
Research Voyage
Research Tips and Infromation

PhD Defence Process: A Comprehensive Guide

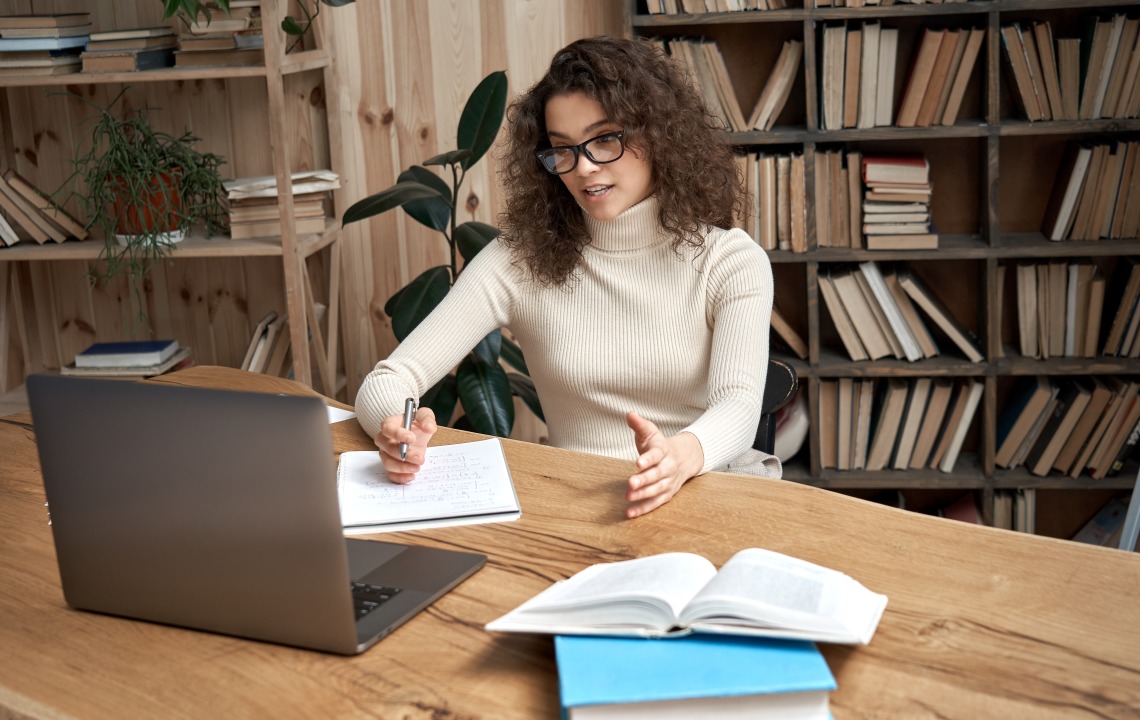
Embarking on the journey toward a PhD is an intellectual odyssey marked by tireless research, countless hours of contemplation, and a fervent commitment to contributing to the body of knowledge in one’s field. As the culmination of this formidable journey, the PhD defence stands as the final frontier, the proverbial bridge between student and scholar.
In this comprehensive guide, we unravel the intricacies of the PhD defence—a momentous occasion that is both a celebration of scholarly achievement and a rigorous evaluation of academic prowess. Join us as we explore the nuances of the defence process, addressing questions about its duration, contemplating the possibility of failure, and delving into the subtle distinctions of language that surround it.
Beyond the formalities, we aim to shed light on the significance of this rite of passage, dispelling misconceptions about its nature. Moreover, we’ll consider the impact of one’s attire on this critical day and share personal experiences and practical tips from those who have successfully navigated the defence journey.
Whether you are on the precipice of your own defence or are simply curious about the process, this guide seeks to demystify the PhD defence, providing a roadmap for success and a nuanced understanding of the pivotal event that marks the transition from student to scholar.
Introduction
A. definition and purpose:, b. overview of the oral examination:, a. general duration of a typical defense, b. factors influencing the duration:, c. preparation and flexibility:, a. preparation and thorough understanding of the research:, b. handling questions effectively:, c. confidence and composure during the presentation:, d. posture of continuous improvement:, a. exploring the possibility of failure:, b. common reasons for failure:, c. steps to mitigate the risk of failure:, d. post-failure resilience:, a. addressing the language variation:, b. conforming to regional preferences:, c. consistency in usage:, d. flexibility and adaptability:, e. navigating language in a globalized academic landscape:, a. debunking myths around the formality of the defense:, b. significance in validating research contributions:, c. post-defense impact:, a. appropriate attire for different settings:, b. professionalism and the impact of appearance:, c. practical tips for dressing success:, b. practical tips for a successful defense:, c. post-defense reflections:, career options after phd.
Embarking on the doctoral journey is a formidable undertaking, where aspiring scholars immerse themselves in the pursuit of knowledge, contributing new insights to their respective fields. At the pinnacle of this academic odyssey lies the PhD defence—a culmination that transcends the boundaries of a mere formality, symbolizing the transformation from a student of a discipline to a recognized contributor to the academic tapestry.
The PhD defence, also known as the viva voce or oral examination, is a pivotal moment in the life of a doctoral candidate.
PhD defence is not merely a ritualistic ceremony; rather, it serves as a platform for scholars to present, defend, and elucidate the findings and implications of their research. The defence is the crucible where ideas are tested, hypotheses scrutinized, and the depth of scholarly understanding is laid bare.
The importance of the PhD defence reverberates throughout the academic landscape. It is not just a capstone event; it is the juncture where academic rigour meets real-world application. The defence is the litmus test of a researcher’s ability to articulate, defend, and contextualize their work—an evaluation that extends beyond the pages of a dissertation.
Beyond its evaluative nature, the defence serves as a rite of passage, validating the years of dedication, perseverance, and intellectual rigour invested in the research endeavour. Success in the defence is a testament to the candidate’s mastery of their subject matter and the originality and impact of their contributions to the academic community.
Furthermore, a successful defence paves the way for future contributions, positioning the scholar as a recognized authority in their field. The defence is not just an endpoint; it is a launchpad, propelling researchers into the next phase of their academic journey as they continue to shape and redefine the boundaries of knowledge.
In essence, the PhD defence is more than a ceremonial checkpoint—it is a transformative experience that validates the intellectual journey, underscores the significance of scholarly contributions, and sets the stage for a continued legacy of academic excellence. As we navigate the intricacies of this process, we invite you to explore the multifaceted dimensions that make the PhD defence an indispensable chapter in the narrative of academic achievement.
What is a PhD Defence?
At its core, a PhD defence is a rigorous and comprehensive examination that marks the culmination of a doctoral candidate’s research journey. It is an essential component of the doctoral process in which the candidate is required to defend their dissertation before a committee of experts in the field. The defence serves multiple purposes, acting as both a showcase of the candidate’s work and an evaluative measure of their understanding, critical thinking, and contributions to the academic domain.
The primary goals of a PhD defence include:
- Presentation of Research: The candidate presents the key findings, methodology, and significance of their research.
- Demonstration of Mastery: The defence assesses the candidate’s depth of understanding, mastery of the subject matter, and ability to engage in scholarly discourse.
- Critical Examination: Committee members rigorously question the candidate, challenging assumptions, testing methodologies, and probing the boundaries of the research.
- Validation of Originality: The defence validates the originality and contribution of the candidate’s work to the existing body of knowledge.
The PhD defence often takes the form of an oral examination, commonly referred to as the viva voce. This oral component adds a dynamic and interactive dimension to the evaluation process. Key elements of the oral examination include:
- Presentation: The candidate typically begins with a formal presentation, summarizing the dissertation’s main components, methodology, and findings. This presentation is an opportunity to showcase the significance and novelty of the research.
- Questioning and Discussion: Following the presentation, the candidate engages in a thorough questioning session with the examination committee. Committee members explore various aspects of the research, challenging the candidates to articulate their rationale, defend their conclusions, and respond to critiques.
- Defence of Methodology: The candidate is often required to defend the chosen research methodology, demonstrating its appropriateness, rigour, and contribution to the field.
- Evaluation of Contributions: Committee members assess the originality and impact of the candidate’s contributions to the academic discipline, seeking to understand how the research advances existing knowledge.
The oral examination is not a mere formality; it is a dynamic exchange that tests the candidate’s intellectual acumen, research skills, and capacity to contribute meaningfully to the scholarly community.
In essence, the PhD defence is a comprehensive and interactive evaluation that encapsulates the essence of a candidate’s research journey, demanding a synthesis of knowledge, clarity of expression, and the ability to navigate the complexities of academic inquiry. As we delve into the specifics of the defence process, we will unravel the layers of preparation and skill required to navigate this transformative academic milestone.
How Long is a PhD Defence?
The duration of a PhD defence can vary widely, but it typically ranges from two to three hours. This time frame encompasses the candidate’s presentation of their research, questioning and discussions with the examination committee, and any additional deliberations or decisions by the committee. However, it’s essential to note that this is a general guideline, and actual defence durations may vary based on numerous factors.
- Sciences and Engineering: Defenses in these fields might lean towards the shorter end of the spectrum, often around two hours. The focus is often on the methodology, results, and technical aspects.
- Humanities and Social Sciences: Given the theoretical and interpretive nature of research in these fields, defences might extend closer to three hours or more. Discussions may delve into philosophical underpinnings and nuanced interpretations.
- Simple vs. Complex Studies: The complexity of the research itself plays a role. Elaborate experiments, extensive datasets, or intricate theoretical frameworks may necessitate a more extended defence.
- Number of Committee Members: A larger committee or one with diverse expertise may lead to more extensive discussions and varied perspectives, potentially elongating the defence.
- Committee Engagement: The level of engagement and probing by committee members can influence the overall duration. In-depth discussions or debates may extend the defence time.
- Cultural Norms: In some countries, the oral defence might be more ceremonial, with less emphasis on intense questioning. In others, a rigorous and extended defence might be the norm.
- Evaluation Practices: Different academic systems have varying evaluation criteria, which can impact the duration of the defence.
- Institutional Guidelines: Some institutions may have specific guidelines on defence durations, influencing the overall time allotted for the process.
Candidates should be well-prepared for a defence of any duration. Adequate preparation not only involves a concise presentation of the research but also anticipates potential questions and engages in thoughtful discussions. Additionally, candidates should be flexible and responsive to the dynamics of the defense, adapting to the pace set by the committee.
Success Factors in a PhD Defence
- Successful defence begins with a deep and comprehensive understanding of the research. Candidates should be well-versed in every aspect of their study, from the theoretical framework to the methodology and findings.
- Thorough preparation involves anticipating potential questions from the examination committee. Candidates should consider the strengths and limitations of their research and be ready to address queries related to methodology, data analysis, and theoretical underpinnings.
- Conducting mock defences with peers or mentors can be invaluable. It helps refine the presentation, exposes potential areas of weakness, and provides an opportunity to practice responding to challenging questions.
- Actively listen to questions without interruption. Understanding the nuances of each question is crucial for providing precise and relevant responses.
- Responses should be clear, concise, and directly address the question. Avoid unnecessary jargon, and strive to convey complex concepts in a manner that is accessible to the entire committee.
- It’s acceptable not to have all the answers. If faced with a question that stumps you, acknowledge it honestly. Expressing a willingness to explore the topic further demonstrates intellectual humility.
- Use questions as opportunities to reinforce key messages from the research. Skillfully link responses back to the core contributions of the study, emphasizing its significance.
- Rehearse the presentation multiple times to build familiarity with the material. This enhances confidence, reduces nervousness, and ensures a smooth and engaging delivery.
- Maintain confident and open body language. Stand tall, make eye contact, and use gestures judiciously. A composed demeanour contributes to a positive impression.
- Acknowledge and manage nervousness. It’s natural to feel some anxiety, but channelling that energy into enthusiasm for presenting your research can turn nervousness into a positive force.
- Engage with the committee through a dynamic and interactive presentation. Invite questions during the presentation to create a more conversational atmosphere.
- Utilize visual aids effectively. Slides or other visual elements should complement the spoken presentation, reinforcing key points without overwhelming the audience.
- View the defence not only as an evaluation but also as an opportunity for continuous improvement. Feedback received during the defence can inform future research endeavours and scholarly pursuits.
In essence, success in a PhD defence hinges on meticulous preparation, adept handling of questions, and projecting confidence and composure during the presentation. A well-prepared and resilient candidate is better positioned to navigate the challenges of the defence, transforming it from a moment of evaluation into an affirmation of scholarly achievement.
Failure in PhD Defence
- While the prospect of failing a PhD defence is relatively rare, it’s essential for candidates to acknowledge that the possibility exists. Understanding this reality can motivate diligent preparation and a proactive approach to mitigate potential risks.
- Failure, if it occurs, should be seen as a learning opportunity rather than a definitive endpoint. It may highlight areas for improvement and offer insights into refining the research and presentation.
- Lack of thorough preparation, including a weak grasp of the research content, inadequate rehearsal, and failure to anticipate potential questions, can contribute to failure.
- Inability to effectively defend the chosen research methodology, including justifying its appropriateness and demonstrating its rigour, can be a critical factor.
- Failing to clearly articulate the original contributions of the research and its significance to the field may lead to a negative assessment.
- Responding defensively to questions, exhibiting a lack of openness to critique, or being unwilling to acknowledge limitations can impact the overall impression.
- Inability to address committee concerns or incorporate constructive feedback received during the defense may contribute to a negative outcome.
- Comprehensive preparation is the cornerstone of success. Candidates should dedicate ample time to understanding every facet of their research, conducting mock defences, and seeking feedback.
- Identify potential weaknesses in the research and address them proactively. Being aware of limitations and articulating plans for addressing them in future work demonstrates foresight.
- Engage with mentors, peers, or advisors before the defence. Solicit constructive feedback on both the content and delivery of the presentation to refine and strengthen the defence.
- Develop strategies to manage stress and nervousness. Techniques such as mindfulness, deep breathing, or visualization can be effective in maintaining composure during the defence.
- Conduct a pre-defense review of all materials, ensuring that the presentation aligns with the dissertation and that visual aids are clear and supportive.
- Approach the defence with an open and reflective attitude. Embrace critique as an opportunity for improvement rather than as a personal affront.
- Clarify expectations with the examination committee beforehand. Understanding the committee’s focus areas and preferences can guide preparation efforts.
- In the event of failure, candidates should approach the situation with resilience. Seek feedback from the committee, understand the reasons for the outcome, and use the experience as a springboard for improvement.
In summary, while the prospect of failing a PhD defence is uncommon, acknowledging its possibility and taking proactive steps to mitigate risks are crucial elements of a well-rounded defence strategy. By addressing common failure factors through thorough preparation, openness to critique, and a resilient attitude, candidates can increase their chances of a successful defence outcome.
PhD Defense or Defence?
- The choice between “defense” and “defence” is primarily a matter of British English versus American English spelling conventions. “Defense” is the preferred spelling in American English, while “defence” is the British English spelling.
- In the global academic community, both spellings are generally understood and accepted. However, the choice of spelling may be influenced by the academic institution’s language conventions or the preferences of individual scholars.
- Academic institutions may have specific guidelines regarding language conventions, and candidates are often expected to adhere to the institution’s preferred spelling.
- Candidates may also consider the preferences of their advisors or committee members. If there is a consistent spelling convention used within the academic department, it is advisable to align with those preferences.
- Consideration should be given to the spelling conventions of scholarly journals in the candidate’s field. If intending to publish research stemming from the dissertation, aligning with the conventions of target journals is prudent.
- If the defense presentation or dissertation will be shared with an international audience, using a more universally recognized spelling (such as “defense”) may be preferred to ensure clarity and accessibility.
- Regardless of the chosen spelling, it’s crucial to maintain consistency throughout the document. Mixing spellings can distract from the content and may be perceived as an oversight.
- In oral presentations and written correspondence related to the defence, including emails, it’s advisable to maintain consistency with the chosen spelling to present a professional and polished image.
- Recognizing that language conventions can vary, candidates should approach the choice of spelling with flexibility. Being adaptable to the preferences of the academic context and demonstrating an awareness of regional variations reflects a nuanced understanding of language usage.
- With the increasing globalization of academia, an awareness of language variations becomes essential. Scholars often collaborate across borders, and an inclusive approach to language conventions contributes to effective communication and collaboration.
In summary, the choice between “PhD defense” and “PhD defence” boils down to regional language conventions and institutional preferences. Maintaining consistency, being mindful of the target audience, and adapting to the expectations of the academic community contribute to a polished and professional presentation, whether in written documents or oral defences.
Is PhD Defense a Formality?
- While the PhD defence is a structured and ritualistic event, it is far from being a mere formality. It is a critical and substantive part of the doctoral journey, designed to rigorously evaluate the candidate’s research contributions, understanding of the field, and ability to engage in scholarly discourse.
- The defence is not a checkbox to be marked but rather a dynamic process where the candidate’s research is evaluated for its scholarly merit. The committee scrutinizes the originality, significance, and methodology of the research, aiming to ensure it meets the standards of advanced academic work.
- Far from a passive or purely ceremonial event, the defence involves active engagement between the candidate and the examination committee. Questions, discussions, and debates are integral components that enrich the scholarly exchange during the defence.
- The defence serves as a platform for the candidate to demonstrate the originality of their research. Committee members assess the novelty of the contributions, ensuring that the work adds value to the existing body of knowledge.
- Beyond the content, the defence evaluates the methodological rigour of the research. Committee members assess whether the chosen methodology is appropriate, well-executed, and contributes to the validity of the findings.
- Successful completion of the defence affirms the candidate’s ability to contribute meaningfully to the academic discourse in their field. It is an endorsement of the candidate’s position as a knowledgeable and respected scholar.
- The defence process acts as a quality assurance mechanism in academia. It ensures that individuals awarded a doctoral degree have undergone a thorough and rigorous evaluation, upholding the standards of excellence in research and scholarly inquiry.
- Institutions have specific criteria and standards for awarding a PhD. The defence process aligns with these institutional and academic standards, providing a consistent and transparent mechanism for evaluating candidates.
- Successful completion of the defence is a pivotal moment that marks the transition from a doctoral candidate to a recognized scholar. It opens doors to further contributions, collaborations, and opportunities within the academic community.
- Research presented during the defence often forms the basis for future publications. The validation received in the defence enhances the credibility of the research, facilitating its dissemination and impact within the academic community.
- Beyond the academic realm, a successfully defended PhD is a key credential for professional advancement. It enhances one’s standing in the broader professional landscape, opening doors to research positions, teaching opportunities, and leadership roles.
In essence, the PhD defence is a rigorous and meaningful process that goes beyond formalities, playing a crucial role in affirming the academic merit of a candidate’s research and marking the culmination of their journey toward scholarly recognition.
Dressing for Success: PhD Defense Outfit
- For Men: A well-fitted suit in neutral colours (black, navy, grey), a collared dress shirt, a tie, and formal dress shoes.
- For Women: A tailored suit, a blouse or button-down shirt, and closed-toe dress shoes.
- Dress codes can vary based on cultural expectations. It’s advisable to be aware of any cultural nuances within the academic institution and to adapt attire accordingly.
- With the rise of virtual defenses, considerations for attire remain relevant. Even in online settings, dressing professionally contributes to a polished and serious demeanor. Virtual attire can mirror what one would wear in-person, focusing on the upper body visible on camera.
- The attire chosen for a PhD defense contributes to the first impression that a candidate makes on the examination committee. A professional and polished appearance sets a positive tone for the defense.
- Dressing appropriately reflects respect for the gravity of the occasion. It acknowledges the significance of the defense as a formal evaluation of one’s scholarly contributions.
- Wearing professional attire can contribute to a boost in confidence. When individuals feel well-dressed and put-together, it can positively impact their mindset and overall presentation.
- The PhD defense is a serious academic event, and dressing professionally fosters an atmosphere of seriousness and commitment to the scholarly process. It aligns with the respect one accords to academic traditions.
- Institutional norms may influence dress expectations. Some academic institutions may have specific guidelines regarding attire for formal events, and candidates should be aware of and adhere to these norms.
- While adhering to the formality expected in academic settings, individuals can also express their personal style within the bounds of professionalism. It’s about finding a balance between institutional expectations and personal comfort.
- Select and prepare the outfit well in advance to avoid last-minute stress. Ensure that the attire is clean, well-ironed, and in good condition.
- Accessories such as ties, scarves, or jewelry should complement the outfit. However, it’s advisable to keep accessories subtle to maintain a professional appearance.
- While dressing professionally, prioritize comfort. PhD defenses can be mentally demanding, and comfortable attire can contribute to a more confident and composed demeanor.
- Pay attention to grooming, including personal hygiene and haircare. A well-groomed appearance contributes to an overall polished look.
- Start preparation well in advance of the defense date. Know your research inside out, anticipate potential questions, and be ready to discuss the nuances of your methodology, findings, and contributions.
- Conduct mock defenses with peers, mentors, or colleagues. Mock defenses provide an opportunity to receive constructive feedback, practice responses to potential questions, and refine your presentation.
- Strike a balance between confidence and humility. Confidence in presenting your research is essential, but being open to acknowledging limitations and areas for improvement demonstrates intellectual honesty.
- Actively engage with the examination committee during the defense. Listen carefully to questions, respond thoughtfully, and view the defense as a scholarly exchange rather than a mere formality.
- Understand the expertise and backgrounds of the committee members. Tailor your presentation and responses to align with the interests and expectations of your specific audience.
- Practice time management during your presentation. Ensure that you allocate sufficient time to cover key aspects of your research, leaving ample time for questions and discussions.
- It’s normal to feel nervous, but practicing mindfulness and staying calm under pressure is crucial. Take deep breaths, maintain eye contact, and focus on delivering a clear and composed presentation.
- Have a plan for post-defense activities. Whether it’s revisions to the dissertation, publications, or future research endeavors, having a roadmap for what comes next demonstrates foresight and commitment to ongoing scholarly contributions.
- After successfully defending, individuals often emphasize the importance of taking time to reflect on the entire doctoral journey. Acknowledge personal and academic growth, celebrate achievements, and use the experience to inform future scholarly pursuits.
In summary, learning from the experiences of others who have successfully defended offers a wealth of practical wisdom. These insights, combined with thoughtful preparation and a proactive approach, contribute to a successful and fulfilling defense experience.
You have plenty of career options after completing a PhD. For more details, visit my blog posts:
7 Essential Steps for Building a Robust Research Portfolio
Exciting Career Opportunities for PhD Researchers and Research Scholars
Freelance Writing or Editing Opportunities for Researchers A Comprehensive Guide
Research Consultancy: An Alternate Career for Researchers
The Insider’s Guide to Becoming a Patent Agent: Opportunities, Requirements, and Challenges
The journey from a curious researcher to a recognized scholar culminates in the PhD defence—an intellectual odyssey marked by dedication, resilience, and a relentless pursuit of knowledge. As we navigate the intricacies of this pivotal event, it becomes evident that the PhD defence is far more than a ceremonial rite; it is a substantive evaluation that validates the contributions of a researcher to the academic landscape.
Upcoming Events
- Visit the Upcoming International Conferences at Exotic Travel Destinations with Travel Plan
- Visit for Research Internships Worldwide

