How to write a research plan: Step-by-step guide
Last updated
30 January 2024
Reviewed by
Short on time? Get an AI generated summary of this article instead
Today’s businesses and institutions rely on data and analytics to inform their product and service decisions. These metrics influence how organizations stay competitive and inspire innovation. However, gathering data and insights requires carefully constructed research, and every research project needs a roadmap. This is where a research plan comes into play.
Read this step-by-step guide for writing a detailed research plan that can apply to any project, whether it’s scientific, educational, or business-related.
- What is a research plan?
A research plan is a documented overview of a project in its entirety, from end to end. It details the research efforts, participants, and methods needed, along with any anticipated results. It also outlines the project’s goals and mission, creating layers of steps to achieve those goals within a specified timeline.
Without a research plan, you and your team are flying blind, potentially wasting time and resources to pursue research without structured guidance.
The principal investigator, or PI, is responsible for facilitating the research oversight. They will create the research plan and inform team members and stakeholders of every detail relating to the project. The PI will also use the research plan to inform decision-making throughout the project.
- Why do you need a research plan?
Create a research plan before starting any official research to maximize every effort in pursuing and collecting the research data. Crucially, the plan will model the activities needed at each phase of the research project .
Like any roadmap, a research plan serves as a valuable tool providing direction for those involved in the project—both internally and externally. It will keep you and your immediate team organized and task-focused while also providing necessary definitions and timelines so you can execute your project initiatives with full understanding and transparency.
External stakeholders appreciate a working research plan because it’s a great communication tool, documenting progress and changing dynamics as they arise. Any participants of your planned research sessions will be informed about the purpose of your study, while the exercises will be based on the key messaging outlined in the official plan.
Here are some of the benefits of creating a research plan document for every project:
Project organization and structure
Well-informed participants
All stakeholders and teams align in support of the project
Clearly defined project definitions and purposes
Distractions are eliminated, prioritizing task focus
Timely management of individual task schedules and roles
Costly reworks are avoided
- What should a research plan include?
The different aspects of your research plan will depend on the nature of the project. However, most official research plan documents will include the core elements below. Each aims to define the problem statement , devising an official plan for seeking a solution.
Specific project goals and individual objectives
Ideal strategies or methods for reaching those goals
Required resources
Descriptions of the target audience, sample sizes , demographics, and scopes
Key performance indicators (KPIs)
Project background
Research and testing support
Preliminary studies and progress reporting mechanisms
Cost estimates and change order processes
Depending on the research project’s size and scope, your research plan could be brief—perhaps only a few pages of documented plans. Alternatively, it could be a fully comprehensive report. Either way, it’s an essential first step in dictating your project’s facilitation in the most efficient and effective way.
- How to write a research plan for your project
When you start writing your research plan, aim to be detailed about each step, requirement, and idea. The more time you spend curating your research plan, the more precise your research execution efforts will be.
Account for every potential scenario, and be sure to address each and every aspect of the research.
Consider following this flow to develop a great research plan for your project:

Define your project’s purpose
Start by defining your project’s purpose. Identify what your project aims to accomplish and what you are researching. Remember to use clear language.
Thinking about the project’s purpose will help you set realistic goals and inform how you divide tasks and assign responsibilities. These individual tasks will be your stepping stones to reach your overarching goal.
Additionally, you’ll want to identify the specific problem, the usability metrics needed, and the intended solutions.
Know the following three things about your project’s purpose before you outline anything else:
What you’re doing
Why you’re doing it
What you expect from it
Identify individual objectives
With your overarching project objectives in place, you can identify any individual goals or steps needed to reach those objectives. Break them down into phases or steps. You can work backward from the project goal and identify every process required to facilitate it.
Be mindful to identify each unique task so that you can assign responsibilities to various team members. At this point in your research plan development, you’ll also want to assign priority to those smaller, more manageable steps and phases that require more immediate or dedicated attention.
Select research methods
Once you have outlined your goals, objectives, steps, and tasks, it’s time to drill down on selecting research methods . You’ll want to leverage specific research strategies and processes. When you know what methods will help you reach your goals, you and your teams will have direction to perform and execute your assigned tasks.
Research methods might include any of the following:
User interviews : this is a qualitative research method where researchers engage with participants in one-on-one or group conversations. The aim is to gather insights into their experiences, preferences, and opinions to uncover patterns, trends, and data.
Field studies : this approach allows for a contextual understanding of behaviors, interactions, and processes in real-world settings. It involves the researcher immersing themselves in the field, conducting observations, interviews, or experiments to gather in-depth insights.
Card sorting : participants categorize information by sorting content cards into groups based on their perceived similarities. You might use this process to gain insights into participants’ mental models and preferences when navigating or organizing information on websites, apps, or other systems.
Focus groups : use organized discussions among select groups of participants to provide relevant views and experiences about a particular topic.
Diary studies : ask participants to record their experiences, thoughts, and activities in a diary over a specified period. This method provides a deeper understanding of user experiences, uncovers patterns, and identifies areas for improvement.
Five-second testing: participants are shown a design, such as a web page or interface, for just five seconds. They then answer questions about their initial impressions and recall, allowing you to evaluate the design’s effectiveness.
Surveys : get feedback from participant groups with structured surveys. You can use online forms, telephone interviews, or paper questionnaires to reveal trends, patterns, and correlations.
Tree testing : tree testing involves researching web assets through the lens of findability and navigability. Participants are given a textual representation of the site’s hierarchy (the “tree”) and asked to locate specific information or complete tasks by selecting paths.
Usability testing : ask participants to interact with a product, website, or application to evaluate its ease of use. This method enables you to uncover areas for improvement in digital key feature functionality by observing participants using the product.
Live website testing: research and collect analytics that outlines the design, usability, and performance efficiencies of a website in real time.
There are no limits to the number of research methods you could use within your project. Just make sure your research methods help you determine the following:
What do you plan to do with the research findings?
What decisions will this research inform? How can your stakeholders leverage the research data and results?
Recruit participants and allocate tasks
Next, identify the participants needed to complete the research and the resources required to complete the tasks. Different people will be proficient at different tasks, and having a task allocation plan will allow everything to run smoothly.
Prepare a thorough project summary
Every well-designed research plan will feature a project summary. This official summary will guide your research alongside its communications or messaging. You’ll use the summary while recruiting participants and during stakeholder meetings. It can also be useful when conducting field studies.
Ensure this summary includes all the elements of your research project . Separate the steps into an easily explainable piece of text that includes the following:
An introduction: the message you’ll deliver to participants about the interview, pre-planned questioning, and testing tasks.
Interview questions: prepare questions you intend to ask participants as part of your research study, guiding the sessions from start to finish.
An exit message: draft messaging your teams will use to conclude testing or survey sessions. These should include the next steps and express gratitude for the participant’s time.
Create a realistic timeline
While your project might already have a deadline or a results timeline in place, you’ll need to consider the time needed to execute it effectively.
Realistically outline the time needed to properly execute each supporting phase of research and implementation. And, as you evaluate the necessary schedules, be sure to include additional time for achieving each milestone in case any changes or unexpected delays arise.
For this part of your research plan, you might find it helpful to create visuals to ensure your research team and stakeholders fully understand the information.
Determine how to present your results
A research plan must also describe how you intend to present your results. Depending on the nature of your project and its goals, you might dedicate one team member (the PI) or assume responsibility for communicating the findings yourself.
In this part of the research plan, you’ll articulate how you’ll share the results. Detail any materials you’ll use, such as:
Presentations and slides
A project report booklet
A project findings pamphlet
Documents with key takeaways and statistics
Graphic visuals to support your findings
- Format your research plan
As you create your research plan, you can enjoy a little creative freedom. A plan can assume many forms, so format it how you see fit. Determine the best layout based on your specific project, intended communications, and the preferences of your teams and stakeholders.
Find format inspiration among the following layouts:
Written outlines
Narrative storytelling
Visual mapping
Graphic timelines
Remember, the research plan format you choose will be subject to change and adaptation as your research and findings unfold. However, your final format should ideally outline questions, problems, opportunities, and expectations.
- Research plan example
Imagine you’ve been tasked with finding out how to get more customers to order takeout from an online food delivery platform. The goal is to improve satisfaction and retain existing customers. You set out to discover why more people aren’t ordering and what it is they do want to order or experience.
You identify the need for a research project that helps you understand what drives customer loyalty . But before you jump in and start calling past customers, you need to develop a research plan—the roadmap that provides focus, clarity, and realistic details to the project.
Here’s an example outline of a research plan you might put together:
Project title
Project members involved in the research plan
Purpose of the project (provide a summary of the research plan’s intent)
Objective 1 (provide a short description for each objective)
Objective 2
Objective 3
Proposed timeline
Audience (detail the group you want to research, such as customers or non-customers)
Budget (how much you think it might cost to do the research)
Risk factors/contingencies (any potential risk factors that may impact the project’s success)
Remember, your research plan doesn’t have to reinvent the wheel—it just needs to fit your project’s unique needs and aims.
Customizing a research plan template
Some companies offer research plan templates to help get you started. However, it may make more sense to develop your own customized plan template. Be sure to include the core elements of a great research plan with your template layout, including the following:
Introductions to participants and stakeholders
Background problems and needs statement
Significance, ethics, and purpose
Research methods, questions, and designs
Preliminary beliefs and expectations
Implications and intended outcomes
Realistic timelines for each phase
Conclusion and presentations
How many pages should a research plan be?
Generally, a research plan can vary in length between 500 to 1,500 words. This is roughly three pages of content. More substantial projects will be 2,000 to 3,500 words, taking up four to seven pages of planning documents.
What is the difference between a research plan and a research proposal?
A research plan is a roadmap to success for research teams. A research proposal, on the other hand, is a dissertation aimed at convincing or earning the support of others. Both are relevant in creating a guide to follow to complete a project goal.
What are the seven steps to developing a research plan?
While each research project is different, it’s best to follow these seven general steps to create your research plan:
Defining the problem
Identifying goals
Choosing research methods
Recruiting participants
Preparing the brief or summary
Establishing task timelines
Defining how you will present the findings
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 18 April 2023
Last updated: 27 February 2023
Last updated: 6 February 2023
Last updated: 6 October 2023
Last updated: 5 February 2023
Last updated: 16 April 2023
Last updated: 9 March 2023
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 4 July 2024
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next.

Users report unexpectedly high data usage, especially during streaming sessions.

Users find it hard to navigate from the home page to relevant playlists in the app.

It would be great to have a sleep timer feature, especially for bedtime listening.

I need better filters to find the songs or artists I’m looking for.
Log in or sign up
Get started for free
New NPM integration: design with fully interactive components from top libraries!
Creating A User Research Plan (with Examples)

UX research helps to test hypothesis you have about users prior to design. Sadly, not every UX design project starts with user research, and that’s because it takes a lot of time to recruit participants, run UX research projects, and sumamrize findings.
Good research, nevertheless, ensures that your product team doesn’t build the wrong functionality that would cost you valuable resources and make you vulnerable to losing customers.
In this article, you’ll see how you can use UX research plan to get stakeholder’s buy-in and create research reports that’s full of valuable advice for product design. Let’s go.
At the end, when you have your research complete, launch the right tool for your design process. For that, try UXPin, an end-to-end design tool for interactive prototyping that brings design and product development together.
Designers can create a powerful prototypes, show them to product managers who can interact with the design instead of just looking at it. Then, they give the design to engineers who can get all the specs and some code to kickstart front-end design with.
Since with UXPin you work faster, you have ample time for UX research before UX design. Try it for free .
Build advanced prototypes
Design better products with States, Variables, Auto Layout and more.
What is a UX Research Plan?
A UX research plan helps to set expectations and document the essentials you need to communicate to stakeholders and clients. Your company needs a strong business case for every user research session, complete with research objectives, goals, methods, and logistical needs for the study.
UX Research Plan Elements
Every UX research plan should start with a solid outline. That’s where templates come in handy. They help you structure your UX research project in a way that team members and stakeholders see value in completing research process.
Master templates are the best way to create a successful and effective UX research plan. Using a template as a starting point makes planning and writing easier and helps you and your team stay focused on the who, what, why, and when of research. Read on for tips and examples for how you can build a user research plan that works.
UX Research Plan Background
The background section should offer your clients and stakeholders a few sentences on why you are creating a user research plan and what it will accomplish. It should orient readers to the needs and expectations behind the purpose of the study. It should also include a problem statement, which is the primary question you’re setting out to answer with your research findings.
Example Background
The purpose of this study is to understand the major pain points users experience in using our website/app and how these contribute to issues such as cart abandonment, returned items, and low customer loyalty.
We will be using usability testing to follow the user’s experience of our website/app and the obstacles they encounter leading up to the point of purchase. We will also be using generative research techniques to better understand the customer’s experience of our brand and the challenges and needs they face in making a purchase.
UX Research Plan Objectives
Before getting into the nitty-gritty of your user research plan, you first want to focus on your research objectives. This step outlines the reasons you are conducting a UX research plan in the first place. Why are you carrying out this research? What are the end goals you have after completing all the work?
Seeking out answers to these questions should be a collaborative effort between you and your stakeholders. It’s also helpful to consider discussions and learnings from past clients and projects to create metrics for your UX research plan.
Objectives and Success Metrics
Research objectives will be different for every project, but they should always be actionable and specific.
Example Objectives
- Understand how users currently go about tracking orders on our website
- Understand what actions customers take when they consider buying a new [product we offer]
- Learn about competitor websites/apps customers are using to buy [product we offer]
- Evaluate pain points customers are experiencing in using our website/app
And here are some examples to help you determine the success of your UX research plan.
Example Success Metrics
- What information are we trying to collect about users?
- What scales/documents/statistics do we intend to create?
- What decisions will these materials help to make?
UX Research Plan Methodology
This step should be a short and sweet description of the research methods you will use to answer the research objectives. It should include both secondary and primary methods. Generative methods, such as user interviews and open-ended questions, help uncover motivations or more general insights, while UX testing helps to evaluate the usability and experience of your product.
Research Scope & Focus Areas
Clearly outlining the research scope and focus areas helps to facilitate efficient user research planning. The more you’re able to hone in on the specifics of what information you are wanting to collect, the less overwhelmed you will be in the process. It also helps avoid inundating your clients with unnecessary information.
To keep research-focused, this section should include:
- 3-6 question topics (e.g. How do users spend their time on a website?)
- Design Focus Components, including interface qualities (e.g. Usability, Training, Efficiency, Satisfaction)
- Primary User Scenarios (e.g. Scenarios in which pain points are most problematic; scenarios you have the least information about, etc.)
Example Methodology
For this study, we’re conducting a 30-minute usability test to evaluate our user’s experience of our app/website. A secondary method will be to conduct one-on-one generative research interviews to better understand our customers and empathize with their needs.
UX Research Plan Participant Profiles
Once you’ve defined objectives methodology and focus areas, it’s time to outline the participants you’ll need to get the required insights. Participant profiles help you determine who you want to recruit, or an approximation of your users, to optimize recruiting efforts. Here are a few examples of how to ensure you’ll get the best participants for your study.
Define your target user by collaborating with internal stakeholders, marketing, sales, and customer support. With their help, you can create approximations about who your users are. This is a great starting point for finding the right participants for your study.
Compare yourself to your competitors and create participant profiles based on their audiences. Recruiting people who use a competitor’s product can be an excellent way to glean insights into how to further improve your product.
Outline a screening process. Participant profiles should include any relevant information concerning your target audience, including behaviors, needs, demographics, geography, etc. Including the right criteria will help you evaluate whether or not to include certain individuals in your user research plan.
This Nielsen Norman article offers some great information about defining and recruiting the right participants for your study.
UX Research Plan Timeline
This is optional, but many UX research plans include a timeline that offers clients and stakeholders a general overview of how long the research will take. It helps to set expectations for the final results as well as allowing you to create a schedule for research sessions, debriefing, follow-up, and deliverables.
Timeline Example:
Approximately 6-8 weeks for identifying objectives, creating participant profiles, recruitment, in-person meetings, qualitative research, and analysis.
Try an End-to-End Design Solution
UX research plan templates are essential tools for executing a successful project. Having a master template helps you to remember what the process entails, communicate essential information to the right people, and stay on track throughout the user research plan.
UXPin, besides being a great prototyping tool, makes creating such research templates fast and easy. Especially since each project will be a little different and plans will need tweaking in terms of structure and content. Try UXPin for free .
Build prototypes that are as interactive as the end product. Try UXPin
by UXPin on 8th October, 2020
UXPin is a product design platform used by the best designers on the planet. Let your team easily design, collaborate, and present from low-fidelity wireframes to fully-interactive prototypes.
No credit card required.
These e-Books might interest you

Design Systems & DesignOps in the Enterprise
Spot opportunities and challenges for increasing the impact of design systems and DesignOps in enterprises.

