© Copyright 2001-Present. American Rhetoric by Michael E. Eidenmuller All rights reserved.


My Favorite Speeches for Rhetorical Analysis: 10 Speeches for Middle School ELA and High School English
Teaching rhetorical analysis is one of my absolute favorite units to complete with my students. I love teaching my students about rhetorical strategies and devices, analyzing what makes an effective and persuasive argument, and reading critical speeches with my students. Here is a quick list of some of my favorite speeches for rhetorical analysis.

I absolutely LOVE teaching rhetorical analysis. I think it might be one of my favorite units to teach to my high school students. There are just so many different text options to choose from. Here is a list of some of my favorite speeches to include in my rhetorical analysis teaching unit.
10 Speeches for Teaching Rhetorical Analysis
1. the gettysburg address (abraham lincoln).

Some notable things to mention in this speech include allusion and parallel structure. To make your analysis more meaningful, point out these devices to students and explain how these devices enhance the meaning of the text.
Teaching Resource : The Gettysburg Address Rhetorical Analysis Activity Packet
2. Lou Gehrig’s Farewell Speech (Lou Gehrig)
This speech is one that many of my athletes love to analyze, and it is an excellent exemplar text to teach pathos. And like The Gettysburg Address, it is short. This is another speech that you can read, analyze, and even write about in one class period.
When I use this speech in my class, I have students look for examples of pathos. Mainly, I have them look at word choice, tone, and mood. How does Lou Gehrig’s choice of words affect his tone and the overall mood of the speech?
3. I Have a Dream (Martin Luther King, Jr.)

In the classroom, it is important to point out the sermonic feel to the speech and also to have your students look for calls to action and pathos. Have your students look for tone, allusions, and word choice to help them notice these rhetoric expressions throughout it.
Teaching Resource : I Have a Dream Close Read and Rhetorical Analysis
4. Speech at the March on Washington (Josephine Baker)
This is another important speech that held a lot of importance for the changes that needed to be made in America. The speech is a shorter one, so in the classroom, it will not take as long to analyze it, and students can understand the significance of the use of rhetoric in a shorter amount of time than some other speeches.
When teaching this speech, I like to remind my students to search for devices that portray an excellent example of the pathos that is so present in this speech. Some of these devices could be mood, repetition, and diction.
5. Steve Jobs’ Commencement Speech (Steve Jobs)

In class, it is good to have your students annotate and analyze the speech just as they have done for the others. The organization of the speech will help them to notice the similarities and differences between each point Jobs makes.
6. Space Shuttle Challenger (Ronald Reagan)
This speech represents a strong sense of pathos as a movement to help the American people cope with loss after the deaths of the astronauts aboard the Challenger. It is another speech that is not too long, so it should not take a long time to both analyze and annotate the entire speech.
When teaching this speech in class, be sure to mention how pathos is the driving force behind the speech, through the tone and the diction. How does Reagan use emotion to focus on the astronauts as humans, rather than solely focusing on the tragedy?
7. The Perils of Indifference (Elie Wiesel)
This speech is a good one to teach because it both makes students question their own lives, but also how the world works. The speech relies on pathos, and a little ethos too, to get the audience to feel the full effect of the tragedy of the Holocaust and what the speaker went through. It is a long speech so it may take longer for the students to fully grasp all the details that make it such a persuasive speech.
When I teach this speech, I like to have students annotate every place they notice an example of pathos, and then have them explain why in their annotations this makes them feel an emotion. The same with the ethos, and then we can further analyze the rest together.
8. 9/11 Address to the Nation (George W. Bush)
This speech shows another example of the use of pathos in the midst of a tragedy. The President wanted to show the American people how much he was feeling for those lost in the tragedy of 9/11. It is not a long speech, but the amount of emotion within the words is significant for students to notice.
When teaching this speech, it is essential that students look very closely at each part of it, noticing each piece that reveals tone, mood, and other literary devices. How do the different devices add to the pathos of the speech?
FREE TEACHING ACTIVITY : September 11 Address to the Nation Sampler
Teaching Resource : September 11 Address to the Nation Rhetorical Analysis Unit
9. We are Virginia Tech (Nikki Giovanni)
This speech is probably the shortest speech on this list but provides one of the most emotional and pathos-filled rhetoric. This describes another tragedy that is spoken about with pathos to give the audience a safe feeling after such an emotional thing. Students can spend time analyzing the different devices that make the piece so strong in its emotion.
In the classroom, make sure your students make a note of the repetition, and what that does for the speech. Does it make the emotion more impactful? How does it make the audience feel like they are a part of something bigger?
10. Woman’s Right to the Suffrage (Susan B. Anthony)
This is another short speech that holds a lot of power within it. A lot of students will enjoy reading this to see how much the country has changed, and how this speech may have some part in influencing this change. It is a great speech to help teach logos in the classroom, and it will not take a long time to analyze.
Make sure your students notice, and they also understand, the use of allusions within the speech. These allusions help to establish the use of logos, as Anthony wants the use of American historical documents to show how logical her argument is.
Ready-For-You Rhetorical Analysis Teaching Unit

You might also be interested in my blog post about 15 rhetorical analysis questions to ask your students.
Teaching rhetorical analysis and speeches in the classroom is a great way to teach informational text reading standards.
Rhetorical Analysis Teaching Resources:
These resources follow reading standards for informational text and are ideal for secondary ELA teachers.
- Rhetorical Analysis Unit with Sticky Notes
- Ethos, Pathos, Logos: Understanding Rhetorical Appeals\
- Rhetorical Analysis Mini Flip Book
Join the Daring English Teacher community!
Subscribe to receive freebies, teaching ideas, and my latest content by email.
I won’t send you spam. Unsubscribe at any time.
Built with ConvertKit
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Leave this field empty

SUBSCRIBE NOW
Home — Essay Samples — Social Issues — I Have a Dream — Rhetorical Analysis of MLK Speech ‘I Have a Dream’
Rhetorical Analysis of Mlk Speech ‘i Have a Dream’
- Categories: I Have a Dream
About this sample

Words: 590 |
Published: Jan 29, 2024
Words: 590 | Page: 1 | 3 min read
Table of contents
Analysis of the speaker, analysis of the audience, analysis of rhetorical appeals, analysis of rhetorical devices, analysis of speech structure.
- Miller, K. (2002). Martin Luther King's "I Have a Dream" Speech: The Rhetorical Situation Revisited. Communication Studies, 53(3-4), 227-231.
- Gibson, D. (2013). 50th Anniversary of MLK's "I Have a Dream" Speech: Revisiting a Lesson in Structure. The History Teacher, 47(1), 125-128.

