
Writing A Research Proposal
8 common (and costly) mistakes to avoid 🤦.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) & David Phair (PhD) . Reviewed By: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | June 2021
At Grad Coach, we review a lot of research proposals , including dissertation proposals and thesis proposals. Some are pretty good, while others are, well, not fantastic. Sadly, many students only approach us after their proposal has been rejected , meaning they’ve wasted a lot of time and effort.
We’ll look at 8 common mistakes and issues we see cropping up in research proposals so that you can craft your proposal with confidence and maximise the chances of it being approved.

Overview: 8 Research Proposal Killers
- The research topic is too broad (or just poorly articulated).
- The research aims, objectives and questions don’t align .
- The research topic is not well justified .
- The study has a weak theoretical foundation .
- The research design is not well articulated well enough.
- Poor writing and sloppy presentation.
- Poor project planning and risk management.
- Not following the university’s specific criteria .
#1: The research topic is too broad.
One of the most common issues we see in dissertation and thesis proposals is that the research topic is simply too broad . In other words, the focus of the research is not ringfenced tightly enough (or just not defined clearly enough), resulting in a proposal that has an unclear direction or attempts to take on too much.
For example, a research project that aims to “investigate trust in the workplace” would be considered very broad. This topic has no specific focus and leaves many questions unanswered, for example:
- What type(s) of trust?
- Between whom?
- Within what types of workplaces?
- Within what industry or industries?
As a general rule of thumb, you should aim for a fairly narrow focus when you craft your research topic. Doing this will allow you to go deep and investigate the topic in-depth , which is what the markers want to see. Quality beats quantity – or rather, depth beats breadth – when it comes to defining and refining your research topic.
A related problem is that oftentimes, students have a more refined topic within their mind, but they don’t articulate it well in their proposal. This often results in the proposal being rejected because the topic is perceived as being too broad. In other words, it’s important to ensure you not only have a clear, sharp focus for your research, but that you communicate that well in your dissertation or thesis proposal. Make sure that you address the who , what , were and when, so that your topic is well defined.
Let’s look at an example.
Sticking with the topic I mentioned earlier, a more refined and well-articulated research aim could be something along the lines of:
“To investigate the factors that cultivate organisational trust (i.e. a customer trusting an organisation) within the UK life insurance industry.”
As you can see, this is a lot more specific and ringfences the topic into a more manageable scope . So, when it comes to your research topic, remember to keep it tight .

#2: The research aims, objectives and questions don’t align.
Another common issue that we see with weaker research proposals is misalignment between the research aims and objectives , as well as with the research questions . Sometimes all three are misaligned , and sometimes there’s only one misfit. Whatever the case, it’s a problem that can lead to proposal rejection, as these three elements need to link together tightly.
Let’s look at an example of a misaligned trio.
Research Aim:
To identify factors that cultivate organisational trust in British insurance brokers.
Research Objectives:
To measure organisational trust levels across different demographic groups within the UK.
To investigate the causes of differences in organisational trust levels between groups.
Research Question:
What factors influence organisational trust between customers and insurance brokers within the UK?
As you can see, the research aim and research question are reasonably aligned (they are both focused on the factors that cultivate trust). However, the research objectives are misaligned, as they focus on measuring trust levels across different groups, rather than identifying what factors stimulate trust. This will result in a study that’s pulling in different directions – not good.
A related issue we see is that students don’t really understand the difference between research aims (the broader goal), research objectives (how you’ll achieve that goal) and research questions (the specific questions you’ll answer within your study). So, when you’re preparing your proposal, make sure that you clearly understand how these differ and make sure they’re all tightly aligned with each other.

#3: The research topic is not well justified.
A good research topic – in other words, a good set of research aims, research objectives and research questions – needs to be well justified to convince your university to approve your research. Poor justification of the research topic is a common reason for proposals to be rejected.
So, how do you justify your research?
For a research topic to be well justified, you need to demonstrate both originality and importance .
Originality means that your proposed research is novel , or at least that it’s novel within its context (for example, within a specific country or industry). While the extent of this novelty will vary depending on your institution, programme and level of study (e.g. Masters vs Doctorate), your research will always need to have some level of originality. In other words, you can’t research something that’s been researched ad nauseam before.
Simply put, your research needs to emerge from a gap in the existing literature . To do this, you need to figure out what’s missing from the current body of knowledge (by undertaking a review of the literature) and carve out your own research to fill that gap. We explain this process in more detail here .
Importance is the second factor. Just because a topic is unique doesn’t mean it’s important . You need to be able to explain what the benefits of undertaking your proposed research would be. Who would benefit? How would they benefit? How could the newly developed knowledge be used in the world, whether in academia or industry?
So, when you’re writing up your research proposal, make sure that you clearly articulate both the originality and importance of your proposed research, or you’ll risk submitting an unconvincing proposal.

#4: The study has a weak theoretical foundation.
As I mentioned in the previous point, your research topic needs to emerge from the existing research . In other words, your research needs to fill a clear gap in the literature – something that hasn’t been adequately researched, or that lacks research in a specific context.
To convince your university that your topic will fill a gap in the research, your proposal needs to have a strong theoretical foundation . In other words, you need to show that you’ve done the necessary reading and are familiar with the existing research. To do this, you need to provide an integrated summary of the existing research and highlight (very clearly) the theoretical gap that exists.
Some common signs of a weak theoretical foundation that we’ve encountered include:
- A general lack of sources and a reliance on personal opinion and anecdotes, rather than academic literature.
- Failing to acknowledge and discuss landmark studies and key literature in the topic area.
- Relying heavily on low-quality sources , such as blog posts, personal websites, opinion pieces, etc.
- Relying heavily on outdated sources and not incorporating more recent research that builds on the “classics”.
While it’s generally not expected that you undertake a comprehensive literature review at the proposal stage, you do still need to justify your topic by demonstrating a need for your study (i.e. the literature gap). So, make sure that you put in the time to develop a sound understanding of the current state of knowledge in your space, and make sure that you communicate that understanding in your proposal by building your topic justification on a solid base of credible literature.

