Purpose and Limitations of Random Assignment
In an experimental study, random assignment is a process by which participants are assigned, with the same chance, to either a treatment or a control group. The goal is to assure an unbiased assignment of participants to treatment options.
Random assignment is considered the gold standard for achieving comparability across study groups, and therefore is the best method for inferring a causal relationship between a treatment (or intervention or risk factor) and an outcome.
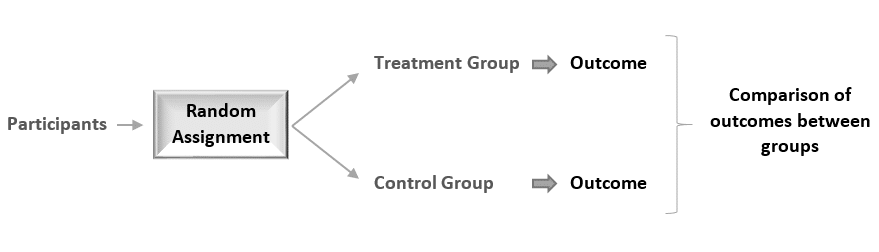
Random assignment of participants produces comparable groups regarding the participants’ initial characteristics, thereby any difference detected in the end between the treatment and the control group will be due to the effect of the treatment alone.

How does random assignment produce comparable groups?
1. random assignment prevents selection bias.
Randomization works by removing the researcher’s and the participant’s influence on the treatment allocation. So the allocation can no longer be biased since it is done at random, i.e. in a non-predictable way.
This is in contrast with the real world, where for example, the sickest people are more likely to receive the treatment.
2. Random assignment prevents confounding
A confounding variable is one that is associated with both the intervention and the outcome, and thus can affect the outcome in 2 ways:
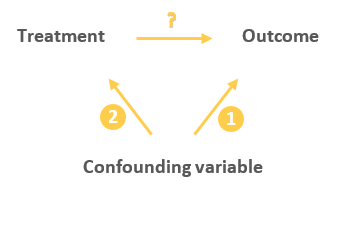
Either directly:

Or indirectly through the treatment:

This indirect relationship between the confounding variable and the outcome can cause the treatment to appear to have an influence on the outcome while in reality the treatment is just a mediator of that effect (as it happens to be on the causal pathway between the confounder and the outcome).
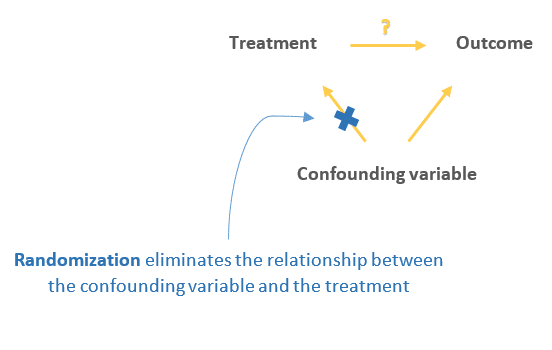
Random assignment eliminates the influence of the confounding variables on the treatment since it distributes them at random between the study groups, therefore, ruling out this alternative path or explanation of the outcome.
3. Random assignment also eliminates other threats to internal validity
By distributing all threats (known and unknown) at random between study groups, participants in both the treatment and the control group become equally subject to the effect of any threat to validity. Therefore, comparing the outcome between the 2 groups will bypass the effect of these threats and will only reflect the effect of the treatment on the outcome.
These threats include:
- History: This is any event that co-occurs with the treatment and can affect the outcome.
- Maturation: This is the effect of time on the study participants (e.g. participants becoming wiser, hungrier, or more stressed with time) which might influence the outcome.
- Regression to the mean: This happens when the participants’ outcome score is exceptionally good on a pre-treatment measurement, so the post-treatment measurement scores will naturally regress toward the mean — in simple terms, regression happens since an exceptional performance is hard to maintain. This effect can bias the study since it represents an alternative explanation of the outcome.
Note that randomization does not prevent these effects from happening, it just allows us to control them by reducing their risk of being associated with the treatment.
What if random assignment produced unequal groups?
Question: What should you do if after randomly assigning participants, it turned out that the 2 groups still differ in participants’ characteristics? More precisely, what if randomization accidentally did not balance risk factors that can be alternative explanations between the 2 groups? (For example, if one group includes more male participants, or sicker, or older people than the other group).
Short answer: This is perfectly normal, since randomization only assures an unbiased assignment of participants to groups, i.e. it produces comparable groups, but it does not guarantee the equality of these groups.
A more complete answer: Randomization will not and cannot create 2 equal groups regarding each and every characteristic. This is because when dealing with randomization there is still an element of luck. If you want 2 perfectly equal groups, you better match them manually as is done in a matched pairs design (for more information see my article on matched pairs design ).
