Thematic Analysis: A Step by Step Guide
Saul McLeod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul McLeod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:

What is Thematic Analysis?
Thematic analysis is a qualitative research method used to identify, analyze, and interpret patterns of shared meaning (themes) within a given data set, which can be in the form of interviews , focus group discussions , surveys, or other textual data.
Thematic analysis is a useful method for research seeking to understand people’s views, opinions, knowledge, experiences, or values from qualitative data.
This method is widely used in various fields, including psychology, sociology, and health sciences.
Thematic analysis minimally organizes and describes a data set in rich detail. Often, though, it goes further than this and interprets aspects of the research topic.
Key aspects of thematic analysis include:
- Flexibility : It can be adapted to suit the needs of various studies, providing a rich and detailed account of the data.
- Coding : The process involves assigning labels or codes to specific data segments that capture a single idea or concept relevant to the research question.
- Themes : Representing a broader level of analysis, encompassing multiple codes that share a common underlying meaning or pattern. They provide a more abstract and interpretive understanding of the data.
- Iterative process : Thematic analysis is recursive, not linear. Researchers move back and forth between phases, refining codes and themes as their understanding of the data evolves.
- Interpretation : The researcher interprets the identified themes to tell a compelling and insightful story about the data.
Many researchers mistakenly treat thematic analysis (TA) as a single, homogenous method. However, as Braun and Clarke emphasize, TA is more accurately described as an “umbrella term” encompassing a diverse family of approaches.
These approaches differ significantly in terms of their procedure and underlying philosophies regarding the nature of knowledge and the role of the researcher.
It’s important to note that the types of thematic analysis are not mutually exclusive, and researchers may adopt elements from different approaches depending on their research questions, goals, and epistemological stance.
The choice of approach should be guided by the research aims, the nature of the data, and the philosophical assumptions underpinning the study.
1. Coding Reliability Thematic Analysis
Coding reliability, frequently employed in the US, leans towards a positivist philosophy . It prioritizes objectivity and replicability, often using predetermined themes or codes.
Coding reliability TA emphasizes using coding techniques to achieve reliable and accurate data coding, which reflects (post)positivist research values.
This approach emphasizes the reliability and replicability of the coding process. It involves multiple coders independently coding the data using a predetermined codebook.
The goal is to achieve a high level of agreement among the coders, which is often measured using inter-rater reliability metrics.
This approach often involves a coding frame or codebook determined in advance or generated after familiarization with the data.
In this type of TA, two or more researchers apply a fixed coding frame to the data, ideally working separately.
Some researchers even suggest that some coders should be unaware of the research question or area of study to prevent bias in the coding process.
Statistical tests are used to assess the level of agreement between coders, or the reliability of coding. Any differences in coding between researchers are resolved through consensus.
This approach is more suitable for research questions that require a more structured and reliable coding process, such as in content analysis or when comparing themes across different data sets.
2. Reflexive Thematic Analysis
Braun and Clarke’s reflexive thematic analysis is an approach to qualitative data analysis that emphasizes researchers’ active role in knowledge construction.
It involves identifying patterns across data, acknowledging how researchers’ perspectives shape theme development, and critically reflecting on the analysis process throughout the study.
It acknowledges that the researcher’s subjectivity, theoretical assumptions, and interpretative framework shape the identification and interpretation of themes.
In reflexive TA, analysis starts with coding after data familiarization. Unlike other TA approaches, there is no codebook or coding frame. Instead, researchers develop codes as they work through the data.
As their understanding grows, codes can change to reflect new insights—for example, they might be renamed, combined with other codes, split into multiple codes, or have their boundaries redrawn.
If multiple researchers are involved, differences in coding are explored to enhance understanding, not to reach a consensus. The finalized coding is always open to new insights and coding.
Reflexive thematic analysis involves a more organic and iterative process of coding and theme development. The researcher continuously reflects on their role in the research process and how their own experiences and perspectives might influence the analysis.
This approach is particularly useful for exploratory research questions and when the researcher aims to provide a rich and nuanced interpretation of the data.
3. Codebook Thematic Analysis
Codebook TA, such as template, framework, and matrix analysis, combines coding reliability and reflexive elements.
Codebook TA, while employing structured coding methods like those used in coding reliability TA, generally prioritizes qualitative research values, such as reflexivity.
In this approach, the researcher develops a codebook based on their initial engagement with the data. The codebook contains a list of codes, their definitions, and examples from the data.
The codebook is then used to systematically code the entire data set. This approach allows for a more detailed and nuanced analysis of the data, as the codebook can be refined and expanded throughout the coding process.
It is particularly useful when the research aims to provide a comprehensive description of the data set.
Codebook TA is often chosen for pragmatic reasons in applied research, particularly when there are predetermined information needs, strict deadlines, and large teams with varying levels of qualitative research experience
The use of a codebook in this context helps to map the developing analysis, which is thought to improve teamwork, efficiency, and the speed of output delivery.
Why coding reliability doesn’t fit with reflexive TA:
- Using coding reliability measures in reflexive TA represents an attempt to quantify and control for subjectivity in a research approach that explicitly values the researcher’s unique contribution to knowledge construction.
- Braun and Clarke argue that such attempts to bridge the “divide” between positivist and qualitative research ultimately undermine the integrity and richness of the reflexive TA approach.
- The emphasis on coding consistency can stifle the very reflexivity that reflexive TA encourages.
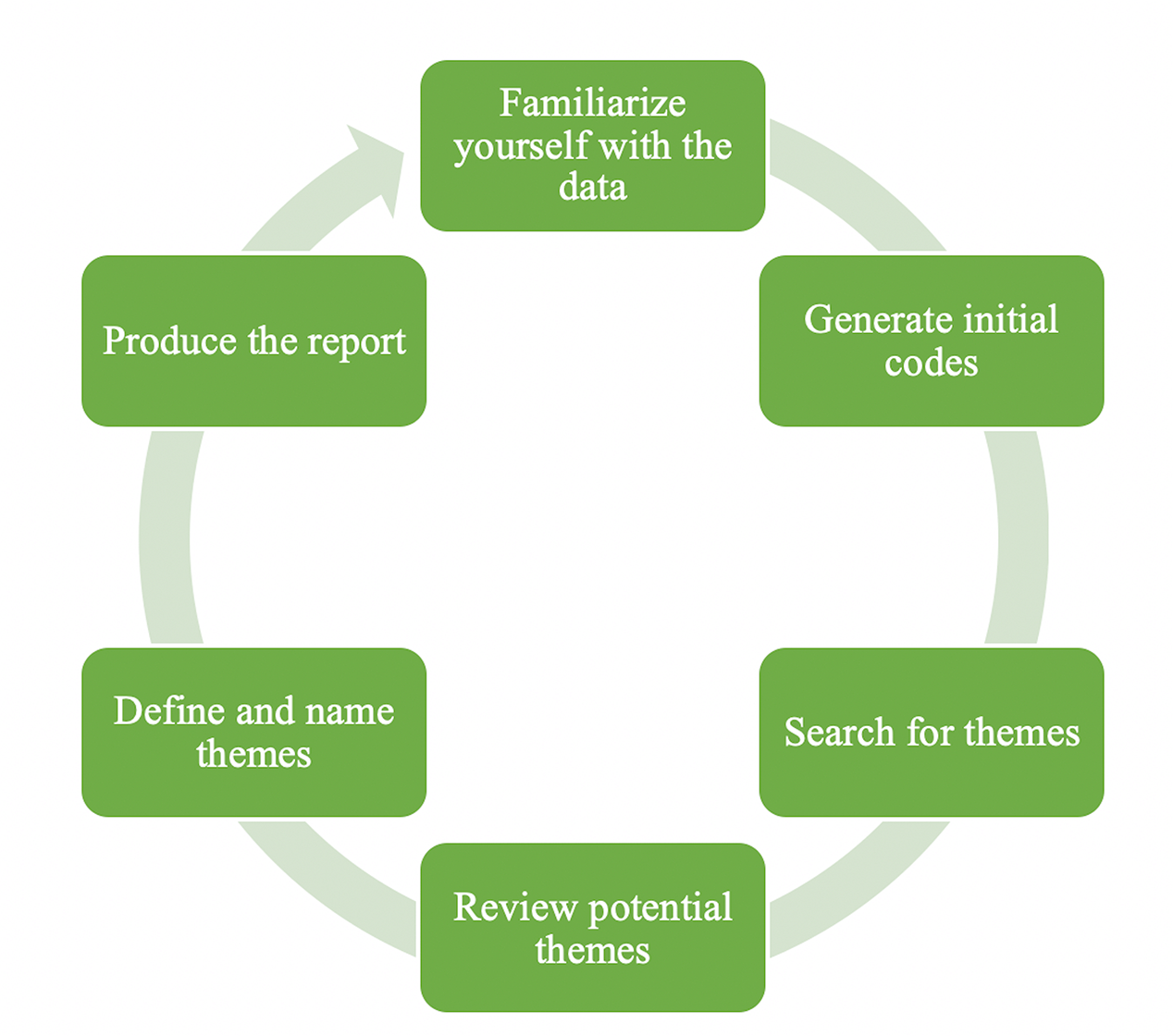
Six Phases Of Reflective Thematic Analysis
Reflexive thematic analysis was developed by Virginia Braun and Victoria Clarke, two prominent qualitative researchers.
The process of thematic analysis is characterized by an iterative movement between the different phases, rather than a strict linear progression.
This means that researchers might revisit earlier phases as their understanding of the data evolves, constantly refining their analysis.
For instance, during the reviewing and developing themes phase, researchers may realize that their initial codes don’t effectively capture the nuances of the data and might need to return to the coding phase.
This back-and-forth movement continues throughout the analysis, ensuring a thorough and evolving understanding of the data.
Here’s a breakdown of the six phases:
- This initial phase involves immersing oneself in the data.
- It includes transcribing audio or video data (if necessary) and engaging in repeated readings of the transcripts.
- The goal is to gain a thorough understanding of the content and begin to notice initial patterns or interesting features.
- This phase involves systematically identifying and labeling segments of data that are relevant to the research question.
- Codes are like labels attached to meaningful chunks of data, helping to organize and categorize information.
- This phase marks the shift from individual codes to broader patterns of meaning.
- The researcher starts grouping codes that seem to cluster together, indicating potential themes.
- It’s crucial to recognize that themes do not simply “emerge” from the data; rather, the researcher actively constructs them based on their interpretation of the coded data.
- This phase involves critically evaluating the initial themes against the coded data and the entire data set.
- It’s a process of quality checking and ensuring that the themes accurately and comprehensively reflect the data.
- Researchers may need to refine, discard, or even generate new themes based on this review process.
- This phase involves developing clear and concise definitions for each theme, capturing their scope and boundaries.
- The researcher aims to identify the “essence” of each theme and ensure that each theme has a distinct and meaningful contribution to the overall analysis.
- This stage also involves developing succinct and evocative names for the themes, conveying their central meaning to the reader.
- The final phase involves weaving the themes together to present a coherent and compelling narrative of the data.
- The write-up should not merely describe the data but should offer insightful interpretations, relate the findings back to the research question, and connect them to existing literature.
Step 1: Familiarization With the Data
Familiarization is crucial, as it helps researchers figure out the type (and number) of themes that might emerge from the data.
Familiarization involves immersing yourself in the data by reading and rereading textual data items, such as interview transcripts or survey responses.
You should read through the entire data set at least once, and possibly multiple times, until you feel intimately familiar with its content.
- Read and re-read the data (e.g., interview transcripts, survey responses, or other textual data) : The researcher reads through the entire data set multiple times to gain a comprehensive understanding of the data’s breadth and depth. This helps the researcher develop a holistic sense of the participants’ experiences, perspectives, and the overall narrative of the data.
- Listen to the audio recordings of the interviews : This helps to pick up on tone, emphasis, and emotional responses that may not be evident in the written transcripts. For instance, they might note a participant’s hesitation or excitement when discussing a particular topic. This is an important step if you didn’t collect or transcribe the data yourself.
- Take notes on initial ideas and observations : Note-making at this stage should be observational and casual, not systematic and inclusive, as you aren’t coding yet. Think of the notes as memory aids and triggers for later coding and analysis. They are primarily for you, although they might be shared with research team members.
- Immerse yourself in the data to gain a deep understanding of its content : It’s not about just absorbing surface meaning like you would with a novel, but about thinking about what the data mean .
By the end of the familiarization step, the researcher should have a good grasp of the overall content of the data, the key issues and experiences discussed by the participants, and any initial patterns or themes that emerge.
This deep engagement with the data sets the stage for the subsequent steps of thematic analysis, where the researcher will systematically code and analyze the data to identify and interpret the central themes.
Step 2: Generating Initial Codes
Codes are concise labels or descriptions assigned to segments of the data that capture a specific feature or meaning relevant to the research question.
Research question(s) and coding
- Braun and Clarke argue that the research question should be at the forefront of the researcher’s mind as they engage with the data, helping them focus their attention on what is relevant and meaningful.
- The research question is not set in stone; it can, and often should, evolve throughout the analysis.
- Braun and Clarke encourage a flexible and iterative dance between the research question and the coding process in reflexive thematic analysis.
- They advocate for a dynamic interplay where the research question guides the analysis while remaining open to refinement and even transformation based on the insights gleaned from deep engagement with the data.
- The coding process, with its close engagement with the data, can reveal new insights, nuances, and avenues for exploration, potentially leading to a reframing or narrowing of the initial research question.
The process of qualitative coding helps the researcher organize and reduce the data into manageable chunks, making it easier to identify patterns and themes relevant to the research question.
Think of it this way: If your analysis is a house, themes are the walls and roof, while codes are the individual bricks and tiles.
Coding is an iterative process, with researchers refining and revising their codes as their understanding of the data evolves.
The ultimate goal is to develop a coherent and meaningful coding scheme that captures the richness and complexity of the participants’ experiences and helps answer the research question(s).
Coding can be done manually (paper transcription and pen or highlighter) or by means of software (e.g. by using NVivo, MAXQDA or ATLAS.ti).
Qualitative data analysis software, such as NVivo can streamline the coding process, help you organize your data, and facilitate searching for patterns.
Example: Instead of manually writing codes on note cards or in separate documents, you can use software to directly tag and categorize segments of text within your data. This allows for easy retrieval and comparison of coded extracts later in the analysis
However, while software can assist with tasks like organizing codes and visually representing relationships, the researcher maintains responsibility for interpreting the data, defining themes, and making analytical decisions.