#5: The research design is not articulated well enough (or is just impractical).
Once you’ve made a strong argument regarding the value of your research (i.e., you’ve justified it), the next matter that your research proposal needs to address is the “how” – in other words, your intended research design and methodology .
A common issue we see is that students don’t provide enough detail in this section. This is often because they don’t really know exactly what they’re going to do and plan to just “figure it out later” (which is not good enough). But sometimes it’s just a case of poor articulation – in other words, they have a clear design worked out in their minds, but they haven’t put their plan to paper.
Whatever the reason, a dissertation or thesis proposal that lacks detail regarding the research design runs a major risk of being rejected. This is because universities want to see that you have a clearly defined, practical plan to achieve your research aims and objectives and answer your research questions.
At a minimum, you should provide detail regarding the following:
- Research philosophy – the set of beliefs your research is based on (positivism, interpretivism, pragmatism)
- Research approach – the broader method you’ll use (inductive, deductive, qualitative and quantitative)
- Research strategy – how you’ll conduct the research (e.g., experimental, action, case study, etc.)
- Time horizon – the number of points in time at which you’ll collect your data (e.g. cross-sectional or longitudinal)
- Techniques and procedures – your intended data collection methods, data analysis techniques, sampling strategies , etc.
For more information about each of these design decisions, check out our post detailing the Research Onion.
Of course, your research design can (and most likely will) evolve along the way , but you still need a starting point. Also, your proposed research design needs to be practical, given your constraints. A brilliant design is pointless if you don’t have the resources (e.g. money, equipment, expertise, etc.) to pull it off. So, get detailed in this section of your proposal and keep it realistic to maximise your chances of approval.
Need a helping hand?
#6: Poor writing and sloppy presentation.
As with any document, poor writing and sloppy presentation can heavily detract from your research proposal, even if you tick all the other boxes. While poor writing and presentation alone probably won’t result in your proposal being rejected, it will definitely put you at a disadvantage , as it gives a negative impression regarding the overall quality of your work.
The main issues we see here are:
- Directionless or scattered writing – for example, writing that jumps from one point to another with poor flow and connectivity, disjointed points, etc.
- Poor argument formation – for example, a lack of premises and conclusions, disconnected conclusions and poor reasoning (you can learn more about argument development here ).
- Inappropriate language – for example, using a very informal or casual tone, slang, etc).
- Grammar and spelling issues, as well as inconsistent use of UK/US English.
- Referencing issues – for example, a lack of references or incorrectly formatted references.
- Table and figure captions – for example, a lack of captions, citations, figure and table numbers, etc.
- Low-quality visuals and diagrams.
The good news is that many of these can be resolved by editing and proofreading your proposal beforehand, so it’s always a good idea to take the time to do this. It’s also a good idea to ask a friend to review your document, as you will invariably suffer from blindspots when editing your own work. If your budget allows, having your work reviewed by an academic editor will ensure you cover all bases and submit a high-quality document.
#7: Poor project planning and risk management.
While different universities will have varying requirements, there is usually a requirement (or at least an expectation) for a project plan of sorts. As I mentioned earlier, a strong research proposal needs to be practical and manageable, given your constraints. Therefore, a well-articulated project plan that considers all the practicalities (and risks) is an important part of a strong research proposal.
We generally recommend that students draw up a fairly detailed Gantt chart , detailing each major task involved in the dissertation writing process. For example, you can break it down into the various chapters ( introduction , literature review, etc.) and the key tasks involved in completing each chapter (research, planning, writing, etc). What’s most important here is to be realistic – things almost always take longer than you expect, especially if you’re a first-time researcher.
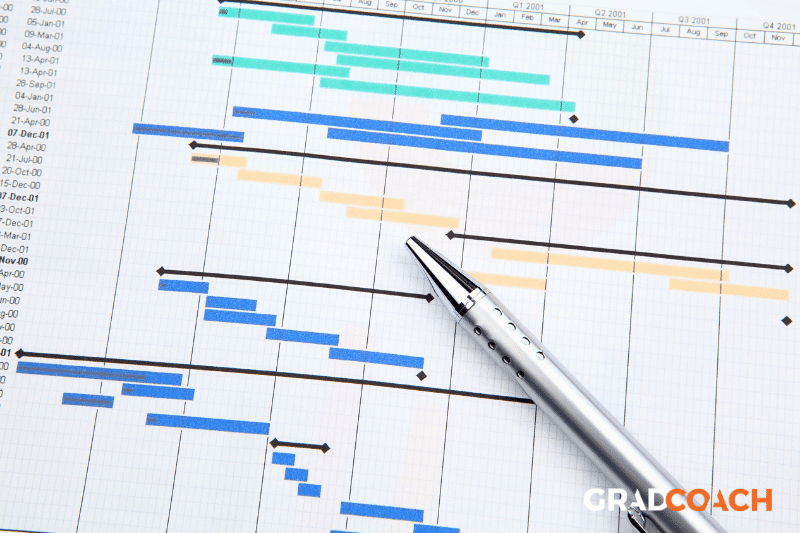
We also recommend including some sort of risk management plan . For this, you could make use of a basic risk register , listing all the potential risks you foresee, as well as your mitigation and response actions, should they occur. For example, the risk of data collection taking longer than anticipated, the risk of not getting enough survey responses , etc.
What’s most important is to demonstrate that you have thought your research through and have a clear plan of action . Of course, as with your research design, plans can (and likely will) change – and that’s okay. However, you still need to have an initial plan, and that plan needs to be realistic and manageable, or you’ll risk your proposal getting rejected.
#8: Not following the university’s specific criteria.
While research proposals are fairly generic in terms of contents and style, and tend to follow a reasonably standardised structure, each university has its nuances in terms of what they want to be included in the dissertation or thesis proposal.
Some universities want more or less detail in certain sections, some want extra sections, and some want a very specific structure and format (down to the font type and size!). So, you need to pay very close attention to whatever institution-specific criteria your university has set out.
Typically, your university will provide some sort of brief or guidance document to direct your proposal efforts, so be sure to study this document thoroughly and ask the faculty for clarity if you’re uncertain about anything. Some universities will also provide a proposal template . Pay careful attention to any specific structure they recommend as well as formatting requirements (such as font, line spacing, margin sizes, referencing format, etc.).
If your university provides an assessment criteria matrix , you’ve hit the jackpot, as that document will detail exactly what you need to achieve in each section of the proposal. Study that matrix inside out and make sure that your research proposal tightly aligns with the assessment criteria.

Recap: 8 Research Proposal Mistakes
We’ve covered a lot here – let’s recap on the 8 common mistakes that can hurt your research proposal or even get it rejected:
- The research design is not articulated well enough.
- Not following the university’s specific criteria.
If you have any questions about these common mistakes, leave a comment below and we’ll do our best to answer. You may also want to have a look at some examples of successful proposals here . If you’d like to get 1-on-1 help with your research proposal , book a free initial consultation with a friendly coach to discuss how we can move you forward.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Research Proposal Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

Thanks a lot for sharing these tips, very usefull and help me a lot, Many thanks
I just want to express my sincere gratitude for everything you guys are doing. You held my hand when I was doing my dissertation. I successfully completed it and got good marks. I just got myself reviewing this so I could help others struggling. May God bless you. May he bless you abundantly.
Thank you so much, I got it very important, and your presentation is also very attractive.
I find the text very educative. I am just preparing to start work on my PhD thesis. I must admit that I have learnt so much about how to organize myself for the task ahead of me. Thank you so much for being there to support people like me.
I found this video highly educative, it gave me a full glance at what is ahead of me – starting my Ph.D. now! Thank you for these amazing facts.
Thanks a lot for such an insightful video and explanation on Research Proposal design. I’m a beginner and pursuing my B.ed , these tips are really helpful to get a good start.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- Career Advice
How to Avoid Failing Your Ph.D. Dissertation
By Daniel Sokol
You have / 5 articles left. Sign up for a free account or log in.

Istock.com/erhui1979
I am a barrister in London who specializes in helping doctoral students who have failed their Ph.D.s. Few people will have had the dubious privilege of seeing as many unsuccessful Ph.D. dissertations and reading as many scathing reports by examination committees. Here are common reasons why students who submit their Ph.D.s fail, with advice on how to avoid such pitfalls. The lessons apply to the United States and the United Kingdom.
Lack of critical reflection. Probably the most common reason for failing a Ph.D. dissertation is a lack of critical analysis. A typical observation of the examination committee is, “The thesis is generally descriptive and a more analytical approach is required.”
For doctoral work, students must engage critically with the subject matter, not just set out what other scholars have said or done. If not, the thesis will not be original. It will not add anything of substance to the field and will fail.
Doctoral students should adopt a reflexive approach to their work. Why have I chosen this methodology? What are the flaws or limitations of this or that author’s argument? Can I make interesting comparisons between this and something else? Those who struggle with this aspect should ask their supervisors for advice on how to inject some analytic sophistication to their thesis.
Lack of coherence. Other common observations are of the type: “The argument running through the thesis needs to be more coherent” or “The thesis is poorly organized and put together without any apparent logic.”
The thesis should be seen as one coherent whole. It cannot be a series of self-contained chapters stitched together haphazardly. Students should spend considerable time at the outset of their dissertation thinking about structure, both at the macro level of the entire thesis and the micro level of the chapter. It is a good idea to look at other Ph.D. theses and monographs to get a sense of what constitutes a logical structure.
Poor presentation. The majority of failed Ph.D. dissertations are sloppily presented. They contain typos, grammatical mistakes, referencing errors and inconsistencies in presentation. Looking at some committee reports randomly, I note the following comments:
- “The thesis is poorly written.”
- “That previous section is long, badly written and lacks structure.”
- “The author cannot formulate his thoughts or explain his reasons. It is very hard to understand a good part of the thesis.”
- “Ensure that the standard of written English is consistent with the standard expected of a Ph.D. thesis.”
- “The language used is simplistic and does not reflect the standard of writing expected at Ph.D. level.”
For committee members, who are paid a fixed and pitiful sum to examine the work, few things are as off-putting as a poorly written dissertation. Errors of language slow the reading speed and can frustrate or irritate committee members. At worst, they can lead them to miss or misinterpret an argument.
Students should consider using a professional proofreader to read the thesis, if permitted by the university’s regulations. But that still is no guarantee of an error-free thesis. Even after the proofreader has returned the manuscript, students should read and reread the work in its entirety.
When I was completing my Ph.D., I read my dissertation so often that the mere sight of it made me nauseous. Each time, I would spot a typo or tweak a sentence, removing a superfluous word or clarifying an ambiguous passage. My meticulous approach was rewarded when one committee member said in the oral examination that it was the best-written dissertation he had ever read. This was nothing to do with skill or an innate writing ability but tedious, repetitive revision.
Failure to make required changes. It is rare for students to fail to obtain their Ph.D. outright at the oral examination. Usually, the student is granted an opportunity to resubmit their dissertation after making corrections.
Students often submit their revised thesis together with a document explaining how they implemented the committee’s recommendations. And they often believe, wrongly, that this document is proof that they have incorporated the requisite changes and that they should be awarded a Ph.D.
In fact, the committee may feel that the changes do not go far enough or that they reveal further misunderstandings or deficiencies. Here are some real observations by dissertation committees:
- “The added discussion section is confusing. The only thing that has improved is the attempt to provide a little more analysis of the experimental data.”
- “The author has tried to address the issues identified by the committee, but there is little improvement in the thesis.”
In short, students who fail their Ph.D. dissertations make changes that are superficial or misconceived. Some revised theses end up worse than the original submission.
Students must incorporate changes in the way that the committee members had in mind. If what is required is unclear, students can usually seek clarification through their supervisors.
In the nine years I have spent helping Ph.D. students with their appeals, I have found that whatever the subject matter of the thesis, the above criticisms appear time and time again in committee reports. They are signs of a poor Ph.D.
Wise students should ask themselves these questions prior to submission of the dissertation:
- Is the work sufficiently critical/analytical, or is it mainly descriptive?
- Is it coherent and well structured?
- Does the thesis look good and read well?
- If a resubmission, have I made the changes that the examination committee had in mind?
Once students are satisfied that the answer to each question is yes, they should ask their supervisors the same questions.