DesignOps Pillar: How We Work Together
Get tips on hiring, onboarding, and structuring a design team with insights from DesignOps leaders.
We use cookies to improve performance and enhance your experience. By using our website you agree to our use of cookies in accordance with our cookie policy.
Integrations
What's new?
In-Product Prompts
Participant Management
Interview Studies
Prototype Testing
Card Sorting
Tree Testing
Live Website Testing
Automated Reports
Templates Gallery
Choose from our library of pre-built mazes to copy, customize, and share with your own users
Browse all templates
Financial Services
Tech & Software
Product Designers
Product Managers
User Researchers
By use case
Concept & Idea Validation
Wireframe & Usability Test
Content & Copy Testing
Feedback & Satisfaction
Content Hub
Educational resources for product, research and design teams
Explore all resources
Question Bank
Research Maturity Model
Guides & Reports
Help Center
Future of User Research Report
The Optimal Path Podcast
Maze Guides | Resources Hub
What is UX Research: The Ultimate Guide for UX Researchers
0% complete
Essential elements of an effective UX research plan (examples + templates)
Conducting UX research without a plan is like moving to another country without knowing the language—confusing and exhausting.
To avoid wasting time and resources, it’s crucial to set achievable research goals and work on developing a research plan that’s clear, comprehensive, and aligned with your overarching business goals and research strategy.
A good UX research plan sets out the parameters for your research, and guides how you’ll gather insights to inform product development. In this chapter, we share a step-by-step guide to creating a research plan, including templates and tactics for you to try. You’ll also find expert tips from Paige Bennett, Senior User Research Manager at Affirm, and Sinéad Davis Cochrane, Research Manager at Workday.

What is a UX research plan?
A UX research plan—not to be confused with a UX research strategy or research design—is a plan to guide individual user experience (UX) research projects.
It's a living document that includes a detailed explanation of tactics, methods, timeline, scope, and task owners. It should be co-created and shared with key stakeholders, so everyone is familiar with the project plan, and product teams can meet strategic goals.
A UX research plan is different to a research strategy and research design in both its purpose and contents. Let’s take a look.
Research plan vs. research design vs. research strategy: What’s the difference?
While your UX research plan should be based on strategy, it’s not the same thing. Your UX strategy is a high-level document that contains goals, budget, vision, and expectations. Meanwhile, a plan is a detailed document explaining how the team will achieve those strategic goals. Research design is the form your research itself takes.
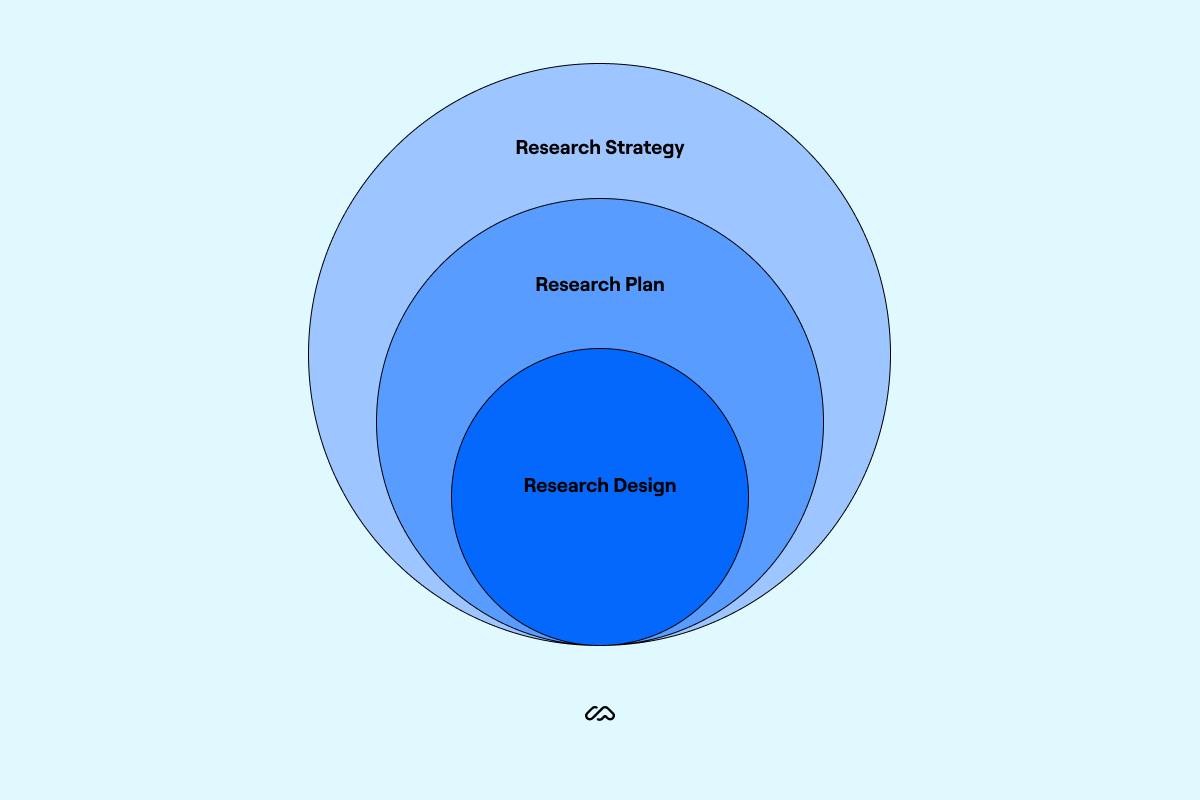
In short, a strategy is a guide, a plan is what drives action, and design is the action itself.
Research design | to be employed and specifics on how they’ll be used in the study (e.g., qualitative interviews, quantitative surveys, experimental trials) that will assist in data collection (sampling size) and how they will be selected | |
|---|---|---|
Research plan | or goals of the research that will be used to gather and analyze data of the project (like budget and personnel) required | |
Research strategy |
What are the benefits of using a UX research plan?
Conducting research without goals and parameters is aimless. A UX research plan is beneficial for your product, user, and business—by building a plan for conducting UX research, you can:
Streamline processes and add structure
Work toward specific, measurable goals, align and engage stakeholders, save time by avoiding rework.
The structure of a research plan allows you to set timelines, expectations, and task owners, so everyone on your team is aligned and empowered to make decisions. Since there’s no second guessing what to do next or which methods to use, you’ll find your process becomes simpler and more efficient. It’s also worth standardizing your process to turn your plan into a template that you can reuse for future projects.
When you set research goals based on strategy, you’ll find it easier to track your team’s progress and keep the project in scope, on time, and on budget. With a solid, strategy-based UX research plan you can also track metrics at different stages of the project and adjust future tactics to get better research findings.
“It’s important to make sure your stakeholders are on the same page with regards to scope, timeline, and goals before you start," explains Paige Bennett, Senior User Research Manager at Affirm. That's because, when stakeholders are aligned, they're much more likely to sign off on product changes that result from UX research.
A written plan is a collaborative way to involve stakeholders in your research and turn them into active participants rather than passive observers. As they get involved, they'll make useful contributions and get a better understanding of your goals.
A UX research plan helps you save time and money quite simply because it’s easier and less expensive to make design or prototype changes than it is to fix usability issues once the product is coded or fully launched. Additionally, having a plan gives your team direction, which means they won’t be conducting research and talking to users without motive, and you’ll be making better use of your resources. What’s more, when everyone is aligned on goals, they’re empowered to make informed decisions instead of waiting for their managers’ approval.
What should a UX research plan include?
In French cuisine, the concept of mise en place—putting in place—allows chefs to plan and set up their workspace with all the required ingredients before cooking. Think of your research plan like this—laying out the key steps you need to go through during research, to help you run a successful and more efficient study.
Here’s what you should include in a UX research plan:
- A brief reminder of the strategy and goals
- An outline of the research objectives
- The purpose of the plan and studies
- A short description of the target audience, sample size, scope, and demographics
- A detailed list of expectations including deliverables, timings, and type of results
- An overview of the test methods and a short explanation of why you chose them
- The test set up or guidelines to outline everything that needs to happen before the study: scenarios, screening questions, and duration of pilot tests
- Your test scripts, questions to ask, or samples to follow
- When and how you’ll present the results
- Cost estimations or requests to go over budget
Collect all UX research findings in one place
Use Maze to run quantitative and qualitative research, influence product design, and shape user-centered products.

How to create a UX research plan
Now we’ve talked through why you need a research plan, let’s get into the how. Here’s a short step-by-step guide on how to write a research plan that will drive results.
- Define the problem statement
- Get stakeholders’ buy-in
- Identify your objectives
- Choose the right research method
- Recruit participants
- Prepare the brief
- Establish the timeline
- Decide how you’ll present your findings
1. Define the problem statement
One of the most important purposes of a research plan is to identify what you’re trying to achieve with the research, and clarify the problem statement. For Paige Bennett , Senior User Research Manager at Affirm, this process begins by sitting together with stakeholders and looking at the problem space.
“We do an exercise called FOG, which stands for ‘Fact, Observation, Guess’, to identify large gaps in knowledge,” says Paige. “Evaluating what you know illuminates questions you still have, which then serves as the foundation of the UX research project.”
You can use different techniques to identify the problem statement, such as stakeholder interviews, team sessions, or analysis of customer feedback. The problem statement should explain what the project is about—helping to define the research scope with clear deliverables and objectives.
2. Identify your objectives
Research objectives need to align with the UX strategy and broader business goals, but you also need to define specific targets to achieve within the research itself—whether that’s understanding a specific problem, or measuring usability metrics . So, before you get into a room with your users and customers, “Think about the research objectives: what you’re doing, why you’re doing it, and what you expect from the UX research process ,” explains Sinéad Davis Cochrane , Research Manager at Workday.
Examples of research objectives might be:
- Learn at what times users interact with your product
- Understand why users return (or not) to your website/app
- Discover what competitor products your users are using
- Uncover any pain points or challenges users find when navigating with your product
- Gauge user interest in and prioritize potential new features
A valuable purpose of setting objectives is ensuring your project doesn't suffer from scope creep. This can happen when stakeholders see your research as an opportunity to ask any question. As a researcher , Sinéad believes your objectives can guide the type of research questions you ask and give your research more focus. Otherwise, anything and everything becomes a research question—which will confuse your findings and be overwhelming to manage.
Sinéad shares a list of questions you should ask yourself and the research team to help set objectives:
- What are you going to do with this information?
- What decisions is it going to inform?
- How are you going to leverage these insights?
Another useful exercise to help identify research objectives is by asking questions that help you get to the core of a problem. Ask these types of questions before starting the planning process:
- Who are the users you’re designing this for?
- What problems and needs do they have?
- What are the pain points of using the product?
- Why are they not using a product like yours?
3. Get stakeholders buy-in
It’s good practice to involve stakeholders at early stages of plan creation to get everyone on board. Sharing your UX research plan with relevant stakeholders means you can gather context, adjust based on comments, and gauge what’s truly important to them. When you present the research plan to key stakeholders, remember to align on the scope of research, and how and when you’ll get back to them with results.
Stakeholders usually have a unique vision of the product, and it’s crucial that you’re able to capture it early on—this doesn’t mean saying yes to everything, but listening to their ideas and having a conversation. Seeing the UX research plan as a living document makes it much easier to edit based on team comments. Plus, the more you listen to other ideas, the easier it will be to evangelize research and get stakeholder buy-in by helping them see the value behind it.
I expect my stakeholders to be participants, and I outline how I expect that to happen. That includes observing interviews, participating in synthesis exercises, or co-presenting research recommendations.

Paige Bennett , Senior User Research Manager at Affirm
4. Choose the right research method

Choose between the different UX research methods to capture different insights from users.
To define the research methods you’ll use, circle back to your research objectives, what stage of the product development process you’re in, and the constraints, resources, and timeline of the project. It’s good research practice to use a mix of different methods to get a more complete perspective of users’ struggles.
For example, if you’re at the start of the design process, a generative research method such as user interviews or field studies will help you generate new insights about the target audience. Or, if you need to evaluate how a new design performs with users, you can run usability tests to get actionable feedback.
It’s also good practice to mix methods that drive quantitative and qualitative results so you can understand context, and catch the user sentiment behind a metric. For instance, if during a remote usability test, you hear a user go ‘Ugh! Where’s the sign up button?’ you’ll get a broader perspective than if you were just reviewing the number of clicks on the same test task.
Examples of UX research methods to consider include:
- Five-second testing
- User interviews
- Field studies
- Card sorting
- Tree testing
- Focus groups
- Usability testing
- Diary studies
- Live website testing
Check out our top UX research templates . Use them as a shortcut to get started on your research.
5. Determine how to recruit participants
Every research plan should include information about the participants you need for your study, and how you’ll recruit them. To identify your perfect candidate, revisit your goals and the questions that need answering, then build a target user persona including key demographics and use cases. Consider the resources you have available already, by asking yourself:
- Do you have a user base you can tap into to collect customer insights ?
- Do you need to hire external participants?
- What’s your budget to recruit users?
- How many users do you need to interact with?
When selecting participants, make sure they represent all your target personas. If different types of people will be using a certain product, you need to make sure that the people you research represent these personas. This means not just being inclusive in your recruitment, but considering secondary personas—the people who may not be your target user base, but interact with your product incidentally.
You should also consider recruiting research participants to test the product on different devices. Paige explains: “If prior research has shown that behavior differs greatly between those who use a product on their phone versus their tablet, I need to better understand those differences—so I’m going to make sure my participants include people who have used a product on both devices.”
During this step, make sure to include information about the required number of participants, how you’ll get them to participate, and how much time you need per user. The main ways to recruit testers are:
- Using an online participant recruitment tool like Maze Panel
- Putting out physical or digital adverts in spaces that are relevant to your product and user
- Reaching out to existing users
- Using participants from previous research
- Recruiting directly from your website or app with a tool like In-Product Prompts
5.1. Determine how you’ll pay them
You should always reward your test participants for their time and insights. Not only because it’s the right thing to do, but also because if they have an incentive they’re more likely to give you complete and insightful answers. If you’re hosting the studies in person, you’ll also need to cover your participants' travel expenses and secure a research space. Running remote moderated or unmoderated research is often considered to be less expensive and faster to complete.
If you’re testing an international audience, remember to check your proposed payment system works worldwide—this might be an Amazon gift card or prepaid Visa cards.
6. Prepare the brief
The next component of a research plan is to create a brief or guide for your research sessions. The kind of brief you need will vary depending on your research method, but for moderated methods like user interviews, field studies, or focus groups, you’ll need a detailed guide and script. The brief is there to remind you which questions to ask and keep the sessions on track.
Your script should cover:
- Introduction: A short message you’ll say to participants before the session begins. This works as a starting point for conversations and helps set the tone for the meeting. If you’re testing without a moderator, you should also include an introductory message to explain what the research is about and the type of answers they should give (in terms of length and specificity).
- Interview questions: Include your list of questions you’ll ask participants during the sessions. These could be examples to help guide the interviews, specific pre-planned questions, or test tasks you’ll ask participants to perform during unmoderated sessions.
- Outro message: Outline what you'll say at the end of the session, including the next steps, asking participants if they are open to future research, and thanking them for their time. This can be a form you share at the end of asynchronous sessions.
It’s crucial you remember to ask participants for their consent. You should do this at the beginning of the test by asking if they’re okay with you recording the session. Use this space to lay out any compensation agreements as well. Then, ask again at the end of the session if they agree with you keeping the results and using the data for research purposes. If possible, explain exactly what you’ll do with their data. Double check and get your legal team’s sign-off on these forms.
7. Establish the timeline
Next in your plan, estimate how long the research project will take and when you should expect to review the findings. Even if not exact, determining an approximate timeline (e.g., two-three weeks) will enable you to manage stakeholders’ expectations of the process and results.
Many people believe UX research is a lengthy process, so they skip it. When you set up a timeline and get stakeholders aligned with it, you can debunk assumptions and put stakeholders’ minds at ease. Plus, if you’re using a product discovery tool like Maze, you can get answers to your tests within days.
8. Decide how you’ll present your findings
When it comes to sharing your findings with your team, presentation matters. You need to make a clear presentation and demonstrate how user insights will influence design and development. If you’ve conducted UX research in the past, share data that proves how implementing user insights has improved product adoption.
Examples of ways you can present your results include:
- A physical or digital PDF report with key statistics and takeaways
- An interactive online report of the individual research questions and their results
- A presentation explaining the results and your findings
- A digital whiteboard, like Miro, to display the results
In your plan, mention how you’ll share insights with the product team. For example, if you’re using Maze, you can start by emailing everyone the ready-to-share report and setting up a meeting with the team to identify how to bring those insights to life. This is key, because your research should be the guiding light for new products or updates, if you want to keep development user-centric. Taking care over how you present your findings will impact whether they’re taken seriously and implemented by other stakeholders.
Your UX research plan template: Free template + example
Whether you’re creating the plan yourself or delegating to your team, a clear UX research plan template cuts your prep time in half.
Find our customizable free UX research plan template here , and keep reading for a filled-in example.

