

10 Most Common Speech-Language Disorders & Impediments
As you get to know more about the field of speech-language pathology you’ll increasingly realize why SLPs are required to earn at least a master’s degree . This stuff is serious – and there’s nothing easy about it.
In 2016 the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders reported that 7.7% of American children have been diagnosed with a speech or swallowing disorder. That comes out to nearly one in 12 children, and gets even bigger if you factor in adults.
Whether rooted in psycho-speech behavioral issues, muscular disorders, or brain damage, nearly all the diagnoses SLPs make fall within just 10 common categories…
Types of Speech Disorders & Impediments
Apraxia of speech (aos).
Apraxia of Speech (AOS) happens when the neural pathway between the brain and a person’s speech function (speech muscles) is lost or obscured. The person knows what they want to say – they can even write what they want to say on paper – however the brain is unable to send the correct messages so that speech muscles can articulate what they want to say, even though the speech muscles themselves work just fine. Many SLPs specialize in the treatment of Apraxia .
There are different levels of severity of AOS, ranging from mostly functional, to speech that is incoherent. And right now we know for certain it can be caused by brain damage, such as in an adult who has a stroke. This is called Acquired AOS.
However the scientific and medical community has been unable to detect brain damage – or even differences – in children who are born with this disorder, making the causes of Childhood AOS somewhat of a mystery. There is often a correlation present, with close family members suffering from learning or communication disorders, suggesting there may be a genetic link.
Mild cases might be harder to diagnose, especially in children where multiple unknown speech disorders may be present. Symptoms of mild forms of AOS are shared by a range of different speech disorders, and include mispronunciation of words and irregularities in tone, rhythm, or emphasis (prosody).
Stuttering – Stammering
Stuttering, also referred to as stammering, is so common that everyone knows what it sounds like and can easily recognize it. Everyone has probably had moments of stuttering at least once in their life. The National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders estimates that three million Americans stutter, and reports that of the up-to-10-percent of children who do stutter, three-quarters of them will outgrow it. It should not be confused with cluttering.
Most people don’t know that stuttering can also include non-verbal involuntary or semi-voluntary actions like blinking or abdominal tensing (tics). Speech language pathologists are trained to look for all the symptoms of stuttering , especially the non-verbal ones, and that is why an SLP is qualified to make a stuttering diagnosis.
The earliest this fluency disorder can become apparent is when a child is learning to talk. It may also surface later during childhood. Rarely if ever has it developed in adults, although many adults have kept a stutter from childhood.
Stuttering only becomes a problem when it has an impact on daily activities, or when it causes concern to parents or the child suffering from it. In some people, a stutter is triggered by certain events like talking on the phone. When people start to avoid specific activities so as not to trigger their stutter, this is a sure sign that the stutter has reached the level of a speech disorder.
The causes of stuttering are mostly a mystery. There is a correlation with family history indicating a genetic link. Another theory is that a stutter is a form of involuntary or semi-voluntary tic. Most studies of stuttering agree there are many factors involved.
Dysarthria is a symptom of nerve or muscle damage. It manifests itself as slurred speech, slowed speech, limited tongue, jaw, or lip movement, abnormal rhythm and pitch when speaking, changes in voice quality, difficulty articulating, labored speech, and other related symptoms.
It is caused by muscle damage, or nerve damage to the muscles involved in the process of speaking such as the diaphragm, lips, tongue, and vocal chords.
Because it is a symptom of nerve and/or muscle damage it can be caused by a wide range of phenomena that affect people of all ages. This can start during development in the womb or shortly after birth as a result of conditions like muscular dystrophy and cerebral palsy. In adults some of the most common causes of dysarthria are stroke, tumors, and MS.
A lay term, lisping can be recognized by anyone and is very common.
Speech language pathologists provide an extra level of expertise when treating patients with lisping disorders . They can make sure that a lisp is not being confused with another type of disorder such as apraxia, aphasia, impaired development of expressive language, or a speech impediment caused by hearing loss.
SLPs are also important in distinguishing between the five different types of lisps. Most laypersons can usually pick out the most common type, the interdental/dentalised lisp. This is when a speaker makes a “th” sound when trying to make the “s” sound. It is caused by the tongue reaching past or touching the front teeth.
Because lisps are functional speech disorders, SLPs can play a huge role in correcting these with results often being a complete elimination of the lisp. Treatment is particularly effective when implemented early, although adults can also benefit.
Experts recommend professional SLP intervention if a child has reached the age of four and still has an interdental/dentalised lisp. SLP intervention is recommended as soon as possible for all other types of lisps. Treatment includes pronunciation and annunciation coaching, re-teaching how a sound or word is supposed to be pronounced, practice in front of a mirror, and speech-muscle strengthening that can be as simple as drinking out of a straw.
Spasmodic Dysphonia
Spasmodic Dysphonia (SD) is a chronic long-term disorder that affects the voice. It is characterized by a spasming of the vocal chords when a person attempts to speak and results in a voice that can be described as shaky, hoarse, groaning, tight, or jittery. It can cause the emphasis of speech to vary considerably. Many SLPs specialize in the treatment of Spasmodic Dysphonia .
SLPs will most often encounter this disorder in adults, with the first symptoms usually occurring between the ages of 30 and 50. It can be caused by a range of things mostly related to aging, such as nervous system changes and muscle tone disorders.
It’s difficult to isolate vocal chord spasms as being responsible for a shaky or trembly voice, so diagnosing SD is a team effort for SLPs that also involves an ear, nose, and throat doctor (otolaryngologist) and a neurologist.
Have you ever heard people talking about how they are smart but also nervous in large groups of people, and then self-diagnose themselves as having Asperger’s? You might have heard a similar lay diagnosis for cluttering. This is an indication of how common this disorder is as well as how crucial SLPs are in making a proper cluttering diagnosis .
A fluency disorder, cluttering is characterized by a person’s speech being too rapid, too jerky, or both. To qualify as cluttering, the person’s speech must also have excessive amounts of “well,” “um,” “like,” “hmm,” or “so,” (speech disfluencies), an excessive exclusion or collapsing of syllables, or abnormal syllable stresses or rhythms.
The first symptoms of this disorder appear in childhood. Like other fluency disorders, SLPs can have a huge impact on improving or eliminating cluttering. Intervention is most effective early on in life, however adults can also benefit from working with an SLP.
Muteness – Selective Mutism
There are different kinds of mutism, and here we are talking about selective mutism. This used to be called elective mutism to emphasize its difference from disorders that caused mutism through damage to, or irregularities in, the speech process.
Selective mutism is when a person does not speak in some or most situations, however that person is physically capable of speaking. It most often occurs in children, and is commonly exemplified by a child speaking at home but not at school.
Selective mutism is related to psychology. It appears in children who are very shy, who have an anxiety disorder, or who are going through a period of social withdrawal or isolation. These psychological factors have their own origins and should be dealt with through counseling or another type of psychological intervention.
Diagnosing selective mutism involves a team of professionals including SLPs, pediatricians, psychologists, and psychiatrists. SLPs play an important role in this process because there are speech language disorders that can have the same effect as selective muteness – stuttering, aphasia, apraxia of speech, or dysarthria – and it’s important to eliminate these as possibilities.
And just because selective mutism is primarily a psychological phenomenon, that doesn’t mean SLPs can’t do anything. Quite the contrary.
The National Institute on Neurological Disorders and Stroke estimates that one million Americans have some form of aphasia.
Aphasia is a communication disorder caused by damage to the brain’s language capabilities. Aphasia differs from apraxia of speech and dysarthria in that it solely pertains to the brain’s speech and language center.
As such anyone can suffer from aphasia because brain damage can be caused by a number of factors. However SLPs are most likely to encounter aphasia in adults, especially those who have had a stroke. Other common causes of aphasia are brain tumors, traumatic brain injuries, and degenerative brain diseases.
In addition to neurologists, speech language pathologists have an important role in diagnosing aphasia. As an SLP you’ll assess factors such as a person’s reading and writing, functional communication, auditory comprehension, and verbal expression.
Speech Delay – Alalia
A speech delay, known to professionals as alalia, refers to the phenomenon when a child is not making normal attempts to verbally communicate. There can be a number of factors causing this to happen, and that’s why it’s critical for a speech language pathologist to be involved.
The are many potential reasons why a child would not be using age-appropriate communication. These can range anywhere from the child being a “late bloomer” – the child just takes a bit longer than average to speak – to the child having brain damage. It is the role of an SLP to go through a process of elimination, evaluating each possibility that could cause a speech delay, until an explanation is found.
Approaching a child with a speech delay starts by distinguishing among the two main categories an SLP will evaluate: speech and language.
Speech has a lot to do with the organs of speech – the tongue, mouth, and vocal chords – as well as the muscles and nerves that connect them with the brain. Disorders like apraxia of speech and dysarthria are two examples that affect the nerve connections and organs of speech. Other examples in this category could include a cleft palette or even hearing loss.
The other major category SLPs will evaluate is language. This relates more to the brain and can be affected by brain damage or developmental disorders like autism. There are many different types of brain damage that each manifest themselves differently, as well as developmental disorders, and the SLP will make evaluations for everything.
Issues Related to Autism
While the autism spectrum itself isn’t a speech disorder, it makes this list because the two go hand-in-hand more often than not.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports that one out of every 68 children in our country have an autism spectrum disorder. And by definition, all children who have autism also have social communication problems.
Speech-language pathologists are often a critical voice on a team of professionals – also including pediatricians, occupational therapists, neurologists, developmental specialists, and physical therapists – who make an autism spectrum diagnosis .
In fact, the American Speech-Language Hearing Association reports that problems with communication are the first detectable signs of autism. That is why language disorders – specifically disordered verbal and nonverbal communication – are one of the primary diagnostic criteria for autism.
So what kinds of SLP disorders are you likely to encounter with someone on the autism spectrum?
A big one is apraxia of speech. A study that came out of Penn State in 2015 found that 64 percent of children who were diagnosed with autism also had childhood apraxia of speech.
This basic primer on the most common speech disorders offers little more than an interesting glimpse into the kind of issues that SLPs work with patients to resolve. But even knowing everything there is to know about communication science and speech disorders doesn’t tell the whole story of what this profession is all about. With every client in every therapy session, the goal is always to have the folks that come to you for help leave with a little more confidence than when they walked in the door that day. As a trusted SLP, you will build on those gains with every session, helping clients experience the joy and freedom that comes with the ability to express themselves freely. At the end of the day, this is what being an SLP is all about.
Ready to make a difference in speech pathology? Learn how to become a Speech-Language Pathologist today
- Emerson College - Master's in Speech-Language Pathology online - Prepare to become an SLP in as few as 20 months. No GRE required. Scholarships available.
- NYU Steinhardt - NYU Steinhardt's Master of Science in Communicative Sciences and Disorders online - ASHA-accredited. Bachelor's degree required. Graduate prepared to pursue licensure.
- Arizona State University - Online - Online Bachelor of Science in Speech and Hearing Science - Designed to prepare graduates to work in behavioral health settings or transition to graduate programs in speech-language pathology and audiology.
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Types of Speech Impediments
Sanjana is a health writer and editor. Her work spans various health-related topics, including mental health, fitness, nutrition, and wellness.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/SanjanaGupta-d217a6bfa3094955b3361e021f77fcca.jpg)
Steven Gans, MD is board-certified in psychiatry and is an active supervisor, teacher, and mentor at Massachusetts General Hospital.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/steven-gans-1000-51582b7f23b6462f8713961deb74959f.jpg)
Phynart Studio / Getty Images
Articulation Errors
Ankyloglossia, treating speech disorders.
A speech impediment, also known as a speech disorder , is a condition that can affect a person’s ability to form sounds and words, making their speech difficult to understand.
Speech disorders generally become evident in early childhood, as children start speaking and learning language. While many children initially have trouble with certain sounds and words, most are able to speak easily by the time they are five years old. However, some speech disorders persist. Approximately 5% of children aged three to 17 in the United States experience speech disorders.
There are many different types of speech impediments, including:
- Articulation errors
This article explores the causes, symptoms, and treatment of the different types of speech disorders.
Speech impediments that break the flow of speech are known as disfluencies. Stuttering is the most common form of disfluency, however there are other types as well.
Symptoms and Characteristics of Disfluencies
These are some of the characteristics of disfluencies:
- Repeating certain phrases, words, or sounds after the age of 4 (For example: “O…orange,” “I like…like orange juice,” “I want…I want orange juice”)
- Adding in extra sounds or words into sentences (For example: “We…uh…went to buy…um…orange juice”)
- Elongating words (For example: Saying “orange joooose” instead of "orange juice")
- Replacing words (For example: “What…Where is the orange juice?”)
- Hesitating while speaking (For example: A long pause while thinking)
- Pausing mid-speech (For example: Stopping abruptly mid-speech, due to lack of airflow, causing no sounds to come out, leading to a tense pause)
In addition, someone with disfluencies may also experience the following symptoms while speaking:
- Vocal tension and strain
- Head jerking
- Eye blinking
- Lip trembling
Causes of Disfluencies
People with disfluencies tend to have neurological differences in areas of the brain that control language processing and coordinate speech, which may be caused by:
- Genetic factors
- Trauma or infection to the brain
- Environmental stressors that cause anxiety or emotional distress
- Neurodevelopmental conditions like attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
Articulation disorders occur when a person has trouble placing their tongue in the correct position to form certain speech sounds. Lisping is the most common type of articulation disorder.
Symptoms and Characteristics of Articulation Errors
These are some of the characteristics of articulation disorders:
- Substituting one sound for another . People typically have trouble with ‘r’ and ‘l’ sounds. (For example: Being unable to say “rabbit” and saying “wabbit” instead)
- Lisping , which refers specifically to difficulty with ‘s’ and ‘z’ sounds. (For example: Saying “thugar” instead of “sugar” or producing a whistling sound while trying to pronounce these letters)
- Omitting sounds (For example: Saying “coo” instead of “school”)
- Adding sounds (For example: Saying “pinanio” instead of “piano”)
- Making other speech errors that can make it difficult to decipher what the person is saying. For instance, only family members may be able to understand what they’re trying to say.
Causes of Articulation Errors
Articulation errors may be caused by:
- Genetic factors, as it can run in families
- Hearing loss , as mishearing sounds can affect the person’s ability to reproduce the sound
- Changes in the bones or muscles that are needed for speech, including a cleft palate (a hole in the roof of the mouth) and tooth problems
- Damage to the nerves or parts of the brain that coordinate speech, caused by conditions such as cerebral palsy , for instance
Ankyloglossia, also known as tongue-tie, is a condition where the person’s tongue is attached to the bottom of their mouth. This can restrict the tongue’s movement and make it hard for the person to move their tongue.
Symptoms and Characteristics of Ankyloglossia
Ankyloglossia is characterized by difficulty pronouncing ‘d,’ ‘n,’ ‘s,’ ‘t,’ ‘th,’ and ‘z’ sounds that require the person’s tongue to touch the roof of their mouth or their upper teeth, as their tongue may not be able to reach there.
Apart from speech impediments, people with ankyloglossia may also experience other symptoms as a result of their tongue-tie. These symptoms include:
- Difficulty breastfeeding in newborns
- Trouble swallowing
- Limited ability to move the tongue from side to side or stick it out
- Difficulty with activities like playing wind instruments, licking ice cream, or kissing
- Mouth breathing
Causes of Ankyloglossia
Ankyloglossia is a congenital condition, which means it is present from birth. A tissue known as the lingual frenulum attaches the tongue to the base of the mouth. People with ankyloglossia have a shorter lingual frenulum, or it is attached further along their tongue than most people’s.
Dysarthria is a condition where people slur their words because they cannot control the muscles that are required for speech, due to brain, nerve, or organ damage.
Symptoms and Characteristics of Dysarthria
Dysarthria is characterized by:
- Slurred, choppy, or robotic speech
- Rapid, slow, or soft speech
- Breathy, hoarse, or nasal voice
Additionally, someone with dysarthria may also have other symptoms such as difficulty swallowing and inability to move their tongue, lips, or jaw easily.
Causes of Dysarthria
Dysarthria is caused by paralysis or weakness of the speech muscles. The causes of the weakness can vary depending on the type of dysarthria the person has:
- Central dysarthria is caused by brain damage. It may be the result of neuromuscular diseases, such as cerebral palsy, Huntington’s disease, multiple sclerosis, muscular dystrophy, Huntington’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, or Lou Gehrig’s disease. Central dysarthria may also be caused by injuries or illnesses that damage the brain, such as dementia, stroke, brain tumor, or traumatic brain injury .
- Peripheral dysarthria is caused by damage to the organs involved in speech. It may be caused by congenital structural problems, trauma to the mouth or face, or surgery to the tongue, mouth, head, neck, or voice box.
Apraxia, also known as dyspraxia, verbal apraxia, or apraxia of speech, is a neurological condition that can cause a person to have trouble moving the muscles they need to create sounds or words. The person’s brain knows what they want to say, but is unable to plan and sequence the words accordingly.
Symptoms and Characteristics of Apraxia
These are some of the characteristics of apraxia:
- Distorting sounds: The person may have trouble pronouncing certain sounds, particularly vowels, because they may be unable to move their tongue or jaw in the manner required to produce the right sound. Longer or more complex words may be especially harder to manage.
- Being inconsistent in their speech: For instance, the person may be able to pronounce a word correctly once, but may not be able to repeat it. Or, they may pronounce it correctly today and differently on another day.
- Grasping for words: The person may appear to be searching for the right word or sound, or attempt the pronunciation several times before getting it right.
- Making errors with the rhythm or tone of speech: The person may struggle with using tone and inflection to communicate meaning. For instance, they may not stress any of the words in a sentence, have trouble going from one syllable in a word to another, or pause at an inappropriate part of a sentence.
Causes of Apraxia
Apraxia occurs when nerve pathways in the brain are interrupted, which can make it difficult for the brain to send messages to the organs involved in speaking. The causes of these neurological disturbances can vary depending on the type of apraxia the person has:
- Childhood apraxia of speech (CAS): This condition is present from birth and is often hereditary. A person may be more likely to have it if a biological relative has a learning disability or communication disorder.
- Acquired apraxia of speech (AOS): This condition can occur in adults, due to brain damage as a result of a tumor, head injury , stroke, or other illness that affects the parts of the brain involved in speech.
If you have a speech impediment, or suspect your child might have one, it can be helpful to visit your healthcare provider. Your primary care physician can refer you to a speech-language pathologist, who can evaluate speech, diagnose speech disorders, and recommend treatment options.
The diagnostic process may involve a physical examination as well as psychological, neurological, or hearing tests, in order to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other causes.
Treatment for speech disorders often involves speech therapy, which can help you learn how to move your muscles and position your tongue correctly in order to create specific sounds. It can be quite effective in improving your speech.
Children often grow out of milder speech disorders; however, special education and speech therapy can help with more serious ones.
For ankyloglossia, or tongue-tie, a minor surgery known as a frenectomy can help detach the tongue from the bottom of the mouth.
A Word From Verywell
A speech impediment can make it difficult to pronounce certain sounds, speak clearly, or communicate fluently.
Living with a speech disorder can be frustrating because people may cut you off while you’re speaking, try to finish your sentences, or treat you differently. It can be helpful to talk to your healthcare providers about how to cope with these situations.
You may also benefit from joining a support group, where you can connect with others living with speech disorders.
National Library of Medicine. Speech disorders . Medline Plus.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Language and speech disorders .
Cincinnati Children's Hospital. Stuttering .
National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders. Quick statistics about voice, speech, and language .
Cleveland Clinic. Speech impediment .
Lee H, Sim H, Lee E, Choi D. Disfluency characteristics of children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptoms . J Commun Disord . 2017;65:54-64. doi:10.1016/j.jcomdis.2016.12.001
Nemours Foundation. Speech problems .
Penn Medicine. Speech and language disorders .
Cleveland Clinic. Tongue-tie .
University of Rochester Medical Center. Ankyloglossia .
Cleveland Clinic. Dysarthria .
National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders. Apraxia of speech .
Cleveland Clinic. Childhood apraxia of speech .
Stanford Children’s Hospital. Speech sound disorders in children .
Abbastabar H, Alizadeh A, Darparesh M, Mohseni S, Roozbeh N. Spatial distribution and the prevalence of speech disorders in the provinces of Iran . J Med Life . 2015;8(Spec Iss 2):99-104.
By Sanjana Gupta Sanjana is a health writer and editor. Her work spans various health-related topics, including mental health, fitness, nutrition, and wellness.
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Heart Disease
- Digestive Health
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Diet & Nutrition
- Supplements
- Health Insurance
- Public Health
- Patient Rights
- Caregivers & Loved Ones
- End of Life Concerns
- Health News
- Thyroid Test Analyzer
- Doctor Discussion Guides
- Hemoglobin A1c Test Analyzer
- Lipid Test Analyzer
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) Analyzer
- What to Buy
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Medical Expert Board
Overcoming Speech Impediment: Symptoms to Treatment
There are many causes and solutions for impaired speech
- Types and Symptoms
- Speech Therapy
- Building Confidence
Speech impediments are conditions that can cause a variety of symptoms, such as an inability to understand language or speak with a stable sense of tone, speed, or fluidity. There are many different types of speech impediments, and they can begin during childhood or develop during adulthood.
Common causes include physical trauma, neurological disorders, or anxiety. If you or your child is experiencing signs of a speech impediment, you need to know that these conditions can be diagnosed and treated with professional speech therapy.
This article will discuss what you can do if you are concerned about a speech impediment and what you can expect during your diagnostic process and therapy.
FG Trade / Getty Images
Types and Symptoms of Speech Impediment
People can have speech problems due to developmental conditions that begin to show symptoms during early childhood or as a result of conditions that may occur during adulthood.
The main classifications of speech impairment are aphasia (difficulty understanding or producing the correct words or phrases) or dysarthria (difficulty enunciating words).
Often, speech problems can be part of neurological or neurodevelopmental disorders that also cause other symptoms, such as multiple sclerosis (MS) or autism spectrum disorder .
There are several different symptoms of speech impediments, and you may experience one or more.
Can Symptoms Worsen?
Most speech disorders cause persistent symptoms and can temporarily get worse when you are tired, anxious, or sick.
Symptoms of dysarthria can include:
- Slurred speech
- Slow speech
- Choppy speech
- Hesitant speech
- Inability to control the volume of your speech
- Shaking or tremulous speech pattern
- Inability to pronounce certain sounds
Symptoms of aphasia may involve:
- Speech apraxia (difficulty coordinating speech)
- Difficulty understanding the meaning of what other people are saying
- Inability to use the correct words
- Inability to repeat words or phases
- Speech that has an irregular rhythm
You can have one or more of these speech patterns as part of your speech impediment, and their combination and frequency will help determine the type and cause of your speech problem.
Causes of Speech Impediment
The conditions that cause speech impediments can include developmental problems that are present from birth, neurological diseases such as Parkinson’s disease , or sudden neurological events, such as a stroke .
Some people can also experience temporary speech impairment due to anxiety, intoxication, medication side effects, postictal state (the time immediately after a seizure), or a change of consciousness.
Speech Impairment in Children
Children can have speech disorders associated with neurodevelopmental problems, which can interfere with speech development. Some childhood neurological or neurodevelopmental disorders may cause a regression (backsliding) of speech skills.
Common causes of childhood speech impediments include:
- Autism spectrum disorder : A neurodevelopmental disorder that affects social and interactive development
- Cerebral palsy : A congenital (from birth) disorder that affects learning and control of physical movement
- Hearing loss : Can affect the way children hear and imitate speech
- Rett syndrome : A genetic neurodevelopmental condition that causes regression of physical and social skills beginning during the early school-age years.
- Adrenoleukodystrophy : A genetic disorder that causes a decline in motor and cognitive skills beginning during early childhood
- Childhood metabolic disorders : A group of conditions that affects the way children break down nutrients, often resulting in toxic damage to organs
- Brain tumor : A growth that may damage areas of the brain, including those that control speech or language
- Encephalitis : Brain inflammation or infection that may affect the way regions in the brain function
- Hydrocephalus : Excess fluid within the skull, which may develop after brain surgery and can cause brain damage
Do Childhood Speech Disorders Persist?
Speech disorders during childhood can have persistent effects throughout life. Therapy can often help improve speech skills.
Speech Impairment in Adulthood
Adult speech disorders develop due to conditions that damage the speech areas of the brain.
Common causes of adult speech impairment include:
- Head trauma
- Nerve injury
- Throat tumor
- Stroke
- Parkinson’s disease
- Essential tremor
- Brain tumor
- Brain infection
Additionally, people may develop changes in speech with advancing age, even without a specific neurological cause. This can happen due to presbyphonia , which is a change in the volume and control of speech due to declining hormone levels and reduced elasticity and movement of the vocal cords.
Do Speech Disorders Resolve on Their Own?
Children and adults who have persistent speech disorders are unlikely to experience spontaneous improvement without therapy and should seek professional attention.
Steps to Treating Speech Impediment
If you or your child has a speech impediment, your healthcare providers will work to diagnose the type of speech impediment as well as the underlying condition that caused it. Defining the cause and type of speech impediment will help determine your prognosis and treatment plan.
Sometimes the cause is known before symptoms begin, as is the case with trauma or MS. Impaired speech may first be a symptom of a condition, such as a stroke that causes aphasia as the primary symptom.
The diagnosis will include a comprehensive medical history, physical examination, and a thorough evaluation of speech and language. Diagnostic testing is directed by the medical history and clinical evaluation.
Diagnostic testing may include:
- Brain imaging , such as brain computerized tomography (CT) or magnetic residence imaging (MRI), if there’s concern about a disease process in the brain
- Swallowing evaluation if there’s concern about dysfunction of the muscles in the throat
- Electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies (aka nerve conduction velocity, or NCV) if there’s concern about nerve and muscle damage
- Blood tests, which can help in diagnosing inflammatory disorders or infections
Your diagnostic tests will help pinpoint the cause of your speech problem. Your treatment will include specific therapy to help improve your speech, as well as medication or other interventions to treat the underlying disorder.
For example, if you are diagnosed with MS, you would likely receive disease-modifying therapy to help prevent MS progression. And if you are diagnosed with a brain tumor, you may need surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation to treat the tumor.
Therapy to Address Speech Impediment
Therapy for speech impairment is interactive and directed by a specialist who is experienced in treating speech problems . Sometimes, children receive speech therapy as part of a specialized learning program at school.
The duration and frequency of your speech therapy program depend on the underlying cause of your impediment, your improvement, and approval from your health insurance.
If you or your child has a serious speech problem, you may qualify for speech therapy. Working with your therapist can help you build confidence, particularly as you begin to see improvement.
Exercises during speech therapy may include:
- Pronouncing individual sounds, such as la la la or da da da
- Practicing pronunciation of words that you have trouble pronouncing
- Adjusting the rate or volume of your speech
- Mouth exercises
- Practicing language skills by naming objects or repeating what the therapist is saying
These therapies are meant to help achieve more fluent and understandable speech as well as an increased comfort level with speech and language.
Building Confidence With Speech Problems
Some types of speech impairment might not qualify for therapy. If you have speech difficulties due to anxiety or a social phobia or if you don’t have access to therapy, you might benefit from activities that can help you practice your speech.
You might consider one or more of the following for you or your child:
- Joining a local theater group
- Volunteering in a school or community activity that involves interaction with the public
- Signing up for a class that requires a significant amount of class participation
- Joining a support group for people who have problems with speech
Activities that you do on your own to improve your confidence with speaking can be most beneficial when you are in a non-judgmental and safe space.
Many different types of speech problems can affect children and adults. Some of these are congenital (present from birth), while others are acquired due to health conditions, medication side effects, substances, or mood and anxiety disorders. Because there are so many different types of speech problems, seeking a medical diagnosis so you can get the right therapy for your specific disorder is crucial.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Language and speech disorders in children .
Han C, Tang J, Tang B, et al. The effectiveness and safety of noninvasive brain stimulation technology combined with speech training on aphasia after stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis . Medicine (Baltimore). 2024;103(2):e36880. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000036880
National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders. Quick statistics about voice, speech, language .
Mackey J, McCulloch H, Scheiner G, et al. Speech pathologists' perspectives on the use of augmentative and alternative communication devices with people with acquired brain injury and reflections from lived experience . Brain Impair. 2023;24(2):168-184. doi:10.1017/BrImp.2023.9
Allison KM, Doherty KM. Relation of speech-language profile and communication modality to participation of children with cerebral palsy . Am J Speech Lang Pathol . 2024:1-11. doi:10.1044/2023_AJSLP-23-00267
Saccente-Kennedy B, Gillies F, Desjardins M, et al. A systematic review of speech-language pathology interventions for presbyphonia using the rehabilitation treatment specification system . J Voice. 2024:S0892-1997(23)00396-X. doi:10.1016/j.jvoice.2023.12.010
By Heidi Moawad, MD Dr. Moawad is a neurologist and expert in brain health. She regularly writes and edits health content for medical books and publications.
- Brain & Nervous System
What to Know About Speech Impairment