Bad-Faith Counteroffers
Black and other minoritized faculty don’t receive equitable ones if they receive them at all, which harms both them a
Share This Article
More from career advice.

A 3-Step Process for Gaining a Tenure-Track Job
Susanna Semerdzhyan, a first-generation college graduate, shares strategies that helped her overcome the obstacles.

Let’s Finally Tackle the Problem of Pay Inequity
Higher ed must go beyond buzz words and stop hiding behind performative equity, which does not create change, w
- Become a Member
- Sign up for Newsletters
- Learning & Assessment
- Diversity & Equity
- Career Development
- Labor & Unionization
- Shared Governance
- Academic Freedom
- Books & Publishing
- Financial Aid
- Residential Life
- Free Speech
- Physical & Mental Health
- Race & Ethnicity
- Sex & Gender
- Socioeconomics
- Traditional-Age
- Adult & Post-Traditional
- Teaching & Learning
- Artificial Intelligence
- Digital Publishing
- Data Analytics
- Administrative Tech
- Alternative Credentials
- Financial Health
- Cost-Cutting
- Revenue Strategies
- Academic Programs
- Physical Campuses
- Mergers & Collaboration
- Fundraising
- Research Universities
- Regional Public Universities
- Community Colleges
- Private Nonprofit Colleges
- Minority-Serving Institutions
- Religious Colleges
- Women's Colleges
- Specialized Colleges
- For-Profit Colleges
- Executive Leadership
- Trustees & Regents
- State Oversight
- Accreditation
- Politics & Elections
- Supreme Court
- Student Aid Policy
- Science & Research Policy
- State Policy
- Colleges & Localities
- Employee Satisfaction
- Remote & Flexible Work
- Staff Issues
- Study Abroad
- International Students in U.S.
- U.S. Colleges in the World
- Intellectual Affairs
- Seeking a Faculty Job
- Advancing in the Faculty
- Seeking an Administrative Job
- Advancing as an Administrator
- Beyond Transfer
- Call to Action
- Confessions of a Community College Dean
- Higher Ed Gamma
- Higher Ed Policy
- Just Explain It to Me!
- Just Visiting
- Law, Policy—and IT?
- Leadership & StratEDgy
- Leadership in Higher Education
- Learning Innovation
- Online: Trending Now
- Resident Scholar
- University of Venus
- Student Voice
- Academic Life
- Health & Wellness
- The College Experience
- Life After College
- Academic Minute
- Weekly Wisdom
- Reports & Data
- Quick Takes
- Advertising & Marketing
- Consulting Services
- Data & Insights
- Hiring & Jobs
- Event Partnerships
4 /5 Articles remaining this month.
Sign up for a free account or log in.
- Create Free Account
- How it works

Failed Dissertation, Coursework, Report, or Exam – What to Do?
Published by Alvin Nicolas at August 13th, 2021 , Revised On June 12, 2024
Each year several hundreds of university students end up failing their dissertation, coursework, exam, or assignment. Receipt of a failing mark can be the most devastating experience for students in the UK.
Failing a dissertation, essay, or assignment can have a devastating effect on your life – from being shocked by hearing the news of their failure to the mental sufferings that follow.
Have you recently failed your dissertation , assignment , exam or coursework ? If yes, then be calm because you are not alone. There are several ways of tackling such a situation. This article presents several options for students who have failed an exam, dissertation, or assignment.
So, please sit back and relax because it’s not the world’s end.
Possible Reasons for Failure
Often students do not get enough help from their tutors to pass an exam, dissertation or coursework, which results in a situation where they start to wait for things to resolve on their own until their problems become too large.
Fortunately, failing mark is not the end of the world, and students can change their circumstances.
There could be numerous reasons as to why you may have failed your dissertation, exam, essay , or report . Some students cannot keep up with course reading during the semester, while others do not have a sufficient understanding of their subject-related theories and knowledge due to various reasons.
The inability to understand key concepts, missing lectures regularly, and lack of understanding of course content are some of the most common reasons for a failing mark.
A sensible thing to do would be to have your paper edited and proofread by an expert to eliminate any grammatical, structural, and spelling errors.
Does your Dissertation Have the Following?
- Great Research/Sources
- Perfect Language
- Accurate Sources
If not, we can help. Our panel of experts makes sure to keep the 3 pillars of Dissertation strong.

Avoiding Failure Before you Even Begin
If you want to avoid failure before it happens, you must take some pre-emptive actions before your problems become too large.
Achieving a graduate or postgraduate qualification is not a walk in the park. Therefore, it is vitally important for students to make sure that they meet their challenges head-on to prevent them from turning into potential failures.
Here are some tips for you to avoid failure before you even start.
- If you know that you are struggling with your dissertation , coursework , or assignment , then take out the time to discuss your problems with your academic supervisor. An academic supervisor or mentor is a member of the faculty assigned to you at your degree course.
Meet with them regularly and let them know of any problems you are facing so they can help you address them promptly.
- Meet the challenges head-on. Don’t wait for your problems to become too large. A small issue can turn into a major crisis if you keep on ignoring it for too long. For example, if you are struggling to collect primary data for your dissertation , it will be appropriate to consult with your mentor to avoid falling behind on deadlines.
Most universities understand that students may face unforeseen challenges now and then due to their finances, family problems, personal limitations, and prolonged sickness. Therefore, it is possible to minimise the damage by filing for extenuating circumstances.
- By completing and submitting the extenuating circumstances form, you will be formally notifying your university that you are lagging on your dissertation or coursework. And do not forget to attach a formal plan to let them know how you will make sure to meet your new deadline so you can be granted an extension to your coursework, exam, or dissertation deadline.
Get an expert academic to help you with your dissertation, assignment, coursework, or essay so they can do the hard work for you. At ResearchProspect , we have masters and PhD qualified writers in all academic subjects. Whether it’s an essay, coursework, exam, dissertation, or assignment, you need help with. Our writers will exceed your expectations.
All you have to do is complete our online order form to place your order , and we will send the completed paper to your email address on or before the specified deadline. You are welcome to view our professional samples , take a look at our service portfolio and learn more about our company before placing your order.
Opportunities for Reassessment
Even if you end up receiving a failing mark, you will have several options to choose from to clean the mess. However, before making any decisions, you must determine whether you have failed the entire module, just an element of a module or the dissertation.
Failing Dissertation
if you have forgotten your dissertation because you will be allowed to resubmit it by the deadline agreed upon by yourself and the university.
However, the marks awarded for a resubmitted dissertation are usually caped to a minimum passing mark as a penalty for your failure in the first place.
A complete dissertation failure in UK universities will only occur if you cannot achieve the minimum passing mark even on your second attempt.
To improve your situation, you should regularly meet with your supervisor and avoid overlooking mandatory draft submissions.
Failing Module
You will be required to either re-sit an exam or re-submit the coursework (in some cases) if you have failed an entire module.
Each module that you take the exam for usually has a unique set of module guidelines associated with it. How you will be reassessed is taken by the board of examiners and the lecturers only after considering these guidelines.
Again, the maximum obtainable mark is usually capped to a bare pass level if you are re-siting an exam or resubmitting coursework.
Failing an Element of Module
If you only failed one piece of an exam or coursework and managed to achieve high marks for other modules, you may not need to resubmit that element.
The bottom line is that if your average coursework mark is above the bare minimum passing mark, you will pass that module even if you failed one piece of it.
For example, receive a failing mark of 35 in one essay coursework that counts for 25% of the overall module mark but pass the remaining 75% module assessment (which can be in the form of an exam or coursework). You can still give the entire module.
However, depending on your university’s regulations, you may have the opportunity to resubmit the failed coursework to improve your overall course grade.
Want to know what essay structure and style will work best for your assignment?
Problem fixed! We can write any type of essay in any referencing style. We ensure every essay written is beyond your expectations.

