Digital Economy: A Leveller or a Source of Economic Inequality - UPSC PDF Download
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? |

Science-Technology
With more and more technological developments, the internet has become a means to make life easier. It has transformed many sectors of the economy and has aided significantly in boosting the country's economic growth. It is no surprise that the digital economy is expanding its reach across the length and breadth of the country and has become an integral part of people’s lives. While going digital has made things simpler in almost all spheres of life (economic, political, social, commercial, etc.), whether it is actually beneficial or not is up for debate. It goes without saying that having a digital economy has made the day to day activities much smoother; it would be incorrect to assume that it hasn’t created problems.
A Leveller or a Cause for Inequality?
The benefits of the digital economy are there for everyone to enjoy. Some of the major advantages offered by the digital economy in India are: -
- An Increase in Online Businesses: Also known as e-commerce, the availability of a well-developed internet network along with facilities such as online banking, trading, video conferencing, etc., makes it so much easier for individuals to carry out their work. Owing to these facilities, marketing, buying and selling, money transactions, etc., have become so much easier, closer to home, and have significantly helped in the empowerment of the underprivileged sections of the Indian society.
- Higher Transparency and More Proof: Once something is on the internet, it stays out there forever, no matter whether you delete it from one domain or another. It never fully disappears. This is a massive advantage, especially when it comes to money transactions and other kinds of agreements entered by the people. For instance, once a person makes a payment online, the transaction record is saved online and is easily accessible as and when required. This has made life simpler for individuals and offers protection in case of instances of fraud, theft, or other forms of cyber-crimes.
- Easy Availability of Services: Not only does the internet provide a means to easily conduct essential activities, but it also allows people to access necessary services conveniently. Information regarding necessary steps, benefits available, documentation required, etc., for different government schemes. Many government agencies have their own apps which allow the users to avail themselves of the essential services within a few minutes.
While the advantages offered by the digital economy are noteworthy, it goes without saying that the digital economy is responsible for creating some inequalities in Indian society as well, such as:
- Unemployment: It goes without saying that an internet driven economy has made life less complicated, but it has also become a cause for concern. With almost everything being done online with the help of software, there is a decrease in the demand for manpower. Fewer and fewer people are required to do a particular work, which has thrown many people into unemployment. For example, when it comes to bank work, the easy availability of banking apps, Paytm, Google Pay, etc., has put many people out of work. Also, for people with a lesser understanding of the internet, it becomes difficult to find a suitable job.
- Increased Cyber Crimes: Even though every activity on the internet can be traced, it does not mean that cybercrime no longer exists. In fact, it is quite the opposite. With almost everyone having access to the internet, some with greater knowledge of its functioning and loopholes, there have been increased cases of cybercrime, including hacking of bank accounts, thefts, illegal transactions, etc., which have eroded the trust of people in the prospects of the digital economy.
- Lack of Security: The ease with which unauthorized entities can access data on the internet can turn out to be quite harmful. Many companies, businesses, and even government agencies store large amounts of data online or on computers. Anyone who knows how to hack into another system, even a secure one, can easily gain access to important and confidential data and can also use it to their advantage.
Steps to Tackle The Issue of Inequality
With constant technological developments, it is good to move along with those changes; it is good to learn new ways of life. However, the problem arises when people get so absorbed in that new life that they do not realize the harm it is causing to themselves and others. In such situations, it becomes important to identify what the problem is and how to find a solution to it. Here are some ways to bridge the gap that was and continues to be created by the digital economy:
- Stricter Cyber Laws: While cybercrime has been on the rise in recent years, thanks to easier access to the internet, the laws for cyber crimes are still not well-defined. There should be improvements in cyber laws so that the victim is provided immediate attention and relief and the culprits are caught in time. There should be increased awareness about such crimes, and efforts should be made to make the internet more secure. Users should be educated about the do’s and don’ts while using the internet to secure their digital space.
- Education: Since almost every sector of the economy uses the internet and its related services to carry out daily functions and run businesses, more and more people should be taught how to use the internet. They should be encouraged to develop skills related to the internet so that they have a better chance of finding employment. This is especially the case with rural areas. While people in small towns and villages do have access to the internet, it is often limited. If they, too, are taught how to perform online banking, purchasing or selling items online, or even promoting a local business online, they would benefit immensely.
- Empowering people: The fact that many business activities are being conducted online and it has become important to have basic knowledge of the functions of the internet for anyone to land a decent job. These trends indirectly contribute to problems such as unemployment. It is the government’s responsibility to create more job opportunities in all sectors and all regions of the country. Efforts must be undertaken by the central government and the state governments to ensure that people, irrespective of their lack of knowledge of the internet, have a way of earning a livelihood.
Over the years, the government has made efforts to transform the traditional economy into a digital economy. It is in no way wrong to hope for an economy that keeps growing steadily while making things easier for the people. But it is also important to be fully aware of the country's situation and its people before giving priority to major changes such as the ones mentioned above. It is necessary to assess both the positive and negative impacts of such a transformation and then develop a balanced approach that satisfies the needs of all stakeholders.
Top Courses for UPSC
FAQs on Digital Economy: A Leveller or a Source of Economic Inequality - UPSC
| 1. Is the digital economy a leveller or a cause for inequality? |
| 2. What steps can be taken to tackle the issue of inequality in the digital economy? |
| 3. How does the digital economy contribute to economic inequality? |
| 4. What are the potential benefits of the digital economy in reducing inequality? |
| 5. How can governments promote a more equitable digital economy? |
| Rating | |
How to Prepare for UPSC
Practice quizzes, semester notes, mock tests for examination, digital economy: a leveller or a source of economic inequality - upsc, objective type questions, extra questions, important questions, video lectures, sample paper, past year papers, viva questions, shortcuts and tricks, previous year questions with solutions, study material.

Digital Economy: A Leveller or a Source of Economic Inequality Free PDF Download
Importance of digital economy: a leveller or a source of economic inequality, digital economy: a leveller or a source of economic inequality notes, digital economy: a leveller or a source of economic inequality upsc questions, study digital economy: a leveller or a source of economic inequality on the app.
| cation olution |
| Join the 10M+ students on EduRev |
Welcome Back
Create your account for free.
Forgot Password
Unattempted tests, change country, practice & revise.

- भाषा : हिंदी
- Classroom Courses
- Our Selections
- Student Login
- About NEXT IAS
- Director’s Desk
- Advisory Panel
- Faculty Panel
- General Studies Courses
- Optional Courses
- Interview Guidance Program
- Postal Courses
- Test Series
- Current Affairs
- Student Portal

The Government is working on a comprehensive legal framework for the digital economy.
| . A new telecom Bill to replace laws made in 1885 and 1930 is at an advanced stage of drafting. . that India is preparing to replace the IT Act of 2000 vintage. , for example the national data framework that is uploaded for consultation. |
- The digital economy is the worldwide network of economic activities, commercial transactions and professional interactions that are enabled by information and communications technologies (ICT) .
- It can be succinctly summed up as the economy based on digital technologies.
- The digital economy reflects the move from the third industrial revolution to the fourth industrial revolution.
- The third industrial revolution, sometimes called the digital revolution, refers to the changes that happened in the late 20th century with the transition from analog electronic and mechanical devices to digital technologies.
- The fourth industrial revolution builds on the digital revolution as technologies today continue to bridge the physical and cyberworlds.
Advantages of The Digital Economy
- Increased productivity: The digital economy has increased the productivity of businesses as they can now use technology to automate their operations and processes.
- Increased competitiveness: Businesses can use technology to improve their products and services. This has increased the competitiveness of businesses.
- Reduced costs: Digitisation has helped businesses replace manual tasks with automated processes. This has reduced the costs of businesses and has led to lower prices of products and services for consumers.
- Better & Convenient Products: Today, digitised businesses can offer their customers better products and services at lower prices. New business models like e-commerce and m-commerce have made it possible for customers to shop anytime, anywhere.
- Increased employment opportunities: The digital economy has generated new job opportunities as new businesses are springing up. It has also created new job roles spread all over the world.
- Improved quality of life: The digital economy has made it possible for people to work from anywhere in the world. This has improved the quality of life of people as they can now balance their work and personal life.
- Faster transactions: The digital economy has made it possible for businesses to conduct transactions faster as they can now use online payment methods.
- Improved efficiency: Digitisation of processes has helped businesses become more efficient by removing error-prone manual tasks.
- Innovation: The digitisation of businesses and its processes leads to innovation with respect to not just offerings but also the way businesses operate.
- Increased transparency: The digital economy has increased the transparency of businesses as they can now use technology to share information with their customers.
- Improved communication: Increased connectedness in the digital economy has made it possible for businesses to communicate with their customers more effectively. They now have a number of channels through which they can reach their customers including social media, email, and SMS.
- DigiLocker: It was launched in 2015 to create a cloud-based platform to issue, exchange and verify essential documents or certificates.
- MyGov: It was launched in 2014 to bring the government closer to the people by providing an interface (online forum) for exchange of ideas.
- BharatNet: It was introduced to connect all 250,000 Gram Panchayats (GPs) in the country and provide 100 Mbps internet connectivity.
- Smart Cities: It was initiated in 2015 to transform all Indian cities into smart cities by leveraging various technologies.
- Digitisation of Post Offices
- Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojna
- Digital India
Disadvantages Of Digital Economy
- The digital divide: One of the biggest disadvantages of the digital economy is the digital divide. This is the gap between those who have access to technology and those who don’t. This has created a new form of inequality in the world.
- Cybercrime: The increased use of technology has also led to an increase in cybercrime. This is because criminals can now use technology to commit crimes like identity theft, fraud, and money laundering.
- Data security: With businesses collecting more and more data about their customers, there is a risk of this data being leaked or stolen. This can lead to a loss of trust between businesses and their customers.
- Unemployment: The digitisation of the economy has led to job losses in some sectors as businesses have replaced human workers with technology. This has increased unemployment in these sectors.
- Privacy concerns: As businesses collect more data about their customers, there are concerns about the misuse of this data.
- Heavy investments: The digitisation of businesses requires heavy investments in technology. This is a challenge for small businesses which might not have the resources to invest in technology.
- Monopoly: The digitisation of the economy has led to the rise of a few big companies which have become very powerful. This has created a monopoly in some sectors.
- Addictive nature: The digital economy is very addictive in nature. This is because it is designed to keep people hooked on their devices. This can lead to a number of problems like addiction, anxiety, and depression.
- Potential environmental impact: The increased use of technology in the digital economy has led to an increase in the number of e-waste and heavy carbon footprint.
- There is a need to leverage today’s emerging technologies , such as IoT and prescriptive analytics, to better connect with existing and potential customers and to be more responsive while also being more efficient and effective.
- To compete in the years ahead, organizations — whether they are for-profit businesses, service-oriented entities, such as healthcare systems, or nonprofit and government institutions — will need both leaders and employees who are able to innovate.
- Become better prepared to explore how best to develop or use emerging technologies or risk being left behind as the digital economy moves forward.
Source : TH
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
Daily current affairs 01-07-2024, daily current affairs 29-06-2024, daily current affairs 28-06-2024, weaponizing the prevention of money laundering act.

