| Effective Technical Writing in the Information Age |
- FRONT MATTER
- TABLE OF CONTENTS

Number System: In-Text Citation
Generally, the number system is favored in fields where you typically report experimental field or lab work. Technical fields such as materials science, aerospace engineering, and chemistry tend to favor the number system.
When you use the number system, your responsibility is to indicate in your text—either in parentheses or brackets—a number that corresponds to a source on your references page. The first source you cite in your text receives the number 1, the second number 2, and so on. If you repeat a reference to a source later in the text, it retains its original number—thus, all references to source number 4 receive a 4 after them in parentheses or brackets. You delay the appropriate punctuation until after the parentheses or brackets:
If the load on the thrust bearing can be decreased by some means, the life of the turbodrill can be significantly increased (1).
Many authors prefer to identify the source at the beginning of the reference, perhaps including the author’s name directly in the text:
Gould et al. (5) found a clear relation between. . .
The number system is especially handy for citing equations, because you can simply insert the citation number logically as you introduce the equation to avoid confusion with any other numbers:
The line’s slope is used in the following equation (7) to calculate. . .
Other In-Text Citation Practices
Slight but important mechanical differences exist among in-text citation practices, in particular when you are trying to conform to a specific style, such as MLA (Modern Language Association) or APA (American Psychological Association). For example, MLA style requires you to provide the page number of your citation in-text, but not the year, while APA style asks you to place a comma between author and year. Please feel welcome to explore all of these nuances for yourself if you wish, and recognize that some professors will insist that you conform to a particular style. When professors do not dictate a particular style, they will usually simply expect you to use the author-year or number system with consistency throughout the paper.
Remember, too, that journals within you field have already made informed decisions about which in-text citation practices they use. To settle on citation particulars, many writers model a journal in their field—mandatory, of course, if you submit material to a journal hoping for publication.
Read up on the specifics of various citation styles, in particular MLA and APA, at the following pages:
"Research and Citation Resources" article from Purdue's Online Writing Lab (OWL)
"Citation Style for Research Papers" article from Long Island University
APA In-Text Citations and Sample Essay 7th Edition
This handout focuses on how to format in-text citations in APA.
Proper citation of sources is a two-part process . You must first cite each source in the body of your essay; these citations within the essay are called in-text citations . You MUST cite all quoted, paraphrased, or summarized words, ideas, and facts from sources. Without in-text citations, you are technically in danger of plagiarism, even if you have listed your sources at the end of the essay.
In-text citations point the reader to the sources’ information on the references page. The in-text citation typically includes the author's last name and the year of publication. If you use a direct quote, the page number is also provided.
More information can be found on p. 253 of the 7th edition of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association.
Citation Rules
Direct quotation with the author named in the text.
Heinze and Lu (2017) stated, “The NFL shifted its responses to institutional change around concussions significantly as the field itself evolved” (p. 509).
Note: The year of publication is listed in parenthesis after the names of the authors, and the page number is listed in parenthesis at the end of the quote.
Direct Quotation without the Author Named in the Text
As the NFL developed as an organization, it “shifted its responses to institutional change around concussions significantly” (Heinze & Lu, 2017, p. 509).
Note: At the end of the quote, the names of the authors, year of publication, and page number are listed in parenthesis.
Paraphrase with 1-2 Authors
As the NFL developed as an organization, its reactions toward concussions also transformed (Heinze & Lu, 2017).
Note: For paraphrases, page numbers are encouraged but not required.
Paraphrase with 3 or More Authors
To work toward solving the issue of violence in prisons begins with determining aspects that might connect with prisoners' violent conduct (Thomson et al., 2019).
Direct Quotation without an Author
The findings were astonishing "in a recent study of parent and adult child relationships" ("Parents and Their Children," 2007, p. 2).
Note: Since the author of the text is not stated, a shortened version of the title is used instead.
Secondary Sources
When using secondary sources, use the phrase "as cited in" and cite the secondary source on the References page.
In 1936, Keynes said, “governments should run deficits when the economy is slow to avoid unemployment” (as cited in Richardson, 2008, p. 257).
Long (Block) Quotations
When using direct quotations of 40 or more words, indent five spaces from the left margin without using quotation marks. The final period should come before the parenthetical citation.
At Meramec, an English department policy states:
To honor and protect their own work and that of others, all students must give credit to proprietary sources that are used for course work. It is assumed that any information that is not documented is either common knowledge in that field or the original work of that student. (St. Louis Community College, 2001, p. 1)
Website Citations
If citing a specific web document without a page number, include the name of the author, date, title of the section, and paragraph number in parentheses:
In America, “Two out of five deaths among U.S. teens are the result of a motor vehicle crash” (National Center for Injury Prevention and Control, 2004, Overview section, para. 1).
Here is a print-friendly version of this content.
Learn more about the APA References page by reviewing this handout .
For information on STLCC's academic integrity policy, check out this webpage .
For additional information on APA, check out STLCC's LibGuide on APA .
Sample Essay
A sample APA essay is available at this link .
University Libraries University of Nevada, Reno
- Skill Guides
- Subject Guides
MLA Citation Guide (MLA 9th Edition): In-Text Citation
- Understanding Core Elements
- Formatting Appendices and Works Cited List
- Writing an Annotated Bibliography
- Academic Honesty and Citation
In-Text Citation
- Charts, Graphs, Images, and Tables
- Class Notes and Presentations
- Encyclopedias and Dictionaries
- Generative AI
- In Digital Assignments
- Interviews and Emails
- Journal and Magazine Articles
- Newspaper Articles
- Social Media
- Special Collections
- Videos and DVDs
- When Information Is Missing
- Citation Software
In-text citations are inserted in the body of your research paper to briefly document the source of your information.
- In-text citations in MLA style follow the general format of author's last name followed by a page number enclosed in parentheses. Here is an example: "Here's a direct quote" (Smith 8).
- If the author's name is not given, use the first word (or words) of the title. Follow the same formatting that is used in the works-cited list, such as quotation marks. Here is an example: This is a paraphrase ("Trouble" 22).
- If the source does not have page numbers (for example, some online articles, websites and e-books), only include the author's name for the in-text citation. Do not estimate or make up page numbers.
- In-text citations point the reader to the works-cited list, which is located at the end of your paper, for more complete bibliographic information.
Repeated Use of Sources
If you use information from a single source more than once in succession (i.e., no other sources referred to in between), you can use a simplified in-text citation. Here is an example:
Cell biology is an area of science that focuses on the structure and function of cells (Smith 15). It revolves around the idea that the cell is a "fundamental unit of life" (17).
Note: If using this simplified in-text citation creates ambiguity regarding the source being referred to, use the full in-text citation format.
In-Text Citation Formatting and Examples
Format: (Author's Last Name Page Number)
Example: (Hunt 358)
Two Authors
Format: (Author's Last Name and Author's Last Name Page Number)
Example: (Case and Daristotle 57)
Three or More Authors
Format: (Author's Last Name et al. Page Number)
Example: (Case et al. 57)
Unknown Author
Where you would normally put the author's last name, instead use the first one, two, or three words from the title. Do not use initial articles such as "A", "An" or "The". Provide enough words to clarify which sources from your works-cited list that you are referencing.
Follow the formatting of the title. For example, if the title in the works-cited list is in italics, italicize the words from the title in the in-text citation, and if the title in the works-cited list is in quotation marks, put quotation marks around the words from the title in the in-text citation.
Format: (Title Page Number)
Examples :
( Cell Biology 12)
("Nursing" 12)
Multiple Sources
To cite more than one source when you are paraphrasing, separate the in-text citations with a semi-colon.
Format: (Author's Last Name Page Number; Author's Last Name Page Number).
(Smith 42; Bennett 71).
( It Takes Two ; Brock 43).
Note: In MLA style, the sources within the in-text citation do not need to be in alphabetical order.
Works Quoted in Another Source
Sometimes an author of a book, article or website will mention another person's work by using a quotation or paraphrased idea from that source. (This may be a secondary source.) For example, the Kirkey article you are reading includes a quotation by Smith that you would like to include in your essay. The basic rule is that in both your Works-Cited List and in-text citation you will still cite Kirkey. Kirkey will appear in your Works Cited list – NOT Smith. Add the words "qtd. in" to your in-text citation.
Examples of in-text citations:
According to a study by Smith (qtd. in Kirkey) 42% of doctors would refuse to perform legal euthanasia.
Smith (qtd. in Kirkey) states that “even if euthanasia was legal, 42% of doctors would be against this method of assisted dying” (A.10).
Example of Works Cited List citation:
Kirkey, Susan. "Euthanasia." The Montreal Gazette , 9 Feb. 2013, p. A.10. Canadian Newsstand Major Dailies.
- << Previous: Academic Honesty and Citation
- Next: How Do I Cite? >>
University of Tasmania, Australia
Referencing guide: in-text citations.
- Systems and Styles
- Using in-text citations
- Using Turnitin
- Managing references
- AGLC This link opens in a new window
- Health & Medicine examples This link opens in a new window
- Transition from Harvard to APA
- General principles
In-text citations
- Works Cited
- Works Cited - Author
- Works Cited - Title
- Works cited - Title of Container
- Works Cited - Other Contributors
- Works Cited - Version & Number
- Works Cited - Publisher & Publication Date
- Works Cited - Location
- Works Cited - Optional Elements
- Works Cited - More Examples
- Simplified Author-date & Writing guide
Use the first element from the entry in the Works Cited list - usually the author’s surname - and page number/s in parenthesis. There is no punctuation between the name and the page number, e.g. (Smith 173). If the author’s name appears in the body of your essay itself, use just the relevant page number/s in the parenthesis, e.g. Smith claims that...applies (173).
More complex citations, such as the ones below, are punctuated for clarity:
multiple sources in a single citation are separated by semicolons, e.g. (Smith 178; Brown 65)
different locations in a single work are separated by commas, e.g. (Smith 11, 17-18, 95)
to identify a location by a paragraph number or another similar method, use a comma to separate the author's name and the paragraph number; use an abbreviation to identify the numbering method, e.g. (Smith, par. 41), (Smith, ch. 7).
The following examples apply to any type of source, in any format.
Single author
Direct quotes
The question of how narrative works “can be answered through analysis of the forms of narrative and the pieces that make up an individual narrative” (Utell 7-8).
Block quotes
If a quotation is a long one - usually more than four lines of prose or three lines of verse - place it in a free-standing block of text (hence called block quotation ), and omit quotation marks. Start the quotation on a new line, with the entire quote indented from the left margin. E.g.
Various opinions have been offered about what makes a narrative. In order to answer this question
we have to look at characters and how they act and feel. We have to look at how events unfold over time, and how those events play out as important. …. We have to look at how people (or animals, or things) are thinking. And we have to look at how all of this information is being communicated to us. (Utell 7-8)
Paraphrasing
To answer the question of how narrative works, Utell suggests that one first needs to examine all the elements which make up a given narrative (15).
To answer the question of how narrative works, one first needs to examine all the elements which make up a given narrative (Utell 15).
Multiple works by the same author
Add a short form of the title after a comma, e.g. (Utell, “Engagements” 15).
Works by multiple authors with the same surname
Add the author’s first initial or, if necessary, the full first name, e.g. (J. Utell 15).
Two authors
Use both authors’ last names connected by and , e.g. (Hill and Gibson 35-36).
Three or more authors
Use the first author’s name followed by et al. , e.g. (Royle et al. 7)
Corporate author
If the author is an organisation, list all the administrative units identified in the Works Cited entry for the source. The units are separated by commas. The commonly abbreviated words, such as Department, should be abbreviated.
The Tasmanian Government recognised the value of enhancing student experience in its recently released Global Education Strategy (State of Tasmania, Dept. of State Growth 14).
When the author of the work is the organisation that also published it , use the title (in italics, abbreviated if necessary) and page number/s in the parenthesis, e.g.
Google has made finding obscure facts easy. Dusty old volumes, such as Who wrote the movie and what else did he write? have largely been consigned to library storage facilities only to emerge on rare occasions when Google proves no help at all in determining the authorship of this obscure screenplay (78).
Google has made finding obscure facts easy. Dusty old volumes containing such facts as the authorship of this obscure screenplay ( Who 78) have largely been consigned to library storage facilities only to emerge on rare occasions when Google proves no help at all.
Pseudonyms, online usernames, etc
Pseudonyms, e.g. George Eliot would be (Eliot 89-90), online usernames, e.g. (@realDonaldTrump), etc, are treated like standard names.
If the work is published without the author's name use the title (in italics, abbreviated if necessary) and page number/s in the parenthesis, e.g. ( Beowulf 17) ; or use just the page number/s if the title appears in the body of your essay. D o not list the author as "anonymous."
Indirect sources
Whenever you cite material taken from a secondary source, not the original work, add the abbreviation of the phrase "quoted in" (qtd. in) to the citation, e.g.
Jim Collins (qtd. in Driscoll 9) places the phenomenon of "high-pop" in reference to "middlebrow" culture.
Original sources should be used whenever possible.
No page numbers; and other location numbering schemes
When the work has no page numbers or any other location numbering, such as a website might, use just the author's surname (or title if no author) in the parenthesis, e.g.
"Allegory...is thought to clear the reader’s lungs of the transient and fill them with a deep breath of transcendence." (Gordimer). In her review of Coetzee's novel The Life and Times of Michael K, she makes a distinction of allegory...
Paragraph numbers; chapter numbers, etc
Use the author's surname, followed by a comma, and the paragraph number/s (abbreviated to par. or pars. ) in the parenthesis, e.g.
Australian laws (Halsbury's, par. 160-920) define the function of a university as follows:
The objects or functions of a university are to provide facilities for teaching and research in such branches of learning as the relevant establishing legislation may determine, to confer degrees and generally to promote university education an d the advancement of knowledge.
Use this method only for works with numbered paragraphs; do not count them yourself.
Time-based media (audio/video recordings)
Give the relevant time or range of times in hours, minutes and seconds, separated by colons - as displayed by the media player, e.g.
Melvyn Bragg calls the eighteenth century "the paradise for the terrible twins - class and snobbery" (Bragg 00:17:07).
Multiple sources in a single citation
List all the sources in the parenthesis, separated by semicolons, e.g. (Smith 178; Brown 65).
Style Manual
If you cannot find an example for what you are looking for here, consult the MLA website , or the MLA Handbook (below)
Need more help?
Ask a librarian
Visit our webpage
- << Previous: General principles
- Next: Works Cited >>
- Last Updated: Jun 12, 2024 12:04 PM
- URL: https://utas.libguides.com/referencing