Recent Posts
- 05 Quick Review, High Impact, Best Research Journals for Submissions for July 2024
- Top Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a Research Paper
- Average Stipend for Research/Academic Internships
- These Institutes Offer Remote Research/Academic Internships
- How to Include Your Journal in the UGC-CARE List? A Guide for Publishers
- All Blog Posts
- Research Career
- Research Conference
- Research Internship
- Research Journal
- Research Tools
- Uncategorized
- Research Conferences
- Research Journals
- Research Grants
- Internships
- Research Internships
- Email Templates
- Conferences
- Blog Partners
- Privacy Policy
Copyright © 2024 Research Voyage
Design by ThemesDNA.com


- PhD Viva Voces – A Complete Guide
- Doing a PhD
- A PhD viva involves defending your thesis in an oral examination with at least two examiners.
- The aim of a PhD viva is to confirm that the work is your own , that you have a deep understanding of your project and, overall, that you are a competent researcher .
- There are no standard durations, but they usually range from one to three hours, with most lasting approximately two hours .
- There are six outcomes of a PhD viva: (1) pass without corrections (2) pass subject to minor corrections, (3) pass subject to major corrections, (4) downgrade to MPhil with no amendments, (5) downgrade to MPhil subject to amendments, (6) immediate fail.
- Almost all students who sit their viva pass it, with the most common outcome being ‘(2) – pass subject to minor corrections’.
What Is a PhD Viva?
A viva voce , more commonly referred to as ‘viva’, is an oral examination conducted at the end of your PhD and is essentially the final hurdle on the path to a doctorate. It is the period in which a student’s knowledge and work are evaluated by independent examiners.
In order to assess the student and their work around their research question, a viva sets out to determine:
- you understand the ideas and theories that you have put forward,
- you can answer questions about elements of your work that the examiners have questions about,
- you understand the broader research in your field and how your work contributes to this,
- you are aware of the limitations of your work and understand how it can be developed further,
- your work makes an original contribution, is your own and has not been plagiarised.
Note: A viva is a compulsory procedure for all PhD students, with the only exception being when a PhD is obtained through publication as opposed to the conventional route of study.
Who Will Attend a Viva?
In the UK, at least two examiners must take part in all vivas. Although you could have more than two examiners, most will not in an attempt to facilitate a smoother questioning process.
One of the two examiners will be internal, i.e. from your university, and the other will be external, i.e. from another university. Regardless, both will be knowledgeable in your research field and have read your thesis beforehand.
In addition to your two examiners, two other people may be present. The first is a chairperson. This is an individual who will be responsible for monitoring the interview and for ensuring proper conduct is followed at all times. The need for an external chairperson will vary between universities, as one of the examiners can also take on this role. The second is your supervisor, whose attendance is decided upon by you in agreement with your examiners. If your supervisor attends, they are prohibited from asking questions or from influencing the outcome of the viva.
To avoid any misunderstandings, we have summarised the above in a table:
| Examiners | Mandatory and minimum of 2 | Your supervisor | Yes |
| Chairperson | Optional | Your university | No |
| Your Supervisor | Optional | You, in agreement of both examiners | No |
Note: In some countries, such as in the United States, a viva is known as a ‘PhD defense’ and is performed publicly in front of a panel or board of examiners and an open audience. In these situations, the student presents their work in the form of a lecture and then faces questions from the examiners and audience which almost acts as a critical appraisal.
How Long Does a Viva Last?
Since all universities have different guidelines , and since all PhDs are unique, there are no standard durations. Typically, however, the duration ranges from one to three hours, with most lasting approximately two hours.
Your examiners will also influence the duration of your viva as some will favour a lengthy discussion, while others may not. Usually, your university will consult your examiners in advance and notify you of the likely duration closer to the day of your viva.
What Happens During a Viva?
Regardless of the subject area, all PhD vivas follow the same examination process format as below.
Introductions
You will introduce yourselves to each other, with the internal examiner normally introducing the external examiner. If an external chairperson is present, they too are introduced; otherwise, this role will be assumed by one of the examiners.
Procedure Explained
After the introductions, the appointed chair will explain the viva process. Although it should already be known to everyone, it will be repeated to ensure the viva remains on track during the forthcoming discussion.
Warm-Up Questions
The examiners will then begin the questioning process. This usually starts with a few simple opening questions, such as asking you to summarise your PhD thesis and what motivated you to carry out the research project.
In-Depth Questions
The viva questions will then naturally increase in difficulty as the examiners go further into the details of your thesis. These may include questions such as “What was the most critical decision you made when determining your research methodology ?”, “Do your findings agree with the current published work?” and “How do your findings impact existing theories or literature? ”. In addition to asking open-ended questions, they will also ask specific questions about the methodology, results and analysis on which your thesis is based.
Closing the Viva
Once the examiners are satisfied that they have thoroughly evaluated your knowledge and thesis, they will invite you to ask any questions you may have, and then bring the oral examination to a close.
What Happens After the Viva?
Once your viva has officially ended, your examiners will ask you to leave the room so that they can discuss your performance. Once a mutual agreement has been reached, which can take anywhere from 10 minutes to an hour, you will be invited back inside and informed of your outcome.
PhD Viva Outcomes
There are six possible outcomes to a viva:
- Immediate award of degree: A rare recommendation – congratulations, you are one of the few people who completely satisfied your examiners the first time around. You do not have to do anything further at this point.
- Minor amendments required: The most common recommendation – you obtain a pass on the condition that you make a number of minor amendments to your thesis, such as clarifying certain points and correcting grammatical errors. The time you have to make these changes depends on the number of them, but is usually one to six months.
- Major amendments required: A somewhat uncommon recommendation – you are requested to make major amendments to your thesis, ranging from further research to collecting more data or rewriting entire sections. Again, the time you have to complete this will depend on the number of changes required, but will usually be six months to one year. You will be awarded your degree once your amended thesis has been reviewed and accepted.
- Immediate award of MPhil: An uncommon recommendation – your examiners believe your thesis does not meet the standard for a doctoral degree but meets the standard for an MPhil (Master of Philosophy), a lower Master’s degree.
- Amendments required for MPhil: A rare recommendation – your examiners believe your thesis does not meet the standard for a doctoral degree, but with several amendments will meet the standard for an MPhil.
- Immediate fail: A very rare recommendation – you are given an immediate fail without the ability to resubmit and without entitlement to an MPhil.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
What Is the Pass Rate for Vivas?
Based on an analysis of 26,076 PhD students who took their viva exam between 2006 and 2017, the PhD viva pass rate in the UK is 96%; of those who passed, about 80% were required to make minor amendments to their thesis. The reason for this high pass rate is that supervisors will only put their students forward for a viva once they confidently believe they are ready for it. As a result, most candidates who sit a viva are already well-versed in their PhD topic before they even start preparing for the exam.
How Do I Arrange a Viva?
Your viva will be arranged either by the examiners or by the chairperson. The viva will be arranged at least one to two months after you have submitted your thesis and will arrange a viva date and venue that is suitable for all participants.
Can I Choose My Examiners?
At most universities, you and your supervisor will choose the internal and external examiners yourselves. This is because the examiners must have extensive knowledge of the thesis topic in order to be able to examine you and, as the author of the thesis in question, who else could better determine who they might be than you and your supervisor. The internal examiner is usually quite easy to find given they will be from your institution, but the external examiner may end up being your second or third preference depending on availability.
Can I Take Notes Into a Viva?
A viva is about testing your competence, not your memory. As such, you are allowed to take notes and other supporting material in with you. However, keep in mind that your examiners will not be overly impressed if you constantly have to refer to your notes to answer each question. Because of this, many students prefer to take an annotated copy of their thesis, with important points already highlighted and key chapters marked with post-it notes.
In addition to an annotated copy of a thesis, some students also take:
- a list of questions they would like to ask the examiners,
- notes that were created during their preparation,
- a list of minor corrections they have already identified from their viva prep work.
How Do I Prepare for a PhD Viva?
There are several ways to prepare for a PhD viva, one of the most effective being a mock viva voce examination . This allows you to familiarise yourself with the type of viva questions you will be asked and identify any weak areas you need to improve. They also give you the opportunity to practise without the pressure, giving you more time to think about your answers which will help to make sure that you know your thesis inside out. However, a mock viva exam is just one of many methods available to you – some of the other viva preparation methods can be found on our “ How to Prepare for a PhD Viva ” page.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.

13 Tips to Prepare for Your PhD Dissertation Defense
How well do you know your project? Years of experiments, analysis of results, and tons of literature study, leads you to how well you know your research study. And, PhD dissertation defense is a finale to your PhD years. Often, researchers question how to excel at their thesis defense and spend countless hours on it. Days, weeks, months, and probably years of practice to complete your doctorate, needs to surpass the dissertation defense hurdle.
In this article, we will discuss details of how to excel at PhD dissertation defense and list down some interesting tips to prepare for your thesis defense.
Table of Contents
What Is Dissertation Defense?
Dissertation defense or Thesis defense is an opportunity to defend your research study amidst the academic professionals who will evaluate of your academic work. While a thesis defense can sometimes be like a cross-examination session, but in reality you need not fear the thesis defense process and be well prepared.
Source: https://www.youtube.com/c/JamesHaytonPhDacademy
What are the expectations of committee members.
Choosing the dissertation committee is one of the most important decision for a research student. However, putting your dissertation committee becomes easier once you understand the expectations of committee members.
The basic function of your dissertation committee is to guide you through the process of proposing, writing, and revising your dissertation. Moreover, the committee members serve as mentors, giving constructive feedback on your writing and research, also guiding your revision efforts.
The dissertation committee is usually formed once the academic coursework is completed. Furthermore, by the time you begin your dissertation research, you get acquainted to the faculty members who will serve on your dissertation committee. Ultimately, who serves on your dissertation committee depends upon you.
Some universities allow an outside expert (a former professor or academic mentor) to serve on your committee. It is advisable to choose a faculty member who knows you and your research work.
How to Choose a Dissertation Committee Member?
- Avoid popular and eminent faculty member
- Choose the one you know very well and can approach whenever you need them
- A faculty member whom you can learn from is apt.
- Members of the committee can be your future mentors, co-authors, and research collaborators. Choose them keeping your future in mind.
How to Prepare for Dissertation Defense?

1. Start Your Preparations Early
Thesis defense is not a 3 or 6 months’ exercise. Don’t wait until you have completed all your research objectives. Start your preparation well in advance, and make sure you know all the intricacies of your thesis and reasons to all the research experiments you conducted.
2. Attend Presentations by Other Candidates
Look out for open dissertation presentations at your university. In fact, you can attend open dissertation presentations at other universities too. Firstly, this will help you realize how thesis defense is not a scary process. Secondly, you will get the tricks and hacks on how other researchers are defending their thesis. Finally, you will understand why dissertation defense is necessary for the university, as well as the scientific community.
3. Take Enough Time to Prepare the Slides
Dissertation defense process harder than submitting your thesis well before the deadline. Ideally, you could start preparing the slides after finalizing your thesis. Spend more time in preparing the slides. Make sure you got the right data on the slides and rephrase your inferences, to create a logical flow to your presentation.
4. Structure the Presentation
Do not be haphazard in designing your presentation. Take time to create a good structured presentation. Furthermore, create high-quality slides which impresses the committee members. Make slides that hold your audience’s attention. Keep the presentation thorough and accurate, and use smart art to create better slides.
5. Practice Breathing Techniques
Watch a few TED talk videos and you will notice that speakers and orators are very fluent at their speech. In fact, you will not notice them taking a breath or falling short of breath. The only reason behind such effortless oratory skill is practice — practice in breathing technique.
Moreover, every speaker knows how to control their breath. Long and steady breaths are crucial. Pay attention to your breathing and slow it down. All you need I some practice prior to this moment.
6. Create an Impactful Introduction
The audience expects a lot from you. So your opening statement should enthrall the audience. Furthermore, your thesis should create an impact on the members; they should be thrilled by your thesis and the way you expose it.
The introduction answers most important questions, and most important of all “Is this presentation worth the time?” Therefore, it is important to make a good first impression , because the first few minutes sets the tone for your entire presentation.
7. Maintain Your Own List of Questions
While preparing for the presentation, make a note of all the questions that you ask yourself. Try to approach all the questions from a reader’s point of view. You could pretend like you do not know the topic and think of questions that could help you know the topic much better.
The list of questions will prepare you for the questions the members may pose while trying to understand your research. Attending other candidates’ open discussion will also help you assume the dissertation defense questions.
8. Practice Speech and Body Language
After successfully preparing your slides and practicing, you could start focusing on how you look while presenting your thesis. This exercise is not for your appearance but to know your body language and relax if need be.
Pay attention to your body language. Stand with your back straight, but relax your shoulders. The correct posture will give you the feel of self-confidence. So, observe yourself in the mirror and pay attention to movements you make.
9. Give Mock Presentation
Giving a trial defense in advance is a good practice. The most important factor for the mock defense is its similarity to your real defense, so that you get the experience that prepares for the actual defense.
10. Learn How to Handle Mistakes
Everyone makes mistakes. However, it is important to carry on. Do not let the mistakes affect your thesis defense. Take a deep breath and move on to the next point.
11. Do Not Run Through the Presentation
If you are nervous, you would want to end the presentation as soon as possible. However, this situation will give rise to anxiety and you will speak too fast, skipping the essential details. Eventually, creating a fiasco of your dissertation defense .
12. Get Plenty of Rest
Out of the dissertation defense preparation points, this one is extremely important. Obviously, sleeping a day before your big event is hard, but you have to focus and go to bed early, with the clear intentions of getting the rest you deserve.
13. Visualize Yourself Defending Your Thesis
This simple exercise creates an immense impact on your self-confidence. All you have to do is visualize yourself giving a successful presentation each evening before going to sleep. Everyday till the day of your thesis defense, see yourself standing in front of the audience and going from one point to another.
This exercise takes a lot of commitment and persistence, but the results in the end are worth it. Visualization makes you see yourself doing the scary thing of defending your thesis.
If you have taken all these points into consideration, you are ready for your big day. You have worked relentlessly for your PhD degree , and you will definitely give your best in this final step.
Have you completed your thesis defense? How did you prepare for it and how was your experience throughout your dissertation defense ? Do write to us or comment below.
The tips are very useful.I will recomend it to our students.
Excellent. As a therapist trying to help a parent of a candidate, I am very impressed and thankful your concise, clear, action-oriented article. Thank you.
Thanks for your sharing. It is so good. I can learn a lot from your ideas. Hope that in my dissertation defense next time I can pass
The tips are effective. Will definitely apply them in my dissertation.
My dissertation defense is coming up in less than two weeks from now, I find this tips quite instructive, I’ll definitely apply them. Thank you so much.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Reporting Research
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for data interpretation
In research, choosing the right approach to understand data is crucial for deriving meaningful insights.…

Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right approach
The process of choosing the right research design can put ourselves at the crossroads of…

- Career Corner
Unlocking the Power of Networking in Academic Conferences
Embarking on your first academic conference experience? Fear not, we got you covered! Academic conferences…

Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making
Research recommendations play a crucial role in guiding scholars and researchers toward fruitful avenues of…

- AI in Academia
Disclosing the Use of Generative AI: Best practices for authors in manuscript preparation
The rapid proliferation of generative and other AI-based tools in research writing has ignited an…
Setting Rationale in Research: Cracking the code for excelling at research
Mitigating Survivorship Bias in Scholarly Research: 10 tips to enhance data integrity
The Power of Proofreading: Taking your academic work to the next level
Facing Difficulty Writing an Academic Essay? — Here is your one-stop solution!

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What would be most effective in reducing research misconduct?