Cite this Essay
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing style below:
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr. Heisenberg
Verified writer
- Expert in: Social Issues

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 861 words
2 pages / 971 words
2 pages / 1110 words
1 pages / 448 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on I Have a Dream
On August 28,1963, Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. delivered a public speech on the steps of the Lincoln Memorial in Washington D.C. This speech would go on to be known as the most famous speech in history, the “I Have a Dream” [...]
On August 28, 1963, Martin Luther King Jr. delivered his iconic "I Have a Dream" speech at the March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom. This historic address not only captured the spirit of the civil rights movement but also [...]
Have you ever wondered what made Martin Luther King Jr.'s "I Have a Dream" speech so iconic? Why is it still remembered and celebrated today, more than half a century after it was delivered? The purpose of this essay is to [...]
The "I Have a Dream" speech delivered by Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. in 1963 is not only a profound moment in American history but also a masterful example of persuasive rhetoric. Dr. King strategically employs various persuasive [...]
On August 28, 1963, Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. delivered a public speech on the steps of the Lincoln Memorial in Washington D.C. This speech would go on to be known as the most famous speech in history, the “I Have a Dream” [...]
In practical subjects, like math, it is often frowned upon to find your own way of doing something. Students are expected to pay attention to their lessons and use the exact same methods that are presented to figure out problems [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
What Is a Rhetorical Analysis and How to Write a Great One

By Helly Douglas

Do you have to write a rhetorical analysis essay? Fear not! We’re here to explain exactly what rhetorical analysis means, how you should structure your essay, and give you some essential “dos and don’ts.”
What is a Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
How do you write a rhetorical analysis, what are the three rhetorical strategies, what are the five rhetorical situations, how to plan a rhetorical analysis essay, creating a rhetorical analysis essay, examples of great rhetorical analysis essays, final thoughts.
A rhetorical analysis essay studies how writers and speakers have used words to influence their audience. Think less about the words the author has used and more about the techniques they employ, their goals, and the effect this has on the audience.

In your analysis essay, you break a piece of text (including cartoons, adverts, and speeches) into sections and explain how each part works to persuade, inform, or entertain. You’ll explore the effectiveness of the techniques used, how the argument has been constructed, and give examples from the text.
A strong rhetorical analysis evaluates a text rather than just describes the techniques used. You don’t include whether you personally agree or disagree with the argument.
Structure a rhetorical analysis in the same way as most other types of academic essays . You’ll have an introduction to present your thesis, a main body where you analyze the text, which then leads to a conclusion.
Think about how the writer (also known as a rhetor) considers the situation that frames their communication:
- Topic: the overall purpose of the rhetoric
- Audience: this includes primary, secondary, and tertiary audiences
- Purpose: there are often more than one to consider
- Context and culture: the wider situation within which the rhetoric is placed
Back in the 4th century BC, Aristotle was talking about how language can be used as a means of persuasion. He described three principal forms —Ethos, Logos, and Pathos—often referred to as the Rhetorical Triangle . These persuasive techniques are still used today.
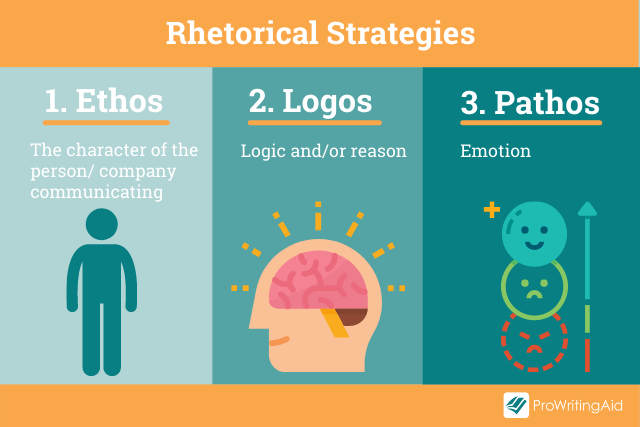
Rhetorical Strategy 1: Ethos
Are you more likely to buy a car from an established company that’s been an important part of your community for 50 years, or someone new who just started their business?
Reputation matters. Ethos explores how the character, disposition, and fundamental values of the author create appeal, along with their expertise and knowledge in the subject area.
Aristotle breaks ethos down into three further categories:
- Phronesis: skills and practical wisdom
- Arete: virtue
- Eunoia: goodwill towards the audience
Ethos-driven speeches and text rely on the reputation of the author. In your analysis, you can look at how the writer establishes ethos through both direct and indirect means.
Rhetorical Strategy 2: Pathos
Pathos-driven rhetoric hooks into our emotions. You’ll often see it used in advertisements, particularly by charities wanting you to donate money towards an appeal.
Common use of pathos includes:
- Vivid description so the reader can imagine themselves in the situation
- Personal stories to create feelings of empathy
- Emotional vocabulary that evokes a response
By using pathos to make the audience feel a particular emotion, the author can persuade them that the argument they’re making is compelling.
Rhetorical Strategy 3: Logos
Logos uses logic or reason. It’s commonly used in academic writing when arguments are created using evidence and reasoning rather than an emotional response. It’s constructed in a step-by-step approach that builds methodically to create a powerful effect upon the reader.
Rhetoric can use any one of these three techniques, but effective arguments often appeal to all three elements.
The rhetorical situation explains the circumstances behind and around a piece of rhetoric. It helps you think about why a text exists, its purpose, and how it’s carried out.
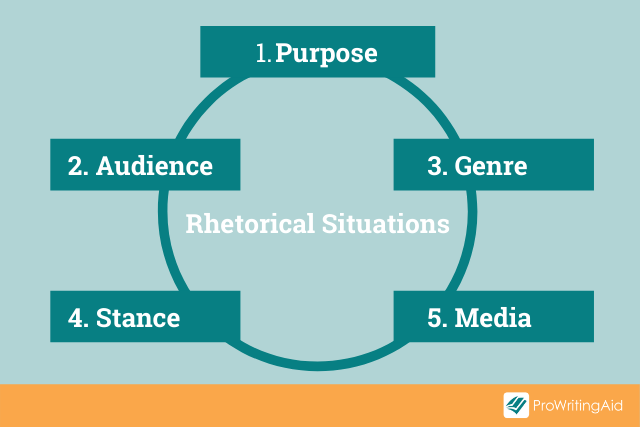
The rhetorical situations are:
- 1) Purpose: Why is this being written? (It could be trying to inform, persuade, instruct, or entertain.)
- 2) Audience: Which groups or individuals will read and take action (or have done so in the past)?
- 3) Genre: What type of writing is this?
- 4) Stance: What is the tone of the text? What position are they taking?
- 5) Media/Visuals: What means of communication are used?
Understanding and analyzing the rhetorical situation is essential for building a strong essay. Also think about any rhetoric restraints on the text, such as beliefs, attitudes, and traditions that could affect the author's decisions.
Before leaping into your essay, it’s worth taking time to explore the text at a deeper level and considering the rhetorical situations we looked at before. Throw away your assumptions and use these simple questions to help you unpick how and why the text is having an effect on the audience.

