- Network Sites:
Changing the World One Wireless RF Chip at a Time
- iHeartRadio
- 3D Printing
- Amateur Radio
- Augmented Reality
- Cloud Computing
- Computers & Peripherals
- Consumer Electronics
- Cyber Security
- .NET Gadgeteer
- Adafruit Playground
- AllThingsTalk
- Amazon Alexa
- Amazon Web Services
- Android SmartThings
- Microcontrollers
- Power Electronics
- RF & Wireless
- Sensors & Actuators
- + Start Project
- + Import Project
- Health & Fitness
- Home Automation
- Industrial IoT
- Machine Learning
- Motor Control
- Security / Identification
- AT&T IoT Platform
- BeagleBoard
- Bosch IoT Suite
- ControlEverything.com

Connect With Us
Make diy homework writing machine at home.
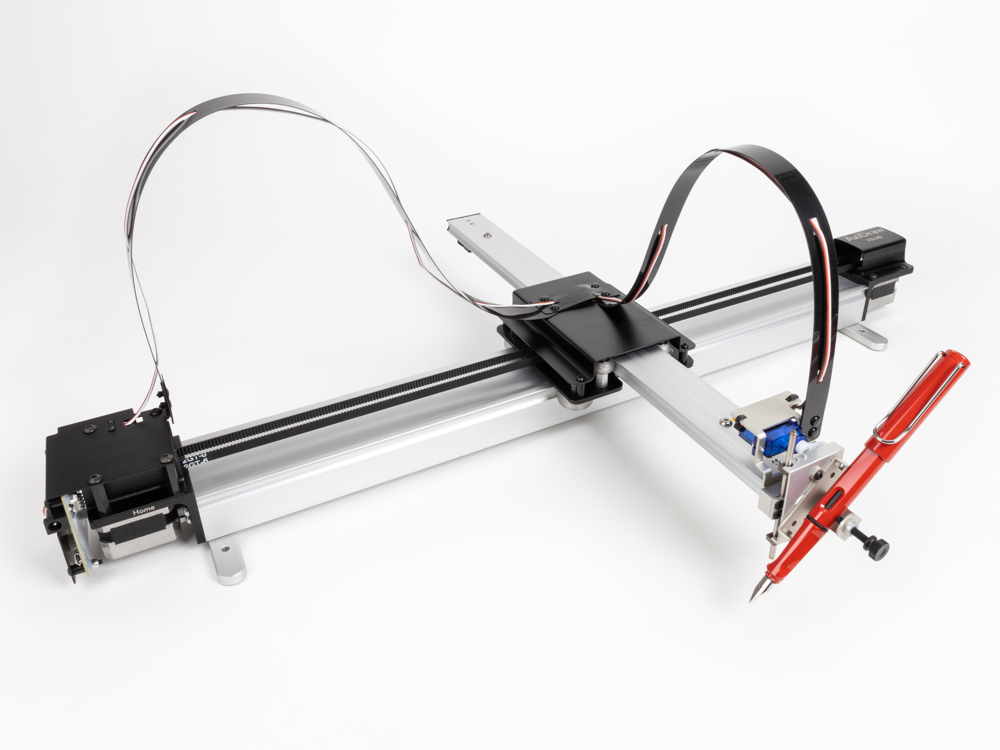
Drawing Robot/Pen Plotter/Drawing Machine is an Open Hardware version of the famous machine AxiDraw which it is a pen pl
| 1 | |||
Introduction: Make DIY Homework Writing Machine at Home
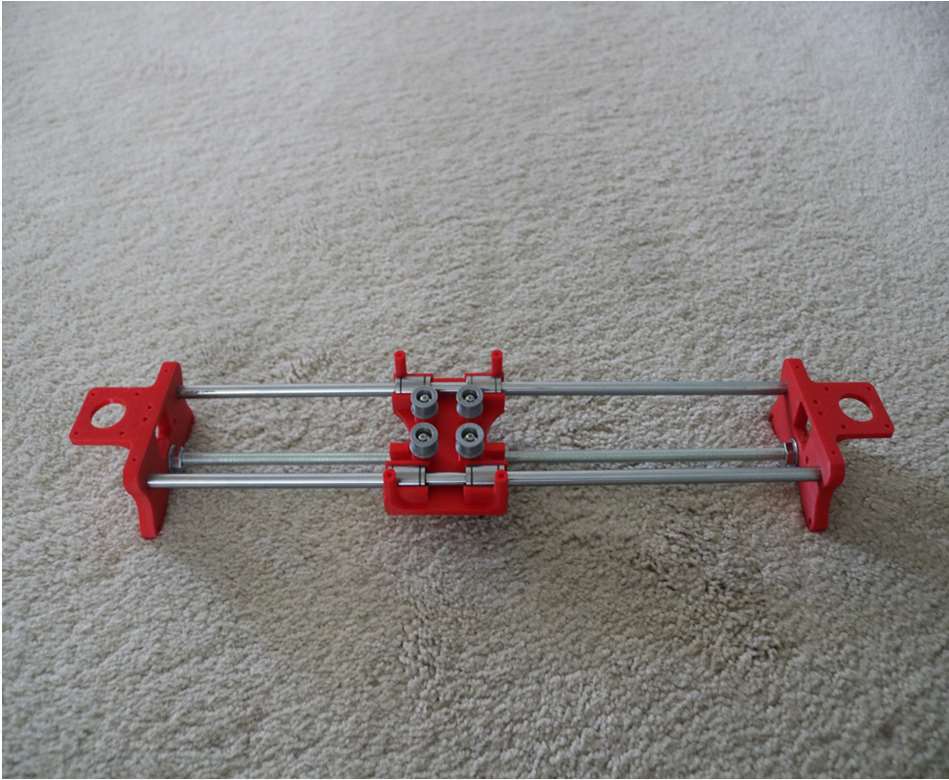
Drawing Robot/Pen Plotter/Drawing Machine is an Open Hardware version of the famous machine AxiDraw which it is a pen plotter, capable of writing or drawing on almost any flat surface. It can write with pens, permanent markers, pencils, and other writing implements to handle an endless variety of applications.
Its unique design features a writing head that extends beyond the machine, making it possible to draw on objects bigger than the machine itself. The biggest advantage of the machine is that it can be placed over the book because of the core XY extending design of the machine.
This Drawing Robot/Pen Plotter/Drawing Machine is similar to the commercially available AxiDraw. It is powered by an Arduino Uno controller, uses a CNC Shield, and GRBL firmware
The cost to build the Drawing Robot is between $75 depending on where you buy your parts and whether you already own some of the parts such as the Arduino.
You can find all of my projects on https://www.diyprojectslab.com/
Maximum drawing area 24 * 30 CM.
Thank You NextPCB
This project is successfully completed because of the help and support from NextPCB. Guys if you have a PCB project, please visit their website and get exciting discounts and coupons.
Free shipping 0$ PCB Prototype: https://www.nextpcb.com/pcb-quote?
Thanksgiving Christmas lucky draw 100% win: https://www.nextpcb.com/christmas-lucky-draw
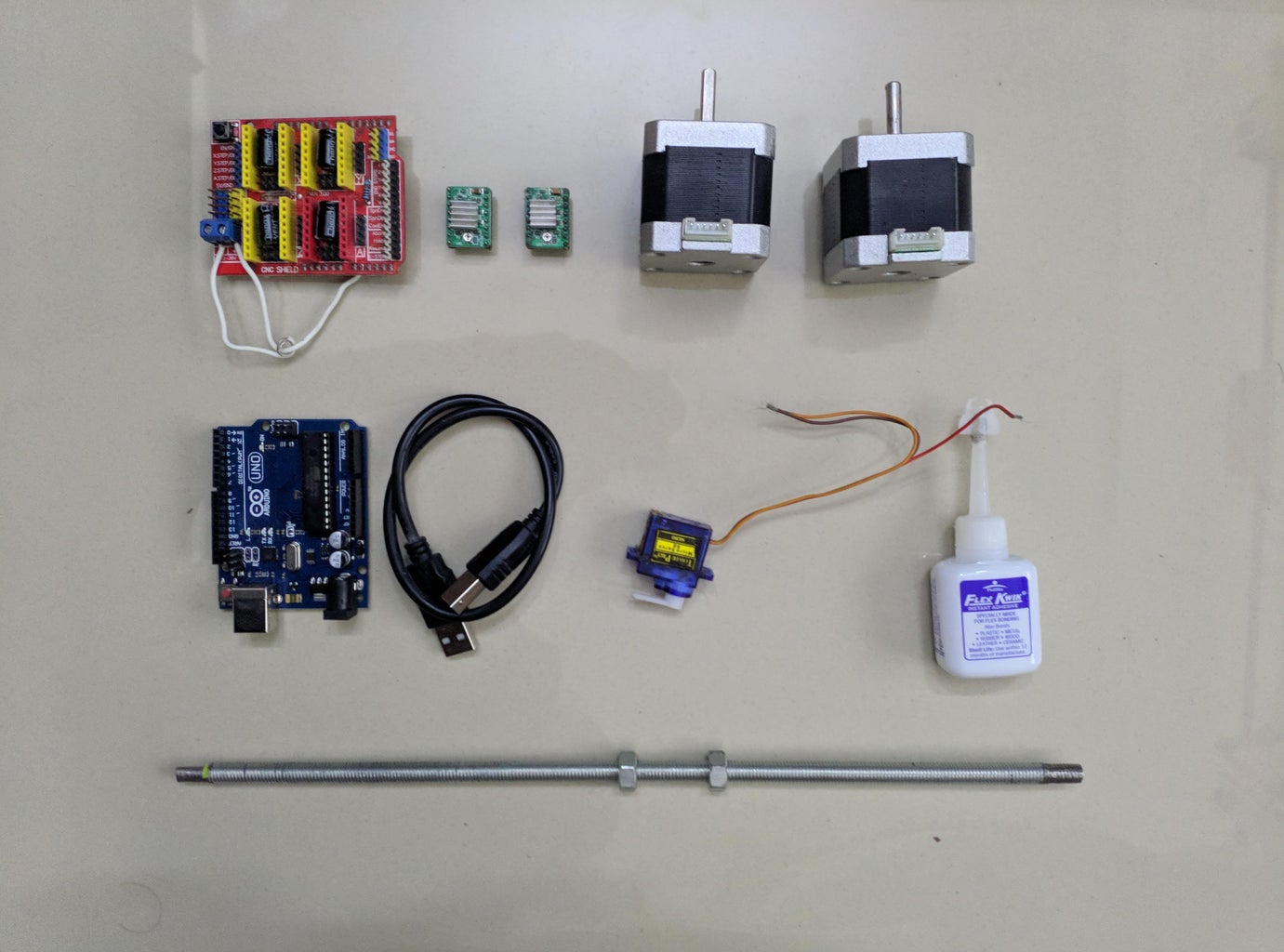
Step 1: Parts and Materials Required
4 x 5/16in washer 4 x M3 washers
2 x Nema 17 Stepper Motors Amazon.com
2 x Linear Rod M8 x 450mm for X Axis Amazon.com
2 x Linear Rod M8 x 350mm for Y Axis Amazon.com
2 x Linear Rod 3mm for Z Axis (you can get it from old CDROM)