Defending Your Dissertation: A Guide

Written by Luke Wink-Moran | Photo by insta_photos
Dissertation defenses are daunting, and no wonder; it’s not a “dissertation discussion,” or a “dissertation dialogue.” The name alone implies that the dissertation you’ve spent the last x number of years working on is subject to attack. And if you don’t feel trepidation for semantic reasons, you might be nervous because you don’t know what to expect. Our imaginations are great at making The Unknown scarier than reality. The good news is that you’ll find in this newsletter article experts who can shed light on what dissertations defenses are really like, and what you can do to prepare for them.
The first thing you should know is that your defense has already begun. It started the minute you began working on your dissertation— maybe even in some of the classes you took beforehand that helped you formulate your ideas. This, according to Dr. Celeste Atkins, is why it’s so important to identify a good mentor early in graduate school.
“To me,” noted Dr. Atkins, who wrote her dissertation on how sociology faculty from traditionally marginalized backgrounds teach about privilege and inequality, “the most important part of the doctoral journey was finding an advisor who understood and supported what I wanted from my education and who was willing to challenge me and push me, while not delaying me. I would encourage future PhDs to really take the time to get to know the faculty before choosing an advisor and to make sure that the members of their committee work well together.”
Your advisor will be the one who helps you refine arguments and strengthen your work so that by the time it reaches your dissertation committee, it’s ready. Next comes the writing process, which many students have said was the hardest part of their PhD. I’ve included this section on the writing process because this is where you’ll create all the material you’ll present during your defense, so it’s important to navigate it successfully. The writing process is intellectually grueling, it eats time and energy, and it’s where many students find themselves paddling frantically to avoid languishing in the “All-But-Dissertation” doldrums. The writing process is also likely to encroach on other parts of your life. For instance, Dr. Cynthia Trejo wrote her dissertation on college preparation for Latin American students while caring for a twelve-year-old, two adult children, and her aging parents—in the middle of a pandemic. When I asked Dr. Trejo how she did this, she replied:
“I don’t take the privilege of education for granted. My son knew I got up at 4:00 a.m. every morning, even on weekends, even on holidays; and it’s a blessing that he’s seen that work ethic and that dedication and the end result.”
Importantly, Dr. Trejo also exercised regularly and joined several online writing groups at UArizona. She mobilized her support network— her partner, parents, and even friends from high school to help care for her son.
The challenges you face during the writing process can vary by discipline. Jessika Iwanski is an MD/PhD student who in 2022 defended her dissertation on genetic mutations in sarcomeric proteins that lead to severe, neonatal dilated cardiomyopathy. She described her writing experience as “an intricate process of balancing many things at once with a deadline (defense day) that seems to be creeping up faster and faster— finishing up experiments, drafting the dissertation, preparing your presentation, filling out all the necessary documents for your defense and also, for MD/PhD students, beginning to reintegrate into the clinical world (reviewing your clinical knowledge and skill sets)!”
But no matter what your unique challenges are, writing a dissertation can take a toll on your mental health. Almost every student I spoke with said they saw a therapist and found their sessions enormously helpful. They also looked to the people in their lives for support. Dr. Betsy Labiner, who wrote her dissertation on Interiority, Truth, and Violence in Early Modern Drama, recommended, “Keep your loved ones close! This is so hard – the dissertation lends itself to isolation, especially in the final stages. Plus, a huge number of your family and friends simply won’t understand what you’re going through. But they love you and want to help and are great for getting you out of your head and into a space where you can enjoy life even when you feel like your dissertation is a flaming heap of trash.”
While you might sometimes feel like your dissertation is a flaming heap of trash, remember: a) no it’s not, you brilliant scholar, and b) the best dissertations aren’t necessarily perfect dissertations. According to Dr. Trejo, “The best dissertation is a done dissertation.” So don’t get hung up on perfecting every detail of your work. Think of your dissertation as a long-form assignment that you need to finish in order to move onto the next stage of your career. Many students continue revising after graduation and submit their work for publication or other professional objectives.
When you do finish writing your dissertation, it’s time to schedule your defense and invite friends and family to the part of the exam that’s open to the public. When that moment comes, how do you prepare to present your work and field questions about it?
“I reread my dissertation in full in one sitting,” said Dr. Labiner. “During all my time writing it, I’d never read more than one complete chapter at a time! It was a huge confidence boost to read my work in full and realize that I had produced a compelling, engaging, original argument.”
There are many other ways to prepare: create presentation slides and practice presenting them to friends or alone; think of questions you might be asked and answer them; think about what you want to wear or where you might want to sit (if you’re presenting on Zoom) that might give you a confidence boost. Iwanksi practiced presenting with her mentor and reviewed current papers to anticipate what questions her committee might ask. If you want to really get in the zone, you can emulate Dr. Labiner and do a full dress rehearsal on Zoom the day before your defense.
But no matter what you do, you’ll still be nervous:
“I had a sense of the logistics, the timing, and so on, but I didn’t really have clear expectations outside of the structure. It was a sort of nebulous three hours in which I expected to be nauseatingly terrified,” recalled Dr. Labiner.
“I expected it to be terrifying, with lots of difficult questions and constructive criticism/comments given,” agreed Iwanski.
“I expected it to be very scary,” said Dr. Trejo.
“I expected it to be like I was on trial, and I’d have to defend myself and prove I deserved a PhD,” said Dr Atkins.
And, eventually, inexorably, it will be time to present.
“It was actually very enjoyable” said Iwanski. “It was more of a celebration of years of work put into this project—not only by me but by my mentor, colleagues, lab members and collaborators! I felt very supported by all my committee members and, rather than it being a rapid fire of questions, it was more of a scientific discussion amongst colleagues who are passionate about heart disease and muscle biology.”
“I was anxious right when I logged on to the Zoom call for it,” said Dr. Labiner, “but I was blown away by the number of family and friends that showed up to support me. I had invited a lot of people who I didn’t at all think would come, but every single person I invited was there! Having about 40 guests – many of them joining from different states and several from different countries! – made me feel so loved and celebrated that my nerves were steadied very quickly. It also helped me go into ‘teaching mode’ about my work, so it felt like getting to lead a seminar on my most favorite literature.”
“In reality, my dissertation defense was similar to presenting at an academic conference,” said Dr. Atkins. “I went over my research in a practiced and organized way, and I fielded questions from the audience.
“It was a celebration and an important benchmark for me,” said Dr. Trejo. “It was a pretty happy day. Like the punctuation at the end of your sentence: this sentence is done; this journey is done. You can start the next sentence.”
If you want to learn more about dissertations in your own discipline, don’t hesitate to reach out to graduates from your program and ask them about their experiences. If you’d like to avail yourself of some of the resources that helped students in this article while they wrote and defended their dissertations, check out these links:
The Graduate Writing Lab
https://thinktank.arizona.edu/writing-center/graduate-writing-lab
The Writing Skills Improvement Program
https://wsip.arizona.edu
Campus Health Counseling and Psych Services
https://caps.arizona.edu
https://www.scribbr.com/
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to prepare an excellent thesis defense
What is a thesis defense?
How long is a thesis defense, what happens at a thesis defense, your presentation, questions from the committee, 6 tips to help you prepare for your thesis defense, 1. anticipate questions and prepare for them, 2. dress for success, 3. ask for help, as needed, 4. have a backup plan, 5. prepare for the possibility that you might not know an answer, 6. de-stress before, during, and after, frequently asked questions about preparing an excellent thesis defense, related articles.
If you're about to complete, or have ever completed a graduate degree, you have most likely come across the term "thesis defense." In many countries, to finish a graduate degree, you have to write a thesis .
A thesis is a large paper, or multi-chapter work, based on a topic relating to your field of study.
Once you hand in your thesis, you will be assigned a date to defend your work. Your thesis defense meeting usually consists of you and a committee of two or more professors working in your program. It may also include other people, like professionals from other colleges or those who are working in your field.
During your thesis defense, you will be asked questions about your work. The main purpose of your thesis defense is for the committee to make sure that you actually understand your field and focus area.
The questions are usually open-ended and require the student to think critically about their work. By the time of your thesis defense, your paper has already been evaluated. The questions asked are not designed so that you actually have to aggressively "defend" your work; often, your thesis defense is more of a formality required so that you can get your degree.
- Check with your department about requirements and timing.
- Re-read your thesis.
- Anticipate questions and prepare for them.
- Create a back-up plan to deal with technology hiccups.
- Plan de-stressing activities both before, and after, your defense.
How long your oral thesis defense is depends largely on the institution and requirements of your degree. It is best to consult your department or institution about this. In general, a thesis defense may take only 20 minutes, but it may also take two hours or more. The length also depends on how much time is allocated to the presentation and questioning part.
Tip: Check with your department or institution as soon as possible to determine the approved length for a thesis defense.
First of all, be aware that a thesis defense varies from country to country. This is just a general overview, but a thesis defense can take many different formats. Some are closed, others are public defenses. Some take place with two committee members, some with more examiners.
The same goes for the length of your thesis defense, as mentioned above. The most important first step for you is to clarify with your department what the structure of your thesis defense will look like. In general, your thesis defense will include:
- your presentation of around 20-30 minutes
- questions from the committee
- questions from the audience (if the defense is public and the department allows it)
You might have to give a presentation, often with Powerpoint, Google slides, or Keynote slides. Make sure to prepare an appropriate amount of slides. A general rule is to use about 10 slides for a 20-minute presentation.
But that also depends on your specific topic and the way you present. The good news is that there will be plenty of time ahead of your thesis defense to prepare your slides and practice your presentation alone and in front of friends or family.
Tip: Practice delivering your thesis presentation in front of family, friends, or colleagues.
You can prepare your slides by using information from your thesis' first chapter (the overview of your thesis) as a framework or outline. Substantive information in your thesis should correspond with your slides.
Make sure your slides are of good quality— both in terms of the integrity of the information and the appearance. If you need more help with how to prepare your presentation slides, both the ASQ Higher Education Brief and James Hayton have good guidelines on the topic.
The committee will ask questions about your work after you finish your presentation. The questions will most likely be about the core content of your thesis, such as what you learned from the study you conducted. They may also ask you to summarize certain findings and to discuss how your work will contribute to the existing body of knowledge.
Tip: Read your entire thesis in preparation of the questions, so you have a refreshed perspective on your work.
While you are preparing, you can create a list of possible questions and try to answer them. You can foresee many of the questions you will get by simply spending some time rereading your thesis.
Here are a few tips on how to prepare for your thesis defense:
You can absolutely prepare for most of the questions you will be asked. Read through your thesis and while you're reading it, create a list of possible questions. In addition, since you will know who will be on the committee, look at the academic expertise of the committee members. In what areas would they most likely be focused?
If possible, sit at other thesis defenses with these committee members to get a feel for how they ask and what they ask. As a graduate student, you should generally be adept at anticipating test questions, so use this advantage to gather as much information as possible before your thesis defense meeting.
Your thesis defense is a formal event, often the entire department or university is invited to participate. It signals a critical rite of passage for graduate students and faculty who have supported them throughout a long and challenging process.
While most universities don't have specific rules on how to dress for that event, do regard it with dignity and respect. This one might be a no-brainer, but know that you should dress as if you were on a job interview or delivering a paper at a conference.
It might help you deal with your stress before your thesis defense to entrust someone with the smaller but important responsibilities of your defense well ahead of schedule. This trusted person could be responsible for:
- preparing the room of the day of defense
- setting up equipment for the presentation
- preparing and distributing handouts
Technology is unpredictable. Life is too. There are no guarantees that your Powerpoint presentation will work at all or look the way it is supposed to on the big screen. We've all been there. Make sure to have a plan B for these situations. Handouts can help when technology fails, and an additional clean shirt can save the day if you have a spill.
One of the scariest aspects of the defense is the possibility of being asked a question you can't answer. While you can prepare for some questions, you can never know exactly what the committee will ask.
There will always be gaps in your knowledge. But your thesis defense is not about being perfect and knowing everything, it's about how you deal with challenging situations. You are not expected to know everything.
James Hayton writes on his blog that examiners will sometimes even ask questions they don't know the answer to, out of curiosity, or because they want to see how you think. While it is ok sometimes to just say "I don't know", he advises to try something like "I don't know, but I would think [...] because of x and y, but you would need to do [...] in order to find out.” This shows that you have the ability to think as an academic.
You will be nervous. But your examiners will expect you to be nervous. Being well prepared can help minimize your stress, but do know that your examiners have seen this many times before and are willing to help, by repeating questions, for example. Dora Farkas at finishyourthesis.com notes that it’s a myth that thesis committees are out to get you.
Two common symptoms of being nervous are talking really fast and nervous laughs. Try to slow yourself down and take a deep breath. Remember what feels like hours to you are just a few seconds in real life.
- Try meditational breathing right before your defense.
- Get plenty of exercise and sleep in the weeks prior to your defense.
- Have your clothes or other items you need ready to go the night before.
- During your defense, allow yourself to process each question before answering.
- Go to dinner with friends and family, or to a fun activity like mini-golf, after your defense.
Allow yourself to process each question, respond to it, and stop talking once you have responded. While a smile can often help dissolve a difficult situation, remember that nervous laughs can be irritating for your audience.
We all make mistakes and your thesis defense will not be perfect. However, careful preparation, mindfulness, and confidence can help you feel less stressful both before, and during, your defense.
Finally, consider planning something fun that you can look forward to after your defense.
It is completely normal to be nervous. Being well prepared can help minimize your stress, but do know that your examiners have seen this many times before and are willing to help, by repeating questions for example if needed. Slow yourself down, and take a deep breath.
Your thesis defense is not about being perfect and knowing everything, it's about how you deal with challenging situations. James Hayton writes on his blog that it is ok sometimes to just say "I don't know", but he advises to try something like "I don't know, but I would think [...] because of x and y, you would need to do [...] in order to find out".
Your Powerpoint presentation can get stuck or not look the way it is supposed to do on the big screen. It can happen and your supervisors know it. In general, handouts can always save the day when technology fails.
- Dress for success.
- Ask for help setting up.
- Have a backup plan (in case technology fails you).
- Deal with your nerves.

Changes are coming to this website. Learn more ➜
Preparing for your phd thesis defence.
As you start thinking about the end stages of your PhD, it’s important to understand the processes and timelines related to the thesis defence so that your degree completion is not delayed. Even if your thesis defence seems far away, there are several planning considerations you can consider early on to help the end stages of your PhD go smoothly.
On this page you will find videos, tools, and information about what the PhD thesis defence is , timelines for the PhD thesis defence , and tips for a successful PhD thesis defence .
All PhD students should also ensure that they read the PhD thesis examination regulations and review the thesis preparation guidelines prior to their oral defence. If your thesis defence will be conducted remotely, you should also review the process for a remote thesis defence .
What is the PhD defence?
Understanding the purpose, processes and possible outcomes of the thesis defence can help you feel more prepared for the defence itself. In this video, you’ll learn about what the defence is, who’s there, what happens, and the deliberation and range of possible outcomes.
Transcript - Demystifying the thesis defence at University of Waterloo (PDF)
You may wish to learn more about some of the topics discussed in this video. Here are some helpful links to learn more:
Examination committee members (including the external examiner): Visit the PhD thesis examination regulations section on the PhD thesis examining committee for more information about the committee members, including information about the external examiner and conflicts of interest.
- Closed thesis defences and non-disclosure agreements: Visit the PhD thesis examination regulations section on guidelines for thesis examination without public disclosure for more information about closed thesis examinations.
- Thesis defence decisions and outcomes: Visit the PhD thesis examination regulations section on decisions for additional information about decisions and outcomes.
- Thesis submission: Visit the thesis submission webpage for information about the thesis submission process, including approvals that must be obtained before submitting your thesis.
- UWSpace: Visit the Library’s UWSpace webpage for information about what UWSpace is and how to submit, or deposit, your thesis to UWSpace.
Timeline to defence
Early planning considerations.
Well before your defence date, there are several considerations to think about that can help make the end stages of your degree go smoothly and ensure your defence date and degree completion are not delayed:
- Being aware of formatting requirements will save you time on revisions later on – the last thing you want to be doing before submitting your thesis to UWSpace is updating page numbers or your table of contents! Consider using the Microsoft Word or LaTeX thesis template produced by Information Systems & Technology.
- The Dissertation Boost Camp can help you develop effective writing practices and strategies for completing your thesis, while the three-part Rock Your Thesis workshop series will provide practical guidance for planning, writing, revising, and submitting your thesis project. You can also book an individual appointment to do backwards planning with an advisor. They can help you utilize the planning tools most effectively, while providing hands-on guidance and feedback.
- If you are using third-party content, including your own previously published work in your thesis, or seeking intellectual property protection (for yourself or another involved party), there may be implications for your thesis or defence. Learn more about copyright for your thesis , and email [email protected] for help with copyright questions related to your thesis.
- Depending on your departmental or discipline’s norms, you may require approval from your entire committee, or just your supervisor. Ensure you talk with your supervisor and/or committee early on to confirm processes and timelines, so you’re not surprised later.
- Depending on your departmental or discipline’s norms, your supervisor may select an external examiner themselves, or they may seek your input. Talk to your supervisor early on about this process, as in some faculties the external examiner may need to be vetted and approved as early as the term before you wish to defend. Remember that there are conflict of interest guidelines around the appointment of the external examiner , and the PhD candidate should not be in communication with the external examiner prior to the defence.
- A PhD thesis must be on display for a minimum of 4 weeks prior to the defence date. To accommodate, you may need to submit your thesis as early as 6-8 weeks prior to your defence. Review your faculty specific backwards planning tool for the thesis submission deadline in your faculty and learn more about the display period in the PhD thesis examination regulations.
- After your successful thesis defence, you will likely have some required revisions to your thesis. It’s important to understand revision timelines , especially if you’re hoping to become “degree complete” before a tuition refund or convocation deadline. Find tuition refund and convocation deadlines in the important dates calendar .
- Following your thesis defence, there are several steps to be taken before your final, approved thesis is accepted in UWSpace. Ensure that you’re aware of these thesis submission steps and timelines in advance.
Backwards planning tools
Graduate Studies and Postdoctoral Affairs, in collaboration with the Faculties, have prepared faculty specific backwards planning tools to help PhD candidates map out the timelines related to their thesis defence and degree completion.
Select your faculty below to download a PDF copy of the backwards planning tool. We encourage you to discuss your ideal timelines with your supervisor(s) and your department graduate program co-ordinator.
- Faculty of Health backwards planning tool (PDF)
- Faculty of Arts backwards planning tool (PDF)
- Faculty of Engineering backwards planning tool (PDF)
- Faculty of Environment backwards planning tool (PDF)
- Faculty of Mathematics backwards planning tool (PDF)
- Faculty of Science backwards planning tool (PDF)
Tips for success
The PhD thesis defence is the culmination of years of hard work! The tips outlined in this video, compiled from recent PhD graduates and experienced thesis defence chairs, cover tips for preparing for your defence, day-of logistics, and defending successfully.
Transcript - Your Thesis Defence: Tips for Success (PDF)
Will your PhD thesis defence be held remotely? We’ve compiled additional tips for success specifically related to the remote defence.

Graduate Studies and Postdoctoral Affairs (GSPA)
Graduate Studies Academic Calendar
Website feedback
- Contact Waterloo
- Maps & Directions
- Accessibility
The University of Waterloo acknowledges that much of our work takes place on the traditional territory of the Neutral, Anishinaabeg, and Haudenosaunee peoples. Our main campus is situated on the Haldimand Tract, the land granted to the Six Nations that includes six miles on each side of the Grand River. Our active work toward reconciliation takes place across our campuses through research, learning, teaching, and community building, and is co-ordinated within the Office of Indigenous Relations .
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Prepare for Your Dissertation Defense

4-minute read
- 1st August 2023
After years of research and study, you’ve finally reached the grand finale of your PhD years: your dissertation defense. Since defending your dissertation is the culmination of all your hard work, it’s essential to do everything you can to prepare for it.
In this post, we’ll take you through how to ready yourself for your dissertation defense so you can focus on your accomplishments and excel during this crucial professional moment.
What is a Dissertation Defense?
The dissertation defense is the crowning moment of years of research – the final examination before a PhD student is awarded their doctoral degree.
During a dissertation defense, the student presents their research, methodology, findings, and conclusions to a committee of faculty members and experts in their field. The committee then engages in a question-and-answer session to assess the student’s understanding of the subject matter, the quality of their research, and their ability to defend their work under scrutiny.
Many PhD students consider it to be the defining moment of their academic career and their chance to prove their expertise in their chosen research field.
If all this sounds overwhelming – don’t worry. If you’re a PhD student, you’ll have plenty of time and opportunity to adequately prepare for your dissertation defense. Below are some strategies to help you get ready for this significant occasion in your career.
1. Know the Requirements
Familiarize yourself with your institution’s guidelines and requirements for the defense process. Understanding the format, time limit, and expectations for the presentation will help you to prepare your material and anticipate any issues.
2. Review Your Dissertation
Even if you think you know it inside and out, review your dissertation from beginning to end. It may have been some time since you’ve last read and considered certain portions of your research and findings. Consider what your committee might ask about your research questions , data analysis, and conclusions.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
3. Work on Starting Strong
To begin your defense on a strong note, work on creating a clear and engaging introduction. You can start by briefly outlining the purpose of your study, research questions, and methodology . Try to stay on topic and don’t veer off track by discussing unrelated or unnecessary information.
4. Practice Presenting
Practice your presentation skills by rehearsing your defense multiple times. Focus on clarity and pacing and try to stay within the allotted time limit. It also helps to record yourself so that you can see yourself from your audience’s point of view.
5. Practice Q&A Sessions
To build your confidence, enlist friends and colleagues to conduct mock question-and-answer sessions. When practicing, remember to pause before answering questions you’re unsure of. It’s better to take your time delivering a response than it is to give an inaccurate or incorrect answer.
6. Seek Feedback
Find out if your institution offers mock defense sessions where peers or mentors play the role of the committee, ask you questions, and give feedback . You can also have colleagues, mentors, or advisors review your presentation and offer practical feedback.
7. Create Visual Aids
Think about any visual aids , such as slides, you may want to use to illustrate your defense and prepare them in advance. Be sure to check that your university allows visuals or images and that they enhance, rather than overwhelm, your presentation.
8. Stay Calm and Confident
It’s natural to feel nervous but try to stay calm and composed during your defense. Take deep breaths and remind yourself of the expertise you’ve gained through the experience of writing your dissertation.
Expert Proofreading Services
The best way to prepare for your dissertation defense is to have your dissertation professionally proofread. Our editing experts have extensive experience with a wide variety of academic subjects and topics and can help ensure your dissertation is ready for presentation. Send in a free sample of 500 words or less and get started today.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
3-minute read
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
How Do I Prepare for a Successful Defence?
Vivas and Presentations
- First Online: 19 October 2023
Cite this chapter

- Sue Reeves ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3017-0559 3 &
- Bartek Buczkowski ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-4146-3664 4
451 Accesses
Once you have submitted your dissertation, you may be asked to do a defence of your dissertation. This could be in the form of an oral presentation, a poster presentation of your findings, or you could be invited to a viva voce. Vivas, as they are usually known, are particularly common for research degrees such as MPhils or PhDs and are essentially a verbal defence of your thesis that is conducted in an interview style format. At a minimum, the viva is a way of checking you authored the thesis yourself and understand the detail, but it is also an opportunity to discuss your research findings and interpretations in depth with experts. Preparation is key for defending your thesis in a viva or a presentation format. With a bit of groundwork, you could even enjoy the discussion, after all the thesis is the culmination of all your hard work, and no one knows it better than you.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or Ebook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Ratcliffe R (2015) How to survive a PhD viva: 17 top tips. https://www.theguardian.com/higher-education-network/2015/jan/08/how-to-survive-a-phd-viva-17-top-tips. Accessed 3 Mar 2023
Further Reading
Levin P, Topping G (2006) Perfect presentations. Open University Press
Google Scholar
Smith P (2014) The PhD viva: how to prepare for your oral examination. Macmillan, New York
Book Google Scholar
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Roehampton, London, UK
Manchester Metropolitan University, Manchester, UK
Bartek Buczkowski
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Reeves, S., Buczkowski, B. (2023). How Do I Prepare for a Successful Defence?. In: Mastering Your Dissertation. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-41911-9_14
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-41911-9_14
Published : 19 October 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-41910-2
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-41911-9
eBook Packages : Biomedical and Life Sciences Biomedical and Life Sciences (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