1: What is the Rhetorical Situation?
- Why is there a need or opportunity for persuasion?
- How do words and references help you identify the time and location?
- What are the rhetoric restraints?
- What historical occasions would lead to this text being created?
2: Who is the Author?
- How do they position themselves as an expert worth listening to?
- What is their ethos?
- Do they have a reputation that gives them authority?
- What is their intention?
- What values or customs do they have?
3: Who is it Written For?
- Who is the intended audience?
- How is this appealing to this particular audience?
- Who are the possible secondary and tertiary audiences?
4: What is the Central Idea?
- Can you summarize the key point of this rhetoric?
- What arguments are used?
- How has it developed a line of reasoning?
5: How is it Structured?
- What structure is used?
- How is the content arranged within the structure?
6: What Form is Used?
- Does this follow a specific literary genre?
- What type of style and tone is used, and why is this?
- Does the form used complement the content?
- What effect could this form have on the audience?
7: Is the Rhetoric Effective?
- Does the content fulfil the author’s intentions?
- Does the message effectively fit the audience, location, and time period?
Once you’ve fully explored the text, you’ll have a better understanding of the impact it’s having on the audience and feel more confident about writing your essay outline.
A great essay starts with an interesting topic. Choose carefully so you’re personally invested in the subject and familiar with it rather than just following trending topics. There are lots of great ideas on this blog post by My Perfect Words if you need some inspiration. Take some time to do background research to ensure your topic offers good analysis opportunities.

Remember to check the information given to you by your professor so you follow their preferred style guidelines. This outline example gives you a general idea of a format to follow, but there will likely be specific requests about layout and content in your course handbook. It’s always worth asking your institution if you’re unsure.
Make notes for each section of your essay before you write. This makes it easy for you to write a well-structured text that flows naturally to a conclusion. You will develop each note into a paragraph. Look at this example by College Essay for useful ideas about the structure.
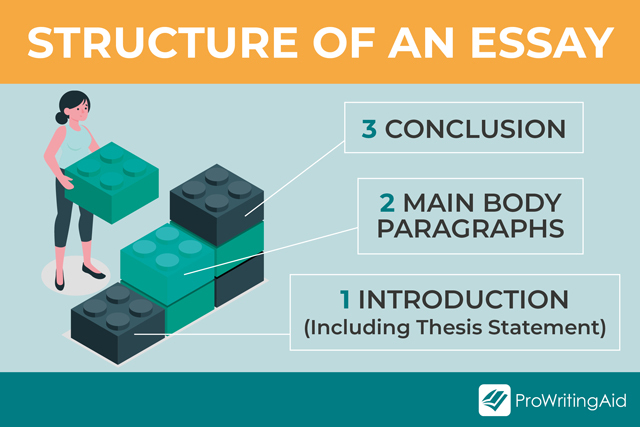
1: Introduction
This is a short, informative section that shows you understand the purpose of the text. It tempts the reader to find out more by mentioning what will come in the main body of your essay.
- Name the author of the text and the title of their work followed by the date in parentheses
- Use a verb to describe what the author does, e.g. “implies,” “asserts,” or “claims”
- Briefly summarize the text in your own words
- Mention the persuasive techniques used by the rhetor and its effect
Create a thesis statement to come at the end of your introduction.
After your introduction, move on to your critical analysis. This is the principal part of your essay.
- Explain the methods used by the author to inform, entertain, and/or persuade the audience using Aristotle's rhetorical triangle
- Use quotations to prove the statements you make
- Explain why the writer used this approach and how successful it is
- Consider how it makes the audience feel and react
Make each strategy a new paragraph rather than cramming them together, and always use proper citations. Check back to your course handbook if you’re unsure which citation style is preferred.
3: Conclusion
Your conclusion should summarize the points you’ve made in the main body of your essay. While you will draw the points together, this is not the place to introduce new information you’ve not previously mentioned.
Use your last sentence to share a powerful concluding statement that talks about the impact the text has on the audience(s) and wider society. How have its strategies helped to shape history?
Before You Submit
Poor spelling and grammatical errors ruin a great essay. Use ProWritingAid to check through your finished essay before you submit. It will pick up all the minor errors you’ve missed and help you give your essay a final polish. Look at this useful ProWritingAid webinar for further ideas to help you significantly improve your essays. Sign up for a free trial today and start editing your essays!
You’ll find countless examples of rhetorical analysis online, but they range widely in quality. Your institution may have example essays they can share with you to show you exactly what they’re looking for.
The following links should give you a good starting point if you’re looking for ideas:
Pearson Canada has a range of good examples. Look at how embedded quotations are used to prove the points being made. The end questions help you unpick how successful each essay is.
Excelsior College has an excellent sample essay complete with useful comments highlighting the techniques used.
Brighton Online has a selection of interesting essays to look at. In this specific example, consider how wider reading has deepened the exploration of the text.