Next Generation Institute for UPSC Civil Services Examination Preparation.
- Video Gallery
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- UPSC CSE Posts
- Testimonials
NEXT IAS (Delhi)
Old rajinder nagar.
- 27-B, Pusa Road, Metro Pillar no.118, Near Karol Bagh Metro, New Delhi-110060
Mukherjee Nagar
- 1422, Main Mukherjee Nagar Road. Near Batra Cinema New Delhi-110009
NEXT IAS (Jaipur)
- NEXT IAS - Plot No - 6 & 7, 3rd Floor, Sree Gopal Nagar, Gopalpura Bypass, Above Zudio Showroom Jaipur (Rajasthan) - 302015
NEXT IAS (Prayagraj)
- 31/31, Sardar Patel Marg, Civil Lines, Prayagraj, Uttar Pradesh - 211001
NEXT IAS (Bhopal)
- Plot No. 46 Zone - 2 M.P Nagar Bhopal - 462011
- 8827664612 ,
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
UPSC Coaching, Study Materials, and Mock Exams
Enroll in ClearIAS UPSC Coaching Join Now Log In
Call us: +91-9605741000
Digital India Programme
Last updated on December 31, 2023 by ClearIAS Team
Digital India is a flagship programme of the Government of India launched in 2015. Read here to know the program in detail.
Digital India is a flagship programme of the Government of India with a vision to transform India into a digitally empowered society and knowledge economy.
It was launched in July 2015.
E-governance initiatives in India gained momentum in the mid-1990s for wider sectoral applications with an emphasis on citizen-centric services.
The major Information and Communication Technology (ICT) initiatives included major projects like railway computerization, land record computerization, etc., which focused mainly on the development of information systems. Later on, many states started individual e-governance projects aimed at providing electronic services to citizens.
These initiatives did not make the expected impact due to isolated and less interactive features. Hence, more comprehensive planning and implementation were required to establish a connected government.
Digital India is an umbrella programme that covers multiple Government Ministries and Departments. It weaves together a large number of ideas and thoughts into a single, comprehensive vision so that each of them can be implemented as part of a larger goal.
Download Timetable and Study Plan ⇓
(1) ⇒ UPSC Mains Test Series 2024
(2) ⇒ UPSC Prelims Test Series 2025
(3) ⇒ UPSC Fight Back 2025
(4) ⇒ UPSC Prelims cum Mains 2025
Table of Contents
e-Kranti: National e-Governance Plan 2.0
The national-level e-governance programme called National e-Governance Plan (NeGP) was initiated in 2006.
- There were 31 Mission Mode Projects under the National e-Governance Plan covering a wide range of domains viz. agriculture , land records , health, education, passports, police, courts, municipalities, commercial taxes, treasuries, etc.
- 24 Mission Mode Projects have been implemented and started delivering either a full or partial range of envisaged services.
All new and ongoing e-governance projects as well as the existing projects, which are being revamped, should now follow the key principles of e-Kranti namely:
- Transformation and not Translation
- Integrated Services and not Individual Services
- Government Process Reengineering (GPR) to be mandatory in every MMP
- ICT Infrastructure on Demand
- Cloud by Default
- Mobile First
- Fast Tracking Approvals
- Mandating Standards and Protocols
- Language Localization
- National GIS (Geo-Spatial Information System)
- Security and Electronic Data Preservation
The portfolio of Mission Mode Projects has increased from 31 to 44 MMPs. Many new social sector projects namely Women and Child Development, Social Benefits, Financial Inclusion, Urban Governance eBhasha, etc., have been added as new MMPs under e-Kranti.
Vision Areas of Digital India
The vision of the Digital India programme is to transform India into a digitally empowered society and knowledge economy.
The Digital India programme is centered on three key vision areas:
1. Digital infrastructure as a core utility to every citizen
- High-speed internet as a core utility
- Cradle-to-grave digital identity
- Participation in digital and financial space through mobiles and banking
- Easy access to a Common Service Centre (CSC)
- Shareable private space on a public cloud
2. Governance and services on demand
- Seamlessly integrated services across departments
- Services available in real-time from online and mobile platforms
- All citizen entitlements to be portable and available on the cloud
- Digital transformation for ease of doing business
- Electronic and cashless financial transactions
- Leveraging Geospatial Information System (GIS) for decision support systems and development
3. Digital empowerment of citizens
- Universal digital library
- Universally accessible digital resources
- All documents/certificates to be available on the cloud
- Availability of digital resources/services in Indian languages
- Collaborative digital platforms for participative governance
Digital India: Programme pillars
Digital India aims to provide the much-needed thrust to the nine pillars of growth areas, namely:
- Broadband Highways
- Universal Access to Mobile Connectivity
- Public Internet Access Programme
- e-Governance: Reforming Government through Technology
- e-Kranti – Electronic Delivery of Services
- Information for All
- Electronics Manufacturing
- IT for Jobs
- Early Harvest Programmes
Digital India Initiatives
The Government has taken up many initiatives under the Digital India campaign:
DigiLockers: This flagship initiative aims at ‘Digital Empowerment’ of the citizen by providing access to authentic digital documents in citizen’s digital document wallet
E-Hospitals: It is a Hospital Management Information System (HMIS) which is a one-stop solution for connecting patients, hospitals, and doctors through a single digital platform. Till February 2021, as many as 420 e-Hospitals had been established under the Digital India campaign
E-Pathshala: Developed by NCERT, e-Pathshala showcases and disseminates all educational e-resources including textbooks, audio, video, periodicals, and a variety of other print and non-print materials through the website and mobile app
BHIM: Bharat Interface for Money is an app that makes payment transactions simple, easy, and quick using Unified Payments Interface (UPI)
Digital India Bhashini: It is India’s Artificial Intelligence (AI) led language translation platform.
Digital India GENESIS: (Gen-next Support for Innovative Startups) is a national deep-tech startup platform to discover, support, grow and make successful startups in Tier-II and Tier-III cities of India.
My Scheme: It is a service discovery platform facilitating access to Government Schemes. It aims to offer a one-stop search and discovery portal where users can find schemes that they are eligible for.
Meri Pehchaan: It is a National Single Sign On (NSSO) for One Citizen Login. It is a user authentication service in which a single set of credentials provide access to multiple online applications or services.
Chips to Startup (C2S) Programme: The C2S Programme aims to train specialized manpower in the area of design of semiconductor chips at bachelor, master, and Research levels, and act as a catalyst for the growth of Startups involved in semiconductor design in the country.
Indiastack global: It is a global repository of key projects implemented under India Stack like Aadhaar , UPI (Unified Payment Interface), Digilocker, Cowin Vaccination Platform, Government e MarketPlace, DIKSHA Platform, and Ayushman Bharat Digital Health Mission .
Digital India week 2022
The Digital India Week 2022 under the Digital India Programme, to strengthen the Ease of Doing Business and Ease of Living.
The theme for the week was ‘Catalyzing New India’s Techade’.
Way forward
The Digital India programme aims at pulling together many existing schemes. These schemes will be restructured, revamped, and re-focused and will be implemented in a synchronized manner. Many elements are only process improvements with minimal cost implications. The common branding of programmes as Digital India highlights their transformative impact.
India’s aim for the digital revolution will help is pushing all sectors and jurisdictions of the economy. The advances in governance, reforms, start-ups , and demographic advantage will push the country towards being the fastest growing digital economy.
Also read: Payments Infrastructure Development Fund (PIDF) scheme

Top 10 Best-Selling ClearIAS Courses
Upsc prelims cum mains (pcm) gs course: unbeatable batch 2025 (online), rs.75000 rs.29000, upsc prelims test series (pts) 2025 (online), rs.9999 rs.4999, upsc mains test series (mts) (online), rs.19999 rs.9999, csat course 2025 (online), current affairs course 2025: important news & analysis (online), ncert foundation course (online), essay writing course for upsc cse (online), ethics course for upsc cse (online), fight back: repeaters program with daily tests (online or offline), rs.55000 rs.25000.

About ClearIAS Team
ClearIAS is one of the most trusted learning platforms in India for UPSC preparation. Around 1 million aspirants learn from the ClearIAS every month.
Our courses and training methods are different from traditional coaching. We give special emphasis on smart work and personal mentorship. Many UPSC toppers thank ClearIAS for our role in their success.
Download the ClearIAS mobile apps now to supplement your self-study efforts with ClearIAS smart-study training.
Reader Interactions
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Don’t lose out without playing the right game!
Follow the ClearIAS Prelims cum Mains (PCM) Integrated Approach.
Join ClearIAS PCM Course Now
UPSC Online Preparation
- Union Public Service Commission (UPSC)
- Indian Administrative Service (IAS)
- Indian Police Service (IPS)
- IAS Exam Eligibility
- UPSC Free Study Materials
- UPSC Exam Guidance
- UPSC Prelims Test Series
- UPSC Syllabus
- UPSC Online
- UPSC Prelims
- UPSC Interview
- UPSC Toppers
- UPSC Previous Year Qns
- UPSC Age Calculator
- UPSC Calendar 2024
- About ClearIAS
- ClearIAS Programs
- ClearIAS Fee Structure
- IAS Coaching
- UPSC Coaching
- UPSC Online Coaching
- ClearIAS Blog
- Important Updates
- Announcements
- Book Review
- ClearIAS App
- Work with us
- Advertise with us
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- Talk to Your Mentor
Featured on

and many more...
ClearIAS Programs: Admissions Open
Thank You 🙌
UPSC CSE 2025: Study Plan
IAS/IPS/IFS Online Coaching: Target CSE 2025

Cover the entire syllabus of UPSC CSE Prelims and Mains systematically.
Subscribe clearias youtube channel.

Get free study materials. Don’t miss ClearIAS updates.
Subscribe Now
Download Self-Study Plan

Analyse Your Performance and Track Your Progress
Download Study Plan
- Our Centers Delhi Bhubaneswar Lucknow
- UPSC Mains Previous Year Questions
- Digital economy: A leveller or a source of economi
Digital economy: A leveller or a source of economic inequality
- Subject Essay

Verifying, please be patient.
Our Centers
DELHI (Karol Bagh)
GS SCORE, 1B, Second Floor, Pusa Road, Karol Bagh, New Delhi - 110005 (Beside Karol Bagh Metro Station Gate No. 8)
Get directions on Google Maps
BHUBANESWAR (Jaydev Vihar)
GS SCORE, Plot No.2298, Jaydev Vihar Square, Near HCG Day Care, BBSR - 751013
LUCKNOW (Aliganj)
GS SCORE, 2nd Floor, B-33, Sangam Chauraha, Sector H, Aliganj, Lucknow, UP - 226024
Delhi (Karol Bagh) Centre
GS SCORE, Second Floor, Metro Tower, 1B, Pusa Road, Karol Bagh, New Delhi - 110005 (Beside Karol Bagh Metro Station Gate No. 8)
Email: [email protected]
Phone: +91 8448496262
Classroom / online / Live programs
- Mains Classes
- Mains Advance Classes
- Ethics & Essay Classes
- IAS Foundation
- Aadhar:NCERT Foundation
- Target PT:Prelims Classes
- Current Affairs Mentorship Program
- Optional Classes
- Optional Q&A (TEST SERIES & Mentorship)
- Mains Previous Year Questions
TEST SERIES/ MENTORSHIP
- ITS:Integrated Test Series & Mentorship
- GS Mains Q&A (Mentorship & Test Series)
- GS Test Series
- Ethics & Essay Test Series
- Samarth - Mains Answer Writing
STUDY MATERIAL
- Prelims Study Material
- Mains Study Material
- Mains Answer Writing Workbook
- Meet the Mentor
- Terms & Conditions
- © 2024 - IAS SCORE
All Rights Reserved.
Welcome to our secure login portal. Access your account with ease.