1 x Threaded Rod M8 x 480mm8 x LM8UU Bearings Amazon.com
1 x Servo Sg901 x Spring 5m (from ball point pen) Amazon.com
2 x GT2 Pulley, 16 teeth Amazon.com
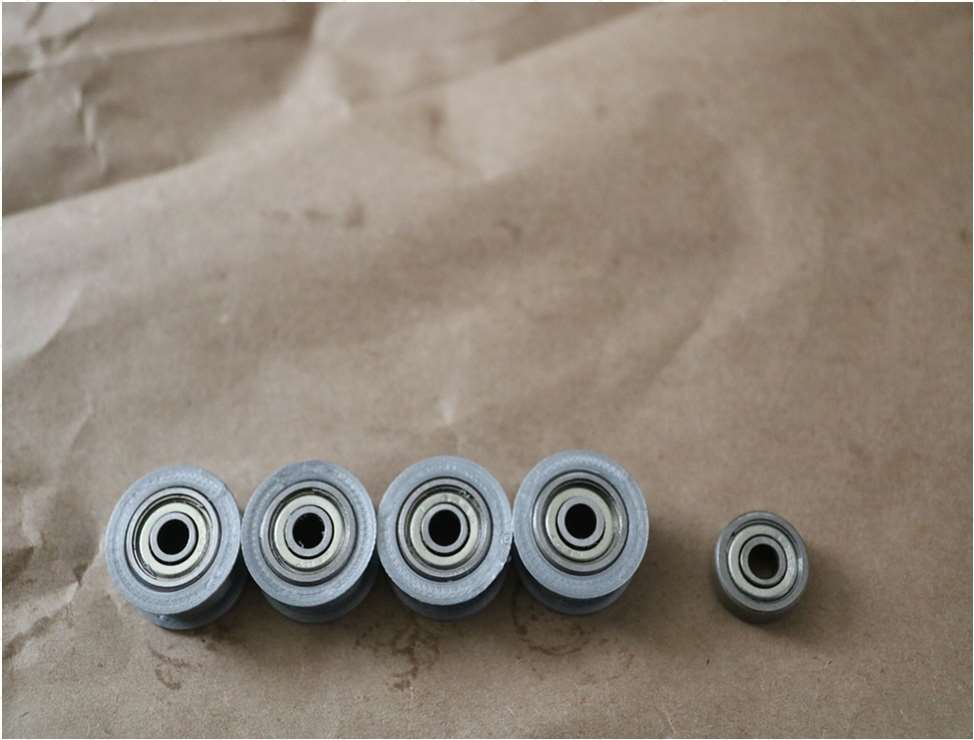
5 x Bearing 624zz Amazon.com
1 x 2000mm GT2 belt Amazon.com
1 x Arduino Uno Amazon.com
1 x CNC Shield Amazon.com
2 x A4988 Stepper driver with heatsink Amazon.com
6 x Jumpers Amazon.com
1 x 12V 2A Power Supply Amazon.com
- 4 x 5/16in-18
- 13 x Phillips M3-0.5 x 16mm
- 4 x Phillips M3-0.5 x 6mm
- 5 x Phillips M4-0.7x 35mm
- 1 x Hex M3-0.5 x 20mm
- 4 x 5/16in washer
- 4 x M3 washers
Step 2: 3D Printing
PLA is fine for this design. I print at 200C on BuildTak. None of the parts require rafts or brims. I suggest supports only for the pen holder and the Z axis end plate which is standing up.
Download the files from Thingiverse
Open the 3D models in Cura or any other slicer.
Use 75% infill on all the parts (An infill of 70 – 100% will work as well)
Printed all the parts with 0.10 – 0.20 mm layer height
Printed with PLA
Use supports on the Penholder, Slider, X_Support_L and the X_Support_R
Note: The longest part took around 10hrs and the shortest took 30 minutes to print
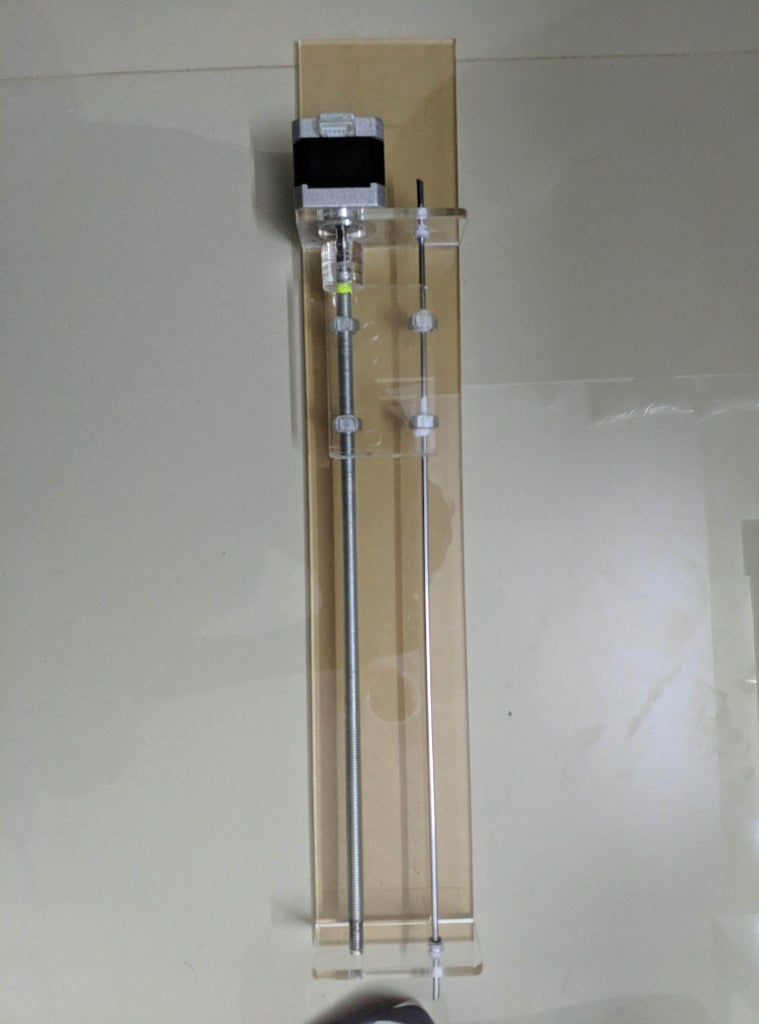
Step 3: Assemble the X-Axis
Now take the threaded rod and insert it in the hole below. Feed a 5/16in washer and 5/16in nut on both sides of the x-support part
Remember that you need (2) 350mm and (2) 450mm long linear rods
Take the (2) 450mm linear rods and insert them into either x-support part
- Use may need to use a round file to smooth out the holes that you insert them in
- Also, you can use a rubber mallet to help insert the rods
Step 4: Assemble the X-Axis Bearing
Slide the clamshell through the 450mm (X-axis) linear rods Use a rubber mallet again to attach the last X-support on the linear rods Make sure that the rods stick out equally on both sides Slide the other end of the threaded rod through the hole on the X-support Put on the last set of nuts and washers to hold the X-support in place Now that the X-axis is complete, you can use (2) Phillips M3-0.5 x 16mm screws per X-support to help keep the linear rods from sliding
Now you want to push the LM8UU bearings into their place on the top and bottom clamshell (The top and bottom clamshell take (4) bearings each)
Take (4) 624zz bearings and push them through the 3D-printed idler pulleys. Leave the 5th bearing for later when you assemble the Y-axis
Assemble the X-Axis (Carriage)
- Get (4) M3-0.5 x 20mm screws, (4) M3 nuts, (4) M3 washers and (4) 624zz bearings with the idler pulleys installed