A speech impairment affects people who have problems speaking in a regular tone of voice or tempo. Speech impairments make it hard for people to communicate properly, and they can happen in both children and adults.
These disorders can cause frustration and embarrassment to the person suffering from them.
What is Speech Impairment?
People who have speech impairments have a hard time pronouncing different speech sounds. They might distort the sounds of some words and leave other sounds out completely.
There are three general categories of speech impairment:
- Fluency disorder. This type can be described as continuity, smoothness, rate, and effort in speech production.
- Voice disorder. A voice disorder means you have an atypical tone of voice. It could be an unusual pitch, quality, resonance, or volume.
- Articulation disorder. If you have an articulation disorder, you might distort certain sounds. You could also fully omit sounds.
Stuttering , or stammering, is a common fluency disorder that affects about 3 million Americans. It usually affects young children who are just learning to speak, but it can continue on into adulthood.
Speech and language impairments are two words that are often used interchangeably, but they are two very different types of problems.
Speech means talking. It uses the jaw muscles, tongue, lips, and vocal chords. Language is a set of words and symbols made to communicate a message. Language and speech disorders can affect you separately, or both can happen at the same time.
Types of Speech Impairments
Speech impairments can begin in childhood and carry on through your adult years. Others can happen due to trauma, or after a medical event like a stroke.
The types of speech impairments are:
- Childhood apraxia of speech. This can happen to children when it’s time for them to start talking. The brain’s signals don’t communicate with the mouth, so the child can’t move their lips and tongue in the way they’re mean to.
- Dysarthria. This type of speech impairment happens when the muscles you use to talk are too weak, and can’t form words properly.
- Orofacial myofunctional disorders (OMD). OMDs are characterized by an abnormal pattern of facial muscle use. OMD interferes with how the facial muscles, including the tongue, are used. People who suffer from OMD might also struggle to breathe through their nose.
- Speech sound disorders. It’s normal for children to struggle to pronounce certain sounds as they learn to talk. But after ages four or five, constant mispronunciation might signal a problem. It can continue into adulthood, or some people get it after a stroke.
- Stuttering. Stuttering can mean repeating words or sounds like “uh” and “um” (disfluencies) involuntarily. Stuttering can be intensified by strong emotions or stress.
- Voice. A voice disorder can mean you “lost” your voice because you stressed it too much. It can also mean a chronic cough or paralysis of the vocal cords, among others.
Health Issues That Affect Speech Impairment
Other than childhood speech impairments, there are a range of reasons you could get one in your adult years. They can happen due to a traumatic event, illness, or surgery.
Dysarthria , aphasia, and voice disturbances can happen in adulthood, and are usually due to these medical events.
Aphasia. Aphasia is the loss of ability to understand words, spoken or written. There are many types of aphasia . It can happen after a stroke or if a tumor reaches the part of the brain where language is processed.
Medical issues that can cause aphasia:
- Head trauma
- Transient ischemic attack (TIA)
- Brain tumor
- Alzheimer’s disease
Dysarthria. Dysarthria is usually caused by a nerve problem. The person suffering from it loses the ability to make certain sounds or might have poor pronunciation. It can also affect your ability to control the tongue, larynx, lips, and vocal chords.
Medical issues that can cause dysarthria:
- Facial trauma
- Diseases that affect your nervous system
- Side effects of certain medication
- Alcoholic intoxication
- Dentures that don’t fit properly
- Transient ischemic attack (TIA)
Voice disturbances. Traumatic events or extreme stress placed on the vocal cords can cause you to “lose” your voice or have a vocal disturbance. Disease can also affect the way your voice sounds.
Cancerous or noncancerous growths or nodules on the vocal cords can make your voice sound different.
Understanding Speech Impairments
Having a speech impairment can be a very frustrating and embarrassing experience for the person experiencing it. It’s important to be patient and understanding when communicating.
Try the following tips to improve communication and foster an accepting environment with someone who has a speech impairment:
- Speak slowly and use hand gestures
- Keep a pen and paper handy in case it’s needed to communicate
- Maintain a calm environment free of stimulating sounds
- Use simple phrases when you speak
- Use your normal tone of voice
Consulting with a mental health care provider can help with feelings of anger and depression that can accompany speech impairments.
Top doctors in ,
Find more top doctors on, related links.
- Brain & Nervous System News & Features
- Brain & Nervous System Reference
- Brain & Nervous System Slideshows
- Brain & Nervous System Quizzes
- Brain & Nervous System Videos
- Find a Neurologist
- Living Better With MS
- Alzheimer's Disease
- Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease
- Guillain-Barré Syndrome
- Lou Gehrig’s Disease (ALS)
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Parkinson's Disease
- Restless Legs Syndrome
- Spinal Muscular Atrophy
- More Related Topics

- Bachelor’s Degrees
- Master’s Degrees
- Doctorate Degrees
- Certificate Programs
- Nursing Degrees
- Cybersecurity
- Human Services
- Science & Mathematics
- Communication
- Liberal Arts
- Social Sciences
- Computer Science
- Admissions Overview
- Tuition and Financial Aid
- Incoming Freshman and Graduate Students
- Transfer Students
- Military Students
- International Students
- Early Access Program
- About Maryville
- Our Faculty
- Our Approach
- Our History
- Accreditation
- Tales of the Brave
- Student Support Overview
- Online Learning Tools
- Infographics
Home / Blog
Speech Impediment Guide: Definition, Causes, and Resources
December 8, 2020

Tables of Contents
What Is a Speech Impediment?
Types of speech disorders, speech impediment causes, how to fix a speech impediment, making a difference in speech disorders.
Communication is a cornerstone of human relationships. When an individual struggles to verbalize information, thoughts, and feelings, it can cause major barriers in personal, learning, and business interactions.
Speech impediments, or speech disorders, can lead to feelings of insecurity and frustration. They can also cause worry for family members and friends who don’t know how to help their loved ones express themselves.
Fortunately, there are a number of ways that speech disorders can be treated, and in many cases, cured. Health professionals in fields including speech-language pathology and audiology can work with patients to overcome communication disorders, and individuals and families can learn techniques to help.

Commonly referred to as a speech disorder, a speech impediment is a condition that impacts an individual’s ability to speak fluently, correctly, or with clear resonance or tone. Individuals with speech disorders have problems creating understandable sounds or forming words, leading to communication difficulties.
Some 7.7% of U.S. children — or 1 in 12 youths between the ages of 3 and 17 — have speech, voice, language, or swallowing disorders, according to the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD). About 70 million people worldwide, including some 3 million Americans, experience stuttering difficulties, according to the Stuttering Foundation.
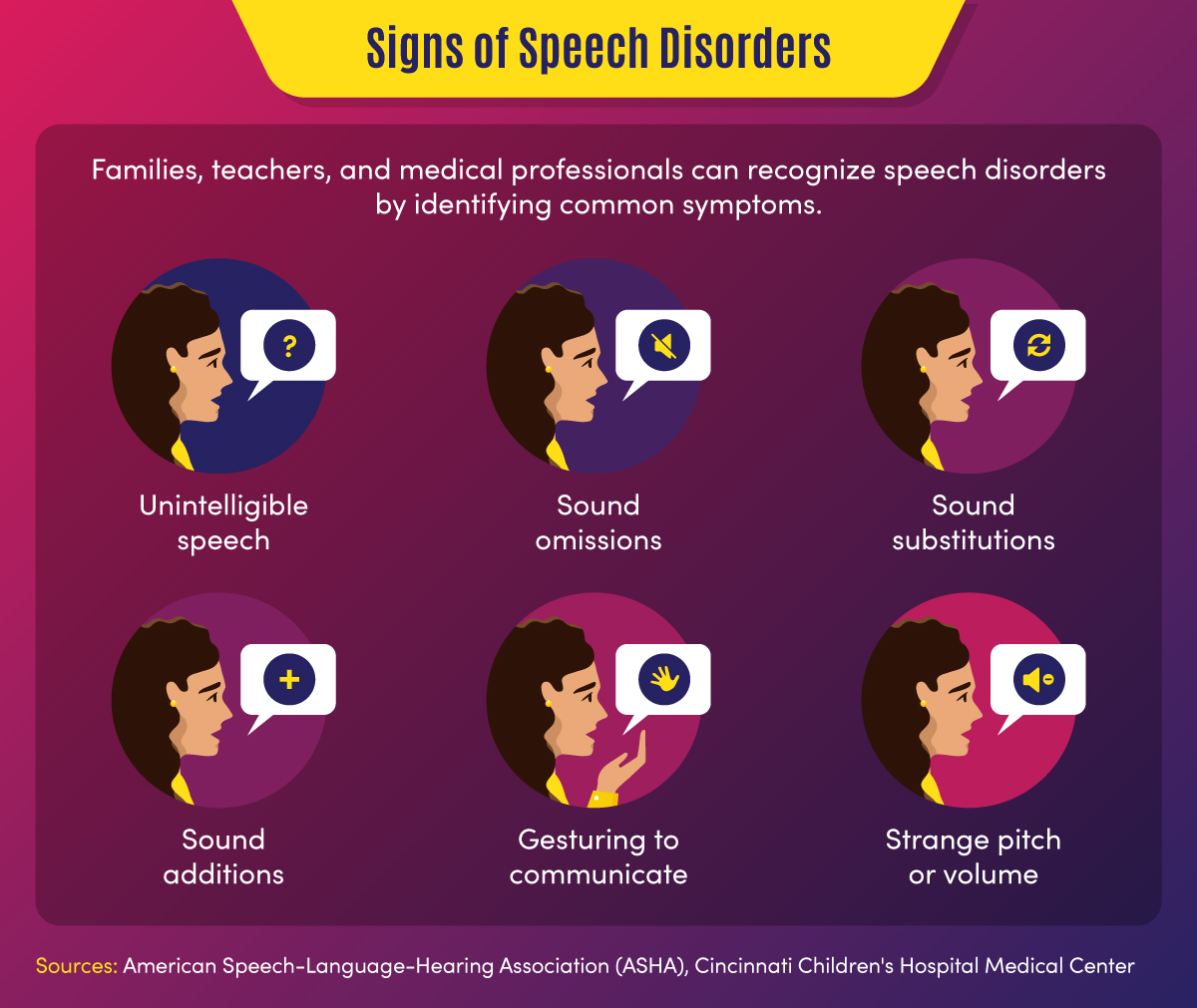
Common signs of a speech disorder
There are several symptoms and indicators that can point to a speech disorder.
- Unintelligible speech — A speech disorder may be present when others have difficulty understanding a person’s verbalizations.
- Omitted sounds — This symptom can include the omission of part of a word, such as saying “bo” instead of “boat,” and may include omission of consonants or syllables.
- Added sounds — This can involve adding extra sounds in a word, such as “buhlack” instead of “black,” or repeating sounds like “b-b-b-ball.”
- Substituted sounds — When sounds are substituted or distorted, such as saying “wabbit” instead of “rabbit,” it may indicate a speech disorder.
- Use of gestures — When individuals use gestures to communicate instead of words, a speech impediment may be the cause.
- Inappropriate pitch — This symptom is characterized by speaking with a strange pitch or volume.
In children, signs might also include a lack of babbling or making limited sounds. Symptoms may also include the incorrect use of specific sounds in words, according to the American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA). This may include the sounds p, m, b, w, and h among children aged 1-2, and k, f, g, d, n, and t for children aged 2-3.
Back To Top
Categories of Speech Impediments
Speech impediments can range from speech sound disorders (articulation and phonological disorders) to voice disorders. Speech sound disorders may be organic — resulting from a motor or sensory cause — or may be functional with no known cause. Voice disorders deal with physical problems that limit speech. The main categories of speech impediments include the following:
Fluency disorders occur when a patient has trouble with speech timing or rhythms. This can lead to hesitations, repetitions, or prolonged sounds. Fluency disorders include stuttering (repetition of sounds) or (rapid or irregular rate of speech).
Resonance disorders are related to voice quality that is impacted by the shape of the nose, throat, and/or mouth. Examples of resonance disorders include hyponasality and cul-de-sac resonance.
Articulation disorders occur when a patient has difficulty producing speech sounds. These disorders may stem from physical or anatomical limitations such as muscular, neuromuscular, or skeletal support. Examples of articulation speech impairments include sound omissions, substitutions, and distortions.
Phonological disorders result in the misuse of certain speech sounds to form words. Conditions include fronting, stopping, and the omission of final consonants.
Voice disorders are the result of problems in the larynx that harm the quality or use of an individual’s voice. This can impact pitch, resonance, and loudness.
Impact of Speech Disorders
Some speech disorders have little impact on socialization and daily activities, but other conditions can make some tasks difficult for individuals. Following are a few of the impacts of speech impediments.
- Poor communication — Children may be unable to participate in certain learning activities, such as answering questions or reading out loud, due to communication difficulties. Adults may avoid work or social activities such as giving speeches or attending parties.
- Mental health and confidence — Speech disorders may cause children or adults to feel different from peers, leading to a lack of self-confidence and, potentially, self-isolation.
Resources on Speech Disorders
The following resources may help those who are seeking more information about speech impediments.
Health Information : Information and statistics on common voice and speech disorders from the NIDCD
Speech Disorders : Information on childhood speech disorders from Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center
Speech, Language, and Swallowing : Resources about speech and language development from the ASHA
Children and adults can suffer from a variety of speech impairments that may have mild to severe impacts on their ability to communicate. The following 10 conditions are examples of specific types of speech disorders and voice disorders.
1. Stuttering
This condition is one of the most common speech disorders. Stuttering is the repetition of syllables or words, interruptions in speech, or prolonged use of a sound.
This organic speech disorder is a result of damage to the neural pathways that connect the brain to speech-producing muscles. This results in a person knowing what they want to say, but being unable to speak the words.
This consists of the lost ability to speak, understand, or write languages. It is common in stroke, brain tumor, or traumatic brain injury patients.
4. Dysarthria
This condition is an organic speech sound disorder that involves difficulty expressing certain noises. This may involve slurring, or poor pronunciation, and rhythm differences related to nerve or brain disorders.
The condition of lisping is the replacing of sounds in words, including “th” for “s.” Lisping is a functional speech impediment.
6. Hyponasality
This condition is a resonance disorder related to limited sound coming through the nose, causing a “stopped up” quality to speech.
7. Cul-de-sac resonance
This speech disorder is the result of blockage in the mouth, throat, or nose that results in quiet or muffled speech.
8. Orofacial myofunctional disorders
These conditions involve abnormal patterns of mouth and face movement. Conditions include tongue thrusting (fronting), where individuals push out their tongue while eating or talking.
9. Spasmodic Dysphonia
This condition is a voice disorder in which spasms in the vocal cords produce speech that is hoarse, strained, or jittery.
10. Other voice disorders
These conditions can include having a voice that sounds breathy, hoarse, or scratchy. Some disorders deal with vocal folds closing when they should open (paradoxical vocal fold movement) or the presence of polyps or nodules in the vocal folds.
Speech Disorders vs. Language Disorders
Speech disorders deal with difficulty in creating sounds due to articulation, fluency, phonology, and voice problems. These problems are typically related to physical, motor, sensory, neurological, or mental health issues.
Language disorders, on the other hand, occur when individuals have difficulty communicating the meaning of what they want to express. Common in children, these disorders may result in low vocabulary and difficulty saying complex sentences. Such a disorder may reflect difficulty in comprehending school lessons or adopting new words, or it may be related to a learning disability such as dyslexia. Language disorders can also involve receptive language difficulties, where individuals have trouble understanding the messages that others are trying to convey.