Home / Guides / Citation Guides / MLA Format / How to Cite an Essay in MLA
How to Cite an Essay in MLA
The guidelines for citing an essay in MLA format are similar to those for citing a chapter in a book. Include the author of the essay, the title of the essay, the name of the collection if the essay belongs to one, the editor of the collection or other contributors, the publication information, and the page number(s).
Citing an Essay
Mla essay citation structure.
Last, First M. “Essay Title.” Collection Title, edited by First M. Last, Publisher, year published, page numbers. Website Title , URL (if applicable).
MLA Essay Citation Example
Gupta, Sanjay. “Balancing and Checking.” Essays on Modern Democracy, edited by Bob Towsky, Brook Stone Publishers, 1996, pp. 36-48. Essay Database, www . databaseforessays.org/modern/modern-democracy.
MLA Essay In-text Citation Structure
(Last Name Page #)
MLA Essay In-text Citation Example
Click here to cite an essay via an EasyBib citation form.
MLA Formatting Guide
MLA Formatting
- Annotated Bibliography
- Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- et al Usage
- In-text Citations
- Paraphrasing
- Page Numbers
- Sample Paper
- Works Cited
- MLA 8 Updates
- MLA 9 Updates
- View MLA Guide
Citation Examples
- Book Chapter
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Website (no author)
- View all MLA Examples
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
To cite your sources in an essay in MLA style, you need to have basic information including the author’s name(s), chapter title, book title, editor(s), publication year, publisher, and page numbers. The templates for in-text citations and a works-cited-list entry for essay sources and some examples are given below:
In-text citation template and example:
For citations in prose, use the first name and surname of the author on the first occurrence. For subsequent citations, use only the surname(s). In parenthetical citations, always use only the surname of the author(s).
Citation in prose:
First mention: Annette Wheeler Cafarelli
Subsequent occurrences: Wheeler Cafarelli
Parenthetical:
….(Wheeler Cafarelli).
Works-cited-list entry template and example:
The title of the chapter is enclosed in double quotation marks and uses title case. The book or collection title is given in italics and uses title case.
Surname, First Name. “Title of the Chapter.” Title of the Book , edited by Editor(s) Name, Publisher, Publication Year, page range.
Cafarelli, Annette Wheeler. “Rousseau and British Romanticism: Women and British Romanticism.” Cultural Interactions in the Romantic Age: Critical Essays in Comparative Literature , edited by Gregory Maertz. State U of New York P, 1998, pp. 125–56.
To cite an essay in MLA style, you need to have basic information including the author(s), the essay title, the book title, editor(s), publication year, publisher, and page numbers. The templates for citations in prose, parenthetical citations, and works-cited-list entries for an essay by multiple authors, and some examples, are given below:
For citations in prose, use the first name and surname of the author (e.g., Mary Strine).
For sources with two authors, use both full author names in prose (e.g., Mary Strine and Beth Radick).
For sources with three or more authors, use the first name and surname of the first author followed by “and others” or “and colleagues” (e.g., Mary Strine and others). In subsequent citations, use only the surname of the first author followed by “and others” or “and colleagues” (e.g., Strine and others).
In parenthetical citations, use only the author’s surname. For sources with two authors, use two surnames (e.g., Strine and Radick). For sources with three or more author names, use the first author’s surname followed by “et al.”
First mention: Mary Strine…
Subsequent mention: Strine…
First mention: Mary Strine and Beth Radick…
Subsequent mention: Strine and Radick…
First mention: Mary Strine and colleagues …. or Mary Strine and others
Subsequent occurrences: Strine and colleagues …. or Strine and others
…. (Strine).
….(Strine and Radick).
….(Strine et al.).
The title of the essay is enclosed in double quotation marks and uses title case. The book or collection title is given in italics and uses title case.
Surname, First Name, et al. “Title of the Essay.” Title of the Book , edited by Editor(s) Name, Publisher, Publication Year, page range.
Strine, Mary M., et al. “Research in Interpretation and Performance Studies: Trends, Issues, Priorities.” Speech Communication: Essays to Commemorate the 75th Anniversary of the Speech Communication Association , edited by Gerald M. Phillips and Julia T. Wood, Southern Illinois UP, 1990, pp. 181–204.
MLA Citation Examples
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started

Basic Principles of Citation
APA Style uses the author–date citation system , in which a brief in-text citation directs readers to a full reference list entry. The in-text citation appears within the body of the paper (or in a table, figure, footnote, or appendix) and briefly identifies the cited work by its author and date of publication. This enables readers to locate the corresponding entry in the alphabetical reference list at the end of the paper.
Each work cited must appear in the reference list, and each work in the reference list must be cited in the text (or in a table, figure, footnote, or appendix).
Both paraphrases and quotations require citations.
The following are guidelines to follow when writing in-text citations:
- Ensure that the spelling of author names and the publication dates in reference list entries match those in the corresponding in-text citations.
- Cite only works that you have read and ideas that you have incorporated into your writing. The works you cite may provide key background information, support or dispute your thesis, or offer critical definitions and data.
- Readers may find a long string of citations difficult to understand, especially if they are using assistive technology such as a screen reader; therefore, include only those citations needed to support your immediate point.
- Cite primary sources when possible, and cite secondary sources sparingly.
- Cite sources to document all facts and figures that you mention that are not common knowledge.
- To cite a specific part of a source , provide an author–date citation for the work plus information about the specific part.
- Even when sources cannot be retrieved (e.g., because they are personal communications ), still credit them in the text (however, avoid using online sources that are no longer recoverable).
Basic principles of citation are covered in the seventh edition APA Style manuals in the Publication Manual Sections 8.1 to 8.36 and the Concise Guide Sections 8.1 to 8.34
Related handouts
- In-Text Citation Checklist (PDF, 227KB)
- Six Steps to Proper Citation (PDF, 112KB)
From the APA Style blog

How to cite your own translations
If you translate a passage from one language into another on your own in your paper, your translation is considered a paraphrase, not a direct quotation.

Key takeaways from the Psi Chi webinar So You Need to Write a Literature Review
This blog post describes key tasks in writing an effective literature review and provides strategies for approaching those tasks.

How to cite a work with a nonrecoverable source
In most cases, nonrecoverable sources such as personal emails, nonarchived social media livestreams (or deleted and unarchived social media posts), classroom lectures, unrecorded webinars or presentations, and intranet sources should be cited only in the text as personal communications.
The “outdated sources” myth
The “outdated sources” myth is that sources must have been published recently, such as the last 5 to 10 years. There is no timeliness requirement in APA Style.

From COVID-19 to demands for social justice: Citing contemporary sources for current events
The guidance in the seventh edition of the Publication Manual makes the process of citing contemporary sources found online easier than ever before.

Citing classical and religious works
A classical or religious work is cited as either a book or a webpage, depending on what version of the source you are using. This post includes details and examples.

Academic Writer—APA’s essential teaching resource for higher education instructors
Academic Writer’s advanced authoring technology and digital learning tools allow students to take a hands-on approach to learning the scholarly research and writing process.

