

Press ESC to close

Essay on Unemployment in India: Look at the Most Essential Topic of India for UPSC
Unemployment in India is proving to be the worst state for the country. It is defined under many classifications but the impact of it is that it is leading the country towards lower GDP and low living standards. Unemployment is the state of actively seeking work but not finding any paid function. Rich people in India continue to grow towards richness and the poor turn out to be poorer. All these miserable situations must be placed in your mind along with the facts and statistics. This state is making the country regressive for the people who do not have money. Are you an aspirant searching for significant topics for the UPSC exam? If you are looking for an upsc essay, you have come to the right place because here is the essay on unemployment in India. Go through this article precisely and grab all the points.
Also Read: Permanent Court of Arbitration: Important Notes for UPSC Exam
Essay on Unemployment in India
Unemployment is defined as the health of the economy of a country. It is a scenario when someone actively searches for work but does not get any paid job . The rate of unemployment in a country is measured by a certain formulation. The formula is: Unemployment rate = (Unemployed Workers / Total labour force) × 100. A national sample survey organization has been set up for calculating such situations in a country. This organization comes under MoSPI. MoSPI is abbreviated as Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation. It calculates the unemployment rate in India under three major approaches. These approaches are written below.
#1. Daily Status Approach
The unemployment rate of the citizens of a country is determined by this process. The unemployment status of a person is measured for each day but in a reference of a week. This is done by noticing that if any person is having no gainful work even for one hour in a day, then the person will be described as unemployed for that day.
#2. Weekly Status Approach
This approach is used effectively for measuring the unemployment rate of a nation. This approach works for highlighting the record of few people who did not have gainful or paid work even for an hour of a day. This is also valid for the unemployed people for an hour on any day of the week. This proceeds the date of the survey. A single day in the entire week is determined by this approach.
#3. Usual Status Approach
This is the most common form of reporting the number of unemployed people in a country. The approach tests the estimates of those individuals who had no gainful work or were unemployed for a major time during the whole year i.e. 365 days. It is calculated for the whole year.
Also Read: Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine: A Very Important Healthcare Topic for UPSC
Causes of Unemployment
Many causes are leading to the increment in the unemployment rates in India. The causes include the given points.
#1. Overpopulation is the most important cause of unemployment.
#2. Lack of education is also contributing largely to the unemployment rates. The status of ineffective educational structures, no or low educational levels along with lesser vocational skills of the working population is a major cause.
#3. Bad quality infrastructure and inadequate growth of industries are a cause along with very few investment rates in the sectors of manufacturing.
Also Read: Recusal of Judges: A Potential Topic for The Next UPSC Exam
Have a Look at Other Major Causes!
#1. Lower concentration towards the agriculture sector causing greater unemployment and low investment in modern agricultural technologies.
#2. The other cause is the division of the larger workforce. The workforce is working for informal functioning due to lack of education and henceforth employment measurements are less. For example, construction workers, domestic helpers, etc.
#3. The most influential cause is the regressive state of women in the country. The subservient and orthodox social norms are deteriorating women from continuing employment.
Unemployment in India Essay
The facts say that India’s unemployment rate in February 2021 was 6.9 percent. It is still very down but has turned out to be better than before considering its downfall from 7.8 percent in February 2020 . It indicates that the country is returning to the pre COVID levels in terms of unemployment. The experts from the economic department say that the labour workforce was depressed even before the outbreak of the pandemic and the situation during COVID has made it worse. The Center for Monitoring Indian Economy has claimed that participation from the labour force and employment rates have remained low. This is the data that is indicating labour fallout from labour markets due to lack of jobs.
Also Read: New IT Rules 2021: Facts to Know for UPSC about New Provisions, Patterns & Rules
People Losing Jobs!
The unemployment rate in India is touching heights because of people losing jobs. The people who had jobs are losing them due to lesser market evolution and functioning. In the metropolitan areas, people are degrading financially and losing jobs. CMIE recently claimed that the unemployment rate is dramatically rising. The post-lockdown era is marked by a noticeable drop of 2.5 percent in employment along with a drop of 6.2 percent in the count of unemployment
There has been a reduction of 2.8 percent in the labour force as well.
Types of Unemployment in India
There are different kinds of unemployment traced in India. Disguised unemployment refers to the state when more than the expected number of people are unemployed which is majorly seen in unorganized sectors and agriculture. Seasonal unemployment is a state of a person being seasonally unemployed. Structural unemployment is a factor that arises due to a lack of requisite skills for a certain organization. It is a mismatch between the individual and industry. Cyclical unemployment is something that arises due to recessions or declines in the economic conditions of the country. Vulnerable unemployment is a state where people are working without a definite income and job contact. Technological unemployment is something that occurs due to a lack of technology. It was stated by the World Bank in 2016 that 69% of jobs are threatened under this case.
Also Read: What is Mission Indradhanush: A Potential UPSC Topic Related to Covid-19 Vaccine
Impact of Unemployment
The impact of unemployment is detrimental to the people. It leads to the generation and growth of poverty. It also increases the crime rates of the nation because the young mind finds some illegal and unlawful things to do when they do not get a potential job. The people become enticed by antisocial elements and start losing faith in the democracy of India. Unemployed people who indulge in drugs and commit suicides that are a loss of resources to the nation. It is a way of decreasing and degrading the economy of the country and pushing it towards devastation.
You must keenly know this UPSC essay to upgrade your learning capabilities regarding the current issues of society.
Initiatives by the Government of India
There are many initiatives taken by the government of India for the betterment of people and giving them employment. The initiative for the rural people was taken in 1980 as Integrated Rural Development Programme (IRDP). In 1979, one scheme was launched that was primarily concerned with self-employment and SC/ST people. It was named Training of Rural Youth for Self-Employment (TRYSEM). It gave employment to youth ranging from the age of 18 to 35. RSETI/RUDSETI was launched by the government to minimize the issues of unemployment. The other schemes include PMKVY, Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana which was launched in 2015 to enable the youth towards learning industry skills and getting a potential job.
Schemes Launched by the Government
The most known scheme is MNREGA which stands for Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act. It came in 2005 for giving the right to work to all the citizens. The main aim of this scheme was to provide social security to the people for 100 days of paid work. It gave employment to many people across the nation. Start-Up India scheme and Stand Up India scheme came out in 2016 to uplift the people by developing an entrepreneurship environment for them and giving loan benefits to the SC/ST people and women respectively. The government has been making tremendous efforts to give employment to the youth and to turn the country into a larger economy and development.
Also Read: Addu Atoll UPSC Topic: Why is Addu Atoll Trending All Over India?
We hope that we have covered the essential points in this article. You must be aware of the problems faced by the country and should work appropriately to modify or upgrade the conditions. You must not read the articles for learning but you must enlighten your soul about the situations popping up before the citizens of the country.
If you are finding it difficult to crack the CSE or prepare for it excellently, you must visit UPSC Pathshala . You will get the best guidance over every hindrance and solutions to all your questions. You just have to click on your device and get connected to the most experienced faculties and experts through the websites. You will become confident and intelligent enough to achieve your goals.

One Comment
Unemployment is the traditional and major cause of India which hinders it’s development. I was looking for an article which has the overall outlook to the unemployment in India so that I could get the precise information. This article has helped me in getting it. Do you guys have same opinion?
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Share Article:
About the Author
Shilpa is a professional web content writer and is in deep love with travelling. She completed her mass communication degree and is now dedicatedly playing with words to guide her readers to get the best for themselves. Developing educational content for UPSC, IELTS aspirants from breakthrough research work is her forte. Strongly driven by her zodiac sign Sagittarius, Shilpa loves to live her life on her own notes and completely agrees with the idea of ‘live and let live. Apart from writing and travelling, most of the time she can be seen in the avatar of 'hooman' mom to her pets and street dogs or else you can also catch her wearing the toque blanche and creating magic in the kitchen on weekends.
You might also like

Operation Kaveri UPSC: Let’s Prepare the UPSC Notes for Current UPSC Topic!

UPSC DPA: Let’s Go Through the Complete Guide for the Examination!

PM SVANidhi Scheme UPSC: Let’s Prepare UPSC Notes for This Significant Topic!
Other stories, ias sonal goel biography: learn about her upsc journey and strategy, what is salwa judum: here’re the important facts to note down for upsc.
Forgot your password?
Lost your password? Please enter your email address. You will receive mail with link to set new password.
Back to login

Present Status of Unemployment In India – Explained Pointwise
ForumIAS announcing GS Foundation Program for UPSC CSE 2025-26 from 27th May. Click Here for more information.
- 1 Present Status of Unemployment in India according to “State of Working India 2023” report
- 2.1 Types of Unemployment
- 3.1 Education and Skills Reasons
- 3.2 Social Reasons
- 3.3 Economic Structure reasons
- 4 Why addressing the present status of unemployment is crucial for India’s development?
- 5 What should be the way forward for addressing the present status of unemployment in India?
Recently released report “State of Working India 2023” has higlighted the present status of unemployment in India. The report has been prepared by Azim Premji University’s Centre for Sustainable Employment. The report highlights the trends of Unemployment in India over the decade.
What is Unemployment, and what are the different types of Unemployment?
Definition- Unemployment refers to a situation where a person who is able and willing to work is not able to find a job. It is often used as a measure of the health of an economy, as high levels of unemployment can indicate a lack of available jobs, which in turn can lead to reduced economic growth and increased social and economic inequality.
Types of Unemployment
Read More- Unemployment Forum IAS