Writing a rhetorical analysis essay can seem daunting, but spending significant time deeply analyzing the text before you write will make it far more achievable and result in a better-quality essay overall.
It can take some time to write a good essay. Aim to complete it well before the deadline so you don’t feel rushed. Use ProWritingAid’s comprehensive checks to find any errors and make changes to improve readability. Then you’ll be ready to submit your finished essay, knowing it’s as good as you can possibly make it.
Try ProWritingAid's Editor for Yourself

Be confident about grammar
Check every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send.
Helly Douglas
Helly Douglas is a UK writer and teacher, specialising in education, children, and parenting. She loves making the complex seem simple through blogs, articles, and curriculum content. You can check out her work at hellydouglas.com or connect on Twitter @hellydouglas. When she’s not writing, you will find her in a classroom, being a mum or battling against the wilderness of her garden—the garden is winning!
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via:
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis Essay–Examples & Template
What is a Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
A rhetorical analysis essay is, as the name suggests, an analysis of someone else’s writing (or speech, or advert, or even cartoon) and how they use not only words but also rhetorical techniques to influence their audience in a certain way. A rhetorical analysis is less interested in what the author is saying and more in how they present it, what effect this has on their readers, whether they achieve their goals, and what approach they use to get there.
Its structure is similar to that of most essays: An Introduction presents your thesis, a Body analyzes the text you have chosen, breaks it down into sections and explains how arguments have been constructed and how each part persuades, informs, or entertains the reader, and a Conclusion section sums up your evaluation.
Note that your personal opinion on the matter is not relevant for your analysis and that you don’t state anywhere in your essay whether you agree or disagree with the stance the author takes.
In the following, we will define the key rhetorical concepts you need to write a good rhetorical analysis and give you some practical tips on where to start.
Key Rhetorical Concepts
Your goal when writing a rhetorical analysis is to think about and then carefully describe how the author has designed their text so that it has the intended effect on their audience. To do that, you need to consider a number of key rhetorical strategies: Rhetorical appeals (“Ethos”, “Logos”, and “Pathos”), context, as well as claims, supports, and warrants.
Ethos, Logos, and Pathos were introduced by Aristotle, way back in the 4th century BC, as the main ways in which language can be used to persuade an audience. They still represent the basis of any rhetorical analysis and are often referred to as the “rhetorical triangle”.
These and other rhetorical techniques can all be combined to create the intended effect, and your job as the one analyzing a text is to break the writer’s arguments down and identify the concepts they are based on.
Rhetorical Appeals
Rhetorical appeal #1: ethos.
Ethos refers to the reputation or authority of the writer regarding the topic of their essay or speech and to how they use this to appeal to their audience. Just like we are more likely to buy a product from a brand or vendor we have confidence in than one we don’t know or have reason to distrust, Ethos-driven texts or speeches rely on the reputation of the author to persuade the reader or listener. When you analyze an essay, you should therefore look at how the writer establishes Ethos through rhetorical devices.
Does the author present themselves as an authority on their subject? If so, how?
Do they highlight how impeccable their own behavior is to make a moral argument?
Do they present themselves as an expert by listing their qualifications or experience to convince the reader of their opinion on something?
Rhetorical appeal #2: Pathos
The purpose of Pathos-driven rhetoric is to appeal to the reader’s emotions. A common example of pathos as a rhetorical means is adverts by charities that try to make you donate money to a “good cause”. To evoke the intended emotions in the reader, an author may use passionate language, tell personal stories, and employ vivid imagery so that the reader can imagine themselves in a certain situation and feel empathy with or anger towards others.
Rhetorical appeal #3: Logos
Logos, the “logical” appeal, uses reason to persuade. Reason and logic, supported by data, evidence, clearly defined methodology, and well-constructed arguments, are what most academic writing is based on. Emotions, those of the researcher/writer as well as those of the reader, should stay out of such academic texts, as should anyone’s reputation, beliefs, or personal opinions.
Text and Context
To analyze a piece of writing, a speech, an advertisement, or even a satirical drawing, you need to look beyond the piece of communication and take the context in which it was created and/or published into account.
Who is the person who wrote the text/drew the cartoon/designed the ad..? What audience are they trying to reach? Where was the piece published and what was happening there around that time?
A political speech, for example, can be powerful even when read decades later, but the historical context surrounding it is an important aspect of the effect it was intended to have.
Claims, Supports, and Warrants
To make any kind of argument, a writer needs to put forward specific claims, support them with data or evidence or even a moral or emotional appeal, and connect the dots logically so that the reader can follow along and agree with the points made.
The connections between statements, so-called “warrants”, follow logical reasoning but are not always clearly stated—the author simply assumes the reader understands the underlying logic, whether they present it “explicitly” or “implicitly”. Implicit warrants are commonly used in advertisements where seemingly happy people use certain products, wear certain clothes, accessories, or perfumes, or live certain lifestyles – with the connotation that, first, the product/perfume/lifestyle is what makes that person happy and, second, the reader wants to be as happy as the person in the ad. Some warrants are never clearly stated, and your job when writing a rhetorical analysis essay is therefore to identify them and bring them to light, to evaluate their validity, their effect on the reader, and the use of such means by the writer/creator.