Tips for preparing your PhD defense [EASY dissertation defense]
Embarking on the final hurdle of your doctoral journey, the PhD dissertation defense, can feel daunting.
This significant event involves presenting and justifying years of research to a committee of field experts, showcasing your comprehension, originality, and critical thinking skills.
With various expectations from committee members, it’s crucial to know what makes a compelling thesis and how to adeptly defend your arguments. Preparation is key; from choosing well-suited examiners to meticulously preparing for potential questions, every step counts.
This article provides easy-to-follow tips for this process, from how to approach revisions to the actual defense duration, ensuring a smoother dissertation defense.
Top tips for your PhD defence process
- Understand Expectations : Understand what your examiners are looking for in your thesis. They expect it to be relevant to the field, have a clear title, a comprehensive abstract, engage with relevant literature, answer clear research questions, provide a consistent argument, and make a significant contribution to knowledge. They also value the ability to show connections between different parts of the thesis and a confident, positive attitude during the defense.
- Choose the Right Examiners : Make strategic decisions when selecting your examiners. They should be experts in your field, open-minded about cross-discipline work, cited in your work, have a constructive approach, align with your methodology, and respect critical viewpoints. Consider your supervisor’s advice, as they can help identify suitable examiners.
- Thorough Preparation : Understand your institute’s specific defense requirements and practice rigorously. Break down your thesis into sections, time your presentation, focus on key points, and prepare for potential questions. Consider setting up a mock defense to familiarize yourself with the process.
- Master Your Content : Understand your work inside out. Rather than cramming as much information as possible, focus on thoroughly comprehending your research. If faced with an unexpected question during the defense, take a moment to formulate an organized response.
- Manage Your Time : Be aware that dissertation defenses usually last between one to three hours, so ensure your presentation fits within this timeframe. Remember, the defense is an opportunity to showcase your hard work. Be confident and composed throughout the process.
What Is Dissertation Defense?
A PhD defense, also known as a viva , is a critical process that marks the completion of a doctoral degree. It varies from one institution to another and between different countries.
It could be a private examination by a panel of experts in the field or a public defense before an audience.
In this defense, you present and justify the research you have conducted over many years.
You’ll engage in a rigorous academic conversation about the different aspects of your research, answer questions, and explain your findings and their implications.
The defense is a chance for the panel to test your comprehension of your chosen subject area, your work’s originality, and its contribution to the field. It also tests your ability to think critically, to articulate your thoughts, and how effectively you can defend your arguments under pressure.
The essence of a PhD defense is not only to assess the validity of the thesis but also to assess the candidate’s proficiency in their subject.
What Are the Expectations of PhD Defence Examiners? Understand your dissertation committee.
Meeting the expectations of committee members in the context of a dissertation is essential for the successful completion of the research.
They will have read your thesis and will be looking for any mistakes or areas that they are unsure about to ask you during your PhD defence.
Here are what PhD defence examiners are looking for in your thesis and may have questions at your oral defence:
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Relevance to Field | The thesis must be clearly relevant to the specific academic field. |
| Clear Title | The thesis should have a clear, descriptive, and concise title. |
| Clear Abstract | The abstract should provide a good overview of the research and its findings. |
| Relevant Literature Review | The thesis should engage with the existing academic literature relevant to the research topic. |
| Research Questions | Research questions should be clear, relevant, and answered in the course of the research. |
| Consistent Argument | The thesis should contain a clear and consistent argument throughout. |
| Conceptual Conclusions | The conclusions should not only summarize the research findings but also relate back to the literature review and conceptual issues raised. |
| Contribution to Knowledge | The thesis should make a significant contribution to the field of knowledge. |
| Ability to think interconnectedly | The ability to show connections between different parts of the thesis is important, as it demonstrates a higher level of thinking. |
| Pleasurable Text | The text should be enjoyable to read, well-written, and explicit in terms of ideas and concepts. |
| Positive Attitude | The candidate should demonstrate confidence, enjoyment, and a positive attitude during the Viva (oral examination), symbolized by smiling with the examiners, not at them. |
| Display of interconnectedness | The thesis should clearly show how various parts are interconnected, ultimately achieving synergy. |
A dissertation committee typically consists of external experts (in a similar field) who will engage in robust discussion about your PhD and submitted thesis.
As committee members, their primary role is to actively engage with the dissertation research, offering constructive feedback and suggestions as well as deciding if you have satisfied the requirements of the university to be awarded a PhD
Here’s my video about the common questions you’ll likely encounter during your defence and how you can answer them:
How to Choose your PhD examiners and committee members
Choosing your PhD examiners requires strategic thinking and insightful conversations with your supervisor. It’s a very important decision and can make your PhD defence much smoother.
During my PhD, I chose examiners that I had cited and based my work on their preliminary investigations.
But there are more things to think about before you write down their names!
Here’s a table checklist for choosing your PhD examiners.
| CHECKLIST | NOTES |
|---|---|
| Expert in relevant field | Your examiners should be well-acquainted with your research topic and be able to provide relevant and informed feedback. |
| Interdisciplinary knowledge | If your thesis spans multiple disciplines, it would be helpful to have examiners who understand all the fields involved. |
| Open-minded about cross-discipline work | Ensure your examiner is open-minded about works integrating different disciplines, as each field has unique ways of presenting findings. |
| Cited in your work | Consider examiners who you have cited in your work, as they are familiar with the type of work you’re doing. |
| Constructive Approach | Avoid examiners known for overly harsh or destructive feedback, you want someone who can critically analyze your work but also provide constructive comments. |
| Alignment with your methodology | The examiner should understand and ideally endorse the methodology you used. This ensures that they can productively critique your work’s design and execution. |
| Respect for critical viewpoints | If you’ve critiqued a particular scholar’s work in your thesis, ensure the scholar is professional enough to respect different viewpoints if considering them as an examiner. |
| Supervisor’s advice | Pay heed to your supervisor’s advice as they have experience in identifying suitable and appropriate examiners. |
First, compile a list of potential examiners who you believe would be appropriate for reviewing your thesis. Discuss your choices with your supervisor, explaining why you consider them suitable.
If your thesis spans multiple disciplines, consider choosing examiners from each discipline; it ensures intricate knowledge of each field is utilized.
However, ensure these examiners are open-minded about cross-discipline work, as disciplines tend to have unique ways of presenting their findings.
Listen to your supervisor’s advice.
They have experience in these matters and know who would be best qualified to examine your work.
Even if a scholar is high-profile or an editor of a favored journal, they might not be suitable due to methodological differences or varying research approaches.
Choosing the right examiner is crucial, as an ill-suited examiner could result in undesired outcomes. The goal is to establish a thoughtful academic conversation about your work.
How to Prepare for Dissertation Defense?
To prepare for your dissertation defense, start by understanding the specific requirements of your institute, as the process can vary across countries.
This could include:
- a presentation,
- a conversation with examiners,
- or a combination of both.
Once you know what to expect, practice vigorously. This should not be your first time discussing your work with others – engage in academic conversation, seek feedback and address challenging questions prior to the defense.
Breakdown your thesis into sections and time yourself on each section to manage length. Focus on the key points and avoid irrelevant details.
Creating a mock defense will be helpful in managing time and getting familiar with the process.
Prepare for potential questions. It’s not about cramming as much information as possible, but about understanding your work inside out. Start by preparing answers to common defense questions. In case of an unexpected question, don’t rush to answer. Take a moment, write down key points, and formulate an organized response.
Remember that the defense is an opportunity to showcase years of hard work.
Be confident, and don’t forget to breathe!
How Long Do Dissertation Defenses Usually Last?
The length of a dissertation defense can vary depending on factors such as the specific requirements of the institution and the complexity of the research being presented.
On average, a dissertation defense usually lasts between one to three hours.
During this time, the candidate will present their research and findings to a panel of experts, often including faculty members and fellow researchers.
The defense typically begins with an introduction by the candidate, followed by a detailed presentation of the research methodology, results, and conclusions.
Panel members then have the opportunity to ask questions and engage in a discussion with the candidate.
It is not unusual for defenses to be quite intense and challenging, as the panel seeks to assess the depth of the candidate’s knowledge and understanding of their research. In some cases, the candidate may be asked to leave the room while the panel deliberates before ultimately reaching a decision on the acceptance or rejection of the dissertation.
Wrapping up
As the culmination of the doctoral journey, the PhD defense demands meticulous preparation and understanding of its unique rigors.
This entails knowing the expectations of your dissertation committee, choosing the right examiners who offer constructive feedback, and putting considerable time into preparing for your oral defense.
The defense process isn’t a mere formality; it’s a critical examination of the candidate’s comprehension, originality, and critical thinking skills.
It provides an opportunity to exhibit your research and its contribution to your field, defend your arguments, and validate your years of labor.
Thus, selecting well-qualified examiners, anticipating potential questions, and honing your presentation skills are vital for a successful defense.
Students must be registered for their PhD program and finalize their dissertation prior to the defense, which can last anywhere from one to three hours, depending on the institution and the complexity of the research.
Any corrections or major revisions suggested by the dissertation committee members must be completed and submitted weeks prior to the conferral date.
A PhD defense isn’t just a rite of passage for doctoral candidates—it’s the final, decisive step on the journey to earning a doctorate.
It requires the full commitment of the candidate, their dissertation advisor, the committee chair, and all members involved, ensuring that the graduate studies department’s requirements are met, and that the student is admitted to the next phase of their academic or professional journey.

Dr Andrew Stapleton has a Masters and PhD in Chemistry from the UK and Australia. He has many years of research experience and has worked as a Postdoctoral Fellow and Associate at a number of Universities. Although having secured funding for his own research, he left academia to help others with his YouTube channel all about the inner workings of academia and how to make it work for you.
Thank you for visiting Academia Insider.
We are here to help you navigate Academia as painlessly as possible. We are supported by our readers and by visiting you are helping us earn a small amount through ads and affiliate revenue - Thank you!

2024 © Academia Insider

Skip to content. | Skip to navigation
Personal tools
- Log in/Register Register

https://www.vitae.ac.uk/doing-research/doing-a-doctorate/completing-your-doctorate/your-viva/your-phd-viva
This page has been reproduced from the Vitae website (www.vitae.ac.uk). Vitae is dedicated to realising the potential of researchers through transforming their professional and career development.
- Vitae members' area
Defending your doctoral thesis: the PhD viva
Format for defending a doctoral thesis.
Every institution will have specific regulations for the thesis defence. In some countries or institutions, the convention is for thesis defences to be public events where you will give a lecture explaining your research, followed by a discussion with a panel of examiners (opponents). Both your examiners and the audience are able to ask questions.
In other countries, including the UK, the oral examination is usually conducted behind closed doors by at least two examiners, usually with at least one being from another institution (external examiner) and an expert in your topic of research. In the UK the supervisor does not participate in the viva, but may be allowed to observe. Sometimes someone from your own institution is appointed as an independent chair. Although it is now becoming more common for the candidate to have an opportunity to give a public lecture in UK institutions, this does not form part of the examination and may or may not be attended by the examiners.
Viva preparation
Take the preparation for your viva seriously and devote a substantial amount of time to it. The viva preparation checklist may be useful to help you prepare.
Your institution may offer courses on viva preparation and there may be opportunities to organise a practice viva. Take advantage of these opportunities: they can be extremely valuable experiences.
Things you may wish to take with you
- your thesis – mildly annotated if you wish
- a list of questions that you might be asked and your planned responses
- any questions that you want to ask your examiners
- additional notes which you have made during your revision
- list of minor corrections that you have come across during your revision.
During the viva
Your study will have strengths and weaknesses: it is essential that you are prepared to discuss both. You could think of any weaknesses as an opportunity to demonstrate your skill at critical appraisal. Examiners will seek to find and discuss weaknesses in all theses. Do not interpret criticism as indication of a possible negative outcome.
Examiners have different personalities, styles and levels of experience. Sometimes a candidate may feel that a challenge is made in a confrontational way. Experienced, effective examiners will not be inappropriately confrontational, but some will. Do not take offence. A relaxed, thoughtful, and non-confrontational response from you will help re-balance the discussion. Having an independent chair can help maintain a constructive environment.
Useful tips for during your viva:
- Ask for clarification of ambiguous questions or ask for the question to be repeated if necessary
- Take time to think before answering
- Be prepared to ask questions and enter into a dialogue with your examiners
- Be prepared to discuss your research in context of other work done in your field
- Be ready to admit if you don't know the answer to a question
- Be prepared to express opinions of your own
You are not expected to have perfect recall of your thesis and everything that you have read and done. If you get flustered, or need to refer to notes your examiners will understand. They have been in your situation themselves!
After your viva
There are several possible outcomes of a thesis defence. Most commonly, your examiners will recommend to your institution that you are awarded your degree subject to minor corrections, although in some instances they might ask for more substantial work.
Bookmark & Share
University of Rochester
Search Rochester.edu
Popular Searches
Resources for
- Prospective students
- Current students
- Faculty and staff
School of Arts & Sciences
Hajim School of Engineering & Applied Sciences
Graduate Education and Postdoctoral Affairs
- PhD Defense
Preparing for a PhD Defense
Table of contents, preparing to start, nominate a faculty member to serve as chair for your defense, selecting a defense date, international students and work visas, registration categories for defense, dissertation writing and guidelines, preparing your dissertation for defense, registering your dissertation for the final oral exam, know the rituals.
- Use PowerPoint
Public Lecture
Dress Professionally
Items to Bring to the Defense
The Closed Examination
Address Questions with Confidence
Student Status
Final corrected copies of the dissertation, publishing your final dissertation, binding your final dissertation, before defense.
Before you can start your thesis you must:
- Complete all courses, exams, and research requirements
- Meet with your advisory committee to ensure that everyone agrees that the work is ready to defend
- Decide on a date for the defense
- Inform your graduate administrator that you have started the process to prepare for your defense
A chair is appointed for each PhD oral defense to monitor and promote fairness and rigor in the conduct of the defense. To help eliminate pre-established judgments on the candidate’s work, the chair should be from a different program/department than the student. For more information about chair responsibilities, read the instructions for the chair .
You must identify a faculty member to serve as chair for your defense. The chair must be:
- A current full-time faculty member at assistant professor rank or higher
- Outside the department offering the degree program, or outside your advisor's department (interdisciplinary degree programs only)
- Someone who has not had prior involvement in your research
The selection of the chair is subject to the approval of the department/program, th Arts, Sciences and Engineering dean of graduate education and postdoctoral affairs, and the University dean of graduate studies.
The chair must be physically present during the entire defense, including the public oral presentation (if applicable) and the questioning session. The chair is welcome to read and comment on the dissertation and/or the defense presentation, but this is not required. The chair does not need to be an expert in your research area.
It is your responsibility to get a copy of the final dissertation to the chair at least one week prior to the defense.
You should begin scheduling the actual defense date three months in advance to ensure that your advisor, committee members, and chair are able to be present and that rooms are available on the date and time selected.
Defenses can be held on any day the University’s Graduate Studies Office is open (not weekends, evenings, holidays, or the days between Christmas and New Year’s). Check the academic calendar for important dates and deadlines.
Use the PhD calendar to determine the deadline dates for getting your paperwork to the Office of Graduate Education and Postdoctoral Affairs and department committee.
When all committee members and your chair agree to a specific date and time for the defense, inform your graduate administrator as soon as you possibly can, but no later than six weeks prior to your defense date . Your graduate administrator will advise you of any program-specific requirements for the defense as well as work with you to prepare for your thesis defense. They will also help you determine who will schedule the room for your thesis defense.
You should provide your committee members at least two weeks to read and comment on your dissertation before the date you need to register your dissertation.
Participating Via Video Conferencing
While you, your advisor, and the chair must all be physically present in the room for the defense, other committee members are allowed to participate in the defense remotely via Skype or other video conferencing technology so long as all committee members agree to the arrangement. This must also be approved by the AS&E dean of graduate education and postdoctoral affairs and the University dean of graduate studies before the dissertation is registered for defense.
Someone other than you and your committee must handle the IT setup and be on standby for any problems. If anyone involved finds that remote participation is interfering with the defense, he or she can request that the defense be rescheduled.
We strongly recommend that international students meet with an International Services Office (ISO) representative as soon as permission to start writing is granted. The ISO will provide information on visa options, documentation, and timelines for applying for a visa for employment in the United States.
You will register for one of the following categories while preparing your defense:
- 999: Dissertation —Indicates the PhD student has completed all of the requirements for the degree except the dissertation and is in residence as a full-time student
- 995 : Continuation of Enrollment —Indicates the PhD student has completed all of the requirements for the degree except the dissertation and is not in residence as a full-time student
See the registration page for more information about these categories.
The Preparing Your Doctoral Dissertation manual is a great resource to help you bring your dissertation up to the required standard of organization, appearance, and format for the University of Rochester. Before preparing the defense copy of your dissertation, check the contents of the manual carefully to help avoid mistakes that can be time-consuming and costly to correct.
Before beginning your dissertation, you should consult with your advisor for your department or program’s preferred style guide (APA, MLA, Chicago).
Including material produced by other authors in your dissertation can serve a legitimate research purpose, but you want to avoid copyright infringement in the process. For detailed instructions on avoiding copyright infringement, please see ProQuest’s Copyright Guide .
The University requires that you provide copies of the dissertation to your committee members and exam chair. You should check with your committee members to see if they prefer printed or electronic copies (or both). Printed copies do not need to be printed on heavyweight, expensive paper unless there is the need to do so for figures and images.
Printing and binding a dissertation can be expensive. You can use the Copy Center or FedEx Office to print and bind your dissertation.
In order to register your dissertation, you or your graduate administrator will need to create a record on the Graduate Studies PhD Completion website . This record will include:
- Degree information
- Past degrees
- Contact information
- The defense version of your dissertation as a PDF
- Other relevant documents
The version of your dissertation attached to your online record is considered the registration copy.
When your PhD completion record is finalized, committee members will receive emails with links to access your record and approve your dissertation to progress to defense. You’ll need to provide copies of the dissertation identical to the registration copy to all members of your committee, including the chair, at least two weeks before the record is finalized. Everyone but the chair is required to comment or sign off on the dissertation before it is submitted.
There may be deadlines for registering your dissertation specific to your program. Consult with your graduate administrator to ascertain those deadlines and follow them carefully.
After all committee members have provided their approval, your thesis will be reviewed by your faculty director/department chair, the AS&E dean of graduate education and postdoctoral affairs, and the office of the University dean of graduate studies. When all of these officials have approved your committee and dissertation for defense, your dissertation is considered registered. You will be able to track these approvals in your online record and will receive a confirmation email when approvals are complete.
The GEPA Office and the AS&E dean of graduate education and postdoctoral affairs, as well as the University Graduate Studies Office, may make corrections to the PDF of your dissertation. This annotated copy of your dissertation, along with the original version, will be stored in the PhD completion website. You are not allow to distribute updated versions of your dissertation prior to the defense, but be sure to incorporate any corrections before uploading your final dissertation to ProQuest®.
After the defense, if the committee has required major revisions to be approved by one or more of its members, it is your responsibility to provide them with the corrected final version for their approval. They will be asked to submit written confirmation of that approval to the University Graduate Studies Office. Failure to do so could delay conferral of your degree.
After the defense, you will receive additional instructions by email for completion of all PhD degree requirements.
It is important to walk into the defense knowing that your committee wants you to pass. Even if criticism is harsh, it is meant to be constructive. The defense is not solely an opportunity for the committee to compliment and congratulate you for the work you have done. It is also meant to challenge you and force you to consider tough questions.
The Defense
The best way to prepare for your defense is to regularly attend the defenses of your colleagues throughout your graduate program, not just several weeks prior to your own defense.
You can also talk to people in your department who already defended to find out what their defenses were like. You should also speak with your advisor to get a sense of his/her specific expectations of a defense.
Guidelines for Presentations
Use PowerPoint or Other Software to Create Slides
You should prepare a presentation of the research that comprises the thesis. Your slides should encapsulate the work and focus on its most salient contributions. In preparing, ask yourself these questions: “What do I want people to know about my thesis? What is the most important information that I can present and talk about?”
Here are some basic tips:
- Use text large enough to be read by the audience (especially text from figures)
- Ensure graphics and tables are clear
- Don’t clutter your slides—if necessary, have things come up on mouse clicks
- Use spell check and proofread your slides
- Practice your presentation with your peers
- Work on pronunciation, if required
- Time your presentation to ensure it will fit the allotted time while allowing time for questions
If your defense includes a public lecture, we recommended that you do a trial run a day or two before in the room that has been booked for your lecture. This will allow you to familiarize yourself with the space and the equipment and to address any problems that arise during the trial run.
Plan your public lecture to allow enough time for questions. Present enough information so that the audience understands what you did, why you did it, what the implications are, and what your suggestions are for future research.
Friends and family are welcome to attend your public lecture. Faculty and students in the audience are given the opportunity to ask questions.
Plan to dress professionally for the defense in the same way you would if presenting a paper at a conference or for a job interview. You will be standing for a long time on the day of your defense. You might want to keep this in mind when selecting the shoes you will wear for your defense.
Essentials for your public lecture include:
- Your presentation
- A laser pointer
- A copy of your dissertation
- A pen or pencil
- A bottle of water
You will be asked to leave the room while your committee reviews your program of study, and decides whether:
- The thesis is acceptable/not acceptable
- Whether members will ask sequential questions or whether each member will be allotted a specific time period for questioning
The person to start the questioning is designated. You will be called back into the examining room and questioning will begin. After all questions have been addressed, you will be asked to leave the room while your committee decides the outcome of the exam. You will be asked to return to the room to be informed of the outcome by the chair of your exam committee.
- Listen to the entire question no matter how long it takes the faculty member or student to ask it (take notes if necessary).
- Pause and think about the question before answering.
- Rephrase the question.
- Answer the question to the best of your ability; if you do not know the answer, remain calm and say so in a professional way.
- Remember that no one will know the ins and outs of the thesis and your research materials as well as you. You are the foremost expert in the thesis topic and YOU know the research involved. Be positive!
Possible outcomes include:
- Acceptable with minor or no revisions (no further approval required)
- Acceptable with major revisions in content or format (in this case, one or more committee members must be responsible for overseeing and approving the major revisions before the final copies are submitted)
- Not acceptable
After the Defense
You can submit the final corrected copies of your dissertation as soon as you address any remaining comments that were brought up during the defense or noted in the registration copy of your dissertation, which will be returned to you usually within a few days before or after the defense. You can take up to one semester following the defense to address any comments, during which you can remain a full-time student. Your degree conferral date will depend on when you submit the final corrected copies of your dissertation.
The day after your defense, you will receive an email from the University dean of graduate studies that provides instructions on how to:
- Submit the final corrected copies of your dissertation through ProQuest
- Provide authorization for the release of your dissertation through UR Research
- Complete a mandatory online exit survey
- Verify to the University dean of graduate studies’ office that the dissertation has been submitted
The University of Rochester requires all doctoral candidates to deposit their dissertations for publication with ProQuest Dissertation Publishing and with the University libraries. Hard copies are not required. The library receives an electronic copy of the dissertation from ProQuest, but students must give the University permission to obtain it.
For questions regarding publishing through ProQuest, contact Author Relations at [email protected] or (800) 521-0600 ext. 77020.
Check with your graduate administrator to see if your department wants a bound copy of your dissertation, and, if so, how the cost of binding is covered.
If you want a bound copy for yourself or your family, you can purchase one through ProQuest .

