CPM Educational Program
Expert textbook solutions.
Browse your textbook to find expert solutions, hints, and answers for all exercises. The solutions are always presented as a clear and concise, step-by-step explanation with included theory and helpful figures, graphs, and diagrams. Mathleaks covers the most commonly adopted textbooks with more than 250000 expert solutions.

Mathleaks Solver
With Mathleaks, you’re not tied to your textbook for solutions. Instead, scan and solve exercises with our math solver, which instantly reads the problem by using the camera on your smartphone or tablet. Access the solver through the Mathleaks app or on our website. The Mathleaks solver works for Pre-Algebra, Algebra 1, and Algebra 2.
Mathleaks Community
Get access to the world's most popular math community with Mathleaks. You can connect with other students all over the US who are studying with the same textbook or in the same math course.
Study math more efficiently using Mathleaks for CPM Educational Program textbooks.
- Core Connections Integrated I, 2013
- Core Connections Algebra 1, 2013
- Core Connections Geometry, 2013
- Core Connections Algebra 2, 2013
- Core Connections Integrated I, 2014
- Core Connections Integrated II, 2015
- Core Connections: Course 1
- Core Connections: Course 2
- Core Connections: Course 3
- Core Connections Integrated III, 2015
CPM Student Tutorials
Cc course 3 etools, other resources.
- Student: CPM eBooks (Student Version)
- Student: eWorkspace
- Parent: eBook Support
- Trouble Shooting
- Creating Desmos eTools
- Creating CPM eTools
- Algebra Videos
- Problem Solving Videos
- Statistics Videos
- TI-84 Graphing Calculator
- Student: Presentation Tools
- CC Course 1 eTools
- CC Course 2 eTools
- CC Algebra eTools
- CC Geometry eTools
- CC Algebra 2 eTools
- CC Integrated I eTools
- CC Integrated II eTools
- CC Integrated III eTools
- Pre-Calc. w/Trig
- Making Connections 1
- Making Connections 2
- Algebra Connections
- Geometry Connections
- Algebra 2 Connections
- Foundations For Algebra 1
- Foundations For Algebra 2
General eTools
- Algebra Tiles (CPM)
- Pattern Tile & Dot Tool (CPM)
- Base Ten Blocks (CPM)
- Area and Perimeter (CPM)
- Desmos Graphing Calculator
- Data Representations (CPM)
- Rigid Transformations eTool (CPM)
- CC3 1.1.2: 1-9 Student eTool (CPM)
- CC3 1.1.2: 1-10 Student eTool (CPM)
- CC3 1.1.4: 1-25b Newton's Revenge Teacher eTool (Desmos)
- CC3 1.2.1: 1-42 Student eTool (Desmos)
- CC3 2.1.4: 2-36 Student eTool (CPM)
- CC3 2.1.5: 2-47 Student eTool (CPM)
- CC3 2.1.5: 2-49a and 2-49b Student eTools (CPM)
- CC3 2.1.6: 2-56a to 2-56f Student eTools (CPM)
- CC3 2.1.6: 2-57 Student eTool (CPM)
- CC3 2.1.7: 2-64, 2-65, 2-66a & 2-66b Student eTools (CPM)
- CC3 2.1.8: 2-72 & 2-74 Student eTools (CPM)