Decide On Your Coding Approach
- Will you use a predefined deductive coding framework with examples (based on theory or prior research), or let codes emerge from the data (inductive coding)?
- Will a piece of data have one code or multiple?
- Will you code everything or selectively? Broader research questions may warrant coding more comprehensively.
Instead of chasing data saturation , Clarke advocates for aiming for “ theoretical sufficiency “. This means coding data until you have enough evidence to confidently and convincingly support your interpretations and answer your research question.
If you decide not to code everything, it’s crucial to:
- Have clear criteria for what you will and won’t code.
- Be transparent about your selection process in the research report write-up.
- Remain open to revisiting uncoded data later in analysis.
Do A First Round Of Coding
- You are not required to code every single line or sentence. The size of the data segment you code can vary depending on what is meaningful and relevant to your research question.
- Go through the data and assign initial codes to chunks that could contribute to answering your research question, even if the connection seems tenuous at first.
- Instead of aiming for absolute certainty, Braun and Clarke suggest researchers consider whether a data segment is “potentially relevant” to the research question.
- Create a code name (a word or short phrase) that captures the essence of each chunk.
- Keep a codebook – a list of your codes with descriptions or definitions.
- Be open to adding, revising or combining codes as you go.
- Recognize that your understanding of the data, and therefore your codes, will likely evolve as you work through the data
After generating your first code, compare each new data extract to see if an existing code applies or if a new one is needed.
Avoid getting bogged down in trying to create the “perfect” set of codes from the outset. Embrace the iterative nature of coding, refining, and adjusting as needed
When grappling with the decision of whether to code a particular data segment, Braun and Clarke advocate for an inclusive approach, particularly in the initial stages of analysis.
They emphasize that it’s easier to discard codes later than to revisit the entire dataset for recording.
Coding can be done at two levels of meaning:
Semantic codes provide a descriptive snapshot of the data, while latent codes offer a more interpretive and deeper understanding of the underlying meanings and assumptions present.
- Semantic: These codes capture the surface meaning or explicit content of the data. They stay close to the participants’ intended meaning, mirroring their language and concepts. Think of semantic codes as a direct representation of what the participant says, with minimal interpretation by the researcher. They provide a concise summary of a portion of data, staying close to the content and the participant’s meaning.
- Latent: Goes beyond the participant’s meaning to provide a conceptual interpretation of the data. They often draw on existing theories or concepts to interpret the data, providing a more conceptual “take” on what the participants are saying. Latent codes require the researcher to dig beneath the surface and make inferences based on their expertise and knowledge.
The decision of whether to use semantic or latent codes, or a mix of both, depends on the research question, the specific data, and the theoretical orientation of the researcher.
Latent coding requires more experience and theoretical knowledge than semantic coding.
Most codes will be a mix of descriptive and conceptual. Novice coders tend to generate more descriptive codes initially, developing more conceptual approaches with experience.
Both types of codes are valuable in thematic analysis and contribute to a more comprehensive and insightful analysis of qualitative data.
Evolution of codes:
Coding in reflexive TA is not a linear, pre-determined process; instead, it’s an iterative process characterized by constant development, refinement, and transformation.
Braun and Clarke underscore that in reflexive TA, codes are not static categories but rather evolving tools that the researcher actively shapes and reshapes in response to the emerging insights from the data.
Don’t be afraid to revisit and adjust your codes —this is a sign of thoughtful engagement, not failure.
Braun and Clark highlight how codes might be:
- Renamed: As the researcher’s understanding of the data deepens, they might find that a code’s initial label no longer accurately reflects the nuances of the meaning it captures. Renaming allows for a more precise and insightful representation of the data.
- Combined: Codes that initially seemed distinct might reveal overlaps or shared connections as the analysis progresses, leading to their merging into a broader, more encompassing code.
- Split: Conversely, a code that initially seemed cohesive might later reveal subtle distinctions within it, prompting the researcher to split it into two or more more focused codes, reflecting a more nuanced understanding of the data.
- Redrawn boundaries: The scope and focus of a code can also shift throughout the analysis, leading to a redrawing of its boundaries to better encapsulate the emerging patterns and insights.
This step ends when:
- All data is fully coded.
- Data relevant to each code has been collated.
You have enough codes to capture the data’s diversity and patterns of meaning, with most codes appearing across multiple data items.
The number of codes you generate will depend on your topic, data set, and coding precision.
Step 3: Generating Initial Themes
Generating initial provisional (candidate) themes begins after all data has been initially coded and collated, resulting in a comprehensive list of codes identified across the data set.
This step involves shifting from the specific, granular codes to a broader, more conceptual level of analysis.
What is the difference between a theme and a code?
- A code is attached to a segment of data (your “coding chunk”) that is potentially relevant to your research question
- Themes are built from codes, meaning they’re more abstract and interpretive.
- Codes capture a single idea or observation, while a theme pulls together multiple codes to create a broader, more nuanced understanding of the data.
- Think of codes as the building blocks, and themes as the structure you create using those blocks.
Themes are higher-level units of analysis that organize and interpret the codes, revealing the overarching stories and key insights within the data. The focus is on making sense of the coded data by identifying connections, similarities, and overarching patterns that address the research question.
Phase 3 of thematic analysis is about actively “generating initial themes” rather than passively “searching for themes.” The distinction highlights that researchers don’t just uncover pre-existing themes hidden within the data.
Thematic analysis is not about “discovering” themes that already exist in the data, but rather actively constructing or generating themes through a careful and iterative process of examination and interpretation.
Themes involve a higher level of abstraction and interpretation. They go beyond merely summarizing the data (what participants said) and require the researcher to synthesize codes into meaningful clusters that offer insights into the underlying meaning and significance of the findings in relation to the research question.
Collating codes into potential themes :
The generating initial themes step helps the researcher move from a granular, code-level analysis to a more conceptual, theme-level understanding of the data.
The process of collating codes into potential themes involves grouping codes that share a unifying feature or represent a coherent and meaningful pattern in the data.
The researcher looks for patterns, similarities, and connections among the codes to develop overarching themes that capture the essence of the data.
It’s important to remember that coding is an organic and ongoing process.
You may need to re-read your entire data set to see if you have missed any data relevant to your themes, or if you need to create any new codes or themes.
Once a potential theme is identified, all coded data extracts associated with the codes grouped under that theme are collated. This ensures a comprehensive view of the data pertaining to each theme.
The researcher should ensure that the data extracts within each theme are coherent and meaningful.
This step helps ensure that your themes accurately reflect the data and are not based on your own preconceptions.
By the end of this step, the researcher will have a collection of candidate themes (and maybe sub-themes), along with their associated data extracts.
However, these themes are still provisional and will be refined in the next step of reviewing the themes.
This process is similar to sculpting, where the researcher shapes the “raw” data into a meaningful analysis. This involves grouping codes that share a unifying feature or represent a coherent pattern in the data:
- Review the list of initial codes and their associated data extracts (e.g., highlighted quotes or segments from interview transcripts).
- Look for codes that seem to share a common idea or concept.
- Group related codes together to form potential themes.
- If using qualitative data analysis software, you can assign the coded extracts to the relevant themes within the software.
- Some codes may form main themes, while others may be sub-themes or may not fit into any theme.
- If a coded extract seems to fit under multiple themes, choose the theme that it most closely aligns with in terms of shared meaning.
Example : The researcher would gather all the data extracts related to “Financial Obstacles and Support,” such as quotes about struggling to pay for tuition, working long hours, or receiving scholarships.
Thematic maps
Thematic maps can help visualize the relationship between codes and themes. These visual aids provide a structured representation of the emerging patterns and connections within the data, aiding in understanding the significance of each theme and its contribution to the overall research question.
- As you identify which theme each coded extract belongs to, copy and paste the extract under the relevant theme in your thematic map or table.
- Include enough context around each extract to ensure its meaning is clear.
Thematic maps often use visual elements like boxes, circles, arrows, and lines to represent different codes and themes and to illustrate how they connect to one another.
Thematic maps typically display themes and subthemes in a hierarchical structure, moving from broader, overarching themes to more specific, nuanced subthemes.
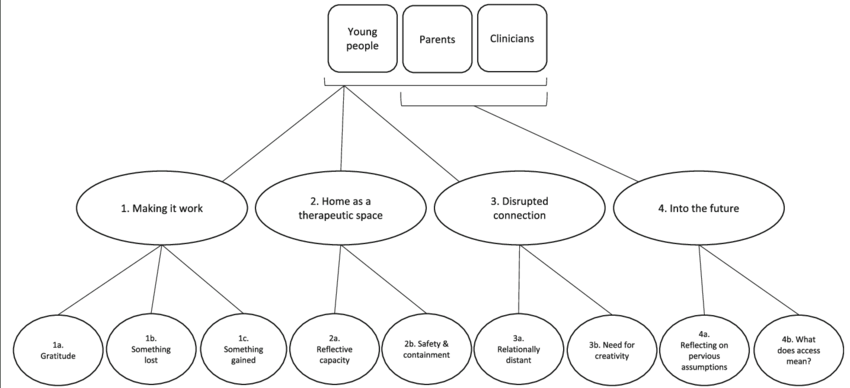
Maps can help researchers visualize the connections and tensions between different themes, revealing how they intersect or diverge to create a more nuanced understanding of the data.
Similar to the iterative nature of thematic analysis itself, thematic maps are fluid and adaptable, changing as the researcher gains a deeper understanding of the data.
Maps can highlight overlaps between themes or areas where a theme might be too broad or too narrow, prompting the researcher to adjust their analysis accordingly.
Example : Studying first-generation college students, the researcher might notice that the codes “financial challenges,” “working part-time,” and “scholarships” all relate to the broader theme of “Financial Obstacles and Support.”
Two main conceptualizations of a theme exist:
- Bucket theme (domain summary) : This approach identifies a pre-defined area of interest (often from interview questions) and summarizes all data relevant to that area.
- Storybook theme (shared meaning) : This approach focuses on identifying broader patterns of meaning that tell a story about the data. These themes go beyond simply summarizing and involve a greater degree of interpretation from the researcher.
Avoid : Themes as Domain Summaries (Shared Topic or “Bucket Themes”)
Domain summary themes are organized around a shared topic but not a shared meaning, and often resemble “buckets” into which data is sorted.
A domain summary organizes data around a shared topic but not a shared meaning.
In this approach, themes simply summarize what participants mentioned about a particular topic, without necessarily revealing a unified meaning.
Domain summaries group data extracts around a common topic or area of inquiry, often reflecting the interview questions or predetermined categories.
The emphasis is on collating all relevant data points related to that topic, regardless of whether they share a unifying meaning or concept.
While potentially useful for organizing data, domain summaries often remain at a descriptive level, failing to offer deeper insights into the data’s underlying meanings and implications.
These themes are often underdeveloped and lack a central organizing concept that ties all the different observations together.
A strong theme has a “central organizing concept” that connects all the observations and interpretations within that theme and goes beyond surface-level observations to uncover implicit meanings and assumptions.
A theme should not just be a collection of unrelated observations of a topic. This means going beyond just describing the “surface” of the data and identifying the assumptions, conceptualizations, and ideologies that inform the data’s meaning.
It’s crucial to avoid creating themes that are merely summaries of data domains or directly reflect the interview questions.
Example 1 : A theme titled “Incidents of homophobia” that merely describes various participant responses about homophobia without delving into deeper interpretations would be a topic summary theme.
Example 2 : A theme titled “Benefits of Being Single” that lists all the positive aspects of singlehood mentioned by participants would be a domain summary. A more insightful theme might explore the underlying reasons behind these benefits, such as “Redefining Independence in Singlehood.”
Tip : Using interview questions as theme titles without further interpretation or relying on generic social functions (“social conflict”) or structural elements (“economics”) as themes often indicates a lack of shared meaning and thorough theme development. Such themes might lack a clear connection to the specific dataset
Ensure : Themes as Shared Meaning (or “Storybook Themes”)
Braun and Clarke stress that a theme should offer more than a mere description of the data; it should tell a story about the data.
Instead, themes should represent a deeper level of interpretation, capturing the essence of the data and providing meaningful insights into the research question.
Shared meaning themes are patterns of shared meaning underpinned by a central organizing concept.
In contrast to domain summaries, shared meaning themes go beyond merely identifying a topic. They are organized around a “ central organizing concept ” that ties together all the observations and interpretations within that theme.
This central organizing concept represents the researcher’s interpretation of the shared meaning that connects seemingly disparate data points.
They reflect a pattern of shared meaning across different data points, even if those points come from different topics.
- Emphasis on interpretation and insight: Shared meaning themes require the researcher to move beyond surface-level descriptions and engage in a more interpretive and nuanced analysis. This involves identifying the underlying assumptions, conceptualizations, and ideologies that shape participants’ experiences and perspectives.
- Themes as interpretive stories: Braun and Clarke use the metaphor of a “storybook” to capture the essence of shared meaning themes. These themes aim to tell a compelling and insightful story about the data, going beyond a mere restatement of what participants said.
Example : The theme “‘There’s always that level of uncertainty’: Compulsory heterosexuality at university” effectively captures the shared experience of fear and uncertainty among LGBT students, connecting various codes related to homophobia and its impact on their lives.
Key considerations for developing shared meaning themes:
- Identifying the “Essence”: Developing a strong shared meaning theme involves identifying the “essence” or “core idea” that underpins a cluster of codes and data extracts. This requires asking questions like: What is the common thread that connects these observations? What underlying assumptions or beliefs are being expressed? What is the larger story that these data points tell about the phenomenon being studied?
- Moving beyond the literal: Shared meaning themes often involve uncovering the implicit or latent meanings embedded within the data. This requires the researcher to look beyond the literal interpretations of participants’ words and consider the broader social and cultural contexts that shape their perspectives.
Step 4: Reviewing Themes
The researcher reviews, modifies, and develops the preliminary themes identified in the previous step, transforming them into final, well-developed themes.
This phase involves a recursive process of checking the themes against the coded data extracts and the entire data set to ensure they accurately reflect the meanings evident in the data.
The purpose is to refine the themes, ensuring they are coherent, consistent, and distinctive.
According to Braun and Clarke, a well-developed theme “captures something important about the data in relation to the research question and represents some level of patterned response or meaning within the data set”.
A well-developed theme will:
- Go beyond paraphrasing the data to analyze the meaning and significance of the patterns identified.
- Provide a detailed analysis of what the theme is about.
- Be supported with a good amount of relevant data extracts.
- Be related to the research question.
Revisions at this stage might involve creating new themes, refining existing themes, or discarding themes that do not fit the data. For example, you might realize that two provisional themes actually overlap significantly and decide to merge them into a single, more nuanced theme.
Level One : Reviewing Themes Against Coded Data Extracts
- Researchers begin by comparing their initial candidate themes against the coded data extracts associated with each theme to ensure they form a coherent pattern.
- This step helps to determine whether each theme is supported by the data and whether it accurately reflects the meaning found in the extracts. Determine if there is enough data to support each theme.
- Look at the relationships between themes and sub-themes in the thematic map. Consider whether the themes work together to tell a coherent story about the data. If the thematic map does not effectively represent the data, consider making adjustments to the themes or their organization.
- If some extracts do not fit well with the rest of the data in a theme, consider whether they might better fit under a different theme or if the theme needs to be refined.
- It’s important to ensure that each theme has a singular focus and is not trying to encompass too much. Themes should be distinct from one another, although they may build on or relate to each other.
- Discarding codes : If certain codes within a theme are not well-supported or do not fit, they can be removed.
- Relocating codes : Codes that fit better under a different theme can be moved.
- Redrawing theme boundaries : The scope of a theme can be adjusted to better capture the relevant data.
- Discarding themes : Entire themes can be abandoned if they do not work.
Level Two : Evaluating Themes Against the Entire Data Set
- Once the themes appear coherent and well-supported by the coded extracts, researchers move on to evaluate them against the entire data set.
- This involves a final review of all the data to ensure that the themes accurately capture the most important and relevant patterns across the entire dataset in relation to the research question.
- During this level, researchers may need to recode some extracts for consistency, especially if the coding process evolved significantly, and earlier data items were not recoded according to these changes.
Level Three : Considering relationships between codes, themes, and different levels of themes (sub-themes)
Once you have gathered all the relevant data extracts under each theme, review the themes to ensure they are meaningful and distinct.
This step involves analyzing how different codes combine to form overarching themes and exploring the hierarchical relationship between themes and sub-themes.
Within a theme, there can be different levels of themes, often organized hierarchically as main themes and sub-themes.
Some themes may be more prominent or overarching (main themes), while others may be secondary or subsidiary (sub-themes).
- Main themes represent the most overarching or significant patterns found in the data. They provide a high-level understanding of the key issues or concepts present in the data.
- Sub-themes are essentially themes within a theme. They represent a further level of nuance and complexity within a broader theme, highlighting specific and important aspects of the central organizing concept of that theme.
Sub-themes provide a way to add depth and richness to your thematic analysis, but they should be used thoughtfully and strategically. A well-structured analysis might rely primarily on clearly defined main themes, using sub-themes selectively to highlight particularly important nuances within those themes.
Too many sub-themes can create a thin, fragmented analysis and suggest that the analysis hasn’t been developed sufficiently to identify the overarching concepts that tie the data together.
It’s important to note that sub-themes are not a necessary feature of a reflexive TA. You can have a robust analysis with just two to six main themes, especially if you are working with a limited word count
The relationship between codes, sub-themes and main themes can be visualized using a thematic map, diagram, or table.
This map helps researchers review and refine themes, ensuring they are internally consistent (homogeneous) and distinct from other themes (heterogeneous).
Refine the thematic map as you continue to review and analyze the data.
Consider how the themes tell a coherent story about the data and address the research question.
If some themes seem to overlap or are not well-supported by the data, consider combining or refining them.
If a theme is too broad or diverse, consider splitting it into separate themes or sub-theme.
Example : The researcher might identify “Academic Challenges” and “Social Adjustment” as other main themes, with sub-themes like “Imposter Syndrome” and “Balancing Work and School” under “Academic Challenges.” They would then consider how these themes relate to each other and contribute to the overall understanding of first-generation college students’ experiences.
Final Questions:
- Does this provisional theme capture something meaningful? Is it coherent, with a central idea that meshes the data and codes together? Does it have clear boundaries?”
- “Can I identify the boundaries of this theme?”
- “Are there enough meaningful data to evidence this theme?”
- “Are there multiple articulations around the core idea, and are they nuanced, complex, and diverse?”
- “Does the theme feel rich?”
- “Are the data contained within each theme too diverse and wide-ranging?”
- “Does the theme convey something important?”
Step 5: Defining and Naming Themes
The themes are finalized when the researcher is satisfied with the theme names and definitions.
If the analysis is carried out by a single researcher, it is recommended to seek feedback from an external expert to confirm that the themes are well-developed, clear, distinct, and capture all the relevant data.
Defining themes means determining the exact meaning of each theme and understanding how it contributes to understanding the data.
This process involves formulating exactly what we mean by each theme. The researcher should consider what a theme says, if there are subthemes, how they interact and relate to the main theme, and how the themes relate to each other.
Themes should not be overly broad or try to encompass too much, and should have a singular focus. They should be distinct from one another and not repetitive, although they may build on one another.
In this phase the researcher specifies the essence of each theme.
- What does the theme tell us that is relevant for the research question?
- How does it fit into the ‘overall story’ the researcher wants to tell about the data?
Naming themes involves developing a clear and concise name that effectively conveys the essence of each theme to the reader. A good name for a theme is informative, concise, and catchy.
- A well-crafted theme name should immediately convey the theme’s central organizing concept and give the reader a sense of the story the theme will tell.
- The researcher develops concise, punchy, and informative names for each theme that effectively communicate its essence to the reader.
- Theme names should be catchy and evocative, giving the reader an immediate sense of what the theme is about.
- Avoid using one-word theme names or names that simply identify the topic, as this often signifies a domain summary rather than a well-developed theme.
- Avoid using jargon or overly complex language in theme names.
- The name should go beyond simply paraphrasing the content of the data extracts and instead interpret the meaning and significance of the patterns within the theme.
- The goal is to make the themes accessible and easily understandable to the intended audience. If a theme contains sub-themes, the researcher should also develop clear and informative names for each sub-theme.
- Theme names can include direct quotations from the data, which helps convey the theme’s meaning. However, researchers should avoid using data collection questions as theme names. Using data collection questions as themes often leads to analyses that present domain summaries of topics rather than fully realized themes.
For example, “‘There’s always that level of uncertainty’: Compulsory heterosexuality at university” is a strong theme name because it captures the theme’s meaning. In contrast, “incidents of homophobia” is a weak theme name because it only states the topic.
For instance, a theme labeled “distrust of experts” might be renamed “distrust of authority” or “conspiracy thinking” after careful consideration of the theme’s meaning and scope.
Step 6: Producing the Report
Braun and Clarke differentiate between two distinct approaches to presenting the analysis in qualitative research: the “establishing the gap model” and the “making the argument model” (p.120).
Establishing the Gap Model:
This model operates on the premise that knowledge gaps exist due to limited research in specific areas or shortcomings in current research.
This approach frames the research’s purpose as filling these identified gaps. Braun and Clarke critique this model as echoing a positivist-empiricist view of research as a quest for definitive truth, which they argue is incongruent with the nature of qualitative research.
They suggest this approach aligns more with a quantitative perspective that seeks to uncover objective truths.
Making the Argument Model:
Braun and Clarke advocate for the “making the argument model,” particularly in the context of qualitative research.
This model situates the research’s rationale within existing knowledge and theoretical frameworks.
Rather than striving to unearth a singular truth, this approach aims to contribute to a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the subject matter by offering a well-supported, contextually grounded, and persuasive perspective on the issue at hand.
This approach might negate the need for a literature review before data analysis, allowing the research findings to guide the exploration of relevant literature.
Method Section of Thematic Analysis
A well-crafted method section goes beyond a superficial summary of the six phases.
It provides a clear and comprehensive account of the analytical journey, allowing readers to trace the researchers’ thought process, assess the trustworthiness of the findings, and understand the rationale behind the methodological choices made.
This transparency is essential for ensuring the rigor and validity of thematic analysis as a qualitative research method.
1. Description of the thematic approach:
The method section should explicitly state the type of thematic analysis undertaken and the specific version used (e.g., reflexive thematic analysis, codebook thematic analysis).
It should also explain the rationale for selecting this specific approach in relation to the research questions.
For instance, if a study focuses on exploring participants’ lived experiences, an inductive (reflexive) approach might be more suitable.
If the research question is driven by a particular theoretical framework, a deductive (codebook) approach may be chosen.
2. Data collection method and data set:
Clearly describe the method used to collect data (e.g., interviews, focus groups , surveys, documents).
Specify the size of the data set (e.g., number of interviews, focus groups, or documents) and the characteristics of the participants or texts included.
3. Reflexivity and transparency:
Braun and Clarke caution against merely listing the six phases of thematic analysis because presenting the phases as a series of steps implies that thematic analysis is a linear and objective process that can be separated from the researcher’s influence.
It should demonstrate an understanding of the principles of reflexivity and transparency.
By embracing reflexivity and transparency, researchers using thematic analysis can move away from a simplistic “recipe” approach and acknowledge the iterative and interpretive nature of qualitative research.
Reflexivity involves acknowledging and critically examining how the researcher’s own subjectivity might be shaping the research process.
It requires reflecting on how personal experiences, beliefs, and assumptions could influence the interpretation of data and the development of themes.
For example, a researcher studying experiences of discrimination might reflect on how their own social identities and experiences with prejudice could impact their understanding of the data.
Transparency involves clearly documenting the decisions made throughout the research process.
This includes explaining the rationale behind coding choices, theme development, and the selection of data extracts to illustrate themes.
For example, the researcher(s) might discuss the process of selecting particular data extracts or how their initial interpretations evolved over time.
Transparency allows readers to understand how the findings were generated and to assess the trustworthiness of the research.
The researcher(s) could provide a detailed account of how they moved from initial codes to broader themes, including examples of how they resolved discrepancies between codes or combined them into overarching categories.
While transparency requires detail and rigor, it should not come at the expense of clarity and accessibility.
Braun and Clarke encourage researchers to write in a clear, engaging style that makes the research process and findings accessible to a wide audience, including those who might not be familiar with qualitative research methods.
Writing About Themes
