
- Lean Six Sigma

8D Problem Solving Report
8D is a problem solving method used globally, mainly in manufacturing industry by Quality Engineers and Operations managers. The purpose of 8D problem solving method is to identify, correct and prevent problems affecting customers and operational efficiency. It is a problem solving approach similar to PDCA cycle (Plan – Do – Check – Act).
8D stands for 8 Disciplines. It is a methodology that emphasizes “No problem should be repeated but fixed permanently”.
8D Problem Solving Method originally evolved during Second World War. But it became an official methodology in 1974, when it was used by US Government for its Military Operations as ‘Military Standard 1520’. Later it was adapted and popularized by Ford Motors with slight modification in the methodology.
As the name indicates 8D has 8 disciplines that any process or operations should follow to solve the problems occurring. The outcome of 8D is a report called ‘8D Report’ that records the problems, root cause(s) and corrective and preventive actions.
The below are the D’s in 8D approach:
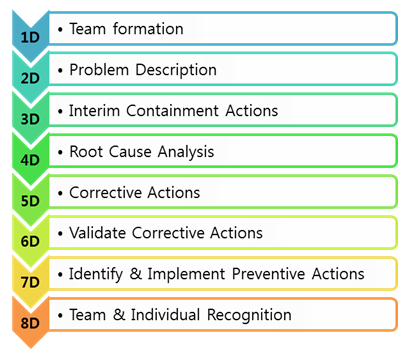
Figure 1: 8D Problem Solving Approach
1D – Team Formation: The first and foremost step not only in 8D but also in any other initiative or project is Team Formation, for any initiative cannot be successful without a right team. The team selected should be committed, competent, co-ordinated, cross-functional with representation from all teams, and should be knowledgeable in 8D methodology.
2D – Problem Description: After selecting the team, our concentration should be on detailing the problem. The team should collect details about the problem, for completely understanding the depth of the problem. All details should be data and fact based.
3D – Interim Containment Actions: Once the problem is described, before heading up to problem solving, the team should fix the effect of the problem, especially on customers. It might involve actions like isolating the items affected, replacing defective parts, before it reaches the customers. This step is mainly to prevent the problem from reaching the market and customers, which might become a competitive disadvantage and reduce customer loyalty.
4D – Root Cause Analysis: After taking containment actions, the team should involve in identifying the root cause(s) for the problem. Methods and tools like 5-Why Analysis , Fishbone diagram , Pareto Analysis , 7 Old QC tools , New QC tools etc. can be used for identifying the root cause. An important point to be noted is: Whatever method is used for RCA , it should be data & fact based.
5D – Formulate Corrective Actions: After successfully arriving at the root cause, the team should formulate corrective actions to be taken to correct the problem. Tools like Brain storming, Affinity diagram etc. can be used.
6D – Validate Corrective Actions: After arriving at the corrective actions, the team should validate whether the solutions are effective. There are several tools like Accelerated life testing , simulation etc. available for this purpose. Then the solution can be implemented in the process. The solution approach from step 4-6 should be repeated until the problem is completely eliminated.
7D – Preventive Action: Identifying and implementing corrective actions is only a temporary solution that keeps the system running or is like ‘Living with the problem by taking counter measures’. The permanent solution is to identify a potential long term solution that will not allow the problem (similar problems) from occurring into the system again. Sometimes corrective action will be a costly, time being measure. Preventive action makes changes in the system, upstream or downstream processes so that the entire system is modified or aligned for ‘Problem Free’ operations.
8D – Team and Individual Recognition: Once the problem is completely solved, the team and the extra-ordinary contributors must be rewarded and recognized appropriately. This will act as a motivation factor for other employees.
These are the steps of 8D methodology. To summarize, 8D is a holistic, systematic and proven methodology for problem solving.
Previous post: Change Management
Next post: Project Portfolio Management
- 10 Things You Should Know About Six Sigma
- Famous Six Sigma People
- Six Sigma Software
Recent Posts
- Control System Expansion
- Energy Audit Management
- Industrial Project Management
- Network Diagram
- Supply Chain and Logistics
- Visual Management
- Utilizing Pareto Charts in Business Analysis
- Privacy Policy

Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
– Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving –
⇓ Introduction to 8D
⇓ What is 8D
⇓ Why Apply 8D
⇓ When to Apply 8D
⇓ How to Apply 8D

Introduction to Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
The Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D) is a problem solving methodology designed to find the root cause of a problem, devise a short-term fix and implement a long-term solution to prevent recurring problems. When it’s clear that your product is defective or isn’t satisfying your customers, an 8D is an excellent first step to improving Quality and Reliability.
Ford Motor Company developed this problem solving methodology, then known as Team Oriented Problem Solving (TOPS), in the 1980s. The early usage of 8D proved so effective that it was adopted by Ford as the primary method of documenting problem solving efforts, and the company continues to use 8D today.
8D has become very popular among manufacturers because it is effective and reasonably easy to teach. Below you’ll find the benefits of an 8D, when it is appropriate to perform and how it is performed.
What is Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
The 8D problem solving process is a detailed, team oriented approach to solving critical problems in the production process. The goals of this method are to find the root cause of a problem, develop containment actions to protect customers and take corrective action to prevent similar problems in the future.
The strength of the 8D process lies in its structure, discipline and methodology. 8D uses a composite methodology, utilizing best practices from various existing approaches. It is a problem solving method that drives systemic change, improving an entire process in order to avoid not only the problem at hand but also other issues that may stem from a systemic failure.
8D has grown to be one of the most popular problem solving methodologies used for Manufacturing, Assembly and Services around the globe. Read on to learn about the reasons why the Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving may be a good fit for your company.
Why Apply Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
The 8D methodology is so popular in part because it offers your engineering team a consistent, easy-to-learn and thorough approach to solving whatever problems might arise at various stages in your production process. When properly applied, you can expect the following benefits:
- Improved team oriented problem solving skills rather than reliance on the individual
- Increased familiarity with a structure for problem solving
- Creation and expansion of a database of past failures and lessons learned to prevent problems in the future
- Better understanding of how to use basic statistical tools required for problem solving
- Improved effectiveness and efficiency at problem solving
- A practical understanding of Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
- Problem solving effort may be adopted into the processes and methods of the organization
- Improved skills for implementing corrective action
- Better ability to identify necessary systemic changes and subsequent inputs for change
- More candid and open communication in problem solving discussion, increasing effectiveness
- An improvement in management’s understanding of problems and problem resolution
8D was created to represent the best practices in problem solving. When performed correctly, this methodology not only improves the Quality and Reliability of your products but also prepares your engineering team for future problems.
When to Apply Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
The 8D problem solving process is typically required when:
- Safety or Regulatory issues has been discovered
- Customer complaints are received
- Warranty Concerns have indicated greater-than-expected failure rates
- Internal rejects, waste, scrap, poor performance or test failures are present at unacceptable levels
How to Apply Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
The 8D process alternates inductive and deductive problem solving tools to relentlessly move forward toward a solution. The Quality-One approach uses a core team of three individuals for inductive activities with data driven tools and then a larger Subject Matter Expert (SME) group for the deductive activities through brainstorming, data-gathering and experimentation.
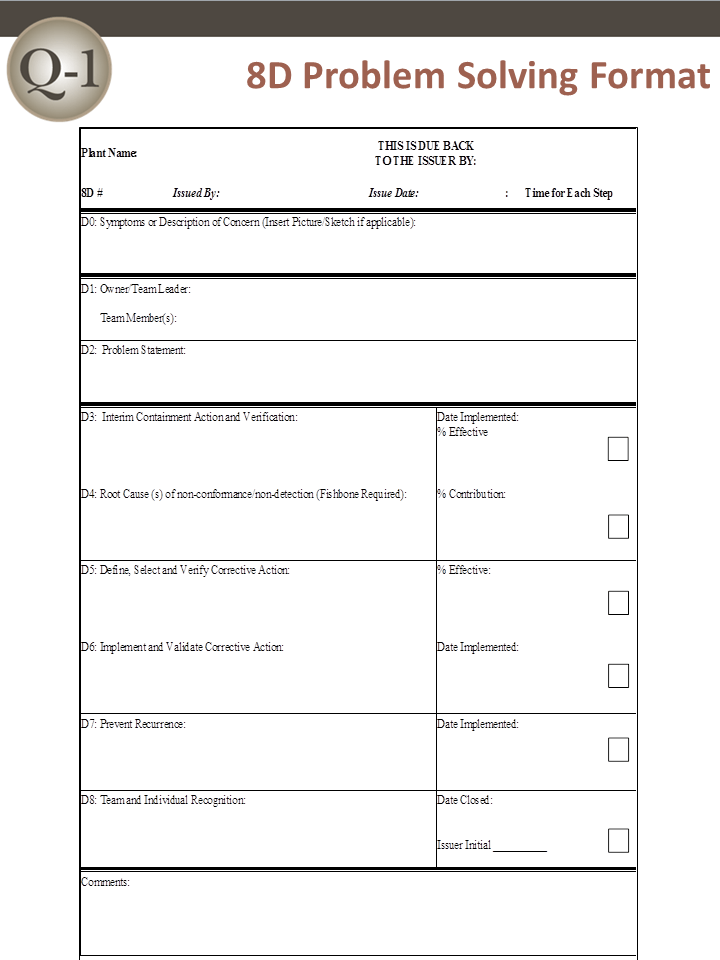
D0: Prepare and Plan for the 8D
Proper planning will always translate to a better start. Thus, before 8D analysis begins, it is always a good idea to ask an expert first for their impressions. After receiving feedback, the following criterion should be applied prior to forming a team:
Collect information on the symptoms
Use a Symptoms Checklist to ask the correct questions
Identify the need for an Emergency Response Action (ERA), which protects the customer from further exposure to the undesired symptoms
D1: Form a Team
A Cross Functional Team (CFT) is made up of members from many disciplines. Quality-One takes this principle one step further by having two levels of CFT:
- The Core Team Structure should involve three people on the respective subjects: product, process and data
- Additional Subject Matter Experts are brought in at various times to assist with brainstorming, data collection and analysis
Teams require proper preparation. Setting the ground rules is paramount. Implementation of disciplines like checklists, forms and techniques will ensure steady progress. 8D must always have two key members: a Leader and a Champion / Sponsor:
- The Leader is the person who knows the 8D process and can lead the team through it (although not always the most knowledgeable about the problem being studied)
- The Champion or Sponsor is the one person who can affect change by agreeing with the findings and can provide final approval on such changes
D2: Describe the Problem
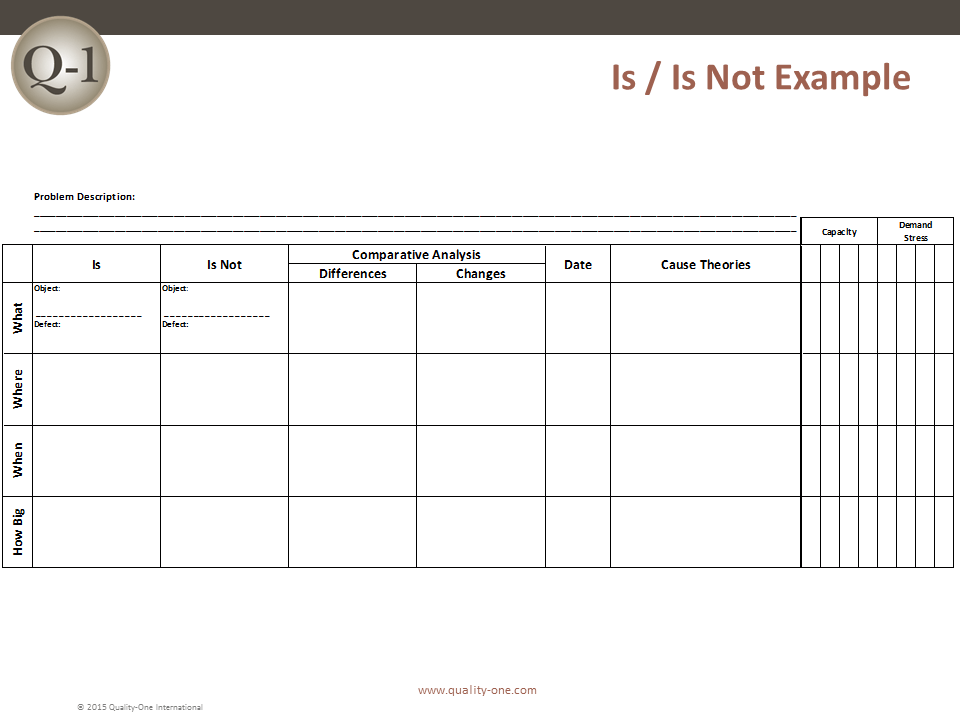
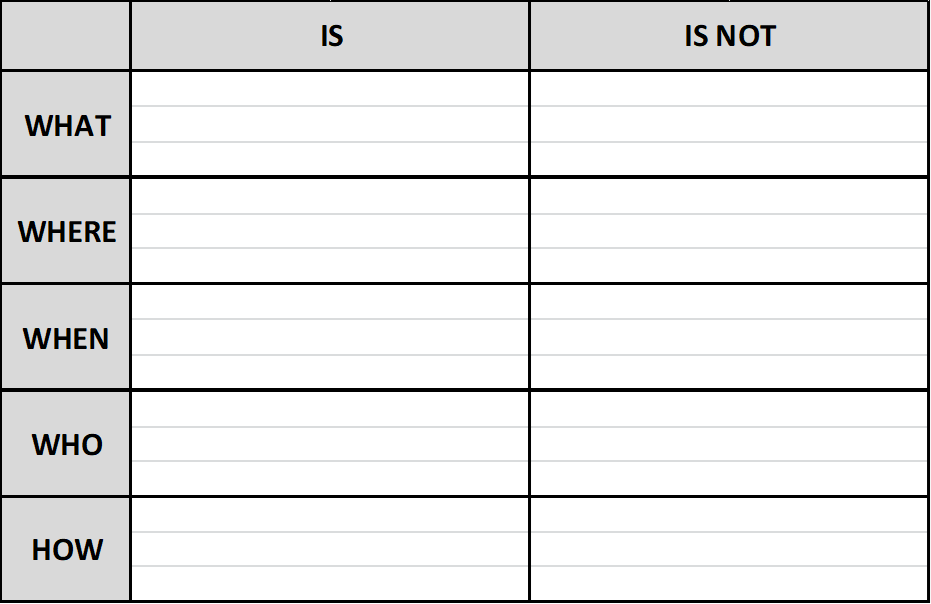
The 8D method’s initial focus is to properly describe the problem utilizing the known data and placing it into specific categories for future comparisons. The “Is” data supports the facts whereas the “Is Not” data does not. As the “Is Not” data is collected, many possible reasons for failure are able to be eliminated. This approach utilizes the following tools:
- Problem Statement
- Affinity Diagram (Deductive tool)
- Fishbone/Ishikawa Diagram (Deductive tool)
- Problem Description
D3: Interim Containment Action
In the interim, before the permanent corrective action has been determined, an action to protect the customer can be taken. The Interim Containment Action (ICA) is temporary and is typically removed after the Permanent Correct Action (PCA) is taken.
- Verification of effectiveness of the ICA is always recommended to prevent any additional customer dissatisfaction calls
D4: Root Cause Analysis (RCA) and Escape Point
The root cause must be identified to take permanent action to eliminate it. The root cause definition requires that it can be turned on or off, at will. Activities in D4 include:
- Comparative Analysis listing differences and changes between “Is” and “Is Not”
- Development of Root Cause Theories based on remaining items
- Verification of the Root Cause through data collection
- Review Process Flow Diagram for location of the root cause
- Determine Escape Point, which is the closest point in the process where the root cause could have been found but was not
D5: Permanent Corrective Action (PCA)
The PCA is directed toward the root cause and removes / changes the conditions of the product or process that was responsible for the problem. Activities in D5 include:
- Establish the Acceptance Criteria which include Mandatory Requirements and Wants
- Perform a Risk Assessment / Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) on the PCA choices
- Based on risk assessment, make a balanced choice for PCA
- Select control-point improvement for the Escape Point
- Verification of Effectiveness for both the PCA and the Escape Point are required
D6: Implement and Validate the Permanent Corrective Action
To successfully implement a permanent change, proper planning is essential. A project plan should encompass: communication, steps to complete, measurement of success and lessons learned. Activities in D6 include:
- Develop Project Plan for Implementation
- Communicate the plan to all stakeholders
- Validation of improvements using measurement
D7: Prevent Recurrence
D7 affords the opportunity to preserve and share the knowledge, preventing problems on similar products, processes, locations or families. Updating documents and procedures / work instructions are expected at this step to improve future use. Activities in D7 include:
- Review Similar Products and Processes for problem prevention
- Develop / Update Procedures and Work Instructions for Systems Prevention
- Capture Standard Work / Practice and reuse
- Assure FMEA updates have been completed
- Assure Control Plans have been updated
D8: Closure and Team Celebration
Teams require feedback to allow for satisfactory closure. Recognizing both team and individual efforts and allowing the team to see the previous and new state solidifies the value of the 8D process. Activities in D8 include:
- Archive the 8D Documents for future reference
- Document Lessons Learned on how to make problem solving better
- Before and After Comparison of issue
- Celebrate Successful Completion
8D and Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
The 8D process has Root Cause Analysis (RCA) imbedded within it. All problem solving techniques include RCA within their structure. The steps and techniques within 8D which correspond to Root Cause Analysis are as follows:
- Problem Symptom is quantified and converted to “Object and Defect”
- Problem Symptom is converted to Problem Statement using Repeated Whys
- Possible and Potential Causes are collected using deductive tools (i.e. Fishbone or Affinity Diagram)
- Problem Statement is converted into Problem Description using Is / Is Not
- Problem Description reduces the number of items on the deductive tool (from step 3)
- Comparative Analysis between the Is and Is Not items (note changes and time)
- Root Cause theories are developed from remaining possible causes on deductive tool and coupled with changes from Is / Is Not
- Compare theories with current data and develop experiments for Root Cause Verification
- Test and confirm the Root Causes
Example: Multiple Why Technique
The Multiple / Repeated Why (Similar to 5 Why) is an inductive tool, which means facts are required to proceed to a more detailed level. The steps required to determine problem statement are:
- Problem Symptom is defined as an Object and Defect i.e. “Passenger Injury”
- Why? In every case “SUV’s Roll Over”
- Why? In every case, it was preceded by a “Blown Tire”
- Why? Many explanations may be applied, therefore the team cannot continue with another repeated why past “Blown Tire”
- Therefore, the Problem Statement is “Blown Tire”
- Why? Low (Air) Pressure, Tire Defect (Degradation of an Interface) and High (Ambient) Temperature
- Counter measures assigned to low pressure and tire defect
This example uses only 4 of the 5 Whys to determine the root causes without going further into the systemic reasons that supported the failure. The Repeated Why is one way to depict this failure chain. Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) could also be used.
Learn More About Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
Quality-One offers Quality and Reliability Support for Product and Process Development through Consulting, Training and Project Support. Quality-One provides Knowledge, Guidance and Direction in Quality and Reliability activities, tailored to your unique wants, needs and desires. Let us help you Discover the Value of 8D Consulting , 8D Training or 8D Project Support .
Contact Us | Discover the Value!
(248) 280-4800 | [email protected]
Remember Me
- Don't have an account? Register
- Lost your password? Click here
- Already have an account? Log in
- Product overview
- All features
- App integrations
CAPABILITIES
- project icon Project management
- Project views
- Custom fields
- Status updates
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- Reporting dashboards
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- Time tracking
- my-task icon Admin and security
- Admin console
- asana-intelligence icon Asana AI
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Campaign management
- Creative production
- Content calendars
- Marketing strategic planning
- Resource planning
- Project intake
- Product launches
- Employee onboarding
- View all uses arrow-right icon
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Work management resources Discover best practices, watch webinars, get insights
- What's new Learn about the latest and greatest from Asana
- Customer stories See how the world's best organizations drive work innovation with Asana
- Help Center Get lots of tips, tricks, and advice to get the most from Asana
- Asana Academy Sign up for interactive courses and webinars to learn Asana
- Developers Learn more about building apps on the Asana platform
- Community programs Connect with and learn from Asana customers around the world
- Events Find out about upcoming events near you
- Partners Learn more about our partner programs
- Support Need help? Contact the Asana support team
- Asana for nonprofits Get more information on our nonprofit discount program, and apply.
Featured Reads