- CC3 2.1.9: 2-82a, 2-82b, & 2-82c Student eTools (CPM)
- CC3 3.1.1: 3-1a & 3-1b Student eTool (CPM)
- CC3 3.1.2: Redwoods: The Tallest Trees Video
- CC3 3.1.2: 3-11&12 John's Giant Redwood Student eTool (Desmos)
- CC3 3.1.3: 3-18 Student eTool (Desmos)
- CC3 3.1.3: 3-19 to 3-22 Student eTool (Desmos)
- CC3 3.2.1: 3-70 Student eTool (CPM)
- CC3 4.1.2: 4-12, 4-13a, 4-13b, and 4-15 Student eTools (CPM)
- CC3 4.1.3: 4-22 Student eTool (Desmos)
- CC3 4.1.7: 4-65 Student eTool (Desmos)
- CC3 5.1.1: 5-2b Student eTool (CPM)
- CC3 5.2.1: Iditarod- Checkpoints Video
- CC3 5.2.1: 5-23 Student eTool (Desmos)
- CC3 5.2.3: 5-42 Student eTool (CPM)
- CC3 6.1.1: Key-Lock Puzzle (CPM)
- CC3 6.1.2: Transformation Challenge 1 & 2 (CPM)
- CC3 6.1.3: 6-18 Student eTool (Desmos)
- CC3 6.1.3: 6-24 Student eTool (CPM)
- CC3 6.2.1: 6-43 Student eTool (Desmos)
- CC3 6.2.2: 6-52, 6-53, & 6-56 Student eTools (Desmos)
- CC3 7.1.2: 7-15 Student eTool (Desmos)
- CC3 7.2.2: 7-43 Student eTool (Desmos)
- CC3 7.2.3: 7-56 & 7-59 Student eTools (Desmos)
- CC3 7.3.1: 7-87 Student eTool (Desmos)
- CC3 7.3.2: 7-97 Student eTool (Desmos)
- CC3 8.1.1: 8-2 and 8-3 Student eTools (Desmos)
- CC3 8.1.2: 8-14 Student eTool (Desmos)
- CC3 8.2.3: Powers of Ten Film
- CC3 9.2.3: 9-85 Student eTool (Desmos)
- CC3 9.2.4: 9-105 ShowMe video
- CC3 9.2.6: 3D Model Box (CPM)
- CC3 9.2.7: Pythagorean Proof Video
- CC3 10.1.3: Volume of a Pyramid Video
- CC3 10.1.3: Volume of a Cone
- CC3 10.1.3: Volume of a Sphere
3 π 2 3 π 2
−135 ° −135 °
7 π 10 7 π 10
α = 150° α = 150°
β = 60° β = 60°
7 π 6 7 π 6
215 π 18 = 37.525 units 215 π 18 = 37.525 units
− 3 π 2 − 3 π 2 rad/s
1655 kilometers per hour
7.2 Right Triangle Trigonometry
sin t = 33 65 , cos t = 56 65 , tan t = 33 56 , sec t = 65 56 , csc t = 65 33 , cot t = 56 33 sin t = 33 65 , cos t = 56 65 , tan t = 33 56 , sec t = 65 56 , csc t = 65 33 , cot t = 56 33
sin ( π 4 ) = 2 2 , cos ( π 4 ) = 2 2 , tan ( π 4 ) = 1 , sec ( π 4 ) = 2 , csc ( π 4 ) = 2 , cot ( π 4 ) = 1 sin ( π 4 ) = 2 2 , cos ( π 4 ) = 2 2 , tan ( π 4 ) = 1 , sec ( π 4 ) = 2 , csc ( π 4 ) = 2 , cot ( π 4 ) = 1
adjacent = 10 ; opposite = 10 3 ; adjacent = 10 ; opposite = 10 3 ; missing angle is π 6 π 6
About 52 ft
7.3 Unit Circle
cos ( t ) = − 2 2 , sin ( t ) = 2 2 cos ( t ) = − 2 2 , sin ( t ) = 2 2
cos ( π ) = − 1 , sin ( π ) = 0 cos ( π ) = − 1 , sin ( π ) = 0
sin ( t ) = − 7 25 sin ( t ) = − 7 25
approximately 0.866025403
- ⓐ cos ( 315° ) = 2 2 , sin ( 315° ) = – 2 2 cos ( 315° ) = 2 2 , sin ( 315° ) = – 2 2
- ⓑ cos ( − π 6 ) = 3 2 , sin ( − π 6 ) = − 1 2 cos ( − π 6 ) = 3 2 , sin ( − π 6 ) = − 1 2
( 1 2 , − 3 2 ) ( 1 2 , − 3 2 )
7.4 The Other Trigonometric Functions
sin t = − 2 2 cos t = 2 2 , tan t = − 1 , s e c t = 2 , csc t = − 2 , cot t = − 1 sin t = − 2 2 cos t = 2 2 , tan t = − 1 , s e c t = 2 , csc t = − 2 , cot t = − 1