Plagiarism – A Serious Offence
All UK universities have strict rules and penalties against students who are caught plagiarising. If you receive a failing mark due to plagiarism , you may not be able to resubmit your dissertation/coursework or re-sit an exam.
So make sure to cite others’ ideas and avoid copying work from other academic sources to prevent your case from being sent to the University Ethics Board, which usually has the power to take a range of measures against you. In most cases, you will not be able to appeal the decision being taken if you are found guilty of plagiarising. So, refrain from it.
To help bring the point home, you can check out the comments and guidelines made by Reading, UK , regarding plagiarism.
Interesting watch: Check out a student’s account of how and why their dissertation went badly (UK institution).
Also read: Consequences of Plagiarism
How to Appeal Against a Failing Mark?
If you believe that you have been disadvantaged in some way or your university did not consider your financial or family problems while awarding you a failing mark. You may have the grounds to appeal against the mark awarded to you.
All UK universities have their own set of rules for lodging student academic appeals. Generally, this is a very lengthy procedure. Make sure that you provide documentary evidence along with the appropriate forms to justify your appeal.
The university exam board will review your case, and you will be allowed to resubmit your work or resit the exam if your application is successful.
Detailed information on appealing procedures is usually available on the university’s website and provided to students before starting their degree.
While no student ever wants to fail an exam, coursework, assignment or dissertation, the unthinkable sometimes can happen. But it would help if you did not get discouraged by the disastrous situation because most universities offer another chance to students who have genuine reasons.
How ResearchProspect Can Help
ResearchProspect is a UK-registered firm to provides academic support to students around the world. We specialise in completing design projects, literature reviews , essays , reports , coursework , exam notes , statistical analysis , primary and empirical research, dissertations , case studies, academic posters , and much more. Getting help from our expert academics is quick and simple. All you have to do is complete our online order form and get your paper delivered to your email address well before your due deadline.
Winning Dissertation Presentations
Don’t let all the paranoia get to you. If you don’t want your dissertation to fail, make sure to take steps to prevent that thing from happening.
Alternatively, checking out some real-life instances of students defending their dissertational research might help, too:
Three Minute Thesis (3MT) 2011 Winner – Matthew Thompson
2014 Three Minute Thesis winning presentation by Emily Johnston
Oxford University’s graduate’s advice for an award-nominated, A-graded dissertation
Furthermore, you can also check out real-life students’ advice about writing a winning dissertation, advice they wish someone had given them.
Further still, if you want to take every last measure, you could also check out what institutions in the UK, such as Birmingham University, require in your dissertation .
Frequently Asked Questions
What does it mean if you fail your dissertation.
Failing a dissertation means not meeting required standards. It may lead to retaking or resubmitting. Understand feedback, identify weaknesses, and seek support to improve and succeed next time.

You May Also Like
This article is a step-by-step guide to how to write statement of a problem in research. The research problem will be half-solved by defining it correctly.
Not sure how to write dissertation title page? All dissertations must have a dissertation title page where necessary information should be clearly presented
Dissertation discussion is where you explore the relevance and significance of results. Here are guidelines to help you write the perfect discussion chapter.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
How to Write a Dissertation Proposal | A Step-by-Step Guide
Published on 14 February 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on 11 November 2022.
A dissertation proposal describes the research you want to do: what it’s about, how you’ll conduct it, and why it’s worthwhile. You will probably have to write a proposal before starting your dissertation as an undergraduate or postgraduate student.
A dissertation proposal should generally include:
- An introduction to your topic and aims
- A literature review of the current state of knowledge
- An outline of your proposed methodology
- A discussion of the possible implications of the research
- A bibliography of relevant sources
Dissertation proposals vary a lot in terms of length and structure, so make sure to follow any guidelines given to you by your institution, and check with your supervisor when you’re unsure.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Step 1: coming up with an idea, step 2: presenting your idea in the introduction, step 3: exploring related research in the literature review, step 4: describing your methodology, step 5: outlining the potential implications of your research, step 6: creating a reference list or bibliography.
Before writing your proposal, it’s important to come up with a strong idea for your dissertation.
Find an area of your field that interests you and do some preliminary reading in that area. What are the key concerns of other researchers? What do they suggest as areas for further research, and what strikes you personally as an interesting gap in the field?
Once you have an idea, consider how to narrow it down and the best way to frame it. Don’t be too ambitious or too vague – a dissertation topic needs to be specific enough to be feasible. Move from a broad field of interest to a specific niche:
- Russian literature 19th century Russian literature The novels of Tolstoy and Dostoevsky
- Social media Mental health effects of social media Influence of social media on young adults suffering from anxiety
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Like most academic texts, a dissertation proposal begins with an introduction . This is where you introduce the topic of your research, provide some background, and most importantly, present your aim , objectives and research question(s) .
Try to dive straight into your chosen topic: What’s at stake in your research? Why is it interesting? Don’t spend too long on generalisations or grand statements:
- Social media is the most important technological trend of the 21st century. It has changed the world and influences our lives every day.
- Psychologists generally agree that the ubiquity of social media in the lives of young adults today has a profound impact on their mental health. However, the exact nature of this impact needs further investigation.
Once your area of research is clear, you can present more background and context. What does the reader need to know to understand your proposed questions? What’s the current state of research on this topic, and what will your dissertation contribute to the field?
If you’re including a literature review, you don’t need to go into too much detail at this point, but give the reader a general sense of the debates that you’re intervening in.
This leads you into the most important part of the introduction: your aim, objectives and research question(s) . These should be clearly identifiable and stand out from the text – for example, you could present them using bullet points or bold font.
Make sure that your research questions are specific and workable – something you can reasonably answer within the scope of your dissertation. Avoid being too broad or having too many different questions. Remember that your goal in a dissertation proposal is to convince the reader that your research is valuable and feasible:
- Does social media harm mental health?
- What is the impact of daily social media use on 18– to 25–year–olds suffering from general anxiety disorder?
Now that your topic is clear, it’s time to explore existing research covering similar ideas. This is important because it shows you what is missing from other research in the field and ensures that you’re not asking a question someone else has already answered.
You’ve probably already done some preliminary reading, but now that your topic is more clearly defined, you need to thoroughly analyse and evaluate the most relevant sources in your literature review .
Here you should summarise the findings of other researchers and comment on gaps and problems in their studies. There may be a lot of research to cover, so make effective use of paraphrasing to write concisely:
- Smith and Prakash state that ‘our results indicate a 25% decrease in the incidence of mechanical failure after the new formula was applied’.
- Smith and Prakash’s formula reduced mechanical failures by 25%.
The point is to identify findings and theories that will influence your own research, but also to highlight gaps and limitations in previous research which your dissertation can address:
- Subsequent research has failed to replicate this result, however, suggesting a flaw in Smith and Prakash’s methods. It is likely that the failure resulted from…
Next, you’ll describe your proposed methodology : the specific things you hope to do, the structure of your research and the methods that you will use to gather and analyse data.
You should get quite specific in this section – you need to convince your supervisor that you’ve thought through your approach to the research and can realistically carry it out. This section will look quite different, and vary in length, depending on your field of study.
You may be engaged in more empirical research, focusing on data collection and discovering new information, or more theoretical research, attempting to develop a new conceptual model or add nuance to an existing one.
Dissertation research often involves both, but the content of your methodology section will vary according to how important each approach is to your dissertation.
Empirical research
Empirical research involves collecting new data and analysing it in order to answer your research questions. It can be quantitative (focused on numbers), qualitative (focused on words and meanings), or a combination of both.
With empirical research, it’s important to describe in detail how you plan to collect your data:
- Will you use surveys ? A lab experiment ? Interviews?
- What variables will you measure?
- How will you select a representative sample ?
- If other people will participate in your research, what measures will you take to ensure they are treated ethically?
- What tools (conceptual and physical) will you use, and why?
It’s appropriate to cite other research here. When you need to justify your choice of a particular research method or tool, for example, you can cite a text describing the advantages and appropriate usage of that method.
Don’t overdo this, though; you don’t need to reiterate the whole theoretical literature, just what’s relevant to the choices you have made.
Moreover, your research will necessarily involve analysing the data after you have collected it. Though you don’t know yet what the data will look like, it’s important to know what you’re looking for and indicate what methods (e.g. statistical tests , thematic analysis ) you will use.
Theoretical research
You can also do theoretical research that doesn’t involve original data collection. In this case, your methodology section will focus more on the theory you plan to work with in your dissertation: relevant conceptual models and the approach you intend to take.
For example, a literary analysis dissertation rarely involves collecting new data, but it’s still necessary to explain the theoretical approach that will be taken to the text(s) under discussion, as well as which parts of the text(s) you will focus on:
- This dissertation will utilise Foucault’s theory of panopticism to explore the theme of surveillance in Orwell’s 1984 and Kafka’s The Trial…
Here, you may refer to the same theorists you have already discussed in the literature review. In this case, the emphasis is placed on how you plan to use their contributions in your own research.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
You’ll usually conclude your dissertation proposal with a section discussing what you expect your research to achieve.
You obviously can’t be too sure: you don’t know yet what your results and conclusions will be. Instead, you should describe the projected implications and contribution to knowledge of your dissertation.
First, consider the potential implications of your research. Will you:
- Develop or test a theory?
- Provide new information to governments or businesses?
- Challenge a commonly held belief?
- Suggest an improvement to a specific process?
Describe the intended result of your research and the theoretical or practical impact it will have:
Finally, it’s sensible to conclude by briefly restating the contribution to knowledge you hope to make: the specific question(s) you hope to answer and the gap the answer(s) will fill in existing knowledge:
Like any academic text, it’s important that your dissertation proposal effectively references all the sources you have used. You need to include a properly formatted reference list or bibliography at the end of your proposal.
Different institutions recommend different styles of referencing – commonly used styles include Harvard , Vancouver , APA , or MHRA . If your department does not have specific requirements, choose a style and apply it consistently.
A reference list includes only the sources that you cited in your proposal. A bibliography is slightly different: it can include every source you consulted in preparing the proposal, even if you didn’t mention it in the text. In the case of a dissertation proposal, a bibliography may also list relevant sources that you haven’t yet read, but that you intend to use during the research itself.
Check with your supervisor what type of bibliography or reference list you should include.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2022, November 11). How to Write a Dissertation Proposal | A Step-by-Step Guide. Scribbr. Retrieved 11 June 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/proposal/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, what is a dissertation | 5 essential questions to get started, what is a literature review | guide, template, & examples, what is a research methodology | steps & tips.
- Future Students
- Current Students
- Faculty/Staff