APA Style webinar on citing works in text
Attend the webinar, “Citing Works in Text Using Seventh Edition APA Style,” on July 14, 2020, to learn the keys to accurately and consistently citing sources in APA Style.
- Subject guides
- Citing and referencing
- In-text citations
Citing and referencing: In-text citations
- Reference list
- Books and book chapters
- Journals/Periodicals
- Newspapers/Magazines
- Government and other reports
- Legal sources
- Websites and social media
- Audio, music and visual media
- Conferences
- Dictionaries/Encyclopedias/Guides
- Theses/Dissertations
- University course materials
- Company and Industry reports
- Patents and Standards
- Tables and Figures
- Abbreviations used in referencing
- Medicine and Health sources
- Foreign language sources
- Music scores
- Journals and periodicals
- Government sources
- News sources
- Web and social media
- Games and apps
- Ancient and sacred sources
- Primary sources
- Audiovisual media and music scores
- Images and captions
- University lectures, theses and dissertations
- Interviews and personal communication
- Archival material
- In-Text Citations: Further Information
- Reference List: Standard Abbreviations
- Data Sheets (inc. Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS))
- Figures & Tables (inc. Images)
- Lecture Materials (inc. PowerPoint Presentations)
- Reports & Technical Reports
- Theses and Dissertations
- Reference list guidelines
- Journal articles
- Government and industry publications
- Websites, newspaper and social media
- Conference papers, theses and university material
- Video and audio
- Images, graphs, tables, data sets
- Personal communications
- In-text Citations
- Journals / Periodicals
- Encyclopedias and Dictionaries
- Interviews and lectures
- Music Scores / Recordings
- Film / Video Recording
- Television / Radio Broadcast
- Online Communication / Social Media
- Live Performances
- Government and Organisation Publications
- Medicine & health sources
- Government/organisational/technical reports
- Images, graphs, tables, figures & data sets
- Websites newspaper & magazine articles, socia media
- Conferences, theses & university materials
- Personal communication & confidential unpublished material
- Video, audio & other media
- Generative AI
- Indigenous knowledges
Vancouver Contents
- Introduction to Vancouver style
- Audio and visual media
- Dictionaries / Encyclopedias
- Drug information sources
- Evidence summaries
- Government / Technical reports
- Standards and Pharmacopoeias
- Tables and figures
- Theses / Dissertations
In-text citing: General notes
Before using this guide check with your faculty, school or department for their specific referencing guidelines
- When you paraphrase someone else's work.
- When you directly quote someone else's work.
- A number is allocated to a source in the order in which it is cited in the text. If the source is referred to again, the same number is used.
- Use Arabic numerals (1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9).
- Either square [ ] or curved brackets ( ) can be used as long as it is consistent. Please check with your faculty/lecturer to see if they have a preference . For consistency in this guide we have chosen to use round brackets for our examples .
- Superscripts can also be used rather than brackets eg. ...was discovered. 1,3
- Reference numbers should be inserted to the left or inside of colons and semi-colons.
- Reference numbers are generally placed outside or after full stops and commas - however, check with your faculty/journal publisher to determine their preference . For consistency in this guide we are placing reference numbers after full stops.
- Whatever format is chosen, it is important that the punctuation is consistently applied to the whole document.
The way you cite information can be important depending on the emphasis you wish to apply:
If you wish to quote or paraphrase an author, and want to emphasise the author, then your citation becomes ' author prominent '. The citation will look something like this:
- ... in his research, Jones (2) asserts....
If you wish to emphasise the information you have paraphrased or quoted from an author, then your citation becomes ' information prominent '. The citation will look something like this:
- ... as evidenced from a recent Australian study.(1)
Multiple works by the same author:
Each individual work by the same author, even if it is published in the same year, has its own reference number.
Citing secondary sources:
A secondary source, or indirect citation, occurs when the ideas on one author are published in another author's work, and you have not accessed or read the original piece of work. Cite the author of the work you have read and also include this source in your reference list.
- ...to highlight the issue Taylor (10) discusses Bridge's research work....
Examples of in-text citations
The in-text citation is placed immediately after the text which refers to the source being cited:
Using round brackets :
...as one author has put it "the darkest days were still ahead".(1)
Using square brackets:
...as one author has put it "the darkest days were still ahead".[1]
Using superscript:
...as one author has put it "the darkest days were still ahead". 1
The author's name can also be integrated into the text
Scholtz 1 has argued that...
Including page numbers with in-text citations :
Page numbers are not usually included with the citation number. However should you wish to specify the page number of the source the page/s should be included in the following format:
...as one author has put it "the darkest days were still ahead". 1(p23)
...as one author has put it "the darkest days were still ahead".(1 p23)
Scholtz (1 p16-18) has argued that...
Citing more than one reference at a time :
The preferred method is to list each reference number separated by a comma, or by a dash for a sequence of consecutive numbers. There should be no spaces between commas or dashes, for example: (1,5,6-8)
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
APA Formatting and Style Guide (7th Edition)

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
In-Text Citations
Resources on using in-text citations in APA style
Reference List
Resources on writing an APA style reference list, including citation formats
Other APA Resources
Essay Writing: In-Text Citations
- Essay Writing Basics
- Purdue OWL Page on Writing Your Thesis This link opens in a new window
- Paragraphs and Transitions
- How to Tell if a Website is Legitimate This link opens in a new window
- Formatting Your References Page
- Cite a Website
- Common Grammatical and Mechanical Errors
- Additional Resources
- Proofread Before You Submit Your Paper
- Structuring the 5-Paragraph Essay
In-text Citations
What are In-Text Citations?
You must cite (give credit) all information sources used in your essay or research paper whenever and wherever you use them.
When citing sources in the text of your paper, you must list:
● The author’s last name
● The year the information was published.
Types of In-Text Citations: Narrative vs Parenthetical
A narrative citation gives the author's name as part of the sentence .
- Example of a Narrative Citation: According to Edwards (2017) , a lthough Smith and Carlos's protest at the 1968 Olympics initially drew widespread criticism, it also led to fundamental reforms in the organizational structure of American amateur athletics.
A parenthetical citation puts the source information in parentheses—first or last—but does not include it in the narrative flow.
- Example of a Parenthetical Citation: Although Tommie Smith and John Carlos paid a heavy price in the immediate aftermath of the protests, they were later vindicated by society at large (Edwards, 2017) .
Full citation for this source (this belongs on the Reference Page of your research paper or essay):
Edwards, H. (2017). The Revolt of the Black Athlete: 50th Anniversary Edition. University of Illinois Press.
Sample In-text Citations
| Studies have shown music and art therapies to be effective in aiding those dealing with mental disorders as well as managing, exploring, and gaining insight into traumatic experiences their patients may have faced. (Stuckey & Nobel, 2010). |
| - FIRST INITIAL, ARTICLE TITLE -- |
| Hint: (Use an when they appear in parenthetical citations.) e.g.: (Jones & Smith, 2022) |
| Stuckey and Nobel (2010) noted, "it has been shown that music can calm neural activity in the brain, which may lead to reductions in anxiety, and that it may help to restore effective functioning in the immune system." |
|
|
Note: This example is a direct quote. It is an exact quotation directly from the text of the article. All direct quotes should appear in quotation marks: "...."
Try keeping direct quotes to a minimum in your writing. You need to show your understanding of the source material by being able to paraphrase or summarize it.
List the author’s last name only (no initials) and the year the information was published, like this:
(Dodge, 2008 ). ( Author , Date).
IF you use a direct quote, add the page number to your citation, like this:
( Dodge , 2008 , p. 125 ).
( Author , Date , page number )
What information should I cite in my paper/essay?
Credit these sources when you mention their information in any way: direct quotation, paraphrase, or summarize.
What should you credit?
Any information that you learned from another source, including:
● statistics
EXCEPTION: Information that is common knowledge: e.g., The Bronx is a borough of New York City.
Quick Sheet: APA 7 Citations
Quick help with apa 7 citations.
- Quick Sheet - Citing Journal Articles, Websites & Videos, and Creating In-Text Citations A quick guide to the most frequently-used types of APA 7 citations.
In-text Citation Tutorial
- Formatting In-text Citations, Full Citations, and Block Quotes In APA 7 Style This presentation will help you understand when, why, and how to use in-text citations in your APA style paper.
Download the In-text Citations presentation (above) for an in-depth look at how to correctly cite your sources in the text of your paper.
SIgnal Phrase Activity
Paraphrasing activity from the excelsior owl, in-text citation quiz.
- << Previous: Formatting Your References Page
- Next: Cite a Website >>
- Last Updated: Jun 25, 2024 3:33 PM
- URL: https://monroecollege.libguides.com/essaywriting
- Research Guides |
- Databases |