- Take one screw and feed a washer through it, the washer will rest on the bearing. The nut will be at the bottom of the carriage, which will secure the bearing in place
Assemble the X-Axis (X-Support)
- Slide the clamshell through the 450mm (X-axis) linear rods
- Use a rubber mallet again to attach the last X-support on the linear rods
- Make sure that the rods stick out equally on both sides
- Slide the other end of the threaded rod through the hole on the X-support
- Put on the last set of nuts and washers to hold the X-support in place
- Now that the X-axis is complete, you can use (2) Phillips M3-0.5 x 16mm screws per X-support to help keep the linear rods from sliding
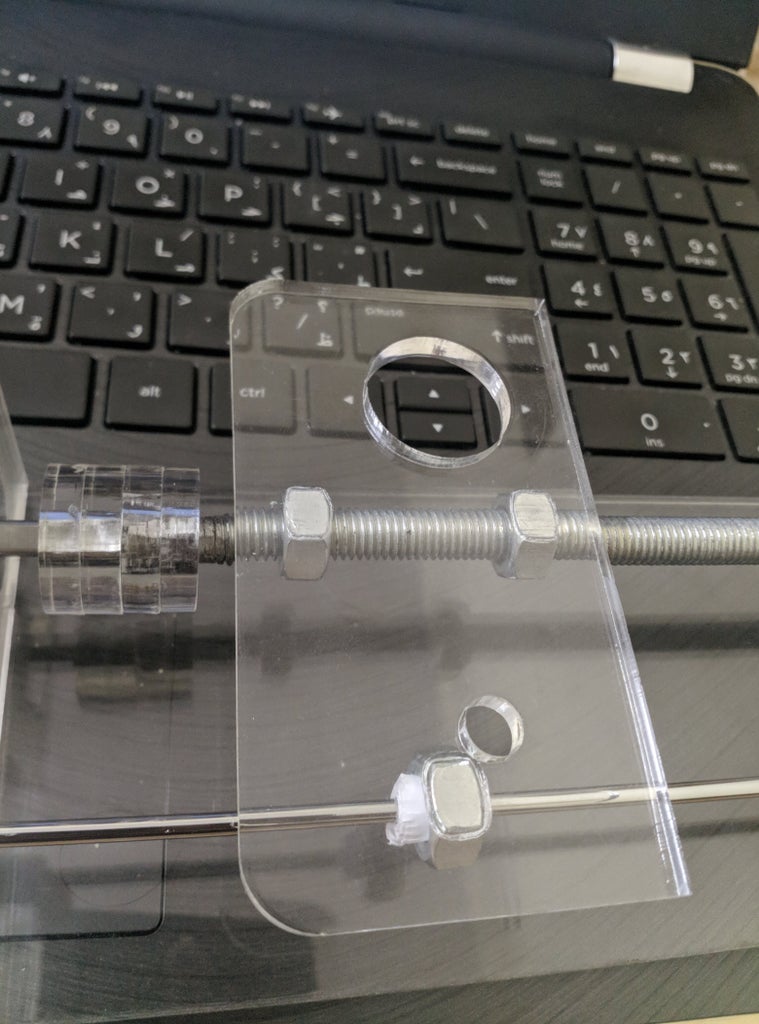
Step 5: Assemble the Y-Axis
- Slide the the linear rods/Y-back piece through the LM8UU bearings and attach the Y-front piece using a rubber mallet
- Take the (2) 350mm linear rods and insert them the Y-back piece by using a rubber mallet
- Get (1) M4-0.5 x 35 screw, (1) M4 nut and the 5th 624zz bearing
- Get (2) M3-0.5 x 16 screws to secure the linear rods
- Slide in the bearing when inserting the screw through the Y-back piece
Step 6: Assemble the X-Y Axis (Belt)
Use a pair of needle nose pliers to help guide the GT2 belt more easily through the clamshell Take the two ends of the belt and slide them through the “teeth” on the Base Slider The belt should be tight and not loose Note that once the GT2 belt is on, it is normal for the clamshell not to move easily
- Use a pair of needle nose pliers to help guide the GT2 belt more easily through the clamshell
- Take the two ends of the belt and slide them through the “teeth” on the Base Slider
- The belt should be tight and not loose
- Note that once the GT2 belt is on, it is normal for the clamshell not to move easily
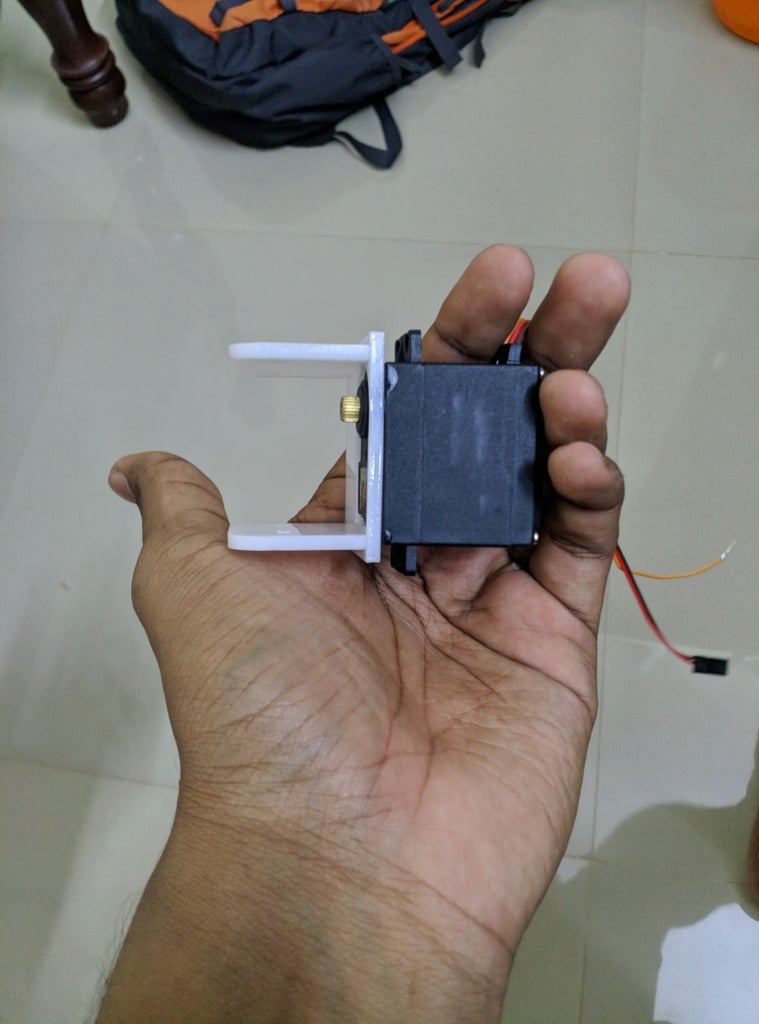
Step 7: Assemble the Z-Axis
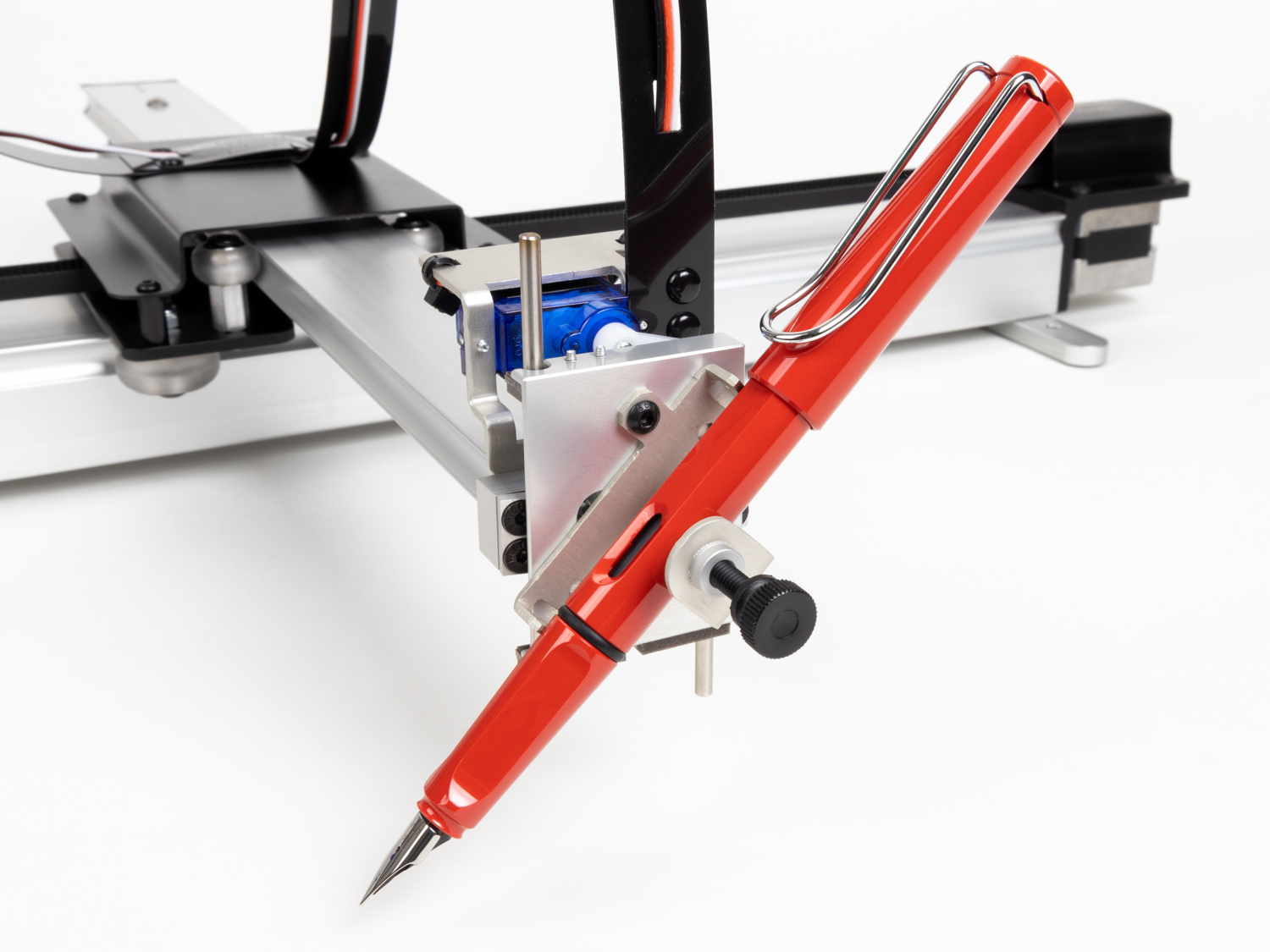
Get (2) 3mm linear rods and the following 3D printed parts (Slider, Pen Holder, Base Slide, 3MM Metric Thumb Screw) Get (1) Hex M3-0.5 x 20mm screw and the Metric Thumb Screw and push them together. Use superglue to keep it together. Get (3) M3-0.5 x 16mm screws which you will use the secure the Base Slide to the Y-Front part. You may need to use (3) M3-0.5 nuts in order to hold it in place Push the Slider and Pen Holder together to make one piece Now take that new part and the (2) 3mm linear rods and slide the rods through the holes. Place a small spring in between the two parts so there is a little bit of pressure to lift the Slider. You may need to cut the spring a bit until there is an adequate amount of pressure on the slider.