Applications and Funding

Career and Networking

Thesis and Dissertation
Watch talks, video talks, webinar recordings, create a talk, view on youtube, recent talk.
How I Got Accepted into an MD-PhD Program
In this video, Caretia Washington shares her journey to getting accepted…
Starting your PhD? Watch this talk.
Academic Writing Club

Online co-writing group every Tuesday and Thursday. Free to join.
No upcoming Webinars
Featured Event
Wondering how to navigate publishing your first academic paper? Listen to our first ever Space on The PhD Place.
Our Mission
Work with us, advertise with us, run a webinar, sponsored posts, write an article, stories, advice and support for your academic journey., from nerves to triumph: your personal guide to dissertation defense.
- August 26, 2023
- Aberystwyth University
- Dissertation Defence/ Viva , Mental Health , Thesis and Dissertation , Thesis Tips , Wellbeing

Picture this: after countless hours of research, writing, and refining, you’re now standing on stage with your cohort, in a gown and funny hat, because … you’ve finally completed that last important milestone in your academic journey – defending your doctoral dissertation. It’s a culmination of years of dedication, determination, and sleepless nights. You’re not there yet—but you’re close. So how do you make it past this final, nerve-wracking hurdle?
In this article, we’ll deep-dive into the dissertation defense process, with tips, strategies, and straight-up information. I’ll share my expertise as a coach whose job it is to get people up on that stage.
What to expect during the dissertation defense
A dissertation defense typically consists of an oral presentation to your dissertation committee, who have already received and read the final draft of your dissertation manuscript. Other members of your cohort and institution, and outside readers or experts, might also be present in the audience.
Without fail, I see two different reactions to this news from my coaching students: either they are terrified of having their work scrutinized by their committee in public, or they are extremely laid back, knowing that they’ve already done all the hard work in the manuscript. (These later students are the ones paying attention to me).
You probably already know the general gist of what happens in a defense presentation: you present the highlights of your study, the committee ask questions, and then they vote on whether you pass or need to complete further revision. So, here are some things you might not yet know:
• The oral defense gives the committee the opportunity to ask you about any areas of your study that are still unclear or weak on paper – so that you can prove they are not unclear or weak in real life. In other words, it’s a chance to get anything that got stuck in your head (rather than making it on to paper) out and in front of your committee.
• Your chair or supervisor and committee should not be allowing you to complete the defense process unless they are already confident that the biggest issues with your work have already been resolved.
• Questions are normal – your committee are working with you because your work interests them (hopefully), so questions are as likely to indicate their excitement about your work as a problem they have spotted.
• Revisions are normal – from requests to polish the grammar to insisting you add more supporting sources or develop your recommendations more thoroughly, “pass with revisions” is a normal, common, and expected end result. To pass with no revisions is pretty rare (although I have had a few students achieve this – looking at you, YY!) – like getting 100% on a calculus test in school.
In short, your defense presentation is nothing to be scared of. You are lined up for defense because both you and your committee feel you know your stuff, and now all you need to do is share what you’ve produced and learned and engage people in discussion about it. You got this!
Preparing for Your Dissertation Defense
Still nervous? Ok, that’s fair enough. As with many things, good preparation can help you get those nerves under control, so here are some top tips to help you get ready.

Tick the Boxes
It’s essential to understand the requirements and expectations of your defense committee. Get familiar with the specific guidelines and procedures set by your institution, and make sure you meet all necessary criteria. If you’re giving them what they ask for, you are definitely off to a strong start.
Know Your Stuff
This defense is about you showing off what you know, so before you stand up in front of the crown, take a deep dive into your own research masterpiece. Thoroughly review your dissertation, scrutinizing each chapter, section, and argument. Make notes. Look for anything that might provoke questions or debate. Remember, this is your opportunity to showcase your expertise and demonstrate the depth of your knowledge.
Seek Wise Counsel
Your advisor and committee members are the best resources you could ask for about defense. They set the guidelines, and they judge whether you have done well. Reach out to them for guidance, feedback, and advice—their collective wisdom and support can be instrumental in honing your presentation. And, if they are not all that … well, remember there are others out there who can help, including coaches, mentors, and past students.
Just like any performance, practice makes perfect. Take the time to rehearse your presentation multiple times, refining your delivery and strengthening your command over the content. By doing so, you’ll build confidence and ensure a smoother delivery when the day arrives. Even more importantly, you’ll settle the key points of your study firmly in your brain, making sure you sound like the expert you are.
Anticipate the Unknown
Obviously, you can’t predict every question or comment that will come up during your defense. However, you can still prepare yourself for potential challenges. Get cozy with the research landscape in your field and the interests of your committee members. Step outside of your own perspective and view your work through a stranger’s eyes to anticipate areas of critique or alternative viewpoints. This will enable you to respond thoughtfully and demonstrate your ability to engage in scholarly discourse.
Managing Nerves and Anxiety
You know what’s coming and you know how to prepare – are you still nervous? If so, know that that is completely normal. Here’s how me and two of my students got their dissertation defense nerves under control.
An Awesome Supervisor
For my own dissertation defense (known as a viva voce in the UK), I was incredibly lucky to have a supervisor with whom I had a strong, supportive, and nurturing relationship. Although the main examination of my work was handled by the external reader, who sat across from me behind a big desk, my supervisor sat behind him and nodded and smiled encouragingly every time I said something. Words can’t describe how much that calmed me down and gave me confidence. If you are as lucky as me and have an awesome supervisor, tell your nerves they can stand down – your supervisor’s got your back!
You Can Get Used to Anything
One of my students, who graduated last year, suffered from terrible defense nerves because she was worried about holding so much complex information in her head and delivering it coherently. Her solution? She practiced endlessly, over the course of about a month.
With me as her coach playing the role of audience, or with her kids and other family members, her cohort peers, her dog, and even other academics, she presented that study until she could do so in her sleep. The point was that, by the time the actual defense day rolled around, presenting the study to people was comfortable, familiar territory. Done and dusted!
Temporary Denial
Another student, who graduated shortly after, took completely the opposite approach to managing dissertation defense nerves. This student was burnt out from a huge rush to meet an unexpectedly tight deadline for the final manuscript when her chair decided to retire at the last minute. Rather than burn herself out further, she hit send on the manuscript, paid a designer to polish the design of the presentation rough draft, and then shut down her devices and went on holiday with her family. For one week, she did not look at or talk about her research at all. Instead, she sat on the beach, ate ice cream, and scrolled Instagram (probably). Then, she returned to work (a week before the presentation), refreshed and feeling excited about her work again. The break enabled her to practice and prepare in a calm frame of mind.
Some Parting Thoughts
I won’t walk you through the other obvious stuff, like what makes a good presentation PowerPoint or how body language and appearance can improve your presentation skills—that stuff is what Google is for. You’re an expert by now at finding the information you need, so get out there and find it. However, know that if you need help getting ready for your defense, there are definitely humans around you (and some dogs) who want to help – whether that’s your chair, your family, or a coach like me. I recommend you find them now and let them tell you just how ready for this you are.
Jennifer Harrison

Non-Academic Job Interviews: 4 Questions to Get Ready For
Are you taking the first steps into careers outside of academia? Anxious about selling yourself to a new audience post-PhD? This is normal, but with the right preparation you can knock your interview out of the park and stand out from the crowd! This article guides you through four important questions to prepare your answers for.

Great ‘Applied’ Expectations: The Importance of Gaining Real-World Experience During Your PhD
A PhD alone can’t give you all the skills and networks you will need to be competitive in the job market. This article guides you through four important benefits of real-world experience during your PhD, and how you can go about gaining this.

I would like to stay in academia after my PhD. What can I do?
Not sure of your options after your PhD? Confused by the different academic job titles, and how they relate to PhD students? Check out these five academia-oriented job options you can consider.
All views expressed are those of the individual authors and do not reflect the views of The PhD Place Ltd. See our Disclaimer
The PhD Place Ltd Is A Registered Limited Company In England & Wales, Number 14300924. C16, Ingenuity Centre, Triumph Road, University Of Nottingham Innovation Park, Nottingham, United Kingdom, NG7 2TU
© Copyright 2023. All Rights Reserved.

The Savvy Scientist
Experiences of a London PhD student and beyond
How to Defend a Thesis: An Introduction to the PhD Viva

The prospect of defending your PhD work can be more than a little daunting. It represents the climax of many years of hard work, you’ll have to defend a thesis in front of experts in your field and the whole PhD viva process can seem cloaked in mystery.
Maybe you’ve seen a labmate go for their PhD viva to then emerge several hours later, relieved but perhaps slightly dazed. Often it’ll be the case that they’ll have forgotten the specifics by the time they’ve left the room. On top of that, horror stories of bad PhD viva experiences pass through many research groups which are enough to make even the most confident and positive PhD students shake in their boots.
Having had my own PhD viva earlier this year, in addition to discussing experiences with many other PhD graduates, I now want to help you through the process.
Before we begin, I want to offer some reassurance. For most people the PhD viva is not at all the horrible experience we occasionally hear about. Even so, it’s still useful to know what to expect. I’ve therefore put together a series to help others understand the PhD viva process and how to defend a thesis.
Defend a Thesis: Overview of the PhD Viva Series
This first post will be an introduction to the PhD viva process and how to defend a thesis. Upcoming posts will cover:
- Viva Preparation: Common PhD Viva Questions
- What is a PhD Viva Like? Sharing Graduates’ Experiences
- How to Choose Your Examiners
If there is anything specific you’d like covered, please let me know! I’ll be sure to include it. If you’d like to subscribe to get notified of upcoming posts as they’re released you can do so here:
How is a PhD Assessed?
Typically the main output expected at the end of your PhD project is a thesis. You’ve put years of work into your PhD and the thesis details your contributions to your chosen research field. But how is the thesis “marked”? Who will decide if what you’ve written is actually any good?
This is where the PhD viva comes in!
The PhD viva involves you discussing and defending your work with experts in your field. The experts act as examiners to determine whether or not the university should award you a PhD based on your thesis and viva performance. The thesis is the written report submitted for a PhD, and the viva is a means of quality control to ensure that only suitable candidates are awarded a PhD by the university.
Although part of the purpose of a PhD viva is to ensure that the work is of a high quality, just as importantly it’s to check that you were the one who carried it out and that you understand what you were doing!
The PhD viva is therefore essentially an exam during which you’ll have to defend a thesis.
Here is the official “mark scheme” for a PhD at Imperial:

I recommend looking at the presentation which this screenshot came from: sadly I only came across it after my own PhD viva whilst putting together this post!
Steps to Completing a PhD
- Submit your thesis for the examiners to read ahead of the viva.
- Have the viva , where you’ll defend a thesis and discuss your research. The examiners will decide from a list of possible outcomes as detailed later in this post.
- Make amendments to the thesis as necessary.
- Optional celebration.
- Have the thesis amendments approved by the examiners and/or your supervisor and confirmation sent to the university.
- Upload the final copy of your thesis to the university.
- Eagerly await notification that you’ve been awarded a PhD by the university!
- Celebrate, Dr!
All celebrations except for the one after making changes to your thesis are mandatory!
PhD Viva vs PhD Defence
The words viva and defence are sometimes used interchangeably, but often are used to reference the different ways that the a PhD is concluded around the world.
A PhD viva (technically a viva voce ) is a formal examination of a PhD. It’s typical in the UK (amongst other countries) and it is a closed-event between yourself and some examiners.
Across much of Europe it is common instead to have a PhD defence . This still involves expert questioning but can be more of a ceremony and may even be open to the public. You can read about Siddartha’s experience , who completed his PhD in the Netherlands.
I went through a PhD viva and that’ll be the focus of this series. Nevertheless, there is overlap and you may still have difficult questions in a PhD defence, so the content in this series should still be useful no matter where you’re based.
In both a PhD viva and a PhD defence you’ll be expected to defend a thesis which represents the culmination of your work during the PhD.
Who is Present During the PhD Viva?
In the UK it is typical for the PhD viva to include:
- One or more experts from your university ( internal examiner ).
- One or more experts in your field from another institution to your own ( external examiner ).
- And sometimes your supervisor, though in my experience this is quite rare unless you actively ask them to be there.
The main role of the internal examiner is to act as a moderator and ensure that the university’s protocols are upheld. They’ll usually still have some questions for you, but on top of that they’ll make sure that the external examiner(s) are reasonable. They will also take charge of documenting the viva.
Often the external examiner will be more specialised to your field than the internal examiner, so expect them to potentially ask more tricky and technical questions.
As mentioned in the previous section, for PhD defences in other countries the event may be less of an exam (viva) and more of a celebration of your work. These can be a lot more open, with access granted to your friends, family or anyone else who is interested in the topic. I quite like this idea, especially when the research has been publicly funded!
How the PhD Viva is Structured
The structure of the viva will vary but a typical format is shown below. The times in brackets are how long the sections for my own viva were, thankfully not all vivas are over five hours long!
- Introductions (2 minutes) – greeting the examiners and they’ll usually quickly give an overview for how they want the viva to go.
- Presentation (10 minutes) – Not all examiners will want you to give a presentation, it’s best to ask them in advance. I believe many examiners like asking for presentations: both to ease into the exam and also to see how you do at distilling years of work into a short presentation.
- Discussion (Over 5 hours, yes, really!) – the long and potentially scary bit.
- A short break (~10 minutes) . You’ll leave the room (or video call!) and the examiners will come to a decision for your PhD outcome.
- Decision and final comments (10 minutes) – where the examiners will tell you what the outcome is of the viva – we’ll cover this in more depth in the next section.
The discussion in the middle of course is the main guts of the PhD viva, and the potentially scary bit. This is where you’ll get questioned about your work and thesis. What you get asked could vary considerably depending on your thesis and examiners.
I’ll save an in-depth discussion of my own viva for another post. In short, I received very few questions relating to the work or any fundamental underlying science. There were practically no questions to quiz my knowledge.
Rather than checking my understanding of the work, the viva was much more of a discussion of how best to present the work in the thesis. We spent roughly an hour going page by page through each chapter. This included suggestions for improvements to figures, changes in terminology and the like.
Possible PhD Viva Outcomes
At the end of the viva the examiners will give you feedback. This will include feedback on your performance in the viva. But as long as they’re satisfied that you carried out the work and that you knew what you’re doing, the bulk of the feedback will in fact revolve around your PhD thesis.
Technically there are lots of potential outcomes, as detailed here:

In reality here are the four main possible outcomes from the viva:
- Pass with no amendments . The examiners didn’t want to make a single alteration to your thesis. Well done you just have to submit the finalised thesis to the university and you’ve finished your PhD! I know a few people who’ve had no revisions but it’s rare.
- Pass with minor amendments Minor amendments include things such as correcting typos, rewording sentences and small alterations to data analysis and presentation. This is by far the most common outcome.
- Referral for resubmission ( major amendments). More substantial changes to the thesis are required or further experimental work is required to fulfil the requirements of a PhD. The examiners will decide whether or not this means having another viva too.
- Fail . Unless there are glaring issues or you didn’t actually do any of the research in your thesis yourself, you should be relieved to hear that practically no one ever fails. If you have failed, it usually points to systematic issues revolving around your supervisor: you shouldn’t have been allowed to get to this point. Usually the examiners would recommend that you be awarded a lower degree, such as a masters in research (MRes).
Slightly up the page is a screenshot from my own examiners’ report. You’ll see that I, like most people, passed with minor amendments.
2022 Update: Starting to prepare for your PhD viva? A set of viva preparation worksheets are now available in the resource library. Click the image below for free access!

Making Changes to Your PhD Thesis
Shortly after the viva you should receive the examiner’s report which includes a list of revisions for you to make.
If you’ve got through the viva with a pass, you can breathe a sigh of relief because the hard work is over! In a separate post I’ll be covering how the process to make my own minor amendments went.
No matter the outcome, it is possible that you’d like to make your own changes to the thesis since it’ll have been many weeks (or months) since submitting the draft copy for your viva. On reflection there may be things you’re not happy with. You are welcome to make changes to the document yourself.
If you’re interested in reading more about how to make the corrections to your thesis, read the article dedicated to it here: Minor Corrections: How To Make Them and Succeed With Your PhD Thesis.
After you’ve made changes, the final stage in getting awarded the PhD is submitting your finalised version of the thesis to the university. Shortly afterwards you’ll get the long-awaited notification that you’ve got your PhD!