This is similar to throwing a die: If you throw it 10 times, the chance of getting a specific outcome will not be 1/6. But it will approach 1/6 if you repeat the experiment a very large number of times and calculate the average number of times the specific outcome turned up.
So randomization will not produce perfectly equal groups for each specific study, especially if the study has a small sample size. But do not forget that scientific evidence is a long and continuous process, and the groups will tend to be equal in the long run when a meta-analysis aggregates the results of a large number of randomized studies.
So for each individual study, differences between the treatment and control group will exist and will influence the study results. This means that the results of a randomized trial will sometimes be wrong, and this is absolutely okay.
BOTTOM LINE:
Although the results of a particular randomized study are unbiased, they will still be affected by a sampling error due to chance. But the real benefit of random assignment will be when data is aggregated in a meta-analysis.
Limitations of random assignment
Randomized designs can suffer from:
1. Ethical issues:
Randomization is ethical only if the researcher has no evidence that one treatment is superior to the other.
Also, it would be unethical to randomly assign participants to harmful exposures such as smoking or dangerous chemicals.
2. Low external validity:
With random assignment, external validity (i.e. the generalizability of the study results) is compromised because the results of a study that uses random assignment represent what would happen under “ideal” experimental conditions, which is in general very different from what happens at the population level.
In the real world, people who take the treatment might be very different from those who don’t – so the assignment of participants is not a random event, but rather under the influence of all sort of external factors.
External validity can be also jeopardized in cases where not all participants are eligible or willing to accept the terms of the study.
3. Higher cost of implementation:
An experimental design with random assignment is typically more expensive than observational studies where the investigator’s role is just to observe events without intervening.
Experimental designs also typically take a lot of time to implement, and therefore are less practical when a quick answer is needed.
4. Impracticality when answering non-causal questions:
A randomized trial is our best bet when the question is to find the causal effect of a treatment or a risk factor.
Sometimes however, the researcher is just interested in predicting the probability of an event or a disease given some risk factors. In this case, the causal relationship between these variables is not important, making observational designs more suitable for such problems.
5. Impracticality when studying the effect of variables that cannot be manipulated:
The usual objective of studying the effects of risk factors is to propose recommendations that involve changing the level of exposure to these factors.
However, some risk factors cannot be manipulated, and so it does not make any sense to study them in a randomized trial. For example it would be impossible to randomly assign participants to age categories, gender, or genetic factors.
6. Difficulty to control participants:
These difficulties include:
- Participants refusing to receive the assigned treatment.
- Participants not adhering to recommendations.
- Differential loss to follow-up between those who receive the treatment and those who don’t.
All of these issues might occur in a randomized trial, but might not affect an observational study.
- Shadish WR, Cook TD, Campbell DT. Experimental and Quasi-Experimental Designs for Generalized Causal Inference . 2nd edition. Cengage Learning; 2001.
- Friedman LM, Furberg CD, DeMets DL, Reboussin DM, Granger CB. Fundamentals of Clinical Trials . 5th ed. 2015 edition. Springer; 2015.
Further reading
- Posttest-Only Control Group Design
- Pretest-Posttest Control Group Design
- Randomized Block Design
Random Assignment in Psychology: Definition & Examples
Julia Simkus
Editor at Simply Psychology
BA (Hons) Psychology, Princeton University
Julia Simkus is a graduate of Princeton University with a Bachelor of Arts in Psychology. She is currently studying for a Master's Degree in Counseling for Mental Health and Wellness in September 2023. Julia's research has been published in peer reviewed journals.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Saul McLeod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul McLeod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
In psychology, random assignment refers to the practice of allocating participants to different experimental groups in a study in a completely unbiased way, ensuring each participant has an equal chance of being assigned to any group.
In experimental research, random assignment, or random placement, organizes participants from your sample into different groups using randomization.
Random assignment uses chance procedures to ensure that each participant has an equal opportunity of being assigned to either a control or experimental group.
The control group does not receive the treatment in question, whereas the experimental group does receive the treatment.
When using random assignment, neither the researcher nor the participant can choose the group to which the participant is assigned. This ensures that any differences between and within the groups are not systematic at the onset of the study.
In a study to test the success of a weight-loss program, investigators randomly assigned a pool of participants to one of two groups.
Group A participants participated in the weight-loss program for 10 weeks and took a class where they learned about the benefits of healthy eating and exercise.
Group B participants read a 200-page book that explains the benefits of weight loss. The investigator randomly assigned participants to one of the two groups.
The researchers found that those who participated in the program and took the class were more likely to lose weight than those in the other group that received only the book.
Importance
Random assignment ensures that each group in the experiment is identical before applying the independent variable.
In experiments , researchers will manipulate an independent variable to assess its effect on a dependent variable, while controlling for other variables. Random assignment increases the likelihood that the treatment groups are the same at the onset of a study.