- Using Password
Not registered yet? register here!
Welcome to our secure register portal. For a brighter future, register now and unlock endless learning opportunities.
User Register
Already have an account? Login
Oops, forgot your password? Don't worry, we've got you covered. Reset it here
Lost your login details? No problem! forgot your password in just a few clicks
Forgot Password
Verify your mobile number, you have successfully logged in.
Join Us on WhatsApp
A Brand of CLT Technologies & Edu-Publishers Pvt. Ltd.
Forgot password
If you haven’t created your account yet, please SIGN UP HERE
Quick Links Testimonials FAQ
Hybrid Classes
We provide offline, online and recorded lectures in the same amount.
Personalised Mentoring
Every aspirant is unique and the mentoring is customised according to the strengths and weaknesses of the aspirant
Topicwise Mindmaps
In every Lecture. Director Sir will provide conceptual understanding with around 800 Mindmaps.
Quality Content
We provide you the best and Comprehensive content which comes directly or indirectly in UPSC Exam.
If you haven’t created your account yet, please SIGNUP HERE
UPSC Courses
IAS Foundation 2024
- C2U-NCERT 2024
- Newspaper Analysis Program
- Basic Daily Answer Writing
Optional Classes
- Geography Crash Course
Current Affairs
- Daily Newspaper Analysis - DNA
- UPSC Facts & Data
- GS Prelims PT Pointers
- Press Information Bureau - PIB
- Good Morning Times - Subject Wise
- EASY TO PICK MONTHLY CURRENT
- GS Paper Wise Current Affairs
- Daily Question Practice (PT-Mains)
Test Series
- RAW Live MCQ
- Oral Test Session By Director Sir
Others Links
- Testimonials
UPSC Prelims Classes 2024
Crash Course
- Sanjeevani @ 60Days
- Morden History
- Science & Technology
Regular Modules 2024
- Mapping & Geography
- Environment
- Economics Basic To Advance
- Polity & History
- News Paper Analysis Programme
- Prelims Test Series
- About Civil Services
- UPSC Prelims Syllabus & Strategy
- UPSC Previous Years Paper
- Prelims Modular Batches
- UPSC Prelims - PT Pointers
- Exclusive Test Series - Mock
- CSAT Classes
- Prelims Sanjeevani 2024 Crash Course
Mains Classes 2024
- RAW GS Crash Course
- Target 50 Program
- Ethics & Case Studies
- Editorial & Current Affairs – QIP
- Writing Skill Development Program
Mains & Interview
- Mains Syllabus & Strategy
- Daily UPSC Answer Writing
- Target 50 For Mains Batch
- Personality Test
- Mains Crash Course
- MAINS Previous Papers
- Optionals Previous Papers
Mains Material
- Mains Kunji
- Prelims (Live-MCQ)
- Prelims PT Tricks-2024
- Daily Answer Writing
Free Study Material
- Important Video Lectures
- Previous Years Papers
- Newspaper Analysis & ENY Notes
- UPSC GS Mains Notes
- 2 nd ARC Report Summary
- Aspire IAS Notes
- Free Download - UPSC Content
- Paid Material(SLP)
- UPSC Optional Notes

DAILY NEWS ANALYSIS
- Download PDF
- SHARE ARTICLE
30 August, 2022
Digital Economy in India UPSC
- Economic Issues
- e-governance
- Cyber Security
- Data privacy
- Telecom sector
- Industrial Revolution
Digital Economy In India
Image Source - Inc42
A comprehensive legislative framework for the digital economy is being developed by the government.
About digital economy
The information and communications technology that enables the global network of economic activity, commercial transactions, and professional relationships is known as the "digital economy" (ICT).
The economy based on digital technologies is a brief summary of it.
The fourth industrial revolution
- The transition from the third to the fourth industrial revolution is reflected in the digital economy.
- The transition from analogue electronic and mechanical devices to digital technology, often known as the third industrial revolution or the digital revolution, occurred in the latter half of the 20th century.
- The fourth industrial revolution expands on the digital revolution as modern technology keeps bridging the real world and the virtual one.
Advantages of The Digital Economy
- Productivity increases as a result of the digital economy because businesses may now employ technology to automate many tasks and procedures.
- Technology can be used by businesses to enhance their goods and services and boost competitiveness . Because of this, commercial competition has intensified.
- Cost savings: Digitization has enabled firms to automate jobs that formerly required manual labour. Due to decreasing operating expenses for firms, consumers now pay less for goods and services.
- Better and more practical items are now available to clients thanks to digitized enterprises, who can also give them more affordable pricing. Customers may now shop whenever and wherever they want thanks to new business models like e- and m-commerce.
- Employment prospects have increased as a result of the emergence of new enterprises in the digital economy. New job positions have also been developed and distributed globally.
- A higher quality of life is now possible thanks to the global reach of the digital economy. People now have the ability to balance their personal and professional lives, which has improved their quality of life.
- Transactions are completed more quickly thanks to the digital economy because firms can now employ online payment options.
- Efficiency gain : By eliminating manual tasks that are prone to error, firms Innovation: As organizations and their processes become more digital, new products and services are developed as well as new ways for them to run.
- Transparency has increased as a result of the digital economy because companies may now utilize technology to communicate information with their clients.
- Communication has been improved as a result of the digital economy's increased connectivity. Businesses can now communicate with customers more successfully. They now have a variety of avenues, such as social media, email, and SMS, via which they can communicate with their clients have become more efficient as a result of process digitization.
Initiatives by the Government
- DigiLocker: This cloud-based platform for issuing, exchanging, and verifying critical documents or certifications was introduced in 2015.
- MyGov: This platform was introduced in 2014 in an effort to improve communication between the public and the government.
- BharatNet: It was established to offer 100 Mbps internet connectivity to all 250,000 Gram Panchayats (GPs) in the nation.
- Smart Cities: In 2015, a plan to use various technologies to make all Indian cities smart cities was launched.
- Post Offices are being digitalized.
- Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojna
- Digital India Program
| Telecom is the first dimension. The writing of a new telecom bill to replace legislation passed in 1885 and 1930 is nearly complete. The Bill for data protection will come in second. Third, India is creating a complete digital India Act to replace the IT Act from 2000. A national data framework is one of the policy frameworks that has been uploaded for review. The concepts of data security and privacy are now widely accepted on a global scale. Any social media network or app that has privacy issues will be held accountable. India would start exporting telecom technologies to other countries by the following year. |
Disadvantages
- The digital gap is one of the most significant drawbacks of the digital economy. This divide exists between people with and without access to technology . As a result, there is now a new kind of inequality throughout the world.
- Cybercrime : As technology is used more frequently, cybercrime has also risen. This is due to the fact that fraud, money laundering, and identity theft are now crimes that may be committed by criminals using technology.
- Data protection : Businesses run the danger of having their consumer data stolen or exposed as they gather more and more information about their clients. This may result in a decline in customer and business trust.
- Unemployment: As firms replaced human labour with technology, the digitalisation of the economy has resulted in job losses in several areas. In several industries, unemployment has increased as a result.
- Privacy worries : As companies gather more information about their customers, there are worries about how this information might be used improperly.
- Heavy investments are needed in technology for the digitalization of businesses. Small businesses may not have the resources to invest in technology, thus this is a barrier for them.
- Monopoly: The digitalization of the economy has resulted in the establishment of a small number of large, extremely strong enterprises. This has led to monopolies in some industries.
- Utilizing current emerging technologies, such as IoT and predictive analytics, can help businesses engage with current and potential customers more effectively, be more responsive, and operate more efficiently.
- Organizations, whether they are for-profit companies, service providers like healthcare systems, or charity and governmental institutions, will need innovative leaders and staff if they want to compete in the years to come.
- Learn more about developing or utilizing emerging technologies, or risk falling behind as the digital economy develops.
Also, Read - National Forensic Science University
Source: The Hindu

- Pradhan Mantri Suryodaya Yojana
Recently, Prime Minister announced Pradhan Mantri Suryodaya Yojana under which 1 crore households will get rooftop solar power systems. India’s Status of Current Solar Capacity India currently stands at 4th place globally in solar power capacity. As per Ministry of New an

- Foreign Contribution Regulation Act (FCRA)- NGO
The Foreign Contribution Regulation Act, 2010 (FCRA) registration of two prominent non-governmental organisations (NGOs) — Centre for Policy Research (CPR) and World Vision India (WVI) have been cancelled this month. What is FCRA? Key provisions of FCRA, 2010 Key aspects Description
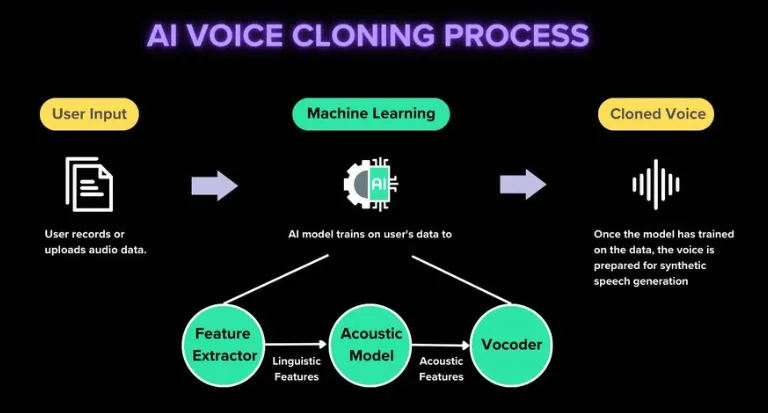
- Voice clone-AI
Voice clone fraud has been on the rise in India. AI voice cloning – It is the process of creating a synthetic replica of a person’s voice through machine learning and speech synthesis technology.It is called as voice deepfakesor audio deepfakes. Objective – To achieve a high level of na
- Science communication- how to promote
Steps taken by India to promote Science Communication Publications and Information Directorate (PID) - An organisation under Council of Science and Industrial Research (CSIR) established in 1951 for publishing and disseminating scientific information in India. National science magazines- The PI
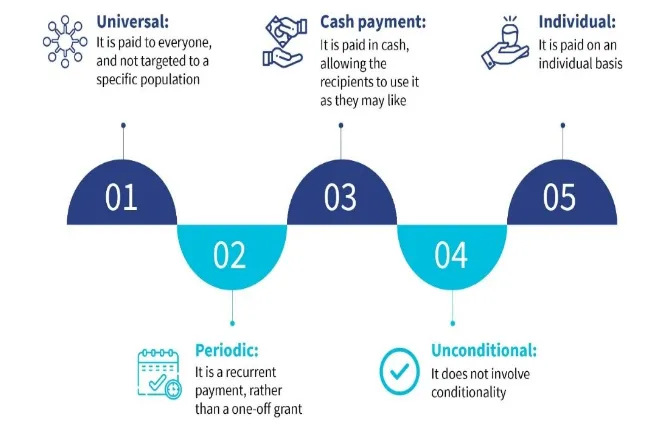
Universal Basic Income (UBI)- Analysis
Universal Basic Income (UBI) can strengthen welfare architecture and unlock the nation’s latent demographic potential. UBI - It is an income support mechanism typically intended to reach all or a very large portion of the population regardless of their earnings or employment status. Objective- To provide enough to co

06 Feb,2024
- Mukhyamantri Gramin Solar Street Light Scheme
- Syndiniales & Corallicolids
- India's stock market
- Naiyandi Melam

Search By Date
Top editorials.
- Union Budget 2024-25: Highlights –Interim Budget
- Acculturation
- I2U2 FOOD PARK
- LABOUR CODE
- Organisation Of Turkic State and India-Turkey Relation
- MPLAD SCHEME
- Quantum Technology in India
- Non-Aligned Movement: Detailed Overview
- CLIMATE CHANGE AND COP 26
- Tribal Welfare
Saarthi Mentorship Programme
Our Popular Courses
Module wise Prelims Batches
Mains Batches
Important Tags
- International Relations
- Miscellaneous
- Human Geography
- Modern History
- Indian Society
- Art and Culture
- Government policies and interventions
- Biodiversity & Environment
- Bilateral Relations
- Important Bills
- Internal security
- Important reports
- Social issues
- Various acts
- International organisation
- International treaties and conventions
- Disaster and Disaster management
- Indian Polity
- World History
- Indian Geography
- Physical Geography
- Developmental Issues
- Indian Economy
- Government Policies & Reports
- Tolerance and Intolerance
- Ancient History
- Add To My Notes
Articles:Geography And Environment
Articles: history culture society, articles: governance & national issues, articles: ir & io, articles: economic development & economic issues, articles: s&t internal security, articles: ethics & others, articles: others, update my notes, newsletter subscription, important links.