Resources on Types of Speech Disorders
The following resources may provide additional information on the types of speech impediments.
Common Speech Disorders: A guide to the most common speech impediments from GreatSpeech
Speech impairment in adults: Descriptions of common adult speech issues from MedlinePlus
Stuttering Facts: Information on stuttering indications and causes from the Stuttering Foundation
Speech disorders may be caused by a variety of factors related to physical features, neurological ailments, or mental health conditions. In children, they may be related to developmental issues or unknown causes and may go away naturally over time.
Physical and neurological issues. Speech impediment causes related to physical characteristics may include:
- Brain damage
- Nervous system damage
- Respiratory system damage
- Hearing difficulties
- Cancerous or noncancerous growths
- Muscle and bone problems such as dental issues or cleft palate
Mental health issues. Some speech disorders are related to clinical conditions such as:
- Autism spectrum disorder
- Down syndrome or other genetic syndromes
- Cerebral palsy or other neurological disorders
- Multiple sclerosis
Some speech impairments may also have to do with family history, such as when parents or siblings have experienced language or speech difficulties. Other causes may include premature birth, pregnancy complications, or delivery difficulties. Voice overuse and chronic coughs can also cause speech issues.
The most common way that speech disorders are treated involves seeking professional help. If patients and families feel that symptoms warrant therapy, health professionals can help determine how to fix a speech impediment. Early treatment is best to curb speech disorders, but impairments can also be treated later in life.
Professionals in the speech therapy field include speech-language pathologists (SLPs) . These practitioners assess, diagnose, and treat communication disorders including speech, language, social, cognitive, and swallowing disorders in both adults and children. They may have an SLP assistant to help with diagnostic and therapy activities.
Speech-language pathologists may also share a practice with audiologists and audiology assistants. Audiologists help identify and treat hearing, balance, and other auditory disorders.
How Are Speech Disorders Diagnosed?
Typically, a pediatrician, social worker, teacher, or other concerned party will recognize the symptoms of a speech disorder in children. These individuals, who frequently deal with speech and language conditions and are more familiar with symptoms, will recommend that parents have their child evaluated. Adults who struggle with speech problems may seek direct guidance from a physician or speech evaluation specialist.
When evaluating a patient for a potential speech impediment, a physician will:
- Conduct hearing and vision tests
- Evaluate patient records
- Observe patient symptoms
A speech-language pathologist will conduct an initial screening that might include:
- An evaluation of speech sounds in words and sentences
- An evaluation of oral motor function
- An orofacial examination
- An assessment of language comprehension
The initial screening might result in no action if speech symptoms are determined to be developmentally appropriate. If a disorder is suspected, the initial screening might result in a referral for a comprehensive speech sound assessment, comprehensive language assessment, audiology evaluation, or other medical services.
Initial assessments and more in-depth screenings might occur in a private speech therapy practice, rehabilitation center, school, childcare program, or early intervention center. For older adults, skilled nursing centers and nursing homes may assess patients for speech, hearing, and language disorders.
How Are Speech Impediments Treated?
Once an evaluation determines precisely what type of speech sound disorder is present, patients can begin treatment. Speech-language pathologists use a combination of therapy, exercise, and assistive devices to treat speech disorders.
Speech therapy might focus on motor production (articulation) or linguistic (phonological or language-based) elements of speech, according to ASHA. There are various types of speech therapy available to patients.
Contextual Utilization — This therapeutic approach teaches methods for producing sounds consistently in different syllable-based contexts, such as phonemic or phonetic contexts. These methods are helpful for patients who produce sounds inconsistently.
Phonological Contrast — This approach focuses on improving speech through emphasis of phonemic contrasts that serve to differentiate words. Examples might include minimal opposition words (pot vs. spot) or maximal oppositions (mall vs. call). These therapy methods can help patients who use phonological error patterns.
Distinctive Feature — In this category of therapy, SLPs focus on elements that are missing in speech, such as articulation or nasality. This helps patients who substitute sounds by teaching them to distinguish target sounds from substituted sounds.
Core Vocabulary — This therapeutic approach involves practicing whole words that are commonly used in a specific patient’s communications. It is effective for patients with inconsistent sound production.
Metaphon — In this type of therapy, patients are taught to identify phonological language structures. The technique focuses on contrasting sound elements, such as loud vs. quiet, and helps patients with unintelligible speech issues.
Oral-Motor — This approach uses non-speech exercises to supplement sound therapies. This helps patients gain oral-motor strength and control to improve articulation.
Other methods professionals may use to help fix speech impediments include relaxation, breathing, muscle strengthening, and voice exercises. They may also recommend assistive devices, which may include:
- Radio transmission systems
- Personal amplifiers
- Picture boards
- Touch screens
- Text displays
- Speech-generating devices
- Hearing aids
- Cochlear implants
Resources for Professionals on How to Fix a Speech Impediment
The following resources provide information for speech therapists and other health professionals.
Assistive Devices: Information on hearing and speech aids from the NIDCD
Information for Audiologists: Publications, news, and practice aids for audiologists from ASHA
Information for Speech-Language Pathologists: Publications, news, and practice aids for SLPs from ASHA
Speech Disorder Tips for Families
For parents who are concerned that their child might have a speech disorder — or who want to prevent the development of a disorder — there are a number of activities that can help. The following are tasks that parents can engage in on a regular basis to develop literacy and speech skills.
- Introducing new vocabulary words
- Reading picture and story books with various sounds and patterns
- Talking to children about objects and events
- Answering children’s questions during routine activities
- Encouraging drawing and scribbling
- Pointing to words while reading books
- Pointing out words and sentences in objects and signs
Parents can take the following steps to make sure that potential speech impediments are identified early on.
- Discussing concerns with physicians
- Asking for hearing, vision, and speech screenings from doctors
- Requesting special education assessments from school officials
- Requesting a referral to a speech-language pathologist, audiologist, or other specialist
When a child is engaged in speech therapy, speech-language pathologists will typically establish collaborative relationships with families, sharing information and encouraging parents to participate in therapy decisions and practices.
SLPs will work with patients and their families to set goals for therapy outcomes. In addition to therapy sessions, they may develop activities and exercises for families to work on at home. It is important that caregivers are encouraging and patient with children during therapy.
Resources for Parents on How to Fix a Speech Impediment
The following resources provide additional information on treatment options for speech disorders.
Speech, Language, and Swallowing Disorders Groups: Listing of self-help groups from ASHA
ProFind: Search tool for finding certified SLPs and audiologists from ASHA
Baby’s Hearing and Communication Development Checklist: Listing of milestones that children should meet by certain ages from the NIDCD
If identified during childhood, speech disorders can be corrected efficiently, giving children greater communication opportunities. If left untreated, speech impediments can cause a variety of problems in adulthood, and may be more difficult to diagnose and treat.
Parents, teachers, doctors, speech and language professionals, and other concerned parties all have unique responsibilities in recognizing and treating speech disorders. Through professional therapy, family engagement, positive encouragement and a strong support network, individuals with speech impediments can overcome their challenges and develop essential communication skills.
Additional Sources
American Speech-Language-Hearing Association, Speech Sound Disorders
Identify the Signs, Signs of Speech and Language Disorders
Intermountain Healthcare, Phonological Disorders
MedlinePlus, Speech disorders – children
National Institutes of Health, National Institutes on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders, “Quick Statistics About Voice, Speech, Language”
Bring us your ambition and we’ll guide you along a personalized path to a quality education that’s designed to change your life.
Take Your Next Brave Step
Receive information about the benefits of our programs, the courses you'll take, and what you need to apply.
Five Common Speech Disorders in Children
You have determined that your child has more than just a speech delay, now what? How do you determine what kind of speech disorder your child has and more importantly, what do you do about it? We have listed below five common speech disorders in children. Of course, we always recommend a visit to your pediatrician if you feel your child has any of these symptoms, and an appointment with an SLP may be necessary to begin an effective speech therapy treatment plan.
5 Common Speech Disorders in Children:
Articulation Disorder: An articulation disorder is a speech sound disorder in which a child has difficulty making certain sounds correctly. Sounds may be omitted or improperly altered during the course of speech. A child may substitute sounds (“wabbit” instead of “rabbit”) or add sounds improperly to words. Young children will typically display articulation issues as they learn to speak, but they are expected to “grow out of it” by a certain age. If the errors persist past a standard developmental age, which varies based on the sound, then that child has an articulation disorder.
The most common articulation disorders are in the form of a “lisp” – when a child does not pronounce the S sound correctly – or when a child cannot pronounce the R sound correctly. He may say “wabbit” instead of “rabbit” or “buhd” or instead of “bird.”
Apraxia of Speech is a communication disorder affecting the motor programming system for speech production. Speech production is difficult – specifically with sequencing and forming sounds. The person may know what he wants to say, but there is a disruption in the part of the brain that sends the signal to the muscle for the movement necessary to produce the sound. That leads to problems with articulation as well as intonation and speaking stress and rhythm errors. Apraxia of Speech can be discovered in childhood (CAS), or might be acquired (AOS) resulting from a brain injury or illness in both children and adults.
Fragile X Syndrome (FXS) is an inherited genetic disorder that is the most common cause of inherited intellectual disabilities in boys as well as autism (about 30% of children with FXS will have autism). It also affects girls, though their symptoms tend to be milder. It is greatly under-recognized and second only to Down syndrome in causing intellectual impairment.
FXS occurs when there is a mutation of FMRI gene and is an inherited disorder. If a child received a pre-mutated X chromosome from one of his parents (as a carrier), then he is at greater risk of developing FXS. Diagnosing Fragile X Syndrome is not easy for parents and doctors at the beginning of a child’s life. Few outward signs are noticeable within the first 9 months. These signs may include an elongated face and protruding eyes.
Intellectual disabilities, speech and language problems, and social anxiety occur most frequently in children with Fragile X. Speech symptoms include repetition of words and phrases, cluttered speech and difficulties with the pragmatics of speech. All of FXS’s symptoms can range from mild to very severe.
Stuttering occurs when speech is disrupted by involuntary repetitions, prolonging of sounds and hesitation or pausing before speech. Stuttering can be developmental, meaning it begins during early speech acquisition, or acquired due to brain trauma. No one knows the exact causes of stuttering in a child. It is considered to have a genetic basis, but the direct link has not yet been found. Children with relatives who stutter are 3 times as likely to develop stuttering. Stuttering is also more typical in children who have congenital disorders like cerebral palsy .
A child who stutters is typically not struggling with the actual production of the sounds—stress and a nervousness trigger many cases of stuttering. Stuttering is variable, meaning if the speaker does not feel anxious when speaking, the stuttering may not affect their speech.
Language disorders can be classified in three different ways: Expressive Language Disorder (ELD), Receptive Language Disorder (RLD) or Expressive-Receptive Language Disorder (ERLD). Children with Expressive Language Disorder do not have problems producing sounds or words, but have an inability to retrieve the right words and formulate proper sentences. Children with Receptive Language Disorder have difficulties comprehending spoken and written language. Finally, children with Expressive-Receptive Language Disorder will exhibit both kinds of symptoms. Grammar is a hard concept for them to understand and they may not use of articles (a, the), prepositions (of, with) and plurals. An early symptom is delay in the early stages of language, so if your child takes longer to formulate words or starting to babble, it can be a sign of ELD.
Children with Receptive Language Disorder may act like they are ignoring you or just repeat words that you say; this is known as “echolalia.” Even when repeating the words you say, they may not understand. An example of this is if you say, “Do you want to go to the park?” and they respond with the exact phrase and do not answer the question. They may not understand you or the fact that you asked them to do something.
Children with Expressive-Receptive Language Disorder can have a mix of these symptoms
These are some of the most common speech disorders in children. No child is the same and you know your child best. If you feel that your child has a speech disorder, contact your pediatrician to discuss treatment options.

- Speech Pathology Master’s Programs: Which is Right for You?
- What Can You Do with a Bachelor’s in Speech Pathology?
- Speech Pathology Doctoral Programs
- Online Masters in Speech Pathology at Emerson College (sponsored program)
- Online Masters in Speech Pathology at New York University (sponsored program)
- How to Become a Speech Pathologist: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Guide to Applying to Speech Pathology School
- How to Make a Career Change to Speech Pathology
- Is a Speech Pathology Degree Worth It?
- 10 Reasons to Love Being a Speech Pathologist
- What Is a CCC-SLP and Why It’s Important
- CCC-SLP Requirements: Become a CCC-SLP
- Guide to Applying for CCC-SLP Certification
- CCC-SLP Salary and Career Outlook
- The Guide to the ASHA Speech Pathology Certification Standards
- State-by-State Guide for Speech Pathology License Requirements
- 8 SLP Certifications that May Help Advance Your Career
- How to Become an Effective ASHA Clinical Fellowship Mentor
- How to Complete the ASHA Clinical Fellowship
- The Guide to Speech Pathology Job and Salary Negotiations
- What to Expect at Your First Speech Pathologist Job
- Bilingual Speech Pathologist Salary and Careers
- Child Speech Therapist Career and Salary Outlook
- Speech Pathology Assistant Careers and Salary Outlook
- How to Choose Your Speech Pathologist Career Setting
- Become a Speech Pathologist in a School Setting
- Become a Speech Pathologist in a Hospital Work Setting
- Opening a Speech Therapy Telepractice: What You Need to Know
- Speech Pathology Internships Guide
- Guide to Speech Therapy Volunteer Opportunities
- Choosing Between Speech Pathology or Occupational Therapy
- How to Become an Audiologist
- Scholarships
- Day in the Life of an SLP Student
- Speech Disorder Resources for College Students
- Common Speech Language Pathology Assessment Tools
- The SLP Guide to Evidence-Based Practice
- When to Take Your Bilingual Child to the Speech Pathologist
- When to Take Your Child to the SLP
Home / Resources
What are the Most Common Speech Disorders?
July 24, 2020
Speech disorders impact millions of people and their ability to communicate. The National Institute of Deafness and Other Communication Disorders estimates that 5% of children in the U.S. ages 3 to 17 have had a speech disorder in the past 12 months. Some speech disorders can be overcome, while others are lifelong conditions. In either case, therapy with a speech pathologist can help a person make the most of their speech capabilities and develop alternative methods of communication.
Speech pathologists or speech therapists complete a master’s program to be able to evaluate a person’s speech and communication, create a treatment plan and provide treatment to improve a person’s speech and other communication methods. Some speech pathologists’ careers deal with research and development treatment guidelines for various speech and language disorders.
What Is a Speech Disorder?
Speech is how people make sounds and words , according to the American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA). Speech problems can include the inability to make sounds clearly, having a raspy voice or stuttering (repeating sounds or pauses when speaking).
Language is not the same thing as speech; it is the words we use to share ideas. Problems with language can include difficulty understanding, talking, reading or writing.
According to ASHA, a speech disorder is an impairment of the articulation of sounds, fluency or voice. It is one of many types of communication disorders, which also include language and hearing disorders.
Types of Speech Disorders
There are three categories of speech disorders :
- Articulation disorders : An unusual production of speech sounds involving substitutions, omissions, additions or distortions that might interfere with whether the sounds are intelligible to others.
- Fluency disorders : Interruptions in the flow of a person’s speech, such as an uncommon rate, rhythm, or repetition of sounds, syllables, words or phrases.
- Voice disorders : An abnormal production or absence of vocal quality, pitch, volume, resonance or duration that’s inappropriate for the person’s age and sex.
Speech Disorder Causes
The medical community doesn’t know the cause of all speech disorders and, for many, the cause can vary. Potential causes for speech disorders include:
- Brain damage : Some speech and other communication disorders are due to a congenital condition. A child or adult who suffers a traumatic brain injury might sustain damage to a portion of the brain that impacts speech. Also, diseases and conditions such as stroke, dementia, Parkinson’s disease, ALS, Huntington’s disease, MS, cerebral palsy, muscular dystrophy, cancer and benign brain tumors can impact speech.
- Nervous system condition : A disorder that affects a person’s nervous system can affect the muscles in their mouth, jaw, lips, or tongue or their vocal folds (voice box).
- Nerve damage : Nerve damage in the voice box can impact the vocal folds and cause voice disorders, which are a type of speech disorder.
- Stress : In some cases, it’s believed that stress can trigger certain speech disorders.
10 Common Speech Disorders
1. childhood apraxia of speech.
To talk, messages from the brain tell the muscles around the mouth and throat to move. In childhood apraxia, the messages don’t get through to the muscles correctly, according to ASHA. The child’s muscles aren’t weak, but they can’t move their mouth or tongue the right way to make the necessary sounds. The severity of this condition can vary. In more severe cases, a child might not be able to talk much.
Childhood apraxia is not a developmental issue that a child can grow out of. With the help of a speech therapist, a child’s speech can improve. But ultimately, the way the child learns to make speech sounds won’t be typical of other children.
2. Adult Apraxia
Apraxia of speech in adults is also called acquired apraxia of speech, verbal apraxia and dyspraxia. Adults suffer from verbal apraxia because of brain damage, such as a stroke, oxygen deprivation or a traumatic brain injury.
Acquired apraxia in adults can affect their speech in various ways. A person might make a new sound, leave out sounds or say something the wrong way. They might not be able to make a sound the right way consistently. A person might have a hard time controlling their mouth, lips and tongue to make the right sounds. They might have to talk slowly. In severe cases, an adult might not be able to talk at all.
3. Dysarthria
Dysarthria is the result of muscle weakness due to brain damage. The severity of the condition can vary, and it can be accompanied by other conditions, like speech apraxia. People with dysarthria might slur their words, speak slowly or too fast, talk softly, sound robotic and not be able to move their mouth or tongue well. Some people’s voices sound different than before their injury.
4. Orofacial Myofunctional Disorders
People of any age can have an orofacial myofunctional disorder (OMD). An OMD might interfere with the development of the bones and muscles in a person’s face and mouth. This can impact a person’s ability to breathe, swallow, eat and talk. Various issues can cause an OMD, including anything that causes a person to rest their tongue in the right place or keep their lips together when at rest.
One type of OMC is called tongue thrusting, which involves children pushing their tongue out when they try to talk, drink or eat.
5. Speech Sound Disorders
A child who can’t correctly make speech sounds by 4 years old might have a speech sound disorder, also known as a phonological disorder or articulation disorder. Speech sound disorders are not only in children, though. Adults might have suffered from a disorder since childhood or acquired this disorder after sustaining brain damage.
With a speech sound disorder, a person might make one sound in place of another, add sounds, change a sound or leave a sound out. The changes can be severe enough to make it hard for others to understand them. It’s important to note that people with accents will do some of these things, like replace one sound with another. An accent or dialect is not a speech sound disorder.
6. Stuttering
A person who stutters might repeat whole words or sounds, stretch out sounds or have a hard time saying certain words. These are known as repetitions, prolongations and blocks, respectively. While everyone might stutter once in a while, stuttering becomes a speech disorder when it gets in the way of a person’s ability to communicate with others and is accompanied by negative feelings about talking.
There’s no specific cause for stuttering. It might be the result of differences in children’s brains. In many cases, there’s a family history of stuttering. Most children start to stutter between the ages of 2 and 6 years. If the stuttering lasts for more than 6 months, then treatment with a speech pathologist might be necessary.
7. Voice Disorders
Several conditions impact a person’s voice, and therefore, their ability to talk. These include:
Chronic cough : A cough that lasts more than four weeks in children and eight weeks in adults is considered chronic. It can alter the sound of a person’s voice or their ability to talk.
Paradoxical vocal fold movement : PVFM is when a person’s vocal folds (inside the voice box) close partly or all the way when they should open. This can cause breathing difficulties, change a person’s voice, or cause someone to lose their voice. PVFM can be triggered by acid reflux, stress, smoke, pollen, other allergens, exercise or breathing cold air, though no one knows the underlying cause.
Spasmodic dysphonia : With this long-term condition, a person’s vocal folds don’t move properly. A person with this disorder might not be able to speak all the time, though, at other times, their voice might sound normal. Their vocal folds might spasm or tighten when they talk, which can make them sound jerky or hoarse. A brain or nervous system disorder can cause this condition.
Vocal fold nodules and polyps : Growths on a person’s vocal folds can change their voice and cause discomfort and pain. This condition is usually caused by vocal abuse — typically long-term overuse or abuse.
Vocal fold paralysis : Vocal fold paralysis happens when one or both of your vocal folds can’t move. If they can’t come together, separate and vibrate, then a person doesn’t have a voice. It also causes issues with breathing and swallowing. When one fold is paralyzed, a person’s voice might be quiet. They might be limited in their pitch and tone and sound breathy. When two folds are paralyzed, the person might need a tracheotomy.
Aphasia is technically a language disorder caused by brain damage to the left side of the brain. People with aphasia might have a hard time understanding other people, speaking, reading or writing. For example, a person with aphasia might hear another person and understand them, but then have a difficult time responding with the correct speech sounds. Aphasia can cause people to not remember the right word, say the wrong word, make up words, have a hard time speaking in full sentences or have a hard time speaking coherent sentences.
9. Selective Mutism
Selective mutism is a childhood language disorder, often associated with a child being extremely shy, afraid of embarrassment, traumatized, wanting to be alone or having an anxiety disorder. A child might refuse to talk in certain situations, say in public or at school.
10. Childhood Speech Delays
A child who is significantly delayed in developing their language and speech skills might have a language disorder. These are called preschool language disorders. Delayed speech is also called alalia. Some children have a hard time with receptive language, which helps them follow directions, understand gestures and answer questions. Others have difficulties with expressive language, like asking questions, naming objects or putting words together for a sentence. Some children have trouble with both.
Speech Disorder Treatments
Many speech disorders cannot be cured, but by receiving speech and language therapy with a licensed speech pathologist, many children and adults can improve their speech or adapt to alternative communication methods.
Speech therapists can help individuals learn the correct way to make a sound, including when and how to move their mouth and tongue, practice saying certain sounds, learn to tell when a sound is correct or wrong and practice using sounds in longer sentences. Speech pathologists can give children and adults exercises to improve their speech. Additionally, depending on the type of speech disorder, other medical or mental health care might be necessary.
Speech disorders impact children and adults from all walks of life. But these disorders don’t have to stand in the way of their communication, education and careers. Licensed speech pathologists can help individuals improve their speaking, and when helpful, learn to use augmentative and alternative communication methods.
Information last updated June 2020
Sponsored online speech pathology programs

Online MS: Pursue SLP Certification. Study FT/PT
Speech@Emerson enables you to earn an MS online and pursue SLP certification in as few as 20 mos. Learn the same curriculum as the on-campus program. Study FT or PT.
- Prepares you to pursue certification as an SLP generalist
- In-person clinical placements at faculty-approved partner sites
- As few as 20 months to complete
info SPONSORED

Want to Become an SLP? Earn an MS Online at NYU
NYU Steinhardt’s online master of science program in Communicative Sciences and Disorders prepares aspiring speech-language pathologists with a comprehensive professional education.
- Prepares students to pursue SLP licensure
- Accredited by ASHA’s Council on Academic Accreditation
- As few as six terms to complete
- Full-time and part-time plans of study
Common Speech Impediments: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, And Support
Speech impediments include a variety of both language and speech disorders, some of which can be addressed through online speech therapy with speech-language pathologists. They can arise because of heredity and genetics, developmental delays, or even damage to Broca’s area—the part of the brain that’s involved in language skills and speech skills. They may also be linked to other conditions like autism spectrum disorder, cerebral palsy, dyslexia, or even hearing loss. It depends on the type and the cause, but most speech impediments and speech impairments can be treated through speech therapy.
That said, recognizing when a speech impediment may be present can help you get yourself or your child the treatment and support they may need for improved academic and/or social functioning and self-confidence.