- Project management |
- What is 8D? A template for efficient pr ...
What is 8D? A template for efficient problem-solving
How you respond when problems arise is one of the most defining qualities of a manager. Luckily, there are tools you can use to master problem-solving. The 8D method of problem-solving combines teamwork and basic statistics to help you reach a logical solution and prevent new issues from arising.
You’ve spent months overseeing the development of your company's newest project. From initiation, planning, and execution, you’re confident this may be your best work yet.
Until the feedback starts rolling in.
There’s no sugar-coating it—things don’t always go as planned. But production or process issues are hardly a signal to throw in the towel. Instead, focus on honing your problem-solving skills to find a solution that keeps it from happening again.
The 8D method of problem solving emphasizes the importance of teamwork to not only solve your process woes but prevent new ones from occurring. In this guide, we’ll break down what 8D is, how to use this methodology, and the benefits it can give to you and your team. Plus, get an 8D template to make solving your issue easier.
What is 8D?
The eight disciplines (8D) method is a problem-solving approach that identifies, corrects, and eliminates recurring problems. By determining the root causes of a problem, managers can use this method to establish a permanent corrective action and prevent recurring issues.
How do you use the 8D method?
The 8D method is a proven strategy for avoiding long-term damage from recurring problems. If you’re noticing issues in your workflow or processes, then it’s a good time to give this problem-solving method a try.
To complete an 8D analysis, follow “the eight disciplines” to construct a statistical analysis of the problem and determine the best solution.
The eight disciplines of problem-solving
8D stands for the eight disciplines you will use to establish an 8D report. As you may notice, this outline starts with zero, which makes nine total disciplines. The “zero stage” was developed later as an initial planning stage.
To illustrate these steps, imagine your organization experienced a decline in team innovation and productivity this past year. Your stakeholders have noticed and want to see changes implemented within the next six months. Below, we’ll use the 8D process to uncover a morale-boosting solution.
![3d vs 8d problem solving [inline illustration] D8 problem solving approach (infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/6ab7c188-3258-4d2e-afe6-9a4a084cc09f/inline-productivity-8d-template-1-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
D0: Prepare and plan
Before starting the problem-solving process, evaluate the problem you want to solve. Understanding the background of the problem will help you identify the root cause in later steps.
Collect information about how the problem has affected a process or product and what the most severe consequences may be. Planning can include:
Gathering data
Determining the prerequisites for solving the problem
Collecting feedback from others involved
![3d vs 8d problem solving [inline illustration] D0 Planning (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/abc3621d-e1ae-47ff-b731-0ee38cff99e9/inline-productivity-8d-template-2-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
If we look back at our example, you may want to figure out whether this decline in morale is organization-wide or only applies to a few departments. Consider interviewing a few employees from different departments and levels of management to gain some perspective. Next, determine what knowledge and skills you will need to solve this lapse in productivity.
D1: Form your team
Create a cross-functional team made up of people who have knowledge of the various products and workflows involved. These team members should have the skills needed to solve the problem and put corrective actions in place.
Steps in this discipline may include:
Appointing a team leader
Developing and implementing team guidelines
Determining team goals and priorities
Assigning individual roles
Arranging team-building activities
![3d vs 8d problem solving [inline illustration] D1 Team members (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/51986017-5150-4dd4-940c-252cd0eb8ba5/inline-productivity-8d-template-3-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
From our example, a solid team would consist of people with first-hand experience with the issues—like representatives from all departments and key people close to workshop-level work. You may also want to pull someone in from your HR department to help design and implement a solution. Most importantly, make sure the people you choose want to be involved and contribute to the solution.
D2: Identify the problem
You may have a good understanding of your problem by now, but this phase aims to break it down into clear and quantifiable terms by identifying the five W’s a and two H’s (5W2H):
Who first reported the problem?
What is the problem about?
When did it occur and how often?
Where did it occur (relating to the sector, supplier, machine, or production line involved)?
Why is solving the problem important?
How was the problem first detected?
How many parts/units/customers are affected?
![3d vs 8d problem solving [inline illustration] D2 Problem statement & description (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/9825ecd6-2bd3-4559-a68c-b1ae8aca2e52/inline-productivity-8d-template-4-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Use your team’s insights to answer these questions. From our example, your team may conclude that:
Employees feel overwhelmed with their current workload.
There is no real structure or opportunity to share new ideas.
Managers have had no training for meetings or innovation settings.
Disgruntled employees know they can achieve more—and want to achieve more—even if they seem disengaged.
Once you answer these questions, record an official problem statement to describe the issue. If possible, include photos, videos, and diagrams to ensure all parties have a clear understanding of the problem. It may also help to create a flowchart of the process that includes various steps related to the problem description.
D3: Develop an interim containment plan
Much like we can expect speedy first aid after an accident, your team should take immediate actions to ensure you contain the problem—especially if the problem is related to customer safety.
An interim containment plan will provide a temporary solution to isolate the problem from customers and clients while your team works to develop a permanent corrective action. This band-aid will help keep your customers informed and safe—and your reputation intact.
![3d vs 8d problem solving [inline illustration] D3 Interim containment action (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/d6279c36-ccc6-4de3-89d2-f221632a1059/inline-productivity-8d-template-5-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Because your findings revealed workers were overworked and managers lacked training, your team suggests scheduling a few mandatory training sessions for leaders of each department covering time and stress management and combating burnout . You may also want to have a presentation outlining the topics of this training to get key managers and stakeholders interested and primed for positive upcoming changes.
D4: Verify root causes and escape points
Refer back to your findings and consult with your team about how the problem may have occurred. The root cause analysis involves mapping each potential root cause against the problem statement and its related test data. Make sure to test all potential causes—fuzzy brainstorming and sloppy analyses may cause you to overlook vital information.
![3d vs 8d problem solving [inline illustration] D4 Root cause & escape points (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/301717c6-0434-4c88-addf-d500dc23ae87/inline-productivity-8d-template-6-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
In our example, focus on the “why” portion of the 5W2H. You and your team identify six root causes:
Managers have never had any training
There is a lack of trust and psychological safety
Employees don’t understand the objectives and goals
Communication is poor
Time management is poor
Employees lack confidence
In addition to identifying the root causes, try to pinpoint where you first detected the problem in the process, and why it went unnoticed. This is called the escape point, and there may be more than one.
D5: Choose permanent corrective actions
Work with your team to determine the most likely solution to remove the root cause of the problem and address the issues with the escape points. Quantitatively confirm that the selected permanent corrective action(s) (PCA) will resolve the problem for the customer.
Steps to choosing a PCA may include:
Determining if you require further expertise
Ensuring the 5W2Hs are defined correctly
Carrying out a decision analysis and risk assessment
Considering alternative measures
Collecting evidence to prove the PCA will be effective
![3d vs 8d problem solving [inline illustration] D5 Permanent corrective action (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/53509966-18dd-4bb4-88a1-c7ca940fde3f/inline-productivity-8d-template-7-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Your team decides to roll out the training used in the interim plan to all employees, with monthly company-wide workshops on improving well-being. You also plan to implement meetings, innovation sessions, and team-coaching training for managers. Lastly, you suggest adopting software to improve communication and collaboration.
D6: Implement your corrective actions
Once all parties have agreed on a solution, the next step is to create an action plan to remove the root causes and escape points. Once the solution is in effect, you can remove your interim containment actions.
After seeing success with the training in the interim phase, your stakeholders approve all of your team’s proposed PCAs. Your representative from HR also plans to implement periodic employee wellness checks to track employee morale .
![3d vs 8d problem solving [inline illustration] D6 PCA implementation plan (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/ca68af4a-afa7-4be4-93cb-8a8321eb5172/inline-productivity-8d-template-8-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
To ensure your corrective action was a success, monitor the results, customer, or employee feedback over a long period of time and take note of any negative effects. Setting up “controls” like employee wellness checks will help you validate whether your solution is working or more needs to be done.
D7: Take preventive measures
One of the main benefits of using the 8D method is the improved ability to identify necessary systematic changes to prevent future issues from occurring. Look for ways to improve your management systems, operating methods, and procedures to not only eliminate your current problem, but stop similar problems from developing later on.
![3d vs 8d problem solving [inline illustration] D7 Preventive measure (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/cdd7b133-fb80-4db7-8935-1285a6b62b69/inline-productivity-8d-template-9-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Based on our example, the training your team suggested is now adopted in the new manager onboarding curriculum. Every manager now has a “meeting system” that all meetings must be guided by, and workloads and projects are managed as a team within your new collaboration software . Innovation is improving, and morale is at an all-time high!
D8: Celebrate with your team
The 8D method of problem-solving is impossible to accomplish without dedicated team members and first-class collaboration. Once notes, lessons, research, and test data are documented and saved, congratulate your teammates on a job well done! Make an effort to recognize each individual for their contribution to uncovering a successful solution.
![3d vs 8d problem solving [inline illustration] 8D Team congratulations & reward (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/d2055965-bf3d-4bf4-a1ea-a0a7c4bf8a32/inline-productivity-8d-template-10-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
8D report template and example
Check out our 8D report template below to help you record your findings as you navigate through the eight disciplines of problem solving. This is a formal report that can be used as a means of communication within companies, which makes for transparent problem-solving that you can apply to the entire production or process chain.
Benefits of using the 8D method
The 8D method is one of the most popular problem-solving strategies for good reason. Its strength lies in teamwork and fact-based analyses to create a culture of continuous improvement —making it one of the most effective tools for quality managers. The benefits of using the 8D method include:
Improved team-oriented problem-solving skills rather than relying on an individual to provide a solution
Increased familiarity with a problem-solving structure
A better understanding of how to use basic statistical tools for problem-solving
Open and honest communication in problem-solving discussions
Prevent future problems from occurring by identifying system weaknesses and solutions
Improved effectiveness and efficiency at problem-solving
Better collaboration = better problem solving
No matter how good a manager you are, production and process issues are inevitable. It’s how you solve them that separates the good from the great. The 8D method of problem solving allows you to not only solve the problem at hand but improve team collaboration, improve processes, and prevent future issues from arising.
Try Asana’s project management tool to break communication barriers and keep your team on track.
Related resources

Data-driven decision making: A step-by-step guide

How Asana uses work management for employee onboarding
4 ways to establish roles and responsibilities for team success
6 ways to develop adaptability in the workplace and embrace change

8D: Tools and Techniques
Author: Daniel Croft
Daniel Croft is an experienced continuous improvement manager with a Lean Six Sigma Black Belt and a Bachelor's degree in Business Management. With more than ten years of experience applying his skills across various industries, Daniel specializes in optimizing processes and improving efficiency. His approach combines practical experience with a deep understanding of business fundamentals to drive meaningful change.
Are you grappling with recurring problems in your organization and searching for a structured way to resolve them once and for all? Look no further than the 8D Problem-Solving Methodology —a comprehensive eight-step approach initially developed in the automotive industry but widely applicable across various sectors.
This systematic method not only aids in diagnosing the root cause of a problem but also offers a roadmap for effective solutions. However, maximizing the potential of the 8D process involves more than just following its steps. It requires the strategic application of specific tools and techniques at each stage. In this educational blog post, we will guide you through the tools and techniques best suited for each of the 8 Disciplines, empowering you to turn challenges into opportunities for improvement. So, let’s delve into this toolkit and make your problem-solving journey as efficient and effective as possible.
D1: Form a Team
The first step in the 8D Problem-Solving Methodology is to form a cross-functional team. A well-assembled team is the backbone of any successful problem-solving initiative. While it may be tempting to rush through this step, investing time and effort here can pay dividends later. Let’s explore some of the key tools that can assist you in forming an effective team.
Suggested Tools:
1. raci matrix.
The RACI Matrix is an invaluable tool for defining roles and responsibilities within the team. The acronym stands for Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed. By using this matrix, you can clearly specify:
- Responsible : Who is doing the task?
- Accountable : Who is ensuring the task gets completed?
- Consulted : Who needs to provide input?
- Informed : Who needs to know the outcome?
Clear delineation of roles prevents overlap, ensures accountability, and minimizes confusion later in the process.

2. Skills Matrix
Selecting team members with the right set of skills is crucial. A Skills Matrix can help you in this aspect by providing a visual representation of each potential team member’s skills and competencies. You can rate skills on a scale (e.g., 1 to 5) and identify gaps that need to be filled. The matrix can include both technical and soft skills like communication, leadership, and domain expertise.
Key Takeaway:
An effective problem-solving team is not just a group of people; it’s a carefully chosen set of individuals with complementary skills and clearly defined roles. Utilizing tools like the RACI Matrix and Skills Matrix can immensely help in this phase, setting the stage for a successful problem-solving endeavor.
By taking the time to carefully form your team and define everyone’s roles and responsibilities, you lay a strong foundation for the rest of the 8D process. Remember, a well-prepared team is more likely to find sustainable solutions and less likely to encounter roadblocks down the line.
D2: Define the Problem
After assembling a competent team, the next critical step in the 8D Problem-Solving Methodology is defining the problem. A well-defined problem serves as a clear roadmap, guiding your team in the right direction from the start. Ambiguity at this stage can lead to misdirection and wasted resources. So what tools can help you clearly and concisely articulate the problem?
1. 5W2H Method
The 5W2H method is a powerful tool for problem definition. It involves asking a series of questions to gain a comprehensive understanding of the issue at hand. These questions include:
- Who is involved or affected?
- What exactly is the problem?
- When did it occur?
- Where did it occur?
- Why is it a problem?
- How did it happen?
- How much is it affecting?
By systematically answering these questions, you define the problem in a manner that is both comprehensive and easily understandable for everyone involved.
2. SMART Criteria
The SMART criteria focus on setting specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound goals for the problem-solving effort. This approach helps ensure that the problem is clearly defined and that the team has a focused, achievable objective to aim for.
- Specific : Clearly define what needs to be achieved.
- Measurable : Set criteria for measuring progress and success.
- Achievable : Ensure the goals are realistic given the resources.
- Relevant : Align the goals with broader organizational objectives.
- Time-bound : Establish a timeline for solving the problem.

Defining the problem is not a mere formality; it is a necessity for effective problem-solving. A well-defined problem ensures that everyone is on the same page and focused on the right issues. Tools like the 5W2H method and SMART criteria offer invaluable frameworks for achieving this clarity. They help dissect the problem into manageable parts, setting the stage for focused root cause analysis.
D3: Contain the Problem
Once you have a team in place and a well-defined problem, the next step in the 8D Problem-Solving Methodology is containment. This stage is often overlooked but is crucial for limiting the damage and preventing the problem from exacerbating. Containment actions are essentially short-term solutions aimed at halting the spread of the issue while you work on finding a permanent fix. Let’s delve into some tools that can guide you in this phase.
1. Check Sheet
A Check Sheet is a simple yet effective tool for collecting and organizing data. It’s often a paper-and-pencil tool that allows for quick data collection in real-time. For example, if the problem is a high rate of defects in a manufacturing line, a Check Sheet could be used to tally the number of defects by type or time of occurrence. This provides valuable insights into the scope and pattern of the problem, aiding in containment.
2. SWIFT Checklist
The SWIFT (Short Window Immediate Fix Technique) Checklist is a tool designed for rapid assessment. It outlines immediate actions that should be taken to contain the issue. The checklist could include questions like:
- Are there safety issues that need immediate attention?
- Can the affected products be quarantined?
- Do stakeholders need to be informed?
By quickly going through the SWIFT Checklist, you can prioritize the most critical containment actions and implement them without delay.
Containment is not just about putting a temporary fix; it’s about preventing the problem from causing further harm or affecting other processes. Tools like the Check Sheet and SWIFT Checklist can be instrumental in quickly assessing the situation and implementing immediate containment actions.
Utilizing these tools allows you to create a rapid response mechanism, thereby minimizing the impact and scope of the problem. As you transition to finding a long-term solution, these containment measures ensure that the situation remains under control.
D4: Root Cause Analysis
Reaching the root cause analysis stage in the 8D Problem-Solving Methodology signifies a pivotal moment. Here, you transition from understanding and containing the problem to actually solving it. Identifying the root cause(s) is fundamental to ensuring that the issue doesn’t recur. While containment measures provide short-term relief, it’s the root cause analysis that offers a long-term solution. Let’s examine some essential tools that can assist in uncovering the underlying issues.
The “ 5 Whys ” is a powerful questioning technique that helps you drill down into the root cause of a problem by asking “Why?” repeatedly. Often, the apparent issue is just a symptom of a deeper problem. The 5 Whys technique encourages you to move beyond the symptoms and discover the underlying cause.
For instance, if the issue is frequent machine breakdowns, asking “Why?” might reveal:
- Why is the machine breaking down? Because of excessive wear and tear.
- Why is there excessive wear and tear? Because maintenance isn’t performed regularly.
- Why isn’t maintenance regular? Because there’s no schedule.
- Why is there no schedule? Because it was never made a priority.
- Why was it never a priority? Because of a lack of awareness about its importance.

2. Pareto Analysis
Pareto Analysis is based on the Pareto Principle, which states that 80% of problems are often due to 20% of causes. By identifying and focusing on these significant causes, you can resolve the majority of issues with minimum effort. Pareto Analysis typically involves collecting data and creating a Pareto Chart to visualize which factors are most impactful.

3. Fishbone Diagram (Ishikawa)
Though also used in problem definition, the Fishbone Diagram is invaluable for root cause analysis as well. It allows you to categorize potential causes and delve deeper into each, often in combination with other tools like the 5 Whys or Pareto Analysis.

Identifying the root cause is not merely a step in the process; it’s the cornerstone for effective corrective action. Tools like the 5 Whys, Pareto Analysis, and Fishbone Diagram provide a structured approach to dig deep into the problem and unearth its roots. Only by understanding the root cause can you implement solutions that are not just quick fixes but long-lasting remedies.
D5: Choose and Verify Corrective Actions
After identifying the root cause of the problem, the next logical step in the 8D Problem-Solving Methodology is to choose and verify corrective actions. It’s crucial to remember that not all solutions are created equal. Some may offer a quick fix but not a long-lasting one, while others could inadvertently introduce new issues. Therefore, this stage involves a delicate balance of selecting an effective solution and ensuring it doesn’t have unintended consequences. Let’s explore some of the tools that can guide you in making informed decisions.
1. FMEA (Failure Mode and Effects Analysis)
FMEA is a structured approach for evaluating the potential failure modes of a proposed solution and their impact. By predicting how things could go wrong, you can proactively address these issues before they occur. The FMEA process involves the identification of failure modes, assessment of their effects, and prioritization based on their severity, occurrence, and detectability. This prioritization helps you focus your resources where they’ll be most effective.
2. Pilot Testing
Before implementing a corrective action on a full scale, it’s prudent to test it on a smaller scale to verify its effectiveness. Pilot testing allows you to:
- Evaluate the impact of the solution without large-scale commitment.
- Identify any adjustments or optimizations needed.
- Collect data to validate the solution’s efficacy.
Pilot tests should be carefully designed to mimic the conditions under which the full-scale implementation will occur. This way, the results are indicative of what you can expect in the broader application.
Choosing a corrective action is a significant milestone, but verifying its effectiveness is equally crucial. Tools like FMEA and Pilot Testing enable you to rigorously evaluate your chosen solutions, mitigating risks and ensuring that the corrective actions will address the root cause without creating new problems.
By diligently applying these tools, you not only select the right corrective action but also build a robust verification mechanism. This two-pronged approach ensures that your solution is not just theoretically sound but practically effective as well.
D6: Implement Corrective Actions
Reaching the implementation phase of the 8D Problem-Solving Methodology is a big step. You’ve formed a team, defined the problem, contained it, identified its root cause, and chosen and verified corrective actions. Now, it’s time to put those actions into play. However, effective implementation is easier said than done. It requires meticulous planning, execution, and monitoring to ensure the corrective actions yield the desired results. Let’s look at some of the tools that can help you master this crucial stage.
1. Gantt Chart
A Gantt Chart is an excellent tool for project planning and tracking. It provides a visual timeline for the tasks involved in implementing the corrective actions. The chart specifies:
- Start and end dates
- Responsible parties
- Dependencies between tasks
This visual representation makes it easier to manage resources and timelines, ensuring that implementation stays on track.

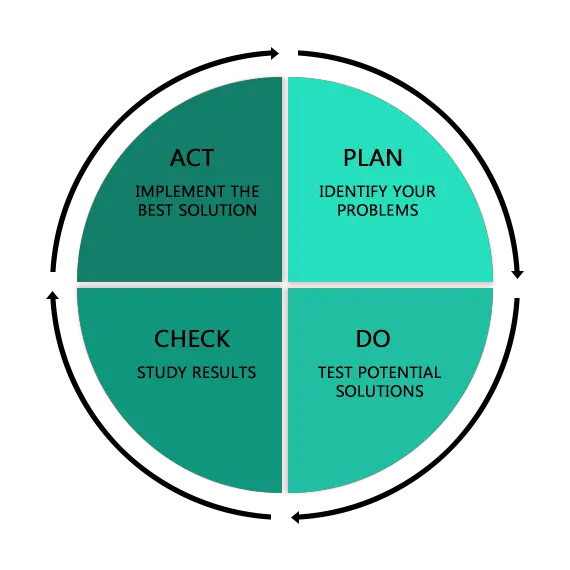
2. PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act)
The PDCA cycle is a four-step approach for implementing changes in a controlled manner. Each step serves a specific purpose:
- Plan : Establish the objectives, processes, and metrics for the corrective action.
- Do : Execute the plan on a small scale initially.
- Check : Measure the outcomes against the planned objectives and analyze the results.
- Act : Make adjustments based on the analysis and either scale the implementation or revisit the plan.
By cycling through these steps, you can continually refine your implementation approach, ensuring it aligns with your objectives.
Implementation is the stage where your problem-solving efforts come to fruition, but it’s not a one-and-done deal. Effective implementation requires continuous monitoring and adjustment. Tools like the Gantt Chart and PDCA cycle provide you with the means to implement corrective actions in a structured, controlled, and measurable way.
Remember, a well-planned implementation not only solves the current problem but also equips your organization with the knowledge and experience to tackle future challenges more effectively.
D7: Prevent Recurrence
Successfully implementing corrective actions is an accomplishment, but the 8D Problem-Solving journey doesn’t end there. The next crucial step is to ensure that the problem doesn’t recur. This phase focuses on institutionalizing the improvements you’ve made, ensuring they are sustainable over the long term. It involves both documentation of new best practices and ongoing monitoring. Let’s explore the tools that can help solidify these new standards.
1. Standard Work
Standard Work refers to the documentation of the new best practices that led to the resolution of the problem. These could be new procedures, guidelines, or checklists that need to be followed. Standard Work serves multiple purposes:
- It provides a clear and easy-to-follow guide for team members.
- It ensures that the successful corrective actions are repeated, thereby making the improvements sustainable.
- It serves as a training resource for new employees or for refresher training for existing staff.

2. Control Charts
Control Charts are used to monitor process performance over time. These charts can help you:
- Identify any variations in the process.
- Distinguish between normal variations and those that need attention.
- Trigger corrective actions if the process goes out of the defined control limits.
Regularly updating and reviewing the Control Charts ensures that you catch any deviations before they turn into bigger problems.

Prevention is indeed better than cure. The most effective problem-solving initiatives are those that not only solve the immediate issue but also prevent its recurrence. Tools like Standard Work and Control Charts offer a structured way to document and monitor the improvements, making them a part of your organizational culture.
By diligently using these tools, you not only secure the gains made but also create a proactive environment where potential issues are identified and addressed before they escalate.
D8: Congratulate the Team
The final step in the 8D Problem-Solving Methodology is often the most overlooked but is crucial for long-term success: congratulating the team. After navigating through a complex problem-solving journey, taking a moment to acknowledge and celebrate the hard work is vital. It not only boosts morale but also encourages a culture of continuous improvement. Let’s delve into some tools and practices that can help you effectively close out your problem-solving initiative.
1. Recognition and Rewards
Acknowledging the hard work and dedication of the team is essential for maintaining a motivated and engaged workforce. Recognition can take various forms:
- Public acknowledgment in team meetings or company-wide announcements.
- Certificates or plaques to commemorate the achievement.
- Small rewards or bonuses, where appropriate.
This recognition serves as a reminder that efforts are appreciated, which in turn fosters a positive work environment.
2. Lessons Learned Document
Closing out a problem-solving initiative offers a prime opportunity to capture what worked and what didn’t. A Lessons Learned Document serves this purpose:
- It details the challenges faced, how they were overcome, and any roadblocks encountered.
- It captures best practices for future reference.
- It identifies areas for improvement, offering a starting point for future problem-solving endeavors.
Sharing this document organization-wide can serve as a valuable resource for other teams facing similar challenges.

A job well done indeed deserves recognition, but it also lays the groundwork for future improvements. Tools like Recognition and Rewards and the Lessons Learned Document not only celebrate success but also institutionalize the knowledge gained. This twofold approach not only marks the successful completion of one problem-solving initiative but sets the stage for ongoing improvements and future successes.
By taking the time to celebrate and reflect, you not only acknowledge the efforts made but also capture valuable insights that can guide your organization’s continuous improvement journey.
Successfully navigating the 8D Problem-Solving Methodology is a commendable achievement, but the journey doesn’t end with implementing a solution. Each step, from forming a team to congratulating them, is a building block in your organization’s culture of continuous improvement.
Employing specific tools like RACI Matrix, 5 Whys, FMEA, and Control Charts at different stages ensures that your problem-solving efforts are not just effective but also sustainable. These tools offer more than just a way to tackle issues; they provide a structured approach to learning from them. Remember, the goal isn’t just to solve a single problem but to refine a system that becomes increasingly resilient and efficient over time. So, take a moment to celebrate your achievements, and then gear up for your next challenge, armed with the knowledge and tools that will make your problem-solving journey even more impactful.
- Sharma, M., Sharma, S. and Sahni, S., 2020. Structured Problem Solving: combined approach using 8D and Six Sigma case study. Engineering Management in Production and Services , 12 (1), pp.57-69.
- Broday, E.E. and Júnior, P.P.A., 2013. Application of a quality management tool (8D) for solving industrial problems. Independent Journal of Management & Production , 4 (2), pp.377-390.
- Engineer, A.T.D., 2016. Managing project using 8D technique. Management , 7 (6), p.67œ76.
Was this helpful?