Challenge UPSC 2024 - PT Tricks
Update Info
- Prelims Sanjeevani 2021 Crash Course
Mains & Interview
- Mains Sanjeevani 7Days Batch (coming soon)
- MAINS Test Series By Toppers
- RAW Prelims Live MCQ 2021
UPSC Resource
- General Studies Notes
- SLP - Paid Notes
- [email protected]
- https://t.me/iasgyanpdfs

- Daily News Analysis
DIGITAL ECONOMY

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
- India’s digital economy and the infrastructure sector has a total potential for $2.5 trillion - Prime Minister Narendra Modi. Addressing a meeting of the BRICS Business Forum, Mr. Modi said the digital transformation unfolding in India had never been seen before on the world stage.
What is the digital economy?
The digital economy refers to economic activity that uses electronic communication and digital technologies to provide goods and services. The main building blocks of the digital economy are
- The internet. This enables firms to offer goods for sale and enables consumers to browse for goods that they need.
- E-mail. Electronic communication enables very cheap, instantaneous communication across the world. It can be used to send information and requests very quickly.
- Digital automation . Firms can use the processing power of computers to make decisions on output, prices and how to reach consumers.
- Digital payments – credit cards, Apple Pay, Google pay, bitcoin, bank transfer. A digital economy is moving us towards a cashless society.
- Increasingly the digital economy relies on AI, mass use of electronic data and automated technology
- Social media . To a lesser extent, social media is an aspect of the digital economy. With individuals using it share recommendations about business.
Essential Elements of Digital Economy
Digital Economy facilitates and executes the buying and selling of products and services through electronic transactions undertaken by means of the internet. Its essential elements are:
- Digitalization and using Information and Communication Technology (ICT), rigorously.
- Knowledge codification
- Conversion of information into commodities
- Organizing work and production in modern ways.
Hyperconnectivity, i.e. emerging interconnectivity of people, firms, systems, etc. as a result of the internet, mobile technology and Internet of Things (IoT).
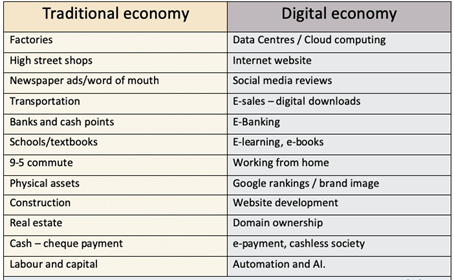
Examples of the digital economy
Airbnb – This enables tourists to book online. It has also made it possible for individual households to let our their house/room to tourists. Before the digital economy it was not practical.
E-commerce site : Amazon market place/Ebay.
Netflix – This enables consumers to purchase tv-series and films over the internet, without need for any physical good.
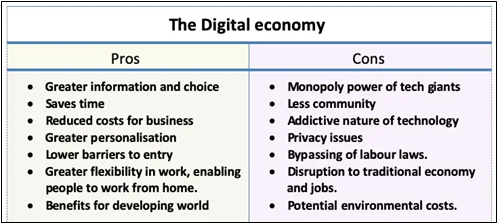
Advantages of the digital economy
Greater information
The internet has enabled consumers to have greater information and choice. For example, it makes it easier to compare prices between firms. It also brings information to a person’s fingertips.
Time saving
For the user, time is a determining factor when making purchases, managing their finances, traveling or even working.
Reduced costs
The digital economy considerably reduces the costs for the merchant and the maintenance of his business.
Increases flexibility
The flexibility that financial technology provides can be seen at all levels of exchange transactions - From the user and the numerous payment methods to the possibility of buying from anywhere in the world.
Provides more information and decision-making power
The power of decision for the user defines many things and the use of the digital economy is exactly that, more information for better decision making.
Process reinvention
The digital economy removes many of the barriers that previously defined the way certain processes are carried out. A clear example is work, which took a 180º turn with technological advances that allow, for example, working from home, making tele-working one of the most widely used alternatives today due to the multiple benefits it combines.
Lower barriers to entry
In some markets, aspects of the digital economy make it easier for new firms to enter. The digital economy has brought many new services which were inconceivable before, such as online home deliveries for grocery to dating apps.
Creates significant data which can give new insights
The mass production of data can help inform governments and charities about what is happening in the economy. For example, in tracking of COVID-19 spread, the use of an app on mobile phones may indicate where local hotspots emerge.
Contributes to Economic Growth:
The widespread digital economy has recorded tremendous growth and innovation as well as it can be broadly applied to other economic sectors.
Creates new jobs
Digital economy has given a boost to jobs too. In the last few years, the development of mobile apps has solely created millions of jobs worldwide.
Improves public services
A set of global access to broadband and a powerful information and communication technology services ecosystem provides a platform to improve service delivery in core sectors.
Rise in e-commerce
A recent growth in e-commerce transactions has been reported in the last few years. And all credit goes to the digitalization of commercial activities, due to which developing, buying, distributing, selling and tracking of products and services, has become much simpler, competitive, and profitable.
Digital delivery of goods and services
From aviation to banking, entertainment to education and insurance to hotel booking, one can easily get the goods and services of their need, online.
Transparency
In the digital economy, major commercial transactions take place online, which eliminates cash transactions, and ultimately increases transparency and reduces corruption.
Expands business opportunities
Digitalization enables small firms and businesses to actively participate in international buying and selling of goods and services.
Limitations of Digital Economy
Cybersecurity
An exponential increase in cyber threats has been reported in recent years due to increasing digitalization in the economy. Except if cybersecurity is countered successfully, it will not be easy to develop a safe and trusted environment, which is conducive to the growing business.
Disruptions in labour markets
Though it is assumed to create new job opportunities, there is also a risk related to the speed of labour market changes and destruction of basic jobs. As everything will be digitized and automated, processes that involve labour and manual work will be avoided and is replaced by technology-oriented work, which will result in loss of jobs and may also widen income inequality.
Strong infrastructure requirement
It requires strong infrastructure concerning internet, telecommunication and mobile industry. For the development of such industries, heavy investment is required, so as to link all the cities, towns and villages.
With the emergence of the digital economy, consumers can get easy and quick access to information, due to the digitization of the content. Moreover, sharing of information with their friends and acquaintances is now just a click away.
Monopoly power
Despite the potential for new start-ups, many aspects of the digital economy have become dominated by firms with monopoly power. For example, Amazon has cornered the market for online sales, meaning many firms have to go through the Amazon market place to reach consumers who go to Amazon out of habit. Similarly, Google and Facebook have all developed very strong brand loyalty and market share in their respective markets. This has made a few tech giants very profitable.
Addictive nature of technology
Whilst, in theory, the internet can save time, e.g. finding bus times is much easier with internet than paper copies, this time saved may be outweighed by the time we waste checking Facebook, twitter, internet searches. Also, the sheer volume of information can cause us to drown in information and lose sight of what we actually need. More choices do not necessarily lead to better outcomes.
Privacy issues
Harvesting and using data has become big business. Facebook collects a large range of data on its users and this has been bought by political interests who can give very targeted political ads to its users.
Bypassing of labour laws
The digital economy has created a trend towards using self-employed freelancers, who are not protected by the same labour laws. For example, delivery drivers for Uber drivers have often been employed on zero-hour contracts. This enables firms to cut labour costs, be more flexible, but it can leave workers without sick pay or employment protections.
Social media has led to more graphic content
The anonymous and distant nature of social media has exacerbated trends to personal attacks and the posting of conspiracy theories or posting of violent/sexual images. The digital economy has enabled the proliferation of content that is damaging to human well-being.
Disruption patterns.
The pace of digitalization can lead to structural unemployment, with some unskilled workers increasingly losing out to skilled workers. Combined with the monopoly power of big tech firms, it is causing an increased inequality in society, which may lead to feelings of alienation and unfairness.
Environmental costs
Digital economy does not always imply a ‘green solution.’ Data centres use electricity and cause CO2 emissions. In the US, data centres account for around two per cent of U.S. electricity use in 2014.
A bigger potential cost is how the digital economy encourages a ‘throw-away’ culture. E.g. the planned obsolescence of mobile phones and computers, encouraging consumers to buy new models, leading to greater use of raw materials.

Some Initiatives taken to digitize India
Infrastructure
Under this initiative, the Government provides multiple programs that facilitate a reliable digital infrastructure. The following are some of the programs under this:
- AADHAR: One of the key strengths of ‘Digital India’, wherein every resident of the country is given a unique identity number.
- Bharat Broadband Network (BBNL): This is the custodian of Digital India. The creation of the National Optical Fiber Network (NOFN) has been mandated in India.
- Centre for Excellence for Internet of Things (CoE-IT): The main objective of the center is for creating domain capability and innovative applications.
- CERT-IN: This is formed with the intention to secure Indian cyberspace.
- Common Services Centres (CSCS): CSCs are the access points for the delivery of essential public utility services, healthcare, social welfare schemes, financial, education, and agriculture services.
- Cyber Swachhta Kendra: The purpose of this is to generate secure cyberspace by detecting botnet infections in India and to notify, enable cleaning, and secure systems of end-users so as to prevent further infections.
- Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Gram Jyoti Yojana : This is one of the flagship programs of the Power Ministry (MoP) and is designed to provide a continuous power supply to the entire rural India.
- DigiLocker : A digital wallet to empower citizens digitally.
- Digital Saksharta Abhiyaan (DISHA): This aims to provide IT training to 52.5. lakh persons.
- Digitize India Platform : This platform provides digitization of scanned document images or physical documents.
Under this initiative, the Government has introduced multiple online services to facilitate greater reach and accessibility:
- Accessible India Campaign and Mobile App : This nation-wide flagship campaign is for achieving universal accessibility for enabling people with disabilities to gain access to equal opportunity.
- Agrimarket App: This mobile application aims to keep farmers abreast with the crop prices and avoid distress sale.
- Beti Bachao Beti Padhao: This aims to provide equal opportunity to a girl child, a chance to be born and be educated.
- BHIM (Bharat Interface For Money): This makes payment easy and quick using UPI.
- Crime and Criminal Tracking Network & Systems (CCTNS): This aims for nationwide networking infrastructure for the evolution of an IT-enabled state-of-the-art tracking system around ‘Investigation of crime and detection of criminals.’
- Crop Insurance Mobile App: This app can be used to compute the insurance premium for notified crops based on the area of coverage, amount, and loan amount in the case of loanee farmers.
- Digital AIIMS: A distinctive health identification number for every patient visiting AIIMS was generated on an Aadhar platform.
- E-Granthalaya, E-Panchayat, E-Hospital, E-Pathshala, E- prison: All of these provide digitalization of services like libraries, hospitals, schools, and prisons.
Empowerment