Example: Improving user adoption of a project management tool called Flows
Now, let’s go through how to fill out this template and create a UX research plan with an example.
Executive summary:
Flows aims to increase user adoption and tool engagement by 30% within the next 12 months. Our B2B project management software has been on the market for 3 years and has 25,000 active users across various industries.
By researching the current product experience with existing users, we’ll learn what works and what doesn’t in order to make adjustments to the product and experience.
Research objectives:
| Objective | Description |
|---|---|
| Objective 1 | Identify pain points and areas of friction in the current user experience that stop adoption and engagement |
| Objective 2 | Understand how team members currently use the tool to manage projects and collaborate |
| Objective 3 | Explore desired features, integrations, and capabilities to enhance productivity and team effectiveness |
Purpose of the plan and studies:
The purpose is to gather actionable insights into user needs, behaviors, and challenges to inform updates that will drive increased adoption and engagement of 30% for the B2B project management tool within 12 months.
Target audience, sample size, scope, and demographics:
| Characteristic | Details |
|---|---|
| Target audience | Current customers (teams) using the project management tool |
| Sample size | 20 teams across different client accounts |
| Scope | Full user experience from onboarding to daily use across all tool features |
| Demographics | Teams of 5-15 members from industries like software, marketing, construction, and consulting |
Expectations, deliverables, timings, and type of results:
| Deliverable | Description | Deadline |
|---|---|---|
| Deliverable 1 | User journey maps highlighting friction points | 3 weeks after research study completion |
| Deliverable 2 | Competitive analysis report | 4 weeks |
| Deliverable 3 | Prioritized feature roadmap | 5 weeks |
| Deliverable 4 | Final report with key findings and recommendations | 6 weeks |
Research methodologies:
| Method | Reason |
|---|---|
| Behavioural analytics | Review product stats to uncover friction points that can inform following research |
| Contextual inquiries (8 teams*): | Observe teams using the tool in their workspace |
| User interviews (12 teams*) | 60-min semi-structured interviews |
| Usability testing (5 teams*) | Unmoderated remote usability tests |
*Some teams will take part in more than one research session.
Research analysis methods:
We are doing a mixed methods study.
User interviews are our primary method for gathering qualitative data, and will be analyzed using thematic analysis .
- Quantitative data will be pulled from usability tests to evaluate the effectiveness of our current design.
- Research set up and guidelines:
- Create baselines surveys to gauge current usage and pain points
- Develop interview/discussion guides and usability testing scenarios
- Pilot test materials with two teams
- User interviews: 60 mins, semi-structured; usability tests: 90 mins
- Findings will be presented in a research report for all stakeholders
Research scripts, questions, and samples:
User interview questions:
- What’s your experience with Flows?
- How does Flows fit into your workflow?
- What is your understanding of Flows’ features?
- What do you wish Flows could do that it currently doesn’t?
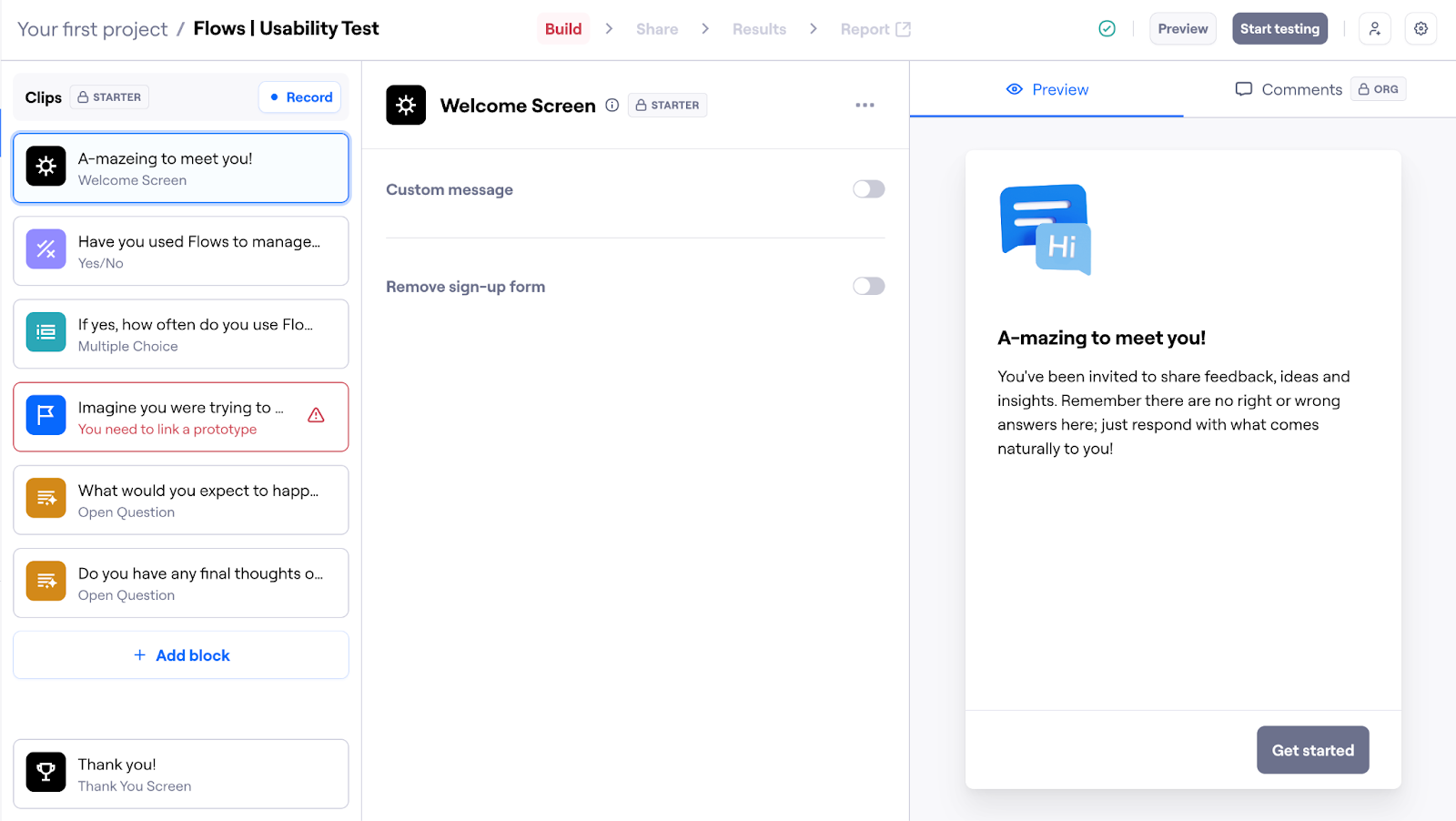
Usability test sample with Maze:
Cost estimations or budget requests/pricing:
Total estimated budget: $8,000
| Item | Estimated costs | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Participant incentives | $4,000 | |
| Remote usability testing platform | $1,000 | |
| Research tools & software | $3,000 |
More free customizable templates for UX research
Whether you’re creating the plan yourself or are delegating this responsibility to your team, here are six research templates to get started:
- UX research plan template : This editable Miro research project plan example helps you brainstorm user and business-facing problems, objectives, and questions
- UX research brief : You need a clear brief before you conduct UX research—Milanote shares a template that will help you simplify the writing process
- User testing synthesis : Trello put together a sample board to organize user testing notes—you can use this as a guide, but change the titles to fit your UX research purposes
- Usability testing templates : At Maze, we’ve created multiple templates for conducting specific UX research methods—this list will help you create different remote usability tests
- Information architecture (IA) tests template : The way you organize the information in your website or app can improve or damage the user experience—use this template to run IA tests easily
- Feedback survey templates : Ask users anything through a survey, and use these templates to get creative and simplify creation
Everything you need to know about UX research plans
We all know that a robust plan is essential for conducting successful UX research. But, in case you want a quick refresher on what we’ve covered:
- Using a UX research strategy as a starting point will make your plan more likely to succeed
- Determine your research objectives before anything else
- Use a mix of qualitative and quantitative research methods
- Come up with clear personas so you can recruit and test a group of individuals that’s representative of your real end users
- Involve stakeholders from the beginning to get buy-in
- Be vocal about timelines, budget, and expected research findings
- Use the insights to power your product decisions and wow your users; building the solution they genuinely want and need
UX research can happen at any stage of the development lifecycle. When you build products with and for users, you need to include them continuously at various stages of the process.
It’s helpful to explore the need for continuous discovery in your UX research plan and look for a tool like Maze that simplifies the process for you. We’ll cover more about the different research methods and UX research tools in the upcoming chapters—ready to go?
Elevate your UX research workflow
Discover how Maze can streamline and operationalize your research plans to drive real product innovation while saving on costs.
Frequently asked questions
What’s the difference between a UX research plan and a UX research strategy?
The difference between a UX research plan and a UX research strategy is that they cover different levels of scope and detail. A UX research plan is a document that guides individual user experience (UX) research projects. UX research plans are shared documents that everyone on the product team can and should be familiar with. A UX research strategy, on the other hand, outlines the high-level goals, expectations, and demographics of the organization’s approach to research.
What should you include in a user research plan?
Here’s what to include in a user research plan:
- Problem statement
- Research objectives
- Research methods
- Participants' demographics
- Recruitment plan
- User research brief
- Expected timeline
- How to present findings
How do you write a research plan for UX design?
Creating a research plan for user experience (UX) requires a clear problem statement and objectives, choosing the right research method, recruiting participants and briefing them, and establishing a timeline for your project. You'll also need to plan how you'll analyze and present your findings.
How do you plan a UX research roadmap?
To plan a UX research roadmap, start by identifying key business goals and user needs. Align research activities with product milestones to ensure timely insights. Prioritize research methods—like surveys, interviews, and usability tests—based on the project phase and objectives. Set clear timelines and allocate resources accordingly. Regularly update stakeholders on progress and integrate feedback to refine the roadmap continuously.
Generative Research: Definition, Methods, and Examples

Home > Blog >
How to write a ux research plan that actually works: 7-step tutorial, saviour egbe, august 29, 2023.
A UX research plan is like a map that will help you navigate the complexity of running a research project. It will help you define your goals, choose the right methods, and collect the data you need to make informed design decisions.
But UX research plans don't have to be boring. In fact, they can be quite funny. For example, one UX researcher I know has a section in his plan called " The Things That Make Me Cry ." This is where he lists all the things that he's learned about his users that make him sad, such as the fact that they often have to deal with frustrating interfaces or unhelpful customer service.
But the primary use of a research plan of course is to make sure that your research is effective. So, while it’s helpful to have a sense of humor, you also need to be serious about your research.
In this article, we'll consider:
- What a UX research plan is and why it's important
- How to create a UX research plan
- An example of a well-structured UX research plan and
- A template for a UX research plan you can use to get started
So, whether you're a UX newbie or a seasoned pro, read on for everything you need to know about UX research plans!
What is a UX Research Plan?
A UX research plan is a document that outlines the goals, methods, and timeline for your research. It's a roadmap that will help you stay on track and ensure that your research is productive.
A good UX research plan should include the following:
- A clear statement of the research goals: What do you hope to learn from your research? What are the specific questions you're trying to answer?
- A description of the target audience: Who are the people you're designing for? What are their needs and pain points?
- A selection of research methods: There are many different research methods available, so it's important to choose the ones that are right for your goals and target audience.
- A timeline and budget: How long will your research take? How much money will it cost?
- A plan for data analysis and presentation: How will you analyze your data and communicate the findings to others?
Why is a UX Research Plan Important?
A UX research plan is important for several reasons. It helps you:
- Stay focused and avoids wasting time and resources.
- Ensures that your research is relevant to the needs of your users.
- Get buy-in from stakeholders & align on the goals for the project.
- Provides a framework for organizing and analyzing your data.
- Helps you communicate the findings of your research to others.
How to Create a UX Research Plan
Creating a UX research plan is an important step in ensuring that your product or service is user-friendly and meets the needs of your target audience. Here are the essential steps to create a research plan that drives meaningful insights and successful user experiences:
Step 1: Alignment & Requirements Gathering
Research rarely will happen in a vacuum. Usually you are working with a team—product, engineering, design, for example.
When the need for a research study arises, the first thing you want to do is meet with your team to understand the questions they're trying to answer.
Depending on how formally set up your research practice is, you may even want to supplement this step with a Research Request document where stakeholders can explain the key questions they'd like to answer, why they're important, and any constraints (budgets, timelines) they're working with.
Step 2: Define Your Goals
Once you've gathered your data, the next step is to clearly define & write out your goals. What do you hope to learn from your research? What specific questions are you trying to answer?
Here are some things to consider when framing your goals:
- What are the business objectives for your product or service? Are you trying to grow active users? Or reduce churn? What should the final results of this research project help you do?
- Who are your target users? These are the people you’d like to learn more about.
- What do you want to learn about their behavior and preferences? This will help you determine your research questions. Ideally the answers to these questions should also tie to your business goals so there’s a clear line between what you’re trying to learn and what that learning will do for the company.
Once you’ve thought about and drafted the answers to these questions, make sure to follow the below steps before starting interviews:
i. Assess Internal Data and Identify Research Needs
Before you start collecting new data, take some time to assess any existing data you have. This could include analytics, customer feedback, or previous research findings. This will help you identify any gaps in your knowledge and determine what areas need to be explored further.
Sometimes you’ll find you already have the answer to your research question in-house—saving you weeks of research effort and thousands of dollars of investment!
If you’re trying to build a repository to help you do this more effectively, check out this definitive guide on research repositories .
ii. Link Research Goals to Business Objectives
It's also important to link your research goals to the business objectives of your organization. This will help you justify the time and resources that will be required for your research. By demonstrating how your research will help you achieve your business goals, you'll be more likely to get the support you need.
As a bonus, once your research is complete, you can go back and track its impact against these business goals. This will help you build a case for your own work and the research practice at your company.
As you proceed through Step 1, keep in mind that your research goals should be Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound (SMART). This framework will help you ensure that your goals are well-defined and actionable.
Step 3: Identify Your Target Audience & Plan a Recruiting Strategy
Knowing your audience is essential for creating a UX research plan that delivers relevant and actionable insights. In this step, we'll talk about how to define your target audience and plan a recruiting strategy for this set of users.
The target audience you’re considering this research study may overlap with your standard target users, or you may want to speak with a subset of this group.
For instance, if you’re doing a research study on why users churn, speaking to a regular active user won’t help. You’ll need to define and recruit users who can actually answer your questions well—in this case it could be “users who have churned in the last 2 weeks”.
When defining the audience for this study, think about whether your target user falls in a specific category based on one of these characteristics:
- Demographics: This includes basic characteristics, such as age, gender, location, and occupation.
- Behaviors and habits: Are you interested in users who have or have not conducted certain actions on your product? For research on how well your Slack integration works, you may want to speak to users who have already installed it, for example.
- Needs and use cases: Sometimes one product can have multiple use cases. For example, a transcription product could be used by researchers, or journalists, or students trying to capture their class notes. Which use case or needs are relevant to your research study?
- Payment type: In today’s world products may have free, freemium / trial, or paid users and each of these groups may behave differently. Think about whether you need one or all of these user types as part of your research.
Now that you know who you need to reach, you also need to think about how to reach them.
Recruiting, as we all know, is a major pain point for (most) researchers. There are some ways to speed it up though.
If you’re running research for a B2C product or an easy to find B2B cohort, you may want to turn to an external recruiting software like UserInterview.com or Respondent.io. There are also local agencies to help you find more local audiences in international markets.
If you are trying to recruit via an external paid channel like this, make sure to budget it in your research plan. These channels are very quick to set up research calls with, but they do come with an added cost.
If you’re running research with a niche B2B audience or are defining your audience based on behaviour on your product (e.g., user who churned in the last 2 weeks), you may need to use internal recruiting methods. This means reaching out to your own users via email, intercom, or via your sales / support team.
If you are recruiting existing customers, make sure to budget in the time it takes to recruit these users. It may take a few days to weeks to gather the relevant user emails and schedule calls, although paid incentives for research help this move much faster.
If you are planning to recruit your own customers, use our Ultimate Guide to Recruiting Your Users for Interviews and Usability Tests . This article has templates for outreach, incentive payment options, and many tactical tips to help you streamline internal recruiting.
Remember, the accuracy and relevance of your research findings depend on the quality of your participants. Take the time to identify and engage users who genuinely reflect your intended audience. This will help you create a research plan that generates insights that drive impactful design decisions.
Step 4: Choose Your Research Methods
Choosing the right research methods is necessary for getting the most out of your UX research plan. Before kicking off your study, make sure to review the possible ways you can answer your research question as well as any constraints you face regarding time, money, or tooling.
If you’re not sure which methods exist, read through this article on UX Research Methods . This article provides an overview of the different methods, so you can choose the ones that are right for your project. It covers everything from usability testing to card sorting, and it includes practical advice on how to conduct each UX research method effectively.
When you’re actually selecting the right method out of the available options, here are the key questions you need to ask yourself:
- Your research goals: What do you hope to learn from your research? The methods you choose should be aligned with your specific goals. For example, if you need to deeply understand user motivations, a user interview is much better fit than a survey.
- Quantitative vs. qualitative: Do you want to collect quantitative data (numbers and statistics) or qualitative insights (in-depth understanding)? Different methods are better suited for different types of data. If you need to know the percentage of users using Zoom vs GoogleMeet, a 5-person user interview won’t get you that data but a 100 person survey with a representative sample might.
- Resources and time: How much time and money do you have to spend on your research? Some methods are more time-consuming or expensive than others. For instance, an ethnographic study where you travel to see your users is obviously more expensive and time-consuming than a 30-minute remote user interview.
By considering these factors, you can choose a combination of research methods that will help you understand your users better.
Step 5: Define your timelines & budgets
Now that you know your target audience (and therefore recruiting method) and your research methods, you can define the timelines and budgets your stakeholders care about.
- Timelines: How long will it take to conduct your research? This will depend on the methods you choose, the number of participants you need to recruit, and the amount of data you need to collect. For example, user interviews can typically be conducted within a few weeks, but usability testing can take anywhere from a few days to a few weeks, depending on the number of participants and the complexity of the product or service being tested.
- Budgets: How much money will you need to conduct your research? This will depend on the methods you choose, the number of participants you need to recruit, and the cost of data collection and analysis. For example, user interviews can be conducted for a few hundred dollars, but usability testing can cost several thousand dollars, depending on the number of participants and the complexity of the product or service being tested.
Step 6: Identify your assumptions
Sometimes without realising it, our research study comes packaged with a set of assumptions about who users are and what they want.
Before kicking off your study, it’s important to identify these assumptions in writing and align on them with your team.
For instance, if you’re running research on how to improve a Slack integration, your in-built assumptions may be:
- Users already use this integration
- It’s worth improving this integration further
Once you’ve laid out these assumptions in advance of your research, you can check them against existing data and keep them in mind when you’re reviewing your research findings.
For example, if analytics data shows that no users use your Slack integration, it may call into question the research you’re running today or change the audience you speak to about it.
Instead of speaking to existing Slack integration users, your audience may need to be companies that have Slack but have not downloaded your Slack integration.
Your research questions may also shift from “Why do you use the Slack integration?” to “Why not? ”
In general, taking a moment to review research assumptions helps you be more aware of them throughout your research study.
Step 7: Define the research questions
This is a pivotal phase in the UX research process. It's when you define the questions that will guide your data collection efforts. These questions will be your compass, directing your research toward meaningful insights that drive product improvements.
Here are some tips for crafting and structuring your research questions:
- Make sure each question is aligned with your overall research objectives. This will ensure that your findings address the core goals of your project.
- Make your questions clear, concise, and specific. Ambiguity can lead to varied interpretations and muddy insights.
- Frame your questions from the user's perspective. Use language that aligns with your target audience to ensure your questions are relatable.
- Avoid leading questions. These are questions that nudge participants towards a particular response. Aim for neutrality to get real insights.
- Use a mix of open-ended and closed-ended questions. Open-ended questions allow participants to provide detailed responses, while closed-ended questions offer predefined answer choices.
- Structure your questions logically, moving from broader inquiries to more specific ones. This will help participants to follow your thought process.
- Limit the number of questions. You want to get comprehensive insights but don't want to overwhelm participants with too many questions.
- Cover the core areas relevant to your project. This could include user pain points, needs, preferences, expectations, and perceptions.
- Pilot-test your questions with a small group of participants. Their feedback can help you to identify unclear or misleading questions.
- Make sure your questions are relevant to the research methods you will be using. For example, usability testing may focus on task-oriented questions, while interviews explore broader experiences.
Here are some examples of well-defined research questions:
1. Usability testing:
- How easily can users navigate the Looppanel account setup process?
- What challenges do users face when uploading their recorded calls to Looppanel?
- How intuitive is the process of setting up Calendar integration on Looppanel?
2. Interviews:
- Can you describe a recent experience you had with the Looppanel customer support?
- What motivated you to sign up for Looppanel for your user research needs instead of other platforms?
- In your view, how does the platform assist in taking your user interview notes effectively?
By carefully defining your research questions, you can ensure that your data collection efforts are focused and meaningful. This will help you to gather the insights you need to improve your product or service and deliver a better experience to your users.
Step 8: Align with your team
Now that you’ve thought through the basics, it's essential to get buy-in from your team and stakeholders on the final plan.
A lot may have happened between your first requirement-gathering meeting and when your plan is finalized. Take the final plan to stakeholders and make sure they are aligned:
- The research question you’re going to answer
- How your study ties to business goals
- Which users you’ll be engaging with
- Which method you’ll be using
- What your timelines look like
- What your budget looks like (if applicable)
This step is really important because if there’s a lack of alignment between you and your key stakeholder, you may end up with findings nobody is going to act on.
Example UX Research Plan
Here is an example UX research plan for improving the onboarding experience of a mobile app. Use this example as a guide to help you create your own plan!
Psst… we also have a template below that you can copy and use!
Project Title: Research study to improve onboarding experience on DuoLingo
Business Goal: We want to increase the activation rate of new users on the app.
Project Goal(s) :
- Identify key drop-off points on the onboarding flow
- Identify why users are dropping off at these points
Target Users: People from the 15-40 age group in North America who have not used Duolingo before.
- MixPanel analytics data to identify existing drop-off points for users
- Usability testing with the think aloud protocol to understand why users are dropping off at those points
Timelines: The study will run for 4 weeks:
- Week 1: Analyzing existing analytics data & recruiting participants
- Week 2: Running usability tests
- Week 3: Analyzing results
- Week 4: Presenting findings
Budget (if applicable): Anticipated spend of $500 on recruiting.
Key Research Questions These are the research questions we’ll be gathering data on :
- At which point(s) in the onboarding process are users most likely to drop off?
- What are the common reasons users cite for discontinuing the onboarding process?
- How do users perceive the clarity of instructions during the initial setup stages?
- Are there any specific usability issues that lead users to abandon the onboarding flow?
- How do users' prior experiences with language learning apps impact their expectations of DuoLingo's onboarding?
UX Research plan template