What are the reasons for present high unemployment in India?
The reasons behind the present status of unemployment in India are the following-
Education and Skills Reasons
Failure of Indian Education system – Although literacy rates have risen in the last few decades, there still remains a fundamental flaw in the education system in India. The degree-oriented system fails when it comes to producing skilled human resources for specific job profiles in the economy.
Higher educational level among youth – Youth unemployment has increased significantly from 2011-12 to 2021-22, nearly doubling during this period. As educational attainment improves , more educated individuals are less inclined to accept unskilled and informal jobs. This is the reason behind high unemployment among graduate youth.
Social Reasons
Joint Family System – It has encouraged disguised unemployment. In big families having large business establishments, many persons don’t do any work and are dependent on the joint income of the family. The joint family system is more prevalent in rural areas, with families employed in the agricultural sector.
Rush for government jobs for social prestige and security – Many educated youth are running behind government jobs due to social pressure, socially respected job profile and social security. This has to a situation where many students choose to remain unemployed during preparation for government jobs.
Low mobility of Labour due to social reasons – People generally avoid migrating to far-off areas of work due to factors like diversity of language, religion, customs and family loyalty . This low labour mobility has contributed to the high unemployment in India.
Expansion of social security measures – The government has increased the distribution of food under the National Food Security Act. This has reduced the pressure on individuals to immediately seek employment. It allows them more time to “search for work, ” which has also contributed to the increase in the unemployment rate.
Economic Structure reasons
Economic growth model promoting informal job creation like Gig Economy – Economic growth model of India has been tilted towards gig economy which is based on informal and contractual jobs. Thus, even though the workers have moved out of the agricultural sector, they have been absorbed in the informal and contractual employment as opposed to formal employment. Ex- Delivery boys, service providers.
The decline of Small Scale and Cottage Industries- Independent India’s preference to large scale industry and new industrial policy of the 1990s has resulted in the decline of small scale industries. This has resulted in high unemployment in rural areas.
Huge dependence on agricultural sector- Agriculture remains the biggest employer in the country. The seasonal nature of employment in the agricultural sector has led to recurring cycles of unemployment for the rural population.
Why addressing the present status of unemployment is crucial for India’s development?
Reaping the demographic dividend – India could get old before it becomes rich if the present status of unemployment is not addressed. The high unemployment in India will prevent us from reaping the benefits that our demographic dividend may provide.
Women’s Empowerment- Increasing the female formal job opportunities will lead to socio-economic upliftment of women in different fields.
Poverty alleviation- Increasing formal employment and addressing the flaws in the informal sector jobs will help India alleviate poverty. This will improve the socio-economic position of the vulnerable sections of the society.
Lead India into the league of developed nations – Addressing the present status of unemployment is indispensable for leveraging the contribution of women and the youth. Both are crucial population segments which will propel India towards becoming a developed economy.
What should be the way forward for addressing the present status of unemployment in India?
Need for National Employment Policy (NEP)- There is a need for formulation of National Employment Policy (NEP) that would encompass a set of multidimensional interventions ranging from social to economic issues.
Special packages for Labour Intensive Industries – Government must provide special packages for labour intensive industries like leather and footwear , food processing, furniture and home decor, textiles and apparel. These industries have high potential for generating more jobs per capital spent.
Focus on resource based development- Decentralisation of Industrial activities based on resources will address the problem of labour mobility and provide employment opportunities in backward regions of the country like Jharkhand, Odisha.
Proper Implementation of New Education Policy – The proper implementation of New Education Policy will reduce the distance between Industry and academia. Incubation centers need to be promoted to cultivate original business ideas that will be financially viable for employment generation.
Removal of social barriers for more women participation- SHGs led women employment schemes like Kudumbashree must be promoted to break the social barriers for entry of women in job market.
Greater public investment – The government must make greater public investment in sectors like health, education, police and judiciary to create many government jobs and associated employment opportunities.
Proper Implementation of the government employment schemes – Government schemes like Atma Nirbhar Bharat Rojgar Yojana (ABRY), Pradhan Mantri Rojgar Protsahan Yojana (PMRPY), Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) etc. must be properly implemented for reducing the present levels of unemployment in India.
Source- Indian Express

Type your email…
Search Articles
Latest articles.
- 10 PM UPSC Current Affairs Quiz 1 June, 2024
- 9 PM UPSC Current Affairs Articles 1st June, 2024
- Significance of the successful test flight of Agnibaan
- Urban Heat Island effect makes cities like Chennai hotter than rural areas
- Issue with juvenile detention in India
- Impact of Methodological Changes on Poverty Data in India’s 2022-23 Household Consumption Expenditure Survey
- Need for One Nation Many Election
- UPSC Prelims Marathon 1st June – Buddhism (Origin, Doctrine, Schools) Jainism and Ajivika sect – 2024
- 10 PM UPSC Current Affairs Quiz 31 May, 2024
- 9 PM UPSC Current Affairs Articles 31st May, 2024
Prelims 2024 Current Affairs
- Art and Culture
- Indian Economy
- Science and Technology
- Environment & Ecology
- International Relations
- Polity & Nation
- Important Bills and Acts
- International Organizations
- Index, Reports and Summits
- Government Schemes and Programs
- Miscellaneous
- Species in news
Download Hallticket For Simulator X
- UPSC IAS Exam Pattern
- UPSC IAS Prelims
- UPSC IAS Mains
- UPSC IAS Interview
- UPSC IAS Optionals
- UPSC Notification
- UPSC Eligibility Criteria
- UPSC Online
- UPSC Admit Card
- UPSC Results
- UPSC Cut-Off
- UPSC Calendar
- Documents Required for UPSC IAS Exam
- UPSC IAS Prelims Syllabus
- General Studies 1
- General Studies 2
- General Studies 3
- General Studies 4
- UPSC IAS Interview Syllabus
- UPSC IAS Optional Syllabus

Unemployment in India – UPSC Economy Notes
Unemployment remains a pervasive and pressing issue in India, posing significant challenges to the country’s economic growth and social stability. With a burgeoning population and an increasingly competitive job market, the problem of unemployment has become deeply entrenched, affecting millions of individuals across various demographic segments. Despite India’s rapid strides in industrialization and technological advancement, job creation has not kept pace with the expanding workforce, resulting in a substantial gap between labor supply and demand. This imbalance has been exacerbated by structural inefficiencies, educational disparities, and economic disruptions, further exacerbating the plight of those seeking gainful employment. As India grapples with the multifaceted ramifications of unemployment, addressing this complex issue has emerged as a critical imperative for policymakers, economists, and society at large.
Table of Contents
Unemployment Rate:
The unemployment rate is a key metric that quantifies the proportion of individuals actively seeking employment but unable to secure a job, expressed as a ratio of the total number of job seekers.
Unemployment in India:
- The number of unemployed persons in India is projected to increase from 18.3 million in 2017 to 18.6 million in 2018 and further to 18.9 million by 2019.
- The unemployment rate is expected to remain static at 3.5 per cent during this period.
- The World Bank emphasizes the need for India to generate a significant number of salaried jobs (formal jobs) to meet the demands of the working population and elevate its growth to that of a middle-income country.
- Approximately 65 percent of India’s population is below the age of 35.
- Unemployment within this demographic segment has the potential to become a significant burden for the country.
- Urban Unemployment: The urban unemployment rate decreased from 4.5% in 2004-05 to 3.4% in 2011-12.
- Rural-Unurban Disparities: Unemployment rates across all religious groups in rural areas were lower compared to urban areas for both males and females.
- Religious Group Variations: Christians had the highest unemployment rates in both rural (4.5%) and urban (5.9%) areas in 2011-12.
- Changes Over Time: While the unemployment rate decreased for Sikhs in rural areas, it slightly increased for Muslims. Hindus had the lowest unemployment rate in urban areas at 3.3%.
- Income Sources: Self-employment remained the major source of income for almost half of the households in rural areas across all religious groups, followed by casual labor.
These insights highlight the complex dynamics of unemployment in India, influenced by demographic factors, urban-rural disparities, and variations across religious groups. The emphasis on creating formal jobs is underscored as a crucial factor for sustainable economic growth.
Labour Force Participation Rate:
The Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR) is a metric that assesses the percentage of individuals within the working-age group (16 – 64 years) who are actively available for employment.
Key Findings from NSSO Report:
- The LFPR in 2017-18 was 49.8%, marking a notable decrease from 55.9% recorded in 2011-12.
- This decline is indicative of changes in the workforce dynamics over the six-year period.
- The LFPR for females experienced a double decline between 2011-12 and 2017-18.
- The proportion of the active labour force among women decreased over the specified period.
- The rural areas witnessed a substantial fall in LFPR, dropping from 67.7% to 58.7%.
- In urban areas, the decline was from 49.3% to 47.6%.
- The gap between LFPR in urban and rural areas narrowed, primarily due to a decline in the active labour force in villages.
- Among men in the working-age group, there was a slight decline in LFPR, potentially attributed to an increasing preference for higher education.
- The reduction in LFPR among children and particularly women is linked to decreasing poverty.
These findings highlight shifts in labour force participation rates, especially the significant decline over the years, gender-related disparities, and the impact of educational preferences and economic conditions on workforce dynamics.
Women’s Participation in the Labour Force:
The relatively low participation of women in the Indian labour force poses a significant challenge to economic progress. Key insights into this issue include:
1. Gender Disparities:
- The labour force participation rate (LFPR) of women in India is notably lower than that of men, with a difference exceeding 50 percentage points, a high figure among G-20 nations according to World Bank data.
- In urban areas, the LFPR for women is even lower compared to rural areas.
2. Reasons for Low Participation:
- Wage Disparities: Women often receive lower wages compared to men, contributing to the disincentive for seeking employment outside the home.
- Lack of Flexibility and Benefits: Inadequate provision of flexibility, childcare benefits, and maternity leaves acts as a deterrent for women to enter the workforce.
- Gender Discrimination: Societal gender discrimination and the lower social status of women in comparison to men impact their participation in the labour force.
- Security Concerns: Security issues further hinder the mobility of women in the labour market.
3. Economic Consequences:
- Studies, including one by the McKinsey Global Institute, suggest that India’s GDP could be significantly higher if women’s participation in the economy were on par with that of men.
- The Asian Development Bank (ADB) estimates that increasing women’s participation in India to levels observed in advanced countries could boost annual GDP by 4.2%.
4. Policy Recommendations (NITI Ayog’s 3 Year Action Agenda):
- Job Creation: Emphasis on creating jobs in industries and services.
- Labour-Market Flexibility: Reforming key laws to enhance flexibility in the labour market.
- Addressing NPAs: Tackling the issue of Non-Performing Assets (NPAs) in banks through strategic measures.
- Sector-Specific Action: Implementing specific action points in sectors such as Apparel, Leather and Footwear, Electronics, Food Processing, Gems and Jewelry, Tourism, Finance, and Real Estate.
Addressing gender disparities in labour force participation is crucial for India’s overall economic development, and the outlined policy recommendations aim to foster a more inclusive and dynamic workforce.
1. What is the current unemployment rate in India?
- As of the latest available data, the unemployment rate in India stands at around X%. However, it’s important to note that this figure can fluctuate due to various economic factors and government policies.
2. What are the main causes of unemployment in India?
- Unemployment in India can be attributed to several factors including rapid population growth, inadequate job creation, technological advancements leading to job displacement, lack of necessary skills among the workforce, and structural issues within the economy.
3. How does unemployment affect the Indian economy?
- Unemployment negatively impacts the Indian economy by reducing consumer spending, lowering tax revenues, increasing social welfare costs, and hampering economic growth. It also leads to social unrest and inequality, hindering overall development.
4. What measures is the Indian government taking to address unemployment?
- The Indian government has implemented various measures such as skill development programs, employment generation schemes like MNREGA (Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act), encouraging entrepreneurship through initiatives like Startup India, and promoting sectors with high employment potential such as manufacturing and agriculture.
5. What can individuals do to mitigate the impact of unemployment?
- Individuals can take proactive steps to enhance their employability by acquiring relevant skills through education, vocational training, or upskilling programs. They can also explore entrepreneurial opportunities, freelance work, or gig economy platforms. Additionally, staying informed about job market trends and networking can increase their chances of securing employment.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here
Visit our YouTube Channel – here
- Shadow Banks – UPSC Economy Notes
- Public Sector Evolution, Reforms, and Performance – UPSC Economy Notes
- Economic Inequality in India – UPSC Economy Notes
- Infrastructure Status – UPSC Economy Notes
Edukemy Team
Zero base budgeting (zbb) – upsc economy notes, monetary policy and credit policy – upsc economy notes, nature of unemployment in india – upsc economy notes, world bank group and covid-19 – upsc economy notes, residex (housing price index) – upsc economy notes, beed model – upsc economy notes, impact of globalization on employment in india – upsc economy..., share and types – upsc economy notes, inflation – concepts, facts, and policy – upsc economy notes, foreign direct investment (fdi) – upsc economy notes, leave a comment cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Our website uses cookies to improve your experience. By using our services, you agree to our use of cookies Got it
Keep me signed in until I sign out
Forgot your password?
A new password will be emailed to you.
Have received a new password? Login here


Unemployment in India: Types, Causes, and the Way Forward | Sociology UPSC | Triumph IAS
Table of Contents
Unemployment in India
(relevant for economics section of general studies paper prelims/mains).