Common symptoms of a speech impediment
There are many different types of speech impediments a person can have, so the symptoms can vary. That said, those listed below are common symptoms that could be initial indicators that you or your child may be experiencing speech problems or challenges:
- Elongating words
- Quiet or muffled speech
- Blinking frequently
- Distorted sounds while talking
- Frequent changes in pitch
- Poor voice quality
- Visible frustration when trying to communicate
- Overall difficulty communicating and expressing thoughts and ideas
- Inability to repeat words
- Inability to pronounce words the same way twice
- A phobia of speaking in public
- Speaking slowly and carefully
- Speech delay
- Frequent pauses when talking
- Limited vocabulary over several years, delayed language development
Some speech and language disorders are consistent with underlying mental health conditions such as autism. You can visit licensed health professionals or speech therapists to receive an accurate diagnosis and find out how to treat a speech impediment or language disorder, and its underlying cause, if applicable.
Key categories of speech impediments
Speech impediments or communication disorders can take many forms, from speech sound disorders to voice-related disorders. While speech sound disorders mostly result from sensory or motor causes, voice-related disorders deal with physical problems regarding speech. Read on for a list of some of the most common categories of speech impediments.
Voice disorders
Voice disorders primarily arise due to issues regarding the health and structure of the larynx or the voice box. They can impact pitch, resonance, volume, and voice quality. Symptoms of a voice disorder may include having a hoarse, quivering, strained, choppy, or weak and whispery voice, which can make it difficult to produce speech sounds.
The root cause of these disorders can be either organic, like alterations to respiratory, laryngeal, or vocal tract mechanisms, or functional, like improper use of the voice. Some risk factors that may contribute to vocal health challenges include allergies, psychological stress, age, excessive alcohol or drug use, screaming, scarring from neck surgery, or even gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Examples of voice disorders include laryngitis, vocal cord paralysis/weakness, polyps or nodes present on the vocal cords, leukoplakia, or muscle tension dysphonia.
Fluency disorders
A person may be diagnosed with a fluency disorder if they have trouble with speech timing and rhythm which makes it difficult to create a normal speech pattern. These disorders are characterized by interruptions in the typical flow of speaking, including abnormal repetitions, hesitation, and prolongations. Their cause is unknown, but it may be genetic. Symptoms can also be exacerbated by stress and anxiety. Stuttering is the most common example of fluency disorders.
Symptoms of a fluency disorder may include dragging out syllables, speaking breathlessly, repetition of words, speaking slowly, and being tense while speaking. Secondary symptoms may include fidgeting, mumbling, saying “um” or “uh” often, not using certain problematic words, rearranging words in sentences, and anxiety around speaking. Treatment options vary depending on the specific disorder. With stuttering, for example, slowing down, practicing, using speech monitors, attending speech therapy, and receiving cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) are all potential treatment options.
Articulation disorders and phonological disorders
Articulation and phonological disorders are two types of speech disorders classified as speech sound disorders that may impact communication. An articulation disorder includes speech that commonly exhibits errors such as substitution, omission, distortion, and/or addition (SODA). Although the actual causes of articulation disorders aren’t well understood, contributing factors may include brain injuries, a cleft palate/cleft lip, or nerve damage. Phonological disorders typically involve producing sounds correctly but using them in the wrong place and are more predictable than articulation errors. There may also be a genetic factor that contributes to both disorders and other families may be impacted as well. A licensed speech-language pathologist (SLP) can determine if an individual may have an articulation disorder or a phonological disorder. Ongoing speech therapy is typically the recommended treatment method.
Speech impediments versus language impairments
A speech impediment is typically characterized by difficulty creating sound due to factors like fluency disorders or other voice problems. These disorders may arise from underlying mental health issues, neurological problems, or physical factors or conditions impacting speech muscles.
Language impairments, on the other hand, are more about difficulty processing, reading, and writing and can be connected to an issue processing receptive language. They’re common in children, especially when they first start school. Language impairments relate to meaning, whereas speech impediments relate to sound. It’s also very common for a language impairment disorder to present alongside a learning disability like dyslexia.

Examples of speech impediments
Below is a brief overview of a few of the most common speech disorders and speech impediments, along with symptoms and potential treatment options.
Apraxia of speech is a speech sound disorder that affects the pathways of the brain. It’s characterized by a person having difficulty expressing their thoughts accurately and consistently. It involves the brain being able to form the words and knowing exactly what to say, but the person then being unable to properly execute the required speech movements to deliver accurate sounds. In mild cases, a person will only have small limitations in their ability to form speech sounds. In severe cases, alternate communication methods may need to be used.
An SLP is the type of provider who can diagnose apraxia. To diagnose speech disorders, including both childhood apraxia (sometimes called verbal apraxia) and acquired apraxia, they may ask the individual to perform simple speech tasks like repeating a particular word several times or repeating a list of words that increase in length. Apraxia generally needs to be monitored by both parents and an SLP over time for an accurate diagnosis to be possible.
There are various treatment options for apraxia, the most common being one-on-one meetings with a speech pathologist. They’ll likely help you or your child build helpful strategies and skills to help strengthen problem areas and communicate more clearly. Some other treatment methods include improving speech intelligibility or using alternate forms of communication, like electronic speech or manual signs and gestures.
The National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders describes aphasia as a communication disorder that results in a person’s inability to speak, write, and/or understand language. Like other communication disorders, it may occur because of damage to the portions of the brain that are involved in language, which is common in those who have experienced a stroke. It may also come on gradually in those who have a tumor or a progressive neurological disease like Alzheimer’s. Symptoms may include saying or writing sentences that don’t make sense, a reduction in a person’s ability to understand a conversation, and substituting certain sounds and words for others.
Since this disorder is usually caused by damage to parts of the brain, it will typically first be recognized in an MRI or CT scan that can confirm the presence of a brain injury. The extent and type of aphasia can generally only be determined by observing the affected part of the brain and determining how extensively it has been damaged, which is often done with the help of an SLP.
Treatment options for aphasia can be restorative (aimed at restoring impaired function) or compensatory (aimed at compensating for deficits).
Dysarthria
Dysarthria is usually caused by brain damage or facial paralysis that affects the muscles of the jaw, tongue, or throat, which may result in deficits in a person’s speech. It may also be caused by other conditions like Lou Gehrig’s disease, Parkinson’s, or a stroke. It’s considered a nervous system disorder, subclassified as a motor speech disorder. It’s commonly seen in those who already have other speech disorders, such as aphasia or apraxia. Symptoms of dysarthria include slurred speech, speaking too slowly, speaking too quickly, speaking very softly, being unable to move one’s lips or jaw, and having monotonous speech.
Dysarthria can be diagnosed by an expert in speech-language pathology through an exam and tests like MRI, CT, electromyography, or the Denver articulation screening examination. Treatment depends upon the severity and rate of progression of the disorder. Some potential examples include tactics like slowing down while talking, doing exercises to help strengthen jaw muscles, moving the lips and tongue more, and learning strategies for speaking more loudly. Hand gestures and speech machines may also help.
The importance of treatment
It is important to treat speech disorders; the consequences of an untreated speech or language impediment can vary widely depending on the type, symptoms, and severity, as well as the age and life situation of the individual. In general, it’s usually helpful to seek professional advice on treating speech disorders as soon as you notice or suspect an impediment present in yours or your child’s speech. Especially for moderate to severe cases, some potential effects of leaving these common speech disorders untreated can include:
- Poor academic performance/dropping out of school
- Decrease in quality of life
- Social anxiety and an inability to connect with people
- Damaged relationships
- Social isolation
- Hospitalization

Seeking professional support
Meeting with an SLP is usually the recommended first step for someone who believes they or their child may have a speech impediment. If you have a teenager with dyslexia, there are resources for dyslexic teens that can give supportive information about the condition. Healthcare providers may also provide helpful insights and ask about your family members’ history when it comes to speech and language-related issues as they can be hereditary. While these professionals can help with the physical aspects of a variety of speech and language impediments, you or your child may also benefit from emotional support in relation to the mental health effects of having an impediment. A therapist may be able to provide this type of guidance. If your child is experiencing a speech impediment, a counselor may be able to work with them to process their feelings of frustration and learn healthy coping mechanisms for stress. They can help you manage the same feelings if you receive a speech or language impediment diagnosis, or may be able to support you in your journey of parenting a child with a speech or language impediment diagnosis.
In addition to support at home, teenagers with a diagnosed speech impairment or impediment can receive special education services at school. The Centers for Disease Control notes that under the Individuals with Disabilities Act (IDEA) and Section 504, schools must provide support and accommodations for students with speech disorders. For some children, support groups can provide outlets for social connections and advice for coping.
Meeting with a therapist in person is an option if there are providers in your area. That said, many people find it less intimidating or more comfortable to meet with a therapist virtually. For example, a teen who is experiencing a speech or language impediment may feel better interacting with a counselor through the online chat feature that virtual therapy platforms like TeenCounseling provide. It may allow them to express themselves more clearly than they could face-to-face or over the phone. Parents who need support in caring for a child with a speech or language impediment may find the availability and convenience of meeting with a therapist through an online therapy service like BetterHelp to be most beneficial. Research suggests that online and in-person therapy offer similar benefits for a variety of conditions, so you can choose the format that’s best for you.

Counselor reviews
See below for reviews of TeenCounseling therapists written by parents who sought help for their children through this service.
“Kathleen has been good for my daughter to talk to. I am thankful for her to give my daughter someone else's perspective other than her parents. Thank you.”
“I love Ms. Jones. She doesn’t over-talk or judge you. She gives really good advice and if you're confused she knows how to break it down or explain whatever it is so you can understand. If you need to talk about anything, she’s always an open ear and responds quickly. Not only does she give you points from others' perspectives but she steps into yours so she can understand why certain things are the way they are. In my first session, I was nervous and I think she could tell. She’ll crack a joke every now and then to make me feel more comfortable. She’s just such a bundle of joy and a good counselor to have.”
Speech and language impediments can vary widely in terms of types, causes, symptoms, and severity. These are diagnosed by professionals in the field of speech and language pathology or by a medical doctor. A therapist can provide emotional support for those who are having difficulty coping with their own or their child’s diagnosis or other related challenges.
What are the 3 speech impediments?
Speech impediments can manifest in a variety of ways. Three of the most common are listed below:
- Voice disorders affect the tone, pitch, quality, and volume of a person’s voice. A person with a voice disorder may have difficulty speaking or being heard clearly by others. Voice disorders can be either functional or organic. Functional disorders occur due to improper use of the parts of the throat that produce speech, such as overuse of the voice leading to vocal fatigue. Organic voice disorders result from physical anatomical changes, such as nodules on the vocal cords.
- Fluency disorders affect the rate, rhythm, and cadence of speech. Those with fluency disorders may speak in a disjointed, choppy, or prolonged fashion, making them difficult for others to understand clearly. While many types of fluency disorders exist, stuttering is likely the best-known. Speech often requires precise timing to convey a message accurately, which fluency disorders can disrupt.
- Speech sound disorders are a broad category of disorders that interferes with a person’s ability to produce sounds and words correctly. Speech sound disorders can present very differently from person to person. Sometimes word sounds are omitted or added where not appropriate, and sometimes word sounds are distorted or substituted completely. A typical example of a speech sound disorder is the substitution of “r” for “w” in words like “rabbit” (becoming “wabbit”). Many children experience that substitution, but it does not become a disorder until the child does not outgrow it.
Other types of disorders can cause problems with expressive communication or tongue-tie those experiencing them, such as developmental language disorder. Language disorders also cause concerns related to expressive communication, but the concerns are due to a lack of understanding of one or more components of language, not an inability to produce or use word sounds.
What do you call a speech impediment?
Speech impediments are typically referred to as speech disorders . Speech refers to the ability to form speech sounds using the vocal cords, mouth, lips, and tongue. Speech also requires that a rhythm and cadence be maintained. Speech disorders indicate a problem producing intelligible speech; word sounds may be omitted or misplaced, the rhythm of the speech may be difficult to follow, or a person’s voice might be strangely pitched or too soft to hear clearly.
It is important not to confuse speech disorders with language disorders . Language disorders arise due to difficulty understanding what words mean, how word sounds fit together, or how to use spoken language to communicate. Language problems may affect how a person speaks, but the root cause of the concern is linked to their understanding of language, not their ability to produce intelligible speech.
How do I know if I have a speech impediment?
If you’re experiencing a sudden onset of impaired speech with no apparent cause, seek medical attention immediately. Strokes, traumatic brain injuries, and other serious medical conditions can cause sudden changes in speaking ability. Gradual changes in speaking ability may also indicate an underlying medical problem. If you’re concerned that your speaking ability has been gradually deteriorating, consider making an appointment with a healthcare provider in the near future.
Most people with a speech disorder are diagnosed in childhood. Parents often identify speech-related concerns in early childhood based on their child’s speech patterns. The child’s pediatrician may also refer the child to a speech-language pathologist, a professional specializing in evaluating and treating speech disorders. If problems persist until the child is in school, teachers and other school officials might initiate a referral for an evaluation if they believe speech concerns are present. Children often receive speech and language therapy that resolves or improves their speech problems.
Speech disorders also appear in adulthood, often due to injury or illness. It is also possible, although rare, for speech problems to be misdiagnosed or missed outright during a person’s childhood. In that case, the speech disorder may have been present since childhood and symptoms persisted into adulthood.
If you’re finding it difficult to communicate verbally with others, have an easily identifiable speech problem (like stuttering), or receive feedback that others have trouble understanding you, consider making an appointment with your doctor for an evaluation and referral to the appropriate healthcare providers.
What are 5 causes of speech impairment?
Speech and language disorders can result from conditions that interfere with the development of perceptual, structural, motor, cognitive, or socioemotional functions. The cause of many speech disorders is unknown, but research has indicated several underlying factors that may be responsible:
- Pre-existing genetic conditions, like Down’s syndrome or Fragile X syndrome. Evidence suggests that genes may play a role even if genetic abnormalities do not result in a diagnosable genetic condition.
- Physical abnormalities, such as damage or improper development of the respiratory system, facial muscles, or cranial nerves.
- Hearing problems, which can delay a child’s acquisition of speech.
- Neurodevelopmental disorders, such as autism spectrum disorder, may interfere with speech development. There is also evidence to suggest that those with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder may have a more challenging time acquiring speech skills.
- Neurological conditions such as cerebral palsy.
Mental health concerns can also cause problems communicating with others. For example, an underlying anxiety disorder may lead to selective mutism , wherein a child speaks only under certain circumstances.
Is speech impediment a disability?
A speech-language disorder is considered a “ communication disability ” under the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). The ADA requires government and businesses to establish “effective communication” with people who have communication disabilities. Effective communication can be established in several ways. For those with a speech disorder, accommodation may be as simple as ensuring the person can get hold of writing materials if they need to express themselves quickly. In some cases, organizations may use a transliterator, or person trained to recognize unclear speech and repeat it clearly.
Because speech disorders are known to lead to academic struggles in K-12 and higher education settings, they are categorized as a disability under the Individuals with Disabilities Education Improvement Act (IDEIA) . The IDEIA sets guidelines for all schools in the United States, public or not public, guaranteeing each child a right to accommodations and interventions for their speech disorder.
Can I fix my speech impediment?
Whether or not a speech disorder can be completely eliminated depends heavily on individual factors. The cause of the disorder, its severity, and the type of speech dysfunction all play a role in determining whether a particular disorder can be completely resolved. While it is not possible to guarantee that a speech disorder can be “cured,” nearly all disorders are treatable, and improvement is likely possible.
Can you treat a speech impediment?
Yes, many speech disorders are highly treatable. Most people receive treatment as children when most speech disorders become apparent. For children, speech-language pathologists will identify the specific speech disorder, search for an underlying cause, and design an intervention that targets that child’s speech problem. For example, a child who struggles with articulation errors and producing word sounds consistently may benefit from a contextual utilization approach . Contextual utilization leverages the fact that one sound is easier or more difficult to pronounce depending on which other sounds surround it.
Speech disorders that emerge in adulthood may be more challenging to treat due to underlying factors, such as brain injury. Suppose an adult experiences a traumatic brain injury that affects their speaking ability. In that case, a speech-language pathologist may help them find alternative communication methods, such as using a computer. They may also help them directly restore some of their speaking ability by leading them through exercises that improve nerve function and muscle control.
Is a speech impediment mental?
Speech disorders can be caused by various factors, many of which have nothing to do with the brain. However, there is a relationship between psychiatric mental health concerns and difficulty with spoken communication . Although researchers are still unsure of the exact cause, studies have identified a significant link between speech disorders and mental health disorders like schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and major depression.
Neurodevelopmental disorders, such as autism spectrum disorder and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, are also associated with an increased risk of developing a speech disorder. Although the link between neurodevelopmental disorders and speech disorders is not fully understood, evidence suggests that treating the speech disorder is still possible.
Finally, speech disorders can also be caused by illness or injury in the brain, such as cancer, an infection, or traumatic brain injury. Although these are not considered mental or developmental disorders, they may affect brain function and mental acuity. Speaking is a complex process, and there are many ways it can be affected.
Is autism a speech impediment?
Autism spectrum disorder is not a speech disorder, but it is heavily associated with communication problems. Those on the autism spectrum often use repetitive or rigid language and may not follow communication norms. They may repeat phrases continuously, use a modified tone of voice, or introduce information that has little to do with the conversation at hand.
Those on the autism spectrum are often able to form word sounds properly. The communication deficits of autism spectrum disorder are more closely related to language disorders than speech disorders. Speech disorders are associated with difficulty producing or using word sounds correctly, whereas language disorders are associated with a lack of understanding of one or more language components.
Autism spectrum disorder is also characterized by difficulties using pragmatic communication, or communication that is appropriate to a specific social situation. Although not a disorder of speech, a limited ability to recognize the socioemotional content of speech can significantly impact interpersonal communication and social interactions.
- Recognizing And Navigating Teen Depression Medically reviewed by Elizabeth Erban , LMFT, IMH-E
- ADHD Signs In Women, Men, And Children Medically reviewed by Julie Dodson , MA
- Relationships and Relations
CogniFit Blog: Brain Health News
Brain Training, Mental Health, and Wellness

Rhotacism: A complete guide to this speech impediment
Remember when you were a child and spoke by making your “R’s” sound like “W’s” and everything thought it was cute? That’s known as rhotacism and some people live with it even as adults. What is rhotacism, what is it like in other languages, and what are its symptoms? What does it look like as a speech impediment and what are some examples? What are its causes? How does it affect the brain ? Is it curable and how can it be fixed? This article will answer all your doubts about rhotacism.
What is rhotacism?
Rhotacism is a speech impediment that is defined by the lack of ability, or difficulty in, pronouncing the sound R . Some speech pathologists, those who work with speech impediments may call this impediment de-rhotacization because the sounds don’t become rhotic, rather they lose their rhotic quality. It could also be called a residual R error.
It’s not such an uncommon phenomenon and actually also happens with the letter L , a phenomenon known as lambdacism . Sometimes people mistake these speech impediments for a lisp, of which they are not. Within the 2000-2001 school year, more than 700,000 students within the American public school system were categorized as having either a language impediment or a speech impediment. Ironically, all three speech impediments contain the troubled letter within them.
The word rhotacism comes from the New Latin rhotacism meaning peculiar or excessive use of [r]. The Latin word came from Ancient Greek word rhōtakismós which means to incorrectly use “rho” which is the equivalent of the Greek R. For language nerds, here’s a really great explanation of how the word came into being.
How does rhotacism work in different languages?
Rhotacism is, in theory , more common among people whose native language has a trilled R. For example, in Spanish the “rr” is a trilled R. Other languages with a trilled R include Bulgarian, Hungarian, Arabic, Finnish, Romanian, Indonesian, Russian , Italian, and most Swedish speakers. Some people might mock Asians, specifically Chinese, for not being able to pronounce the English word “broccoli” correctly- rather pronouncing it “browccoli”. This isn’t due to a rhotacism, however. It’s actually due to the fact that Mandarin (Chinese) words can have an “r” sound in the beginning of a word, but not in the middle or end of a word. This leads them to have issues in their phonotactics and creates an inability to pronounce the English “R” in the middle of words.
The leader of Hezbollah, Hasan Nasrallah, is a Lebanese leader and is mocked for his rhotacism when he says, “ Amwīka ” and “ Iswā’īl ” for the Arabic Amrīka (America), and Isrā’īl (Israel). He is a native Arabic speaker- a language which has the trilled R. Notice how he puts a W sound in those two words where the R sound usually is.
Symptoms of rhotacism
- Some people try to hide their impediment by avoiding words with R ’s in them.
- An overall inability to say R sounds
- Using trilled R’s or guttural R’s (such as the French R) when trying to pronounce the regular English R.
Rhotacism as a speech impediment
Using a strict classification, only about 5%-10% of the human population speaks in a completely normal way. Everyone else suffers from some type of speech disorder or another. For children of any language, the R sounds are usually the hardest to master and often end up being the last ones a child learns. That’s why baby talk if you think about it, doesn’t really use explicit or strong R sounds. In English, rhotacism often comes off as a W sound which is why “Roger Rabbit” sounds like “Woger Wabbit”. R is often more difficult because a child has to learn the different combination of the /r/ sounds, not just the letter itself, unlike other letters. For example, when it comes before and after vowel sounds. The combination of a vowel with the /r/ sound is called a phenome and in English, there are eight combinations of these:
– The prevocalic R , such as “rain”
– The RL , such as “girl”
– The IRE, such as “tire”
– The AR, such as “car”
– The EAR , “such as “beer”
– The OR , such as “seashore”
– The ER , such as “butter”
– The AIR , such as “software”
A speech impediment is a speech disorder , not a language disorder . Speech disorders are problems in being able to produce the sounds of speech whereas language disorders are problems with understanding and/or being able to use words. Language disorders, unlike speech disorders, have nothing to do with speech production.
Often what happens is that the person speaking isn’t tensing their tongue enough, or not moving their tongue correctly (up and backward depending on the dialect) which makes the W or “uh” sound come out. It may also be that the person is moving their lips instead of their tongue.