- In-Text Citation and Notes
Citing Sources in the Text of your Paper
When writers use an outside source, they must give credit to the original writer or creator of that source. This also allows a reader to easily make note of the source’s bibliographic entry. Just as each style guide has rules for creating a citation in a bibliography at the end of a text, each guide also has certain rules for citing the use of sources within the text of the essay.
The following are basic guidelines for citing sources in the text of your paper when using the MLA, APA, Chicago, ASA, or Turabian style guides. These guidelines may not account for every citation situation. Since citing sources is not a creative enterprise, you should consult the appropriate print version of the style guide when you have questions about citation.
MLA: In-Text Citations
MLA citation style requires that writers cite a source within the text of their essay at the end of the sentence in which the source is used.
General Guidance on in-text citations (or reference to your source) The parenthetical reference should be inserted after the last quotation mark but before the period at the end of the sentence.
General Form: (Author Last Name Page #)
Example: (Smith 42)
If two quotations from different sources are used in the same sentence The in-text citation associated with a particular quote should be placed as close to the quotation as possible without interrupting the flow of the sentence.
Example for two sources in one sentence: According to one researcher, “the design thinking process is not meant to be a formula,” (Spencer 58) whereas others might argue that steps and formulas are in fact important like Walker suggests: “following a specific path towards design success is necessary for achieving outlined goals,” (21).
If a paragraph includes several quotations from a single source A single in-text citation may be placed at the end of the paragraph. Page numbers should be included for each quotation organized by placement in the paragraph. In the following example, the first quotation from Smith appeared on page 43 of the text. The second quotation used in the paragraph came from page 12.
Example: (Smith 43, 12)
If the author is included more than once on the Works Cited page The following form should be used. Note that the format of the title on the Works Cited sheet should be mirrored in the in-text citation.
General Form: (Author Last, “Title Fragment” Page #) or (Author Last, Title Fragment Page #)
Examples: (Smith, “Who Moved” 42) or (Smith, Big Changes 172)
If you have more than one author:
Two: (Brown and Sullivan 42)
Three: (Brown, Sullivan, and Grayson 158)
Four or more: (Brown, et al. 38)
If there is no author A title fragment should be used to make a connection between the use of the source and the citation for the source on the Works Cited page.
General Form: (“Title Fragment” Page #) or ( Title Fragment Page #)
Examples: (“Library Links” 13) or ( Building a Bookshelf 42)
For more information related to MLA in-text citations, see the MLA Handbook , 8th ed. (pages 54-58). This title is on reserve at the circulation desk at the front of the library on the 3rd floor near the main entrance.
APA: Parenthetical In-Text Citations
To cite a source in the text of an essay, APA advocates two methods: in-text citations and attribution within the essay’s content. in-text citations should be included immediately after the quotation marks used in direct quotations or immediately after the use of the source, even if this means including the parenthetical reference in the middle of the sentence.
The following is the general form for parenthetical citations in APA style:
In-text citation: (Author Last Name, Year of Publication) Example: (Smith, 1988)
To make the citation of the source less distracting The APA also suggests mentioning the author in the essay’s content so that only the year of publication and page number may be required in the parenthetical reference.
Attribution in text: Author Last Name (Year of Publication) has argued this point. Example: Smith (1988) has argued this point.
Page numbers are not required in APA in-text citations. However, it is highly suggested that these be included. To include references to a specific part of the text, add the page number or chapter number after the year.
Examples: Smith (1988, p. 244) has written that… or Smith (1988, chap. 5) has written that…
When a work has two authors Both names should be cited every time the reference is required. Use an ampersand (&) to separate the names of authors. If a text has been authored by more than five individuals, the full listing of authors is not required in the first reference or any subsequent in-text references.
The first mention of the reference: Johnson, Smith, and Brown (1999) agree that… Subsequent mention: Johnson et al. (1999) agree that…
If a group or corporation is the author The full name of the group or corporation should be included in place of the author’s name. If an organization has a recognizable abbreviation, this may be used in subsequent references.
The first mention of the reference: (American Medical Association, 2002) Subsequent mention: (AMA, 2002)
If no author is given for a specific text Use the first couple of words of the title in place of the author’s last name. Title fragments should be formatted using the same punctuation as titles on the References page.
Examples of attribution in the text:
The recent publication Plagiarism and You (2002) offers some explanation…
In “Five Ways to Protect Yourself” (2000) one can find…
Examples of attribution at the end of the sentence: ( Plagiarism and You , 2002) or (“Five Ways to Protect Yourself,” 2000)
When no date is given for the publication of a text (as is the case with many websites) Include the abbreviation “n.d.” (which stands for “no date”) in place of the year of publication.
Example: In the article “Five Ways to Protect Yourself” (n.d.) one can find…
For more information related to in-text citations (or in-text referencing) using the APA format, see the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association , 7th ed. pages 261-269. A copy of this manual is available on the 3rd floor of the library at the circulation desk.
Chicago: Notes Style
In Chicago’s Documentation Style 1, also known as notes form, the use of research sources is indicated in the text with a numerical subscript that corresponds to an entry at the end of the paper. These are called endnotes. Although footnotes (or notes at the bottom of the page) are sometimes required, endnotes have become the predominant form of notes citations.
When using endnotes to indicate the use of research sources, writers must also include a bibliography at the end of the essay. The note and the bibliographic entry include almost identical information but in a different format.
As the formats for notes are contingent on the format of the source for which the note is written, examples of note formats are included with the bibliographic examples available through the Citing Sources link. The B: entry would be included in the Bibliography at the end of the paper, while the N: entry gives examples to be used in footnotes or endnotes.
For further information on note format or other issues related to citing sources using the Chicago style, see The Chicago Manual of Style , 16th ed.
Chicago: Author/Date Style
Documentation 2, also called the Author-Date style, requires the use of parenthetical references in the text of the essay as well as a list of References.
Parenthetical references should be placed at the end of the sentence, before the period, when a resource has been used. If the sentence is either long enough or complex enough so that the cited portion of the sentence is not obvious, the parenthetical reference may instead be inserted immediately after the use of information from the source. Page numbers should be included whenever possible.
General Form: (Author Last Name Year of Publication, Page #)
Example: (Smith 1992, 142)
The following examples illustrate parenthetical reference formats for works with more than one author.
(Smith and Johnson 1998, 14)
(Smith, Johnson, and White 2001, 42)
(Smith et al. 1998, 203)
(National Alliance for Social Consideration 1932, 11)
When organizations or corporate authors are the author of a text, the name of the organization may be shortened to its most basic title. Abbreviations for the organization are not encouraged.
In the Chicago style, daily newspapers are rarely included in a list of References. Instead, attribution may be given to information from a daily newspaper in a parenthetical reference.
General Form: ( Newspaper Name , Day Month Year of Publication, Section and Page #)
Examples: ( San Antonio Express-News , 2 June 2005, B2)
( New York Times , 2 June 2005, A2)
( Durant Daily Democrat , 2 June 2005, 3)
The Chicago style guide does not offer examples for creating parenthetical references when there is no given author. Standard practice has been to include the title of the work in place of the author. The title should be formatted in the same manner as the formatting in the References list entry.
( Plagiarism and You 2002, 142)
(“Five Ways to Protect Yourself” 2000, 33)
Electronic sources commonly lack a date of publication, as do other sources. When there is no date of publication listed for a source, include the abbreviation “n.d.” in place of the date.
(Statistics for Water Rights n.d.)
For further information on citing sources using the Chicago style, see The Chicago Manual of Style, 16th ed.
If the author’s name is mentioned in the text, use a parenthetical reference to show the year of publication at the end of the sentence.
…Welch contends that this is not the case (1991).
If the author’s name is not mentioned in the text, it should be included with the year of publication within parentheses.
…but it has been argued that this was not the case (Welch 1991).
Page numbers should be included within parentheses after the year of publication. These are separated by a colon and no spaces.
…but it has been argued that this was not the case (Welch 1991:136).
The following forms should be used for multiple authors:
A recent study confirmed her belief (Johnson and Smith 1995:34).
This was reinforced by recent research on the topic (Johnson, Smith, and Marcus 1999)
If a text has more than three authors, the term “et al.” with no additional punctuation marks may be used after the first author listed in the publication credits.
This was not accurate according to a recent study (Johnson et al. 2003).
If multiple sources are cited for the same statement, the author and publication year should be distinguished from other texts with a colon. Cited texts should be arranged by author name or by date; arrangement should be consistent throughout the paper.
Some studies have refuted these arguments (Benson 1993; Nguyen 1999; Brown and Goggans 2000).
For additional information on in-text citation using the ASA style, see the American Sociological Association Style Guide , Third ed., pp. 45-47.
In the Turabian citation style, writers may use one of two forms in citing their resources: endnotes or author/date parenthetical references. Writers using the Turabian style may use the Chicago formats for both endnotes as references and for parenthetical references. Refer to Kate L. Turabian’s A Manual for Writers , 7th ed., pp. 143-145 (notes style) and pp. 217-220 (author-date style) for more information.
Citation Sources
- MLA Style, 9th ed.
- APA Style, 7th ed.
- Chicago (Notes-Bibliography Style), 17th ed.
- Chicago (Author-Date Style), 17th ed.
- See also the online version of the Chicago Manual of Style
- Turabian (Notes-Bibliography Style), 9th ed.
- Turabian (Author-Date Style), 9th ed.
- ASA Style, 6th ed.
Citing Sources in the Text of a Paper
Including a list of Works Cited at the end of an essay is not enough. Learn how to cite the use of a source in the text of your paper.
Using Information from Sources in the Text of a Paper
Review five different methods for including the words of another writer or information from a research resource into the text of your paper.
Citing Creative Commons Materials
Find models and suggestions for citing Creative Commons images, video clips, music, or other materials.
Suggested Readings on Academic Integrity
Find books, articles and websites which deal with academic integrity issues.
Creating an Annotated Bibliography
Learn how to create an annotated bibliography for a class assignment or for your own use as a researcher and writer.
Learn more about Zotero – a citation management tool to help you keep track of and organize various references for papers and projects.
Avoiding Plagiarism
See Trinity University’s definitions of plagiarism and consider how to avoid these situations.
Detecting Plagiarized Material
Information and links for faculty members and others to use in detecting plagiarized materials.
BibGuru Blog
Be more productive in school
- Citation Styles
Citation styles with numbers [Updated 2023]
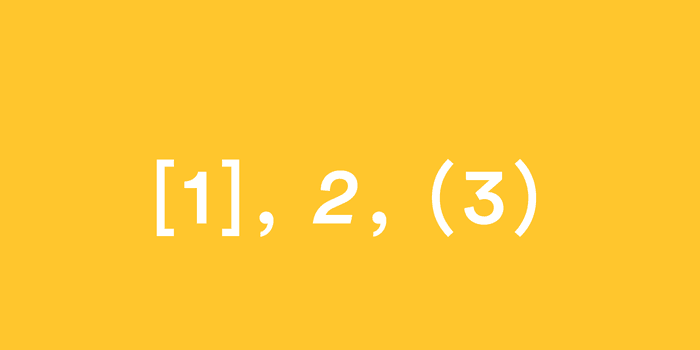
Citation styles can take many forms, like author-date, author-page, footnotes, numeric, etc. In this post, we discuss the most frequently used citation formats with numbers and provide examples of references in each style.
#1 Vancouver

Vancouver style is a numeric citation system used in biomedical, health and other sciences. This style consists of in-text citations that use either superscript or bracketed numbers.
The same number is used throughout the paper to refer to the same source. The reference list at the end of the paper lists the full bibliographic citations for each source. This list is ordered sequentially, not alphabetically.
Vancouver style resources
🌐 Official Vancouver style guidelines
📝 Vancouver citation generator
🗂 Estilo Vancouver (in Spanish)
Vancouver style examples
Here is an example of an in-text citation in Vancouver style:
A similar study was carried out in 2015 ¹ .
Here is a reference list entry in Vancouver style:
1. Aprile A, Gulino A, Storto M, Villa I, Beretta S, Merelli I, et al. Hematopoietic stem cell function in β-thalassemia is impaired and is rescued by targeting the bone marrow niche. Blood [Internet]. 2020; Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1182/blood.2019002721

The American Medical Association (AMA) style is a numeric citation format used in many medical fields. This style features in-text references with superscript numbers and a reference list that includes full bibliographic references for each source.
AMA style resources
🌐 Official AMA style guidelines
🗂 AMA style guide
📝 AMA citation generator
AMA style examples
Here is an example of an in-text citation in AMA style:
The rising hospitalizations and deaths across New York City boroughs ¹ .
Here is a reference list entry in AMA style:
1. Wadhera RK, Wadhera P, Gaba P, et al. Variation in COVID-19 hospitalizations and deaths across New York City boroughs. JAMA. 2020. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.7197

Nature is one of the most renowned science journals in the world and they have their own numeric referencing style. Its system requires in-text citations with numbers in superscript, which are referenced in full in a sequential list at the end of the paper.
Nature style resources
🌐 Official Nature style guidelines
🗂 Nature style guide
Nature style examples
Here is an example of an in-text citation in Nature style:
A great revelation in the genomes field ¹ .
Here is a reference list entry in Nature style:
1. Skov, L. et al . The nature of Neanderthal introgression revealed by 27,566 Icelandic genomes. Nature (2020) doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2225-9.

CSE (Council of Science Editors) style is is the standard format used in the physical and life sciences. This style features three types of citation systems: citation-sequence, name-year, and citation-name.
• Name-Year : In-text citations of this type feature the author’s last name and the year of publication in brackets. A bibliography at the end lists all references in full.
• Citation-Sequence : Every source is assigned a superscript number that is used as an in-text reference. The bibliography at the end lists all numbers with their references in the order in which they appeared in the text.
• Citation-Name : The reference list is organized alphabetically by authors’ last names; each name is assigned a number which can be placed in superscript as an in-text reference.
CSE style resources
🌐 Official CSE style guidelines
📝 CSE citation generator
CSE style examples
Here is an example of an in-text citation in CSE citation-sequence style:
Therefore, the translocation of wild plants was tracked ¹ .
Here is a bibliography entry in CSE citation-sequence style:
1. Hofman CA, Rick TC. 2018. Ancient Biological Invasions and Island Ecosystems: Tracking Translocations of Wild Plants and Animals. J. Archaeol. [accessed 2019 Mar 11]; 26(1): 65–11. doi.org/10.1007/s10814-017-9105-3.
Science is a peer-reviewed journal published by the American Association for the Advancement of Science. This journal features a numeric citation style that consists of in-text references and notes with an italicized number in parentheses. Each reference is given a unique number that is later added to a reference list.
Science style resources
🌐 Official Science style guidelines
Science style examples
Here is an example of an in-text citation in Science style:
This clearly contrasts with the single-donor gene transfers associated with endosymbiosis ( 22 ) .
Here is a reference list entry in Science style:
22. X. Fan, H. Qiu, W. Han, Y. Wang, D. Xu, X. Zhang, D. Bhattacharya, N. Ye, Phytoplankton pangenome reveals extensive prokaryotic horizontal gene transfer of diverse functions. Sci. Adv. 6 , eaba0111 (2020).

IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) style is used for engineering and science papers. This style uses a numeric, in-text citation format, with a number in square brackets. This number corresponds to a reference list entry at the end of the paper.
IEEE style resources
🌐 Official IEEE style guidelines
🗂 IEEE style guide
📝 IEEE citation generator
IEEE style examples
Here is an example of an in-text citation in IEEE style:
As seen in a multi-camera study [1] ...
Here is a bibliography entry in IEEE style:
[1] E. Nuger and B. Benhabib, “Multi-Camera Active-Vision for Markerless Shape Recovery of Unknown Deforming Objects,” J. Intell. Rob. Syst. , vol. 92, no. 2, pp. 223–264, Oct. 2018.
Frequently Asked Questions about citation styles with numbers
A numbered, or numeric, citation style uses superscripted numbers or numbers in brackets for in-text citations. The numbers correspond to a reference list at the end of the paper that features full bibliographic citations for each source.
A numeric style is not necessarily better or worse than an author-date style. The decision to use either one will depend on the topic you’re writing about, the field you’re studying, or your instructor’s preferences for the assignment.
Numeric citation styles use Arabic numerals (1, 2, 3, etc.).
Science and Nature use their own numeric citation styles. Science uses a numeric citation style with italicized numbers in parentheses. Nature , however, uses a style with superscript numbers.