Unemployment
Unemployment takes place when an individual actively seeking employment faces the inability to secure a job. Unemployment is frequently employed as an indicator of the economic well-being of a nation.
Types of unemployment
- Disguised Unemployment : This phenomenon occurs when there are more employed individuals than necessary. This is particularly evident in India’s agricultural and unorganized sectors.
- Seasonal Unemployment: This type of unemployment takes place during specific periods of the year. Agricultural labourers in India frequently experience periods of joblessness due to the seasonal nature of their work.
- Structural Unemployment : This category of unemployment arises from a mismatch between job opportunities available in the market and the skill sets possessed by the available workforce.
- Cyclical Unemployment : This form of unemployment is a consequence of the business cycle, where joblessness increases during economic downturns and decreases during periods of economic growth.
- Technological Unemployment : This refers to job losses caused by technological advancements that render certain roles obsolete.
- Frictional Unemployment: Also known as Search Unemployment , this type refers to the transitional phase when individuals are between jobs or actively seeking new employment opportunities.
- Vulnerable Employment : This pertains to informal labour where individuals lack proper job contracts and legal protections. Since their work is not documented, they are considered “unemployed .” This type of unemployment is prevalent in India.
Causes of Unemployment in India
- Social Factors: The caste system is prevalent in India, leading to certain castes being prohibited from certain types of work in specific regions.
- Within large joint families engaged in significant business ventures, there often exist individuals who do not actively participate in work and instead rely on the collective family income.
- Rapid Population Growth: The continuous increase in population has emerged as a significant challenge in India, serving as a key contributor to unemployment.
- Agricultural Dominance : Despite significant technological advancements, nearly half of India’s workforce remains dependent on agriculture, which itself is underdeveloped and provides seasonal employment.
- Decline of Cottage and Small Industries : The advancement of large-scale industries has adversely affected cottage and small-scale enterprises. The output of cottage industries has dwindled, leading to unemployment among artisans.
- Labour Immobility : The mobility of labour in India remains limited. Ties to family and local communities often deter individuals from seeking work in distant locations. Additionally, factors such as language, religion, and climate further impede mobility.
- Flaws in the Education System : In a rapidly evolving job market, specialization has become crucial. However, India’s education system often fails to equip individuals with the necessary skills for specialized jobs, resulting in unemployment for those willing to work but lacking the required expertise.
Way forward
- Encouraging Labour-Intensive Sectors: Numerous labour-intensive manufacturing fields exist in India, including food processing, leather and footwear, woodworking, furniture production, textiles, apparel, and garment manufacturing. Tailored initiatives for each sector are necessary to generate employment opportunities.
- Decentralization of Industries: The dispersion of industrial activities across regions is essential to ensure employment opportunities are accessible to people in every area. Focusing on rural development can help curb the migration of rural residents to urban centers, subsequently reducing pressure on urban job markets.
- Formulating a National Employment Policy: Establishing a comprehensive National Employment Policy (NEP) is imperative. Such a policy should encompass a wide range of multidimensional interventions addressing diverse social and economic concerns that impact various policy domains, extending beyond labour and employment matters.
Sample Question for UPSC Sociology Optional Paper:
Question 1: What is the impact of the caste system on unemployment in India? Answer : The caste system contributes to unemployment by restricting certain castes from specific types of work, thereby limiting employment opportunities.
Question 2: How does rapid population growth contribute to unemployment in India? Answer : Rapid population growth in India exacerbates unemployment by increasing the number of job seekers, thereby outstripping the rate at which new jobs are created.
Question 3 : Why is vulnerable employment considered a type of unemployment in India? Answer : Vulnerable employment is considered a type of unemployment because individuals in this category lack proper job contracts and legal protections, making their work status unstable.
Question 4 : What are the limitations of India’s education system in addressing unemployment? Answer : The education system often fails to provide individuals with the specialized skills required in a rapidly evolving job market, resulting in a mismatch between job opportunities and skill sets.
Question 5 : How can decentralization of industries help in reducing unemployment in India? Answer : Decentralization can help in spreading employment opportunities across regions, reducing the migration pressure on urban job markets and providing employment in rural areas.
Related Blogs …
To master these intricacies and fare well in the Sociology Optional Syllabus , aspiring sociologists might benefit from guidance by the Best Sociology Optional Teacher and participation in the Best Sociology Optional Coaching . These avenues provide comprehensive assistance, ensuring a solid understanding of sociology’s diverse methodologies and techniques.
Unemployment in India, Types of Unemployment, Causes of Unemployment, Labour-Intensive Sectors, National Employment Policy, Decentralization of Industries, Education System Flaws, Social Factors, Unemployment in India, Types of Unemployment, Causes of Unemployment, Labour-Intensive Sectors, National Employment Policy, Decentralization of Industries, Education System Flaws, Social Factors

Choose T he Best Sociology Optional Teacher for IAS Preparation?
At the beginning of the journey for Civil Services Examination preparation, many students face a pivotal decision – selecting their optional subject. Questions such as “ which optional subject is the best? ” and “ which optional subject is the most scoring? ” frequently come to mind. Choosing the right optional subject, like choosing the best sociology optional teacher , is a subjective yet vital step that requires a thoughtful decision based on facts. A misstep in this crucial decision can indeed prove disastrous.
Ever since the exam pattern was revamped in 2013, the UPSC has eliminated the need for a second optional subject. Now, candidates have to choose only one optional subject for the UPSC Mains , which has two papers of 250 marks each. One of the compelling choices for many has been the sociology optional. However, it’s strongly advised to decide on your optional subject for mains well ahead of time to get sufficient time to complete the syllabus. After all, most students score similarly in General Studies Papers; it’s the score in the optional subject & essay that contributes significantly to the final selection.
“ A sound strategy does not rely solely on the popular Opinion of toppers or famous YouTubers cum teachers. ”
It requires understanding one’s ability, interest, and the relevance of the subject, not just for the exam but also for life in general. Hence, when selecting the best sociology teacher, one must consider the usefulness of sociology optional coaching in General Studies, Essay, and Personality Test.
The choice of the optional subject should be based on objective criteria, such as the nature, scope, and size of the syllabus, uniformity and stability in the question pattern, relevance of the syllabic content in daily life in society, and the availability of study material and guidance. For example, choosing the best sociology optional coaching can ensure access to top-quality study materials and experienced teachers. Always remember, the approach of the UPSC optional subject differs from your academic studies of subjects. Therefore, before settling for sociology optional , you need to analyze the syllabus, previous years’ pattern, subject requirements (be it ideal, visionary, numerical, conceptual theoretical), and your comfort level with the subject.
This decision marks a critical point in your UPSC – CSE journey , potentially determining your success in a career in IAS/Civil Services. Therefore, it’s crucial to choose wisely, whether it’s the optional subject or the best sociology optional teacher . Always base your decision on accurate facts, and never let your emotional biases guide your choices. After all, the search for the best sociology optional coaching is about finding the perfect fit for your unique academic needs and aspirations.
To master these intricacies and fare well in the Sociology Optional Syllabus , aspiring sociologists might benefit from guidance by the Best Sociology Optional Teacher and participation in the Best Sociology Optional Coaching . These avenues provide comprehensive assistance, ensuring a solid understanding of sociology’s diverse methodologies and techniques. Sociology, Social theory, Best Sociology Optional Teacher, Best Sociology Optional Coaching, Sociology Optional Syllabus. Best Sociology Optional Teacher, Sociology Syllabus, Sociology Optional, Sociology Optional Coaching, Best Sociology Optional Coaching, Best Sociology Teacher, Sociology Course, Sociology Teacher, Sociology Foundation, Sociology Foundation Course, Sociology Optional UPSC, Sociology for IAS,
Follow us :
🔎 https://www.instagram.com/triumphias
🔎 www.triumphias.com
🔎https://www.youtube.com/c/TriumphIAS
https://t.me/VikashRanjanSociology

Find More Blogs
One comment.
- Pingback: Current Affairs 10 October 2023 Important News | GS | #1 Best Sociology Optional Coaching
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

- भाषा : हिंदी
- Classroom Courses
- Our Selections
- Student Login
- About NEXT IAS
- Director’s Desk
- Advisory Panel
- Faculty Panel
- General Studies Courses
- Optional Courses
- Interview Guidance Program
- Postal Courses
- Test Series
- Current Affairs
- Student Portal

- Recently, the Centre for Monitoring the Indian Economy (CMIE) released data stating that India’s unemployment rate in August 2022 rose to 8.3%.
Key Findings
- This is the highest unemployment rate in the past 12 months. In August 2021, the unemployment rate was 8.35%.
- In August, urban unemployment was 9.6% and rural was 7.7%.
- Only in two months — February and June — has the rural unemployment rate been higher than the urban unemployment rate.
- There is a significant variance in the unemployment rate across states.
- Haryana, J&K and Rajasthan have the highest levels of unemployment rate — each with over 30% of the unemployment rate.
- In sharp contrast, there are many states with remarkably low unemployment rates as well.
- Chhattisgarh has an unemployment rate of just 0.4%.
- Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha and Meghalaya — all have unemployment rates well below 3%.
- Since the unemployment rate is essentially a ratio between the total unemployed and the total labour force, it can go up whenever the number of unemployed increases more than the increase in the total labour force.
- while the labour force increased by 4 million, the economy instead of creating new jobs, actually shed 2.6 million existing jobs.
- In August while the total number of unemployed went up by 6.6 million, the labour force only went up by 4 million. Hence the spike in the unemployment rate.
Unemployment Rate
- The unemployment rate is essentially the percentage of working-age people (15 years and above) who are demanding work but not able to get a job. Both aspects of the definition are important.
- It is calculated by looking at all the people of the working age who are demanding work and then finding out what percentage of them are unable to land a job. That percentage is the unemployment rate.
- Unemployment rate = [Total unemployed / Total Labour Force]
- In other words, unemployment rates are expressed as a percentage of the labour force, not the total population.
- The underlying size of the labour force — that is, the percentage of working-age people demanding work — itself varies over time and is measured by the Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR).
Challenges/Impacts of Jobless growth
- Between 2010 and 2020, the number of working women in India dropped to 19% from 26%, according to data compiled by the World Bank.
- CMIE estimated that female labour force participation plummeted to 9% by 2022.
- A growing reserve of frustrated, unemployed youth threatens to turn India’s demographic dividend of having a young population into a curse.
- The proportion of Indians employed in agriculture had been falling for decades, but this process flattened some years ago and was reversed by the covid crisis.
- Those who move out of farming mostly find themselves in low-paying construction work and informal services.
- India’s economic growth has been largely services led, with a small pool of skills at the upper end, given a glaring failure in mass education.
- India presents a paradox of skill shortages while being labour surplus.
- Trucks are idle because of the shortage of drivers. The steel industry needs more metallurgists.
- The healthcare sector is short of nurses and technicians.
- The construction sector needs civil engineers, hi-tech welders, bricklayers, and so on.
- It is the government’s responsibility to take initiative and create adequate roles for unemployed people within the main economy.
- Government support for enhancing infrastructure is particularly essential for small and medium-sized enterprises.
Source : IE
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
Daily current affairs 01-06-2024, daily current affairs 31-05-2024, daily current affairs 30-05-2024, us-china trade war could help and hurt india.