We’ve also created a UX Research plan template you can use easily duplicate and use for your own work.
Click here to get Looppanel's UX Research Plan template.
This template contains sections for:
- Project Title
- Business Goals
- Project Goals
- Target Users
- Research Methods
- Timelines & Budgets
- Key Research Questions
Follow us on
Get the best resources for ux research, in your inbox, related articles.

Resources & Guides
April 21, 2023
15 Best UX Research Tools for User Researchers, 2024

August 1, 2023
How to Choose the Right UX Research Method

November 8, 2022
A Definitive Guide to the UX Research Repository [2024]
Looppanel automatically records your calls, transcribes them, and centralizes all your research data in one place
The User Research and Insights Tool for Design and Product Teams
How to Create a UX Research Plan [Free Template Inside]
Benjamin Franklin once said, “If you fail to plan, you’re planning to fail”. While Benjamin Franklin wasn’t talking about UX research, the statement applies.
Many researchers fail to plan because they assume they understand user research well enough to create a budget, timeline, process, and more. They conveniently forget that planning is the cornerstone of a successful project and expertise is never enough to see anything through.
Creating a UX research plan allows you to leverage multiple perspectives from project stakeholders and teammates. Stakeholders can help you understand where techniques might not work, timelines may be too tight, or budget insufficient to execute a research project.
Research planning prevents surprises that may come up along the way. It reduces cost and helps you determine how each step of the UX research will be executed to ensure success.
In this guide, we’ll lead you through the steps of creating a UX research plan. You’ll also get a free template so you can create your first research plan immediately.
What Is UX Research?
UX research is the study of user interaction to obtain insights that improve the design process. UX researchers study a group of target users to collect and analyze data that leads to user-friendly products.
The primary goal of UX research is to build products for the end-user based on real data not what you think the user wants. When you conduct UX research, you can give your audience the best solutions because you know what they need.
As a UX researcher, you could begin with qualitative research methods to collect data and understand the user’s needs and motivation. Next, you use quantitative measures such as usability testing to test your hypothesis and results.
What Is a UX Research Plan?
A UX research plan is a document that sets expectations and highlights the most important information you need to communicate with stakeholders in a research project. It is usually a collaboration between all stakeholders to ensure it meets the goals and objectives you’ve laid out.
A user research plan acts as a starting point to help you write easily and keep your team focused on the who, what, why, and when of a UX research project.
What Are the Benefits of Planning User Research?
Show Project Sponsors and Senior Executives the ROI of Your Research
In most scenarios, project sponsors do not care about the process or the user research techniques you choose. They want to know what your research will achieve and how much it will cost to execute. A brief research plan lays out the objective of the research and how it will benefit product design.
Engage Stakeholders
A written research plan is also a great way to engage stakeholders and ensure they’re involved with the research project and the results. You’ll also be leveraging the experience of team members who’ve conducted similar research in the past.
Keeps You Accountable
When you write something down, it looks different from what you pictured in your head. It eliminates the risk of missing steps in the process, going above budget, or losing sight of your research objectives. Think of a research plan as a list of checkpoints to make sure you’ve achieved each goal in your research.
Easier to Plug Holes in Your Process
A research plan helps you to learn what works or doesn’t work and questions you need to be asking. As you write down your plan and process, you can find holes and improve your research plan. It makes it easier to focus and prepare for the study.
How to Create a User Research Plan?
1. Write the Background of the Research
The background section should be brief. Tell stakeholders and clients about the recent history of the project, why you’re conducting the research, and what you’re going to accomplish. In a few sentences (no more than five lines of text), everyone should understand the purpose of the study.
The background section should also include the problem statement. A few ways to identify the problem statement include interviews with stakeholders, a deep analysis of the current data, or team sessions to brainstorm.
2. What Are the Objectives of the Research?
You must have an objective before getting in a room with users. The research objective drives all the research questions you’ll be asking participants during the user interview process.
Why are you conducting user research? What problems do you hope to solve? What is the end goal after completing the research?
Getting answers to these questions should be a collaborative effort between stakeholders and team members involved in the project.
3. Define Stakeholders
Who are the stakeholders that will benefit from the results? Research project stakeholders could be employees in sales, customer support, C-level executives, or product teams.
When you’ve listed everyone you think should be involved, set up a meeting to brainstorm ideas and collect input. It’s easier to deliver the right insights when you’re involving the right stakeholders in your project.
4 . Study Existing Solutions
Have any studies been done on this topic in the past? Perhaps your competitors or in-house teammates have published previous findings that will work as the basis of your research? The answers will help you determine where to begin.
If your team uses Aurelius as a research repository , you’ll be able to easily search through past research projects to quickly find information and make Cross-Project Insights and recommendations from past research with your current project.
5. Recruit Participants
After defining the problem and objectives, it’s time to create a participant profile. Choosing the right participants is one of the most crucial parts of a project.
When creating participant profiles start with characteristics such as occupation, age group, geography, and level of engagement with the product. Next, determine the number of participants to recruit for each UX research method.
We advise internal collaboration with all stakeholders such as sales, marketing, and customer support teams to brainstorm a hypothesis on who your ideal user is. Analyze your competitors to see what type of users they have in their audience.
If you have a database, consider looking inwards to customers who already know your product. If you don’t, use a research recruitment platform to find participants.
When recruiting externally, use a screener to hone in on your ideal participant. Is there a particular behavior you’re looking for? A qualifying action they must have taken within a specific timeframe? Do they need to be a certain age? Screeners ensure you’re bringing in the right users for your research.
6. Establish KPIs and Metrics of Success
How will success be determined? What criteria will you use to check milestone achievements? Examples of success metrics include:
- Time on task
- Specific information about the user
- Decisions that the collected data will help you make
- Statistics you intend to create
7. Outline Scope and Focus of Research
Outlining the focus areas leads to efficient research planning. The deeper you’re able to hone in on the specific information you want to collect from the research, the more clarity you’ll have.
8. Write Research Questions
This is the section where you’ll write down the research questions to ask during user interviews. Start by examining what you already know about the problem such as insights from previous research . Find the knowledge gaps and create questions to answer them.
When brainstorming research questions, it’s important to determine if the goal is to create a new design or to fix an existing design.
If your objective is to build the right design, then your questions will focus on observing user behavior and leveraging mental models.
If the goal is to fix an existing design, then you’ll ask questions about usability to improve the current design. Whatever the goal is, aim for open-ended questions.
Here’s a comprehensive list of questions to ask when conducting UX research interviews
9. Determine Your Budget
Budget plays a role in the amount of data you gather and how you conduct research. More budget equals flexibility to outsource to a dedicated recruitment service, run paid campaigns to attract more people, or even increase the incentives for participants.
More money also makes it easier to choose the right UX research methods that translate into quality insight. Conversely, with a small budget, you have to think of ways to stretch your funds such as using zoom over in-person meetings, limiting the number of research participants, or choosing inexpensive research techniques.
10. Establish Project Timeline
Having a timeline for executing the research plan lets stakeholders and clients know how long the research will take. There might be different expectations between what you think the timeline should be versus the client’s expectation.
When establishing a timeline consider the following:
- The scale of the project
- The time needed to collect data for research analysis
- Time for recruiting research participants
- Number of teammates to engage in research activities
- Unforeseen circumstances such as participants showing up late or needing to reschedule for another day
11. Develop Research Protocols
The research protocol is a list of questions and tasks you’ll cover during in-person sessions. It also includes a list of research methods you’ve chosen.
A common practice is to write down the opening and closing statement of your UX interview. It begins with an explanation of the product, research objectives, and how long each interview session will take. In the end, you thank the participant for their time and answer any questions they might have.
Make sure you get feedback from stakeholders on the research questions as well as the following:
- The duration of each session
- Tasks each research participant will complete during usability testing
- A script to guide each session
- How to record interviews and protect participant data
12. Determine the Research Methods
In this section, you’ll discuss the UX research methods you’ll use during the research and explain why you’ve chosen these techniques.
While there are dozens of research methods to choose from, your choices should be informed by your research questions. Some, like A/B tests and surveys, are suited for quantitative research while others like user interviews and contextual inquiries work best for qualitative research .
Learn more about how to choose a UX research method plus options to choose from during user research
13. Choose UX Research Tools
Similar to research protocols, the research tools you choose should be based on your research objectives and questions.
When choosing UX research tools, consider the following:
- Are you recruiting participants internally from your database or externally?
- Is it going to be a usability test?
- Will you conduct interviews via video conferencing?
- How will you store and analyze research data ?
- Are you going to A/B test certain elements for conversion?
- Will you conduct surveys to collect mass feedback?
There are different tools that fulfill each of these objectives. For example, you can recruit participants from platforms like User Interviews and Userbrain . You can build a research repository to store data and get insights with Aurelius . Tools like Optimizely and Crazy Egg are great for A/B testing.
Get a comprehensive list of UX research tools to complete each stage of the research process in this article
14. Draw Insights and Present your Research Findings
This is the final stage when creating a UX research plan. The insights will be determined by the goals of the research. Is the goal to improve an existing product or create a new product? Which stakeholders will need access to the result?
Make sure you document your process and include details about setbacks you faced along the way, methodologies used, and session materials. This way, your team can have an overview to look back on when conducting the next research project.
To get insight from your research data, use Aurelius to analyze dozens of notes, audio/video recordings as well as spreadsheets.
Create a new project in Aurelius, import your data from anywhere, find information quickly with Tags, search for patterns with Keywords, highlight major findings with Key Insights and make suggestions with Recommendations.
Aurelius turns your recommendations and key insights into shareable reports that you can customize as you like. You can share or present your research findings via email, a PDF, or a live link to your report.
Learn More About How Aurelius Can Help You Improve the Research Process
Asides from having a plan of action for research issues, you must have a plan for working with research participants.
A few things to do during the first interaction with research participants include:
- Inform users about the background of the research and what they’re signing up for
- Tell them how you plan to store their data
- Ask for permission to record the process
- Ask for permission to use their data for research purposes only
- Share details about the UX research process
- Tell them the methods you’re using to collect data
If you feel like it’s too much information, remember that it’s better to overshare than to not give sufficient information.
Use a Template to Streamline UX Research Planning
Templates help you create research plans quickly. Think of it as a starting point for your research project. It includes all the essential elements you need to conduct research and communicate your findings.
Go ahead and download our free UX research plan template. Then, use the tips above to fill out the template.
Download our free UX research plan template
Filter by Keywords
10 Free Research Plan Templates for Teams and Professionals
February 13, 2024
Starting a new research project from scratch can feel overwhelming. Without the right tools and templates, you’re left with a blank page and no direction. With them, starting a new project or organizing an existing one feels like a breeze.
That’s why you need to build a library of the best research plan templates. And we’re here to help you do it.
Stick with us as we run through the benefits of using a research plan template and share some of our favorites—all designed to help make your research projects run like magic.
What is a Research Plan Template?
What makes a good research plan template, 1. clickup user research plan template, 2. clickup market research template, 3. clickup research whiteboard template, 4. clickup equity research report template, 5. clickup seo research & management template, 6. clickup research report template, 7. clickup data analysis findings template, 8. clickup personal swot analysis template, 9. clickup case study template, 10. clickup investigation report template, how to write a research plan.
A research plan template is a document that’s designed to help you build the best research management plan possible. Instead of starting from scratch with a blank screen, a research plan document gives you the building blocks to fill in—so you won’t miss anything important.
There are a lot of solid research plan documents out there—covering everything from UX research (user experience) to case study templates . These templates can be helpful for any team, whether you’re working on product development prototypes or research objectives for a marketing project. They’re especially helpful for product design , UX research, and project management teams.
Some of the most popular research plan templates include:
- UX research plan templates
- Usability testing research templates
- Data analysis findings templates
- Project proposal templates
- Case study templates
- Research process templates
- Market research templates
- Competitive analysis templates
- Request for proposal templates
Each is there to guide you towards collecting, reviewing, and reporting on your research in a more strategic and organized way. Think of the research plan as your helpful research buddy—there to make things easier, provide guidance, and help you ace your project execution .
We’re all looking for something different when it comes to project templates. You might favor simplicity and order, while another team might prefer a more creative approach with lots of color and prompts.
Even though your needs are unique, there are some elements that almost always make a research plan template stand out above all the rest.
The best research plan templates:
- Keep you and your product team organized
- Help you standardize the research process and research method you use
- Keep you focused on the key project goals and deliverables
- Give you suggestions for metrics to record and analyze
- Help you keep your research questions in one place
- Help you stay on target with your project timeline
- Give you a defined place to store your thoughts and research findings
There’s no one perfect template for any individual or team. Consider what your purpose or goal is, what your project management workstreams look like, and which areas you need the most support or guidance in. This will help you choose which templates to feature and how you can use wiki software to build a collection of your go-to templates.
10 Research Plan Templates to Use in 2024
There are hundreds of research plan templates out there, but they’re not all alike. Some of them bring out the best of your project management skills , while others hinder them.
We’ve brought together the best of the best, to share with you the ultimate list of research plan templates to add to your workflow this year. Want to know what’s even better? You don’t need to get buy-in for an expensive pricing plan—these templates are all free!
One of the first things that comes to mind when you say “research plan template” is user research. For development and project teams, this is one step of the process where strategy and staying organized is essential.
The User Research Plan Template by ClickUp makes it easy for you to achieve that and more. There’s space to share your project overview and research goals, research objectives, hypotheses, and more—plus a bonus Interview Research Debrief doc.
This template acts as a central resource for all the stakeholders. Use it to bring your team together, reaffirm your goals and objectives, and stay on track as you execute your qualitative research project.
Bonus: UX design tools !
Planning your market research is a must-have if you want to get the best possible data. Give your team everything they need in one place and it helps your process run smoothly.
To help keep your team informed and ready to go, we developed the Market Research Template by ClickUp . It’s a Task template that brings you key information, all in one place.
Our Market Research Template features five custom fields—a research presentation link, market research type, report document link, data collection technique, and research stage. Add your clickable links, and use the dropdowns to assign the correct stage or type as you progress.