Under this initiative, the Government provides e-governance, skill development, and infrastructure development initiatives:
- Aadhar Enabled Payment System (AEPS)
- Digidhan Abhiyaan
- National Mission on Education using ICT
- North East BPO Promotion Scheme (NEBPS)
- NREGA – Soft
- PayGov India
- Smart Cities
- Pradhan Mantri Jan- Dhan Yojana (PMJDY)
- Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY)
- PAHAL (DBTL)
- Targeted Public Distribution System (TPDS)
- Visvesvaraya PhD Scheme For Electronics and IT
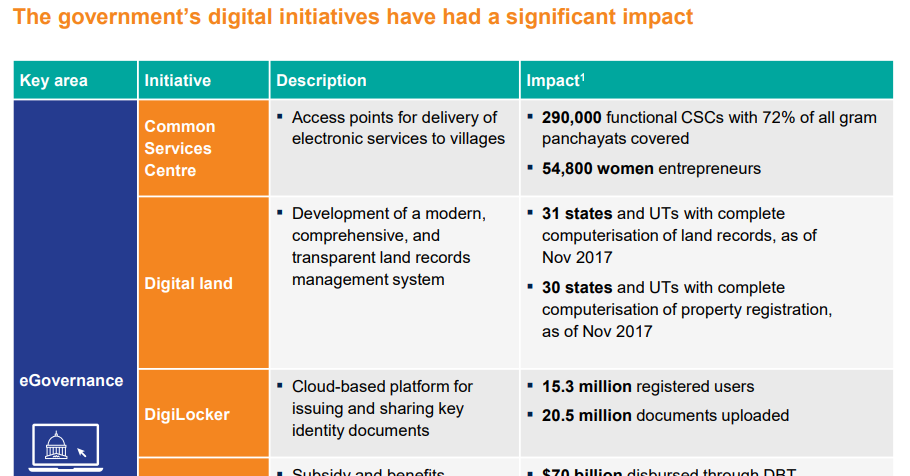
Significant achievements made by India in this field
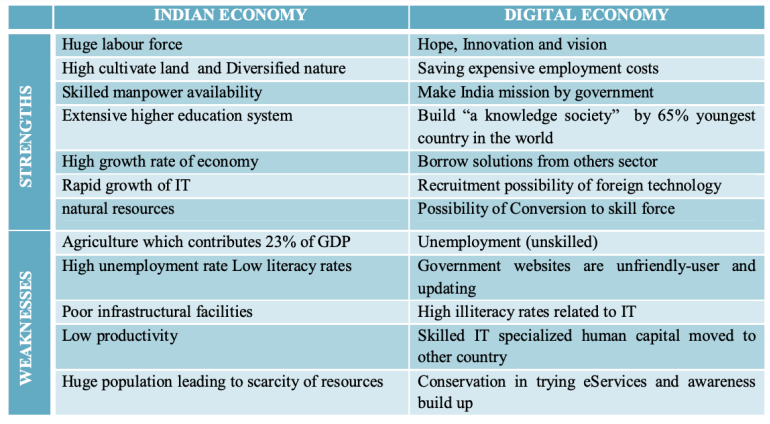
SWOT Analysis of India in this field
Future Potential

https://epaper.thehindu.com/Home/ShareArticle?OrgId=GP49V1KRL.1&imageview=0
1.png)
- About APTI PLUS
- Our Results
- Couselling at your college
- Daily Current Affairs
- IAS Gazette Magazine
- Daily Editorial
- Prelims Xpress
Help Centre
- Feedback/Suggestions
- Free Couselling Form
- Payment Methods
Legal Stuff
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
- Refund Policy
- Forgot Password?
Not a member yet? Sign-up Now!
Already a member? Sign-in Here!
Impact of Digital Economy in India – Essay for UPSC
In 2016 Prime Minister Narendra Modi, came up with a demonetization with the goal of checking corruption, black money, and counterfeit currency. Later the goal was shifted toward making India into a digital economy. To spread economic benefits to all sections of society. However, World Development Report published by UNDP , highlights that India has the highest offline population in the world. What is the impact of digital economy in India? Is India ready for the Digital economy? How digital economy can benefit society? What are the threats of the digital economy?
We try our best to provide you with a 1000+ words essay on the Impact of Digital Economy in India. Further, we will discuss the digital economy in India issues and challenges .
Impact of Digital India on Society
The digital economy can be understood as performing economic activities through the internet and Communication Technology. Moreover, the economy basically has four components. Firstly, the sale and purchase of goods and services, utilization of resources, impact on society, and the international sphere. The digital economy provides an avenue for free moments of goods and services across the world, the very principle of capitalism. Thus, an economy like India can produce goods at a lower price by selling to a developed nation like the US, leading to income redistribution.
Even with society, it can lead to an inclusive and equitable society. For instance, tribals of the Bastar region namely “HO”, “Munda”, and others are utilizing the digital platform for selling their goods made with traditional knowledge with a brand of “Bastar Arts”. Similarly, in Papua New Guinea, old age people rather than make them dependent. The public departments also use digital platforms to get advice or share the experiences of retired officials. India has also come up with a similar portal “Anubhav”. Hence, effective utilization of resources within society.
Further, the digital economy transcends Nation state borders and opens new avenues for quality education and healthcare. For instance, Coursera , a web platform provides online courses from top universities like Oxford to different parts of the world. It not only generates economic activity for universities and service providers. But, it has positive externalities in producing quality human resources in the next generation. India has also come up with a similar platform with the name “SWAYAM” to reduce social inequalities in education.

Report on the Impact of Digital Economy in India
Similarly, telemedicine provides a new platform for assessable Healthcare. In the present situation, only the tertiary health sector is utilizing it in India, which earns about 920 crores through medical tourism. However, the government is working to introduce it at the local level.
Not only this but also as per reports, if India shifts completely to the digital economy, then it can save 1 lakh trees from cutting by saving paper per month. As per a World Bank report, on average 4.25 lakh trees are planted in India in a month. Protection of the environment will benefit the coming generation. India along with Japan came up with the Asia-Africa growth corridor through the digital economy. It consists of building cyber-infrastructure in Asia & Africa.
India will provide soft skills, education, and health through it to turn its demographic into human capital. It will benefit both India as well as Africa. Not only boosts the economy in current times but also transcends to the coming generation with better human capital.
Challenges of the Digital Economy
One of the biggest challenges of the digital economy highlighted in the World Development Report of UNDP is the creation of social inequalities. India the fastest growing economy has internet access to only 20 crore people out of 130 crores. In rural India, only 9% of people have internet access. If we talk about high-speed internet it is less than one percent even in urban areas.
At the next level, digital illiteracy is a challenge that further makes inequality between the haves and the haves not. Rather than building social equality, it can pave the way for monopoly in the economy, which is why social inequality. At present, India has only 42 % of people have digital literacy, which is just about doing basic work on a computer or on other ICT devices. Big companies, which have deep pockets are using digital platforms with predatory pricing. For instance, Samsung dealers sell products on Flipkart and Amazon for less than cost making. These monopolistic trends can further disturb the social fabric of society.
Recently, digital currency like Bitcoin came into the picture to boost the digital economy. It has become an avenue for terrorist activities, which is again a threat to a peaceful society. Digital platforms have become a bane rather than a bone. Women trafficking through a digital platform and bidding across borders is growing day by day. CRY(Child Rights and You), a non-government organization, shows its concern in its annual report. Which, with the advent of the digitalization of the economy, child trafficking has increased from 4 children per day in metro cities to 16 children per day (a 400% increase).
The steps were taken toward Digital Economy in India
Apprehension related to trafficking and economic inequalities transcending to social inequalities is a wearing trend. But, we need to understand digitalization or ICT platforms are just a tool. For effective utilization, we need to work towards various measures. For instance, the Government of India plans “Bharat net” to connect all the village panchayats. Similarly, the government introduced free Wi-Fi in public places like Railways to improve internet access. Moreover, World Bank is funding projects across the world to improve internet accessibility.
Further, to empower people, the Government came up with “Adhar Pay” in which people can transact without an internet connection. It will not only boost the economy but also empower the most deprived section of society. In schools, computer education is made compulsory. Further, the “Skill India Program” is also Introduced.
To check monopolies, the government has also come up with a digital India program that not only provides a platform for selling goods and services but also makes farmers aware to improve their productivity.
To further strengthen the digital economy and check the misuse of the Cyber platform, WTO decided on various faults and form a committee with the collaboration of the representatives of different nations. Moreover, digital challenges are bound to come. So, we need to upgrade the capability of security forces to check the misuse of cyber technology. To fight all the corrupt practices and remove them from root and shoot, ethics and morality are panaceas to build a just society. Which is socially inclusive, economically inclusive, and environmentally sustainable. Indeed, the digital economy can benefit society in achieving these goals in the coming future.
Also Read:- Similar Essays for UPSC in 1000+ Words!
Share this:
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
Vikramjit Singh
Vikramjit Singh, founder of Newscoop, an esteemed UPSC educational website, helps aspirants prepare for UPSC CSE with 5 years of experience, offering a deep understanding of crucial concepts.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Recent posts.

- Commercialization of Agriculture: British India

- Feminization of Agriculture in India: Causes & Impacts

- National Parks of Rajasthan: Map & Features

- Uttaramerur Inscription: Elections & Local Governance

- Difference Between the Cabinet and Council of Ministers

Shadow Cabinet: Origin & Functions in India

Indus River Dolphin: IUCN Status & Threats
Krishnadevaraya: Mother, Wives & Children | Achievements & Ashtadiggajas
You are wrong shivaji maharaj has eight wives 1. Sai bai 2. Soyrabai 3. Putalabai 4.Sakwarbai 5. kashibai 6. Laxmibai…
Thanks for sharing this information about "Artificial Lakes in India"
Enough information for us I like it
Best best best..
Moreover, Khanderao was treated for a long time but he could not survive.
Copyright © Newscoop IAS | All rights reserved.

Digital Rupee: Advantages and Challenges – Explained, pointwise
ForumIAS announcing GS Foundation Program for UPSC CSE 2025-26 from 26th June. Click Here for more information.
- 1 Introduction
- 2 What is a Central Bank Digital Currency?
- 3 About the status of CBDC at the global level
- 4 About the steps announced by the Finance Minister on digital currency(Digital Rupee)?
- 5 Will other digital currencies be allowed in India?
- 6 What are the prerequisites before releasing the Digital Rupee?
- 7 What are the advantages of announcing a digital rupee or CBDC?
- 8 What are the challenges associated with issuing a digital rupee?
- 9 What should be done to improve the performance of the digital rupee?
| For Archives click → |
Introduction
The Union Minister for Finance & Corporate Affairs has tabled the Union Budget 2022-23 in the Parliament. One of the major highlights of this year’s budget is the announcement of Government’s decision to launch Digital Rupee – India’s version of a Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC).
The announcement is a reiteration of the SC Garg Committee that had asked the RBI to introduce its own digital currency and ban private cryptocurrencies completely.
What is a Central Bank Digital Currency?
A Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC), or national digital currency , is the digital form of a country’s fiat currency. Instead of printing paper currency or minting coins, the central bank issues electronic tokens. This token value is backed by the full faith and credit of the Government.
About the status of CBDC at the global level

Currently, 9 countries already use digital currencies. Among the nine countries with active CBDCs, eight are small island nations in the Caribbean. Currently, at least 87 countries are researching or developing CBDCs, including 14 who are running pilot programmes.
1) Sweden is conducting real-world trials of their digital currency (Krona) ; 2) The Bahamas has already issued their digital currency “ Sand Dollar ” to all citizens; 3) In October 2021, Nigeria became the latest country to introduce a digital currency, e-Naira . 4) China started a trial run of their digital currency e-RMB amid pandemic. They plan to implement pan-China in 2022. This is the first national digital currency operated by a major economy.
Countries like Japan, Singapore are currently examining the various facets of such a transition. A few days ago, the US Federal Reserve also released a report outlining the costs and benefits of issuing a central bank-backed digital dollar.
| : CBDC is just a wallet or an electronic purse, issued by a central bank. There are many such wallets operating in the Indian financial system. The CBDC will be one of them, but with a difference that it will be issued by the nation’s central bank. |
About the steps announced by the Finance Minister on digital currency(Digital Rupee)?