Daniel Croft
Daniel Croft is a seasoned continuous improvement manager with a Black Belt in Lean Six Sigma. With over 10 years of real-world application experience across diverse sectors, Daniel has a passion for optimizing processes and fostering a culture of efficiency. He's not just a practitioner but also an avid learner, constantly seeking to expand his knowledge. Outside of his professional life, Daniel has a keen Investing, statistics and knowledge-sharing, which led him to create the website www.learnleansigma.com, a platform dedicated to Lean Six Sigma and process improvement insights.

Scatter Plots

The Importance of Data Driven Decision Making in Lean Six Sigma
Free lean six sigma templates.
Improve your Lean Six Sigma projects with our free templates. They're designed to make implementation and management easier, helping you achieve better results.

5S Floor Marking Best Practices
In lean manufacturing, the 5S System is a foundational tool, involving the steps: Sort, Set…
How to Measure the ROI of Continuous Improvement Initiatives
When it comes to business, knowing the value you’re getting for your money is crucial,…
8D Problem-Solving: Common Mistakes to Avoid
In today’s competitive business landscape, effective problem-solving is the cornerstone of organizational success. The 8D…
The Evolution of 8D Problem-Solving: From Basics to Excellence
In a world where efficiency and effectiveness are more than just buzzwords, the need for…
Are you grappling with recurring problems in your organization and searching for a structured way…
How to Select the Right Lean Six Sigma Projects: A Comprehensive Guide
Going on a Lean Six Sigma journey is an invigorating experience filled with opportunities for…

What Is an 8D Report? Understanding the 8 Disciplines of Problem-Solving
Someone probably asked you (or told you) to make one... but what is it? Where does it come from? And how to do it?
Have you ever faced a problem that seems too complex to solve? Do you feel like you're stuck and not sure where to begin? This is where the 8D report comes in. Developed in the 1980s as part of the Ford Motor Company's problem-solving methodology, the 8D report is a step-by-step approach to solve complex problems effectively. It combines data analysis, critical thinking, and teamwork to identify the root cause of a problem and develop a sustainable solution.
The Origins of the 8D Report
The 8D report has a rich history that dates back to the 1950s. During that time, a quality control consultant named Kaoru Ishikawa developed the Ishikawa diagram, also known as the fishbone diagram. This approach highlighted a visual way to identify the potential causes of a problem.
The Ishikawa diagram is a tool used to identify the root causes of a problem. It is also known as a fishbone diagram because of its shape. The diagram is made up of a central line that represents the problem, with branches extending out to represent the potential causes. The branches are labeled with categories such as people, process, equipment, and materials to help identify the source of the problem.
Then, in the 1960s, Motorola developed the 7-step approach to quality control, which became a standard for problem-solving across many industries. This approach focused on identifying the root cause of a problem and implementing a solution to prevent it from happening again.
The Birth of the 8D Methodology
Fast-forward to the 1980s, where Ford Motor Company faced a significant problem with their new vehicles. They noticed an increasing number of customer complaints and expensive repairs, which led to a reputation loss and diminished profitability. In response, Ford developed the 8D methodology, a documented process that rigorously addressed recurring and complex issues.
The 8D methodology is an eight-step problem-solving process that is used to identify, correct, and prevent recurring problems. The process involves a team of people working together to identify the root cause of the problem, develop and implement a solution, and monitor the effectiveness of the solution.
The eight steps of the 8D methodology are:
- Establish the team
- Describe the problem
- Implement and verify interim containment actions
- Define and verify root causes
- Choose and verify permanent corrective actions
- Implement and validate corrective actions
- Prevent recurrence
- Congratulate the team
The Role of Ford Motor Company in Popularizing 8D
The widespread success of the 8D methodology at Ford Motor Company put it on the map. Other industries and businesses soon adopted the approach, and it became a standard in the automotive industry, aviation, healthcare, and many others. It has been refined and enhanced to suit many different needs, but its core principles remain unchanged.
The 8D methodology is a powerful tool for problem-solving and continuous improvement. By following the eight steps, teams can identify the root cause of a problem, develop and implement a solution, and prevent the problem from recurring. This approach has helped many organizations improve their quality, reduce costs, and increase customer satisfaction.
The 8 Disciplines of Problem-Solving
Problem-solving is an essential skill for any organization. The ability to identify and resolve issues quickly and effectively can make a significant difference in achieving business objectives. The 8D report is a structured problem-solving methodology that can help organizations address complex problems. The methodology involves eight disciplines, each representing a different phase of the process.
D1: Establish the Team
The first step is to establish an interdisciplinary team that will be responsible for generating solutions. The team should consist of individuals from different departments, with different skill sets, and areas of expertise. The team identifies key stakeholders and people who may be affected by the problem or have a stake in the solution. This helps to ensure that the team has a comprehensive understanding of the problem and can develop a solution that meets the needs of all stakeholders.
D2: Define and Describe the Problem
The second step is to define the problem as precisely as possible. This is done by gathering information about when, where, and how the problem occurs, its frequency, and its severity. The team should also identify any patterns or trends that may be contributing to the problem. This helps to ensure that the team has a clear understanding of the problem and can develop an effective solution.
D3: Develop an Interim Containment Plan
The third step involves developing a temporary solution that helps to contain the problem while the team works on finding a permanent solution. The interim containment plan should be designed to prevent the problem from getting worse and minimize the impact on stakeholders. This helps to ensure that the team has time to develop an effective permanent solution.
D4: Determine Root Causes
The fourth step is to determine the root cause of the problem. This involves analyzing data, conducting experiments, and brainstorming to identify all possible causes. The team should also consider the impact of the problem on different stakeholders and identify any underlying issues that may be contributing to the problem. This helps to ensure that the team can develop a permanent solution that addresses the root cause of the problem.
D5: Identify and Verify Permanent Corrective Actions
The fifth step involves developing a permanent and effective solution. The team identifies the best course of action to take, evaluates its feasibility, and verifies its effectiveness. The team should also consider the impact of the solution on different stakeholders and ensure that the solution meets the needs of all stakeholders. This helps to ensure that the team can develop a permanent solution that addresses the root cause of the problem and meets the needs of all stakeholders.
D6: Implement and Validate Permanent Corrective Actions
The sixth step involves implementing the selected solution and validating its effectiveness. The team monitors the situation to ensure that the problem does not recur. The team should also communicate the solution to all stakeholders and ensure that they understand how the solution will be implemented. This helps to ensure that the solution is effectively implemented and the problem does not recur.
D7: Prevent Recurrence
The seventh step involves putting measures in place that ensure the problem does not happen again. This includes developing and implementing preventive measures that address the causes of the problem. The team should also monitor the situation to ensure that the preventive measures are effective and adjust them as necessary. This helps to ensure that the problem does not recur and the organization can avoid similar issues in the future.
D8: Congratulate the Team and Share Lessons Learned
The eighth and final step involves congratulating the team for their hard work and sharing the lessons learned with the broader stakeholder base. This helps to improve the organization's problem-solving capabilities and establish best practices for future issues. The team should also document the entire process, including the problem, the solution, and the lessons learned. This helps to ensure that the organization can learn from the experience and apply the knowledge gained to future issues.
The Benefits of Using an 8D Report
The 8D methodology has become increasingly popular in recent years as a problem-solving tool. It provides a structured approach to problem-solving that has several advantages for businesses and problem solvers alike.
Improved Problem-Solving Skills
One of the most significant benefits of using the 8D methodology is that it sharpens your problem-solving skills. By breaking down the problem into manageable steps, the methodology helps you think critically and analyze the situation. This, in turn, helps build a culture that values critical thinking and analysis, making it easier to solve problems in the future. Additionally, by reducing the time it takes to solve problems, the 8D methodology saves valuable resources that can be used elsewhere.
Enhanced Teamwork and Collaboration
The interdisciplinary team is one of the critical components of the 8D methodology. By bringing together team members from different disciplines, the methodology encourages collaboration and a diverse range of perspectives. This leads to better solutions and a more inclusive culture in the organization. By working together, team members can identify problems more quickly and develop more effective solutions.
Reduced Recurrence of Issues
Another significant benefit of the 8D method is that it provides a robust and effective solution to recurring problems. The structured approach breaks down the problem into manageable steps that ensure that it is entirely resolved, and the cause is eliminated. This reduces the likelihood of the problem recurring in the future, saving time and resources that would otherwise be spent addressing the same issue repeatedly.
Increased Customer Satisfaction
By using the 8D methodology, businesses can identify and solve problems before they impact their customers. This leads to an improvement in customer satisfaction, as customers are less likely to experience issues with the product or service. Ultimately, this increased customer satisfaction leads to increased retention and revenue for the business.
In conclusion, the 8D methodology is an effective problem-solving tool that has several benefits for businesses and problem solvers. By improving problem-solving skills, enhancing teamwork and collaboration, reducing the recurrence of issues, and increasing customer satisfaction, the 8D methodology can help businesses become more efficient and effective.
The 8D methodology is a proven and effective problem-solving approach. It helps businesses tackle complex issues with a structured and rigorous approach that leads to sustainable solutions. By focusing on the root cause of the problem and implementing preventive measures, the 8D report reduces the recurrence of problems, increases customer satisfaction, and enhances the organization's problem-solving skills. Implementing the 8D methodology can save businesses time, money, and valuable resources.
Supplios can help you (and your suppliers) complete 8D reports, SCAR, and other important Quality processes much faster and more efficiently than before. Our fully automated system can be configured to match your specific process, and we integrate with many ERP and QMS systems.
Inquire with our team to get a custom demo of the platform today!
Are you a ComplianceQuest Customer?
8D Management (8 Disciplines Management)

8D Management & The 8D of Problem Solving
Problems are a part of life and a business is no exception. Even with the best of intentions and systems, some errors can creep in and be hard to detect. It may be nothing serious or can have serious repercussions such as reputation damage, heavy fines, product recall, property loss, and so on. It becomes essential to identify the problem, its consequences on the one hand, and causes on the other to be able to not only resolve it for now but also ensure prevention of its recurrence. One of the methodologies, popular amongst engineers and professionals mainly in the automotive industry but now applied across several industries is the eight disciplines (8D) model. It helps to identify, correct, and eliminate recurring problems, affecting improvement in product and process.
Related Assets
Whenever organizations tackle problems and generate solutions based out of root cause analysis, they tend to generate a lot of…
Key Highlights: 8D is an extremely effective, proven problem-solving framework, especially in the manufacturing and automotive sector. However, to truly…
From a quality management standpoint, a problem may be reported in an organization from one of the following processes: Complaints…

What is 8D?
The 8D is a systematic, holistic and proven methodology designed to identify the root cause of a problem, plan a quick fix, and implement corrective actions and preventive actions to avoid their recurrence. If your product is defective or not meeting your customer requirements, then 8D is an excellent first step to improve Quality and Reliability.
One of the core parts of introducing 8D problem solving, greatly accepted by most disciplines of industries, and having huge effectiveness levels in improving product and process quality, would be 8D (Eight Disciplines). Key steps in the 8D methodology are forming a team, defining the problem, identifying and implementing interim containment, identifying the root causes, implementing and verifying permanent corrective actions, and avoiding future recurrence of problems. The 8D process for root cause analysis concludes by highlighting that the team members not only play a vital role but also recognizes them, hence reinforcing that this approach is a collaborative one. 8D has become very popular among manufacturers, assembly, and services around the globe because it is effective and comparatively easy to teach.
Introduction to 8d Problem Solving
The 8D approach to problem-solving, also known as the 8D methodology, is a systematic and comprehensive method used to address and resolve complex issues, particularly in manufacturing and other industries.
This 8D troubleshooting methodology involves a structured process designed to identify, correct, and prevent issues, ensuring that similar problems do not occur in the future.
By following the 8D process steps, teams can effectively perform root cause analysis and implement corrective actions.
The 8D structured problem-solving process is highly valued for its ability to provide a clear framework for identifying and eliminating the root cause of a problem, thereby enhancing overall operational efficiency.

Why to Apply 8D Problem Solving Methodology?
The 8D methodology, developed to represent the best practices in problem solving, provides the engineering teams with an effective and efficient team-oriented problem solving skill, a better understanding of Root Cause Analysis (RCA) and how to use basic statistical tools required for problem solving. 8D helps the management understand and resolve problems better, identify necessary systemic changes and inputs for change , and facilitate a more candid and open communication in problem solving discussions.
8D improves the Quality and Reliability of your products, and if performed correctly, prepares the engineering team for future problems.
When to Apply 8D Problem Solving Process?
The 8D problem solving process is used to solve major, critical, chronic, and recurring problems. The 8D is typically required during safety or regulatory issues, customer complaints , warranty concerns, poor performance or test failures, internal rejects, and to minimize waste and scrap.

How to Use Root Cause Analysis to Transform Your Safety Program
8d problem solving approach.
The 8D is a systematic process for the introduction and improvement of quality, and elimination of problems. Here we will show you the step by step approach of the problem solving tools that can make you proficient at identifying causes of problems, defining problems, and errors. Additionally, it helps identify root causes and take actions to solve and prevent identified problems in processes. So, let’s take a peep inside:

D0: Planning and preparing for the 8D
Proper planning and preparation are always a good start before taking any action. So, you need to consider the following before forming a team:
- Problem description
- Timeframe for the resolution
- The number of resources to accomplish this

D1: Team establishment
Create a team with people who varied backgrounds and experiences which will lead to the best quality inputs and a complete solution. For the team to function smoothly, define clear roles, and responsibilities for your people, and have a team leader.

D2: Problem description
The 8D method’s primary focus is to describe the problem appropriately and objectively such that it captures all the vital information. During this analysis, repeated 5W1H (why, what, who, where, when, and how) are required to be asked to develop a clear description.

D3: Problem containment plan
A temporary problem containment plan is sometimes needed to minimize the impact of the problem until you develop permanent solutions. On developing the plan based on the hypothetical cases, the resources for addressing the main problem can be released. At times, new processes may be required to work around the problem until you have a permanent fix.

D4: Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
With the problem temporarily contained, you can now turn to identify all of the root causes of the nonconformance . There are several tools to identify the actual root cause of an issue including the 5W1H to understand the problem in-depth, Fishbone diagrams to visually categorize causes, and Pareto charts to identify the vital causes.

D5: Permanent Corrective Action
Once the root cause of the problem is determined, the team can start brainstorming permanent corrections to identify what the best long-term solution will be. Brainstorming sessions combined with tools such as affinity diagrams help organize ideas based on their relationships and determine the best course of action.

D6: Implement and Validate the Permanent Corrective Action
Once the solution is identified, the management needs to implement and verify the corrective action using the PDCA (plan-do-check-act) approach for small-scale testing before large-scale rollout. Thus, the outcomes and corrective actions are tracked to ensure expected results. To successfully implement a permanent change, a project plan should incorporate:
- Development of the project plan for implementation
- Communicating the plan to all stakeholders
- Validating improvements using measurement

D7: Prevent Recurrence
A complete solution of problems means preventing them from occurring. Besides, preventative measures should also be implemented for corrective actions in the 8D methodology. This requires reviewing management processes, operating procedures, and training manuals to ensure that best practices are followed.
At this stage, organizations should consider actions including updating process audit questions and regularly verifying them based on corrective actions to reduce risk in other processes, presenting poka-yoke or error-proofing devices to big-risk processes, and conducting red rabbit tests to see how long it takes poka-yoke devices to detect defective product.

D8: Verification and Team Celebration
Once the problem is solved, the ultimate step is to congratulate the team. It’s important to recognize their efforts and share their success across the organization because teams require feedback to allow for satisfactory closure. This facilitates motivation and employee engagement while helping you improve quality control, execute process improvements, and aid change management as you grow.

Create a team with people who are having varied backgrounds and experiences which will lead to the best quality inputs and a complete solution. For the team to function smoothly, define clear roles, and responsibilities for your people, and have a team leader.

A complete solution of problems means preventing them from occurring initially. Besides, preventative measures should also be implemented for corrective actions in the 8D methodology. This requires reviewing management processes, operating procedures, and training manuals to ensure that best practices are followed.
8D Root Cause Analysis (RCA) and 8D Corrective Action Process
The 8D Root Cause Analysis, as well as the 8D Corrective Action process, is a widely systematic approach in quality management , especially concerning 8D in quality control. This method includes eight comprehensive steps that are devised to problem solving by dealing with root causes of the problems comprehensively. The steps of the 8D process start with the formation of a team, a clear definition of the problem, and move on to interim containment actions. This is then followed by detailed root-cause analysis using the 8D RCA process, development and verification of permanent corrective actions, implementation, and recurrence preventing efforts. Encouraging details in the analysis: the 8D methodology steps encompass collaborative efforts and documentation that ensure durable solutions and continuous improvement in organizational processes. Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is embedded within the 8D process and includes the following steps and techniques:

Problem Symptom is measured and transformed to “Object and Defect”

Problem Symptom is reformed to Problem Statement using the 5W1H process

Potential Causes are gathered using the tools like Fishbone or Affinity Diagram

Problem Statement should fit using both the “is” and the “isn’t” sections of the question

Root Cause concepts are developed from remaining possible causes on the tool and related changes from is/is not

Compare theories with recent data and develop experiments for Root Cause Verification

Test and confirm the Root Causes

Customer Success
3 Women Leaders Making a Powerful Impact in Global Quality and Safety Management
How to use the 8d approach.
8D portrays 8 steps of a structured approach to solve difficult, recurring, or critical problems by providing transparency, driving a team approach, and increasing the chances of solving the problem.
Proper plan for solving the problem and identify the prerequisites.
Team creation
Gather a cross-functional team with product/process knowledge.
Problem description and definition
Use the data and information to specify the problem by identifying in quantifiable terms the who, what, where, when, why, how, and how many (the 5W1H) for the problem.
Problem Containment Plan development
Develop and implement interim actions to eliminate the problem from any customer in the future.
Specify and assess Root Causes
Identify and review all relevant causes and sources of variation that analyze why the problem has occurred and figure out why the problem was not noticed at first using 5W1H or diagrams.
Verify Permanent Solutions
After collecting data confirm that the possible solutions will actually resolve the problem.
Implement and Validate Corrective Actions
Discuss and review results and develop plans to implement the best solutions or countermeasures.
Preventive measures
Transform the operation systems, management systems, procedures, and practices to avoid the recurrence of similar problems.
Compliment your team
Recognize the collective efforts of your team and formally thank them for their involvement.
8D Problem Solving Tools and Techniques
The 8D problem solving methodology is the set of tools and methods aiming for complex quality issues. 8D problem solving techniques are basically comprised of a fishbone diagram, 5 Whys analysis, Pareto charts, process flowcharts, and Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) to come to terms with the 8D framework. Integration with statistical tools and data analysis in every step of 8D analysis is sure to make the most accurate identification of the root cause.
This approach would ensure that cross-functional teams' participation would not only be present in the brainstorming sessions but also in the 8D problem solving process at the problem solving stage.

Training in 8D Methodology
8D training is an inevitable imperative that makes its deployment in organizations effective. The 8D methodology provides all the necessary details that the teams could apply to the skills and knowledge required at every step in 8D of quality control . Training the workforce on 8D methodology will make them able to apply these aspects when dealing with real-world problems, which will better off the quality and efficiency of the entire organization. It ensures that all these measures and strategies have been inducted to make sure that 8D problem solving approaches are not just tools for problem solution but have been inducted to lay down the base for sustainable quality improvement and prevention practices in the organizational processes.

How to Enhance Quality and Efficiency in 8D Manufacturing?
Understand the Basics of the 8D Approach to Problem Solving
- Familiarize yourself with the principles of the 8D methodology.
- Recognize that the 8D process steps include team formation, problem
Form a Cross-Functional Team
- Assemble a team with diverse skills and perspectives.
- Ensure each member understands their role in the 8D structured problem solving process.
- Use precise language to describe the problem.
- Implement tools like the 5 Whys to aid in the root cause analysis 8d problem solving phase.
Implement Interim Containment Actions
- Take immediate steps to prevent the problem from worsening.
- Document these actions as part of the 8D troubleshooting methodology
Identify and Verify Root Causes
- Conduct a thorough root cause analysis to pinpoint the underlying issues.
- Utilize techniques like fishbone diagrams and Pareto charts in the 8D RCA process.
Develop Permanent Corrective Actions
- Propose solutions that address the root causes identified.
- Ensure these solutions are sustainable and prevent recurrence.
Validate the Corrective Actions
- Test the solutions to ensure they effectively resolve the problem.
- Collect data to confirm the effectiveness of the root cause analysis and the 8Dd corrective action process.
Implement and Monitor Solutions
- Roll out the verified solutions across relevant areas.
- Continuously monitor the impact to ensure long-term success.
Prevent Recurrence
- Update processes and documentation to incorporate the new solutions.
- Train employees on the new procedures to embed them in daily operations.
Recognize and Celebrate Success
- Acknowledge the efforts of the team in solving the problem.
- Use this opportunity to reinforce the importance of the 8D methodology in maintaining quality and efficiency.
Ensuring compliance with FDA regulations is crucial for medical device manufacturers to maintain market access and ensure patient safety. Medical Device Compliance Software plays a pivotal role in helping companies align with these stringent requirements. Here’s how:
Great product, support, and people to work with!
We have rolled-out CQ across our company to automate various elements of QMS requirements such as Document Management, Complaints, Non-conformances, Corrective Action (8D and A3), Supplier Management and Audit Management. We have been using the software for more than 2 years. We are glad to see how well the system is being used across the company. We have several thousand users on the system currently and working to scale the usage further. CQ solution has been configured to meet our needs, works elegantly across languages, across time zones, and business verticals. With integration between CQ and SAP to exchange critical data, the process automation provides a lot of productivity.
CQ configuration team and support have worked hard to ensure that our needs continue to be met. They consistently go above and beyond. We cannot be more pleased with our use of CQ QMS capabilities and would definitely recommend to anyone who is looking for a modern cloud based EQMS solution especially if you want a scalable EQMS solution.
Lia Budiman, Continental Contitech

8D Process Improvement in Different Industries
Automotive Industry
- Application of 8D Methodology: Essential for addressing recurring quality issues and customer complaints.
- Root Cause Analysis 8D Problem Solving: Identifies underlying issues affecting vehicle performance and safety.
- 8D Structured Problem Solving: Used to enhance manufacturing processes and reduce defects.
- 8D Process Steps: Followed rigorously to maintain high safety and quality standards in vehicle production
Aerospace Industry
- 8D Troubleshooting Methodology: Critical for resolving complex technical issues and ensuring compliance with stringent safety regulations.
- 8D RCA Process: Applied to investigate and eliminate root causes of system failures.
- 8D Corrective Action Process: Ensures that preventive measures are implemented to avoid the recurrence of problems.
- 8D Manufacturing: Focuses on precision and reliability in the production of aerospace components.
Electronics Industry
- 8D Approach to Problem Solving: Used to tackle issues related to product design and manufacturing.
- Root Cause Analysis and the 8D Corrective Action Process: Vital for maintaining product quality and reducing warranty claims.
- 8D Process Steps: Helps in identifying and addressing defects in electronic components and assemblies.
- 8D Methodology: Ensures continuous improvement and innovation in electronics manufacturing processes.
Healthcare Industry
- 8D Structured Problem Solving: Applied to improve patient care and operational efficiency in healthcare facilities.
- 8D Problem-Solving Steps: Utilized to address issues related to medical equipment and procedural errors.
- Root Cause Analysis 8D Problem Solving: Enhances patient safety by identifying and eliminating causes of medical errors.
- 8D Troubleshooting Methodology: Ensures that corrective actions are taken to prevent the recurrence of adverse events.
Food and Beverage Industry
- 8D Manufacturing: Ensures product quality and safety throughout the production process.
- 8D Approach to Problem-Solving: Addresses contamination issues and improves production line efficiency.
- Root Cause Analysis and the 8D Corrective Action Process: Essential for maintaining food safety standards.
- 8D Process Steps: Used to investigate and resolve quality issues in food production systematically.
Pharmaceutical Industry
- 8D Methodology: Applied to ensure the consistency and safety of pharmaceutical products.
- 8D RCA Process: Identifies and addresses root causes of deviations in manufacturing processes.
- 8D Corrective Action Process: Implements preventive measures to ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
- 8D Troubleshooting Methodology: Enhances production efficiency and reduces the risk of product recalls.
Consumer Goods Industry
- 8D Structured Problem Solving: Used to resolve product design and manufacturing issues.
- 8D Process Steps: Ensures consistent product quality and customer satisfaction.
- Root Cause Analysis 8D Problem Solving: Identifies and eliminates causes of defects in consumer products.
- 8D Manufacturing: Focuses on improving production processes and reducing waste.
Energy Industry
- 8D Approach to Problem Solving: Applied to address equipment failures and improve operational reliability.
- Root Cause Analysis and the 8D Corrective Action Process: Ensures the continuous improvement of energy production processes.
- 8D Troubleshooting Methodology: Helps resolve complex technical issues in energy plants.
- 8D RCA Process: Identifies and eliminates causes of energy generation and distribution inefficiencies.
8D Process Metrics and KPIs
- Problem Resolution Time: This metric tracks the time taken from problem identification to resolution in the 8D root cause analysis process, ensuring timely corrective actions are implemented to prevent recurrence.
- Recurrence Rate: By measuring how often a similar problem reappears after the 8D corrective action process, this KPI helps assess the effectiveness of the implemented solutions and continuous improvement efforts.
- Root Cause Identification Accuracy: This KPI evaluates the precision and accuracy with which the root causes are identified during the 8D root cause analysis, ensuring that the correct issues are being addressed.
- Corrective Action Implementation Rate: This metric tracks the percentage of corrective actions successfully implemented within the stipulated timeline, indicating the efficiency of the 8D corrective action process.
- Customer Satisfaction Improvement: Monitoring changes in customer satisfaction levels following the 8D corrective action process can highlight the impact of the process on overall product quality and customer perception.