Examples of rhotacism
- Barry Kripke from the TV show The Big Bang Theory has both rhotacism and lambdacism- meaning he has issues pronouncing both his R ’s and his L ’s.
- The most famous of rhotacism would be Elmer Fudd from Looney Tunes . He pronounces the word “rabbit” [ˈɹ̠ʷæbɪ̈t] as “wabbit” [ˈwæbɪ̈t]
- In Monty Python’s Life of Brian , the 1979 film’s character Pilate suffers from rhotacism. In the film, people mock him for his inability to be understood easily.
Here’s a video with a woman who suffers from rhotacism. She explains how difficult it can be to have the speech impediment.
Causes of rhotacism
For many people, the causes of rhotacism are relatively unknown-, especially in adults. However, scientists theorize that the biggest cause is that the person grew up in an environment where they heard R ’s in a weird way, the shape of their mouths are different than normal, or their tongues and lips never learned how to produce the letter. In children, this could happen because the parents or adults around think the way the child talks (using baby talk) is cute and the child never actually learns how to produce it.
For one internet forum user, it has to do with how they learned the language , “I speak various languages, I pronounce the “R” normal in Dutch, French, and Spanish, but I have a rhotacism when speaking English. It’s the way I learnt it.”
For other people, speech issues are a secondary condition to an already existing, serious condition. Physically, it would be a cleft lip or a cleft palate. Neurologically, it could be a condition such as cerebral palsy. It may also be a tongue tie . Almost everyone has a stretch of skin that runs along the bottom of their tongue. If that skin is too tight and reaches the tip of the tongue, it can make pronouncing (and learning how to pronounce) R ’s and L ’s difficult. If the tongue tie isn’t fixed early on, it can be incredibly difficult to fix and learn how to pronounce later.
How the brain affects rhotacism
The brain affects rhotacism only for those who suffer from it not due to a physical impediment (such as a cleft palate). For some, this could happen because the brain doesn’t have the phonemic awareness and never actually learned what the letter R is supposed to sound like. This is common with kids whose parents spoke to them in “baby talk” and encouraged the child’s baby talk, too. This kind of behavior only strengthens a child’s inner concept that / R / is pronounced like “w” or “uh”.
Another reason could be that the brain connections simply don’t allow the lips or mouth to move in the way they need to in order to pronounce the R . This inability has little to do with physical incapabilities and more to do with mental ones. Some people with rhotacism have an issue with their oral-motor skills which means that there isn’t sufficient communication in the parts of the brain responsible for speech production.
Treatment for rhotacism
Is rhotacism curable.
It can have negative social effects- especially among younger children, such as bullying, which lowers self-esteem and can have a lasting effect. However, if the impediment is caught early enough on and is treated rather quickly, there is a good overall prognosis meaning it’s curable.
However, some people never end up being able to properly pronounce that R and they end up substituting other sounds, such as the velar approximant (like w sounds) , the uvular approximant (also known as the “French R ”), and the uvular trill ( like the trilled R in Spanish).
How to fix rhotacism
Rhotacism is fixed by speech therapy . Before anything else, there needs to be an assessment from a Speech Language Pathologist (SLP) who will help decide if the problem can be fixed. If a child is involved, the SLP would predict if the child can outgrow the problem or not. After the diagnosis, a speech therapist will work with the person who suffers from the speech impediment by possibly having weekly visits with some homework and practice instructions. Therapy happens in spouts- a period of a few weeks and a break. There is a follow-up to see if there has been an improvement in pronunciation. In the U.S., children who are in school and have a speech disorder are placed in a special education program. Most school districts provide these children with speech therapy during school hours.
Another option, often used alongside speech therapy, is using a speech therapy hand-held tool that helps isolate the sound being pronounced badly and gives an image of the proper tongue placement to enable better pronunciation.
One study tested a handheld tactical tool (known as Speech Buddies) and the traditional speech therapy methods. The study found that students who used the hand-held tool (alongside speech therapy) improved 33% faster than those who used only the traditional speech therapy methods.
Have you or someone you know ever struggled with rhotacism? Let us know what you think in the comments below!
- Category: Wellness
- Tag: language , Language Disorder

- Overcoming Anxiety At Work: Steps to Promote Wellness Towards Successful Career

Pin It on Pinterest
Share this post with your friends!
Speech Blubs
by Blub Blub
Browse topics
All blog posts 404
Popular topics
100+ fun activities for kids that will keep them entertained for hours! Target speech development through play and games. They won’t even know they are learning!
Learn about your baby and toddler developmental milestones! Check if you are on track, when to worry, and how to work on skills like language, potty training, and feeding!
Every child is different! Here are speech and language tips and tools for kids with learning differences, alongside information for parents provided by speech therapists.
Parenting starts with your well-being! Here is some advice on how to teach life skills, work from home, distance learning, along with tips for developing parenting coping skills.
We help kids speak no matter their speech challenges! Speech therapists advise parents about late talkers, speech delay, stuttering, apraxia, articulation, and other speech impediments.
From your first worry to your first appointment, and your last speech therapy session – find the information you need to help your child thrive and gain necessary speech skills.
Parent's Academy › Speech Disorders › Speech Impediments › 6 Types of Speech Impediments
6 Types of Speech Impediments
Stacie bennett.
Speech-Language Pathologist , Trenton , New Jersey
Jan 28, 2022 ‘Speech and language impediment’ is a very broad term that refers to a communication disorder in an individual that has depressed social, language, communication, hearing, or fluency skills.
In This Article
Speech therapy exercises with speech blubs, apraxia of speech, speech sound disorder, specific language impairment, language-based learning disabilities, key takeaways about speech impediments.
A speech impediment relates to the way an individual produces or articulates specific sounds. One example of this is stuttering. Under the umbrella of a speech impairment lies several different types of disorders with which a child or adult can be diagnosed.
A language impairment involves understanding and sharing thoughts and ideas. For example, this person may not have adequate or “age-appropriate” vocabulary and grammar skills. Again, there are several different language disorders that fall under this category that will be addressed in this blog.
Speech Blubs is a language therapy app with a vast library of more than 1,500 activities, face filters, voice-activated activities, and educational bonus videos.
The more you practice, the more it carries over! Try the Speech Blubs app for fun and engaging therapy sessions with your little one.
Boost Your Child’s Speech Development!
Improve language & communication skills with fun learning!

3 Types of Speech Disorders
Apraxia of speech is a neurogenic (starts in the nervous system) communication disorder that involves the planning system for speech.
Individuals with Apraxia know what they want to say, but there is a disconnect in the part of the brain that tells a specific muscle to move. When someone is diagnosed with apraxia of speech , they may have signs of groping, which is where the mouth searches for the position to create the sound.
When this occurs, it affects how long or short the sounds are, and could lead to odd pitch or volume issues and to sounds being distorted or substituted. A tell-tale sign of someone who has apraxia is that they lose the ability to produce sounds that they previously could say.
For instance, if you ask a child to say the word “dog,” which they do successfully and then ask them to say the same word again 10 minutes later, they will not be able to do it.
Speech sound disorders may be of two varieties: articulation (the production of sounds) or phonological processes (sound patterns).
An articulation disorder may take the form of substitution, omission, addition, or distortion of normal speech sounds.
Phonological process disorders may involve more systematic difficulties with the production of particular types of sounds, such as those made in the back of the mouth, like “k” and “g” (ASHA 2018).
Educating a child on the appropriate ways to produce a speech sound and encouraging the child to practice this articulation over time may produce natural speech.
For additional reading on articulation and phonological disorders, check these blogs:
- What Are Phonological Processes
- Process of Articulation Therapy
Stuttering is a disruption in the fluency of an individual’s speech, which begins in childhood and may persist over a lifetime.
Stuttering is a form of disfluency (an inability to produce fluent speech). Disfluency becomes a problem because it impedes successful communication between two parties. Disfluencies may be due to unwanted repetitions of sounds (e.g., “I-I-I want ice cream”), or the extension of speech sounds (e.g., “S——tart the wash”), syllables (e.g., “Na-na-na nasty”), or words (e.g., “go-go-go to the store”). Disfluencies also incorporate unintentional pauses in speech, in which the individual is unable to produce speech sounds (ASHA 2016).
Unfortunately, the cause of stuttering is unknown, which makes it more difficult to treat. Treatment can vary from person to person depending on the severity and type of stuttering that is occurring.

Read more on how to distinguish stuttering as a part of typical speech development from stuttering as a speech disorder!
3 Types of Language Disorders
Specific Learning Impairment (SLI) is diagnosed when a child’s language is not developing as rapidly or as typically as other children. In order for a child to be diagnosed with SLI, they cannot have Autism Spectrum Disorder, Apraxia, hearing loss, or an abnormality of the speech mechanisms. If those disorders are present, they do not have SLI and are exhibiting speech patterns typical of those diagnoses. Usually, the first indication of SLI is that the child is later than usual in starting to speak and subsequently is delayed in putting words together to form sentences. Spoken language may be immature. In many children with SLI, understanding of language , or receptive language, is also impaired, though this may not be obvious unless the child is given a formal assessment. This diagnosis is reserved for children whose language difficulties persist into school age, not for children who are speech delayed and eventually catch up to their peers.
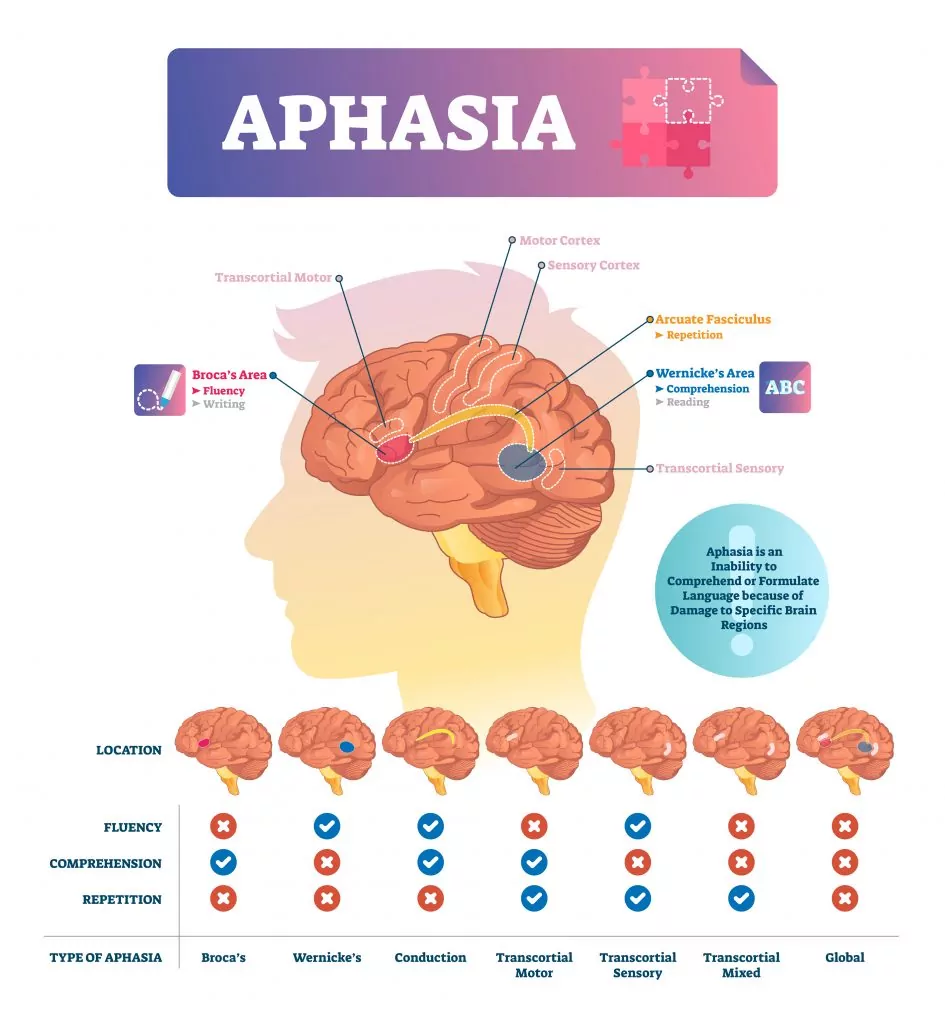
Aphasia is an inability to comprehend or formulate language because of damage to specific brain regions.
The major causes are a cerebral vascular accident (stroke), or head trauma, but aphasia can also be the result of brain tumors, brain infections, or neurodegenerative diseases such as dementia (ASHA 2017).
The difficulties of people with aphasia can range from occasional trouble finding words, to losing the ability to speak, read, or write; intelligence, however, is unaffected. Any person of any age can develop aphasia, given that it is often caused by a traumatic injury. However, people who are middle-aged and older are the most likely to experience the problem.
Language-based learning disabilities occur in children who are falling behind their same-aged peers. These children will have difficulties with spelling, reading, and/or writing, but have normal intelligence levels. This is a common source of academic struggles in young children and can often be misdiagnosed or missed in typical assessments.
The key to supporting students with LBLD is knowing how to adjust curriculum and instruction to ensure they develop proficient language and literacy skills . Most individuals with LBLD need instruction that is specialized, explicit, structured, and multisensory, as well as ongoing, guided practice aimed at remediating their specific areas of weakness.
There are a lot of speech and language impediments that can occur in children and adults. This blog only scratches the surface of these disorders, so please stay tuned and check out Speech Blubs regularly for more in-depth blogs regarding these subjects.
If there’s a topic you’d like to know more about, please reach out to us and we will get working on it! As always, if you feel like your child is exhibiting any signs or symptoms of these disorders, it’s important that you make an appointment with a speech-language pathologist as soon as possible to get a full evaluation.
Speech Blubs is helping kids speak. Download now for fun & educational content to practice speech at home!
Have a question for our Speech Therapists?