Next generation institute for the preparation of UPSC Civil Services Examination
- Video Gallery
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- UPSC CSE Posts
- Testimonials
NEXT IAS (Delhi)
Old rajinder nagar.
- 27-B, Pusa Road, Metro Pillar no.118, Near Karol Bagh Metro, New Delhi-110060
Mukherjee Nagar
- 1422, Main Mukherjee Nagar Road. Near Batra Cinema New Delhi-110009
NEXT IAS (Bhopal)
- Plot No. 46 Zone - 2 M.P Nagar Bhopal - 462011
- 8827664612 ,
NEXT IAS (Jaipur)
- NEXT IAS - Plot No - 6 & 7, 3rd Floor, Sree Gopal Nagar, Gopalpura Bypass, Above Zudio Showroom Jaipur (Rajasthan) - 302015
NEXT IAS (Prayagraj)
- 31/31, Sardar Patel Marg, Civil Lines, Prayagraj, Uttar Pradesh - 211001
Unemployment Essay
500+ words essay on unemployment.
Unemployment is a serious problem among young people. There are thousands of people who do not have any work to do and cannot find work for themselves. Unemployment refers to the situation where a person wants to work but cannot find employment in the labour market. One of the major reasons that contribute to unemployment is the large population of India and the limited availability of resources. In this essay on unemployment, we will discuss all these issues responsible for unemployment in India and how we can overcome this problem. Students must go through this unemployment essay to get ideas on how to write an effective essay on the topic related to unemployment. Also, they can practice more CBSE essays on different topics to boost their writing skills.
Unemployment is measured by the unemployment rate, defined as the number of people actively looking for a job as a percentage of the labour force. The unemployment rate for the year 2013-14 in rural India was 4.7%, whereas it was 5.5% for urban India. In the short term, unemployment significantly reduces a person’s income and, in the long term, it reduces their ability to save for retirement and other goals. Unemployment is a loss of valuable productive resources to the economy. The impact of job loss in rural and regional areas flows through the local community, damaging businesses.
Reason for Unemployment
An unemployed person is one who is an active member of the labour force and is seeking work but is unable to find any work for himself. There are multiple reasons behind the unemployment of a person. One of them is the slow economic growth, due to which jobs in adequate numbers are not created. Excessive dependence on agriculture and slow growth of non-farm activities also limit employment generation. Unemployment in urban areas is mainly the result of substantial rural migration to urban areas. This has also resulted in a labour workforce in cities. The lack of technology and proper machinery has also contributed to unemployment.
The present educational system is based on theoretical knowledge instead of practical work. Thus, it lacks the development of aptitude and technical qualifications required for various types of work among job seekers. This has created a mismatch between the need and availability of relevant skills and training. This results in unemployment, especially among the youth and educated people with high degrees and qualifications. Apart from it, the lack of investment and infrastructure has led to inadequate employment opportunities in different sectors.
Steps to Eliminate Unemployment
Various strategies and proposals have been implemented to generate employment. Many Employment programmes and policies have been introduced and undertaken to boost self-employment and help unemployed people engage in public works. The Government of India has taken several policy measures to fight the problem of unemployment. Some of the measures are the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA), National Skill Development Mission, Swarna Jayanti Shahari Rozgar Yojana (SJSRY), Regional Rural Banks (RRBs).
Despite the measures taken by the government, India remains a country experiencing severe unemployment problems. It can be resolved by imparting education in such a way that youth get the necessary skills so as to get employment easily. Setting up various vocational training and vocational courses for undergraduate and postgraduate students will help in finding employment for youth. The government needs to emphasise these courses at the primary level and make them a compulsory part of the curriculum to make students proficient in their early stages of life. Career counselling should be provided within schools and colleges so that students can choose a better career option based on their interests and ability. Government should create more job opportunities for the youth and graduates.
India is a fast-growing economy. There is an enormous scope for improvement in the unemployment sector. The various measures and steps taken by the government to increase the employment rate have succeeded to a great extent. The widespread skill development programmes have gained popularity across the nation. With better enforcement of the strategies, the employment level can be significantly improved. Although, we have to go a long way before we can say that all the people in India will get employment.
We hope this essay on unemployment must have helped students in boosting their essay-writing skills. Keep learning and visiting the BYJU’S website for more study material.
Frequently Asked Questions on Unemployment Essay
Is unemployment still an existing problem in india.
Yes, unemployment is still a serious issue in our country. Steps need to be taken by the government and also by the youngsters in India to improve this situation.
Is it necessary for schoolchildren to be informed about unemployment?
Students at this young age should definitely be informed about this topic as it will motivate them to study and aim for higher scores in exams.
What points are to be added to an essay topic on Unemployment?
Add details about different age groups of people suffering from this state of employment. You can focus on the fact that poverty is an indirect reason for unemployment and vice-versa. Then, suggest steps that can be taken to bring about an improvement in education and increase the percentage of literacy.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
- Skip to main content
India’s Largest Career Transformation Portal
Essay on Unemployment for Students in English | 500 Words Essay
December 20, 2020 by Sandeep
Essay on Unemployment: It is a serious social issue in India and a big global concern too. There are thousands of people who are not employed owing to the rising population and a steady decline in jobs, leading to unemployment. Automation of jobs, illiteracy, stiff competition, unavailability of resources, unqualified, political factors, etc. has given way to unemployment. Unemployment causes financial distress in families, hampers mental health and causes depression, anxiety, stress and other physical ailments.
Essay on Unemployment 500 Words in English
Below we have provided Unemployment Essay in English, suitable for class 6, 7, 8, 9 and 10 school students.
There is saying that “Give a man a fish, and he will be hungry again tomorrow; teach him to catch a fish, and he will be richer for all his life.” The importance of jobs in life is very significant to afford a good quality of life. Due to the increasing population and high competition, people are not able to grab jobs. This has led to recession and burden on the economy.
What is Unemployment: It is defined as a situation in which a person who is willing to do a job fails to find a job that earns him/her a living. It does not include people who are not looking for jobs.
Types of Unemployment
The unemployment rates are increasing, showing the slowdown in the economy. Unemployment can be classified mainly in two categories one in urban areas and others in rural areas. The major part of India’s population lives in rural areas. There are different types of unemployment – open, disguised, and seasonal. In Urban areas, the infrastructure is well developed, and there are a lot of advancements in technology. The main types of unemployment here are Industrial, educated, and technological development.
- Open – It is a case in which there is no work to do. People are willing to work, but there is no work available.
- Disguised – It is a situation in which some individuals are noticeably employed but are literally unemployed. It is in the agricultural sector where there are way more people working than required.
- Seasonal – It means the needs of the workers are only in particular seasons. It points to a time period where there is less requirement than normal season.
- Industrial – The illiterate people who can work in manufacturing industries are eager to do work but not getting any work in urban areas. It is called Industrial unemployment
- Educated – When the person is educated but not able to find a job according to his academic qualifications. Then, it is called educated unemployment.
- Technological – Technological unemployment happens because of the advancement in technology. It has a significant impact on the organization, as productivity increases and efficiency enhances.
The most common types of unemployment in India is seasonal and disguised unemployment.
Reasons for Unemployment
- There are multiple reasons causing a great jump in the rate of unemployment. The biggest reason is the increasing rate of population. There is consistent growth in the population of India. The greater the population, the more the demands of the job seekers, but the advancement in technology causes a decrease in the labour force required.
- Another reason is the lack of education and skills among the youth. Job seekers are more, and well-skilled people are very less for the country. It is also called structural unemployment, where the skills needed for the job do not match the skills of the worker.
- The advancement in technology in this modern era is also taking away the jobs that can be handled by machines and systems. It has replaced unskilled labour, and the results are more effective and accurate. The production is faster, and the cost is minimised.
- Lack of capital threatens companies to pay for its operations. It makes it difficult to prepare for emergencies and sometimes difficult to pay its employees.
Consequences of Unemployment
There are severe consequences of unemployment, causing the economy to suffer. Mainly the people who are affected by it have to go through it. It causes an increase in suicide cases, stress levels boost up, crime rates surge, etc. Unemployed people get demotivated and degrade their skills, which is bad for the economy. There are big impacts which include the loss of productive labour force in the country, which can help in growing GDP. It deteriorates the growth of businesses as well.
As many unemployed people cannot afford basic commodities, it causes fewer sales in businesses. Social causes of long term employment are very substantial. It affects the health of individuals and their families. There is less consumption of nutritious diet, including fruits and vegetables. It can stop their physical and mental development. Again, not creating a valuable asset for the economy in the long run.
Initiative by Government
The government has taken several steps to solve this significant issue. Some initiatives were launched to curb this problem of unemployment. These initiatives include IRDP (Integrated Rural Development Programme), training for self-employment, NRY (Nehru Rozgar Yojana), Drought Prone area program, PMGSY (Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana), Employment Guarantee Scheme and more.
The Employment Guarantee Scheme ensures a minimum of 100 working days with wages to do unskilled work. Training for self-employment aims at reducing employment among the youth. Moreover, the government is spending on irrigation, farms, and roads, etc. The government can take some more steps to reduce unemployment like population control, more Small- medium enterprises, good education system and improvement in agriculture.
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
UPSC Coaching, Study Materials, and Mock Exams
Enroll in ClearIAS UPSC Coaching Join Now Log In
Call us: +91-9605741000
India-Afghanistan Relations – Everything you need to know
Last updated on September 27, 2023 by ClearIAS Team
A period of adjustment has become essential following US President Donald Trump’s unilateral announcement that he is pulling US troops out of Afghanistan.
The US withdrawal from Afghan not only affects Indian policy on Afghan but also changes the regional balance of power in fundamental ways.
The diplomatic mandarins of New Delhi are apprehensive about the growing influence of the Taliban in Afghan and the centrality of the Taliban in ensuing peace processes.
We should delve into the history of Afghan and India’s role in various stages of this history to grasp the complete relevance of Afghan’s stability for India.
Table of Contents
Afghan – a ‘Graveyard of empires’
Afghan is considered as ‘Graveyard of empires’. The fall of Alexander (in Bactria), disintegration of USSR , and the decline of US hegemony were started in this region. There is an ever-growing perception that it is difficult to come out of Afghan quagmire.
The present US situation rings testimony to this quagmire.