A thematic analysis report should provide a convincing and clear, yet complex story about the data that is situated within a scholarly field.
A balance should be struck between the narrative and the data presented, ensuring that the report convincingly explains the meaning of the data, not just summarizes it.
To achieve this, the report should include vivid, compelling data extracts illustrating the themes and incorporate extracts from different data sources to demonstrate the themes’ prevalence and strengthen the analysis by representing various perspectives within the data.
The report should be written in first-person active tense, unless otherwise stated in the reporting requirements.
The analysis can be presented in two ways :
- Integrated Results and Discussion section: This approach is suitable when the analysis has strong connections to existing research and when the analysis is more theoretical or interpretive.
- Separate Discussion section: This approach presents the data interpretation separately from the results.
Regardless of the presentation style, researchers should aim to “show” what the data reveals and “tell” the reader what it means in order to create a convincing analysis.
- Presentation order of themes: Consider how to best structure the presentation of the themes in the report. This may involve presenting the themes in order of importance, chronologically, or in a way that tells a coherent story. The order in which themes are presented should be logical and meaningful, creating a clear storyline for the reader.
- Subheadings: Use subheadings to clearly delineate each theme and its sub-themes, making the report easy to navigate and understand.
Themes should connect logically and meaningfully and, if relevant, should build on previous themes to tell a coherent story about the data.
Avoid using phrases like “themes emerged” as it suggests that the themes were pre-existing entities in the data, waiting to be discovered. This undermines the active role of the researcher in interpreting and constructing themes from the data.
Themes should be supported with compelling data extracts that illustrate the identified patterns.
Data extracts serve as evidence for the themes identified in TA. Without them, the analysis becomes unsubstantiated and potentially unconvincing to the reader.
The report should include vivid, compelling data extracts that clearly illustrate the theme being discussed and should incorporate extracts from different data sources, rather than relying on a single source.
Not all data extracts are equally effective. Choose extracts that vividly and concisely illustrate the theme’s central organizing concept.
Although it is tempting to rely on one source when it eloquently expresses a particular aspect of the theme, using multiple sources strengthens the analysis by representing a wider range of perspectives within the data.
Having too few data extracts for a theme weakens the analysis and makes it appear “thin and sketchy”. This may leave the reader unconvinced about the theme’s validity and prevalence within the data.
The analysis should go beyond a simple summary of the participant’s words and instead interpret the meaning of the data.
Data extracts should not be presented without being integrated into the analytic narrative. They should be used to illustrate and support the interpretation of the data, not just reiterate what the participants said.
Researchers should strive to maintain a balance between the amount of narrative and the amount of data presented.
A good thematic analysis strikes a balance between presenting data extracts and providing analytic commentary. A common rule of thumb is to aim for a 50/50 ratio.
The importance of examining contradictory data
A robust thematic analysis acknowledges and explores the full range of data, including those that challenge the dominant patterns.
Ignoring data that doesn’t neatly fit into identified themes is a significant pitfall in thematic analysis.
Failing to acknowledge and explore contradictory data can lead to an incomplete or misleading analysis, potentially obscuring valuable insights.
- Data sets are rarely completely uniform : Human experiences and perspectives are complex and often contradictory. It’s unrealistic to expect that every piece of data will perfectly align with the identified themes.
- Contradictory data can challenge assumptions : Data that contradicts the emerging themes can challenge the researcher’s assumptions and interpretations, leading to a more nuanced and insightful understanding of the data.
- Ignoring contradictions can create an overly simplistic analysis : An analysis that smooths over contradictions or presents a completely unified picture of the data might lack depth and fail to capture the complexities of the phenomenon being studied.
- Alternative interpretations : Contradictory data might suggest alternative interpretations or explanations that need to be considered and addressed in the analysis.
- Value of outliers : Instead of dismissing data that doesn’t fit, view it as potentially valuable. These outliers might reveal limitations in the analysis, highlight the influence of contextual factors, or uncover new avenues for inquiry.
Embracing contradictions and exploring their potential meanings leads to a more comprehensive and insightful analysis.
Discussion Section
The discussion section should engage critically with the findings, connect them to existing knowledge, and contribute to a deeper understanding of the phenomenon under investigation.
Braun and Clarke emphasize that the discussion section should not merely summarize the themes but rather weave a compelling and insightful narrative that connects the analysis back to the research question, existing literature, and broader theoretical discussions.
While each theme should have a distinct focus, the discussion should also draw connections between themes, creating a cohesive and interconnected narrative.
They advocate for a style that engages the reader, convinces them of the validity of the findings, and leaves them with a sense of “ so what? ” – a clear understanding of the significance and implications of the research.
- Connecting themes and building a narrative: The discussion section should move beyond simply describing individual themes to explore the relationships and connections between them. The goal is to present a coherent and nuanced narrative that addresses the research questions.
- Interpreting the findings: The discussion section should interpret the significance of the findings about the research questions and existing literature. It should go beyond merely summarizing the data to offer insights into what the themes mean, why they might have emerged, and what their implications are. Asking questions like “So what?” and “What is relevant or useful here to addressing my question?” can help you guide the interpretation of the data.
- Integrating literature: The discussion section should connect the findings to relevant scholarly literature. This could involve comparing and contrasting the findings with previous research, exploring how the study supports or challenges existing theories, or discussing the implications of the findings in light of existing knowledge.
- Theoretical insights: For analyses that go beyond the semantic level, the discussion section should explore the theoretical insights that emerge from the data. This could involve identifying underlying assumptions, ideologies, or power dynamics that shape the experiences or perspectives of the participants.
- Critical reflection on the method: Reflect on the methodological choices made during the analysis and their potential implications for the findings. This could involve discussing the benefits and limitations of the chosen thematic analysis approach, acknowledging any potential biases, and suggesting areas for future research.
Potential Pitfalls to Avoid
- Failing to analyze the data : Thematic analysis should involve more than simply presenting data extracts without an analytic narrative. The researcher must provide an interpretation and make sense of the data, telling the reader what it means and how it relates to the research questions.
- Using data collection questions as themes : Themes should be identified across the entire dataset, not just based on the questions asked during data collection. Reporting data collection questions as themes indicates a lack of thorough analytic work to identify patterns and meanings in the data.
- Confusing themes with summaries : Themes are not merely summaries of what participants said about a topic. Instead, they represent rich and multifaceted patterns of shared meaning organized around a central concept and are generated by the researcher through intense analytic engagement with the data. Good themes often uncover the implicit or latent meanings behind the data rather than just summarizing what’s explicitly stated.
- Conducting a weak or unconvincing analysis : Themes should be distinct, internally coherent, and consistent, capturing the majority of the data or providing a rich description of specific aspects. A weak analysis may have overlapping themes, fail to capture the data adequately, or lack sufficient examples to support the claims made.
- Ignoring contradictory data : An analysis that smooths over contradictions or presents a completely unified picture of the data might lack depth and fail to capture the complexities of the phenomenon being studied. Acknowledging and exploring data that does not fit neatly into identified themes can lead to more nuanced findings.
- Mismatch between data and analytic claims : The researcher’s interpretations and analytic points must be consistent with the data extracts presented. Claims that are not supported by the data, contradict the data, or fail to consider alternative readings or variations in the account are problematic.
- Misalignment between theory, research questions, and analysis : The interpretations of the data should be consistent with the theoretical framework used. For example, an experiential framework would not typically make claims about the social construction of the topic. The form of thematic analysis used should also align with the research questions.
- Neglecting to clarify assumptions, purpose, and process : A good thematic analysis should spell out its theoretical assumptions, clarify how it was undertaken, and for what purpose. Without this crucial information, the analysis is lacking context and transparency, making it difficult for readers to evaluate the research.
Reducing Bias
Braun and Clarke’s approach to thematic analysis, which they term “reflexive TA,” places the researcher’s subjectivity and reflexivity at the forefront of the research process.
Rather than striving for an illusory objectivity, reflexive TA recognizes and values the researcher’s active role in shaping the research, from data interpretation to theme construction.
When researchers are both reflexive and transparent in their thematic analysis, it strengthens the trustworthiness and rigor of their findings.
The explicit acknowledgement of potential biases and the detailed documentation of the analytical process provide a stronger foundation for the interpretation of the data, making it more likely that the findings reflect the perspectives of the participants rather than the biases of the researcher.
Reflexivity
Reflexivity involves critically examining one’s own assumptions and biases, is crucial in qualitative research to ensure the trustworthiness of findings.
It requires acknowledging that researcher subjectivity is inherent in the research process and can influence how data is collected, analyzed, and interpreted.
Identifying and Challenging Assumptions:
Braun and Clarke argue that the researcher’s background, experiences, theoretical commitments, and social position inevitably shape how they approach and make sense of the data.
Reflexivity encourages researchers to explicitly acknowledge their preconceived notions, theoretical leanings, and potential biases.
Reflexivity involves critically examining how these personal and professional experiences influence the research process, particularly during data interpretation and theme development.
Researchers are encouraged to make these influences transparent in their methodology and throughout their analysis, fostering a more honest and nuanced account of the research.
Memos offer a space for researchers to step back from the data and ask themselves probing questions about their own perspectives and potential biases.
Researchers can ask: How might my background or beliefs be shaping my interpretation of this data? Am I overlooking alternative explanations? Am I imposing my own values or expectations on the participants?
By actively reflecting on how these factors might influence their interpretation of the data, researchers can take steps to mitigate their impact.
This might involve seeking alternative explanations, considering contradictory evidence, or discussing their interpretations with others to gain different perspectives.
Reflexivity as an Ongoing Process
Reflexivity is not a one-time activity but an ongoing process that should permeate all stages of the research, from the initial design to the final write-up.
This involves constantly questioning one’s assumptions, interpretations, and reactions to the data, considering alternative perspectives, and remaining open to revising initial understandings.
Braun and Clarke provide a series of probing questions that researchers can ask themselves throughout the analytic process to encourage this reflexivity.
- “Why might I be reacting to the data in this way?”
- “What does my interpretation rely on?”
- “How would I feel if I was in that situation? (Is this different from or similar to how the person feels, and why might that be?)”
Transparency
Transparency refers to clearly documenting the research process, including coding decisions, theme development, and the rationale behind behind theme development.
Transparency is not merely about documenting what was done but also about clearly articulating why and how specific analytic choices were made throughout the research process, from study design to data interpretation.
This transparency allows readers to understand the researchers’ perspectives, the rationale behind their decisions, and the potential influences on the findings, ultimately strengthening the credibility and trustworthiness of the research
This transparency helps ensure the trustworthiness and rigor of the findings, allowing other researchers to assess the credibility of the findings and potentially replicate the analysis.
Transparency in Braun and Clarke’s approach to thematic analysis is not merely about adhering to a set of reporting guidelines; it’s about embracing an ethos of openness, reflexivity, and accountability throughout the research process.
By illuminating the “messiness” of qualitative research and clearly articulating the researchers’ perspectives and decisions, reflexive TA promotes a more honest, trustworthy, and ultimately, more insightful form of qualitative inquiry.
Documenting Decision-Making:
Transparency requires researchers to provide a clear and detailed account of their analytical choices throughout the research process.
This includes documenting the rationale behind coding decisions, the process of theme development, and any changes made to the analytical approach during the study.
- Data selection and sampling: Why were particular data sources chosen? How were participants selected, and what were the inclusion/exclusion criteria?
- Coding strategies: How were codes developed? Was the coding primarily inductive, deductive, or a combination of both? Did the coding process evolve, and if so, how? Were any coding tools or software used?
- Theme development: How were themes identified, refined, and named? What was the process of moving from codes to themes? How was the final thematic structure decided upon?
By making these decisions transparent, researchers allow others to scrutinize their work and assess the potential for bias.
Practical Strategies for Reflexivity and Transparency in Thematic Analysis:
- Maintaining a reflexive journal: Researchers can keep a journal throughout the research process to document their thoughts, assumptions, and potential biases. This journal serves as a record of the researcher’s evolving understanding of the data and can help identify potential blind spots in their analysis.
- Engaging in team-based analysis: Collaborative analysis, involving multiple researchers, can enhance reflexivity by providing different perspectives and interpretations of the data. Discussing coding decisions and theme development as a team allows researchers to challenge each other’s assumptions and ensure a more comprehensive analysis.
- Clearly articulating the analytical process: In reporting the findings of thematic analysis, researchers should provide a detailed account of their methods, including the rationale behind coding decisions, the process of theme development, and any challenges encountered during analysis. This transparency allows readers to understand the steps taken to ensure the rigor and trustworthiness of the analysis.
- Flexibility: Thematic analysis is a flexible method, making it adaptable to different research questions and theoretical frameworks. It can be employed with various epistemological approaches, including realist, constructionist, and contextualist perspectives. For example, researchers can focus on analyzing meaning across the entire data set or examine a particular aspect in depth.
- Accessibility: Thematic analysis is an accessible method, especially for novice qualitative researchers, as it doesn’t demand extensive theoretical or technical knowledge compared to methods like Discourse Analysis (DA) or Conversation Analysis (CA). It is considered a foundational qualitative analysis method.
- Rich Description: Thematic analysis facilitates a rich and detailed description of data9. It can provide a thorough understanding of the predominant themes in a data set, offering valuable insights, particularly in under-researched areas.
- Theoretical Freedom: Thematic analysis is not restricted to any pre-existing theoretical framework, allowing for diverse applications. This distinguishes it from methods like Grounded Theory or Interpretative Phenomenological Analysis (IPA), which are more closely tied to specific theoretical approaches
Disadvantages
- Subjectivity and Interpretation: The flexibility of thematic analysis, while an advantage, can also be a disadvantage. The method’s openness can lead to a wide range of interpretations of the same data set, making it difficult to determine which aspects to emphasize. This potential subjectivity might raise concerns about the analysis’s reliability and consistency.
- Limited Interpretive Power: Unlike methods like narrative analysis or biographical approaches, thematic analysis may not capture the nuances of individual experiences or contradictions within a single account. The focus on patterns across interviews could result in overlooking unique individual perspectives.
- Oversimplification: Thematic analysis might oversimplify complex phenomena by focusing on common themes, potentially missing subtle but important variations within the data. If not carefully executed, the analysis may present a homogenous view of the data that doesn’t reflect the full range of perspectives.
- Lack of Established Theoretical Frameworks: Thematic analysis does not inherently rely on pre-existing theoretical frameworks. While this allows for inductive exploration, it can also limit the interpretive power of the analysis if not anchored within a relevant theoretical context. The absence of a theoretical foundation might make it challenging to draw meaningful and generalizable conclusions.
- Difficulty in Higher-Phase Analysis: While thematic analysis is relatively easy to initiate, the flexibility in its application can make it difficult to establish specific guidelines for higher-phase analysis1. Researchers may find it challenging to navigate the later stages of analysis and develop a coherent and insightful interpretation of the identified themes.
- Potential for Researcher Bias: As with any qualitative research method, thematic analysis is susceptible to researcher bias. Researchers’ preconceived notions and assumptions can influence how they code and interpret data, potentially leading to skewed results.
Reading List
- Braun, V., & Clarke, V. (2006). Using thematic analysis in psychology . Qualitative Research in Psychology, 3 (2), 77–101.
- Braun, V., & Clarke, V. (2013). Successful qualitative research: A practical guide for beginners. Sage.
- Braun, V., & Clarke, V. (2019). Reflecting on reflexive thematic analysi s. Qualitative Research in Sport, Exercise and Health, 11 (4), 589–597.
- Braun, V., & Clarke, V. (2021). One size fits all? What counts as quality practice in (reflexive) thematic analysis? Qualitative Research in Psychology, 18 (3), 328–352.
- Braun, V., & Clarke, V. (2021). To saturate or not to saturate? Questioning data saturation as a useful concept for thematic analysis and sample-size rationales . Qualitative Research in Sport, Exercise and Health, 13 (2), 201–216.
- Braun, V., & Clarke, V. (2022). Conceptual and design thinking for thematic analysis . Qualitative psychology , 9 (1), 3.
- Braun, V., & Clarke, V. (2022b). Thematic analysis: A practical guide . Sage.
- Braun, V., Clarke, V., & Hayfield, N. (2022). ‘A starting point for your journey, not a map’: Nikki Hayfield in conversation with Virginia Braun and Victoria Clarke about thematic analysis. Qualitative research in psychology , 19 (2), 424-445.
- Finlay, L., & Gough, B. (Eds.). (2003). Reflexivity: A practical guide for researchers in health and social sciences. Blackwell Science.
- Gibbs, G. R. (2013). Using software in qualitative analysis. In U. Flick (ed.) The Sage handbook of qualitative data analysis (pp. 277–294). London: Sage.
- McLeod, S. (2024, May 17). Qualitative Data Coding . Simply Psychology. https://www.simplypsychology.org/qualitative-data-coding.html
- Terry, G., & Hayfield, N. (2021). Essentials of thematic analysis . American Psychological Association.
- Trainor, L. R., & Bundon, A. (2021). Developing the craft: Reflexive accounts of doing reflexive thematic analysis . Qualitative research in sport, exercise and health , 13 (5), 705-726.
Examples of Good Practice
- Anderson, S., Clarke, V., & Thomas, Z. (2023). The problem with picking: Permittance, escape and shame in problematic skin picking . Psychology and Psychotherapy: Theory, Research and Practice , 96 (1), 83-100.
- Braun, V., Terry, G., Gavey, N., & Fenaughty, J. (2009). ‘ Risk’and sexual coercion among gay and bisexual men in Aotearoa/New Zealand–key informant accounts . Culture, Health & Sexuality , 11 (2), 111-124.
- Clarke, V., & Kitzinger, C. (2004). Lesbian and gay parents on talk shows: resistance or collusion in heterosexism? . Qualitative Research in Psychology , 1 (3), 195-217.
- Hayfield, N., Jones, B., Carter, J., & Jowett, A. (2024). Exploring civil partnership from the perspective of those in mixed-sex relationships: Embracing a clean slate of equality . Journal of Family Issues , 45 (8), 1925-1948.
- Hayfield, N., Moore, H., & Terry, G. (2024). “Friends? Supported. Partner? Not so much…”: Women’s experiences of friendships, family, and relationships during perimenopause and menopause . Feminism & Psychology , 09593535241242563.
- Lovell, D., Hayfield, N., & Thomas, Z. (2023). “No one has ever asked me and I’m grateful that you have” men’s experiences of their partner’s female sexual pain . Sexual and Relationship Therapy , 1-24.
- Wheeler, L., Fragkiadaki, E., Clarke, V., & DiCaccavo, A. (2022). ‘Sunshine’,‘angels’ and ‘rainbows’: language developed by mothers bereaved by perinatal loss. British Journal of Midwifery , 30 (7), 368-374.
- Answers to frequently asked questions about thematic analysis
- Thematic analysis – data for coding exercise
- University of Auckland – Thematic Analysis Resources
How to do thematic analysis
Last updated
8 February 2023
Reviewed by
Miroslav Damyanov
Short on time? Get an AI generated summary of this article instead
Uncovering themes in data requires a systematic approach. Thematic analysis organizes data so you can easily recognize the context.
- What is thematic analysis?
Thematic analysis is a method for analyzing qualitative data that involves reading through a data set and looking for patterns to derive themes . The researcher's subjective experience plays a central role in finding meaning within the data.
Streamline your thematic analysis
Find patterns and themes across all your qualitative data when you analyze it in Dovetail
- What are the main approaches to thematic analysis?
Inductive thematic analysis approach
Inductive thematic analysis entails deriving meaning and identifying themes from data with no preconceptions. You analyze the data without any expected outcomes.
Deductive thematic analysis approach
In the deductive approach, you analyze data with a set of expected themes. Prior knowledge, research, or existing theory informs this approach.
Semantic thematic analysis approach
With the semantic approach, you ignore the underlying meaning of data. You take identifying themes at face value based on what is written or explicitly stated.
Latent thematic analysis approach
Unlike the semantic approach, the latent approach focuses on underlying meanings in data and looks at the reasons for semantic content. It involves an element of interpretation where you theorize meanings and don’t just take data at face value.
- When should thematic analysis be used?
Thematic analysis is beneficial when you’re working with large bodies of data. It allows you to divide and categorize huge quantities of data in a way that makes it far easier to digest.
The following scenarios warrant the use of thematic analysis:
You’re new to qualitative analysis
You need to identify patterns in data
You want to involve participants in the process
Thematic analysis is particularly useful when you’re looking for subjective information such as experiences and opinions in surveys , interviews, conversations, or social media posts.
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of thematic analysis?
Thematic analysis is a highly flexible approach to qualitative data analysis that you can modify to meet the needs of many studies. It enables you to generate new insights and concepts from data.
Beginner researchers who are just learning how to analyze data will find thematic analysis very accessible. It’s easy for most people to grasp and can be relatively quick to learn.
The flexibility of thematic analysis can also be a disadvantage. It can feel intimidating to decide what’s important to emphasize, as there are many ways to interpret meaning from a data set.
- What is the step-by-step process for thematic analysis?
The basic thematic analysis process requires recognizing codes and themes within a data set. A code is a label assigned to a piece of data that you use to identify and summarize important concepts within a data set. A theme is a pattern that you identify within the data. Relevant steps may vary based on the approach and type of thematic analysis, but these are the general steps you’d take:
1. Familiarize yourself with the data(pre-coding work)
Before you can successfully work with data, you need to understand it. Get a feel for the data to see what general themes pop up. Transcribe audio files and observe any meanings and patterns across the data set. Read through the transcript, and jot down notes about potential codes to create.
2. Create the initial codes (open code work)
Create a set of initial codes to represent the patterns and meanings in the data. Make a codebook to keep track of the codes. Read through the data again to identify interesting excerpts and apply the appropriate codes. You should use the same code to represent excerpts with the same meaning.
3. Collate codes with supporting data (clustering of initial code)
Now it's time to group all excerpts associated with a particular code. If you’re doing this manually, cut out codes and put them together. Thematic analysis software will automatically collate them.
4. Group codes into themes (clustering of selective codes)
Once you’ve finalized the codes, you can sort them into potential themes. Themes reflect trends and patterns in data. You can combine some codes to create sub-themes.
5. Review, revise, and finalize the themes (final revision)
Now you’ve decided upon the initial themes, you can review and adjust them as needed. Each theme should be distinct, with enough data to support it. You can merge similar themes and remove those lacking sufficient supportive data. Begin formulating themes into a narrative.
6. Write the report
The final step of telling the story of a set of data is writing the report. You should fully consider the themes to communicate the validity of your analysis.
A typical thematic analysis report contains the following:
An introduction
A methodology section
Results and findings
A conclusion
Your narrative must be coherent, and it should include vivid quotes that can back up points. It should also include an interpretive analysis and argument for your claims. In addition, consider reporting your findings in a flowchart or tree diagram, which can be independent of or part of your report.
In conclusion, a thematic analysis is a method of analyzing qualitative data. By following the six steps, you will identify common themes from a large set of texts. This method can help you find rich and useful insights about people’s experiences, behaviors, and nuanced opinions.
- How to analyze qualitative data
Qualitative data analysis is the process of organizing, analyzing, and interpreting non-numerical and subjective data . The goal is to capture themes and patterns, answer questions, and identify the best actions to take based on that data.
Researchers can use qualitative data to understand people’s thoughts, feelings, and attitudes. For example, qualitative researchers can help business owners draw reliable conclusions about customers’ opinions and discover areas that need improvement.
In addition to thematic analysis, you can analyze qualitative data using the following:
Content analysis
Content analysis examines and counts the presence of certain words, subjects, and contexts in documents and communication artifacts, such as:
Text in various formats
This method transforms qualitative input into quantitative data. You can do it manually or with electronic tools that recognize patterns to make connections between concepts.
Free AI content analysis generator
Make sense of your research by automatically summarizing key takeaways through our free content analysis tool.
Narrative analysis
Narrative analysis interprets research participants' stories from testimonials, case studies, interviews, and other text or visual data. It provides valuable insights into the complexity of people's feelings, beliefs, and behaviors.
Discourse analysis
In discourse analysis , you analyze the underlying meaning of qualitative data in a particular context, including:
Historical
This approach allows us to study how people use language in text, audio, and video to unravel social issues, power dynamics, or inequalities.
For example, you can look at how people communicate with their coworkers versus their bosses. Discourse analysis goes beyond the literal meaning of words to examine social reality.