sin π 3 = 3 2 , cos π 3 = 1 2 , tan π 3 = 3 , s e c π 3 = 2 , c s c π 3 = 2 3 3 , c o t π 3 = 3 3 sin π 3 = 3 2 , cos π 3 = 1 2 , tan π 3 = 3 , s e c π 3 = 2 , c s c π 3 = 2 3 3 , c o t π 3 = 3 3
sin ( − 7 π 4 ) = 2 2 , cos ( − 7 π 4 ) = 2 2 , tan ( − 7 π 4 ) = 1 , sec ( − 7 π 4 ) = 2 , csc ( − 7 π 4 ) = 2 , cot ( − 7 π 4 ) = 1 sin ( − 7 π 4 ) = 2 2 , cos ( − 7 π 4 ) = 2 2 , tan ( − 7 π 4 ) = 1 , sec ( − 7 π 4 ) = 2 , csc ( − 7 π 4 ) = 2 , cot ( − 7 π 4 ) = 1
sin t sin t
cos t = − 8 17 , sin t = 15 17 , tan t = − 15 8 csc t = 17 15 , cot t = − 8 15 cos t = − 8 17 , sin t = 15 17 , tan t = − 15 8 csc t = 17 15 , cot t = − 8 15
sin t = − 1 , cos t = 0 , tan t = Undefined sec t = Undefined, csc t = − 1 , cot t = 0 sin t = − 1 , cos t = 0 , tan t = Undefined sec t = Undefined, csc t = − 1 , cot t = 0
sec t = 2 , csc t = 2 , tan t = 1 , cot t = 1 sec t = 2 , csc t = 2 , tan t = 1 , cot t = 1
≈ − 2.414 ≈ − 2.414
7.1 Section Exercises
Whether the angle is positive or negative determines the direction. A positive angle is drawn in the counterclockwise direction, and a negative angle is drawn in the clockwise direction.
Linear speed is a measurement found by calculating distance of an arc compared to time. Angular speed is a measurement found by calculating the angle of an arc compared to time.
4 π 3 4 π 3
2 π 3 2 π 3
7 π 2 ≈ 11.00 in 2 7 π 2 ≈ 11.00 in 2
81 π 20 ≈ 12.72 cm 2 81 π 20 ≈ 12.72 cm 2
π 2 π 2 radians
−3 π −3 π radians
π π radians
5 π 6 5 π 6 radians
5.02 π 3 ≈ 5.26 5.02 π 3 ≈ 5.26 miles
25 π 9 ≈ 8.73 25 π 9 ≈ 8.73 centimeters
21 π 10 ≈ 6.60 21 π 10 ≈ 6.60 meters
104.7198 cm 2
0.7697 in 2
8 π 9 8 π 9
1320 1320 rad/min 210.085 210.085 RPM
7 7 in./s, 4.77 RPM , 28.65 28.65 deg/s
1 , 809 , 557.37 mm/min = 1 , 809 , 557.37 mm/min = 30.16 m/s 30.16 m/s
5.76 5.76 miles
794 miles per hour
2,234 miles per hour
11.5 inches
7.2 Section Exercises
The tangent of an angle is the ratio of the opposite side to the adjacent side.
For example, the sine of an angle is equal to the cosine of its complement; the cosine of an angle is equal to the sine of its complement.
b = 20 3 3 , c = 40 3 3 b = 20 3 3 , c = 40 3 3
a = 10,000 , c = 10,00.5 a = 10,000 , c = 10,00.5
b = 5 3 3 , c = 10 3 3 b = 5 3 3 , c = 10 3 3
5 29 29 5 29 29
5 41 41 5 41 41
c = 14 , b = 7 3 c = 14 , b = 7 3
a = 15 , b = 15 a = 15 , b = 15
b = 9.9970 , c = 12.2041 b = 9.9970 , c = 12.2041
a = 2.0838 , b = 11.8177 a = 2.0838 , b = 11.8177
a = 55.9808 , c = 57.9555 a = 55.9808 , c = 57.9555
a = 46.6790 , b = 17.9184 a = 46.6790 , b = 17.9184
a = 16.4662 , c = 16.8341 a = 16.4662 , c = 16.8341
498.3471 ft
22.6506 ft
368.7633 ft
7.3 Section Exercises
The unit circle is a circle of radius 1 centered at the origin.