Make your life easier with our productivity and writing resources.
For students and teachers.
- Plagiarism and grammar
- Citation guides
Citation Machine® — Write Smarter
Start a new citation or manage your existing bibliographies.
Scan your paper for plagiarism and grammar errors.
Check your paper for grammar and plagiarism
Catch plagiarism and grammar mistakes with our paper checker
Use Citation Machine® Plus to get smart recommendations!
Scan your paper for unintentional plagiarism and get advanced recommendations for sentence structure, writing style, grammar and more!
- expert check

Know you're citing correctly
No matter what citation style you're using (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.) we'll help you create the right bibliography
Check for unintentional plagiarism
Scan your paper the way your teacher would to catch unintentional plagiarism. Then, easily add the right citation
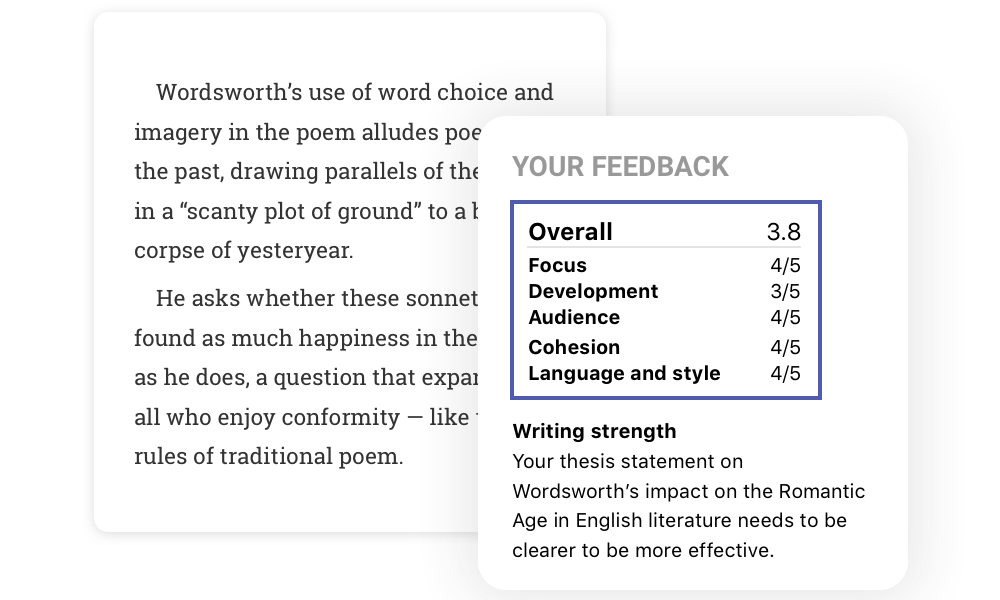
Strengthen your writing
Give your paper an in-depth check. Receive feedback within 24 hours from writing experts on your paper's main idea, structure, conclusion, and more.


Find and fix grammar errors
Don't give up sweet paper points for small mistakes. Our algorithms flag grammar and writing issues and provide smart suggestions
Citation Machine® Guides & Resources
Mla format: everything you need to know and more.
Filled with a wide variety of examples and visuals, our Citation Machine® MLA guide will help you master the citation process. Learn how to cite websites, books, journal articles, magazines, newspapers, films, social media, and more!
MLA Citation Generator | Website | Books | Journal Articles | YouTube | Images | Movies | Interview | PDFs
Comprehensive Guide to APA Format
Our Citation Machine® APA guide is a one-stop shop for learning how to cite in APA format. Read up on what APA is, or use our citing tools and APA examples to create citations for websites, books, journals, and more!
APA Citation Generator | Website | Books | Journal Articles | YouTube | Images | Movies | Interview | PDFs
Everything You Need to Know About Chicago Style
Creating citations in Chicago style has never been easier thanks to our extensive Citation Machine® Chicago style guide and tools. Learn about footnotes, endnotes, and everything in between, or easily create citations for websites, books, journal articles, and more!
Chicago Citation Generator | Website | Books | Journal Articles | YouTube | Images | Movies | Interview | PDFs
Citation Machine®’s Ultimate Writing Guides
Whether you’re a student, writer, foreign language learner, or simply looking to brush up on your grammar skills, our comprehensive grammar guides provide an extensive overview on over 50 grammar-related topics. Confused about reflexive verbs, demonstrative adjectives, or conjunctive adverbs? Look no further! Learn about these grammar topics and many, many more in our thorough and easy to understand reference guides!
Citing Sources Guide | Grammar Guide | Plagiarism Guide | Writing Tips
Student Blog
Stay up to date! Get research tips and citation information or just enjoy some fun posts from our student blog.
- Citation Machine® Plus
- Citation Guides
- Chicago Style
- Harvard Referencing
- Terms of Use
- Global Privacy Policy
- Cookie Notice
- DO NOT SELL MY INFO
- Free Tools for Students
- APA Citation Generator
Free APA Citation Generator
Generate citations in APA format quickly and automatically, with MyBib!

🤔 What is an APA Citation Generator?
An APA citation generator is a software tool that will automatically format academic citations in the American Psychological Association (APA) style.
It will usually request vital details about a source -- like the authors, title, and publish date -- and will output these details with the correct punctuation and layout required by the official APA style guide.
Formatted citations created by a generator can be copied into the bibliography of an academic paper as a way to give credit to the sources referenced in the main body of the paper.
👩🎓 Who uses an APA Citation Generator?
College-level and post-graduate students are most likely to use an APA citation generator, because APA style is the most favored style at these learning levels. Before college, in middle and high school, MLA style is more likely to be used. In other parts of the world styles such as Harvard (UK and Australia) and DIN 1505 (Europe) are used more often.
🙌 Why should I use a Citation Generator?
Like almost every other citation style, APA style can be cryptic and hard to understand when formatting citations. Citations can take an unreasonable amount of time to format manually, and it is easy to accidentally include errors. By using a citation generator to do this work you will:
- Save a considerable amount of time
- Ensure that your citations are consistent and formatted correctly
- Be rewarded with a higher grade
In academia, bibliographies are graded on their accuracy against the official APA rulebook, so it is important for students to ensure their citations are formatted correctly. Special attention should also be given to ensure the entire document (including main body) is structured according to the APA guidelines. Our complete APA format guide has everything you need know to make sure you get it right (including examples and diagrams).
⚙️ How do I use MyBib's APA Citation Generator?
Our APA generator was built with a focus on simplicity and speed. To generate a formatted reference list or bibliography just follow these steps:
- Start by searching for the source you want to cite in the search box at the top of the page.
- MyBib will automatically locate all the required information. If any is missing you can add it yourself.
- Your citation will be generated correctly with the information provided and added to your bibliography.
- Repeat for each citation, then download the formatted list and append it to the end of your paper.
MyBib supports the following for APA style:
| ⚙️ Styles | APA 6 & APA 7 |
|---|---|
| 📚 Sources | Websites, books, journals, newspapers |
| 🔎 Autocite | Yes |
| 📥 Download to | Microsoft Word, Google Docs |

Daniel is a qualified librarian, former teacher, and citation expert. He has been contributing to MyBib since 2018.
Does citation polarity help evaluate the quality of academic papers?
- Published: 23 May 2023
- Volume 128 , pages 4065–4087, ( 2023 )
Cite this article

- Linhong Xu 1 , 2 ,
- Kun Ding ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-9805-3554 1 ,
- Yuan Lin 1 &
- Chunbo Zhang 1
584 Accesses
3 Citations
Explore all metrics
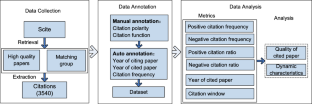
Citation frequency is an important metric for the evaluation of academic papers, but it assumes that all citations are of equal value. The purpose of this study is to determine the validity of citation polarity, which contains evaluative information such as criticism or praise, in the evaluation of paper quality. In this paper, 3538 citation sentences in papers from ACL conferences were selected and manually annotated for citation polarity. They were divided into best paper group and matching paper group, and tested in heterologous pairs to determine whether there were differences in the positive and negative citations of the two groups, and to further investigate the trend of citation polarity with the increase of citation window. The results of the study showed that the best paper and the matching paper had significant differences in the number of positive and negative citations, and the mean and median values of positive citations in the best group were about 1.5 times higher than those in the matching group. As the citation window increased, the best papers maintained both positive and negative citation dominance over 5 years, and the peak citation in the best group was about three times higher than that in the matching group. Therefore, the metric of citation polarity can help evaluate the quality of papers and provide new ideas for scientific and objective evaluation of academic papers.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or Ebook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Influence Evaluation of Academic Papers via Citation Characteristics Analysis
Evaluation by citation: trends in publication behavior, evaluation criteria, and the strive for high impact publications.