Reserve Bank of India will launch a Digital Rupee by 2022-23. The CBDC will be backed by the blockchain and other technologies. The digital rupee will be the digital form of the physical rupee and will be regulated by the RBI.
The budget announcement was made after consultations with the RBI, and the RBI will decide by when it is ready to launch the digital rupee.
According to the Prime Minister, the digital rupee could be exchanged for cash and will open new opportunities in the fintech sector.
Recently, RBI Deputy Governor has said that the central bank is “working towards a phased implementation strategy ” and will examine the CBDCs in the wholesale and retail segments.
Will other digital currencies be allowed in India?
According to the Secretary, Department of Economic Affairs, “ digital rupee will be the first and only digital currency in India.” He also explained that the taxation of crypto assets does not legitimize their usage, as crypto-assets do not mean cryptocurrencies alone. According to him, Crypto, in a general sense, is a digital asset that uses crypto technology.
The Budget has used the term “Virtual Digital Assets” (VDAs) . VDAs are a superset for all digital assets being transacted on the blockchain, such as cryptos, non-fungible tokens (NFTs), or any other virtual asset.
Note : The draft Cryptocurrency and Regulation of Official Digital Currency Bill, 2021 aims to prohibit all private cryptocurrencies. The Bill also aims to lay down the regulatory framework for the launch of an “official digital currency”.
What are the prerequisites before releasing the Digital Rupee?
First , the design of the currency with regard to how it will be issued, the degree of anonymity it will have, the kind of technology that is to be used, etc., needs to be sorted out.
Second , CBDC would need an entirely new centralized payment system . This system has to be linked to electronic wallets that reside on prepaid cards, smartphones, or other electronic devices.
Third , the government has to develop an interoperable system between the other virtual digital assets (VDAs) and the digital rupee for seamless transfer of funds.
Fourth , digital money will be programmable money. Hence, the government has to come out with suitable products and services using the digital rupee, such as smart contracts.
What are the advantages of announcing a digital rupee or CBDC?

According to the Prime Minister, the Central bank digital currency or the digital rupee will make online payments more secure and risk-free and boost the digital economy in the years to come. He also mentioned that the digital rupee will lead to ease in the development of a global digital payment system .
Further, introducing the digital rupee will revolutionise the fintech sector by creating new opportunities and lessen the burden in handling, printing, logistics management of cash .
Digital Rupee will lead to a whole lot of improvement in terms of digitization of the economy, ease of transfer , not just within the country but across jurisdictions. Further, the Digital rupee will prevent counterfeiting of currency and a boost to the war on black money and corruption.
The Digital Rupee will accelerate financial inclusion, lower costs for financial transactions , especially in the case of cross-border transactions, the advantages of an alternate payments system , the creation of another instrument in the monetary policy arsenal of central banks.
Commercial banks sometimes fail, and depositors lose a big chunk of their money despite the deposit guarantee scheme, but when the money is parked with the central bank there is no risk of default .
CBDC will reduce the need for card networks, payment gateways . There are 1.2 billion mobile phone connections in India right now, but only 582 million bank accounts exist. The CBDC could help to bridge the disconnect.
The other advantages include,
Reducing systemic risk: There are about 3,000 privately issued cryptocurrencies in the world. According to IMF, the key reason for considering national digital currency is to counter the growth of private forms of digital money.
Industry estimates suggest there are 15 million to 20 million crypto investors in India, with total crypto holdings of around 400 billion rupees (US$5.37 billion). Most cryptocurrency exchanges are asking people to invest and trade in cryptos without providing basic information about the product and the inherent risks.
There is a possibility of these companies going bankrupt without any protection. But the digital rupee has government backing in case of any financial crisis.
Reduce volatility: The national digital currency will be regulated by the RBI. So, there will be less volatility compared to other digital currencies .
Negative interest rate : In tough times, a Central Bank might want people to spend money, hence the concept of negative interest rates. But, presently it can’t do so as people will simply withdraw their money from the banks. CBDCs will solve this problem. A negative interest rate could be easily mandated on CBDCs kept in the wallets.
Complement blockchain-led decentralised finance : All crypto assets’ final returns will be in sovereign currency, and therefore the digital rupee will aid the virtual digital asset(VDA) markets by bridging the gap between fiat money and decentralised finance.
What are the challenges associated with issuing a digital rupee?
Globally, pilot projects on CBDC have been underway since 2014. However, progress is slow because this seemingly simple innovation can have unforeseen consequences. These include,
Challenges to the entire banking system : The impact of the digital rupee on the banking system is not clearly understood e.g., if CBDCs are indeed efficient vehicles for retail savers, this could adversely affect bank deposits. Hence, there might be an impact on the role of banks in credit creation, RBI’s monetary policy, etc.
Further, Sweden’s Riksbank , which launched its e-krona project in 2017, is still studying the need and potential impact of e-krona on Sweden’s economy.
Threat to financial stability : If the RBI offered interest rates on the digital rupee, then it will directly compete with banks. If the regulator ends up competing with the regulated entities, the banking system may see erosion in deposits, threatening the financial sector’s stability.
No incentive to switch to digital rupee for user: From a user’s standpoint, there is no real incentive to switch to a CBDC as a growing proportion of retail transactions are already done digitally or by using UPI-based fast payment systems .
Potential cybersecurity threat: India is already facing many cyber security threats . With the advent of digital currency, cyberattacks might increase and threaten digital theft like the Mt Gox bankruptcy case.
End of privacy : The digital currency must collect certain basic information of an individual so that the person can prove that he’s the holder of that digital currency. This basic information can be sensitive ones such as the person’s identity, fingerprints etc.
Further, CBDCs will leave a digital trail even with the phone turned off. For instance, trails such as paying for food, fare and lodging.
Operational issues : There will be many operational issues for the implementation of CBDC, including the KYC (know your customer) norms and privacy of data.
What should be done to improve the performance of the digital rupee?
The Government should work towards an interoperable system between the virtual digital asset and the digital rupee. It will unleash opportunities for not only those working or wanting to work in the decentralised finance space (VDAs), but also for traditional finance industry exponents.
Creation of adequate cybersecurity methods: Before the introduction of National Digital currency, the Government has to create certain important things, such as, training of the law enforcement agencies, creating a policy of basic information assessed while issuing, verifying someone’s digital currency.
The RBI needs to create a regulatory sandbox , with limited participants and pre-specified uses, before launching its own digital currency. Only then can the rupee hold its own against other currencies.
Preserving the financial sector stability : The digital rupee can be issued via a distributed ledger , synchronised between the banks and the RBI and not a centralised ledger, held solely by the RBI. This decentralised model will not end up in competition between RBI and other banks.
Though the introduction of a digital rupee provides various advantages for the government, the government has to create necessary safeguards before rolling it out and must bridge the digital divide.

Type your email…
Search Articles
Latest articles.
- 10 PM UPSC Current Affairs Quiz 1 July, 2024
- 9 PM UPSC Current Affairs Articles 1st July, 2024
- UPSC Prelims Marathon 1st July – Freedom Struggle under Extremist Phase (1905-1917) and India and Neighborhood policy – 2024
- 10 PM Daily UPSC Current Affairs 30th June – 2024 | Revision Test
- [Answered] UPSC Mains Answer Writing 29th June 2024 I Mains Marathon
- UPSC Prelims Marathon 30th June – Revision – 2024
- 10 PM UPSC Current Affairs Quiz 29 June, 2024
- 9 PM UPSC Current Affairs Articles 29th June, 2024
- [Answered] UPSC Mains Answer Writing 28th June 2024 I Mains Marathon
- UPSC Prelims Marathon 29th June – Political organizations prior to 1885 and Freedom Struggle under Moderate Phase – 2024
Prelims 2024 Current Affairs
- Art and Culture
- Indian Economy
- Science and Technology
- Environment & Ecology
- International Relations
- Polity & Nation
- Important Bills and Acts
- International Organizations
- Index, Reports and Summits
- Government Schemes and Programs
- Miscellaneous
- Species in news
All India Open Test(Simulator X)

- TRP for UPSC Personality Test
- Interview Mentorship Programme – 2023
- Daily News & Analysis
- Daily Current Affairs Quiz
- Baba’s Explainer
- Dedicated TLP Portal
- 60 Day – Rapid Revision (RaRe) Series – 2024
- English Magazines
- Hindi Magazines
- Yojana & Kurukshetra Gist
- Gurukul Foundation
- Gurukul Advanced
- TLP Connect – 2025
- TLP (+) Plus – 2025
- Integrated Learning Program (ILP) – 2025
- TLP Plus – 2024
- Public Administration FC – 2024
- Anthropology Foundation Course
- Anthropology Optional Test Series
- Sociology Foundation Course – 2024
- Sociology Test Series – 2023
- Geography Optional Foundation Course
- Geography Optional Test Series – Coming Soon!
- PSIR Foundation Course
- PSIR Test Series – Coming Soon
- ‘Mission ಸಂಕಲ್ಪ’ – KPSC Foundation Course
- ‘Mission ಸಂಕಲ್ಪ’ – KPSC Prelims Crash Course
- CTI (COMMERCIAL TAX INSPECTOR) Test Series & Video Classes
- Monthly Magazine
UPI- India’s Digital Payment Revolution
- February 7, 2020
UPSC Articles

Indian Economy
Topic: General Studies 3 Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment. Science & Technology
Google writing a letter to the US Federal Reserve two months ago asking them to learn from Indian digital payments
Also, digital payment transactions on the Universal Payment Interface (UPI) platform rose from 0.1 million in October 2016 to 1.3 billion in January 2020
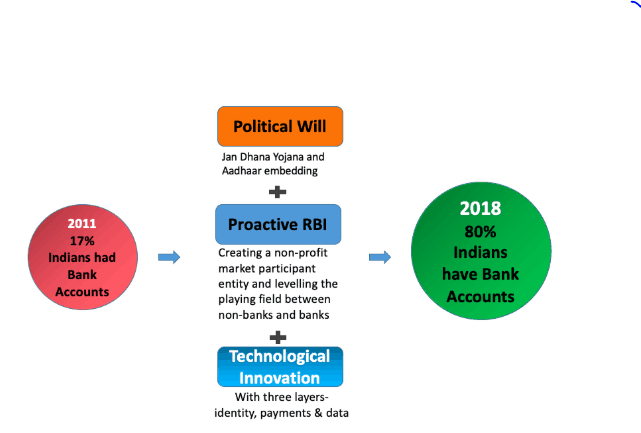
Daily Current Affairs IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 7th February 2020
India’s payment revolution comes from
- A clear vision – shifting the system from low volume, high value, and high cost to high volume, low value, low cost
- A clear strategy -regulated and unregulated private players innovating on top of public infrastructure (UPI)
- Trade-offs balanced by design -regulation vs innovation, privacy vs personalisation, and ease-of-use vs fraud prevention
- It is a common platform through which a person can transfer money from his bank account to any other bank account in the country instantly using nothing but his/her UPI ID.
- Launched in 2016 as Mobile First digital payments platform
- Immediate money transfer through mobile device round the clock 24*7 and 365 days based on the Immediate Payment Service (IMPS) platform.
- UPI is completely interoperable and as such, it is unique in the world, where you have an interoperable system on the ‘send’ and ‘receive’ side
- Developed by: National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) under the guidance from RBI
Significance of UPI
- It created interoperability between all sources and recipients of funds (consumers, businesses, fintechs, wallets, 140 member banks),
- Settled instantly inside the central bank in fiat money – Convenience to consumers and merchants and
- Blunted data monopolies -big tech firms have strong autonomy but weak fiduciary responsibilities over customer data).
UPI offers the following policy lessons .
- First, th e India stack — interconnected yet independent platforms or open APIs — are a public good that lowers costs, spurs innovation, and blunts the natural digital winner-takes-all..
- Second, collaboration can create ecosystems that overcome existing obstacles — the execution deficit of government, the trust deficit of private companies, and the scale deficit of nonprofits.
- Third, complementary policy interventions are important. Demonetisation and GST acted as a catalyst for the transition to digital payments .
- Fourth, human capital and diversity matter . This revolution needed career bureaucrats to partner with academics, tech entrepreneurs, venture capitalists, global giants and private firms.
However, more needs to be done
- The central government must deadline digitising all its payments.
- The RBI must implement the 100-plus action items (outlines in RBI’s Vision 2021 document) and the recommendations of Nandan Nilekani Committee for Deepening Digital Payments .
- RBI should make use of RuPay and UPI to tap the remittances market – which presently stands at 70billion USD and is largely in informal domain
- RBI must replicate the core design of UPI — fierce but sustainable private and public competition — in bank credit to increase our present 50% Credit-to -GDP ratio to atleast 100%(OECD level)
- This experience shows that India doesn’t need to be Western or Chinese to be modern. If our policymakers had copied Alipay or US banks, we wouldn’t have witnessed this digital payments revolution
- Replicating similar model in education, healthcare, and government services will help in achieving the socio-economic goals outlined in our Constitution
Connecting the Dots
- UPI 2.0 launched on August 2018
- Nandan Nilekani Committee for Deepening Digital Payments.
- More about NPCI
For a dedicated peer group, Motivation & Quick updates, Join our official telegram channel – https://t.me/IASbabaOfficialAccount
Subscribe to our YouTube Channel HERE to watch Explainer Videos, Strategy Sessions, Toppers Talks & many more…