Coterminal angles are angles that share the same terminal side. A reference angle is the size of the smallest acute angle, t , t , formed by the terminal side of the angle t t and the horizontal axis.
The sine values are equal.
60° , 60° , Quadrant IV, sin ( 300° ) = − 3 2 sin ( 300° ) = − 3 2 , cos ( 300° ) = 1 2 cos ( 300° ) = 1 2
45° , 45° , Quadrant II, sin ( 135° ) = 2 2 sin ( 135° ) = 2 2 , cos ( 135° ) = − 2 2 cos ( 135° ) = − 2 2
60° , 60° , Quadrant II, sin ( 120° ) = 3 2 sin ( 120° ) = 3 2 , cos ( 120° ) = − 1 2 cos ( 120° ) = − 1 2
30° , 30° , Quadrant II, sin ( 150° ) = 1 2 sin ( 150° ) = 1 2 , cos ( 150° ) = − 3 2 cos ( 150° ) = − 3 2
π 6 , π 6 , Quadrant III, sin ( 7 π 6 ) = − 1 2 sin ( 7 π 6 ) = − 1 2 , cos ( 7 π 6 ) = − 3 2 cos ( 7 π 6 ) = − 3 2
π 4 , π 4 , Quadrant II, sin ( 3 π 4 ) = 2 2 sin ( 3 π 4 ) = 2 2 , cos ( 4 π 3 ) = − 2 2 cos ( 4 π 3 ) = − 2 2
π 3 , π 3 , Quadrant II, sin ( 2 π 3 ) = 3 2 sin ( 2 π 3 ) = 3 2 , cos ( 2 π 3 ) = − 1 2 cos ( 2 π 3 ) = − 1 2
π 4 , π 4 , Quadrant IV, sin ( 7 π 4 ) = − 2 2 , cos ( 7 π 4 ) = 2 2 sin ( 7 π 4 ) = − 2 2 , cos ( 7 π 4 ) = 2 2
− 15 4 − 15 4
( −10 , 10 3 ) ( −10 , 10 3 )
( –2.778 , 15.757 ) ( –2.778 , 15.757 )
[ –1 , 1 ] [ –1 , 1 ]
sin t = 1 2 , cos t = − 3 2 sin t = 1 2 , cos t = − 3 2
sin t = − 2 2 , cos t = − 2 2 sin t = − 2 2 , cos t = − 2 2
sin t = 3 2 , cos t = − 1 2 sin t = 3 2 , cos t = − 1 2
sin t = − 2 2 , cos t = 2 2 sin t = − 2 2 , cos t = 2 2
sin t = 0 , cos t = − 1 sin t = 0 , cos t = − 1
sin t = − 0.596 , cos t = 0.803 sin t = − 0.596 , cos t = 0.803
sin t = 1 2 , cos t = 3 2 sin t = 1 2 , cos t = 3 2
sin t = − 1 2 , cos t = 3 2 sin t = − 1 2 , cos t = 3 2
sin t = 0.761 , cos t = − 0.649 sin t = 0.761 , cos t = − 0.649
sin t = 1 , cos t = 0 sin t = 1 , cos t = 0
− 6 4 − 6 4
( 0 , –1 ) ( 0 , –1 )
37.5 seconds, 97.5 seconds, 157.5 seconds, 217.5 seconds, 277.5 seconds, 337.5 seconds

7.4 Section Exercises
Yes, when the reference angle is π 4 π 4 and the terminal side of the angle is in quadrants I and III. Thus, a x = π 4 , 5 π 4 , x = π 4 , 5 π 4 , the sine and cosine values are equal.
Substitute the sine of the angle in for y y in the Pythagorean Theorem x 2 + y 2 = 1. x 2 + y 2 = 1. Solve for x x and take the negative solution.
The outputs of tangent and cotangent will repeat every π π units.