History of India-Afghan relations
Relations between the people of Afghanistan and India can be traced back to the Indus Valley Civilisation . Following Alexander the Great’s brief occupation, the successor state of the Seleucid Empire controlled the region known today as Afghanistan. In 305 BCE, they ceded much of it to the Indian Maurya Empire as part of an alliance treaty. The Mauryans brought Buddhism from India and controlled the area south of the Hindu Kush.
From the 10th century to the mid 18th century, northern India has been invaded by a number of invaders based in what today is Afghanistan. Some of them were Ghaznavids, Khaljis, Mughals, Durranis etc. During these eras, many Afghans began immigrating to India due to political unrest in their regions.
Khan Abdul Ghaffar Khan of Afghan was a prominent leader of the Indian independence movement and active supporter of the Indian National Congress.
India-Afghanistan Relations – Strategic, Economic, and Security Interests
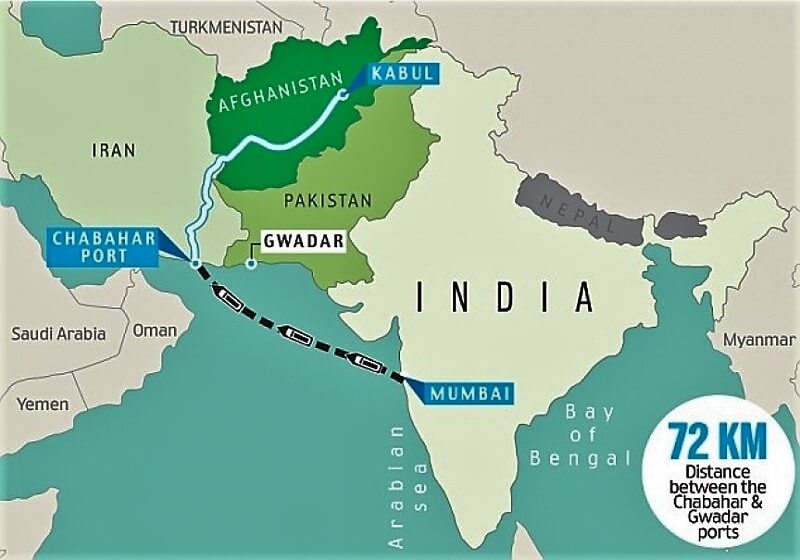
India-Afghanistan: Strategic interests
- India is interested in retaining Afghanistan as a friendly state from which it has the capacity to monitor Pakistan and cultivate assets to influence activities in Pakistan.
- While India is keenly interested in cultivating a significant partnership with Afghanistan, Pakistan is trying to deny India these very opportunities.
- India’s interest in Afghan is more than mere Pakistan-centrist and reflects its aspiration to be and to be seen as a regional power.
- Islamic fundamentalism in Pakistan and Afghan has deleterious effects in the domestic social fabric of India, as Hindu fundamentalism in India is triggered by these external developments.
- In Medieval times it was between Persian and Mughal Empire .
- During colonial times it was between Russia and Britain.
India-Afghanistan: Economic interests
- Afghanistan has a mineral wealth of about $1-3 trillion of Iron ore, Lithium, Chromium, Natural Gas, Petroleum etc.
- Safeguarding Indian investments and personnel in Afghan is utmost important to India as Indian investment in Afghan amounts to about $3bn.
India-Afghanistan: Security interests
- Pakistan has raised and supported several militant groups such as Lashkar-e-Taiba, Harkat-ul-Mujahideen/Harkat-ul-Ansar, and Harkat-ul-Jihad-al-Islami among others, which operate in India.
- All of these groups have trained in Afghanistan, with varying proximity to the Taliban and by extension al-Qaeda.
- Thus India is absolutely adamant that Afghanistan should not again become a terrorist safe haven.
- Radical ideologies and terrorism spreading in this region are a security threat for India .
- With Pakistan increasing its strategic depth in Afghan, it can reverse the gain of India in Afghan brought through much cost. Pakistan can incubate and move around various anti-India groups in Afghan especially in Loya Paktia.
- The golden crescent comprising of Iran, Afghan, and Pakistan is a worry for India, especially with respect to the issue of drug abuse in Punjab.
- Islamic State is using Afghan as an outpost in Asia as it comes under stress in Iraq and Syria.
History of Indian engagement in Afghan post Independence
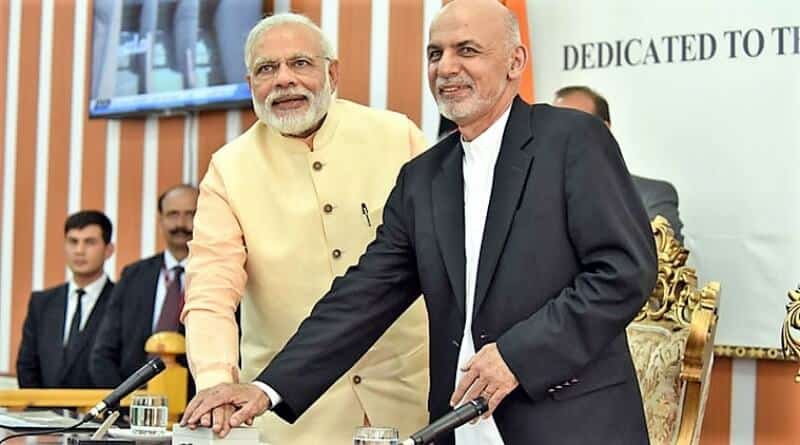

- India has sought to establish its presence in Afghanistan from the early days of its independence in 1947.
- In 1950, Afghanistan and India signed a “Friendship Treaty.”
- India had robust ties with Afghan King Zahir Shah’s regime.
- Prior to the Soviet invasion in 1979, New Delhi had formalized agreements and protocols with various pro-Soviet regimes in Kabul.
- While India’s role in Afghanistan was constrained during the anti-Soviet jihad, between 1979 and 1989, India expanded its development activities in Afghanistan, focusing upon industrial, irrigation, and hydroelectric projects.
- After the Taliban consolidated their hold on Afghanistan in the mid-1990s, India struggled to maintain its presence and to support anti-Taliban forces.
- However, Indian objectives in Afghanistan remained modest given the constrained environment. India aimed to undermine the ability of the Taliban to consolidate its power over Afghanistan, principally by supporting the Northern Alliance in tandem with other regional actors.
- Working with Iran, Russia, and Tajikistan, India provided important resources to the Northern Alliance, the only meaningful challenge to the Taliban in Afghanistan.
- Since 2001, India has relied upon development projects and other forms of humanitarian assistance.
Debate on India’s role in Afghan
There is a debate among major players in Afghan on the optimal role for India in Afghanistan’s reconstruction in light of the enduring security competition between India and Pakistan .
- Expanding India’s presence in Afghanistan through increased Indian training of Afghan civilian and military personnel, development projects, and expanded economic ties.
- Caution against India’s involvement.
- Indian and Pakistani competition in Afghanistan is seen as a new “Great Game” and argues that Afghanistan can be pacified only through a regional solution that resolves once and for all the intractable Indo-Pakistan dispute over Kashmir.
Afghan History
Phase i – until the end of the cold war.
Monarchy under King Zahir Shah lasted till 1973 and was overthrown by a coup led by Mohammed Daoud Khan. He declared Afghanistan as a republic. Against his repressive rule, protest became widespread leading to Communist Revolution or Saur Revolution in 1978 and the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan came into being. The event proved to be the catalyst for decades of unrest and bloodshed in Afghan. There were protests against the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan and to stabilize the communist regime, USSR intervened in 1979.
The Democratic Republic of Afghanistan, renamed in 1987 to the Republic of Afghanistan, commonly known as Afghanistan, existed from 1978 to 1992, during which time the socialist People’s Democratic Party of Afghanistan (PDPA) ruled Afghanistan.

- India had an upper hand as the diplomatic and cultural ties were strong with the Afghan regime during these periods.
- India was the only South Asian nation to recognize the Soviet-backed Democratic Republic of Afghanistan and the Soviet Union’s military presence in Afghan territories.
Meanwhile, US-Pakistan interest coincided in Afghan. After the Iranian revolution, Iran came out of US influence in the Middle Eastern region. So the US was apprehensive of growing Soviet influence in Afghan. Thus CIA-ISI worked together to destabilize the communist government in Afghan, which led to USSR intervention in 1979. The intervention lasted from 1979 to 1989.
Mujahadeen succeeded in toppling communist regime in Afghan in 1989. Mujahadeen was Pakistani supported alliance by seven Afghan Mujahideen parties fighting against the Soviet-backed the Democratic Republic of Afghan forces in Soviet-Afghan war.
India, however, recognized the Mujahadeen government. Following the withdrawal of the Soviet armed forces from Afghanistan in 1989, India continued to support Najibullah’s government (Mujahadeen government) with humanitarian aid.
Taliban to power
- Even though the Mujahadeen government came into power by the backing of US-Pakistan, the government comprised of different warlords. This lead to the power struggle between them and there was a law & order crisis.
- Moreover, the then president, Najibullah, become pro-India.
- This lead to the promotion of Taliban by Pakistan.
Who are the Taliban?
- Taliban means students.
- They are refugees of Afghan civil war and are located in NWFP in Pakistan.
- They were educated in Madrasas financed by Saudi Arabia and indoctrinated with Wahabism-Salafism.
- Wahabism is a puritan movement in Islam who wants Shariat rule.
After fall of Mujahadeen government, India together with the international community supported the coalition government that took control, but relations and contacts ended with the outbreak of another civil war, which brought to power the Taliban. The Taliban regime was recognized only by Pakistan, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates (UAE). The destruction of the Bamiyan Buddha monuments by the Taliban led to outrage and angry protests by India. In 1999, the hijacked Indian Airlines Flight 814 landed and stayed in Kandahar in Afghanistan and the Taliban were suspected of supporting them. India became one of the key supporters of the anti-Taliban Northern Alliance.
Phase II – since the end of the cold war
- India tried to repair the relations since the 1990s. But the emergence of the Taliban with Pakistan’s support limited India’s options. India continued to support anti-Taliban forces in Afghanistan.
The war in Afghan (2001-present)
- Meanwhile, post-cold war scenario changed the regional dynamics and US war on terror in 2001 lead to the defeat of the Taliban.
- US war in Afghan was started in 2001. The war’s public aims were to dismantle al-Qaeda and to deny it a safe base of operations in Afghanistan by removing the Taliban from power
- The US demanded extradition of Osama-bin-Laden from Taliban post 9/11. Taliban didn’t comply and the US launched the war on Afghan under the war on terror. Northern Alliance, which was fighting the Taliban since the 1990s, offered assistance to the US in this endeavour. Thus all the powers, including India, Russia, the US fought against the Taliban. Taliban was ousted and went underground in Pakistan.
- Zaranj–Delaram road in 2009.
- Construction of Afghan parliament.
- After the US invasion of Iraq in 2003, the concentration of US was shifted to Iraq. This lead to Taliban insurgency in 2005 and they regrouped from Pakistan hideouts.
- Since then the US is looking to come out of the war in Afghan but the war is being protracted without an end in sight.
- Recently US-Taliban talks were held in Doha and US announced that there has been an in-principle agreement on key issues: US troop will leave Afghan and in return, the Taliban promised that Afghan will not be used by terrorists.
Thus from 2001 to present, the Taliban has emerged as an important central player in the Afghan peace process. Now major players like US, Russia, China have accepted this centrality of the Taliban. Since only Pakistan has influence over the Taliban, this turn of events can be considered as a diplomatic victory of Pakistan whereas India is increasingly being sidelined in these proceedings.
Pakistan’s policy on Afganistan
- Pakistan is an unnatural nation that suffers from a crisis of nation-building. Since the beginning, it has been witnessing ethnic conflicts between Punjabis-Sindhis, between native inhabitants and Muhasir, Shia-Sunni, Baluch etc.
- Its biggest fear is the possibility of the creation of greater Pashtunistan. NWFP, south & central Pakistan is * *dominated by Pashtoons. They don’t recognize the legitimacy of the Durand line and treat it as a colonial boundary. The Pashtoon government of Afghan is inspired by integration of the region in Afghan.
- Pakistan wants a strategic depth in Afghan – it wants whosoever rules Afghan is completely controlled by Pakistan. Pakistan is not ready to tolerate even the minimum presence of India (diplomatic also).
- Pakistan has tensions over India’s presence in Afghanistan and the presence of India is seen as a provocation in Islamabad and as evidence of an Indian strategy of encirclement.
Indian policy on Afghanistan