Should You Strive For No Amendments?
In my opinion it’s not worth the effort of trying to get no amendments.
I’d personally rather spend slightly less time up front, knowing that more than likely I would have to made some amendments. You can never put in enough work to ensure there will be nothing your examiners want changed!
You could spent hundreds of extra hours endlessly going through your thesis meticulously before submission but your examiners can always find something they want you to change. In comparison, my own minor amendments only took two days of work.
Sometimes you’ll see someone mention on their CV that they passed with no revisions but it doesn’t really have any bearing on your PhD. Unlike most other qualifications, there aren’t really grades for PhDs: you either have one or you don’t.
During an early PhD assessment my assessor made a poignant joke about medical degrees: “What do you call the person who graduates bottom of their class in medical school? A doctor!” And it’s essentially the same with PhDs!
If you’d like personalised help with preparing for your PhD viva I am now starting to offer a small number of one-to-one sessions. Please contact me to find out more or click here to book a call.
I hope this introduction to PhD vivas and how to defend a thesis has been useful. Let me know if you have any specific questions or concerns you’d like to see addressed in the following posts.
As always you can stay up to date with content by subscribing here:
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
Related Posts

Minor Corrections: How To Make Them and Succeed With Your PhD Thesis
2nd June 2024 2nd June 2024

How to Master Data Management in Research
25th April 2024 27th April 2024

Thesis Title: Examples and Suggestions from a PhD Grad
23rd February 2024 23rd February 2024
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Privacy Overview

How to prepare for your PhD thesis defence
What's the best way to prepare for your thesis defence? The tips below will help you in the final few weeks before the exam, but the real preparation begins as soon as you start your PhD .
Talking to people and discussing your work regularly over a long period of time is the best preparation. Don't let your thesis defence be the first time you get feedback on your work!
Know the format of your thesis defence
The format of a thesis defence varies from country to country. Having studied in the UK, my viva-voce defence was essentially an interview with one internal and one external examiner. In other countries, it's common to have public examinations with a whole panel of examiners and an audience of colleagues, family and friends. The first and most obvious tip, then, is to make sure you know what the format of your exam will be; whether you will have to prepare a presentation and so on.
Prepare and practice your presentation
If you have to give a presentation, check any time restrictions so you can prepare accordingly. You don't want to show up with 100 slides for a 15-minute presentation, nor do you want to show up with 10 slides for a 1-hour presentation. The most important thing to do for any presentation is to practice so that;
You know the material inside out
You know how long it takes
You can refine the presentation
You can practice on your own or with an audience, and you should do both if possible. Practicing on your own and speaking out loud to an empty room may feel silly, but overcoming that discomfort is good preparation for the discomfort of facing an actual audience. Practicing with an audience of peers is then a good way of getting feedback and finding out what questions people ask.
See also: How to design outstanding PowerPoint slides
The dreaded "awkward question"
Whether you have to give a presentation or not, one of the scariest aspects of the defence is the possibility of being asked a question you can't answer. It's tempting to try to read a ton of literature to prepare for this, but since it's very difficult to predict what the examiners will ask and it's impossible to read everything, this approach isn't always effective or reassuring (it might just make you realise how much you don't know).
You aren't expected to know everything. Sometimes, an examiner will ask a question they don't know the answer to, either out of interest (since you are the expert in your research) or because they want to see how you think. While it is OK, sometimes, to just say "I don't know", you could also say something like,
"I don't know, but I would think that [...] because of x and y , but you would need to do [...] in order to find out" .
This shows that you have the ability to think as an academic.
Core content
Of course, there is some core content which you will be expected to know well, but this is set by you, not the examiner. To a large extent, the content of the examination is determined by the content in your thesis.
When you choose what to cover in your thesis you are choosing your battleground for the thesis defence, so the best strategy is to stick to the material you know best in your writing!
Dealing with nerves
You will be nervous before your examination. You will almost certainly get an adrenaline rush, which can set your heart racing, give you sweaty palms, make your stomach churn and make you want to go to the toilet 10 times in 20 minutes. This is normal!
The worst part is the waiting before you start because there isn't much you can do to use up all that nervous energy. But once the defence starts, you can do some things to keep it under control.
One symptom of nerves is to talk really fast and to try to show how much you know and speak in this kind of long stream of consciousness that diverges away from the question until you forget what the actual question was but then you don't know how to get back to the point and so you just keep talking and that makes you more nervous and how are you going to get off this train of thought...
Try to slow down and give yourself time to breathe. Try to remember the question* and come back to the point. Once you have answered, stop talking!
*If you forget the question, it's OK to say, "sorry, I got lost in my train of though there, what was the question, again?"
The examiners expect you to be nervous
Remember that the examiners expect you to be a bit nervous in your thesis defence, and they will help you through if necessary. It is OK to ask them to repeat or clarify a question. It is OK to pause to think. It is OK to take a sip of water if you need to!
Ultimately...
Success or failure is determined mainly by the content of your thesis. If your research is good, and you actually did the work, it is highly unlikely that a nervous performance in your defence will lead to failure. Generally speaking, once your thesis is submitted, there isn't much you can do to affect the outcome (positively or negatively). Read through your thesis, read up on one or two key points if necessary, practice your presentation, and trust that whatever happens you will be OK.
An easy way to update your literature review
How to write a thesis you can defend easily
Your final PhD year: Moving towards completion
An easy way to update your literature review quickly
Stay up to date
Get the latest posts in your inbox
Just one more step! Please check your inbox and confirm your subscription

Just one more step! Please check your inbox and confirm your email
Recovering physicist. I used to work in nanoscience before moving on to bigger things. After finishing my PhD in 2007 I completed 2 postdoc contracts before becoming starting coaching PhD students full-time in late 2010. In 2015 I published the book
How to design outstanding PowerPoint slides
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CAREER COLUMN
- 30 March 2020
How to defend a PhD remotely
- Alyssa Frederick 0
Alyssa Frederick is a postdoctoral scholar at the Bodega Marine Laboratory in Bodega Bay, California, part of the University of California, Davis.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
In November 2019, I conducted my PhD defence using the videoconferencing software Zoom.
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-020-00971-z
This is an article from the Nature Careers Community, a place for Nature readers to share their professional experiences and advice. Guest posts are encouraged .
Related Articles

- Peer review
- Conferences and meetings

How PhD students and other academics are fighting the mental-health crisis in science
News Feature 09 JUL 24

How can I break into industry if my CV keeps disappearing into a black hole?
Career Feature 08 JUL 24

Harrowing trends: how endangered-species researchers find hope in the dark
Who will make AlphaFold3 open source? Scientists race to crack AI model
News 23 MAY 24

Pay researchers to spot errors in published papers
World View 21 MAY 24

Plagiarism in peer-review reports could be the ‘tip of the iceberg’
Nature Index 01 MAY 24

How to network with the brightest minds in science
Career Feature 26 JUN 24

How I overcame my stage fright in the lab
Career Column 30 MAY 24

China promises more money for science in 2024
News 08 MAR 24
Postdoctoral Fellowship - Graph Database Developer
Postdoctoral Fellowship - Graph Database Developer Organization National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD and surro...
Bethesda, Maryland
National Institutes of Health/National Library of Medicine
Postdoctoral Fellow - Boyi Gan lab
New postdoctoral positions are open in a cancer research laboratory located within The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. The lab curre...
Houston, Texas (US)
The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center - Experimental Radiation Oncology
Senior Research Associates x 3 – Bioinformatician Team
The Genomics and Bioinformatics Core (GBC) within the Institute of Metabolic Science – Metabolic Research Laboratories at the Clinical School, Univers
Cambridge, Cambridgeshire
University of Cambridge
Al Medical Engineering at School of Biomedical Engineering
Tsinghua BME offers faculty positions in the emerging research direction of AI Medical Engineering
Beijing, China
Tsinghua University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University Global Recruitment
Interested applicants can send CV to the relevant department/school.
Shanghai, China
Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
- Perspective
- Conversation
- About the Blog
- More about CSP
- Careers at CSP
Erin Zimmerman
Plant biologist turned science writer and illustrator with a BSc in plant biology and physics from the University of Guelph and an MSc and PhD in fungal genetics and molecular systematics, respectively, from the Université de Montréal.
The Last Big Hurdle: How to Prepare for a Successful PhD Defence
It’s the moment almost everyone who completes a PhD both dreads and looks ahead to for years—the defence. It signals a major achievement, but in people’s imaginations, it can seem like the stuff of nightmares… standing frozen in front of everyone, unable to answer a tricky question posed by a committee member and feeling like you must look incompetent. The format of a doctoral defence varies from field to field, but the worst fears of the candidates remain largely the same. Though most people know it probably won’t go so badly, the open-ended-ness can certainly be intimidating- you’re up there alone in front of a panel of experts who get to ask you whatever they’d like, and you may have to deliver your answers in front of an audience of your peers. There are few experiences in academic life more geared to be stressful for the person at the centre of them.
It doesn’t have to be that bad. I spent the weeks leading up to my PhD defence in a state of near panic, but I can honestly say that once it actually got underway, I sort of enjoyed it. You’re the star of the show and get to walk your peers through the finer points of your research. It can be a really invigorating experience. So let’s try to break this down into bite-sized chunks and look at strategies and tips for making your defence an event you might actually look back fondly on.
What the committee wants
Let’s start with what the committee is actually looking for. They want to see a firm grasp of the subject matter, an understanding of the implications of the work, and the ability to see weaknesses in the methodology and possible routes to take for future work. This means creating a presentation that gives a clear, logical overview of your topic, the question you’re addressing, what you did, your results and conclusions, and where the research can go from here. Remember, your jury members are not out to get you. The questions you receive from them will generally fall under one of three headings- those that test your subject knowledge, those that clarify a confusing point, and those that arise from genuine curiosity. If your presentation does a good job of conveying your knowledge of your topic, you can expect more questions from the second and third categories, allowing you to think of the defense more as a conversation amongst experts than a test from on high.
How to prepare
Practice is obviously very important here. Once you’ve put your talk together, find a trusted friend or mentor (ideally, several of them) who knows your field to go through it with you. They can both help you to pare down unnecessary parts and point out logical leaps you may not have noticed because you’re so close to the subject matter. You also want this to be a person who will ask you tough questions and try to spot holes in your reasoning, so choose your test audience carefully. It can be tempting to spend a lot of time obsessing over your slides, trying to make them perfect, but there’s a lot of studying you’ll need to do to be ready for more tangential questions, so don’t lose too much time this way.
Even though you have lived and breathed your thesis topic for years, it’s a good idea to give your thesis a complete re-read just to make sure you really know what’s in there. It may have been months since you finished writing it, and parts may have gotten a little fuzzy since then. Make sure you know why you used the methodology that you did, be able to justify any conclusions you’ve made, and if there are mistakes, admit them openly at the defence and be able to talk about what you should have done differently—the committee isn’t looking for perfection, they’re looking for clear thinking and thorough consideration of methodology.
This is also a good time to review important topics that are peripheral to your work; this will allow you to answer some of the questions designed to test the limits of your broader knowledge of your field. One of the best pieces of defence preparation advice I’ve ever heard is to find out what each of your committee members’ professional interests are, and do a bit of reading on those topics. There’s a very good chance that they’ll ask you something that’s related to their own work, because that’s familiar ground to them, and you may be able to anticipate these questions this way.
Finally, though it’s less and less of a problem as technology improves, you’ll want to make very sure ahead of time that all your presentation gear works and connects properly to the display equipment in the room where your defence will be. No one wants to be running around at the last moment looking for a dongle they didn’t think they needed, or have their laptop’s battery run out partway through the defence. Check that your slides look the same way on the projection screen as they do on your computer- not cut off or too dark. It also doesn’t hurt just to spend time in the room in which you’ll be presenting, to get a feel for the place and see where everything will be positioned.
Common questions and ideas to think about
- What makes your project original, and how does it answer a previously unanswered question? What have you contributed to the body of knowledge on this topic?
- Why was this question important to ask? Why do we care about what your findings reveal? (Hint: “Just for the sake of knowing” is not an acceptable answer here.)
- Did the focus of your project change over its course? If so, explain how and why.
Methodology
- Why did you choose your methodological approach (including your statistical analyses)? Why is it superior to or more appropriate than all other methodologies?
- Talk about the difficulties you experienced with your methodology and how you addressed them.
- What are the limitations of your study design/methodology?
- Explain how your data represent an appropriate source of measurement to address your question.
- Is the amount of data gathered sufficient to address your question? Why or why not?
- If you could do it again with unlimited time and funds, how would your methodology change?
Conclusions
- What would you say is the most important “take-away” message of your work?
- Does your work have wider implications for other disciplines in your field?
- How do your conclusions support or contradict the existing literature?
- Are there alternative ways your data could have been interpreted?
- Speculate about what broader implications your research could have, but which aren’t addressed by your data, or were outside the scope of your project.
- If you were to continue on with this area of research, what would you do next to further your results? Is there a closely related “spin-off” question that needs to be answered?
- Propose an experimental design to test this related question. What results might you expect to see?
- Where do you think this field of study is headed in the next five to ten years?
Tips, tricks, and stress management
- Practice the first few minutes of your talk until you can do it on ‘autopilot’; this will give you a bit of time to relax into your presentation, get your thoughts in order, and begin talking more confidently.
- If your defence is open to the public, ask a few supportive friends or colleagues to sit where you can easily make eye contact while you’re talking. Seeing a friendly, smiling face can be encouraging and help you to relax.
- Don’t forget to review the newest literature in the weeks leading up to your defence—one or more important papers may have been published in your field since you wrote your thesis, and you’ll want to know about them.
- Have a hard copy of your thesis on hand during the defence. It’s much faster to flip to a physical page when asked about a particular section of the text. If this really isn’t for you, be sure you have a quick way to move through pages on your computer.
- Eat and drink the same things you normally would on the day of your defence. Your stomach may be extra sensitive in response to the stress, and you don’t want to surprise it with anything new. And go easy on the caffeine… jittery-ness will not help you to manage your stress!
- Try to let your enthusiasm for your subject matter show; your audience will feel more positive about your talk if they can see that you really find the work fascinating.
- It’s fine to take a moment to think about your answer before responding. The silence isn’t as long or as deafening as you think it is. And if you don’t know, just admit you don’t know—it’s okay to not know everything.
- Dress well, but comfortably, and try to project confidence. If you can speak to your committee as a group of your peers, it will reflect well on your growth as a scientist in training- and demonstrate you are someone who deserves to be awarded their doctorate.
- Don’t forget to publicly thank your advisor, your committee, and any other key people involved with your project for their time commitment and investment in your career.
- When planning post-defence festivities, be aware that you may be more tired, both mentally and emotionally, than you expected. Don’t ask too much of yourself in the hours following the event.
A bit of encouragement
Above all, there are two things you need to remember while preparing for your defence. First, your advisor and committee would not have allowed you to proceed to this point if they didn’t think you were ready. They want to see you succeed and, altruism aside, it would reflect badly on them as well if you were to fail. Trust that they’ve made the right decision. Second, after years of delving into your little corner of the scientific world, no one knows your thesis topic better than you do—not even your committee. Marshall your facts and feel confident in knowing that on this topic, you’re the world expert.
What is your best advice to prep for a PhD defence?
You might also like

Dr. Lisa Venier takes on a new role at the Canadian Journal of Forest Research

Chasing Arctic dreams: A conversation with Dr. Mark Mallory

Reflections from women in Canadian chemistry
- Scholar's Toolbox
What? Why? How? A list of potential PhD defense questions