Do negative citations reduce the impact of cited papers?
Abujbara, A., Ezra, J., & Radev, D. (2013). Purpose and polarity of citation: Towards NLP-based bibliometrics. Conference of the North American chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human language technologies. Atlanta, Georgia, USA: Association for Computational Linguistics (pp. 596–606).
Aljuaid, H., Iftikhar, R., Ahmad, S., et al. (2020). Important citation identification using sentiment analysis of in-text citations. Telematics and Informatics, 56 (2), 1–18.
Google Scholar
Athar, A., & Teufel, S. (2012). Context-enhanced citation sentiment detection. Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Montrèal, Canada: Association for Computational Linguistics (pp. 597–601).
Bordignon, F. (2020). Self-correction of science: A comparative study of negative citations and post-publication peer review. Scientometrics, 124 (2), 1225–1239.
Article Google Scholar
Bordignon, F. (2022). Critical citations in knowledge construction and citation analysis: From paradox to definition. Scientometrics, 127 (1), 959–972.
Bornmann, L. (2015). Inter-rater reliability and convergent validity of F1000Prime peer review. Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology, 66 (12), 2415–2426.
Bornmann, L. (2017). Is collaboration among scientists related to the citation impact of papers because their quality increases with collaboration? An analysis based on data from F1000Prime and normalized citation scores. Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology, 68 (4), 1036–1047.
Brembs, B. (2018). Prestigious science journals struggle to reach even average reliability. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 12 (2), 1–2.
Bridgstock, M. (1991). The quality of single and multiple authored papers: An unresolved problem. Scientometrics, 21 (1), 37–48.
Brooks, T. A. (1986). Evidence of complex citer motivations. Journal of the American Society for Information Science, 37 (1), 34–36.
Case, D. O., & Higgins, G. M. (2000). How can we investigate citation behavior? A study of reasons for citing literature in communication. Journal of the American Society for Information Science, 51 (7), 635–645.
Catalini, C., Lacetera, N., & Oettl, A. (2015). The incidence and role of negative citations in science. PNAS, 112 (45), 13823–13826.
Chubin, D. E., & Moitra, S. D. (1975). Content analysis of references: Adjunct or alternative to citation counting?[J]. Social Studies of Science, 5 (4), 423–441.
Cohen, J. (1960). A coefficient of agreement for nominal scales. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 20 (1), 37–46.
Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences (2nd ed.). Lawrence Erlbaum.
MATH Google Scholar
Cronin, B., & Meho, L. (2006). Using the h-Index to rank influential information scientists. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 57 (9), 1275–1278.
Dunaiski, M., Visser, W., & Geldenhuys, J. (2016). Evaluating paper and author ranking algorithms using impact and contribution awards. Journal of Informetrics, 10 (2), 392–407.
Farys, R., & Wolbring, T. (2017). Matched control groups for modeling events in citation data: An illustration of nobel prize effects in citation networks. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 68 (9), 2201–2210.
Garfield, E. (1964). Can citation indexing be automated? Proceedings of the Symposium on Statistical Association . Washington (pp. 84–90).
Geng, S., & Yang, J. (2018). A method to evaluate the academic influence of papers based on citation sentiment. Information Studies: Theory & Application, 41 (12), 93–98.
Geras, A., Siudem, G., & Gagolewski, M. (2020). Should we introduce a dislike button for academic articles? Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology, 71 (2), 221–229.
Ghosh, S., & Shah, C. (2020). Identifying citation sentiment and its influence while indexing scientific papers. Proceedings of the 53rd Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Hawaii, USA: HICSS 2517–2526.
Hu, Y. (2015). The relationship between citations of academic papers and academic quality. Library Forum, 35 (5), 56–59.
Ikram, M. T., & Afzal, M. T. (2019). Aspect based citation sentiment analysis using linguistic patterns for better comprehension of scientific knowledge. Scientometrics, 119 (1), 73–95.
Jiang, C., & Wei, Q. (2017). Construction of evaluation index system of representative paper in humanities and social sciences and its realization mechanism. Gansu Social Sciences, 44 (2), 97–106.
Jiang, L., & Zhang, Q. (2020). Research on academic evaluation based on fine-grain citation sentimental quantification. Data Analysis and Knowledge Discovery, 4 (6), 129–138.
MathSciNet Google Scholar
Kumar, S. (2016). Structure and dynamics of signed citation networks. International Conference Companion on World Wide Web, Montreal, Canada: ACM 63–64.
Liang, G. Q., Hou, H. Y., Ren, P., Wang, Y. J., Huang, F., Wang, J. X., & Hu, Z. G. (2018). Analysis of correlation between usage count and times cited of high quality literatures. Journal of Intelligence, 37 (4), 147–153.
Liao, H., Xiao, R., Cimini, G., & Medo, M. (2014). Network-driven reputation in online scientific communities. PLoS ONE, 9 (12), 1–18.
Liu, Y., Wu, Q., Wu, S., & Gao, Y. (2021). Weighted citation based on ranking-related contribution: A new index for evaluating article impact. Scientometrics, 126 (10), 8653–8672.
Lu, Y., Luo, J., Xiao, Y., & Zhu, H. (2021). Text representation model of scientific papers based on fusing multi-viewpoint information and its quality evaluation. Scientometrics, 126 (8), 6937–6963.
Macilwain, C. (2013). Halt the avalanche of performance metrics. Nature, 500 (7462), 255.
Martin, B. R., & Irvine, J. (1983). Assessing basic research: Some partial indicators of scientific progress in radio astronomy. Research Policy, 12 (2), 61–90.
Min, C., Bu, Y., Wu, D., Ding, Y., & Zhang, Y. (2021). Identifying citation patterns of scientific breakthroughs: A perspective of dynamic citation process. Information Processing & Management, 58 (1), 1–21.
Moravcsik, M. J., & Murugesan, P. (1975). Some results on the function and quality of citations. Social Studies of Science, 5 (1), 86–92.
Munkhdalai, T., Lalor, J. P., & Yu, H. (2016). Citation analysis with neural attention models. International Workshop on Health Text Mining and Information Analysis, Austin, Texas, USA: Association for Computational Linguistics (pp. 69–77).
Muppidi, S., Gorripati, S. K., & Kishore, B. (2020). An approach for bibliographic citation sentiment analysis using deep learning. International Journal of Knowledge-Based and Intelligent Engineering Systems, 24 (4), 353–362.
Newman, M. E. J. (2009). The first-mover advantage in scientific publication. Europhysics Letters, 86 (6), 68001–68006.
Newman, M. E. J. (2014). Prediction of highly cited papers. Europhysics Letters, 105 (2), 1–6.
Nicholson, J. M., Mordaunt, M., Lopez, P., Uppala, A., Rosati, D., Rodrigues, N. P., Grabitz, P., & Rife, S. C. (2021). scite: A smart citation index that displays the context of citations and classifies their intent using deep learning. Quantitative Science Studies, 2 (3), 882–898.
Niu, Q., Zhou, J., Zeng, A., Fan, Y., & Di, Z. (2016). Which publication is your representative work? Journal of Informetrics, 10 (3), 842–853.
Salimi, N. (2017). Quality assessment of scientific outputs using the BWM. Scientometrics, 112 (1), 195–213.
Shadish, W. R., Tolliver, D., Gray, M., & Sen Gupta, S. K. (1995). Author judgements about works they cite: Three studies from psychology journals. Social Studies of Science, 25 (3), 477–498.
Song, D., Wang, W., Fan, Y., Xing, Y., & Zeng, A. (2022). Quantifying the structural and temporal characteristics of negative links in signed citation networks. Information Processing & Management, 59 (4), 102996.
Suelzer, E. M., Deal, J., Hanus, K. L., Ruggeri, B., Sieracki, R., & Witkowski, E. (2019). Evaluation of citations of the retracted article by Wakefield et al. with fraudulent claims of an association between vaccination and autism. JAMA Network Open, 2 (11), 1–10.
Suo, C., & Gai, S. (2018). An analysis on the quality and influence of scientific paper based on citations. Information Studies: Theory & Application, 41 (5), 11–15.
Teufel, S., Siddharthan, A., & Tidhar, D. (2006). Automatic classification of citation function. Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Sydney, Australia: Association for Computational Linguistics (pp. 103–110).
Vinkler, P. (1987). Quasi-quantitative citation model. Scientometrics, 12 (1–2), 47–72.
Wang, D., Song, C., & Barabási, A. (2013). Quantifying long-term scientific impact. Science, 342 (6154), 127–132.
Wang, H., Tan, Z., & Chen, T. (2016). Research on the factors affecting papers’ citation frequency. Studies in Science of Science, 34 (2), 171–177.
Xie, Z., Ma, J. X., & Hu, W. (2021). Evaluation of academic representative works: Methods review and research prospects. Information Studies: Theory & Application, 44 (12), 190–196.
Xu, L., Ding, K., Chen, N., & Li, B. (2020). Corpus construction for citation sentiment in Chinese literature. Journal of the China Society for Scientific and Technical Information, 39 (1), 25–37.
Xu, L., Ding, K., & Lin, Y. (2022). Do negative citations reduce the impact of cited papers? Scientometrics, 127 (2), 1161–1186.
Yan, E., Chen, Z., & Li, K. (2020). Authors’ status and the perceived quality of their work: Measuring citation sentiment change in Nobel articles. Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology, 71 (3), 314–324.
Yang, P., Sun, X., & Li, W. et al. (2018). Automatic academic paper rating based on modularized hierarchical convolutional neural network. Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of ACL. Melbourne, Australia, Association for Computational Linguistics (pp. 496–502).
Yousif, A., Niu, Z., & Nyamawe, A. S. et al. (2018). Improving citation sentiment and purpose classification using hybrid deep neural network model. Proceedings of the International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Systems and Informatics, Cairo, Egypt: Springer (pp. 327–336).
Yousif, A., Niu, Z., Tarus, J. K., & Ahmad, A. (2019a). A survey on sentiment analysis of scientific citations. Artificial Intelligence Review, 52 , 1805–1838.
Yousif, A., Niu, Z., Chambua, J., & Khan, Z. Y. (2019b). Multi-task learning model based on recurrent convolutional neural networks for citation sentiment and purpose classification. Neurocomputing, 335 (3), 195–205.
Zeng, A., Shen, Z., Zhou, J., Wu, J., Fan, Y., Wang, Y., & Stanley, H. E. (2017). The science of science: From the perspective of complex systems. Physics Reports, 714 (16), 1–73.
Article MathSciNet MATH Google Scholar
Zhang, C., & Li, Z. (2019). Extracting sentences of research originality from full text academic articles. Data Analysis and Knowledge Discovery, 3 (10), 12–19.
Zhang, P., Wang, P., & Wu, Q. (2018). How are the best JASIST papers cited? Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 69 (6), 857–860.
Zhou, J., Zeng, A., Fan, Y., & Di, Z. (2018). The representative works of scientists. Scientometrics, 117 (3), 1721–1732.
Zhou, L., Amadi, U., & Zhang, D. (2020). Is self-citation biased? An investigation via the lens of citation polarity, density, and location. Information Systems Frontiers, 22 (1), 77–90.
Zhou, Y., Lü, L., & Li, M. (2012). Quantifying the influence of scientists and their publications: Distinguishing between prestige and popularity. New Journal of Physics, 14 (3), 1–18.
Download references
Acknowledgements
This work is partially supported by grant from the Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 61772103, 61806038, 61976036). We also thank the anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
WISE Lab, Institute of Science of Science and Technology Management, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, 116024, China
Linhong Xu, Kun Ding, Yuan Lin & Chunbo Zhang
Software Institute, Dalian University of Foreign Languages, Dalian, 116044, China
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Kun Ding .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Xu, L., Ding, K., Lin, Y. et al. Does citation polarity help evaluate the quality of academic papers?. Scientometrics 128 , 4065–4087 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-023-04734-1
Download citation
Received : 28 October 2022
Accepted : 04 May 2023
Published : 23 May 2023
Issue Date : July 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-023-04734-1
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Citation polarity
- Quality of academic papers
- Positive citation
- Negative citation
- Research evaluation
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

Publications — Over 100 years of publishing excellence
- Book Author Resources
- Submit a Book Proposal
- AMS Rights, Licensing, and Permissions
- Open Math Notes
- Frequently asked questions
- Member Journals
- Research Journals
- Translation Journals
- Distributed Journals
- Open Access Journals
- Guidelines and Policies
- Journal Author Resources
Librarian Resources
- eBook Collections
- COUNTER Usage Statistics
- My Subscriptions
- Subscription Information
- Licensing Information
Mathematical Reviews/MathSciNet®
- MathSciNet ®
- Reviewer Home
- MathSciNet ® Subscriptions
Membership — Welcome to your membership center
Join the ams, renew your membership, give a membership, individual membership.
- Member Benefits
- Member Directory
- Reciprocating Societies
- Members in Developing Countries
Institutional Membership
- Domestic Institutions
- International Institutions
- Two-Year Institutions
- Graduate Student Chapter Program
Other Member Types
- Corporate Memberships
- Associate Memberships
Meetings & Conferences — Engage with colleagues and the latest research
National meetings.
- Joint Mathematics Meetings
- Upcoming JMMs
- Previous JMMs
- Special Lectures
- Professional Enhancement Programs (PEPs)
Sectional Meetings
- Upcoming Sectionals
- Previous Sectionals
- Presenting Papers
- Hosting Sectionals
Other Meetings, Conferences & Workshops
- Mathematics Research Communities
- Education Mini-conference
- International Meetings
- Mathematics Calendar
- Short Courses
- Workshop for Department Chairs and Leaders
Meetings Resources
- Suggest a Speaker
- AMS Meetings Grants
- Submitting Abstracts
- Welcoming Environment Policy
- MathSafe – supporting safe meetings
News & Outreach — Explore news, images, posters, and mathematical essays
News from the ams.
- AMS News Releases
- Feature Stories
- Information for Journalists
- In Memory Of
Math Voices
- Feature Column
- Math in the Media
- Column on Teaching and Learning
Explorations
- Recognizing Diverse Mathematicians
- AMS Posters
- Mathematics & Music
- Mathematical Imagery
- Mathematical Moments
Professional Programs — Resources and opportunities to further your mathematical pursuits
Professional development.
- Employment Services
- Mathjobs.org
- BEGIN Career Initiative
- Mathprograms.org
- Mathematical Opportunities Database
- Research Seminars
Institutional Information and Data
- Annual Survey of the Mathematical and Statistical Sciences
- CBMS Survey
- Other Sources of Data
- Directory of Institutions in the Mathematical Sciences
- Professional Directory
Grants & Support
- AMS-Simons Grants for PUI Faculty
- Travel Grants
- Fellowships & Scholarships
- Epsilon Fund
- Child Care Grants
Awards & Recognition
- AMS Prizes & Awards
- Fellows of the AMS
Education — Resources to support advanced mathematics teaching and learning
For students.
- Information for Undergraduate and High School Students
- Research Experiences for Undergraduates (REUs)
- Considering Grad School
- Find Grad Programs
- Applying to Grad School
- What do Mathematicians Do?
For Teachers
- Teaching Online
- Teaching Resources
- Inclusive Classrooms
- Assessing Student Learning
- Education Webinars
For Department Leaders & Mentors
- Information for Department Leaders
- paraDIGMS (Diversity in Graduate Mathematical Sciences)
Government Relations — Advocating for the mathematical sciences
Elevating mathematics in congress.
- Our Mission
- Letters, Statements, & Legislation
- Congressional Briefings
Legislative Priorities
- Federal Issues of Concern
- Federal Budget Process
Get Involved
- Advocacy Resources
- Take Action
DC-Based Fellowships
- Congressional Fellowship
- Mass Media Fellowship
- Catalyzing Advocacy in Science & Engineering (CASE) Fellowship
Giving to the AMS — Your gifts make great things happen for mathematics Make a Gift
What you can support.
- The 2020 Fund
- Next Generation Fund
- Birman Fellowship for Women Scholars
- JMM Child Care Grants
- MathSciNet for Developing Countries
Create a Legacy
- Make a Tribute Gift
- Create a Permanent Fund
- Establish a Prize, Award or Fellowship
- Bequests and Charitable Estate Planning
Honoring Your Gift
- Donor Stories
- Donor Wall of Honor
- Thomas S. Fiske Society
- AMS Contributors Society
- AMS Gardens
Giving Resources
- AMS Development Committee
- AMS Gift Acceptance Policy
About the AMS — Advancing research. Connecting the mathematics community.
Our organization.
- Executive Staff
- Equity, Diversity, & Inclusion
- Jobs at AMS
- Customer Service
Our Governance
- Board of Trustees
- Executive Committee
Governance Operations
- Calendar of Meetings
- Policy Statements & Guidelines