You can collect user research in so many ways. Questionnaires, user interviews, focus groups, user research sessions, or social media. Another super engaging way to do this is with a whiteboard.
Collaboration and user research feels interactive and fun with the Research Whiteboard Template by ClickUp . Encourage your team to share the insights they’ve collected in this highly visual template, with digital sticky notes instead of empty white boxes.
Use this ClickUp whiteboard template as a more engaging way to view your user research. You can also use this as a tool for internal research projects—invite your stakeholders by link and ask them to comment directly.
If you’re in the business of advising investors on what to do with their money, an equity report is a must-have. Instead of manually writing a new report every time, a research plan template can help you shortcut the process and get straight to the details.
Enter the Equity Research Report Template by ClickUp . It’s designed to help you share what you know in a more strategic way. Share an insight into the company overview, management team, performance, market valuation, and recommendations.
This research plan template has everything you need to present your findings to investors in an organized and effective way. Look like a pro to your investor clients and partners, and store all your data in a meaningful way to reflect on later.
Staying on top of your company’s SEO performance is no easy task. There are so many moving parts, tools, projects, goals, and team members that you need a way to stay organized and productive.
Luckily for you, the SEO Research & Management Template by ClickUp is here to help simplify the process—and make you look good to your boss. This Folder template gives you a dedicated place to work on your SEO goals, with SEO-related custom fields and plenty of custom task types to help your team communicate progress and see roadblocks in your research plan.
Use this template to see at a glance where your SEO projects are, so you can be more proactive about how your team is working. You can also dive in to details and understand time estimates, publish dates, and where your rankings are at.
Check out these AI SEO Tools !
There’s no need to start from scratch every time you’re asked to put a research report together—instead use a template to make all your research questions and study reports as impressive as the last one.
Shortcut your way to success with the Research Report Template by ClickUp . There are sections for your executive summary, introduction, research method and techniques, results & discussion, references, and appendices. Add a report author and contributors, so you can recognize everyone that contributed to the report.
Share your research methods, approach, and findings with stakeholders and clients with this impressive template. It’s a useful foundation to help your team get organized and find a better way to update stakeholders on progress.

The Data Analysis Findings Template by ClickUp helps you present your data to everyone in a more meaningful way. Instead of presenting numbers and graphs, this template can help you go deeper into the problem statement, scope, analysis and research method, findings, and conclusion.
Use this template to help you organize your thoughts and communicate the results of your study in a transparent and easy-to-read way. Explain the context and background information alongside your approach, so your stakeholders can fully understand what the data shows.

A personal SWOT analysis can help you understand your (or your team’s) strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. This information can not only help you work better, but it means you can be more intentional about your impact on the wider company.
The Personal SWOT Analysis Template by ClickUp can help you remember to work on your SWOT analysis. Find your strengths, weaknesses or pain points, opportunities, and threats. This Task template features several custom fields designed to help you monitor your progress—including your objective, timeline, and completion rate.
This template can be a helpful reminder to focus on your personal SWOT analysis, so you can be more intentional and aware of how you contribute to your team and company’s goals and objectives. Use your personal SWOT to help you set professional goals for work and make a bigger impact.

Case studies give you a powerful insight into what your brands, clients, or competitors are doing. They’re an in-depth look into a specific area of the business, based on your personal research and findings.
Simplify the process of building your case studies with the Case Study Template by ClickUp . This template gives you a strong foundation for presenting clear, insightful case studies with your team, stakeholders, or clients. Introduce the company, your case study objective, solutions and statistics, and your insights.
Use this template to help you create case studies at scale. Present your data in a clear and concise way, with all the context your team or stakeholders need to extract the most value from the case study as possible.
Often our research helps us understand the market, our competitors, or what our own company is doing. Sometimes, it’s to help us understand incidents and challenges instead.
That’s where the Investigation Report Template by ClickUp comes in. This template is designed to help you report on accidents, complaints, incidents, and violations. Explain the case details including a summary and evidence, then move into cross-examination with space for interview questions and answers, and your conclusion.
This template is a must-have for teams and companies that want to demonstrate how they overcome challenges or handle incidents. It’s great for transparency and trust-building, and serves as a useful way to document a trail of evidence for when you need it.
Now that you have a template for your research plan, let’s dive into the details of how to write one. Follow these steps to create an effective research plan that will guide your research and help you achieve your goals.

Step 1: Identify Your Research Question
The first step in writing a research plan is to clearly define your research question or topic. This will serve as the foundation for all of your research and help guide your methods and analysis. Make sure your question is specific, relevant, and achievable within the scope of your project.
Step 2: Outline Your Objectives
Next, you should outline the specific objectives or goals of your research. These objectives should be aligned with your research question and provide a clear roadmap for your project. Be sure to make them measurable and achievable.
Step 3: Choose Your Research Methods
Based on your research question and objectives, you can now determine the appropriate methods for gathering data and conducting analysis. This may include surveys, experiments, interviews, or literature reviews. It’s important to choose methods that are suitable for your research topic and will provide reliable and accurate results.
Step 4: Create a Timeline
A research plan should include a detailed timeline for each stage of the project. This will help you stay on track and ensure that you have enough time to complete each task. Be realistic with your timeline and build in some buffer time for unexpected delays or challenges.
Step 5: Consider Ethical Implications
When conducting research, it’s important to consider any potential ethical implications. This may include obtaining consent from participants, ensuring privacy and confidentiality, or following ethical guidelines set by your institution or governing body.
Step 6: Anticipate Potential Outcomes
As with any research project, there are always potential outcomes that can arise. These could be both positive and negative, and it’s important to anticipate and plan for them. This will help you be prepared for any potential challenges or changes that may occur during your research.
Step 7: Revise and Refine Your Plan
Once you have completed the previous steps, it’s essential to review and revise your research plan as needed. It’s common for plans to change as the project progresses, so be open to making adjustments and tweaking your methods or timeline as needed.
Stay Organized with the Best Research Plan Templates
Nobody likes a disorganized project—especially a research project. Let your team breathe a sigh of relief and make your stakeholders smile when they realize you’ve got it all under control.
Use these free research plan templates to help you get organized, streamline your workflows, and keep everyone informed. Build a collection of templates that work for your projects, and make them a central part of the way you work as a team. Standardize, simplify, and get productive.
All of these research plan templates are available right now, for free, inside our template library . Get access to these user-friendly templates, 100MB of storage, 1,000+ integrations, and more with ClickUp—free now, and forever!
Questions? Comments? Visit our Help Center for support.
Receive the latest WriteClick Newsletter updates.
Thanks for subscribing to our blog!
Please enter a valid email
- Free training & 24-hour support
- Serious about security & privacy
- 99.99% uptime the last 12 months
UX Research Plan
This UX Research Plan template is designed for UX researchers, UX Designers, Product Designers, and anyone else who wants to conduct an in-depth research session.
This template includes outcomes, objectives, questions, research audience, participants, and many more. All the important information to help give the foundation for a great research plan.
How to use the research plan template?
On the board, you will find a detailed imaginary project example of how to use the research plan. You can then share the link to the completed template with members of your team and any stakeholders.
- Research & Design
- UX & Design
- Into the Miroverse
- Design Sprints
- Strategy & Planning

Submit your template →
Do you have a great board to share with the world? We' ll help you turn it into a template to share with the community.
Similar templates

Sustainability infused User Journey Mapping

AJ&Smart's Remote Design Sprint

Design Principles

How to create a UX research plan

Steven Carr

The concept of research planning can be met with mixed emotions. Some may say that planning delays action. However, a good plan should really do the opposite by providing a clear guide for action and deliverables. In this post, we’ll detail how a well-conceived UX research plan will help streamline your research and foster understanding and engagement from all stakeholders involved.
What is a UX research plan?
A UX research plan can take many forms. It can be a document, spreadsheet, set of slides, or anything else you can imagine as long as it acts as an overview for kicking off the project.
While a UX research plan doesn’t have to be a formal document, it shouldn’t only live in the mind of a single person. Consolidating ideas, milestones, and deliverables together in one, accessible place allows for a guided conversation that has major benefits on the outcomes of a set of research.
What are the benefits of building a UX research plan?
When it comes to user research, it may seem daunting to be too prescriptive when building your UX research plan. After all, how can you account for everything a user might need, say, or want? Nonetheless, it’s important to try, because making progress on your goals is rarely made through random activity. And, there’s nothing wrong with making adjustments as you go.
Even when faced with uncertainty—often compounded by the everchanging world we live in—effective planning facilitates progress.
The benefits of a UX research plan are numerous, but some include:
- Fosters alignment : Rarely does UX research involve a single stakeholder. With a written UX research plan, you can ensure that all team members involved are on the same page, marching toward agreed-upon goals. Not to mention, a plan allows you to spot conflicting interests before you’re too far down the line.
- Engages stakeholders : An effective UX research plan ensures stakeholders are properly engaged with the study and its results. Without a written plan, there’s a greater chance that stakeholders won’t feel invested and may become observers of the research rather than active participants.
- Ensures UX goals are achieved : A UX research plan should clearly map desired outcomes as well as mileposts to define progress. These provide a standard for assessing how the plan is progressing and if adjustments need to be made to keep the plan on track.
Every organization is different, so the teams within them may be responsible for different business goals. This means that there isn’t a one-size-fits-all approach to creating a UX research plan.
In this section, we’ll provide an overview of steps to consider when creating your plan.
A well-oiled UX research plan should include:
- A clear problem statement
- Objectives for the research
- The research method(s) needed to execute the research
- An overview of the participants
- A test plan
- How you’ll present your findings
Let’s get started.
1. Craft a clear problem statement
As with most plans, you should start by clearly identifying and stating the problem that you’re trying to solve. A UX research plan is no different. Your problem statement should be clear, specific, and give enough detail that stakeholders understand what the research is trying to solve.
Problem statements don’t just stem from nowhere. Some great sources for inspiration might be your support team which deals with customer issues on a daily basis, customer reviews on your website, or feedback from social media. Understanding what data already exists—and what you still need to know—is a fantastic starting point for building a strong UX research plan. Let's take a closer look at some of the steps involved in creating a great problem statement:
Defining the problem:
Begin by articulating the issue in a manner that is concise yet comprehensive. A well-crafted problem statement should communicate the essence of the issue succinctly, making it immediately apparent to all stakeholders what the research will address. It’s important that this statement avoids generalities and is rooted in specific user experiences or observed difficulties. For example, instead of saying "improve website navigation," specify "users are struggling to locate the search function on the homepage, which is impacting conversion rates."
Gathering preliminary data:
Before formalizing your problem statement, gather preliminary data to understand the context better. Chat to your customer support team to identify common complaints or challenges users face. Review customer feedback collected through surveys, feedback forms on your website, or direct interactions. Social media platforms can also be a goldmine of user opinions and issues, often providing raw, unfiltered feedback on what users like or struggle with regarding your product or service.
Analyzing existing data:
Analyze the data you’ve gathered to detect patterns or recurring themes. This analysis might reveal that users feel a particular feature is too complicated or that there are barriers to completing a purchase. Such insights help refine your problem statement by focusing on specific user challenges that your research needs to address.
Crafting a detailed problem statement:
With a clear understanding of user challenges, refine your problem statement to reflect these specifics. Ensure it encapsulates the user's perspective, focusing on their experiences and the difficulties they encounter. For instance, if users find an application form daunting due to its length and complexity, your problem statement could be, "Users are abandoning the application form because its length and complex questions create a perception that the process is tedious and time-consuming."
Communicating the significance:
Ensure your problem statement communicates why addressing this issue is crucial for the business or product. Link the problem directly to business outcomes, such as improved user satisfaction, increased sales, or reduced customer churn. This not only highlights the importance of the research but also aligns it with broader business goals, facilitating stakeholder buy-in.
Seeking feedback:
Once you have a draft, share it with key stakeholders—include team members from design, development, marketing, customer service etc. This will help provide new insights, validate the problem’s relevance, and make sure it resonates across all areas of the business. This feedback might prompt revisions that make the statement more inclusives and more robust.
Finalizing the problem statement:
Once you've used that feedback to refine your problem statement, you'll have a well-defined statement that will lead to powerful and useful reseaarch insights.
Once you’ve put together your problem statement, it’s time to define your objectives.
2. Define your objectives
Think about defining your objectives as telling the story of what you’re doing, why you’re doing it, and what you expect to learn from your UX research . The objectives you set should be the driving force behind every task you assign and every question that you ask research participants.
This means it’s important to be specific. Setting clear objectives will help you define the project scope and the questions you have to ask participants to get the information you need. If the scope is too broad, anything and everything becomes a research question—which becomes overwhelming to manage.
If you like to think visually, consider this chart.
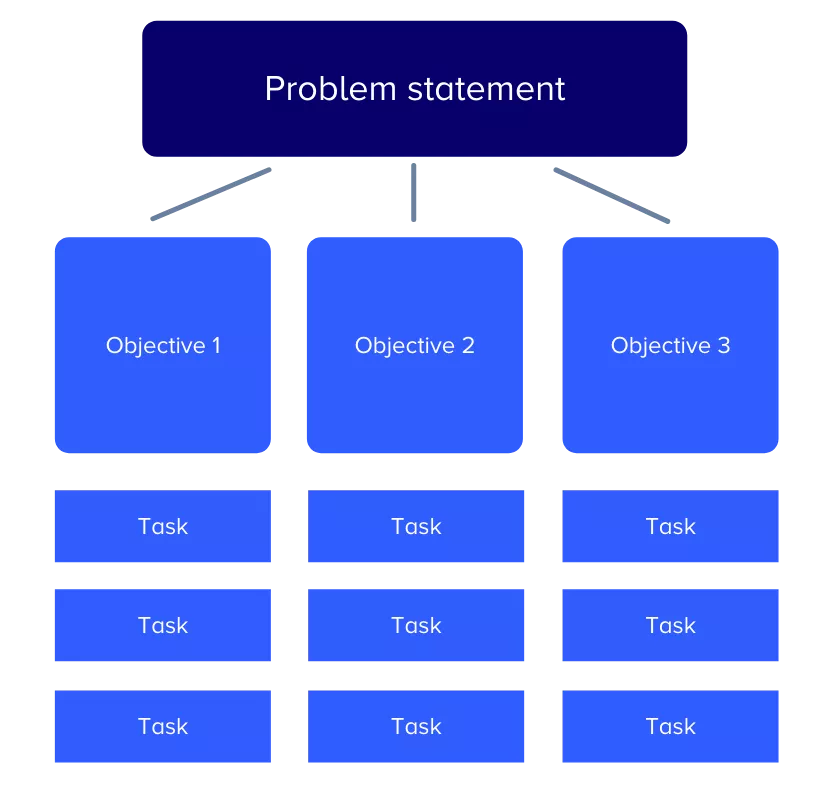
Avoiding the rabbit hole
A well-defined objective keeps you from falling into the rabbit hole of scope creep. Without specific targets, your project can easily grow unwieldy, trying to cover too much ground and diluting the impact of your findings. To avoid this, break down large goals into smaller, focused tasks that you can tackle effectively. For instance, if improving website navigation is your goal, you could focus specifically on enhancing the visibility of the main menu, reducing clicks to reach key content, or improving search functionality.
Using SMART goals
To make your objectives really work for you, frame them using the SMART criteria—Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. Here’s how you might apply these to a UX project:
- Specific : Nail down exactly what you want to achieve. Instead of a broad "improve website usability," aim for something like "cut down the time it takes users to complete a purchase by 20%."
- Measurable : Set up ways to measure your success. You could track the average time it takes users to check out before and after you make site improvements.
- Achievable : Keep your objectives realistic, considering the resources and time you have. If user access is limited, opt for in-depth feedback from a smaller user group instead of surface-level input from many.
- Relevant : Tie your objectives to your broader business goals. If increasing online sales is the target, streamlining the checkout process is a no-brainer.
- Time-bound : Put deadlines on your goals to keep the project moving forward. Plan out when you'll conduct phases of research, analysis, and implementation.
Iterative review and adaptation
Objectives aren’t set in stone. As you dive into your research and start gathering data, be ready to tweak and refine your objectives based on what you learn. UX research is inherently iterative, and being flexible allows you to pivot as you uncover new insights or face unexpected challenges. Regularly revisiting your objectives ensures your research stays relevant and aligned with both user needs and business priorities.
By keeping your objectives clear and focused, you make sure that your UX research is effective, impactful, and tightly connected to enhancing user experience. This isn't just about sticking to a plan—it's about making the plan work hard for you, every step of the way.
Start with a problem statement, define the objectives you need to address the problem, then build out tasks and questions that will uncover the necessary information from your participants.
Once you have a clear understanding of what your problem is and how you’re going to aim to solve it, you’ll need to choose the right research method for your plan.
3. Selecting the right UX research method
Next, you'll have to choose the research method that will achieve your stated goals—based on the objectives you've already identified. Before we jump into individual research methods, or the tactics used for conducting UX research, there are big-picture questions that need to be addressed first. And that’s: What types of UX research are there?
We won’t dive too deep into this here, but here’s some additional reading that might help you understand the type of research you’ll need to conduct:
- Qualitative vs. quantitative research : Qualitative methods are all about the 'why' behind user behaviors, giving you insights through interviews, observations, and open-ended interactions. Quantitative methods crunch the numbers—you’ll get stats, percentages, and graphs that show what users are doing at scale.
- Attitudinal vs. behavioral research : Are you looking to find out what users say they do or what they actually do? Attitudinal research focuses on opinions, preferences, and beliefs, often gathered through surveys or interviews. Behavioral research, on the other hand, observes the real actions users take, often in usability tests or through analytics.
- Generative vs. evaluation research : Starting fresh and need ideas? Generative research helps you understand problems and identify new opportunities, perfect when you’re at the drawing board. Evaluation research is your go-to when you’ve got something to test, checking if your designs are hitting the mark or missing it by a mile.
Choosing a method that fits
Now that you’ve got a lay of the land, it’s time to match your research method to your project goals. Here’s how you can ensure the method you pick will deliver the goods:
- Match the method to your objective : If your goal is to understand how users feel about a new feature, a survey might give you broad quantitative data, but in-depth interviews could unveil deeper insights about their feelings and reactions.
- Consider your resources : Some methods, like extensive field studies, can be resource-heavy. Have a think about what’s realistic in terms of time, budget, and available tools.
- Think about the outcome : What kind of data do you need at the end? Numbers that prove a point, or stories that give you direction? Choose a method that aligns with the kind of evidence that will best inform your design decisions.
Mix and match for best results
Often, no single method will tell the whole story. Consider using a mix of approaches to get both the depth and breadth of insights you need. For instance, you might start with a survey to get a general sense of user satisfaction and follow up with interviews to dive deeper into specific issues highlighted by the survey results.Once you understand the types of results you're trying to achieve, make sure that the research method you choose delivers the evidence you need to make informed decisions.
Related reading: The UX research methodology guidebook
4. Select your participants
One of the most important factors that contribute to a successful UX research plan lies in choosing the right participants (and the right number of them). There’s some debate out there over how many participants you should include in UX research, and the right answer depends on what you’re trying to learn.
Figuring out the right number of participants Let’s unpack this a bit:
- The rule of five : Research shows that five test participants will uncover 85% of a product’s usability issues . This is particularly handy when you’re looking to iron out kinks in a prototype or an existing product.
- Looking for trends? Go bigger : If your mission is to catch broader user trends or get data that you can really hang your hat on, you’ll need a bigger crowd. This means pulling in more folks to get that robust quantitative data that’ll make your stakeholders sit up and listen.
Selecting the right participants is more than just filling seats—it’s about ensuring that every voice you hear from can directly contribute to richer, more actionable insights. So take your time, think it through, and choose wisely to make your UX research as impactful as possible.
Ensuring a good fit
Finally, make sure they’re a good fit for what you’re trying to learn:
- Screen effectively : Develop screening surveys or questions that help you verify that potential participants really do match the profile you’re looking for.
- Keep it balanced : Try to maintain a balance in your participant group to avoid skewing your data. If you’re only hearing from one type of user, you might miss out on insights that could be critical for another segment of your audience.
Recruiting the right participants
Finding these people and convincing them to take part in your study is next on the agenda. Here are a few strategies:
- Leverage existing data : Start with what you know. Use your app’s analytics to identify users who fit your criteria, or sift through customer service logs to find people who’ve faced relevant issues.
- Consider your reach : Depending on your resources and the scale of your project, think about how you’ll reach out to these potential participants. Email blasts, social media calls, or leveraging a professional recruiting service can all be effective, depending on your needs and budget.
Matching participants to your target audience
But it’s not just about numbers. Who these people are matters a ton. Here’s how to get the right mix:
- Broad vs. specific : You’ve got two paths here. Either you go broad, casting a wide net to gather a diverse range of insights across a general demographic, which is great for more exploratory or generative research. Or, you get laser-focused, targeting a very specific group of users who represent your core audience or a particular user scenario. This approach is fantastic when your research goals are tightly defined.
- Align with your objectives : Circle back to what you’re aiming to learn. If your goal is to improve the check-out process for a shopping app, your best bet is to zero in on users who’ve abandoned their cart recently. That’s your goldmine for insights.
Defining who your participants should be will require you to go back to the goals you’ve set and the questions that need answering.
5. Build your test plan
There's a certain art to crafting a great test plan. Admittedly, it can take a bit of practice. From moderated user interviews to unmoderated usability tests to prototyping—test plans can take many different shapes and sizes. Lucky for you, our education and research teams have come together to build out this outstanding resource for building test plans.
Check out all of our articles on the UserTesting Knowledgebase for building a test plan .
6. Lock in a timeline
Establishing your research project’s timeline is an essential step in creating a UX research plan. Estimating how long the research project will take place and when the findings could be expected are necessary considerations in any project.
Even if not exact, determining an approximate timeline (e.g., 2-3 weeks) will enable you to manage stakeholders’ expectations of the process and the results.
Let’s dive into how to effectively map out the time your research will take and when you can expect to roll out the findings.
Planning your research timeline
Here’s how you can approach it:
- Start with the end in mind : Think about when you need the results and work backward from there. Are there product development deadlines or marketing launches that your research needs to feed into? Pin these dates down first.
- Break it down : Segment your research into phases like planning, recruitment, execution, analysis, and presentation of findings. Assign realistic time frames to each phase based on the complexity of the tasks involved.
Be realistic and flexible
While it’s great to have a timeline, it’s also important to stay flexible:
- Allow for buffers : Research can be unpredictable. Participants might cancel, or you might stumble upon a vein of insights that requires deeper exploration. Build in buffer days to accommodate these uncertainties without throwing off your entire schedule.
- Continuous updates : Keep your stakeholders in the loop with regular updates. If timelines shift, communicate this early and clearly, explaining the reasons and the new expected dates.
Managing expectations
An accurate timeline helps in setting and managing expectations:
- Transparent scheduling : Share your timeline with everyone involved in the project. This transparency helps manage expectations and allows team members to align their schedules and responsibilities accordingly.
- Prepare for adjustments : Be prepared to adjust your timeline based on feedback from interim findings or logistical hiccups. This flexibility can be crucial for maintaining the quality and relevance of your research.
Locking in a timeline isn’t just about sticking to dates. It’s about creating a structured approach to your research that allows for informed planning, anticipates adjustments, and aligns with the broader goals of your project. By taking the time to map out each phase and communicate this effectively, you ensure that your UX research delivers valuable insights in a timely and efficient manner.
7. Present the results
Finally, determining how you’ll present the findings of your project from the start ensures they will be impactful and implemented across the organization. Setting this understanding from the beginning will also determine if all of your stakeholders have been properly identified. It can be frustrating to find out that you need to present to an executive halfway through a project.
Ultimately, for the purpose of your UX research plan, it’s important to choose a presentation medium that’s appropriate for your key stakeholders. Perhaps it’s a UX research report , a set of slides, or even a Jira ticket for your product team; the point is, you want to deliver the information to stakeholders in a way they’re comfortable with—and will be most receptive to.
Using a UX research plan template
So now you’ve built a UX research plan from scratch. While it may seem like an arduous process, we can assure you that it’s well worth your time. Being able to confidently embark on a project with clear deliverables, milestones, stakeholder buy-in, and a plan for presenting results is a major feat—one that will be recognized and appreciated by all of those involved.
Nevertheless, time is money. So once you’ve gone through an entire UX research project, we encourage you to hold a retrospective meeting to identify all the ways you could improve the process. Once you uncover what went well and what can be improved, turn your UX research plan into a template for you and your peers to leverage within your organization.
Need some inspiration for your next UX research project? Check out our list of curated test templates to get you started.
In this Article
Get started now