Related Posts :
Uniform code of pharmaceutical marketing practices, abortion – amendments to medical termination of pregnancy(mtp) act -mixed bag.

- [PRELIMS RESULT] UPSC/IAS Civil Services Examination, Prelims 2024 Result Declared!
- DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 1st July 2024
- UPSC Quiz – 2024 : IASbaba’s Daily Current Affairs Quiz 1st July 2024
- [New Batch] ILP 2025 – INTEGRATED LEARNING PROGRAM – The Most Comprehensive and Trusted 365 Days Plan recommended by Toppers for UPSC 2025 – With Surprising Features – Video Classes and Mentorship!
- IASbaba’s TLP 2024 (Phase 2): UPSC Mains Answer Writing – GS2 Questions [1st July, 2024] – Day 7
- DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam –29th June 2024
- UPSC Quiz – 2024 : IASbaba’s Daily Current Affairs Quiz 29th June 2024
- IASbaba’s TLP 2024 (Phase 2): UPSC Mains Answer Writing – GS1 Questions [29th June, 2024] – Day 6
- DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 28th June 2024
- UPSC Quiz – 2024 : IASbaba’s Daily Current Affairs Quiz 28th June 2024
Don’t lose out on any important Post and Update. Learn everyday with Experts!!
Email Address
Search now.....
Sign up to receive regular updates.
Sign Up Now !


- OUR CENTERS Bangalore Delhi Lucknow Mysuru Srinagar Dharwad Hyderabad
Call us @ 08069405205

Search Here

- An Introduction to the CSE Exam
- Personality Test
- Annual Calendar by UPSC-2024
- Common Myths about the Exam
- About Insights IAS
- Our Mission, Vision & Values
- Director's Desk
- Meet Our Team
- Our Branches
- Careers at Insights IAS
- Daily Current Affairs+PIB Summary
- Insights into Editorials
- Insta Revision Modules for Prelims
- Current Affairs Quiz
- Static Quiz
- Current Affairs RTM
- Insta-DART(CSAT)
- Insta 75 Days Revision Tests for Prelims 2024
- Secure (Mains Answer writing)
- Secure Synopsis
- Ethics Case Studies
- Insta Ethics
- Weekly Essay Challenge
- Insta Revision Modules-Mains
- Insta 75 Days Revision Tests for Mains
- Secure (Archive)
- Anthropology
- Law Optional
- Kannada Literature
- Public Administration
- English Literature
- Medical Science
- Mathematics
- Commerce & Accountancy
- Monthly Magazine: CURRENT AFFAIRS 30
- Content for Mains Enrichment (CME)
- InstaMaps: Important Places in News
- Weekly CA Magazine
- The PRIME Magazine
- Insta Revision Modules-Prelims
- Insta-DART(CSAT) Quiz
- Insta 75 days Revision Tests for Prelims 2022
- Insights SECURE(Mains Answer Writing)
- Interview Transcripts
- Previous Years' Question Papers-Prelims
- Answer Keys for Prelims PYQs
- Solve Prelims PYQs
- Previous Years' Question Papers-Mains
- UPSC CSE Syllabus
- Toppers from Insights IAS
- Testimonials
- Felicitation
- UPSC Results
- Indian Heritage & Culture
- Ancient Indian History
- Medieval Indian History
- Modern Indian History
- World History
- World Geography
- Indian Geography
- Indian Society
- Social Justice
- International Relations
- Agriculture
- Environment & Ecology
- Disaster Management
- Science & Technology
- Security Issues
- Ethics, Integrity and Aptitude

- Indian Heritage & Culture
- Enivornment & Ecology

UPSC EDITORIAL ANALYSIS : Big Reforms Push
Source: indian express.
- Prelims: Indian Economy(GDP, GVA, fiscal policy, MGNREGA, budget, economic survey, budget, Employment etc )
- Mains GS Paper III: Fiscal policy, Monetary policy, GDP, Issues related to planning etc.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
- The 2024-25 budget i s expected to present a long-term vision for the Indian economy.
- The Finance minister before elections presented an interim budget, rather than a comprehensive annual budget.
INSIGHTS ON THE ISSUE
- expenditure
- taxes it plans to levy
- other transactions which affect the economy and lives of citizens.
- Article 112 of the Indian Constitution: Union Budget of a year is referred to as the Annual Financial Statement (AFS).
- The Budget Division of the Department of Economic Affairs in the Finance Ministry is the nodal body responsible for preparing the Budget.
- deficit indicators.
- Depending on the manner in which they are defined, there can be many classifications and indicators of expenditure, receipts and deficits.
Interim Budget:
- paying salaries, ongoing programmes in various sectors etc — with no changes in the taxation structure
- Until a new government takes over and presents a full Budget that is revised for the full fiscal.
Key elements of the Budget:
- In 2023, India’s per capita income grew at 9.2 percent i n nominal dollar terms.
- To sustain these growth rates, India will become an upper middle-income country by 2030 and higher income by 2042 .
- It needs to boost all those cylinder s comprising private consumption, investment, exports, and imports.
- The budget plays a catalytic role t o firepower each of these components.
- India needs a boost to labour-intensive manufacturing to enable seizing the demographic dividend.
- Factor market reforms are possibly an important driver.
- An auction process with a large uptake, with alternative forms of compensation and accelerating the digitization of land records would all contribute towards this.
Fiscal policy choices:
- Move to public debt to GDP ratio as a medium-term anchor for fiscal policy, with the fiscal deficit as an operational target.
- It can create unnecessary uncertainty
- It can undermine the ability of monetary policy to control inflation
- Influence real economic activity in the usual ways.
- India’s debt to GDP remains high i n comparison with peer groups.
- It is higher than the average of 10 percent a cross emerging markets.
- Deleveraging by the sovereign would be essential to convert the outlook upgrade by rating agencies into an actual ratings increase.
Institutional side:
- FRBM review committee recommended setting up an independent Fiscal Council.
- It will provide independent forecasts on key macro variables like real and nominal GDP growth, tax buoyancy, commodity prices
- Ex-post monitoring role , and serve as the institution to advise on triggering the escape clause and specify a path of return.
- The introduction of a Fiscal Council could perhaps be revisited.
Way Forward
- 10 percent real growth can happen.
- Through sustaining our achievements of macroeconomic and political stability, along with a continued push to physical and digital infrastructure.
- There is a need to create an enabling environment for businesses t o thrive, the focus on environment-related issues, and the upliftment of the marginalized section of society
- Focus on the quality of growth to ensure that it is equitable, sustainable and green.
QUESTION FOR PRACTICE
- Explain intergenerational and intragenerational issues of equity from the perspective of inclusive growth and sustainable growth.(UPSC 2020)
(200 WORDS, 10 MARKS)
Editorial Analysis – 29 June 2024 [PDF ]

- Our Mission, Vision & Values
- Director’s Desk
- Commerce & Accountancy
- Previous Years’ Question Papers-Prelims
- Previous Years’ Question Papers-Mains
- Environment & Ecology
- Science & Technology