8D Problem Solving Report
8D problem solving reports and templates are useful tools to initiate a problem solving process. These reports are used to explain what 8D is and including information about each step so that one will know what needs to be done by attempting this to solve problems. Keeping these reports easily available can avoid repeating work on the same problems over and over again.
8D reports must be detailed and incorporate information at every step within the 8D process. Those who are working on the problem should provide sufficient information when completing a report so that someone who was not on the current 8D team can pull it out and understand what the problem was and what solutions were implemented.
Improve quality, eliminate problems and identify the root cause of a problem with 8d Methodology
Who can 8d help.
The 8D methodology is universally applicable for every organization that needs solving. Although, there are a few industries and sectors where this 8D approach is successfully used such as manufacturing, the automotive industry , engineering companies that manufacture products or parts, and medium and large-scale enterprises.

Related Checklists

Quality Assurance Checklist – Part A (Project Management)
Checklist | September 7th, 2022

Quality Assurance Checklist – Part B (Project Deliverables)

Quality Control Area Safety Audit Checklist for Pharmaceutical Companies
Checklist | April 22nd, 2022
Implementing the 8D Root Cause Analysis

Establish the Team
- Assemble a cross-functional team: Ensure diverse perspectives and expertise.
- Define roles and responsibilities: Clarify each member's contributions.
- Team leader selection: Choose someone with strong leadership and problem-solving skills.
Describe the Problem
- Problem statement creation: Define the issue clearly and concisely.
- Use of data and evidence: Gather and present data to illustrate the problem.
- Scope and impact: Detail how the problem affects processes, products, or customers.
- Immediate actions: Implement temporary measures to contain the problem.
- Verification of ICAs: Ensure the containment actions are effective.
- Monitoring: Continuously monitor the situation until a permanent solution is found.
Determine Root Causes
- Root cause analysis techniques: Utilize tools like the 5 Whys and Fishbone diagrams.
- Data analysis: Examine data to identify patterns and anomalies.
- Identify multiple root causes: Look beyond the obvious to find all contributing factors.
Develop Permanent Corrective Actions (PCAs)
- Brainstorm solutions: Generate potential corrective actions.
- Evaluate effectiveness: Assess the feasibility and impact of each solution.
- Select the best solution: Choose the most effective and sustainable corrective action.
Implement and Validate PCAs
- Action plan creation: Develop a detailed plan to implement corrective actions.
- Execution: Carry out the corrective actions according to the plan.
- Validation: Verify that the corrective actions resolve the problem effectively.
- Standardization: Update processes, procedures, and documentation to include the new solutions.
- Training: Educate employees on the new procedures to ensure consistent application.
- Monitoring and review: Regularly review the effectiveness of the implemented solutions.
Recognize the Team and Celebrate Success
- Team recognition: Acknowledge the contributions of each team member.
- Celebrate achievements: Celebrate the success of solving the problem.
- Document lessons learned: Record insights and lessons learned for future reference.
Quality-centric Companies Rely on CQ QMS

Frequently Asked Questions
The 8D methodology is often used since it provides a consistent, simple, and thorough approach to solving raised problems at various stages. If properly applied, it gives several advantages such as:
A systematic approach for improving team-oriented problem solving skills
A clear understanding of basic statistical tools needed for problem solving
A practical understanding of the ‘ root cause analysis’ tool
Creating and expanding relative information about past failures and lessons learned to avoid future problems in the organization
Improving skills for corrective action deployment
When the team is trying to find the root cause of the problem and deploy corrective actions, some defective products will continue to be manufactured. To prevent these defective parts from reaching the customer, interim containment ensures that the defects are contained in the facility till the problem is completely solved. If defective parts reach the customer, it may result in warranty claims, field failures, and customer complaints.
To implement the 8D process successfully, the following factors are crucial:
The right team
An accurate description of the problem
Avoiding skipping through steps
Ensuring cooperation within the team and management support
Understanding the difference between real causes and possible causes
Related Insights

5 Dos and Don’ts When Choosing a QMS Solution for Your Enterprise
Every investment a business makes should have a measurable impact. In the case of an EQMS, the ROI is based…
Root Cause Analysis – Definition, Benefits and Process
All Quality and Safety Management Standards emphasize the importance of…
5 Why vs. Pareto Chart vs. Fishbone Diagram – Pros and Cons of Each of These RCA Techniques
All Quality Management Standards emphasize the importance of identifying the…
Automated CAPA with RCA and 5 Why to Make Your Workplace Healthy and Safe
PGT Innovations (PGT), pioneers in the impact-resistant window and door…
Connect with a CQ Expert
Learn about all features of our Product, Quality, Safety, and Supplier suites. Please fill the form below to access our comprehensive demo video.

Please confirm your details
By submitting this form you agree that we can store and process your personal data as per our Privacy Statement. We will never sell your personal information to any third party.
In Need of Smarter Ways Forward? Get in Touch.
Got questions we can help.
Chat with a CQ expert, we will answer all your questions.

Certainty Blog
Mastering 8d problem solving: a comprehensive guide for businesses.
Table of contents
- What is 8D Problem Solving?
- The 8 Disciples of Problem Solving
- Implementing 8D Problem Solving Methodology
Example of Successful 8D Problem Solving
- Common Challenges and Best Practices
Measuring the Effectiveness of 8D Problem-Solving Efforts
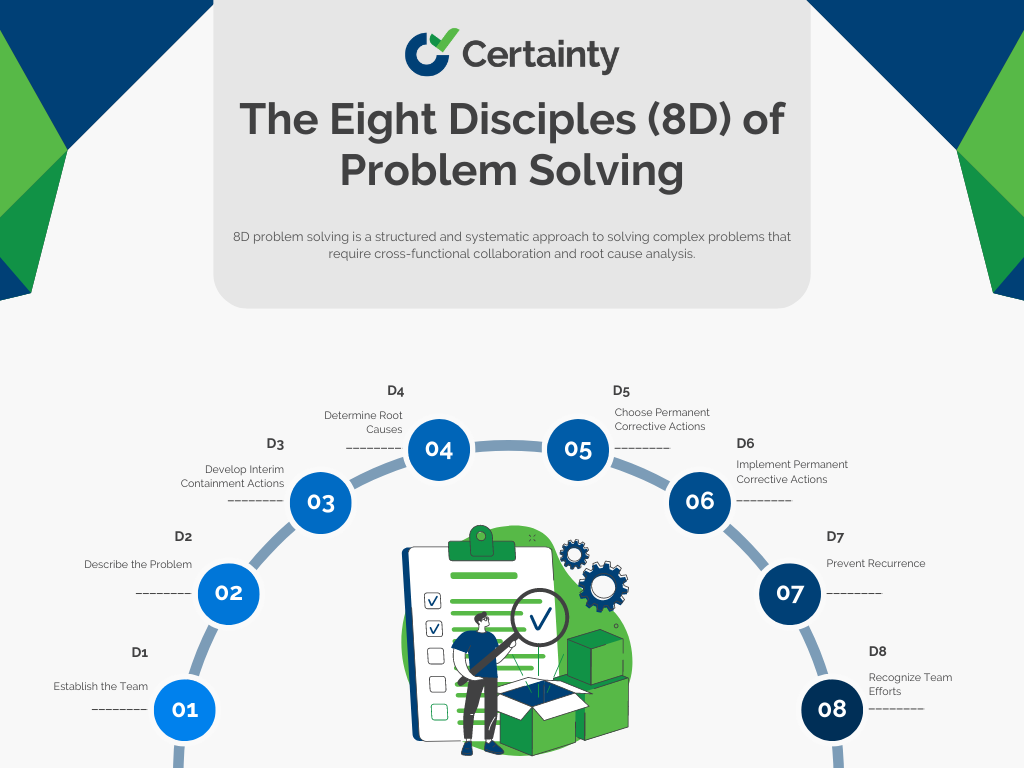
Problem solving is a vital skill for any business that wants to survive and thrive in today’s competitive and dynamic environment. However, not all problems are created equal. Some are simple and straightforward, while others are complex and multifaceted. How can businesses effectively tackle these challenging problems and prevent them from recurring?
One of the most powerful and proven problem-solving methodologies is 8D problem solving. 8D stands for eight disciplines, which are a series of steps that guide teams through the process of identifying, analyzing, resolving, and preventing problems. 8D problem solving can help businesses improve their quality, reduce their costs, and enhance their customer satisfaction.
What is 8D Problem Solving
8D problem solving is a structured and systematic approach to solving complex problems that require cross-functional collaboration and root cause analysis. It was developed by Ford Motor Company in the late 1980s as a way to address customer complaints and improve product quality. Since then, it has been widely adopted by many organizations across various sectors.
The core principles and objectives of 8D problem solving are:
- Focus on the customer’s needs and expectations
- Involve a multidisciplinary team with relevant expertise and authority
- Use data and facts to support decision making
- Identify and eliminate the root causes of the problem
- Implement corrective actions that prevent reoccurrence
- Document and communicate the problem-solving process and results
The 8D methodology differs from other problem-solving approaches in several ways. First, it emphasizes team-oriented problem-solving. Second, it follows a sequential and logical order of steps that ensures thoroughness and consistency. Third, it uses various tools and techniques to facilitate analysis and action. Fourth, it incorporates feedback loops and verification methods to ensure effectiveness and sustainability.
The Eight Disciples of Problem Solving
D1: establish the team.
The first step in the 8D approach is to form a team that will work on the problem. The team should consist of members who have knowledge, experience, or involvement in the problem area. The team should also have a leader who will coordinate the activities and communicate with stakeholders.
The purpose of establishing the team is to:
- Define the roles and responsibilities of each team member
- Establish the scope and boundaries of the problem
- Set the goals and expectations for the problem-solving process
- Allocate the resources and time required for the process
D2: Describe the Problem
The second step in this problem-solving method is to define and describe the problem in detail. The team should use data and facts to describe the problem as accurately as possible. The team should also use tools such as the 5W2H method (who, what, where, when, why, how, how much), Six Sigma, or an IS/IS NOT matrix to clarify the aspects of the problem.
Defining and describing the problem allows businesses to:
- Establish a common understanding of the problem among the team members
- Identify the symptoms, effects, and impacts of the problem
- Quantify the magnitude and frequency of the problem
- Specify the criteria for evaluating potential solutions
D3: Develop Interim Containment Actions
The third step in 8D problem solving is to develop interim containment actions that will prevent or minimize the negative consequences of the problem until a permanent solution is found. The team should identify and implement actions that will isolate, control, or eliminate the causes or sources of variation that contribute to the problem.
When you develop interim containment actions, you:
- Protect the customer from defective products or services
- Reduce the risk of further damage or harm
- Maintain operational continuity and stability
- Buy time for root cause analysis and corrective actions
D4: Determine Root Causes
The fourth step in the 8D method is to determine the root causes responsible for creating or allowing the problem to occur. The team should use data analysis tools such as Pareto charts, histograms, scatter plots, or fishbone diagrams to identify possible causes. The team should also use root cause analysis techniques such as 5 Whys, fault tree analysis, or Failure Modes and Effect Analysis (FMEA) to verify or validate the causes.
The purpose of determining root causes is to:
- Understand why the problem happened
- Identify all possible factors that influence or contribute to the problem
- Eliminate superficial or symptomatic causes
- Prevent jumping to conclusions or making assumptions
D5: Choose Permanent Corrective Actions
The fifth step in 8D problem solving is to choose permanent corrective actions that will address or remove root causes permanently. The team should generate multiple possible solutions using brainstorming techniques such as SCAMPER (substitute, combine, adapt, modify, put to another use, eliminate, reverse) or TRIZ (theory of inventive problem solving). The team should also evaluate each solution using criteria such as feasibility, effectiveness, cost, risk, or impact.
Choosing permanent corrective actions helps to:
- Select the best solution that meets customer needs and expectations
- Ensure that root causes are eliminated or prevented from recurring
- Consider trade-offs between different solutions
- Plan for implementation challenges or barriers

30+ Audit and inspection checklists free for download.
D6: implement permanent corrective actions.
The sixth step in 8D problem solving is to implement permanent corrective actions that were chosen in D5. The team should develop an action plan that specifies who will do what by when using tools such as Gantt charts or PDCA cycles (plan-do-check-act). The team should also execute the action plan according to schedule using tools such as checklists or standard operating procedures.
The purpose of implementing permanent corrective actions is to:
- Put the chosen solution into practice
- Monitor progress and performance during implementation
- Resolve any issues or problems that arise during the implementation
- Document changes or modifications made during implementation
D7: Prevent Recurrence
The seventh step in 8D problem solving is to prevent recurrence by ensuring that permanent corrective actions are effective and sustainable. The team should verify that root causes have been eliminated using tools such as control charts or statistical process control (SPC). The team should also validate that customer requirements have been met using tools such as surveys or audits.
Preventing reoccurrence helps to:
- Confirm that permanent corrective actions have solved the problem
- Evaluate customer satisfaction with products or services after implementation
- Identify opportunities for further improvement or optimization
- Standardize best practices or lessons learned from implementation
D8: Recognize Team Efforts
The eighth step in 8D problem solving is recognizing team efforts by acknowledging their contributions and achievements throughout the process. The team should celebrate their success by sharing their results with stakeholders using tools such as reports or presentations. The team should also appreciate their efforts by rewarding them with recognition or incentives.
The purpose of recognizing team efforts is to:
- Motivate team members for future challenges
- Build trust and rapport among team members
- Enhance team morale and cohesion
- Promote a culture of continuous improvement
Implementing 8D Problem-Solving Methodology
Implementing an 8D problem-solving methodology can be challenging for many businesses due to various factors such as organizational culture, resources, or complexity. However, with proper planning, preparation, and execution, it can be done successfully.
Here is some practical guidance on how businesses can effectively implement the 8D process:
Define clear roles & responsibilities for each discipline
One of the key factors for successful implementation is having clear roles & responsibilities for each discipline within the 8D process. Each discipline requires specific skills, knowledge, or authority that may not be available within a single person or department.
Therefore, it is important to assign appropriate roles & responsibilities for each discipline based on their expertise & involvement in the problem area.
Some examples of roles & responsibilities are:
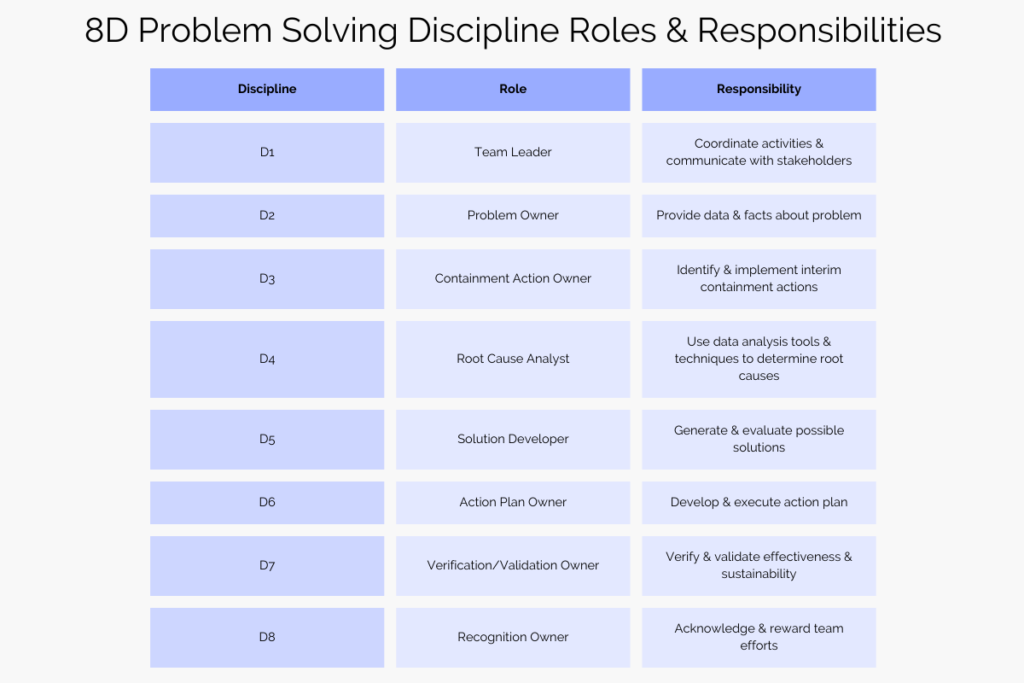
By defining clear roles & responsibilities for each discipline, businesses can ensure accountability, transparency, and collaboration throughout the process.
Establish a common language & framework for communication
Another key factor for successful implementation is having a common language & framework for communication among team members & stakeholders. Communication is essential for sharing information, ideas, or feedback during the process.
However, communication can also be challenging due to different backgrounds, perspectives, or expectations among team members & stakeholders. Therefore, it is important to establish a common language & framework for communication that can facilitate understanding, alignment, and agreement throughout the process. Some examples of common language & framework are:
- Using standard terminology & definitions for the 8D process
- Implementing visual tools & templates to document & present the 8D process
- Using common metrics & criteria to measure & evaluate the 8D process
- Establishing feedback mechanisms & channels to communicate & collaborate during the 8D process
By establishing a common language & framework for communication, businesses can ensure clarity, consistency, and quality throughout the process.
Provide adequate training & support for team members
A third key factor for successful implementation is providing adequate training & support for team members who are involved in the 8D process. Team members need to have sufficient knowledge, skills, or confidence to perform their roles & responsibilities effectively. However, team members may not have prior experience or exposure to the 8D process or its tools & techniques. Therefore, it is important to provide adequate training & support for team members that can enhance their competence & capability during the process. Some examples of training & support are:
- Providing formal training sessions or workshops on the 8D process or its tools & techniques
- Offering coaching or mentoring from experts or experienced practitioners on the 8D process or its tools & techniques
- Contributing access to resources or references on the 8D process or its tools & techniques
- Maintaining feedback or recognition of team members’ performance or improvement during the 8D process
By providing adequate training & support for team members, businesses can ensure effectiveness, efficiency, and engagement throughout the process.
To illustrate the versatility and applicability of 8D problem solving across different industries and contexts, here is a hypothetical example of successful 8D problem solving:
Example: Reducing Customer Complaints in a Food Manufacturing Company
A food manufacturing company was facing a high rate of customer complaints due to foreign materials found in their products. The company used 8D problem solving to address this issue and improve product quality. Here are the steps they took within each discipline:
The company formed a cross-functional team consisting of representatives from quality assurance, production, engineering, and customer service. The team leader was the quality assurance manager who had the authority and responsibility to coordinate the activities and communicate with stakeholders.
The team defined and described the problem using data and facts from customer complaints and product inspection records. The team used the 5W2H method to clarify the aspects of the problem. The problem statement was: “In the past six months, we have received 25 customer complaints due to foreign materials such as metal shavings, plastic pieces, or wood chips found in our products.”
The team developed interim containment actions that would prevent or minimize the occurrence of foreign materials in their products until a permanent solution was found. The team identified and implemented measures such as increasing the frequency and intensity of product inspection, installing additional metal detectors and filters in the production line, and segregating and quarantining any products that were suspected or confirmed to contain foreign materials.
The team determined the root causes that were responsible for creating or allowing foreign materials to enter their products. They then used data analysis tools such as Pareto charts and fishbone diagrams to identify potential causes. Root cause analysis techniques such as 5 Whys to verify or validate the causes were also implemented.
Ultimately, they found that there were three main root causes:
- inadequate maintenance of equipment that resulted in metal shavings or plastic pieces falling off during operation;
- improper handling of raw materials that resulted in wood chips or other contaminants being mixed in during storage or transportation;
- lack of awareness or training of staff on how to prevent or detect foreign materials in products.
The team chose permanent corrective actions that would address or remove root causes permanently. The team generated multiple possible solutions using brainstorming techniques such as SCAMPER and TRIZ. They also evaluated each solution using criteria such as feasibility, effectiveness, cost, risk, or impact. Eventually, they selected the best solutions that met customer needs and expectations.
The solutions were:
- implementing a preventive maintenance program for equipment that included regular inspection, cleaning, and replacement of parts;
- establishing a quality control system for raw materials that included verification, testing, and labeling of incoming materials;
- conducting a training program for staff on how to prevent, detect, and report foreign materials in products.
The team implemented permanent corrective actions that were chosen in D5. An action plan that specified who would do what by when using tools such as Gantt charts and PDCA cycles was then developed. They then executed the action plan according to schedule using tools such as checklists and standard operating procedures.
The team prevented recurrence by ensuring that permanent corrective actions were effective and sustainable. They first verified that root causes had been eliminated using tools such as control charts and statistical process control (SPC). Next, they validated that customer requirements had been met using tools such as surveys and audits. After implementing permanent corrective actions, the rate of customer complaints due to foreign materials dropped by 90%.
Team efforts were recognized by acknowledging their contributions and achievements throughout the process. The team celebrated their success by sharing their results with stakeholders using tools such as reports and presentations. Management also appreciated their efforts by rewarding them with recognition or incentives such as certificates, gift cards, or bonuses.
Common Challenges and Best Practices in 8D Problem Solving
Despite its benefits and advantages,
8D problem solving can also pose some challenges for businesses that want to implement it effectively. Some of these challenges are:
- Resistance to change from staff or management who are used to existing processes or practices
- Lack of commitment or support from senior leaders who do not see the value or urgency of problem-solving
- Difficulty in defining or measuring problems
- Insufficient data or information to support analysis or decision making
- Conflicts or disagreements among team members or stakeholders due to different opinions or interests
To overcome these challenges and ensure successful 8D problem solving, businesses can adopt some best practices such as:
- Communicating the benefits and objectives of 8D problem solving to staff and management
- Securing the buy-in and sponsorship of senior leaders who can provide direction and resources
- Using clear and objective criteria to define and measure problems
- Collecting and analyzing relevant and reliable data or information
- Resolving conflicts or disagreements through constructive dialogue and compromise
To ensure that 8D problem-solving efforts are not wasted or forgotten, businesses need to measure the effectiveness and impact of their initiatives. Measuring the effectiveness of 8D problem-solving efforts can help businesses:
- Assess whether they have achieved their goals and expectations
- Evaluate whether they have improved their performance and customer satisfaction
- Identify areas for further improvement or optimization
- Demonstrate their value and credibility to stakeholders
To measure the effectiveness of 8D problem-solving efforts, businesses can use various methods such as:
- Key performance indicators (KPIs) that can be used to quantify the results or outcomes of 8D problem-solving initiatives. Some examples of KPIs are customer satisfaction scores, defect rates, cycle times, or cost savings.
- Data collection and analysis tools that can be used to gather and interpret data or information related to 8D problem-solving initiatives. Some examples of data collection and analysis tools are surveys, audits, control charts, or statistical process control (SPC).
- Periodic reviews and feedback mechanisms can be used to monitor and evaluate the progress and performance of 8D problem-solving initiatives. Some examples of periodic reviews and feedback mechanisms are reports, presentations, meetings, or feedback forms.
By measuring the effectiveness of 8D problem-solving efforts, businesses can ensure that they are continuously improving their quality, efficiency, and customer satisfaction.
You might also be interested in:
How to Use Key Risk Indicators to Manage Risks and Improve Performance
ISO 19011: A Comprehensive Guide to Quality Management Auditing
Certainty Software is a proven solution for any audit/inspection based performance improvement program in virtually all sectors of the economy from global Fortune 500 multinationals in food manufacturing to leading national companies in the hospitality sector.
Email: [email protected] Tel (Canada): + 1 888 871 0027
Quick Links
- Technical Support
- Book a Demo
- Getting Started
Download the app