What are the Five Rhetorical Situations?
A “rhetorical situation” refers to the circumstance behind a text or other piece of communication that arises from a given context. It explains why a rhetorical piece was created, what its purpose is, and how it was constructed to achieve its aims.
Rhetorical situations can be classified into the following five categories:
Asking such questions when you analyze a text will help you identify all the aspects that play a role in the effect it has on its audience, and will allow you to evaluate whether it achieved its aims or where it may have failed to do so.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline
Analyzing someone else’s work can seem like a big task, but as with every assignment or writing endeavor, you can break it down into smaller, well-defined steps that give you a practical structure to follow.
To give you an example of how the different parts of your text may look when it’s finished, we will provide you with some excerpts from this rhetorical analysis essay example (which even includes helpful comments) published on the Online Writing Lab website of Excelsior University in Albany, NY. The text that this essay analyzes is this article on why one should or shouldn’t buy an Ipad. If you want more examples so that you can build your own rhetorical analysis template, have a look at this essay on Nabokov’s Lolita and the one provided here about the “Shitty First Drafts” chapter of Anne Lamott’s writing instruction book “Bird by Bird”.
Analyzing the Text
When writing a rhetorical analysis, you don’t choose the concepts or key points you think are relevant or want to address. Rather, you carefully read the text several times asking yourself questions like those listed in the last section on rhetorical situations to identify how the text “works” and how it was written to achieve that effect.
Start with focusing on the author : What do you think was their purpose for writing the text? Do they make one principal claim and then elaborate on that? Or do they discuss different topics?
Then look at what audience they are talking to: Do they want to make a group of people take some action? Vote for someone? Donate money to a good cause? Who are these people? Is the text reaching this specific audience? Why or why not?
What tone is the author using to address their audience? Are they trying to evoke sympathy? Stir up anger? Are they writing from a personal perspective? Are they painting themselves as an authority on the topic? Are they using academic or informal language?
How does the author support their claims ? What kind of evidence are they presenting? Are they providing explicit or implicit warrants? Are these warrants valid or problematic? Is the provided evidence convincing?
Asking yourself such questions will help you identify what rhetorical devices a text uses and how well they are put together to achieve a certain aim. Remember, your own opinion and whether you agree with the author are not the point of a rhetorical analysis essay – your task is simply to take the text apart and evaluate it.
If you are still confused about how to write a rhetorical analysis essay, just follow the steps outlined below to write the different parts of your rhetorical analysis: As every other essay, it consists of an Introduction , a Body (the actual analysis), and a Conclusion .
Rhetorical Analysis Introduction
The Introduction section briefly presents the topic of the essay you are analyzing, the author, their main claims, a short summary of the work by you, and your thesis statement .
Tell the reader what the text you are going to analyze represents (e.g., historically) or why it is relevant (e.g., because it has become some kind of reference for how something is done). Describe what the author claims, asserts, or implies and what techniques they use to make their argument and persuade their audience. Finish off with your thesis statement that prepares the reader for what you are going to present in the next section – do you think that the author’s assumptions/claims/arguments were presented in a logical/appealing/powerful way and reached their audience as intended?
Have a look at an excerpt from the sample essay linked above to see what a rhetorical analysis introduction can look like. See how it introduces the author and article , the context in which it originally appeared , the main claims the author makes , and how this first paragraph ends in a clear thesis statement that the essay will then elaborate on in the following Body section:
Cory Doctorow ’s article on BoingBoing is an older review of the iPad , one of Apple’s most famous products. At the time of this article, however, the iPad was simply the latest Apple product to hit the market and was not yet so popular. Doctorow’s entire career has been entrenched in and around technology. He got his start as a CD-ROM programmer and is now a successful blogger and author. He is currently the co-editor of the BoingBoing blog on which this article was posted. One of his main points in this article comes from Doctorow’s passionate advocacy of free digital media sharing. He argues that the iPad is just another way for established technology companies to control our technological freedom and creativity . In “ Why I Won’t Buy an iPad (and Think You Shouldn’t, Either) ” published on Boing Boing in April of 2010, Cory Doctorow successfully uses his experience with technology, facts about the company Apple, and appeals to consumer needs to convince potential iPad buyers that Apple and its products, specifically the iPad, limit the digital rights of those who use them by controlling and mainstreaming the content that can be used and created on the device .
Doing the Rhetorical Analysis
The main part of your analysis is the Body , where you dissect the text in detail. Explain what methods the author uses to inform, entertain, and/or persuade the audience. Use Aristotle’s rhetorical triangle and the other key concepts we introduced above. Use quotations from the essay to demonstrate what you mean. Work out why the writer used a certain approach and evaluate (and again, demonstrate using the text itself) how successful they were. Evaluate the effect of each rhetorical technique you identify on the audience and judge whether the effect is in line with the author’s intentions.
To make it easy for the reader to follow your thought process, divide this part of your essay into paragraphs that each focus on one strategy or one concept , and make sure they are all necessary and contribute to the development of your argument(s).
One paragraph of this section of your essay could, for example, look like this:
One example of Doctorow’s position is his comparison of Apple’s iStore to Wal-Mart. This is an appeal to the consumer’s logic—or an appeal to logos. Doctorow wants the reader to take his comparison and consider how an all-powerful corporation like the iStore will affect them. An iPad will only allow for apps and programs purchased through the iStore to be run on it; therefore, a customer must not only purchase an iPad but also any programs he or she wishes to use. Customers cannot create their own programs or modify the hardware in any way.
As you can see, the author of this sample essay identifies and then explains to the reader how Doctorow uses the concept of Logos to appeal to his readers – not just by pointing out that he does it but by dissecting how it is done.
Rhetorical Analysis Conclusion
The conclusion section of your analysis should restate your main arguments and emphasize once more whether you think the author achieved their goal. Note that this is not the place to introduce new information—only rely on the points you have discussed in the body of your essay. End with a statement that sums up the impact the text has on its audience and maybe society as a whole:
Overall, Doctorow makes a good argument about why there are potentially many better things to drop a great deal of money on instead of the iPad. He gives some valuable information and facts that consumers should take into consideration before going out to purchase the new device. He clearly uses rhetorical tools to help make his case, and, overall, he is effective as a writer, even if, ultimately, he was ineffective in convincing the world not to buy an iPad .
Frequently Asked Questions about Rhetorical Analysis Essays
What is a rhetorical analysis essay.
A rhetorical analysis dissects a text or another piece of communication to work out and explain how it impacts its audience, how successfully it achieves its aims, and what rhetorical devices it uses to do that.
While argumentative essays usually take a stance on a certain topic and argue for it, a rhetorical analysis identifies how someone else constructs their arguments and supports their claims.
What is the correct rhetorical analysis essay format?
Like most other essays, a rhetorical analysis contains an Introduction that presents the thesis statement, a Body that analyzes the piece of communication, explains how arguments have been constructed, and illustrates how each part persuades, informs, or entertains the reader, and a Conclusion section that summarizes the results of the analysis.
What is the “rhetorical triangle”?
The rhetorical triangle was introduced by Aristotle as the main ways in which language can be used to persuade an audience: Logos appeals to the audience’s reason, Ethos to the writer’s status or authority, and Pathos to the reader’s emotions. Logos, Ethos, and Pathos can all be combined to create the intended effect, and your job as the one analyzing a text is to break the writer’s arguments down and identify what specific concepts each is based on.
Let Wordvice help you write a flawless rhetorical analysis essay!
Whether you have to write a rhetorical analysis essay as an assignment or whether it is part of an application, our professional proofreading services feature professional editors are trained subject experts that make sure your text is in line with the required format, as well as help you improve the flow and expression of your writing. Let them be your second pair of eyes so that after receiving paper editing services or essay editing services from Wordvice, you can submit your manuscript or apply to the school of your dreams with confidence.
And check out our editing services for writers (including blog editing , script editing , and book editing ) to correct your important personal or business-related work.
How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis: Full Guide