- Classroom Programme
- Interview Guidance
- Online Programme
- Drishti Store
- My Bookmarks
- My Progress
- Change Password
- From The Editor's Desk
- How To Use The New Website
- Help Centre
Achievers Corner
- Topper's Interview
- About Civil Services
- UPSC Prelims Syllabus
- GS Prelims Strategy
- Prelims Analysis
- GS Paper-I (Year Wise)
- GS Paper-I (Subject Wise)
- CSAT Strategy
- Previous Years Papers
- Practice Quiz
- Weekly Revision MCQs
- 60 Steps To Prelims
- Prelims Refresher Programme 2020
Mains & Interview
- Mains GS Syllabus
- Mains GS Strategy
- Mains Answer Writing Practice
- Essay Strategy
- Fodder For Essay
- Model Essays
- Drishti Essay Competition
- Ethics Strategy
- Ethics Case Studies
- Ethics Discussion
- Ethics Previous Years Q&As
- Papers By Years
- Papers By Subject
- Be MAINS Ready
- Awake Mains Examination 2020
- Interview Strategy
- Interview Guidance Programme
Current Affairs
- Daily News & Editorial
- Daily CA MCQs
- Sansad TV Discussions
- Monthly CA Consolidation
- Monthly Editorial Consolidation
- Monthly MCQ Consolidation
Drishti Specials
- To The Point
- Important Institutions
- Learning Through Maps
- PRS Capsule
- Summary Of Reports
- Gist Of Economic Survey
Study Material
- NCERT Books
- NIOS Study Material
- IGNOU Study Material
- Yojana & Kurukshetra
- Chhatisgarh
- Uttar Pradesh
- Madhya Pradesh
Test Series
- UPSC Prelims Test Series
- UPSC Mains Test Series
- UPPCS Prelims Test Series
- UPPCS Mains Test Series
- BPSC Prelims Test Series
- RAS/RTS Prelims Test Series
- Daily Editorial Analysis
- YouTube PDF Downloads
- Strategy By Toppers
- Ethics - Definition & Concepts
- Mastering Mains Answer Writing
- Places in News
- UPSC Mock Interview
- PCS Mock Interview
- Interview Insights
- Prelims 2019
- Product Promos
Indian Economy
Make Your Note
The Big Picture – Cashless Economy
- 11 Jul 2019
- 10 min read
- GS Paper - 3
- GS Paper - 2
- E-Governance
Presenting the Union Budget for 2019-20 , the Finance Minister said that 2% tax deducted at source (TDS) will be levied on cash withdrawals exceeding Rs 1 crore in a year from a bank account to discourage the practice of making business payments in cash.
Also, the government has said that businesses with an annual turnover of over Rs 50 crore can offer low-cost digital modes of payments and no charges on Merchant Discount Rate (MDR) will be imposed on them or their customers.
The Reserve Bank of India and banks will absorb these costs from the savings that will accrue to them on account of handling less cash as people move to these digital modes of payment .
Analysis of the Proposals Made in the Budget
- In the year 2005, the government introduced more or less same proposal i.e. Banking Cash Transaction Tax (BCTT) . The BCTT of 0.1% was introduced for withdrawal of cash on a single day of over Rs 25,000. The 2006 budget showed that only 350 crores had been collected by the banks for paying government on that account. The amount was not considered enough to continue with the implementation of the program.
- This proposal will incentivise merchants to offer the option of digital payments including UPI, credit/debit cards, RTGS, NEFT to their customers.
- It is based on the number of transactions rather than the value of transactions as in the case of TDS proposal.
- A penalty of Rs. 5,000 a if the merchants do not offer digital modes of payments to their customers by a particular date makes it binding to the merchants .
- The boost to digitisation should not result in losses to anyone, expecting the banks and companies having a turnover of over Rs 50 crore to bear the cost of digitization is not fair. It is quite possible that such companies may witness a negative impact on their transactions.
- There is a need to create incentives and disincentives structure by which people automatically get encouraged to move towards more digital transactions.
Cashless Economy
- It is not that any economy can ever be completely cashless, cash will continue to play its role. Even in the developed countries, the prevalence of cash is not completely being eliminated.
- If one reduces the use of cash, the compliance level in various things gets better. For example, better recognition of economic activities, more efficient collection of tax etc.
- The GDP can get positively impacted by 0.5-0.6% due to digitization.
- However, using cash in small amounts has its own set of benefits. It offers security and protects the privacy of an individual. Also, it does not have an associated cyberthreat as in the case of digital transactions.
- Transition to cashless economy also has the burden of financial exclusion due to lack of digital literacy, especially in the case of poor and elderly .
The Government’s Initiatives for Digitizing the Economy
- The proponents of the demonetisation argue that if it had not happened, further quick measures to encourage digital transactions like increase in the number of point of sale machines, introduction of mobile wallets like Paytm and PhonePe had not happened.
- There were 18 trillion rupees approximately in circulation before the demonetisation, at the end of that fiscal it was around 13.5 million and presently, 20-21.5 trillion, less by 4.5 around trillion.
- In the year 2013, the value of digital transactions was around 0.7 trillion, it is now 5 times i.e. 3.5 trillion. This can be the result of the 4.5 trillion rupees being less in circulation now.
- Some see the growth of digital transactions during demonetisation as a bit of compulsion as there was not enough cash in the economy.
- The National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) created the Unified Payments Interface (UPI) which is a payment platform in which funds can be transferred between the banks effortlessly. It created the digital infrastructure for private players to come and offer apps for payment services to the citizens. PhonePe, Paytms, mobiquicks are examples. The private players also helped in popularising the digitisation in the economy.
- The government and the private sector have also started using Big Data techniques for improving the financial services provided by them. Credit offerings are now being based on the transaction history of the consumers.
Way Forward
- Presently, 10% of the internet users in the world are in India and per month use of data in India is 9GB, that means that people are moving towards digitization.
- Also, India needs to have a consistent broadband network and power connection in order to include the rural consumers . The government has already launched Bharatnet in this direction and background infrastructure for rural area is expanding slowly.
- All the government transactions should be done using digital payments.
- The government should facilitate payment of tolls, purchase of railway tickets, subsidy payments to farmers through a digital medium.
- The government should create cash-in cash-out machines (CICO) instead of ATMS which are now becoming very bulky and difficult to build and maintain. CICO machines can operate with a sim card whereas ATMs require a broadband connection.
- India’s transition to a cashless economy needs more focus on behavioral change (as observed during demonetization). The government is moving in the right direction as supply of digital infrastructure will eventually create demand for digitalization. This can have a multiplier effect on the economy.
- Sweden and China are leading in digitization. In China, a reasonable amount of money is transacted through ‘Wechat’. Whatsapp is trying the same in India but is suffering due to data localisation issues . Such issues needs to be resolved soon.
The switch to digital economy should not be based on compulsions and should be left on the market forces. Incentivizing is better than imposing financial burden on either companies or banks. Also, the policy framing in this regard should be more inclined towards the consumer and less on the digital companies.
India’s demographic dividend offers hope to this transition. Private sector participation and rural inclusion should remain the focus areas while moving forward towards ‘Digital India’.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Significance and Increasing Scope of the Digital Economy: The digital economy is gaining prominence and impacting various aspects of economic activity globally. It emphasizes that the digital economy is no longer limited to a specific sector but is permeating every corner of the economy. India's Recognition of the Digital Economy: India's ...
India's Digital Economy. Digital Economy refers to the full range of economic, social and cultural activities supported by the Internet and related information and communications technologies. Some experts regard it as the third industrial revolution. Some people consider the digital economy as a major growth enabler.
The different technologies and economic aspects of the digital economy can be broken down into three broad components: 1. Core aspects of the digital economy: It comprises of fundamental innovations (semiconductors, processors), core technologies (computers, telecommunication devices) and enabling infrastructures (Internet and telecoms networks).
India's digital economy and the infrastructure sector has a total potential for $2.5 trillion. There are more than 100 unicorns in over 70,000 start-ups in India, and their number continues to grow. The value of the Indian digital economy will reach $1 trillion by 2025. Advantages of a Digital Economy. Removal of Black Economy: By restricting ...
In Depth - Digital India. India is amongst the top 2 countries globally, just behind China on many dimensions of digital adoption. By 2022, India's digital economy is likely to cross $1 trillion. This was the focus at the India Digital Summit 2019, held in New Delhi. The summit deliberated on what India needs to become a trillion dollar ...
Introduction of Digital Economy: A Leveller or a Source of Economic Inequality in English is available as part of our UPSC preparation & Digital Economy: A Leveller or a Source of Economic Inequality in Hindi for UPSC courses. Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for UPSC Exam by signing up for free.
Source: The Indian Express. Prelims: 4G, 5G, Governance(Adhar, UIDAI, KYC,Bharatnet, CSCs, drones. Mains GS Paper II: Digital India, Important aspects of governance(e governance, accountability), Application of drones. ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS. Recently the Prime Minister said that Digital India is a transformative programme to deliver that every Indian must have a smartphone in his hand and every ...
The Government is working on a comprehensive legal framework for the digital economy. First is Telecom. A new telecom Bill to replace laws made in 1885 and 1930 is at an advanced stage of drafting. Second will be the data protection Bill. Third is a comprehensive digital India Act that India is preparing to replace the IT Act of 2000 vintage.
The State of India's Digital Economy (SIDE) 2023 was released by ICRIER-Prosus Centre for Internet and Digital Economy (IPCIDE) in Feb 2023. What does the report say about India's digital economy and its progress? Know more in this article for the IAS exam Indian economy segment. India's Digital Economy 2023 Report. Key Finding of the Report:
Digital India has empowered the nation by creating opportunities for individuals, expansion of businesses and growth of economy on the whole. Given its potential, it is paramount that this 'digital revolution' must take into account concerns regarding equity and affordability. Examine. (250 words) Difficulty level: Tough
Digital India is a flagship programme of the Government of India with a vision to transform India into a digitally empowered society and knowledge economy. It was launched in July 2015. E-governance initiatives in India gained momentum in the mid-1990s for wider sectoral applications with an emphasis on citizen-centric services.
IAS 2025-26: Samarth - UPSC Answer Writing Program New IAS 2026: 2 Year Integrated (Pre-Cum-Mains) Test Series
UBI - It is an income support mechanism typically intended to reach all or a very large portion of the population regardless of their earnings or employment status. Objective- To provide enough to co. A comprehensive legislative framework for the digital economy In India (UPSC ) is being developed by the government.
A digital economy is moving us towards a cashless society. Increasingly the digital economy relies on AI, mass use of electronic data and automated technology; Social media. To a lesser extent, social media is an aspect of the digital economy. With individuals using it share recommendations about business. Essential Elements of Digital Economy
India is amongst the top 2 countries globally, just behind China on many dimensions of digital adoption. By 2022, India's digital economy is likely to cross $1 trillion. This was the focus at the India Digital Summit 2019, held in New Delhi. The summit deliberated on what India needs to become a trillion dollar digital economy, the challenges ...
Digital economy: A leveller or a source of economic inequality (2016) Lesson 23 of 29 • 14 upvotes • 14:25mins. Dipesh Saini. Digital economy: A leveller or a source of economic inequality. Continue on app (Hindi) UPSC CSE Mains 2017 - Essay Discussion. 29 lessons • 6h 35m . 1. Course Overview (in Hindi) 1:49mins. 2. Destiny of a Nation ...
The digital economy provides an avenue for free moments of goods and services across the world, the very principle of capitalism. Thus, an economy like India can produce goods at a lower price by selling to a developed nation like the US, leading to income redistribution. Even with society, it can lead to an inclusive and equitable society.
The digital sector has been the fastest-growing sector in the country. This kind of exponential growth has never been experienced before. Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman said that India's digital economy is expected to witness exponential growth to $800 billion by 2030 on the back of rising internet penetration and increasing incomes.
According to the Prime Minister, the Central bank digital currency or the digital rupee will make online payments more secure and risk-free and boost the digital economy in the years to come. He also mentioned that the digital rupee will lead to ease in the development of a global digital payment system .
As we celebrate the six years of completion of Digital India, here are the six concrete steps that can aid the digital transformation of the nation in the new normal for Digital 4.0 contributing to India's success story and fulfilling the five trillion-dollar economy dream. Inculcation of scientific temper, where perception doesn't drive ...
Also, digital payment transactions on the Universal Payment Interface (UPI) platform rose from 0.1 million in October 2016 to 1.3 billion in January 2020. Daily Current Affairs IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam - 7th February 2020. India's payment revolution comes from. A clear vision - shifting the system from low volume, high value, and ...
This paper details the methodology used to nowcast the growth rate of the information and communication technology (ICT) sector in the "The growth outlook of the ICT sector" chapter of the OECD Digital Economy Outlook 2024, Volume 1.In an era of rapid digital transformation, innovative data sources for economic measurement are crucial.
New AI Preparedness Index Dashboard tracks 174 economies based on their digital infrastructure, human capital, labor policies, innovation, integration and regulation ... Measuring preparedness is challenging, partly because the institutional requirements for economy-wide integration of AI are still uncertain. As the dashboard shows, different ...
This, in turn, increases the revenue of the government - thus resulting in the growth of the overall financial status of the country. Empowerment to People: One of the biggest advantages of moving towards a digital economy is that it empowers citizens. One example of that would be the LPG subsidy that the government gives to the common people.
Source: Indian Express Prelims: Indian Economy(GDP, GVA, fiscal policy, MGNREGA, budget, economic survey, budget, Employment etc ) Mains GS Paper III: Fiscal policy, Monetary policy, GDP, Issues related to planning etc. ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS. The 2024-25 budget is expected to present a long-term vision for the Indian economy.; The Finance minister before elections presented an interim budget ...
This report explores how human rights are exercised, protected and promoted in the digital age. By examining this topic from three perspectives - rights, technological developments, and policy developments - the paper supports policy makers in shaping digital transformation so that it puts people at the centre.
The International Transactions in Operational Research (ITOR), the flagship journal published by the International Federation of Operational Research Societies, will publish a special issue dedicated to managing supply chain resilience in the digital economy era.. Supply chains are increasingly exposed to disruptions, which may arise from uncertainties in trade policies, economy, new ...
OECD Digital Economy Papers 20 June 2024 Download PDF. Cite this publication. Cite this content as: Close. OECD (2024), "New ... and promote a more secure and resilient digital ecosystem. In the same series. See all publications. Working paper. The OECD Truth Quest Survey. 28 June 2024. Working paper. Shaping a rights-oriented digital ...
The Government's Initiatives for Digitizing the Economy. The first move taken was the demonetisation in November 2016. At the time of demonetisation, India's cash to GDP ratio was around 12%. After demonetisation, that ratio came down to around 9% of the GDP. But after that, it grew at a lower pace but steadily.