The author’s views are entirely his or her own and may not necessarily reflect the views of Blub Blub Inc. All content provided on this website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for independent professional medical judgement, advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.
Related articles
25 speech and language terms every parent should know.
Whether we are speaking to teachers, health visitors, or speech therapists, there is a lot of new information for any parent to digest and understand. So,...
Innovating Speech Therapy: A Closer Look at the Dorchester District No. 2 Webinar
The recent collaboration between Speech Blubs Pro and Dorchester School District No. 2 represents a significant step forward in applying digital tools to speech therapy….
Get started with Speech Blubs
Cancel anytime, hassle-free!
American Speech-Language-Hearing Association
- Certification
- Publications
- Continuing Education
- Practice Management
- Audiologists
- Speech-Language Pathologists
- Academic & Faculty
- Audiology & SLP Assistants
Speech Sound Disorders-Articulation and Phonology
View All Portal Topics
See the Speech Sound Disorders Evidence Map for summaries of the available research on this topic.
The scope of this page is speech sound disorders with no known cause—historically called articulation and phonological disorders —in preschool and school-age children (ages 3–21).
Information about speech sound problems related to motor/neurological disorders, structural abnormalities, and sensory/perceptual disorders (e.g., hearing loss) is not addressed in this page.
See ASHA's Practice Portal pages on Childhood Apraxia of Speech and Cleft Lip and Palate for information about speech sound problems associated with these two disorders. A Practice Portal page on dysarthria in children will be developed in the future.
Speech Sound Disorders
Speech sound disorders is an umbrella term referring to any difficulty or combination of difficulties with perception, motor production, or phonological representation of speech sounds and speech segments—including phonotactic rules governing permissible speech sound sequences in a language.
Speech sound disorders can be organic or functional in nature. Organic speech sound disorders result from an underlying motor/neurological, structural, or sensory/perceptual cause. Functional speech sound disorders are idiopathic—they have no known cause. See figure below.
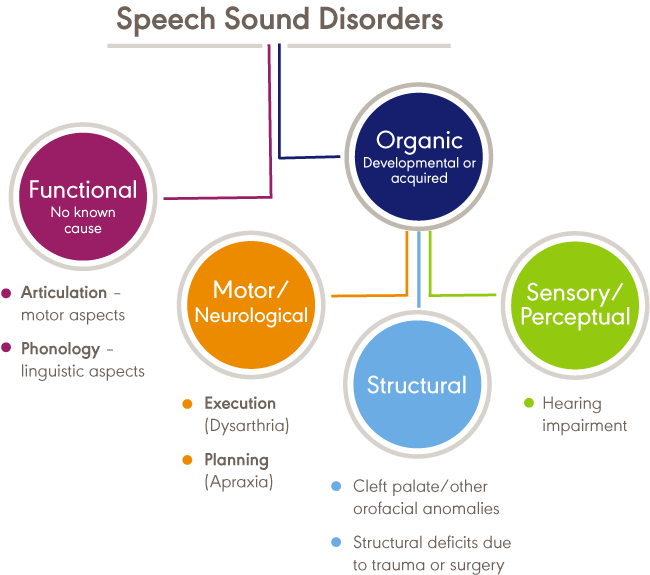
Organic Speech Sound Disorders
Organic speech sound disorders include those resulting from motor/neurological disorders (e.g., childhood apraxia of speech and dysarthria), structural abnormalities (e.g., cleft lip/palate and other structural deficits or anomalies), and sensory/perceptual disorders (e.g., hearing loss).
Functional Speech Sound Disorders
Functional speech sound disorders include those related to the motor production of speech sounds and those related to the linguistic aspects of speech production. Historically, these disorders are referred to as articulation disorders and phonological disorders , respectively. Articulation disorders focus on errors (e.g., distortions and substitutions) in production of individual speech sounds. Phonological disorders focus on predictable, rule-based errors (e.g., fronting, stopping, and final consonant deletion) that affect more than one sound. It is often difficult to cleanly differentiate between articulation and phonological disorders; therefore, many researchers and clinicians prefer to use the broader term, "speech sound disorder," when referring to speech errors of unknown cause. See Bernthal, Bankson, and Flipsen (2017) and Peña-Brooks and Hegde (2015) for relevant discussions.
This Practice Portal page focuses on functional speech sound disorders. The broad term, "speech sound disorder(s)," is used throughout; articulation error types and phonological error patterns within this diagnostic category are described as needed for clarity.
Procedures and approaches detailed in this page may also be appropriate for assessing and treating organic speech sound disorders. See Speech Characteristics: Selected Populations [PDF] for a brief summary of selected populations and characteristic speech problems.
Incidence and Prevalence
The incidence of speech sound disorders refers to the number of new cases identified in a specified period. The prevalence of speech sound disorders refers to the number of children who are living with speech problems in a given time period.
Estimated prevalence rates of speech sound disorders vary greatly due to the inconsistent classifications of the disorders and the variance of ages studied. The following data reflect the variability:
- Overall, 2.3% to 24.6% of school-aged children were estimated to have speech delay or speech sound disorders (Black, Vahratian, & Hoffman, 2015; Law, Boyle, Harris, Harkness, & Nye, 2000; Shriberg, Tomblin, & McSweeny, 1999; Wren, Miller, Peters, Emond, & Roulstone, 2016).
- A 2012 survey from the National Center for Health Statistics estimated that, among children with a communication disorder, 48.1% of 3- to 10-year old children and 24.4% of 11- to 17-year old children had speech sound problems only. Parents reported that 67.6% of children with speech problems received speech intervention services (Black et al., 2015).
- Residual or persistent speech errors were estimated to occur in 1% to 2% of older children and adults (Flipsen, 2015).
- Reports estimated that speech sound disorders are more prevalent in boys than in girls, with a ratio ranging from 1.5:1.0 to 1.8:1.0 (Shriberg et al., 1999; Wren et al., 2016).
- Prevalence rates were estimated to be 5.3% in African American children and 3.8% in White children (Shriberg et al., 1999).
- Reports estimated that 11% to 40% of children with speech sound disorders had concomitant language impairment (Eadie et al., 2015; Shriberg et al., 1999).
- Poor speech sound production skills in kindergarten children have been associated with lower literacy outcomes (Overby, Trainin, Smit, Bernthal, & Nelson, 2012). Estimates reported a greater likelihood of reading disorders (relative risk: 2.5) in children with a preschool history of speech sound disorders (Peterson, Pennington, Shriberg, & Boada, 2009).
Signs and Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of functional speech sound disorders include the following:
- omissions/deletions —certain sounds are omitted or deleted (e.g., "cu" for "cup" and "poon" for "spoon")
- substitutions —one or more sounds are substituted, which may result in loss of phonemic contrast (e.g., "thing" for "sing" and "wabbit" for "rabbit")
- additions —one or more extra sounds are added or inserted into a word (e.g., "buhlack" for "black")
- distortions —sounds are altered or changed (e.g., a lateral "s")
- syllable-level errors —weak syllables are deleted (e.g., "tephone" for "telephone")
Signs and symptoms may occur as independent articulation errors or as phonological rule-based error patterns (see ASHA's resource on selected phonological processes [patterns] for examples). In addition to these common rule-based error patterns, idiosyncratic error patterns can also occur. For example, a child might substitute many sounds with a favorite or default sound, resulting in a considerable number of homonyms (e.g., shore, sore, chore, and tore might all be pronounced as door ; Grunwell, 1987; Williams, 2003a).
Influence of Accent
An accent is the unique way that speech is pronounced by a group of people speaking the same language and is a natural part of spoken language. Accents may be regional; for example, someone from New York may sound different than someone from South Carolina. Foreign accents occur when a set of phonetic traits of one language are carried over when a person learns a new language. The first language acquired by a bilingual or multilingual individual can influence the pronunciation of speech sounds and the acquisition of phonotactic rules in subsequently acquired languages. No accent is "better" than another. Accents, like dialects, are not speech or language disorders but, rather, only reflect differences. See ASHA's Practice Portal pages on Multilingual Service Delivery in Audiology and Speech-Language Pathology and Cultural Responsiveness .
Influence of Dialect
Not all sound substitutions and omissions are speech errors. Instead, they may be related to a feature of a speaker's dialect (a rule-governed language system that reflects the regional and social background of its speakers). Dialectal variations of a language may cross all linguistic parameters, including phonology, morphology, syntax, semantics, and pragmatics. An example of a dialectal variation in phonology occurs with speakers of African American English (AAE) when a "d" sound is used for a "th" sound (e.g., "dis" for "this"). This variation is not evidence of a speech sound disorder but, rather, one of the phonological features of AAE.
Speech-language pathologists (SLPs) must distinguish between dialectal differences and communicative disorders and must
- recognize all dialects as being rule-governed linguistic systems;
- understand the rules and linguistic features of dialects represented by their clientele; and
- be familiar with nondiscriminatory testing and dynamic assessment procedures, such as identifying potential sources of test bias, administering and scoring standardized tests using alternative methods, and analyzing test results in light of existing information regarding dialect use (see, e.g., McLeod, Verdon, & The International Expert Panel on Multilingual Children's Speech, 2017).
See ASHA's Practice Portal pages on Multilingual Service Delivery in Audiology and Speech-Language Pathology and Cultural Responsiveness .
The cause of functional speech sound disorders is not known; however, some risk factors have been investigated.
Frequently reported risk factors include the following:
- Gender —the incidence of speech sound disorders is higher in males than in females (e.g., Everhart, 1960; Morley, 1952; Shriberg et al., 1999).
- Pre- and perinatal problems —factors such as maternal stress or infections during pregnancy, complications during delivery, preterm delivery, and low birthweight were found to be associated with delay in speech sound acquisition and with speech sound disorders (e.g., Byers Brown, Bendersky, & Chapman, 1986; Fox, Dodd, & Howard, 2002).
- Family history —children who have family members (parents or siblings) with speech and/or language difficulties were more likely to have a speech disorder (e.g., Campbell et al., 2003; Felsenfeld, McGue, & Broen, 1995; Fox et al., 2002; Shriberg & Kwiatkowski, 1994).
- Persistent otitis media with effusion —persistent otitis media with effusion (often associated with hearing loss) has been associated with impaired speech development (Fox et al., 2002; Silva, Chalmers, & Stewart, 1986; Teele, Klein, Chase, Menyuk, & Rosner, 1990).
Roles and Responsibilities
Speech-language pathologists (SLPs) play a central role in the screening, assessment, diagnosis, and treatment of persons with speech sound disorders. The professional roles and activities in speech-language pathology include clinical/educational services (diagnosis, assessment, planning, and treatment); prevention and advocacy; and education, administration, and research. See ASHA's Scope of Practice in Speech-Language Pathology (ASHA, 2016).
Appropriate roles for SLPs include the following:
- Providing prevention information to individuals and groups known to be at risk for speech sound disorders, as well as to individuals working with those at risk
- Educating other professionals on the needs of persons with speech sound disorders and the role of SLPs in diagnosing and managing speech sound disorders
- Screening individuals who present with speech sound difficulties and determining the need for further assessment and/or referral for other services
- Recognizing that students with speech sound disorders have heightened risks for later language and literacy problems
- Conducting a culturally and linguistically relevant comprehensive assessment of speech, language, and communication
- Taking into consideration the rules of a spoken accent or dialect, typical dual-language acquisition from birth, and sequential second-language acquisition to distinguish difference from disorder
- Diagnosing the presence or absence of a speech sound disorder
- Referring to and collaborating with other professionals to rule out other conditions, determine etiology, and facilitate access to comprehensive services
- Making decisions about the management of speech sound disorders
- Making decisions about eligibility for services, based on the presence of a speech sound disorder
- Developing treatment plans, providing intervention and support services, documenting progress, and determining appropriate service delivery approaches and dismissal criteria
- Counseling persons with speech sound disorders and their families/caregivers regarding communication-related issues and providing education aimed at preventing further complications related to speech sound disorders
- Serving as an integral member of an interdisciplinary team working with individuals with speech sound disorders and their families/caregivers (see ASHA's resource on interprofessional education/interprofessional practice [IPE/IPP] )
- Consulting and collaborating with professionals, family members, caregivers, and others to facilitate program development and to provide supervision, evaluation, and/or expert testimony (see ASHA's resource on person- and family-centered care )
- Remaining informed of research in the area of speech sound disorders, helping advance the knowledge base related to the nature and treatment of these disorders, and using evidence-based research to guide intervention
- Advocating for individuals with speech sound disorders and their families at the local, state, and national levels
As indicated in the Code of Ethics (ASHA, 2023), SLPs who serve this population should be specifically educated and appropriately trained to do so.
See the Assessment section of the Speech Sound Disorders Evidence Map for pertinent scientific evidence, expert opinion, and client/caregiver perspective.
Screening is conducted whenever a speech sound disorder is suspected or as part of a comprehensive speech and language evaluation for a child with communication concerns. The purpose of the screening is to identify individuals who require further speech-language assessment and/or referral for other professional services.
Screening typically includes
- screening of individual speech sounds in single words and in connected speech (using formal and or informal screening measures);
- screening of oral motor functioning (e.g., strength and range of motion of oral musculature);
- orofacial examination to assess facial symmetry and identify possible structural bases for speech sound disorders (e.g., submucous cleft palate, malocclusion, ankyloglossia); and
- informal assessment of language comprehension and production.
See ASHA's resource on assessment tools, techniques, and data sources .
Screening may result in
- recommendation to monitor speech and rescreen;
- referral for multi-tiered systems of support such as response to intervention (RTI) ;
- referral for a comprehensive speech sound assessment;
- recommendation for a comprehensive language assessment, if language delay or disorder is suspected;
- referral to an audiologist for a hearing evaluation, if hearing loss is suspected; and
- referral for medical or other professional services, as appropriate.
Comprehensive Assessment
The acquisition of speech sounds is a developmental process, and children often demonstrate "typical" errors and phonological patterns during this acquisition period. Developmentally appropriate errors and patterns are taken into consideration during assessment for speech sound disorders in order to differentiate typical errors from those that are unusual or not age appropriate.
The comprehensive assessment protocol for speech sound disorders may include an evaluation of spoken and written language skills, if indicated. See ASHA's Practice Portal pages on Spoken Language Disorders and Written Language Disorders .
Assessment is accomplished using a variety of measures and activities, including both standardized and nonstandardized measures, as well as formal and informal assessment tools. See ASHA's resource on assessment tools, techniques, and data sources .
SLPs select assessments that are culturally and linguistically sensitive, taking into consideration current research and best practice in assessing speech sound disorders in the languages and/or dialect used by the individual (see, e.g., McLeod et al., 2017). Standard scores cannot be reported for assessments that are not normed on a group that is representative of the individual being assessed.
SLPs take into account cultural and linguistic speech differences across communities, including
- phonemic and allophonic variations of the language(s) and/or dialect(s) used in the community and how those variations affect determination of a disorder or a difference and
- differences among speech sound disorders, accents, dialects, and patterns of transfer from one language to another. See phonemic inventories and cultural and linguistic information across languages .
Consistent with the World Health Organization's (WHO) International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF) framework (ASHA, 2016a; WHO, 2001), a comprehensive assessment is conducted to identify and describe
- impairments in body structure and function, including underlying strengths and weaknesses in speech sound production and verbal/nonverbal communication;
- co-morbid deficits or conditions, such as developmental disabilities, medical conditions, or syndromes;
- limitations in activity and participation, including functional communication, interpersonal interactions with family and peers, and learning;
- contextual (environmental and personal) factors that serve as barriers to or facilitators of successful communication and life participation; and
- the impact of communication impairments on quality of life of the child and family.
See ASHA's Person-Centered Focus on Function: Speech Sound Disorder [PDF] for an example of assessment data consistent with ICF.
Assessment may result in
- diagnosis of a speech sound disorder;
- description of the characteristics and severity of the disorder;
- recommendations for intervention targets;
- identification of factors that might contribute to the speech sound disorder;
- diagnosis of a spoken language (listening and speaking) disorder;
- identification of written language (reading and writing) problems;
- recommendation to monitor reading and writing progress in students with identified speech sound disorders by SLPs and other professionals in the school setting;
- referral for multi-tiered systems of support such as response to intervention (RTI) to support speech and language development; and
- referral to other professionals as needed.
Case History
The case history typically includes gathering information about
- the family's concerns about the child's speech;
- history of middle ear infections;
- family history of speech and language difficulties (including reading and writing);
- languages used in the home;
- primary language spoken by the child;
- the family's and other communication partners' perceptions of intelligibility; and
- the teacher's perception of the child's intelligibility and participation in the school setting and how the child's speech compares with that of peers in the classroom.
See ASHA's Practice Portal page on Cultural Responsiveness for guidance on taking a case history with all clients.
Oral Mechanism Examination
The oral mechanism examination evaluates the structure and function of the speech mechanism to assess whether the system is adequate for speech production. This examination typically includes assessment of
- dental occlusion and specific tooth deviations;
- structure of hard and soft palate (clefts, fistulas, bifid uvula); and
- function (strength and range of motion) of the lips, jaw, tongue, and velum.
Hearing Screening
A hearing screening is conducted during the comprehensive speech sound assessment, if one was not completed during the screening.
Hearing screening typically includes
- otoscopic inspection of the ear canal and tympanic membrane;
- pure-tone audiometry; and
- immittance testing to assess middle ear function.
Speech Sound Assessment
The speech sound assessment uses both standardized assessment instruments and other sampling procedures to evaluate production in single words and connected speech.
Single-word testing provides identifiable units of production and allows most consonants in the language to be elicited in a number of phonetic contexts; however, it may or may not accurately reflect production of the same sounds in connected speech.
Connected speech sampling provides information about production of sounds in connected speech using a variety of talking tasks (e.g., storytelling or retelling, describing pictures, normal conversation about a topic of interest) and with a variety of communication partners (e.g., peers, siblings, parents, and clinician).
Assessment of speech includes evaluation of the following:
- Accurate productions
- sounds in various word positions (e.g., initial, within word, and final word position) and in different phonetic contexts;
- sound combinations such as vowel combinations, consonant clusters, and blends; and
- syllable shapes —simple CV to complex CCVCC.
- Speech sound errors
- consistent sound errors;
- error types (e.g., deletions, omissions, substitutions, distortions, additions); and
- error distribution (e.g., position of sound in word).
- Error patterns (i.e., phonological patterns)—systematic sound changes or simplifications that affect a class of sounds (e.g., fricatives), sound combinations (e.g., consonant clusters), or syllable structures (e.g., complex syllables or multisyllabic words).
See Age of Acquisition of English Consonants (Crowe & McLeaod, 2020) [PDF] and ASHA's resource on selected phonological processes (patterns) .
Severity Assessment
Severity is a qualitative judgment made by the clinician indicating the impact of the child's speech sound disorder on functional communication. It is typically defined along a continuum from mild to severe or profound. There is no clear consensus regarding the best way to determine severity of a speech sound disorder—rating scales and quantitative measures have been used.
A numerical scale or continuum of disability is often used because it is time-efficient. Prezas and Hodson (2010) use a continuum of severity from mild (omissions are rare; few substitutions) to profound (extensive omissions and many substitutions; extremely limited phonemic and phonotactic repertoires). Distortions and assimilations occur in varying degrees at all levels of the continuum.
A quantitative approach (Shriberg & Kwiatkowski, 1982a, 1982b) uses the percentage of consonants correct (PCC) to determine severity on a continuum from mild to severe.
To determine PCC, collect and phonetically transcribe a speech sample. Then count the total number of consonants in the sample and the total number of correct consonants. Use the following formula:
PCC = (correct consonants/total consonants) × 100
A PCC of 85–100 is considered mild, whereas a PCC of less than 50 is considered severe. This approach has been modified to include a total of 10 such indices, including percent vowels correct (PVC; Shriberg, Austin, Lewis, McSweeny, & Wilson, 1997).
Intelligibility Assessment
Intelligibility is a perceptual judgment that is based on how much of the child's spontaneous speech the listener understands. Intelligibility can vary along a continuum ranging from intelligible (message is completely understood) to unintelligible (message is not understood; Bernthal et al., 2017). Intelligibility is frequently used when judging the severity of the child's speech problem (Kent, Miolo, & Bloedel, 1994; Shriberg & Kwiatkowski, 1982b) and can be used to determine the need for intervention.
Intelligibility can vary depending on a number of factors, including
- the number, type, and frequency of speech sound errors (when present);
- the speaker's rate, inflection, stress patterns, pauses, voice quality, loudness, and fluency;
- linguistic factors (e.g., word choice and grammar);
- complexity of utterance (e.g., single words vs. conversational or connected speech);
- the listener's familiarity with the speaker's speech pattern;
- communication environment (e.g., familiar vs. unfamiliar communication partners, one-on-one vs. group conversation);
- communication cues for listener (e.g., nonverbal cues from the speaker, including gestures and facial expressions); and
- signal-to-noise ratio (i.e., amount of background noise).
Rating scales and other estimates that are based on perceptual judgments are commonly used to assess intelligibility. For example, rating scales sometimes use numerical ratings like 1 for totally intelligible and 10 for unintelligible, or they use descriptors like not at all, seldom, sometimes, most of the time, or always to indicated how well speech is understood (Ertmer, 2010).
A number of quantitative measures also have been proposed, including calculating the percentage of words understood in conversational speech (e.g., Flipsen, 2006; Shriberg & Kwiatkowski, 1980). See also Kent et al. (1994) for a comprehensive review of procedures for assessing intelligibility.
Coplan and Gleason (1988) developed a standardized intelligibility screener using parent estimates of how intelligible their child sounded to others. On the basis of the data, expected intelligibility cutoff values for typically developing children were as follows:
22 months—50%
37 months—75%
47 months—100%
See the Resources section for resources related to assessing intelligibility and life participation in monolingual children who speak English and in monolingual children who speak languages other than English.
Stimulability Testing
Stimulability is the child's ability to accurately imitate a misarticulated sound when the clinician provides a model. There are few standardized procedures for testing stimulability (Glaspey & Stoel-Gammon, 2007; Powell & Miccio, 1996), although some test batteries include stimulability subtests.
Stimulability testing helps determine
- how well the child imitates the sound in one or more contexts (e.g., isolation, syllable, word, phrase);
- the level of cueing necessary to achieve the best production (e.g., auditory model; auditory and visual model; auditory, visual, and verbal model; tactile cues);
- whether the sound is likely to be acquired without intervention; and
- which targets are appropriate for therapy (Tyler & Tolbert, 2002).
Speech Perception Testing
Speech perception is the ability to perceive differences between speech sounds. In children with speech sound disorders, speech perception is the child's ability to perceive the difference between the standard production of a sound and his or her own error production—or to perceive the contrast between two phonetically similar sounds (e.g., r/w, s/ʃ, f/θ).
Speech perception abilities can be tested using the following paradigms:
- Auditory Discrimination —syllable pairs containing a single phoneme contrast are presented, and the child is instructed to say "same" if the paired items sound the same and "different" if they sound different.
- Picture Identification —the child is shown two to four pictures representing words with minimal phonetic differences. The clinician says one of these words, and the child is asked to point to the correct picture.
- Speech production–perception task —using sounds that the child is suspected of having difficulty perceiving, picture targets containing these sounds are used as visual cues. The child is asked to judge whether the speaker says the item correctly (e.g., picture of a ship is shown; speaker says, "ship" or "sip"; Locke, 1980).
- Mispronunciation detection task —using computer-presented picture stimuli and recorded stimulus names (either correct or with a single phoneme error), the child is asked to detect mispronunciations by pointing to a green tick for "correct" or a red cross for "incorrect" (McNeill & Hesketh, 2010).
- Lexical decision/judgment task —using target pictures and single-word recordings, this task assesses the child's ability to identify words that are pronounced correctly or incorrectly. A picture of the target word (e.g., "lake") is shown, along with a recorded word—either "lake" or a word with a contrasting phoneme (e.g., "wake"). The child points to the picture of the target word if it was pronounced correctly or to an "X" if it was pronounced incorrectly (Rvachew, Nowak, & Cloutier, 2004).
Considerations For Assessing Young Children and/or Children Who Are Reluctant or Have Less Intelligible Speech
Young children might not be able to follow directions for standardized tests, might have limited expressive vocabulary, and might produce words that are unintelligible. Other children, regardless of age, may produce less intelligible speech or be reluctant to speak in an assessment setting.
Strategies for collecting an adequate speech sample with these populations include
- obtaining a speech sample during the assessment session using play activities;
- using pictures or toys to elicit a range of consonant sounds;
- involving parents/caregivers in the session to encourage talking;
- asking parents/caregivers to supplement data from the assessment session by recording the child's speech at home during spontaneous conversation; and
- asking parents/caregivers to keep a log of the child's intended words and how these words are pronounced.
Sometimes, the speech sound disorder is so severe that the child's intended message cannot be understood. However, even when a child's speech is unintelligible, it is usually possible to obtain information about his or her speech sound production.
For example:
- A single-word articulation test provides opportunities for production of identifiable units of sound, and these productions can usually be transcribed.
- It may be possible to understand and transcribe a spontaneous speech sample by (a) using a structured situation to provide context when obtaining the sample and (b) annotating the recorded sample by repeating the child's utterances, when possible, to facilitate later transcription.
Considerations For Assessing Bilingual/Multilingual Populations
Assessment of a bilingual individual requires an understanding of both linguistic systems because the sound system of one language can influence the sound system of another language. The assessment process must identify whether differences are truly related to a speech sound disorder or are normal variations of speech caused by the first language.
When assessing a bilingual or multilingual individual, clinicians typically
- gather information, including
- language history and language use to determine which language(s) should be assessed,
- phonemic inventory, phonological structure, and syllable structure of the non-English language, and
- dialect of the individual;
- assess phonological skills in both languages in single words as well as in connected speech;
- account for dialectal differences, when present; and
- identify and assess the child's
- common substitution patterns (those seen in typically developing children),
- uncommon substitution patterns (those often seen in individuals with a speech sound disorder), and
- cross-linguistic effects (the phonological system of one's native language influencing the production of sounds in English, resulting in an accent—that is, phonetic traits from a person's original language (L1) that are carried over to a second language (L2; Fabiano-Smith & Goldstein, 2010).
See phonemic inventories and cultural and linguistic information across languages and ASHA's Practice Portal page on Multilingual Service Delivery in Audiology and Speech-Language Pathology . See the Resources section for information related to assessing intelligibility and life participation in monolingual children who speak English and in monolingual children who speak languages other than English.
Phonological Processing Assessment
Phonological processing is the use of the sounds of one's language (i.e., phonemes) to process spoken and written language (Wagner & Torgesen, 1987). The broad category of phonological processing includes phonological awareness , phonological working memory , and phonological retrieval .
All three components of phonological processing (see definitions below) are important for speech production and for the development of spoken and written language skills. Therefore, it is important to assess phonological processing skills and to monitor the spoken and written language development of children with phonological processing difficulties.
- Phonological Awareness is the awareness of the sound structure of a language and the ability to consciously analyze and manipulate this structure via a range of tasks, such as speech sound segmentation and blending at the word, onset-rime, syllable, and phonemic levels.
- Phonological Working Memory involves storing phoneme information in a temporary, short-term memory store (Wagner & Torgesen, 1987). This phonemic information is then readily available for manipulation during phonological awareness tasks. Nonword repetition (e.g., repeat "/pæɡ/") is one example of a phonological working memory task.
- Phonological Retrieval is the ability to retrieve phonological information from long-term memory. It is typically assessed using rapid naming tasks (e.g., rapid naming of objects, colors, letters, or numbers). This ability to retrieve the phonological information of one's language is integral to phonological awareness.
Language Assessments
Language testing is included in a comprehensive speech sound assessment because of the high incidence of co-occurring language problems in children with speech sound disorders (Shriberg & Austin, 1998).
Spoken Language Assessment (Listening and Speaking)
Typically, the assessment of spoken language begins with a screening of expressive and receptive skills; a full battery is performed if indicated by screening results. See ASHA's Practice Portal page on Spoken Language Disorders for more details.
Written Language Assessment (Reading and Writing)
Difficulties with the speech processing system (e.g., listening, discriminating speech sounds, remembering speech sounds, producing speech sounds) can lead to speech production and phonological awareness difficulties. These difficulties can have a negative impact on the development of reading and writing skills (Anthony et al., 2011; Catts, McIlraith, Bridges, & Nielsen, 2017; Leitão & Fletcher, 2004; Lewis et al., 2011).
For typically developing children, speech production and phonological awareness develop in a mutually supportive way (Carroll, Snowling, Stevenson, & Hulme, 2003; National Institute for Literacy, 2009). As children playfully engage in sound play, they eventually learn to segment words into separate sounds and to "map" sounds onto printed letters.
The understanding that sounds are represented by symbolic code (e.g., letters and letter combinations) is essential for reading and spelling. When reading, children have to be able to segment a written word into individual sounds, based on their knowledge of the code and then blend those sounds together to form a word. When spelling, children have to be able to segment a spoken word into individual sounds and then choose the correct code to represent these sounds (National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, 2000; Pascoe, Stackhouse, & Wells, 2006).
Components of the written language assessment include the following, depending on the child's age and expected stage of written language development:
- Print Awareness —recognizing that books have a front and back, recognizing that the direction of words is from left to right, and recognizing where words on the page start and stop.
- Alphabet Knowledge —including naming/printing alphabet letters from A to Z.
- Sound–Symbol Correspondence —knowing that letters have sounds and knowing the sounds for corresponding letters and letter combinations.
- Reading Decoding —using sound–symbol knowledge to segment and blend sounds in grade-level words.
- Spelling —using sound–symbol knowledge to spell grade-level words.
- Reading Fluency —reading smoothly without frequent or significant pausing.
- Reading Comprehension —understanding grade-level text, including the ability to make inferences.
See ASHA's Practice Portal page on Written Language Disorders for more details.
See the Treatment section of the Speech Sound Disorders Evidence Map for pertinent scientific evidence, expert opinion, and client/caregiver perspective.
The broad term "speech sound disorder(s)" is used in this Portal page to refer to functional speech sound disorders, including those related to the motor production of speech sounds (articulation) and those related to the linguistic aspects of speech production (phonological).
It is often difficult to cleanly differentiate between articulation and phonological errors or to differentially diagnose these two separate disorders. Nevertheless, we often talk about articulation error types and phonological error types within the broad diagnostic category of speech sound disorder(s). A single child might show both error types, and those specific errors might need different treatment approaches.
Historically, treatments that focus on motor production of speech sounds are called articulation approaches; treatments that focus on the linguistic aspects of speech production are called phonological/language-based approaches.
Articulation approaches target each sound deviation and are often selected by the clinician when the child's errors are assumed to be motor based; the aim is correct production of the target sound(s).
Phonological/language-based approaches target a group of sounds with similar error patterns, although the actual treatment of exemplars of the error pattern may target individual sounds. Phonological approaches are often selected in an effort to help the child internalize phonological rules and generalize these rules to other sounds within the pattern (e.g., final consonant deletion, cluster reduction).
Articulation and phonological/language-based approaches might both be used in therapy with the same individual at different times or for different reasons.
Both approaches for the treatment of speech sound disorders typically involve the following sequence of steps:
- Establishment —eliciting target sounds and stabilizing production on a voluntary level.
- Generalization —facilitating carry-over of sound productions at increasingly challenging levels (e.g., syllables, words, phrases/sentences, conversational speaking).
- Maintenance —stabilizing target sound production and making it more automatic; encouraging self-monitoring of speech and self-correction of errors.
Target Selection
Approaches for selecting initial therapy targets for children with articulation and/or phonological disorders include the following:
- Developmental —target sounds are selected on the basis of order of acquisition in typically developing children.
- Complexity —focuses on more complex, linguistically marked phonological elements not in the child's phonological system to encourage cascading, generalized learning of sounds (Gierut, 2007; Storkel, 2018).
- Dynamic systems —focuses on teaching and stabilizing simple target phonemes that do not introduce new feature contrasts in the child's phonological system to assist in the acquisition of target sounds and more complex targets and features (Rvachew & Bernhardt, 2010).
- Systemic —focuses on the function of the sound in the child's phonological organization to achieve maximum phonological reorganization with the least amount of intervention. Target selection is based on a distance metric. Targets can be maximally distinct from the child's error in terms of place, voice, and manner and can also be maximally different in terms of manner, place of production, and voicing (Williams, 2003b). See Place, Manner and Voicing Chart for English Consonants (Roth & Worthington, 2018) .
- Client-specific —selects targets based on factors such as relevance to the child and his or her family (e.g., sound is in child's name), stimulability, and/or visibility when produced (e.g., /f/ vs. /k/).
- Degree of deviance and impact on intelligibility —selects targets on the basis of errors (e.g., errors of omission; error patterns such as initial consonant deletion) that most effect intelligibility.
See ASHA's Person-Centered Focus on Function: Speech Sound Disorder [PDF] for an example of goal setting consistent with ICF.
Treatment Strategies
In addition to selecting appropriate targets for therapy, SLPs select treatment strategies based on the number of intervention goals to be addressed in each session and the manner in which these goals are implemented. A particular strategy may not be appropriate for all children, and strategies may change throughout the course of intervention as the child's needs change.
"Target attack" strategies include the following:
- Vertical —intense practice on one or two targets until the child reaches a specific criterion level (usually conversational level) before proceeding to the next target or targets (see, e.g., Fey, 1986).
- Horizontal —less intense practice on a few targets; multiple targets are addressed individually or interactively in the same session, thus providing exposure to more aspects of the sounds system (see, e.g., Fey, 1986).
- Cyclical —incorporating elements of both horizontal and vertical structures; the child is provided with practice on a given target or targets for some predetermined period of time before moving on to another target or targets for a predetermined period of time. Practice then cycles through all targets again (see, e.g., Hodson, 2010).
Treatment Options
The following are brief descriptions of both general and specific treatments for children with speech sound disorders. These approaches can be used to treat speech sound problems in a variety of populations. See Speech Characteristics: Selected Populations [PDF] for a brief summary of selected populations and characteristic speech problems.