In August 2020, I defended my PhD successfully. In the preceding months, I had generated a list of potential defense questions by using various different sources (websites, other defenses I watched, colleagues, and my supervisors). The list ended up helping me a lot. Today I shared this list with a colleague who is soon defending, and I thought: Why not share it publicly?
Note: The questions were compiled with a Finnish PhD defense in mind. In Finland, the defense is at the very end of the research process, and no changes to the PhD will be made after the event. The defense is also a public event.
The list was last edited: November 3rd, 2022
Title and cover.
- Why did you choose this title? Were there any other kinds of titles you were considering?
- Why did you choose this photo/image as your thesis cover? (if there is one)
Topic and contribution to the field
- Why did you choose this research topic?
- Why do you think this topic is important? For whom is it important?
- What do you think your work has added to the discipline/field/study of this topic?
- How is your study original?
- [Your topic] seems to be something that is usually studied discipline X. However, your thesis represents discipline Y. How did you navigate the interdisciplinarity of your work?
Paradigm/theory/concepts
- How did you decide to use this particular conceptual/theoretical framework?
- How did your chosen framework help you to explore your research problem?
- How would someone using another theoretical framework interpret your results?
- What are the shortcomings of this particular theory/conceptual framework?
- How would you describe/define/summarise … [insert a term]
- In your work, you introduce a new concept/theory. Why did you decide to do that instead of using an existing concept/theory?
- Could you describe your theoretical/methodological framework in a way that the audience also understands it? (for public defenses)
Literature review
- Why did your literature review cover these areas but not others?
- The literature review looks very tidy – doesn’t anything challenge it?
- Why did you (not) include the work by X in your study?
- Which scholar(s) have you been influenced by the most?
Research question(s)
- How did you come to formulate this particular research question / these research questions?
- How did your research questions/problem changed during the research process?
- Were there research questions you decided to add/remove during the research process?
- Why don’t you have a research question?
- How did you decide to use these particular methods of data collection/analysis? Were there other options you considered?
- Why did you choose quantitative/qualitative/mixed methods approach?
- What informed your choice of methods?
- What are the advantages/disadvantages of the chosen methods?
- How did you select your participants/this particular data?
- Describe how you generated your data.
- Why did you analyse your data in this way? What other ways were there available? Why didn’t you choose those methods?
- If you could still improve this measure/procedure/etc., how would you do it?
- How would you explain the low/high response rate of your survey?
- How did you triangulate your data?
- If you could do your study all over again with unlimited resources, how would you do it?
- How do you explain the discrepancy between your findings and the findings of previous studies?
- Did you expect these kinds of results? Why (not)?
- What is the most important result of your work?
- Who should care about your work and the results?
- How generalizable are your findings and why?
- Were there any other ways to present your results?
- Based on your findings, how would you develop [your topic]?
- What is common or different to these substudies included in your dissertation?
- What did [your approach] reveal that other approaches could not have reveal?
- What did you not see because you did your work [in this way]?
- How could [x] now be rethought in the light of COVID-19?
- What kinds of implications do your results have for further research/practice/policy?
Research process
- How did your own position/background/bias affect your research?
- Describe your researcher positionality.
- What were the biggest challenges during the research process?
- Were there any surprises during your research, pleasant or unpleasant?
- What was the most interesting part of your work?
- How did you address research ethics during your research?
- What implications do your findings have for [your topic]?
- What do you see as the problems in your study? What limitations do these impose on what you can say? How would you address these limitations in future studies?
- What could you not study in the end? Why?
- What kind of a dissertation did you want to do originally? Why did your plans change?
- If you could now redo the work, what would you differently?
- Is there anything else that you would like to tell us about your thesis which you have not had the opportunity to tell us during the defense?
Future research
- What do you plan to do next with your data?
- What would be the next logical study to do as a follow-up to this one?
- What will you study next?
- How does gaining a doctorate advance your career plans?
Photo by Vadim Bogulov on Unsplash
Leave a reply cancel reply.
- Scholar’s Toolbox
- In the Spotlight
- Working in Academia
- Miscellanea
- Contributors
- About ECHER
Preparing for Your PhD Defence
Completing your dissertation isn’t the final hurdle to earning your PhD, the oral defence (called a viva voce or viva in the UK) is. But once the date has been set and the examiners are confirmed, how do you start to prepare? Here are some tips to help you beat the nerves and rock your defence.
Know What You’re in For
If defences are public in your department, try to attend a couple before your own. Attending someone else’s defence is a great learning experience and will help you see what works and what doesn't. Notice things like how the candidate dresses, how they address the examiners, and the sort of questions the committee asks. What makes their talk compelling? Watching a live defence is the best way to understand the format and what will be expected of you when it’s your turn.
Reread Your Dissertation
This is a very important step. A PhD is a multi-year endeavour and it may have been a few years since you did some of the research in your dissertation. Go through each chapter and summarize your main arguments. Then zoom out about your dissertation as a whole. While the committee will question you about the details, they will also ask you to consider your work in a broader context. What are the implications of your findings? What does your thesis contribute to the field? It’s also a good idea to take note of any weaknesses or mistakes so you’re prepared if they’re discussed during the defence.
Prepare Your Talk
After rereading your thesis, you will be in a good position to put your talk together. Your talk should address what you did, why you did it, how you did it, what you found, and what it means. Remember you will only have about 20 minutes. Preparation is more than just building a slide deck, you must also practice giving your talk. Practice giving your talk multiple times both on your own and in front of groups—and remember to rehearse the question part too. Fielding questions from your test audience will help you get better at thinking on your feet when facing unexpected questions.
Basic Question Types
It’s impossible to predict every question you will be asked during your defence so instead prepare for questions in these five common categories: General questions, the context of your work, your methods and research design, analysis of your results, and discussion. You can also familiarize yourself with the work of your committee members as they are more likely to ask questions about their own area of expertise.
Defence preparation shouldn’t be purely academic. Don’t forget to prepare yourself mentally and physically as well by eating well, exercising, and getting enough sleep.
Discover related jobs
Discover similar employers
Accelerate your academic career
Dutch Academic Job Titles Explained
What's the difference between a universitair docent and a hoogleraar? Wh...
German Academic Job Titles Explained
German job titles are slightly different from their American equivalents...
Moving to Denmark to Research or Study
Denmark attracts thousands of students and researchers each year. Here a...
What is a PhD?
How long does it take to do a PhD? Do you have to be a super genius to d...
Keep Calm and Ace Your Interview
These tips to help manage your nerves before, during, and after the inte...
Overcoming Impostor Syndrome
Impostor syndrome is a nagging feeling of self-doubt and unworthiness th...
Jobs by field
- Electrical Engineering 217
- Programming Languages 181
- Machine Learning 178
- Artificial Intelligence 169
- Molecular Biology 166
- Mechanical Engineering 150
- Materials Engineering 147
- Electronics 145
- Cell Biology 140
- Engineering Physics 119
Jobs by type
- Postdoc 366
- Assistant / Associate Professor 158
- Professor 120
- Researcher 109
- Engineer 101
- Research assistant 100
- Lecturer / Senior Lecturer 75
- Management / Leadership 56
- Tenure Track 47
Jobs by country
- Belgium 399
- Netherlands 172
- Switzerland 120
- Morocco 115
- Luxembourg 68
Jobs by employer
- KU Leuven 145
- Mohammed VI Polytechnic Unive... 119
- Ghent University 83
- Eindhoven University of Techn... 82
- University of Luxembourg 67
- KTH Royal Institute of Techno... 60
- ETH Zürich 58
- University of Antwerp 53
- Karolinska Institutet 43
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
What questions to prepare for PhD defense?
I will soon defend my PhD in social science in Sweden. I want to ask what questions the evaluation committee will ask me during the defense? If they ask me some questions outside my thesis, what shall I do? Is it enough only know well my own research? What quality I need to successfully defend my PhD?
- answering-questions
- 9 Have you not gone to other people's defenses before? Have you asked your advisor? – xLeitix Commented Mar 30, 2015 at 11:19
- 4 I don't recall ever hearing any restrictions on what I can ask in a thesis defense. Ordinarily, I ask about things in the thesis, prerequisites for things in the thesis, and things that the candidate happens to mention during the defense. I could, in principle, ask a completely off-topic question, to which the candidate might well reply "I have no idea"; presumably, such an answer wouldn't damage the outcome of the defense (unless the other 4 examiners agree with my craziness). – Andreas Blass Commented Mar 30, 2015 at 13:37
- 5 Whatever field you study and whatever type of presentation you give, always be prepared for questions asking you why you made certain decisions. It won't hurt preparing for them and it might actually improve your presentation if you hadn't thought about it before. – Mast Commented Mar 30, 2015 at 13:49
- 5 Obligatory XKCD: xkcd.com/1403 – Corey Ogburn Commented Mar 30, 2015 at 18:17
- 4 I was asked "who is Maud Menten?" (see 1910's at famouscanadianwomen.com/famous%20firsts/… ) Since I used the Michaelis-Menten equation in my work, it was borderline relevant. Luckily there is a plaque to her on the U of T campus, so I knew both the equation half of the answer and the trivia question half. That was the only question that examiner asked. Seriously, know your thesis well and ask your supervisor if you can expect anything unusual, and you'll be ok. They don't generally let you defend if they don't think you're ready. – Kate Gregory Commented Mar 30, 2015 at 18:32
4 Answers 4
Generally speaking, PhD defenses come in two flavors, and it is not possible to say a priori which one yours will fall into:
- A real thesis "defense" focuses on the thesis, and all questions will relate to the scope of the research work. In this case, knowing your own work and its context well enough should be sufficient, but it is of course possible that somebody asks you why you used method A rather than B. In this case, saying that you don't know B may not fly as an answer. However, you should not get a completely disconnected question just to test your general subject area knowledge.
- A "Rigorosum" ( dict.leo translated this for me to "doctoral viva", no idea if this is a well-known term) is a general final exam for a doctoral candidate. Typically, this will also include questions about the disseration, but anybody in the exam commission is free to ask about other topics in the field as well. Typically, the questions are getting "easier" (more high-level) the farther they are away from the topic of the dissertation. The claim here is that a fresh PhD should have both, depth and breadth in her/his knowledge.
There are a number of ways to figure out which class your defense will fall into:
- Attend other defenses . Typically, PhD defenses are public, and it is highly recommended that any PhD candidate should visit a few before her/his own, to get to know the procedure and get a feel for what the defense talk is supposed to look like.
- Ask your advisor . The advisor should obviously know what the requirements of the defense are, exactly.
- Look it up in the programme description . Usually, the programme description will contain exam regulations for the defense, and this should describe the exam procedure and who is supposed to ask what kind of questions. This approach has two dangers: (1) you may misunderstand what the exam regulations are saying - as they are more legalese text, you may misunderstand the gist of it, and (2) the actual exam may happen differently than specified - there is no telling whether the exam regulation exactly captures the real spirit of the defense. Hence, you should really also talk to your advisor and/or attend other defenses as well.
- 9 Typically, there's a non-public part of the defense after the public part where the general public is asked to leave and the committee can grill the candidate in private. That's where the interesting/hard/potentially embarrassing questions are likely to come. This is harder to prepare for and benefits from asking your advisor and recent other students for guidance. – Bill Barth Commented Mar 30, 2015 at 13:24
- 4 @BillBarth Ok, I was not aware of that. In all universities that I was aware of, everything needs to be public to have traceability of decisions. – xLeitix Commented Mar 30, 2015 at 16:42
- "Viva" (short for viva voce ) is the term used in the UK (and some other countries?), I'm not sure if use of this term corresponds to your two categories or not. At my UK university you are expected to answer questions generally on your field as well as your thesis. – MJeffryes Commented Mar 30, 2015 at 16:48
- 3 In addition to that, vivas in the UK are typically behind closed doors in their entirety - only two(ish) examiners and the candidate, with even the advisor being absent. – E.P. Commented Mar 30, 2015 at 22:28
- good answer. i would like to add that the OP should look into their supervisor's reviews of the thesis. in some countries/unis these are provided beforehand. they contain the main criticism and these will come up also in the defense. the defense talk itself should already address them. – henning no longer feeds AI Commented Jul 12, 2015 at 16:11
Some types of questions that often come up:
Questions about some detail of your work. The point of such questions is often not so much the correctness of this small part of your dissertation, but rather to get you to demonstrate your ability to explain what you've done. This also helps to balance out the presentation, which typically covered the whole thesis in much less detail. For example, in mathematics you might be asked to go over the proof of one of your theorems in detail. Since you've spent more time working on these details than any of the examiners, and assuming that the examiner hasn't spotted a substantial error, you should be in a good position to answer such a question. Don't panic and assume that you've made some huge mistake, but rather go through the material carefully and convince the examiner that you're correct.
What are the broader implications of your work? This is actually a hard question for most students to answer because they've been so focused on the details of their thesis that they may not have taken time to see how it fits into the broader picture of progress in their discipline. This will also be an important question when you eventually interview for faculty positions.
Can this method be applied to some other problem Y? You may be asked how the techniques used in your dissertation could be applied to a different problem. If the answer is that the technique doesn't extend in that direction, then you should be prepared to explain why not.
Questions about what exactly is new in your work. You should have been extremely careful in writing your dissertation to properly cite earlier work and distinguish your new contributions from that earlier work. If this isn't clear to the examiners, you may be asked to clarify.
I attended about a dozen PhD defenses and recently defended my own PhD. Based on my (very limited) experiences, questions can be roughly categorized into two types:
Knowledge : the first set of questions or statements are usually to test your knowledge on your topic, the related work and whatever you have written down in your thesis and/or papers. If you have done all the work, these are mostly fairly easy to answer and are your way to demonstrate the awesome work you have done. These questions are to clarify, justify and frame your work related to others, in order to get a solid understanding of your contribution. Examples:
- Can you explain what you mean with #concept you introduce#?
- Why did you categorize or describe #your concept# in this way?
- I believe #your topic# relates to #other guys theory# in such a way, which introduces an interesting contradiction. Can you comment or elaborate on this?
- What is the main limitation of your work, and how could you address it?
Reasoning : committee members may also ask provocative or even harsh questions to see how strong you believe in your work but also whether you can transcend your topic and reason on a higher level. These questions or statements can be directly related to your topic but can also be more general. These types of questions are usually given to see how well the candidate performs when put under pressure and when they are questioned about things beyond their thesis. These can be interpreted as "nasty" questions, but remember that you can turn the questions around to your advantage. Examples:
- Why do you believe this is science? What is science?
- You spend #x# years researching this? Why did you choose the topic and why should we and the community care about it?
- I don't see the contribution in your work, can you explain?
- Why do you think you deserve a PhD?
- Why did you choose this specific application domain?
Again, this is based on my personal limited experience, but it applied to my PhD defense as well.
You do not have much influence on the questions from the committee. If your PhD studies were more or less normal and you got that far, everyone wants you to succeed. They will not ask anything incredible (if they are relatively normal as well).
As for the public questions, my experiences are :
the friends you gave questions to. You have to choose the ones who have good reflexes to jump up and down when time for public questions come. You also have to train the "what a surprising question look"
the odd colleague who decided to ask a question about something related to your field, but far enough for you to have no idea. You sweat a lot, visualize him hanging on a tree and hope for the best. Best is to answer whatever you know on the subject and everyone acts happy. If he persists then you ask him what is his view on the subject so that he sits down ashamed mumbling "I have no idea"
finally the 173 years old professor who absolutely wants you to discuss his article from 1952. You thank for the question and talk about the article from 2012 someone wrote on a related subject.
(events described above actually happened to me in the course of my 2 hours defence)
- 1 Even though I will not ever have to go though a PhD defense anymore, it would have been great to understand the downvotes. – WoJ Commented Jul 12, 2015 at 17:59
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged phd defense answering-questions ..
- Featured on Meta
- We spent a sprint addressing your requests — here’s how it went
- Upcoming initiatives on Stack Overflow and across the Stack Exchange network...
Hot Network Questions
- Simple BJT circuit problem
- Is it an option for the ls utility specified in POSIX.1-2017?
- Is it possible to go back to the U.S. after overstaying as a child?
- Equivalence of first/second choice with naive probability - I don't buy it
- Is infinity a number?
- Combinatoric Problem in Stardew Valley about Keg Layout
- Why are metal ores dredged from coastal lagoons rather than being extracted directly from the mother lode?
- Which interpreter for "Unicode text, UTF-8 text executable"
- Judging a model through the TP, TN, FP, and FN values
- Identify the story about an author whose work-in-progress is completed by a computer
- Mysterious creaking on (mainly) the right pedal stroke even after replacing usual suspects
- The center of gravity of a triangle on a parabola lies on the axis of symmetry
- Why does King Aegon speak to his dragon in the Common Tongue (English)?
- When is it appropriate to report mistakes in a paper?
- How to choose between 3/4 and 6/8 time?
- Why does Macbeth well deserve his name?
- Looking for two tables to start at the same height
- Can a MicroSD card help speed up my Mini PC?
- What should I do so that the length of the brackets remains constant when I color the table?
- What's the shape of the Control Weather spell? (if any)
- Intelligence vs Wisdom in D&D
- Identify this bouncing ball screensaver in DOS
- French Election 2024 - seat share based on first round only
- Help understanding the implications of Security Breach section of an NDA
The Grad Student Way
Your One Stop Grad School and PhD Resource
- Second Income Ebook
- Twitter GradStudentWay
- LinkedIn GradStudentWay
- Facebook Page
- RSS Feed GradStudentWay
- Networking Guide
- 10 Ways To Successfully Defend Your PhD
First, what does it take to give a successful PhD Defense? How can you prepare, keep the stress levels low, and make sure you have the highest chance of success?
I’ll just say that everyone’s PhD Defense is unique and is unpredictable. Your talk/presentation is only as good as you want it to be. And you cannot fully prepare for all the endless possibility of questions. If you wrote a 200 page thesis, your thesis commitee can pick apart an error bar on a graph on page 133. They can ask you what you meant by a word in a random sentence in any given paragraph. Keep in mind, this is all just apart of the PhD hazing process, and in a sense is just to humble you. At the end of the day, if you wrote a good quality thesis and are CONFIDENT, you should have no problem successfully defending and leaving that room with a sense of relief. Either way, I wanted to share my experience while it is still fresh in my mind
1) Do not underestimate how long it takes to prepare your slides/talk and make sure you give multiple practice talks
When I turned in my thesis two weeks ahead of time to my committee, I thought the hard part was over. Although a very important milestone, don’t let your guard down. If you already have most your slides ready to go, then you are lucky. I ended up getting data at the last minute and my story changed. I had to make many model slides from scratch.
If you want to give a GOOD thesis talk, you need to practice multiple times . And this means that you don’t cram it all in a couple of days right before your talk. I’m not talking about giving just one practice talk. You need to give multiple group practice talks. In between, you need to practice on your own.
You certainly don’t have to memorize every word of your thesis defense talk, but you should have it well-polished. There is no limit (or requirement) on how many practice talks you should give, but give as many talks as it takes until you feel like you are ready. If you are unsure of the quality of your talk (or being “ready”), tape record yourself or watch a video of yourself to see just how good it is. You might be surprised when you play it back to yourself.
You should also time your talk. I noticed that I tend to talk faster (by about 5 minutes) when giving the actual public talk vs. when I practice on my own. The length of the talk can depend on many departmental factors. My talk was ~45-50 minutes long which also leaves time for questions.
Either way, do not procrastinate on your slides and/or talk until days before. Make sure you use the full two weeks to perfect your slides, polish your talk (and be very concise about your words), and review material you are unsure about.
2) Listen to other thesis defense talks
The best way to mentally prepare for your thesis defense talk is to listen to other thesis defense talks. I actually went and got a few talks on DVD (the good ones that I remembered). If their research is on a similar topic as your own, this would be more ideal-but take what you can get. When you watch the talk, ask yourself what makes it good or bad? Were they enthusiastic and sincere? Did they keep the energy throughout the talk? Were there some rough areas of the talk? When nerves are running high, talks may not go as expected. You can battle this nervousness by showing up well-prepared. If you are, the thesis defense talk is just a formality.
If you cannot obtain any thesis defense talks on video, make sure that you go to actual public thesis defense talks. At least go to one so that you have a good idea of how to TIE the whole story together and give your audience the big picture. Keep in mind that you are giving a talk to a general audience . This means that use of jargon and highly technical terms will only put your audience to sleep. Make sure it is clear and understandable. Simplify it the best that you can and put it in the larger context of your research field. Use cartoons or model slides (if necessary) to give your audience the general, overall picture.
3) Have your friends, labmates, and others drill you with questions
What’s the best way to prepare for unforeseen questions? Have others that are familiar with your work drill you with questions. Chances are that even though these questions may not be the actual questions you will be asked either by the public and/or your thesis committee, it prepares you to think on your feet. It also builds your confidence . And the questions that your labmates or friends ask you may just be the same question you will get asked on your defense day.
4) Re-read over your entire thesis and write out your own list of questions
You may be sick of reading your entire thesis over and over by now, but you need to keep everything fresh in your mind. I actually read over my entire thesis multiple times during my final two weeks and came up with my own list of questions that I thought my committee would ask me. In addition, I also came up with a list of questions that I had of my own (questions that I was unsure of or that I thought were a weakness of mine). If you cannot come up with a list of good questions, then you are not trying hard enough.
Even though my committee didn’t ask me my exact list of questions, the process of coming up with my own list of questions-then finding the answers to those questions (beyond my thesis)-actually helped me gained a deeper understanding of my project. And it was a confidence booster in disguise.
5) Don’t let distractions get to you
Completing your thesis is a huge milestone. Those last two weeks until defense day can be stressful. Whether you are doing job interviews, applying to other jobs, or you want to “jump the gun” and finally start your post-PhD life, don’t give into temptation. Keep your guard up until your actual defense day. This is key to giving a good talk. You need to go in with the mindset that you will kill your presentation and give a long lasting impression to your audience. I have actually heard that some people who gave great thesis defense talks were offered a position shortly after (i.e. a postdoc).
You are going to want to do all those little tasks that you have been putting off for so long because you have spent X amount of months writing your thesis in solitude and you had no time to do them. Your list could be very long. I can tell you that one of the things on my list was to keep publishing blog articles and keep my blog running. I simply did not have enough time. Prioritize and focus on your defense talk and nothing else . If you are looking for jobs during this time period, I will be writing about this in Part 3 of this series.
6) Get plenty of sleep, keep your diet in check, and take care of yourself
This might be the most difficult thing for anyone. I struggled with this the most while writing my thesis. Skipping meals, late nights, overloading your system with caffeine just to stay awake. You have to fight it the best that you can. A month before my defense talk, I hit the gym 3x a week (for the first time in months). Everyone handles the anxiety of their defense talk differently. I am someone who thinks about it constantly. So it becomes hard to focus on other things, like taking care of yourself.
Once your thesis is turned in to your committee members, during those final two weeks- sleep and a proper diet are KEY. The day of your defense, make sure you are well-rested (don’t stay up all night stressing about it) and eat well. Don’t sell yourself short. By taking care of yourself, you ensure that you have the highest probability for giving a great thesis defense talk and showing your committee members that you are confident about your project.
7) Keep your cool and relax
When your defense day comes, you have to remember that you have put in a lot of HARD WORK to get to this point. You know your topic better than anyone . Because of this, you have no reason to be stressed out.
When your committee pushes you and asks you questions, they again will push you to your limits. You will meet a point where you won’t know the answer. Also, a question could simply be a future direction/experiment that you simply haven’t tested yet. Remember that they are simply trying to test your knowledge and humble you. You don’t have to know all the answers. Therefore, when you are answering questions, keep your cool and relax. Answer the questions the best that you can and you should have no problem passing. And in all honesty, the prelim (or qualifying exam) was much harder than the actual defense…
8) Don’t focus on the after-party until you have actually reached the after-party
Who doesn’t want to spend their final two weeks planning the celebration? Although I did have an after-party, I did not go to great efforts to plan it like a wedding party. As I said in #5, prioritize and focus on your thesis defense talk and nothing else. Plan your after-party while you are on break from your practice talk/preparing for questions/working on slides but do not make it a number one priority. Once you have passed, then you can change your focus. The feeling is indescribable (see #10).
9) Have a good structure
A good thesis talk also has a good introduction before going on to the next idea or slide. It should flow in a logical manner and be smooth. That is why #1 is important, because many people don’t spend enough time in the creation of good powerpoint slides. Your slides and talk have to MATCH up , meaning you can’t have really good slides and a mediocre talk (or vice versa) if you want it to go well.
This is why practice is important, and if you spend enough time on BOTH the talk/slides you will give a very good talk. A lot of times while I was actually practicing my talk, I had to go back and change the order/wording of slides or how I introduced certain slides (the wording) so that the flow would be better.
Be formal in how you word things (i.e. say “our data show that”… vs. “you see here that”…). To give a good introduction, it might be wise to use slides that ask a question in between. This question slide (break) in-between your next idea allows for your general audience to CATCH UP and understand your logic . Why are you doing this experiment? If you just show a bunch of your published data with no introduction (and maybe a title that gives an interpretation/punchline), you will overwhelm and bore your audience.
Many scientists forget that although they are an expert on their topic, what seems easy and understandable to them-does not apply to others outside of their field .
Before you go to your next data slides introduce the idea (based on this data I wanted to ask this question). Then tell them WHY you performed this particular experiment (which is basically in the form of a question). Once your audience understands why, go on to the next slide and give them your interpretation. In other words, don’t just jump to the interpretation . This will keep your audience’s attention and make sure that your thesis defense talk gets a lot of positive feedback and leaves a good impression on your committee members (it really does show).
10) Visualize yourself giving your defense each day and think about how good it will feel when it’s over
This one is pretty self explanatory. I will say that when it is all said and done, it feels like a huge burden has been lifted off your shoulders. It is emotional and you finally feel that all that hard work and time that you put in over the years-was all worth it in the end. Good luck to all those who are preparing for their defense talk in the future! Think about what it will be like to get up in front of a large audience and show everyone how you moved a field forward. This is YOUR moment to show everyone you are an expert in your field. The more you keep this mentality, the better your talk will be. Keep your cool and relax (#7) and everything will be fine.
If you would like to see an example video of a defense talk that illustrates the advice I’ve given, a link to my PhD defense can be found here: http://bit.ly/1sAIT7O
Best of luck to all!
Search The Grad Student Way
Most recent posts.
- PhD Career Series: Finding and Developing Your Inner Leader
- Top 11 Alternative Entry Level PhD Science Careers To Skip the PostDoc
- PhD Myth Busters: Making the Transition From Academia to Industry
- How A Rock Band Helped Save My PhD
- Is A PhD Really Worth It? Or A Waste of Time?
- Dealing With PhD Stress The Right Way: Advice From 3 PhD Graduates
- Write Your PhD Thesis In One Month Or Less
- PhD Career Series: Product Management
- 5 Ways to Gain Valuable Skills Outside of Your Academic Training
- A PhD Student’s Race Against Time – How To Win/Graduate Faster
- Going Freelance Out of Graduate School
- Considering Grad School? Important Things You Should Know Before, During, and After Applying
- Short and Sweet: Five Job Hunting Mistakes PhD Graduates Should Avoid
- Welcome To The ‘Academic Fight Club’
Second Income
- Career Development
- Cool Research
- Entrepreneurship
- Grad School Finance
- Grad School Hardships
- Grad School Humor
- Grad School Insights
- Grad School Poetry
- Grad Student Advice Series
- Grad Student Way Background
- Guest Posts
- PhD Careers In-Depth
- Popular Posts
- Post-Doctoral Related
- Professional Development
- Scientific Discoveries
- Transition From Academia Into Industry
- What's The Worst That Can Happen?
Further Reading
| M | T | W | T | F | S | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 29 | 30 | 31 | ||||
Recent Comments
- Andrew Martin on Top 11 Alternative Entry Level PhD Science Careers To Skip the PostDoc
- Ryan Raver on Is A PhD Really Worth It? Or A Waste of Time?
- Ya-Huei Huang on 10 Ways To Successfully Defend Your PhD
- Krutika I on 10 Ways To Successfully Defend Your PhD
- HABIB ULLAH SIDDIQUI on Grad Student Advice Series: 10 Ways To Be A Successful PhD Student
- sgo on 10 Ways To Successfully Defend Your PhD
- Tuscon Peter on 7 Easy Ways For Graduate Or College Students To Earn Alternative Income Or Make Money Online
- Jim on 7 Easy Ways For Graduate Or College Students To Earn Alternative Income Or Make Money Online
Recent Posts
- October 2018
- November 2015
- January 2015
- December 2014
- November 2013
- September 2013
- August 2013
- February 2013
- January 2013
- December 2012
- October 2012
- September 2012
- August 2012
- Entries feed
- Comments feed
- WordPress.org
Grad School Networking
Featured Posts
Grad Student Advice Series: What to do with your PhD: Post Doc or Real Job?
6 Ways To Survive Grad School and Achieve Work-Life Balance
7 Easy Ways For Graduate Or College Students To Earn Alternative Income Or Make Money Online
Return to top of page
Copyright © 2024 · eleven40 Child Theme on Genesis Framework · WordPress · Log in
Hyperspectral Characterization of Forest Health, Sylvia Park PhD Defense
Please join us on July 10th at 1 PM to support Sylvia Park as she defends her Ph.D thesis "Hyperspectral Characterization of Forest Health."
We hope to see you in LILY, room 2-425 or online through zoom .
Faculty Advisors: Dr. John Couture and Dr. Douglass Jacobs

Related Events
PhD Defence Lisheng Wang | Advanced packaging for SiC power modules
Advanced packaging for SiC power modules
Lisheng Wang is a PhD student in the Department of Power Electronics. Promotors are dr.ir. R.J.E. Hueting and prof.dr.ir. G. Rietveld from the Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Mathematics and Computer Science.