- Current Students Hub

Doctoral handbook
You are here
- Dissertation Proposal
On this page:
Proposal Overview and Format
Proposal committee, proposal hearing or meeting.
- Printing Credit for Use in School of Education Labs
Students are urged to begin thinking about a dissertation topic early in their degree program. Concentrated work on a dissertation proposal normally begins after successful completion of the Second-Year Review, which often includes a “mini” proposal, an extended literature review, or a theoretical essay, plus advancement to doctoral candidacy. In defining a dissertation topic, the student collaborates with their faculty advisor or dissertation advisor (if one is selected) in the choice of a topic for the dissertation.
The dissertation proposal is a comprehensive statement on the extent and nature of the student’s dissertation research interests. Students submit a draft of the proposal to their dissertation advisor between the end of the seventh and middle of the ninth quarters. The student must provide a written copy of the proposal to the faculty committee no later than two weeks prior to the date of the proposal hearing. Committee members could require an earlier deadline (e.g., four weeks before the hearing).
The major components of the proposal are as follows, with some variations across Areas and disciplines:
- A detailed statement of the problem that is to be studied and the context within which it is to be seen. This should include a justification of the importance of the problem on both theoretical and educational grounds.
- A thorough review of the literature pertinent to the research problem. This review should provide proof that the relevant literature in the field has been thoroughly researched. Good research is cumulative; it builds on the thoughts, findings, and mistakes of others.
- its general explanatory interest
- the overall theoretical framework within which this interest is to be pursued
- the model or hypotheses to be tested or the research questions to be answered
- a discussion of the conceptual and operational properties of the variables
- an overview of strategies for collecting appropriate evidence (sampling, instrumentation, data collection, data reduction, data analysis)
- a discussion of how the evidence is to be interpreted (This aspect of the proposal will be somewhat different in fields such as history and philosophy of education.)
- If applicable, students should complete a request for approval of research with human subjects, using the Human Subjects Review Form ( http://humansubjects.stanford.edu/ ). Except for pilot work, the University requires the approval of the Administrative Panel on Human Subjects in Behavioral Science Research before any data can be collected from human subjects.
Registration (i.e., enrollment) is required for any quarter during which a degree requirement is completed, including the dissertation proposal. Refer to the Registration or Enrollment for Milestone Completion section for more details.
As students progress through the program, their interests may change. There is no commitment on the part of the student’s advisor to automatically serve as the dissertation chair. Based on the student’s interests and the dissertation topic, many students approach other GSE professors to serve as the dissertation advisor, if appropriate.
A dissertation proposal committee is comprised of three academic council faculty members, one of whom will serve as the major dissertation advisor. Whether or not the student’s general program advisor serves on the dissertation proposal committee and later the reading committee will depend on the relevance of that faculty member’s expertise to the topic of the dissertation, and their availability. There is no requirement that a program advisor serve, although very often they do. Members of the dissertation proposal committee may be drawn from other area committees within the GSE, from other departments in the University, or from emeriti faculty. At least one person serving on the proposal committee must be from the student’s area committee (CTE, DAPS, SHIPS). All three members must be on the Academic Council; if the student desires the expertise of a non-Academic Council member, it may be possible to petition. After the hearing, a memorandum listing the changes to be made will be written and submitted with the signed proposal cover sheet and a copy of the proposal itself to the Doctoral Programs Officer.
Review and approval of the dissertation proposal occurs normally during the third year. The proposal hearing seeks to review the quality and feasibility of the proposal. The Second-Year Review and the Proposal Hearing are separate milestones and may not occur as part of the same hearing or meeting.
The student and the dissertation advisor are responsible for scheduling a formal meeting or hearing to review the proposal; the student and proposal committee convene for this evaluative period. Normally, all must be present at the meeting either in person or via conference phone call.
At the end of this meeting, the dissertation proposal committee members should sign the Cover Sheet for Dissertation Proposal and indicate their approval or rejection of the proposal. This signed form should be submitted to the Doctoral Programs Officer. If the student is required to make revisions, an addendum is required with the written approval of each member of the committee stating that the proposal has been revised to their satisfaction.
After submitting the Proposal Hearing material to the Doctoral Programs Officer, the student should make arrangements with three faculty members to serve on their Dissertation Reading Committee. The Doctoral Dissertation Reading Committee form should be completed and given to the Doctoral Programs Officer to enter in the University student records system. Note: The proposal hearing committee and the reading committee do not have to be the same three faculty members. Normally, the proposal hearing precedes the designation of a Dissertation Reading Committee, and faculty on either committee may differ (except for the primary dissertation advisor). However, some students may advance to Terminal Graduate Registration (TGR) status before completing their dissertation proposal hearing if they have established a dissertation reading committee. In these cases, it is acceptable for the student to form a reading committee prior to the dissertation proposal hearing. The reading committee then serves as the proposal committee.
The proposal and reading committee forms and related instructions are on the GSE website, under current students>forms.
Printing Credit for Use in GSE Labs
Upon completion of their doctoral dissertation proposal, GSE students are eligible for a $300 printing credit redeemable in any of the GSE computer labs where students are normally charged for print jobs. Only one $300 credit per student will be issued, but it is usable throughout the remainder of her or his doctoral program until the balance is exhausted. The print credit can be used only at the printers in Cubberley basement and CERAS, and cannot be used toward copying.
After submitting the signed dissertation proposal cover sheet to the Doctoral Programs Officer indicating approval (see above), students can submit a HELP SU ticket online at helpsu.stanford.edu to request the credit. When submitting the help ticket, the following should be selected from the drop-down menus for HELP SU:
Request Category : Computer, Handhelds (PDAs), Printers, Servers Request Type : Printer Operating System : (whatever system is used by the student, e.g., Windows XP.)
The help ticket will be routed to the GSE's IT Group for processing; they will in turn notify the student via email when the credit is available.
- Printer-friendly version
Handbook Contents
- Timetable for the Doctoral Degree
- Degree Requirements
- Registration or Enrollment for Milestone Completion
- The Graduate Study Program
- Student Virtual and Teleconference Participation in Hearings
- First Year (3rd Quarter) Review
- Second Year (6th Quarter) Review
- Committee Composition for First- and Second-Year Reviews
- Advancement to Candidacy
- Academic Program Revision
- Dissertation Content
- Dissertation Reading Committee
- University Oral Examination
- Submitting the Dissertation
- Registration and Student Statuses
- Graduate Financial Support
- GSE Courses
- Curriculum Studies and Teacher Education (CTE)
- Developmental and Psychological Sciences (DAPS)
- Learning Sciences and Technology Design (LSTD)
- Race, Inequality, and Language in Education (RILE)
- Social Sciences, Humanities, and Interdisciplinary Policy Studies in Education (SHIPS)
- Contact Information
- Stanford University Honor Code
- Stanford University Fundamental Standard
- Doctoral Programs Degree Progress Checklist
- GSE Open Access Policies
PhD students, please contact