- Get (2) 3mm linear rods and the following 3D printed parts (Slider, Pen Holder, Base Slide, 3MM Metric Thumb Screw)
- Get (1) Hex M3-0.5 x 20mm screw and the Metric Thumb Screw and push them together. Use superglue to keep it together.
- Get (3) M3-0.5 x 16mm screws which you will use the secure the Base Slide to the Y-Front part. You may need to use (3) M3-0.5 nuts in order to hold it in place
- Push the Slider and Pen Holder together to make one piece
- Now take that new part and the (2) 3mm linear rods and slide the rods through the holes. Place a small spring in between the two parts so there is a little bit of pressure to lift the Slider. You may need to cut the spring a bit until there is an adequate amount of pressure on the slider.
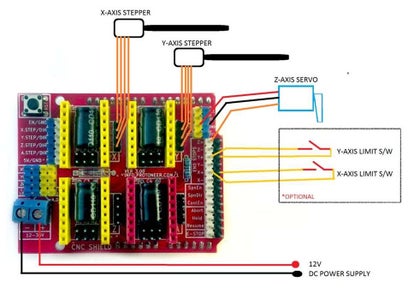
Step 8: ELECTRONICS
To find the coils of the stepper motors, use a multimeter. If there's resistance between the two wires, you have a coil. On the schematic, the coils are represented by two wires of the same color.
ELECTRONICS
i prefer you can use Arduino uno CNC Shield
Ready to your all circuit
1) 4pcs A4988 Stepper Motor Driver
2) Expansion Board A4988 Driver
3)Arduino UNO First of all take hit sink and stick on A4988 motor Driver.
4pcs A4988 Stepper motor driver connect on expansion board A4988 driver module, then connect the arduino with expansion board and connect all wiring The shield also has a built-in micro stepping control - meaning that instead of using full steps or half steps like a large CNC would do, we can make the motors move by 1/16 or 1/32 of a step to make the laser move with the maximal precision possible. However, the motors will consume more electricity: they will get hot quicker.
To use the micro stepping modes, short some of the mode pins together. Different combinations give different resolutions. Take a look at the chart for the different configurations possible. When the shield is programmed, add the A4988 drivers to it and wire up the rest of the electronics.
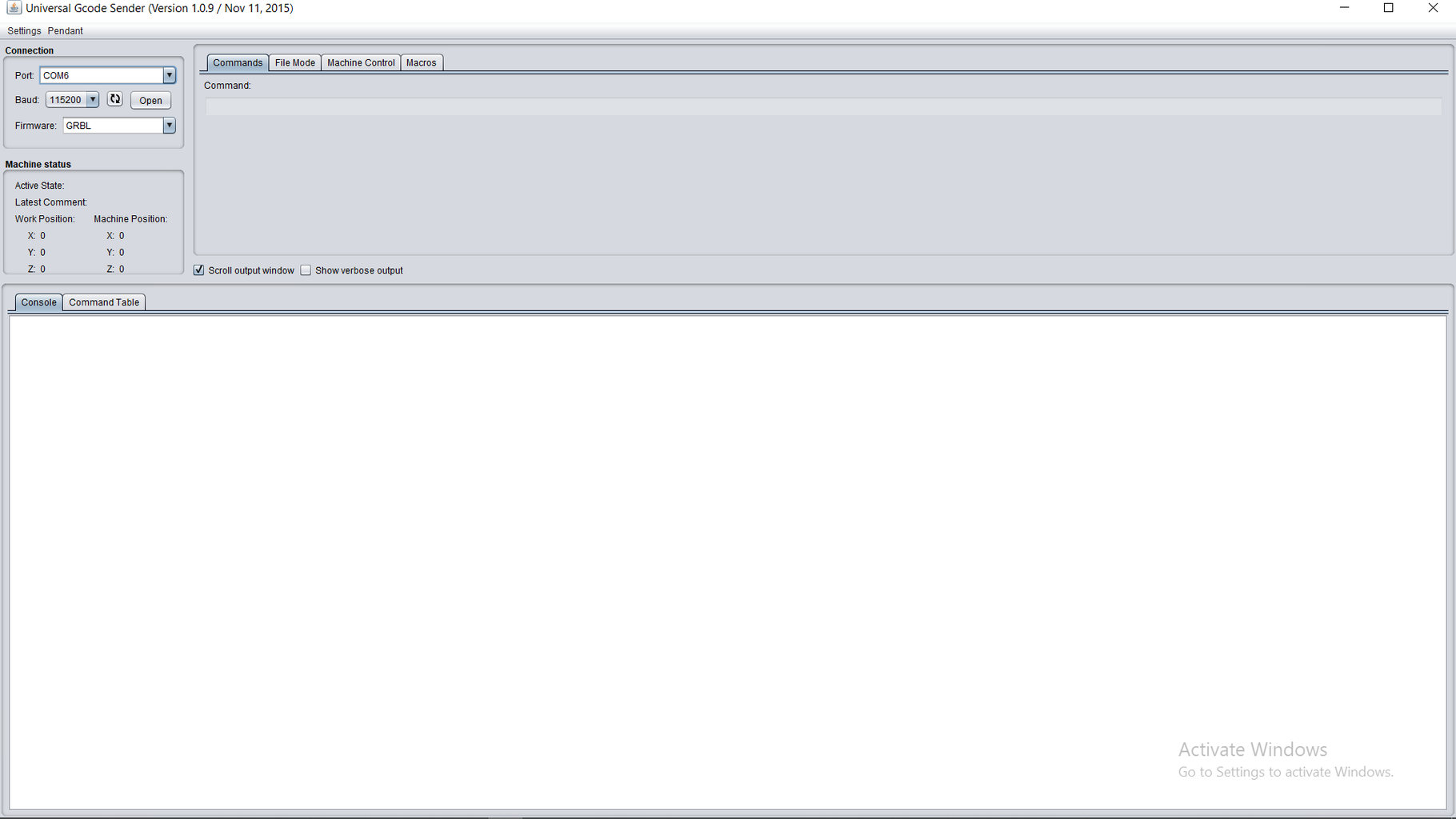
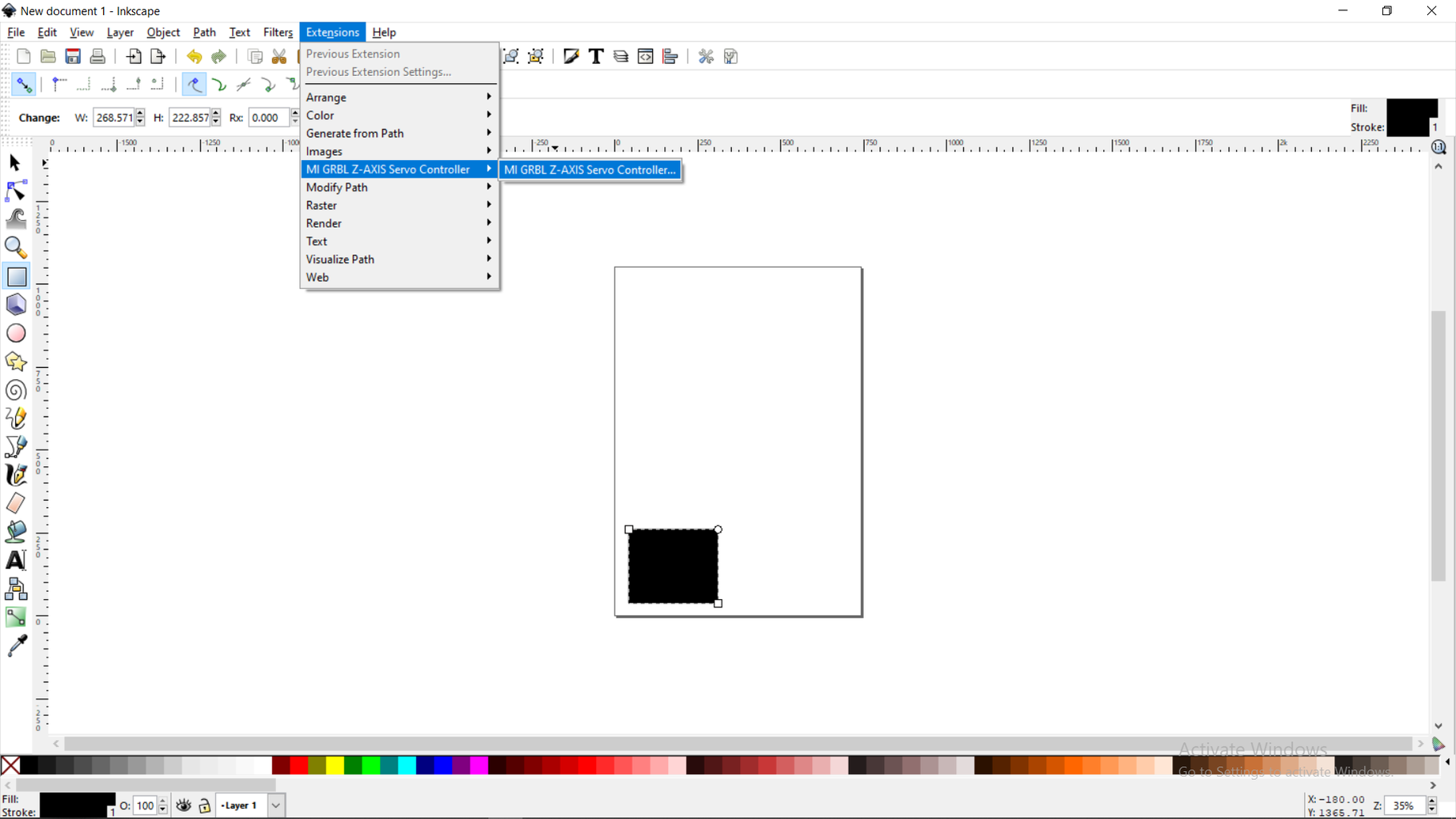
Step 9: SOFTWARE
Inkscape which is the graphics design software (draw or import graphics)
Inkscape MI GRBL Extension (convert graphics to G-Code)Universal G Code Sender (sends the G-Code to the robot causing drawing motion)GRBL which is the Arduino firmware (programmed into the Arduino Uno)
Arduino: https://www.arduino.cc/en/software
Universal G-code sender: https://winder.github.io/ugs_website/...