2 3 3 2 3 3
− 2 3 3 − 2 3 3
− 3 3 − 3 3
sin t = − 2 2 3 sin t = − 2 2 3 , sec t = − 3 sec t = − 3 , csc t = − 3 2 4 csc t = − 3 2 4 , tan t = 2 2 tan t = 2 2 , cot t = 2 4 cot t = 2 4
sec t = 2 , sec t = 2 , csc t = 2 3 3 , csc t = 2 3 3 , tan t = 3 , tan t = 3 , cot t = 3 3 cot t = 3 3
− 2 2 − 2 2
sin t = 2 2 sin t = 2 2 , cos t = 2 2 cos t = 2 2 , tan t = 1 tan t = 1 , cot t = 1 cot t = 1 , sec t = 2 sec t = 2 , csc t = 2 csc t = 2
sin t = − 3 2 sin t = − 3 2 , cos t = − 1 2 cos t = − 1 2 tan t = 3 tan t = 3 , cot t = 3 3 cot t = 3 3 , sec t = − 2 sec t = − 2 , csc t = − 2 3 3 csc t = − 2 3 3
sin ( t ) ≈ 0.79 sin ( t ) ≈ 0.79
csc t ≈ 1.16 csc t ≈ 1.16
sin t cos t = tan t sin t cos t = tan t
13.77 hours, period: 1000 π 1000 π
3.46 inches
Review Exercises
− 7 π 6 − 7 π 6
10.385 meters
2 π 11 2 π 11
1036.73 miles per hour
a = 10 3 , c = 2 106 3 a = 10 3 , c = 2 106 3
a = 5 3 2 , b = 5 2 a = 5 3 2 , b = 5 2
369.2136 ft
all real numbers
cosine, secant
Practice Test
6.283 centimeters
3.351 feet per second, 2 π 75 2 π 75 radians per second
a = 9 2 , b = 9 3 2 a = 9 2 , b = 9 3 2
real numbers
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/algebra-and-trigonometry/pages/1-introduction-to-prerequisites
- Authors: Jay Abramson
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Algebra and Trigonometry
- Publication date: Feb 13, 2015
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/algebra-and-trigonometry/pages/1-introduction-to-prerequisites
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/algebra-and-trigonometry/pages/chapter-7
© Dec 8, 2021 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
CHAPTER 7 KEYS:
Reviews & skills keys:.

Home > INT2 > Chapter 7 > Lesson 7.1.3
Lesson 7.1.1, lesson 7.1.2, lesson 7.1.3, lesson 7.1.4, lesson 7.1.5, lesson 7.2.1, lesson 7.2.2, lesson 7.2.3.
© 2022 CPM Educational Program. All rights reserved.
7.2.3.5 Packet Tracer – Troubleshooting EIGRP for IPv4 Instructions Answers
Packet tracer – troubleshooting eigrp for ipv4 (instructor version).
Instructor Note : Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only.
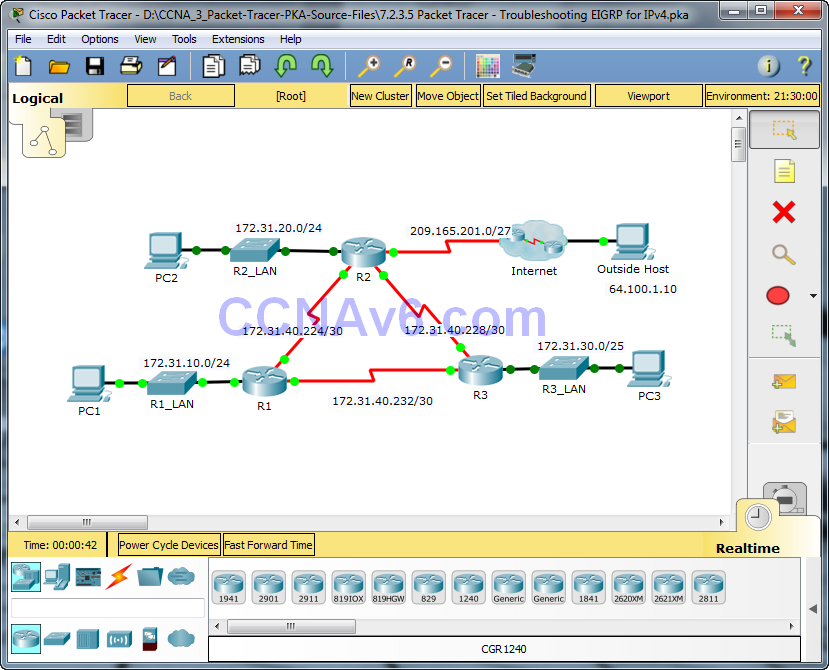
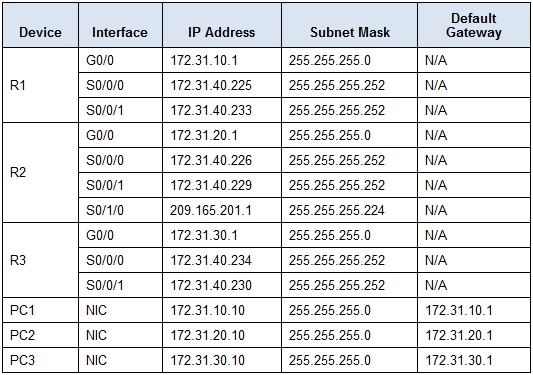
Addressing Table
In this activity, you will troubleshoot EIGRP neighbor issues. Use show commands to identify errors in the network configuration. Then, you will document the errors you discover and implement an appropriate solution. Finally, you will verify full end-to-end connectivity is restored.