Treatment selection will depend on a number of factors, including the child's age, the type of speech sound errors, the severity of the disorder, and the degree to which the disorder affects overall intelligibility (Williams, McLeod, & McCauley, 2010). This list is not exhaustive, and inclusion does not imply an endorsement from ASHA.
Contextual Utilization Approaches
Contextual utilization approaches recognize that speech sounds are produced in syllable-based contexts in connected speech and that some (phonemic/phonetic) contexts can facilitate correct production of a particular sound.
Contextual utilization approaches may be helpful for children who use a sound inconsistently and need a method to facilitate consistent production of that sound in other contexts. Instruction for a particular sound is initiated in the syllable context(s) where the sound can be produced correctly (McDonald, 1974). The syllable is used as the building block for practice at more complex levels.
For example, production of a "t" may be facilitated in the context of a high front vowel, as in "tea" (Bernthal et al., 2017). Facilitative contexts or "likely best bets" for production can be identified for voiced, velar, alveolar, and nasal consonants. For example, a "best bet" for nasal consonants is before a low vowel, as in "mad" (Bleile, 2002).
Phonological Contrast Approaches
Phonological contrast approaches are frequently used to address phonological error patterns. They focus on improving phonemic contrasts in the child's speech by emphasizing sound contrasts necessary to differentiate one word from another. Contrast approaches use contrasting word pairs as targets instead of individual sounds.
There are four different contrastive approaches— minimal oppositions, maximal oppositions , treatment of the empty set, and multiple oppositions.
- Minimal Oppositions (also known as "minimal pairs" therapy)—uses pairs of words that differ by only one phoneme or single feature signaling a change in meaning. Minimal pairs are used to help establish contrasts not present in the child's phonological system (e.g., "door" vs. "sore," "pot" vs. "spot," "key" vs. "tea"; Blache, Parsons, & Humphreys, 1981; Weiner, 1981).
- Maximal Oppositions —uses pairs of words containing a contrastive sound that is maximally distinct and varies on multiple dimensions (e.g., voice, place, and manner) to teach an unknown sound. For example, "mall" and "call" are maximal pairs because /m/ and /k/ vary on more than one dimension—/m/ is a bilabial voiced nasal, whereas /k/ is a velar voiceless stop (Gierut, 1989, 1990, 1992). See Place, Manner and Voicing Chart for English Consonants (Roth & Worthington, 2018) .
- Treatment of the Empty Set —similar to the maximal oppositions approach but uses pairs of words containing two maximally opposing sounds (e.g., /r/ and /d/) that are unknown to the child (e.g., "row" vs. "doe" or "ray" vs. "day"; Gierut, 1992).
- Multiple Oppositions —a variation of the minimal oppositions approach but uses pairs of words contrasting a child's error sound with three or four strategically selected sounds that reflect both maximal classification and maximal distinction (e.g., "door," "four," "chore," and "store," to reduce backing of /d/ to /g/; Williams, 2000a, 2000b).
Complexity Approach
The complexity approach is a speech production approach based on data supporting the view that the use of more complex linguistic stimuli helps promote generalization to untreated but related targets.
The complexity approach grew primarily from the maximal oppositions approach. However, it differs from the maximal oppositions approach in a number of ways. Rather than selecting targets on the basis of features such as voice, place, and manner, the complexity of targets is determined in other ways. These include hierarchies of complexity (e.g., clusters, fricatives, and affricates are more complex than other sound classes) and stimulability (i.e., sounds with the lowest levels of stimulability are most complex). In addition, although the maximal oppositions approach trains targets in contrasting word pairs, the complexity approach does not. See Baker and Williams (2010) and Peña-Brooks and Hegde (2015) for detailed descriptions of the complexity approach.
Core Vocabulary Approach
A core vocabulary approach focuses on whole-word production and is used for children with inconsistent speech sound production who may be resistant to more traditional therapy approaches.
Words selected for practice are those used frequently in the child's functional communication. A list of frequently used words is developed (e.g., based on observation, parent report, and/or teacher report), and a number of words from this list are selected each week for treatment. The child is taught his or her "best" word production, and the words are practiced until consistently produced (Dodd, Holm, Crosbie, & McIntosh, 2006).
Cycles Approach
The cycles approach targets phonological pattern errors and is designed for children with highly unintelligible speech who have extensive omissions, some substitutions, and a restricted use of consonants.
Treatment is scheduled in cycles ranging from 5 to 16 weeks. During each cycle, one or more phonological patterns are targeted. After each cycle has been completed, another cycle begins, targeting one or more different phonological patterns. Recycling of phonological patterns continues until the targeted patterns are present in the child's spontaneous speech (Hodson, 2010; Prezas & Hodson, 2010).
The goal is to approximate the gradual typical phonological development process. There is no predetermined level of mastery of phonemes or phoneme patterns within each cycle; cycles are used to stimulate the emergence of a specific sound or pattern—not to produce mastery of it.
Distinctive Feature Therapy
Distinctive feature therapy focuses on elements of phonemes that are lacking in a child's repertoire (e.g., frication, nasality, voicing, and place of articulation) and is typically used for children who primarily substitute one sound for another. See Place, Manner and Voicing Chart for English Consonants (Roth & Worthington, 2018) .
Distinctive feature therapy uses targets (e.g., minimal pairs) that compare the phonetic elements/features of the target sound with those of its substitution or some other sound contrast. Patterns of features can be identified and targeted; producing one target sound often generalizes to other sounds that share the targeted feature (Blache & Parsons, 1980; Blache et al., 1981; Elbert & McReynolds, 1978; McReynolds & Bennett, 1972; Ruder & Bunce, 1981).
Metaphon Therapy
Metaphon therapy is designed to teach metaphonological awareness —that is, the awareness of the phonological structure of language. This approach assumes that children with phonological disorders have failed to acquire the rules of the phonological system.
The focus is on sound properties that need to be contrasted. For example, for problems with voicing, the concept of "noisy" (voiced) versus "quiet" (voiceless) is taught. Targets typically include processes that affect intelligibility, can be imitated, or are not seen in typically developing children of the same age (Dean, Howell, Waters, & Reid, 1995; Howell & Dean, 1994).
Naturalistic Speech Intelligibility Intervention
Naturalist speech intelligibility intervention addresses the targeted sound in naturalistic activities that provide the child with frequent opportunities for the sound to occur. For example, using a McDonald's menu, signs at the grocery store, or favorite books, the child can be asked questions about words that contain the targeted sound(s). The child's error productions are recast without the use of imitative prompts or direct motor training. This approach is used with children who are able to use the recasts effectively (Camarata, 2010).
Nonspeech Oral–Motor Therapy
Nonspeech oral–motor therapy involves the use of oral-motor training prior to teaching sounds or as a supplement to speech sound instruction. The rationale behind this approach is that (a) immature or deficient oral-motor control or strength may be causing poor articulation and (b) it is necessary to teach control of the articulators before working on correct production of sounds. Consult systematic reviews of this treatment to help guide clinical decision making (see, e.g., Lee & Gibbon, 2015 [PDF]; McCauley, Strand, Lof, Schooling, & Frymark, 2009 ). See also the Treatment section of the Speech Sound Disorders Evidence Map filtered for Oral–Motor Exercises .
Speech Sound Perception Training
Speech sound perception training is used to help a child acquire a stable perceptual representation for the target phoneme or phonological structure. The goal is to ensure that the child is attending to the appropriate acoustic cues and weighting them according to a language-specific strategy (i.e., one that ensures reliable perception of the target in a variety of listening contexts).
Recommended procedures include (a) auditory bombardment in which many and varied target exemplars are presented to the child, sometimes in a meaningful context such as a story and often with amplification, and (b) identification tasks in which the child identifies correct and incorrect versions of the target (e.g., "rat" is a correct exemplar of the word corresponding to a rodent, whereas "wat" is not).
Tasks typically progress from the child judging speech produced by others to the child judging the accuracy of his or her own speech. Speech sound perception training is often used before and/or in conjunction with speech production training approaches. See Rvachew, 1994; Rvachew et al., 2004; Rvachew, Rafaat, & Martin, 1999; Wolfe, Presley, & Mesaris, 2003.
Traditionally, the speech stimuli used in these tasks are presented via live voice by the SLP. More recently, computer technology has been used—an advantage of this approach is that it allows for the presentation of more varied stimuli representing, for example, multiple voices and a range of error types.
Treatment Techniques and Technologies
Techniques used in therapy to increase awareness of the target sound and/or provide feedback about placement and movement of the articulators include the following:
- Using a mirror for visual feedback of place and movement of articulators
- Using gestural cueing for place or manner of production (e.g., using a long, sweeping hand gesture for fricatives vs. a short, "chopping" gesture for stops)
- Using ultrasound imaging (placement of an ultrasound transducer under the chin) as a biofeedback technique to visualize tongue position and configuration (Adler-Bock, Bernhardt, Gick, & Bacsfalvi, 2007; Lee, Wrench, & Sancibrian, 2015; Preston, Brick, & Landi, 2013; Preston et al., 2014)
- Using palatography (various coloring agents or a palatal device with electrodes) to record and visualize contact of the tongue on the palate while the child makes different speech sounds (Dagenais, 1995; Gibbon, Stewart, Hardcastle, & Crampin, 1999; Hitchcock, McAllister Byun, Swartz, & Lazarus, 2017)
- Amplifying target sounds to improve attention, reduce distractibility, and increase sound awareness and discrimination—for example, auditory bombardment with low-level amplification is used with the cycles approach at the beginning and end of each session to help children perceive differences between errors and target sounds (Hodson, 2010)
- Providing spectral biofeedback through a visual representation of the acoustic signal of speech (McAllister Byun & Hitchcock, 2012)
- Providing tactile biofeedback using tools, devices, or substances placed within the mouth (e.g., tongue depressors, peanut butter) to provide feedback on correct tongue placement and coordination (Altshuler, 1961; Leonti, Blakeley, & Louis, 1975; Shriberg, 1980)
Considerations for Treating Bilingual/Multilingual Populations
When treating a bilingual or multilingual individual with a speech sound disorder, the clinician is working with two or more different sound systems. Although there may be some overlap in the phonemic inventories of each language, there will be some sounds unique to each language and different phonemic rules for each language.
One linguistic sound system may influence production of the other sound system. It is the role of the SLP to determine whether any observed differences are due to a true communication disorder or whether these differences represent variations of speech associated with another language that a child speaks.
Strategies used when designing a treatment protocol include
- determining whether to use a bilingual or cross-linguistic approach (see ASHA's Practice Portal page on Multilingual Service Delivery in Audiology and Speech-Language Pathology );
- determining the language in which to provide services, on the basis of factors such as language history, language use, and communicative needs;
- identifying alternative means of providing accurate models for target phonemes that are unique to the child's language, when the clinician is unable to do so; and
- noting if success generalizes across languages throughout the treatment process (Goldstein & Fabiano, 2007).
Considerations for Treatment in Schools
Criteria for determining eligibility for services in a school setting are detailed in the Individuals with Disabilities Education Improvement Act of 2004 (IDEA). In accordance with these criteria, the SLP needs to determine
- if the child has a speech sound disorder;
- if there is an adverse effect on educational performance resulting from the disability; and
- if specially designed instruction and/or related services and supports are needed to help the student make progress in the general education curriculum.
Examples of the adverse effect on educational performance include the following:
- The speech sound disorder affects the child's ability or willingness to communicate in the classroom (e.g., when responding to teachers' questions; during classroom discussions or oral presentations) and in social settings with peers (e.g., interactions during lunch, recess, physical education, and extracurricular activities).
- The speech sound disorder signals problems with phonological skills that affect spelling, reading, and writing. For example, the way a child spells a word reflects the errors made when the word is spoken. See ASHA's resource language in brief and ASHA's Practice Portal pages on Spoken Language Disorders and Written Language Disorders for more information about the relationship between spoken and written language
Eligibility for speech-language pathology services is documented in the child's individualized education program, and the child's goals and the dismissal process are explained to parents and teachers. For more information about eligibility for services in the schools, see ASHA's resources on eligibility and dismissal in schools , IDEA Part B Issue Brief: Individualized Education Programs and Eligibility for Services , and 2011 IDEA Part C Final Regulations .
If a child is not eligible for services under IDEA, they may still be eligible to receive services under the Rehabilitation Act of 1973, Section 504. 29 U.S.C. § 701 (1973) . See ASHA's Practice Portal page on Documentation in Schools for more information about Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973.
Dismissal from speech-language pathology services occurs once eligibility criteria are no longer met—that is, when the child's communication problem no longer adversely affects academic achievement and functional performance.
Children With Persisting Speech Difficulties
Speech difficulties sometimes persist throughout the school years and into adulthood. Pascoe et al. (2006) define persisting speech difficulties as "difficulties in the normal development of speech that do not resolve as the child matures or even after they receive specific help for these problems" (p. 2). The population of children with persistent speech difficulties is heterogeneous, varying in etiology, severity, and nature of speech difficulties (Dodd, 2005; Shriberg et al., 2010; Stackhouse, 2006; Wren, Roulstone, & Miller, 2012).
A child with persisting speech difficulties (functional speech sound disorders) may be at risk for
- difficulty communicating effectively when speaking;
- difficulty acquiring reading and writing skills; and
- psychosocial problems (e.g., low self-esteem, increased risk of bullying; see, e.g., McCormack, McAllister, McLeod, & Harrison, 2012).
Intervention approaches vary and may depend on the child's area(s) of difficulty (e.g., spoken language, written language, and/or psychosocial issues).
In designing an effective treatment protocol, the SLP considers
- teaching and encouraging the use of self-monitoring strategies to facilitate consistent use of learned skills;
- collaborating with teachers and other school personnel to support the child and to facilitate his or her access to the academic curriculum; and
- managing psychosocial factors, including self-esteem issues and bullying (Pascoe et al., 2006).
Transition Planning
Children with persisting speech difficulties may continue to have problems with oral communication, reading and writing, and social aspects of life as they transition to post-secondary education and vocational settings (see, e.g., Carrigg, Baker, Parry, & Ballard, 2015). The potential impact of persisting speech difficulties highlights the need for continued support to facilitate a successful transition to young adulthood. These supports include the following:
- Transition Planning —the development of a formal transition plan in middle or high school that includes discussion of the need for continued therapy, if appropriate, and supports that might be needed in postsecondary educational and/or vocational settings (IDEA, 2004).
- Disability Support Services —individualized support for postsecondary students that may include extended time for tests, accommodations for oral speaking assignments, the use of assistive technology (e.g., to help with reading and writing tasks), and the use of methods and devices to augment oral communication, if necessary.
The Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990 (ADA) and Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973 provide protections for students with disabilities who are transitioning to postsecondary education. The protections provided by these acts (a) ensure that programs are accessible to these students and (b) provide aids and services necessary for effective communication (U.S. Department of Education, Office for Civil Rights, 2011).
For more information about transition planning, see ASHA's resource on Postsecondary Transition Planning .
Service Delivery
See the Service Delivery section of the Speech Sound Disorders Evidence Map for pertinent scientific evidence, expert opinion, and client/caregiver perspective.
In addition to determining the type of speech and language treatment that is optimal for children with speech sound disorders, SLPs consider the following other service delivery variables that may have an impact on treatment outcomes:
- Dosage —the frequency, intensity, and duration of service
- Format —whether a person is seen for treatment one-on-one (i.e., individual) or as part of a group
- Provider —the person administering the treatment (e.g., SLP, trained volunteer, caregiver)
- Setting —the location of treatment (e.g. home, community-based, school [pull-out or within the classroom])
- Timing —when intervention occurs relative to the diagnosis.
Technology can be incorporated into the delivery of services for speech sound disorders, including the use of telepractice as a format for delivering face-to-face services remotely. See ASHA's Practice Portal page on Telepractice .
The combination of service delivery factors is important to consider so that children receive optimal intervention intensity to ensure that efficient, effective change occurs (Baker, 2012; Williams, 2012).
ASHA Resources
- Consumer Information: Speech Sound Disorders
- Interprofessional Education/Interprofessional Practice (IPE/IPP)
- Let's Talk: For People With Special Communication Needs
- Person- and Family-Centered Care
- Person-Centered Focus on Function: Speech Sound Disorder [PDF]
- Phonemic Inventories and Cultural and Linguistic Information Across Languages
- Postsecondary Transition Planning
- Selected Phonological Processes (Patterns)
Other Resources
- Age of Acquisition of English Consonants (Crowe & McLeod, 2020) [PDF]
- American Cleft Palate–Craniofacial Association
- English Consonant and Vowel Charts (University of Arizona)
- Everyone Has an Accent
- Free Resources for the Multiple Oppositions approach - Adventures in Speech Pathology
- Multilingual Children's Speech: Overview
- Multilingual Children's Speech: Intelligibility in Context Scale
- Multilingual Children's Speech: Speech Participation and Activity Assessment of Children (SPAA-C)
- Phonetics: The Sounds of American English (University of Iowa)
- Phonological and Phonemic Awareness
- Place, Manner and Voicing Chart for English Consonants (Roth & Worthington, 2018)
- RCSLT: New Long COVID Guidance and Patient Handbook
- The Development of Phonological Skills (WETA Educational Website)
- The Speech Accent Archive (George Mason University)
Adler-Bock, M., Bernhardt, B. M., Gick, B., & Bacsfalvi, P. (2007). The use of ultrasound in remediation of North American English /r/ in 2 adolescents. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 16, 128–139.
Altshuler, M. W. (1961). A therapeutic oral device for lateral emission. Journal of Speech and Hearing Disorders, 26, 179–181.
American Speech-Language-Hearing Association. (2016a). Code of ethics [Ethics]. Available from www.asha.org/policy/
American Speech-Language-Hearing Association. (20016b). Scope of practice in speech-language-pathology [Scope of Practice]. Available from www.asha.org/policy/
Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990, P.L. 101-336, 42 U.S.C. §§ 12101 et seq.
Anthony, J. L., Aghara, R. G., Dunkelberger, M. J., Anthony, T. I., Williams, J. M., & Zhang, Z. (2011). What factors place children with speech sound disorders at risk for reading problems? American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 20, 146–160.
Baker, E. (2012). Optimal intervention intensity. International Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 14, 401–409.
Baker, E., & Williams, A. L. (2010). Complexity approaches to intervention. In S. F. Warren & M. E. Fey (Series Eds.). & A. L. Williams, S. McLeod, & R. J. McCauley (Volume Eds.), Intervention for speech sound disorders in children (pp. 95–115). Baltimore, MD: Brookes.
Bernthal, J., Bankson, N. W., & Flipsen, P., Jr. (2017). Articulation and phonological disorders: Speech sound disorders in children . New York, NY: Pearson.
Blache, S., & Parsons, C. (1980). A linguistic approach to distinctive feature training. Language, Speech, and Hearing Services in Schools, 11, 203–207.
Blache, S. E., Parsons, C. L., & Humphreys, J. M. (1981). A minimal-word-pair model for teaching the linguistic significant difference of distinctive feature properties. Journal of Speech and Hearing Disorders, 46, 291–296.
Black, L. I., Vahratian, A., & Hoffman, H. J. (2015). Communication disorders and use of intervention services among children aged 3–17 years; United States, 2012 (NHS Data Brief No. 205). Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics.
Bleile, K. (2002). Evaluating articulation and phonological disorders when the clock is running. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 11, 243–249.
Byers Brown, B., Bendersky, M., & Chapman, T. (1986). The early utterances of preterm infants. British Journal of Communication Disorders, 21, 307–320.
Camarata, S. (2010). Naturalistic intervention for speech intelligibility and speech accuracy. In A. L. Williams, S. McLeod, & R. J. McCauley (Eds.), Interventions for speech sound disorders in children (pp. 381–406). Baltimore, MD: Brookes.
Campbell, T. F., Dollaghan, C. A., Rockette, H. E., Paradise, J. L., Feldman, H. M., Shriberg, L. D., . . . Kurs-Lasky, M. (2003). Risk factors for speech delay of unknown origin in 3-year-old children. Child Development, 74, 346–357.
Carrigg, B., Baker, E., Parry, L., & Ballard, K. J. (2015). Persistent speech sound disorder in a 22-year-old male: Communication, educational, socio-emotional, and vocational outcomes. Perspectives on School-Based Issues, 16, 37–49.
Carroll, J. M., Snowling, M. J., Stevenson, J., & Hulme, C. (2003). The development of phonological awareness in preschool children. Developmental Psychology, 39, 913–923.
Catts, H. W., McIlraith, A., Bridges, M. S., & Nielsen, D. C. (2017). Viewing a phonological deficit within a multifactorial model of dyslexia. Reading and Writing, 30, 613–629.
Coplan, J., & Gleason, J. R. (1988). Unclear speech: Recognition and significance of unintelligible speech in preschool children. Pediatrics, 82, 447–452.
Crowe, K., & McLeod, S. (2020). Children’s English consonant acquisition in the United States: A review. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 29 (4), 2155-2169. https://doi.org/10.1044/2020_AJSLP-19-00168.
Dagenais, P. A. (1995). Electropalatography in the treatment of articulation/phonological disorders. Journal of Communication Disorders, 28, 303–329.
Dean, E., Howell, J., Waters, D., & Reid, J. (1995). Metaphon: A metalinguistic approach to the treatment of phonological disorder in children. Clinical Linguistics & Phonetics, 9, 1–19.
Dodd, B. (2005). Differential diagnosis and treatment of children with speech disorder . London, England: Whurr.
Dodd, B., Holm, A., Crosbie, S., & McIntosh, B. (2006). A core vocabulary approach for management of inconsistent speech disorder. International Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 8, 220–230.
Eadie, P., Morgan, A., Ukoumunne, O. C., Eecen, K. T., Wake, M., & Reilly, S. (2015). Speech sound disorder at 4 years: Prevalence, comorbidities, and predictors in a community cohort of children. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology, 57, 578–584.
Elbert, M., & McReynolds, L. V. (1978). An experimental analysis of misarticulating children's generalization. Journal of Speech and Hearing Research, 21, 136–149.
Ertmer, D. J. (2010). Relationship between speech intelligibility and word articulation scores in children with hearing loss. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 53, 1075–1086.
Everhart, R. (1960). Literature survey of growth and developmental factors in articulation maturation. Journal of Speech and Hearing Disorders, 25, 59–69.
Fabiano-Smith, L., & Goldstein, B. A. (2010). Phonological acquisition in bilingual Spanish–English speaking children. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 53, 1 60–178.
Felsenfeld, S., McGue, M., & Broen, P. A. (1995). Familial aggregation of phonological disorders: Results from a 28-year follow-up. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 38, 1091–1107.
Fey, M. (1986). Language intervention with young children . Boston, MA: Allyn & Bacon.
Flipsen, P. (2006). Measuring the intelligibility of conversational speech in children. Clinical Linguistics & Phonetics, 20, 202–312.
Flipsen, P. (2015). Emergence and prevalence of persistent and residual speech errors. Seminars in Speech Language, 36, 217–223.
Fox, A. V., Dodd, B., & Howard, D. (2002). Risk factors for speech disorders in children. International Journal of Language and Communication Disorders, 37, 117–132.
Gibbon, F., Stewart, F., Hardcastle, W. J., & Crampin, L. (1999). Widening access to electropalatography for children with persistent sound system disorders. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 8, 319–333.
Gierut, J. A. (1989). Maximal opposition approach to phonological treatment. Journal of Speech and Hearing Research, 54, 9–19.
Gierut, J. A. (1990). Differential learning of phonological oppositions. Journal of Speech and Hearing Research, 33, 540–549.
Gierut, J. A. (1992). The conditions and course of clinically induced phonological change. Journal of Speech and Hearing Research, 35, 1049–1063.
Gierut, J. A. (2007). Phonological complexity and language learnability. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 16, 6–17.
Glaspey, A. M., & Stoel-Gammon, C. (2007). A dynamic approach to phonological assessment. Advances in Speech-Language Pathology, 9, 286–296.
Goldstein, B. A., & Fabiano, L. (2007, February 13). Assessment and intervention for bilingual children with phonological disorders. The ASHA Leader, 12, 6–7, 26–27, 31.
Grunwell, P. (1987). Clinical phonology (2nd ed.). London, England: Chapman and Hall.
Hitchcock, E. R., McAllister Byun, T., Swartz, M., & Lazarus, R. (2017). Efficacy of electropalatography for treating misarticulations of /r/. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 26, 1141–1158.
Hodson, B. (2010). Evaluating and enhancing children's phonological systems: Research and theory to practice. Wichita, KS: PhonoComp.
Howell, J., & Dean, E. (1994). Treating phonological disorders in children: Metaphon—Theory to practice (2nd ed.). London, England: Whurr.
Individuals with Disabilities Education Improvement Act of 2004, P. L. 108-446, 20 U.S.C. §§ 1400 et seq. Retrieved from http://idea.ed.gov/
Kent, R. D., Miolo, G., & Bloedel, S. (1994). The intelligibility of children's speech: A review of evaluation procedures. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 3, 81–95.
Law, J., Boyle, J., Harris, F., Harkness, A., & Nye, C. (2000). Prevalence and natural history of primary speech and language delay: Findings from a systematic review of the literature. International Journal of Language and Communication Disorders, 35, 165–188.
Lee, A. S. Y., & Gibbon, F. E. (2015). Non-speech oral motor treatment for children with developmental speech sound disorders. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 2015 (3), 1–42.
Lee, S. A. S., Wrench, A., & Sancibrian, S. (2015). How to get started with ultrasound technology for treatment of speech sound disorders. Perspectives on Speech Science and Orofacial Disorders, 25, 66–80.
Leitão, S., & Fletcher, J. (2004). Literacy outcomes for students with speech impairment: Long-term follow-up. International Journal of Language and Communication Disorders, 39, 245–256.
Leonti, S., Blakeley, R., & Louis, H. (1975, November). Spontaneous correction of resistant /ɚ/ and /r/ using an oral prosthesis. Paper presented at the annual convention of the American Speech and Hearing Association, Washington, DC.
Lewis, B. A., Avrich, A. A., Freebairn, L. A., Hansen, A. J., Sucheston, L. E., Kuo, I., . . . Stein, C. M. (2011). Literacy outcomes of children with early childhood speech sound disorders: Impact of endophenotypes. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 54, 1628–1643.
Locke, J. (1980). The inference of speech perception in the phonologically disordered child. Part I: A rationale, some criteria, the conventional tests. Journal of Speech and Hearing Disorders, 45, 431–444.
McAllister Byun, T., & Hitchcock, E. R. (2012). Investigating the use of traditional and spectral biofeedback approaches to intervention for /r/ misarticulation. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 21, 207–221.
McCauley, R. J., Strand, E., Lof, G. L., Schooling, T., & Frymark, T. (2009). Evidence-based systematic review: Effects of nonspeech oral motor exercises on speech. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 18, 343–360.
McCormack, J., McAllister, L., McLeod, S., & Harrison, L. (2012). Knowing, having, doing: The battles of childhood speech impairment. Child Language Teaching and Therapy, 28, 141–157.
McDonald, E. T. (1974). Articulation testing and treatment: A sensory motor approach. Pittsburgh, PA: Stanwix House.
McLeod, S., & Crowe, K. (2018). Children's consonant acquisition in 27 languages: A cross-linguistic review. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 27, 1546–1571.
McLeod, S., Verdon, S., & The International Expert Panel on Multilingual Children's Speech. (2017). Tutorial: Speech assessment for multilingual children who do not speak the same language(s) as the speech-language pathologist. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 26, 691–708.
McNeill, B. C., & Hesketh, A. (2010). Developmental complexity of the stimuli included in mispronunciation detection tasks. International Journal of Language & Communication Disorders, 45, 72–82.
McReynolds, L. V., & Bennett, S. (1972). Distinctive feature generalization in articulation training. Journal of Speech and Hearing Disorders, 37, 462–470.
Morley, D. (1952). A ten-year survey of speech disorders among university students. Journal of Speech and Hearing Disorders, 17, 25–31.
National Institute for Literacy. (2009). Developing early literacy: Report of the National Early Literacy Panel. A scientific synthesis of early literacy development and implications for intervention. Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Education.
National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. (2000). Teaching children to read: An evidence-based assessment of the scientific research literature on reading and its implications for reading instruction [Report of the National Reading Panel]. Washington, DC: Author.
Overby, M.S., Trainin, G., Smit, A. B., Bernthal, J. E., & Nelson, R. (2012). Preliteracy speech sound production skill and later literacy outcomes: A study using the Templin Archive. Language, Speech, and Hearing Services in Schools, 43, 97–115.
Pascoe, M., Stackhouse, J., & Wells, B. (2006). Persisting speech difficulties in children: Children's speech and literacy difficulties, Book 3. West Sussex, England: Whurr.
Peña-Brooks, A., & Hegde, M. N. (2015). Assessment and treatment of articulation and phonological disorders in children . Austin, TX: Pro-Ed.
Peterson, R. L., Pennington, B. F., Shriberg, L. D., & Boada, R. (2009). What influences literacy outcome in children with speech sound disorder? Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 52, 1175-1188.
Powell, T. W., & Miccio, A. W. (1996). Stimulability: A useful clinical tool. Journal of Communication Disorders, 29, 237–253.
Preston, J. L., Brick, N., & Landi, N. (2013). Ultrasound biofeedback treatment for persisting childhood apraxia of speech. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 22, 627–643.
Preston, J. L., McCabe, P., Rivera-Campos, A., Whittle, J. L., Landry, E., & Maas, E. (2014). Ultrasound visual feedback treatment and practice variability for residual speech sound errors. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 57, 2102–2115.
Prezas, R. F., & Hodson, B. W. (2010). The cycles phonological remediation approach. In A. L. Williams, S. McLeod, & R. J. McCauley (Eds.), Interventions for speech sound disorders in children (pp. 137–158). Baltimore, MD: Brookes.
Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973, P.L. No. 93-112, 29 U.S.C. § 794.
Roth, F. P., & Worthington, C. K. (2018). Treatment resource manual for speech-language pathology . San Diego, CA: Plural Publishing.
Ruder, K. F., & Bunce, B. H. (1981). Articulation therapy using distinctive feature analysis to structure the training program: Two case studies. Journal of Speech and Hearing Disorders, 46, 59–65.
Rvachew, S. (1994). Speech perception training can facilitate sound production learning. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 37, 347–357.
Rvachew, S., & Bernhardt, B. M. (2010). Clinical implications of dynamic systems theory for phonological development. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 19, 34–50.
Rvachew, S., Nowak, M., & Cloutier, G. (2004). Effect of phonemic perception training on the speech production and phonological awareness skills of children with expressive phonological delay. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 13, 250–263.
Rvachew, S., Rafaat, S., & Martin, M. (1999). Stimulability, speech perception skills, and treatment of phonological disorders. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 8, 33–43.
Shriberg, L. D. (1980). An intervention procedure for children with persistent /r/ errors. Language, Speech, and Hearing Services in Schools, 11, 102–110.
Shriberg, L. D., & Austin, D. (1998). Comorbidity of speech-language disorders: Implications for a phenotype marker for speech delay. In R. Paul (Ed.), The speech-language connection (pp. 73–117). Baltimore, MD: Brookes.
Shriberg, L. D., Austin, D., Lewis, B., McSweeny, J. L., & Wilson, D. L. (1997). The percentage of consonants correct (PCC) metric: Extensions and reliability data. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 40, 708–722.
Shriberg, L. D., Fourakis, M., Hall, S. D., Karlsson, H. B., Lohmeier, H. L., McSweeny, J. L., . . . Wilson, D. L. (2010). Extensions to the speech disorders classification system (SDCS). Clinical Linguistics & Phonetics, 24, 795–824.
Shriberg, L. D., & Kwiatkowski, J. (1980). Natural Process Analysis (NPA): A procedure for phonological analysis of continuous speech samples. New York, NY: Macmillan.
Shriberg, L. D., & Kwiatkowski, J. (1982a). Phonological disorders II: A conceptual framework for management. Journal of Speech and Hearing Disorders, 47, 242–256.
Shriberg, L. D., & Kwiatkowski, J. (1982b). Phonological disorders III: A procedure for assessing severity of involvement. Journal of Speech and Hearing Disorders, 47, 256–270.
Shriberg, L. D., & Kwiatkowski, J. (1994). Developmental phonological disorders I: A clinical profile. Journal of Speech and Hearing Research, 37, 1100–1126.
Shriberg, L. D., Tomblin, J. B., & McSweeny, J. L. (1999). Prevalence of speech delay in 6-year-old children and comorbidity with language impairment. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 42, 1461–1481.
Silva, P. A., Chalmers, D., & Stewart, I. (1986). Some audiological, psychological, educational and behavioral characteristics of children with bilateral otitis media with effusion. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 19, 165–169.
Stackhouse, J. (2006). Speech and spelling difficulties: Who is at risk and why? In M. Snowling & J. Stackhouse (Eds.), Dyslexia speech and language: A practitioner's handbook (pp. 15–35). West Sussex, England: Whurr.
Storkel, H. L. (2018). The complexity approach to phonological treatment: How to select treatment targets. Language, Speech, and Hearing Sciences in Schools, 49, 463–481.
Storkel, Holly. (2019). Using Developmental Norms for Speech Sounds as a Means of Determining Treatment Eligibility in Schools. Perspectives of the ASHA Special Interest Groups, 4, 67-75.
Teele, D. W., Klein, J. O., Chase, C., Menyuk, P., & Rosner, B. A. (1990). Otitis media in infancy and intellectual ability, school achievement, speech, and language at 7 years. Journal of Infectious Disease, 162, 685–694.
Tyler, A. A., & Tolbert, L. C. (2002). Speech-language assessment in the clinical setting. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 11, 215–220.
U.S. Department of Education, Office for Civil Rights. (2011). Transition of students with disabilities to postsecondary education: A guide for high school educators . Washington, DC: Author. Retrieved from http://www2.ed.gov/about/offices/list/ocr/transitionguide.html
Wagner, R. K., & Torgesen, J. K. (1987). The nature of phonological processing and its causal role in the acquisition of reading skills. Psychological Bulletin, 101, 192–212.
Weiner, F. (1981). Treatment of phonological disability using the method of meaningful minimal contrast: Two case studies. Journal of Speech and Hearing Disorders, 46, 97–103.
Williams, A. L. (2000a). Multiple oppositions: Case studies of variables in phonological intervention. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 9, 289–299.
Williams, A. L. (2000b). Multiple oppositions: Theoretical foundations for an alternative contrastive intervention approach. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 9, 282–288.
Williams, A. L. (2003a). Speech disorders resource guide for preschool children. Clifton Park, NY: Delmar Learning.
Williams, A. L. (2003b). Target selection and treatment outcomes. Perspectives on Language Learning and Education, 10, 12–16.
Williams, A. L. (2012). Intensity in phonological intervention: Is there a prescribed amount? International Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 14, 456–461.
Williams, A. L., McLeod, S., & McCauley, R. J. (2010). Direct speech production intervention. In A. L. Williams, S. McLeod, & R. J. McCauley (Eds.), Interventions for speech sound disorders in children (pp. 27–39). Baltimore, MD: Brookes.
Wolfe, V., Presley, C., & Mesaris, J. (2003). The importance of sound identification training in phonological intervention. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 12, 282–288.
World Health Organization. (2001). International classification of functioning, disability and health. Geneva, Switzerland: Author.
Wren, Y., Miller, L. L., Peters, T. J., Emond, A., & Roulstone, S. (2016). Prevalence and predictors of persistent speech sound disorder at eight years old: Findings from a population cohort study. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research , 59, 647–673.
Wren, Y. E., Roulstone, S. E., & Miller, L. L. (2012). Distinguishing groups of children with persistent speech disorder: Findings from a prospective population study. Logopedics Phoniatrics Vocology, 37, 1–10.
About This Content
Acknowledgements .
Content for ASHA's Practice Portal is developed through a comprehensive process that includes multiple rounds of subject matter expert input and review. ASHA extends its gratitude to the following subject matter experts who were involved in the development of the Speech Sound Disorders: Articulation and Phonology page:
- Elise M. Baker, PhD
- John E. Bernthal, PhD, CCC-A/SLP
- Caroline Bowen, PhD
- Cynthia W. Core, PhD, CCC-SLP
- Sharon B. Hart, PhD, CCC-SLP
- Barbara W. Hodson, PhD, CCC-SLP
- Sharynne McLeod, PhD
- Susan Rvachew, PhD, S-LP(C)
- Cheryl C. Sancibrian, MS, CCC-SLP
- Holly L. Storkel, PhD, CCC-SLP
- Judith E. Trost-Cardamone, PhD, CCC-SLP
- Lynn Williams, PhD, CCC-SLP
Citing Practice Portal Pages
The recommended citation for this Practice Portal page is:
American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (n.d.) Speech Sound Disorders: Articulation and Phonology. (Practice Portal). Retrieved month, day, year, from www.asha.org/Practice-Portal/Clinical-Topics/Articulation-and-Phonology/ .