ROI of UserTesting
About the author(s).
Steven is a Marketing Content Strategist. When he’s not inserting oxford commas where they belong, you can find him shooting pool at a local dive or building killer playlists on Spotify.
Related Blog Posts

What is customer journey mapping?

Investing in UX research

What is an ethnographic study?
Human understanding. Human experiences.
Get the latest news on events, research, and product launches
Oh no! We're unable to display this form.
Please check that you’re not running an adblocker and if you are please whitelist usertesting.com.
If you’re still having problems please drop us an email .
By submitting the form, I agree to the Privacy Policy and Terms of Use .
updated on:
UX Research Plan Template. From Objective to Timeline
min to read

Masha Panchenko
Writer at Eleken
UX research is a complex process. To get the most of it, the process has to be organized. Even if your research consists of just a few interviews, you need a plan to make it effective and focused and not to end up with vague conversations.
With a good research plan, all the team will be on the same page, the deadlines will be met, and the research report will be relevant to the objectives.
As a design agency , we do UX research for each project we work on. One thing we can say for sure is that there is no universal template for UX research. Each project needs an individual approach. Yet there are some general steps that help us organize the research and build a structure around it.

So, how to create a UX research plan?
When you think of research strategy, a great guide is the DECIDE framework described in the book Interaction Design by Preece, Rogers, and Sharp. Here are the main steps:
- D etermine the goals .
- E xplore the questions .
- C hoose the evaluation approach and methods .
- I dentify the practical issues .
- D ecide how to deal with ethical issues.
- E valuate, analyze, interpret and present the data .
However, what works great for the user research strategy may not work as well when you have to make a concise UX research plan, short and clear. What is great in this framework is attention to ethical issues. On the other side, in an actual research plan, you might need to focus more on practical issues, such as budget, schedule, user database.
Here we suggest breaking the plan into more practical points.
Study existing situation
First of all, a researcher needs to understand the subject well, conduct interviews with team members, understand how the team is working. At this stage, they can also check the findings and results of previous researches, as well as related studies conducted with other products on the market.
This step may take more time for a product that is already on market, and less for the one that is yet to be developed. However, even in the latter case, there is always a certain background that is important to consider before the start.
When we start working on a product, one of the very first steps of the research is to ask questions to the team, before even talking to users. Here is a sneak peek to our working process with Acadeum, an educational SaaS for whom we did the UI/UX services . Each sticky note is a question that opens new possibilities to the product design.

Defining the user research objectives is crucial to understanding if the research was successful or not.
“Understanding our users better” is a vague objective. Of course, we should not underestimate the importance of empathizing with the customers. Most researchers are inherently directed at this “understanding” and it is awesome. Even if you just talked to your customers and got to know them better, the research can’t be considered “unsuccessful”. However, to get the most out of UX research, you need a more concrete objective.
For example, here is how we did UX research for Gridle , a CRM platform . While the research consisted of just a few in-depth interviews the result was the creation of a whole empathy map, a tangible version of “understanding”. It was short, just a few in-depth interviews, but the result was not just “better understanding”, it was an empathy map. It can also be a customer journey map or a detailed buyer persona profile. These are the things that can be used by other team members and won’t be lost when the researcher will stop working on the project.

The other extreme is too much “KPI-oriented” objective. “Increase revenue”, “improve conversion rates” sounds very concrete and measurable. However, UX research alone can’t fix these issues. It can suggest a certain hypothesis, but after that, the changes have to be made and the hypothesis has to be tested to finally reach those KPIs and improve metrics.
Here are some examples of user research objectives that are both concrete and feasible:
- What are the weak points in user flow?
- What are the main factors of users dissatisfaction?
- What are the a-ha moments of customer journey?
Estimated budget
At this stage, there is no need to define a detailed budget. What we are looking for here is to estimate the amount of money the client is ready to allocate for the research. Depending on the budget, the research methods and the number of users researched will vary. For example, an email survey can be run at a very low cost, while eye tracking requires costly technical resources and software.
At the final stages, the budget needs to be revisited. Only when the plan is done can we estimate the real budget.
Research methods
There are so many different UX research methods, that it is easy to get lost among them. Fundamental research may use all of them, but in most cases combining just a few is enough to get answers to the focus questions.
If you know little about all these UX research techniques, here is a quick guide on choosing the right one for your project:

As you can see, there is no way to avoid talking directly to users. Try integrating elements of an interview in every step of the research where you get access to the users. To learn more options and choose wisely, check out our list of 14 essential UX research methods .
If the product is at the very initial stages of development, generative research with deep interviews and competitors study works great. When the development is taking off, card sorting and contextual inquiry would help. When the product or prototype is ready and needs to be assessed, it is time for usability testing and email surveys.
In any case, a good practice is to combine quantitative and qualitative research, evaluative and generative research.
Choice of UX research techniques affects the tools. This might be even harder than picking the methods, but we’ve got a list of best UX research tools to help.
Participant profiles
Picking the right participants is a key to success. In many cases, you would not have a defined user persona before running UX research. Start with basic characteristics: age group, occupation, geography, and, what is important, the level of their engagement with the product (active users/prospect users/other options).
Some of these characteristics would not be relevant for your case, while others will be important. When you are done with a profile, define the minimum number of participants you need for each research method.
At this step, you should also think of ways to recruit the participants. There are many services and tools that help to find people for UX research sessions. It may be a great choice when you are just about to launch a product and not sure where to look for the participants. If you already have a user database, recruiting some of them would be more efficient than relying on the participants found by a third party.
The research protocol contains specific guidelines for each selected research method. Interview questions have to be phrased correctly and correspond to the objectives.
A good practice is to write down the opening and closing of a user interview. At the beginning it is a short presentation of the product, an explanation of the study and its objectives, noting the amount of time it would take. At the end of the interview, there should be an expression of gratitude for the participation and asking if the interviewee has any questions.
Survey questions have to be planned in a similar way, as well as usability testing and even field research. “Just observe the users” isn’t a very effective approach. It is important to know what you are focusing on and what the questions are, even if there is no direct user interview planned.
Once you have decided on research methods and the number of participants, a timeline should not be a hard task. The problem here might be that the time period that the client has planned for the research is shorter than what a researcher thinks is needed. Maybe hiring a research assistant can help save time. Another benefit of a clear and concise UX research plan is that it allows engaging other people to work, even if they are not familiar with the project in detail.
How long should UX research be? The timing depends on the scale of each project. Based on our experience, research takes on average from 1 to 5 weeks. When making an estimate, consider these factors:
- Time needed for the collection of data and time needed for the analysis
- The number of team members you can engage in user interviews and other research activities
- Time for the recruitment
- Human factor. People might be late, absent, or simply not available for an interview the next few days.
Make sure you plan with some spare time, so you won’t have to do the analysis in a rush: this is the key element of the UX research plan.
Ethics is the last but not least part of the DECIDE framework. Yet it is overlooked way too often in user research plan. Should we give special attention to ethics when we just ask some people to interact with an app and tell their experience? Whatever your opinion is, the rule of thumb with ethics consideration is better to overdo than do not enough.
What are the most common points that you should consider?
- Receive the permission to record/film the process
- Receive the permission to use the information for research purposes (if it is needed for publication, it has to be stated clearly)
- Inform the participants of all the details of the UX research process
Explaining to all the participants the background of the research, the methods used, and the purpose can be annoying and many researchers deem it unnecessary. Yet people have to know what they give and what they get.
The best way to save time on explanations and secure the ethics issues is to prepare a Research Participation Agreement (RPA). The document does not have to be long and there is no need to engage a lawyer in writing it. Follow this RPA template to make sure you inserted all the necessary info.
Budget (again)
Now that all parts of the plan are ready, it is time to check if the final budget fits into the initial one. There is no need to write a detailed budget into the UX research plan when it is just a part of the product design process, but often it is useful for researchers to know the sums to be able to estimate the costs in the future.
UX research plan graphic templates
Now that we are long gone into the process of crafting a UX research plan, and the process is far from any real template… Here are some templates that help you visually organize the plan (or at least the most important parts of it).

Miro UX research plan template. Goals&questions-oriented
Airtable template. Timeline-oriented
Milanote template. Brief
An example of organizing all the user insights in Trello
This template is more of a how-to instruction. That is because UX research is a complex process that needs to be tailored to each project. Having some guides helps make the planning a bit easier.
If you need professional UX research for your project, contact us and we’ll present you an efficient and realistic plan.

Want to get maximum UX insights from user interviews? We cover all whats, whys and hows in this comprehensive guide!

Examine a list of the top 10 UX research tools suggested by experienced designers to make your research a success.
.png)
Want to learn how to make the most out of usability tests with limited resources? Read on!

What is A/B testing? How can it improve your business performance? And how do you do it? All the answers in our post!

Learn how to use ChatGPT in the research process and explore examples where ChatGPT can be helpful for UX researchers.

Learn to carry out the 4-step UX research process to make your product shine bright like a diamond for the target user.

What do UX researchers actually do? What are the best ways to get inside the mind of users? Find out with these simple but efficient UX research methods.