Newsletter Signup

8D Methodology: the power to stop and solve problems

With the 8D Methodology, errors are no longer solved with intuition alone. Find out how this structured approach prepares you for any problem.
Even with the most rigorous planning, problems are bound to stifle production flows in any company. While some managers may try a systematic approach to address them, the length of the process and the pressure to get things back to normal as soon as possible are powerful deterrents. But although quick-fixes and patches may cut it in the short-run, they often fail to underlying causes, resulting in repeated issues and lack of stability.
This is where the 8D Methodology comes in: a comprehensive problem solving approach focusing precisely on the cause s . Among other features, it contradicts the notion that “stopping is dying”, and devotes time and attention to solving the problem once and for all. This is what the 8D methodology means and how to apply it.
What is the 8D Methodology and why is it important?
The 8D Methodology is a troubleshooting tool that follows 8 steps. The focus is on identifying the root-cause of the problem, implementing short-term fixes, and testing long-term measures to prevent it from happening again.
The consequences of consecutive errors show just how important such tools can be for a company. After all, making mistakes is human, but when they happen successively, they become a pattern and reflect on the company.
Take Boeing, for instance, one of the most prominent victims of repeated mistakes. Two accidents, both with the 737 MAX fuselage , left hundreds of casualties and the company reeling with the consequences. But Boeing could have seen it coming. In fact, Boeing had already suspended deliveries for 5 months because of the same problems involving the 737 MAX.
The healthcare sector is also plagued with ineffective problem-solving. Reports indicate that nurses spend 33 minutes of a 7.5-hour shift solving problems with artisanal solutions that are not part of their work. As a result of these unplanned tasks, productivity is bound to fall.
How to implement the 8D methodology?
As the name implies, implementing the 8D Methodology follows a set of 8 sequential steps, from planning to lessons learned.
D0: Draw up a plan
First, it is important to create a plan and assess whether the 8D Methodology applies to the problem at hand. Since this tool is laborious and involves several steps and people, it should be applied in critical situations or when the problem is recurring. At this stage, managers should define the problem, the deadline for its resolution and the human and material resources.
D1: Define a team
At this stage, managers set the problem-solving team, a task-force of sorts focusing on its long-term eradication. The selected people must have a deep knowledge of the problem to enable multiple visions and experiences. It is also vital to define functions and responsibilities of each individual.
D2: Describe the problem
It is fundamental to summarize the problem objectively, leaving personal opinions and bias aside. To do so, gather all available information, such as data, photographs, samples and documents, and interpret them in such a way as to make the nature of the problem very explicit.
D3: Develop a plan to contain the problem
In this step, the goal is to contain the problem to prevent further damage from happening while the investigation takes place. However, even if they are just provisional measures, they must be planned with time to be effective.
D4: Identify and eliminate the root cause of the problem
With the problem temporarily contained, it is time to investigate it in depth and find its cause. Some companies use cause analysis methods, such as the Ishikawa Diagram or 5W1H, to help identify the source of the problem.
D5: Verify proposed solutions
This step evaluates the effectiveness of the previous solutions. They may prove effective, insufficient, or even counterproductive. Thus, it is important to create verification criteria to make sure that actions effectively solve the long-term problem.
D6: Implement a permanent solution
When actions are proven effective, they can now be implemented to solve issues definitively. It is also important to monitor implementation to ensure compliance with the planned scope.
D7: Prevent reappearances
Besides the corrective solution, a preventive solution should also be implemented – the whole point of the 8D Methodology. Thus, it is important to evaluate other factors that may give rise to the problem again, which usually implies reviewing the management processes and operational procedures.
D8: Celebrate Success
Last, not least, celebrate the results. Recognition is key to keeping a team motivated and reinforces the collective involvement and commitment in the company, something even more important as the business grows.
Best Practices for Implementing the 8D Methodology
To implement the 8D Methodology, it is not enough to simply follow each step. It is vital that everyone shares a specific mindset of openness to error and stops if necessary for the process to take place prudently, carefully and safely.
For example, the 8D Methodology may seem, at first glance, quite intuitive, so much so that some managers may think they already use it. But this apparent simplicity is misleading – just stopping to address the root-cause rather than carry on with the work as soon as machines start up again can prove quite challenging.
For example, the simple act of setting up a team is often undervalued. When that doesn’t happen, each person ends up trying to solve the same problem in their own way: the production team can adjust their processes, the engineering team can change the design–and both think they’re making progress, but in fact they’re just generating more chaos. That’s why these first steps, usually ignored, are so powerful–they make everyone stop, prevent each member of the team from addressing problem solving with their own bias and prevent confusion.
In addition, the current paradigm in most companies is to avoid stopping production at all costs, because it affects deadlines and the bottom line. But if this does not happen in certain situations, customers will continue to be subject to problems, sometimes with dire consequences as with Boeing.
Fortunately, there are also positive examples in this field. The Peloton brand made the difficult decision to stop the Bike Plus bike production line because the pedals were not working properly in the mechanical tolerance tests. The bikes were already being mass-produced, but the brand stopped production all the same and brought the old pedal design back into production. Of course, there were implications for deadlines and margins, but if this had not happened, the consequences could have been much more damaging.
That’s why the discipline of the 8D Methodology it is important: it requires that all steps be followed, without exception, which would not happen if the problem was addressed only with intuition and the predominant “never stop” mindset. It is worth investing time to stop, slow down, and focus on effective troubleshooting.
Somengil and the commitment to Quality
Implement the 8D Methodology it is a challenging investment, which can take weeks or months, but ensures that problems within a company or project are solved definitively. When these 8 steps become part of the DNA of the business, they are more prepared for any obstacle that may arise.
Achieving this goal also implies having the right equipment, inspired by the same rigorous execution. This is the case of MultiWasher , a state-of-the-art industrial washing machine that sanitizes any type of utensils, from pots, plates, trays, supermarket carts, or hospital equipment. Schedule a webinar to see this machine running and the impact it might have on your business.

What is NFC and what is it for?

It’s in our hands: how to improve Food Safety and Hygiene
Hospital Hygiene: 5 good practices that promote patient health
Talk with us..
Zona Industrial de Vagos, Lote 41, 3840-385 Vagos Portugal
(+351) 234 797 345
- Consumptions
- Industrial Washing
- Sin categoria
- Sustainability
Login and registration
- Forgot Username?
- Forgot Password?
8D method (8 disciplines)
Origins of the 8d method, steps of the 8d method.
D1: Form a team
- Objective : Assemble a cross-functional team with the necessary skills to solve the problem.
- Select members based on their technical expertise, process knowledge, and problem-solving ability.
- Appoint a team leader responsible for oversight and coordination.
D2: Describe the problem
- Objective : Clearly understand the problem using factual data.
- Gather and document data and facts.
- Conduct a preliminary analysis to identify some probable major causes and detail the problem. Tools like "5W2H" (what, who, where, when, how, and why) can be used for this purpose.
- Ensure the problem is well-defined so everyone understands the same thing.
D3: Implement urgent actions (if necessary)
- Objective : Provide an urgent, likely temporary, solution to prevent the problem from spreading.
- Identify and implement temporary measures to contain the problem based on the preliminary analysis conducted in the previous step.
- Inform relevant parties about these actions.
D4: Identify and verify root causes
- Objective : Discover the true cause of the problem to avoid only treating the symptoms.
- Use analysis tools such as the 5 Whys, Ishikawa diagram (fishbone diagram), or Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA).
- Validate the root cause by ensuring that eliminating it makes the problem disappear.
D5: Developp permanent actions
- Objective : Develop solutions to eliminate the root cause.
- Brainstorm to identify potential solutions.
- Select the best solution based on costs, available resources, and potential impacts.
- Test the chosen solution to ensure its effectiveness.
D6: Implement permanent actions
- Objective : Implement the long-term solution to permanently eliminate the problem.
- Deploy the solution on a large scale.
- Train relevant parties and update the necessary documentation.
D7: Prevent recurrence
- Objective : Ensure the problem will not reoccur in the future.
- Review and modify processes, standards, or systems to prevent a recurrence of the problem.
- Regularly monitor to verify that the corrective actions remain effective.
- Update any relevant documentation, be it manuals, standards, or specifications to reflect the changes made.
D8: Congratulate the team
- Objective : Recognize the team's efforts and reinforce a problem-solving culture.
- Celebrate successes.
- Share lessons learned with the entire organization.
- Encourage a culture of continuous improvement.
Pros and cons of the 8D method
The 8D method is widely used for problem-solving, especially in the automotive industry. However, like any approach, it has its advantages and disadvantages compared to other popular methods like DMAIC, A3, or PDCA. Here's an overview of the pros and cons of the 8D method compared to these methods.
Advantages of the 8D method :
Explicit emergency action : The 8D method includes a dedicated step (D3) for implementing emergency actions to immediately contain the issue. This allows for a quick response to at least partially address the problem, which none of the other three methods specify as explicitly.
Emphasis on team recognition : Step D8, focused on team recognition, emphasizes the importance of team dynamics and motivation, which can boost morale and encourage active participation in the future. Although recognizing individuals is also often part of other methods, it's not as explicitly defined in them.
Disadvantages of the 8D method :
Less emphasis on data analysis : Unlike DMAIC, which heavily emphasizes data analysis, the 8D method might sometimes not delve as deeply into quantitative analysis, possibly leading to less optimal solutions in some situations.
Structural rigidity : The linear structure of 8D, though providing clarity, can sometimes feel rigid. But this is also the case with the DMAIC and A3 methods (though the former has only 5 steps instead of 8, and the latter is less specified). The PDCA, with its cyclical nature, is noticeably more flexible allowing for a smoother iteration.
Possibly perceived as too action-oriented : The emphasis on emergency and corrective actions can sometimes overshadow the need for deep thinking and thorough analysis, especially if teams feel pressured to quickly solve issues.
Less suited for broader or systemic problems : While 8D is excellent for specific issues, methods like DMAIC or A3 might be better suited to tackle more complex or systemic problems that require deeper analysis.
8D: a method for addressing urgent, low-complexity problems?
- As time and resources are limited, that's always less to dedicate to researching the root causes of problems. Thus, if the problem is complex, we're less likely to implement the right methods to durably solve the problem.
- Since actions are taken in step D3, there's a risk that one might settle for them, at least initially... before realizing the problem isn't solved.
- Moreover, as actions are put into place in step D3, there's a risk that it might be more challenging to successfully implement other actions with the individuals who have to carry them out (classic phenomenon of staff mobilization, resistance to change, credibility of management in implementing successive actions...).
When you subscribe to the blog, we will send you an e-mail when there are new updates on the site so you wouldn't miss them.
Related Posts
A3 is a principle, not a problem-solving method !!
The pdca cycle or deming wheel: how and why to use it, the 5 whys method: how and when to use it, 5w2h or 5w1h methods: how and when to use them, ishikawa diagram and root cause analysis, comparison of problem-solving methods and techniques, continuous improvement process : a challenge for significant benefits, dmaic process: a methodology to implement six sigma, what is an operational audit of the organisation, improvement and innovation excellence.
8D Problem Solving Process