In This Section
- Practice Portal Home
- Clinical Topics
- Professional Issues
- Advertising Disclaimer
- Advertise with us
Evidence Maps
- ASHA Evidence Maps
Peer Connections
- Connect with your colleagues in the ASHA Community
- ASHA Special Interest Groups
ASHA Related Content
- Find related products in ASHA's Store
- Search for articles on ASHAWire
- ASHA Stream
Content Disclaimer: The Practice Portal, ASHA policy documents, and guidelines contain information for use in all settings; however, members must consider all applicable local, state and federal requirements when applying the information in their specific work setting.
ASHA Corporate Partners
- Become A Corporate Partner

The American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA) is the national professional, scientific, and credentialing association for 234,000 members, certificate holders, and affiliates who are audiologists; speech-language pathologists; speech, language, and hearing scientists; audiology and speech-language pathology assistants; and students.
- All ASHA Websites
- Work at ASHA
- Marketing Solutions
Information For
Get involved.
- ASHA Community
- Become a Mentor
- Become a Volunteer
- Special Interest Groups (SIGs)
Connect With ASHA
American Speech-Language-Hearing Association 2200 Research Blvd., Rockville, MD 20850 Members: 800-498-2071 Non-Member: 800-638-8255
MORE WAYS TO CONNECT
Media Resources
- Press Queries
Site Help | A–Z Topic Index | Privacy Statement | Terms of Use © 1997- American Speech-Language-Hearing Association

COMMENTS
Spasmodic Dysphonia (SD) is a chronic long-term disorder that affects the voice. It is characterized by a spasming of the vocal chords when a person attempts to speak and results in a voice that can be described as shaky, hoarse, groaning, tight, or jittery. It can cause the emphasis of speech to vary considerably.
For example, some speech impediments improve as children grow older. If a medical condition causes speech issues, your speech is likely to improve as you get better. But there are situations when people need long-term speech therapy so they can communicate. If you have a speech impediment, your healthcare provider is your best resource for ...
However, some speech disorders persist. Approximately 5% of children aged three to 17 in the United States experience speech disorders. There are many different types of speech impediments, including: Disfluency. Articulation errors. Ankyloglossia. Dysarthria. Apraxia. This article explores the causes, symptoms, and treatment of the different ...
Speech disorders affect a person's ability to produce sounds that create words, and they can make verbal communication more difficult. Types of speech disorder include stuttering, apraxia, and ...
Common causes of childhood speech impediments include: Autism spectrum disorder: A neurodevelopmental disorder that affects social and interactive development. Cerebral palsy: A congenital (from birth) disorder that affects learning and control of physical movement. Hearing loss: Can affect the way children hear and imitate speech.
There are three general categories of speech impairment: Fluency disorder. This type can be described as continuity, smoothness, rate, and effort in speech production. Voice disorder. A voice ...
Speech and Language Disorders. Speech is how we say sounds and words. People with speech problems may: not say sounds clearly. have a hoarse or raspy voice. repeat sounds or pause when speaking, called stuttering. Language is the words we use to share ideas and get what we want. A person with a language disorder may have problems:
Speech impediments can cause communication problems and feelings of insecurity. Learn about causes and types of speech disorders and how they can be treated. ... Examples of articulation speech impairments include sound omissions, substitutions, and distortions. Phonological disorders result in the misuse of certain speech sounds to form words ...
Signs and Symptoms of Speech Sound Disorders. Your child may substitute one sound for another, leave sounds out, add sounds, or change a sound. It can be hard for others to understand them. It is normal for young children to say the wrong sounds sometimes. For example, your child may make a "w" sound for an "r" and say "wabbit" for "rabbit."
5 Common Speech Disorders in Children: Articulation Disorder: An articulation disorder is a speech sound disorder in which a child has difficulty making certain sounds correctly. Sounds may be omitted or improperly altered during the course of speech. A child may substitute sounds ("wabbit" instead of "rabbit") or add sounds improperly ...
2. Adult Apraxia. Apraxia of speech in adults is also called acquired apraxia of speech, verbal apraxia and dyspraxia. Adults suffer from verbal apraxia because of brain damage, such as a stroke, oxygen deprivation or a traumatic brain injury. Acquired apraxia in adults can affect their speech in various ways.
Examples of speech impediments. Below is a brief overview of a few of the most common speech disorders and speech impediments, along with symptoms and potential treatment options. Apraxia. Apraxia of speech is a speech sound disorder that affects the pathways of the brain. It's characterized by a person having difficulty expressing their ...
Stuttering also may include tension and negative feelings about talking. It may get in the way of how you talk to others. You may want to hide your stuttering. So, you may avoid certain words or situations. For example, you may not want to talk on the phone if that makes you stutter more.
Articulation disorder is a common condition when your child can't make specific sounds. For example, they may always replace "r" with "w" or "th" with "s.". The disorder isn't related to any issues with their brain, mouth or hearing. A speech-language pathologist can diagnose the condition and help your child communicate ...
Disorders of speech and language are common in preschool age children. Disfluencies are disorders in which a person repeats a sound, word, or phrase. Stuttering may be the most serious disfluency. It may be caused by: Genetic abnormalities. Emotional stress. Any trauma to brain or infection.
Rhotacism as a speech impediment. Using a strict classification, only about 5%-10% of the human population speaks in a completely normal way. Everyone else suffers from some type of speech disorder or another. For children of any language, the R sounds are usually the hardest to master and often end up being the last ones a child learns.
This week we cover what goes on behind the scenes of speech disorders. Often this is the most talked about type of problem that speech therapists help, but i...
A speech impediment relates to the way an individual produces or articulates specific sounds. One example of this is stuttering. Under the umbrella of a speech impairment lies several different types of disorders with which a child or adult can be diagnosed. A language impairment involves understanding and sharing thoughts and ideas. For ...
Speech and language impediment is a very broad term that refers to a communication disorder in a... This video will tell you about 6 types of speech impediment.
See the Speech Sound Disorders Evidence Map for summaries of the available research on this topic.. The scope of this page is speech sound disorders with no known cause—historically called articulation and phonological disorders—in preschool and school-age children (ages 3-21).. Information about speech sound problems related to motor/neurological disorders, structural abnormalities, and ...
Dysarthria (pronounced "dis-AR-three-uh") is a motor speech disorder that makes it difficult to form and pronounce words. Motor speech disorders occur when damage to your nervous system prevents you from fully controlling parts of your body that control speech, like your tongue, voice box (larynx) and jaw. Dysarthria makes it challenging to ...