Mathematics of Computation
Published by the American Mathematical Society since 1960 (published as Mathematical Tables and other Aids to Computation 1943-1959), Mathematics of Computation is devoted to research articles of the highest quality in computational mathematics.
ISSN 1088-6842 (online) ISSN 0025-5718 (print)
The 2020 MCQ for Mathematics of Computation is 1.78 . What is MCQ? The Mathematical Citation Quotient (MCQ) measures journal impact by looking at citations over a five-year period. Subscribers to MathSciNet may click through for more detailed information.
- Articles in press
- Recently published
- All issues : 1943 – Present
Contents of Volume 93, Number 349 HTML articles powered by AMS MathViewer View front and back matter from the print issue
- Search Menu
- Sign in through your institution
- Supplements
- Advance articles
- Editor's Choice
- Special Issues
- Author Guidelines
- Submission Site
- Why Publish With Us?
- Open Access
- About Nicotine & Tobacco Research
- About Society for Nicotine & Tobacco Research
- Editorial Board
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Journals Career Network
- Self-Archiving Policy
- Dispatch Dates
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic
Article Contents
“ keep it a secret ”: leaked documents suggest philip morris international, and its japanese affiliate, continue to exploit science for profit.
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
Sophie Braznell, Louis Laurence, Iona Fitzpatrick, Anna B Gilmore, “ Keep it a secret ”: leaked documents suggest Philip Morris International, and its Japanese affiliate, continue to exploit science for profit, Nicotine & Tobacco Research , 2024;, ntae101, https://doi.org/10.1093/ntr/ntae101
- Permissions Icon Permissions
The tobacco industry has a long history of manipulating science to conceal the harms of its products. As part of its proclaimed transformation, the world’s largest tobacco company, Philip Morris International (PMI), states it conducts “ transparent science ”. This paper uses recently leaked documents from PMI and its Japanese affiliate, Philip Morris Japan (PMJ), to examine its contemporary scientific practices.
23 documents dating 2012 through 2020 available from Truth Tobacco Industry Documents Library were examined using Forster's hermeneutic approach to analysing corporate documentation. Thematic analysis using the Science for Profit Model was conducted to assess whether PMI/PMJ employed known corporate strategies to influence science in their interests.
PMJ contracted a third-party external research organisation, CMIC, to covertly fund a study on smoking cessation conducted by Kyoto University academics. No public record of PMJ’s funding or involvement in this study was found. PMJ paid life sciences consultancy, FTI-Innovations, ¥3,000,000 (approx. £20,000) a month between 2014 and 2019 to undertake extensive science-adjacent work, including building relationships with key scientific opinion leaders and using academic events to promote PMI’s science, products and messaging. FTI-Innovation’s work was hidden internally and externally. These activities resemble known strategies to influence the conduct, publication and reach of science, and conceal scientific activities.
The documents reveal PMI/PMJ’s recent activities mirror past practices to manipulate science, undermining PMI’s proclaimed transformation. Tobacco industry scientific practices remain a threat to public health, highlighting the urgent need for reform to protect science from the tobacco industry’s vested interests.
Implications: Japan is a key market for PMI, being a launch market for IQOS and having the highest heated tobacco product use globally. Our findings, in conjunction with other recent evidence, challenge PMI’s assertion that it is a source of credible science and cast doubt on the quality and ethical defensibility of its research, especially its studies conducted in Japan. This, in turn, brings into question the true public health impacts of its products. There is urgent need to reform the way tobacco-related science is funded and conducted. Implementation of models through which research can be funded using the industry’s profits while minimising its influence should be explored.
Supplementary data
| Month: | Total Views: |
|---|---|
| June 2024 | 340 |
| July 2024 | 208 |
Email alerts
Citing articles via.
- About Nicotine & Tobacco Research
- Recommend to your Library
Affiliations
- Online ISSN 1469-994X
- Copyright © 2024 Society for Research on Nicotine and Tobacco
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
Scribbr APA Citation Generator
Accurate APA citations, verified by experts, trusted by millions.
Scribbr for Chrome: Your shortcut to APA citations
Cite any page or article with a single click right from your browser. The extension does the hard work for you by automatically grabbing the title, author(s), publication date, and everything else needed to whip up the perfect APA citation.
Add to Chrome. It's free!
| ⚙️ Styles | APA 7 & APA 6 |
|---|---|
| 📚 Source types | Websites, books, articles |
| 🔎 Autocite | Search by title, URL, DOI, or ISBN |

Rely on accurate APA citations, verified by experts.
You don’t want points taken off for incorrect citations. That’s why our APA citation experts have invested countless hours perfecting our algorithms. As a result, we’re proud to be recommended by teachers worldwide.
Enjoy the APA Citation Generator with minimal distraction.
Staying focused is already challenging enough. You don’t need video pop-ups and flickering banner ads slowing you down. At Scribbr, we keep distractions to a minimum while also keeping the APA Citation Generator free for everyone.
Citation Generator features you'll love
Search for your source by title, URL, DOI, ISBN, and more to retrieve the relevant information automatically.
APA 6th & 7th edition
Scribbr's Citation Generator supports both APA 6 and APA 7 (as well as MLA and Harvard ). No matter what edition you're using, we’ve got you covered!
Export to Bib(La)TeX
Easily export in BibTeX format and continue working in your favorite LaTeX editor.
Export to Word
Reference list finished? Export to Word with perfect indentation and spacing set up for you.
Sorting, grouping, and filtering
Organize the reference list the way you want: from A to Z, new to old, or grouped by source type.
Save multiple lists
Stay organized by creating a separate reference list for each of your assignments.
Choose between Times New Roman, Arial, Calibri, and more options to match your style.
Industry-standard technology
The Scribbr Citation Generator is built using the same citation software (CSL) as Mendeley and Zotero, but with an added layer for improved accuracy.
Annotations
Create perfectly formatted annotated bibliographies with just a few clicks.
Explanatory tips help you get the details right to ensure accurate citations.
Citation guides
Getting to grips with citation is simple with the help of our highly rated APA citation guides and videos .
Secure backup
Your work is saved automatically after every change and stored securely in your Scribbr account.
- Introduction
- Parenthetical vs. narrative
- Multiple authors
Missing information
- Sources to include
Tools and resources
- Scroll to top