Problem solving processes for product and manufacturing companies have many names 8D, 5C, Issue Management, Corrective Action, etc., however, they all address the key goal of identifying, managing, correcting, and preventing issues affecting internal and external stakeholders. A favorite in the industry is the 8D Problem Solving Process (8D), because it is a team-oriented and structured problem-solving methodology that emphasizes the idea that problems should not be repeated but fixed permanently. This process focuses on the origin of the problem by determining root causes and establishing permanent corrective and preventive actions.
Additionally, what makes the 8D process widely used is the fact that other problem solving processes such as the 5 Whys, 5C, Process Flow Charting, Is/Is Not Analysis, Fishbone Diagram, Process Variables Mapping, Comparative Analysis, Root Cause Verification, and Process Control Plans are an integral part of the overall 8D process. This allows the process to be easily adapted and updated to specific needs.
The U.S. government first standardized the 8D Problem Solving Process during the Second World War. It was later improved and popularized by the Ford Motor Company in the early ‘90s and has become an integral process within the largest and most successful companies to date.
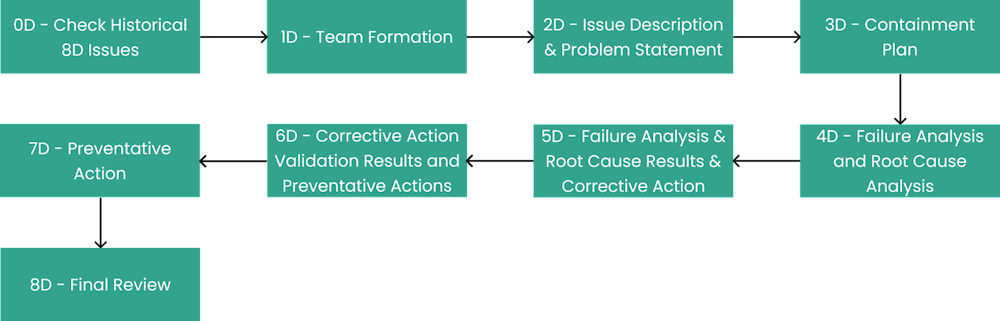
0D - Check Historical 8D Issues
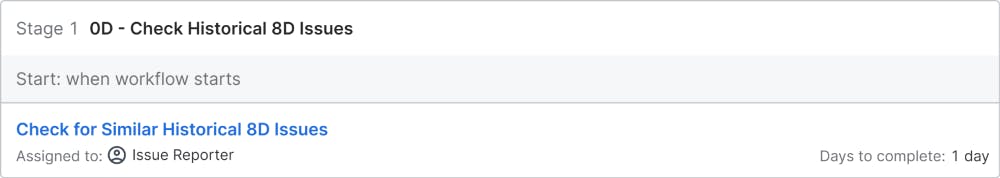
The goal of this stage is to look through your historical problem solving archive for similar issues to be used as a basis and framework to help accelerate a path to issue resolution. If Regrello is used for this process, the data will automatically be archived and searchable.
1D - Team Formation
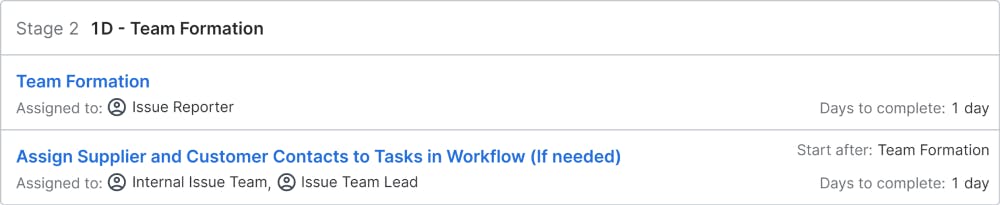
Assign an Issue Team Lead and an Internal Issue Team, responsible for driving the issue to resolution. The Issue Team Lead should be an internal user that can drive cross functional action to address the issue. The Internal Issue Team should be a small internal and/or external group with the process and/or product knowledge, allocated time, authority, and skills in the required technical disciplines to solve the issue and implement corrective / preventative actions.
2D - Issue Description & Problem Statement
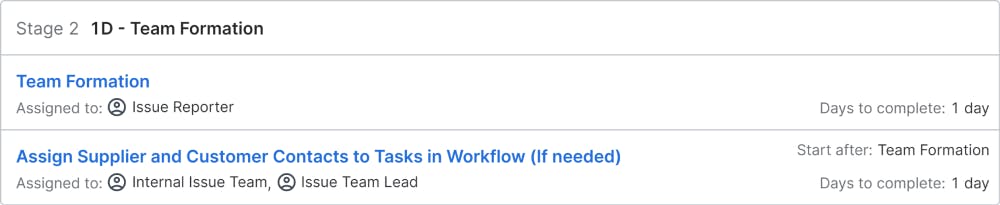
The team should collect details about the problem, typically a preliminary Failure Analysis (FA) and/or Root Cause Analysis to help get a complete understanding of the problem. The team then develops a clear problem statement and problem description by identifying “what is wrong with what” and detailing the problem in quantifiable terms.
3D - Containment Plan
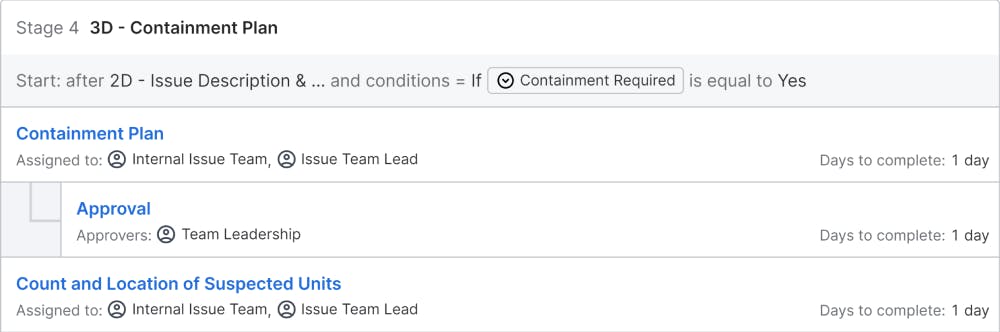
This is an optional stage depending on the issue that is getting resolved. This stage defines, verifies and implements containment action to isolate the effects of the issue from any internal and/or external customer until permanent corrective (preventive) actions are implemented. Key steps in this stage might involve actions like isolating the items affected, stopping production, and replacing defective parts. This stage’s goal is to prevent the issue from getting worse and reaching the market and customers.
4D - Failure Analysis and Root Cause Analysis
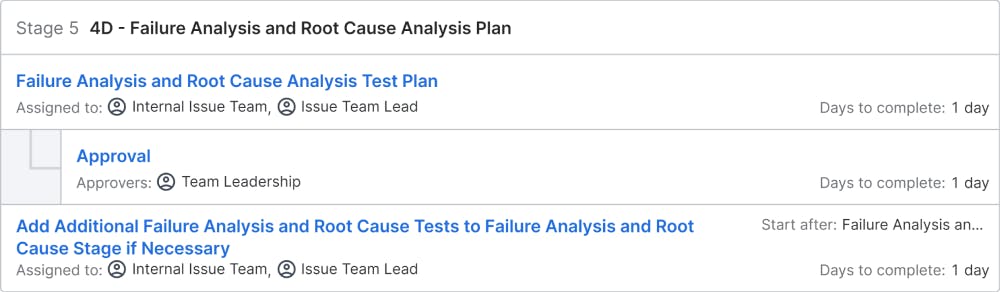
This stage utilizes Failure Analysis and Root Cause Analysis to identify, isolate, and verify the failure and root cause of the issue that could have been detected and contained but was not. Teams should ensure they have enough or gather more data to learn more about the issue and its possible causes.
The goal of the Failure Analysis is to determine the mechanism and the cause of the failure, essentially how and why the product failed. This will lead to a Root Cause Analysis that will be used in conjunction with the Failure Analysis to identify the key equipment failures, process failures, environmental factors, or human errors that will help identify the Corrective Actions that need to be taken to fix the issue. The outcome of this stage should have a defined test plan with test owners who execute and verify the test.
5D - Corrective Actions
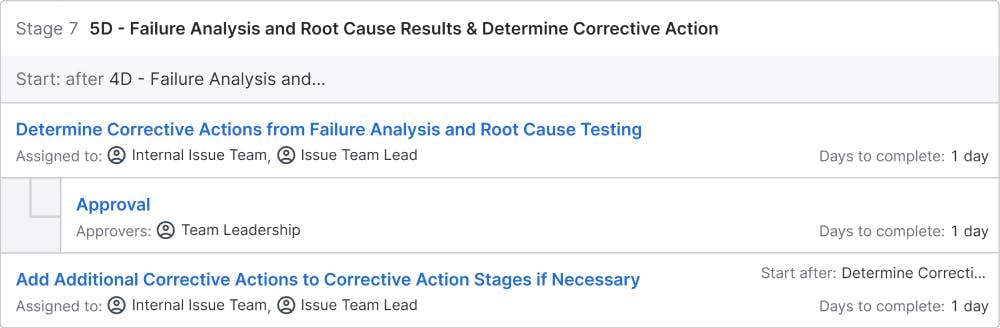
This stage looks at the Failure Analysis and Root Cause results to determine the key Root Causes and the potential Corrective Actions that will fix the issue. These Corrective Actions need to address the root cause and failure points in the process. Additionally, Corrective Actions need to be tracked and verified to ensure that the solution is successful and does not cause any other issues. Corrective Actions can be short-term fixes until longer-term Preventative Actions can be implemented. The outcome of this stage should have a defined Corrective Action Test Plan with test owners who execute and verify the test.
6D - Corrective Action Validation
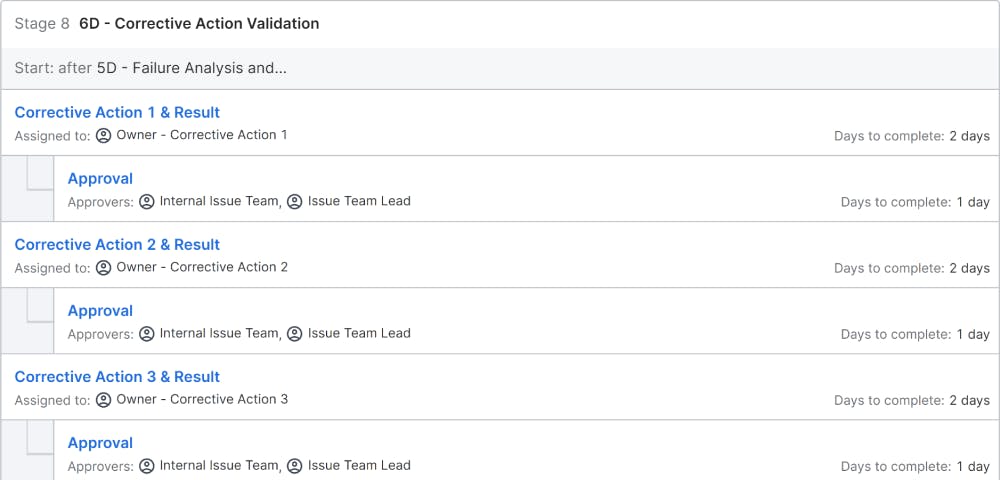
This stage is where the team executes the Corrective Action Test Plan and validates if the Corrective Actions are effective in addressing the root cause and failure points in the process as well as ensuring the fix is not causing other issues. The team will then deliver and review the results of the Corrective Actions to determine if the issue is addressed. If the issue is not completely addressed, the team can repeat stages “4D - Failure Analysis and Root Cause Analysis” and “5D - Corrective Actions” until a solution is found.
7D - Preventative Actions
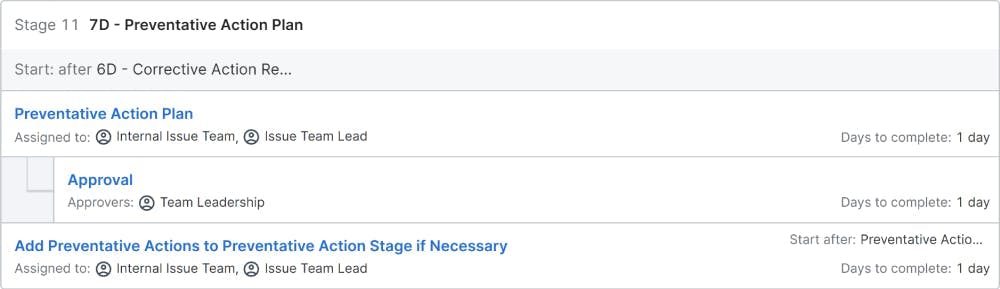
This stage looks at the Corrective Action results to determine Preventative Actions to identify a potential long term solution that will not allow the issue or similar issues from occurring. These Preventative Actions may make changes in the system, software, people, products, and or upstream or downstream processes etc.
The outcome of this stage should have a defined Preventative Action Plan with owners who implement and verify the Preventative Actions. The team needs to monitor the long-term results of these Preventative Actions to ensure its effectiveness.
8D - Final Review & Lessons Learned
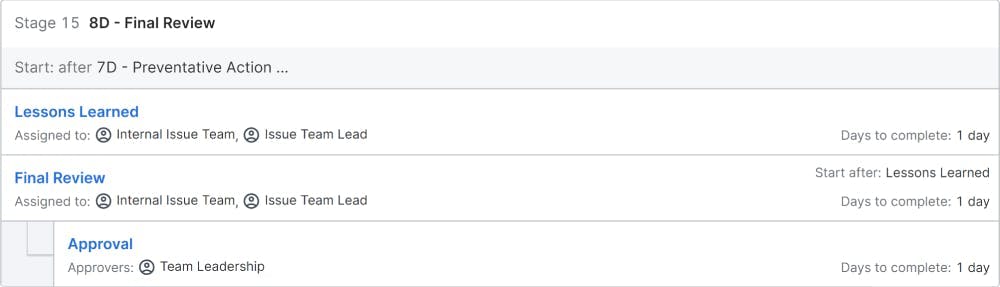
This stage is where the team delivers their Lessons Learned from the 8D issue process, conducts a Final Review, and has a future check in on the effectiveness of the implemented Corrective and Preventative Actions.
Lessons Learned are the documented positive and negative experiences or lessons learned while working through an issue. These Lessons Learned are important to the overall 8D process as they become a database to capture learnings from one issue and preserve them for future issues. They allow the team to understand efficiencies from previous 8D solutions and to avoid repeating mistakes or problems.
The Final Review should include all relevant stakeholders and their leaders if necessary. In this Final Review, teams should discuss if they should integrate the findings and lessons learned into the 8D Problem Solving Process.
The Corrective & Preventative Action Check In confirms that the Corrective and/or Preventative Actions implemented are continuing to fix the issues as expected and identify opportunities to improve them.
WHO SHOULD USE THIS PROCESS
Like many of Regrello’s Compendiums, the 8D Problem Solving Process is most applicable for mid to large size companies that develop or manufacture products, as the structure, vocabulary, and author’s experience lie in that field. It can be, with modification, applied to other areas. Smaller entities can definitely use what’s presented, and it should help avoid common pitfalls, however the documentation expected and roles outlined may be beyond Kickstarter startups or first-product operations. Similarly, global entities with established processes may already have much of what’s outlined incorporated within their existing structure. While they too can usually benefit from thinking holistically about the process, their main benefit from Regrellos’ compendiums will come from the high-level visibility provided by moving communication out of email and into a specific project-focused workflow, enabling reporting and cross-product learning.
Otherwise, this guide should be of benefit to everyone who develops or manufactures products, be it in-house or in collaboration with a supplier, a more rigid Contract Manufacturer (CM), Electronic Manufacturing Services Provider (EMS), or Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) structure, or a more-closely constructed partnership.
WHY USE THIS PROCESS
The main benefits of this 8D Compendium lie in the standardized and automated structure of the blueprint. Breaking down the process into clearly defined stages that allow flexibility to solve any problem as well as give a historical library of the challenges, issues, and risks within production while also enabling personnel to get up to speed on projects more quickly. In addition, by documenting the issues, root cause, and solutions, past projects become learning material for new employees, allowing lessons learned to be easily accessible and help guide future decisions.
Implementing a standard, methodical, and referenceable Problem Solving Process drastically reduces risk, provides visibility, and accelerates the issue resolution by providing a clear method and guide to solve inherently variable problems. Delays in addressing and fixing issues result in delivery delays, wasted components and labor dollars, and negative relationships with your partners. Improving the control, visibility and reliability of this process is of primary importance to leadership in any product or manufacturing company.
- Choosing the Right Corrective Action Form
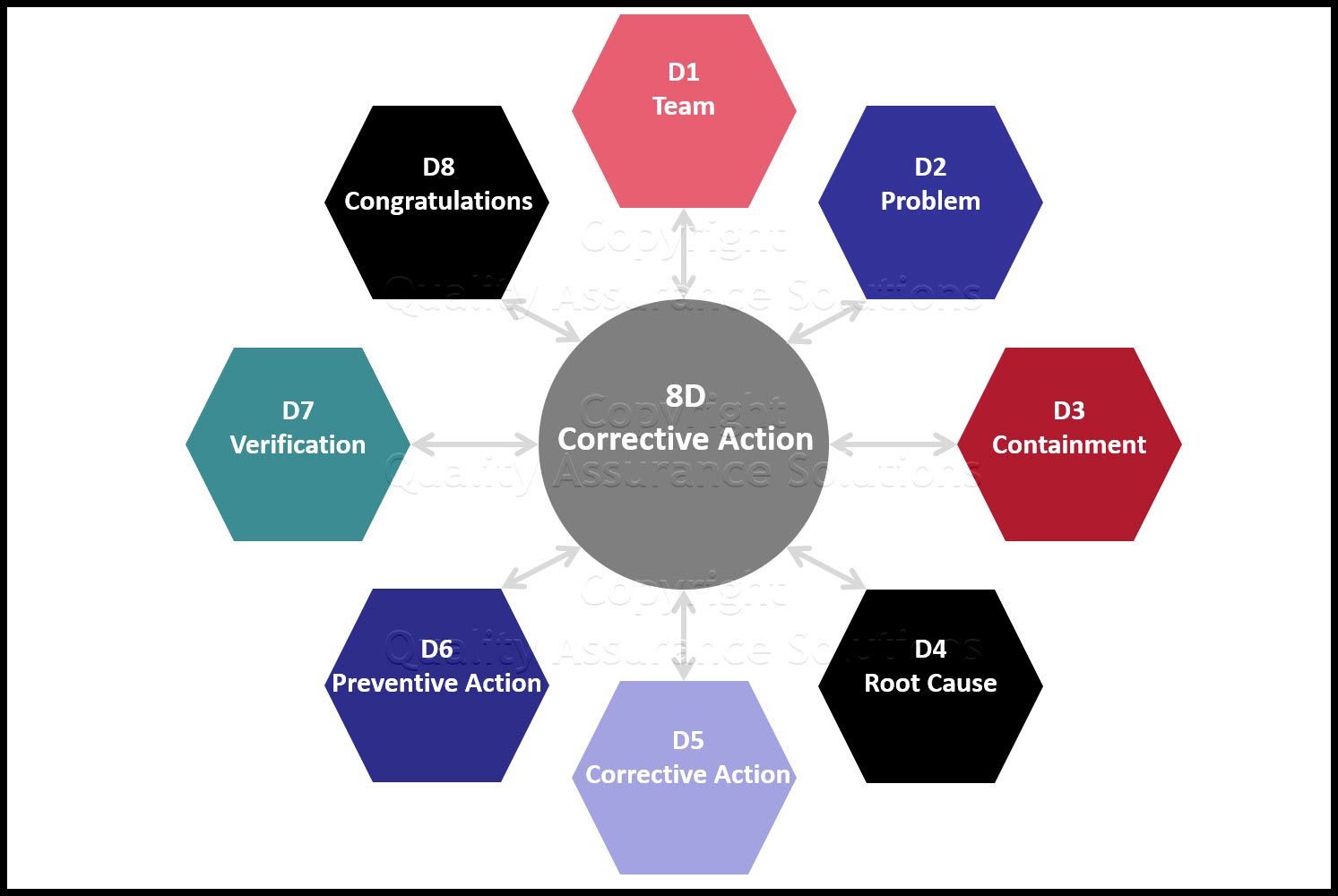
To choose the right corrective action form you need to understand the D(s) involved with corrective action. The D stands for Discipline. There are 3 main corrective action types and these are 5D, 8D, and 9D. There are 9 different Ds that support each type. These are D1, D2, D3, D4, D5, D6, D7, D8 and D9.
This article explains the differences between the Dx steps and how to select a corrective action method that fits a given situation.
D1, D2, D3, D4, D5, D6, D7, D8 and D9 are the individual steps within a corrective action process.
5D, 8D, and 9D are the full corrective action methods. They consist of the Dx (where x is 5, 8 and 9) corrective action steps and include the previous steps. 8D consist of D1, D2, D3, D4, D5, D6, D7 and D8 steps. 5D consist of the D1, D2, D3, D4 and D5 steps. 9D consist of the D1, D2, D3, D4, D5, D6, D7, D8 and D9 steps.
If you create a 5D corrective action form, you need to make sure you include the D1, D2, D3, D4 and D5 steps. The same is true for a 8D and 9D corrective action form.

8D Manager Software with 5D, 8D, 9D, and RMA report generator. Corrective action software for every company needs.
The Dx Steps of the Corrective Action Form
D1 stands for forming a team.
D2 stands for identifying a problem.
D3 describes the containment actions you take to prevent the problem from getting to a customer. Or if it is at the customer, how you get it away from the customer.
D4 stands for identifying the root cause of the problem.
D5 describes the corrective actions you take to permanently fix or remove the problem.
D6 describes the preventive actions you take to further prevent the problem from occurring again.
D7 identifies the verification steps you take to make sure D3 through D7 (and D9) are complete.
D8 stands for congratulating the team.
D9 stands for risk and / or safety actions taken as the result of the corrective action.
For more details on the Dx steps, see this article .
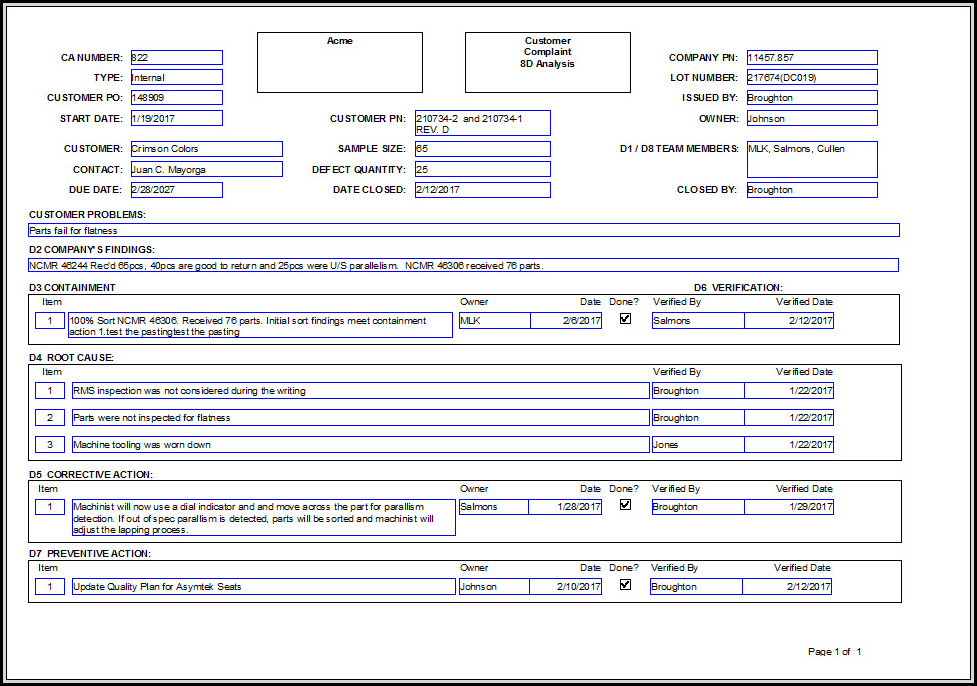
Differences between Corrective Actions
Short corrective action form usually require a 5D investigation. Which means you form a team, you identify a problem, you take containment actions, you identify the root cause and you issue corrective action.
More important corrective actions require an 8D investigation. This includes the 5D investigation plus you conduct preventive actions, you verify all the previous actions and you congratulate the team.
Some companies require an 9D investigation which includes the 8D and add Risk / Safety Actions.
Selecting a Corrective Action Form Method.
Many companies struggle with determining the corrective action method that best suits them. In fact, for many small companies, or companies new to corrective action, they may have not documented their method or given it much thought. Because of this, they may use different approaches depending on the individual handling the complaint. This causes an unwanted amount of variation when it comes to conducting corrective actions. Further, this causes confusion at the customer location, confusion with auditors and confusion with management.
I recommend a multi method approach based on the situation. Below is a flowchart that you can use for selecting a corrective action form depending on the situation. Please download and edit to your needs.
You can use this flowchart whether the problem / complaint / defect / issue started internally or externally.
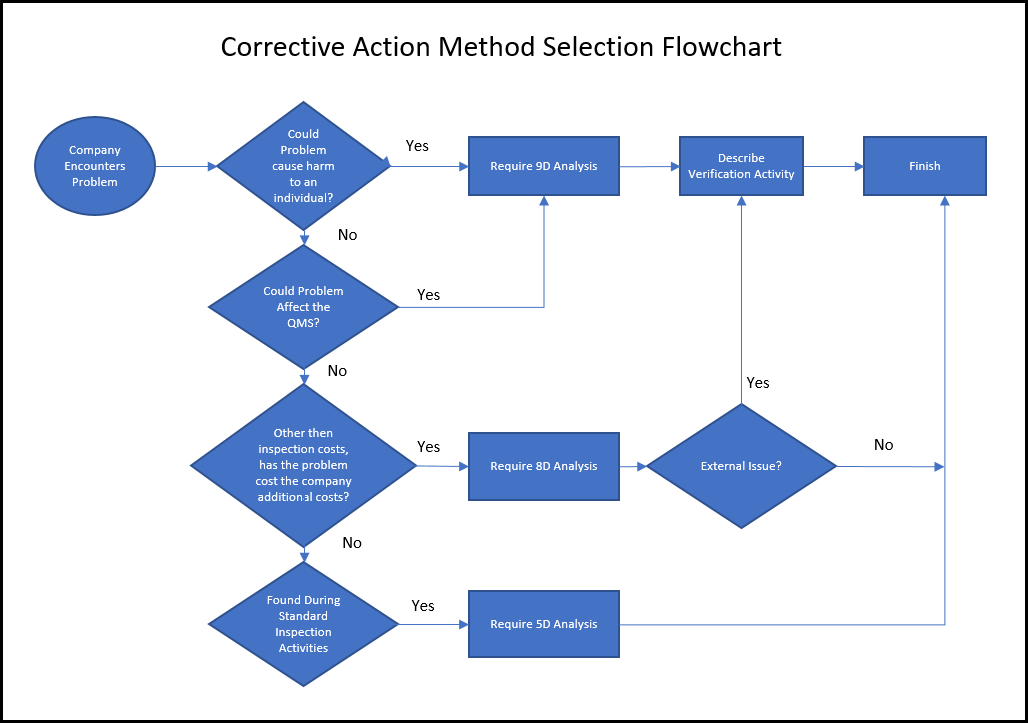
| Download the Corrective Action Method Selection Flowchart |
Harmful to the Individual
The first question, you should answer... could this problem cause harm to an individual? If this defect can hurt someone then conduct a full 9D investigation. You need to make sure these defects don’t escape your company. Your corrective action must assure you permanently fix the problem. In addition you need to make sure the root cause of the defect doesn’t spread to other parts. If people were harmed or could be harmed, you need to address this too. The 9D investigation assures these actions occur.
Does the Problem Affect the QMS?
The new requirements of ISO 9001:2015 requires Risk Analysis. Plus, ISO based most of the other QMS standards on the ISO 9001:2015 standard. Auditors now audit for Risk Management and how it affects your QMS. If the problem or defect affects the QMS, you need to conduct Risk Analysis on that issue. This means you should conduct a 9D corrective action form investigation and make sure the identified risks feed into your corrective action software ( 8D Manager! ) and your QMS Management review.
Normal vs Non Normal Issue
Company’s usually set up inspection stages to catch possible normal issues. Inspections include process, final, receiving, SPC, shipping and many others. If the issue got past the inspection and caused any unsuspected costs to the company, then issue an 8D Analysis.
What kind of unsuspected costs?
- Machine Damage
- Production Delay
- Management Meetings
If the issue was found at your customer receiving inspection, how do you classify this? It is up to your company and your customer. They may require an 8D Analysis. Or they may require a simpler 5D Analysis. For example if the customer finds a label issue, then 5D may be sufficient. If they find defects and the customer cannot use the parts then 8D may be needed.
If your customer found the issue during their processing with your parts, then classify that as unsuspected costs and you should issue an 8D Analysis.
Normal Inspection Problem
If the defect was found during normal internal inspection then this would only require a 5D analysis. The inspection is there to catch that issue. The 5D will find the root cause and implement the actions to further prevent it. If you find the issue to be constantly reoccurring then you may want to upgrade the corrective action to an 8D analysis
Document Verification Actions
For 8D corrective action process you need to verify the actions were completed. You usually prove this with just a name and date of the verification. You want to make sure the verification takes place by someone different than the person conducting the action.
However, when addressing external (found by a customer) issues with the 8D process and with any 9D corrective action, you should describe how you conducted the verification. Describe exactly what the person did to make sure the action was executed.
8D Manager Software
This article discussed the differences between D8 steps and the 8D steps. It also provided a flowchart for selecting an appropriate corrective action method.
Companies face the difficulties of issuing the exact corrective action approach and keeping everything for corrective action together. 8D Manager lets you simplify all of this. You can quickly issue 5D, 8D, 9D corrective actions and create professional reports. 8D Manager assures you don’t skip a step. 8D Manager lets the corrective action be as simple or as complex as you need. 8D Manager stores them all in one location and you can review and edit any of them quickly and easily.
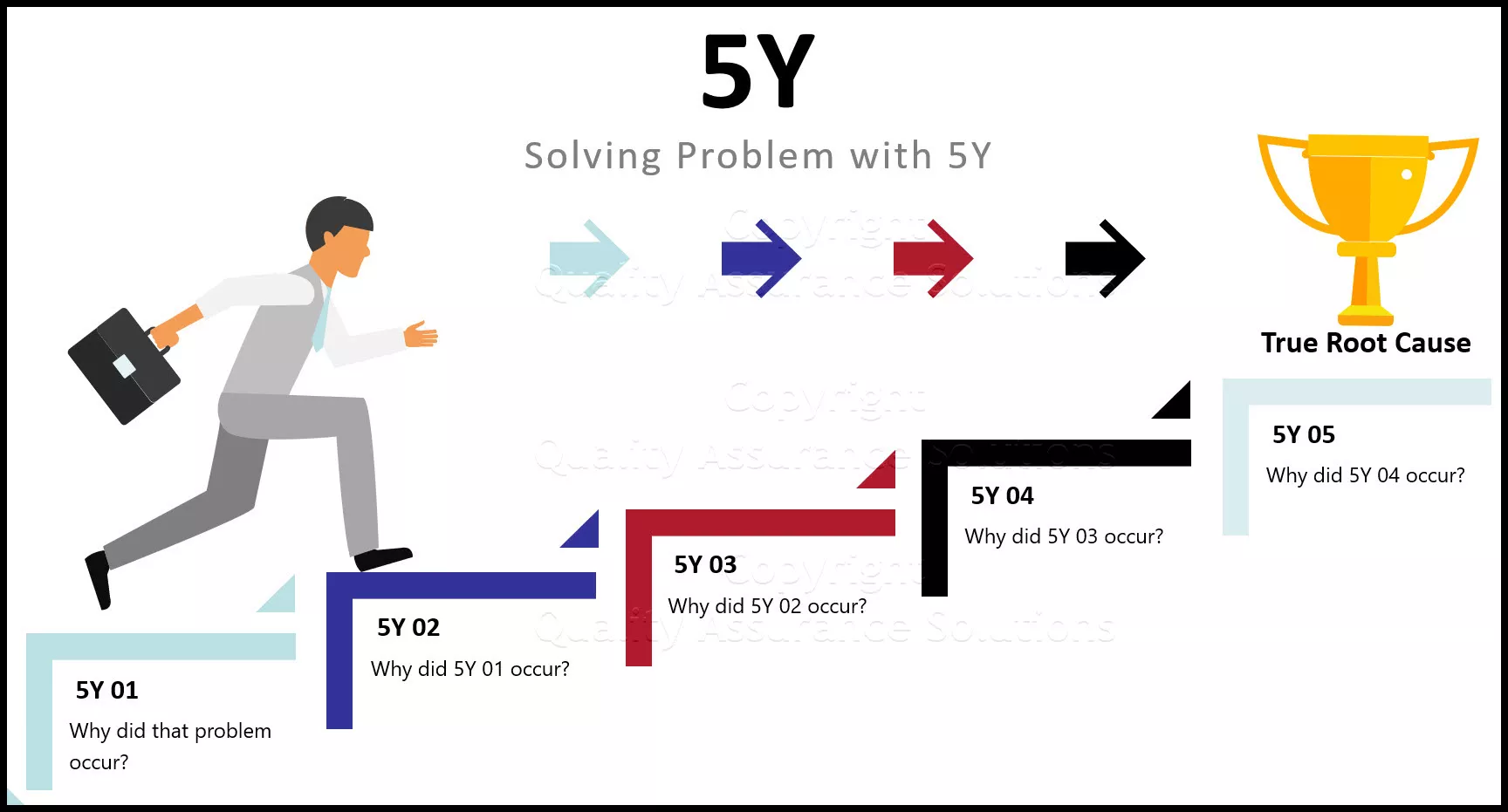
5 Why Problem Solving
Learn 5 why problem solving and how this connects to 8D problem solving. See how to use 5Y analysis for customer corrective actions.