Troubleshooting Process
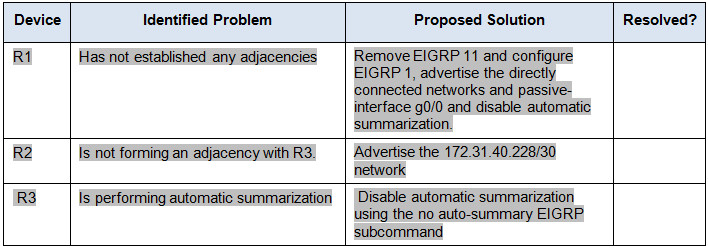
a. Use testing commands to discover connectivity problems in the network and document the problem in the Documentation Table.
b. Use verification commands to discover the source of the problem and devise an appropriate solution to implement. Document the proposed solution in the Documentation Table.
c. Implement each solution one at a time and verify if the problem is resolved. Indicate the resolution status in the Documentation Table.
d. If the problem is not resolved, it may be necessary to first remove the implemented solution before returning to Step 2.
e. Once all identified problems are resolved, test for full end-to-end connectivity.
Documentation Table
Download Packet Tracer (.pka) file:
7.2.3.5 packet tracer - troubleshooting eigrp for ipv4.pka 136.61 kb 3855 downloads.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
CPM Education Program proudly works to offer more and better math education to more students.
Illustrative Mathematics Grade 7 Open Up Resources OURUnit 2 Lesson 3More resources available at: mathhelp.cusd.com
CPM Education Program proudly works to offer more and better math education to more students.
Our resource for Core Connections Integrated 3 includes answers to chapter exercises, as well as detailed information to walk you through the process step by step. With Expert Solutions for thousands of practice problems, you can take the guesswork out of studying and move forward with confidence. Find step-by-step solutions and answers to Core ...
Mathleaks offers the ultimate homework help and much of the content is free to use. Browse the textbooks below or by downloading the Mathleaks app for free on Google Play or the App Store. Start CPM Educational Program. Show more. Core Connections Integrated I, 2013. ISBN: 9781603283083. undefined Textbooks Show chapters.
Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy-to-learn solution you can count on. Question: Exercise 7.2.3: Algebraic and geometric multiplicity Consider the matrix A= 1-4 0 0 01 JO -4 0 0 | 2 2 0 (3 4 -1 -4] (a) What are the eigenvalues of A and what is their algebraic multiplicity? (b) What is the geometric multiplicity of X = 2 ...