Grounded theory analysis
In grounded theory analysis, you develop theories by examining real-world data. The process involves creating hypotheses and theories by systematically collecting and evaluating this data. While this approach is helpful for studying lesser-known phenomena, it might be overwhelming for a novice researcher.
- Challenges with analyzing qualitative data
While qualitative data can answer questions that quantitative data can't, it still comes with challenges.
If done manually, qualitative data analysis is very time-consuming.
It can be hard to choose a method.
Avoiding bias is difficult.
Human error affects accuracy and consistency.
To overcome these challenges, you should fine-tune your methods by using the appropriate tools in collaboration with teammates.
Learn more about thematic analysis software
What is thematic analysis in qualitative research.
Thematic analysis is a method of analyzing qualitative data. It is applied to texts, such as interviews or transcripts. The researcher closely examines the data to identify common patterns and themes.
Can thematic analysis be done manually?
You can do thematic analysis manually, but it is very time-consuming without the help of software.
What are the two types of thematic analysis?
The two main types of thematic analysis include codebook thematic analysis and reflexive thematic analysis.
Codebook thematic analysis uses predetermined codes and structured codebooks to analyze from a deductive perspective. You draw codes from a review of the data or an initial analysis to produce the codebooks.
Reflexive thematic analysis is more flexible and does not use a codebook. Researchers can change, remove, and add codes as they work through the data.
What makes a good thematic analysis?
The goal of thematic analysis is more than simply summarizing data; it's about identifying important themes. Good thematic analysis interprets, makes sense of data, and explains it. It produces trustworthy and insightful findings that are easy to understand and apply.
What are examples of themes in thematic analysis?
Grouping codes into themes summarize sections of data in a useful way to answer research questions and achieve objectives. A theme identifies an area of data and tells the reader something about it. A good theme can sit alone without requiring descriptive text beneath it.
For example, if you were analyzing data on wildlife, codes might be owls, hawks, and falcons. These codes might fall beneath the theme of birds of prey. If your data were about the latest trends for teenage girls, codes such as mini skirts, leggings, and distressed jeans would fall under fashion.
Thematic analysis is straightforward and intuitive enough that most people have no trouble applying it.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 9 November 2024
Last updated: 24 October 2024
Last updated: 11 January 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 4 July 2024
Last updated: 12 October 2023
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 31 January 2024
Last updated: 23 January 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Last updated: 20 December 2023
Latest articles
Related topics, a whole new way to understand your customer is here, log in or sign up.
Get started for free