The specific research objectives of this dissertation are:
(a) To perform a comprehensive review of topside interconnections for wide bandgap (WBG) power semiconductor packaging, examining materials, failure modes, advantages, challenges of existing technologies, and future trends.
(b) To develop a new embedded concept with improved thermal management and reduced thermo-mechanical interfacial stress, and to address the limitations of the narrow laser drilling process window compared to conventional embedded technologies.
(c) To introduce a cost-effective alternative bonding scheme and process for large-size substrate attachment coupled with reliable metal-plated metallisation for aluminium (Al) surfaces.
A comprehensive literature review of topside interconnection technologies for WBG semiconductor power devices and modules has been performed. First, the challenges and driving factors for the interconnection of WBG semiconductor dies are discussed. Then, the technical details and innovative features of state-of-the-art interconnection techniques are summarised for commercially-used WBG semiconductors, namely SiC and gallium nitride (GaN). The review categorises and compares existing topside interconnection materials, highlighting their advantages, challenges, and failure modes. Based on this discussion, potential future directions for interconnection technology development are suggested, concluding that superior performance of WBG semiconductors can be achieved by combining novel materials with innovative designs for topside interconnections.
Subsequently, a ceramic substrate-embedded design with a planar copper topside interconnection has been developed to improve the laser drilling process window, and to enhance both reliability and thermal conductance. First, a detailed study was performed of the interaction between ceramic substrates, FR-4 resin (i.e., a woven glass fibre-reinforced epoxy resin laminated composite material, which is Flame Retardant-4), and the lamination and curing processes. It is found that aluminium nitride (AlN), despite its high thermal conductivity, is unsuitable as a ceramic substrate for this application due to its lower flexural strength. Instead, a 0.32 mm thick silicon nitride (Si 3 N 4 ) ceramic substrate has been selected given its superior combination of thermal conductivity and flexural strength, offering a 30% safety margin against ceramic breakage as verified by warpage testing of the fabricated proposed module. The proposed module incorporates a pre-sintered die top system (DTS) layer on the source, gate, and Kelvin source pads, which improves the laser drilling process and reduces interfacial stress in the topside interconnection. Thermal and thermo-mechanical simulations demonstrated that the novel power module achieves significantly lower thermal resistance and von Mises stress, which are 5.8% and 29%, respectively, of those in conventional embedded modules. Electrical testing confirmed that the SiC dies in the embedded module exhibit comparable static electrical performance, and a buck converter using this module showed higher efficiency due to reduced parasitics. Manufacturing results further validated the design's reproducibility and process stability, achieving a 100% production yield for 8 samples, attributed to the effective DTS layer protection, clean laser-drilled micro vias, and excellent plating quality.
Subsequent exploration focuses on the reliability of plated Nickel (Ni)/Silver (Ag) metallisation on Al for sintered Ag joints and development of a new plated Ni/Copper (Cu)/Ag metallisation stack for enhanced reliability. Shear strength, thermal shock (TS), and high-temperature storage (HTS) reliability of sintered Ag joints across different metallisation layers have been analysed, alongside microstructural and elemental analyses to understand failure modes. Traditional Ni/Ag metallisation shows limited reliability due to poor adhesion between Ni and Ag, while the Ni/Cu/Ag metallisation stack exhibited superior performance, with shear strengths consistently above 40 MPa for up to 500 TS cycles, and failure modes predominantly involving Al/Ni delamination and cohesive failure. Longer sintering times further enhance shear strength of both metallisation stacks, reaching values between 100 MPa and 130 MPa. Additionally, a new failure mode has been observed in the Ni/Cu/Ag joints, suggesting a reduced impact of Al/Ni metallisation weakness. This confirms that the new metallisation stack effectively addresses delamination issues in sintered Ag joints with Al heatsinks and direct bonded aluminium (DBA) substrates, thereby maximising the potential of sintered Ag joints.
Further investigations involved shear strength tests on different solder, sintered Ag and transient liquid phase (TLP) joint samples as a function of aging via thermal cycling and high-temperature storage tests. The joint microstructure and failure modes have been analysed using a scanning electron microscope (SEM) with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS). The findings show that sintered Ag has the maximum shear strength of around 70 MPa both before and after aging, while solder joints have the lowest shear strength that decreases from 50 MPa to about 35 MPa after thermal cycling and aging. TLP bonding demonstrates a stable shear strength of approximately 50 MPa after aging due to intermetallic compound growth. TLP bonding thus has a higher reliability than solder joints and is a cost-effective bonding alternative to Ag sintering.
Lastly, a novel wet placement process for Ag sintering of large-size power devices utilising a newly-developed vacuum-assisted fixture has been developed. Experiments of this new placement process show that the pre-heating temperature plays a critical role in determining the shear strength and bonding quality of large-size sintered Ag joints. Elevated pre-heating temperatures (105 °C, 130 °C) led to violent volatilisation processes, resulting in joints with higher void fractions (5.7%, 10.2%) and reduced shear strength (around 70 MPa). Conversely, low preheating temperatures like 60 °C lead to insufficient volatilisation, compromising production efficiency due to the very long heating times needed. Optimal shear strength (77 MPa) and minimal void fraction (0.1%) have been achieved at a pre-heating temperature of 80 °C. The STPak sub-module power devices realised with this process demonstrate full functionality after sintering at 230 °C, 15 MPa, and 10 mins.
In summary, this research fills a crucial gap in the research and application of WBG semiconductors by providing a comprehensive overview of topside interconnection for WBG semiconductors, serving as a valuable reference for packaging engineers. Additionally, it outlines potential future directions, guiding further research in this area. Moreover, this study contributes significantly to the field of power electronics by addressing critical interconnection packaging challenges for SiC power modules. The proposed and validated innovative solutions enhance the processability, reliability, cost-effectiveness, and thermal performance of SiC-based power modules, potentially expanding their application in high-power and high-frequency applications. This advancement not only benefits traditional power modules but also shows huge potential for embedded and system-level integrated power modules, further enriching the field.
More events

PhD Defense: Hybrid Memory Hierarchies for Next Generation HPC Systems
IRB IRB-5165
https://umd.zoom.us/j/6565459667?omn=96827661262 Demands on computational performance, power efficiency, data transfer, resource capacity, and resilience for next generation high performance computing (HPC) systems present a new host of challenges. There is a growing disparity between computational performance vs. network and storage device throughput and among the energy costs of computational, memory, and communication operations. Chapel is a powerful, high-level, parallel, PGAS language designed to streamline development by addressing code complexities and uses a shared memory model for handling large, distributed memory systems. We propose to extend the capabilities of Chapel by providing support of persistent memory with intrinsic and programmatic features for HPC systems. In our approach we will explore the efficacy of persistent memory in a hybrid-PGAS environment through latency hiding analysis via cache monitoring, identification and mitigation of performance bottlenecks via data-centric analysis, and hardware profiling to assess performance cost vs benefits and energy footprint. To manage persistency and ensure resiliency we propose to develop a transaction system with ACID properties that supports hybrid-PGAS virtual addressing and distributed checkpoint system.
Share Options
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Linkedin
Ph.D. Defense Presentation by Jiechao Gao
Computer Science Department
Event Actions
- Add to iCal
- Add to Google
Towards private and accurate IoT applications
Abstract .
Over the past years, the fast-growing trend of Internet of Things (IoT) is bringing millions of new smart devices and sensors into homes, office buildings and industries. These smart devices and sensors enable smart IoT applications (e.g., energy prediction, activity recognition, etc.) to increase the quality and efficiency of our lives. To achieve promising performance for smart IoT applications, it requires massive data from different users and sensors to guarantee the performance due to machine learning and deep learning purposes. However, the edge devices of IoT applications often collect and store only limited data, which is insufficient for training modern learning models. Collaboratively training sets steps to achieve better application performance among different devices while introducing the concern of data privacy. On the other hand, directly applying privacy-preserving techniques such as differential privacy can dramatically degrade the performance of IoT applications.
In this research, we aim to achieve privacy-first smart IoT applications while ensuring their accurate performance for multi-user and multi-sensor scenarios. First, we propose Personalized Federated Deep Reinforcement Learning~(PFDRL), a system that helps local users achieve private and accurate energy management. PFDRL replaces the central server with a decentralized federated learning (DFL) framework and enables personalized federated reinforcement learning to tackle the standby energy reduction in residential buildings. Next, we propose PFed-LDP, a personalized federated local differential privacy framework for global users. The PFed-LDP design includes a weight-enhanced local differential privacy (LDP) with a dynamic layer-sharing mechanism in the federated learning framework to accomplish privacy-preserving, personalized and communication efficient IoT applications. Finally, we introduce PrivateHub, a system that utilizes contrastive learning with diffusion models for synthetic data generation in multi-sensor scenarios. PrivateHub helps to prevent the private applications' identification from multi-sensor environments while ensuring the accurate performance of the non-private applications.
Committee:
- Yangfeng Ji, Committee Chair (CS/SEAS/UVA)
- Bradford Campbell, Advisor (CS, ECE/SEAS/UVA)
- Lu Feng (CS, SIE/SEAS/UVA)
- Cong Shen (ECE/SEAS/UVA)
- Jorge Ortiz (ECE/School of Eng/Rutgers)
Alumni Spotlight: Recent PhD in Pharmacological Sciences Graduate Huda Barhoosh Showcased “Activity-Based DNA-Encoded Library Screening for Inhibitors of Eukaryotic Translation” Dissertation Defense

“I am very thankful to have had a great graduate school experience that was positive in many aspects,” said Huda Barhoosh, a recent graduate of the UC Irvine School of Pharmacy & Pharmaceutical Sciences’ PhD in Pharmacological Sciences program. “I feel blessed to have a supportive advisor who has helped shape me into a well-rounded scientist. My fellow graduate students have been welcoming and supportive, and I have built lasting friendships.”
A graduate of Qatar University’s BSc in Pharmacy program, Barhoosh chose to pursue her PhD in Pharmacological Sciences at UCI, stating that the program “offered the perfect combination of rigorous research, exceptional faculty, interdisciplinary opportunities, a supportive community, and outstanding resources.”
During her time in the PhD program, Barhoosh served as a student representative for the UCI Diverse Educational Community and Doctoral Experience (DECADE) initiative, which aims to foster inclusivity and guide the success of women and underrepresented minorities who are pursuing graduate degrees. She was on the UCI School of Pharmacy & Pharmaceutical Sciences’ Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI) committee as well. She also mentored first-year PhD students and was an organizer for the Synthetic and Chemical Biology Club .
Barhoosh completed a 10-week rotation in the Alachkar Lab in her first year at UCI, assisting with research that studied the impact of prenatal stress on mice offspring. Then, she joined the Paegel Lab , contributing to the research team’s studies of miniaturization.
“I worked on developing a miniaturized droplet-based high-throughput screening assay to screen DNA-encoded libraries for inhibitors of eukaryotic translation. A large number of drug targets are currently inaccessible to small-molecule therapeutics due to the nature of the protein target. By inhibiting translation, we can circumvent this and prevent the disease target from being produced in the first place. I’ve designed an assay that can screen small-molecules for translation inhibition and have used it to screen large libraries built in our lab and have discovered novel translation inhibitors,” she shared. “I am fortunate to be part of a research lab that conducts cutting-edge research, which has expanded my skills and knowledge and includes amazing individuals who have enriched my graduate school journey.”
On June 4, Barhoosh presented the culmination of her research at UCI with “Activity-Based DNA-Encoded Library Screening for Inhibitors of Eukaryotic Translation.”
“Small molecule probes exist for only ~2% of human proteins because most lack functional binding pockets or cannot be assayed for high-throughput screening (HTS). Selective translation modulation is a possible mechanism to circumvent canonical druggability constraints and can be evaluated via in vitro transcription translation (IVTT),” she explained in the summary of her dissertation defense. “We developed a plug-and-play IVTT activity assay by fusing a GFP reporter to various target gene sequences and screened these constructs in microfluidic droplets using DNA-encoded libraries (DEL). This work sets the stage for scaling microfluidic IVTT screening to the entirety of the human proteome as a universal biochemical assay, and perhaps more broadly across the tree of life.”
With the completion of her studies, Barhoosh is ready to apply what she has learned to her upcoming professional endeavors.
“The interdisciplinary nature of the PhD in Pharmacological Sciences program has exposed me to a wide range of research areas, broadening my knowledge and perspective. The available resources and facilities have significantly advanced my research,” she said. “I aim to join the pharmaceutical industry and establish my career as a scientist. I hope to use the skills and knowledge that I’ve gained through my training to advance the field of drug discovery.”
Share this post:

Integrated Multi-Physics Laboratory Department of Mechanical Engineering
Congratulations to dr. wang for passing his phd defense :).


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The PhD defence, also known as the viva voce or oral examination, is a pivotal moment in the life of a doctoral candidate. PhD defence is not merely a ritualistic ceremony; rather, it serves as a platform for scholars to present, defend, and elucidate the findings and implications of their research. The defence is the crucible where ideas are ...
Learn what a PhD viva is, who attends, how long it lasts, what happens during and after, and what are the possible outcomes. A PhD viva is an oral examination of your thesis by two examiners, one internal and one external, to confirm your competence as a researcher.
And, PhD dissertation defense is a finale to your PhD years. Often, researchers question how to excel at their thesis defense and spend countless hours on it. Days, weeks, months, and probably years of practice to complete your doctorate, needs to surpass the dissertation defense hurdle.
Learn from experts how to prepare for your dissertation defense, from choosing an advisor to writing, presenting, and answering questions. Find out what to expect, how to cope with challenges, and how to celebrate your achievement.
How to prepare for a thesis defense quick guide. Check with your department about requirements and timing. Re-read your thesis. Anticipate questions and prepare for them. Create a back-up plan to deal with technology hiccups. Plan de-stressing activities both before, and after, your defense.
Learn what the PhD defence is, who's involved, and how to prepare for it. Find out the steps, deadlines, and resources for submitting your thesis, choosing your committee, and completing your degree.
The dissertation defense is the crowning moment of years of research - the final examination before a PhD student is awarded their doctoral degree. During a dissertation defense, the student presents their research, methodology, findings, and conclusions to a committee of faculty members and experts in their field.
Getting a Ph.D. is a once-in-a-lifetime event, so enjoy it and take satisfaction in what you've accomplished. Patricia Gosling and Bart Noordam are the authors of Mastering Your Ph.D.: Survival and Success in the Doctoral Years and Beyond ( Springer, 2006 ). Gosling is a senior medical writer at Novartis Vaccines and Diagnostics in Germany and ...
Learn what to expect and how to prepare for a viva or an oral presentation of your dissertation. Find out the common questions, tips, and outcomes of different levels of assessment.
tips from former PhD stude nts and super visors, this book. unpacks the principles and unwritten rules underpinning. the defence. Addressing planning and preparing for the. doctoral defence, and ...
A PhD defense isn't just a rite of passage for doctoral candidates—it's the final, decisive step on the journey to earning a doctorate. It requires the full commitment of the candidate, their dissertation advisor, the committee chair, and all members involved, ensuring that the graduate studies department's requirements are met, and ...
Learn how to prepare for and conduct yourself during the oral examination of your PhD thesis. Find out about the format, tips, and possible outcomes of the viva in different countries and institutions.
ur department Chair will approve the thesis for registration using the same online system. Then, requests for review and approval will go to the Arts, Sciences and Engineering Dean of G. duate Studies office and finally to the office of the University Dean of Graduate Studies. When all of these officials have appro.
Learn how to prepare for your PhD defense at the University of Rochester, including choosing a chair, selecting a date, registering your dissertation, and following the guidelines. Find out the requirements, deadlines, and resources for international students and work visas.
This defense is about you showing off what you know, so before you stand up in front of the crown, take a deep dive into your own research masterpiece. Thoroughly review your dissertation, scrutinizing each chapter, section, and argument. ... A PhD herself, she has coached and supervised first-generation, ESL, and non-traditional students in ...
PhD Viva vs PhD Defence. The words viva and defence are sometimes used interchangeably, but often are used to reference the different ways that the a PhD is concluded around the world. A PhD viva (technically a viva voce) is a formal examination of a PhD. It's typical in the UK (amongst other countries) and it is a closed-event between ...
Learn how to deal with the format, presentation, questions and nerves of your thesis defence. Find out how to practice, what to expect and how to trust your research in this guide by James Hayton.
Videoconferencing technology can help researchers to conduct oral exams remotely. Credit: Getty. In November 2019, I conducted my PhD defence using the videoconferencing software Zoom.
It's the moment almost everyone who completes a PhD both dreads and looks ahead to for years—the defence. It signals a major achievement, but in people's imaginations, it can seem like the stuff of nightmares… standing frozen in front of everyone, unable to answer a tricky question posed by a committee member and feeling like you must look incompetent.
In August 2020, I defended my PhD successfully. In the preceding months, I had generated a list of potential defense questions by using various different sources (websites, other defenses I watched, and my supervisors). The list ended up helping me a lot. Today I shared this list with a colleague who is soon defending, and I thought: Why not share it publicly?
It's also a good idea to take note of any weaknesses or mistakes so you're prepared if they're discussed during the defence. Prepare Your Talk. After rereading your thesis, you will be in a good position to put your talk together. Your talk should address what you did, why you did it, how you did it, what you found, and what it means.
23. Generally speaking, PhD defenses come in two flavors, and it is not possible to say a priori which one yours will fall into: A real thesis "defense" focuses on the thesis, and all questions will relate to the scope of the research work. In this case, knowing your own work and its context well enough should be sufficient, but it is of course ...
5) Don't let distractions get to you. Completing your thesis is a huge milestone. Those last two weeks until defense day can be stressful. Whether you are doing job interviews, applying to other jobs, or you want to "jump the gun" and finally start your post-PhD life, don't give into temptation.
Hyperspectral Characterization of Forest Health, Sylvia Park PhD Defense. Please join us on July 10th at 1 PM to support Sylvia Park as she defends her Ph.D thesis "Hyperspectral Characterization of Forest Health." We hope to see you in LILY, room 2-425 or online through zoom. Faculty Advisors: Dr. John Couture and Dr. Douglass Jacobs
The PhD defence of Lisheng Wang will take place in the Waaier building of the University of Twente and can be followed by a live stream. Live Stream. Lisheng Wang is a PhD student in the Department of Power Electronics. Promotors are dr.ir. R.J.E. Hueting and prof.dr.ir. G. Rietveld from the Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Mathematics and ...
PhD Defense: Planning and Perception for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles in Object and Environmental Monitoring Harnaik Dhami. Talk. 07.09.2024 13:00 to 15:00. IRB-5165. PhD Defense: Enhancing Modern Query Federation Systems: Execution Optimization, Performance Prediction, and Systems Assessment Chujun Song.
Share Ph.D defense - Emmannuel WAngila on LinkedIn; I'm Interested. About this Event (NANO) Nanoscale Material Science & Engineering Building, 105 View map Add to calendar Save to Google Calendar Save to iCal Save to Outlook. 731 W Dickson St, Fayetteville, AR 72701. #Dissertation defense ...
Towards private and accurate IoT applications Abstract Over the past years, the fast-growing trend of Internet of Things (IoT) is bringing millions of new smart devices and sensors into homes, office buildings and industries. These smart devices and sensors enable smart IoT applications (e.g., energy prediction, activity recognition, etc.) to increase the quality and efficiency of our lives.
Alumni Spotlight: Recent PhD in Pharmacological Sciences Graduate Huda Barhoosh Showcased "Activity-Based DNA-Encoded Library Screening for Inhibitors of Eukaryotic Translation" Dissertation Defense "I am very thankful to have had a great graduate school experience that was positive in many aspects," said Huda Barhoosh, a recent graduate of the UC Irvine School of Pharmacy & ...
Rio Tinto Kennecott Mechanical Engineering Bldg. 1495 E. 100 S. (1550 MEK) Salt Lake City, UT 84112