- Afghan is India’s natural partner, not just to balance Pakistan but also for the fulfilment of energy-economic interest.
- Indian policy in Afghan can be described as the dichotomy between its aspiration for a larger role in its northwestern neighbourhood and the real constraints on it.
- In 2011 India became the first country Afghanistan signed a strategic partnership agreement . Until then India was following US demand of India’s limited cooperation with Afghan.
- India has repeatedly stressed that its relationship with Afghan is independent of Pakistan.
- In both the 1965 and 1971 wars, Afghanistan was non-committal and did not support India.
- On the Kashmir issue, Afghanistan has not publicly supported India
- India has not entered the debate on the Durand Line.
- The delivery marks the first time India has gifted offensive combat capability to Afghanistan, a sensitive topic in the past due to strong objections by Pakistan.
- Under the agreement, India will also train Afghan defence personnel on operations.
US policy on Afghanistan
- US policy on Afghan had not been consistent. On the one hand, the US thinks that it needs the assistance of Pakistan to solve the issue because of the geographic proximity of Pakistan to Afghan. On the other hand, the US is also wary of Pakistan’s double game of supporting the US and Taliban at the same time.
- Because of this inherent inconsistency of US policy regarding Afghan, US has not been able to decide what should be the extent of India’s role in Afghan.
- India’s reconstruction program in Afghan is inconvenient for the US for the fear of provocation of Pakistan.
Under the Obama government
- Obama policy was of regional diplomacy along with providing additional troops in Afghan.
- The aim was to draw down forces from 2011 and by 2014 Afghan will take over security.
- But Taliban increased attacks thus exposing the weakness of Afghan capability to take over.
Under Trump government
- Donald Trump endorsed that the Afghan war should be ended at the earliest possible time.
- But hasty withdrawal would create a vacuum as the ground situation had become more complicated with various terrorist outfits including ISIS and al-Qaeda gaining space in Afghan.
- Followed Obama policy of a modest increase in troops.
- Initiated New Afghan policy.
New Afghan strategy of US
- Military commitment without a deadline.
- Open acknowledgement of Pakistan’s role in providing sanctuary to Afghan-based militant groups.
- Acknowledgement of India’s’ role in stabilizing Afghan.
- US.’s new Afghanistan-Pakistan-India policy builds India’s economic assistance into its own strategy for Afghanistan.
Under the strategy, the US held back its aid to Pakistan until Islamabad demonstrates action against terrorist groups. However, China came in aid of Pakistan by arguing that Pakistan has also been affected by terrorism.
After the US released this new Afghanistan strategy, Defense Minister Nirmala Sitharaman visited the US. India put forward its Afghan strategy:
- There will be no Indian boots-on-ground in Afghan.
- India will provide economic assistance and capacity building.
- India will sign MoU with Afghan to train its police force.
- India will assist Afghan in its own way and not the way desired by the US, that is boots-on-ground.
- Countered the argument of Pakistan Prime Minister that India has zero political and zero military role in Afghan.
However, President Donald Trump now appears reconciled to Pakistan’s centrality to the endgame in the region. He unilaterally announced his plan of pulling US troops out of Afghan. A “framework” deal between the US and Afghan Taliban signed at Doha. Washington’s hasty timetable of 18 months to disentangle itself from the Afghan quagmire has narrowed the US’s options. Due to this India is trapped in a strategic blind-spot in Afghanistan.
Regional Powers
- China’s role in Afghanistan is gradually evolving towards more engagement in various areas. China has evolved into a notable though not yet major player in Afghanistan in the areas of investment, economic and humanitarian assistance.
- This increasing engagement reflects both China’s concerns about the deterioration of security in Afghanistan and its interest in benefiting from a reconstructed Afghanistan.
- Afghan’s geographic location at the crossroads of Central and South Asia, between India in the South and Russia in the North, is of great strategic value to China. In addition, Afghanistan’s vast natural resources are also an attraction.
- China’s interest in ensuring stability in Afghan reflects its growing worries about an eruption of insecurity that could endanger its security of its border province Xinjiang, its investments in the Central Asian region and also its OBOR initiative.
- Beijing is concerned about possible links between its Muslim minorities in Xinjiang and the Taliban, as well as other Islamist groups in Afghanistan.
- Beijing remains reluctant to consider a security role in Afghanistan but has made major diplomatic efforts to promote the Afghan peace process.
- China is holding talks in Islamabad since early 2016 along with Afghanistan, the US, and Pakistan (the Quadrilateral Coordination Group). China is also holding peace talks between the Afghan government and the Taliban.
- China’s role as a mediator and confidence-builder may be crucial, as its pressure has kept Pakistan peacefully engaged.
- What Afghanistan needs is long-term and sustainable support – and China would be in a position to provide it, be it in the frame of its OBOR scheme or other initiatives.
- This could include joint infrastructure projects and training and professionalization for Afghans.
- India and China have agreed for joint projects in Afghan in the Wuhan summit in 2018.
- Like India, Russia, China, and the U.S., Iran would want to see a steady hand at the helm in Afghanistan.
- Iranian Revolution 1979 can be seen as a precursor to Afghan turmoil. Iranian Revolution led to two developments in the region:
- Iran came out of US influence. The US thus intervened in Afghan to counter USSR influence in the region. This lead to USSR intervention in Afghan in 1979.
- Iranian Revolution consolidated Shia sect in Iran. This threatened Saudi and UAE lead by Sunni sects. This, in turn, led them to finance Wahabism-Salafism and thus Taliban.
- Since Saudi was promoting Wahhabi Islam through the Taliban, Iran supported the overthrow of the Taliban in 2001.
- After deterioration of US-Iran ties, Iran began to support the Taliban in its borders to ward off US presence from their borders.
- Amidst the crippling sanctions on its economy, Iran can benefit from a stable trading partner in its neighbourhood. In 2017 it supplanted Pakistan as Afghanistan’s largest trading partner.
- Russia has increased its involvement in Afghanistan.
- Russia established ties with the Taliban in 2007 to discuss the issue of drug trafficking through the central Asian region.
- Moreover mutual fear of IS has brought the Taliban and Russians closer.
- After the Syrian crisis, Russia is trying to flex its muscle in this region to boost its global power status.
Peace conferences and processes
There are many peace conferences and processes to solve the crisis. Bonn Agreement 2001 was the first international pact on Afghanistan for peace and reconciliation. Let us look at some of the important among them, their consequences and India’s role or stand in them.
There are two major international peace efforts that are currently underway – the American push for peace led by Zalmay Khalilzad (Special Representative for Afghanistan Reconciliation, Khalilzad) and the Moscow-led consultations.
Zalmay Khalilzad has held talks with different stakeholders – Pakistan, Saudi Arabia, Qatar and the Taliban with the intention to deliver a deal in six months. Appointment of Khalizad indicates the US urge to get out of Afghan at the earliest possible time.
Moscow consultations are called ‘Moscow-format consultations on Afghanistan’. Moscow consultation is one of the few peace processes which have managed to get the Taliban and Afghanistan at the same table of talks notwithstanding its inconclusiveness.
Heart of Asia Conference, Kabul process etc. are some of the other peace conferences.
India’s stand in the Peace Conferences
- In peace conferences, India’s stand is that it should be Afghan-led, Afghan-owned and Afghan-controlled and with the participation of the government of Afghanistan. India is also wary of talks with the Taliban and the distinction of ‘good Taliban-bad Taliban’.
Recent events
- Much to India’s chagrin, U.S. and Russia have accepted the idea that peace in Afghanistan is not possible without major concessions to the Taliban. Taliban has become the centre stage in all the peace conferences.
- This is evident in the talks facilitated by Russia in Moscow in February 2019, with mainstream Afghan politicians sitting around the table with Taliban leaders and recent U.S.-Taliban talks in Qatar.
- The U.S. and Russia have, in their respective peace processes, agreed to sidestep the Ashraf Ghani regime in Kabul, and accepted the Taliban’s condition that it will not negotiate with the elected Afghan government at this stage.
- And both the Russian and U.S. processes are dependent on cooperation from Pakistan, which retains its influence over the Taliban leadership.
- Current talks with the Taliban are not Afghan-led, owned or controlled, and the Taliban has not abjured violence, or sworn allegiance to the Afghan constitution before joining talks.
- For India, which has built on its centuries-old ties with Afghanistan with $3 billion in development assistance over the last 10 years, the spectre of a Pakistan proxy in power in Kabul is now looming large.
- Holding no trump cards in this game, India is now engaging with China and Iran, and with a range of Afghan actors including former President Hamid Karzai, who is said to be playing a key role in the US-Taliban process.
- India aims to secure its own strategic and economic interests in Afghanistan while backing the position taken by the government in Kabul on the talks.
- According to foreign policy experts, India may have to think of reaching out to the Taliban in near-future, at least sections of it that are independent minded.
Trade and Connectivity between India-Afghan
- India wants to improve transport connectivity and economic collaboration with countries in Central and South Asia through Afghan.
- There is a land route through Waga Atari route. But Pakistan doesn’t allow India-Afghan trade through this route.
- Indian investment in Chabahar port in southeastern Iran will serve as a hub for the transportation of transit goods.
- India builds Deleram- Zaranj highway in Afghan.
- India-Afghan established two air corridors to facilitate bilateral trade.
- India helped Afghans in the reconstruction of Salma Dam in the Herat province.
- India has also constructed a new Parliament complex for the Afghan government.
- There is an India Afghan joint working group on trade, commerce, investment.
- TIR facilitates trade and international road transport by permitting customs sealed vehicles and containers to transmit nations without inspected at borders.
- Afghan Pakistan are contracting parties of TIR
- TIR may boost trade between India-Afghan through Pakistan.
- But Pakistan did not allow the agreement to be used by India for transit.
- Afghan is in favour of India joining the agreement, but Pakistan rejected this proposition.
Donald Trump is the third US President who is trying to end the Afghan war. However many experts opine that the announcement of drawdown before getting anything concrete from the Taliban is a strategic blunder for the US. It will lead to instability in Afghan that will not only affect India’s interest but also regional stability.
The current US move has been a diplomatic victory for Pakistan. The US will require Pakistan’s support to implement the interim deal as only Pakistan has influence over the Taliban.
Fully aware of the deadline, the Taliban are trying to secure maximum concessions from Zalmay Khalilzad without offering anything meaningful in return.
With the US withdrawing from Afghanistan, India must find ways to maintain its presence. Despite being an important stakeholder in Afghanistan, India finds itself increasingly marginalized in negotiations involving the key regional players. New Delhi is concerned about the vital role that all the powers are giving to Pakistan. Iran and Russia, two of India’s closest allies during the Northern Alliance’s battle against the Taliban regime in the 1990s, seem out of sync with New Delhi’s interests.
India’s developmental approach has earned it immense goodwill among the Afghan people. However, the “soft power” strategy has limitations. The recent mocking of Donald Trump of New Delhi’s role in war-torn Afghanistan is a manifestation of this limitation. However, there is a domestic consensus in India that boots-on-ground is not an option. Thus India is in the dilemma between continued soft-power or to aggressively push its hard power.
Trump’s recent strategy of engaging with the Taliban without the consideration of India has cast a shadow over the US’s role as a strategic ally of India in the region.
- While India’s principled position that it will not directly or publicly talk to the Taliban until it engages the Afghan government remains valid, it is necessary that India stays abreast of all negotiations and isn’t cut out of the resolution process.
- It is hoped that a robust channel is open between Indian intelligence agencies and all important groups in Afghanistan*, *including the Taliban, in order to ensure that Indian interests, development projects, and citizens are kept secure.
- New Delhi should leverage the goodwill it enjoys among the Afghan people. India must intensify its dialogue with regional and global stakeholders, and impress upon them that any dialogue with the Taliban must not come at the cost of the hard-fought victories of the Afghan people in the past two decades: on establishing constitutional democracy and the rule of law, and securing the rights of women and minorities.
India’s army chief, General Bipin Rawat, recently asserted that India “cannot be out of the bandwagon” because if “you are not sitting on the high table you will not know what is happening”. It is time for New Delhi to engage the Taliban to secure its interests. India also needs to reassess its policy choices in close coordination with Russia and Iran, constantly reminding them that complete surrender to the Taliban’s demands will be detrimental to their own security.
References : The Hindu, Indian Express, The Diplomat, The Wire, Foreign Policy, Wikipedia, Does The Elephant Dance
Article by – Sethu Krishnan M