Work With Us
Private Coaching
Done-For-You
Short Courses
Client Reviews
Free Resources
What Is Thematic Analysis?
Plain-Language Explanation, Definition & Examples

T hematic analysis is one of the most popular qualitative analysis techniques we see students opting for at Grad Coach – and for good reason. Despite its relative simplicity, thematic analysis can be a very powerful analysis technique when used correctly. In this post, we’ll unpack thematic analysis using plain language (and loads of examples) so that you can conquer your analysis with confidence.
Thematic Analysis 101
- Basic terminology relating to thematic analysis
- What is thematic analysis
- When to use thematic analysis
- The main approaches to thematic analysis
- The three types of thematic analysis
- How to “do” thematic analysis (the process)
- Tips and suggestions
First, the lingo…
Before we begin, let’s first lay down some terminology. When undertaking thematic analysis, you’ll make use of codes . A code is a label assigned to a piece of text, and the aim of using a code is to identify and summarise important concepts within a set of data, such as an interview transcript.
For example, if you had the sentence, “My rabbit ate my shoes”, you could use the codes “rabbit” or “shoes” to highlight these two concepts. The process of assigning codes is called qualitative coding . If this is a new concept to you, be sure to check out our detailed post about qualitative coding .
Codes are vital as they lay a foundation for themes . But what exactly is a theme? Simply put, a theme is a pattern that can be identified within a data set. In other words, it’s a topic or concept that pops up repeatedly throughout your data. Grouping your codes into themes serves as a way of summarising sections of your data in a useful way that helps you answer your research question(s) and achieve your research aim(s).
Alright – with that out of the way, let’s jump into the wonderful world of thematic analysis…
What is thematic analysis?
Thematic analysis is the study of patterns to uncover meaning . In other words, it’s about analysing the patterns and themes within your data set to identify the underlying meaning. Importantly, this process is driven by your research aims and questions , so it’s not necessary to identify every possible theme in the data, but rather to focus on the key aspects that relate to your research questions .
Although the research questions are a driving force in thematic analysis (and pretty much all analysis methods), it’s important to remember that these questions are not necessarily fixed . As thematic analysis tends to be a bit of an exploratory process, research questions can evolve as you progress with your coding and theme identification.
When should you use thematic analysis?
There are many potential qualitative analysis methods that you can use to analyse a dataset. For example, content analysis , discourse analysis , and narrative analysis are popular choices. So why use thematic analysis?
Thematic analysis is highly beneficial when working with large bodies of data , as it allows you to divide and categorise large amounts of data in a way that makes it easier to digest. Thematic analysis is particularly useful when looking for subjective information , such as a participant’s experiences, views, and opinions. For this reason, thematic analysis is often conducted on data derived from interviews , conversations, open-ended survey responses , and social media posts.
Your research questions can also give you an idea of whether you should use thematic analysis or not. For example, if your research questions were to be along the lines of:
- How do dog walkers perceive rules and regulations on dog-friendly beaches?
- What are students’ experiences with the shift to online learning?
- What opinions do health professionals hold about the Hippocratic code?
- How is gender constructed in a high school classroom setting?
These examples are all research questions centering on the subjective experiences of participants and aim to assess experiences, views, and opinions. Therefore, thematic analysis presents a possible approach.
In short, thematic analysis is a good choice when you are wanting to categorise large bodies of data (although the data doesn’t necessarily have to be large), particularly when you are interested in subjective experiences .
What are the main approaches?
Broadly speaking, there are two overarching approaches to thematic analysis: inductive and deductive . The approach you take will depend on what is most suitable in light of your research aims and questions. Let’s have a look at the options.
The inductive approach
The inductive approach involves deriving meaning and creating themes from data without any preconceptions . In other words, you’d dive into your analysis without any idea of what codes and themes will emerge, and thus allow these to emerge from the data.
For example, if you’re investigating typical lunchtime conversational topics in a university faculty, you’d enter the research without any preconceived codes, themes or expected outcomes. Of course, you may have thoughts about what might be discussed (e.g., academic matters because it’s an academic setting), but the objective is to not let these preconceptions inform your analysis.
The inductive approach is best suited to research aims and questions that are exploratory in nature , and cases where there is little existing research on the topic of interest.
The deductive approach
In contrast to the inductive approach, a deductive approach involves jumping into your analysis with a pre-determined set of codes . Usually, this approach is informed by prior knowledge and/or existing theory or empirical research (which you’d cover in your literature review ).
For example, a researcher examining the impact of a specific psychological intervention on mental health outcomes may draw on an existing theoretical framework that includes concepts such as coping strategies, social support, and self-efficacy, using these as a basis for a set of pre-determined codes.
The deductive approach is best suited to research aims and questions that are confirmatory in nature , and cases where there is a lot of existing research on the topic of interest.
Regardless of whether you take the inductive or deductive approach, you’ll also need to decide what level of content your analysis will focus on – specifically, the semantic level or the latent level.
A semantic-level focus ignores the underlying meaning of data , and identifies themes based only on what is explicitly or overtly stated or written – in other words, things are taken at face value.
In contrast, a latent-level focus concentrates on the underlying meanings and looks at the reasons for semantic content. Furthermore, in contrast to the semantic approach, a latent approach involves an element of interpretation , where data is not just taken at face value, but meanings are also theorised.
“But how do I know when to use what approach?”, I hear you ask.
Well, this all depends on the type of data you’re analysing and what you’re trying to achieve with your analysis. For example, if you’re aiming to analyse explicit opinions expressed in interviews and you know what you’re looking for ahead of time (based on a collection of prior studies), you may choose to take a deductive approach with a semantic-level focus.
On the other hand, if you’re looking to explore the underlying meaning expressed by participants in a focus group, and you don’t have any preconceptions about what to expect, you’ll likely opt for an inductive approach with a latent-level focus.
Simply put, the nature and focus of your research, especially your research aims , objectives and questions will inform the approach you take to thematic analysis.

What are the types of thematic analysis?
Now that you’ve got an understanding of the overarching approaches to thematic analysis, it’s time to have a look at the different types of thematic analysis you can conduct. Broadly speaking, there are three “types” of thematic analysis:
- Reflexive thematic analysis
- Codebook thematic analysis
- Coding reliability thematic analysis
Let’s have a look at each of these:
Reflexive thematic analysis takes an inductive approach, letting the codes and themes emerge from that data. This type of thematic analysis is very flexible, as it allows researchers to change, remove, and add codes as they work through the data. As the name suggests, reflexive thematic analysis emphasizes the active engagement of the researcher in critically reflecting on their assumptions, biases, and interpretations, and how these may shape the analysis.
Reflexive thematic analysis typically involves iterative and reflexive cycles of coding, interpreting, and reflecting on data, with the aim of producing nuanced and contextually sensitive insights into the research topic, while at the same time recognising and addressing the subjective nature of the research process.
Codebook thematic analysis , on the other hand, lays on the opposite end of the spectrum. Taking a deductive approach, this type of thematic analysis makes use of structured codebooks containing clearly defined, predetermined codes. These codes are typically drawn from a combination of existing theoretical theories, empirical studies and prior knowledge of the situation.
Codebook thematic analysis aims to produce reliable and consistent findings. Therefore, it’s often used in studies where a clear and predefined coding framework is desired to ensure rigour and consistency in data analysis.
Coding reliability thematic analysis necessitates the work of multiple coders, and the design is specifically intended for research teams. With this type of analysis, codebooks are typically fixed and are rarely altered.
The benefit of this form of analysis is that it brings an element of intercoder reliability where coders need to agree upon the codes used, which means that the outcome is more rigorous as the element of subjectivity is reduced. In other words, multiple coders discuss which codes should be used and which shouldn’t, and this consensus reduces the bias of having one individual coder decide upon themes.

Quick Recap: Thematic analysis approaches and types
To recap, the two main approaches to thematic analysis are inductive , and deductive . Then we have the three types of thematic analysis: reflexive, codebook and coding reliability . Which type of thematic analysis you opt for will need to be informed by factors such as:
- The approach you are taking. For example, if you opt for an inductive approach, you’ll likely utilise reflexive thematic analysis.
- Whether you’re working alone or in a group . It’s likely that, if you’re doing research as part of your postgraduate studies, you’ll be working alone. This means that you’ll need to choose between reflexive and codebook thematic analysis.
Now that we’ve covered the “what” in terms of thematic analysis approaches and types, it’s time to look at the “how” of thematic analysis.