Inkscape: https://inkscape.org/release/inkscape..
4xiDraw & km laser: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1YO8-...
Processing: https://processing.org/download/
drawing to G-code processing: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1PIFx...
watch video for full setup
Step 10: Drawing Machine at Work
@diy.projects.lab
Related Content
- Virtual Reality
- CNC Machine
- Diyprojectslab
You May Also Like
Welcome back.
Don't have a Maker account? Create one now .
Forgot your password? Click here .
Join Our Community of Makers
Register for our site & newsletters. This gives you access to start a project, collaborate with others, and more!
This is the name that will be shown with your messages. You may use any name you wish. Once set, this cannot be changed.
Entering a password is required.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
- Online Text to STL
- 3D Printed Soldering Helper
- 3D Printed Coin Vault
- 3D Printed FLARE GUN (PROP/REPLICA) MULTI PART
- 3D Printed Mini Container with PET Bottle Cap Size
TEST 3D PRINTS
Easy & Fun Things to 3D Print
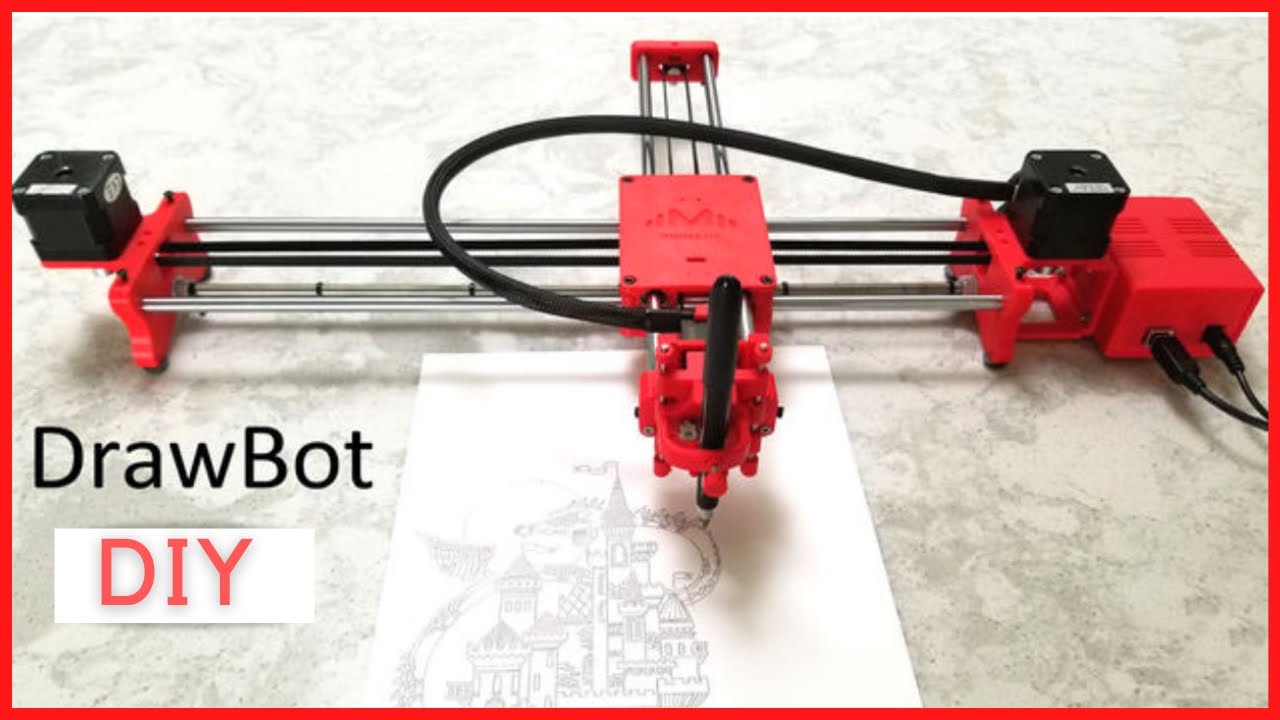
How To Make DIY Pen Plotter / Homework Writing Machine at Home
This Drawing Robot/Pen Plotter/Drawing Machine is similar to the commercially available AxiDraw. It is powered by an Arduino Uno controller, uses a CNC Shield, and GRBL firmware.
The cost to build the Drawing Robot is between $75 and $100 depending on where you buy your parts and whether you already own some of the parts such as the Arduino.
Parts and Materials Required
- 2 x Nema 17 Stepper Motors
- 2 x Linear Rod M8 x 450mm for X Axis
- 2 x Linear Rod M8 x 350mm for Y Axis
- 2 x Linear Rod 3mm for Z Axis (you can get it from old CDROM)
- 1 x Threaded Rod M8 x 480mm
- 8 x LM8UU Bearings
- 1 x Servo Sg90
- 1 x Spring 5m (from ball point pen)
- 2 x GT2 Pulley, 16 teeth
- 5 x Bearing 624zz
- 1 x 2000mm GT2 belt
- 1 x Arduino Uno
- 1 x CNC Shield
- 2 x A4988 Stepper driver with heatsink
- 6 x Jumpers
- 1 x 12V 2A Power Supply
- 4 x 5/16in-18
- 13 x Phillips M3-0.5 x 16mm
- 4 x Phillips M3-0.5 x 6mm
- 5 x Phillips M4-0.7x 35mm
- 1 x Hex M3-0.5 x 20mm
- 4 x 5/16in washer
- 4 x M3 washers
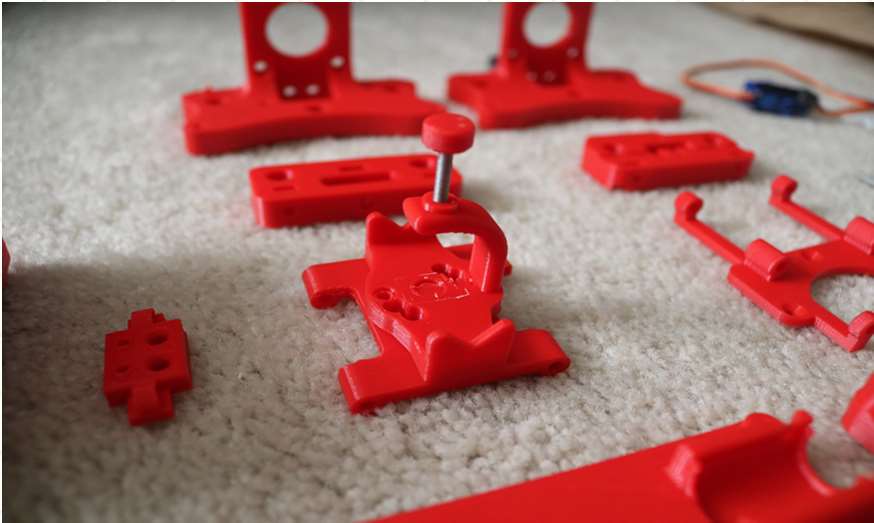
3D Printing
- Download the files from Thingiverse
- Open the 3D models in Cura or any other slicer(Sli3er, Simplify 3D, etc.)