Aim IAS, IPS, or IFS?

About ClearIAS Team
ClearIAS is one of the most trusted learning platforms in India for UPSC preparation. Around 1 million aspirants learn from the ClearIAS every month.
Our courses and training methods are different from traditional coaching. We give special emphasis on smart work and personal mentorship. Many UPSC toppers thank ClearIAS for our role in their success.
Download the ClearIAS mobile apps now to supplement your self-study efforts with ClearIAS smart-study training.
Reader Interactions
March 5, 2019 at 9:01 am
Awesome.really appreciate..good efforts for IAS aspirant by clearias team.. thanks a lot
March 5, 2019 at 8:55 pm
This is the best article that i have read on India – Afghan relationship. The astute analyse reveals the hard work and patience of the author. Thank you Sethu Krishnan and Clear IAS team.
April 13, 2019 at 10:13 pm
Concept is really worth reading
May 1, 2019 at 8:03 am
great content…keep going!
October 23, 2019 at 2:06 am
It means India is in trouble and the recent move of abrogating article 370 will have bad consequences for Indian security.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Don’t lose out without playing the right game!
Follow the ClearIAS Prelims cum Mains (PCM) Integrated Approach.
Join ClearIAS PCM Course Now
UPSC Online Preparation
- Union Public Service Commission (UPSC)
- Indian Administrative Service (IAS)
- Indian Police Service (IPS)
- IAS Exam Eligibility
- UPSC Free Study Materials
- UPSC Exam Guidance
- UPSC Prelims Test Series
- UPSC Syllabus
- UPSC Online
- UPSC Prelims
- UPSC Interview
- UPSC Toppers
- UPSC Previous Year Qns
- UPSC Age Calculator
- UPSC Calendar 2024
- About ClearIAS
- ClearIAS Programs
- ClearIAS Fee Structure
- IAS Coaching
- UPSC Coaching
- UPSC Online Coaching
- ClearIAS Blog
- Important Updates
- Announcements
- Book Review
- ClearIAS App
- Work with us
- Advertise with us
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- Talk to Your Mentor
Featured on

and many more...
Take ClearIAS Mock Exams: Analyse Your Progress
Analyse Your Performance and Track Your All-India Ranking
Ias/ips/ifs online coaching: target cse 2025.

Are you struggling to finish the UPSC CSE syllabus without proper guidance?

SIMPLIFYING UPSC IAS EXAM PREPARATION
- OUR CENTERS Bangalore Delhi Lucknow Mysuru Srinagar Dharwad Hyderabad
Call us @ 08069405205

Search Here

- An Introduction to the CSE Exam
- Personality Test
- Annual Calendar by UPSC-2024
- Common Myths about the Exam
- About Insights IAS
- Our Mission, Vision & Values
- Director's Desk
- Meet Our Team
- Our Branches
- Careers at Insights IAS
- Daily Current Affairs+PIB Summary
- Insights into Editorials
- Insta Revision Modules for Prelims
- Current Affairs Quiz
- Static Quiz
- Current Affairs RTM
- Insta-DART(CSAT)
- Insta 75 Days Revision Tests for Prelims 2024
- Secure (Mains Answer writing)
- Secure Synopsis
- Ethics Case Studies
- Insta Ethics
- Weekly Essay Challenge
- Insta Revision Modules-Mains
- Insta 75 Days Revision Tests for Mains
- Secure (Archive)
- Anthropology
- Law Optional
- Kannada Literature
- Public Administration
- English Literature
- Medical Science
- Mathematics
- Commerce & Accountancy
- Monthly Magazine: CURRENT AFFAIRS 30
- Content for Mains Enrichment (CME)
- InstaMaps: Important Places in News
- Weekly CA Magazine
- The PRIME Magazine
- Insta Revision Modules-Prelims
- Insta-DART(CSAT) Quiz
- Insta 75 days Revision Tests for Prelims 2022
- Insights SECURE(Mains Answer Writing)
- Interview Transcripts
- Previous Years' Question Papers-Prelims
- Answer Keys for Prelims PYQs
- Solve Prelims PYQs
- Previous Years' Question Papers-Mains
- UPSC CSE Syllabus
- Toppers from Insights IAS
- Testimonials
- Felicitation
- UPSC Results
- Indian Heritage & Culture
- Ancient Indian History
- Medieval Indian History
- Modern Indian History
- World History
- World Geography
- Indian Geography
- Indian Society
- Social Justice
- International Relations
- Agriculture
- Environment & Ecology
- Disaster Management
- Science & Technology
- Security Issues
- Ethics, Integrity and Aptitude