How to “do” thematic analysis
At this point, you’re ready to get going with your analysis, so let’s dive right into the thematic analysis process. Keep in mind that what we’ll cover here is a generic process, and the relevant steps will vary depending on the approach and type of thematic analysis you opt for.
Step 1: Get familiar with the data
The first step in your thematic analysis involves getting a feel for your data and seeing what general themes pop up. If you’re working with audio data, this is where you’ll do the transcription , converting audio to text.
At this stage, you’ll want to come up with preliminary thoughts about what you’ll code , what codes you’ll use for them, and what codes will accurately describe your content. It’s a good idea to revisit your research topic , and your aims and objectives at this stage. For example, if you’re looking at what people feel about different types of dogs, you can code according to when different breeds are mentioned (e.g., border collie, Labrador, corgi) and when certain feelings/emotions are brought up.
As a general tip, it’s a good idea to keep a reflexivity journal . This is where you’ll write down how you coded your data, why you coded your data in that particular way, and what the outcomes of this data coding are. Using a reflexive journal from the start will benefit you greatly in the final stages of your analysis because you can reflect on the coding process and assess whether you have coded in a manner that is reliable and whether your codes and themes support your findings.
As you can imagine, a reflexivity journal helps to increase reliability as it allows you to analyse your data systematically and consistently. If you choose to make use of a reflexivity journal, this is the stage where you’ll want to take notes about your initial codes and list them in your journal so that you’ll have an idea of what exactly is being reflected in your data. At a later stage in the analysis, this data can be more thoroughly coded, or the identified codes can be divided into more specific ones.
Need a helping hand?
Step 2: Search for patterns or themes in the codes
Step 2! You’re going strong. In this step, you’ll want to look out for patterns or themes in your codes. Moving from codes to themes is not necessarily a smooth or linear process. As you become more and more familiar with the data, you may find that you need to assign different codes or themes according to new elements you find. For example, if you were analysing a text talking about wildlife, you may come across the codes, “pigeon”, “canary” and “budgerigar” which can fall under the theme of birds.
As you work through the data, you may start to identify subthemes , which are subdivisions of themes that focus specifically on an aspect within the theme that is significant or relevant to your research question. For example, if your theme is a university, your subthemes could be faculties or departments at that university.
Step 3: Review themes
By now you’ll have a good idea of your codes, themes, and potentially subthemes. Now it’s time to review all the themes you’ve identified . In this step, you’ll want to check that everything you’ve categorised as a theme actually fits the data, whether the themes do indeed exist in the data, whether there are any themes missing , and whether you can move on to the next step knowing that you’ve coded all your themes accurately and comprehensively . If you find that your themes have become too broad and there is far too much information under one theme, it may be useful to split this into more themes so that you’re able to be more specific with your analysis.

Step 4: Finalise Themes
By this point, your analysis will really start to take shape. In the previous step, you reviewed and refined your themes, and now it’s time to label and finalise them . It’s important to note here that, just because you’ve moved onto the next step, it doesn’t mean that you can’t go back and revise or rework your themes. In contrast to the previous step, finalising your themes means spelling out what exactly the themes consist of, and describe them in detail . If you struggle with this, you may want to return to your data to make sure that your data and coding do represent the themes, and if you need to divide your themes into more themes (i.e., return to step 3).
When you name your themes, make sure that you select labels that accurately encapsulate the properties of the theme . For example, a theme name such as “enthusiasm in professionals” leaves the question of “who are the professionals?”, so you’d want to be more specific and label the theme as something along the lines of “enthusiasm in healthcare professionals”.
It is very important at this stage that you make sure that your themes align with your research aims and questions . When you’re finalising your themes, you’re also nearing the end of your analysis and need to keep in mind that your final report (discussed in the next step) will need to fit in with the aims and objectives of your research.
In your reflexivity journal, you’ll want to write down a few sentences describing your themes and how you decided on these. Here, you’ll also want to mention how the theme will contribute to the outcomes of your research, and also what it means in relation to your research questions and focus of your research.

Step 5: Produce your report
You’re nearly done! Now that you’ve analysed your data, it’s time to report on your findings. A typical thematic analysis report consists of:
- An introduction
- A methodology section
- Your results and findings
- A conclusion
When writing your report, make sure that you provide enough information for a reader to be able to evaluate the rigour of your analysis. In other words, the reader needs to know the exact process you followed when analysing your data and why. The questions of “what”, “how”, “why”, “who”, and “when” may be useful in this section.
So, what did you investigate? How did you investigate it? Why did you choose this particular method? Who does your research focus on, and who are your participants? When did you conduct your research, when did you collect your data, and when was the data produced? Your reflexivity journal will come in handy here as within it you’ve already labelled, described, and supported your themes.
If you’re undertaking a thematic analysis as part of a dissertation or thesis, this discussion will be split across your methodology, results and discussion chapters . For more information about those chapters, check out our detailed post about dissertation structure .
Quick Recap: How to “do” thematic analysis
Getting familiar with your data: Here you’ll read through your data and get a general overview of what you’re working with. At this stage, you may identify a few general codes and themes that you’ll make use of in the next step.
Search for patterns or themes in your codes : Here you’ll dive into your data and pick out the themes and codes relevant to your research question(s).
Review themes : In this step, you’ll revisit your codes and themes to make sure that they are all truly representative of the data, and that you can use them in your final report.
Finalise themes : Here’s where you “solidify” your analysis and make it report-ready by describing and defining your themes.
Produce your report : This is the final step of your thematic analysis process, where you put everything you’ve found together and report on your findings.
Tips & Suggestions
In the video below, we share 6 time-saving tips and tricks to help you approach your thematic analysis as effectively and efficiently as possible.
Wrapping Up
In this article, we’ve covered the basics of thematic analysis – what it is, when to use it, the different approaches and types of thematic analysis, and how to perform a thematic analysis.
If you have any questions about thematic analysis, drop a comment below and we’ll do our best to assist. If you’d like 1-on-1 support with your thematic analysis, be sure to check out our research coaching services here .

Learn More About Methodology

How To Choose A Tutor For Your Dissertation
Hiring the right tutor for your dissertation or thesis can make the difference between passing and failing. Here’s what you need to consider.

5 Signs You Need A Dissertation Helper
Discover the 5 signs that suggest you need a dissertation helper to get unstuck, finish your degree and get your life back.

Triangulation: The Ultimate Credibility Enhancer
Triangulation is one of the best ways to enhance the credibility of your research. Learn about the different options here.

Research Limitations 101: What You Need To Know
Learn everything you need to know about research limitations (AKA limitations of the study). Includes practical examples from real studies.

In Vivo Coding 101: Full Explainer With Examples
Learn about in vivo coding, a popular qualitative coding technique ideal for studies where the nuances of language are central to the aims.
📄 FREE TEMPLATES
Research Topic Ideation
Proposal Writing
Literature Review
Methodology & Analysis
Academic Writing
Referencing & Citing
Apps, Tools & Tricks
The Grad Coach Podcast
27 Comments
I really appreciate the help
Hello Sir, how many levels of coding can be done in thematic analysis? We generate codes from the transcripts, then subthemes from the codes and themes from subthemes, isn’t it? Should these themes be again grouped together? how many themes can be derived?can you please share an example of coding through thematic analysis in a tabular format?
I’ve found the article very educative and useful
Excellent. Very helpful and easy to understand.
This article so far has been most helpful in understanding how to write an analysis chapter. Thank you.
My research topic is the challenges face by the school principal on the process of procurement . Thematic analysis is it sutable fir data analysis ?
It is a great help. Thanks.
Best advice. Worth reading. Thank you.
Where can I find an example of a template analysis table ?
Finally I got the best article . I wish they also have every psychology topics.
Hello, Sir/Maam
I am actually finding difficulty in doing qualitative analysis of my data and how to triangulate this with quantitative data. I encountered your web by accident in the process of searching for a much simplified way of explaining about thematic analysis such as coding, thematic analysis, write up. When your query if I need help popped up, I was hesitant to answer. Because I think this is for fee and I cannot afford. So May I just ask permission to copy for me to read and guide me to study so I can apply it myself for my gathered qualitative data for my graduate study.
Thank you very much! this is very helpful to me in my Graduate research qualitative data analysis.
Thank you very much. I find your guidance here helpful. Kindly let help me understand how to write findings and discussions.
i am having troubles with the concept of framework analysis which i did not find here and i have been an assignment on framework analysis
I was discouraged and felt insecure because after more than a year of writing my thesis, my work seemed lost its direction after being checked. But, I am truly grateful because through the comments, corrections, and guidance of the wisdom of my director, I can already see the bright light because of thematic analysis. I am working with Biblical Texts. And thematic analysis will be my method. Thank you.
lovely and helpful. thanks
very informative information.
thank you very much!, this is very helpful in my report, God bless……..
Thank you for the insight. I am really relieved as you have provided a super guide for my thesis.
Thanks a lot, really enlightening
excellent! very helpful thank a lot for your great efforts
I am currently conducting a research on the Economic challenges to migrant integration. Using interviews to understand the challenges by interviewing professionals working with migrants. Wouks appreciate help with how to do this using the thematic approach. Thanks
The article cleared so many issues that I was not certain of. Very informative. Thank you.
i really appreciate the learning that learned from here
This was absolutely informative! I’ll certainly be using Grad Coach often 🙂 thank you!
Hi can you use thematic analysis on two variables?
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment
- Print Friendly
- - Google Chrome
Intended for healthcare professionals
- Access provided by Google Indexer
- My email alerts
- BMA member login
- Username * Password * Forgot your log in details? Need to activate BMA Member Log In Log in via OpenAthens Log in via your institution

Search form
- Advanced search
- Search responses
- Search blogs
- Practical thematic...
Practical thematic analysis: a guide for multidisciplinary health services research teams engaging in qualitative analysis
- Related content
- Peer review
- on behalf of the Coproduction Laboratory
- 1 Dartmouth Health, Lebanon, NH, USA
- 2 Dartmouth Institute for Health Policy and Clinical Practice, Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth College, Lebanon, NH, USA
- 3 Center for Primary Care and Public Health (Unisanté), Lausanne, Switzerland
- 4 Jönköping Academy for Improvement of Health and Welfare, School of Health and Welfare, Jönköping University, Jönköping, Sweden
- 5 Highland Park, NJ, USA
- 6 Division of Public Health Sciences, Department of Surgery, Washington University School of Medicine, St Louis, MO, USA
- Correspondence to: C H Saunders catherine.hylas.saunders{at}dartmouth.edu
- Accepted 26 April 2023
Qualitative research methods explore and provide deep contextual understanding of real world issues, including people’s beliefs, perspectives, and experiences. Whether through analysis of interviews, focus groups, structured observation, or multimedia data, qualitative methods offer unique insights in applied health services research that other approaches cannot deliver. However, many clinicians and researchers hesitate to use these methods, or might not use them effectively, which can leave relevant areas of inquiry inadequately explored. Thematic analysis is one of the most common and flexible methods to examine qualitative data collected in health services research. This article offers practical thematic analysis as a step-by-step approach to qualitative analysis for health services researchers, with a focus on accessibility for patients, care partners, clinicians, and others new to thematic analysis. Along with detailed instructions covering three steps of reading, coding, and theming, the article includes additional novel and practical guidance on how to draft effective codes, conduct a thematic analysis session, and develop meaningful themes. This approach aims to improve consistency and rigor in thematic analysis, while also making this method more accessible for multidisciplinary research teams.
Through qualitative methods, researchers can provide deep contextual understanding of real world issues, and generate new knowledge to inform hypotheses, theories, research, and clinical care. Approaches to data collection are varied, including interviews, focus groups, structured observation, and analysis of multimedia data, with qualitative research questions aimed at understanding the how and why of human experience. 1 2 Qualitative methods produce unique insights in applied health services research that other approaches cannot deliver. In particular, researchers acknowledge that thematic analysis is a flexible and powerful method of systematically generating robust qualitative research findings by identifying, analysing, and reporting patterns (themes) within data. 3 4 5 6 Although qualitative methods are increasingly valued for answering clinical research questions, many researchers are unsure how to apply them or consider them too time consuming to be useful in responding to practical challenges 7 or pressing situations such as public health emergencies. 8 Consequently, researchers might hesitate to use them, or use them improperly. 9 10 11
Although much has been written about how to perform thematic analysis, practical guidance for non-specialists is sparse. 3 5 6 12 13 In the multidisciplinary field of health services research, qualitative data analysis can confound experienced researchers and novices alike, which can stoke concerns about rigor, particularly for those more familiar with quantitative approaches. 14 Since qualitative methods are an area of specialisation, support from experts is beneficial. However, because non-specialist perspectives can enhance data interpretation and enrich findings, there is a case for making thematic analysis easier, more rapid, and more efficient, 8 particularly for patients, care partners, clinicians, and other stakeholders. A practical guide to thematic analysis might encourage those on the ground to use these methods in their work, unearthing insights that would otherwise remain undiscovered.
Given the need for more accessible qualitative analysis approaches, we present a simple, rigorous, and efficient three step guide for practical thematic analysis. We include new guidance on the mechanics of thematic analysis, including developing codes, constructing meaningful themes, and hosting a thematic analysis session. We also discuss common pitfalls in thematic analysis and how to avoid them.
Summary points
Qualitative methods are increasingly valued in applied health services research, but multidisciplinary research teams often lack accessible step-by-step guidance and might struggle to use these approaches
A newly developed approach, practical thematic analysis, uses three simple steps: reading, coding, and theming
Based on Braun and Clarke’s reflexive thematic analysis, our streamlined yet rigorous approach is designed for multidisciplinary health services research teams, including patients, care partners, and clinicians
This article also provides companion materials including a slide presentation for teaching practical thematic analysis to research teams, a sample thematic analysis session agenda, a theme coproduction template for use during the session, and guidance on using standardised reporting criteria for qualitative research
In their seminal work, Braun and Clarke developed a six phase approach to reflexive thematic analysis. 4 12 We built on their method to develop practical thematic analysis ( box 1 , fig 1 ), which is a simplified and instructive approach that retains the substantive elements of their six phases. Braun and Clarke’s phase 1 (familiarising yourself with the dataset) is represented in our first step of reading. Phase 2 (coding) remains as our second step of coding. Phases 3 (generating initial themes), 4 (developing and reviewing themes), and 5 (refining, defining, and naming themes) are represented in our third step of theming. Phase 6 (writing up) also occurs during this third step of theming, but after a thematic analysis session. 4 12
Key features and applications of practical thematic analysis
Step 1: reading.
All manuscript authors read the data
All manuscript authors write summary memos
Step 2: Coding
Coders perform both data management and early data analysis
Codes are complete thoughts or sentences, not categories
Step 3: Theming
Researchers host a thematic analysis session and share different perspectives
Themes are complete thoughts or sentences, not categories
Applications
For use by practicing clinicians, patients and care partners, students, interdisciplinary teams, and those new to qualitative research
When important insights from healthcare professionals are inaccessible because they do not have qualitative methods training
When time and resources are limited