CC3 6.1.1: Key-Lock Puzzle (CPM) CC3 6.1.2: Transformation Challenge 1 & 2 (CPM) CC3 6.1.3: 6-18 Student eTool (Desmos) CC3 6.1.3: 6-24 Student eTool (CPM) CC3 6.2.1: 6-43 Student eTool (Desmos) CC3 6.2.2: 6-52, 6-53, & 6-56 Student eTools (Desmos)
Exercise 68. Exercise 69. Exercise 70. Exercise 71. Find step-by-step solutions and answers to Core Connections Course 3 - 9781603280914, as well as thousands of textbooks so you can move forward with confidence.
Introduction to Systems of Equations and Inequalities; 11.1 Systems of Linear Equations: Two Variables; 11.2 Systems of Linear Equations: Three Variables; 11.3 Systems of Nonlinear Equations and Inequalities: Two Variables; 11.4 Partial Fractions; 11.5 Matrices and Matrix Operations; 11.6 Solving Systems with Gaussian Elimination; 11.7 Solving Systems with Inverses; 11.8 Solving Systems with ...
Chapter 7 Team Quiz Review KEY.pdf. Review for Team Quiz HW Key.pdf. Ch 7 Review HW KEY.pdf
Question: 7.2.3 Use the differential equation approach to find i0 (t) for t>0 in the network in Fig. P7.2.3. Show transcribed image text. There are 2 steps to solve this one. Expert-verified.
Step 1. To determine whether there is significant evidence for Ha (alternative hypothesis) in each of the si... 7.2.3 For each of the following situations, suppose H 0: μ1 = μ2 is being tested against H A:μ1 =μ2. State whether or not there is significant evidence for H A. a. P -value =0.085,a=0.10. b. P -value =0.065,a=0.050.
7-53. Solve this problem by defining a variable, writing an equation, and solving it. Write your solution in a sentence. The number of students attending the fall play was 150 fewer than three times the number of adults. Together, students and adults purchased 1778 tickets. How many students attended the fall play? Bringing more math to more ...
Our resource for enVisionmath 2.0: Grade 7, Volume 2 includes answers to chapter exercises, as well as detailed information to walk you through the process step by step. With Expert Solutions for thousands of practice problems, you can take the guesswork out of studying and move forward with confidence. Find step-by-step solutions and answers ...
SRWE Final Skills Exam (PTSA) Final Exam. CCNA 2 v7 FINAL Exam Answers. Test. CCNA Semester 2 (SRWE v7.0) Packet Tracer Activity (Answers) 1.3.6 Packet Tracer - Configure SSH. 1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Configure Router Interfaces. 1.5.10 Packet Tracer - Verify Directly Connected Networks.
OUR 7.2.3 Practice Problems • Teacher Guide - Desmos ... Loading...
CPM Education Program proudly works to offer more and better math education to more students.
Here's the best way to solve it. ACTIVITY 7.2.3: Exce: Confidence intervals for a proportion Click this link to download the spreadsheet for use in this activity Critical values for quick reference during this activity. Confidence level Critical value 0.90 z = 1.645 0.95 z* = 1.960 0.99 * = 2.576 Start The manager of a bookstore with a coffee ...
Troubleshooting Process. a. Use testing commands to discover connectivity problems in the network and document the problem in the Documentation Table. b. Use verification commands to discover the source of the problem and devise an appropriate solution to implement. Document the proposed solution in the Documentation Table.
In Exercise 7.2.3 problem \#8, you were asked to write an equation for a polynomial function containing the given features. This polynomial will be of the form f (x)= a(x+4)(x+b)(x−c). Please select the following correct values for the variables a,b, and c : a= b= c= All zeros for f (x) have a multiplicity of As x approaches infinity, f (x ...
Step 7 of 8. For Exercise 7.2.4, Let be the random sample of size from , the corresponding probability mass function is, The likelihood function is, Thus, differentiating the log-likelihood function, then, Setting it to zero, Step 8 of 8. Solving the equation, it implies that the M.L.E. is,
Computer Science questions and answers. 4. Exercise 19. Referring to example 7.2.3, assume that records with the following ID numbers are to be placed in sequence in Table 7.2.1. Find the position into which each record is placed. a. 417302072 b. 364981703 C. 283090787.