- Indian Heritage & Culture
- Enivornment & Ecology

- How to Study Art & Culture?
- What is Art and Culture? What is the difference between the two?
- Indus Civilization
- Evolution of rock-cut architecture in India
- Important rock-cut caves
- The contribution of Pallavas to Rock-cut architecture
- Comparision of art form found at Ellora and Mahabalipuram
- Buddhist Architecture
- Early Temples in India
- Basic form of Hindu temple
- Dravida style of temple architecture
- Nagara Style or North India Temple style
- Vesara style of temple architecture
- Characteristic features of Indo-Islamic form of architecture
- Styles of Islamic architecture in the Indian subcontinent
- Types of buildings in Islamic architecture in the Indian subcontinent
- Evolution of this form of architecture during the medieval period
- Modern Architecture
- Post-Independence architecture
- Indus Civilization Sculpture
- Bharhut Sculptures
- Sanchi Sculptures
- Gandhara School of Sculpture
- Mathura School of Sculpture
- Amaravati School of Sculpture
- Gupta Sculpture
- Medieval School of Sculpture
- Modern Indian Sculpture
- Pre Historic Painting
- Mural Paintings & Cave Paintings
- Pala School
- Mughal Paintings
- Bundi School of Painting
- Malwa School
- Mewar School
- Basohli School
- Kangra School
- Decanni School of Painting
- Madhubani Paintings or Mithila paintings
- Pattachitra
- Kalighat Painting
- Modern Indian Paintings
- Personalities Associated to Paintings
- Christianity
- Zoroastrianism
- Six Schools of Philosophy
- Lokayata / Charvaka
- Hindustani Music
- Carnatic Music
- Folk Music Tradition
- Modern Music
- Personalities associated with Music
- Bharatanatyam
- Mohiniattam
- Folk Dances
- Modern Dance in India
- Sanskrit Theatre
- Folk Theatre
- Modern Theatre
- Personalities associated with Theatre
- History of Puppetry
- String Puppetry
- Shadow Puppetry
- Rod Puppetry
- Glove Puppetry
- Indian Cinema and Circus
- Shankaracharya
- Ramanujacharya (1017-1137AD)
- Madhvacharya
- Vallabhacharya
- Kabir (1440-1510 AD)
- Guru Nanak (1469-1538 AD)
- Chaitanya Mahaprabhu
- Shankar Dev
- Purandaradasa
- Samard Ramdas
- Classical Languages
- Scheduled Languages
- Literature in Ancient India
- Buddhist and Jain Literature
- Tamil (Sangam) Literature
- Malayalam Literature
- Telugu Literature
- Medieval Literature
- Modern Literature
- Important characteristics of Fairs and Festivals of India
- Some of the major festivals that are celebrated in India
- Art & Crafts
- Ancient Science & Technology
- Medieval Science & Technology
- Famous Personalities in Science & Technology
- Tangible Cultural Heritage
- Intangible Cultural Heritage
- Cultural Heritage Sites
- Natural Heritage Sites
- Important Institutions
- Important programmes related to promotion and preservation of Indian heritage
- Ochre Colored Pottery (OCP)
- Black and Red Ware (BRW)
- Painted Grey-Ware (PGW)
- Northern Black Polished Ware (NBPW)
- Origin of Martial arts in India
- Various forms of Martial arts in India
- Branches of economics
- Different types of sectors in an economy
- Different types of economic systems
- Difference between economic growth vs economic development
- The concept of demand and supply in an economy
- Factors of production
- National Income
- Importance of quantifying economic growth
- Various types of economic indicators or concepts related to measuring economic growth
- Output Method
- Expenditure Method
- Income method
- Determinants of National Income
- Issues associated with National Income accounting in India
- Possible solutions to Issues with National Accounting
- Indian economy at the time of independence: Basic characteristics
- Basic characteristics of the Indian economy in present times
- Features of Indian Economy
- Role of Agriculture in India
- Growth of Services sector in India
- Status of Human Resource in India
- Status of Natural Resource in India
- Challenges with Indian Economy
- Overall Solutions to achieve a New India by 2022
- Historical evolution of planning in India
- Functions of Planning Commission
- Framework of planning under the commission
- Growth of Indian economy under the various-five year plans of the Planning commission
- Analysis of the working of Planning commission
- Framework of planning under the AYOG
- Performance of the AYOG since its inception
- Issues plaguing the AYOG and measures to resolve these issues
- Definition of a resource
- Types of resources
- Need for mobilizing resource in an economy
- Sources of resource mobilization in India
- Role of Fiscal Policy in Resource Mobilization
- Role of Tax in Resource Mobilization
- Role of Capital/ Financial Markets in Resource Mobilization
- Role of Banking/ Banks in Resource Mobilization
- Issues faced in resource mobilization in recent times
- Steps to be taken to address issues resource mobilization
- Definition of inclusive growth
- Salient Features of Inclusive Growth
- Elements of Inclusive growth
- Need for Inclusion
- Reasons for Inequality in India
- Dimensions of Inclusive Growth
- Measuring Inclusive Growth
- Experience of Indian in ushering in Inclusive growth since independence
- Measures taken by India since independence to ensure inclusive growth in the economy
- Reasons why India has not been able to achieve inclusive growth in the economy
- Rural economy based growth
- Sustainable and inclusive agricultural growth
- Holistic approach to combat poverty in India
- Social sector development
- Role of public and private partnership in this regard
- Balanced regional growth
- Industrial growth and its role in ushering inclusive growth
- Definition of budget
- Types of budget
- Various important terminologies associated with budget
- Budgeting process in India
- Some recent reforms introduced in the budgeting process
- Issues associated with budgeting process in India
- Measures required to address issues related to Budgeting
- Definition, types and objectives of Fiscal policy
- Important concepts/terms related to Government revenue and expenditure
- Types of deficit
- Methods of financing deficits in India
- Changes in FRBMA policies since its introduction
- Analysis of implementation of FRBMA
- Recommendations made with regards to FRBMA policies
- Function of Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
- Definition of monetary policy
- Quantitative tools of monetary policy of RBI
- Qualitative tools of Monetary policy of RBI
- Major monetary policy reforms introduced in recent times
- An objective analysis on the efficacy of monetary policy in India
- Recommendations made by various committees and economists to improve monetary policy framework in India
- Amendments introduced in RBI act over the years
- Issues associated with RBI functioning
- Measures to address the issues plaguing RBI
- Definition of Inflation
- Types of Inflation
- Factors causing Inflation
- Indicators used to measure Inflation
- Effect of Inflation in Indian economy
- Inflation Targeting in India
- Pros and cons of Inflation targeting in India
- Various other methods of combating Inflation
- Government steps to control inflation
- Present trend of Inflation in the economy
- Definition of Taxation
- Objectives behind Taxation
- Types of taxes
- Direct taxes in India
- Indirect taxes in India
- Major taxation related reforms introduced in recent times
- Trend of tax collection in India
- Issues associated with taxation system in India
- Measures suggested/recommendations made to address issues associated with taxation system in India
- Historical evolution of banking system in India
- Functions of banks in an economy
- Scheduled banks
- Non-scheduled banks
- Nationalization of banks
- Narasimhan committee recommendation on Banking sector
- Banking reforms introduced in India in recent times
- Issues associated with banking system in India
- Way Forward : Fifth Generation Banking
- Definition of Money Market and Capital Market
- Importance of Money Market and Capital Market for an Economy
- Money Market Instruments
- Regulatory framework of Indian money market
- Money Market Reforms
- Issues / Challenges related to Money Market in India
- Gilt-Edged Market
- The Industrial Securities Market
- Historical evolution of stock market in India
- Importance of stock exchanges
- Various stock exchanges in India
- Regulatory framework of Capital Market in India
- Capital Market Reforms
- Recommendations for Further Improving Capital Market in India
- Definition of investment
- Importance of investment for an economy
- Classification of investment
- Factors affecting investment
- Public investment model
- Private investment model
- Public private partnership model
- Issues associated with PPP model
- Reforms undertaken to better PPP model in recent times
- Harrod-Domar model
- Solow Swan model
- Feldman- Mahalanobis model
- Rao- Manmohan model
- Relationship between infrastructure and economic development
- Transport system in India’s economic development
- Growth in Indian railways
- Roads and road transport system in India
- Water transport in India
- Civil Aviation in India
- Communication Infrastructure in India
- Urban infrastructure
- Infrastructural reforms taken in the above sectors
- An objective analysis of the present infrastructure in the country
- Measures to further improve infrastructure in the country
- Concept of social sector and social infrastructure
- Development of Education In India
- Health and Family Welfare and The Development of Health Infrastructure
- Indian agriculture at the time of independence
- Land reforms
- Indian agriculture under the five year plans
- Food security in India
- Organization of agricultural credit in India
- Agriculture Marketing and Warehousing
- Agricultural labour
- Agriculture and Food processing industries
- Growth trajectory
- Issues plaguing Indian agriculture
- Programmes and policies introduced in India in recent times to address the issues
- Some more measures or recommendations made by the committee to improve agricultural growth in India
- Indian industry at the eve of independence
- Industrial growth under five year planning
- Major Industrial policies introduced in India since independence
- Basic characteristics of Indian industries in the present times
- Measures taken in recent times to increase the industrial growth in the country
- Issues plaguing industrial growth in India despite the measures
- Suggestions and recommendations given by various committees to increase the industrial growth in the country
- Present foreign trade of India
- Foreign trade policies
- Impact of globalization on Indian economy
- India’s balance of payments
- GATT, WTO and India’s foreign trade
- IMF and World Bank
- Recent reforms taken by Indian in this domain
- Definition of Poverty
- Classification of Poverty
- Poverty in India at the eve of Independence
- Growth of Industry in India
- Poverty Alleviation Programmes since Independence
- Impact of LPG reform on reducing poverty in India
- Reasons why poverty still exists in India
- Actions required to address the above issues
- Definition of Unemployment
- Types of unemployment
- Measurement of Unemployment in India
- Unemployment Trends in India
- Causes of unemployment in India
- Programmes, policies and measures taken to address Unemployment in India since Independence
Home » Economy » Poverty and unemployment
Poverty and unemployment
- Unemployment

- Our Mission, Vision & Values
- Director’s Desk
- Commerce & Accountancy
- Previous Years’ Question Papers-Prelims
- Previous Years’ Question Papers-Mains
- Environment & Ecology
- Science & Technology

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Unemployment is often used as a measure of the health of the economy. The most frequent measure of unemployment is the unemployment rate, which is the number of unemployed people divided by the number of people in the labor force. ... UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year's Questions (PYQs) Mains. Q. ... Filter By Papers. GS Paper 1 ...
If you are looking for an upsc essay, you have come to the right place because here is the essay on unemployment in India. Go through this article precisely and grab all the points. Also Read: Permanent Court of Arbitration: Important Notes for UPSC Exam. Essay on Unemployment in India. Unemployment is defined as the health of the economy of a ...
India's unemployment rate for individuals aged 15 and above has dropped to 3.1% in 2023, marking the lowest in the past three years. The unemployment rate was at 3.6% in 2022 and 4.2% in 2021. There is a decline in the unemployment rate among females to 3% in 2023 from 3.3% in 2022 and 3.4% in 2021.
For candidates preparing for UPSC, unemployment in India can be asked in GS I or as an essay question. Therefore, this article will discuss detailed information on unemployment in India, types of unemployment, causes and government initiatives to control unemployment in India. Candidates appearing for UPSC 2023 can go through the following links:
GS Paper 3: Topics Covered: Employment Related issues. Context: According to the latest Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) released by the National Statistical Office (NSO):. India's urban unemployment rate jumped to 12.6 per cent in the April-June quarter of 2021, compared to 9.3 per cent in the January-March quarter.; It, however, eased from the 20.8 per cent level seen during the first ...
Rate of Unemployment- The overall unemployment rate has reduced to 6.6 per cent in 2021-22 from 8.7 per cent in 2017-18. Unemployment based on education and age group - Over 42 per cent of India's graduates under 25 were unemployed in 2021-22. Unemployment figure stands at 21.4 per cent for those who have completed higher secondary ...
Casual Unemployment. When a person is employed on a day-to-day basis, casual unemployment may occur due to short-term contracts, shortage of raw materials, fall in demand, change of ownership etc. Chronic Unemployment. If unemployment continues to be a long term feature of a country, it is called chronic unemployment.
Causes of Unemployment in India. This can be attributed to various factors, both structural and cyclical. Here are some of the major causes: Population Growth: The supply of labor surpasses the available job opportunities, leading to higher unemployment rates. Lack of Skill Development: There is often a mismatch between the skills possessed by the workforce and the skills demanded by the ...
The number of unemployed persons in India is projected to increase from 18.3 million in 2017 to 18.6 million in 2018 and further to 18.9 million by 2019. The unemployment rate is expected to remain static at 3.5 per cent during this period. World Bank's Report on India's Economy:
NIDHI GOYAL RANK 91 UPSC CSE 2023 Essay Test Copy | When women do better, economies do better. IAS, AYAN JAIN RANK 16 UPSC CSE 2023 Essay Test Copy | Artificial intelligence will either be the be… MANISH BHARDWAJ RANK 215 UPSC CSE 2023 Essay Test Copy | Nature, as we know her, is no saint.
Why in News. According to data from the Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy (CMIE), India's unemployment rate touched a four-month high of 7.9% in December 2021.. With Covid-19 cases on the rise amid the threat posed by the Omicron variant and many states imposing fresh curbs, economic activity and consumption levels have been affected.; This could adversely affect economic recovery further ...
2319. Recently, the Centre for Monitoring the Indian Economy (CMIE) released data stating that India's unemployment rate in August 2022 rose to 8.3%. This is the highest unemployment rate in the past 12 months. In August 2021, the unemployment rate was 8.35%.
Cyclical unemployment. Cyclical unemployment exists when individuals lose their jobs as a result of a downturn in aggregate demand (AD) If the decline in aggregate demand is persistent, it is either called demand deficient, general, or Keynesian unemployment. When companies experience a reduction in the demand for their products or services ...
The unemployment rate for the year 2013-14 in rural India was 4.7%, whereas it was 5.5% for urban India. In the short term, unemployment significantly reduces a person's income and, in the long term, it reduces their ability to save for retirement and other goals. Unemployment is a loss of valuable productive resources to the economy.
UPSC Buddy. India's Largest Career Transformation Portal. ... Essay on Unemployment: It is a serious social issue in India and a big global concern too. There are thousands of people who are not employed owing to the rising population and a steady decline in jobs, leading to unemployment. Automation of jobs, illiteracy, stiff competition ...
India-Afghanistan: Economic interests. Afghanistan has a mineral wealth of about $1-3 trillion of Iron ore, Lithium, Chromium, Natural Gas, Petroleum etc. Safeguarding Indian investments and personnel in Afghan is utmost important to India as Indian investment in Afghan amounts to about $3bn.
The unemployment rate was 6.6% for men and 9.4% for women (9.3% and 11.6% in July-September 2021). The WPR is defined as the percentage of employed persons in the population. The WPR in urban areas for persons aged 15 and above stood at 44.5% (42.3% in July-September 2021).
Insights IAS: Simplifying UPSC IAS Exam Preparation. InsightsIAS has redefined, revolutionized and simplified the way aspirants prepare for UPSC IAS Civil Services Exam. Today, it's India's top website and institution when it comes to imparting quality content, guidance and teaching for the IAS Exam.
Introduce by writing the unemployment scenario of India. Discuss the reasons for large scale unemployment in India. Suggest measures can be taken to tackle this unemployment wave in India. Introduction. Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) data show an increase in the worker to population ratio (WPR) from 34.7% in 2017-18 to 38.2% in 2019-20.
As the world shrinks with technological and communication changes, terrorists, weapons and funds are also able to move across national boundaries easily. International co-operation between law enforcement authorities in this area is a sine qua non for combating such cross-border challenges.
An Opportunity for India-Russia Ties. This editorial is based on "Resetting Putin's Red Carpet" which was published in Indian Express on 06/12/2021. It talks about reviving the stagnant India-Russia economic ties. Recently, the 21 st India-Russia annual summit took place at New Delhi which also included the first 2+2 ministerial dialogue ...