Dealing with Customer Complaints
Best methods when dealing with customer complaints. We recommend reaction to business complaints, consumers complaints, and product complaints.
Corrective and Preventive Action Management Systems for ISO 9001.
We break down the differences between corrective and preventive action management systems and preventive maintenance for ISO 9001
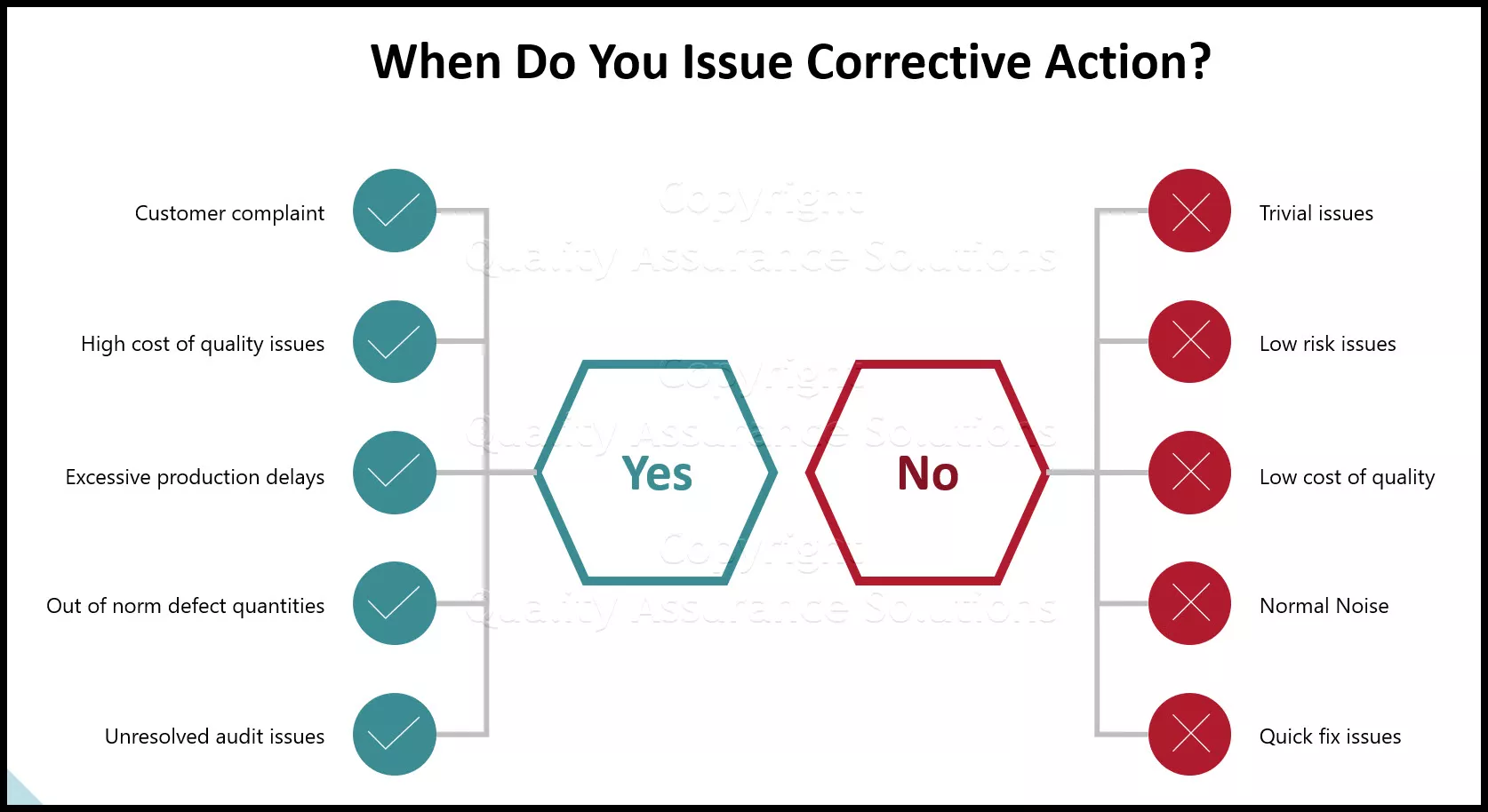
Corrective Action Forms Implementation and Measurement Tips
Tips on issuing corrective action forms, measuring corrective actions preventive action and creating an effective corrective action system.
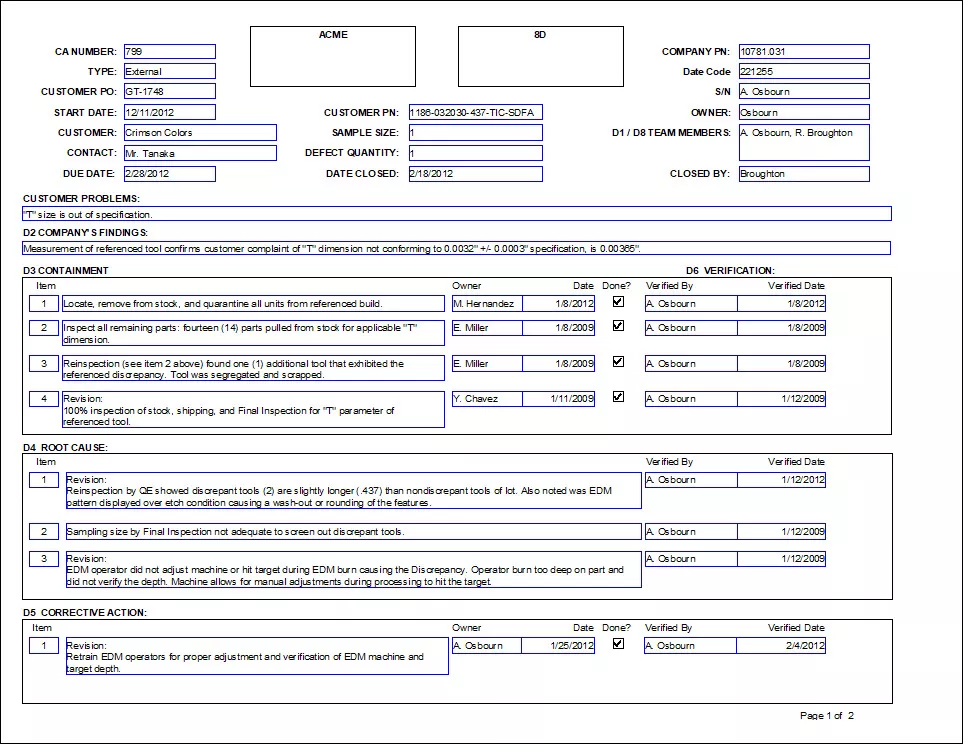
Root Cause Corrective Action System documentation
Describes the important items to include in your Root Cause Corrective Action System. Corrective Action is critical to your ISO 9001 certification.
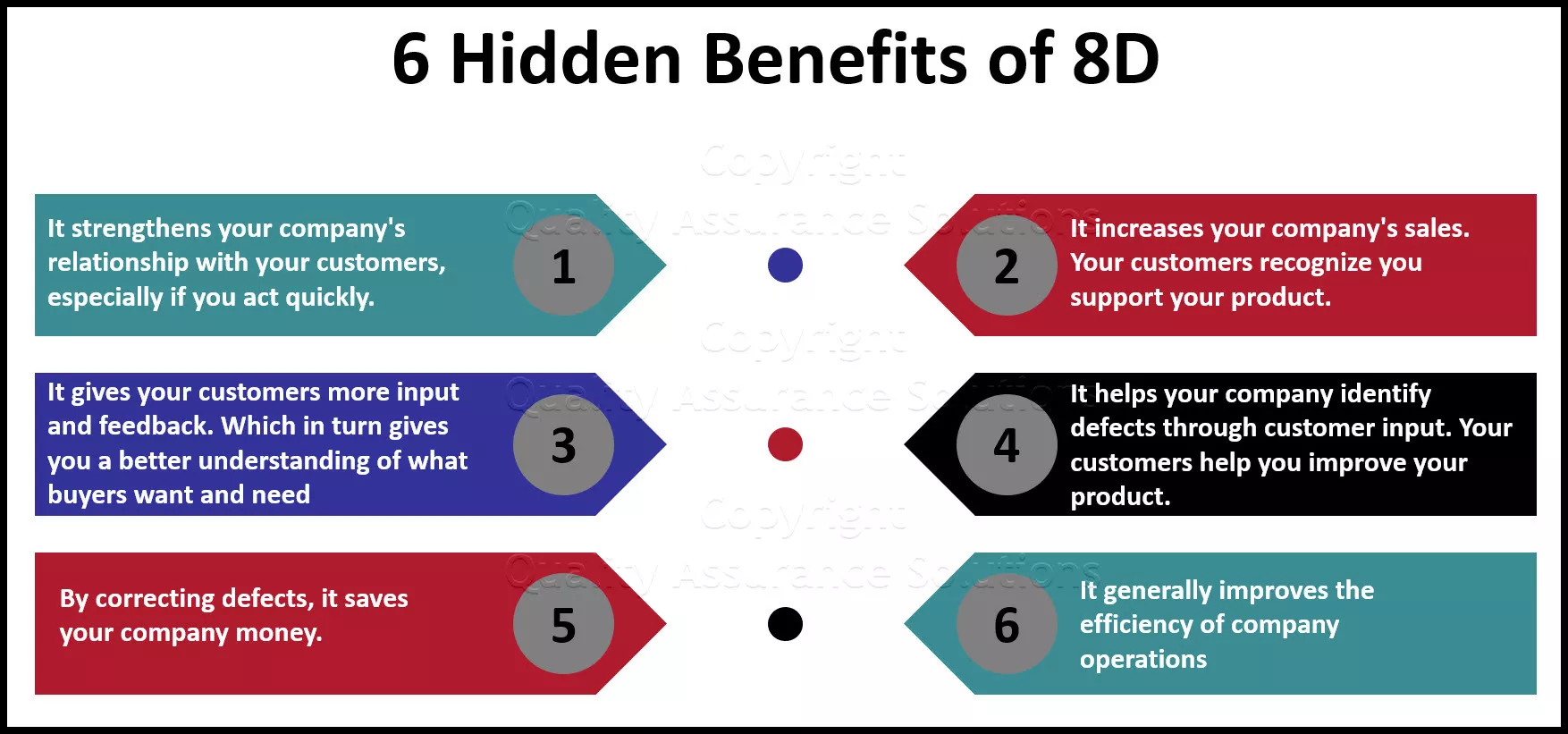
Learn 8D Eight Disciplines!
Learn the 8D Eight Disciplines, see it in action, and apply global 8D software to your business.
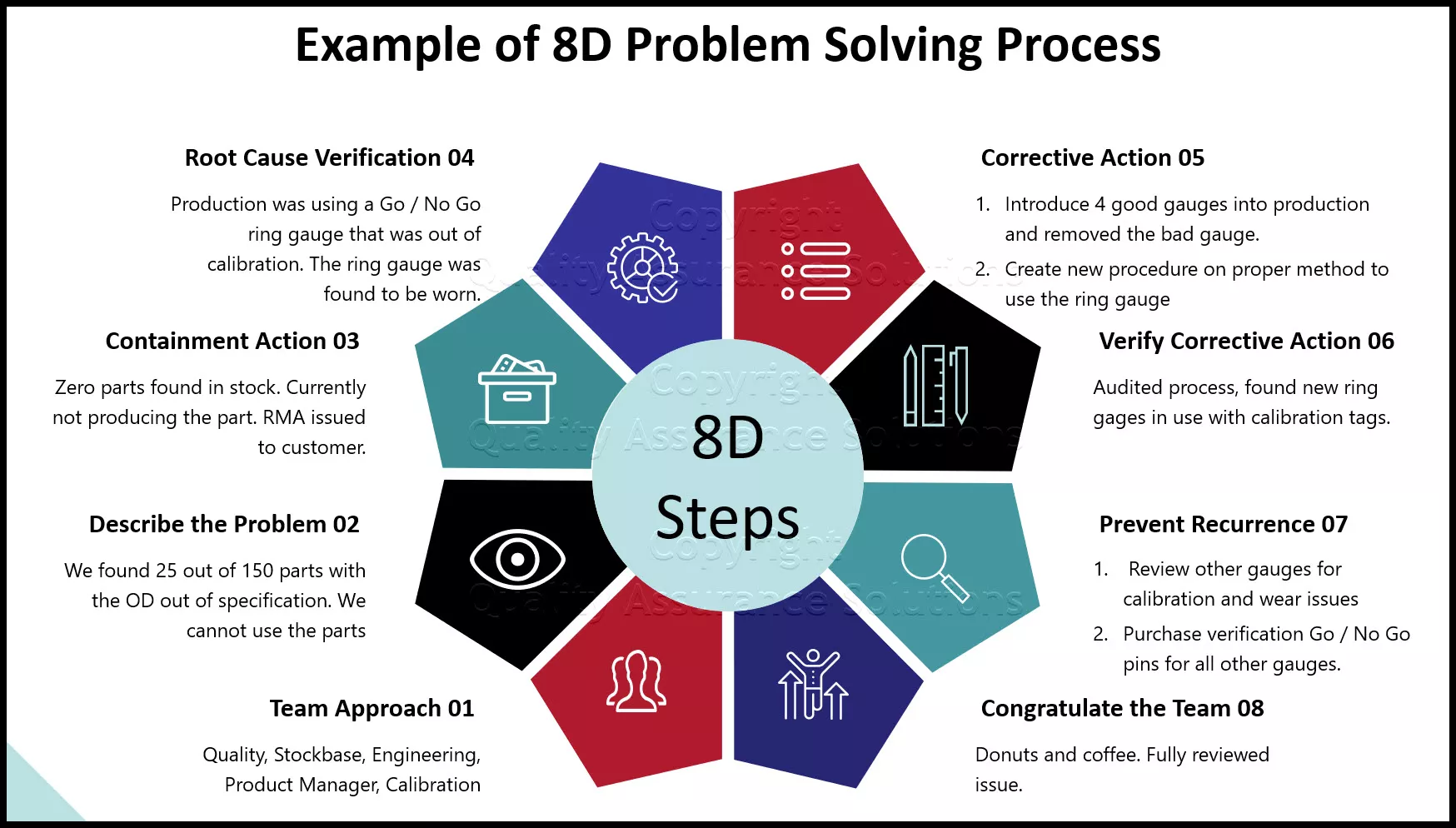
Corrective Action Software in Action
See how to use corrective action software to solve customer complaints. Here is a detailed example of 8D Manager in Action.
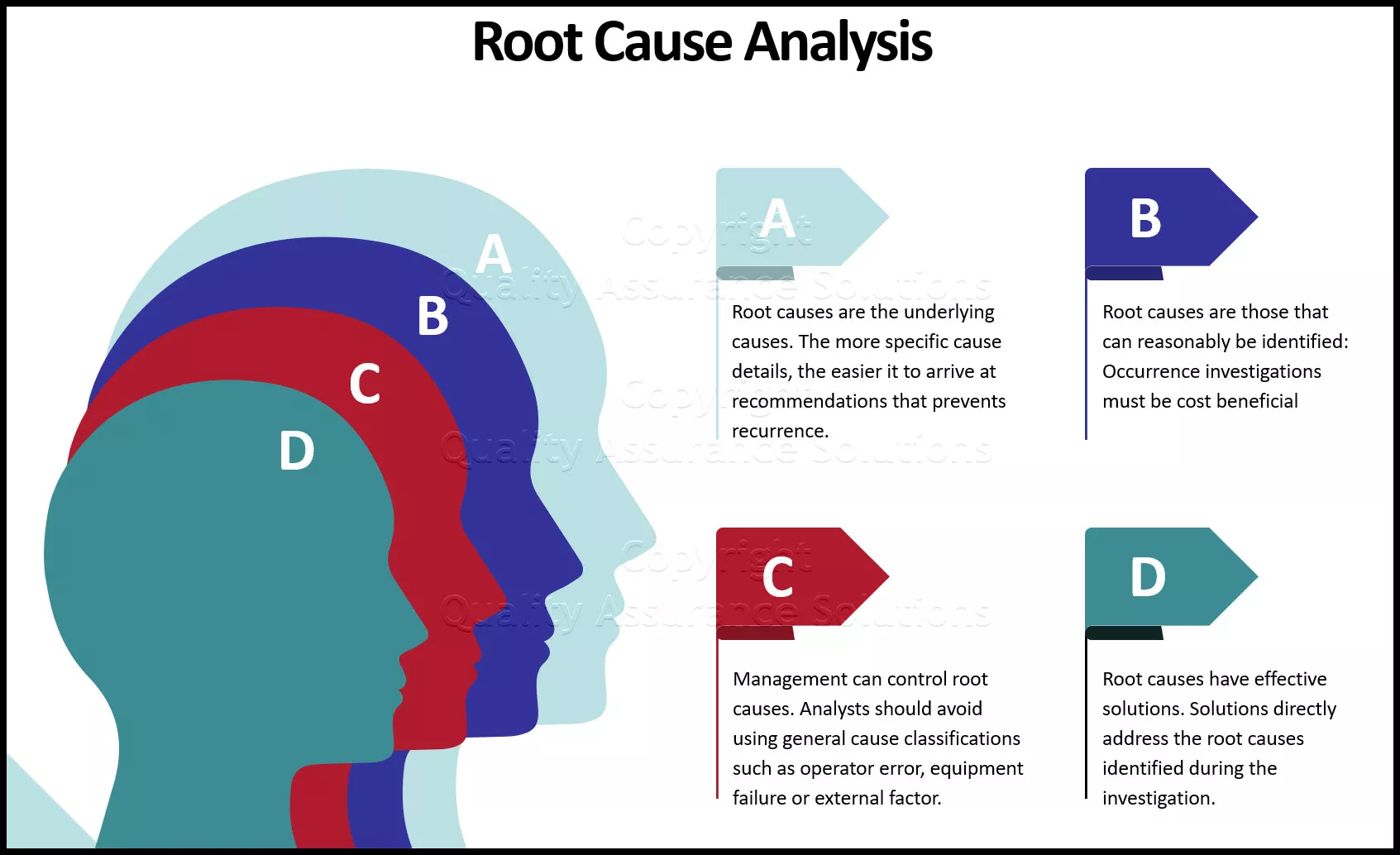
Root cause analysis
Root cause analysis (RCA) is a process designed for use in investigating and categorizing the root ...
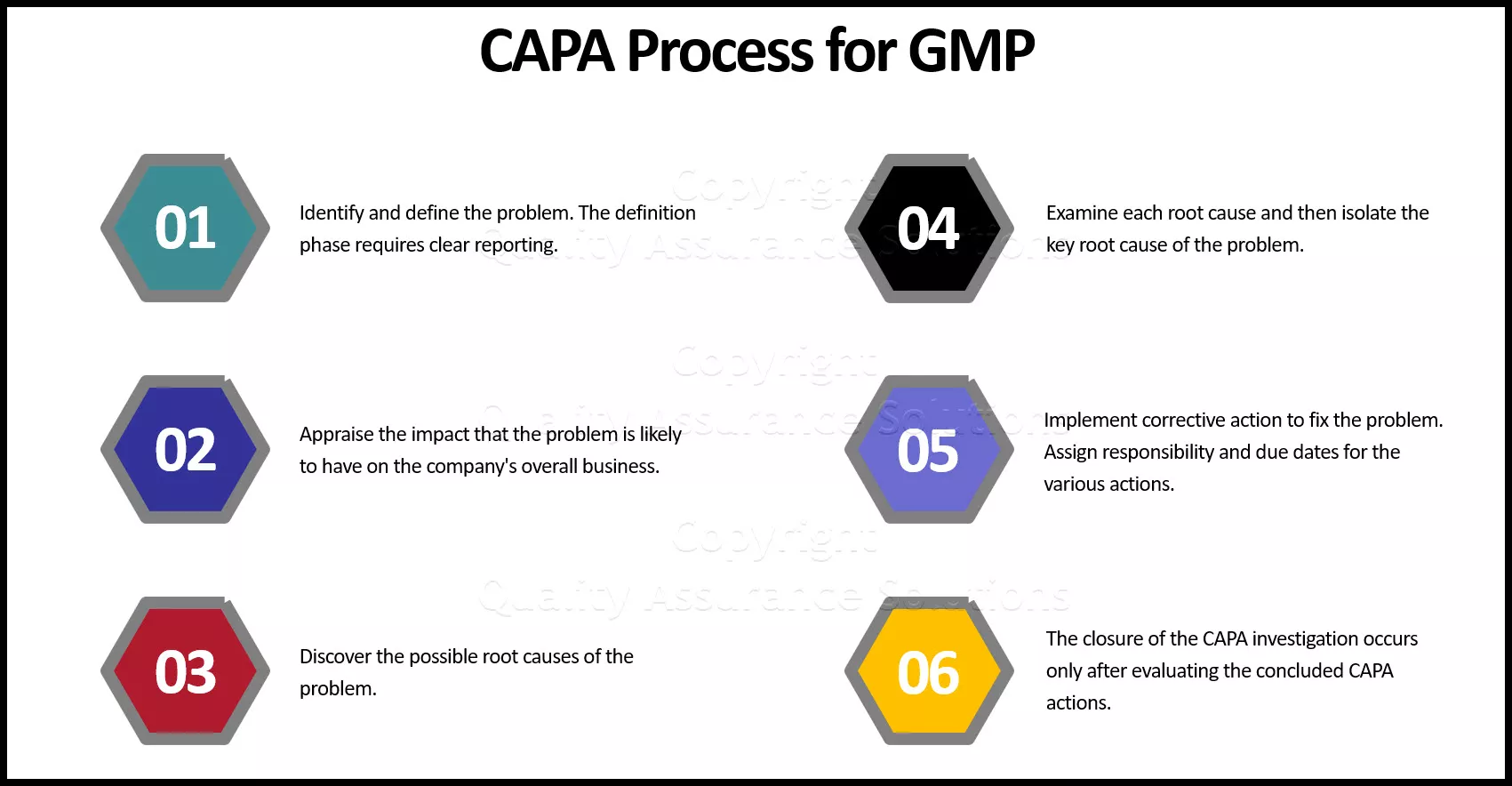
Preventive Corrective Action With 6 Steps
An effective Preventive Corrective Action may require many integral processes that function together for best results. These processes may include
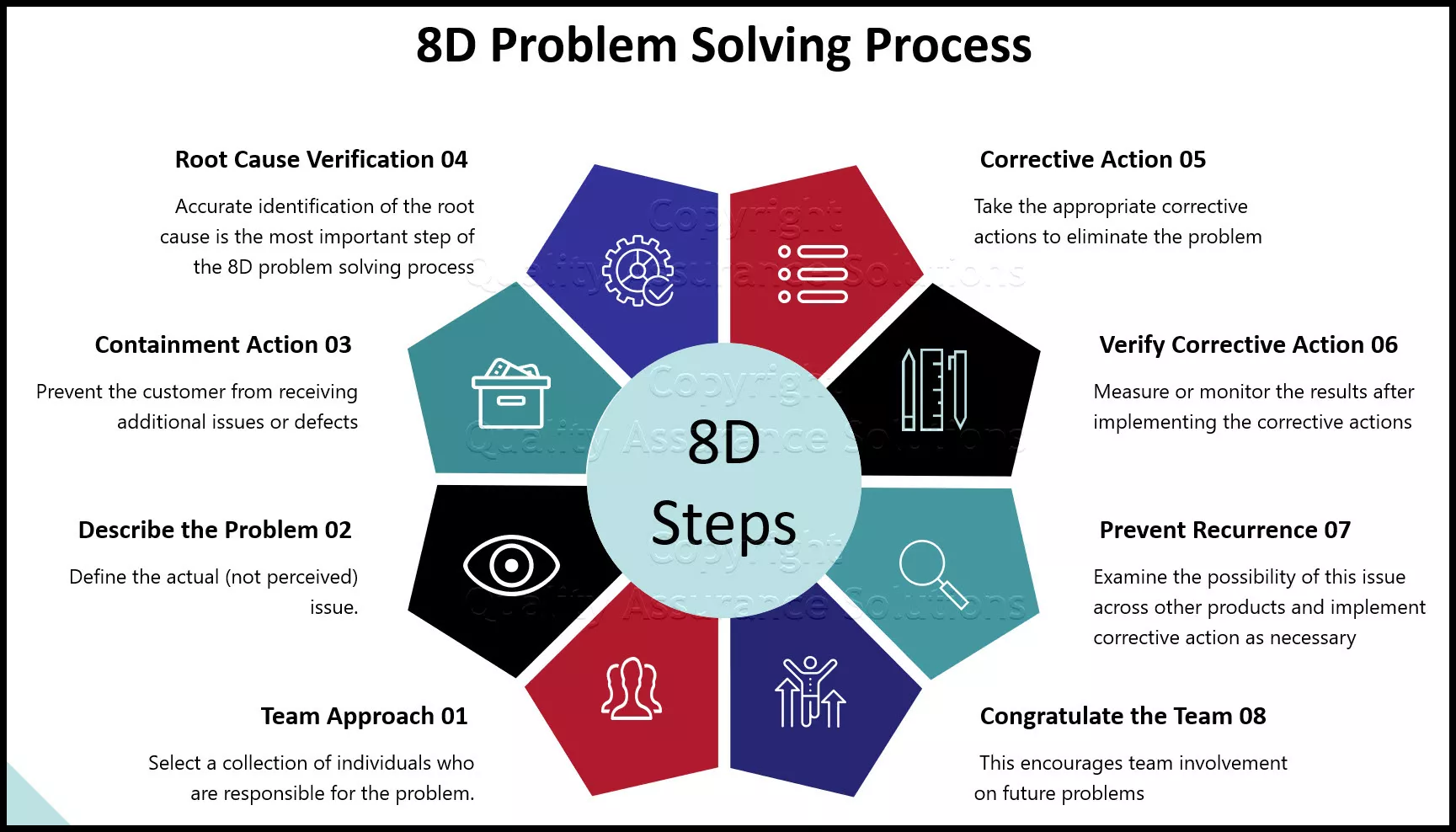
Discusses 8D Problem Solving Details and 8D Reports.
Review this for detail information on 8D problem solving. This article discusses your customer requirements for 8D reports.