MA POLS and MA/PP students, please contact

EDS, ICE/IEPA, Individually Designed, LDT, MA/JD, MA/MBA students, please contact

Stanford Graduate School of Education
482 Galvez Mall Stanford, CA 94305-3096 Tel: (650) 723-2109
- Contact Admissions
- GSE Leadership
- Site Feedback
- Web Accessibility
- Career Resources
- Faculty Open Positions
- Explore Courses
- Academic Calendar
- Office of the Registrar
- Cubberley Library
- StanfordWho
- StanfordYou
Improving lives through learning

- Stanford Home
- Maps & Directions
- Search Stanford
- Emergency Info
- Terms of Use
- Non-Discrimination
- Accessibility
© Stanford University , Stanford , California 94305 .
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
- How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
Published on October 12, 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on November 21, 2023.

A research proposal describes what you will investigate, why it’s important, and how you will conduct your research.
The format of a research proposal varies between fields, but most proposals will contain at least these elements:
Introduction
Literature review.
- Research design
Reference list
While the sections may vary, the overall objective is always the same. A research proposal serves as a blueprint and guide for your research plan, helping you get organized and feel confident in the path forward you choose to take.
Table of contents
Research proposal purpose, research proposal examples, research design and methods, contribution to knowledge, research schedule, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about research proposals.
Academics often have to write research proposals to get funding for their projects. As a student, you might have to write a research proposal as part of a grad school application , or prior to starting your thesis or dissertation .
In addition to helping you figure out what your research can look like, a proposal can also serve to demonstrate why your project is worth pursuing to a funder, educational institution, or supervisor.
| Show your reader why your project is interesting, original, and important. | |
| Demonstrate your comfort and familiarity with your field. Show that you understand the current state of research on your topic. | |
| Make a case for your . Demonstrate that you have carefully thought about the data, tools, and procedures necessary to conduct your research. | |
| Confirm that your project is feasible within the timeline of your program or funding deadline. |
Research proposal length
The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor’s or master’s thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
One trick to get started is to think of your proposal’s structure as a shorter version of your thesis or dissertation , only without the results , conclusion and discussion sections.
Download our research proposal template
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We’ve included a few for you below.
- Example research proposal #1: “A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management”
- Example research proposal #2: “Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use”
Like your dissertation or thesis, the proposal will usually have a title page that includes:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- Your institution and department
The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project. Make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why.
Your introduction should:
- Introduce your topic
- Give necessary background and context
- Outline your problem statement and research questions
To guide your introduction , include information about:
- Who could have an interest in the topic (e.g., scientists, policymakers)
- How much is already known about the topic
- What is missing from this current knowledge
- What new insights your research will contribute
- Why you believe this research is worth doing
As you get started, it’s important to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review shows your reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory. It also shows that you’re not simply repeating what other people have already done or said, but rather using existing research as a jumping-off point for your own.
In this section, share exactly how your project will contribute to ongoing conversations in the field by:
- Comparing and contrasting the main theories, methods, and debates
- Examining the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches
- Explaining how will you build on, challenge, or synthesize prior scholarship
Following the literature review, restate your main objectives . This brings the focus back to your own project. Next, your research design or methodology section will describe your overall approach, and the practical steps you will take to answer your research questions.
| ? or ? , , or research design? | |
| , )? ? | |
| , , , )? | |
| ? |
To finish your proposal on a strong note, explore the potential implications of your research for your field. Emphasize again what you aim to contribute and why it matters.
For example, your results might have implications for:
- Improving best practices
- Informing policymaking decisions
- Strengthening a theory or model
- Challenging popular or scientific beliefs
- Creating a basis for future research
Last but not least, your research proposal must include correct citations for every source you have used, compiled in a reference list . To create citations quickly and easily, you can use our free APA citation generator .
Some institutions or funders require a detailed timeline of the project, asking you to forecast what you will do at each stage and how long it may take. While not always required, be sure to check the requirements of your project.
Here’s an example schedule to help you get started. You can also download a template at the button below.
Download our research schedule template
| Research phase | Objectives | Deadline |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Background research and literature review | 20th January | |
| 2. Research design planning | and data analysis methods | 13th February |
| 3. Data collection and preparation | with selected participants and code interviews | 24th March |
| 4. Data analysis | of interview transcripts | 22nd April |
| 5. Writing | 17th June | |
| 6. Revision | final work | 28th July |
If you are applying for research funding, chances are you will have to include a detailed budget. This shows your estimates of how much each part of your project will cost.
Make sure to check what type of costs the funding body will agree to cover. For each item, include:
- Cost : exactly how much money do you need?
- Justification : why is this cost necessary to complete the research?
- Source : how did you calculate the amount?
To determine your budget, think about:
- Travel costs : do you need to go somewhere to collect your data? How will you get there, and how much time will you need? What will you do there (e.g., interviews, archival research)?
- Materials : do you need access to any tools or technologies?
- Help : do you need to hire any research assistants for the project? What will they do, and how much will you pay them?
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement .
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
The best way to remember the difference between a research plan and a research proposal is that they have fundamentally different audiences. A research plan helps you, the researcher, organize your thoughts. On the other hand, a dissertation proposal or research proposal aims to convince others (e.g., a supervisor, a funding body, or a dissertation committee) that your research topic is relevant and worthy of being conducted.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, November 21). How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved June 13, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/research-proposal/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a problem statement | guide & examples, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, how to write a literature review | guide, examples, & templates, what is your plagiarism score.
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.
- Skip to content
- Skip to navigation
Thesis Defense Announcement for Matthew Beach – 06/19/2024 at 2:00 PM
June 14, 2024
Thesis Title: A proposal for a graphical user interface application for querying the unmanned aerial system integration safety and security technology ontology When: 06/19/2024 2:00 PM Where: Simrall 228 Candidate: Matthew Beach Degree: Master of Science in Electrical & Computer Engineering Committee Members: Dr. Samee Khan, Dr. John Ball, Dr. Chaomin Luo
Abstract: Unmanned aerial systems (UAS) have become wildly popular over the past decade. With the increased demand of these systems, it is imperative for agencies such as the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) to integrate rules and regulations of UAS into the National Airspace System (NAS). In 2023, a UAS Integration Safety and Security Technology Ontology (ISSTO) was developed in the Web Ontology Language (OWL) to aid in this integration. To further aid UAS integration into the NAS, it becomes necessary to develop methods for training new pilots, air traffic control operators, drone operators, etc. This paper proposes a query application that allows new operators to query through ISSTO and efficiently access UAS and counter-UAS information from the knowledge domains contained within the ontology. These knowledge domains include information on various FAA regulations and authorizations, National Airspace classifications, counter-UAS procedures and more. The application developed in this thesis serves as a proof of concept for a commercialized training product.
Category: Dissertations and Theses
- Share full article