Have you ever been completely fascinated by a speech or ad, wondering how it managed to convince you so effectively? From powerful political speeches to catchy commercials, persuasion is all around us, shaping our thoughts and choices every day.
In this guide, we'll explain all about a rhetorical analysis essay. We'll break down the clever tricks writers and speakers use to win over their audience, like how they choose their words carefully and play with our emotions. This article will give you the tools you need to understand and analyze texts more deeply. So, let’s jump right in and start by understanding the nature of this assignment first.
What is a Rhetorical Analysis Essay
A rhetorical analysis essay is a type of essay where you examine how authors or speakers use words, phrases, and other techniques to influence or persuade their audience. This type of essay focuses on analyzing the strategies used by the writer or speaker to achieve their purpose, whether it's to inform, persuade, entertain, or provoke.
You'll dissect the text or speech into its components, looking at how each part contributes to the overall message. This might involve examining the introduction, thesis statement, body paragraphs, evidence, and conclusion.
Once you've identified the strategies used, you'll assess their effectiveness in achieving the author's or speaker's purpose. This involves considering the intended audience, context, and the impact of the communication.
As per our essay writing service , some common topics for rhetorical analysis include analyzing speeches by influential leaders, dissecting political advertisements, or examining the rhetoric used in literary works.

Wednesday Addams
Mysterious, dark, and sarcastic
You’re the master of dark humor and love standing out with your unconventional style. Your perfect costume? A modern twist on Wednesday Addams’ gothic look. You’ll own Halloween with your unapologetically eerie vibe. 🖤🕸️
Do You Want to Ease Your Academic Burden?
Order a rhetorical analysis essay from our expert writers today and experience the power of top-notch academic writing.
Rhetorical Analysis Topic Ideas
Now that we've grasped the essence of a rhetorical analysis essay let's explore some potential topics you might consider for your own analysis. Here are 15 specific ideas to get you started:
- The Use of Metaphors in Barack Obama's 'Yes We Can' Speech
- Visual Rhetoric in Dove's 'Real Beauty' Advertising Campaign
- The Role of Irony in Jonathan Swift's 'A Modest Proposal'
- The Manipulation of Emotions in Coca-Cola's 'Share a Coke' Campaign
- The Repetition Technique in Winston Churchill's 'We Shall Fight on the Beaches' Speech
- The Argument Structure in Michelle Obama's Speech on Education
- The Use of Imagery in Edgar Allan Poe's 'The Raven'
- Gender Stereotypes in Old Spice's 'The Man Your Man Could Smell Like' Ad
- Satirical Elements in George Orwell's 'Animal Farm'
- The Influence of Tone in Greta Thunberg's Climate Change Speeches
- Political Symbolism in Banksy's Street Art
- Humor as Persuasion in Ellen DeGeneres' Stand-Up Comedy
- The Power of Silence in Emma Watson's UN Speech on Gender Equality
- Ethical Appeals in ASPCA's Animal Rights Advertisements
- The Cultural References in Super Bowl Commercials: A Case Study
How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis
Understanding how to start a rhetorical analysis essay involves dissecting a piece of communication to learn how it works and what effect it aims to achieve. This analytical process typically includes five paragraphs and three main parts: an introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Below, our analytical essay writing service will explain each in more detail
.webp)
Major Rhetorical Elements
Before heading towards the analysis process, it's essential to grasp some key rhetorical concepts that will help guide your examination of the text or speech. These concepts provide a framework for understanding how authors and speakers use language to persuade and influence their audience.
Ethos, pathos logos in rhetorical analysis form the foundation of persuasive communication and are often intertwined in rhetorical strategies. Ethos refers to the credibility or authority of the speaker or author. Pathos involves appealing to the audience's emotions, while logos appeals to reason and logic.
There are also other rhetorical devices that are specific techniques or patterns of language used to convey meaning or evoke particular responses. Examples include metaphor, simile, imagery, irony, repetition, and hyperbole. Recognizing and analyzing these devices can provide insight into the author's intended message and its impact on the audience.
Tone and mood also play crucial roles in shaping the audience's perception and response to the communication. Tone refers to the author's attitude toward the subject matter, while mood describes the emotional atmosphere created by the text.
Whether you ask us - write my essay , or tackle the task yourself, familiarizing yourself with these concepts will help you analyze the text and persuade the audience more effectively.
Understanding Rhetorical Appeals
.webp)
First off, what is ethos in rhetorical analysis? Well, it revolves around establishing the credibility and authority of the speaker or author. This appeal seeks to convince the audience that the communicator is trustworthy, knowledgeable, and reliable. Ethos in rhetorical analysis can be built through various means, including:
- Professional Credentials : Demonstrating expertise in the subject matter through relevant qualifications or experience.
- Personal Character : Highlighting traits such as honesty, integrity, and sincerity to engender trust and respect.
- Association : Aligning oneself with respected individuals, institutions, or causes to enhance credibility by association.
For instance, in a health-related speech, a doctor might leverage their medical expertise and professional experience (credentials) to establish ethos. Similarly, a celebrity endorsing a product is using their fame and reputation (association) to persuade consumers.
Now, let's understand what is pathos in rhetorical analysis. Pathos involves appealing to the audience's emotions, aiming to evoke feelings such as empathy, sympathy, joy, anger, or fear. This emotional connection can be a powerful tool for persuasion, as it resonates with the audience on a personal level. Strategies for employing pathos in rhetorical analysis include:
- Vivid Imagery : Painting a vivid picture or narrative that elicits strong emotional responses from the audience.
- Anecdotes : Sharing personal stories or anecdotes that evoke empathy or sympathy and make the message more relatable.
- Language Choice : Using emotive language, sensory details, and rhetorical devices to evoke specific emotional reactions.
For example, in a charity advertisement for children in need, images of impoverished and suffering children coupled with heart-wrenching stories (anecdotes) are used to evoke feelings of compassion and a desire to help.
Lastly, what is logos in rhetorical analysis, you may ask. It appeals to reason and logic, aiming to persuade the audience through rational argumentation and evidence. This appeal relies on facts, statistics, logical reasoning, and sound arguments to convince the audience of the validity of the message. Strategies for employing logos in rhetorical analysis include:
- Factual Evidence : Providing empirical data, research findings, or expert opinions to support the argument.
- Logical Reasoning : Presenting a well-structured argument with clear premises and conclusions that logically follow one another.
- Counterarguments : Addressing potential counterarguments and refuting them with logical reasoning and evidence.
For instance, in a persuasive essay advocating for environmental conservation, the author might present scientific data on climate change (factual evidence) and use logical reasoning to explain the consequences of inaction.
Text and Context
Text analysis involves closely examining the language, structure, and rhetorical devices employed within the communication. This includes identifying key themes, rhetorical appeals, persuasive strategies, and stylistic elements used by the author or speaker to convey their message.