Thus, any changes that result from the independent variable can be assumed to be a result of the treatment of interest. This is particularly important for eliminating sources of bias and strengthening the internal validity of an experiment.
Random assignment is the best method for inferring a causal relationship between a treatment and an outcome.
Random Selection vs. Random Assignment
Random selection (also called probability sampling or random sampling) is a way of randomly selecting members of a population to be included in your study.
On the other hand, random assignment is a way of sorting the sample participants into control and treatment groups.
Random selection ensures that everyone in the population has an equal chance of being selected for the study. Once the pool of participants has been chosen, experimenters use random assignment to assign participants into groups.
Random assignment is only used in between-subjects experimental designs, while random selection can be used in a variety of study designs.
Random Assignment vs Random Sampling
Random sampling refers to selecting participants from a population so that each individual has an equal chance of being chosen. This method enhances the representativeness of the sample.
Random assignment, on the other hand, is used in experimental designs once participants are selected. It involves allocating these participants to different experimental groups or conditions randomly.
This helps ensure that any differences in results across groups are due to manipulating the independent variable, not preexisting differences among participants.

When to Use Random Assignment
Random assignment is used in experiments with a between-groups or independent measures design.
In these research designs, researchers will manipulate an independent variable to assess its effect on a dependent variable, while controlling for other variables.
There is usually a control group and one or more experimental groups. Random assignment helps ensure that the groups are comparable at the onset of the study.
How to Use Random Assignment
There are a variety of ways to assign participants into study groups randomly. Here are a handful of popular methods:
- Random Number Generator : Give each member of the sample a unique number; use a computer program to randomly generate a number from the list for each group.
- Lottery : Give each member of the sample a unique number. Place all numbers in a hat or bucket and draw numbers at random for each group.
- Flipping a Coin : Flip a coin for each participant to decide if they will be in the control group or experimental group (this method can only be used when you have just two groups)
- Roll a Die : For each number on the list, roll a dice to decide which of the groups they will be in. For example, assume that rolling 1, 2, or 3 places them in a control group and rolling 3, 4, 5 lands them in an experimental group.
When is Random Assignment not used?
- When it is not ethically permissible: Randomization is only ethical if the researcher has no evidence that one treatment is superior to the other or that one treatment might have harmful side effects.
- When answering non-causal questions : If the researcher is just interested in predicting the probability of an event, the causal relationship between the variables is not important and observational designs would be more suitable than random assignment.
- When studying the effect of variables that cannot be manipulated: Some risk factors cannot be manipulated and so it would not make any sense to study them in a randomized trial. For example, we cannot randomly assign participants into categories based on age, gender, or genetic factors.
Drawbacks of Random Assignment
While randomization assures an unbiased assignment of participants to groups, it does not guarantee the equality of these groups. There could still be extraneous variables that differ between groups or group differences that arise from chance. Additionally, there is still an element of luck with random assignments.
Thus, researchers can not produce perfectly equal groups for each specific study. Differences between the treatment group and control group might still exist, and the results of a randomized trial may sometimes be wrong, but this is absolutely okay.
Scientific evidence is a long and continuous process, and the groups will tend to be equal in the long run when data is aggregated in a meta-analysis.
Additionally, external validity (i.e., the extent to which the researcher can use the results of the study to generalize to the larger population) is compromised with random assignment.
Random assignment is challenging to implement outside of controlled laboratory conditions and might not represent what would happen in the real world at the population level.
Random assignment can also be more costly than simple observational studies, where an investigator is just observing events without intervening with the population.
Randomization also can be time-consuming and challenging, especially when participants refuse to receive the assigned treatment or do not adhere to recommendations.
What is the difference between random sampling and random assignment?
Random sampling refers to randomly selecting a sample of participants from a population. Random assignment refers to randomly assigning participants to treatment groups from the selected sample.
Does random assignment increase internal validity?
Yes, random assignment ensures that there are no systematic differences between the participants in each group, enhancing the study’s internal validity .
Does random assignment reduce sampling error?
Yes, with random assignment, participants have an equal chance of being assigned to either a control group or an experimental group, resulting in a sample that is, in theory, representative of the population.
Random assignment does not completely eliminate sampling error because a sample only approximates the population from which it is drawn. However, random sampling is a way to minimize sampling errors.
When is random assignment not possible?
Random assignment is not possible when the experimenters cannot control the treatment or independent variable.
For example, if you want to compare how men and women perform on a test, you cannot randomly assign subjects to these groups.
Participants are not randomly assigned to different groups in this study, but instead assigned based on their characteristics.
Does random assignment eliminate confounding variables?
Yes, random assignment eliminates the influence of any confounding variables on the treatment because it distributes them at random among the study groups. Randomization invalidates any relationship between a confounding variable and the treatment.
Why is random assignment of participants to treatment conditions in an experiment used?