The Disturbing Truth About Hair Relaxers
They’ve been linked to reproductive disorders and cancers. Why are they still being marketed so aggressively to Black women?
A woman at a salon having relaxer applied to her hair. Credit... Naila Ruechel for The New York Times
Supported by
By Linda Villarosa
Linda Villarosa, a contributing writer for the magazine, interviewed dozens of people, including scientists, government officials and legal plaintiffs, for this article.
- June 13, 2024
The phone rang incessantly in Dr. Tamarra James-Todd’s office at Harvard’s T.H. Chan School of Public Health. “I’m sorry,” she said, excusing herself for the third time. “It’s happening a lot,” she explained after pausing to take another call, “with the F.D.A. thing.”
Listen to this article, read by Robin Miles
James-Todd, an associate professor of environmental reproductive epidemiology, is a pioneer who has conducted or been a co-author of nearly 70 scientific investigations over the past 20 years to establish the connection between the chemicals in hair products that generations of Black women have used to straighten their hair and the reproductive-health racial disparities that scientists have struggled to explain for decades. And on that day last October, she was receiving calls because the Food and Drug Administration had announced a proposal for a ban on the use of formaldehyde as an ingredient in hair relaxers, citing its link to cancer and other long-term adverse health effects.
Her early and sustained interest has also inspired other scientists — most of them Black women like her — to add questions about the use of hair relaxers and other products to large longitudinal studies with tens of thousands of subjects as they pursue explanations for these racial disparities. The scientists are driven by their own intimate experience: As children, they sat in salon chairs or in kitchens having chemical relaxers, colloquially called “creamy crack,” applied to their hair as they waited for it to go from “kinky” to smooth and silky as the products promised. Decades later, they still recall the harsh smell and the sensation of their scalps being aflame. “I go all the way back to: I was right,” James-Todd said. “That stuff that was burning on my head — it wasn’t safe.”