For example, in a political speech advocating for healthcare reform, text analysis might involve identifying the use of rhetorical appeals such as ethos (e.g., highlighting the speaker's experience in healthcare policy), pathos (e.g., sharing anecdotes of individuals struggling with medical costs), and logos (e.g., presenting statistics on healthcare affordability).
Contextual analysis involves considering the broader social, cultural, and historical factors that shape communication and influence its reception. This includes examining the audience demographics, the political and cultural climate, the historical events surrounding the communication, and any relevant societal norms or values.
For instance, when analyzing a historical speech advocating for civil rights, contextual research paper writers might involve considering the social and political context of the time, including prevailing attitudes towards race, ongoing civil rights movements, and recent legislative developments.
Claims, Supports, and Warrants
A claim is a statement or assertion that the author or speaker is advocating for or seeking to prove. Claims can take various forms, including factual claims (assertions of fact), value claims (judgments about what is good or bad), and policy claims (proposals for action). For example, in an argumentative essay about the importance of exercise, the claim might be that regular physical activity is essential for maintaining good health.
Supports are the evidence, reasoning, or examples provided to substantiate and strengthen the claims being made. Supports can take many forms, including empirical data, expert testimony, personal anecdotes, logical reasoning, and analogies. The quality and relevance of the supports provided play a critical role in the persuasiveness of the argument.
Continuing with the example of the argumentative essay about exercise, supports might include scientific studies demonstrating the health benefits of physical activity, testimonials from fitness experts, and personal stories of individuals who have experienced positive changes from incorporating exercise into their routine.
Warrants are the underlying assumptions or principles that connect the supports to the claims. They provide the reasoning or justification for why the supports are relevant and valid evidence for supporting the claims. Warrants are often implicit rather than explicit and require careful analysis to uncover. In the context of the essay on exercise, the warrant connecting the supports to the claim might be the assumption that actions that promote good health are inherently valuable and worthy of pursuit.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline
Whether you opt for the option to buy essay or start writing it yourself, it's important to use a clear plan to organize your thoughts well. This plan usually includes four main steps, each looking at different parts of your analysis.
Analyzing the Text
Before writing a rhetorical analysis, take the time to thoroughly analyze the text you'll be examining. This means more than just skimming through it; it requires a thorough understanding of its subtleties and complexities. Here are some questions to guide your analysis:
- How does the text try to sway its audience? What methods does it use to convince or influence them?
- Which rhetorical appeals—ethos (credibility), pathos (emotion), logos (logic)—does the author use, and how do they contribute to the overall argument?
- What specific rhetorical devices and strategies does the author employ to effectively convey their message? Are there any patterns or recurring motifs?
- How does the structure of the text contribute to its persuasive power or overall impact?
- Are there any cultural, historical, or contextual factors that influence how the text is perceived or understood?
By scrutinizing the text in this manner, you'll gain a deeper understanding of how it functions and the techniques employed by the author to achieve their desired effect.
Rhetorical Analysis Introduction
The introduction sets the stage for your analysis by providing essential context and framing the discussion. Start by introducing the text you're analyzing, including the author's name and the title of the work. Provide some background information to give context to your analysis. For example, if you're analyzing a speech, mention the occasion or event where it was delivered.
Next, summarize the main arguments or claims made by the author. Highlight the rhetorical techniques they use to persuade their audience. Are they appealing to logic, emotion, credibility, or a combination of these? Use specific examples from the text to illustrate these techniques discussed by our dissertation service .
For instance, if you're analyzing a speech on climate change, mention the speaker's expertise in environmental science to establish credibility. Summarize the key points they make about the consequences of inaction and the urgent need for change.
Finally, conclude your introduction with a clear thesis statement. This statement should encapsulate the main argument or purpose of your analysis.
Rhetorical Analysis Body Paragraph
The body paragraphs form the crux of your analysis, where you delve into the details of the text and dissect its rhetorical strategies. Each paragraph should focus on a specific aspect of the text, such as the use of ethos, pathos, logos, or specific rhetorical devices.
Utilize Aristotle's rhetorical triangle and other key concepts introduced earlier to guide your analysis. Provide quotations or examples from the text to illustrate your points and explain why the author chose certain approaches. Evaluate the effectiveness of these strategies in achieving the author's goals and persuading the audience.
For instance, if you're discussing the use of pathos in a marketing campaign, analyze the emotional appeal of the imagery or language used and consider how it resonates with the target audience.
Rhetorical Analysis Conclusion
In the conclusion, it's crucial to reinforce your main arguments and evaluate the author's effectiveness in achieving their goals, whether you're writing an MLA or APA essay format . Reflect on the overall impact of the text on both its immediate audience and society at large, underscoring the importance of your analysis.
Resist the temptation to introduce new ideas in the conclusion. Instead, draw upon the points you've already explored in the body of your essay to strengthen your analysis. Conclude with a poignant statement that resonates with your readers, encapsulating the essence of your interpretation and leaving a lasting impression. This final remark should tie together the threads of your analysis, leaving the reader with a deeper understanding of the text's rhetorical strategies and significance.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
In this section, you'll discover two essay samples that skillfully demonstrate the application of rhetorical analysis. These examples offer insightful insights into the effective use of rhetorical techniques in writing.
5 Rhetorical Analysis Essay Tips
Here are five focused tips that will help you lay a solid foundation for your examination.
- Dissect Rhetorical Strategies : Break down the text to identify specific rhetorical devices such as metaphor, simile, or parallelism.
- Evaluate Tone and Diction : Pay attention to the author's tone and word choice. Analyze how these elements contribute to the overall mood of the text.
- Probe Ethos, Pathos, Logos : Explore how the author establishes credibility (ethos), evokes emotions (pathos), and employs logic (logos) to sway the audience.
- Contextualize Historical Significance : Consider the historical, cultural, and social backdrop against which the text was written.
- Craft a Structured Analysis : Organize your essay with a clear introduction, body paragraphs focusing on specific rhetorical elements, and a conclusion that synthesizes your findings.
Final Words
As we near the end, it's important to analyze carefully whether you're examining a speech, an advertisement, or a story. Pay attention to the smart tactics that influence our thinking. It's all about revealing how we communicate and relate to one another. Ultimately, understanding rhetoric offers a fresh perspective on the world beyond just academic success.
Looking to Take Your Academic Performance to the Next Level?
Say goodbye to stress, endless research, and sleepless nights - and hello to a brighter academic future.
What is a Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
How to structure a rhetorical analysis essay, how to write a rhetorical analysis essay.