While UX designers are hunting for users’ problems to solve, customer support is sitting on a pile of insights. Learn how you can benefit from these insights.

Learn what concrete benefits customer feedback gives, how to collect it, and what to do after you’ve gathered these valuable insights.

Wondering if UX research without users is possible? In fact, it is. Read this article to learn the most effective methods and tricks!
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- What Is a Research Design | Types, Guide & Examples
What Is a Research Design | Types, Guide & Examples
Published on June 7, 2021 by Shona McCombes . Revised on November 20, 2023 by Pritha Bhandari.
A research design is a strategy for answering your research question using empirical data. Creating a research design means making decisions about:
- Your overall research objectives and approach
- Whether you’ll rely on primary research or secondary research
- Your sampling methods or criteria for selecting subjects
- Your data collection methods
- The procedures you’ll follow to collect data
- Your data analysis methods
A well-planned research design helps ensure that your methods match your research objectives and that you use the right kind of analysis for your data.
Table of contents
Step 1: consider your aims and approach, step 2: choose a type of research design, step 3: identify your population and sampling method, step 4: choose your data collection methods, step 5: plan your data collection procedures, step 6: decide on your data analysis strategies, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about research design.
- Introduction
Before you can start designing your research, you should already have a clear idea of the research question you want to investigate.
There are many different ways you could go about answering this question. Your research design choices should be driven by your aims and priorities—start by thinking carefully about what you want to achieve.
The first choice you need to make is whether you’ll take a qualitative or quantitative approach.
| Qualitative approach | Quantitative approach |
|---|---|
| and describe frequencies, averages, and correlations about relationships between variables |
Qualitative research designs tend to be more flexible and inductive , allowing you to adjust your approach based on what you find throughout the research process.
Quantitative research designs tend to be more fixed and deductive , with variables and hypotheses clearly defined in advance of data collection.
It’s also possible to use a mixed-methods design that integrates aspects of both approaches. By combining qualitative and quantitative insights, you can gain a more complete picture of the problem you’re studying and strengthen the credibility of your conclusions.
Practical and ethical considerations when designing research
As well as scientific considerations, you need to think practically when designing your research. If your research involves people or animals, you also need to consider research ethics .
- How much time do you have to collect data and write up the research?
- Will you be able to gain access to the data you need (e.g., by travelling to a specific location or contacting specific people)?
- Do you have the necessary research skills (e.g., statistical analysis or interview techniques)?
- Will you need ethical approval ?
At each stage of the research design process, make sure that your choices are practically feasible.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Within both qualitative and quantitative approaches, there are several types of research design to choose from. Each type provides a framework for the overall shape of your research.
Types of quantitative research designs
Quantitative designs can be split into four main types.
- Experimental and quasi-experimental designs allow you to test cause-and-effect relationships
- Descriptive and correlational designs allow you to measure variables and describe relationships between them.
| Type of design | Purpose and characteristics |
|---|---|
| Experimental | relationships effect on a |
| Quasi-experimental | ) |
| Correlational | |
| Descriptive |
With descriptive and correlational designs, you can get a clear picture of characteristics, trends and relationships as they exist in the real world. However, you can’t draw conclusions about cause and effect (because correlation doesn’t imply causation ).
Experiments are the strongest way to test cause-and-effect relationships without the risk of other variables influencing the results. However, their controlled conditions may not always reflect how things work in the real world. They’re often also more difficult and expensive to implement.
Types of qualitative research designs
Qualitative designs are less strictly defined. This approach is about gaining a rich, detailed understanding of a specific context or phenomenon, and you can often be more creative and flexible in designing your research.
The table below shows some common types of qualitative design. They often have similar approaches in terms of data collection, but focus on different aspects when analyzing the data.
| Type of design | Purpose and characteristics |
|---|---|
| Grounded theory | |
| Phenomenology |
Your research design should clearly define who or what your research will focus on, and how you’ll go about choosing your participants or subjects.
In research, a population is the entire group that you want to draw conclusions about, while a sample is the smaller group of individuals you’ll actually collect data from.
Defining the population
A population can be made up of anything you want to study—plants, animals, organizations, texts, countries, etc. In the social sciences, it most often refers to a group of people.
For example, will you focus on people from a specific demographic, region or background? Are you interested in people with a certain job or medical condition, or users of a particular product?
The more precisely you define your population, the easier it will be to gather a representative sample.
- Sampling methods
Even with a narrowly defined population, it’s rarely possible to collect data from every individual. Instead, you’ll collect data from a sample.
To select a sample, there are two main approaches: probability sampling and non-probability sampling . The sampling method you use affects how confidently you can generalize your results to the population as a whole.
| Probability sampling | Non-probability sampling |
|---|---|
Probability sampling is the most statistically valid option, but it’s often difficult to achieve unless you’re dealing with a very small and accessible population.
For practical reasons, many studies use non-probability sampling, but it’s important to be aware of the limitations and carefully consider potential biases. You should always make an effort to gather a sample that’s as representative as possible of the population.
Case selection in qualitative research
In some types of qualitative designs, sampling may not be relevant.
For example, in an ethnography or a case study , your aim is to deeply understand a specific context, not to generalize to a population. Instead of sampling, you may simply aim to collect as much data as possible about the context you are studying.
In these types of design, you still have to carefully consider your choice of case or community. You should have a clear rationale for why this particular case is suitable for answering your research question .
For example, you might choose a case study that reveals an unusual or neglected aspect of your research problem, or you might choose several very similar or very different cases in order to compare them.
Data collection methods are ways of directly measuring variables and gathering information. They allow you to gain first-hand knowledge and original insights into your research problem.
You can choose just one data collection method, or use several methods in the same study.
Survey methods
Surveys allow you to collect data about opinions, behaviors, experiences, and characteristics by asking people directly. There are two main survey methods to choose from: questionnaires and interviews .
| Questionnaires | Interviews |
|---|---|
| ) |
Observation methods
Observational studies allow you to collect data unobtrusively, observing characteristics, behaviors or social interactions without relying on self-reporting.
Observations may be conducted in real time, taking notes as you observe, or you might make audiovisual recordings for later analysis. They can be qualitative or quantitative.
| Quantitative observation | |
|---|---|
Other methods of data collection
There are many other ways you might collect data depending on your field and topic.
| Field | Examples of data collection methods |
|---|---|
| Media & communication | Collecting a sample of texts (e.g., speeches, articles, or social media posts) for data on cultural norms and narratives |
| Psychology | Using technologies like neuroimaging, eye-tracking, or computer-based tasks to collect data on things like attention, emotional response, or reaction time |
| Education | Using tests or assignments to collect data on knowledge and skills |
| Physical sciences | Using scientific instruments to collect data on things like weight, blood pressure, or chemical composition |
If you’re not sure which methods will work best for your research design, try reading some papers in your field to see what kinds of data collection methods they used.
Secondary data
If you don’t have the time or resources to collect data from the population you’re interested in, you can also choose to use secondary data that other researchers already collected—for example, datasets from government surveys or previous studies on your topic.
With this raw data, you can do your own analysis to answer new research questions that weren’t addressed by the original study.
Using secondary data can expand the scope of your research, as you may be able to access much larger and more varied samples than you could collect yourself.
However, it also means you don’t have any control over which variables to measure or how to measure them, so the conclusions you can draw may be limited.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