Steps in practical thematic analysis
- Download figure
- Open in new tab
- Download powerpoint
We present linear steps, but as qualitative research is usually iterative, so too is thematic analysis. 15 Qualitative researchers circle back to earlier work to check whether their interpretations still make sense in the light of additional insights, adapting as necessary. While we focus here on the practical application of thematic analysis in health services research, we recognise our approach exists in the context of the broader literature on thematic analysis and the theoretical underpinnings of qualitative methods as a whole. For a more detailed discussion of these theoretical points, as well as other methods widely used in health services research, we recommend reviewing the sources outlined in supplemental material 1. A strong and nuanced understanding of the context and underlying principles of thematic analysis will allow for higher quality research. 16
Practical thematic analysis is a highly flexible approach that can draw out valuable findings and generate new hypotheses, including in cases with a lack of previous research to build on. The approach can also be used with a variety of data, such as transcripts from interviews or focus groups, patient encounter transcripts, professional publications, observational field notes, and online activity logs. Importantly, successful practical thematic analysis is predicated on having high quality data collected with rigorous methods. We do not describe qualitative research design or data collection here. 11 17
In supplemental material 1, we summarise the foundational methods, concepts, and terminology in qualitative research. Along with our guide below, we include a companion slide presentation for teaching practical thematic analysis to research teams in supplemental material 2. We provide a theme coproduction template for teams to use during thematic analysis sessions in supplemental material 3. Our method aligns with the major qualitative reporting frameworks, including the Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research (COREQ). 18 We indicate the corresponding step in practical thematic analysis for each COREQ item in supplemental material 4.
Familiarisation and memoing
We encourage all manuscript authors to review the full dataset (eg, interview transcripts) to familiarise themselves with it. This task is most critical for those who will later be engaged in the coding and theming steps. Although time consuming, it is the best way to involve team members in the intellectual work of data interpretation, so that they can contribute to the analysis and contextualise the results. If this task is not feasible given time limitations or large quantities of data, the data can be divided across team members. In this case, each piece of data should be read by at least two individuals who ideally represent different professional roles or perspectives.
We recommend that researchers reflect on the data and independently write memos, defined as brief notes on thoughts and questions that arise during reading, and a summary of their impressions of the dataset. 2 19 Memoing is an opportunity to gain insights from varying perspectives, particularly from patients, care partners, clinicians, and others. It also gives researchers the opportunity to begin to scope which elements of and concepts in the dataset are relevant to the research question.
Data saturation
The concept of data saturation ( box 2 ) is a foundation of qualitative research. It is defined as the point in analysis at which new data tend to be redundant of data already collected. 21 Qualitative researchers are expected to report their approach to data saturation. 18 Because thematic analysis is iterative, the team should discuss saturation throughout the entire process, beginning with data collection and continuing through all steps of the analysis. 22 During step 1 (reading), team members might discuss data saturation in the context of summary memos. Conversations about saturation continue during step 2 (coding), with confirmation that saturation has been achieved during step 3 (theming). As a rule of thumb, researchers can often achieve saturation in 9-17 interviews or 4-8 focus groups, but this will vary depending on the specific characteristics of the study. 23
Data saturation in context
Braun and Clarke discourage the use of data saturation to determine sample size (eg, number of interviews), because it assumes that there is an objective truth to be captured in the data (sometimes known as a positivist perspective). 20 Qualitative researchers often try to avoid positivist approaches, arguing that there is no one true way of seeing the world, and will instead aim to gather multiple perspectives. 5 Although this theoretical debate with qualitative methods is important, we recognise that a priori estimates of saturation are often needed, particularly for investigators newer to qualitative research who might want a more pragmatic and applied approach. In addition, saturation based, sample size estimation can be particularly helpful in grant proposals. However, researchers should still follow a priori sample size estimation with a discussion to confirm saturation has been achieved.
Definition of coding
We describe codes as labels for concepts in the data that are directly relevant to the study objective. Historically, the purpose of coding was to distil the large amount of data collected into conceptually similar buckets so that researchers could review it in aggregate and identify key themes. 5 24 We advocate for a more analytical approach than is typical with thematic analysis. With our method, coding is both the foundation for and the beginning of thematic analysis—that is, early data analysis, management, and reduction occur simultaneously rather than as different steps. This approach moves the team more efficiently towards being able to describe themes.
Building the coding team
Coders are the research team members who directly assign codes to the data, reading all material and systematically labelling relevant data with appropriate codes. Ideally, at least two researchers would code every discrete data document, such as one interview transcript. 25 If this task is not possible, individual coders can each code a subset of the data that is carefully selected for key characteristics (sometimes known as purposive selection). 26 When using this approach, we recommend that at least 10% of data be coded by two or more coders to ensure consistency in codebook application. We also recommend coding teams of no more than four to five people, for practical reasons concerning maintaining consistency.
Clinicians, patients, and care partners bring unique perspectives to coding and enrich the analytical process. 27 Therefore, we recommend choosing coders with a mix of relevant experiences so that they can challenge and contextualise each other’s interpretations based on their own perspectives and opinions ( box 3 ). We recommend including both coders who collected the data and those who are naive to it, if possible, given their different perspectives. We also recommend all coders review the summary memos from the reading step so that key concepts identified by those not involved in coding can be integrated into the analytical process. In practice, this review means coding the memos themselves and discussing them during the code development process. This approach ensures that the team considers a diversity of perspectives.
Coding teams in context
The recommendation to use multiple coders is a departure from Braun and Clarke. 28 29 When the views, experiences, and training of each coder (sometimes known as positionality) 30 are carefully considered, having multiple coders can enhance interpretation and enrich findings. When these perspectives are combined in a team setting, researchers can create shared meaning from the data. Along with the practical consideration of distributing the workload, 31 inclusion of these multiple perspectives increases the overall quality of the analysis by mitigating the impact of any one coder’s perspective. 30
Coding tools
Qualitative analysis software facilitates coding and managing large datasets but does not perform the analytical work. The researchers must perform the analysis themselves. Most programs support queries and collaborative coding by multiple users. 32 Important factors to consider when choosing software can include accessibility, cost, interoperability, the look and feel of code reports, and the ease of colour coding and merging codes. Coders can also use low tech solutions, including highlighters, word processors, or spreadsheets.
Drafting effective codes
To draft effective codes, we recommend that the coders review each document line by line. 33 As they progress, they can assign codes to segments of data representing passages of interest. 34 Coders can also assign multiple codes to the same passage. Consensus among coders on what constitutes a minimum or maximum amount of text for assigning a code is helpful. As a general rule, meaningful segments of text for coding are shorter than one paragraph, but longer than a few words. Coders should keep the study objective in mind when determining which data are relevant ( box 4 ).
Code types in context
Similar to Braun and Clarke’s approach, practical thematic analysis does not specify whether codes are based on what is evident from the data (sometimes known as semantic) or whether they are based on what can be inferred at a deeper level from the data (sometimes known as latent). 4 12 35 It also does not specify whether they are derived from the data (sometimes known as inductive) or determined ahead of time (sometimes known as deductive). 11 35 Instead, it should be noted that health services researchers conducting qualitative studies often adopt all these approaches to coding (sometimes known as hybrid analysis). 3
In practical thematic analysis, codes should be more descriptive than general categorical labels that simply group data with shared characteristics. At a minimum, codes should form a complete (or full) thought. An easy way to conceptualise full thought codes is as complete sentences with subjects and verbs ( table 1 ), although full sentence coding is not always necessary. With full thought codes, researchers think about the data more deeply and capture this insight in the codes. This coding facilitates the entire analytical process and is especially valuable when moving from codes to broader themes. Experienced qualitative researchers often intuitively use full thought or sentence codes, but this practice has not been explicitly articulated as a path to higher quality coding elsewhere in the literature. 6
Example transcript with codes used in practical thematic analysis 36
- View inline
Depending on the nature of the data, codes might either fall into flat categories or be arranged hierarchically. Flat categories are most common when the data deal with topics on the same conceptual level. In other words, one topic is not a subset of another topic. By contrast, hierarchical codes are more appropriate for concepts that naturally fall above or below each other. Hierarchical coding can also be a useful form of data management and might be necessary when working with a large or complex dataset. 5 Codes grouped into these categories can also make it easier to naturally transition into generating themes from the initial codes. 5 These decisions between flat versus hierarchical coding are part of the work of the coding team. In both cases, coders should ensure that their code structures are guided by their research questions.
Developing the codebook
A codebook is a shared document that lists code labels and comprehensive descriptions for each code, as well as examples observed within the data. Good code descriptions are precise and specific so that coders can consistently assign the same codes to relevant data or articulate why another coder would do so. Codebook development is iterative and involves input from the entire coding team. However, as those closest to the data, coders must resist undue influence, real or perceived, from other team members with conflicting opinions—it is important to mitigate the risk that more senior researchers, like principal investigators, exert undue influence on the coders’ perspectives.
In practical thematic analysis, coders begin codebook development by independently coding a small portion of the data, such as two to three transcripts or other units of analysis. Coders then individually produce their initial codebooks. This task will require them to reflect on, organise, and clarify codes. The coders then meet to reconcile the draft codebooks, which can often be difficult, as some coders tend to lump several concepts together while others will split them into more specific codes. Discussing disagreements and negotiating consensus are necessary parts of early data analysis. Once the codebook is relatively stable, we recommend soliciting input on the codes from all manuscript authors. Yet, coders must ultimately be empowered to finalise the details so that they are comfortable working with the codebook across a large quantity of data.
Assigning codes to the data
After developing the codebook, coders will use it to assign codes to the remaining data. While the codebook’s overall structure should remain constant, coders might continue to add codes corresponding to any new concepts observed in the data. If new codes are added, coders should review the data they have already coded and determine whether the new codes apply. Qualitative data analysis software can be useful for editing or merging codes.
We recommend that coders periodically compare their code occurrences ( box 5 ), with more frequent check-ins if substantial disagreements occur. In the event of large discrepancies in the codes assigned, coders should revise the codebook to ensure that code descriptions are sufficiently clear and comprehensive to support coding alignment going forward. Because coding is an iterative process, the team can adjust the codebook as needed. 5 28 29
Quantitative coding in context
Researchers should generally avoid reporting code counts in thematic analysis. However, counts can be a useful proxy in maintaining alignment between coders on key concepts. 26 In practice, therefore, researchers should make sure that all coders working on the same piece of data assign the same codes with a similar pattern and that their memoing and overall assessment of the data are aligned. 37 However, the frequency of a code alone is not an indicator of its importance. It is more important that coders agree on the most salient points in the data; reviewing and discussing summary memos can be helpful here. 5
Researchers might disagree on whether or not to calculate and report inter-rater reliability. We note that quantitative tests for agreement, such as kappa statistics or intraclass correlation coefficients, can be distracting and might not provide meaningful results in qualitative analyses. Similarly, Braun and Clarke argue that expecting perfect alignment on coding is inconsistent with the goal of co-constructing meaning. 28 29 Overall consensus on codes’ salience and contributions to themes is the most important factor.
Definition of themes
Themes are meta-constructs that rise above codes and unite the dataset ( box 6 , fig 2 ). They should be clearly evident, repeated throughout the dataset, and relevant to the research questions. 38 While codes are often explicit descriptions of the content in the dataset, themes are usually more conceptual and knit the codes together. 39 Some researchers hypothesise that theme development is loosely described in the literature because qualitative researchers simply intuit themes during the analytical process. 39 In practical thematic analysis, we offer a concrete process that should make developing meaningful themes straightforward.
Themes in context
According to Braun and Clarke, a theme “captures something important about the data in relation to the research question and represents some level of patterned response or meaning within the data set.” 4 Similarly, Braun and Clarke advise against themes as domain summaries. While different approaches can draw out themes from codes, the process begins by identifying patterns. 28 35 Like Braun and Clarke and others, we recommend that researchers consider the salience of certain themes, their prevalence in the dataset, and their keyness (ie, how relevant the themes are to the overarching research questions). 4 12 34