- Use 75% infill on all the parts (An infill of 70 – 100% will work as well)
- Printed all the parts with 0.10 – 0.20 mm layer height
- Printed with Hatchbox Red PLA
- Use supports on the Penholder, Slider, X_Support_L and the X_Support_R
Note: The longest part took around 9hrs and the shortest took 30 minutes to print
3D Printed Parts

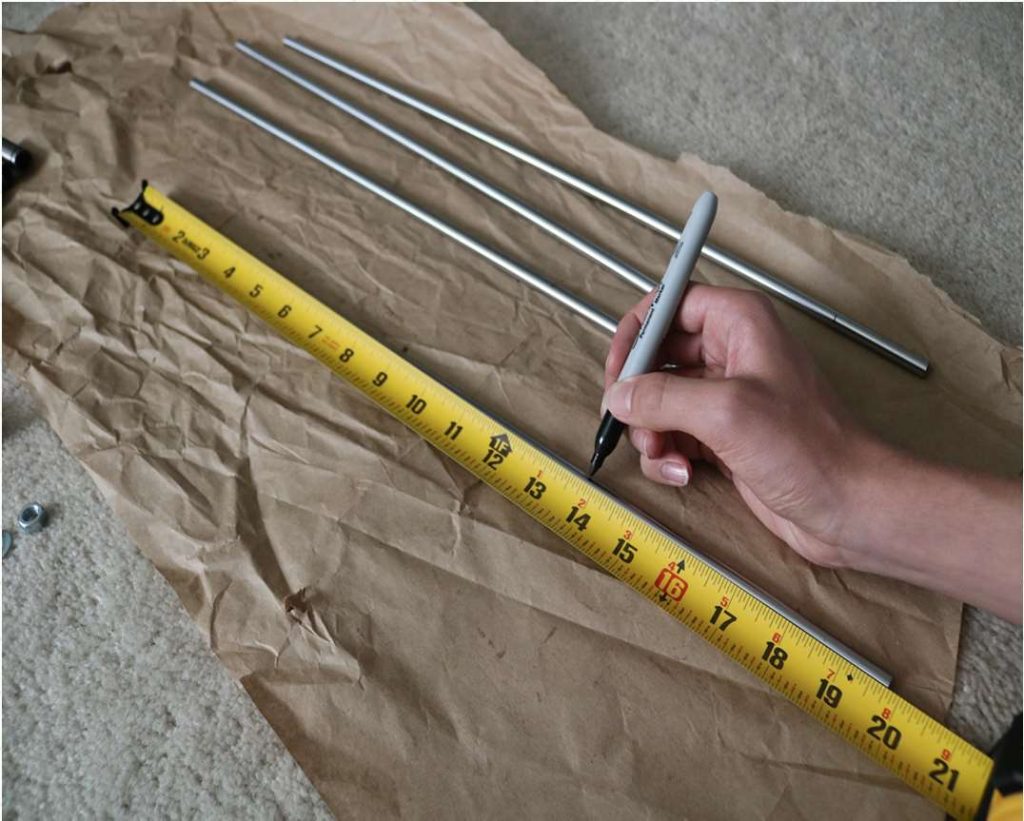
Cut your Linear Rods
Use a measuring tape and sharpie to mark the spots where the rods need to be cut
- Use a vise to hold the rods in place when you cut them
- Remember that you need (2) 350mm and (2) 450mm long linear rods
- On the threaded rod, mark your cutting point at 470mm

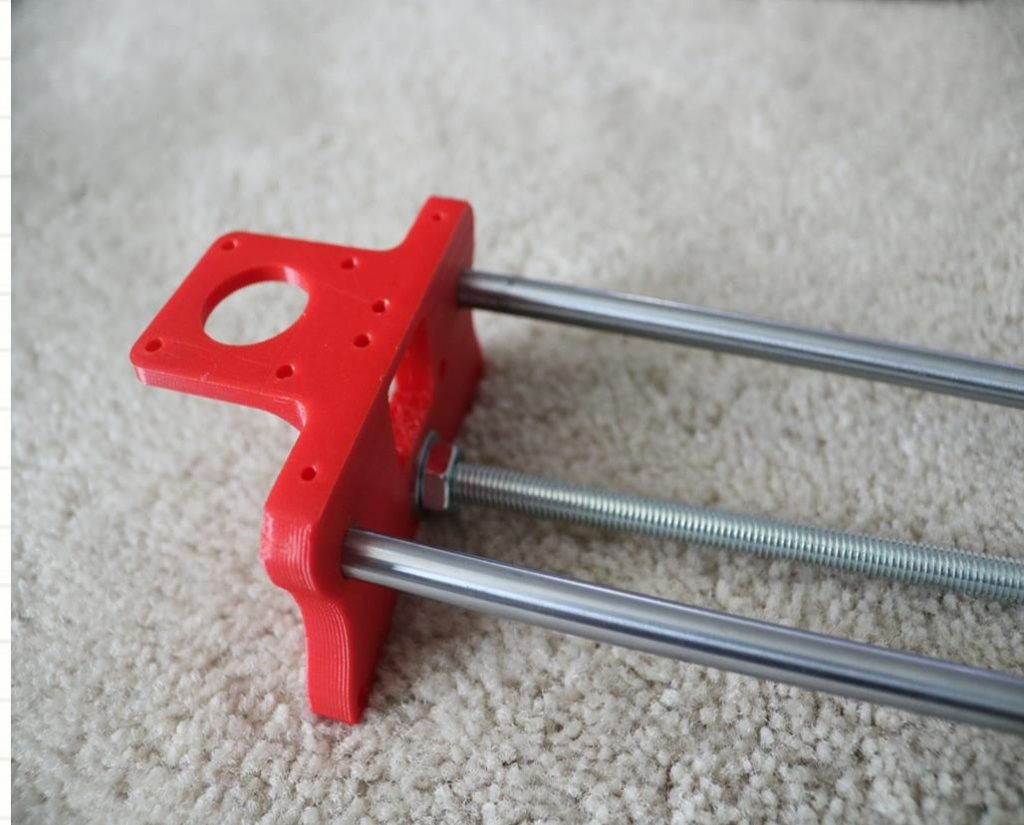
Assemble the X-Axis (Linear/Threaded Rods)
Take the (2) 450mm linear rods and insert them into either x-support part
- Use may need to use a round file to smooth out the holes that you insert them in
- Also, you can use a rubber mallet to help insert the rods
Now take the threaded rod and insert it in the hole below. Feed a 5/16in washer and 5/16in nut on both sides of the x-support part

Assemble the X-Axis (Bearings)
Now you want to push the LM8UU bearings into their place on the top and bottom clamshell (The top and bottom clamshell take (4) bearings each)
Take (4) 624zz bearings and push them through the 3D-printed idler pulleys. Leave the 5th bearing for later when you assemble the Y-axis

Assemble the X-Axis (Carriage)
- Get (4) M3-0.5 x 20mm screws, (4) M3 nuts, (4) M3 washers and (4) 624zz bearings with the idler pulleys installed
- Take one screw and feed a washer through it, the washer will rest on the bearing. The nut will be at the bottom of the carriage, which will secure the bearing in place

Assemble the X-Axis (X-Support)
- Slide the clamshell through the 450mm (X-axis) linear rods
- Use a rubber mallet again to attach the last X-support on the linear rods
- Make sure that the rods stick out equally on both sides
- Slide the other end of the threaded rod through the hole on the X-support
- Put on the last set of nuts and washers to hold the X-support in place
- Now that the X-axis is complete, you can use (2) Phillips M3-0.5 x 16mm screws per X-support to help keep the linear rods from sliding

Assemble the X-Axis (Stepper Motors)
- Use an appropriate sized allen wrench to attach the 16 teeth pulleys on the stepper motor shafts
- Flipping the entire chassis around will make it easier to attach the stepper motors
- Use (8) M3-0.5 x 6mm screws and a Phillips screwdriver to attach the (2) stepper motors
Assemble the Y-Axis (Clamshell)
(Optional if you have problems keeping belt on bearings)
- Grab (4) M4-0.5 x 35mm screws and (4) M4 nuts
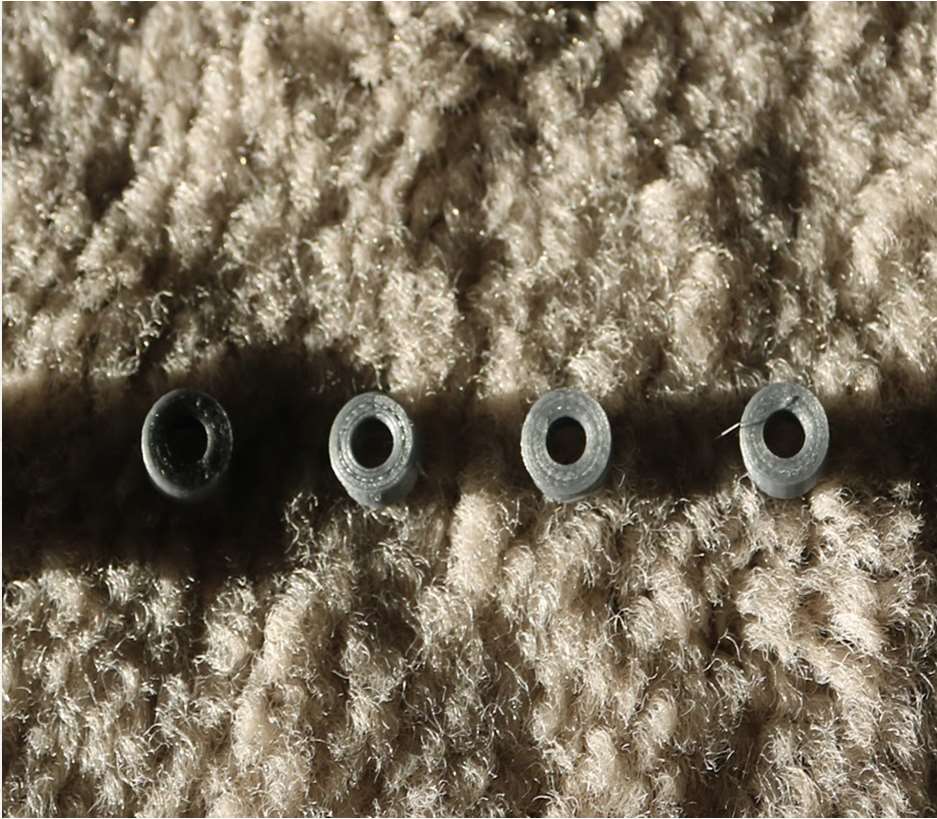
- Make sure that you have the (4) idler pulleys ( Download from Thingiversa ) and the (4) washers printed
- Insert the washers in between the two clamshells, with a screw in between