As well as deciding on your methods, you need to plan exactly how you’ll use these methods to collect data that’s consistent, accurate, and unbiased.
Planning systematic procedures is especially important in quantitative research, where you need to precisely define your variables and ensure your measurements are high in reliability and validity.
Operationalization
Some variables, like height or age, are easily measured. But often you’ll be dealing with more abstract concepts, like satisfaction, anxiety, or competence. Operationalization means turning these fuzzy ideas into measurable indicators.
If you’re using observations , which events or actions will you count?
If you’re using surveys , which questions will you ask and what range of responses will be offered?
You may also choose to use or adapt existing materials designed to measure the concept you’re interested in—for example, questionnaires or inventories whose reliability and validity has already been established.
Reliability and validity
Reliability means your results can be consistently reproduced, while validity means that you’re actually measuring the concept you’re interested in.
| Reliability | Validity |
|---|---|
| ) ) |
For valid and reliable results, your measurement materials should be thoroughly researched and carefully designed. Plan your procedures to make sure you carry out the same steps in the same way for each participant.
If you’re developing a new questionnaire or other instrument to measure a specific concept, running a pilot study allows you to check its validity and reliability in advance.
Sampling procedures
As well as choosing an appropriate sampling method , you need a concrete plan for how you’ll actually contact and recruit your selected sample.
That means making decisions about things like:
- How many participants do you need for an adequate sample size?
- What inclusion and exclusion criteria will you use to identify eligible participants?
- How will you contact your sample—by mail, online, by phone, or in person?
If you’re using a probability sampling method , it’s important that everyone who is randomly selected actually participates in the study. How will you ensure a high response rate?
If you’re using a non-probability method , how will you avoid research bias and ensure a representative sample?
Data management
It’s also important to create a data management plan for organizing and storing your data.
Will you need to transcribe interviews or perform data entry for observations? You should anonymize and safeguard any sensitive data, and make sure it’s backed up regularly.
Keeping your data well-organized will save time when it comes to analyzing it. It can also help other researchers validate and add to your findings (high replicability ).
On its own, raw data can’t answer your research question. The last step of designing your research is planning how you’ll analyze the data.
Quantitative data analysis
In quantitative research, you’ll most likely use some form of statistical analysis . With statistics, you can summarize your sample data, make estimates, and test hypotheses.
Using descriptive statistics , you can summarize your sample data in terms of:
- The distribution of the data (e.g., the frequency of each score on a test)
- The central tendency of the data (e.g., the mean to describe the average score)
- The variability of the data (e.g., the standard deviation to describe how spread out the scores are)
The specific calculations you can do depend on the level of measurement of your variables.
Using inferential statistics , you can:
- Make estimates about the population based on your sample data.
- Test hypotheses about a relationship between variables.
Regression and correlation tests look for associations between two or more variables, while comparison tests (such as t tests and ANOVAs ) look for differences in the outcomes of different groups.
Your choice of statistical test depends on various aspects of your research design, including the types of variables you’re dealing with and the distribution of your data.
Qualitative data analysis
In qualitative research, your data will usually be very dense with information and ideas. Instead of summing it up in numbers, you’ll need to comb through the data in detail, interpret its meanings, identify patterns, and extract the parts that are most relevant to your research question.
Two of the most common approaches to doing this are thematic analysis and discourse analysis .
| Approach | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Thematic analysis | |
| Discourse analysis |
There are many other ways of analyzing qualitative data depending on the aims of your research. To get a sense of potential approaches, try reading some qualitative research papers in your field.
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
A research design is a strategy for answering your research question . It defines your overall approach and determines how you will collect and analyze data.
A well-planned research design helps ensure that your methods match your research aims, that you collect high-quality data, and that you use the right kind of analysis to answer your questions, utilizing credible sources . This allows you to draw valid , trustworthy conclusions.
Quantitative research designs can be divided into two main categories:
- Correlational and descriptive designs are used to investigate characteristics, averages, trends, and associations between variables.
- Experimental and quasi-experimental designs are used to test causal relationships .
Qualitative research designs tend to be more flexible. Common types of qualitative design include case study , ethnography , and grounded theory designs.
The priorities of a research design can vary depending on the field, but you usually have to specify:
- Your research questions and/or hypotheses
- Your overall approach (e.g., qualitative or quantitative )
- The type of design you’re using (e.g., a survey , experiment , or case study )
- Your data collection methods (e.g., questionnaires , observations)
- Your data collection procedures (e.g., operationalization , timing and data management)
- Your data analysis methods (e.g., statistical tests or thematic analysis )
A sample is a subset of individuals from a larger population . Sampling means selecting the group that you will actually collect data from in your research. For example, if you are researching the opinions of students in your university, you could survey a sample of 100 students.
In statistics, sampling allows you to test a hypothesis about the characteristics of a population.
Operationalization means turning abstract conceptual ideas into measurable observations.
For example, the concept of social anxiety isn’t directly observable, but it can be operationally defined in terms of self-rating scores, behavioral avoidance of crowded places, or physical anxiety symptoms in social situations.
Before collecting data , it’s important to consider how you will operationalize the variables that you want to measure.
A research project is an academic, scientific, or professional undertaking to answer a research question . Research projects can take many forms, such as qualitative or quantitative , descriptive , longitudinal , experimental , or correlational . What kind of research approach you choose will depend on your topic.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, November 20). What Is a Research Design | Types, Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved July 10, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/research-design/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, guide to experimental design | overview, steps, & examples, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, ethical considerations in research | types & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Research Plan
Define how to conduct a research activity by writing the protocol before starting., applied for.
Stakeholders
also called
Research Protocol
related content
Hypothesis Generation
Interview Guide
Diary Study
The research plan is a document that clarifies how to approach the research, touching upon research goals, selected methodologies, types of participants and tools used, timeline and locations. This planning activity needs to be done upfront, before starting the actual research, and help maximizing the effort and modeling the activities in the best way possible, according to the specific research purpose. The plan becomes even more important when the research requires to travel in the field, or coordinate different teams in various locations.
Design the research and explain the approach to other team members or stakeholders.
remember to
Include debriefing sessions in the schedule in order to make the work effective and avoid team burnout.
Grow with us! Share your case studies
The collection is always evolving, following the development of our practice. If you have any interesting tools or example of application to share, please get in touch.
This website uses cookies to collect anonymized usage statistics so that we can improve the overall user experience. If you want to know more or change your preferences, read our Cookie Policy . By clicking Accept you are giving consent to the use of cookies.
No, thank you.
FLEET LIBRARY | Research Guides
Rhode island school of design, create a research plan: research plan.
- Research Plan
- Literature Review
- Ulrich's Global Serials Directory
- Related Guides
A research plan is a framework that shows how you intend to approach your topic. The plan can take many forms: a written outline, a narrative, a visual/concept map or timeline. It's a document that will change and develop as you conduct your research. Components of a research plan
1. Research conceptualization - introduces your research question
2. Research methodology - describes your approach to the research question
3. Literature review, critical evaluation and synthesis - systematic approach to locating,
reviewing and evaluating the work (text, exhibitions, critiques, etc) relating to your topic
4. Communication - geared toward an intended audience, shows evidence of your inquiry
Research conceptualization refers to the ability to identify specific research questions, problems or opportunities that are worthy of inquiry. Research conceptualization also includes the skills and discipline that go beyond the initial moment of conception, and which enable the researcher to formulate and develop an idea into something researchable ( Newbury 373).
Research methodology refers to the knowledge and skills required to select and apply appropriate methods to carry through the research project ( Newbury 374) .
Method describes a single mode of proceeding; methodology describes the overall process.
Method - a way of doing anything especially according to a defined and regular plan; a mode of procedure in any activity
Methodology - the study of the direction and implications of empirical research, or the sustainability of techniques employed in it; a method or body of methods used in a particular field of study or activity *Browse a list of research methodology books or this guide on Art & Design Research
Literature Review, critical evaluation & synthesis
A literature review is a systematic approach to locating, reviewing, and evaluating the published work and work in progress of scholars, researchers, and practitioners on a given topic.
Critical evaluation and synthesis is the ability to handle (or process) existing sources. It includes knowledge of the sources of literature and contextual research field within which the person is working ( Newbury 373).
Literature reviews are done for many reasons and situations. Here's a short list:
| to learn about a field of study to understand current knowledge on a subject to formulate questions & identify a research problem to focus the purpose of one's research to contribute new knowledge to a field personal knowledge intellectual curiosity | to prepare for architectural program writing academic degrees grant applications proposal writing academic research planning funding |
Sources to consult while conducting a literature review:
Online catalogs of local, regional, national, and special libraries
meta-catalogs such as worldcat , Art Discovery Group , europeana , world digital library or RIBA
subject-specific online article databases (such as the Avery Index, JSTOR, Project Muse)
digital institutional repositories such as Digital Commons @RISD ; see Registry of Open Access Repositories
Open Access Resources recommended by RISD Research LIbrarians
works cited in scholarly books and articles
print bibliographies
the internet-locate major nonprofit, research institutes, museum, university, and government websites
search google scholar to locate grey literature & referenced citations
trade and scholarly publishers
fellow scholars and peers
Communication
Communication refers to the ability to
- structure a coherent line of inquiry
- communicate your findings to your intended audience
- make skilled use of visual material to express ideas for presentations, writing, and the creation of exhibitions ( Newbury 374)
Research plan framework: Newbury, Darren. "Research Training in the Creative Arts and Design." The Routledge Companion to Research in the Arts . Ed. Michael Biggs and Henrik Karlsson. New York: Routledge, 2010. 368-87. Print.
About the author
Except where otherwise noted, this guide is subject to a Creative Commons Attribution license
source document
Routledge Companion to Research in the Arts
- Next: Literature Review >>
- Last Updated: Sep 20, 2023 5:05 PM
- URL: https://risd.libguides.com/researchplan
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- Product Demos
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Employee Exit Interviews
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Artificial Intelligence
Market Research
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Sydney.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
- The Ultimate Guide to Market Research
- Market Research Templates
Try Qualtrics for free
Market research & templates: a complete guide.
18 min read Interested in market research but need some templates to start with? In this guide, we unpack market research, survey planning best practice and share some of our best templates for brand, customer, product and employee research.
What is a market research template?
While you’re no doubt familiar with the concept of market research and how it can help you to reach your target audiences and improve your product or service , the real challenge is designing a market research plan that is conducive to excellent results.
All of this starts with the right market research template(s) to help you analyse specific target audiences, collect the right data and uncover insights that can drive actionable change .
In this article, we’re going to:
- talk about market research and its use cases,
- provide you with a standard template that allows you to plan your research,
- and share several other templates to help you with specific types of market research
You can also check out our free template library.
But first, let’s revisit market research.
What is market research?
Market research is the process of determining the viability of a new service or product through surveys and questionnaires with prospects and/or customers. It involves gathering information about market needs and prospect/customer preferences .
Through market research, you can discover and/or refine your target market, get opinions and feedback on what you provide to them and uncover further prospect/customer pain points and expectations of your service or product .
Market research can be conducted in-house, either by you and your research team, or through a third-party company that specialises in it (they will typically have their own research panels or be capable of creating a research panel to suit your requirements).
The four common types of market research
There are lots of different ways to conduct market research to collect customer data and feedback , test product concepts , and do brand research, but the four most common are:
The most commonly used form of market research, surveys are a form of qualitative research that asks respondents a series of open or closed-ended questions , delivered either as an on-screen questionnaire or email.
Surveys are incredibly popular because they’re cheap, easy to produce, and can capture data very quickly, leading to faster insights.
2) Focus groups
Why not bring together a carefully selected group of people in your target market using focus groups? Though more expensive and complex than surveys and interviews, focus groups can offer deeper insight into prospect and customer behaviour – from how users experience your products and services to what marketing messages really resonate with them.
Of course, as a market research method that’s reliant on a moderator to steer conversation, it can be subject to bias (as different moderators might have preferred questions or be more forceful) and if you cut corners (not asking all the necessary questions or making assumptions based on responses), the data could get skewed.
3) Observation
As if you were a fly-on-the-wall, the observation market research method can be incredibly powerful. Rather than interviewing or surveying users, you simply take notes while someone from your target market/target audience engages with your product . How are they using it? What are they struggling with? Do they look as though they have concerns?
Observing your target audience/target market in this fashion is a great alternative to the other more traditional methods on this list. It’s less expensive and far more natural as it isn’t guided by a moderator or a predefined set of questions. The only issue is that you can’t get feedback directly from the mouth of the user, so it’s worth combining this type of research with interviews, surveys, and/or focus groups.
4) Interviews
Interviews allow for face-to-face discussions (both in-person and virtually), allowing for more natural conversations with participants.
For gleaning deeper insights (especially with non-verbal cues giving greater weight to opinions), there’s nothing better than face-to-face interviews. Any kind of interview will provide excellent information, helping you to better understand your prospects and target audience/target market.
Use cases for market research
When you want to understand your prospects and/or customers, but have no existing data to set a benchmark – or want to improve your products and services quickly – market research is often the go-to.
Market research (as mentioned above), helps you to discover how prospects and customers feel about your products and services, as well as what they would like to see .
But there are more use cases and benefits to market research than the above.
Reduce risk of product and business failure
With any new venture, there’s no guarantee that the new idea will be successful. As such, it’s up to you to establish the market’s appetite for your product or service. The easiest way to do this is through market research – you can understand the challenges prospects face and quickly identify where you can help. With the data from your market survey, you can then create a solution that addresses the needs and expectations of would-be customers.
Forecast future trends
Market research doesn’t just help you to understand the current market – it also helps you to forecast future needs. As you conduct your research and analyse the findings, you can identify trends – for example, how brands and businesses are adopting new technology to improve customer experiences or how sustainability is becoming a core focus for packaging. Whatever it is you’re looking to understand about the future of business in your market, comprehensive market research can help you to identify it.
Stay ahead of the competition
Understanding your market and what prospects and customers want from you will help to keep you ahead of the competition . The fact is that the top businesses frequently invest in market research to get an edge, and those that don’t tap into the insights of their audience are missing low-hanging fruit.
As well as helping you to stay in front, you can also use market research to identify gaps in the market, e.g. your competitors’ strengths and weaknesses . Just have participants answer questions about competitor products/services – or even use the products/services – and work out how you can refine your offerings to address these issues.
Plan more strategically
What’s the foundation of your business strategy? If it’s based on evidence, e.g. what people expect of your products and services, it’ll be much easier to deliver something that works. Rather than making assumptions about what you should do, market research gives you a clear, concrete understanding of what people want to see.
Check out our guide to market research for a more comprehensive breakdown.
How do you write a market research plan/template?
A market research plan is very similar to a brief in that it documents the most vital information and steps about your project. Consider it a blueprint that outlines your main objective (summary), key questions and outcomes, target audience and size, your timeline, budget, and other key variables.
Let’s talk about them in more detail.
Elements of a great market research plan
1) overview or summary.
Use the first section of your market research plan to outline the background to the problem that you are attempting to solve (this is usually your problem statement or problem question). Include background information on the study’s purpose and the business to provide context to those who would read the report, as well as the need for the research. Keep the overview simple and concise; focus on the most salient elements.
2) Objectives
What is it that you hope to achieve with this survey? Your objectives are the most important part of the survey. Make sure to list 3-5 of the decisions or initiatives that the research will influence.
For example:
Understand the most-used channels for customer engagement and purchasing to decide where to prioritise marketing and sales budget in Q1 2022. Determine what’s causing customer churn at the later stages of the buyer journey and implement a new retention and sales strategy to address it.
Your objectives should be smart, that is: Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, and Timely.
3) Deliverables (or outcomes)
This section should focus on what you expect to have at the end of the project. How many responses are you looking for? How will the data be presented? Who will the data be shared with? (Stakeholders, executives) What are your next steps? Make sure you state how you will collect and analyse the data once it’s available.
Products such as Qualtrics CoreXM make this process fast and incredibly easy to do, drastically reducing the time to insights so you can make more meaningful changes, faster.
4) Target audience
Not to be confused with your market research sample, your target audience represents who you want to research. Of course, your sample may include ideal buyers from your target audience. Here you want to define the main variables or factors of your audience: demographic , age, location , product interaction, experience, and so on. It’s worth building out your buyer personas (if you haven’t already) and including a quick breakdown of them here.
5) Sample plan
How many participants do you want to research and what kind of groups do you want to reach? Depending on these two variables, you may have to use qualitative, quantitative , or multi-method approaches.
6) Research methods
What methods will you use in your market research project? The insights (and the granularity of those insights) will depend on the methods and tools you choose. For example, and as mentioned earlier, surveys are often the go-to for many organisations as they’re affordable and straightforward, but if you want to get more personal views from your respondents, one-to-one interviews might be more applicable. You might even want to take a hands-off approach and simply observe participants as they use your products, or try a combination of research methods. Make sure to outline what methods you will use as part of your research plan.
7) Timeline
How long will your research project run? It’s worth putting together a Gantt chart to highlight key milestones in the project, along with dependencies, and to break down tasks as much as possible. Schedule in contingency time in case some tasks or research runs over – or you need more responses.
Set a budget for the overall program and list it in your plan. Though this might be the most difficult aspect of any research plan, it helps you to be more strategic about tasks and hold people accountable at each stage of the process. If costs go over, that’s good to know for future market research. If costs are lower than anticipated, you then have the opportunity to do further research or prop up other areas of the study.
9) Ethical concerns or conflicts of interest
One of the most important parts of your market research plan, you should highlight any ethical concerns. To begin with, it’s your duty to state whether or not responses will be kept confidential and anonymous as part of the study. It’s also important to allow participants to remain anonymous and ensure you protect their privacy at all times.
Another issue to consider is stereotyping. Any analysis of real populations needs to make approximations and place individuals into groups, but if conducted irresponsibly, stereotyping can lead to undesirable results.
Lastly, conflicts of interest – it may be that researchers have interests in the outcome of the project that lead to a personal advantage that might compromise the integrity of your market research project. You should clearly state in your market research report that any potential conflicts of interest are highlighted and addressed before continuing.
But I want a faster solution!
Well, there’s a quicker and far easier way to do all of the above and get the data you need – just use a market research survey template. In our next section, we’re going to share a whole list of templates that you can use.
Free market research survey templates
No matter what kind of research you want to conduct, we have templates that will remove the complexity of the task and empower you to get more from your data. Below we’ve compiled a list of templates for four key experience areas: Brand Equity , Customer , Employee , and Product .
All of our research templates are free. All you need to do is sign up for a free Qualtrics account to access them.
Brand experience market research templates:
- Logo testing : Collect feedback to help you evaluate and iterate on your logo designs and concepts
- Brand awareness : Track the level of brand awareness in your target market, including current and potential future customers
- Ad testing : Evaluate your consumers’ reaction to an advertisement so you know which campaigns to deploy before you invest
- A/B testing : Quickly and easily compare to versions or options in a study, whether it’s a design, headline, color palette or a mock-up of your latest ad campaign
Customer experience market research templates
- Student satisfaction : Gather feedback on how your institution is delivering on the student experience
- Net promoter score (NPS) : Measure customer loyalty and understand how they feel about your product or service using one of the world’s best-recognized metrics
- Customer satisfaction : Evaluate how satisfied your customers are with your company, including the products and services you provide, and how they are treated when they buy from you
- Customer service : Gain insights into the contact centre experience, so you can achieve and maintain optimum levels of customer experience (CX) performance
- Event feedback : Measure the effectiveness of your events and how well they meet attendee expectations so that you can continuously improve your offering
- IT help desk : Understand how satisfied your employees and customers are with your IT help desk experience
- Website suggestion box : Collect visitor feedback on how your website can be improved
- Website satisfaction : Find out how satisfied visitors are with your website’s design, usability, and performance
- Store purchase feedback : Capture customer experience data at the point of purchase to help you improve the in-store experience
- Online purchase feedback : Find out how well your online shopping experience performs against customer needs and expectations
Employee experience market research templates
- Employee satisfaction : Get an overview of your current employee experience
- Manager feedback : Improve your skills as a leader with valuable feedback from your team
- Employee engagement : Find out how employees find the current experience at your workplace with this entry-level engagement survey
- Employee exit interview : Understand why your employees are leaving and how they’ll speak about your company once they’re gone with this survey template
- Employee onboarding : Improve your onboarding program by understanding what’s working and what’s not
- Team event planning : Collect inputs from employees to plan a team event that works for everyone
- Meeting feedback : Check-in with team members after a meeting to see how well your company is running and what improvements can be made
- Interview feedback : Improve your candidate experience by gathering actionable insights about the interview process
- Employee suggestion box : Gather anonymous data to help address concerns and improve the employee experience in your organization
- Candidate experience : Improve your candidate experience to increase brand perception, offer acceptance rates, and hiring process efficiency with this single-touchpoint survey template
- Employee suggestion action : Take employee feedback a step further by working with your staff to quantify solutions based on their experience data
Product experience market research templates
- Product research : Evaluate your consumers’ reaction to a new product or product feature across every stage of the product development journey
- Pricing : Understand how to set the exact price point for your product or service, according to your target consumers
- Feature prioritisation : Compare and contrast product features using conjoint analysis to find the optimal mix for your customers
- Product package testing : Collect feedback on your product packaging to see how well it meets the needs and expectations of your customers
Armed with the right market research templates, getting the information you need across brand, product, customer and employee disciplines — as well as beyond — is significantly easier.
But if you want help putting together complex market research and scaling your in-house research team to get agile insights, check out our guide to building an agile research function.
Insights are more important than ever, especially during times of change, but building a great team takes a lot of time and money.
In our eBook, we’ll explain how you can:
- Scale your research team
- Build a smart partner strategy
- Ensure you have the right technology for market research and data analysis
Tackle your market research with our agile market research eBook
Related resources
Market intelligence tools 10 min read, qualitative research questions 11 min read, primary vs secondary research 14 min read, business research methods 12 min read, ethnographic research 11 min read, business research 10 min read, qualitative research design 12 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?

COMMENTS
Here's an example outline of a research plan you might put together: Project title. Project members involved in the research plan. Purpose of the project (provide a summary of the research plan's intent) Objective 1 (provide a short description for each objective) Objective 2. Objective 3.
The 7 core components of a user research plan: The background of the research project detailing why we are conducting this study. This can also include the internal stakeholders involved. The objectives and goals of the research, what the teams want to learn from the research, or what they would like the outcome to be.
A research plan is a comprehensive document that outlines the entirety of your research project. It details the research process, from defining the problem statement and research objectives to selecting the research method and outlining the expected outcomes. This plan serves as a blueprint for your research activities, ensuring a focused and ...
Master templates are the best way to create a successful and effective UX research plan. Using a template as a starting point makes planning and writing easier and helps you and your team stay focused on the who, what, why, and when of research. Read on for tips and examples for how you can build a user research plan that works.
6. Prepare the brief. The next component of a research plan is to create a brief or guide for your research sessions. The kind of brief you need will vary depending on your research method, but for moderated methods like user interviews, field studies, or focus groups, you'll need a detailed guide and script.
A UX research plan, also known as a user research plan, is a brief reference document that outlines your research project's goals, key contributors, important dates, and timelines. Think of your research plan as a UX-focused kick-off document for your project. The plan offers an overview of the research initiative, encourages well-defined and ...
Step 1: Alignment & Requirements Gathering. Research rarely will happen in a vacuum. Usually you are working with a team—product, engineering, design, for example. When the need for a research study arises, the first thing you want to do is meet with your team to understand the questions they're trying to answer.
How to plan a UX research study. This is a step-by-step guide to planning user research. It explains the process by which a research plan comes together into a shareable document (like the one above) that enables team alignment, accountability, and efficiency throughout your study. 1. Identify your research goals.
By completing this Research Plan Template, you'll have a clear roadmap for conducting your research activities effectively and gathering valuable insights to inform your UX design decisions. Remember that a well-planned research phase sets the foundation for a successful and user-centered design process. Happy researching!
A research plan example is a document that introduces your main question and how you intend to uncover the answer. They often include details like the surrounding context, objectives, methods, budget, timeline, and more to help you learn more about and eventually solve a customer's pain point or an ineffective interface.
A research plan communicates important information about the who, what, why, when of research. Together with the research roadmap and protocol, these documents ensure everyone is aligned and know their roles in the research. To create research plans quickly, I have a master template to use as a starting point for every project.
UX research is the study of user interaction to obtain insights that improve the design process. UX researchers study a group of target users to collect and analyze data that leads to user-friendly products. The primary goal of UX research is to build products for the end-user based on real data not what you think the user wants.
If you want to learn how to write your own plan for your research project, consider the following seven steps: 1. Define the project purpose. The first step to creating a research plan for your project is to define why and what you're researching. Regardless of whether you're working with a team or alone, understanding the project's purpose can ...
1. ClickUp User Research Plan Template. ClickUp User Research Plan Template. One of the first things that comes to mind when you say "research plan template" is user research. For development and project teams, this is one step of the process where strategy and staying organized is essential.
This UX Research Plan template is designed for UX researchers, UX Designers, Product Designers, and anyone else who wants to conduct an in-depth research session. ... Creating impactful, optimised experiences through research, analysis, and design. Proud recipient of the Miro Choice Award 2023 - Research & Design category 🥇🎉. Join me on ...
Craft a clear problem statement. As with most plans, you should start by clearly identifying and stating the problem that you're trying to solve. A UX research plan is no different. Your problem statement should be clear, specific, and give enough detail that stakeholders understand what the research is trying to solve.
UX Research Process & UX Research Plan Template. UX research is a fairly complex process with a wide array of ins and outs — all essential to extracting actionable insight to inform your design ...
142 users. Open in FigJam. About. Comments 0. Use this template to align your team on the goals of your research, and the methods, timelines and budgets required for your project. This template is part of a larger article: How to Write a UX Research Plan That Actually Works: 7-Step Tutorial. Made with ️ by the team at Looppanel.
UX Research Plan Template. From Objective to Timeline. UX research is a complex process. To get the most of it, the process has to be organized. Even if your research consists of just a few interviews, you need a plan to make it effective and focused and not to end up with vague conversations. With a good research plan, all the team will be on ...
Step 1: Consider your aims and approach. Step 2: Choose a type of research design. Step 3: Identify your population and sampling method. Step 4: Choose your data collection methods. Step 5: Plan your data collection procedures. Step 6: Decide on your data analysis strategies. Other interesting articles.
The research plan is a document that clarifies how to approach the research, touching upon research goals, selected methodologies, types of participants and tools used, timeline and locations. This planning activity needs to be done upfront, before starting the actual research, and help maximizing the effort and modeling the activities in the ...
A research plan is a framework that shows how you intend to approach your topic. The plan can take many forms: a written outline, a narrative, a visual/concept map or timeline. It's a document that will change and develop as you conduct your research. Components of a research plan. 1. Research conceptualization - introduces your research question.
Design Research Plan. Discuss and document how you will gather the information you need to build your product. Identify the activities, timeline and budget your team will need to test and validate assumptions or answer open questions with all potential stakeholders.
What is a market research template? While you're no doubt familiar with the concept of market research and how it can help you to reach your target audiences and improve your product or service, the real challenge is designing a market research plan that is conducive to excellent results.. All of this starts with the right market research template(s) to help you analyse specific target ...
Use this infographic template for PowerPoint to design your next portfolio. It contains 34 well-made, unique infographic slide options. It also features: ... PowerPoint infographic templates like this help you pitch a business plan. Use this fully customizable, well-organized PPT to show what keeps your team moving. ... research; business and ...