Use of themes in practical thematic analysis
Constructing meaningful themes
After coding all the data, each coder should independently reflect on the team’s summary memos (step 1), the codebook (step 2), and the coded data itself to develop draft themes (step 3). It can be illuminating for coders to review all excerpts associated with each code, so that they derive themes directly from the data. Researchers should remain focused on the research question during this step, so that themes have a clear relation with the overall project aim. Use of qualitative analysis software will make it easy to view each segment of data tagged with each code. Themes might neatly correspond to groups of codes. Or—more likely—they will unite codes and data in unexpected ways. A whiteboard or presentation slides might be helpful to organise, craft, and revise themes. We also provide a template for coproducing themes (supplemental material 3). As with codebook justification, team members will ideally produce individual drafts of the themes that they have identified in the data. They can then discuss these with the group and reach alignment or consensus on the final themes.
The team should ensure that all themes are salient, meaning that they are: supported by the data, relevant to the study objectives, and important. Similar to codes, themes are framed as complete thoughts or sentences, not categories. While codes and themes might appear to be similar to each other, the key distinction is that the themes represent a broader concept. Table 2 shows examples of codes and their corresponding themes from a previously published project that used practical thematic analysis. 36 Identifying three to four key themes that comprise a broader overarching theme is a useful approach. Themes can also have subthemes, if appropriate. 40 41 42 43 44
Example codes with themes in practical thematic analysis 36
Thematic analysis session
After each coder has independently produced draft themes, a carefully selected subset of the manuscript team meets for a thematic analysis session ( table 3 ). The purpose of this session is to discuss and reach alignment or consensus on the final themes. We recommend a session of three to five hours, either in-person or virtually.
Example agenda of thematic analysis session
The composition of the thematic analysis session team is important, as each person’s perspectives will shape the results. This group is usually a small subset of the broader research team, with three to seven individuals. We recommend that primary and senior authors work together to include people with diverse experiences related to the research topic. They should aim for a range of personalities and professional identities, particularly those of clinicians, trainees, patients, and care partners. At a minimum, all coders and primary and senior authors should participate in the thematic analysis session.
The session begins with each coder presenting their draft themes with supporting quotes from the data. 5 Through respectful and collaborative deliberation, the group will develop a shared set of final themes.
One team member facilitates the session. A firm, confident, and consistent facilitation style with good listening skills is critical. For practical reasons, this person is not usually one of the primary coders. Hierarchies in teams cannot be entirely flattened, but acknowledging them and appointing an external facilitator can reduce their impact. The facilitator can ensure that all voices are heard. For example, they might ask for perspectives from patient partners or more junior researchers, and follow up on comments from senior researchers to say, “We have heard your perspective and it is important; we want to make sure all perspectives in the room are equally considered.” Or, “I hear [senior person] is offering [x] idea, I’d like to hear other perspectives in the room.” The role of the facilitator is critical in the thematic analysis session. The facilitator might also privately discuss with more senior researchers, such as principal investigators and senior authors, the importance of being aware of their influence over others and respecting and eliciting the perspectives of more junior researchers, such as patients, care partners, and students.
To our knowledge, this discrete thematic analysis session is a novel contribution of practical thematic analysis. It helps efficiently incorporate diverse perspectives using the session agenda and theme coproduction template (supplemental material 3) and makes the process of constructing themes transparent to the entire research team.
Writing the report
We recommend beginning the results narrative with a summary of all relevant themes emerging from the analysis, followed by a subheading for each theme. Each subsection begins with a brief description of the theme and is illustrated with relevant quotes, which are contextualised and explained. The write-up should not simply be a list, but should contain meaningful analysis and insight from the researchers, including descriptions of how different stakeholders might have experienced a particular situation differently or unexpectedly.
In addition to weaving quotes into the results narrative, quotes can be presented in a table. This strategy is a particularly helpful when submitting to clinical journals with tight word count limitations. Quote tables might also be effective in illustrating areas of agreement and disagreement across stakeholder groups, with columns representing different groups and rows representing each theme or subtheme. Quotes should include an anonymous label for each participant and any relevant characteristics, such as role or gender. The aim is to produce rich descriptions. 5 We recommend against repeating quotations across multiple themes in the report, so as to avoid confusion. The template for coproducing themes (supplemental material 3) allows documentation of quotes supporting each theme, which might also be useful during report writing.
Visual illustrations such as a thematic map or figure of the findings can help communicate themes efficiently. 4 36 42 44 If a figure is not possible, a simple list can suffice. 36 Both must clearly present the main themes with subthemes. Thematic figures can facilitate confirmation that the researchers’ interpretations reflect the study populations’ perspectives (sometimes known as member checking), because authors can invite discussions about the figure and descriptions of findings and supporting quotes. 46 This process can enhance the validity of the results. 46
In supplemental material 4, we provide additional guidance on reporting thematic analysis consistent with COREQ. 18 Commonly used in health services research, COREQ outlines a standardised list of items to be included in qualitative research reports ( box 7 ).
Reporting in context
We note that use of COREQ or any other reporting guidelines does not in itself produce high quality work and should not be used as a substitute for general methodological rigor. Rather, researchers must consider rigor throughout the entire research process. As the issue of how to conceptualise and achieve rigorous qualitative research continues to be debated, 47 48 we encourage researchers to explicitly discuss how they have looked at methodological rigor in their reports. Specifically, we point researchers to Braun and Clarke’s 2021 tool for evaluating thematic analysis manuscripts for publication (“Twenty questions to guide assessment of TA [thematic analysis] research quality”). 16
Avoiding common pitfalls
Awareness of common mistakes can help researchers avoid improper use of qualitative methods. Improper use can, for example, prevent researchers from developing meaningful themes and can risk drawing inappropriate conclusions from the data. Braun and Clarke also warn of poor quality in qualitative research, noting that “coherence and integrity of published research does not always hold.” 16
Weak themes
An important distinction between high and low quality themes is that high quality themes are descriptive and complete thoughts. As such, they often contain subjects and verbs, and can be expressed as full sentences ( table 2 ). Themes that are simply descriptive categories or topics could fail to impart meaningful knowledge beyond categorisation. 16 49 50
Researchers will often move from coding directly to writing up themes, without performing the work of theming or hosting a thematic analysis session. Skipping concerted theming often results in themes that look more like categories than unifying threads across the data.
Unfocused analysis
Because data collection for qualitative research is often semi-structured (eg, interviews, focus groups), not all data will be directly relevant to the research question at hand. To avoid unfocused analysis and a correspondingly unfocused manuscript, we recommend that all team members keep the research objective in front of them at every stage, from reading to coding to theming. During the thematic analysis session, we recommend that the research question be written on a whiteboard so that all team members can refer back to it, and so that the facilitator can ensure that conversations about themes occur in the context of this question. Consistently focusing on the research question can help to ensure that the final report directly answers it, as opposed to the many other interesting insights that might emerge during the qualitative research process. Such insights can be picked up in a secondary analysis if desired.
Inappropriate quantification
Presenting findings quantitatively (eg, “We found 18 instances of participants mentioning safety concerns about the vaccines”) is generally undesirable in practical thematic analysis reporting. 51 Descriptive terms are more appropriate (eg, “participants had substantial concerns about the vaccines,” or “several participants were concerned about this”). This descriptive presentation is critical because qualitative data might not be consistently elicited across participants, meaning that some individuals might share certain information while others do not, simply based on how conversations evolve. Additionally, qualitative research does not aim to draw inferences outside its specific sample. Emphasising numbers in thematic analysis can lead to readers incorrectly generalising the findings. Although peer reviewers unfamiliar with thematic analysis often request this type of quantification, practitioners of practical thematic analysis can confidently defend their decision to avoid it. If quantification is methodologically important, we recommend simultaneously conducting a survey or incorporating standardised interview techniques into the interview guide. 11
Neglecting group dynamics
Researchers should concertedly consider group dynamics in the research team. Particular attention should be paid to power relations and the personality of team members, which can include aspects such as who most often speaks, who defines concepts, and who resolves disagreements that might arise within the group. 52
The perspectives of patient and care partners are particularly important to cultivate. Ideally, patient partners are meaningfully embedded in studies from start to finish, not just for practical thematic analysis. 53 Meaningful engagement can build trust, which makes it easier for patient partners to ask questions, request clarification, and share their perspectives. Professional team members should actively encourage patient partners by emphasising that their expertise is critically important and valued. Noting when a patient partner might be best positioned to offer their perspective can be particularly powerful.
Insufficient time allocation
Researchers must allocate enough time to complete thematic analysis. Working with qualitative data takes time, especially because it is often not a linear process. As the strength of thematic analysis lies in its ability to make use of the rich details and complexities of the data, we recommend careful planning for the time required to read and code each document.
Estimating the necessary time can be challenging. For step 1 (reading), researchers can roughly calculate the time required based on the time needed to read and reflect on one piece of data. For step 2 (coding), the total amount of time needed can be extrapolated from the time needed to code one document during codebook development. We also recommend three to five hours for the thematic analysis session itself, although coders will need to independently develop their draft themes beforehand. Although the time required for practical thematic analysis is variable, teams should be able to estimate their own required effort with these guidelines.
Practical thematic analysis builds on the foundational work of Braun and Clarke. 4 16 We have reframed their six phase process into three condensed steps of reading, coding, and theming. While we have maintained important elements of Braun and Clarke’s reflexive thematic analysis, we believe that practical thematic analysis is conceptually simpler and easier to teach to less experienced researchers and non-researcher stakeholders. For teams with different levels of familiarity with qualitative methods, this approach presents a clear roadmap to the reading, coding, and theming of qualitative data. Our practical thematic analysis approach promotes efficient learning by doing—experiential learning. 12 29 Practical thematic analysis avoids the risk of relying on complex descriptions of methods and theory and places more emphasis on obtaining meaningful insights from those close to real world clinical environments. Although practical thematic analysis can be used to perform intensive theory based analyses, it lends itself more readily to accelerated, pragmatic approaches.
Strengths and limitations
Our approach is designed to smooth the qualitative analysis process and yield high quality themes. Yet, researchers should note that poorly performed analyses will still produce low quality results. Practical thematic analysis is a qualitative analytical approach; it does not look at study design, data collection, or other important elements of qualitative research. It also might not be the right choice for every qualitative research project. We recommend it for applied health services research questions, where diverse perspectives and simplicity might be valuable.
We also urge researchers to improve internal validity through triangulation methods, such as member checking (supplemental material 1). 46 Member checking could include soliciting input on high level themes, theme definitions, and quotations from participants. This approach might increase rigor.
Implications
We hope that by providing clear and simple instructions for practical thematic analysis, a broader range of researchers will be more inclined to use these methods. Increased transparency and familiarity with qualitative approaches can enhance researchers’ ability to both interpret qualitative studies and offer up new findings themselves. In addition, it can have usefulness in training and reporting. A major strength of this approach is to facilitate meaningful inclusion of patient and care partner perspectives, because their lived experiences can be particularly valuable in data interpretation and the resulting findings. 11 30 As clinicians are especially pressed for time, they might also appreciate a practical set of instructions that can be immediately used to leverage their insights and access to patients and clinical settings, and increase the impact of qualitative research through timely results. 8
Practical thematic analysis is a simplified approach to performing thematic analysis in health services research, a field where the experiences of patients, care partners, and clinicians are of inherent interest. We hope that it will be accessible to those individuals new to qualitative methods, including patients, care partners, clinicians, and other health services researchers. We intend to empower multidisciplinary research teams to explore unanswered questions and make new, important, and rigorous contributions to our understanding of important clinical and health systems research.
Acknowledgments
All members of the Coproduction Laboratory provided input that shaped this manuscript during laboratory meetings. We acknowledge advice from Elizabeth Carpenter-Song, an expert in qualitative methods.
Coproduction Laboratory group contributors: Stephanie C Acquilano ( http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1215-5531 ), Julie Doherty ( http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5279-6536 ), Rachel C Forcino ( http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9938-4830 ), Tina Foster ( http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6239-4031 ), Megan Holthoff, Christopher R Jacobs ( http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5324-8657 ), Lisa C Johnson ( http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7448-4931 ), Elaine T Kiriakopoulos, Kathryn Kirkland ( http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9851-926X ), Meredith A MacMartin ( http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6614-6091 ), Emily A Morgan, Eugene Nelson, Elizabeth O’Donnell, Brant Oliver ( http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7399-622X ), Danielle Schubbe ( http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9858-1805 ), Gabrielle Stevens ( http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9001-178X ), Rachael P Thomeer ( http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5974-3840 ).
Contributors: Practical thematic analysis, an approach designed for multidisciplinary health services teams new to qualitative research, was based on CHS’s experiences teaching thematic analysis to clinical teams and students. We have drawn heavily from qualitative methods literature. CHS is the guarantor of the article. CHS, AS, CvP, AMK, JRK, and JAP contributed to drafting the manuscript. AS, JG, CMM, JAP, and RWY provided feedback on their experiences using practical thematic analysis. CvP, LCL, SLB, AVC, GE, and JKL advised on qualitative methods in health services research, given extensive experience. All authors meaningfully edited the manuscript content, including AVC and RKS. The corresponding author attests that all listed authors meet authorship criteria and that no others meeting the criteria have been omitted.
Funding: This manuscript did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Competing interests: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form at https://www.icmje.org/disclosure-of-interest/ and declare: no support from any organisation for the submitted work; no financial relationships with any organisations that might have an interest in the submitted work in the previous three years; no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
- Ziebland S ,
- ↵ A Hybrid Approach to Thematic Analysis in Qualitative Research: Using a Practical Example. 2018. https://methods.sagepub.com/case/hybrid-approach-thematic-analysis-qualitative-research-a-practical-example .
- Maguire M ,
- Vindrola-Padros C ,
- Vindrola-Padros B
- ↵ Vindrola-Padros C. Rapid Ethnographies: A Practical Guide . Cambridge University Press 2021. https://play.google.com/store/books/details?id=n80HEAAAQBAJ
- Schroter S ,
- Merino JG ,
- Barbeau A ,
- ↵ Padgett DK. Qualitative and Mixed Methods in Public Health . SAGE Publications 2011. https://play.google.com/store/books/details?id=LcYgAQAAQBAJ
- Scharp KM ,
- Korstjens I
- Barnett-Page E ,
- ↵ Guest G, Namey EE, Mitchell ML. Collecting Qualitative Data: A Field Manual for Applied Research . SAGE 2013. https://play.google.com/store/books/details?id=-3rmWYKtloC
- Sainsbury P ,
- Emerson RM ,
- Saunders B ,
- Kingstone T ,
- Hennink MM ,
- Kaiser BN ,
- Hennink M ,
- O’Connor C ,
- ↵ Yen RW, Schubbe D, Walling L, et al. Patient engagement in the What Matters Most trial: experiences and future implications for research. Poster presented at International Shared Decision Making conference, Quebec City, Canada. July 2019.
- ↵ Got questions about Thematic Analysis? We have prepared some answers to common ones. https://www.thematicanalysis.net/faqs/ (accessed 9 Nov 2022).
- ↵ Braun V, Clarke V. Thematic Analysis. SAGE Publications. 2022. https://uk.sagepub.com/en-gb/eur/thematic-analysis/book248481 .
- Kalpokas N ,
- Radivojevic I
- Campbell KA ,
- Durepos P ,
- ↵ Understanding Thematic Analysis. https://www.thematicanalysis.net/understanding-ta/ .
- Saunders CH ,
- Stevens G ,
- CONFIDENT Study Long-Term Care Partners
- MacQueen K ,
- Vaismoradi M ,
- Turunen H ,
- Schott SL ,
- Berkowitz J ,
- Carpenter-Song EA ,
- Goldwag JL ,
- Durand MA ,
- Goldwag J ,
- Saunders C ,
- Mishra MK ,
- Rodriguez HP ,
- Shortell SM ,
- Verdinelli S ,
- Scagnoli NI
- Campbell C ,
- Sparkes AC ,
- McGannon KR
- Sandelowski M ,
- Connelly LM ,
- O’Malley AJ ,

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Using a comprehensive framework, this paper gives a flexible and methodical method for thematic analysis in qualitative research. This six-stage procedure goes above and beyond a purely inductive analysis of data by including deductive features.
Thematic analysis is a method of analyzing qualitative data. It is usually applied to a set of texts, such as an interview or transcripts. The researcher closely examines the data to identify common themes – topics, ideas and patterns of meaning that come up repeatedly.
Thematic analysis is a qualitative research method used to identify, analyze, and interpret patterns of shared meaning (themes) within a given data set, which can be in the form of interviews, focus group discussions, surveys, or other textual data.
Thematic analysis is a method for analyzing qualitative data that involves reading through a data set and looking for patterns to derive themes. The researcher's subjective experience plays a central role in finding meaning within the data.
Thematic analysis is the study of patterns to uncover meaning. In other words, it’s about analysing the patterns and themes within your data set to identify the underlying meaning.
Thematic analysis is a qualitative research method used to identify, analyze, and interpret patterns of shared meaning (themes) within a given data set, which can be in...
Thematic analysis is an apt qualitative method that can be used when working in research teams and analyzing large qualitative data sets. Our step-by-step approach provides a detailed description and pragmatic approach to conduct a thematic analysis.
Thematic analysis. In Liamputtong P. (Ed.), Handbook of research methods in health social sciences (pp. 843–860). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-5251-4_103. Google Scholar. Kidder L. H., Fine M. (1987). Qualitative and quantitative methods: When stories converge.
Thematic Analysis (TA) is an accessible, flexible, and increasingly popular method of qualitative data analysis. Learning to do it provides the qualitative researcher with a foundation in the basic skills needed to engage with other approaches to qualitative data analysis.
This article offers practical thematic analysis as a step-by-step approach to qualitative analysis for health services researchers, with a focus on accessibility for patients, care partners, clinicians, and others new to thematic analysis.