- Screw the top and bottom clamshells together

Assemble the Y-Axis (Y- Back/Front)
- Take the (2) 350mm linear rods and insert them the Y-back piece by using a rubber mallet
- Get (1) M4-0.5 x 35 screw, (1) M4 nut and the 5th 624zz bearing
- Get (2) M3-0.5 x 16 screws to secure the linear rods
- Slide in the bearing when inserting the screw through the Y-back piece
- Slide the the linear rods/Y-back piece through the LM8UU bearings and attach the Y-front piece using a rubber mallet
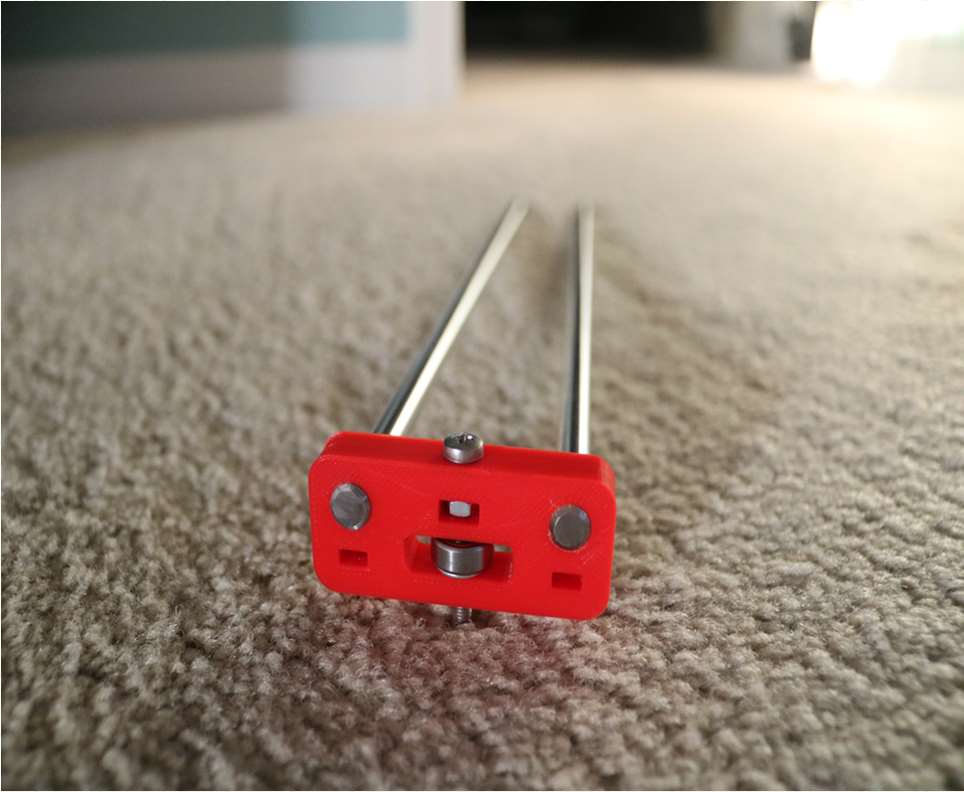

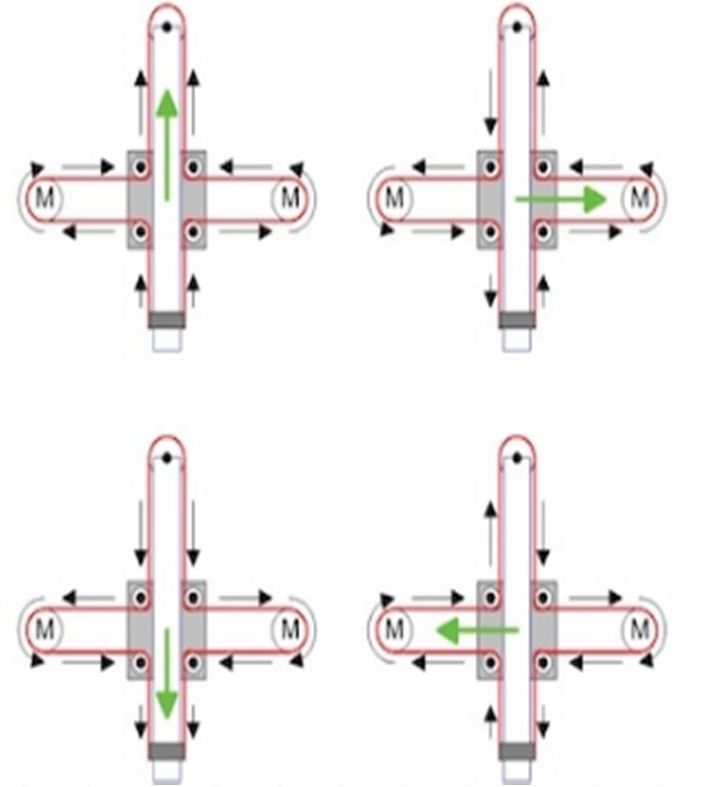
Assemble the X-Y Axis (Belt)
- Use a pair of needle nose pliers to help guide the GT2 belt more easily through the clamshell
- Take the two ends of the belt and slide them through the “teeth” on the Base Slider
- The belt should be tight and not loose
- Note that once the GT2 belt is on, it is normal for the clamshell not to move easily
Belt Diagram
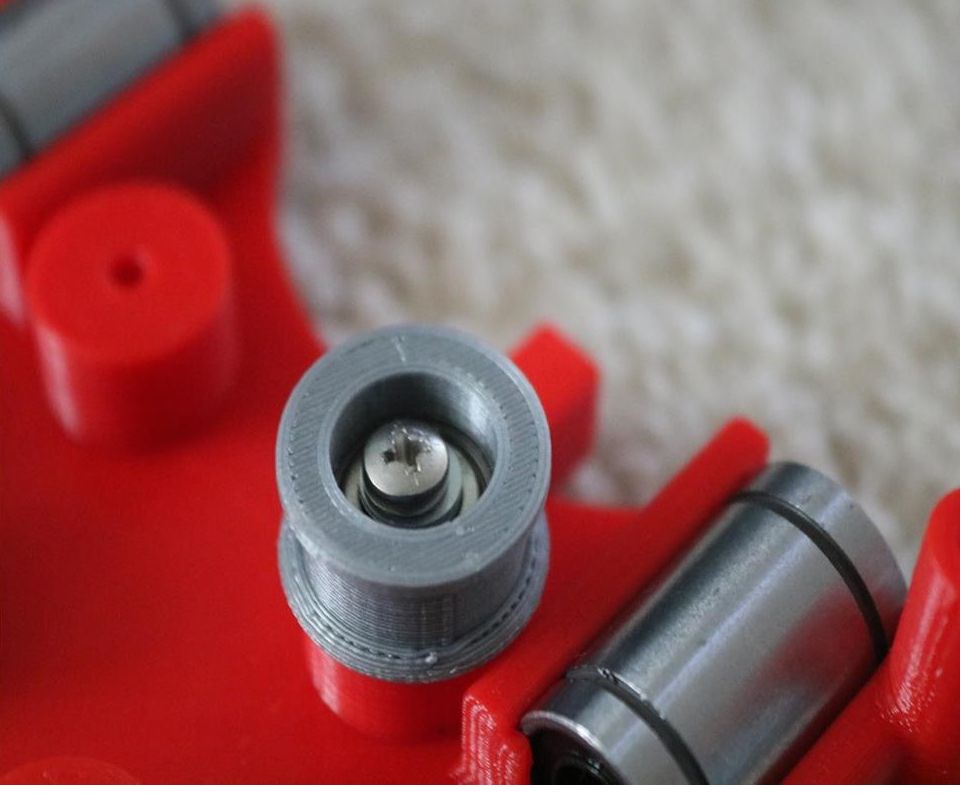
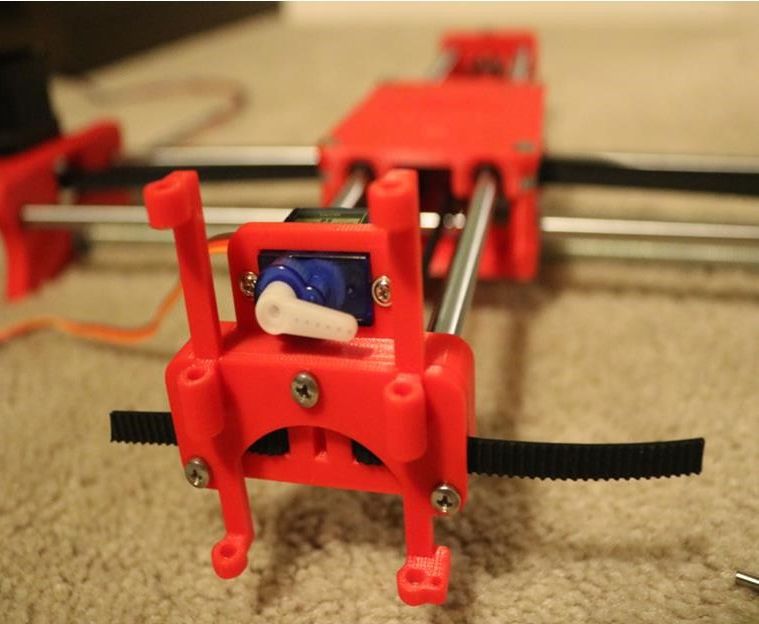
Assemble the Z-Axis
- Get (2) 3mm linear rods and the following 3D printed parts (Slider, Pen Holder, Base Slide, 3MM Metric Thumb Screw)
- Get (1) Hex M3-0.5 x 20mm screw and the Metric Thumb Screw and push them together. Use superglue to keep it together.
- Get (3) M3-0.5 x 16mm screws which you will use the secure the Base Slide to the Y-Front part. You may need to use (3) M3-0.5 nuts in order to hold it in place
- Push the Slider and Pen Holder together to make one piece
- Now take that new part and the (2) 3mm linear rods and slide the rods through the holes. Place a small spring in between the two parts so there is a little bit of pressure to lift the Slider. You may need to cut the spring a bit until there is an adequate amount of pressure on the slider.
Step By Step Video
The Original Instructions by Henry Arnold Jonathan K
- 3D Printed Hairy Lion →
12 thoughts on “ How To Make DIY Pen Plotter / Homework Writing Machine at Home ”
i constructed all the machine but when i press X+ the both X and Y axis are moving what is the problem
double check the steppers wiring
Have you solved it? I have the same problem with my machine, when I press X+, it’s necessary both motors move at same time, but, only one of them move…
Did you solve this problem?
Same problem how to solve ,?
Is it true that you didn’t use the microswitches in the final design?
Hello how to co figurę this machine to RUN on GRBL. What I mean is that GRBL interprets commands for x axis and y axis independently and if I look on your belt diagram it looks like both Motors have to run at the same time in order to move the carriage along y axis… How did you do that?
Have you solved it?
Thank you, thank you. It’s a very good built.
Is it possible to modify it to draw using brush ang oil based paint ?
Could you please tell what software/plug in and which version do you use to generate g-code for this machine?