How to create APA citations
APA Style is widely used by students, researchers, and professionals in the social and behavioral sciences. Scribbr’s free citation generator automatically generates accurate references and in-text citations.
This citation guide outlines the most important citation guidelines from the 7th edition APA Publication Manual (2020).
- Cite a webpage
- Cite a book
- Cite a journal article
- Cite a YouTube video
APA in-text citations
APA in-text citations include the author’s last name, publication date, and, if relevant, a locator such as a page number or timestamp. For example, (Smith, 2021, p. 170) . See it as a shorter version of the entry in the reference list .
You should include in-text citations every time you’re quoting or paraphrasing someone else’s ideas or words. In doing so, you give credit to the original author and avoid plagiarism .
Parenthetical vs. narrative citation
The in-text citation can take two forms: parenthetical and narrative. Both types are generated automatically when citing a source with Scribbr’s APA Citation Generator.
- Parenthetical citation: According to new research … (Smith, 2020) .
- Narrative citation: Smith (2020) notes that …
Multiple authors and corporate authors
The in-text citation changes slightly when a source has multiple authors or an organization as an author. Pay attention to punctuation and the use of the ampersand (&) symbol.
| Author type | Parenthetical citation | Narrative citation |
|---|---|---|
| One author | (Smith, 2020) | Smith (2020) |
| Two authors | (Smith & Jones, 2020) | Smith and Jones (2020) |
| Three or more authors | (Smith et al., 2020) | Smith et al. (2020) |
| Organization | (Scribbr, 2020) | Scribbr (2020) |
When the author, publication date or locator is unknown, take the steps outlined below.
| Missing element | What to do | Parenthetical citation |
|---|---|---|
| Author | Use the source title.* | ( , 2020) |
| Date | Write “n.d.” for “no date.” | (Smith, n.d.) |
| Page number | Either use an or omit the page number. | (Smith, 2020, Chapter 3) or (Smith, 2020) |
APA Citation Generator
Generate accurate APA citations in seconds
Get started
APA references
APA references generally include information about the author , publication date , title , and source . Depending on the type of source, you may have to include extra information that helps your reader locate the source.
It is not uncommon for certain information to be unknown or missing, especially with sources found online. In these cases, the reference is slightly adjusted.
| Missing element | What to do | Reference format |
|---|---|---|
| Author | Start the reference entry with the source title. | Title. (Date). Source. |
| Date | Write “n.d.” for “no date”. | Author. (n.d.). Title. Source. |
| Title | Describe the work in square brackets. | Author. (Date). [Description]. Source. |
Formatting the APA reference page
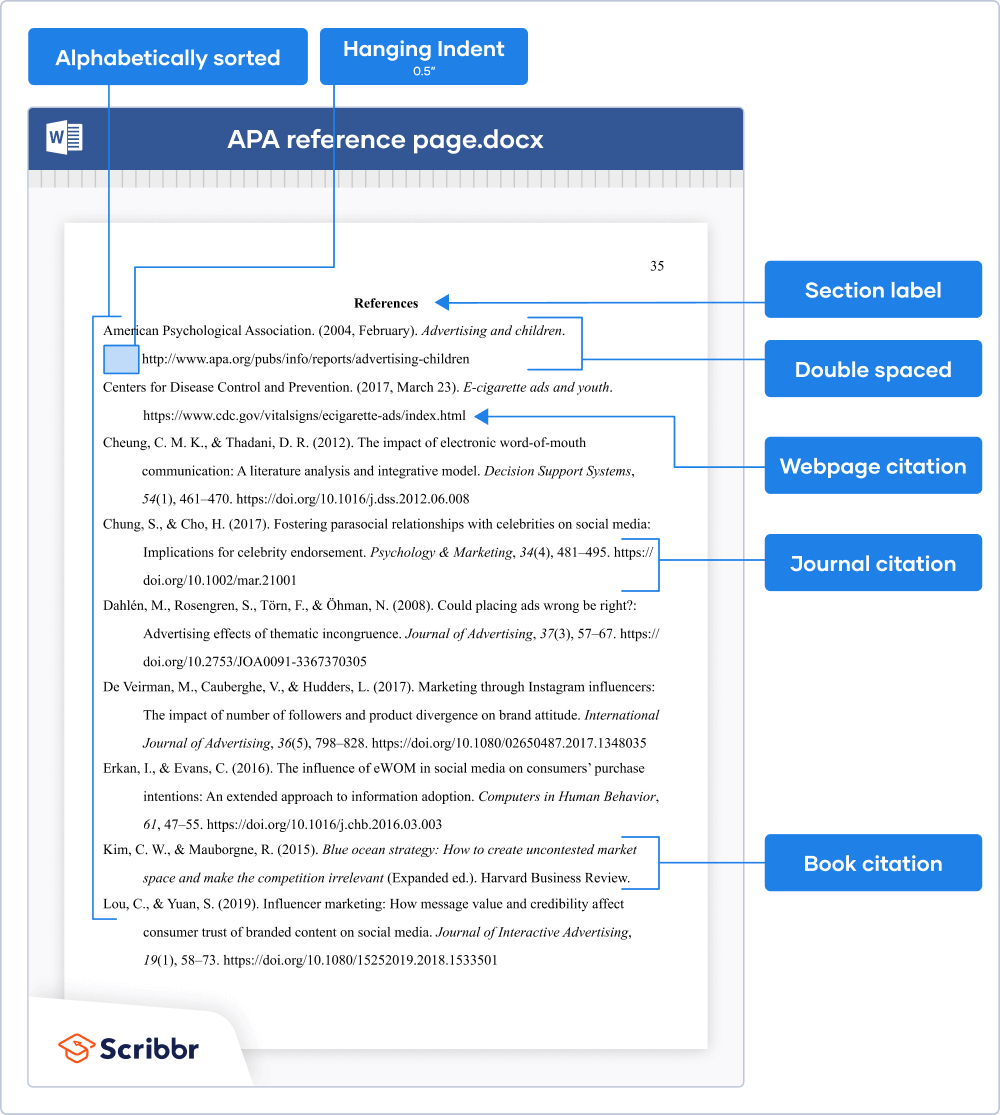
On the first line of the page, write the section label “References” (in bold and centered). On the second line, start listing your references in alphabetical order .
Apply these formatting guidelines to the APA reference page:
- Double spacing (within and between references)
- Hanging indent of ½ inch
- Legible font (e.g. Times New Roman 12 or Arial 11)
- Page number in the top right header
Which sources to include
On the reference page, you only include sources that you have cited in the text (with an in-text citation ). You should not include references to personal communications that your reader can’t access (e.g. emails, phone conversations or private online material).
In addition to the APA Citation Generator, Scribbr provides many more tools and resources that help millions of students and academics every month.
- Citation Generator : Generate flawless citations in APA, MLA , and Harvard style .
- Citation Checker : Upload your paper and have artificial intelligence check your citations for errors and inconsistencies.
- Free plagiarism checker : Detect plagiarism with unparalleled accuracy with Scribbr’s free plagiarism checker.
- AI Proofreader : Upload and improve unlimited documents and earn higher grades on your assignments. Try it for free!
- Paraphrasing tool: Avoid accidental plagiarism and make your text sound better.
- Grammar checker : Eliminate pesky spelling and grammar mistakes.
- Summarizer: Read more in less time. Distill lengthy and complex texts down to their key points.
- AI detector: Find out if your text was written with ChatGPT or any other AI writing tool. ChatGPT 2 & ChatGPT 3 supported.
- Proofreading services : Have a professional editor (or team of editors) improve your writing so you can submit your paper with pride and confidence. Scribbr offers admission essay editing , paper editing , and academic editing .
- Guides and videos : Explore hundreds of articles, bite-sized videos, time-saving templates, and handy checklists that guide you through the process of research, writing, and citation.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In-text citations most commonly take the form of short parenthetical statements indicating the author and publication year of the source, as well as the page number if relevant. Example: APA Style in-text citation (Jackson, 2005, p. 16) We also offer a free citation generator and in-depth guides to the main citation styles.
Reference citations in text are covered on pages 261-268 of the Publication Manual. What follows are some general guidelines for referring to the works of others in your essay. Note: ... you may reference another logical identifying element: a paragraph, a chapter number, a section number, a table number, or something else. Older works (like ...
When you use the number system, your responsibility is to indicate in your text—either in parentheses or brackets—a number that corresponds to a source on your references page. The first source you cite in your text receives the number 1, the second number 2, and so on. If you repeat a reference to a source later in the text, it retains its ...
These citations within the essay are called in-text citations. You must cite all quoted, paraphrased, or summarized words, ideas, and facts from sources. Without in-text citations, you are in danger of plagiarism, even if you have listed your sources at the end of the essay. In-text citations point the reader to the sources' information in ...
In-text citations briefly identify the source of information in the body text. They correspond to a full reference entry at the end of your paper. APA in-text citations consist of the author's last name and publication year. When citing a specific part of a source, also include a page number or range, for example (Parker, 2020, p.
In-text citations point the reader to the sources' information on the references page. The in-text citation typically includes the author's last name and the year of publication. If you use a direct quote, the page number is also provided. More information can be found on p. 253 of the 7th edition of the Publication Manual of the American ...
In-text citations: Author-page style. MLA format follows the author-page method of in-text citation. This means that the author's last name and the page number (s) from which the quotation or paraphrase is taken must appear in the text, and a complete reference should appear on your Works Cited page. The author's name may appear either in the ...
To cite more than one source when you are paraphrasing, separate the in-text citations with a semi-colon. Format: (Author's Last Name Page Number; Author's Last Name Page Number). Examples: (Smith 42; Bennett 71). (It Takes Two; Brock 43). Note: In MLA style, the sources within the in-text citation do not need to be in alphabetical order.
In-text citations are covered in the seventh edition APA Style manuals in the Publication Manual Chapter 8 and the Concise Guide Chapter 8. Last updated: June 2024 Date created: September 2019. APA Style provides guidelines to help writers determine the appropriate level of citation and how to avoid plagiarism and self-plagiarism.
In-text citations. Use the first element from the entry in the Works Cited list - usually the author's surname - and page number/s in parenthesis. There is no punctuation between the name and the page number, e.g. (Smith 173). If the author's name appears in the body of your essay itself, use just the relevant page number/s in the ...
Create manual citation. The guidelines for citing an essay in MLA format are similar to those for citing a chapter in a book. Include the author of the essay, the title of the essay, the name of the collection if the essay belongs to one, the editor of the collection or other contributors, the publication information, and the page number (s).
The following are guidelines to follow when writing in-text citations: Ensure that the spelling of author names and the publication dates in reference list entries match those in the corresponding in-text citations. Cite only works that you have read and ideas that you have incorporated into your writing. The works you cite may provide key ...
When you directly quote someone else's work. General rules of in-text citation: A number is allocated to a source in the order in which it is cited in the text. If the source is referred to again, the same number is used. Use Arabic numerals (1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9). Either square [ ] or curved brackets ( ) can be used as long as it is consistent.
In-Text Citations. Resources on using in-text citations in APA style. The Basics General guidelines for referring to the works of others in your essay Author/Authors How to refer to authors in-text, including single and multiple authors, unknown authors, organizations, etc. Reference List. Resources on writing an APA style reference list ...
The Bluebook: A Uniform System of Citation is the main style guide for legal citations in the US. It's widely used in law, and also when legal materials need to be cited in other disciplines. Bluebook footnote citation. 1 David E. Pozen, Freedom of Information Beyond the Freedom of Information Act, 165, U. P🇦 .
When citing sources in the text of your paper, you must list: The author's last name. The year the information was published. Types of In-Text Citations: Narrative vs Parenthetical. A narrative citation gives the author's name as part of the sentence. Example of a Narrative Citation: According to Edwards (2017), although Smith and Carlos's ...
In-text citation: (Author Last Name, Year of Publication) Example: (Smith, 1988) To make the citation of the source less distracting. The APA also suggests mentioning the author in the essay's content so that only the year of publication and page number may be required in the parenthetical reference.
Vancouver style is a numeric citation system used in biomedical, health and other sciences. This style consists of in-text citations that use either superscript or bracketed numbers. The same number is used throughout the paper to refer to the same source. The reference list at the end of the paper lists the full bibliographic citations for ...
Scroll down to find the proper format for the source you're citing or referencing. If you would like help citing your sources, CitationMachine.com has a citation generator that will help make the APA citation process much easier for you. To start, simply click on the source type you're citing: Website. Books.
Stay up to date! Get research tips and citation information or just enjoy some fun posts from our student blog. Citation Machine® helps students and professionals properly credit the information that they use. Cite sources in APA, MLA, Chicago, Turabian, and Harvard for free.
Our APA generator was built with a focus on simplicity and speed. To generate a formatted reference list or bibliography just follow these steps: Start by searching for the source you want to cite in the search box at the top of the page. MyBib will automatically locate all the required information. If any is missing you can add it yourself.
The total citation frequency, number of positive citations, and number of negative citations for each paper of the two groups are presented in Table 1, and the table is sorted by the total citation frequency of the best paper.The citation frequencies of the best and matching papers ranged from 7-666 to 7-602 respectively.
An old article by White House press secretary Karine Jean-Pierre resurfaced on Wednesday amid a growing number of calls for Biden to drop out of the 2024 race. The post 'Everything Is Going ...
Revised on July 23, 2023. Numbers can be written either as words (e.g., one hundred) or numerals (e.g., 100). In this article we follow the guidelines of APA Style, one of the most common style guides used in academic writing. In general, words should be used for numbers from zero through nine, and numerals should be used from 10 onwards.
Contents of Volume 377, Number 7 HTML articles powered by AMS MathViewer View front and back matter from the print issue Optimal convex domains for the first curl eigenvalue in dimension three Alberto Enciso, Wadim Gerner and Daniel Peralta-Salas; Trans. Amer. Math. Soc. 377 (2024), 4519-4540
Contents of Volume 93, Number 349 HTML articles powered by AMS MathViewer View front and back matter from the print issue An Eulerian finite element method for tangential Navier-Stokes equations on evolving surfaces Maxim A. Olshanskii, Arnold Reusken and Paul Schwering; Math. Comp. 93 (2024), 2031-2065
The tobacco industry has a long history of manipulating science to conceal the harms of its products. As part of its proclaimed transformation, the world's largest tobacco company, Philip Morris International (PMI), states it conducts "transparent science".This paper uses recently leaked documents from PMI and its Japanese affiliate, Philip Morris Japan (PMJ), to examine its contemporary ...
Table of contents for Applied Psychological Measurement, 48, 4-5, Jul 01, 2024
The year 2024 is notable for the large number of elections being held worldwide: at least 97 countries, home to nearly half of the global population, will vote, including eight of the world's 10 most populous nations - Bangladesh, Brazil, India, Indonesia, Mexico, Pakistan, Russia, and the United States; in addition, the European Union held ...
Scribbr's free APA Citation Generator lets you generate perfect APA Style citations in seconds. ... Thesis Paper AI Proofreader Essay Checker PhD dissertation APA editing Academic editing College admissions essay Personal ... and, if relevant, a locator such as a page number or timestamp. For example, (Smith, 2021, p. 170). See it as a ...