Random assignment is used to ensure that all groups are comparable at the start of a study. This allows researchers to conclude that the outcomes of the study can be attributed to the intervention at hand and to rule out alternative explanations for study results.
Further Reading
- Bogomolnaia, A., & Moulin, H. (2001). A new solution to the random assignment problem . Journal of Economic theory , 100 (2), 295-328.
- Krause, M. S., & Howard, K. I. (2003). What random assignment does and does not do . Journal of Clinical Psychology , 59 (7), 751-766.
All Subjects
Experimental Design
Study guides for every class, that actually explain what's on your next test, random assignment, from class:.
Random assignment is a technique used in experimental research to ensure that participants are allocated to different groups or conditions in a way that is not influenced by any biases or pre-existing differences. This process helps to create equivalent groups, enhancing the credibility of the experiment's conclusions by minimizing confounding variables.
congrats on reading the definition of Random Assignment . now let's actually learn it.
5 Must Know Facts For Your Next Test
- Random assignment helps eliminate selection bias, ensuring that differences between groups are due to the experimental treatment rather than other variables.
- This technique is crucial for internal validity, as it strengthens causal inferences by demonstrating that changes in outcomes can be attributed to the manipulated variables.
- It allows researchers to generalize their findings to a larger population since it creates groups that are statistically equivalent on all relevant characteristics.
- Random assignment can be achieved through methods like flipping a coin, using random number generators, or drawing lots to assign participants to groups.
- It's essential for designing both between-subjects and within-subjects experiments, influencing how treatments are administered and compared.
Review Questions
- Random assignment enhances internal validity by ensuring that each participant has an equal chance of being placed in any experimental group. This process reduces the likelihood of pre-existing differences between groups affecting the outcomes. By balancing out participant characteristics across conditions, researchers can confidently attribute observed effects to the treatment rather than other variables.
- In between-subjects designs, random assignment helps create equivalent groups by randomly allocating different participants to separate conditions. In within-subjects designs, although all participants experience all conditions, random assignment can still be applied to determine the order in which they encounter those conditions. This approach minimizes order effects and ensures that any differences observed are due to the treatments themselves.
- Stratified random sampling involves dividing a population into subgroups and then randomly selecting from these groups to ensure representation across key characteristics. When combined with random assignment in an experiment, researchers first use stratified sampling to form a diverse participant pool and then employ random assignment to allocate these individuals into experimental groups. This integration ensures that the groups are both representative of the overall population and balanced in terms of critical variables, enhancing both internal and external validity of the findings.
Related terms
A group of participants that does not receive the experimental treatment, allowing researchers to compare outcomes against those who do receive it.
A method used to select participants for a study where each individual has an equal chance of being chosen, aiming to ensure the sample represents the broader population.
A technique where participants and/or researchers are kept unaware of which group participants belong to, reducing bias in the treatment administration and outcome assessment.
" Random Assignment " also found in:
Subjects ( 28 ).
- AP Psychology
- AP Statistics
- Abnormal Psychology
- Advanced Communication Research Methods
- Applied Impact Evaluation
- Art Therapy
- Biostatistics
- Causal Inference
- Cognitive Psychology
- College Introductory Statistics
- Communication Research Methods
- Data, Inference, and Decisions
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational Psychology
- Honors Statistics
- Intro to Business Statistics
- Intro to Psychology
- Introduction to Biostatistics
- Introduction to Political Research
- Language and Cognition
- Market Research: Tools and Techniques for Data Collection and Analysis
- Marketing Strategy
- Media Effects
- Philosophy of Science
- Physiology of Motivated Behaviors
- Probability and Statistics
- Professionalism and Research in Nursing
- Social Psychology
© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.
Ap® and sat® are trademarks registered by the college board, which is not affiliated with, and does not endorse this website..

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Experiments use random assignment to avoid which of the following? a. Random selection. b. Carryover effects. c. Selection effects.
Random assignment is an important part of control in experimental research, because it helps strengthen the internal validity of an experiment and avoid biases. In experiments, researchers manipulate an …
Random assignment is a process used in experimental research to allocate subjects into different groups—such as treatment and control groups—using a random …
Random assignment prevents selection bias. Randomization works by removing the researcher’s and the participant’s influence on the treatment allocation. So the allocation can no longer be biased since it is done at …
Random assignment or random placement is an experimental technique for assigning human participants or animal subjects to different groups in an experiment (e.g., a treatment group …
In psychology, random assignment refers to the practice of allocating participants to different experimental groups in a study in a completely unbiased way, ensuring each participant has an equal chance of being …
Random assignment is valuable because it ensures independence of treatment from potential outcomes. That is how it leads to unbiased estimates of the average treatment effect. But …
Random assignment is a technique used in experimental research to ensure that participants are allocated to different groups or conditions in a way that is not influenced by any biases or …