How to Handle Customer Complaints
Learn to how to handle customer complaints. Your intitial response sets the tone and builds a relationship with your customer.

Sound Containment Theory is Important to Keeping Customers.
Execution of containment theory prevents escaping defects and improves customer satisfaction. We describe the best approaches to containing defects.

8D Manager, Corrective Action Software for Instant Download.
Download 8D Manager Today. Only $89. Prevent corrective action mistakes that may harm your relationship with your customer. Use 8D Manager for your corrective action software. Satisfaction guaranteed.
8D Manager FAQ
Concerns for Business Owners
Dealing with concerns for business owners and a golden book that helps address them.

Block Out Negative Comments
Tips to block out negative comments. What to do for your business, before, during and after you receive a negative review.
| Quality Assurance Solutions Robert Broughton (805) 419-3344 USA |
| Facebook Twitter Pinterest |
Would you prefer to share this page with others by linking to it?
- Click on the HTML link code below.
- Copy and paste it, adding a note of your own, into your blog, a Web page, forums, a blog comment, your Facebook account, or anywhere that someone would find this page valuable.
Stay in Touch
- Contact & Follow
- The QA Blog
- StreamLining
- Data Analysis
- Brainstorming
- Benchmarking
- Control Plan
- Cost of Quality
- On Time Delivery
- Corrective Action
- Calibration
- Document Control
- Traceability
- Material Control
- Preventive Action
- Risk Management
- Knowledge Mgmt
- Staff Suggestions
- Training Software
- Team Building
- Employee Evaluation
- Communication
- Characteristics
- Setting Goals
- Project Management
- Virtual Teams
Other Business
- Public Speaking
- Copywriting
- Building Security
- Information Security
Website Info
- Terms & Conditions
- Anti Spam Policy
- Privacy Policy
|
Software, Videos, Manuals, On-Line Certifications | ||
| An Organizational Task Management System. Projects, Meetings, Audits & more | ||
|
Corrective Action Software | ||
|
Plan and Track Training | ||
|
AQL Inspection Software |
|
450+ Editable Slides with support links | ||
|
Learn and Train TRIZ | ||
|
Editable Template | ||
|
Templates, Guides, QA Manual, Audit Checklists | ||
|
EMS Manual, Procedures, Forms, Examples, Audits, Videos | ||
|
Six Sigma, Risk Management, SCRUM | ||
|
Software, Videos, Manuals, On-Line Certifications |
The Lean Post / Articles / Dueling Methods: 8D and A3
Problem Solving
Dueling Methods: 8D and A3
By David Verble
August 20, 2020
One of the scores of questions sent in by attendees at our recent webinar on the A3 problem-solving process was what's the difference between it and the 8Ds. Webinar presenter and continuous improvement coach David Verble explains.
Several hundred managers and continuous improvement professionals attended the recent Lean Enterprise Institute webinar “ Beyond Problem-Solving: Other Facets of the A3 Process You Should Know and Practice ” — and sent in scores of questions.
They were more than presenter David Verble could answer in an hour, so he’ll tackle them in follow-up articles on the Lean Post . Here is the first. (Make sure you are subscribed to the Lean Post to get alerts when we post new content.)
Q: What’s the difference between A3 and 8Ds and when or in what kind of problems do I need to use each?
David: The 8Ds or eight disciplines were developed by Ford in the 1980s as a team problem-solving approach. The A3 process is a Toyota-pioneered practice of getting the problem, analysis, corrective actions, and action plan on a single sheet of large (A3) paper, often with the use of graphics. The main difference is that the 8Ds, summarized below, are oriented toward organizing and leading a team through a structured problem-solving process.
The 8Ds (which start with plan for solving the problem; determine prerequisites):
- Form a team with product or process knowledge
- Describe the problem in quantifiable terms such as what, where, how many, etc.
- Implement containment actions to isolate the problem from customers.
- Determine and verify all applicable causes
- Select and verify permanent corrections
- Implement the best corrective actions
- Take actions to prevent the problem from recurring
- Recognize and congratulate the team
By the way, I like the term “corrective actions.” I think it allows for more options than “countermeasures” because it’s broader and includes countermeasures plus temporary actions.
A Report Is Just a Report
It’s important to remember that 8D reports and A3 reports describe the problem-solving after it has happened. Filling out the reports does not — in either case — do the problem-solving. You can use the reports to document your progress, but you don’t do the problem-solving by completing the report. You must do the problem-solving work before you enter anything in the reports.
There is a similarity between the 8Ds and the problem-solving process used by Toyota’s quality circles, which follow a cycle of forming teams and clarifying roles. But the 8Ds shouldn’t be confused with Toyota’s eight-step problem-solving process , which is not oriented toward teams.
Toyota’s 8-Step Process:
- Clarify the problem
- Breakdown the problem
- Set a target
- Analyze the root cause
- Develop countermeasures
- Implement countermeasures
- Monitor the process and results
- Standardize successful processes
The process starts with clarifying the problem, which is essentially grasping the problem situation, understanding what’s going on, and pinpointing the problem. The next step, breaking down the problem, is a key feature that is unique to Toyota’s problem-solving process. I’m not aware of another method that has this emphasis on identifying the problem as a gap in performance and then examining the work in the underperforming process or procedure to learn what is contributing to the gap.
The A3 Emphasis
If you read Managing to Learn , which is about how to use the A3 problem-solving process, middle manager character Desi Porter ultimately captures the current flow of a language translation process, which had caused a host of problems and created many more for the operation . He leads people in the process of agreeing on a future-state workflow that eliminates the problems.
As part of the process, you may have to — as Porter did — collect data and sort out the different types of defects or delays. That’s part of breaking down the problem, but sooner or later, you’re going to end up examining the process or procedure that has the issues in timing or delivery that you’re concerned about. And you are going to look for the specific things that are not working as they should in the workflow resulting in that performance gap. That’s what Toyota means by “breakdown the problem.”
In that way, it is like using value- stream mapping. First, you visualize the current workflow, identify the things about the way the work is being done that are affecting flow and timing, and then decide what changes need to be made to create a better performing future-state process.
I’m obviously biased, but I think the A3 process goes into a depth of problem-solving thinking that most other methods don’t. For instance, I don’t believe the 8D process goes as deep into monitoring results or checking what happened during execution, reflection, and making decisions on next steps: should you standardize, continue problem-solving, or start over? In other words, it does not seem to put the kind of emphasis on completing the plan-do-check-adjust ( PDCA ) cycle that A3 problem-solving and Toyota’s eight-step problem-solving do.
The Big Difference Between A3 and 8D
I have seen both approaches used successfully with most kinds of problems. I saw a variation of 8D used effectively at NUMMI, the Toyota-General Motors joint-venture plant in California. It was an effective means of engaging teams of operators in dealing with problems in the scope of their work. A simplified A3 process was the method used by Toyota Quality Circles. In fact, the A3 format originated as a tool for quality circles to report their problem-solving work to management.
The biggest difference in how the two methods are used that I see is in the scope of problems they are used to tackle. The 8D process seems to be more frequently used at the operational and staff levels to investigate and resolve problems within their work environments.
The A3 problem-solving process and the A3 report — at least as they are done in Toyota — are most often used for management level problems which are often cross-functional or strategic.
After starting out as a report format for quality circles, the A3 was taught to Toyota managers to level up their PDCA problem-solving thinking and skills. (See the Lean Posts How the A3 Process Developed to Help Build Better Managers Parts 1 and 2 by John Shook and Isao Yoshino for more information).
In Toyota, the A3 format is used as a communication and reporting tool in strategy deployment , multi-leveling planning for major projects, cross-functional process improvement initiatives (such Porter’s translation project), and performance improvement efforts at the department, value stream , operating unit, and group levels. It is the primary tool for leading and managing the many organizational change, improvement, and problem-solving processes based on the PDCA cycle.
Keep Learning
- Watch the webinar with David Verble.
- For a deep-dive into the A3 problem-solving method, register for the comprehensive online workshop, Managing to Learn . Learn more about the curriculum and enroll.
Managing to Learn
An Introduction to A3 Leadership and Problem-Solving.
Written by:

About David Verble
A performance improvement consultant and leadership coach since 2000, David has been an LEI faculty member for 17 years. Recognized as one of the first Toyota-trained managers to bring A3 thinking from Japan to the United States, he has conducted A3 problem-solving and leadership programs for 30 years. Overall, his…
The difference is how they do cause finding.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Revolutionizing Logistics: DHL eCommerce’s Journey Applying Lean Thinking to Automation
Podcast by Matthew Savas

Transforming Corporate Culture: Bestbath’s Approach to Scaling Problem-Solving Capability

Teaching Lean Thinking to Kids: A Conversation with Alan Goodman
Podcast by Alan Goodman and Matthew Savas
Related books

A3 Getting Started Guide
by Lean Enterprise Institute

The Power of Process – A Story of Innovative Lean Process Development
by Eric Ethington and Matt Zayko
Related events
September 26, 2024 | Morgantown, PA or Remond, WA
Building a Lean Operating and Management System
October 02, 2024 | Coach-Led Online and In-Person (Oakland University in Rochester, MI)
Explore topics
Subscribe to get the very best of lean thinking delivered right to your inbox
Privacy overview.

- Search forums
- National and International Business System Standards
- ISO 9000, ISO 9001, and ISO 9004 Quality Management Systems Standards
5D and 8D as an option, can it be both or one of them in the system?
- Thread starter YAZIDM
- Start date Jul 29, 2010
- Jul 29, 2010
Hi, Our system just practice 5D as for our Corrective Action record. Since most of the customer asking for 8D , should i remove 5D from the procedure and replace it with 8D or is it possible to have both? My boss is asking can it be both in the procedure since he want the 5D to be used internally.
YAZIDM said: Hi, Our system just practice 5D as for our Corrective Action record. Since most of the customer asking for 8D , should i remove 5D from the procedure and replace it with 8D or is it possible to have both? My boss is asking can it be both in the procedure since he want the 5D to be used internally. Click to expand...
Hi Jane / qusys, Actually this is the first time I saw 5D, fyi, I’m the freshie new guy who taking care the QMS. Our 5D consist; D1: Define the Problem D2: Define & Verify the Root Cause(s) D3: Identify & Verify Proposed Permanent Corrective Action D4: Implement Permanent Corrective Action D5: Action to Prevent Re-occurrence While for 8D ; D1: Identify Team Member/Roles & Responsibilities D2. Define the Problem D3. Implement & Verify Interim Containment Actions(s) D4. Define & Verify Root Cause(s) D5. Identify & Verify Proposed Permanent Corrective Action(s) D6. Implement Permanent Corrective Action(s) D7. Action(s) to Prevent Re-Occurrence D8. Communicate Results & Recognize Team As we all well know, nowadays ALL customers demanding 8D. But my supr. asking me whether is it possible to have them both in the system, reason is 5D for internal use and 8D for external. To me, i will agree with qusys....I’m not sure about this. The procedure only mentions one report that is 5D. My boss wants them both which is ‘as an option’. My concern is will I face any problem in future especially during audits? I believe it’s explainable as what my boss said, but in term of requirement or possibility or necessary maybe logic? Beside "add-in" 8D as an option, should I amend anything on the procedure? Please review attachment. Were gonna arrange Internal audit this coming sept and ISO audit is soon after that. thanks in advance
Attachments
- QA,PROC-13-01,MAL EDI 1 Corrective Action_.pdf 54.1 KB · Views: 1,248
- QA,PROC-13-03,MAL EDI 1 Customer Complain.pdf 134.9 KB · Views: 767
There's nothing wrong with using multiple models, but as some have pointed out, people need to know which to use when. To me the 5D is simply the 8D without use of a team. Many problems do not require a team.
YAZIDM said: ................. should i remove 5D from the procedure and replace it with 8D or is it possible to have both?.................... Click to expand...
Duke Okes said: There's nothing wrong with using multiple models, but as some have pointed out, people need to know which to use when. To me the 5D is simply the 8D without use of a team. Many problems do not require a team. Click to expand...
- May 15, 2015
Does anyone know where I can download a thorough 5D CAR form?
Similar threads
- Feb 6, 2024
- Mar 15, 2024
- Manufacturing and Related Processes
- Jan 30, 2024
- Sep 6, 2023
- Inspection, Prints (Drawings), Testing, Sampling and Related Topics
- DariusPlumdon
- Jul 4, 2023
- IATF 16949 - Automotive Quality Systems Standard
- This site uses cookies to help personalise content, tailor your experience and to keep you logged in if you register. By continuing to use this site, you are consenting to the use of cookies. Accept Learn more…

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The 8D problem solving model establishes a permanent corrective action based on statistical analysis of the problem and focuses on the origin of the problem by determining its root causes. Although it originally comprised eight stages, or disciplines, the eight disciplines system was later augmented by an initial planning stage. ...
The purpose of 8D problem solving method is to identify, correct and prevent problems affecting customers and operational efficiency. It is a problem solving approach similar to PDCA cycle (Plan - Do - Check - Act). 8D stands for 8 Disciplines. It is a methodology that emphasizes "No problem should be repeated but fixed permanently".
Eight Disciplines Methodology (8D) is a method or model developed at Ford Motor Company used to approach and to resolve problems, typically employed by quality engineers or other professionals. Focused on product and process improvement, its purpose is to identify, correct, and eliminate recurring problems. It establishes a permanent corrective action based on statistical analysis of the ...
The 8D problem solving process is a detailed, team oriented approach to solving critical problems in the production process. The goals of this method are to find the root cause of a problem, develop containment actions to protect customers and take corrective action to prevent similar problems in the future. The strength of the 8D process lies ...
The eight disciplines (8D) method is a problem-solving approach that identifies, corrects, and eliminates recurring problems. By determining the root causes of a problem, managers can use this method to establish a permanent corrective action and prevent recurring issues. First introduced by Ford, the 8D method offers a consistent way of ...
Two approaches to problem solving are the 8D report and the A3 report. Although organizations may use these approaches interchangeably, the 8D report is better suited for problem solving due to root cause analysis (RCA)—such as identifying the specific cause of a scrapped part—and the A3 report is optimal for continuous improvement (CI)—such as finding and eliminating causes of scrap in ...
8D Problem Solving is a systematic and structured approach used to solve business related problems. It names has been given by the fact there are 8 steps or 8 disciplines that are followed to identify, correct and eliminate recurring problems. 8D Problem Solving is regarded as robust methodology that has proven its worth across multiple ...
The final step in the 8D Problem-Solving Methodology is often the most overlooked but is crucial for long-term success: congratulating the team. After navigating through a complex problem-solving journey, taking a moment to acknowledge and celebrate the hard work is vital. It not only boosts morale but also encourages a culture of continuous ...
The Ford Motor Company® developed the 8D (8 Disciplines) Problem Solving Process, and published it in their 1987 manual, "Team Oriented Problem Solving (TOPS)." In the mid-90s, Ford added an additional discipline, D0: Plan. The process is now Ford's global standard, and is called Global 8D. Ford created the 8D Process to help teams deal with ...
Abstract. Nothing causes anxiety for a team quite like the release of a corrective action preventive action (CAPA) system and accompanying eight disciplines (8D) model. Questions of value come immediately and consistently. The denial phase is inevitable, but the team can accelerate the progression of forming, storming and norming, and emerge ...
The 8D report is a structured problem-solving methodology that can help organizations address complex problems. The methodology involves eight disciplines, each representing a different phase of the process. The first step is to establish an interdisciplinary team that will be responsible for generating solutions.
8D is the baseline problem solving format and 4D/2D are adaptions that only use some of the steps (and tools) to smaller lower complexity problems. 4D/2D version are not suffient to solve a problem involving a customer escape of a facility. It should be 2D and 4D but RM13000 recommends those
Some of the different actions that comprise this step in the 8D problem-solving process include: Naming team members and setting up the team. Appointing a team leader. Developing and sharing team guidelines. Going over team goals and priorities. Arranging team-building exercises, if needed. 3.
The 8D approach to problem-solving, also known as the 8D methodology, is a systematic and comprehensive method used to address and resolve complex issues, particularly in manufacturing and other industries. This 8D troubleshooting methodology involves a structured process designed to identify, correct, and prevent issues, ensuring that similar ...
8D problem solving is a structured and systematic approach to solving complex problems that require cross-functional collaboration and root cause analysis. It was developed by Ford Motor Company in the late 1980s as a way to address customer complaints and improve product quality. Since then, it has been widely adopted by many organizations ...
The 8D Methodology is a troubleshooting tool that follows 8 steps. The focus is on identifying the root-cause of the problem, implementing short-term fixes, and testing long-term measures to prevent it from happening again. The consequences of consecutive errors show just how important such tools can be for a company.
The 8D method is widely used for problem-solving, especially in the automotive industry. However, like any approach, it has its advantages and disadvantages compared to other popular methods like DMAIC, A3, or PDCA. Here's an overview of the pros and cons of the 8D method compared to these methods. Advantages of the 8D method:
There are different problem-solving tools that are shown in the problem - solving pyramid depending on time/complexity and the percentage of problems. 5 Why Figure 1: problem-solving pyramid 8D is one of these systematic methods used to tackle and solve problems. The primary aims of the 8D methodology are to identify the root cause, correct and
The 8D Problem Solving Process (8D) is a team-oriented and structured problem-solving methodology that emphasizes the idea that problems should not be repeated but fixed permanently. This process focuses on the origin of the problem by determining root causes and establishing permanent corrective and preventive actions.
To choose the right corrective action form you need to understand the D (s) involved with corrective action. The D stands for Discipline. There are 3 main corrective action types and these are 5D, 8D, and 9D. There are 9 different Ds that support each type. These are D1, D2, D3, D4, D5, D6, D7, D8 and D9.
David: The 8Ds or eight disciplines were developed by Ford in the 1980s as a team problem-solving approach. The A3 process is a Toyota-pioneered practice of getting the problem, analysis, corrective actions, and action plan on a single sheet of large (A3) paper, often with the use of graphics. The main difference is that the 8Ds, summarized ...
Our 5D consist; D1: Define the Problem. D2: Define & Verify the Root Cause (s) D3: Identify & Verify Proposed Permanent Corrective Action. D4: Implement Permanent Corrective Action. D5: Action to Prevent Re-occurrence. While for 8D; D1: Identify Team Member/Roles & Responsibilities. D2.