Daniel Parker
is a seasoned educational writer focusing on scholarship guidance, research papers, and various forms of academic essays including reflective and narrative essays. His expertise also extends to detailed case studies. A scholar with a background in English Literature and Education, Daniel’s work on EssayPro blog aims to support students in achieving academic excellence and securing scholarships. His hobbies include reading classic literature and participating in academic forums.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
.webp)

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Full text and audio database of Top 100 American Speeches by Rank Order.
Here is a quick list of some of my favorite speeches for rhetorical analysis. Teaching rhetorical analysis is one of my absolute favorite units to complete with my students. I love teaching my students about rhetorical strategies and devices, analyzing what makes an effective and persuasive argument, and reading critical speeches with my students.
The Gettysburg Address is one of the most famous speeches in American history, delivered by President Abraham Lincoln in 1863 during the Civil War. In this essay, I will conduct a rhetorical analysis of the Gettysburg Address, examining the strategies Lincoln used to persuade and inspire his audience. By exploring the speech's rhetorical ...
Letter From Birmingham Jail Rhetorical Analysis Sample Essay. In his renowned "Letter from Birmingham Jail," Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. employs a powerful rhetorical strategy to advocate for the civil rights movement and address the criticisms of his opponents. Through the skillful use of [...]
Martin Luther King Jr.'s "I Have a Dream" speech is one of the most iconic and influential speeches in American history. Delivered on August 28, 1963, during the March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom, the speech played a crucial role in the civil rights movement and continues to inspire people around the world.
A rhetorical analysis essay analyzes how a text uses different elements to make an argument about that work. In this article, learn how to write a strong rhetorical analysis essay.
A rhetorical analysis is structured similarly to other essays: an introduction presenting the thesis, a body analyzing the text directly, and a conclusion to wrap up. This article defines some key rhetorical concepts and provides tips on how to write a rhetorical analysis.
A rhetorical analysis essay reviews how a text uses rhetorical appeals to make an argument. See examples and learn how to write a strong rhetorical analysis.
Writing a rhetorical analysis usually involves the following steps: Identify the Rhetorical Strategies: Analyzing the author's use of ethos, pathos, and logos. Examine the Audience: Considering who the author is targeting and how they appeal to them.
In this post, we’ll review how to write a rhetorical analysis essay, including: Understanding the assignment guidelines; Introducing your essay topic; Examining the rhetorical strategies; Summarizing your main points; Keep reading for a step-by-step guide to rhetorical analysis. What Is a Rhetorical Strategy?