Hello, what is the width of your belt? 6mm or 10mm? Thanks!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

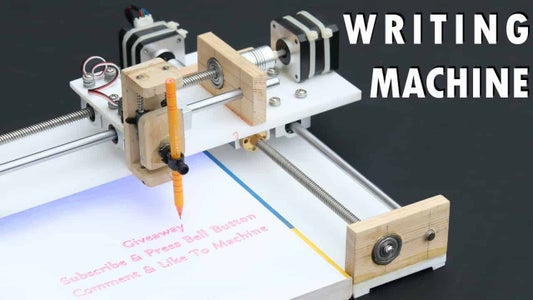
Homework Writing Machine with Arduino and Servo Motor
Homework writing machine is an auto writing machine through which you can make your your work easy by programing your project. As per the title this is a simple project using Arduino to make Homework writing machine at your home.This machine can draw any design and write any type of fonts.You can see sharpness and perfection of writing in photos. The machine uses a gantry to move the writing tip along the X and Y axes. The flexible-nib pen is mounted on a servo motor which rotates the tip onto the writing surface, taking care of the third axis.
Mechanical Kit will be shipped to you and you can learn and build using tutorials. You can start for free today!
1. 3D Printer
2. Automobile Prototyping
3. CNC Machine using Arduino
4. Project Management with Primavera
Homework writing machine project description:
- Servo Motor: A servomotor is a rotary actuator or linear actuator that allows for precise control of angular or linear position, velocity and acceleration.It consists of a suitable motor coupled to a sensor for position feedback. It also requires a relatively sophisticated controller, often a dedicated module designed specifically for use with servomotors. 1 threaded rod
- Wood: Wood is a porous and fibrous structural tissue found in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic material, a natural composite of cellulose fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin that resists compression.
Latest projects on Mechanical
Want to develop practical skills on Mechanical? Checkout our latest projects and start learning for free
- Arduno uno: Arduino is an open source computer hardware and software company, project, and user community that designs and manufactures single-board microcontrollers and microcontroller kits for building digital devices and interactive objects that can sense and control objects in the physical and digital world. The project's products are distributed as open-source hardware and software, which are licensed under the GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL) or the GNU General Public License (GPL),permitting the manufacture of Arduino boards and software distribution by anyone. Arduino boards are available commercially in preassembled form, or as do-it-yourself (DIY) kits.
- Grbl shield: =The Arduino grblShield is a complete hardware solution for Dank's CNC motion control system called grbl. Compatible with the Uno and other 328p versions of the Arduino development platform. (Note: grbl 0.6 is not compatible with 168-based Arduinos (nor will it ever be), and currently grbl does not support the Arduino Megas).
- Driver motors : = motor driver is a little current amplifier; the function of motor drivers is to take a low-current control signal and then turn it into a higher-current signal that can drive a motor.
- 9 gram servo : = A servomotor is a rotary actuator or linear actuator that allows for precise control of angular or linear position, velocity and acceleration.[1] It consists of a suitable motor coupled to a sensor for position feedback. It also requires a relatively sophisticated controller, often a dedicated module designed specifically for use with servomotors. Benbox software
Skyfi Labs helps students learn practical skills by building real-world projects.
You can enrol with friends and receive kits at your doorstep
You can learn from experts, build working projects, showcase skills to the world and grab the best jobs. Get started today!
- Arduino uno
- Servo Motor
- Grbl shield
- Driver motors
- Benbox software
Homework Writing Machine
Join 250,000+ students from 36+ countries & develop practical skills by building projects
Get kits shipped in 24 hours. Build using online tutorials.
More Project Ideas on Mechanical
Subscribe to receive more project ideas.
Stay up-to-date and build projects on latest technologies
☎ Have a Query?

Embed the widget on your own site

Drawing Robot/Pen Plotter/Drawing Machine is an Open Hardware version of the famous machine AxiDraw which it is a pen plotter, capable of wr

Make DIY Homework Writing Machine at Home
Step 1: parts and materials required, step 2: 3d printing, step 3: assemble the x-axis, step 4: assemble the x-axis bearing, step 5: assemble the y-axis.
- Step 6: Assemble the X-Y Axis (Belt
Step 7: Assemble the Z-Axis
Step 8: electronics, step 9: software, step 10: drawing machine at work.
- Comments (8)























IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
DIY Homework Writing Machine: In this Instructable, I'll show you how to create a completely functional 3D-printed writing machine for your science fair project at school or college. This project was created as part of my second-year engineering project at Gujarat's Chandubhai S…
Get (1) Hex M3-0.5 x 20mm screw and the Metric Thumb Screw and push them together. Use superglue to keep it together. Get (3) M3-0.5 x 16mm screws which you will use the secure the Base Slide to the Y-Front part. You may need to use (3) M3-0.5 nuts in order to hold it in place.
Make DIY Homework Writing Machine at Home: Drawing Robot/Pen Plotter/Drawing Machine is an Open Hardware version of the famous machine AxiDraw which it is a pen plotter, capable of writing or drawing on almost any flat surface. It can write with pens, permanent markers, pencils, and other wr…
Step 1: Assembly - Y Axis. Take the 2040mm profile and attach the base plates to both the ends. Use the sliding nuts and m4 bolts to attach the base plates to the profiles. Now turn the profile and attach rubber feet to the bottom slots of the base plates. These rubber feet will hold the machine in place on smooth surfaces.
In this video we make homework writing machine using Arduino uno and stepper motors.This writing machine can be used for writing and drawing in science proje...
This is the Version 2.0 of the Arduino Homework Writing Machine - 2D CNC Plotter. this version comes with a lot of upgrades from the previous one, which incl...
How to Make Homework Machine at homeLearn How to make homework writing and drawing machine at home using Stepper motor.You can make this type of automatic wr...
Get (2) 3mm linear rods and the following 3D printed parts (Slider, Pen Holder, Base Slide, 3MM Metric Thumb Screw) Get (1) Hex M3-0.5 x 20mm screw and the Metric Thumb Screw and push them together. Use superglue to keep it together. Get (3) M3-0.5 x 16mm screws which you will use the secure the Base Slide to the Y-Front part.
Homework writing machine project description: Servo Motor: A servomotor is a rotary actuator or linear actuator that allows for precise control of angular or linear position, velocity and acceleration.It consists of a suitable motor coupled to a sensor for position feedback. It also requires a relatively sophisticated controller, often a dedicated module designed specifically for use with ...
Learn how to build a DIY Arduino Writing/Drawing Machine - 2D Pen Plotter with this tutorial video. See the machine in action and get the code and schematics.
Take the (2) 350mm linear rods and insert them the Y-back piece by using a rubber mallet. Get (1) M4-0.5 x 35 screw, (1) M4 nut and the 5th 624zz bearing. Get (2) M3-0.5 x 16 screws to secure the linear rods. Slide in the bearing when inserting the screw through the Y-back piece. Y-Front.
Get (1) Hex M3-0.5 x 20mm screw and the Metric Thumb Screw and push them together. Use superglue to keep it together. Get (3) M3-0.5 x 16mm screws which you will use the secure the Base Slide to the Y-Front part. You may need to use (3) M3-0.5 nuts in order to hold it in place.
This homework writing machine project features a DIY writing machine that uses a typical pen. It can do outline writing and digital signature or even a real text. The main system uses a 2 axis stepper motor driver board with Nema stepper motors and Mg90S Metal Gear Servo control. The 2 axis stepper motor driver board serves as the main controller.
DOWNLOAD OUR NEW APPLICATION TO GET ALL SCIENCE DIY PROJECTS AT ONE PLACE.TO DOWNLOAD CLICK BELOW. CLICK HERE >>>>>DIY PROJECTS Hi guys , As per the title this is a simple project using Arduino to make Homework writing machine at your home.This machine can draw any design and write any type of fonts.You can see sharpness and perfection of writing in photos.
This Drawing Robot/Pen Plotter/Drawing Machine is similar to the commercially available AxiDraw. It is powered by an Arduino Uno controller, uses a CNC Shiel...
The document describes how to build a DIY homework writing machine at home. It can be used to write or draw on surfaces larger than the machine itself using pens, pencils or other writing implements. The machine uses an Arduino Uno controller and CNC shield to control two Nema 17 stepper motors that move a writing head along an X-Y axis. It can be built for around $75 and has a maximum drawing ...
Step 2: Building X and Y Axis Carriages. Take out the stepper Motor from dvd writer as in the picture. You need to open 2 dvd writers carefully without damaging anything inside it. Screw one carriage which contained the stepper motor to the 1ft.x1ft. board, this is the X-axis motor carriage. Keep some gap for Y axis motor carriage to be placed ...
How to make Homework Writing Machine at homeFiles: https://goo.gl/uCwzvRUNO R3 Arduino: https://goo.gl/bpbfJiArduino CNC Shield V3: https://goo.gl/VzsXqh3D P...
Simple, modern, and precise pen plotters. AxiDraw machines work with a variety of writing instruments, including permanent markers and fountain pens. The unique writing head extends beyond the base of the machine, making it possible to write or draw on almost any flat surface. AxiDraw is the real deal: Designed, manufactured, and supported in ...
Hello Friends, in this video i will show you DIY EleksDraw XY Plotter Pen Drawing Writing Robot Drawing Machine.It is an extremely versatile machine, designe...
Step 4: ATTACHING THE ELECTRIC MOTOR. Attach to Electric motor to the base of a Tie rod, reference the image. Make two of these. This will serve as the medium of moving the machine. Make sure the wheels of the electric motor directly fits in on the tie rod attached to the ply wood and ensure its free movement to and fro the surface.
🔗Product Links:Easydraw v3 - https://shopmakerq.com/product/easydraw-v3-writing-and-drawing-machine-fully-assembled/Inkscape Software Tutorial - https://you...
Step 16: Creating the GCODE FILE. Open Inkscape. Import the desired image and convert it to path. In Extensions, Use the MI GRBL EXTENSION. Press apply and create the GCODE FILE. Open File mode in GCODE Sender. choose the file. hit send. SIT BACK AND LET THE MACHINE DRAW.