The research has finally begun to bear fruit: A robust body of scientific evidence has now shown that straighteners and other hair products marketed to Black girls and women have been linked to endocrine-disrupting substances associated with the early onset of menstruation and many of the reproductive-health issues that follow, from uterine fibroids, preterm birth and infertility to breast, ovarian and uterine cancer. Many of these hormone-health-related problems are more common in Black women than in other women, including an aggressive form of breast cancer that contributes to a death rate from the disease that is 28 percent higher than the rate for white women.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .
Advertisement
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
What percentage of PhD theses are rejected nowadays?
What percentage of PhD theses (e.g., physics ones) are rejected nowadays? And why?
- 1 Probably varies widely by department, location, etc. You shouldn't have to narrow it down, but might you want to? – Nick Stauner Commented Jan 16, 2014 at 4:43
- 33 What do you mean by "rejected"? For example, that a thesis defense takes place but the student fails and leaves graduate school without a Ph.D.? What if the student fails but is told to try again later after doing a little more work? What about a student who thinks he/she should graduate but whose thesis committee disagrees and won't schedule a defense? You might be able to find statistics for failed defenses, but by itself that data may not tell you much. (My impression is that most borderline theses never make it to the defense.) – Anonymous Mathematician Commented Jan 16, 2014 at 8:49
- 11 At many universities (my experience is exclusively EU-centric) there are at least two self-censorship filters before it comes to a defense. Firstly, and most importantly, it's the thesis supervisor who must approve your manuscript as defensible. Secondly, you often also need a dean's approval for moving on towards an actual defense. There are many theses which do not make it through these safeguard filters on their first attempt, but if the system works, you almost never see an officially failed defense/rejected thesis. Hence the numbers on the actual "failure rate" do not really exist. – walkmanyi Commented Jan 16, 2014 at 10:20
- 3 @walkmanyi Same for Austria and Switzerland. I have never heard of somebody 'failing' their defense (that would be an affront against the advisor just as much as against the student), but certainly there are people that just never finish their PhD. I would say, in my group drop-out rate was around 25% - 33%, but I never bothered to count. – xLeitix Commented Jan 16, 2014 at 13:26
- 2 In some graduate schools (e.g. the one I'm confronted with at Harvard), one factor is the 'qualifying exam'. I know of someone with a good publication record, whose adviser think she/he perfectly qualifies for the PhD, and who failed her/his qualifying exam. No PhD for that person, although the quality of the work far exceeds the one of the average thesis I have seen in the field. – Cape Code Commented Feb 12, 2015 at 13:48
2 Answers 2
I'm only personally aware of one student who failed his PhD defense (this is at an R1 US university). After his advisor refused to approve his thesis, he went over his head and got the department chair to schedule the defense anyway. Results were predictable.
On the other hand, "major revisions" are very common, especially, I hear, in the humanities (in engineering, it's far more common to receive token feedback -- if the committee reads the thesis at all! -- than demands for substantial changes).
Outright failing a student during a defense is an extreme embarassment, for the department, for the PhD committee, for the advisor, and of course for the student, so there is every incentive to ensure that a thesis that goes to defense will pass. Moreover, since most theses these days are compilations of previously-published work, it is very easy to tell well in advance if the student is expected to pass.
So if an advisor has doubts about the quality of a student's thesis, he will either ask the student to spend more time improving it, or "suggest" the student start looking for jobs in industry.
Very small, as every failed PhD defence is also a shame for the professor. As a result, the professor will not allow to proceed with defence of the really weak work. And he will listen for other professors that would usually tell in advance they think to vote against.
Hence, most likely, the following will happen:
- If a PhD student just does not work enough, the professor will not allow to continue studies after some time.
- If a PhD student is mad with some own theory or topic that academic community unlikely to accept, the professor will not allow to defend such a work.
- If it is really a bad luck with your topic, the professor will change the topic.
- If the professor has made a strategic mistake and your diligent work does not give results that could be published in a good journal, the professor should normally try to publish anyway in less reputable sources, good enough for PhD defence.
The PhD supervisor is more interested in your success than a lecturer is interested in the progress of the student. Same professor that writes low grades with relatively little attention (as long as he is sure the student deserves) will spend more time when acting as a PhD supervisor, will try to help, will try to fix the topic. This is because PhD project is also his research project. And who would want ones research project to fail? Of course, the professor tries to find a good PhD student for his project, or, if this was not successful, at least to fire lazy or uncooperative student in the first year. But this is way before the actual PhD defence.
If to ask differently, how many PhD students do not get they degree at the end, this really depends a lot on the traditions inside the institution. However in all places I have seen this was below 20 % or about. The first post doctoral position is also seldom a problem.
The next serious threshold you will need to pass is the professor position or at least a permanent researcher position, if you want to stay in science.
- 2 Can you provide a link to a university that requires the advisor to approve the thesis before being submitted. In my experience this is not how it works in the US or UK. – StrongBad Commented Jan 16, 2014 at 14:14
- 6 Regardless of the rules, it is very uncommon to go to defence against the will of the supervisor, and you really cannot expect to pass if you are in such a conflict, at least in European system. I have seen cases in Germany, Switzerland and Lithuania. – algorithmic_fungus Commented Jan 16, 2014 at 14:23
- 2 To say differently, if the supervisor thinks you will pass, you will most likely pass. And, with the help of your supervisor, it should not be extremely difficult to bring your PhD into good shape. The PhD supervisor is more interested in your success than a lecturer is interested in the progress of the student. But if you are in a conflict instead, chances to succeed are minor. For such a case, I would suggest to change the supervisor instead, even if this would mean changing the university as well. – algorithmic_fungus Commented Jan 16, 2014 at 14:52
- 1 @DanielE.Shub: just a quick example of a university requiring an approval of a thesis supervisor before engaging a panel of examiners/reviewers: TU Delft. See article 18.2 (pg. 24), as well as the formal process description (row 6 in table pg. 8) in the TU Delft doctorate regulations . – walkmanyi Commented Jan 16, 2014 at 15:26
- 1 In short. Trust your supervisors. If you have a good relationship with them (or even a bad one honestly), and they think you will pass, then you will almost certainly pass. If: you go over your supervisors head, your supervisors have been sub-par or not supportive, your supervisors have not thoroughly read your thesis, then you have more cause for concern. – DryLabRebel Commented Jun 19, 2021 at 2:13
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged phd thesis science ..
- Featured on Meta
- Upcoming sign-up experiments related to tags
Hot Network Questions
- In Mandarin, can you use 我爱你 platonically?
- Why can real number operations be applied to complex numbers?
- Cannot install MacOS Sonoma to external SSD on MacBook
- Domino equation derivation
- Would a series of gravitational waves from a supernova affect time on a 200 year old clock just as water waves affected clocks on ships in rough seas?
- What would happen to 'politicians' in this world?
- Origin of "That tracks" to mean "That makes sense."
- Show or movie where a blue alien is discovered by kids in a storm drain or sewer and cuts off its own foot
- Problems when extracting chars from data imported from csv file
- Should I tell my class I am neurodivergent?
- Is it epistemologically self-consistent to use the scientific method to justify some beliefs and non-scientific justifications for others?
- Where is "Import Images as Planes" in 4.2?
- Are all representations of the geometric étale fundamental group subquotients of representations of the arithmetic étale fundamental group?
- Whats the time dependency of r and angle in Hohmann transfer?
- Is there a maximum amount of time I should spend on an exercise bike
- Orthodox recognition of Reform bar mitzvah
- Are these called ring binders in American English or files?
- Limitations on pain and pleasure, and the ratio of extremes assuming perfect technology
- Understanding the discrepancy between Input and Output power in ZVS Induction heater
- How do I efficiently update myself on what's expected of me as a postdoc?
- I'm looking for a short story I read 10-15 years ago about a man exploring post-apocalyptic Britain
- A short story about a woman who does not have dissociative identity disorder pretends to have it
- Kubuntu 24.04 LTS doesn't boot right after install. Grub option allows boot but breaks brightness and night color control. Intel integrated graphics
- Why aren't the plains people conquering the city people?
Get the Reddit app
Discussion forum for current, past, and future students of any discipline completing post-graduate studies - taught or research.
Didn’t pass my thesis proposal
I was given a conditional pass. My committee said they thought my written proposal was clear, but there was concern that I didn’t have a firm hold on the existing literature and wasn’t using the right terminology to communicate my ideas. My advisor wants me to reread a landmark paper and send her a summary discussing the weaknesses and strengths of the paper, as well as how it applies to my research.
She’ll send me a document with additional feedback for me to look over. Their feedback I received during my presentation is extremely valid - I’m just struggling really hard accepting it. I’ve worked really hard on my proposal and my presentation, so it seems like if I worked that hard for those things but I did them wrong, then I mustn’t be smart enough to succeed in science.
I also feel kind of blindsided by my advisor. While she’s always given me feedback which I’ve tried to incorporate and never actually said my proposal was excellent in the first place, I feel like she’s never outright, explicitly said what’s wrong. Yet, during my proposal, was telling me all my faults in front of my committee. Is that what science is supposed be? Figuring out on your own what you’re doing wrong?
I’m a huge advocate for learning from your mistakes and understand that graduate school is a place to learn how to do research, but I just feel so silly and embarrassed. I’m not sure how to move forward from here. I feel like every time I move one step forward, I move two steps back.
Edit: forgot to mention that this is for a master program.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Overview: 8 Research Proposal Killers. The research topic is too broad (or just poorly articulated). The research aims, objectives and questions don't align. The research topic is not well justified. The study has a weak theoretical foundation. The research design is not well articulated well enough. Poor writing and sloppy presentation.
The majority of failed Ph.D. dissertations are sloppily presented. They contain typos, grammatical mistakes, referencing errors and inconsistencies in presentation. Looking at some committee reports randomly, I note the following comments: "The thesis is poorly written.". "That previous section is long, badly written and lacks structure.".
Thesis/dissertation proposal often serve as a contract between the the committee and the student. It also serves as a blue print to keep the student on track. Most chairs won't let a student defend unless he/she is relatively sure that it will pass (with corrections) at least. Sometimes a major flaw might slip passed the chair, but that is rare.
The thesis and thesis defense is less about having the results you wanted to have, and more about demonstrating that you know how to do good quality research and can work on that somewhat independently. ... That being said, there are people who have failed during the proposal if their project is especially unoriginal and basic. So, in my ...
He refused to look at individual chapters of my proposal ("I have to see the whole before I can render judgment.") and acted similarly with my dissertation. He never read a single page prior ...
Generally, this is a very lengthy procedure. Make sure that you provide documentary evidence along with the appropriate forms to justify your appeal. The university exam board will review your case, and you will be allowed to resubmit your work or resit the exam if your application is successful.
Writing a proposal or prospectus can be a challenge, but we've compiled some examples for you to get your started. Example #1: "Geographic Representations of the Planet Mars, 1867-1907" by Maria Lane. Example #2: "Individuals and the State in Late Bronze Age Greece: Messenian Perspectives on Mycenaean Society" by Dimitri Nakassis.
Other faculty may attend the dissertation proposal defense, but the members of the student's dissertation proposal committee make the final decision on a candidate. Is it common to fail a dissertation? Yes, it is possible to fail your dissertation. A dissertation is a meaningful academic project that requires thorough research, critical ...
Table of contents. Step 1: Coming up with an idea. Step 2: Presenting your idea in the introduction. Step 3: Exploring related research in the literature review. Step 4: Describing your methodology. Step 5: Outlining the potential implications of your research. Step 6: Creating a reference list or bibliography.
Proposal Overview and Format. Students are urged to begin thinking about a dissertation topic early in their degree program. Concentrated work on a dissertation proposal normally begins after successful completion of the Second-Year Review, which often includes a "mini" proposal, an extended literature review, or a theoretical essay, plus advancement to doctoral candidacy.
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management".
My husband beamed at the compliment and I felt light pushing out the darkness. Dan and I both had failed marriages in our past, but ours had been "meant-to-be" from our six and a half hour meet-cute at Starbucks. I did get past this failed dissertation defense, too. I failed, but I am not a failure. 4 claps.
No. Universities will not let you defend if there is the slightest chance you will fail. It reflects very poorly on the department in front of external examiners if PhD candidates fail a defense. Also planning the defense is a lot of hassle for your department, no one wants to do the work twice. You will be ok.
So basically, I somewhat "failed" the proposal defense although the panel reworked it as a "consultation" so that I wouldn't be failing. I have to pass a new proposal to my adviser this December. ... Overcome this, rewrite your thesis, schedule a 1-2 hr meeting with your advisor and give them a few weeks to read your proposal before ...
A journal paper is a more scoped contribution compared roughly to one chapter of your PhD thesis. Having one journal paper published does not guarantee you a PhD. I am aware of some candidates with 5+ journal publications, who failed their defence because they rushed and did not write an adequate PhD dissertation. It definitely happens.
The document discusses getting help from dissertation writing services after failing a dissertation proposal. It describes the difficulties of writing a dissertation proposal and how a failed proposal can damage students' confidence and academic progress. It then introduces HelpWriting.net, which understands students' struggles and provides high-quality, customized dissertations and proposals ...
Thesis Title: A proposal for a graphical user interface application for querying the unmanned aerial system integration safety and security technology ontology When: 06/19/2024 2:00 PM Where: Simrall 228 Candidate: Matthew Beach Degree: Master of Science in Electrical & Computer Engineering Committee Members: Dr. Samee Khan, Dr. John Ball, Dr. Chaomin Luo Abstract: Unmanned aerial
What does happen however (sometimes) is that people quit before they start to write. It could be lack of funding, bad supervision, change of heart, bad project, etc etc. But the general consensus seem to be that if you're determined and if you actually have something to write about, then you will pass.
US Secretary of State Antony Blinken on Wednesday expressed frustration that Hamas has submitted "numerous changes" to a US-backed proposal for a ceasefire and release of hostages in Gaza ...
For the project that would become her dissertation, James-Todd spent two years interviewing 300 women she recruited from nail and hair salons, churches, workplaces, restaurants and laundromats.
But this is way before the actual PhD defence. If to ask differently, how many PhD students do not get they degree at the end, this really depends a lot on the traditions inside the institution. However in all places I have seen this was below 20 % or about. The first post doctoral position is also seldom a problem.
It is much better to fail at the proposal stage rather than a more devastating failure during the final defense. In some programs, if you fail the final defense, you will need to re-take the proposal phase all over again with a (presumably) brand new topic and study, pretty much a waste of effort into that perspective. 5.
that she filed a thesis with the French government, as required for a doctorate under ... findings regarding each one - in a January 5, 2021 "Notice of Proposal to. Suspend/Remove" that she sent to Ms. Sieg. Although styled as a letter, this proposal is ... The agency had failed to provide the Committee with. this report for approximately ...
These are treaty drafts from March 17 and April 15, 2022, presenting competing proposals from both sides and points of agreement, and a private "communique" from personal talks in Istanbul on ...
This thesis is 13000 words of horseshit. I don't know how I'm going to survive my presentation. I'm so stressed that my stomach hurts. There's so much I would've done differently. I hate myselfffffff. There's a saying I've heard that I like repeating to myself whenever I'm disappointed in my progress: a good dissertation is a finished ...
Didn't pass my thesis proposal. I was given a conditional pass. My committee said they thought my written proposal was clear, but there was concern that I didn't have a firm hold on the existing literature and wasn't using the right terminology to communicate my ideas. My advisor wants me to reread a landmark paper and send her a summary ...