigation. A research ...
A research problem can be theoretical in nature, focusing on an area of academic research that is lacking in some way. Alternatively, a research problem can be more applied in nature, focused on finding a practical solution to an established problem within an industry or an organisation. In other words, theoretical research problems are motivated by the desire to grow the overall body of ...
Research is a procedure based on a sequence and a research problem aids in following and completing the research in a sequence. Repetition of existing literature is something that should be avoided in research. Therefore research problem in a dissertation or an essay needs to be well thought out and presented with a clear purpose.
The research problem, therefore, is the main organizing principle guiding the analysis of your research. The problem under investigation establishes an occasion for writing and a focus that governs what you want to say. It represents the core subject matter of scholarly communication and the means by which scholars arrive at other topics of ...
Step 3: Set your aims and objectives. Finally, the problem statement should frame how you intend to address the problem. Your goal here should not be to find a conclusive solution, but rather to propose more effective approaches to tackling or understanding it. The research aim is the overall purpose of your research.
The first question asks for a ready-made solution, and is not focused or researchable. The second question is a clearer comparative question, but note that it may not be practically feasible. For a smaller research project or thesis, it could be narrowed down further to focus on the effectiveness of drunk driving laws in just one or two countries.
A research problem statement should be clear, concise, and specific, outlining the issue, its context, and significance. While a research problem is a broad statement of the primary issue ...
A research problem has two essential roles in setting your research project on a course for success. 1. They set the scope. The research problem defines what problem or opportunity you're looking at and what your research goals are. It stops you from getting side-tracked or allowing the scope of research to creep off-course.
A research problem, or phenomenon as it might be called in many forms of qualitative methodology, is the topic you would like to address, investigate, or study, whether descriptively or experimentally. It is the focus or reason for engaging in your research. It is typically a topic, phenomenon, or challenge that you are interested in
Learn about the related concepts of research problems and problem statements. Whether you're an academic researcher, a student, or simply someone interested ...
5. Select and include important variables. A clear and manageable research problem typically includes the variables that are most relevant to the study. A research team summarizes how they plan to consider and use these variables and how they might influence the results of the study. Selecting the most important variables can help the study's ...
Alternatively, research problems can be identified by reviewing recent literature, reports, or databases in your field. Often the section on "recommendations for future studies" provided at the end of journal articles or doctoral dissertations suggests potential research problems. In addition, major reports and databases in the field may ...
Defining a research problem is the fuel that drives the scientific process, and is the foundation of any research method and experimental design, from true experiment to case study. It is one of the first statements made in any research paper and, as well as defining the research area, should include a quick synopsis of how the hypothesis was ...
Formulating a research problem is usually done under the first step of research process, i.e., defining the research problem. Identification, clarification and formulation of a research problem is done using different steps as: Discover the Management Dilemma. Define the Management Question. Define the Research Question.
A research problem outlines the precise field of inquiry and knowledge gaps that the research attempts to address, defining the scope and objective of a study. Photo by Scott Graham on Unsplash. Learn the procedure involved in defining research problems, highlighting important considerations and steps researchers should take.
A research problem is a statement about an area of concern, a condition to be improved, a difficulty to be eliminated, or a troubling question that exists in scholarly literature, in theory, or in practice that points to the need for meaningful understanding and deliberate investigation. In some social science disciplines the research problem is typically posed in the form of a question.
A well-defined research problem is more than just a question; it is a gateway to understanding, a key to unlocking the mysteries of the universe, and a catalyst for innovation. Here's why it is so crucial: 1. Precision and Focus. A research problem carves a path through the dense forest of potential research areas.
Research shows that the global insect population is declining at approximately 1.5% annually, even though prairie vegetation is double what it was 20 years ago. This has led to a 37% decline in grasshopper populations in the Konza Prairie during that same period. "Insect declines are a wicked problem that has a lot of moving parts," he said.
A research problem is a specific issue or gap in existing knowledge that you aim to address in your research. You may choose to look for practical problems aimed at contributing to change, or theoretical problems aimed at expanding knowledge. Some research will do both of these things, but usually the research problem focuses on one or the other.
A recall is issued when a manufacturer or NHTSA determines that a vehicle, equipment, car seat, or tire creates an unreasonable safety risk or fails to meet minimum safety standards. Most decisions to conduct a recall and remedy a safety defect are made voluntarily by manufacturers prior to any involvement by NHTSA.
A research problem is a definite or clear expression [statement] about an area of concern, a condition to be improved upon, a difficulty to be eliminated, or a troubling question that exists in scholarly literature, in theory, or within existing practice that points to a need for meaningful understanding and deliberate investigation.
Pew Research Center conducted this study to understand voters' political values related to cultural issues in the context of the 2024 election. For this analysis, we surveyed 8,709 adults, including 7,166 registered voters, from April 8 to 14, 2024. Everyone who took part in this survey is a member of the Center's American Trends Panel (ATP ...
Patients with diabetes face a host of potential health problems as they work to manage the chronic disease. Still, one concern that seems to weigh heavily is the risk of losing their sight through ...
Retailers have long been a target for cyberattacks, whether through supply chain breaches or point-of-sale hacks.They also handle billions of dollars a day and are tasked with keeping consumer credit card data safe. To combat threats, 68 percent of these organizations operate between 10 and 49 security tools or platforms, according to the 2024 CDW Cybersecurity Research Report.